User login
Electronic consultation (e-consult) is designed to increase access to specialty care by facilitating communication between primary care and specialty clinicians without the need for outpatient face-to-face encounters.1–4 In 2011, the US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) implemented an e-consult program as a component of its overall strategy to increase access to specialty services, reduce costs of care, and reduce appointment travel burden on patients.
E-consult has substantially increased within the VA since its implementation.5,6 Consistent with limited evaluations from other health care systems, evaluations of the VA e-consult program demonstrated reduced costs, reduced travel time for patients, and improved access to specialty care.2,5–11 However, there is wide variation in e-consult use across VA specialties, facilities, and regions.5,6,12,13 For example, hematology, preoperative evaluation, neurosurgery, endocrinology, and infectious diseases use e-consults more frequently when compared with in-person consults in the VA.6 Reasons for this variation or specific barriers and facilitators of using e-consults have not been described.
Prior qualitative studies report that primary care practitioners (PCPs) describe e-consults as convenient, educational, beneficial for patient care, and useful for improving patient access to specialty care.8,14,15 One study identified limited PCP knowledge of e-consults as a barrier to use.16 Specialists have reported that e-consult improves clinical communication, but increases their workload.1,14,17,18 These studies did not assess perspectives from both clinicians who initiate e-consults and those who respond to them. This is the first qualitative study to assess e-consult perceptions from perspectives of both PCPs and specialists among a large, national sample of VA clinicians who use e-consults. The objective of this study was to understand perspectives of e-consults between PCPs and specialists that may be relevant to increasing adoption in the VA.
Methods
The team (CL, ML, PG, 2 analysts under the guidance of GS and JS and support from RRK, and a biostatistician) conducted semistructured interviews with PCPs, specialists, and specialty division leaders who were employed by VA in 2016 and 2017. Specialties of interest were identified by the VA Office of Specialty Care and included cardiology, endocrinology, gastroenterology, and hematology.
E-Consult Procedures
Within the VA, the specific procedures used to initiate, triage and manage e-consults are coordinated at VA medical centers (VAMCs) and at the Veterans Integrated Service Network (VISN) regional level. E-consult can be requested by any clinician. Generally, e-consults are initiated by PCPs through standardized, specialty-specific templates. Recipients, typically specialists, respond by answering questions, suggesting additional testing and evaluation, or requesting an in-person visit. Communication is documented in the patient’s electronic health record (EHR). Specialists receive different levels of workload credit for responding to e-consults similar to a relative value unit reimbursement model. Training in the use of e-consults is available to practitioners but may vary at local and regional levels.
Recruitment
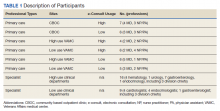
Our sample included PCPs, specialists, and specialty care division leaders. We first quantified e-consult rates (e-consults per 100 patient visits) between July 2016 and June 2017 at VA facilities within primary care and the 4 priority specialties and identified the 30 sites with the highest e-consult rates and 30 sites with the lowest e-consult rates. Sites with < 500 total visits, < 3 specialties, or without any e-consult visit during the study period were excluded. E-consult rates at community-based outpatient clinics were included with associated VAMCs. We then stratified PCPs by whether they were high or low users of e-consults (determined by the top and bottom users within each site) and credentials (MD vs nurse practitioner [NP] or physician assistant [PA]). Specialists were sampled based on their rate of use relative to colleagues within their site and the use rate of their division. We sampled division chiefs and individuals who had > 300 total visits and 1 e-consult during the study period. To recruit participants, the primary investigator sent an initial email and 2 reminder emails. The team followed up with respondents to schedule an interview.
Interview guides were designed to elicit rich descriptions of barriers and facilitators to e-consult use (eAppendix available at doi:10.12788/fp.0214). The team used the Practical Robust Implementation and Sustainability Model (PRISM), which considers factors along 6 domains for intervention planning, implementation, and sustainment.19 Telephone interviews lasted about 20 minutes and were conducted between September 2017 and March 2018. Interviews were recorded and transcribed verbatim.
Analysis
The team used an iterative, team-based, inductive/deductive approach to conventional content analysis.20,21 Initial code categories were created so that we could identify e-consult best practices—facilitators of e-consult that were recommended by both PCPs and specialists. Inductive codes or labels applied to identify meaningful quotations, phrases, or key terms were used to identify emergent ideas and were added throughout coding after discussion among team members. Consensus was reached using a team-based approach.21 Four analysts independently coded the same 3 transcripts and met to discuss points of divergence and convergence. Analyses continued with emergent themes, categories, and conclusions. Atlas.ti. v.7 was used for coding and data management.22
Results
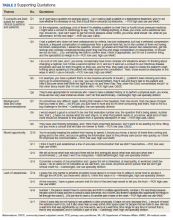
We conducted 34 interviews with clinicians (Table 1) from 13 VISNs. Four best-practice themes emerged among both PCPs and specialists, including that e-consults (1) are best suited for certain clinical questions and patients; (2) require relevant background information from requesting clinicians and clear recommendations from responding clinicians; (3) are a novel opportunity to provide efficient, transparent care; and (4) may not be fully adopted due to low awareness. Supporting quotations for the following findings are provided in Table 2.
Specific Clinical Questions and Patients
PCPs described specific patients and questions for which they most frequently used e-consults, such as for medication changes (Q1), determining treatment steps (Q2,3), and or clarifying laboratory or imaging findings. PCPs frequently used e-consults for patients who did not require a physical examination or when specialists could make recommendations without seeing patients face-to-face (Q3). An important use of e-consults described by PCPs was for treating conditions they could manage within primary care if additional guidance were available (Q4). Several PCPs and specialists also noted that e-consults were particularly useful for patients who were unable to travel or did not want face-to-face appointments (Q5). Notably, PCPs and specialists mentioned situations for which e-consults were inappropriate, including when a detailed history or physical examination was needed, or if a complex condition was suspected (Q6).
