User login
Transplantation palliative care: The time is ripe
Over 10 years ago, a challenge was made in a surgical publication for increased collaboration between the fields of transplantation and palliative care.1
Since that time not much progress has been made bringing these fields together in a consistent way that would mutually benefit patients and the specialties. However, other progress has been made, particularly in the field of palliative care, which could brighten the prospects and broaden the opportunities to accomplish collaboration between palliative care and transplantation.
Growth of palliative services
During the past decade there has been a robust proliferation of hospital-based palliative care programs in the United States. In all, 67% of U.S. hospitals with 50 or more beds report palliative care teams, up from 63% in 2011 and 53% in 2008.
Only a decade ago, critical care and palliative care were generally considered mutually exclusive. Evidence is trickling in to suggest that this is no longer the case. Although palliative care was not an integral part of critical care at that time, patients, families, and even practitioners began to demand these services. Cook and Rocker have eloquently advocated the rightful place of palliative care in the ICU.2
Studies in recent years have shown that the integration of palliative care into critical care decreases in length of ICU and hospital stay, decreases costs, enhances patient/family satisfaction, and promotes a more rapid consensus about goals of care, without increasing mortality. The ICU experience to date could be considered a reassuring precedent for transplantation palliative care.
Integration of palliative care with transplantation
Early palliative care intervention has been shown to improve symptom burden and depression scores in end-stage liver disease patients awaiting transplant. In addition, early palliative care consultation in conjunction with cancer treatment has been associated with increased survival in non–small-cell lung cancer patients. It has been demonstrated that early integration of palliative care in the surgical ICU alongside disease-directed curative care can be accomplished without change in mortality, while improving end-of-life practice in liver transplant patients.3
What palliative care can do for transplant patients
What does palliative care mean for the person (and family) awaiting transplantation? For the cirrhotic patient with cachexia, ascites, and encephalopathy, it means access to the services of a team trained in the management of these symptoms. Palliative care teams can also provide psychosocial and spiritual support for patients and families who are intimidated by the complex navigation of the health care system and the existential threat that end-stage organ failure presents to them. Skilled palliative care and services can be the difference between failing and extended life with a higher quality of life for these very sick patients
Resuscitation of a patient, whether through restoration of organ function or interdicting the progression of disease, begins with resuscitation of hope. Nothing achieves this more quickly than amelioration of burdensome symptoms for the patient and family.
The barriers for transplant surgeons and teams referring and incorporating palliative care services in their practices are multiple and profound. The unique dilemma facing the transplant team is to balance the treatment of the failing organ, the treatment of the patient (and family and friends), and the best use of the graft, a precious gift of society.
Palliative surgery has been defined as any invasive procedure in which the main intention is to mitigate physical symptoms in patients with noncurable disease without causing premature death. The very success of transplantation over the past 3 decades has obscured our memory of transplantation as a type of palliative surgery. It is a well-known axiom of reconstructive surgery that the reconstructed site should be compared to what was there, not to “normal.” Even in the current era of improved immunosuppression and posttransplant support services, one could hardly describe even a successful transplant patient’s experience as “normal.” These patients’ lives may be extended and/or enhanced but they need palliative care before, during, and after transplantation. The growing availability of trained palliative care clinicians and teams, the increased familiarity of palliative and end-of-life care to surgical residents and fellows, and quality metrics measuring palliative care outcomes will provide reassurance and guidance to address reservations about the convergence of the two seemingly opposite realities.
A modest proposal
We propose that palliative care be presented to the entire spectrum of transplantation care: on the ward, in the ICU, and after transplantation. More specific “triggers” for palliative care for referral of transplant patients should be identified. Wentlandt et al.4 have described a promising model for an ambulatory clinic, which provides early, integrated palliative care to patients awaiting and receiving organ transplantation. In addition, we propose an application for grant funding for a conference and eventual formation of a work group of transplant surgeons and team members, palliative care clinicians, and patient/families who have experienced one of the aspects of the transplant spectrum. We await the subspecialty certification in hospice and palliative medicine of a transplant surgeon. Outside of transplantation, every other surgical specialty in the United States has diplomates certified in hospice and palliative medicine. We await the benefits that will accrue from research about the merging of these fields.
1. Molmenti EP, Dunn GP: Transplantation and palliative care: The convergence of two seemingly opposite realities. Surg Clin North Am. 2005;85:373-82.
2. Cook D, Rocker G. Dying with dignity in the intensive care unit. N Engl J Med. 2014;370:2506-14.
3. Lamba S, Murphy P, McVicker S, Smith JH, and Mosenthal AC. Changing end-of-life care practice for liver transplant patients: structured palliative care intervention in the surgical intensive care unit. J Pain Symptom Manage. 2012; 44(4):508-19.
4. Wentlandt, K., Dall’Osto, A., Freeman, N., Le, L. W., Kaya, E., Ross, H., Singer, L. G., Abbey, S., Clarke, H. and Zimmermann, C. (2016), The Transplant Palliative Care Clinic: An early palliative care model for patients in a transplant program. Clin Transplant. 2016 Nov 4; doi: 10.1111/ctr.12838.
Dr. Azoulay is a transplantation specialist of Assistance Publique – Hôpitaux de Paris, and the University of Paris. Dr. Dunn is medical director of the Palliative Care Consultation Service at the University of Pittsburgh Medical Center Hamot, and vice-chair of the ACS Committee on Surgical Palliative Care.
Over 10 years ago, a challenge was made in a surgical publication for increased collaboration between the fields of transplantation and palliative care.1
Since that time not much progress has been made bringing these fields together in a consistent way that would mutually benefit patients and the specialties. However, other progress has been made, particularly in the field of palliative care, which could brighten the prospects and broaden the opportunities to accomplish collaboration between palliative care and transplantation.
Growth of palliative services
During the past decade there has been a robust proliferation of hospital-based palliative care programs in the United States. In all, 67% of U.S. hospitals with 50 or more beds report palliative care teams, up from 63% in 2011 and 53% in 2008.
Only a decade ago, critical care and palliative care were generally considered mutually exclusive. Evidence is trickling in to suggest that this is no longer the case. Although palliative care was not an integral part of critical care at that time, patients, families, and even practitioners began to demand these services. Cook and Rocker have eloquently advocated the rightful place of palliative care in the ICU.2
Studies in recent years have shown that the integration of palliative care into critical care decreases in length of ICU and hospital stay, decreases costs, enhances patient/family satisfaction, and promotes a more rapid consensus about goals of care, without increasing mortality. The ICU experience to date could be considered a reassuring precedent for transplantation palliative care.
Integration of palliative care with transplantation
Early palliative care intervention has been shown to improve symptom burden and depression scores in end-stage liver disease patients awaiting transplant. In addition, early palliative care consultation in conjunction with cancer treatment has been associated with increased survival in non–small-cell lung cancer patients. It has been demonstrated that early integration of palliative care in the surgical ICU alongside disease-directed curative care can be accomplished without change in mortality, while improving end-of-life practice in liver transplant patients.3
What palliative care can do for transplant patients
What does palliative care mean for the person (and family) awaiting transplantation? For the cirrhotic patient with cachexia, ascites, and encephalopathy, it means access to the services of a team trained in the management of these symptoms. Palliative care teams can also provide psychosocial and spiritual support for patients and families who are intimidated by the complex navigation of the health care system and the existential threat that end-stage organ failure presents to them. Skilled palliative care and services can be the difference between failing and extended life with a higher quality of life for these very sick patients
Resuscitation of a patient, whether through restoration of organ function or interdicting the progression of disease, begins with resuscitation of hope. Nothing achieves this more quickly than amelioration of burdensome symptoms for the patient and family.
The barriers for transplant surgeons and teams referring and incorporating palliative care services in their practices are multiple and profound. The unique dilemma facing the transplant team is to balance the treatment of the failing organ, the treatment of the patient (and family and friends), and the best use of the graft, a precious gift of society.
Palliative surgery has been defined as any invasive procedure in which the main intention is to mitigate physical symptoms in patients with noncurable disease without causing premature death. The very success of transplantation over the past 3 decades has obscured our memory of transplantation as a type of palliative surgery. It is a well-known axiom of reconstructive surgery that the reconstructed site should be compared to what was there, not to “normal.” Even in the current era of improved immunosuppression and posttransplant support services, one could hardly describe even a successful transplant patient’s experience as “normal.” These patients’ lives may be extended and/or enhanced but they need palliative care before, during, and after transplantation. The growing availability of trained palliative care clinicians and teams, the increased familiarity of palliative and end-of-life care to surgical residents and fellows, and quality metrics measuring palliative care outcomes will provide reassurance and guidance to address reservations about the convergence of the two seemingly opposite realities.
A modest proposal
We propose that palliative care be presented to the entire spectrum of transplantation care: on the ward, in the ICU, and after transplantation. More specific “triggers” for palliative care for referral of transplant patients should be identified. Wentlandt et al.4 have described a promising model for an ambulatory clinic, which provides early, integrated palliative care to patients awaiting and receiving organ transplantation. In addition, we propose an application for grant funding for a conference and eventual formation of a work group of transplant surgeons and team members, palliative care clinicians, and patient/families who have experienced one of the aspects of the transplant spectrum. We await the subspecialty certification in hospice and palliative medicine of a transplant surgeon. Outside of transplantation, every other surgical specialty in the United States has diplomates certified in hospice and palliative medicine. We await the benefits that will accrue from research about the merging of these fields.
1. Molmenti EP, Dunn GP: Transplantation and palliative care: The convergence of two seemingly opposite realities. Surg Clin North Am. 2005;85:373-82.
2. Cook D, Rocker G. Dying with dignity in the intensive care unit. N Engl J Med. 2014;370:2506-14.
3. Lamba S, Murphy P, McVicker S, Smith JH, and Mosenthal AC. Changing end-of-life care practice for liver transplant patients: structured palliative care intervention in the surgical intensive care unit. J Pain Symptom Manage. 2012; 44(4):508-19.
4. Wentlandt, K., Dall’Osto, A., Freeman, N., Le, L. W., Kaya, E., Ross, H., Singer, L. G., Abbey, S., Clarke, H. and Zimmermann, C. (2016), The Transplant Palliative Care Clinic: An early palliative care model for patients in a transplant program. Clin Transplant. 2016 Nov 4; doi: 10.1111/ctr.12838.
Dr. Azoulay is a transplantation specialist of Assistance Publique – Hôpitaux de Paris, and the University of Paris. Dr. Dunn is medical director of the Palliative Care Consultation Service at the University of Pittsburgh Medical Center Hamot, and vice-chair of the ACS Committee on Surgical Palliative Care.
Over 10 years ago, a challenge was made in a surgical publication for increased collaboration between the fields of transplantation and palliative care.1
Since that time not much progress has been made bringing these fields together in a consistent way that would mutually benefit patients and the specialties. However, other progress has been made, particularly in the field of palliative care, which could brighten the prospects and broaden the opportunities to accomplish collaboration between palliative care and transplantation.
Growth of palliative services
During the past decade there has been a robust proliferation of hospital-based palliative care programs in the United States. In all, 67% of U.S. hospitals with 50 or more beds report palliative care teams, up from 63% in 2011 and 53% in 2008.
