User login
How to explain physician compounding to legislators
In Ohio, new limits on drug compounding in physicians’ offices went into effect in April and have become a real hindrance to care for dermatology patients. The State of Ohio Board of Pharmacy has defined compounding as combining two or more prescription drugs and has required that physicians who perform this “compounding” must obtain a “Terminal Distributor of Dangerous Drugs” license. Ohio is the “test state,” and these rules, unless vigorously opposed, will be coming to your state.
[polldaddy:9779752]
The rules state that “compounded” drugs used within 6 hours of preparation must be prepared in a designated clean medication area with proper hand hygiene and the use of powder-free gloves. “Compounded” drugs that are used more than 6 hours after preparation, require a designated clean room with access limited to authorized personnel, environmental control devices such as a laminar flow hood, and additional equipment and training of personnel to maintain an aseptic environment. A separate license is required for each office location.
The state pharmacy boards are eager to restrict physicians – as well as dentists and veterinarians – and to collect annual licensing fees. Additionally, according to an article from the Ohio State Medical Association, noncompliant physicians can be fined by the pharmacy board.
We are talking big money, power, and dreams of clinical relevancy (and billable activities) here.
What can dermatologists do to prevent this regulatory overreach? I encourage you to plan a visit to your state representative, where you can demonstrate how these restrictions affect you and your patients – an exercise that should be both fun and compelling. All you need to illustrate your case is a simple kit that includes a syringe (but no needles in the statehouse!), a bottle of lidocaine with epinephrine, a bottle of 8.4% bicarbonate, alcohol pads, and gloves.
First, explain to your audience that there is a skin cancer epidemic with more than 5.4 million new cases a year and that, over the past 20 years, the incidence of skin cancer has doubled and is projected to double again over the next 20 years. Further, explain that dermatologists treat more than 70% of these cases in the office setting, under local anesthesia, at a huge cost savings to the public and government (it costs an average of 12 times as much to remove these cancers in the outpatient department at the hospital). Remember, states foot most of the bill for Medicaid and Medicare gap indigent coverage.
Take the bottle of lidocaine with epinephrine and open the syringe pack (Staffers love this demonstration; everyone is fascinated with shots.). Put on your gloves, wipe the top of the lidocaine bottle with an alcohol swab, and explain that this medicine is the anesthetic preferred for skin cancer surgery. Explain how it not only numbs the skin, but also causes vasoconstriction, so that the cancer can be easily and safely removed in the office.
Then explain that, in order for the epinephrine to be stable, the solution has to be very acidic (a pH of 4.2, in fact). Explain that this makes it burn like hell unless you add 0.1 cc per cc of 8.4% bicarbonate, in which case the perceived pain on a 10-point scale will drop from 8 to 2. Then pick up the bottle of bicarbonate and explain that you will no longer be able to mix these two components anymore without a “Terminal Distributor of Dangerous Drugs” license because your state pharmacy board considers this compounding. Your representative is likely to give you looks of astonishment, disbelief, and then a dawning realization of the absurdity of the situation.
Follow-up questions may include “Why can’t you buy buffered lidocaine with epinephrine from the compounding pharmacy?” Easy answer: because each patient needs an individual prescription, and you may not know in advance which patient will need it, and how much the patient will need, and it becomes unstable once it has been buffered. It also will cost the patient $45 per 5-cc syringe, and it will be degraded by the time the patient returns from the compounding pharmacy. Explain further that it costs you only 84 cents to make a 5-cc syringe of buffered lidocaine; that some patients may need as many as 10 syringes; and that these costs are all included in the surgery (free!) if the physician draws it up in the office.
A simple summary is – less pain, less cost – and no history of infections or complications.
It is an eye-opener when you demonstrate how ridiculous the compounding rules being imposed are for physicians and patients. I’ve used this demonstration at the state and federal legislative level, and more recently, at the Food and Drug Administration.
If you get the chance, when a state legislator is in your office, become an advocate for your patients and fellow physicians. Make sure physician offices are excluded from these definitions of com
This column was updated June 22, 2017.
Dr. Coldiron is in private practice but maintains a clinical assistant professorship at the University of Cincinnati. He cares for patients, teaches medical students and residents, and has several active clinical research projects. Dr. Coldiron is the author of more than 80 scientific letters, papers, and several book chapters, and he speaks frequently on a variety of topics. He is a past president of the American Academy of Dermatology. Write to him at dermnews@frontlinemedcom.com.
In Ohio, new limits on drug compounding in physicians’ offices went into effect in April and have become a real hindrance to care for dermatology patients. The State of Ohio Board of Pharmacy has defined compounding as combining two or more prescription drugs and has required that physicians who perform this “compounding” must obtain a “Terminal Distributor of Dangerous Drugs” license. Ohio is the “test state,” and these rules, unless vigorously opposed, will be coming to your state.
[polldaddy:9779752]
The rules state that “compounded” drugs used within 6 hours of preparation must be prepared in a designated clean medication area with proper hand hygiene and the use of powder-free gloves. “Compounded” drugs that are used more than 6 hours after preparation, require a designated clean room with access limited to authorized personnel, environmental control devices such as a laminar flow hood, and additional equipment and training of personnel to maintain an aseptic environment. A separate license is required for each office location.
The state pharmacy boards are eager to restrict physicians – as well as dentists and veterinarians – and to collect annual licensing fees. Additionally, according to an article from the Ohio State Medical Association, noncompliant physicians can be fined by the pharmacy board.
We are talking big money, power, and dreams of clinical relevancy (and billable activities) here.
What can dermatologists do to prevent this regulatory overreach? I encourage you to plan a visit to your state representative, where you can demonstrate how these restrictions affect you and your patients – an exercise that should be both fun and compelling. All you need to illustrate your case is a simple kit that includes a syringe (but no needles in the statehouse!), a bottle of lidocaine with epinephrine, a bottle of 8.4% bicarbonate, alcohol pads, and gloves.
First, explain to your audience that there is a skin cancer epidemic with more than 5.4 million new cases a year and that, over the past 20 years, the incidence of skin cancer has doubled and is projected to double again over the next 20 years. Further, explain that dermatologists treat more than 70% of these cases in the office setting, under local anesthesia, at a huge cost savings to the public and government (it costs an average of 12 times as much to remove these cancers in the outpatient department at the hospital). Remember, states foot most of the bill for Medicaid and Medicare gap indigent coverage.
Take the bottle of lidocaine with epinephrine and open the syringe pack (Staffers love this demonstration; everyone is fascinated with shots.). Put on your gloves, wipe the top of the lidocaine bottle with an alcohol swab, and explain that this medicine is the anesthetic preferred for skin cancer surgery. Explain how it not only numbs the skin, but also causes vasoconstriction, so that the cancer can be easily and safely removed in the office.
Then explain that, in order for the epinephrine to be stable, the solution has to be very acidic (a pH of 4.2, in fact). Explain that this makes it burn like hell unless you add 0.1 cc per cc of 8.4% bicarbonate, in which case the perceived pain on a 10-point scale will drop from 8 to 2. Then pick up the bottle of bicarbonate and explain that you will no longer be able to mix these two components anymore without a “Terminal Distributor of Dangerous Drugs” license because your state pharmacy board considers this compounding. Your representative is likely to give you looks of astonishment, disbelief, and then a dawning realization of the absurdity of the situation.
Follow-up questions may include “Why can’t you buy buffered lidocaine with epinephrine from the compounding pharmacy?” Easy answer: because each patient needs an individual prescription, and you may not know in advance which patient will need it, and how much the patient will need, and it becomes unstable once it has been buffered. It also will cost the patient $45 per 5-cc syringe, and it will be degraded by the time the patient returns from the compounding pharmacy. Explain further that it costs you only 84 cents to make a 5-cc syringe of buffered lidocaine; that some patients may need as many as 10 syringes; and that these costs are all included in the surgery (free!) if the physician draws it up in the office.
A simple summary is – less pain, less cost – and no history of infections or complications.
It is an eye-opener when you demonstrate how ridiculous the compounding rules being imposed are for physicians and patients. I’ve used this demonstration at the state and federal legislative level, and more recently, at the Food and Drug Administration.
If you get the chance, when a state legislator is in your office, become an advocate for your patients and fellow physicians. Make sure physician offices are excluded from these definitions of com
This column was updated June 22, 2017.
Dr. Coldiron is in private practice but maintains a clinical assistant professorship at the University of Cincinnati. He cares for patients, teaches medical students and residents, and has several active clinical research projects. Dr. Coldiron is the author of more than 80 scientific letters, papers, and several book chapters, and he speaks frequently on a variety of topics. He is a past president of the American Academy of Dermatology. Write to him at dermnews@frontlinemedcom.com.
In Ohio, new limits on drug compounding in physicians’ offices went into effect in April and have become a real hindrance to care for dermatology patients. The State of Ohio Board of Pharmacy has defined compounding as combining two or more prescription drugs and has required that physicians who perform this “compounding” must obtain a “Terminal Distributor of Dangerous Drugs” license. Ohio is the “test state,” and these rules, unless vigorously opposed, will be coming to your state.
[polldaddy:9779752]
The rules state that “compounded” drugs used within 6 hours of preparation must be prepared in a designated clean medication area with proper hand hygiene and the use of powder-free gloves. “Compounded” drugs that are used more than 6 hours after preparation, require a designated clean room with access limited to authorized personnel, environmental control devices such as a laminar flow hood, and additional equipment and training of personnel to maintain an aseptic environment. A separate license is required for each office location.
The state pharmacy boards are eager to restrict physicians – as well as dentists and veterinarians – and to collect annual licensing fees. Additionally, according to an article from the Ohio State Medical Association, noncompliant physicians can be fined by the pharmacy board.
We are talking big money, power, and dreams of clinical relevancy (and billable activities) here.
What can dermatologists do to prevent this regulatory overreach? I encourage you to plan a visit to your state representative, where you can demonstrate how these restrictions affect you and your patients – an exercise that should be both fun and compelling. All you need to illustrate your case is a simple kit that includes a syringe (but no needles in the statehouse!), a bottle of lidocaine with epinephrine, a bottle of 8.4% bicarbonate, alcohol pads, and gloves.
First, explain to your audience that there is a skin cancer epidemic with more than 5.4 million new cases a year and that, over the past 20 years, the incidence of skin cancer has doubled and is projected to double again over the next 20 years. Further, explain that dermatologists treat more than 70% of these cases in the office setting, under local anesthesia, at a huge cost savings to the public and government (it costs an average of 12 times as much to remove these cancers in the outpatient department at the hospital). Remember, states foot most of the bill for Medicaid and Medicare gap indigent coverage.
Take the bottle of lidocaine with epinephrine and open the syringe pack (Staffers love this demonstration; everyone is fascinated with shots.). Put on your gloves, wipe the top of the lidocaine bottle with an alcohol swab, and explain that this medicine is the anesthetic preferred for skin cancer surgery. Explain how it not only numbs the skin, but also causes vasoconstriction, so that the cancer can be easily and safely removed in the office.
Then explain that, in order for the epinephrine to be stable, the solution has to be very acidic (a pH of 4.2, in fact). Explain that this makes it burn like hell unless you add 0.1 cc per cc of 8.4% bicarbonate, in which case the perceived pain on a 10-point scale will drop from 8 to 2. Then pick up the bottle of bicarbonate and explain that you will no longer be able to mix these two components anymore without a “Terminal Distributor of Dangerous Drugs” license because your state pharmacy board considers this compounding. Your representative is likely to give you looks of astonishment, disbelief, and then a dawning realization of the absurdity of the situation.
Follow-up questions may include “Why can’t you buy buffered lidocaine with epinephrine from the compounding pharmacy?” Easy answer: because each patient needs an individual prescription, and you may not know in advance which patient will need it, and how much the patient will need, and it becomes unstable once it has been buffered. It also will cost the patient $45 per 5-cc syringe, and it will be degraded by the time the patient returns from the compounding pharmacy. Explain further that it costs you only 84 cents to make a 5-cc syringe of buffered lidocaine; that some patients may need as many as 10 syringes; and that these costs are all included in the surgery (free!) if the physician draws it up in the office.
A simple summary is – less pain, less cost – and no history of infections or complications.
It is an eye-opener when you demonstrate how ridiculous the compounding rules being imposed are for physicians and patients. I’ve used this demonstration at the state and federal legislative level, and more recently, at the Food and Drug Administration.
If you get the chance, when a state legislator is in your office, become an advocate for your patients and fellow physicians. Make sure physician offices are excluded from these definitions of com
This column was updated June 22, 2017.
Dr. Coldiron is in private practice but maintains a clinical assistant professorship at the University of Cincinnati. He cares for patients, teaches medical students and residents, and has several active clinical research projects. Dr. Coldiron is the author of more than 80 scientific letters, papers, and several book chapters, and he speaks frequently on a variety of topics. He is a past president of the American Academy of Dermatology. Write to him at dermnews@frontlinemedcom.com.
Finding Your Voice in Advocacy
Dear Friends,
Since moving to Missouri a little over 2 years ago, I got involved with the Missouri GI Society. They held their inaugural in-person meeting in September, and it was exciting to see and meet gastroenterologists and associates from all over the state. The meeting sparked conversations about challenges in practices and ways to improve patient care. It was incredibly inspiring to see the beginnings and bright future of a society motivated to mobilize change in the community. On a national scale, AGA Advocacy Day 2025 this fall was another example of how to make an impact for the field. I am grateful that local and national GI communities can be a platform for our voices.
In this issue’s “In Focus,” Dr. Colleen R. Kelly discusses the approach for weight management for the gastroenterologist, including how to discuss lifestyle modifications, anti-obesity medications, endoscopic therapies, and bariatric surgeries. In the “Short Clinical Review,” Dr. Ekta Gupta, Dr. Carol Burke, and Dr. Carole Macaron review available non-invasive blood and stool tests for colorectal cancer screening, including guidelines recommendations and evidence supporting each modality.
In the “Early Career” section, Dr. Mayada Ismail shares her personal journey in making the difficult decision of leaving her first job as an early career gastroenterologist, outlining the challenges and lessons learned along the way.
Dr. Alicia Muratore, Dr. Emily V. Wechsler, and Dr. Eric D. Shah provide a practical guide to tech and device development in the “Finance/Legal” section of this issue, outlining everything from intellectual property ownership to building the right team, and selecting the right incubator.
If you are interested in contributing or have ideas for future TNG topics, please contact me (tjudy@wustl.edu) or Danielle Kiefer (dkiefer@gastro.org), Communications/Managing Editor of TNG.
Until next time, I leave you with a historical fun fact because we would not be where we are now without appreciating where we were: screening colonoscopy for colorectal cancer was only first introduced in the mid-1990s with Medicare coverage for high-risk individuals starting in 1998, followed by coverage for average-risk patients in 2001.
Yours truly,
Judy A. Trieu, MD, MPH
Editor-in-Chief
Assistant Professor of Medicine
Interventional Endoscopy, Division of Gastroenterology
Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis
Dear Friends,
Since moving to Missouri a little over 2 years ago, I got involved with the Missouri GI Society. They held their inaugural in-person meeting in September, and it was exciting to see and meet gastroenterologists and associates from all over the state. The meeting sparked conversations about challenges in practices and ways to improve patient care. It was incredibly inspiring to see the beginnings and bright future of a society motivated to mobilize change in the community. On a national scale, AGA Advocacy Day 2025 this fall was another example of how to make an impact for the field. I am grateful that local and national GI communities can be a platform for our voices.
In this issue’s “In Focus,” Dr. Colleen R. Kelly discusses the approach for weight management for the gastroenterologist, including how to discuss lifestyle modifications, anti-obesity medications, endoscopic therapies, and bariatric surgeries. In the “Short Clinical Review,” Dr. Ekta Gupta, Dr. Carol Burke, and Dr. Carole Macaron review available non-invasive blood and stool tests for colorectal cancer screening, including guidelines recommendations and evidence supporting each modality.
In the “Early Career” section, Dr. Mayada Ismail shares her personal journey in making the difficult decision of leaving her first job as an early career gastroenterologist, outlining the challenges and lessons learned along the way.
Dr. Alicia Muratore, Dr. Emily V. Wechsler, and Dr. Eric D. Shah provide a practical guide to tech and device development in the “Finance/Legal” section of this issue, outlining everything from intellectual property ownership to building the right team, and selecting the right incubator.
If you are interested in contributing or have ideas for future TNG topics, please contact me (tjudy@wustl.edu) or Danielle Kiefer (dkiefer@gastro.org), Communications/Managing Editor of TNG.