Background Data and Clear Recommendations
Participants described necessary data that should be included in high-quality e-consults. Specialists voiced frustration in time-consuming chart reviews that were often necessary when these data were not provided by the requestor. In some cases, specialists were unable to access necessary EHR data, which delayed responses (Q7). PCPs noted that the most useful responses carefully considered the question, used current patient information to determine treatments, provided clear recommendations, and defined who was responsible for next steps (Q8). PCPs and specialists stated that e-consult templates that required relevant information facilitated high-quality e-consults. Neither wanted to waste the other clinician's time (Q8).
A Novel Opportunity
Many PCPs felt that e-consults improved communication (eg, efficiency, response time), established new communication between clinicians, and reduced patients’ appointment burden (Q10, Q11). Many specialists felt that e-consults improved documentation of communication between clinicians and increased transparency of clinical decisions (Q12). Additionally, many specialists mentioned that e-consults capture previously informal curbside consults, enabling them to receive workload credit (Q13).
Lack of Awareness
Some noted that the biggest barrier to e-consults was not being aware of them generally, or which specialties offer e-consults (Q14). One PCP described e-consults as the best kept secret and found value in sharing the utility of e-consults with colleagues (Q15). All participants, including those who did not frequently use e-consults, felt that e-consults improved the quality of care by providing more timely care or better answers to clinical questions (Q16). Several practitioners also felt that e-consults increased access to specialty care. For example, specialists reported that e-consults enabled them to better manage patient load by using e-consults to answer relatively simple questions, reserving face-to-face consults for more complex patients (Q17).
Discussion
The objective of this study was to identify potential best practices for e-consults that may help increase their quality and use within the VA. We built on prior studies that offered insights on PCP and specialists’ overall satisfaction with e-consult by identifying several themes relevant to the further adoption of e-consults in the VA and elsewhere without a face-to-face visit.8,13,14,16–18 Future work may be beneficial in identifying whether the study themes identified can explain variation in e-consult use or whether addressing these factors might lead to increased or higher quality e-consult use. We are unaware of any qualitative study of comparable scale in a different health care system. Further, this is the first study to assess perspectives on e-consults among those who initiate and respond to them within the same health care system. Perhaps the most important finding from this study is that e-consults are generally viewed favorably, which is a necessary leverage point to increase their adoption within the system.
Clinicians reported several benefits to e-consults, including timely responses to clinical questions, efficient communication, allow for documentation of specialist recommendations, and help capture workload. These benefits are consistent with prior literature that indicates both PCPs and specialists in the VA and other health care systems feel that e-consults improves communication, decreases unnecessary visits, and improves quality of care.1,14,17,18 In particular, clinicians reported that e-consults improve their practice efficiency and efficacy. This is of critical importance given the pressures of providing timely access to primary and specialty care within the VA. Interestingly, many VA practitioners were unaware which specialties offered e-consults within their facilities, reflecting previous work showing that PCPs are often unaware of e-consult options.16 This may partially explain variation in e-consult use. Increasing awareness and educating clinicians on the benefits of e-consults may help promote use among non- and low users.
A common theme reported by both groups was the importance of providing necessary information within e-consult questions and responses. Specialists felt there was a need to ensure that PCPs provide relevant and patient-specific information that would enable them to efficiently and accurately answer questions without the need for extensive EHR review. This reflects previous work showing that specialists are often unable to respond to e-consult requests because they do not contain sufficient information.22 PCPs described a need to ensure that specialists’ responses included information that was detailed enough to make clinical decisions without the need for a reconsult. This highlights a common challenge to medical consultation, in that necessary or relevant information may not be apparent to all clinicians. To address this, there may be a role in developing enhanced, flexible templating that elicits necessary patient-specific information. Such a template may automatically pull relevant data from the EHR and prompt clinicians to provide important information. We did not assess how perspectives of templates varied, and further work could help define precisely what constitutes an effective template, including how it should capture appropriate patient data and how this impacts acceptability or use of e-consults generally. Collaboratively developed service agreements and e-consult templates could help guide PCPs and specialists to engage in efficient communication.
Another theme among both groups was that e-consult is most appropriate within specific clinical scenarios. Examples included review of laboratory results, questions about medication changes, or for patients who were reluctant to travel to appointments. Identifying and promoting specific opportunities for e-consults may help increase their use and align e-consult practices with scenarios that are likely to provide the most benefit to patients. For example, it could be helpful to understand the distance patients must travel for specialty care. Providing that information during clinical encounters could trigger clinicians to consider e-consults as an option. Future work might aim to identify clinical scenarios that clinicians feel are not well suited for e-consults and determine how to adapt them for those scenarios.
Limitations
Generalizability of these findings is limited given the qualitative study design. Participants’ descriptions of experiences with e-consults reflect the experiences of clinicians in the VA and may not reflect clinicians in other settings. We also interviewed a sample of clinicians who were already using e-consults. Important information could be learned from future work with those who have not yet adopted e-consult procedures or adopted and abandoned them.
Conclusions
E-consult is perceived as beneficial by VA PCPs and specialists. Participants suggested using e-consults for appropriate questions or patients and including necessary information and next steps in both the initial e-consult and response. Finding ways to facilitate e-consults with these suggestions in mind may increase delivery of high-quality e-consults. Future work could compare the findings of this work to similar work assessing clinicians perceptions of e-consults outside of the VA.
1. Battaglia C, Lambert-Kerzner A, Aron DC, et al. Evaluation of e-consults in the VHA: provider perspectives. Fed Pract. 2015;32(7):42-48.
2. Haverhals LM, Sayre G, Helfrich CD, et al. E-consult implementation: lessons learned using consolidated framework for implementation research. Am J Manag Care. 2015;21(12):e640-e647. Published 2015 Dec 1.
3. Sewell JL, Telischak KS, Day LW, Kirschner N, Weissman A. Preconsultation exchange in the United States: use, awareness, and attitudes. Am J Manag Care. 2014;20(12):e556-e564. Published 2014 Dec 1.
4. Horner K, Wagner E, Tufano J. Electronic consultations between primary and specialty care clinicians: early insights. Issue Brief (Commonw Fund). 2011;23:1-14.
5. Kirsh S, Carey E, Aron DC, et al. Impact of a national specialty e-consultation implementation project on access. Am J Manag Care. 2015;21(12):e648-654. Published 2015 Dec 1.
