User login
Assessment and treatment of many of the more common behavioral disorders in childhood, such as ADHD and anxiety, should be considered within a pediatrician’s scope of practice, a stance made very clear by a recent policy statement published by the American Academy of Pediatrics entitled “Mental health competencies for pediatric practice.”1 These competencies include medication treatment. As stated in the article, “certain disorders (ADHD, common anxiety disorders, depression), if associated with no more than moderate impairment, are amenable to primary care medication management because there are indicated medications with a well-established safety profile.”
This shift to shared ownership when it comes to mental health care is likely coming from multiple sources, not the least of them being necessity and an acknowledgment that there simply aren’t enough psychiatrists to take over the mental health care of every youth with a diagnosable psychiatric disorder. While the number of child and adolescent psychiatrists remains relatively flat, the youth suicide rate is rising, as are the numbers presenting to emergency departments in crisis – all for reasons still to be fully understood. And these trends all are occurring as the medical community overall is appreciating more and more that good mental health is a cornerstone of all health.
The response from the pediatric community, whether it be because of personal conviction or simply a lack of options, largely has been to step up to the plate and take on these new responsibilities and challenges while trying to get up to speed with the latest information about mental health best practices. From my own experience doing evaluations and consultations from area primary care clinicians for over 15 years, the shift is noticeable. The typical patient now coming in has already seen a mental health counselor and tried at least one medication, while evaluations for diagnosis and treatment recommendations for things like uncomplicated and treatment-naive ADHD symptoms, for example, are becoming much more infrequent – although still far from extinct.
Nevertheless, there remain concerns about the extent of these new charges. Joe Nasca, MD, an experienced pediatrician who has been practicing in rural Vermont for decades, is worried that there is simply too much already for pediatricians to know and do to be able to add extensive mental health care. “There is so much to know in general peds [pediatrics] that I would guess a year or more of additional residency and experience would adequately prepare me to take this on,” he said in an interview. In comparing psychiatric care to other specialties, Dr. Nasca went on to say that, “I would not presume to treat chronic renal failure without the help of a nephrologist or a dilated aortic arch without a cardiologist.”
In a similar vein, however, it also is true that a significant percentage of children presenting to pediatricians for orthopedic problems, infections, asthma, and rashes are managed without referrals to specialists. The right balance, of course, will vary from clinician to clinician based on that pediatrician’s level of interest, experience, and available resources in the community. The AAP position papers don’t mandate or even encourage the notion that all pediatricians need to be at the same place when it comes to competency in assessment and treatment of mental health problems, although it is probably fair to say that there is a push for the pediatric community as a whole to raise the collective bar at least a notch or two.
In response, the mental health community has moved to support the primary care community in their expanded role. These efforts have taken many forms, most notably the model of integrated care, in which mental health clinicians of various types see patients in primary care offices rather than making patients come to them. There also are new consultation programs that provide easy access to a child psychiatrist or other mental health professional for case-related questions delivered by phone, email, or for single in-person consultations. Additional training and educational offerings also are now available for pediatricians either in training and for those already in practice. These initiatives are bolstered by research showing that, not only can good mental health care be delivered in pediatric settings, but there are cost savings that can be realized, particularly for nonpsychiatric medical care.2 Despite these promising leads, however, there will remain some for whom anything less than the increased availability of a psychiatrist to “take over” a patient’s mental health care will be seen as a falling short of the clinical need.