Until next time, I leave you with a historical fun fact because we would not be where we are now without appreciating where we were: screening colonoscopy for colorectal cancer was only first introduced in the mid-1990s with Medicare coverage for high-risk individuals starting in 1998, followed by coverage for average-risk patients in 2001.
Yours truly,
Judy A. Trieu, MD, MPH
Editor-in-Chief
Assistant Professor of Medicine
Interventional Endoscopy, Division of Gastroenterology
Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis
Dear Friends,
Since moving to Missouri a little over 2 years ago, I got involved with the Missouri GI Society. They held their inaugural in-person meeting in September, and it was exciting to see and meet gastroenterologists and associates from all over the state. The meeting sparked conversations about challenges in practices and ways to improve patient care. It was incredibly inspiring to see the beginnings and bright future of a society motivated to mobilize change in the community. On a national scale, AGA Advocacy Day 2025 this fall was another example of how to make an impact for the field. I am grateful that local and national GI communities can be a platform for our voices.
In this issue’s “In Focus,” Dr. Colleen R. Kelly discusses the approach for weight management for the gastroenterologist, including how to discuss lifestyle modifications, anti-obesity medications, endoscopic therapies, and bariatric surgeries. In the “Short Clinical Review,” Dr. Ekta Gupta, Dr. Carol Burke, and Dr. Carole Macaron review available non-invasive blood and stool tests for colorectal cancer screening, including guidelines recommendations and evidence supporting each modality.
In the “Early Career” section, Dr. Mayada Ismail shares her personal journey in making the difficult decision of leaving her first job as an early career gastroenterologist, outlining the challenges and lessons learned along the way.
Dr. Alicia Muratore, Dr. Emily V. Wechsler, and Dr. Eric D. Shah provide a practical guide to tech and device development in the “Finance/Legal” section of this issue, outlining everything from intellectual property ownership to building the right team, and selecting the right incubator.
If you are interested in contributing or have ideas for future TNG topics, please contact me (tjudy@wustl.edu) or Danielle Kiefer (dkiefer@gastro.org), Communications/Managing Editor of TNG.
Until next time, I leave you with a historical fun fact because we would not be where we are now without appreciating where we were: screening colonoscopy for colorectal cancer was only first introduced in the mid-1990s with Medicare coverage for high-risk individuals starting in 1998, followed by coverage for average-risk patients in 2001.
Yours truly,
Judy A. Trieu, MD, MPH
Editor-in-Chief
Assistant Professor of Medicine
Interventional Endoscopy, Division of Gastroenterology
Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis
Non-Invasive Blood and Stool CRC Screening Tests: Available Modalities and Their Clinical Application
Introduction
Colorectal cancer (CRC) screening significantly reduces CRC incidence and mortality, but only 65% of eligible individuals report being up-to-date with screening.1 Colonoscopy is the most widely used opportunistic screening method in the United States and is associated with many barriers to uptake. Providing patients a choice of colonoscopy and/or stool-based tests, improves screening adherence in randomized controlled trials.2,3 Non-invasive screening options have expanded from stool occult blood and multi-target DNA tests, to multi-target stool RNA tests, and novel blood-based tests, the latter only U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved for patients who refuse colonoscopy and stool-based tests.
Stool Occult Blood Tests
Guaiac-based fecal occult blood testing (gFOBT) significantly reduces CRC mortality by 33%-35% when implemented on an annual or biennial basis.4,5 Fecal immunochemical testing (FIT) has supplanted gFOBT with advantages including independence from dietary restriction and medication-related interference, use of antibodies specific to human globin, and the need for only a single stool sample.
The most common threshold for a positive FIT in the U.S. is ≥ 20 micrograms (μg) of hemoglobin per gram (g) of stool. FIT is approved by the FDA as a qualitative positive or negative result based on a threshold value.6 A meta-analysis summarized test characteristics of commercially available FITs at various detection thresholds.7 The CRC sensitivity and specificity was 75% and 95% for ≥ 20 ug hemoglobin/g stool, and 91% and 90% for 10 ug hemoglobin/g stool, respectively. The sensitivity for advanced adenomas ranged from 25% at 20 μg/g to 40% at a 10 μg/g. Programmatic use of FIT in adults ages ≥ 50 years at 20 ug/g of stool, in cohort and case control studies, has been shown to significantly reduce CRC mortality by 33%-40% and advanced stage CRC by 34%.8,9
Over 57,000 average-risk individuals ages 50–69 years were randomized to biennial FIT or one-time colonoscopy and followed for 10 years.10 CRC mortality and incidence was similar between the groups: 0.22% with FIT vs. 0.24% with colonoscopy and 1.13% with FIT vs. 1.22% with colonoscopy, respectively. Thus, confirming biennial FIT screening is non-inferior to one-time colonoscopy in important CRC-related outcomes.
Multi-Target Stool Tests
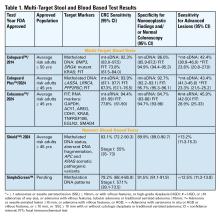
Two multitarget stool DNA tests (mt-sDNA) known as Cologuard™ and Cologuard Plus™ have been approved by the FDA. Both tests include a FIT (with a positivity threshold of 20 μg hemoglobin per gram of stool) combined with DNA methylation markers. The test result is qualitative, reported as a positive or negative. Cologuard™ markers include methylated BMP3, NDRG4, and mutant KRAS while Cologuard Plus™ assesses methylated LASS4, LRRC4, and PPP2R5C. The respective mt-sDNA tests were studied in 9989 of 12,776 and 20,176 of 26,758 average-risk individuals undergoing colonoscopy and the results were compared to a commercially available FIT (with a positivity threshold of 20 μg hemoglobin/gram of stool).11,12 In both trials, the sensitivity for CRC and advanced precancerous lesions was higher with the mt-sDNA tests compared to FIT but had a significantly lower specificity for advanced precancerous lesions versus FIT (see Table 1). An age-related decline in specificity was noted in both trials with mt-sDNA, a trend not observed with FIT. This reduction may be attributed to age-related DNA methylation.
Multi-Target Stool RNA Test
A multi-target stool RNA test (mt-sRNA) commercially available as ColoSense™ is FDA-approved. It combines FIT (at a positivity threshold of 20 μg hemoglobin/gram of stool) with RNA-based stool markers. The combined results of the RNA markers, FIT, and smoking status provide a qualitative single test result. In the trial, 8,920 adults aged ≥45 underwent the mt-sRNA test and FIT followed by colonoscopy (13). The mt-sRNA showed higher sensitivity for CRC than FIT (94.4% versus 77.8%) and advanced adenomas (45.9% versus 28.9%) but lower CRC specificity (84.7% vs 94.7%) (Table 1). Unlike mt-sDNA-based tests, mt-sRNA showed consistent performance across age groups, addressing concerns about age-related declines in specificity attributed to DNA methylation.
Blood-Based Tests
In 2014, the first blood-based (BBT) CRC screening test known as Epi proColon™ was FDA but not Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) approved for average-risk adults ≥50 years of age who are offered and refused other U.S Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) endorsed CRC screening tests. It is a qualitative test for detection of circulating methylated Septin 9 (mSeptin9). The accuracy of mSeptin9 to detect CRC was assessed in a subset of 7941 asymptomatic average risk adults undergoing screening colonoscopy.14 The sensitivity and specificity for CRC were 48% and 91.5%, respectively. The sensitivity for advanced adenomas was 11.2%. An increase in sensitivity to 63.9% and reduction in specificity to 88.4% for CRC was demonstrated in a sub-analysis of available samples where an additional (third) polymerase chain replicate was performed. Epi proColon™ is not currently reimbursed by Medicare and not endorsed in the latest USPSTF guidelines.
Technologic advancements have improved the detection of circulating tumor markers in the blood. The Shield™ BBT approved by the FDA in 2024 for average risk adults ≥ 45 years integrates three types of cfDNA data (epigenetic changes resulting in the aberrant methylation or fragmentation patterns, and genomic changes resulting in somatic mutations) into a positive or negative test result. In the trial, 22,877 average-risk, asymptomatic individuals ages 45–84 were enrolled and clinical validation was performed in 7,861 of the participants.15 The sensitivity for CRC was 83.1% which decreased to 55% for stage I tumors (see Table 1). CRC specificity was 89.6% and the sensitivity for advanced adenomas and large sessile serrated lesions was 13.2%.
Another BBT SimpleScreen™, which is not yet FDA-approved, analyzed circulating, cell-free DNA methylation patterns in 27,010 evaluable average-risk, asymptomatic adults ages 45–85 years undergoing screening colonoscopy.16 The sensitivity and specificity for CRC was 79.2% and 91.5%, respectively. Similar to Shield, the sensitivity for stage I CRC was low at 57.1%. The sensitivity for advanced precancerous lesions, a secondary endpoint, was 12.5% which did not meet the prespecified study criteria.
Effectiveness and Cost Effectiveness
Modeling studies have evaluated novel noninvasive CRC screening tests compared to FIT and colonoscopy.17-20 One compared a hypothetical BBT performed every 3 years that meets the minimum CMS threshold CRC sensitivity and specificity of 74% and 90%, respectively, to other established CRC screening tests beginning at age 45.17 Every 3-year BBT reduced CRC incidence and mortality by 40% and 52%, respectively compared to no screening. However, the reductions were much lower than yearly FIT (72% and 76%, respectively), every 10 year colonoscopy (79% and 81%, respectively), and triennial mt-sDNA (68% and 73%, respectively). The BBT resulted in fewer quality-adjusted life-years per person compared to the alternatives.
Additionally, FIT, colonoscopy, and mt-sDNA were less costly and more effective. Advanced precancerous lesion detection was a key measure for a test’s effectiveness. BBT characteristics would require a CRC sensitivity and specificity of >90% and 90%, respectively, and 80% sensitivity for advanced precancerous lesions at a cost of ≤$120–$140 to be cost-effective compared to FIT at comparable participation rates.
Another analysis simulated colorectal neoplasia progression and compared clinical effectiveness and cost between annual FIT, every 3 year stool mt-sRNA, every 3 year stool mt-sDNA tests, every 3 year stool Shield™; these outcomes were compared to colonoscopy every 10 years and no screening in adults ≥ age 45 over different adherence rates.19 At real-world adherence rates of 60%, colonoscopy prevented most CRC cases and associated deaths. FIT was the most cost-effective strategy at all adherence levels. Between the multi-target stool tests and Shield™, mt-sRNA was the most cost-effective. Compared to FIT, mt-sRNA reduced CRC cases and deaths by 1% and 14%.
The third study evaluated CRC incidence and mortality, quality-adjusted life-years and costs with annual FIT, colonoscopy every 10 years, mt- sDNA tests, mt-sRNA test, and BBTs.20 The latest mt-sDNA (Colguard plus™) and mt-sRNA achieved benefits approaching FIT but the Shield™ test was substantially less effective. The authors hypothesized that if 15% of the population substituted Shield™ for current effective CRC screening strategies, an increase in CRC deaths would occur and require 9-10% of the unscreened population to uptake screening with Shield to avert the increases in CRC deaths due to the substitution effect.
Clinical Implications
The effectiveness of non-invasive screening strategies depends on their diagnostic performance, adherence, and ensuring a timely colonoscopy after a positive test. Two claims-based studies found 47.9% and 49% of patients underwent follow-up colonoscopy within 6 months of an abnormal stool or BBT CRC screening test, respectively.21-22
Conclusions
Non-invasive stool mt-sDNA and mt-sRNA have higher effectiveness than the new BBTs. BBTs can lead to increased CRC mortality if substituted for the FDA and CMS-approved, USPSTF-endorsed, CRC screening modalities. If future BBTs increase their sensitivity for CRC (including early-stage CRC) and advanced precancerous lesions and decrease their cost, they may prove to have similar cost-effectiveness to stool-based tests. Currently, BBTs are not a substitute for colonoscopy or other stool tests and should be offered to patients who refuse other CRC screening modalities. A personalized, risk-adapted approach, paired with improved adherence and follow-up are essential to optimize the population-level impact of CRC screening and ensure equitable, effective cancer prevention.
Dr. Gupta is based at the Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, Department of Medicine, University of Maryland School of Medicine, Baltimore. Dr. Burke and Dr. Macaron are based at the Department of Gastroenterology, Hepatology, and Nutrition, Cleveland Clinic, Cleveland, Ohio. Dr. Gupta and Dr. Macaron declared no conflicts of interest in regard to this article. Dr. Burke declared research support from Emtora Biosciences. She is a current consultant for Lumabridge, and has been a consultant for Sebela and Almirall. She also disclosed support from Myriad, Genzyme, Ferring, Merck, Sharp and Dohme, Abbvie, Salix, and Natera.
References
1. Benavidez GA, Sedani AE, Felder TM, Asare M, Rogers CR. Rural-urban disparities and trends in cancer screening: an analysis of Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance System data (2018-2022). JNCI Cancer Spectr. 2024 Nov 1;8(6):pkae113
2. Galoosian A, Dai H, Croymans D, et al. Population Health Colorectal Cancer Screening Strategies in Adults Aged 45 to 49 Years: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA. 2025 Aug 4:e2512049. doi: 10.1001/jama.2025.12049. Epub ahead of print.
3. Pilonis ND, Bugajski M, Wieszczy P, et al. Participation in Competing Strategies for Colorectal Cancer Screening: A Randomized Health Services Study (PICCOLINO Study). Gastroenterology. 2021 Mar;160(4):1097-1105.
4. Shaukat A, Mongin SJ, Geisser MS, et al. Long-term mortality after screening for colorectal cancer. N Engl J Med. 2013;369(12):1106–1114.
5. Kronborg O, Fenger C, Olsen J, Jørgensen OD, Søndergaard O. Randomised study of screening for colorectal cancer with faecal-occult-blood test. Lancet. 1996 Nov 30;348(9040):1467-71. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(96)03430-7. PMID: 8942774.
6. Burke CA, Lieberman D, Feuerstein JD. AGA Clinical Practice Update on Approach to the Use of Noninvasive Colorectal Cancer Screening Options: Commentary. Gastroenterology. 2022 Mar;162(3):952-956. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2021.09.075. Epub 2022 Jan 28. PMID: 35094786.
7. Imperiale TF, Gruber RN Stump TE, et al. Performance characteristics of fecal immunochemical tests for colorectal cancer and advanced adenomatous polyps: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann Intern Med 2019; 170(5):319-329
8. Doubeni CA, Corley DA, Jensen CD, et al. Fecal Immunochemical Test Screening and Risk of Colorectal Cancer Death. JAMA Netw Open. 2024 Jul 1;7(7):e2423671. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.23671.
9. Chiu HM, Jen GH, Wang YW, et al. Long-term effectiveness of faecal immunochemical test screening for proximal and distal colorectal cancers. Gut. 2021 Dec;70(12):2321-2329. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2020-322545. Epub 2021 Jan 25.
10. Castells A, Quintero E, Bujanda L, et al; COLONPREV study investigators. Effect of invitation to colonoscopy versus fecal immunochemical test screening on colorectal cancer mortality (COLONPREV): a pragmatic, randomised, controlled, non-inferiority trial. Lancet. 2025;405(10486):1231–1239
11. Imperiale TF, Ransohoff DF, Itzkowitz SH, et al. Multitarget stool DNA testing for colorectal-cancer screening. N Engl J Med. 2014;370(14):1287-1297
12. Imperiale TF, Porter K, Zella J, et al. Next-Generation Multitarget Stool DNA Test for Colorectal Cancer Screening. N Engl J Med. 2024 Mar 14;390(11):984-993
13. Barnell EK, Wurtzler EM, La Rocca J, et al. Multitarget Stool RNA Test for Colorectal Cancer Screening. JAMA. 2023 Nov 14;330(18):1760-1768.
14. Church TR, Wandell M, Lofton-Day C, et al. Prospective evaluation of methylated SEPT9 in plasma for detection of asymptomatic colorectal cancer. Gut 2014; 63:317–325.
15. Chung DC, Gray DM 2nd, Singh H, et al. A Cell-free DNA Blood-Based Test for Colorectal Cancer Screening. N Engl J Med. 2024 Mar 14;390(11):973-983.
16. Shaukat A, Burke CA, Chan AT, et al. Clinical Validation of a Circulating Tumor DNA-Based Blood Test to Screen for Colorectal Cancer. JAMA. 2025 Jul 1;334(1):56-63.
