User login
Ancillary Testing for Rotavirus
Rotavirus gastroenteritis (RGE) accounts for approximately 70,000 pediatric hospitalizations annually in the United States.1 Costly microbiological assays are frequently performed in these patients to exclude concurrent serious bacterial infection (SBI), though the actual incidence of SBI is quite low.28 Our objectives were to describe the incidence of SBI in children evaluated at a community hospital and subsequently diagnosed with laboratory‐confirmed RGE and to determine whether ancillary testing was associated with prolonged length of stay (LOS) in hospitalized patients.
Materials and Methods
Study Design and Setting
This retrospective cohort study was conducted at the Albert Einstein Medical Center (AEMC, Philadelphia, PA) and approved by the AEMC institutional review board. During the study period, there were approximately 20,000 pediatric outpatient evaluations and 2000 pediatric hospitalizations per year.
Participants, Study Protocol, and Data Collection
Children under 18 years of age were included if they were evaluated in the pediatric clinic, emergency department (ED), or admitted to the pediatric floor at AEMC between January 1, 1998 and May 31, 2003 and tested positive for stool rotavirus antigen. Study patients were identified using 3 methods: first, International Classification of Diseases, ninth revision, Clinical Modification (ICD‐9‐CM) discharge diagnosis code for enteritis due to rotavirus (ICD‐9‐CM, 008.61); then, pediatric ward admission logs identified gastroenteritis patients; and finally, review of microbiology laboratory records confirmed the presence of a positive stool rotavirus antigen test. Patients with nosocomial RGE, defined by gastroenteritis symptoms manifesting 3 or more days after hospitalization, were excluded.
Study Definitions
Prolonged LOS was defined as hospitalization of 3 days as this value represented the 75th percentile for LOS in our cohort. Patients discharged directly from the ED were classified as not having a prolonged LOS. Bacteremia was defined as isolation of a known bacterial pathogen from blood culture, excluding isolates that reflected commensal skin flora. Fever was defined as temperature >38.0C. Tachypnea and tachycardia were defined using previously published age‐specific definitions.9 Bacterial meningitis required isolation of a bacterial pathogen from the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) or, in patients who received antibiotics prior to evaluation, the combination of CSF pleocytosis (defined as white blood cell count 8/mm3) and bacteria detectable on CSF Gram stain. Urinary tract infection was defined as growth of a single pathogen yielding 50,000 colony forming units (cfu)/mL from a catheterized specimen. Significant past medical history constituted any preexisting medical diagnosis.
Stool samples were assayed for rotaviral antigen by means of ImmunoCard STAT! Rotavirus (Meridian Bioscience, Cincinnati, OH). Abstracted data was entered onto standardized data collection forms and included demographic identifiers, clinical presentation, past medical history, laboratory investigations, and subsequent hospital course.
Data Analysis
Data were analyzed using STATA version 9.2 (Stata Corporation, College Station, TX). Categorical variables were described using counts and percentages. Continuous variables were described using median and interquartile range (IQR) values. Bivariate analyses were conducted to determine the association between potential risk factors and prolonged LOS. Categorical values were compared using either the 2 or the Fisher exact test. Continuous variables were compared with the Wilcoxon rank‐sum test. Adjusted analyses, using logistic regression, were then performed to identify factors independently associated with prolonged LOS. Variables with a P‐value <0.2 were considered for inclusion in the multivariable model. Candidate variables were entered into the model using a purposeful selection approach and included in the final multivariable model if they remained significant on adjusted analysis or if they were involved in confounding. Confounding was assumed to be present if adjustment for a variable produced an odds ratio (OR) that was >15% different than the unadjusted OR. Since prolonged LOS was defined as LOS >75th percentile for the cohort, we had 80% power (alpha = 0.05) to detect an OR of 4 or more for variables with a prevalence of 40% or greater in the study cohort.
Results
One hundred cases of RGE were initially identified; 6 patients were excluded4 with negative rotavirus stool antigen tests and 2 because the infection was nosocomially‐acquired. The remaining 94 cases were included in the analysis. Fifty‐eight (61.7%) of the patients were male, and 80 (85.1%) were African‐American. The median age was 8 months (IQR, 1 month to 16 years) and 83 patients (88.3%) were admitted to hospital. Fifty patients (53.2%) were febrile at presentation. The median length of stay was 2 days (IQR, 1‐3 days).
There were no patients with SBI (95% confidence interval [CI], 0%‐3.8%). Ten patients (12%) had received antibiotics in the 72 hours prior to evaluation; 6 of these 10 patients had blood cultures obtained. Peripheral blood cultures were drawn from 47 patients (50%). Of these, 43 (91.5%) were negative. Three cultures yielded viridans group streptococci, and 1 culture yielded vancomycin‐resistant Enterococcus species (VRE). The cultures yielding viridans group streptococci were drawn from 3 infants aged 42 days, 4 months, and 12 months. All 3 infants were febrile at presentation. In 2 of the 3 infants, 2 sets of blood cultures were drawn and viridans group streptococci was isolated from only 1 of the 2 cultures. The third infant made a rapid clinical recovery without antibiotic intervention and was discharged in less than 48 hours, belying microbiological evidence of bacteremia. Therefore, we classified all 3 viridans group streptococci cultures as contaminated specimens. The difference in the frequency with which blood cultures were performed in children younger than (59%) or older than (44%) 6 months of age was not statistically significant (2, P = 0.143).
The patient with VRE isolated from blood culture was a 4‐month‐old male who presented with 2 days of vomiting and diarrhea and a fever to 38.7C. The VRE culture, while potentially representing bacterial translocation in the setting of RGE, was presumed to be a contaminant when a repeat peripheral culture was negative. The patient had received amoxicillin for the treatment of otitis media prior to presentation and acquisition of cultures. The susceptibility testing results for ampicillin or amoxicillin were not available; however, the patient did not receive antibiotics for treatment of the VRE blood culture isolate.