6. Saxon DR, Kaboli PJ, Haraldsson B, Wilson C, Ohl M, Augustine MR. Growth of electronic consultations in the Veterans Health Administration. Am J Manag Care. 2021;27(1):12-19. doi:10.37765/ajmc.2021.88572
7. Olayiwola JN, Anderson D, Jepeal N, et al. Electronic consultations to improve the primary care-specialty care interface for cardiology in the medically underserved: a cluster-randomized controlled trial. Ann Fam Med. 2016;14(2):133-140. doi:10.1370/afm.1869
8. Schettini P, Shah KP, O’Leary CP, et al. Keeping care connected: e-Consultation program improves access to nephrology care. J Telemed Telecare. 2019;25(3):142-150. doi:10.1177/1357633X17748350
9. Whittington MD, Ho PM, Kirsh SR, et al. Cost savings associated with electronic specialty consultations. Am J Manag Care. 2021;27(1):e16-e23. Published 2021 Jan 1. doi:10.37765/ajmc.2021.88579
10. Shipherd JC, Kauth MR, Matza A. Nationwide interdisciplinary e-consultation on transgender care in the Veterans Health Administration. Telemed J E Health. 2016;22(12):1008-1012. doi:10.1089/tmj.2016.0013
11. Strymish J, Gupte G, Afable MK, et al. Electronic consultations (E-consults): advancing infectious disease care in a large Veterans Affairs Healthcare System. Clin Infect Dis. 2017;64(8):1123-1125. doi:10.1093/cid/cix058
12. Williams KM, Kirsh S, Aron D, et al. Evaluation of the Veterans Health Administration’s Specialty Care Transformational Initiatives to promote patient-centered delivery of specialty care: a mixed-methods approach. Telemed J E-Health. 2017;23(7):577-589. doi:10.1089/tmj.2016.0166
13. US Department of Veterans Affairs, Veterans Health Administration, Specialty Care Transformational Initiative Evaluation Center. Evaluation of specialty care initiatives. Published 2013.
14. Vimalananda VG, Gupte G, Seraj SM, et al. Electronic consultations (e-consults) to improve access to specialty care: a systematic review and narrative synthesis. J Telemed Telecare. 2015;21(6):323-330. doi:10.1177/1357633X15582108
15. Lee M, Leonard C, Greene P, et al. Perspectives of VA primary care clinicians toward electronic consultation-related workload burden. JAMA Netw Open. 2020;3(10):e2018104. Published 2020 Oct 1. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.18104
16. Deeds SA, Dowdell KJ, Chew LD, Ackerman SL. Implementing an opt-in eConsult program at seven academic medical centers: a qualitative analysis of primary care provider experiences. J Gen Intern Med. 2019;34(8):1427-1433. doi:10.1007/s11606-019-05067-7
17. Rodriguez KL, Burkitt KH, Bayliss NK, et al. Veteran, primary care provider, and specialist satisfaction with electronic consultation. JMIR Med Inform. 2015;3(1):e5. Published 2015 Jan 14. doi:10.2196/medinform.3725
18. Gupte G, Vimalananda V, Simon SR, DeVito K, Clark J, Orlander JD. Disruptive innovation: implementation of electronic consultations in a Veterans Affairs Health Care System. JMIR Med Inform. 2016;4(1):e6. Published 2016 Feb 12. doi:10.2196/medinform.4801
19. Feldstein AC, Glasgow RE. A practical, robust implementation and sustainability model (PRISM) for integrating research findings into practice. Jt Comm J Qual Patient Saf. 2008;34(4):228-243. doi:10.1016/s1553-7250(08)34030-6
20. Patton MQ. Qualitative Research and Evaluation Methods. 3rd ed. Sage Publications; 2002.
21. Bradley EH, Curry LA, Devers KJ. Qualitative data analysis for health services research: developing taxonomy, themes, and theory. Health Serv Res. 2007;42(4):1758-1772. doi:10.1111/j.1475-6773.2006.00684.x
22. Kim EJ, Orlander JD, Afable M, et al. Cardiology electronic consultation (e-consult) use by primary care providers at VA medical centres in New England. J Telemed Telecare. 2019;25(6):370-377. doi:10.1177/1357633X18774468
Electronic consultation (e-consult) is designed to increase access to specialty care by facilitating communication between primary care and specialty clinicians without the need for outpatient face-to-face encounters.1–4 In 2011, the US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) implemented an e-consult program as a component of its overall strategy to increase access to specialty services, reduce costs of care, and reduce appointment travel burden on patients.
E-consult has substantially increased within the VA since its implementation.5,6 Consistent with limited evaluations from other health care systems, evaluations of the VA e-consult program demonstrated reduced costs, reduced travel time for patients, and improved access to specialty care.2,5–11 However, there is wide variation in e-consult use across VA specialties, facilities, and regions.5,6,12,13 For example, hematology, preoperative evaluation, neurosurgery, endocrinology, and infectious diseases use e-consults more frequently when compared with in-person consults in the VA.6 Reasons for this variation or specific barriers and facilitators of using e-consults have not been described.
Prior qualitative studies report that primary care practitioners (PCPs) describe e-consults as convenient, educational, beneficial for patient care, and useful for improving patient access to specialty care.8,14,15 One study identified limited PCP knowledge of e-consults as a barrier to use.16 Specialists have reported that e-consult improves clinical communication, but increases their workload.1,14,17,18 These studies did not assess perspectives from both clinicians who initiate e-consults and those who respond to them. This is the first qualitative study to assess e-consult perceptions from perspectives of both PCPs and specialists among a large, national sample of VA clinicians who use e-consults. The objective of this study was to understand perspectives of e-consults between PCPs and specialists that may be relevant to increasing adoption in the VA.
Methods
The team (CL, ML, PG, 2 analysts under the guidance of GS and JS and support from RRK, and a biostatistician) conducted semistructured interviews with PCPs, specialists, and specialty division leaders who were employed by VA in 2016 and 2017. Specialties of interest were identified by the VA Office of Specialty Care and included cardiology, endocrinology, gastroenterology, and hematology.