17. Ladabaum U, Mannalithara A, Weng Y, et al. Comparative Effectiveness and Cost-Effectiveness of Colorectal Cancer Screening with Blood-Based Biomarkers (Liquid Biopsy) vs Fecal Tests or Colonoscopy. Gastroenterology. 2024 Jul;167(2):378-391.
18. van den Puttelaar R, Nascimento de Lima P, Knudsen AB, et al. Effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of colorectal cancer screening with a blood test that meets the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services coverage decision. Gastroenterology 2024;167:368–377.
19. Shaukat A, Levin TR, Liang PS. Cost-effectiveness of Novel Noninvasive Screening Tests for Colorectal Neoplasia. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2025 Jun 23:S1542-3565(25)00525-7. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2025.06.006. Epub ahead of print. PMID: 40562290.
20. Ladabaum U, Mannalithara A, Schoen RE, Dominitz JA, Lieberman D. Projected Impact and Cost-Effectiveness of Novel Molecular Blood-Based or Stool-Based Screening Tests for Colorectal Cancer. Ann Intern Med. 2024 Dec;177(12):1610-1620.
20. Ciemins EL, Mohl JT, Moreno CA, Colangelo F, Smith RA, Barton M. Development of a Follow-Up Measure to Ensure Complete Screening for Colorectal Cancer. JAMA Netw Open. 2024 Mar 4;7(3):e242693. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.2693.
21. Zaki TA, Zhang NJ, Forbes SP, Raymond VM, Das AK, May FP. Colonoscopic Follow-up After Abnormal Blood-Based Colorectal Cancer Screening Results. Gastroenterology. 2025 Jul 21:S0016-5085(25)05775-0. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2025.07.019. Epub ahead of print. PMID: 40744392.
Introduction
Colorectal cancer (CRC) screening significantly reduces CRC incidence and mortality, but only 65% of eligible individuals report being up-to-date with screening.1 Colonoscopy is the most widely used opportunistic screening method in the United States and is associated with many barriers to uptake. Providing patients a choice of colonoscopy and/or stool-based tests, improves screening adherence in randomized controlled trials.2,3 Non-invasive screening options have expanded from stool occult blood and multi-target DNA tests, to multi-target stool RNA tests, and novel blood-based tests, the latter only U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved for patients who refuse colonoscopy and stool-based tests.
Stool Occult Blood Tests
Guaiac-based fecal occult blood testing (gFOBT) significantly reduces CRC mortality by 33%-35% when implemented on an annual or biennial basis.4,5 Fecal immunochemical testing (FIT) has supplanted gFOBT with advantages including independence from dietary restriction and medication-related interference, use of antibodies specific to human globin, and the need for only a single stool sample.
The most common threshold for a positive FIT in the U.S. is ≥ 20 micrograms (μg) of hemoglobin per gram (g) of stool. FIT is approved by the FDA as a qualitative positive or negative result based on a threshold value.6 A meta-analysis summarized test characteristics of commercially available FITs at various detection thresholds.7 The CRC sensitivity and specificity was 75% and 95% for ≥ 20 ug hemoglobin/g stool, and 91% and 90% for 10 ug hemoglobin/g stool, respectively. The sensitivity for advanced adenomas ranged from 25% at 20 μg/g to 40% at a 10 μg/g. Programmatic use of FIT in adults ages ≥ 50 years at 20 ug/g of stool, in cohort and case control studies, has been shown to significantly reduce CRC mortality by 33%-40% and advanced stage CRC by 34%.8,9
Over 57,000 average-risk individuals ages 50–69 years were randomized to biennial FIT or one-time colonoscopy and followed for 10 years.10 CRC mortality and incidence was similar between the groups: 0.22% with FIT vs. 0.24% with colonoscopy and 1.13% with FIT vs. 1.22% with colonoscopy, respectively. Thus, confirming biennial FIT screening is non-inferior to one-time colonoscopy in important CRC-related outcomes.
Multi-Target Stool Tests
Two multitarget stool DNA tests (mt-sDNA) known as Cologuard™ and Cologuard Plus™ have been approved by the FDA. Both tests include a FIT (with a positivity threshold of 20 μg hemoglobin per gram of stool) combined with DNA methylation markers. The test result is qualitative, reported as a positive or negative. Cologuard™ markers include methylated BMP3, NDRG4, and mutant KRAS while Cologuard Plus™ assesses methylated LASS4, LRRC4, and PPP2R5C. The respective mt-sDNA tests were studied in 9989 of 12,776 and 20,176 of 26,758 average-risk individuals undergoing colonoscopy and the results were compared to a commercially available FIT (with a positivity threshold of 20 μg hemoglobin/gram of stool).11,12 In both trials, the sensitivity for CRC and advanced precancerous lesions was higher with the mt-sDNA tests compared to FIT but had a significantly lower specificity for advanced precancerous lesions versus FIT (see Table 1). An age-related decline in specificity was noted in both trials with mt-sDNA, a trend not observed with FIT. This reduction may be attributed to age-related DNA methylation.
Multi-Target Stool RNA Test
A multi-target stool RNA test (mt-sRNA) commercially available as ColoSense™ is FDA-approved. It combines FIT (at a positivity threshold of 20 μg hemoglobin/gram of stool) with RNA-based stool markers. The combined results of the RNA markers, FIT, and smoking status provide a qualitative single test result. In the trial, 8,920 adults aged ≥45 underwent the mt-sRNA test and FIT followed by colonoscopy (13). The mt-sRNA showed higher sensitivity for CRC than FIT (94.4% versus 77.8%) and advanced adenomas (45.9% versus 28.9%) but lower CRC specificity (84.7% vs 94.7%) (Table 1). Unlike mt-sDNA-based tests, mt-sRNA showed consistent performance across age groups, addressing concerns about age-related declines in specificity attributed to DNA methylation.
Blood-Based Tests
In 2014, the first blood-based (BBT) CRC screening test known as Epi proColon™ was FDA but not Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) approved for average-risk adults ≥50 years of age who are offered and refused other U.S Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) endorsed CRC screening tests. It is a qualitative test for detection of circulating methylated Septin 9 (mSeptin9). The accuracy of mSeptin9 to detect CRC was assessed in a subset of 7941 asymptomatic average risk adults undergoing screening colonoscopy.14 The sensitivity and specificity for CRC were 48% and 91.5%, respectively. The sensitivity for advanced adenomas was 11.2%. An increase in sensitivity to 63.9% and reduction in specificity to 88.4% for CRC was demonstrated in a sub-analysis of available samples where an additional (third) polymerase chain replicate was performed. Epi proColon™ is not currently reimbursed by Medicare and not endorsed in the latest USPSTF guidelines.
Technologic advancements have improved the detection of circulating tumor markers in the blood. The Shield™ BBT approved by the FDA in 2024 for average risk adults ≥ 45 years integrates three types of cfDNA data (epigenetic changes resulting in the aberrant methylation or fragmentation patterns, and genomic changes resulting in somatic mutations) into a positive or negative test result. In the trial, 22,877 average-risk, asymptomatic individuals ages 45–84 were enrolled and clinical validation was performed in 7,861 of the participants.15 The sensitivity for CRC was 83.1% which decreased to 55% for stage I tumors (see Table 1). CRC specificity was 89.6% and the sensitivity for advanced adenomas and large sessile serrated lesions was 13.2%.
Another BBT SimpleScreen™, which is not yet FDA-approved, analyzed circulating, cell-free DNA methylation patterns in 27,010 evaluable average-risk, asymptomatic adults ages 45–85 years undergoing screening colonoscopy.16 The sensitivity and specificity for CRC was 79.2% and 91.5%, respectively. Similar to Shield, the sensitivity for stage I CRC was low at 57.1%. The sensitivity for advanced precancerous lesions, a secondary endpoint, was 12.5% which did not meet the prespecified study criteria.
Effectiveness and Cost Effectiveness
Modeling studies have evaluated novel noninvasive CRC screening tests compared to FIT and colonoscopy.17-20 One compared a hypothetical BBT performed every 3 years that meets the minimum CMS threshold CRC sensitivity and specificity of 74% and 90%, respectively, to other established CRC screening tests beginning at age 45.17 Every 3-year BBT reduced CRC incidence and mortality by 40% and 52%, respectively compared to no screening. However, the reductions were much lower than yearly FIT (72% and 76%, respectively), every 10 year colonoscopy (79% and 81%, respectively), and triennial mt-sDNA (68% and 73%, respectively). The BBT resulted in fewer quality-adjusted life-years per person compared to the alternatives.
Additionally, FIT, colonoscopy, and mt-sDNA were less costly and more effective. Advanced precancerous lesion detection was a key measure for a test’s effectiveness. BBT characteristics would require a CRC sensitivity and specificity of >90% and 90%, respectively, and 80% sensitivity for advanced precancerous lesions at a cost of ≤$120–$140 to be cost-effective compared to FIT at comparable participation rates.
Another analysis simulated colorectal neoplasia progression and compared clinical effectiveness and cost between annual FIT, every 3 year stool mt-sRNA, every 3 year stool mt-sDNA tests, every 3 year stool Shield™; these outcomes were compared to colonoscopy every 10 years and no screening in adults ≥ age 45 over different adherence rates.19 At real-world adherence rates of 60%, colonoscopy prevented most CRC cases and associated deaths. FIT was the most cost-effective strategy at all adherence levels. Between the multi-target stool tests and Shield™, mt-sRNA was the most cost-effective. Compared to FIT, mt-sRNA reduced CRC cases and deaths by 1% and 14%.
The third study evaluated CRC incidence and mortality, quality-adjusted life-years and costs with annual FIT, colonoscopy every 10 years, mt- sDNA tests, mt-sRNA test, and BBTs.20 The latest mt-sDNA (Colguard plus™) and mt-sRNA achieved benefits approaching FIT but the Shield™ test was substantially less effective. The authors hypothesized that if 15% of the population substituted Shield™ for current effective CRC screening strategies, an increase in CRC deaths would occur and require 9-10% of the unscreened population to uptake screening with Shield to avert the increases in CRC deaths due to the substitution effect.
Clinical Implications
The effectiveness of non-invasive screening strategies depends on their diagnostic performance, adherence, and ensuring a timely colonoscopy after a positive test. Two claims-based studies found 47.9% and 49% of patients underwent follow-up colonoscopy within 6 months of an abnormal stool or BBT CRC screening test, respectively.21-22
Conclusions
Non-invasive stool mt-sDNA and mt-sRNA have higher effectiveness than the new BBTs. BBTs can lead to increased CRC mortality if substituted for the FDA and CMS-approved, USPSTF-endorsed, CRC screening modalities. If future BBTs increase their sensitivity for CRC (including early-stage CRC) and advanced precancerous lesions and decrease their cost, they may prove to have similar cost-effectiveness to stool-based tests. Currently, BBTs are not a substitute for colonoscopy or other stool tests and should be offered to patients who refuse other CRC screening modalities. A personalized, risk-adapted approach, paired with improved adherence and follow-up are essential to optimize the population-level impact of CRC screening and ensure equitable, effective cancer prevention.
Dr. Gupta is based at the Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, Department of Medicine, University of Maryland School of Medicine, Baltimore. Dr. Burke and Dr. Macaron are based at the Department of Gastroenterology, Hepatology, and Nutrition, Cleveland Clinic, Cleveland, Ohio. Dr. Gupta and Dr. Macaron declared no conflicts of interest in regard to this article. Dr. Burke declared research support from Emtora Biosciences. She is a current consultant for Lumabridge, and has been a consultant for Sebela and Almirall. She also disclosed support from Myriad, Genzyme, Ferring, Merck, Sharp and Dohme, Abbvie, Salix, and Natera.
References
1. Benavidez GA, Sedani AE, Felder TM, Asare M, Rogers CR. Rural-urban disparities and trends in cancer screening: an analysis of Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance System data (2018-2022). JNCI Cancer Spectr. 2024 Nov 1;8(6):pkae113
2. Galoosian A, Dai H, Croymans D, et al. Population Health Colorectal Cancer Screening Strategies in Adults Aged 45 to 49 Years: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA. 2025 Aug 4:e2512049. doi: 10.1001/jama.2025.12049. Epub ahead of print.
3. Pilonis ND, Bugajski M, Wieszczy P, et al. Participation in Competing Strategies for Colorectal Cancer Screening: A Randomized Health Services Study (PICCOLINO Study). Gastroenterology. 2021 Mar;160(4):1097-1105.
4. Shaukat A, Mongin SJ, Geisser MS, et al. Long-term mortality after screening for colorectal cancer. N Engl J Med. 2013;369(12):1106–1114.
5. Kronborg O, Fenger C, Olsen J, Jørgensen OD, Søndergaard O. Randomised study of screening for colorectal cancer with faecal-occult-blood test. Lancet. 1996 Nov 30;348(9040):1467-71. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(96)03430-7. PMID: 8942774.
6. Burke CA, Lieberman D, Feuerstein JD. AGA Clinical Practice Update on Approach to the Use of Noninvasive Colorectal Cancer Screening Options: Commentary. Gastroenterology. 2022 Mar;162(3):952-956. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2021.09.075. Epub 2022 Jan 28. PMID: 35094786.
7. Imperiale TF, Gruber RN Stump TE, et al. Performance characteristics of fecal immunochemical tests for colorectal cancer and advanced adenomatous polyps: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann Intern Med 2019; 170(5):319-329
8. Doubeni CA, Corley DA, Jensen CD, et al. Fecal Immunochemical Test Screening and Risk of Colorectal Cancer Death. JAMA Netw Open. 2024 Jul 1;7(7):e2423671. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.23671.
9. Chiu HM, Jen GH, Wang YW, et al. Long-term effectiveness of faecal immunochemical test screening for proximal and distal colorectal cancers. Gut. 2021 Dec;70(12):2321-2329. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2020-322545. Epub 2021 Jan 25.
10. Castells A, Quintero E, Bujanda L, et al; COLONPREV study investigators. Effect of invitation to colonoscopy versus fecal immunochemical test screening on colorectal cancer mortality (COLONPREV): a pragmatic, randomised, controlled, non-inferiority trial. Lancet. 2025;405(10486):1231–1239
11. Imperiale TF, Ransohoff DF, Itzkowitz SH, et al. Multitarget stool DNA testing for colorectal-cancer screening. N Engl J Med. 2014;370(14):1287-1297
12. Imperiale TF, Porter K, Zella J, et al. Next-Generation Multitarget Stool DNA Test for Colorectal Cancer Screening. N Engl J Med. 2024 Mar 14;390(11):984-993
13. Barnell EK, Wurtzler EM, La Rocca J, et al. Multitarget Stool RNA Test for Colorectal Cancer Screening. JAMA. 2023 Nov 14;330(18):1760-1768.
14. Church TR, Wandell M, Lofton-Day C, et al. Prospective evaluation of methylated SEPT9 in plasma for detection of asymptomatic colorectal cancer. Gut 2014; 63:317–325.
15. Chung DC, Gray DM 2nd, Singh H, et al. A Cell-free DNA Blood-Based Test for Colorectal Cancer Screening. N Engl J Med. 2024 Mar 14;390(11):973-983.
16. Shaukat A, Burke CA, Chan AT, et al. Clinical Validation of a Circulating Tumor DNA-Based Blood Test to Screen for Colorectal Cancer. JAMA. 2025 Jul 1;334(1):56-63.
17. Ladabaum U, Mannalithara A, Weng Y, et al. Comparative Effectiveness and Cost-Effectiveness of Colorectal Cancer Screening with Blood-Based Biomarkers (Liquid Biopsy) vs Fecal Tests or Colonoscopy. Gastroenterology. 2024 Jul;167(2):378-391.
18. van den Puttelaar R, Nascimento de Lima P, Knudsen AB, et al. Effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of colorectal cancer screening with a blood test that meets the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services coverage decision. Gastroenterology 2024;167:368–377.
19. Shaukat A, Levin TR, Liang PS. Cost-effectiveness of Novel Noninvasive Screening Tests for Colorectal Neoplasia. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2025 Jun 23:S1542-3565(25)00525-7. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2025.06.006. Epub ahead of print. PMID: 40562290.
20. Ladabaum U, Mannalithara A, Schoen RE, Dominitz JA, Lieberman D. Projected Impact and Cost-Effectiveness of Novel Molecular Blood-Based or Stool-Based Screening Tests for Colorectal Cancer. Ann Intern Med. 2024 Dec;177(12):1610-1620.
20. Ciemins EL, Mohl JT, Moreno CA, Colangelo F, Smith RA, Barton M. Development of a Follow-Up Measure to Ensure Complete Screening for Colorectal Cancer. JAMA Netw Open. 2024 Mar 4;7(3):e242693. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.2693.