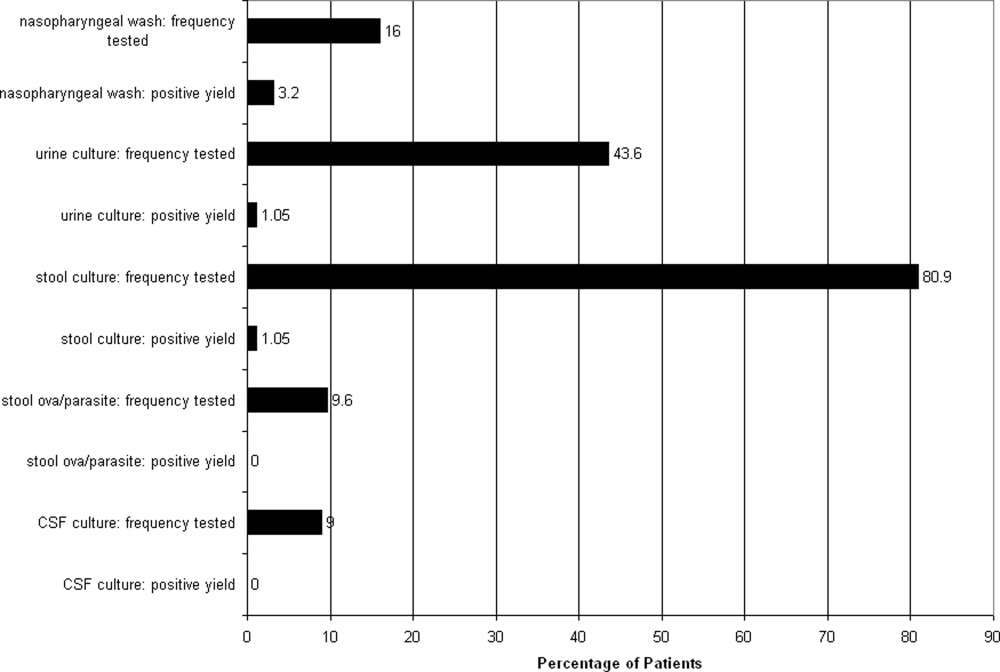
Multiple microbiological assays were performed (Figure 1). Many of the detected organisms were considered nonpathogenic. Stool bacterial cultures were obtained in 76 patients (80.9%) with only 1 (1.3%) positive isolate, Proteus mirabilis, considered nonpathogenic. Urine cultures from 41 patients (43.6%) yielded only 1 (2.4%) positive result, Staphylococcus aureus, deemed a contaminant. Nasopharyngeal washes from 15 patients (16%) revealed 3 (20%) positive results (respiratory syncytial virus in 2 patients and influenza virus in 1). Stool assayed for ova and parasites in 9 patients (9.6%) was negative. CSF cultured in 9 patients was also negative, although 3 samples demonstrated pleocytosis. Nonmicrobiological assays included 4 normal chest radiographs, 2 normal urinalyses, and 3 arterial blood gases revealing metabolic acidosis.

A complete blood count was obtained in 77 patients (81.9%). The median peripheral white blood cell count was 8800/mm3 (IQR, 6800 to 11,800). There were no differences between those with and without prolonged LOS on univariate analysis with regard to vital signs or initial symptoms such as tachypnea, fever, tachycardia, or other features associated with illness severity (eg, extent of dehydration). There were no differences in hematological or chemical parameters or with the performance of any other testing. In bivariate analyses, age 6 months (unadjusted OR, 3.43; 95% CI, 1.26‐9.50; P < 0.01) and collection of peripheral blood culture (OR, 3.12; 95% CI, 1.13‐8.98; P < 0.01) were associated with prolonged LOS. Other variables considered for inclusion in the multivariable model included duration of symptoms, presence of a preexisting medical condition, and performance of a nasopharyngeal wash for respiratory virus detection. In multivariable analysis, age <6 months (adjusted OR, 3.01; 95% CI, 1.17‐7.74; P = 0.022) and the performance of a blood culture (adjusted OR, 2.71; 95% CI, 1.03‐7.13; P = 0.043) were independently associated with a prolonged LOS.
Discussion
The absence of SBI in our relatively small cohort of children admitted to a community hospital with laboratory‐confirmed RGE supports earlier estimates of an incidence of less than 1%,5, 7 an incidence similar to that of occult bacteremia in febrile children 2 to 36 months of age following introduction of the heptavalent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine in 2000.10, 11 We found 13 cases reported in the English literature (Table 1). Several salient features are noted when comparing these case reports. All cases of SBI following laboratory‐confirmed RGE were characterized by the development of a second fever after the resolution of initial symptoms. These fevers presented at a mean day of hospitalization of 2.8 (range, 2‐5). Second fevers were high (mean, 39.2C; range, 38.2C to 40C). Cultures obtained other than peripheral blood cultures were only positive in 1 patient; this patient also had cellulitis and Escherichia coli was isolated from both blood and wound cultures.3 One of the reported children with bacteremia died, 2 cases of SBI following RGE were complicated by disseminated intravascular coagulopathy, and 1 case by acute renal failure. Enterobacter cloacae (n = 4) and Klebsiella pneumoniae (n = 3) were the most commonly isolated organisms from peripheral blood culture.
| References | Age (months)/Sex | Hospital day of bacteremia | Second fever (C)* | Organism Cultured from Peripheral Blood | Other Culture Results | Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||||
| Adler et al.2 | 9/♂ | 3 | 39.5 | Klebsiella pneumoniae | None | Full recovery after uncomplicated course |
| Adler et al.2 | 9/♂ | 2 | 40 | Escherichia coli | None | Full recovery after uncomplicated course |
| Adler et al.2 | 0.74/♀ | 3 | 39 | Klebsiella pneumoniae | Urine, CSF cultures negative | ARF, resolved to full recovery |
| Carneiro et al.4 | 10/♀ | 3 | 39.1 | ESBL‐producing Escherichia coli | Wound culture (cellulitis) from day 3 in PICU yielded ESBL‐producing Escherichia coli | Full recovery after DIC and transfer to PICU |
| Cicchetti et al.3 | 18/♂ | 2 | high | Pantoea agglomerans | None | DIC resolved with Protein C concentrate infusions |
| Gonzalez‐Carretero et al.5 | 1.5/♂ | 3 | 39.3 | Streptococcus viridans | Urine, CSF cultures negative | Full recovery after uncomplicated course |
| Gonzalez‐Carretero et al.5 | 10/♂ | 5 | 38.3 | Enterobacter cloacae | Stool culture negative | Full recovery after uncomplicated course |
| Kashiwagi et al.6 | 12/♂ | 7 | 38.0 | Klebsiella oxytoca | Not reported | Died |
| Lowenthal et. al7 | 6/♂ | 3 | 40 | Enterobacter cloacae | Urine culture negative | Full recovery after uncomplicated course |
| Lowenthal et. al7 | 4/♀ | 2 | 39.5 | Enterobacter cloacae | Urine culture negative | Full recovery after uncomplicated course without antibiotic therapy |
| Lowenthal et. al7 | 0.5/♀ | 3 | 38.2 | Klebsiella pneumoniae | CSF and urine cultures negative | Full recovery after uncomplicated course |
| Lowenthal et. al7 | 13/♀ | 2 | 39.3 | Enterobacter cloacae | Urine culture negative | Full recovery after uncomplicated course |
| Mel et. al8 | 16/♀ | 5 | 39.8 | ESBL‐producing Escherichia coli | Urine culture negative | Full recovery after uncomplicated course |
Many children in our study had ancillary laboratory testing performed. The results of these tests were typically normal and rarely affected clinical management in a positive manner. Bacteria and parasites are relatively rare causes of gastroenteritis in the United States in comparison with rotavirus, particularly during the winter months. However, stool was sent for bacterial culture in over 80% of patients and for ova and parasite detection in almost 10% of patients ultimately diagnosed with RGE. Furthermore, despite the relatively low prevalence of bacteremia since licensure of the Haemophilus influenzae type b vaccine, a majority of children had a complete blood count performed while one‐half also had blood obtained for culture. In our cohort, children 6 months and younger and those from whom a blood culture was collected were at an increased risk for prolonged LOS. It was not clear from medical record review whether children with prolonged LOS were kept in the hospital longer for the sole purpose of awaiting the results of blood cultures.