E-Consult Procedures
Within the VA, the specific procedures used to initiate, triage and manage e-consults are coordinated at VA medical centers (VAMCs) and at the Veterans Integrated Service Network (VISN) regional level. E-consult can be requested by any clinician. Generally, e-consults are initiated by PCPs through standardized, specialty-specific templates. Recipients, typically specialists, respond by answering questions, suggesting additional testing and evaluation, or requesting an in-person visit. Communication is documented in the patient’s electronic health record (EHR). Specialists receive different levels of workload credit for responding to e-consults similar to a relative value unit reimbursement model. Training in the use of e-consults is available to practitioners but may vary at local and regional levels.
Recruitment
Our sample included PCPs, specialists, and specialty care division leaders. We first quantified e-consult rates (e-consults per 100 patient visits) between July 2016 and June 2017 at VA facilities within primary care and the 4 priority specialties and identified the 30 sites with the highest e-consult rates and 30 sites with the lowest e-consult rates. Sites with < 500 total visits, < 3 specialties, or without any e-consult visit during the study period were excluded. E-consult rates at community-based outpatient clinics were included with associated VAMCs. We then stratified PCPs by whether they were high or low users of e-consults (determined by the top and bottom users within each site) and credentials (MD vs nurse practitioner [NP] or physician assistant [PA]). Specialists were sampled based on their rate of use relative to colleagues within their site and the use rate of their division. We sampled division chiefs and individuals who had > 300 total visits and 1 e-consult during the study period. To recruit participants, the primary investigator sent an initial email and 2 reminder emails. The team followed up with respondents to schedule an interview.
Interview guides were designed to elicit rich descriptions of barriers and facilitators to e-consult use (eAppendix available at doi:10.12788/fp.0214). The team used the Practical Robust Implementation and Sustainability Model (PRISM), which considers factors along 6 domains for intervention planning, implementation, and sustainment.19 Telephone interviews lasted about 20 minutes and were conducted between September 2017 and March 2018. Interviews were recorded and transcribed verbatim.
Analysis
The team used an iterative, team-based, inductive/deductive approach to conventional content analysis.20,21 Initial code categories were created so that we could identify e-consult best practices—facilitators of e-consult that were recommended by both PCPs and specialists. Inductive codes or labels applied to identify meaningful quotations, phrases, or key terms were used to identify emergent ideas and were added throughout coding after discussion among team members. Consensus was reached using a team-based approach.21 Four analysts independently coded the same 3 transcripts and met to discuss points of divergence and convergence. Analyses continued with emergent themes, categories, and conclusions. Atlas.ti. v.7 was used for coding and data management.22
Results
We conducted 34 interviews with clinicians (Table 1) from 13 VISNs. Four best-practice themes emerged among both PCPs and specialists, including that e-consults (1) are best suited for certain clinical questions and patients; (2) require relevant background information from requesting clinicians and clear recommendations from responding clinicians; (3) are a novel opportunity to provide efficient, transparent care; and (4) may not be fully adopted due to low awareness. Supporting quotations for the following findings are provided in Table 2.
Specific Clinical Questions and Patients
PCPs described specific patients and questions for which they most frequently used e-consults, such as for medication changes (Q1), determining treatment steps (Q2,3), and or clarifying laboratory or imaging findings. PCPs frequently used e-consults for patients who did not require a physical examination or when specialists could make recommendations without seeing patients face-to-face (Q3). An important use of e-consults described by PCPs was for treating conditions they could manage within primary care if additional guidance were available (Q4). Several PCPs and specialists also noted that e-consults were particularly useful for patients who were unable to travel or did not want face-to-face appointments (Q5). Notably, PCPs and specialists mentioned situations for which e-consults were inappropriate, including when a detailed history or physical examination was needed, or if a complex condition was suspected (Q6).
Background Data and Clear Recommendations
Participants described necessary data that should be included in high-quality e-consults. Specialists voiced frustration in time-consuming chart reviews that were often necessary when these data were not provided by the requestor. In some cases, specialists were unable to access necessary EHR data, which delayed responses (Q7). PCPs noted that the most useful responses carefully considered the question, used current patient information to determine treatments, provided clear recommendations, and defined who was responsible for next steps (Q8). PCPs and specialists stated that e-consult templates that required relevant information facilitated high-quality e-consults. Neither wanted to waste the other clinician's time (Q8).
A Novel Opportunity
Many PCPs felt that e-consults improved communication (eg, efficiency, response time), established new communication between clinicians, and reduced patients’ appointment burden (Q10, Q11). Many specialists felt that e-consults improved documentation of communication between clinicians and increased transparency of clinical decisions (Q12). Additionally, many specialists mentioned that e-consults capture previously informal curbside consults, enabling them to receive workload credit (Q13).
Lack of Awareness
Some noted that the biggest barrier to e-consults was not being aware of them generally, or which specialties offer e-consults (Q14). One PCP described e-consults as the best kept secret and found value in sharing the utility of e-consults with colleagues (Q15). All participants, including those who did not frequently use e-consults, felt that e-consults improved the quality of care by providing more timely care or better answers to clinical questions (Q16). Several practitioners also felt that e-consults increased access to specialty care. For example, specialists reported that e-consults enabled them to better manage patient load by using e-consults to answer relatively simple questions, reserving face-to-face consults for more complex patients (Q17).
Discussion
The objective of this study was to identify potential best practices for e-consults that may help increase their quality and use within the VA. We built on prior studies that offered insights on PCP and specialists’ overall satisfaction with e-consult by identifying several themes relevant to the further adoption of e-consults in the VA and elsewhere without a face-to-face visit.8,13,14,16–18 Future work may be beneficial in identifying whether the study themes identified can explain variation in e-consult use or whether addressing these factors might lead to increased or higher quality e-consult use. We are unaware of any qualitative study of comparable scale in a different health care system. Further, this is the first study to assess perspectives on e-consults among those who initiate and respond to them within the same health care system. Perhaps the most important finding from this study is that e-consults are generally viewed favorably, which is a necessary leverage point to increase their adoption within the system.