21. Zaki TA, Zhang NJ, Forbes SP, Raymond VM, Das AK, May FP. Colonoscopic Follow-up After Abnormal Blood-Based Colorectal Cancer Screening Results. Gastroenterology. 2025 Jul 21:S0016-5085(25)05775-0. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2025.07.019. Epub ahead of print. PMID: 40744392.
Introduction
Colorectal cancer (CRC) screening significantly reduces CRC incidence and mortality, but only 65% of eligible individuals report being up-to-date with screening.1 Colonoscopy is the most widely used opportunistic screening method in the United States and is associated with many barriers to uptake. Providing patients a choice of colonoscopy and/or stool-based tests, improves screening adherence in randomized controlled trials.2,3 Non-invasive screening options have expanded from stool occult blood and multi-target DNA tests, to multi-target stool RNA tests, and novel blood-based tests, the latter only U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved for patients who refuse colonoscopy and stool-based tests.
Stool Occult Blood Tests
Guaiac-based fecal occult blood testing (gFOBT) significantly reduces CRC mortality by 33%-35% when implemented on an annual or biennial basis.4,5 Fecal immunochemical testing (FIT) has supplanted gFOBT with advantages including independence from dietary restriction and medication-related interference, use of antibodies specific to human globin, and the need for only a single stool sample.
The most common threshold for a positive FIT in the U.S. is ≥ 20 micrograms (μg) of hemoglobin per gram (g) of stool. FIT is approved by the FDA as a qualitative positive or negative result based on a threshold value.6 A meta-analysis summarized test characteristics of commercially available FITs at various detection thresholds.7 The CRC sensitivity and specificity was 75% and 95% for ≥ 20 ug hemoglobin/g stool, and 91% and 90% for 10 ug hemoglobin/g stool, respectively. The sensitivity for advanced adenomas ranged from 25% at 20 μg/g to 40% at a 10 μg/g. Programmatic use of FIT in adults ages ≥ 50 years at 20 ug/g of stool, in cohort and case control studies, has been shown to significantly reduce CRC mortality by 33%-40% and advanced stage CRC by 34%.8,9
Over 57,000 average-risk individuals ages 50–69 years were randomized to biennial FIT or one-time colonoscopy and followed for 10 years.10 CRC mortality and incidence was similar between the groups: 0.22% with FIT vs. 0.24% with colonoscopy and 1.13% with FIT vs. 1.22% with colonoscopy, respectively. Thus, confirming biennial FIT screening is non-inferior to one-time colonoscopy in important CRC-related outcomes.
Multi-Target Stool Tests
Two multitarget stool DNA tests (mt-sDNA) known as Cologuard™ and Cologuard Plus™ have been approved by the FDA. Both tests include a FIT (with a positivity threshold of 20 μg hemoglobin per gram of stool) combined with DNA methylation markers. The test result is qualitative, reported as a positive or negative. Cologuard™ markers include methylated BMP3, NDRG4, and mutant KRAS while Cologuard Plus™ assesses methylated LASS4, LRRC4, and PPP2R5C. The respective mt-sDNA tests were studied in 9989 of 12,776 and 20,176 of 26,758 average-risk individuals undergoing colonoscopy and the results were compared to a commercially available FIT (with a positivity threshold of 20 μg hemoglobin/gram of stool).11,12 In both trials, the sensitivity for CRC and advanced precancerous lesions was higher with the mt-sDNA tests compared to FIT but had a significantly lower specificity for advanced precancerous lesions versus FIT (see Table 1). An age-related decline in specificity was noted in both trials with mt-sDNA, a trend not observed with FIT. This reduction may be attributed to age-related DNA methylation.
Multi-Target Stool RNA Test
A multi-target stool RNA test (mt-sRNA) commercially available as ColoSense™ is FDA-approved. It combines FIT (at a positivity threshold of 20 μg hemoglobin/gram of stool) with RNA-based stool markers. The combined results of the RNA markers, FIT, and smoking status provide a qualitative single test result. In the trial, 8,920 adults aged ≥45 underwent the mt-sRNA test and FIT followed by colonoscopy (13). The mt-sRNA showed higher sensitivity for CRC than FIT (94.4% versus 77.8%) and advanced adenomas (45.9% versus 28.9%) but lower CRC specificity (84.7% vs 94.7%) (Table 1). Unlike mt-sDNA-based tests, mt-sRNA showed consistent performance across age groups, addressing concerns about age-related declines in specificity attributed to DNA methylation.
Blood-Based Tests
In 2014, the first blood-based (BBT) CRC screening test known as Epi proColon™ was FDA but not Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) approved for average-risk adults ≥50 years of age who are offered and refused other U.S Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) endorsed CRC screening tests. It is a qualitative test for detection of circulating methylated Septin 9 (mSeptin9). The accuracy of mSeptin9 to detect CRC was assessed in a subset of 7941 asymptomatic average risk adults undergoing screening colonoscopy.14 The sensitivity and specificity for CRC were 48% and 91.5%, respectively. The sensitivity for advanced adenomas was 11.2%. An increase in sensitivity to 63.9% and reduction in specificity to 88.4% for CRC was demonstrated in a sub-analysis of available samples where an additional (third) polymerase chain replicate was performed. Epi proColon™ is not currently reimbursed by Medicare and not endorsed in the latest USPSTF guidelines.
Technologic advancements have improved the detection of circulating tumor markers in the blood. The Shield™ BBT approved by the FDA in 2024 for average risk adults ≥ 45 years integrates three types of cfDNA data (epigenetic changes resulting in the aberrant methylation or fragmentation patterns, and genomic changes resulting in somatic mutations) into a positive or negative test result. In the trial, 22,877 average-risk, asymptomatic individuals ages 45–84 were enrolled and clinical validation was performed in 7,861 of the participants.15 The sensitivity for CRC was 83.1% which decreased to 55% for stage I tumors (see Table 1). CRC specificity was 89.6% and the sensitivity for advanced adenomas and large sessile serrated lesions was 13.2%.
Another BBT SimpleScreen™, which is not yet FDA-approved, analyzed circulating, cell-free DNA methylation patterns in 27,010 evaluable average-risk, asymptomatic adults ages 45–85 years undergoing screening colonoscopy.16 The sensitivity and specificity for CRC was 79.2% and 91.5%, respectively. Similar to Shield, the sensitivity for stage I CRC was low at 57.1%. The sensitivity for advanced precancerous lesions, a secondary endpoint, was 12.5% which did not meet the prespecified study criteria.
Effectiveness and Cost Effectiveness
Modeling studies have evaluated novel noninvasive CRC screening tests compared to FIT and colonoscopy.17-20 One compared a hypothetical BBT performed every 3 years that meets the minimum CMS threshold CRC sensitivity and specificity of 74% and 90%, respectively, to other established CRC screening tests beginning at age 45.17 Every 3-year BBT reduced CRC incidence and mortality by 40% and 52%, respectively compared to no screening. However, the reductions were much lower than yearly FIT (72% and 76%, respectively), every 10 year colonoscopy (79% and 81%, respectively), and triennial mt-sDNA (68% and 73%, respectively). The BBT resulted in fewer quality-adjusted life-years per person compared to the alternatives.
Additionally, FIT, colonoscopy, and mt-sDNA were less costly and more effective. Advanced precancerous lesion detection was a key measure for a test’s effectiveness. BBT characteristics would require a CRC sensitivity and specificity of >90% and 90%, respectively, and 80% sensitivity for advanced precancerous lesions at a cost of ≤$120–$140 to be cost-effective compared to FIT at comparable participation rates.
Another analysis simulated colorectal neoplasia progression and compared clinical effectiveness and cost between annual FIT, every 3 year stool mt-sRNA, every 3 year stool mt-sDNA tests, every 3 year stool Shield™; these outcomes were compared to colonoscopy every 10 years and no screening in adults ≥ age 45 over different adherence rates.19 At real-world adherence rates of 60%, colonoscopy prevented most CRC cases and associated deaths. FIT was the most cost-effective strategy at all adherence levels. Between the multi-target stool tests and Shield™, mt-sRNA was the most cost-effective. Compared to FIT, mt-sRNA reduced CRC cases and deaths by 1% and 14%.
The third study evaluated CRC incidence and mortality, quality-adjusted life-years and costs with annual FIT, colonoscopy every 10 years, mt- sDNA tests, mt-sRNA test, and BBTs.20 The latest mt-sDNA (Colguard plus™) and mt-sRNA achieved benefits approaching FIT but the Shield™ test was substantially less effective. The authors hypothesized that if 15% of the population substituted Shield™ for current effective CRC screening strategies, an increase in CRC deaths would occur and require 9-10% of the unscreened population to uptake screening with Shield to avert the increases in CRC deaths due to the substitution effect.
Clinical Implications
The effectiveness of non-invasive screening strategies depends on their diagnostic performance, adherence, and ensuring a timely colonoscopy after a positive test. Two claims-based studies found 47.9% and 49% of patients underwent follow-up colonoscopy within 6 months of an abnormal stool or BBT CRC screening test, respectively.21-22
Conclusions
Non-invasive stool mt-sDNA and mt-sRNA have higher effectiveness than the new BBTs. BBTs can lead to increased CRC mortality if substituted for the FDA and CMS-approved, USPSTF-endorsed, CRC screening modalities. If future BBTs increase their sensitivity for CRC (including early-stage CRC) and advanced precancerous lesions and decrease their cost, they may prove to have similar cost-effectiveness to stool-based tests. Currently, BBTs are not a substitute for colonoscopy or other stool tests and should be offered to patients who refuse other CRC screening modalities. A personalized, risk-adapted approach, paired with improved adherence and follow-up are essential to optimize the population-level impact of CRC screening and ensure equitable, effective cancer prevention.
Dr. Gupta is based at the Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, Department of Medicine, University of Maryland School of Medicine, Baltimore. Dr. Burke and Dr. Macaron are based at the Department of Gastroenterology, Hepatology, and Nutrition, Cleveland Clinic, Cleveland, Ohio. Dr. Gupta and Dr. Macaron declared no conflicts of interest in regard to this article. Dr. Burke declared research support from Emtora Biosciences. She is a current consultant for Lumabridge, and has been a consultant for Sebela and Almirall. She also disclosed support from Myriad, Genzyme, Ferring, Merck, Sharp and Dohme, Abbvie, Salix, and Natera.
References
1. Benavidez GA, Sedani AE, Felder TM, Asare M, Rogers CR. Rural-urban disparities and trends in cancer screening: an analysis of Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance System data (2018-2022). JNCI Cancer Spectr. 2024 Nov 1;8(6):pkae113
2. Galoosian A, Dai H, Croymans D, et al. Population Health Colorectal Cancer Screening Strategies in Adults Aged 45 to 49 Years: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA. 2025 Aug 4:e2512049. doi: 10.1001/jama.2025.12049. Epub ahead of print.
3. Pilonis ND, Bugajski M, Wieszczy P, et al. Participation in Competing Strategies for Colorectal Cancer Screening: A Randomized Health Services Study (PICCOLINO Study). Gastroenterology. 2021 Mar;160(4):1097-1105.
4. Shaukat A, Mongin SJ, Geisser MS, et al. Long-term mortality after screening for colorectal cancer. N Engl J Med. 2013;369(12):1106–1114.
5. Kronborg O, Fenger C, Olsen J, Jørgensen OD, Søndergaard O. Randomised study of screening for colorectal cancer with faecal-occult-blood test. Lancet. 1996 Nov 30;348(9040):1467-71. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(96)03430-7. PMID: 8942774.
6. Burke CA, Lieberman D, Feuerstein JD. AGA Clinical Practice Update on Approach to the Use of Noninvasive Colorectal Cancer Screening Options: Commentary. Gastroenterology. 2022 Mar;162(3):952-956. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2021.09.075. Epub 2022 Jan 28. PMID: 35094786.
7. Imperiale TF, Gruber RN Stump TE, et al. Performance characteristics of fecal immunochemical tests for colorectal cancer and advanced adenomatous polyps: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann Intern Med 2019; 170(5):319-329
8. Doubeni CA, Corley DA, Jensen CD, et al. Fecal Immunochemical Test Screening and Risk of Colorectal Cancer Death. JAMA Netw Open. 2024 Jul 1;7(7):e2423671. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.23671.
9. Chiu HM, Jen GH, Wang YW, et al. Long-term effectiveness of faecal immunochemical test screening for proximal and distal colorectal cancers. Gut. 2021 Dec;70(12):2321-2329. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2020-322545. Epub 2021 Jan 25.
10. Castells A, Quintero E, Bujanda L, et al; COLONPREV study investigators. Effect of invitation to colonoscopy versus fecal immunochemical test screening on colorectal cancer mortality (COLONPREV): a pragmatic, randomised, controlled, non-inferiority trial. Lancet. 2025;405(10486):1231–1239
11. Imperiale TF, Ransohoff DF, Itzkowitz SH, et al. Multitarget stool DNA testing for colorectal-cancer screening. N Engl J Med. 2014;370(14):1287-1297
12. Imperiale TF, Porter K, Zella J, et al. Next-Generation Multitarget Stool DNA Test for Colorectal Cancer Screening. N Engl J Med. 2024 Mar 14;390(11):984-993
13. Barnell EK, Wurtzler EM, La Rocca J, et al. Multitarget Stool RNA Test for Colorectal Cancer Screening. JAMA. 2023 Nov 14;330(18):1760-1768.
14. Church TR, Wandell M, Lofton-Day C, et al. Prospective evaluation of methylated SEPT9 in plasma for detection of asymptomatic colorectal cancer. Gut 2014; 63:317–325.
15. Chung DC, Gray DM 2nd, Singh H, et al. A Cell-free DNA Blood-Based Test for Colorectal Cancer Screening. N Engl J Med. 2024 Mar 14;390(11):973-983.
16. Shaukat A, Burke CA, Chan AT, et al. Clinical Validation of a Circulating Tumor DNA-Based Blood Test to Screen for Colorectal Cancer. JAMA. 2025 Jul 1;334(1):56-63.
17. Ladabaum U, Mannalithara A, Weng Y, et al. Comparative Effectiveness and Cost-Effectiveness of Colorectal Cancer Screening with Blood-Based Biomarkers (Liquid Biopsy) vs Fecal Tests or Colonoscopy. Gastroenterology. 2024 Jul;167(2):378-391.
18. van den Puttelaar R, Nascimento de Lima P, Knudsen AB, et al. Effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of colorectal cancer screening with a blood test that meets the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services coverage decision. Gastroenterology 2024;167:368–377.
19. Shaukat A, Levin TR, Liang PS. Cost-effectiveness of Novel Noninvasive Screening Tests for Colorectal Neoplasia. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2025 Jun 23:S1542-3565(25)00525-7. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2025.06.006. Epub ahead of print. PMID: 40562290.
20. Ladabaum U, Mannalithara A, Schoen RE, Dominitz JA, Lieberman D. Projected Impact and Cost-Effectiveness of Novel Molecular Blood-Based or Stool-Based Screening Tests for Colorectal Cancer. Ann Intern Med. 2024 Dec;177(12):1610-1620.
20. Ciemins EL, Mohl JT, Moreno CA, Colangelo F, Smith RA, Barton M. Development of a Follow-Up Measure to Ensure Complete Screening for Colorectal Cancer. JAMA Netw Open. 2024 Mar 4;7(3):e242693. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.2693.
21. Zaki TA, Zhang NJ, Forbes SP, Raymond VM, Das AK, May FP. Colonoscopic Follow-up After Abnormal Blood-Based Colorectal Cancer Screening Results. Gastroenterology. 2025 Jul 21:S0016-5085(25)05775-0. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2025.07.019. Epub ahead of print. PMID: 40744392.
‘So You Have an Idea…’: A Practical Guide to Tech and Device Development for the Early Career GI
You are in the middle of a busy clinic day and think, “there has to be a better way to do this.” Suddenly, a better way to do something becomes obvious. Maybe it’s a tool that simplifies documentation, a device that improves patient comfort, or an app that bridges a clinical gap. Many physicians, especially early career gastroenterologists, have ideas like this, but few know what to do next.
This article is for the curious innovator at the beginning of their clinical career. It offers practical, real-world guidance on developing a clinical product: whether that be hardware, software, or a hybrid. It outlines what questions to ask, who to consult, and how to protect your work, using personal insights and business principles learned through lived experience.
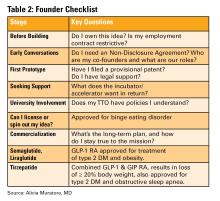
1. Understand Intellectual Property (IP): Know Its Value and Ownership
What is IP?