SBI rarely occurs in the context of RGE. While secondary fever seems to be a common manifestation, the sensitivity of secondary fever as a marker for SBI after RGE in this population is unknown. However, given the very low incidence, the potentially serious complications of SBI following laboratory confirmed RGE, and the likely successful management of these complications in the hospital setting, slightly longer hospitalizations for children under 1 year of age must be weighed against earlier discharges with instructions from clinicians to caregivers for careful monitoring of fever and outpatient follow‐up shortly after discharge.
This study has several limitations. First, the timing of the availability of the results of rotavirus antigen testing is not known. It is possible that the rapid availability of rotavirus test results in some circumstances encouraged clinicians to abandon tests seeking other sources of infection. Conversely, children with gastroenteritis in the context of a concurrent bacterial infection may have been less likely to undergo rotavirus stool antigen testing. This latter possibility would bias our findings toward underestimating the prevalence of concurrent bacterial infection among children with RGE. Second, this study was performed prior to licensure and widespread use of the currently‐licensed vaccine against rotavirus (Rotateq; Merck and Company, Whitehouse Station, NJ). Reductions in the burden of gastroenteritis caused by rotavirus may have a much more dramatic impact on resource utilization in the treatment of gastroenteritis than reductions in ancillary testing. Finally, this study was performed at a single urban community hospital and therefore cannot be generalized to other settings such as academic tertiary care centers. Furthermore, test ordering patterns may be local or regional and other community hospitals may exhibit different patterns. Further clarification of the role of ancillary testing in children presenting with diarrhea during the winter months is warranted since reducing the extent of such testing would dramatically reduce resource utilization for this illness. Finally, a blood culture was not obtained from all patients. Therefore, occult bacteremia attributable to RGE could not be detected. Since no patient in our study underwent subsequent clinical deterioration, we presume that any case of occult bacteremia resolved spontaneously and was not of clinical consequence, although such occurrences would cause us to underestimate the prevalence of SBI in this population.
Resource utilization in our cohort was high, while yield from microbiological investigations was low. This finding challenges the need to perform invasive, costly assays to exclude concurrent SBI in this population. It is possible that children with viral gastroenteritis caused by pathogens other than rotavirus are also at low risk of SBI. However, the diagnostic strategy that best identifies patients at risk for SBI following acute gastroenteritis is unknown. Further studies are needed to determine an ideal clinical approach to the infant with RGE.
- ,,,,,.Hospitalizations associated with rotavirus gastroenteritis in the United States, 1993‐2002.Pediatr Infect Dis J.2006;25(6):489–493.
- ,,,.Enteric gram‐negative sepsis complicating rotavirus gastroenteritis in previously healthy infants.Clin Pediatr (Phila).2005;44(4):351–354.
- ,,, et al.Septic shock complicating acute rotavirus‐associated diarrhea.Pediatr Infect Dis J.2006;25(6):571–572.
- ,,,,,.Pantoea agglomerans sepsis after rotavirus gastroenteritis.Pediatr Infect Dis J.2006;25(3):280–281.
- ,,.Rotavirus gastroenteritis leading to secondary bacteremia in previously healthy infants.Pediatrics.2006;118(5):2255–2256; author reply2256–2257.
- ,,, et al.Klebsiella oxytoca septicemia complicating rotavirus‐associated acute diarrhea.Pediatr Infect Dis J.2007;26(2):191–192.
- ,,,,.Secondary bacteremia after rotavirus gastroenteritis in infancy.Pediatrics.2006;117(1):224–226.
- ,,,.Extended spectrum beta‐lactamase‐positive Escherichia coli bacteremia complicating rotavirus gastroenteritis.Pediatr Infect Dis J.2006;25(10):962.
- ,,,.The Philadelphia Guide: Inpatient Pediatrics.Philadelphia:Lippincott Williams and Wilkins;2005.
- ,,, et al.Changing epidemiology of outpatient bacteremia in 3‐ to 36‐month‐old children after the introduction of the heptavalent‐conjugated pneumococcal vaccine.Pediatr Infect Dis J.2006;25(4):293–300.
- ,.Incidence of occult bacteremia among highly febrile young children in the era of the pneumococcal conjugate vaccine: a study from a Children's Hospital Emergency Department and Urgent Care Center.Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med.2004;158(7):671–675.
Rotavirus gastroenteritis (RGE) accounts for approximately 70,000 pediatric hospitalizations annually in the United States.1 Costly microbiological assays are frequently performed in these patients to exclude concurrent serious bacterial infection (SBI), though the actual incidence of SBI is quite low.28 Our objectives were to describe the incidence of SBI in children evaluated at a community hospital and subsequently diagnosed with laboratory‐confirmed RGE and to determine whether ancillary testing was associated with prolonged length of stay (LOS) in hospitalized patients.
Materials and Methods
Study Design and Setting
This retrospective cohort study was conducted at the Albert Einstein Medical Center (AEMC, Philadelphia, PA) and approved by the AEMC institutional review board. During the study period, there were approximately 20,000 pediatric outpatient evaluations and 2000 pediatric hospitalizations per year.