Only a decade ago, critical care and palliative care were generally considered mutually exclusive. Evidence is trickling in to suggest that this is no longer the case. Although palliative care was not an integral part of critical care at that time, patients, families, and even practitioners began to demand these services. Cook and Rocker have eloquently advocated the rightful place of palliative care in the ICU.2
Studies in recent years have shown that the integration of palliative care into critical care decreases in length of ICU and hospital stay, decreases costs, enhances patient/family satisfaction, and promotes a more rapid consensus about goals of care, without increasing mortality. The ICU experience to date could be considered a reassuring precedent for transplantation palliative care.
Integration of palliative care with transplantation
Early palliative care intervention has been shown to improve symptom burden and depression scores in end-stage liver disease patients awaiting transplant. In addition, early palliative care consultation in conjunction with cancer treatment has been associated with increased survival in non–small-cell lung cancer patients. It has been demonstrated that early integration of palliative care in the surgical ICU alongside disease-directed curative care can be accomplished without change in mortality, while improving end-of-life practice in liver transplant patients.3
What palliative care can do for transplant patients
What does palliative care mean for the person (and family) awaiting transplantation? For the cirrhotic patient with cachexia, ascites, and encephalopathy, it means access to the services of a team trained in the management of these symptoms. Palliative care teams can also provide psychosocial and spiritual support for patients and families who are intimidated by the complex navigation of the health care system and the existential threat that end-stage organ failure presents to them. Skilled palliative care and services can be the difference between failing and extended life with a higher quality of life for these very sick patients
Resuscitation of a patient, whether through restoration of organ function or interdicting the progression of disease, begins with resuscitation of hope. Nothing achieves this more quickly than amelioration of burdensome symptoms for the patient and family.
The barriers for transplant surgeons and teams referring and incorporating palliative care services in their practices are multiple and profound. The unique dilemma facing the transplant team is to balance the treatment of the failing organ, the treatment of the patient (and family and friends), and the best use of the graft, a precious gift of society.
Palliative surgery has been defined as any invasive procedure in which the main intention is to mitigate physical symptoms in patients with noncurable disease without causing premature death. The very success of transplantation over the past 3 decades has obscured our memory of transplantation as a type of palliative surgery. It is a well-known axiom of reconstructive surgery that the reconstructed site should be compared to what was there, not to “normal.” Even in the current era of improved immunosuppression and posttransplant support services, one could hardly describe even a successful transplant patient’s experience as “normal.” These patients’ lives may be extended and/or enhanced but they need palliative care before, during, and after transplantation. The growing availability of trained palliative care clinicians and teams, the increased familiarity of palliative and end-of-life care to surgical residents and fellows, and quality metrics measuring palliative care outcomes will provide reassurance and guidance to address reservations about the convergence of the two seemingly opposite realities.
A modest proposal
We propose that palliative care be presented to the entire spectrum of transplantation care: on the ward, in the ICU, and after transplantation. More specific “triggers” for palliative care for referral of transplant patients should be identified. Wentlandt et al.4 have described a promising model for an ambulatory clinic, which provides early, integrated palliative care to patients awaiting and receiving organ transplantation. In addition, we propose an application for grant funding for a conference and eventual formation of a work group of transplant surgeons and team members, palliative care clinicians, and patient/families who have experienced one of the aspects of the transplant spectrum. We await the subspecialty certification in hospice and palliative medicine of a transplant surgeon. Outside of transplantation, every other surgical specialty in the United States has diplomates certified in hospice and palliative medicine. We await the benefits that will accrue from research about the merging of these fields.
1. Molmenti EP, Dunn GP: Transplantation and palliative care: The convergence of two seemingly opposite realities. Surg Clin North Am. 2005;85:373-82.
2. Cook D, Rocker G. Dying with dignity in the intensive care unit. N Engl J Med. 2014;370:2506-14.
3. Lamba S, Murphy P, McVicker S, Smith JH, and Mosenthal AC. Changing end-of-life care practice for liver transplant patients: structured palliative care intervention in the surgical intensive care unit. J Pain Symptom Manage. 2012; 44(4):508-19.
4. Wentlandt, K., Dall’Osto, A., Freeman, N., Le, L. W., Kaya, E., Ross, H., Singer, L. G., Abbey, S., Clarke, H. and Zimmermann, C. (2016), The Transplant Palliative Care Clinic: An early palliative care model for patients in a transplant program. Clin Transplant. 2016 Nov 4; doi: 10.1111/ctr.12838.
Dr. Azoulay is a transplantation specialist of Assistance Publique – Hôpitaux de Paris, and the University of Paris. Dr. Dunn is medical director of the Palliative Care Consultation Service at the University of Pittsburgh Medical Center Hamot, and vice-chair of the ACS Committee on Surgical Palliative Care.
SVS Now Accepting Abstracts for VAM 2017
Abstracts for the 2017 Vascular Annual Meeting are now being accepted. The submission site opened Monday, Nov. 14 for the meeting, to be held May 31 to June 3, 2017, in San Diego. Plenary sessions and exhibits will be June 1 to 3.
Participants may submit abstracts into any of 14 categories and a number of presentation types, including videos. In 2016, organizers selected approximately two-thirds of the submitted abstracts, and this year the VAM Program Committee is seeking additional venues for people to present their work in, including more sessions and other presentation formats.
Click here for abstract guidelines and more information. Abstracts themselves may be submitted here.
Abstracts for the 2017 Vascular Annual Meeting are now being accepted. The submission site opened Monday, Nov. 14 for the meeting, to be held May 31 to June 3, 2017, in San Diego. Plenary sessions and exhibits will be June 1 to 3.
Participants may submit abstracts into any of 14 categories and a number of presentation types, including videos. In 2016, organizers selected approximately two-thirds of the submitted abstracts, and this year the VAM Program Committee is seeking additional venues for people to present their work in, including more sessions and other presentation formats.
Click here for abstract guidelines and more information. Abstracts themselves may be submitted here.
Abstracts for the 2017 Vascular Annual Meeting are now being accepted. The submission site opened Monday, Nov. 14 for the meeting, to be held May 31 to June 3, 2017, in San Diego. Plenary sessions and exhibits will be June 1 to 3.
Participants may submit abstracts into any of 14 categories and a number of presentation types, including videos. In 2016, organizers selected approximately two-thirds of the submitted abstracts, and this year the VAM Program Committee is seeking additional venues for people to present their work in, including more sessions and other presentation formats.
Click here for abstract guidelines and more information. Abstracts themselves may be submitted here.
Best Practices: Protecting Dry Vulnerable Skin with CeraVe® Healing Ointment
A supplement to Dermatology News. This advertising supplement is sponsored by Valeant Pharmaceuticals.
- Reinforcing the Skin Barrier
- NEA Seal of Acceptance
- A Preventative Approach to Dry, Cracked Skin
- CeraVe Ointment in the Clinical Setting
Faculty/Faculty Disclosure
Sheila Fallon Friedlander, MD
Professor of Clinical Dermatology & Pediatrics
Director, Pediatric Dermatology Fellowship Training Program
University of California at San Diego School of Medicine
Rady Children’s Hospital,
San Diego, California
Dr. Friedlander was compensated for her participation in the development of this article.
CeraVe is a registered trademark of Valeant Pharmaceuticals International, Inc. or its affiliates.
A supplement to Dermatology News. This advertising supplement is sponsored by Valeant Pharmaceuticals.
- Reinforcing the Skin Barrier
- NEA Seal of Acceptance
- A Preventative Approach to Dry, Cracked Skin
- CeraVe Ointment in the Clinical Setting
Faculty/Faculty Disclosure
Sheila Fallon Friedlander, MD
Professor of Clinical Dermatology & Pediatrics
Director, Pediatric Dermatology Fellowship Training Program
University of California at San Diego School of Medicine
Rady Children’s Hospital,
San Diego, California
Dr. Friedlander was compensated for her participation in the development of this article.
CeraVe is a registered trademark of Valeant Pharmaceuticals International, Inc. or its affiliates.
A supplement to Dermatology News. This advertising supplement is sponsored by Valeant Pharmaceuticals.
- Reinforcing the Skin Barrier
- NEA Seal of Acceptance
- A Preventative Approach to Dry, Cracked Skin
- CeraVe Ointment in the Clinical Setting
Faculty/Faculty Disclosure
Sheila Fallon Friedlander, MD
Professor of Clinical Dermatology & Pediatrics
Director, Pediatric Dermatology Fellowship Training Program
University of California at San Diego School of Medicine
Rady Children’s Hospital,
San Diego, California
Dr. Friedlander was compensated for her participation in the development of this article.
CeraVe is a registered trademark of Valeant Pharmaceuticals International, Inc. or its affiliates.
Primary Care Clinician and Patient Knowledge, Interest, and Use of Integrative Treatment Options for Chronic Low Back Pain Management
Primary Care Clinician and Patient Knowledge, Interest, and Use of Integrative Treatment Options for Chronic Low Back Pain Management
More than 50 million US adults report experiencing chronic pain, with nearly 7% experiencing high-impact chronic pain.1-3 Chronic pain negatively affects daily function, results in lost productivity, is a leading cause of disability, and is more prevalent among veterans compared with the general population.1,2,4-6 Estimates from 2021 suggest the prevalence of chronic pain among veterans exceeds 30%; > 11% experienced high-impact chronic pain.1
Primary care practitioners (PCPs) have a prominent role in chronic pain management. Pharmacologic options for treating pain, once a mainstay of therapy, present several challenges for patients and PCPs, including drug-drug interactions and adverse effects.7 The US opioid epidemic and shift to a biopsychosocial model of chronic pain care have increased emphasis on nonpharmacologic treatment options.8,9 These include integrative modalities, which incorporate conventional approaches with an array of complementary health approaches.10-12
Integrative therapy is a prominent feature in whole person care, which may be best exemplified by the US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) Whole Health System of care.13-14 Whole health empowers an individual to take charge of their health and well-being so they can “live their life to the fullest.”14 As implemented in the Veterans Health Administration (VHA), whole health includes the use of evidence-based
METHODS
Using a cross-sectional survey design, PCPs and patients with chronic back pain affiliated with the VA Ann Arbor Healthcare System were invited to participate in separate but similar surveys to assess knowledge, interest, and use of nonpharmacologic integrative modalities for the treatment of chronic pain. In May, June, and July 2023, 78 PCPs received 3 email
Both survey instruments are available upon request, were developed by the study team, and included a mix of yes/no questions, “select all that apply” items, Likert scale response items, and open-ended questions. For one question about which modalities they would like available, the respondent was instructed to select up to 5 modalities. The instruments were extensively pretested by members of the study team, which included 2 PCPs and a nonveteran with chronic back pain.
The list of integrative modalities included in the survey was derived from the tier 1 and tier 2 complementary and integrative health modalities identified in a VHA Directive on complementary and integrative health.15,16 Tier 1 approaches are considered to have sufficient evidence and must be made available to veterans either within a VA medical facility or in the community. Tier 2 approaches are generally considered safe and may be made available but do not have sufficient evidence to mandate their provision. For participant ease, the integrative modalities were divided into 5 subgroups: manual therapies, energy/biofield therapies, mental health therapies, nutrition counseling, and movement therapies. The clinician survey assessed clinicians’ training and interest, clinical and personal use, and perceived barriers to providing integrative modalities for chronic pain. Professional and personal demographic data were also collected. Similarly, the patient survey assessed use of integrative therapies, perceptions of and interest in integrative modalities, and potential barriers to use. Demographic and health-related information was also collected.