Intellectual property refers to your original creations: inventions, designs, software, and more. This is what you want to protect legally through patents, trademarks, or copyrights.
Who owns your idea?
This is the first and most important question to ask. If you are employed (especially by a hospital or academic center), your contract may already give your employer rights to any inventions you create, even those developed in your personal time.
What to ask:
- Does my employment contract include an “assignment of inventions” clause?
- Does the institution claim rights to anything developed with institutional resources?
- Are there moonlighting or external activity policies that affect this?
If you are developing an idea on your personal time, with your own resources, and outside your scope of clinical duties, it might still be considered “theirs” under some contracts. Early legal consultation is critical. A specialized IP attorney can help you understand what you own and how to protect it. This should be done early, ideally before you start building anything.
2. Lawyers Aren’t Optional: They’re Essential Early Partners
You do not need a full legal team, but you do need a lawyer early. An early consultation with an IP attorney can clarify your rights, guide your filing process (e.g. provisional patents), and help you avoid costly missteps.
Do this before sharing your idea publicly, including in academic presentations, pitch competitions, or even on social media. Public disclosure can start a clock ticking for application to protect your IP.
3. Build a Founding Team with Intent
Think of your startup team like a long-term relationship: you’re committing to build something together through uncertainty, tension, and change.
Strong early-stage teams often include:
- The Visionary – understands the clinical need and vision
- The Builder – engineer, developer, or designer
- The Doer – project manager or operations lead
Before forming a company, clearly define:
- Ownership (equity percentages)
- Roles and responsibilities
- Time commitments
- What happens if someone exits
Have these discussions early and document your agreements. Avoid informal “handshake” deals that can lead to serious disputes later.
4. You Don’t Need to Know Everything on Day One
You do not need to know how to write code, build a prototype, or get FDA clearance on day one. Successful innovators are humble learners. Use a Minimum Viable Product (MVP), a simple, functional version of your idea, to test assumptions and gather feedback. Iterate based on what you learn. Do not chase perfection; pursue progress. Consider using online accelerators like Y Combinator’s startup school or AGA’s Center for GI Innovation and Technology.
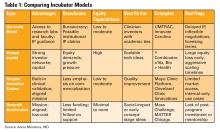
5. Incubators: Use them Strategically
Incubators can offer mentorship, seed funding, legal support, and technical resources, but they vary widely in value (see Table 1). Many may want equity, and not all offer when you truly need.
Ask Yourself:
- Do I need technical help, business mentorship, or just accountability?
- What does this incubator offer in terms of IP protection, exposure, and connections?
- Do I understand the equity trade-off?
- What services and funding do they provide?
- Do they take equity? How much and when?
- What’s their track record with similar ventures?
- Are their incentives aligned with your vision?
6. Academic Institutions: Partners or Pitfalls?
Universities can provide credibility, resources, and early funding through their tech transfer office (TTO).
Key Questions to Ask:
- Will my IP be managed by the TTO?
- How much say do I have in licensing decisions?
- Are there royalty-sharing agreements in place?
- Can I form a startup while employed here?
You may need to negotiate if you want to commercialize your idea independently.
7. Do it for Purpose, Not Payday
Most founders end up owning only a small percentage of their company by the time a product reaches the market. Do not expect to get rich. Do it because it solves a problem you care about. If it happens to come with a nice paycheck, then that is an added bonus.
Your clinical training and insight give you a unique edge. You already know what’s broken. Use that as your compass.
Conclusion
Innovation isn’t about brilliance, it’s about curiosity, structure, and tenacity (see Table 2). Start small. Protect your work. Choose the right partners. Most importantly, stay anchored in your mission to make GI care better.
Dr. Muratore is based at UNC Rex Digestive Health, Raleigh, North Carolina. She has no conflicts related to this article. Dr. Wechsler is based at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Chapel Hill, North Carolina. She holds a patent assigned to Trustees of Dartmouth College. Dr. Shah is based at the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, Michigan. He consults for Ardelyx, Laborie, Neuraxis, Salix, Sanofi, and Takeda and holds a patent with the Regents of the University of Michigan.
You are in the middle of a busy clinic day and think, “there has to be a better way to do this.” Suddenly, a better way to do something becomes obvious. Maybe it’s a tool that simplifies documentation, a device that improves patient comfort, or an app that bridges a clinical gap. Many physicians, especially early career gastroenterologists, have ideas like this, but few know what to do next.
This article is for the curious innovator at the beginning of their clinical career. It offers practical, real-world guidance on developing a clinical product: whether that be hardware, software, or a hybrid. It outlines what questions to ask, who to consult, and how to protect your work, using personal insights and business principles learned through lived experience.
1. Understand Intellectual Property (IP): Know Its Value and Ownership
What is IP?
Intellectual property refers to your original creations: inventions, designs, software, and more. This is what you want to protect legally through patents, trademarks, or copyrights.
Who owns your idea?
This is the first and most important question to ask. If you are employed (especially by a hospital or academic center), your contract may already give your employer rights to any inventions you create, even those developed in your personal time.
What to ask:
- Does my employment contract include an “assignment of inventions” clause?
- Does the institution claim rights to anything developed with institutional resources?
- Are there moonlighting or external activity policies that affect this?
If you are developing an idea on your personal time, with your own resources, and outside your scope of clinical duties, it might still be considered “theirs” under some contracts. Early legal consultation is critical. A specialized IP attorney can help you understand what you own and how to protect it. This should be done early, ideally before you start building anything.
2. Lawyers Aren’t Optional: They’re Essential Early Partners
You do not need a full legal team, but you do need a lawyer early. An early consultation with an IP attorney can clarify your rights, guide your filing process (e.g. provisional patents), and help you avoid costly missteps.
Do this before sharing your idea publicly, including in academic presentations, pitch competitions, or even on social media. Public disclosure can start a clock ticking for application to protect your IP.
3. Build a Founding Team with Intent
Think of your startup team like a long-term relationship: you’re committing to build something together through uncertainty, tension, and change.
Strong early-stage teams often include:
- The Visionary – understands the clinical need and vision
- The Builder – engineer, developer, or designer
- The Doer – project manager or operations lead
Before forming a company, clearly define:
- Ownership (equity percentages)
- Roles and responsibilities
- Time commitments
- What happens if someone exits
Have these discussions early and document your agreements. Avoid informal “handshake” deals that can lead to serious disputes later.
4. You Don’t Need to Know Everything on Day One
You do not need to know how to write code, build a prototype, or get FDA clearance on day one. Successful innovators are humble learners. Use a Minimum Viable Product (MVP), a simple, functional version of your idea, to test assumptions and gather feedback. Iterate based on what you learn. Do not chase perfection; pursue progress. Consider using online accelerators like Y Combinator’s startup school or AGA’s Center for GI Innovation and Technology.
5. Incubators: Use them Strategically
Incubators can offer mentorship, seed funding, legal support, and technical resources, but they vary widely in value (see Table 1). Many may want equity, and not all offer when you truly need.
Ask Yourself:
- Do I need technical help, business mentorship, or just accountability?
- What does this incubator offer in terms of IP protection, exposure, and connections?
- Do I understand the equity trade-off?
- What services and funding do they provide?
- Do they take equity? How much and when?
- What’s their track record with similar ventures?
- Are their incentives aligned with your vision?
6. Academic Institutions: Partners or Pitfalls?
Universities can provide credibility, resources, and early funding through their tech transfer office (TTO).
Key Questions to Ask:
- Will my IP be managed by the TTO?
- How much say do I have in licensing decisions?
- Are there royalty-sharing agreements in place?
- Can I form a startup while employed here?
You may need to negotiate if you want to commercialize your idea independently.
7. Do it for Purpose, Not Payday
Most founders end up owning only a small percentage of their company by the time a product reaches the market. Do not expect to get rich. Do it because it solves a problem you care about. If it happens to come with a nice paycheck, then that is an added bonus.
Your clinical training and insight give you a unique edge. You already know what’s broken. Use that as your compass.
Conclusion
Innovation isn’t about brilliance, it’s about curiosity, structure, and tenacity (see Table 2). Start small. Protect your work. Choose the right partners. Most importantly, stay anchored in your mission to make GI care better.
Dr. Muratore is based at UNC Rex Digestive Health, Raleigh, North Carolina. She has no conflicts related to this article. Dr. Wechsler is based at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Chapel Hill, North Carolina. She holds a patent assigned to Trustees of Dartmouth College. Dr. Shah is based at the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, Michigan. He consults for Ardelyx, Laborie, Neuraxis, Salix, Sanofi, and Takeda and holds a patent with the Regents of the University of Michigan.
You are in the middle of a busy clinic day and think, “there has to be a better way to do this.” Suddenly, a better way to do something becomes obvious. Maybe it’s a tool that simplifies documentation, a device that improves patient comfort, or an app that bridges a clinical gap. Many physicians, especially early career gastroenterologists, have ideas like this, but few know what to do next.
This article is for the curious innovator at the beginning of their clinical career. It offers practical, real-world guidance on developing a clinical product: whether that be hardware, software, or a hybrid. It outlines what questions to ask, who to consult, and how to protect your work, using personal insights and business principles learned through lived experience.
1. Understand Intellectual Property (IP): Know Its Value and Ownership
What is IP?
Intellectual property refers to your original creations: inventions, designs, software, and more. This is what you want to protect legally through patents, trademarks, or copyrights.
Who owns your idea?
This is the first and most important question to ask. If you are employed (especially by a hospital or academic center), your contract may already give your employer rights to any inventions you create, even those developed in your personal time.
What to ask:
- Does my employment contract include an “assignment of inventions” clause?
- Does the institution claim rights to anything developed with institutional resources?
- Are there moonlighting or external activity policies that affect this?
If you are developing an idea on your personal time, with your own resources, and outside your scope of clinical duties, it might still be considered “theirs” under some contracts. Early legal consultation is critical. A specialized IP attorney can help you understand what you own and how to protect it. This should be done early, ideally before you start building anything.
2. Lawyers Aren’t Optional: They’re Essential Early Partners
You do not need a full legal team, but you do need a lawyer early. An early consultation with an IP attorney can clarify your rights, guide your filing process (e.g. provisional patents), and help you avoid costly missteps.
Do this before sharing your idea publicly, including in academic presentations, pitch competitions, or even on social media. Public disclosure can start a clock ticking for application to protect your IP.
3. Build a Founding Team with Intent
Think of your startup team like a long-term relationship: you’re committing to build something together through uncertainty, tension, and change.
Strong early-stage teams often include:
- The Visionary – understands the clinical need and vision
- The Builder – engineer, developer, or designer
- The Doer – project manager or operations lead
Before forming a company, clearly define:
- Ownership (equity percentages)
- Roles and responsibilities
- Time commitments
- What happens if someone exits
Have these discussions early and document your agreements. Avoid informal “handshake” deals that can lead to serious disputes later.
4. You Don’t Need to Know Everything on Day One
You do not need to know how to write code, build a prototype, or get FDA clearance on day one. Successful innovators are humble learners. Use a Minimum Viable Product (MVP), a simple, functional version of your idea, to test assumptions and gather feedback. Iterate based on what you learn. Do not chase perfection; pursue progress. Consider using online accelerators like Y Combinator’s startup school or AGA’s Center for GI Innovation and Technology.
5. Incubators: Use them Strategically
Incubators can offer mentorship, seed funding, legal support, and technical resources, but they vary widely in value (see Table 1). Many may want equity, and not all offer when you truly need.
Ask Yourself:
- Do I need technical help, business mentorship, or just accountability?
- What does this incubator offer in terms of IP protection, exposure, and connections?
- Do I understand the equity trade-off?
- What services and funding do they provide?
- Do they take equity? How much and when?
- What’s their track record with similar ventures?
- Are their incentives aligned with your vision?
6. Academic Institutions: Partners or Pitfalls?
Universities can provide credibility, resources, and early funding through their tech transfer office (TTO).
Key Questions to Ask:
- Will my IP be managed by the TTO?
- How much say do I have in licensing decisions?
- Are there royalty-sharing agreements in place?
- Can I form a startup while employed here?
You may need to negotiate if you want to commercialize your idea independently.
7. Do it for Purpose, Not Payday
Most founders end up owning only a small percentage of their company by the time a product reaches the market. Do not expect to get rich. Do it because it solves a problem you care about. If it happens to come with a nice paycheck, then that is an added bonus.
Your clinical training and insight give you a unique edge. You already know what’s broken. Use that as your compass.
Conclusion
Innovation isn’t about brilliance, it’s about curiosity, structure, and tenacity (see Table 2). Start small. Protect your work. Choose the right partners. Most importantly, stay anchored in your mission to make GI care better.
Dr. Muratore is based at UNC Rex Digestive Health, Raleigh, North Carolina. She has no conflicts related to this article. Dr. Wechsler is based at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Chapel Hill, North Carolina. She holds a patent assigned to Trustees of Dartmouth College. Dr. Shah is based at the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, Michigan. He consults for Ardelyx, Laborie, Neuraxis, Salix, Sanofi, and Takeda and holds a patent with the Regents of the University of Michigan.
When Your First Job Isn’t Forever: Lessons from My Journey and What Early-Career GIs Need to Know
Introduction
For many of us in gastroenterology, landing that first attending job feels like the ultimate victory lap — the reward for all those years of training. We sign the contract, relocate, and imagine this will be our “forever job.” Reality often plays out differently.
In fact, 43% of physicians change jobs within five years, while 83% changed employers at least once in their careers.1 Even within our field — which is always in demand — turnover is high; 1 in 3 gastroenterologists are planning to leave their current role within two years.2 Why does this happen? More importantly, how do we navigate this transition with clarity and confidence as an early-career GI?
My Story: When I Dared to Change My “Forever Job”
When I signed my first attending contract, I didn’t negotiate a single thing. My priorities were simple: family in Toronto and visa requirements. After a decade of medical school, residency, and fellowship, everything else felt secondary. I was happy to be back home.
The job itself was good — reasonable hours, flexible colleagues, and ample opportunity to enhance my procedural skills. As I started carving out my niche in endobariatrics, the support I needed to grow further was not there. I kept telling myself that this job fulfilled my values and I needed to be patient: “this is my forever job. I am close to my family and that’s what matters.”
Then, during a suturing course at the American Society of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy, I had a casual chat with the course director (now my boss). It took me by surprise, but as the conversation continued, he offered me a job. It was tempting: the chance to build my own endobariatrics program with real institutional backing. The catch? It was in a city I had never been to, with no family or friends around. I politely said “no, thank you, I can’t.” He smiled, gave me his number, and said, “think about it.”
For the first time, I allowed myself to ask, “could I really leave my forever job?”
The Power of a Circle and a Spreadsheet
I leaned on my circle — a close group of fellowship friends who each took a turn being someone’s lifeline. We have monthly Zoom calls to talk about jobs, family, and career aspirations. When I shared my dilemma, I realized I wasn’t alone; one friend was also unhappy with her first job. Suddenly, we were asking one another, “can we really leave?”
I hired a career consultant familiar with physician visa issues — hands down, the best money I ever invested. The job search felt like dating: each interview was a first date; some needed a second or third date before I knew if it could be a match.
After every interview, I’d jump on Zoom with my circle. We’d screen-share my giant Excel spreadsheet — our decision matrix — with columns for everything I cared about:
- Institute
- Administrative Time
- Endobariatric support
- Director Title
- Salary
- On-call
- Vacation
- Proximity to airport
- Cost of living
- RVU percentage
- Endoscopy center buy-in
- Contract duration
- Support staff
- CME
We scored each job, line by line, and not a single job checked all the boxes. As I sat there in a state of decision paralysis, it became clear that this was not a simple decision.
The GI Community: A Small, Supportive World
The GI community is incredibly close-knit and kind-hearted. At every conference, I made a point to chat with as many colleagues as I could, to hear their perspectives on jobs and how they made tough career moves. Those conversations were real — no Google search or Excel sheet could offer the perspective and insight I gained by simply asking and leaning on the GI community.
Meanwhile, the person who had first offered me that job kept checking in, catching up at conferences, and bonding over our love for food and baking. With him, I never felt like I was being ‘interviewed’ — I felt valued. It did not feel like he was trying to fill a position with just anyone to improve the call pool. He genuinely wanted to understand what my goals were and how I envisioned my future. Through those conversations, he reminded me of my original passions, which were sidelined when so immersed in the daily routine.