Participants, Study Protocol, and Data Collection
Children under 18 years of age were included if they were evaluated in the pediatric clinic, emergency department (ED), or admitted to the pediatric floor at AEMC between January 1, 1998 and May 31, 2003 and tested positive for stool rotavirus antigen. Study patients were identified using 3 methods: first, International Classification of Diseases, ninth revision, Clinical Modification (ICD‐9‐CM) discharge diagnosis code for enteritis due to rotavirus (ICD‐9‐CM, 008.61); then, pediatric ward admission logs identified gastroenteritis patients; and finally, review of microbiology laboratory records confirmed the presence of a positive stool rotavirus antigen test. Patients with nosocomial RGE, defined by gastroenteritis symptoms manifesting 3 or more days after hospitalization, were excluded.
Study Definitions
Prolonged LOS was defined as hospitalization of 3 days as this value represented the 75th percentile for LOS in our cohort. Patients discharged directly from the ED were classified as not having a prolonged LOS. Bacteremia was defined as isolation of a known bacterial pathogen from blood culture, excluding isolates that reflected commensal skin flora. Fever was defined as temperature >38.0C. Tachypnea and tachycardia were defined using previously published age‐specific definitions.9 Bacterial meningitis required isolation of a bacterial pathogen from the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) or, in patients who received antibiotics prior to evaluation, the combination of CSF pleocytosis (defined as white blood cell count 8/mm3) and bacteria detectable on CSF Gram stain. Urinary tract infection was defined as growth of a single pathogen yielding 50,000 colony forming units (cfu)/mL from a catheterized specimen. Significant past medical history constituted any preexisting medical diagnosis.
Stool samples were assayed for rotaviral antigen by means of ImmunoCard STAT! Rotavirus (Meridian Bioscience, Cincinnati, OH). Abstracted data was entered onto standardized data collection forms and included demographic identifiers, clinical presentation, past medical history, laboratory investigations, and subsequent hospital course.
Data Analysis
Data were analyzed using STATA version 9.2 (Stata Corporation, College Station, TX). Categorical variables were described using counts and percentages. Continuous variables were described using median and interquartile range (IQR) values. Bivariate analyses were conducted to determine the association between potential risk factors and prolonged LOS. Categorical values were compared using either the 2 or the Fisher exact test. Continuous variables were compared with the Wilcoxon rank‐sum test. Adjusted analyses, using logistic regression, were then performed to identify factors independently associated with prolonged LOS. Variables with a P‐value <0.2 were considered for inclusion in the multivariable model. Candidate variables were entered into the model using a purposeful selection approach and included in the final multivariable model if they remained significant on adjusted analysis or if they were involved in confounding. Confounding was assumed to be present if adjustment for a variable produced an odds ratio (OR) that was >15% different than the unadjusted OR. Since prolonged LOS was defined as LOS >75th percentile for the cohort, we had 80% power (alpha = 0.05) to detect an OR of 4 or more for variables with a prevalence of 40% or greater in the study cohort.
Results
One hundred cases of RGE were initially identified; 6 patients were excluded4 with negative rotavirus stool antigen tests and 2 because the infection was nosocomially‐acquired. The remaining 94 cases were included in the analysis. Fifty‐eight (61.7%) of the patients were male, and 80 (85.1%) were African‐American. The median age was 8 months (IQR, 1 month to 16 years) and 83 patients (88.3%) were admitted to hospital. Fifty patients (53.2%) were febrile at presentation. The median length of stay was 2 days (IQR, 1‐3 days).
There were no patients with SBI (95% confidence interval [CI], 0%‐3.8%). Ten patients (12%) had received antibiotics in the 72 hours prior to evaluation; 6 of these 10 patients had blood cultures obtained. Peripheral blood cultures were drawn from 47 patients (50%). Of these, 43 (91.5%) were negative. Three cultures yielded viridans group streptococci, and 1 culture yielded vancomycin‐resistant Enterococcus species (VRE). The cultures yielding viridans group streptococci were drawn from 3 infants aged 42 days, 4 months, and 12 months. All 3 infants were febrile at presentation. In 2 of the 3 infants, 2 sets of blood cultures were drawn and viridans group streptococci was isolated from only 1 of the 2 cultures. The third infant made a rapid clinical recovery without antibiotic intervention and was discharged in less than 48 hours, belying microbiological evidence of bacteremia. Therefore, we classified all 3 viridans group streptococci cultures as contaminated specimens. The difference in the frequency with which blood cultures were performed in children younger than (59%) or older than (44%) 6 months of age was not statistically significant (2, P = 0.143).
The patient with VRE isolated from blood culture was a 4‐month‐old male who presented with 2 days of vomiting and diarrhea and a fever to 38.7C. The VRE culture, while potentially representing bacterial translocation in the setting of RGE, was presumed to be a contaminant when a repeat peripheral culture was negative. The patient had received amoxicillin for the treatment of otitis media prior to presentation and acquisition of cultures. The susceptibility testing results for ampicillin or amoxicillin were not available; however, the patient did not receive antibiotics for treatment of the VRE blood culture isolate.
Multiple microbiological assays were performed (Figure 1). Many of the detected organisms were considered nonpathogenic. Stool bacterial cultures were obtained in 76 patients (80.9%) with only 1 (1.3%) positive isolate, Proteus mirabilis, considered nonpathogenic. Urine cultures from 41 patients (43.6%) yielded only 1 (2.4%) positive result, Staphylococcus aureus, deemed a contaminant. Nasopharyngeal washes from 15 patients (16%) revealed 3 (20%) positive results (respiratory syncytial virus in 2 patients and influenza virus in 1). Stool assayed for ova and parasites in 9 patients (9.6%) was negative. CSF cultured in 9 patients was also negative, although 3 samples demonstrated pleocytosis. Nonmicrobiological assays included 4 normal chest radiographs, 2 normal urinalyses, and 3 arterial blood gases revealing metabolic acidosis.