Data analysis included descriptive statistics (eg, frequency counts, means, medians) and visual graphic displays. Separate analyses were conducted for clinicians and patients in addition to a comparative analysis of the use and potential interest in integrative modalities. Analysis were conducted using R software. This study was deemed nonresearch quality improvement by the VA Ann Arbor Healthcare System facility research oversight board and institutional review board approval was not solicited.
RESULTS
Twenty-eight clinicians completed the survey, yielding a participation rate of 36%. Participating clinicians had a median (IQR) age of 48 years (9.5), 15 self-identified as White (54%), 8 as Asian (29%), 15 as female (54%), 26 as non-Hispanic (93%), and 25 were medical doctors or doctors of osteopathy (89%). Nineteen (68%) worked at the main hospital outpatient clinic, and 9 practiced at community-based outpatient clinics (CBOCs). Thirteen respondents (46%) reported having no formal education or training in integrative approaches. Among those with prior training, 8 clinicians had nutrition counseling (29%) and 7 had psychologic therapy training (25%). Thirteen respondents (46%) also reported using integrative modalities for personal health needs: 8 used psychological therapies, 8 used movement therapies, 10 used integrative modalities for stress management or relaxation, and 8 used them for physical symptoms (Table 1).
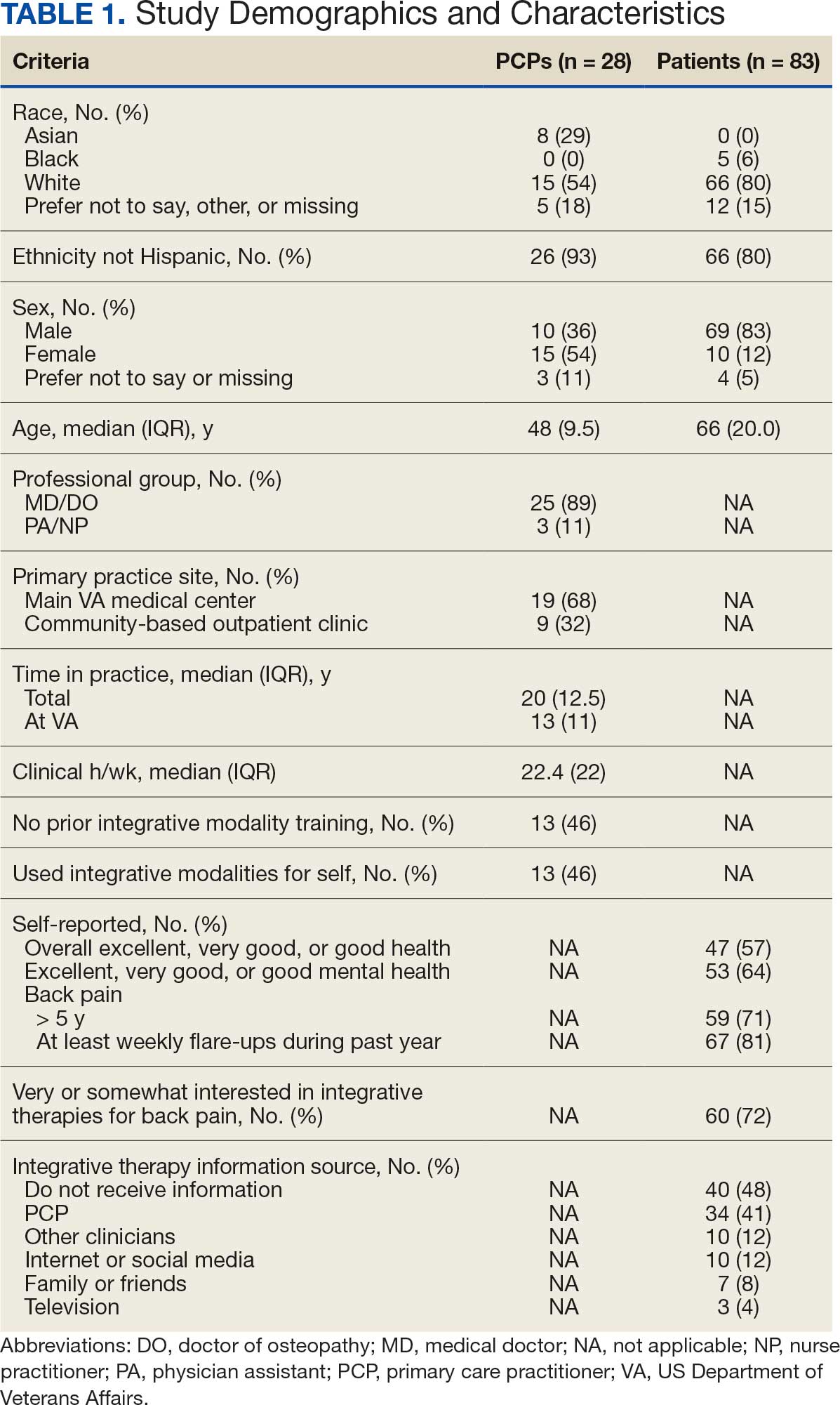
Overall, 85 of 200 patients (43%) responded to the study survey. Two patients indicated they did not have chronic back pain and were excluded. Patients had a median (IQR) age of 66 (20) years, with 66 self-identifying as White (80%), 69 as male (83%), and 66 as non-Hispanic (80%). Forty-four patients (53%) received care at CBOCs. Forty-seven patients reported excellent, very good, or good overall health (57%), while 53 reported excellent, very good, or good mental health (64%). Fifty-nine patients reported back pain duration > 5 years (71%), and 67 (81%) indicated experiencing back pain flare-ups at least once per week over the previous 12 months. Sixty patients (72%) indicated they were somewhat or very interested in using integrative therapies as a back pain treatment; however, 40 patients (48%) indicated they had not received information about these therapies. Among those who indicated they had received information, the most frequently reported source was their PCP (41%). Most patients (72%) also reported feeling somewhat to very comfortable discussing integrative medicine therapies with their PCP.
Integrative Therapy Recommendations and Use
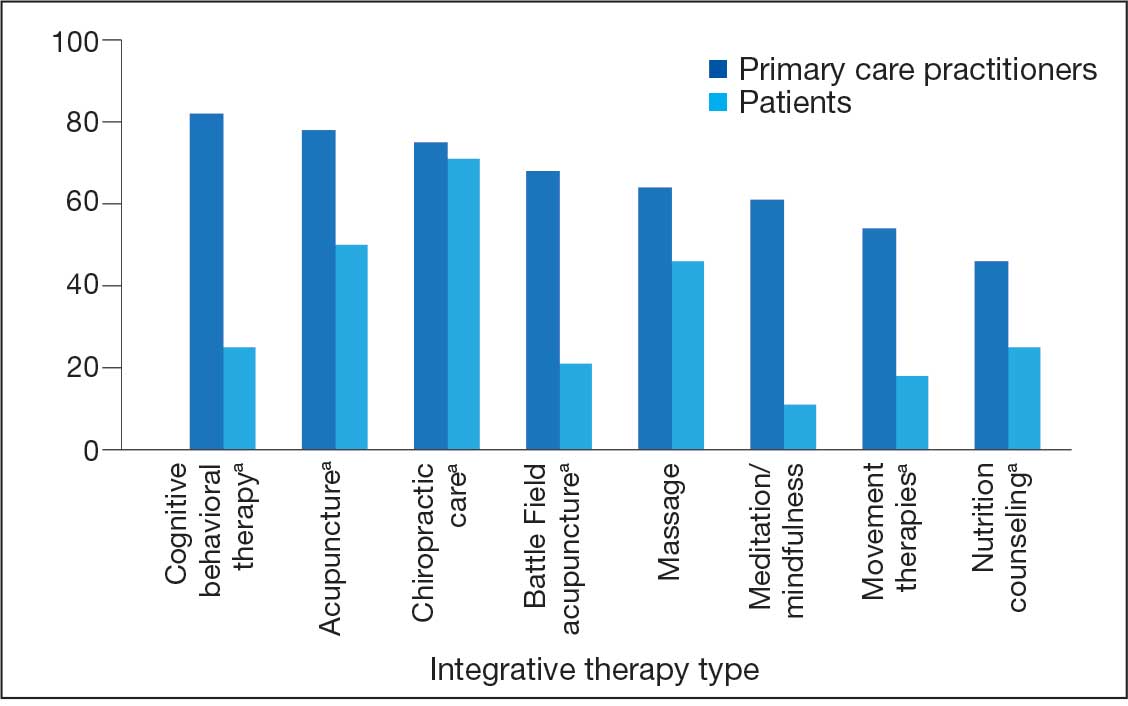
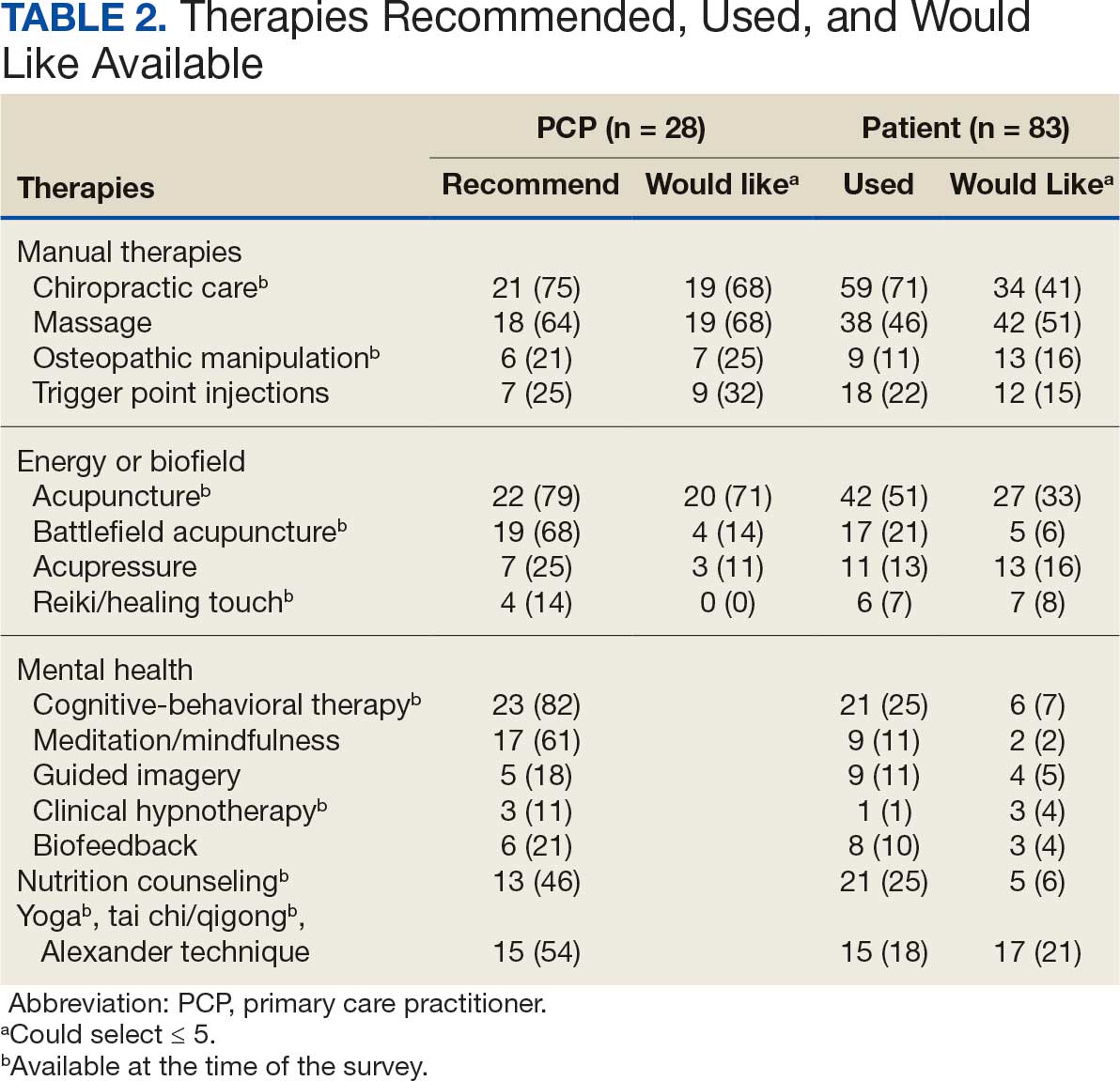
PCPs reported recommending multiple integrative modalities: 23 (82%) recommended cognitive-behavioral therapy, 22 (79%) recommended acupuncture, 21 (75%) recommended chiropractic, 19 (68%) recommended battlefield acupuncture, recommended massage 18 (64%), 17 (61%) recommended meditation or mindfulness, and 15 (54%) recommended movement therapies such as yoga or tai chi/qigong (Figure 1). The only therapies used by at least half of the patients were chiropractic used by 59 patients (71%) and acupuncture by 42 patients (51%). Thirty-eight patients (46%) reported massage use and 21 patients (25%) used cognitive-behavioral therapy (Table 2).