Clinicians reported several benefits to e-consults, including timely responses to clinical questions, efficient communication, allow for documentation of specialist recommendations, and help capture workload. These benefits are consistent with prior literature that indicates both PCPs and specialists in the VA and other health care systems feel that e-consults improves communication, decreases unnecessary visits, and improves quality of care.1,14,17,18 In particular, clinicians reported that e-consults improve their practice efficiency and efficacy. This is of critical importance given the pressures of providing timely access to primary and specialty care within the VA. Interestingly, many VA practitioners were unaware which specialties offered e-consults within their facilities, reflecting previous work showing that PCPs are often unaware of e-consult options.16 This may partially explain variation in e-consult use. Increasing awareness and educating clinicians on the benefits of e-consults may help promote use among non- and low users.
A common theme reported by both groups was the importance of providing necessary information within e-consult questions and responses. Specialists felt there was a need to ensure that PCPs provide relevant and patient-specific information that would enable them to efficiently and accurately answer questions without the need for extensive EHR review. This reflects previous work showing that specialists are often unable to respond to e-consult requests because they do not contain sufficient information.22 PCPs described a need to ensure that specialists’ responses included information that was detailed enough to make clinical decisions without the need for a reconsult. This highlights a common challenge to medical consultation, in that necessary or relevant information may not be apparent to all clinicians. To address this, there may be a role in developing enhanced, flexible templating that elicits necessary patient-specific information. Such a template may automatically pull relevant data from the EHR and prompt clinicians to provide important information. We did not assess how perspectives of templates varied, and further work could help define precisely what constitutes an effective template, including how it should capture appropriate patient data and how this impacts acceptability or use of e-consults generally. Collaboratively developed service agreements and e-consult templates could help guide PCPs and specialists to engage in efficient communication.
Another theme among both groups was that e-consult is most appropriate within specific clinical scenarios. Examples included review of laboratory results, questions about medication changes, or for patients who were reluctant to travel to appointments. Identifying and promoting specific opportunities for e-consults may help increase their use and align e-consult practices with scenarios that are likely to provide the most benefit to patients. For example, it could be helpful to understand the distance patients must travel for specialty care. Providing that information during clinical encounters could trigger clinicians to consider e-consults as an option. Future work might aim to identify clinical scenarios that clinicians feel are not well suited for e-consults and determine how to adapt them for those scenarios.
Limitations
Generalizability of these findings is limited given the qualitative study design. Participants’ descriptions of experiences with e-consults reflect the experiences of clinicians in the VA and may not reflect clinicians in other settings. We also interviewed a sample of clinicians who were already using e-consults. Important information could be learned from future work with those who have not yet adopted e-consult procedures or adopted and abandoned them.
Conclusions
E-consult is perceived as beneficial by VA PCPs and specialists. Participants suggested using e-consults for appropriate questions or patients and including necessary information and next steps in both the initial e-consult and response. Finding ways to facilitate e-consults with these suggestions in mind may increase delivery of high-quality e-consults. Future work could compare the findings of this work to similar work assessing clinicians perceptions of e-consults outside of the VA.
Electronic consultation (e-consult) is designed to increase access to specialty care by facilitating communication between primary care and specialty clinicians without the need for outpatient face-to-face encounters.1–4 In 2011, the US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) implemented an e-consult program as a component of its overall strategy to increase access to specialty services, reduce costs of care, and reduce appointment travel burden on patients.
E-consult has substantially increased within the VA since its implementation.5,6 Consistent with limited evaluations from other health care systems, evaluations of the VA e-consult program demonstrated reduced costs, reduced travel time for patients, and improved access to specialty care.2,5–11 However, there is wide variation in e-consult use across VA specialties, facilities, and regions.5,6,12,13 For example, hematology, preoperative evaluation, neurosurgery, endocrinology, and infectious diseases use e-consults more frequently when compared with in-person consults in the VA.6 Reasons for this variation or specific barriers and facilitators of using e-consults have not been described.
Prior qualitative studies report that primary care practitioners (PCPs) describe e-consults as convenient, educational, beneficial for patient care, and useful for improving patient access to specialty care.8,14,15 One study identified limited PCP knowledge of e-consults as a barrier to use.16 Specialists have reported that e-consult improves clinical communication, but increases their workload.1,14,17,18 These studies did not assess perspectives from both clinicians who initiate e-consults and those who respond to them. This is the first qualitative study to assess e-consult perceptions from perspectives of both PCPs and specialists among a large, national sample of VA clinicians who use e-consults. The objective of this study was to understand perspectives of e-consults between PCPs and specialists that may be relevant to increasing adoption in the VA.
Methods
The team (CL, ML, PG, 2 analysts under the guidance of GS and JS and support from RRK, and a biostatistician) conducted semistructured interviews with PCPs, specialists, and specialty division leaders who were employed by VA in 2016 and 2017. Specialties of interest were identified by the VA Office of Specialty Care and included cardiology, endocrinology, gastroenterology, and hematology.
E-Consult Procedures
Within the VA, the specific procedures used to initiate, triage and manage e-consults are coordinated at VA medical centers (VAMCs) and at the Veterans Integrated Service Network (VISN) regional level. E-consult can be requested by any clinician. Generally, e-consults are initiated by PCPs through standardized, specialty-specific templates. Recipients, typically specialists, respond by answering questions, suggesting additional testing and evaluation, or requesting an in-person visit. Communication is documented in the patient’s electronic health record (EHR). Specialists receive different levels of workload credit for responding to e-consults similar to a relative value unit reimbursement model. Training in the use of e-consults is available to practitioners but may vary at local and regional levels.
Recruitment
Our sample included PCPs, specialists, and specialty care division leaders. We first quantified e-consult rates (e-consults per 100 patient visits) between July 2016 and June 2017 at VA facilities within primary care and the 4 priority specialties and identified the 30 sites with the highest e-consult rates and 30 sites with the lowest e-consult rates. Sites with < 500 total visits, < 3 specialties, or without any e-consult visit during the study period were excluded. E-consult rates at community-based outpatient clinics were included with associated VAMCs. We then stratified PCPs by whether they were high or low users of e-consults (determined by the top and bottom users within each site) and credentials (MD vs nurse practitioner [NP] or physician assistant [PA]). Specialists were sampled based on their rate of use relative to colleagues within their site and the use rate of their division. We sampled division chiefs and individuals who had > 300 total visits and 1 e-consult during the study period. To recruit participants, the primary investigator sent an initial email and 2 reminder emails. The team followed up with respondents to schedule an interview.