A complete blood count was obtained in 77 patients (81.9%). The median peripheral white blood cell count was 8800/mm3 (IQR, 6800 to 11,800). There were no differences between those with and without prolonged LOS on univariate analysis with regard to vital signs or initial symptoms such as tachypnea, fever, tachycardia, or other features associated with illness severity (eg, extent of dehydration). There were no differences in hematological or chemical parameters or with the performance of any other testing. In bivariate analyses, age 6 months (unadjusted OR, 3.43; 95% CI, 1.26‐9.50; P < 0.01) and collection of peripheral blood culture (OR, 3.12; 95% CI, 1.13‐8.98; P < 0.01) were associated with prolonged LOS. Other variables considered for inclusion in the multivariable model included duration of symptoms, presence of a preexisting medical condition, and performance of a nasopharyngeal wash for respiratory virus detection. In multivariable analysis, age <6 months (adjusted OR, 3.01; 95% CI, 1.17‐7.74; P = 0.022) and the performance of a blood culture (adjusted OR, 2.71; 95% CI, 1.03‐7.13; P = 0.043) were independently associated with a prolonged LOS.
Discussion
The absence of SBI in our relatively small cohort of children admitted to a community hospital with laboratory‐confirmed RGE supports earlier estimates of an incidence of less than 1%,5, 7 an incidence similar to that of occult bacteremia in febrile children 2 to 36 months of age following introduction of the heptavalent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine in 2000.10, 11 We found 13 cases reported in the English literature (Table 1). Several salient features are noted when comparing these case reports. All cases of SBI following laboratory‐confirmed RGE were characterized by the development of a second fever after the resolution of initial symptoms. These fevers presented at a mean day of hospitalization of 2.8 (range, 2‐5). Second fevers were high (mean, 39.2C; range, 38.2C to 40C). Cultures obtained other than peripheral blood cultures were only positive in 1 patient; this patient also had cellulitis and Escherichia coli was isolated from both blood and wound cultures.3 One of the reported children with bacteremia died, 2 cases of SBI following RGE were complicated by disseminated intravascular coagulopathy, and 1 case by acute renal failure. Enterobacter cloacae (n = 4) and Klebsiella pneumoniae (n = 3) were the most commonly isolated organisms from peripheral blood culture.
| References | Age (months)/Sex | Hospital day of bacteremia | Second fever (C)* | Organism Cultured from Peripheral Blood | Other Culture Results | Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||||
| Adler et al.2 | 9/♂ | 3 | 39.5 | Klebsiella pneumoniae | None | Full recovery after uncomplicated course |
| Adler et al.2 | 9/♂ | 2 | 40 | Escherichia coli | None | Full recovery after uncomplicated course |
| Adler et al.2 | 0.74/♀ | 3 | 39 | Klebsiella pneumoniae | Urine, CSF cultures negative | ARF, resolved to full recovery |
| Carneiro et al.4 | 10/♀ | 3 | 39.1 | ESBL‐producing Escherichia coli | Wound culture (cellulitis) from day 3 in PICU yielded ESBL‐producing Escherichia coli | Full recovery after DIC and transfer to PICU |
| Cicchetti et al.3 | 18/♂ | 2 | high | Pantoea agglomerans | None | DIC resolved with Protein C concentrate infusions |
| Gonzalez‐Carretero et al.5 | 1.5/♂ | 3 | 39.3 | Streptococcus viridans | Urine, CSF cultures negative | Full recovery after uncomplicated course |
| Gonzalez‐Carretero et al.5 | 10/♂ | 5 | 38.3 | Enterobacter cloacae | Stool culture negative | Full recovery after uncomplicated course |
| Kashiwagi et al.6 | 12/♂ | 7 | 38.0 | Klebsiella oxytoca | Not reported | Died |
| Lowenthal et. al7 | 6/♂ | 3 | 40 | Enterobacter cloacae | Urine culture negative | Full recovery after uncomplicated course |
| Lowenthal et. al7 | 4/♀ | 2 | 39.5 | Enterobacter cloacae | Urine culture negative | Full recovery after uncomplicated course without antibiotic therapy |
| Lowenthal et. al7 | 0.5/♀ | 3 | 38.2 | Klebsiella pneumoniae | CSF and urine cultures negative | Full recovery after uncomplicated course |
| Lowenthal et. al7 | 13/♀ | 2 | 39.3 | Enterobacter cloacae | Urine culture negative | Full recovery after uncomplicated course |
| Mel et. al8 | 16/♀ | 5 | 39.8 | ESBL‐producing Escherichia coli | Urine culture negative | Full recovery after uncomplicated course |
Many children in our study had ancillary laboratory testing performed. The results of these tests were typically normal and rarely affected clinical management in a positive manner. Bacteria and parasites are relatively rare causes of gastroenteritis in the United States in comparison with rotavirus, particularly during the winter months. However, stool was sent for bacterial culture in over 80% of patients and for ova and parasite detection in almost 10% of patients ultimately diagnosed with RGE. Furthermore, despite the relatively low prevalence of bacteremia since licensure of the Haemophilus influenzae type b vaccine, a majority of children had a complete blood count performed while one‐half also had blood obtained for culture. In our cohort, children 6 months and younger and those from whom a blood culture was collected were at an increased risk for prolonged LOS. It was not clear from medical record review whether children with prolonged LOS were kept in the hospital longer for the sole purpose of awaiting the results of blood cultures.
SBI rarely occurs in the context of RGE. While secondary fever seems to be a common manifestation, the sensitivity of secondary fever as a marker for SBI after RGE in this population is unknown. However, given the very low incidence, the potentially serious complications of SBI following laboratory confirmed RGE, and the likely successful management of these complications in the hospital setting, slightly longer hospitalizations for children under 1 year of age must be weighed against earlier discharges with instructions from clinicians to caregivers for careful monitoring of fever and outpatient follow‐up shortly after discharge.
This study has several limitations. First, the timing of the availability of the results of rotavirus antigen testing is not known. It is possible that the rapid availability of rotavirus test results in some circumstances encouraged clinicians to abandon tests seeking other sources of infection. Conversely, children with gastroenteritis in the context of a concurrent bacterial infection may have been less likely to undergo rotavirus stool antigen testing. This latter possibility would bias our findings toward underestimating the prevalence of concurrent bacterial infection among children with RGE. Second, this study was performed prior to licensure and widespread use of the currently‐licensed vaccine against rotavirus (Rotateq; Merck and Company, Whitehouse Station, NJ). Reductions in the burden of gastroenteritis caused by rotavirus may have a much more dramatic impact on resource utilization in the treatment of gastroenteritis than reductions in ancillary testing. Finally, this study was performed at a single urban community hospital and therefore cannot be generalized to other settings such as academic tertiary care centers. Furthermore, test ordering patterns may be local or regional and other community hospitals may exhibit different patterns. Further clarification of the role of ancillary testing in children presenting with diarrhea during the winter months is warranted since reducing the extent of such testing would dramatically reduce resource utilization for this illness. Finally, a blood culture was not obtained from all patients. Therefore, occult bacteremia attributable to RGE could not be detected. Since no patient in our study underwent subsequent clinical deterioration, we presume that any case of occult bacteremia resolved spontaneously and was not of clinical consequence, although such occurrences would cause us to underestimate the prevalence of SBI in this population.