I’ve learned that feeling valued doesn’t come from grand gestures in recruitment. It’s in the quiet signs of respect, trust, and being seen. He wasn’t looking for just anyone; he was looking for someone whose goals aligned with his group’s and someone in whom he wanted to invest. While others might chase the highest salary, the most flexible schedule, or the strongest ancillary support, I realized I valued something I did not realize that I was lacking until then: mentorship.
What I Learned: There is No Such Thing As “The Perfect Job”
After a full year of spreadsheets, Zoom calls, conference chats, and overthinking, I came to a big realization: there’s no perfect job — there’s no such thing as an ideal “forever job.” The only constant for humans is change. Our circumstances change, our priorities shift, our interests shuffle, and our finances evolve. The best job is simply the one that fits the stage of life you’re in at that given moment. For me, mentorship and growth became my top priorities, even if it meant moving away from family.
What Physicians Value Most in a Second Job
After their first job, early-career gastroenterologists often reevaluate what really matters. Recent surveys highlight four key priorities:
- Work-life balance:
In a 2022 CompHealth Group healthcare survey, 85% of physicians ranked work-life balance as their top job priority.3
- Mentorship and growth:
Nearly 1 in 3 physicians cited lack of mentorship or career advancement as their reason for leaving a first job, per the 2023 MGMA/Jackson Physician Search report.4
- Compensation:
While not always the main reason for leaving, 77% of physicians now list compensation as a top priority — a big jump from prior years.3
- Practice support:
Poor infrastructure, administrative overload, or understaffed teams are common dealbreakers. In the second job, physicians look for well-run practices with solid support staff and reduced burnout risk.5
Conclusion
Welcome the uncertainty, talk to your circle, lean on your community, and use a spreadsheet if you need to — but don’t forget to trust your gut. There’s no forever job or the perfect path, only the next move that feels most true to who you are in that moment.
Dr. Ismail (@mayyismail) is Assistant Professor of Clinical Medicine (Gastroenterology) at Temple University in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. She declares no conflicts of interest.
References
1. CHG Healthcare. Survey: 62% of physicians made a career change in the last two years. CHG Healthcare blog. June 10, 2024. Accessed August 5, 2025.
2. Berg S. Physicians in these 10 specialties are less likely to quit. AMA News. Published June 24, 2025. Accessed July 2025.
3. Saley C. Survey: Work/life balance is #1 priority in physicians’ job search. CHG Healthcare Insights. March 10, 2022. Accessed August 2025.
4. Medical Group Management Association; Jackson Physician Search. Early‑Career Physician Recruiting & Retention Playbook. October 23, 2023. Accessed August 2025.
5. Von Rosenvinge EC, et al. A crisis in scope: Recruitment and retention challenges reported by VA gastroenterology section chiefs. Fed Pract. 2024 Aug. doi:10.12788/fp.0504.
Introduction
For many of us in gastroenterology, landing that first attending job feels like the ultimate victory lap — the reward for all those years of training. We sign the contract, relocate, and imagine this will be our “forever job.” Reality often plays out differently.
In fact, 43% of physicians change jobs within five years, while 83% changed employers at least once in their careers.1 Even within our field — which is always in demand — turnover is high; 1 in 3 gastroenterologists are planning to leave their current role within two years.2 Why does this happen? More importantly, how do we navigate this transition with clarity and confidence as an early-career GI?
My Story: When I Dared to Change My “Forever Job”
When I signed my first attending contract, I didn’t negotiate a single thing. My priorities were simple: family in Toronto and visa requirements. After a decade of medical school, residency, and fellowship, everything else felt secondary. I was happy to be back home.
The job itself was good — reasonable hours, flexible colleagues, and ample opportunity to enhance my procedural skills. As I started carving out my niche in endobariatrics, the support I needed to grow further was not there. I kept telling myself that this job fulfilled my values and I needed to be patient: “this is my forever job. I am close to my family and that’s what matters.”
Then, during a suturing course at the American Society of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy, I had a casual chat with the course director (now my boss). It took me by surprise, but as the conversation continued, he offered me a job. It was tempting: the chance to build my own endobariatrics program with real institutional backing. The catch? It was in a city I had never been to, with no family or friends around. I politely said “no, thank you, I can’t.” He smiled, gave me his number, and said, “think about it.”
For the first time, I allowed myself to ask, “could I really leave my forever job?”
The Power of a Circle and a Spreadsheet
I leaned on my circle — a close group of fellowship friends who each took a turn being someone’s lifeline. We have monthly Zoom calls to talk about jobs, family, and career aspirations. When I shared my dilemma, I realized I wasn’t alone; one friend was also unhappy with her first job. Suddenly, we were asking one another, “can we really leave?”
I hired a career consultant familiar with physician visa issues — hands down, the best money I ever invested. The job search felt like dating: each interview was a first date; some needed a second or third date before I knew if it could be a match.
After every interview, I’d jump on Zoom with my circle. We’d screen-share my giant Excel spreadsheet — our decision matrix — with columns for everything I cared about:
- Institute
- Administrative Time
- Endobariatric support
- Director Title
- Salary
- On-call
- Vacation
- Proximity to airport
- Cost of living
- RVU percentage
- Endoscopy center buy-in
- Contract duration
- Support staff
- CME
We scored each job, line by line, and not a single job checked all the boxes. As I sat there in a state of decision paralysis, it became clear that this was not a simple decision.
The GI Community: A Small, Supportive World
The GI community is incredibly close-knit and kind-hearted. At every conference, I made a point to chat with as many colleagues as I could, to hear their perspectives on jobs and how they made tough career moves. Those conversations were real — no Google search or Excel sheet could offer the perspective and insight I gained by simply asking and leaning on the GI community.
Meanwhile, the person who had first offered me that job kept checking in, catching up at conferences, and bonding over our love for food and baking. With him, I never felt like I was being ‘interviewed’ — I felt valued. It did not feel like he was trying to fill a position with just anyone to improve the call pool. He genuinely wanted to understand what my goals were and how I envisioned my future. Through those conversations, he reminded me of my original passions, which were sidelined when so immersed in the daily routine.
I’ve learned that feeling valued doesn’t come from grand gestures in recruitment. It’s in the quiet signs of respect, trust, and being seen. He wasn’t looking for just anyone; he was looking for someone whose goals aligned with his group’s and someone in whom he wanted to invest. While others might chase the highest salary, the most flexible schedule, or the strongest ancillary support, I realized I valued something I did not realize that I was lacking until then: mentorship.
What I Learned: There is No Such Thing As “The Perfect Job”
After a full year of spreadsheets, Zoom calls, conference chats, and overthinking, I came to a big realization: there’s no perfect job — there’s no such thing as an ideal “forever job.” The only constant for humans is change. Our circumstances change, our priorities shift, our interests shuffle, and our finances evolve. The best job is simply the one that fits the stage of life you’re in at that given moment. For me, mentorship and growth became my top priorities, even if it meant moving away from family.
What Physicians Value Most in a Second Job
After their first job, early-career gastroenterologists often reevaluate what really matters. Recent surveys highlight four key priorities:
- Work-life balance:
In a 2022 CompHealth Group healthcare survey, 85% of physicians ranked work-life balance as their top job priority.3
- Mentorship and growth:
Nearly 1 in 3 physicians cited lack of mentorship or career advancement as their reason for leaving a first job, per the 2023 MGMA/Jackson Physician Search report.4
- Compensation:
While not always the main reason for leaving, 77% of physicians now list compensation as a top priority — a big jump from prior years.3
- Practice support:
Poor infrastructure, administrative overload, or understaffed teams are common dealbreakers. In the second job, physicians look for well-run practices with solid support staff and reduced burnout risk.5
Conclusion
Welcome the uncertainty, talk to your circle, lean on your community, and use a spreadsheet if you need to — but don’t forget to trust your gut. There’s no forever job or the perfect path, only the next move that feels most true to who you are in that moment.
Dr. Ismail (@mayyismail) is Assistant Professor of Clinical Medicine (Gastroenterology) at Temple University in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. She declares no conflicts of interest.
References
1. CHG Healthcare. Survey: 62% of physicians made a career change in the last two years. CHG Healthcare blog. June 10, 2024. Accessed August 5, 2025.
2. Berg S. Physicians in these 10 specialties are less likely to quit. AMA News. Published June 24, 2025. Accessed July 2025.
3. Saley C. Survey: Work/life balance is #1 priority in physicians’ job search. CHG Healthcare Insights. March 10, 2022. Accessed August 2025.
4. Medical Group Management Association; Jackson Physician Search. Early‑Career Physician Recruiting & Retention Playbook. October 23, 2023. Accessed August 2025.
5. Von Rosenvinge EC, et al. A crisis in scope: Recruitment and retention challenges reported by VA gastroenterology section chiefs. Fed Pract. 2024 Aug. doi:10.12788/fp.0504.
Introduction
For many of us in gastroenterology, landing that first attending job feels like the ultimate victory lap — the reward for all those years of training. We sign the contract, relocate, and imagine this will be our “forever job.” Reality often plays out differently.
In fact, 43% of physicians change jobs within five years, while 83% changed employers at least once in their careers.1 Even within our field — which is always in demand — turnover is high; 1 in 3 gastroenterologists are planning to leave their current role within two years.2 Why does this happen? More importantly, how do we navigate this transition with clarity and confidence as an early-career GI?
My Story: When I Dared to Change My “Forever Job”
When I signed my first attending contract, I didn’t negotiate a single thing. My priorities were simple: family in Toronto and visa requirements. After a decade of medical school, residency, and fellowship, everything else felt secondary. I was happy to be back home.
The job itself was good — reasonable hours, flexible colleagues, and ample opportunity to enhance my procedural skills. As I started carving out my niche in endobariatrics, the support I needed to grow further was not there. I kept telling myself that this job fulfilled my values and I needed to be patient: “this is my forever job. I am close to my family and that’s what matters.”
Then, during a suturing course at the American Society of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy, I had a casual chat with the course director (now my boss). It took me by surprise, but as the conversation continued, he offered me a job. It was tempting: the chance to build my own endobariatrics program with real institutional backing. The catch? It was in a city I had never been to, with no family or friends around. I politely said “no, thank you, I can’t.” He smiled, gave me his number, and said, “think about it.”
For the first time, I allowed myself to ask, “could I really leave my forever job?”
The Power of a Circle and a Spreadsheet
I leaned on my circle — a close group of fellowship friends who each took a turn being someone’s lifeline. We have monthly Zoom calls to talk about jobs, family, and career aspirations. When I shared my dilemma, I realized I wasn’t alone; one friend was also unhappy with her first job. Suddenly, we were asking one another, “can we really leave?”
I hired a career consultant familiar with physician visa issues — hands down, the best money I ever invested. The job search felt like dating: each interview was a first date; some needed a second or third date before I knew if it could be a match.
After every interview, I’d jump on Zoom with my circle. We’d screen-share my giant Excel spreadsheet — our decision matrix — with columns for everything I cared about:
- Institute
- Administrative Time
- Endobariatric support
- Director Title
- Salary
- On-call
- Vacation
- Proximity to airport
- Cost of living
- RVU percentage
- Endoscopy center buy-in
- Contract duration
- Support staff
- CME
We scored each job, line by line, and not a single job checked all the boxes. As I sat there in a state of decision paralysis, it became clear that this was not a simple decision.
The GI Community: A Small, Supportive World
The GI community is incredibly close-knit and kind-hearted. At every conference, I made a point to chat with as many colleagues as I could, to hear their perspectives on jobs and how they made tough career moves. Those conversations were real — no Google search or Excel sheet could offer the perspective and insight I gained by simply asking and leaning on the GI community.
Meanwhile, the person who had first offered me that job kept checking in, catching up at conferences, and bonding over our love for food and baking. With him, I never felt like I was being ‘interviewed’ — I felt valued. It did not feel like he was trying to fill a position with just anyone to improve the call pool. He genuinely wanted to understand what my goals were and how I envisioned my future. Through those conversations, he reminded me of my original passions, which were sidelined when so immersed in the daily routine.
I’ve learned that feeling valued doesn’t come from grand gestures in recruitment. It’s in the quiet signs of respect, trust, and being seen. He wasn’t looking for just anyone; he was looking for someone whose goals aligned with his group’s and someone in whom he wanted to invest. While others might chase the highest salary, the most flexible schedule, or the strongest ancillary support, I realized I valued something I did not realize that I was lacking until then: mentorship.
What I Learned: There is No Such Thing As “The Perfect Job”
After a full year of spreadsheets, Zoom calls, conference chats, and overthinking, I came to a big realization: there’s no perfect job — there’s no such thing as an ideal “forever job.” The only constant for humans is change. Our circumstances change, our priorities shift, our interests shuffle, and our finances evolve. The best job is simply the one that fits the stage of life you’re in at that given moment. For me, mentorship and growth became my top priorities, even if it meant moving away from family.
What Physicians Value Most in a Second Job
After their first job, early-career gastroenterologists often reevaluate what really matters. Recent surveys highlight four key priorities:
- Work-life balance:
In a 2022 CompHealth Group healthcare survey, 85% of physicians ranked work-life balance as their top job priority.3
- Mentorship and growth:
Nearly 1 in 3 physicians cited lack of mentorship or career advancement as their reason for leaving a first job, per the 2023 MGMA/Jackson Physician Search report.4
- Compensation:
While not always the main reason for leaving, 77% of physicians now list compensation as a top priority — a big jump from prior years.3
- Practice support:
Poor infrastructure, administrative overload, or understaffed teams are common dealbreakers. In the second job, physicians look for well-run practices with solid support staff and reduced burnout risk.5
Conclusion
Welcome the uncertainty, talk to your circle, lean on your community, and use a spreadsheet if you need to — but don’t forget to trust your gut. There’s no forever job or the perfect path, only the next move that feels most true to who you are in that moment.
Dr. Ismail (@mayyismail) is Assistant Professor of Clinical Medicine (Gastroenterology) at Temple University in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. She declares no conflicts of interest.
References
1. CHG Healthcare. Survey: 62% of physicians made a career change in the last two years. CHG Healthcare blog. June 10, 2024. Accessed August 5, 2025.
2. Berg S. Physicians in these 10 specialties are less likely to quit. AMA News. Published June 24, 2025. Accessed July 2025.
3. Saley C. Survey: Work/life balance is #1 priority in physicians’ job search. CHG Healthcare Insights. March 10, 2022. Accessed August 2025.
4. Medical Group Management Association; Jackson Physician Search. Early‑Career Physician Recruiting & Retention Playbook. October 23, 2023. Accessed August 2025.
5. Von Rosenvinge EC, et al. A crisis in scope: Recruitment and retention challenges reported by VA gastroenterology section chiefs. Fed Pract. 2024 Aug. doi:10.12788/fp.0504.
Turning the Cancer Research Problem Into an Opportunity
Turning the Cancer Research Problem Into an Opportunity
The War on Cancer, declared by President Richard Nixon some 50 years ago, has been canceled during the second Trump administration in 2025 — so saith The New York Times Sunday magazine cover story on September 14, 2025. This war seems now to be best described as "The War on Cancer Research."
To our horror and disbelief, we've witnessed the slow but persistent drift of much of the United States citizenry away from science and the sudden and severe movement of the US government to crush much medical research. But it is not as if we were not warned.
In August 2024, on these pages and without political bias, I urged Medscape readers to pay attention to Project 2025. A great deal of what we as a population are now experiencing was laid out as a carefully constructed plan.
What is surprising is the cruel ruthlessness of the "move fast and break things" approach, taken with little apparent concern about the resultant human tragedies (workforce and patients) and no clear care about the resulting fallout. As we've now learned, destroying something as grand as our cancer research enterprise can be accomplished very quickly. Rebuilding it is certain to be slow and difficult and perhaps can never be accomplished.
In this new anti-science, anti-research, and anti-researcher reality, what can we now do?
First and foremost, we must recognize that the war on cancer is not over. Cancer is not canceled, even if much of the US government's research effort/funding has been. Those of us in medicine and public health often speak in quantification of causes of death of our populations. As such, I'll remind Medscape readers that cancer afflicts some 20 million humans worldwide each year, killing nearly 10 million. Although two-thirds of Americans diagnosed with a potentially lethal malignancy are cured, cancer still kills roughly 600,000 Americans each year. Cancer has been the second most frequent cause of death of Americans for 75 years.
Being inevitable and immutable, death itself is not the enemy. We all die. Disease, disability, pain, and human suffering are the real enemies of us all. Cancer maims, pains, diabetes, and torments some 20 million humans worldwide each year. That is a huge humanitarian problem that should be recognized by individuals of all creeds and backgrounds.