Interview guides were designed to elicit rich descriptions of barriers and facilitators to e-consult use (eAppendix available at doi:10.12788/fp.0214). The team used the Practical Robust Implementation and Sustainability Model (PRISM), which considers factors along 6 domains for intervention planning, implementation, and sustainment.19 Telephone interviews lasted about 20 minutes and were conducted between September 2017 and March 2018. Interviews were recorded and transcribed verbatim.
Analysis
The team used an iterative, team-based, inductive/deductive approach to conventional content analysis.20,21 Initial code categories were created so that we could identify e-consult best practices—facilitators of e-consult that were recommended by both PCPs and specialists. Inductive codes or labels applied to identify meaningful quotations, phrases, or key terms were used to identify emergent ideas and were added throughout coding after discussion among team members. Consensus was reached using a team-based approach.21 Four analysts independently coded the same 3 transcripts and met to discuss points of divergence and convergence. Analyses continued with emergent themes, categories, and conclusions. Atlas.ti. v.7 was used for coding and data management.22
Results
We conducted 34 interviews with clinicians (Table 1) from 13 VISNs. Four best-practice themes emerged among both PCPs and specialists, including that e-consults (1) are best suited for certain clinical questions and patients; (2) require relevant background information from requesting clinicians and clear recommendations from responding clinicians; (3) are a novel opportunity to provide efficient, transparent care; and (4) may not be fully adopted due to low awareness. Supporting quotations for the following findings are provided in Table 2.
Specific Clinical Questions and Patients
PCPs described specific patients and questions for which they most frequently used e-consults, such as for medication changes (Q1), determining treatment steps (Q2,3), and or clarifying laboratory or imaging findings. PCPs frequently used e-consults for patients who did not require a physical examination or when specialists could make recommendations without seeing patients face-to-face (Q3). An important use of e-consults described by PCPs was for treating conditions they could manage within primary care if additional guidance were available (Q4). Several PCPs and specialists also noted that e-consults were particularly useful for patients who were unable to travel or did not want face-to-face appointments (Q5). Notably, PCPs and specialists mentioned situations for which e-consults were inappropriate, including when a detailed history or physical examination was needed, or if a complex condition was suspected (Q6).
Background Data and Clear Recommendations
Participants described necessary data that should be included in high-quality e-consults. Specialists voiced frustration in time-consuming chart reviews that were often necessary when these data were not provided by the requestor. In some cases, specialists were unable to access necessary EHR data, which delayed responses (Q7). PCPs noted that the most useful responses carefully considered the question, used current patient information to determine treatments, provided clear recommendations, and defined who was responsible for next steps (Q8). PCPs and specialists stated that e-consult templates that required relevant information facilitated high-quality e-consults. Neither wanted to waste the other clinician's time (Q8).
A Novel Opportunity
Many PCPs felt that e-consults improved communication (eg, efficiency, response time), established new communication between clinicians, and reduced patients’ appointment burden (Q10, Q11). Many specialists felt that e-consults improved documentation of communication between clinicians and increased transparency of clinical decisions (Q12). Additionally, many specialists mentioned that e-consults capture previously informal curbside consults, enabling them to receive workload credit (Q13).
Lack of Awareness
Some noted that the biggest barrier to e-consults was not being aware of them generally, or which specialties offer e-consults (Q14). One PCP described e-consults as the best kept secret and found value in sharing the utility of e-consults with colleagues (Q15). All participants, including those who did not frequently use e-consults, felt that e-consults improved the quality of care by providing more timely care or better answers to clinical questions (Q16). Several practitioners also felt that e-consults increased access to specialty care. For example, specialists reported that e-consults enabled them to better manage patient load by using e-consults to answer relatively simple questions, reserving face-to-face consults for more complex patients (Q17).
Discussion
The objective of this study was to identify potential best practices for e-consults that may help increase their quality and use within the VA. We built on prior studies that offered insights on PCP and specialists’ overall satisfaction with e-consult by identifying several themes relevant to the further adoption of e-consults in the VA and elsewhere without a face-to-face visit.8,13,14,16–18 Future work may be beneficial in identifying whether the study themes identified can explain variation in e-consult use or whether addressing these factors might lead to increased or higher quality e-consult use. We are unaware of any qualitative study of comparable scale in a different health care system. Further, this is the first study to assess perspectives on e-consults among those who initiate and respond to them within the same health care system. Perhaps the most important finding from this study is that e-consults are generally viewed favorably, which is a necessary leverage point to increase their adoption within the system.
Clinicians reported several benefits to e-consults, including timely responses to clinical questions, efficient communication, allow for documentation of specialist recommendations, and help capture workload. These benefits are consistent with prior literature that indicates both PCPs and specialists in the VA and other health care systems feel that e-consults improves communication, decreases unnecessary visits, and improves quality of care.1,14,17,18 In particular, clinicians reported that e-consults improve their practice efficiency and efficacy. This is of critical importance given the pressures of providing timely access to primary and specialty care within the VA. Interestingly, many VA practitioners were unaware which specialties offered e-consults within their facilities, reflecting previous work showing that PCPs are often unaware of e-consult options.16 This may partially explain variation in e-consult use. Increasing awareness and educating clinicians on the benefits of e-consults may help promote use among non- and low users.