Resource utilization in our cohort was high, while yield from microbiological investigations was low. This finding challenges the need to perform invasive, costly assays to exclude concurrent SBI in this population. It is possible that children with viral gastroenteritis caused by pathogens other than rotavirus are also at low risk of SBI. However, the diagnostic strategy that best identifies patients at risk for SBI following acute gastroenteritis is unknown. Further studies are needed to determine an ideal clinical approach to the infant with RGE.
Rotavirus gastroenteritis (RGE) accounts for approximately 70,000 pediatric hospitalizations annually in the United States.1 Costly microbiological assays are frequently performed in these patients to exclude concurrent serious bacterial infection (SBI), though the actual incidence of SBI is quite low.28 Our objectives were to describe the incidence of SBI in children evaluated at a community hospital and subsequently diagnosed with laboratory‐confirmed RGE and to determine whether ancillary testing was associated with prolonged length of stay (LOS) in hospitalized patients.
Materials and Methods
Study Design and Setting
This retrospective cohort study was conducted at the Albert Einstein Medical Center (AEMC, Philadelphia, PA) and approved by the AEMC institutional review board. During the study period, there were approximately 20,000 pediatric outpatient evaluations and 2000 pediatric hospitalizations per year.
Participants, Study Protocol, and Data Collection
Children under 18 years of age were included if they were evaluated in the pediatric clinic, emergency department (ED), or admitted to the pediatric floor at AEMC between January 1, 1998 and May 31, 2003 and tested positive for stool rotavirus antigen. Study patients were identified using 3 methods: first, International Classification of Diseases, ninth revision, Clinical Modification (ICD‐9‐CM) discharge diagnosis code for enteritis due to rotavirus (ICD‐9‐CM, 008.61); then, pediatric ward admission logs identified gastroenteritis patients; and finally, review of microbiology laboratory records confirmed the presence of a positive stool rotavirus antigen test. Patients with nosocomial RGE, defined by gastroenteritis symptoms manifesting 3 or more days after hospitalization, were excluded.
Study Definitions
Prolonged LOS was defined as hospitalization of 3 days as this value represented the 75th percentile for LOS in our cohort. Patients discharged directly from the ED were classified as not having a prolonged LOS. Bacteremia was defined as isolation of a known bacterial pathogen from blood culture, excluding isolates that reflected commensal skin flora. Fever was defined as temperature >38.0C. Tachypnea and tachycardia were defined using previously published age‐specific definitions.9 Bacterial meningitis required isolation of a bacterial pathogen from the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) or, in patients who received antibiotics prior to evaluation, the combination of CSF pleocytosis (defined as white blood cell count 8/mm3) and bacteria detectable on CSF Gram stain. Urinary tract infection was defined as growth of a single pathogen yielding 50,000 colony forming units (cfu)/mL from a catheterized specimen. Significant past medical history constituted any preexisting medical diagnosis.
Stool samples were assayed for rotaviral antigen by means of ImmunoCard STAT! Rotavirus (Meridian Bioscience, Cincinnati, OH). Abstracted data was entered onto standardized data collection forms and included demographic identifiers, clinical presentation, past medical history, laboratory investigations, and subsequent hospital course.
Data Analysis
Data were analyzed using STATA version 9.2 (Stata Corporation, College Station, TX). Categorical variables were described using counts and percentages. Continuous variables were described using median and interquartile range (IQR) values. Bivariate analyses were conducted to determine the association between potential risk factors and prolonged LOS. Categorical values were compared using either the 2 or the Fisher exact test. Continuous variables were compared with the Wilcoxon rank‐sum test. Adjusted analyses, using logistic regression, were then performed to identify factors independently associated with prolonged LOS. Variables with a P‐value <0.2 were considered for inclusion in the multivariable model. Candidate variables were entered into the model using a purposeful selection approach and included in the final multivariable model if they remained significant on adjusted analysis or if they were involved in confounding. Confounding was assumed to be present if adjustment for a variable produced an odds ratio (OR) that was >15% different than the unadjusted OR. Since prolonged LOS was defined as LOS >75th percentile for the cohort, we had 80% power (alpha = 0.05) to detect an OR of 4 or more for variables with a prevalence of 40% or greater in the study cohort.
Results
One hundred cases of RGE were initially identified; 6 patients were excluded4 with negative rotavirus stool antigen tests and 2 because the infection was nosocomially‐acquired. The remaining 94 cases were included in the analysis. Fifty‐eight (61.7%) of the patients were male, and 80 (85.1%) were African‐American. The median age was 8 months (IQR, 1 month to 16 years) and 83 patients (88.3%) were admitted to hospital. Fifty patients (53.2%) were febrile at presentation. The median length of stay was 2 days (IQR, 1‐3 days).
There were no patients with SBI (95% confidence interval [CI], 0%‐3.8%). Ten patients (12%) had received antibiotics in the 72 hours prior to evaluation; 6 of these 10 patients had blood cultures obtained. Peripheral blood cultures were drawn from 47 patients (50%). Of these, 43 (91.5%) were negative. Three cultures yielded viridans group streptococci, and 1 culture yielded vancomycin‐resistant Enterococcus species (VRE). The cultures yielding viridans group streptococci were drawn from 3 infants aged 42 days, 4 months, and 12 months. All 3 infants were febrile at presentation. In 2 of the 3 infants, 2 sets of blood cultures were drawn and viridans group streptococci was isolated from only 1 of the 2 cultures. The third infant made a rapid clinical recovery without antibiotic intervention and was discharged in less than 48 hours, belying microbiological evidence of bacteremia. Therefore, we classified all 3 viridans group streptococci cultures as contaminated specimens. The difference in the frequency with which blood cultures were performed in children younger than (59%) or older than (44%) 6 months of age was not statistically significant (2, P = 0.143).