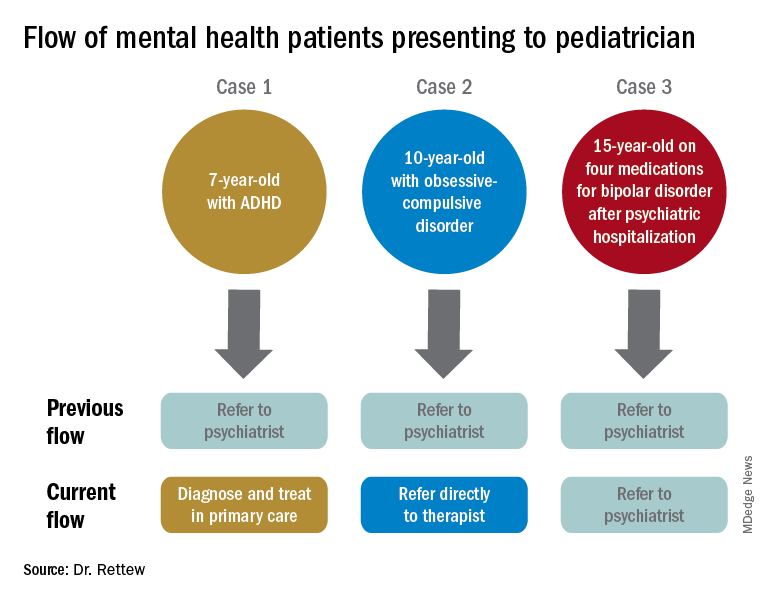
To illustrate how things have and continue to change, consider the following three common clinical scenarios that generally present to a pediatrician:
- New presentation of ADHD symptoms.
- Anxiety or obsessive-compulsive problems.
- Return of a patient who has been psychiatrically hospitalized and now is taking multiple medications.
In the past, all three cases often would have resulted in a referral to a psychiatrist. Today, however, it is quite likely that only one of these cases would be referred because ADHD could be well diagnosed and managed within the primary care setting, and problems like anxiety and obsessive-compulsive disorder are sent first not to a psychiatrist but to a non-MD psychotherapist.
Moving forward, today’s pediatricians are expected to do more for the mental health care of patients themselves instead of referring to a psychiatrist. Most already do, despite having had little in the way of formal training. As the evidence grows that the promotion of mental well-being can be a key to future overall health, as well as to the cost of future health care, there are many reasons to be optimistic that support for pediatricians and collaborative care models for clinicians trying to fulfill these new responsibilities will get only stronger.
References
1. Pediatrics. 2019 Nov;144(5). pii: e20192757.
2. Pediatrics. 2019 Jul;144(1). pii: e20183243.
Dr. Rettew is a child and adolescent psychiatrist and associate professor of psychiatry and pediatrics at the University of Vermont, Burlington. Follow him on Twitter @PediPsych. Email him at pdnews@mdedge.com. Looking for more mental health training? Attend the 14th annual Child Psychiatry in Primary Care conference in Burlington on May 8, 2020 (http://www.med.uvm.edu/cme/conferences).
Assessment and treatment of many of the more common behavioral disorders in childhood, such as ADHD and anxiety, should be considered within a pediatrician’s scope of practice, a stance made very clear by a recent policy statement published by the American Academy of Pediatrics entitled “Mental health competencies for pediatric practice.”1 These competencies include medication treatment. As stated in the article, “certain disorders (ADHD, common anxiety disorders, depression), if associated with no more than moderate impairment, are amenable to primary care medication management because there are indicated medications with a well-established safety profile.”

This shift to shared ownership when it comes to mental health care is likely coming from multiple sources, not the least of them being necessity and an acknowledgment that there simply aren’t enough psychiatrists to take over the mental health care of every youth with a diagnosable psychiatric disorder. While the number of child and adolescent psychiatrists remains relatively flat, the youth suicide rate is rising, as are the numbers presenting to emergency departments in crisis – all for reasons still to be fully understood. And these trends all are occurring as the medical community overall is appreciating more and more that good mental health is a cornerstone of all health.
The response from the pediatric community, whether it be because of personal conviction or simply a lack of options, largely has been to step up to the plate and take on these new responsibilities and challenges while trying to get up to speed with the latest information about mental health best practices. From my own experience doing evaluations and consultations from area primary care clinicians for over 15 years, the shift is noticeable. The typical patient now coming in has already seen a mental health counselor and tried at least one medication, while evaluations for diagnosis and treatment recommendations for things like uncomplicated and treatment-naive ADHD symptoms, for example, are becoming much more infrequent – although still far from extinct.