A common theme reported by both groups was the importance of providing necessary information within e-consult questions and responses. Specialists felt there was a need to ensure that PCPs provide relevant and patient-specific information that would enable them to efficiently and accurately answer questions without the need for extensive EHR review. This reflects previous work showing that specialists are often unable to respond to e-consult requests because they do not contain sufficient information.22 PCPs described a need to ensure that specialists’ responses included information that was detailed enough to make clinical decisions without the need for a reconsult. This highlights a common challenge to medical consultation, in that necessary or relevant information may not be apparent to all clinicians. To address this, there may be a role in developing enhanced, flexible templating that elicits necessary patient-specific information. Such a template may automatically pull relevant data from the EHR and prompt clinicians to provide important information. We did not assess how perspectives of templates varied, and further work could help define precisely what constitutes an effective template, including how it should capture appropriate patient data and how this impacts acceptability or use of e-consults generally. Collaboratively developed service agreements and e-consult templates could help guide PCPs and specialists to engage in efficient communication.
Another theme among both groups was that e-consult is most appropriate within specific clinical scenarios. Examples included review of laboratory results, questions about medication changes, or for patients who were reluctant to travel to appointments. Identifying and promoting specific opportunities for e-consults may help increase their use and align e-consult practices with scenarios that are likely to provide the most benefit to patients. For example, it could be helpful to understand the distance patients must travel for specialty care. Providing that information during clinical encounters could trigger clinicians to consider e-consults as an option. Future work might aim to identify clinical scenarios that clinicians feel are not well suited for e-consults and determine how to adapt them for those scenarios.
Limitations
Generalizability of these findings is limited given the qualitative study design. Participants’ descriptions of experiences with e-consults reflect the experiences of clinicians in the VA and may not reflect clinicians in other settings. We also interviewed a sample of clinicians who were already using e-consults. Important information could be learned from future work with those who have not yet adopted e-consult procedures or adopted and abandoned them.
Conclusions
E-consult is perceived as beneficial by VA PCPs and specialists. Participants suggested using e-consults for appropriate questions or patients and including necessary information and next steps in both the initial e-consult and response. Finding ways to facilitate e-consults with these suggestions in mind may increase delivery of high-quality e-consults. Future work could compare the findings of this work to similar work assessing clinicians perceptions of e-consults outside of the VA.
1. Battaglia C, Lambert-Kerzner A, Aron DC, et al. Evaluation of e-consults in the VHA: provider perspectives. Fed Pract. 2015;32(7):42-48.
2. Haverhals LM, Sayre G, Helfrich CD, et al. E-consult implementation: lessons learned using consolidated framework for implementation research. Am J Manag Care. 2015;21(12):e640-e647. Published 2015 Dec 1.
3. Sewell JL, Telischak KS, Day LW, Kirschner N, Weissman A. Preconsultation exchange in the United States: use, awareness, and attitudes. Am J Manag Care. 2014;20(12):e556-e564. Published 2014 Dec 1.
4. Horner K, Wagner E, Tufano J. Electronic consultations between primary and specialty care clinicians: early insights. Issue Brief (Commonw Fund). 2011;23:1-14.
5. Kirsh S, Carey E, Aron DC, et al. Impact of a national specialty e-consultation implementation project on access. Am J Manag Care. 2015;21(12):e648-654. Published 2015 Dec 1.
6. Saxon DR, Kaboli PJ, Haraldsson B, Wilson C, Ohl M, Augustine MR. Growth of electronic consultations in the Veterans Health Administration. Am J Manag Care. 2021;27(1):12-19. doi:10.37765/ajmc.2021.88572
7. Olayiwola JN, Anderson D, Jepeal N, et al. Electronic consultations to improve the primary care-specialty care interface for cardiology in the medically underserved: a cluster-randomized controlled trial. Ann Fam Med. 2016;14(2):133-140. doi:10.1370/afm.1869
8. Schettini P, Shah KP, O’Leary CP, et al. Keeping care connected: e-Consultation program improves access to nephrology care. J Telemed Telecare. 2019;25(3):142-150. doi:10.1177/1357633X17748350
9. Whittington MD, Ho PM, Kirsh SR, et al. Cost savings associated with electronic specialty consultations. Am J Manag Care. 2021;27(1):e16-e23. Published 2021 Jan 1. doi:10.37765/ajmc.2021.88579
10. Shipherd JC, Kauth MR, Matza A. Nationwide interdisciplinary e-consultation on transgender care in the Veterans Health Administration. Telemed J E Health. 2016;22(12):1008-1012. doi:10.1089/tmj.2016.0013
11. Strymish J, Gupte G, Afable MK, et al. Electronic consultations (E-consults): advancing infectious disease care in a large Veterans Affairs Healthcare System. Clin Infect Dis. 2017;64(8):1123-1125. doi:10.1093/cid/cix058
12. Williams KM, Kirsh S, Aron D, et al. Evaluation of the Veterans Health Administration’s Specialty Care Transformational Initiatives to promote patient-centered delivery of specialty care: a mixed-methods approach. Telemed J E-Health. 2017;23(7):577-589. doi:10.1089/tmj.2016.0166
13. US Department of Veterans Affairs, Veterans Health Administration, Specialty Care Transformational Initiative Evaluation Center. Evaluation of specialty care initiatives. Published 2013.
14. Vimalananda VG, Gupte G, Seraj SM, et al. Electronic consultations (e-consults) to improve access to specialty care: a systematic review and narrative synthesis. J Telemed Telecare. 2015;21(6):323-330. doi:10.1177/1357633X15582108
15. Lee M, Leonard C, Greene P, et al. Perspectives of VA primary care clinicians toward electronic consultation-related workload burden. JAMA Netw Open. 2020;3(10):e2018104. Published 2020 Oct 1. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.18104
16. Deeds SA, Dowdell KJ, Chew LD, Ackerman SL. Implementing an opt-in eConsult program at seven academic medical centers: a qualitative analysis of primary care provider experiences. J Gen Intern Med. 2019;34(8):1427-1433. doi:10.1007/s11606-019-05067-7
17. Rodriguez KL, Burkitt KH, Bayliss NK, et al. Veteran, primary care provider, and specialist satisfaction with electronic consultation. JMIR Med Inform. 2015;3(1):e5. Published 2015 Jan 14. doi:10.2196/medinform.3725
18. Gupte G, Vimalananda V, Simon SR, DeVito K, Clark J, Orlander JD. Disruptive innovation: implementation of electronic consultations in a Veterans Affairs Health Care System. JMIR Med Inform. 2016;4(1):e6. Published 2016 Feb 12. doi:10.2196/medinform.4801
19. Feldstein AC, Glasgow RE. A practical, robust implementation and sustainability model (PRISM) for integrating research findings into practice. Jt Comm J Qual Patient Saf. 2008;34(4):228-243. doi:10.1016/s1553-7250(08)34030-6