The patient with VRE isolated from blood culture was a 4‐month‐old male who presented with 2 days of vomiting and diarrhea and a fever to 38.7C. The VRE culture, while potentially representing bacterial translocation in the setting of RGE, was presumed to be a contaminant when a repeat peripheral culture was negative. The patient had received amoxicillin for the treatment of otitis media prior to presentation and acquisition of cultures. The susceptibility testing results for ampicillin or amoxicillin were not available; however, the patient did not receive antibiotics for treatment of the VRE blood culture isolate.
Multiple microbiological assays were performed (Figure 1). Many of the detected organisms were considered nonpathogenic. Stool bacterial cultures were obtained in 76 patients (80.9%) with only 1 (1.3%) positive isolate, Proteus mirabilis, considered nonpathogenic. Urine cultures from 41 patients (43.6%) yielded only 1 (2.4%) positive result, Staphylococcus aureus, deemed a contaminant. Nasopharyngeal washes from 15 patients (16%) revealed 3 (20%) positive results (respiratory syncytial virus in 2 patients and influenza virus in 1). Stool assayed for ova and parasites in 9 patients (9.6%) was negative. CSF cultured in 9 patients was also negative, although 3 samples demonstrated pleocytosis. Nonmicrobiological assays included 4 normal chest radiographs, 2 normal urinalyses, and 3 arterial blood gases revealing metabolic acidosis.

A complete blood count was obtained in 77 patients (81.9%). The median peripheral white blood cell count was 8800/mm3 (IQR, 6800 to 11,800). There were no differences between those with and without prolonged LOS on univariate analysis with regard to vital signs or initial symptoms such as tachypnea, fever, tachycardia, or other features associated with illness severity (eg, extent of dehydration). There were no differences in hematological or chemical parameters or with the performance of any other testing. In bivariate analyses, age 6 months (unadjusted OR, 3.43; 95% CI, 1.26‐9.50; P < 0.01) and collection of peripheral blood culture (OR, 3.12; 95% CI, 1.13‐8.98; P < 0.01) were associated with prolonged LOS. Other variables considered for inclusion in the multivariable model included duration of symptoms, presence of a preexisting medical condition, and performance of a nasopharyngeal wash for respiratory virus detection. In multivariable analysis, age <6 months (adjusted OR, 3.01; 95% CI, 1.17‐7.74; P = 0.022) and the performance of a blood culture (adjusted OR, 2.71; 95% CI, 1.03‐7.13; P = 0.043) were independently associated with a prolonged LOS.
Discussion
The absence of SBI in our relatively small cohort of children admitted to a community hospital with laboratory‐confirmed RGE supports earlier estimates of an incidence of less than 1%,5, 7 an incidence similar to that of occult bacteremia in febrile children 2 to 36 months of age following introduction of the heptavalent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine in 2000.10, 11 We found 13 cases reported in the English literature (Table 1). Several salient features are noted when comparing these case reports. All cases of SBI following laboratory‐confirmed RGE were characterized by the development of a second fever after the resolution of initial symptoms. These fevers presented at a mean day of hospitalization of 2.8 (range, 2‐5). Second fevers were high (mean, 39.2C; range, 38.2C to 40C). Cultures obtained other than peripheral blood cultures were only positive in 1 patient; this patient also had cellulitis and Escherichia coli was isolated from both blood and wound cultures.3 One of the reported children with bacteremia died, 2 cases of SBI following RGE were complicated by disseminated intravascular coagulopathy, and 1 case by acute renal failure. Enterobacter cloacae (n = 4) and Klebsiella pneumoniae (n = 3) were the most commonly isolated organisms from peripheral blood culture.
| References | Age (months)/Sex | Hospital day of bacteremia | Second fever (C)* | Organism Cultured from Peripheral Blood | Other Culture Results | Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||||
| Adler et al.2 | 9/♂ | 3 | 39.5 | Klebsiella pneumoniae | None | Full recovery after uncomplicated course |
| Adler et al.2 | 9/♂ | 2 | 40 | Escherichia coli | None | Full recovery after uncomplicated course |
| Adler et al.2 | 0.74/♀ | 3 | 39 | Klebsiella pneumoniae | Urine, CSF cultures negative | ARF, resolved to full recovery |
| Carneiro et al.4 | 10/♀ | 3 | 39.1 | ESBL‐producing Escherichia coli | Wound culture (cellulitis) from day 3 in PICU yielded ESBL‐producing Escherichia coli | Full recovery after DIC and transfer to PICU |
| Cicchetti et al.3 | 18/♂ | 2 | high | Pantoea agglomerans | None | DIC resolved with Protein C concentrate infusions |
| Gonzalez‐Carretero et al.5 | 1.5/♂ | 3 | 39.3 | Streptococcus viridans | Urine, CSF cultures negative | Full recovery after uncomplicated course |
| Gonzalez‐Carretero et al.5 | 10/♂ | 5 | 38.3 | Enterobacter cloacae | Stool culture negative | Full recovery after uncomplicated course |
| Kashiwagi et al.6 | 12/♂ | 7 | 38.0 | Klebsiella oxytoca | Not reported | Died |
| Lowenthal et. al7 | 6/♂ | 3 | 40 | Enterobacter cloacae | Urine culture negative | Full recovery after uncomplicated course |
| Lowenthal et. al7 | 4/♀ | 2 | 39.5 | Enterobacter cloacae | Urine culture negative | Full recovery after uncomplicated course without antibiotic therapy |
| Lowenthal et. al7 | 0.5/♀ | 3 | 38.2 | Klebsiella pneumoniae | CSF and urine cultures negative | Full recovery after uncomplicated course |
| Lowenthal et. al7 | 13/♀ | 2 | 39.3 | Enterobacter cloacae | Urine culture negative | Full recovery after uncomplicated course |
| Mel et. al8 | 16/♀ | 5 | 39.8 | ESBL‐producing Escherichia coli | Urine culture negative | Full recovery after uncomplicated course |
Many children in our study had ancillary laboratory testing performed. The results of these tests were typically normal and rarely affected clinical management in a positive manner. Bacteria and parasites are relatively rare causes of gastroenteritis in the United States in comparison with rotavirus, particularly during the winter months. However, stool was sent for bacterial culture in over 80% of patients and for ova and parasite detection in almost 10% of patients ultimately diagnosed with RGE. Furthermore, despite the relatively low prevalence of bacteremia since licensure of the Haemophilus influenzae type b vaccine, a majority of children had a complete blood count performed while one‐half also had blood obtained for culture. In our cohort, children 6 months and younger and those from whom a blood culture was collected were at an increased risk for prolonged LOS. It was not clear from medical record review whether children with prolonged LOS were kept in the hospital longer for the sole purpose of awaiting the results of blood cultures.