Integrative Therapies Desired
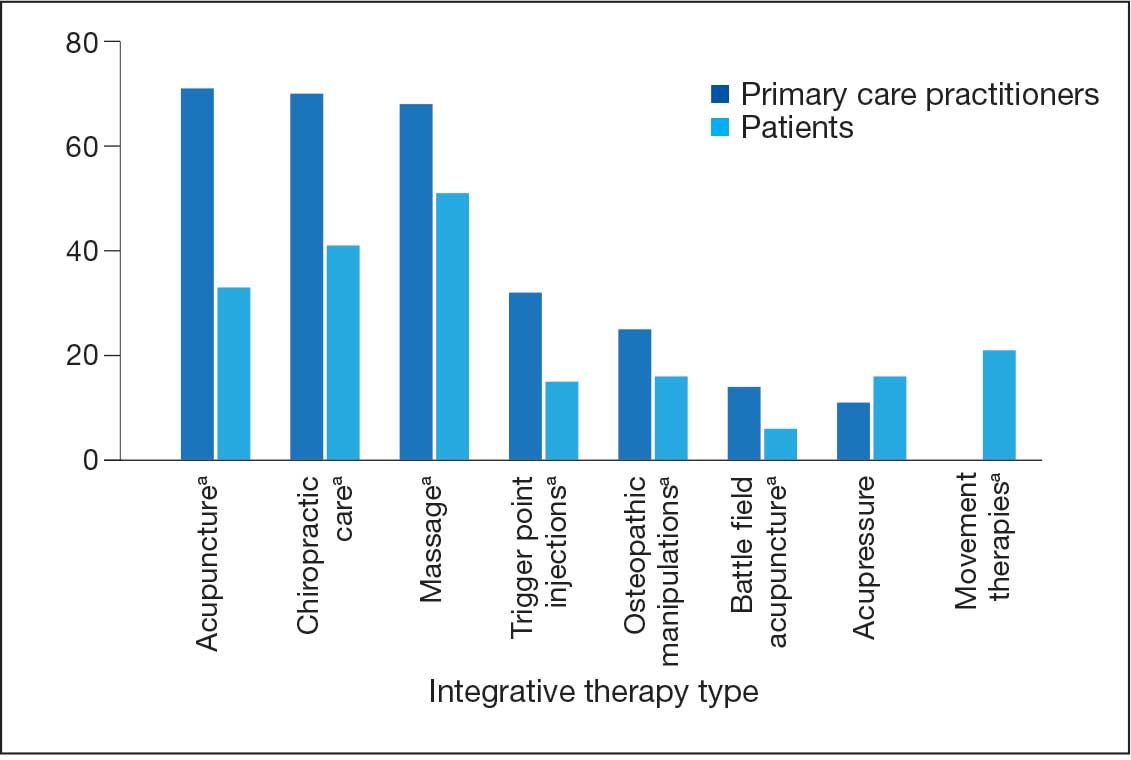
A majority of PCPs identified acupuncture (n = 20, 71%), chiropractic (n = 19, 68%), and massage (n = 19, 68%) as therapies they would most like to have available for patients with chronic pain (Figure 2). Similarly, patients identified massage (n = 42, 51%), chiropractic (n = 34, 41%), and acupuncture (n = 27, 33%) as most desired. Seventeen patients (21%) expressed interest in movement therapies.
Barriers to Integrative Therapies Use
When asked about barriers to use, 26 PCPs (93%) identified access to services as a somewhat or extremely likely barrier, and 22 identified time constraints (79%) (Table 3). However, 17 PCPs (61%) noted lack of familiarity, and 18 (64%) noted a lack of scientific evidence as barriers to recommending integrative modalities. Among patients, 33 (40%) indicated not knowing what services were available at their facility as a barrier, 32 (39%) were not familiar with specific therapies, and 21 (25%) indicated a lack of clarity about the benefits of a specific therapy. Only 14 patients (17%) indicated that there were no obstacles to use.

DISCUSSION
Use of integrative therapies, including complementary treatments, is an increasingly important part of chronic pain management. This survey study suggests VA PCPs are willing to recommend integrative therapies and patients with chronic back pain both desire and use several therapies. Moreover, both groups expressed interest in greater availability of similar therapies. The results also highlight key barriers, such as knowledge gaps, that should be addressed to increase the uptake of integrative modalities for managing chronic pain.
An increasing number of US adults are using complementary health approaches, an important component of integrative therapy.12 This trend includes an increase in use for pain management, from 42.3% in 2002 to 49.2% in 2022; chiropractic care, acupuncture, and massage were most frequently used.12 Similarly, chiropractic, acupuncture and massage were most often used by this sample of veterans with chronic back pain and were identified by the highest percentages of PCPs and patients as the therapies they would most like available.
There were areas where the opinions of patients and clinicians differed. As has been seen previously reported, clinicians largely recommended cognitive-behavioral therapy while patients showed less interest.17 Additionally, while patients expressed interest in the availability of movement therapies, such as yoga, PCPs expressed more interest in other strategies, such as trigger point injections. These differences may reflect true preference or a tendency for clinicians and patients to select therapies with which they are more familiar. Additional research is needed to better understand the acceptability and potential use of integrative health treatments across a broad array of therapeutic options.
Despite VHA policy requiring facilities to provide certain complementary and integrative health modalities, almost all PCPs identified access to services as a major obstacle.15 Based on evidence and a rigorous vetting process, services currently required on-site, via telehealth, or through community partners include acupuncture and battlefield acupuncture (battlefield auricular acupuncture), biofeedback, clinical hypnosis, guided imagery, medical massage therapy, medication, tai chi/qigong, and yoga. Optional approaches, which may be made available to veterans, include chiropractic and healing touch. Outside the VHA, some states have introduced or enacted legislation mandating insurance coverage of nonpharmacological pain treatments.18 However, these requirements and mandates do not help address challenges such as the availability of trained/qualified practitioners.19,20 Ensuring access to complementary and integrative health treatments requires a more concerted effort to ensure that supply meets demand. It is also important to acknowledge the budgetary and physical space constraints that further limit access to services. Although expansion and integration of integrative medicine services remain a priority within the VA Whole Health program, implementation is contingent on available financial and infrastructure resources.
Time was also identified by PCPs as a barrier to recommending integrative therapies to patients. Developing and implementing time-efficient communication strategies for patient education such as concise talking points and informational handouts could help address this barrier. Furthermore, leveraging existing programs and engaging the entire health care team in patient education and referral could help increase integrative and complementary therapy uptake and use.
Although access and time were identified as major barriers, these findings also suggest that PCP and patient knowledge are another target area for enhancing the use of complementary and integrative therapies. Like prior research, most clinicians identified a lack of familiarity with certain services and a lack of scientific evidence as extremely or somewhat likely to affect their ability to offer integrative services to patients with chronic pain.21 Likewise, about 40% of patients identified being unfamiliar with a specific therapy as one of the major obstacles to receiving integrative therapies, with a similar number identifying PCPs as a source of information. The lack of familiarity may be due in part to the evolving nomenclature, with terms such as alternative, complementary, and integrative used to describe approaches outside what is often considered conventional medicine.10 On the other hand, there has also been considerable expansion in the number of therapies within this domain, along with an expanding evidence base. This suggests a need for targeted educational strategies for clinicians and patients, which can be rapidly deployed and continuously adapted as new therapies and evidence emerge.
Limitations
There are some inherent limitations with a survey-based approach, including sampling, non-response, and social desirability biases. In addition, this study only included PCPs and patients affiliated with a single VA medical center. Steps to mitigate these limitations included maintaining survey anonymity and reporting information about respondent characteristics to enhance transparency about the representativeness of the study findings.
CONCLUSIONS
Expanding the use of nonpharmacological pain treatments, including integrative modalities, is essential for safe and effective chronic pain management and reducing opioid use. Our findings show that VA PCPs and patients with chronic back pain are interested in and have some experience with certain integrative therapies. However, even within the context of a health care system that supports the use of integrative therapies for chronic pain as part of whole person care, increasing uptake will require addressing access and time-related constraints as well as ongoing clinician and patient education.
- Rikard SM, Strahan AE, Schmit KM, et al. Chronic pain among adults — United States, 2018-2021. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2023;72:379-385. doi:10.15585/mmwr.mm7215a1
- Yong RJ, Mullins PM, Bhattacharyya N. Prevalence of chronic pain among adults in the United States. Pain. 2022;163:E328-E332. doi:10.1097/j.pain.0000000000002291
- Nahin RL, Feinberg T, Kapos FP, Terman GW. Estimated rates of incident and persistent chronic pain among US adults, 2019-2020. JAMA Netw Open. 2023;6:e2313563. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.13563
- Ferrari AJ, Santomauro DF, Aali A, et al. Global incidence, prevalence, years lived with disability (YLDs), disability-adjusted life-years (DALYs), and healthy life expectancy (HALE) for 371 diseases and injuries in 204 countries and territories and 811 subnational locations, 1990–2021: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2021. The Lancet. 2024;403:2133-2161. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(24)00757-8 5.