20. Patton MQ. Qualitative Research and Evaluation Methods. 3rd ed. Sage Publications; 2002.
21. Bradley EH, Curry LA, Devers KJ. Qualitative data analysis for health services research: developing taxonomy, themes, and theory. Health Serv Res. 2007;42(4):1758-1772. doi:10.1111/j.1475-6773.2006.00684.x
22. Kim EJ, Orlander JD, Afable M, et al. Cardiology electronic consultation (e-consult) use by primary care providers at VA medical centres in New England. J Telemed Telecare. 2019;25(6):370-377. doi:10.1177/1357633X18774468
1. Battaglia C, Lambert-Kerzner A, Aron DC, et al. Evaluation of e-consults in the VHA: provider perspectives. Fed Pract. 2015;32(7):42-48.
2. Haverhals LM, Sayre G, Helfrich CD, et al. E-consult implementation: lessons learned using consolidated framework for implementation research. Am J Manag Care. 2015;21(12):e640-e647. Published 2015 Dec 1.
3. Sewell JL, Telischak KS, Day LW, Kirschner N, Weissman A. Preconsultation exchange in the United States: use, awareness, and attitudes. Am J Manag Care. 2014;20(12):e556-e564. Published 2014 Dec 1.
4. Horner K, Wagner E, Tufano J. Electronic consultations between primary and specialty care clinicians: early insights. Issue Brief (Commonw Fund). 2011;23:1-14.
5. Kirsh S, Carey E, Aron DC, et al. Impact of a national specialty e-consultation implementation project on access. Am J Manag Care. 2015;21(12):e648-654. Published 2015 Dec 1.
6. Saxon DR, Kaboli PJ, Haraldsson B, Wilson C, Ohl M, Augustine MR. Growth of electronic consultations in the Veterans Health Administration. Am J Manag Care. 2021;27(1):12-19. doi:10.37765/ajmc.2021.88572
7. Olayiwola JN, Anderson D, Jepeal N, et al. Electronic consultations to improve the primary care-specialty care interface for cardiology in the medically underserved: a cluster-randomized controlled trial. Ann Fam Med. 2016;14(2):133-140. doi:10.1370/afm.1869
8. Schettini P, Shah KP, O’Leary CP, et al. Keeping care connected: e-Consultation program improves access to nephrology care. J Telemed Telecare. 2019;25(3):142-150. doi:10.1177/1357633X17748350
9. Whittington MD, Ho PM, Kirsh SR, et al. Cost savings associated with electronic specialty consultations. Am J Manag Care. 2021;27(1):e16-e23. Published 2021 Jan 1. doi:10.37765/ajmc.2021.88579
10. Shipherd JC, Kauth MR, Matza A. Nationwide interdisciplinary e-consultation on transgender care in the Veterans Health Administration. Telemed J E Health. 2016;22(12):1008-1012. doi:10.1089/tmj.2016.0013
11. Strymish J, Gupte G, Afable MK, et al. Electronic consultations (E-consults): advancing infectious disease care in a large Veterans Affairs Healthcare System. Clin Infect Dis. 2017;64(8):1123-1125. doi:10.1093/cid/cix058
12. Williams KM, Kirsh S, Aron D, et al. Evaluation of the Veterans Health Administration’s Specialty Care Transformational Initiatives to promote patient-centered delivery of specialty care: a mixed-methods approach. Telemed J E-Health. 2017;23(7):577-589. doi:10.1089/tmj.2016.0166
13. US Department of Veterans Affairs, Veterans Health Administration, Specialty Care Transformational Initiative Evaluation Center. Evaluation of specialty care initiatives. Published 2013.
14. Vimalananda VG, Gupte G, Seraj SM, et al. Electronic consultations (e-consults) to improve access to specialty care: a systematic review and narrative synthesis. J Telemed Telecare. 2015;21(6):323-330. doi:10.1177/1357633X15582108
15. Lee M, Leonard C, Greene P, et al. Perspectives of VA primary care clinicians toward electronic consultation-related workload burden. JAMA Netw Open. 2020;3(10):e2018104. Published 2020 Oct 1. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.18104
16. Deeds SA, Dowdell KJ, Chew LD, Ackerman SL. Implementing an opt-in eConsult program at seven academic medical centers: a qualitative analysis of primary care provider experiences. J Gen Intern Med. 2019;34(8):1427-1433. doi:10.1007/s11606-019-05067-7
17. Rodriguez KL, Burkitt KH, Bayliss NK, et al. Veteran, primary care provider, and specialist satisfaction with electronic consultation. JMIR Med Inform. 2015;3(1):e5. Published 2015 Jan 14. doi:10.2196/medinform.3725
18. Gupte G, Vimalananda V, Simon SR, DeVito K, Clark J, Orlander JD. Disruptive innovation: implementation of electronic consultations in a Veterans Affairs Health Care System. JMIR Med Inform. 2016;4(1):e6. Published 2016 Feb 12. doi:10.2196/medinform.4801
19. Feldstein AC, Glasgow RE. A practical, robust implementation and sustainability model (PRISM) for integrating research findings into practice. Jt Comm J Qual Patient Saf. 2008;34(4):228-243. doi:10.1016/s1553-7250(08)34030-6
20. Patton MQ. Qualitative Research and Evaluation Methods. 3rd ed. Sage Publications; 2002.
21. Bradley EH, Curry LA, Devers KJ. Qualitative data analysis for health services research: developing taxonomy, themes, and theory. Health Serv Res. 2007;42(4):1758-1772. doi:10.1111/j.1475-6773.2006.00684.x
22. Kim EJ, Orlander JD, Afable M, et al. Cardiology electronic consultation (e-consult) use by primary care providers at VA medical centres in New England. J Telemed Telecare. 2019;25(6):370-377. doi:10.1177/1357633X18774468