With this depletion of our domestic government basic and applied cancer research program, what can we do?
- Think globally and look to the international scientific research enterprises — relying on them, much as they have relied on us.
- Defend the universal importance of reliable and available literature on medical science.
- Continue to translate and apply the vast amount of available published research in clinical practice and publish the results.
- Urge private industries to expand their research budgets into areas of study that may not produce quickly tangible positive bottom-line results.
- Remind the Secretary of the Department of Health and Human Services (for whom chronic diseases seem paramount) that cancer is the second leading American chronic disease by morbidity.
- Redouble efforts of cancer prevention, especially urging the FDA to ban combustible tobacco and strive more diligently to decrease obesity.
- Appeal to our vast philanthropic universe to increase its funding of nonprofit organizations active in the cancer investigation, diagnosis, and management space.
One such 501c3 organization is California-based Cancer Commons. (Disclosure: I named it in 2010 and serve as its editor in chief).
A commons is a space shared by a community to use for the common interest. As we originally envisioned it, a cancer commons is an open access internet location where individuals and organizations (eg, corporations, universities, government agencies, philanthropies) will voluntarily share their data to work together to defeat the common enemy of humans: cancer.
On September 8, 2025, Cancer Commons was the 15th annual Lundberg Institute Lecturer at the Commonwealth Club of California in San Francisco. At the lecture, Cancer Commons founder (and long-term survivor of metastatic malignant melanoma), Jay Martin "Martin" Tenenbaum, PhD, spoke of the need for a cancer commons and the founder's vision. Emma Shtivelman, PhD, the long-time compassionate chief scientist, described some of the thousands of patients with advanced cancer that she has helped — all free of charge. And newly named CEO Clifford Reid, MBA, PhD, used his entrepreneurial prowess to envision an ambitious future.
Cancer Commons has always focused on patients with cancer who are beyond standards of curative care. As Cancer Commons evolves, it anticipates focusing on patients with cancer who are beyond National Comprehensive Cancer Network Guidelines. The organization intends to greatly expand its 1000 patients per year with "high touch" engagement with PhD clinical scientists to many thousands by including artificial intelligence. It plans to extend its N-of-One approach to create new knowledge — especially regarding the hundreds of drugs that are FDA-approved for use in treating cancer but have not been further assessed for the utility in actually treating patients with cancer.
The war on cancer is not over. It remains a persistent foe that causes immense disability, pain, and human suffering. With government support depleted, the burden now shifts to the private sector and philanthropic organizations, such as Cancer Commons, to serve as the new vital infrastructure in the fight for a cure. Now, we must redouble our efforts to ensure that these research endeavors are supported if the US government will not do its part.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The War on Cancer, declared by President Richard Nixon some 50 years ago, has been canceled during the second Trump administration in 2025 — so saith The New York Times Sunday magazine cover story on September 14, 2025. This war seems now to be best described as "The War on Cancer Research."
To our horror and disbelief, we've witnessed the slow but persistent drift of much of the United States citizenry away from science and the sudden and severe movement of the US government to crush much medical research. But it is not as if we were not warned.
In August 2024, on these pages and without political bias, I urged Medscape readers to pay attention to Project 2025. A great deal of what we as a population are now experiencing was laid out as a carefully constructed plan.
What is surprising is the cruel ruthlessness of the "move fast and break things" approach, taken with little apparent concern about the resultant human tragedies (workforce and patients) and no clear care about the resulting fallout. As we've now learned, destroying something as grand as our cancer research enterprise can be accomplished very quickly. Rebuilding it is certain to be slow and difficult and perhaps can never be accomplished.
In this new anti-science, anti-research, and anti-researcher reality, what can we now do?
First and foremost, we must recognize that the war on cancer is not over. Cancer is not canceled, even if much of the US government's research effort/funding has been. Those of us in medicine and public health often speak in quantification of causes of death of our populations. As such, I'll remind Medscape readers that cancer afflicts some 20 million humans worldwide each year, killing nearly 10 million. Although two-thirds of Americans diagnosed with a potentially lethal malignancy are cured, cancer still kills roughly 600,000 Americans each year. Cancer has been the second most frequent cause of death of Americans for 75 years.
Being inevitable and immutable, death itself is not the enemy. We all die. Disease, disability, pain, and human suffering are the real enemies of us all. Cancer maims, pains, diabetes, and torments some 20 million humans worldwide each year. That is a huge humanitarian problem that should be recognized by individuals of all creeds and backgrounds.
With this depletion of our domestic government basic and applied cancer research program, what can we do?
- Think globally and look to the international scientific research enterprises — relying on them, much as they have relied on us.
- Defend the universal importance of reliable and available literature on medical science.
- Continue to translate and apply the vast amount of available published research in clinical practice and publish the results.
- Urge private industries to expand their research budgets into areas of study that may not produce quickly tangible positive bottom-line results.
- Remind the Secretary of the Department of Health and Human Services (for whom chronic diseases seem paramount) that cancer is the second leading American chronic disease by morbidity.
- Redouble efforts of cancer prevention, especially urging the FDA to ban combustible tobacco and strive more diligently to decrease obesity.
- Appeal to our vast philanthropic universe to increase its funding of nonprofit organizations active in the cancer investigation, diagnosis, and management space.
One such 501c3 organization is California-based Cancer Commons. (Disclosure: I named it in 2010 and serve as its editor in chief).
A commons is a space shared by a community to use for the common interest. As we originally envisioned it, a cancer commons is an open access internet location where individuals and organizations (eg, corporations, universities, government agencies, philanthropies) will voluntarily share their data to work together to defeat the common enemy of humans: cancer.
On September 8, 2025, Cancer Commons was the 15th annual Lundberg Institute Lecturer at the Commonwealth Club of California in San Francisco. At the lecture, Cancer Commons founder (and long-term survivor of metastatic malignant melanoma), Jay Martin "Martin" Tenenbaum, PhD, spoke of the need for a cancer commons and the founder's vision. Emma Shtivelman, PhD, the long-time compassionate chief scientist, described some of the thousands of patients with advanced cancer that she has helped — all free of charge. And newly named CEO Clifford Reid, MBA, PhD, used his entrepreneurial prowess to envision an ambitious future.
Cancer Commons has always focused on patients with cancer who are beyond standards of curative care. As Cancer Commons evolves, it anticipates focusing on patients with cancer who are beyond National Comprehensive Cancer Network Guidelines. The organization intends to greatly expand its 1000 patients per year with "high touch" engagement with PhD clinical scientists to many thousands by including artificial intelligence. It plans to extend its N-of-One approach to create new knowledge — especially regarding the hundreds of drugs that are FDA-approved for use in treating cancer but have not been further assessed for the utility in actually treating patients with cancer.
The war on cancer is not over. It remains a persistent foe that causes immense disability, pain, and human suffering. With government support depleted, the burden now shifts to the private sector and philanthropic organizations, such as Cancer Commons, to serve as the new vital infrastructure in the fight for a cure. Now, we must redouble our efforts to ensure that these research endeavors are supported if the US government will not do its part.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The War on Cancer, declared by President Richard Nixon some 50 years ago, has been canceled during the second Trump administration in 2025 — so saith The New York Times Sunday magazine cover story on September 14, 2025. This war seems now to be best described as "The War on Cancer Research."
To our horror and disbelief, we've witnessed the slow but persistent drift of much of the United States citizenry away from science and the sudden and severe movement of the US government to crush much medical research. But it is not as if we were not warned.
In August 2024, on these pages and without political bias, I urged Medscape readers to pay attention to Project 2025. A great deal of what we as a population are now experiencing was laid out as a carefully constructed plan.
What is surprising is the cruel ruthlessness of the "move fast and break things" approach, taken with little apparent concern about the resultant human tragedies (workforce and patients) and no clear care about the resulting fallout. As we've now learned, destroying something as grand as our cancer research enterprise can be accomplished very quickly. Rebuilding it is certain to be slow and difficult and perhaps can never be accomplished.
In this new anti-science, anti-research, and anti-researcher reality, what can we now do?
First and foremost, we must recognize that the war on cancer is not over. Cancer is not canceled, even if much of the US government's research effort/funding has been. Those of us in medicine and public health often speak in quantification of causes of death of our populations. As such, I'll remind Medscape readers that cancer afflicts some 20 million humans worldwide each year, killing nearly 10 million. Although two-thirds of Americans diagnosed with a potentially lethal malignancy are cured, cancer still kills roughly 600,000 Americans each year. Cancer has been the second most frequent cause of death of Americans for 75 years.
Being inevitable and immutable, death itself is not the enemy. We all die. Disease, disability, pain, and human suffering are the real enemies of us all. Cancer maims, pains, diabetes, and torments some 20 million humans worldwide each year. That is a huge humanitarian problem that should be recognized by individuals of all creeds and backgrounds.
With this depletion of our domestic government basic and applied cancer research program, what can we do?
- Think globally and look to the international scientific research enterprises — relying on them, much as they have relied on us.
- Defend the universal importance of reliable and available literature on medical science.
- Continue to translate and apply the vast amount of available published research in clinical practice and publish the results.
- Urge private industries to expand their research budgets into areas of study that may not produce quickly tangible positive bottom-line results.
- Remind the Secretary of the Department of Health and Human Services (for whom chronic diseases seem paramount) that cancer is the second leading American chronic disease by morbidity.
- Redouble efforts of cancer prevention, especially urging the FDA to ban combustible tobacco and strive more diligently to decrease obesity.
- Appeal to our vast philanthropic universe to increase its funding of nonprofit organizations active in the cancer investigation, diagnosis, and management space.
One such 501c3 organization is California-based Cancer Commons. (Disclosure: I named it in 2010 and serve as its editor in chief).
A commons is a space shared by a community to use for the common interest. As we originally envisioned it, a cancer commons is an open access internet location where individuals and organizations (eg, corporations, universities, government agencies, philanthropies) will voluntarily share their data to work together to defeat the common enemy of humans: cancer.
On September 8, 2025, Cancer Commons was the 15th annual Lundberg Institute Lecturer at the Commonwealth Club of California in San Francisco. At the lecture, Cancer Commons founder (and long-term survivor of metastatic malignant melanoma), Jay Martin "Martin" Tenenbaum, PhD, spoke of the need for a cancer commons and the founder's vision. Emma Shtivelman, PhD, the long-time compassionate chief scientist, described some of the thousands of patients with advanced cancer that she has helped — all free of charge. And newly named CEO Clifford Reid, MBA, PhD, used his entrepreneurial prowess to envision an ambitious future.
Cancer Commons has always focused on patients with cancer who are beyond standards of curative care. As Cancer Commons evolves, it anticipates focusing on patients with cancer who are beyond National Comprehensive Cancer Network Guidelines. The organization intends to greatly expand its 1000 patients per year with "high touch" engagement with PhD clinical scientists to many thousands by including artificial intelligence. It plans to extend its N-of-One approach to create new knowledge — especially regarding the hundreds of drugs that are FDA-approved for use in treating cancer but have not been further assessed for the utility in actually treating patients with cancer.
The war on cancer is not over. It remains a persistent foe that causes immense disability, pain, and human suffering. With government support depleted, the burden now shifts to the private sector and philanthropic organizations, such as Cancer Commons, to serve as the new vital infrastructure in the fight for a cure. Now, we must redouble our efforts to ensure that these research endeavors are supported if the US government will not do its part.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Turning the Cancer Research Problem Into an Opportunity
Turning the Cancer Research Problem Into an Opportunity
Is AI a Cure for Clinician Burnout?
The practice of medicine is evolving rapidly, with clinicians facing enhanced pressure to maximize productivity while managing increasingly complex patients and related clinical documentation. Indeed, clinicians are spending less time seeing patients, and more time in front of a computer screen.
Despite the many rewards of clinical medicine, rates of clinical practice attrition have increased among physicians in all specialties since 2013 with enhanced administrative burdens identified as a prominent driver. Among its many applications, artificial intelligence (AI) has immense potential to reduce the administrative and cognitive burdens that contribute to clinician burnout and attrition through tools such as AI scribes – these technologies have been rapidly adopted across healthcare systems and are already in use by ~30% of physician practices. The hope is that AI scribes will significantly reduce documentation time, leading to improvements in clinician wellbeing and expanding capacity for patient care. Indeed, some studies have shown up to a 20-30% improvement in documentation efficiency.
So, is AI a cure for physician burnout? The answer depends on what is done with these efficiency gains. If healthcare organizations respond to this enhanced efficiency by increasing patient volume expectations rather than allowing clinicians to recapture some of this time for meaningful work and professional wellbeing, it could create a so-called “workload paradox” where modest time savings are offset by greater productivity demands and the cognitive burden of reviewing AI-generated errors. that prioritizes clinician well-being and patient safety in addition to productivity.
In our final issue of 2025, we highlight a recent RCT from Annals of Internal Medicine finding that fecal microbiota transplantation is at least as effective as vancomycin in treating primary C. difficile infection. In this month’s Member Spotlight, we feature Andrew Ofosu, MD, MPH (University of Cincinnati Health), who stresses the importance of transparency and compassion in communicating effectively with patients, particularly around complex diagnoses. We hope you enjoy this and all the exciting content in our December issue.
Megan A. Adams, MD, JD, MSc
Editor in Chief
The practice of medicine is evolving rapidly, with clinicians facing enhanced pressure to maximize productivity while managing increasingly complex patients and related clinical documentation. Indeed, clinicians are spending less time seeing patients, and more time in front of a computer screen.
Despite the many rewards of clinical medicine, rates of clinical practice attrition have increased among physicians in all specialties since 2013 with enhanced administrative burdens identified as a prominent driver. Among its many applications, artificial intelligence (AI) has immense potential to reduce the administrative and cognitive burdens that contribute to clinician burnout and attrition through tools such as AI scribes – these technologies have been rapidly adopted across healthcare systems and are already in use by ~30% of physician practices. The hope is that AI scribes will significantly reduce documentation time, leading to improvements in clinician wellbeing and expanding capacity for patient care. Indeed, some studies have shown up to a 20-30% improvement in documentation efficiency.
So, is AI a cure for physician burnout? The answer depends on what is done with these efficiency gains. If healthcare organizations respond to this enhanced efficiency by increasing patient volume expectations rather than allowing clinicians to recapture some of this time for meaningful work and professional wellbeing, it could create a so-called “workload paradox” where modest time savings are offset by greater productivity demands and the cognitive burden of reviewing AI-generated errors. that prioritizes clinician well-being and patient safety in addition to productivity.
In our final issue of 2025, we highlight a recent RCT from Annals of Internal Medicine finding that fecal microbiota transplantation is at least as effective as vancomycin in treating primary C. difficile infection. In this month’s Member Spotlight, we feature Andrew Ofosu, MD, MPH (University of Cincinnati Health), who stresses the importance of transparency and compassion in communicating effectively with patients, particularly around complex diagnoses. We hope you enjoy this and all the exciting content in our December issue.
Megan A. Adams, MD, JD, MSc
Editor in Chief
The practice of medicine is evolving rapidly, with clinicians facing enhanced pressure to maximize productivity while managing increasingly complex patients and related clinical documentation. Indeed, clinicians are spending less time seeing patients, and more time in front of a computer screen.
Despite the many rewards of clinical medicine, rates of clinical practice attrition have increased among physicians in all specialties since 2013 with enhanced administrative burdens identified as a prominent driver. Among its many applications, artificial intelligence (AI) has immense potential to reduce the administrative and cognitive burdens that contribute to clinician burnout and attrition through tools such as AI scribes – these technologies have been rapidly adopted across healthcare systems and are already in use by ~30% of physician practices. The hope is that AI scribes will significantly reduce documentation time, leading to improvements in clinician wellbeing and expanding capacity for patient care. Indeed, some studies have shown up to a 20-30% improvement in documentation efficiency.
So, is AI a cure for physician burnout? The answer depends on what is done with these efficiency gains. If healthcare organizations respond to this enhanced efficiency by increasing patient volume expectations rather than allowing clinicians to recapture some of this time for meaningful work and professional wellbeing, it could create a so-called “workload paradox” where modest time savings are offset by greater productivity demands and the cognitive burden of reviewing AI-generated errors. that prioritizes clinician well-being and patient safety in addition to productivity.
In our final issue of 2025, we highlight a recent RCT from Annals of Internal Medicine finding that fecal microbiota transplantation is at least as effective as vancomycin in treating primary C. difficile infection. In this month’s Member Spotlight, we feature Andrew Ofosu, MD, MPH (University of Cincinnati Health), who stresses the importance of transparency and compassion in communicating effectively with patients, particularly around complex diagnoses. We hope you enjoy this and all the exciting content in our December issue.