- Qureshi AR, Patel M, Neumark S, et al. Prevalence of chronic non-cancer pain among military veterans: a systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies. BMJ Mil Health. 2025;171:310-314. doi:10.1136/military-2023-002554
- Feldman DE, Nahin RL. Disability among persons with chronic severe back pain: results from a nationally representative population-based sample. J Pain. 2022;23:2144-2154. doi:10.1016/j.jpain.2022.07.016
- Qaseem A, Wilt TJ, McLean RM, Forciea MA. Noninvasive treatments for acute, subacute, and chronic low back pain: a clinical practice guideline from the American College of Physicians. Ann Intern Med. 2017;166:514-530. doi:10.7326/M16-2367
- van Erp RMA, Huijnen IPJ, Jakobs MLG, Kleijnen J, Smeets RJEM. Effectiveness of primary care interventions using a biopsychosocial approach in chronic low back pain: a systematic review. Pain Practice. 2019;19:224-241. doi:10.1111/papr.12735
- Chou R, Deyo R, Friedly J, et al. Nonpharmacologic therapies for low back pain: a systematic review for an American College of physicians clinical practice guideline. Ann Intern Med. 2017;166:493-505. doi:10.7326/M16-2459
- Complementary, alternative, or integrative health: what’s in a name? National Institutes of Health, National Center for Complementary and Integrative Health. Updated April 2021. Accessed December 15, 2025. https://www.nccih.nih.gov/health/complementary-alternative-or-integrative-health-whats-in-a-name.
- Taylor SL, Elwy AR. Complementary and alternative medicine for US veterans and active duty military personnel promising steps to improve their health. Med Care. 2014;52:S1-S4. doi:10.1097/MLR.0000000000000270.
- Nahin RL, Rhee A, Stussman B. Use of complementary health approaches overall and for pain management by US adults. JAMA. 2024;331:613-615. doi:10.1001/jama.2023.26775
- Gantt CJ, Donovan N, Khung M. Veterans Affairs’ Whole Health System of Care for transitioning service members and veterans. Mil Med. 2023;188:28-32. doi:10.1093/milmed/usad047
- Bokhour BG, Hyde J, Kligler B, et al. From patient outcomes to system change: evaluating the impact of VHA’s implementation of the Whole Health System of Care. Health Serv Res. 2022;57:53-65. doi:10.1111/1475-6773.13938
- Department of Veterans Affairs VHA. VHA Policy Directive 1137: Provision of Complementary and Integrative Health. December 2022. Accessed December 15, 2025. https://www.va.gov/VHApublications/ViewPublication.asp?pub_ID=10072
- Giannitrapani KF, Holliday JR, Miake-Lye IM, Hempel S, Taylor SL. Synthesizing the strength of the evidence of complementary and integrative health therapies for pain. Pain Med. 2019;20:1831-1840. doi:10.1093/pm/pnz068
- Belitskaya-Levy I, David Clark J, Shih MC, Bair MJ. Treatment preferences for chronic low back pain: views of veterans and their providers. J Pain Res. 2021;14:161-171. doi:10.2147/JPR.S290400
- Onstott TN, Hurst S, Kronick R, Tsou AC, Groessl E, McMenamin SB. Health insurance mandates for nonpharmacological pain treatments in 7 US states. JAMA Netw Open. 2024;7:E245737. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.5737
- Sullivan M, Leach M, Snow J, Moonaz S. The North American yoga therapy workforce survey. Complement Ther Med. 2017;31:39-48. doi:10.1016/j.ctim.2017.01.006
- Bolton R, Ritter G, Highland K, Larson MJ. The relationship between capacity and utilization of nonpharmacologic therapies in the US Military Health System. BMC Health Serv Res. 2022;22. doi:10.1186/s12913-022-07700-4
- Stussman BJ, Nahin RL, Barnes PM, Scott R, Feinberg T, Ward BW. Reasons office-based physicians in the United States recommend common complementary health approaches to patients: an exploratory study using a national survey. J Integr Complement Med. 2022;28:651-663. doi:10.1089/jicm.2022.0493
More than 50 million US adults report experiencing chronic pain, with nearly 7% experiencing high-impact chronic pain.1-3 Chronic pain negatively affects daily function, results in lost productivity, is a leading cause of disability, and is more prevalent among veterans compared with the general population.1,2,4-6 Estimates from 2021 suggest the prevalence of chronic pain among veterans exceeds 30%; > 11% experienced high-impact chronic pain.1
Primary care practitioners (PCPs) have a prominent role in chronic pain management. Pharmacologic options for treating pain, once a mainstay of therapy, present several challenges for patients and PCPs, including drug-drug interactions and adverse effects.7 The US opioid epidemic and shift to a biopsychosocial model of chronic pain care have increased emphasis on nonpharmacologic treatment options.8,9 These include integrative modalities, which incorporate conventional approaches with an array of complementary health approaches.10-12
Integrative therapy is a prominent feature in whole person care, which may be best exemplified by the US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) Whole Health System of care.13-14 Whole health empowers an individual to take charge of their health and well-being so they can “live their life to the fullest.”14 As implemented in the Veterans Health Administration (VHA), whole health includes the use of evidence-based
METHODS
Using a cross-sectional survey design, PCPs and patients with chronic back pain affiliated with the VA Ann Arbor Healthcare System were invited to participate in separate but similar surveys to assess knowledge, interest, and use of nonpharmacologic integrative modalities for the treatment of chronic pain. In May, June, and July 2023, 78 PCPs received 3 email
Both survey instruments are available upon request, were developed by the study team, and included a mix of yes/no questions, “select all that apply” items, Likert scale response items, and open-ended questions. For one question about which modalities they would like available, the respondent was instructed to select up to 5 modalities. The instruments were extensively pretested by members of the study team, which included 2 PCPs and a nonveteran with chronic back pain.
The list of integrative modalities included in the survey was derived from the tier 1 and tier 2 complementary and integrative health modalities identified in a VHA Directive on complementary and integrative health.15,16 Tier 1 approaches are considered to have sufficient evidence and must be made available to veterans either within a VA medical facility or in the community. Tier 2 approaches are generally considered safe and may be made available but do not have sufficient evidence to mandate their provision. For participant ease, the integrative modalities were divided into 5 subgroups: manual therapies, energy/biofield therapies, mental health therapies, nutrition counseling, and movement therapies. The clinician survey assessed clinicians’ training and interest, clinical and personal use, and perceived barriers to providing integrative modalities for chronic pain. Professional and personal demographic data were also collected. Similarly, the patient survey assessed use of integrative therapies, perceptions of and interest in integrative modalities, and potential barriers to use. Demographic and health-related information was also collected.
Data analysis included descriptive statistics (eg, frequency counts, means, medians) and visual graphic displays. Separate analyses were conducted for clinicians and patients in addition to a comparative analysis of the use and potential interest in integrative modalities. Analysis were conducted using R software. This study was deemed nonresearch quality improvement by the VA Ann Arbor Healthcare System facility research oversight board and institutional review board approval was not solicited.
RESULTS
Twenty-eight clinicians completed the survey, yielding a participation rate of 36%. Participating clinicians had a median (IQR) age of 48 years (9.5), 15 self-identified as White (54%), 8 as Asian (29%), 15 as female (54%), 26 as non-Hispanic (93%), and 25 were medical doctors or doctors of osteopathy (89%). Nineteen (68%) worked at the main hospital outpatient clinic, and 9 practiced at community-based outpatient clinics (CBOCs). Thirteen respondents (46%) reported having no formal education or training in integrative approaches. Among those with prior training, 8 clinicians had nutrition counseling (29%) and 7 had psychologic therapy training (25%). Thirteen respondents (46%) also reported using integrative modalities for personal health needs: 8 used psychological therapies, 8 used movement therapies, 10 used integrative modalities for stress management or relaxation, and 8 used them for physical symptoms (Table 1).

Overall, 85 of 200 patients (43%) responded to the study survey. Two patients indicated they did not have chronic back pain and were excluded. Patients had a median (IQR) age of 66 (20) years, with 66 self-identifying as White (80%), 69 as male (83%), and 66 as non-Hispanic (80%). Forty-four patients (53%) received care at CBOCs. Forty-seven patients reported excellent, very good, or good overall health (57%), while 53 reported excellent, very good, or good mental health (64%). Fifty-nine patients reported back pain duration > 5 years (71%), and 67 (81%) indicated experiencing back pain flare-ups at least once per week over the previous 12 months. Sixty patients (72%) indicated they were somewhat or very interested in using integrative therapies as a back pain treatment; however, 40 patients (48%) indicated they had not received information about these therapies. Among those who indicated they had received information, the most frequently reported source was their PCP (41%). Most patients (72%) also reported feeling somewhat to very comfortable discussing integrative medicine therapies with their PCP.
Integrative Therapy Recommendations and Use
PCPs reported recommending multiple integrative modalities: 23 (82%) recommended cognitive-behavioral therapy, 22 (79%) recommended acupuncture, 21 (75%) recommended chiropractic, 19 (68%) recommended battlefield acupuncture, recommended massage 18 (64%), 17 (61%) recommended meditation or mindfulness, and 15 (54%) recommended movement therapies such as yoga or tai chi/qigong (Figure 1). The only therapies used by at least half of the patients were chiropractic used by 59 patients (71%) and acupuncture by 42 patients (51%). Thirty-eight patients (46%) reported massage use and 21 patients (25%) used cognitive-behavioral therapy (Table 2).


Integrative Therapies Desired
A majority of PCPs identified acupuncture (n = 20, 71%), chiropractic (n = 19, 68%), and massage (n = 19, 68%) as therapies they would most like to have available for patients with chronic pain (Figure 2). Similarly, patients identified massage (n = 42, 51%), chiropractic (n = 34, 41%), and acupuncture (n = 27, 33%) as most desired. Seventeen patients (21%) expressed interest in movement therapies.

Barriers to Integrative Therapies Use
When asked about barriers to use, 26 PCPs (93%) identified access to services as a somewhat or extremely likely barrier, and 22 identified time constraints (79%) (Table 3). However, 17 PCPs (61%) noted lack of familiarity, and 18 (64%) noted a lack of scientific evidence as barriers to recommending integrative modalities. Among patients, 33 (40%) indicated not knowing what services were available at their facility as a barrier, 32 (39%) were not familiar with specific therapies, and 21 (25%) indicated a lack of clarity about the benefits of a specific therapy. Only 14 patients (17%) indicated that there were no obstacles to use.

DISCUSSION
Use of integrative therapies, including complementary treatments, is an increasingly important part of chronic pain management. This survey study suggests VA PCPs are willing to recommend integrative therapies and patients with chronic back pain both desire and use several therapies. Moreover, both groups expressed interest in greater availability of similar therapies. The results also highlight key barriers, such as knowledge gaps, that should be addressed to increase the uptake of integrative modalities for managing chronic pain.
An increasing number of US adults are using complementary health approaches, an important component of integrative therapy.12 This trend includes an increase in use for pain management, from 42.3% in 2002 to 49.2% in 2022; chiropractic care, acupuncture, and massage were most frequently used.12 Similarly, chiropractic, acupuncture and massage were most often used by this sample of veterans with chronic back pain and were identified by the highest percentages of PCPs and patients as the therapies they would most like available.