Nevertheless, there remain concerns about the extent of these new charges. Joe Nasca, MD, an experienced pediatrician who has been practicing in rural Vermont for decades, is worried that there is simply too much already for pediatricians to know and do to be able to add extensive mental health care. “There is so much to know in general peds [pediatrics] that I would guess a year or more of additional residency and experience would adequately prepare me to take this on,” he said in an interview. In comparing psychiatric care to other specialties, Dr. Nasca went on to say that, “I would not presume to treat chronic renal failure without the help of a nephrologist or a dilated aortic arch without a cardiologist.”
In a similar vein, however, it also is true that a significant percentage of children presenting to pediatricians for orthopedic problems, infections, asthma, and rashes are managed without referrals to specialists. The right balance, of course, will vary from clinician to clinician based on that pediatrician’s level of interest, experience, and available resources in the community. The AAP position papers don’t mandate or even encourage the notion that all pediatricians need to be at the same place when it comes to competency in assessment and treatment of mental health problems, although it is probably fair to say that there is a push for the pediatric community as a whole to raise the collective bar at least a notch or two.
In response, the mental health community has moved to support the primary care community in their expanded role. These efforts have taken many forms, most notably the model of integrated care, in which mental health clinicians of various types see patients in primary care offices rather than making patients come to them. There also are new consultation programs that provide easy access to a child psychiatrist or other mental health professional for case-related questions delivered by phone, email, or for single in-person consultations. Additional training and educational offerings also are now available for pediatricians either in training and for those already in practice. These initiatives are bolstered by research showing that, not only can good mental health care be delivered in pediatric settings, but there are cost savings that can be realized, particularly for nonpsychiatric medical care.2 Despite these promising leads, however, there will remain some for whom anything less than the increased availability of a psychiatrist to “take over” a patient’s mental health care will be seen as a falling short of the clinical need.
To illustrate how things have and continue to change, consider the following three common clinical scenarios that generally present to a pediatrician:
- New presentation of ADHD symptoms.
- Anxiety or obsessive-compulsive problems.
- Return of a patient who has been psychiatrically hospitalized and now is taking multiple medications.
In the past, all three cases often would have resulted in a referral to a psychiatrist. Today, however, it is quite likely that only one of these cases would be referred because ADHD could be well diagnosed and managed within the primary care setting, and problems like anxiety and obsessive-compulsive disorder are sent first not to a psychiatrist but to a non-MD psychotherapist.
Moving forward, today’s pediatricians are expected to do more for the mental health care of patients themselves instead of referring to a psychiatrist. Most already do, despite having had little in the way of formal training. As the evidence grows that the promotion of mental well-being can be a key to future overall health, as well as to the cost of future health care, there are many reasons to be optimistic that support for pediatricians and collaborative care models for clinicians trying to fulfill these new responsibilities will get only stronger.
References
1. Pediatrics. 2019 Nov;144(5). pii: e20192757.
2. Pediatrics. 2019 Jul;144(1). pii: e20183243.
Dr. Rettew is a child and adolescent psychiatrist and associate professor of psychiatry and pediatrics at the University of Vermont, Burlington. Follow him on Twitter @PediPsych. Email him at pdnews@mdedge.com. Looking for more mental health training? Attend the 14th annual Child Psychiatry in Primary Care conference in Burlington on May 8, 2020 (http://www.med.uvm.edu/cme/conferences).
Assessment and treatment of many of the more common behavioral disorders in childhood, such as ADHD and anxiety, should be considered within a pediatrician’s scope of practice, a stance made very clear by a recent policy statement published by the American Academy of Pediatrics entitled “Mental health competencies for pediatric practice.”1 These competencies include medication treatment. As stated in the article, “certain disorders (ADHD, common anxiety disorders, depression), if associated with no more than moderate impairment, are amenable to primary care medication management because there are indicated medications with a well-established safety profile.”

This shift to shared ownership when it comes to mental health care is likely coming from multiple sources, not the least of them being necessity and an acknowledgment that there simply aren’t enough psychiatrists to take over the mental health care of every youth with a diagnosable psychiatric disorder. While the number of child and adolescent psychiatrists remains relatively flat, the youth suicide rate is rising, as are the numbers presenting to emergency departments in crisis – all for reasons still to be fully understood. And these trends all are occurring as the medical community overall is appreciating more and more that good mental health is a cornerstone of all health.