Megan A. Adams, MD, JD, MSc
Editor in Chief
Celebrating VA Physicians in Gastroenterology
Last month, I had the privilege of joining more than one hundred physician colleagues in Washington, DC, for AGA Advocacy Day. While standing amidst the majesty of the Capital, I found myself deeply appreciative for those who dedicate their time and energy to public service. Many of these dedicated federal workers choose to be in DC because of a sincere belief in their mission.
Among these mission-driven public servants are federal employees who work in the Department of Veterans Affairs (VA). As a member of this group, I come to work energized by the mission to care for those who have served in our military. In my clinical practice, I am reminded regularly of the sacrifices of veterans and their families. This month, and especially on Veterans Day, I hope we will take a moment to express gratitude to veterans for their service to our country.
Many young gastroenterologists may not know that it was the landmark VA Cooperative Study #380, led by Dr. David Lieberman (Portland VA) that helped push Medicare to cover reimbursement for screening colonoscopy. Today, one of the most important ongoing studies in our field – VA Cooperative Study #577 – continues the VA tradition of high-impact health services research. Launched in 2012, the study has enrolled 50,000 veterans to compare FIT and colonoscopy. It is led by Dr. Jason Dominitz (Seattle VA) and Dr. Doug Robertson (White River Junction VA).
Beyond research, VA gastroenterologists play a critical role in training the next generation of clinicians. Over 700 gastroenterologists count the VA as a clinical home, making it the largest GI group practice in the country. Many of us — myself included — were trained or mentored by VA physicians whose dedication to service and science has shaped our careers and the field at large.
This month’s issue of GI & Hepatology News has stories about other important contributions to our field. The stories and perspective pieces on Artificial Intelligence are particularly poignant given the announcement last month on the awarding of the Nobel Prize in economics to researchers who study “creative destruction,” the way in which one technological innovation renders others obsolete. Perhaps this award offers another reason to reemphasize and embrace the “art” of medicine.
The views expressed here are my own and do not necessarily reflect the official policy or position of the U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs or the United States Government.
Ziad Gellad, MD, MPH, AGAF
Associate Editor
Last month, I had the privilege of joining more than one hundred physician colleagues in Washington, DC, for AGA Advocacy Day. While standing amidst the majesty of the Capital, I found myself deeply appreciative for those who dedicate their time and energy to public service. Many of these dedicated federal workers choose to be in DC because of a sincere belief in their mission.
Among these mission-driven public servants are federal employees who work in the Department of Veterans Affairs (VA). As a member of this group, I come to work energized by the mission to care for those who have served in our military. In my clinical practice, I am reminded regularly of the sacrifices of veterans and their families. This month, and especially on Veterans Day, I hope we will take a moment to express gratitude to veterans for their service to our country.
Many young gastroenterologists may not know that it was the landmark VA Cooperative Study #380, led by Dr. David Lieberman (Portland VA) that helped push Medicare to cover reimbursement for screening colonoscopy. Today, one of the most important ongoing studies in our field – VA Cooperative Study #577 – continues the VA tradition of high-impact health services research. Launched in 2012, the study has enrolled 50,000 veterans to compare FIT and colonoscopy. It is led by Dr. Jason Dominitz (Seattle VA) and Dr. Doug Robertson (White River Junction VA).
Beyond research, VA gastroenterologists play a critical role in training the next generation of clinicians. Over 700 gastroenterologists count the VA as a clinical home, making it the largest GI group practice in the country. Many of us — myself included — were trained or mentored by VA physicians whose dedication to service and science has shaped our careers and the field at large.
This month’s issue of GI & Hepatology News has stories about other important contributions to our field. The stories and perspective pieces on Artificial Intelligence are particularly poignant given the announcement last month on the awarding of the Nobel Prize in economics to researchers who study “creative destruction,” the way in which one technological innovation renders others obsolete. Perhaps this award offers another reason to reemphasize and embrace the “art” of medicine.
The views expressed here are my own and do not necessarily reflect the official policy or position of the U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs or the United States Government.
Ziad Gellad, MD, MPH, AGAF
Associate Editor
Last month, I had the privilege of joining more than one hundred physician colleagues in Washington, DC, for AGA Advocacy Day. While standing amidst the majesty of the Capital, I found myself deeply appreciative for those who dedicate their time and energy to public service. Many of these dedicated federal workers choose to be in DC because of a sincere belief in their mission.
Among these mission-driven public servants are federal employees who work in the Department of Veterans Affairs (VA). As a member of this group, I come to work energized by the mission to care for those who have served in our military. In my clinical practice, I am reminded regularly of the sacrifices of veterans and their families. This month, and especially on Veterans Day, I hope we will take a moment to express gratitude to veterans for their service to our country.
Many young gastroenterologists may not know that it was the landmark VA Cooperative Study #380, led by Dr. David Lieberman (Portland VA) that helped push Medicare to cover reimbursement for screening colonoscopy. Today, one of the most important ongoing studies in our field – VA Cooperative Study #577 – continues the VA tradition of high-impact health services research. Launched in 2012, the study has enrolled 50,000 veterans to compare FIT and colonoscopy. It is led by Dr. Jason Dominitz (Seattle VA) and Dr. Doug Robertson (White River Junction VA).
Beyond research, VA gastroenterologists play a critical role in training the next generation of clinicians. Over 700 gastroenterologists count the VA as a clinical home, making it the largest GI group practice in the country. Many of us — myself included — were trained or mentored by VA physicians whose dedication to service and science has shaped our careers and the field at large.
This month’s issue of GI & Hepatology News has stories about other important contributions to our field. The stories and perspective pieces on Artificial Intelligence are particularly poignant given the announcement last month on the awarding of the Nobel Prize in economics to researchers who study “creative destruction,” the way in which one technological innovation renders others obsolete. Perhaps this award offers another reason to reemphasize and embrace the “art” of medicine.
The views expressed here are my own and do not necessarily reflect the official policy or position of the U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs or the United States Government.
Ziad Gellad, MD, MPH, AGAF
Associate Editor
Letter: Another View on Private Equity in GI
An October 1 article in GI & Hepatology News cautioned physicians against partnering with private equity firms, warning that they target “quick profits and quick exits, which can be inconsistent with quality long-term patient care.”
But several recent studies – and my own experience – show that .
A 2024 study conducted by Avalere Health found that per-beneficiary Medicare expenditures for physicians who shifted from an unaffiliated practice model to a PE-affiliated model declined by $963 in the 12 months following the transition. By contrast, per-beneficiary Medicare expenditures for physicians who shifted from an unaffiliated model to a hospital-affiliated one increased more than $1,300.
A 2025 peer-reviewed study published in Journal of Market Access & Health Policy found that physicians affiliated with private equity were far more likely to perform common high-volume procedures in the lowest-cost site of care – an ambulatory surgery center or medical office – than in higher-cost hospital outpatient departments. Physicians affiliated with hospitals were far more likely to perform procedures in HOPDs.
Partnering with a private equity-backed management services organization has enabled my practice to afford advanced technologies we never could have deployed on our own. Those technologies have helped improve our polyp detection rates, reduce the incidence of colon cancer, and more efficiently care for patients with ulcerative colitis. We also now provide patients seamless access to digital platforms that help them better manage chronic conditions.
Independent medical practice is under duress. Partnering with a private equity-backed management services organization is one of the most effective ways for a physician practice to retain its independence – and continue offering patients affordable, high-quality care.
George Dickstein, MD, AGAF, is senior vice president of clinical affairs, Massachusetts, for Gastro Health, and chairperson of Gastro Health’s Physician Leadership Council. He is based in Framingham, Mass. GI & Hepatology News encourages readers to submit letters to the editor to debate topics raised in the newspaper.
An October 1 article in GI & Hepatology News cautioned physicians against partnering with private equity firms, warning that they target “quick profits and quick exits, which can be inconsistent with quality long-term patient care.”
But several recent studies – and my own experience – show that .
A 2024 study conducted by Avalere Health found that per-beneficiary Medicare expenditures for physicians who shifted from an unaffiliated practice model to a PE-affiliated model declined by $963 in the 12 months following the transition. By contrast, per-beneficiary Medicare expenditures for physicians who shifted from an unaffiliated model to a hospital-affiliated one increased more than $1,300.
A 2025 peer-reviewed study published in Journal of Market Access & Health Policy found that physicians affiliated with private equity were far more likely to perform common high-volume procedures in the lowest-cost site of care – an ambulatory surgery center or medical office – than in higher-cost hospital outpatient departments. Physicians affiliated with hospitals were far more likely to perform procedures in HOPDs.
Partnering with a private equity-backed management services organization has enabled my practice to afford advanced technologies we never could have deployed on our own. Those technologies have helped improve our polyp detection rates, reduce the incidence of colon cancer, and more efficiently care for patients with ulcerative colitis. We also now provide patients seamless access to digital platforms that help them better manage chronic conditions.
Independent medical practice is under duress. Partnering with a private equity-backed management services organization is one of the most effective ways for a physician practice to retain its independence – and continue offering patients affordable, high-quality care.
George Dickstein, MD, AGAF, is senior vice president of clinical affairs, Massachusetts, for Gastro Health, and chairperson of Gastro Health’s Physician Leadership Council. He is based in Framingham, Mass. GI & Hepatology News encourages readers to submit letters to the editor to debate topics raised in the newspaper.
An October 1 article in GI & Hepatology News cautioned physicians against partnering with private equity firms, warning that they target “quick profits and quick exits, which can be inconsistent with quality long-term patient care.”
But several recent studies – and my own experience – show that .
A 2024 study conducted by Avalere Health found that per-beneficiary Medicare expenditures for physicians who shifted from an unaffiliated practice model to a PE-affiliated model declined by $963 in the 12 months following the transition. By contrast, per-beneficiary Medicare expenditures for physicians who shifted from an unaffiliated model to a hospital-affiliated one increased more than $1,300.
A 2025 peer-reviewed study published in Journal of Market Access & Health Policy found that physicians affiliated with private equity were far more likely to perform common high-volume procedures in the lowest-cost site of care – an ambulatory surgery center or medical office – than in higher-cost hospital outpatient departments. Physicians affiliated with hospitals were far more likely to perform procedures in HOPDs.
Partnering with a private equity-backed management services organization has enabled my practice to afford advanced technologies we never could have deployed on our own. Those technologies have helped improve our polyp detection rates, reduce the incidence of colon cancer, and more efficiently care for patients with ulcerative colitis. We also now provide patients seamless access to digital platforms that help them better manage chronic conditions.
Independent medical practice is under duress. Partnering with a private equity-backed management services organization is one of the most effective ways for a physician practice to retain its independence – and continue offering patients affordable, high-quality care.
George Dickstein, MD, AGAF, is senior vice president of clinical affairs, Massachusetts, for Gastro Health, and chairperson of Gastro Health’s Physician Leadership Council. He is based in Framingham, Mass. GI & Hepatology News encourages readers to submit letters to the editor to debate topics raised in the newspaper.
Bridging the Funding Gap
Federal grants have supported cutting-edge research in scientific and biomedical fields since the mid-20th century, fueling public health breakthroughs and health innovations. This crucial support has been greatly diminished in recent months with deep cuts to federal research dollars.
As these acute policy changes continue to disrupt academic institutions and their investigators, introducing financial strain and operational uncertainty, the importance of research support from professional societies and foundations has become increasingly evident. Their targeted funding plays a critical role in sustaining biomedical research, which directly impacts clinical innovation and patient care. As one example, the AGA Research Foundation provides over $2 million annually to spur discoveries in gastroenterology and hepatology. This vital research support, awarded to 74 unique recipients (including 7 early-career Research Scholar Award recipients) in 2025, represents one of the most important investments that AGA makes in the future of gastroenterology and the patients we treat.
While foundation awards such as these cannot completely close the federal funding gap, they serve as an important lifeline both in supporting the core work of early career and established investigators in an uncertain funding environment and in funding high-risk, high-reward research that more conservative funders are often hesitant to invest in. – now more than ever, the funding it provides has tremendous impact.
In this issue of GI & Hepatology News, we update you on the FDA’s recent approval of semaglutide as a treatment for MASH with fibrosis and highlight a recent target trial emulation study that casts doubt on our traditional understanding regarding the link between common medications such as PPIs and NSAIDs and microscopic colitis in older adults. We also summarize newly-released, global guidelines for pregnancy and IBD, which deserve a careful read. In this month’s Member Spotlight, we feature Pascale White, MD, MBA, MS (Mount Sinai), a recent recipient of the AGA-Pfizer Beacon of Hope Award for Gender and Health Equity, who shares her inspirational work to improve colorectal cancer screening among underserved, high-risk patients in East Harlem. We hope you enjoy this and all the exciting content in our October issue.
Megan A. Adams, MD, JD, MSc
Editor in Chief
Federal grants have supported cutting-edge research in scientific and biomedical fields since the mid-20th century, fueling public health breakthroughs and health innovations. This crucial support has been greatly diminished in recent months with deep cuts to federal research dollars.
As these acute policy changes continue to disrupt academic institutions and their investigators, introducing financial strain and operational uncertainty, the importance of research support from professional societies and foundations has become increasingly evident. Their targeted funding plays a critical role in sustaining biomedical research, which directly impacts clinical innovation and patient care. As one example, the AGA Research Foundation provides over $2 million annually to spur discoveries in gastroenterology and hepatology. This vital research support, awarded to 74 unique recipients (including 7 early-career Research Scholar Award recipients) in 2025, represents one of the most important investments that AGA makes in the future of gastroenterology and the patients we treat.
While foundation awards such as these cannot completely close the federal funding gap, they serve as an important lifeline both in supporting the core work of early career and established investigators in an uncertain funding environment and in funding high-risk, high-reward research that more conservative funders are often hesitant to invest in. – now more than ever, the funding it provides has tremendous impact.
In this issue of GI & Hepatology News, we update you on the FDA’s recent approval of semaglutide as a treatment for MASH with fibrosis and highlight a recent target trial emulation study that casts doubt on our traditional understanding regarding the link between common medications such as PPIs and NSAIDs and microscopic colitis in older adults. We also summarize newly-released, global guidelines for pregnancy and IBD, which deserve a careful read. In this month’s Member Spotlight, we feature Pascale White, MD, MBA, MS (Mount Sinai), a recent recipient of the AGA-Pfizer Beacon of Hope Award for Gender and Health Equity, who shares her inspirational work to improve colorectal cancer screening among underserved, high-risk patients in East Harlem. We hope you enjoy this and all the exciting content in our October issue.
Megan A. Adams, MD, JD, MSc
Editor in Chief
Federal grants have supported cutting-edge research in scientific and biomedical fields since the mid-20th century, fueling public health breakthroughs and health innovations. This crucial support has been greatly diminished in recent months with deep cuts to federal research dollars.
As these acute policy changes continue to disrupt academic institutions and their investigators, introducing financial strain and operational uncertainty, the importance of research support from professional societies and foundations has become increasingly evident. Their targeted funding plays a critical role in sustaining biomedical research, which directly impacts clinical innovation and patient care. As one example, the AGA Research Foundation provides over $2 million annually to spur discoveries in gastroenterology and hepatology. This vital research support, awarded to 74 unique recipients (including 7 early-career Research Scholar Award recipients) in 2025, represents one of the most important investments that AGA makes in the future of gastroenterology and the patients we treat.
While foundation awards such as these cannot completely close the federal funding gap, they serve as an important lifeline both in supporting the core work of early career and established investigators in an uncertain funding environment and in funding high-risk, high-reward research that more conservative funders are often hesitant to invest in. – now more than ever, the funding it provides has tremendous impact.
In this issue of GI & Hepatology News, we update you on the FDA’s recent approval of semaglutide as a treatment for MASH with fibrosis and highlight a recent target trial emulation study that casts doubt on our traditional understanding regarding the link between common medications such as PPIs and NSAIDs and microscopic colitis in older adults. We also summarize newly-released, global guidelines for pregnancy and IBD, which deserve a careful read. In this month’s Member Spotlight, we feature Pascale White, MD, MBA, MS (Mount Sinai), a recent recipient of the AGA-Pfizer Beacon of Hope Award for Gender and Health Equity, who shares her inspirational work to improve colorectal cancer screening among underserved, high-risk patients in East Harlem. We hope you enjoy this and all the exciting content in our October issue.
Megan A. Adams, MD, JD, MSc
Editor in Chief