SBI rarely occurs in the context of RGE. While secondary fever seems to be a common manifestation, the sensitivity of secondary fever as a marker for SBI after RGE in this population is unknown. However, given the very low incidence, the potentially serious complications of SBI following laboratory confirmed RGE, and the likely successful management of these complications in the hospital setting, slightly longer hospitalizations for children under 1 year of age must be weighed against earlier discharges with instructions from clinicians to caregivers for careful monitoring of fever and outpatient follow‐up shortly after discharge.
This study has several limitations. First, the timing of the availability of the results of rotavirus antigen testing is not known. It is possible that the rapid availability of rotavirus test results in some circumstances encouraged clinicians to abandon tests seeking other sources of infection. Conversely, children with gastroenteritis in the context of a concurrent bacterial infection may have been less likely to undergo rotavirus stool antigen testing. This latter possibility would bias our findings toward underestimating the prevalence of concurrent bacterial infection among children with RGE. Second, this study was performed prior to licensure and widespread use of the currently‐licensed vaccine against rotavirus (Rotateq; Merck and Company, Whitehouse Station, NJ). Reductions in the burden of gastroenteritis caused by rotavirus may have a much more dramatic impact on resource utilization in the treatment of gastroenteritis than reductions in ancillary testing. Finally, this study was performed at a single urban community hospital and therefore cannot be generalized to other settings such as academic tertiary care centers. Furthermore, test ordering patterns may be local or regional and other community hospitals may exhibit different patterns. Further clarification of the role of ancillary testing in children presenting with diarrhea during the winter months is warranted since reducing the extent of such testing would dramatically reduce resource utilization for this illness. Finally, a blood culture was not obtained from all patients. Therefore, occult bacteremia attributable to RGE could not be detected. Since no patient in our study underwent subsequent clinical deterioration, we presume that any case of occult bacteremia resolved spontaneously and was not of clinical consequence, although such occurrences would cause us to underestimate the prevalence of SBI in this population.
Resource utilization in our cohort was high, while yield from microbiological investigations was low. This finding challenges the need to perform invasive, costly assays to exclude concurrent SBI in this population. It is possible that children with viral gastroenteritis caused by pathogens other than rotavirus are also at low risk of SBI. However, the diagnostic strategy that best identifies patients at risk for SBI following acute gastroenteritis is unknown. Further studies are needed to determine an ideal clinical approach to the infant with RGE.
- ,,,,,.Hospitalizations associated with rotavirus gastroenteritis in the United States, 1993‐2002.Pediatr Infect Dis J.2006;25(6):489–493.
- ,,,.Enteric gram‐negative sepsis complicating rotavirus gastroenteritis in previously healthy infants.Clin Pediatr (Phila).2005;44(4):351–354.
- ,,, et al.Septic shock complicating acute rotavirus‐associated diarrhea.Pediatr Infect Dis J.2006;25(6):571–572.
- ,,,,,.Pantoea agglomerans sepsis after rotavirus gastroenteritis.Pediatr Infect Dis J.2006;25(3):280–281.
- ,,.Rotavirus gastroenteritis leading to secondary bacteremia in previously healthy infants.Pediatrics.2006;118(5):2255–2256; author reply2256–2257.
- ,,, et al.Klebsiella oxytoca septicemia complicating rotavirus‐associated acute diarrhea.Pediatr Infect Dis J.2007;26(2):191–192.
- ,,,,.Secondary bacteremia after rotavirus gastroenteritis in infancy.Pediatrics.2006;117(1):224–226.
- ,,,.Extended spectrum beta‐lactamase‐positive Escherichia coli bacteremia complicating rotavirus gastroenteritis.Pediatr Infect Dis J.2006;25(10):962.
- ,,,.The Philadelphia Guide: Inpatient Pediatrics.Philadelphia:Lippincott Williams and Wilkins;2005.
- ,,, et al.Changing epidemiology of outpatient bacteremia in 3‐ to 36‐month‐old children after the introduction of the heptavalent‐conjugated pneumococcal vaccine.Pediatr Infect Dis J.2006;25(4):293–300.
- ,.Incidence of occult bacteremia among highly febrile young children in the era of the pneumococcal conjugate vaccine: a study from a Children's Hospital Emergency Department and Urgent Care Center.Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med.2004;158(7):671–675.
- ,,,,,.Hospitalizations associated with rotavirus gastroenteritis in the United States, 1993‐2002.Pediatr Infect Dis J.2006;25(6):489–493.
- ,,,.Enteric gram‐negative sepsis complicating rotavirus gastroenteritis in previously healthy infants.Clin Pediatr (Phila).2005;44(4):351–354.
- ,,, et al.Septic shock complicating acute rotavirus‐associated diarrhea.Pediatr Infect Dis J.2006;25(6):571–572.
- ,,,,,.Pantoea agglomerans sepsis after rotavirus gastroenteritis.Pediatr Infect Dis J.2006;25(3):280–281.
- ,,.Rotavirus gastroenteritis leading to secondary bacteremia in previously healthy infants.Pediatrics.2006;118(5):2255–2256; author reply2256–2257.
- ,,, et al.Klebsiella oxytoca septicemia complicating rotavirus‐associated acute diarrhea.Pediatr Infect Dis J.2007;26(2):191–192.
- ,,,,.Secondary bacteremia after rotavirus gastroenteritis in infancy.Pediatrics.2006;117(1):224–226.
- ,,,.Extended spectrum beta‐lactamase‐positive Escherichia coli bacteremia complicating rotavirus gastroenteritis.Pediatr Infect Dis J.2006;25(10):962.
- ,,,.The Philadelphia Guide: Inpatient Pediatrics.Philadelphia:Lippincott Williams and Wilkins;2005.
- ,,, et al.Changing epidemiology of outpatient bacteremia in 3‐ to 36‐month‐old children after the introduction of the heptavalent‐conjugated pneumococcal vaccine.Pediatr Infect Dis J.2006;25(4):293–300.
- ,.Incidence of occult bacteremia among highly febrile young children in the era of the pneumococcal conjugate vaccine: a study from a Children's Hospital Emergency Department and Urgent Care Center.Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med.2004;158(7):671–675.
Copyright © 2009 Society of Hospital Medicine