User login
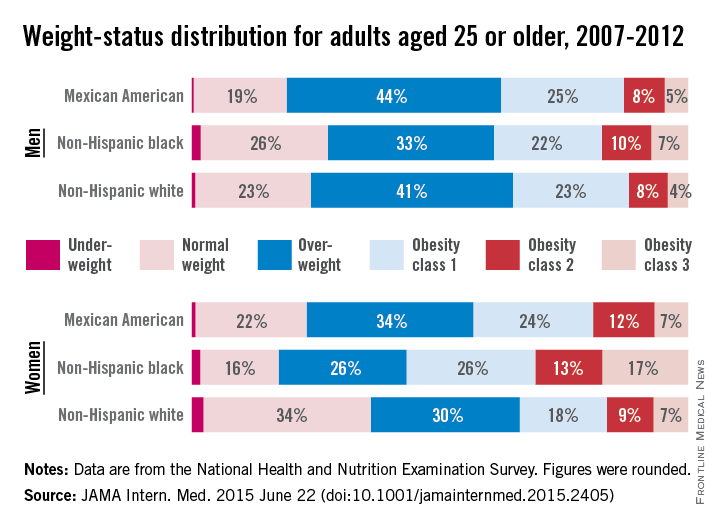
Three-quarters of men and two-thirds of women aged 25 years or older in the United States are either overweight or obese, according to a study published online June 22 in JAMA Internal Medicine.
During 2007-2012, about 40% of men were overweight and 35% were obese. For women, almost 30% were overweight and 37% were obese, Lin Yang, Ph.D., and Dr. Graham A. Colditz of Washington University, St. Louis, reported in a research letter (JAMA Intern. Med. 2015 June 22 [doi:10.1001/jamainternmed.2015.2405]).
Weight-status distributions across racial groups show that non-Hispanic whites were generally less obese than non-Hispanic blacks and Mexican Americans – an effect that was more pronounced among women. About 34% of white women were obese, compared with 57% of black women, with over 17% occupying the heaviest of three obesity levels, according to the investigators’ analysis of the most recent data from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey.
Weight groups in the study were defined by body mass index: underweight (< 18.5 kg/m2), normal weight (18.5-24.9), overweight (25.0-29.9), obesity class 1 (30.0-34.9), obesity class 2 (35.0-39.9), and obesity class 3 (≥ 40).
Compared with an earlier study reporting data for 1988-1994, “the greatest increase in the proportion of patients in the obesity class 3 category was among non-Hispanic black women,” Dr. Yang and Dr. Colditz wrote. Health and policy decision-makers should consider “population-based strategies helping to reduce modifiable risk factors such as physical environment interventions, enhancing primary care efforts to prevent and treat obesity, and altering societal norms of behavior,” they added.
The study was funded by the Washington University Transdiscliplinary Research on Energetics and Cancer Center, the Foundation for Barnes-Jewish Hospital, and the Breast Cancer Research Foundation. The investigators did not report any conflicts.
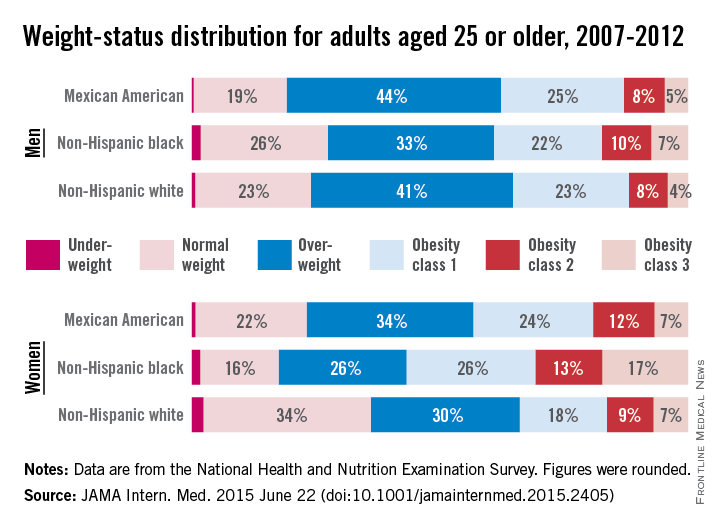
Three-quarters of men and two-thirds of women aged 25 years or older in the United States are either overweight or obese, according to a study published online June 22 in JAMA Internal Medicine.
During 2007-2012, about 40% of men were overweight and 35% were obese. For women, almost 30% were overweight and 37% were obese, Lin Yang, Ph.D., and Dr. Graham A. Colditz of Washington University, St. Louis, reported in a research letter (JAMA Intern. Med. 2015 June 22 [doi:10.1001/jamainternmed.2015.2405]).
Weight-status distributions across racial groups show that non-Hispanic whites were generally less obese than non-Hispanic blacks and Mexican Americans – an effect that was more pronounced among women. About 34% of white women were obese, compared with 57% of black women, with over 17% occupying the heaviest of three obesity levels, according to the investigators’ analysis of the most recent data from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey.
Weight groups in the study were defined by body mass index: underweight (< 18.5 kg/m2), normal weight (18.5-24.9), overweight (25.0-29.9), obesity class 1 (30.0-34.9), obesity class 2 (35.0-39.9), and obesity class 3 (≥ 40).
Compared with an earlier study reporting data for 1988-1994, “the greatest increase in the proportion of patients in the obesity class 3 category was among non-Hispanic black women,” Dr. Yang and Dr. Colditz wrote. Health and policy decision-makers should consider “population-based strategies helping to reduce modifiable risk factors such as physical environment interventions, enhancing primary care efforts to prevent and treat obesity, and altering societal norms of behavior,” they added.
The study was funded by the Washington University Transdiscliplinary Research on Energetics and Cancer Center, the Foundation for Barnes-Jewish Hospital, and the Breast Cancer Research Foundation. The investigators did not report any conflicts.

Three-quarters of men and two-thirds of women aged 25 years or older in the United States are either overweight or obese, according to a study published online June 22 in JAMA Internal Medicine.
During 2007-2012, about 40% of men were overweight and 35% were obese. For women, almost 30% were overweight and 37% were obese, Lin Yang, Ph.D., and Dr. Graham A. Colditz of Washington University, St. Louis, reported in a research letter (JAMA Intern. Med. 2015 June 22 [doi:10.1001/jamainternmed.2015.2405]).
Weight-status distributions across racial groups show that non-Hispanic whites were generally less obese than non-Hispanic blacks and Mexican Americans – an effect that was more pronounced among women. About 34% of white women were obese, compared with 57% of black women, with over 17% occupying the heaviest of three obesity levels, according to the investigators’ analysis of the most recent data from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey.
Weight groups in the study were defined by body mass index: underweight (< 18.5 kg/m2), normal weight (18.5-24.9), overweight (25.0-29.9), obesity class 1 (30.0-34.9), obesity class 2 (35.0-39.9), and obesity class 3 (≥ 40).
Compared with an earlier study reporting data for 1988-1994, “the greatest increase in the proportion of patients in the obesity class 3 category was among non-Hispanic black women,” Dr. Yang and Dr. Colditz wrote. Health and policy decision-makers should consider “population-based strategies helping to reduce modifiable risk factors such as physical environment interventions, enhancing primary care efforts to prevent and treat obesity, and altering societal norms of behavior,” they added.
The study was funded by the Washington University Transdiscliplinary Research on Energetics and Cancer Center, the Foundation for Barnes-Jewish Hospital, and the Breast Cancer Research Foundation. The investigators did not report any conflicts.

FROM JAMA INTERNAL MEDICINE