There were areas where the opinions of patients and clinicians differed. As has been seen previously reported, clinicians largely recommended cognitive-behavioral therapy while patients showed less interest.17 Additionally, while patients expressed interest in the availability of movement therapies, such as yoga, PCPs expressed more interest in other strategies, such as trigger point injections. These differences may reflect true preference or a tendency for clinicians and patients to select therapies with which they are more familiar. Additional research is needed to better understand the acceptability and potential use of integrative health treatments across a broad array of therapeutic options.
Despite VHA policy requiring facilities to provide certain complementary and integrative health modalities, almost all PCPs identified access to services as a major obstacle.15 Based on evidence and a rigorous vetting process, services currently required on-site, via telehealth, or through community partners include acupuncture and battlefield acupuncture (battlefield auricular acupuncture), biofeedback, clinical hypnosis, guided imagery, medical massage therapy, medication, tai chi/qigong, and yoga. Optional approaches, which may be made available to veterans, include chiropractic and healing touch. Outside the VHA, some states have introduced or enacted legislation mandating insurance coverage of nonpharmacological pain treatments.18 However, these requirements and mandates do not help address challenges such as the availability of trained/qualified practitioners.19,20 Ensuring access to complementary and integrative health treatments requires a more concerted effort to ensure that supply meets demand. It is also important to acknowledge the budgetary and physical space constraints that further limit access to services. Although expansion and integration of integrative medicine services remain a priority within the VA Whole Health program, implementation is contingent on available financial and infrastructure resources.
Time was also identified by PCPs as a barrier to recommending integrative therapies to patients. Developing and implementing time-efficient communication strategies for patient education such as concise talking points and informational handouts could help address this barrier. Furthermore, leveraging existing programs and engaging the entire health care team in patient education and referral could help increase integrative and complementary therapy uptake and use.
Although access and time were identified as major barriers, these findings also suggest that PCP and patient knowledge are another target area for enhancing the use of complementary and integrative therapies. Like prior research, most clinicians identified a lack of familiarity with certain services and a lack of scientific evidence as extremely or somewhat likely to affect their ability to offer integrative services to patients with chronic pain.21 Likewise, about 40% of patients identified being unfamiliar with a specific therapy as one of the major obstacles to receiving integrative therapies, with a similar number identifying PCPs as a source of information. The lack of familiarity may be due in part to the evolving nomenclature, with terms such as alternative, complementary, and integrative used to describe approaches outside what is often considered conventional medicine.10 On the other hand, there has also been considerable expansion in the number of therapies within this domain, along with an expanding evidence base. This suggests a need for targeted educational strategies for clinicians and patients, which can be rapidly deployed and continuously adapted as new therapies and evidence emerge.
Limitations
There are some inherent limitations with a survey-based approach, including sampling, non-response, and social desirability biases. In addition, this study only included PCPs and patients affiliated with a single VA medical center. Steps to mitigate these limitations included maintaining survey anonymity and reporting information about respondent characteristics to enhance transparency about the representativeness of the study findings.
CONCLUSIONS
Expanding the use of nonpharmacological pain treatments, including integrative modalities, is essential for safe and effective chronic pain management and reducing opioid use. Our findings show that VA PCPs and patients with chronic back pain are interested in and have some experience with certain integrative therapies. However, even within the context of a health care system that supports the use of integrative therapies for chronic pain as part of whole person care, increasing uptake will require addressing access and time-related constraints as well as ongoing clinician and patient education.
More than 50 million US adults report experiencing chronic pain, with nearly 7% experiencing high-impact chronic pain.1-3 Chronic pain negatively affects daily function, results in lost productivity, is a leading cause of disability, and is more prevalent among veterans compared with the general population.1,2,4-6 Estimates from 2021 suggest the prevalence of chronic pain among veterans exceeds 30%; > 11% experienced high-impact chronic pain.1
Primary care practitioners (PCPs) have a prominent role in chronic pain management. Pharmacologic options for treating pain, once a mainstay of therapy, present several challenges for patients and PCPs, including drug-drug interactions and adverse effects.7 The US opioid epidemic and shift to a biopsychosocial model of chronic pain care have increased emphasis on nonpharmacologic treatment options.8,9 These include integrative modalities, which incorporate conventional approaches with an array of complementary health approaches.10-12
Integrative therapy is a prominent feature in whole person care, which may be best exemplified by the US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) Whole Health System of care.13-14 Whole health empowers an individual to take charge of their health and well-being so they can “live their life to the fullest.”14 As implemented in the Veterans Health Administration (VHA), whole health includes the use of evidence-based
METHODS
Using a cross-sectional survey design, PCPs and patients with chronic back pain affiliated with the VA Ann Arbor Healthcare System were invited to participate in separate but similar surveys to assess knowledge, interest, and use of nonpharmacologic integrative modalities for the treatment of chronic pain. In May, June, and July 2023, 78 PCPs received 3 email
Both survey instruments are available upon request, were developed by the study team, and included a mix of yes/no questions, “select all that apply” items, Likert scale response items, and open-ended questions. For one question about which modalities they would like available, the respondent was instructed to select up to 5 modalities. The instruments were extensively pretested by members of the study team, which included 2 PCPs and a nonveteran with chronic back pain.
The list of integrative modalities included in the survey was derived from the tier 1 and tier 2 complementary and integrative health modalities identified in a VHA Directive on complementary and integrative health.15,16 Tier 1 approaches are considered to have sufficient evidence and must be made available to veterans either within a VA medical facility or in the community. Tier 2 approaches are generally considered safe and may be made available but do not have sufficient evidence to mandate their provision. For participant ease, the integrative modalities were divided into 5 subgroups: manual therapies, energy/biofield therapies, mental health therapies, nutrition counseling, and movement therapies. The clinician survey assessed clinicians’ training and interest, clinical and personal use, and perceived barriers to providing integrative modalities for chronic pain. Professional and personal demographic data were also collected. Similarly, the patient survey assessed use of integrative therapies, perceptions of and interest in integrative modalities, and potential barriers to use. Demographic and health-related information was also collected.
Data analysis included descriptive statistics (eg, frequency counts, means, medians) and visual graphic displays. Separate analyses were conducted for clinicians and patients in addition to a comparative analysis of the use and potential interest in integrative modalities. Analysis were conducted using R software. This study was deemed nonresearch quality improvement by the VA Ann Arbor Healthcare System facility research oversight board and institutional review board approval was not solicited.
RESULTS
Twenty-eight clinicians completed the survey, yielding a participation rate of 36%. Participating clinicians had a median (IQR) age of 48 years (9.5), 15 self-identified as White (54%), 8 as Asian (29%), 15 as female (54%), 26 as non-Hispanic (93%), and 25 were medical doctors or doctors of osteopathy (89%). Nineteen (68%) worked at the main hospital outpatient clinic, and 9 practiced at community-based outpatient clinics (CBOCs). Thirteen respondents (46%) reported having no formal education or training in integrative approaches. Among those with prior training, 8 clinicians had nutrition counseling (29%) and 7 had psychologic therapy training (25%). Thirteen respondents (46%) also reported using integrative modalities for personal health needs: 8 used psychological therapies, 8 used movement therapies, 10 used integrative modalities for stress management or relaxation, and 8 used them for physical symptoms (Table 1).

Overall, 85 of 200 patients (43%) responded to the study survey. Two patients indicated they did not have chronic back pain and were excluded. Patients had a median (IQR) age of 66 (20) years, with 66 self-identifying as White (80%), 69 as male (83%), and 66 as non-Hispanic (80%). Forty-four patients (53%) received care at CBOCs. Forty-seven patients reported excellent, very good, or good overall health (57%), while 53 reported excellent, very good, or good mental health (64%). Fifty-nine patients reported back pain duration > 5 years (71%), and 67 (81%) indicated experiencing back pain flare-ups at least once per week over the previous 12 months. Sixty patients (72%) indicated they were somewhat or very interested in using integrative therapies as a back pain treatment; however, 40 patients (48%) indicated they had not received information about these therapies. Among those who indicated they had received information, the most frequently reported source was their PCP (41%). Most patients (72%) also reported feeling somewhat to very comfortable discussing integrative medicine therapies with their PCP.
Integrative Therapy Recommendations and Use
PCPs reported recommending multiple integrative modalities: 23 (82%) recommended cognitive-behavioral therapy, 22 (79%) recommended acupuncture, 21 (75%) recommended chiropractic, 19 (68%) recommended battlefield acupuncture, recommended massage 18 (64%), 17 (61%) recommended meditation or mindfulness, and 15 (54%) recommended movement therapies such as yoga or tai chi/qigong (Figure 1). The only therapies used by at least half of the patients were chiropractic used by 59 patients (71%) and acupuncture by 42 patients (51%). Thirty-eight patients (46%) reported massage use and 21 patients (25%) used cognitive-behavioral therapy (Table 2).


Integrative Therapies Desired
A majority of PCPs identified acupuncture (n = 20, 71%), chiropractic (n = 19, 68%), and massage (n = 19, 68%) as therapies they would most like to have available for patients with chronic pain (Figure 2). Similarly, patients identified massage (n = 42, 51%), chiropractic (n = 34, 41%), and acupuncture (n = 27, 33%) as most desired. Seventeen patients (21%) expressed interest in movement therapies.

Barriers to Integrative Therapies Use
When asked about barriers to use, 26 PCPs (93%) identified access to services as a somewhat or extremely likely barrier, and 22 identified time constraints (79%) (Table 3). However, 17 PCPs (61%) noted lack of familiarity, and 18 (64%) noted a lack of scientific evidence as barriers to recommending integrative modalities. Among patients, 33 (40%) indicated not knowing what services were available at their facility as a barrier, 32 (39%) were not familiar with specific therapies, and 21 (25%) indicated a lack of clarity about the benefits of a specific therapy. Only 14 patients (17%) indicated that there were no obstacles to use.

DISCUSSION
Use of integrative therapies, including complementary treatments, is an increasingly important part of chronic pain management. This survey study suggests VA PCPs are willing to recommend integrative therapies and patients with chronic back pain both desire and use several therapies. Moreover, both groups expressed interest in greater availability of similar therapies. The results also highlight key barriers, such as knowledge gaps, that should be addressed to increase the uptake of integrative modalities for managing chronic pain.
An increasing number of US adults are using complementary health approaches, an important component of integrative therapy.12 This trend includes an increase in use for pain management, from 42.3% in 2002 to 49.2% in 2022; chiropractic care, acupuncture, and massage were most frequently used.12 Similarly, chiropractic, acupuncture and massage were most often used by this sample of veterans with chronic back pain and were identified by the highest percentages of PCPs and patients as the therapies they would most like available.
There were areas where the opinions of patients and clinicians differed. As has been seen previously reported, clinicians largely recommended cognitive-behavioral therapy while patients showed less interest.17 Additionally, while patients expressed interest in the availability of movement therapies, such as yoga, PCPs expressed more interest in other strategies, such as trigger point injections. These differences may reflect true preference or a tendency for clinicians and patients to select therapies with which they are more familiar. Additional research is needed to better understand the acceptability and potential use of integrative health treatments across a broad array of therapeutic options.