The response from the pediatric community, whether it be because of personal conviction or simply a lack of options, largely has been to step up to the plate and take on these new responsibilities and challenges while trying to get up to speed with the latest information about mental health best practices. From my own experience doing evaluations and consultations from area primary care clinicians for over 15 years, the shift is noticeable. The typical patient now coming in has already seen a mental health counselor and tried at least one medication, while evaluations for diagnosis and treatment recommendations for things like uncomplicated and treatment-naive ADHD symptoms, for example, are becoming much more infrequent – although still far from extinct.
Nevertheless, there remain concerns about the extent of these new charges. Joe Nasca, MD, an experienced pediatrician who has been practicing in rural Vermont for decades, is worried that there is simply too much already for pediatricians to know and do to be able to add extensive mental health care. “There is so much to know in general peds [pediatrics] that I would guess a year or more of additional residency and experience would adequately prepare me to take this on,” he said in an interview. In comparing psychiatric care to other specialties, Dr. Nasca went on to say that, “I would not presume to treat chronic renal failure without the help of a nephrologist or a dilated aortic arch without a cardiologist.”
In a similar vein, however, it also is true that a significant percentage of children presenting to pediatricians for orthopedic problems, infections, asthma, and rashes are managed without referrals to specialists. The right balance, of course, will vary from clinician to clinician based on that pediatrician’s level of interest, experience, and available resources in the community. The AAP position papers don’t mandate or even encourage the notion that all pediatricians need to be at the same place when it comes to competency in assessment and treatment of mental health problems, although it is probably fair to say that there is a push for the pediatric community as a whole to raise the collective bar at least a notch or two.
In response, the mental health community has moved to support the primary care community in their expanded role. These efforts have taken many forms, most notably the model of integrated care, in which mental health clinicians of various types see patients in primary care offices rather than making patients come to them. There also are new consultation programs that provide easy access to a child psychiatrist or other mental health professional for case-related questions delivered by phone, email, or for single in-person consultations. Additional training and educational offerings also are now available for pediatricians either in training and for those already in practice. These initiatives are bolstered by research showing that, not only can good mental health care be delivered in pediatric settings, but there are cost savings that can be realized, particularly for nonpsychiatric medical care.2 Despite these promising leads, however, there will remain some for whom anything less than the increased availability of a psychiatrist to “take over” a patient’s mental health care will be seen as a falling short of the clinical need.
To illustrate how things have and continue to change, consider the following three common clinical scenarios that generally present to a pediatrician:
- New presentation of ADHD symptoms.
- Anxiety or obsessive-compulsive problems.
- Return of a patient who has been psychiatrically hospitalized and now is taking multiple medications.
In the past, all three cases often would have resulted in a referral to a psychiatrist. Today, however, it is quite likely that only one of these cases would be referred because ADHD could be well diagnosed and managed within the primary care setting, and problems like anxiety and obsessive-compulsive disorder are sent first not to a psychiatrist but to a non-MD psychotherapist.
Moving forward, today’s pediatricians are expected to do more for the mental health care of patients themselves instead of referring to a psychiatrist. Most already do, despite having had little in the way of formal training. As the evidence grows that the promotion of mental well-being can be a key to future overall health, as well as to the cost of future health care, there are many reasons to be optimistic that support for pediatricians and collaborative care models for clinicians trying to fulfill these new responsibilities will get only stronger.
References
1. Pediatrics. 2019 Nov;144(5). pii: e20192757.
2. Pediatrics. 2019 Jul;144(1). pii: e20183243.
Dr. Rettew is a child and adolescent psychiatrist and associate professor of psychiatry and pediatrics at the University of Vermont, Burlington. Follow him on Twitter @PediPsych. Email him at pdnews@mdedge.com. Looking for more mental health training? Attend the 14th annual Child Psychiatry in Primary Care conference in Burlington on May 8, 2020 (http://www.med.uvm.edu/cme/conferences).