Despite VHA policy requiring facilities to provide certain complementary and integrative health modalities, almost all PCPs identified access to services as a major obstacle.15 Based on evidence and a rigorous vetting process, services currently required on-site, via telehealth, or through community partners include acupuncture and battlefield acupuncture (battlefield auricular acupuncture), biofeedback, clinical hypnosis, guided imagery, medical massage therapy, medication, tai chi/qigong, and yoga. Optional approaches, which may be made available to veterans, include chiropractic and healing touch. Outside the VHA, some states have introduced or enacted legislation mandating insurance coverage of nonpharmacological pain treatments.18 However, these requirements and mandates do not help address challenges such as the availability of trained/qualified practitioners.19,20 Ensuring access to complementary and integrative health treatments requires a more concerted effort to ensure that supply meets demand. It is also important to acknowledge the budgetary and physical space constraints that further limit access to services. Although expansion and integration of integrative medicine services remain a priority within the VA Whole Health program, implementation is contingent on available financial and infrastructure resources.
Time was also identified by PCPs as a barrier to recommending integrative therapies to patients. Developing and implementing time-efficient communication strategies for patient education such as concise talking points and informational handouts could help address this barrier. Furthermore, leveraging existing programs and engaging the entire health care team in patient education and referral could help increase integrative and complementary therapy uptake and use.
Although access and time were identified as major barriers, these findings also suggest that PCP and patient knowledge are another target area for enhancing the use of complementary and integrative therapies. Like prior research, most clinicians identified a lack of familiarity with certain services and a lack of scientific evidence as extremely or somewhat likely to affect their ability to offer integrative services to patients with chronic pain.21 Likewise, about 40% of patients identified being unfamiliar with a specific therapy as one of the major obstacles to receiving integrative therapies, with a similar number identifying PCPs as a source of information. The lack of familiarity may be due in part to the evolving nomenclature, with terms such as alternative, complementary, and integrative used to describe approaches outside what is often considered conventional medicine.10 On the other hand, there has also been considerable expansion in the number of therapies within this domain, along with an expanding evidence base. This suggests a need for targeted educational strategies for clinicians and patients, which can be rapidly deployed and continuously adapted as new therapies and evidence emerge.
Limitations
There are some inherent limitations with a survey-based approach, including sampling, non-response, and social desirability biases. In addition, this study only included PCPs and patients affiliated with a single VA medical center. Steps to mitigate these limitations included maintaining survey anonymity and reporting information about respondent characteristics to enhance transparency about the representativeness of the study findings.
CONCLUSIONS
Expanding the use of nonpharmacological pain treatments, including integrative modalities, is essential for safe and effective chronic pain management and reducing opioid use. Our findings show that VA PCPs and patients with chronic back pain are interested in and have some experience with certain integrative therapies. However, even within the context of a health care system that supports the use of integrative therapies for chronic pain as part of whole person care, increasing uptake will require addressing access and time-related constraints as well as ongoing clinician and patient education.
- Rikard SM, Strahan AE, Schmit KM, et al. Chronic pain among adults — United States, 2018-2021. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2023;72:379-385. doi:10.15585/mmwr.mm7215a1
- Yong RJ, Mullins PM, Bhattacharyya N. Prevalence of chronic pain among adults in the United States. Pain. 2022;163:E328-E332. doi:10.1097/j.pain.0000000000002291
- Nahin RL, Feinberg T, Kapos FP, Terman GW. Estimated rates of incident and persistent chronic pain among US adults, 2019-2020. JAMA Netw Open. 2023;6:e2313563. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.13563
- Ferrari AJ, Santomauro DF, Aali A, et al. Global incidence, prevalence, years lived with disability (YLDs), disability-adjusted life-years (DALYs), and healthy life expectancy (HALE) for 371 diseases and injuries in 204 countries and territories and 811 subnational locations, 1990–2021: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2021. The Lancet. 2024;403:2133-2161. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(24)00757-8 5.
- Qureshi AR, Patel M, Neumark S, et al. Prevalence of chronic non-cancer pain among military veterans: a systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies. BMJ Mil Health. 2025;171:310-314. doi:10.1136/military-2023-002554
- Feldman DE, Nahin RL. Disability among persons with chronic severe back pain: results from a nationally representative population-based sample. J Pain. 2022;23:2144-2154. doi:10.1016/j.jpain.2022.07.016
- Qaseem A, Wilt TJ, McLean RM, Forciea MA. Noninvasive treatments for acute, subacute, and chronic low back pain: a clinical practice guideline from the American College of Physicians. Ann Intern Med. 2017;166:514-530. doi:10.7326/M16-2367
- van Erp RMA, Huijnen IPJ, Jakobs MLG, Kleijnen J, Smeets RJEM. Effectiveness of primary care interventions using a biopsychosocial approach in chronic low back pain: a systematic review. Pain Practice. 2019;19:224-241. doi:10.1111/papr.12735
- Chou R, Deyo R, Friedly J, et al. Nonpharmacologic therapies for low back pain: a systematic review for an American College of physicians clinical practice guideline. Ann Intern Med. 2017;166:493-505. doi:10.7326/M16-2459
- Complementary, alternative, or integrative health: what’s in a name? National Institutes of Health, National Center for Complementary and Integrative Health. Updated April 2021. Accessed December 15, 2025. https://www.nccih.nih.gov/health/complementary-alternative-or-integrative-health-whats-in-a-name.
- Taylor SL, Elwy AR. Complementary and alternative medicine for US veterans and active duty military personnel promising steps to improve their health. Med Care. 2014;52:S1-S4. doi:10.1097/MLR.0000000000000270.
- Nahin RL, Rhee A, Stussman B. Use of complementary health approaches overall and for pain management by US adults. JAMA. 2024;331:613-615. doi:10.1001/jama.2023.26775
- Gantt CJ, Donovan N, Khung M. Veterans Affairs’ Whole Health System of Care for transitioning service members and veterans. Mil Med. 2023;188:28-32. doi:10.1093/milmed/usad047
- Bokhour BG, Hyde J, Kligler B, et al. From patient outcomes to system change: evaluating the impact of VHA’s implementation of the Whole Health System of Care. Health Serv Res. 2022;57:53-65. doi:10.1111/1475-6773.13938
- Department of Veterans Affairs VHA. VHA Policy Directive 1137: Provision of Complementary and Integrative Health. December 2022. Accessed December 15, 2025. https://www.va.gov/VHApublications/ViewPublication.asp?pub_ID=10072
- Giannitrapani KF, Holliday JR, Miake-Lye IM, Hempel S, Taylor SL. Synthesizing the strength of the evidence of complementary and integrative health therapies for pain. Pain Med. 2019;20:1831-1840. doi:10.1093/pm/pnz068
- Belitskaya-Levy I, David Clark J, Shih MC, Bair MJ. Treatment preferences for chronic low back pain: views of veterans and their providers. J Pain Res. 2021;14:161-171. doi:10.2147/JPR.S290400
- Onstott TN, Hurst S, Kronick R, Tsou AC, Groessl E, McMenamin SB. Health insurance mandates for nonpharmacological pain treatments in 7 US states. JAMA Netw Open. 2024;7:E245737. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.5737
- Sullivan M, Leach M, Snow J, Moonaz S. The North American yoga therapy workforce survey. Complement Ther Med. 2017;31:39-48. doi:10.1016/j.ctim.2017.01.006
- Bolton R, Ritter G, Highland K, Larson MJ. The relationship between capacity and utilization of nonpharmacologic therapies in the US Military Health System. BMC Health Serv Res. 2022;22. doi:10.1186/s12913-022-07700-4
- Stussman BJ, Nahin RL, Barnes PM, Scott R, Feinberg T, Ward BW. Reasons office-based physicians in the United States recommend common complementary health approaches to patients: an exploratory study using a national survey. J Integr Complement Med. 2022;28:651-663. doi:10.1089/jicm.2022.0493
- Rikard SM, Strahan AE, Schmit KM, et al. Chronic pain among adults — United States, 2018-2021. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2023;72:379-385. doi:10.15585/mmwr.mm7215a1
- Yong RJ, Mullins PM, Bhattacharyya N. Prevalence of chronic pain among adults in the United States. Pain. 2022;163:E328-E332. doi:10.1097/j.pain.0000000000002291
- Nahin RL, Feinberg T, Kapos FP, Terman GW. Estimated rates of incident and persistent chronic pain among US adults, 2019-2020. JAMA Netw Open. 2023;6:e2313563. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.13563
- Ferrari AJ, Santomauro DF, Aali A, et al. Global incidence, prevalence, years lived with disability (YLDs), disability-adjusted life-years (DALYs), and healthy life expectancy (HALE) for 371 diseases and injuries in 204 countries and territories and 811 subnational locations, 1990–2021: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2021. The Lancet. 2024;403:2133-2161. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(24)00757-8 5.
- Qureshi AR, Patel M, Neumark S, et al. Prevalence of chronic non-cancer pain among military veterans: a systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies. BMJ Mil Health. 2025;171:310-314. doi:10.1136/military-2023-002554
- Feldman DE, Nahin RL. Disability among persons with chronic severe back pain: results from a nationally representative population-based sample. J Pain. 2022;23:2144-2154. doi:10.1016/j.jpain.2022.07.016
- Qaseem A, Wilt TJ, McLean RM, Forciea MA. Noninvasive treatments for acute, subacute, and chronic low back pain: a clinical practice guideline from the American College of Physicians. Ann Intern Med. 2017;166:514-530. doi:10.7326/M16-2367
- van Erp RMA, Huijnen IPJ, Jakobs MLG, Kleijnen J, Smeets RJEM. Effectiveness of primary care interventions using a biopsychosocial approach in chronic low back pain: a systematic review. Pain Practice. 2019;19:224-241. doi:10.1111/papr.12735
- Chou R, Deyo R, Friedly J, et al. Nonpharmacologic therapies for low back pain: a systematic review for an American College of physicians clinical practice guideline. Ann Intern Med. 2017;166:493-505. doi:10.7326/M16-2459
- Complementary, alternative, or integrative health: what’s in a name? National Institutes of Health, National Center for Complementary and Integrative Health. Updated April 2021. Accessed December 15, 2025. https://www.nccih.nih.gov/health/complementary-alternative-or-integrative-health-whats-in-a-name.
- Taylor SL, Elwy AR. Complementary and alternative medicine for US veterans and active duty military personnel promising steps to improve their health. Med Care. 2014;52:S1-S4. doi:10.1097/MLR.0000000000000270.
- Nahin RL, Rhee A, Stussman B. Use of complementary health approaches overall and for pain management by US adults. JAMA. 2024;331:613-615. doi:10.1001/jama.2023.26775
- Gantt CJ, Donovan N, Khung M. Veterans Affairs’ Whole Health System of Care for transitioning service members and veterans. Mil Med. 2023;188:28-32. doi:10.1093/milmed/usad047
- Bokhour BG, Hyde J, Kligler B, et al. From patient outcomes to system change: evaluating the impact of VHA’s implementation of the Whole Health System of Care. Health Serv Res. 2022;57:53-65. doi:10.1111/1475-6773.13938
- Department of Veterans Affairs VHA. VHA Policy Directive 1137: Provision of Complementary and Integrative Health. December 2022. Accessed December 15, 2025. https://www.va.gov/VHApublications/ViewPublication.asp?pub_ID=10072
- Giannitrapani KF, Holliday JR, Miake-Lye IM, Hempel S, Taylor SL. Synthesizing the strength of the evidence of complementary and integrative health therapies for pain. Pain Med. 2019;20:1831-1840. doi:10.1093/pm/pnz068
- Belitskaya-Levy I, David Clark J, Shih MC, Bair MJ. Treatment preferences for chronic low back pain: views of veterans and their providers. J Pain Res. 2021;14:161-171. doi:10.2147/JPR.S290400
- Onstott TN, Hurst S, Kronick R, Tsou AC, Groessl E, McMenamin SB. Health insurance mandates for nonpharmacological pain treatments in 7 US states. JAMA Netw Open. 2024;7:E245737. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.5737
- Sullivan M, Leach M, Snow J, Moonaz S. The North American yoga therapy workforce survey. Complement Ther Med. 2017;31:39-48. doi:10.1016/j.ctim.2017.01.006
- Bolton R, Ritter G, Highland K, Larson MJ. The relationship between capacity and utilization of nonpharmacologic therapies in the US Military Health System. BMC Health Serv Res. 2022;22. doi:10.1186/s12913-022-07700-4
- Stussman BJ, Nahin RL, Barnes PM, Scott R, Feinberg T, Ward BW. Reasons office-based physicians in the United States recommend common complementary health approaches to patients: an exploratory study using a national survey. J Integr Complement Med. 2022;28:651-663. doi:10.1089/jicm.2022.0493
Primary Care Clinician and Patient Knowledge, Interest, and Use of Integrative Treatment Options for Chronic Low Back Pain Management
Primary Care Clinician and Patient Knowledge, Interest, and Use of Integrative Treatment Options for Chronic Low Back Pain Management
Development and Validation of an Administrative Algorithm to Identify Veterans With Epilepsy
Development and Validation of an Administrative Algorithm to Identify Veterans With Epilepsy
Epilepsy affects about 4.5 million people in the United States and 150,000 new individuals are diagnosed each year.1,2 In 2019, epilepsy-attributable health care spending for noninstitutionalized people was around $5.4 billion and total epilepsy-attributable and epilepsy or seizure health care-related costs totaled $54 billion.3
Accurate surveillance of epilepsy in large health care systems can potentially improve health care delivery and resource allocation. A 2012 Institute of Medicine (IOM) report identified 13 recommendations to guide public health action on epilepsy, including validation of standard definitions for case ascertainment, identification of epilepsy through screening programs or protocols, and expansion of surveillance to better understand disease burden.4
A systematic review of validation studies concluded that it is reasonable to use administrative data to identify people with epilepsy in epidemiologic research. Combining The International Classification of Diseases (ICD) codes for epilepsy (ICD-10, G40-41; ICD-9, 345) with antiseizure medications (ASMs) could provide high positive predictive values (PPVs) and combining symptoms codes for convulsions (ICD-10, R56; ICD-9, 780.3, 780.39) with ASMs could lead to high sensitivity.5 However, identifying individuals with epilepsy from administrative data in large managed health care organizations is challenging.6 The IOM report noted that large managed health care organizations presented varying incidence and prevalence estimates due to differing methodology, geographic area, demographics, and definitions of epilepsy.
The Veterans Health Administration (VHA) is the largest integrated US health care system, providing care to > 9.1 million veterans.7 To improve the health and well-being of veterans with epilepsy (VWEs), a network of sites was established in 2008 called the US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) Epilepsy Centers of Excellence (ECoE). Subsequent to the creation of the ECoE, efforts were made to identify VWEs within VHA databases.8,9 Prior to fiscal year (FY) 2016, the ECoE adopted a modified version of a well-established epilepsy diagnostic algorithm developed by Holden et al for large managed care organizations.10 The original algorithm identified patients by cross-matching ASMs with ICD-9 codes for an index year. But it failed to capture a considerable number of stable patients with epilepsy in the VHA due to incomplete documentation, and had false positives due to inclusion of patients identified from diagnostic clinics. The modified algorithm the ECoE used prior to FY 2016 considered additional prior years and excluded encounters from diagnostic clinics. The result was an improvement in the sensitivity and specificity of the algorithm. Researchers evaluating 500 patients with epilepsy estimated that the modified algorithm had a PPV of 82.0% (95% CI, 78.6%-85.4%).11
After implementation of ICD-10 codes in the VHA in FY 2016, the task of reliably and efficiently identifying VWE led to a 3-tier algorithm. This article presents a validation of the different tiers of this algorithm after the implementation of ICD-10 diagnosis codes and summarizes the surveillance data collected over the years within the VHA showing the trends of epilepsy.
Methods
The VHA National Neurology office commissioned a Neurology Cube dashboard in FY 2021 in collaboration with VHA Support Service Center (VSSC) for reporting and surveillance of VWEs as a quality improvement initiative. The Neurology Cube uses a 3-tier system for identifying VWE in the VHA databases. VSSC programmers extract data from the VHA Corporate Data Warehouse (CDW) and utilize Microsoft SQL Server and Microsoft Power BI for Neurology Cube reports. The 3-tier system identifies VWE and divides them into distinct groups. The first tier identifies VWE with the highest degree of confidence; Tiers 2 and 3 represent identification with successively lesser degrees of confidence (Figure 1).
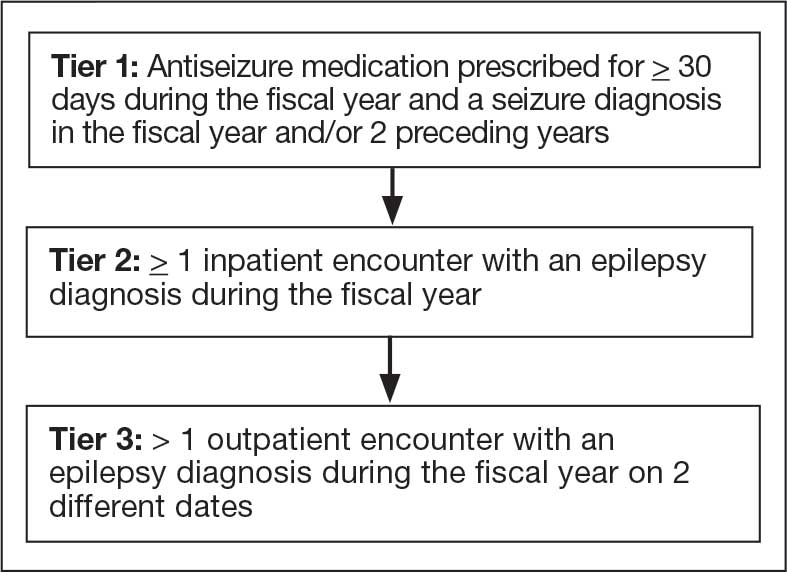
Tier 1
Definition. For a given index year and the preceding 2 years, any of following diagnosis codes on ≥ 1 clinical encounter are considered: 345.xx (epilepsy in ICD-9), 780.3x (other convulsions in ICD-9), G40.xxx (epilepsy in ICD-10), R40.4 (transient alteration of awareness), R56.1 (posttraumatic seizures), or R56.9 (unspecified convulsions). To reduce false positive rates, EEG clinic visits, which may include long-term monitoring, are excluded. Patients identified with ICD codes are then evaluated for an ASM prescription for ≥ 30 days during the index year. ASMs are listed in Appendix 1.
Validation. The development and validation of ICD-9 diagnosis codes crossmatched with an ASM prescription in the VHA has been published elsewhere.11 In FY 2017, after implementation of ICD-10 diagnostic codes, Tier 1 development and validation was performed in 2 phases. Even though Tier 1 study phases were conducted and completed during FY 2017, the patients for Tier 1 were identified from evaluation of FY 2016 data (October 1, 2015, to September 30, 2016). After the pilot analysis, the Tier 1 definition was implemented, and a chart review of 625 randomized patients was conducted at 5 sites for validation. Adequate preliminary data was not available to perform a sample size estimation for this study. Therefore, a practical target of 125 patients was set for Tier 1 from each site to obtain a final sample size of 625 patients. This second phase validated that the crossmatch of ICD-10 diagnosis codes with ASMs had a high PPV for identifying VWE.
Tiers 2 and 3
Definitions. For an index year, Tier 2 includes patients with ≥ 1 inpatient encounter documentation of either ICD-9 345.xx or ICD-10 G40.xxx, excluding EEG clinics. Tier 3 Includes patients who have had ≥ 2 outpatient encounters with diagnosis codes 345.xx or G40.xxx on 2 separate days, excluding EEG clinics. Tiers 2 and 3 do not require ASM prescriptions; this helps to identify VWEs who may be getting their medications outside of VHA or those who have received a new diagnosis.
Validations. Tiers 2 and 3 were included in the epilepsy identification algorithm in FY 2021 after validation was performed on a sample of 8 patients in each tier. Five patients were subsequently identified as having epilepsy in Tier 2 and 6 patients were identified in Tier 3. A more comprehensive validation of Tiers 2 and 3 was performed during FY 2022 that included patients at 5 sites seen during FY 2019 to FY 2022. Since yearly trends showed only about 8% of total patients were identified as having epilepsy through Tiers 2 and 3 we sought ≥ 20 patients per tier for the 5 sites for a total of 200 patients to ensure representation across the VHA. The final count was 126 patients for Tier 2 and 174 patients for Tier 3 (n = 300).
Gold Standard Criteria for Epilepsy Diagnosis
We used the International League Against Epilepsy (ILAE) definition of epilepsy for the validation of the 3 algorithm tiers. ILAE defines epilepsy as ≥ 2 unprovoked (or reflex) seizures occurring > 24 hours apart or 1 unprovoked (or reflex) seizure and a probability of further seizures similar to the general recurrence risk (≥ 60%) after 2 unprovoked seizures, occurring over the next 10 years.12
A standard protocol was provided to evaluators to identify patients using the VHA Computerized Patient Record System (Appendix 1). After review, evaluators categorized each patient in 1 of 4 ways: (1) Yes, definite: The patient’s health care practitioner (HCP) believes the patient has epilepsy and is treating with medication; (2) Yes, uncertain: The HCP has enough suspicion of epilepsy that a medication is prescribed, but uncertainty is expressed of the diagnosis; (3) No, definite: The HCP does not believe the patient has epilepsy and is therefore not treating with medication for seizure; (4) No, uncertain: The HCP is not treating with medication for epilepsy, because the diagnostic suspicion is not high enough, but there is suspicion for epilepsy.
As a quality improvement operational project, the Epilepsy National Program Office approved this validation project and determined that institutional review board approval was not required.
Statistical Analysis
Counts and percentages were computed for categories of epilepsy status. PPV of each tier was estimated with asymptotic 95% CIs.
Results
ICD-10 codes for 480 patients were evaluated in Tier 1 phase 1; 13.8% were documented with G40.xxx, 27.9% with R56.1, 34.4% with R56.9, and 24.0% with R40.4 (Appendix 2). In total, 68.1% fulfilled the criteria of epilepsy, 19.2% did not, and 12.7% were uncertain). From the validation of Tier 1 phase 2 (n = 625), the PPV of the algorithm for patients presumed to have epilepsy (definite and uncertain) was 85.1% (95% CI, 82.1%-87.8%) (Table).
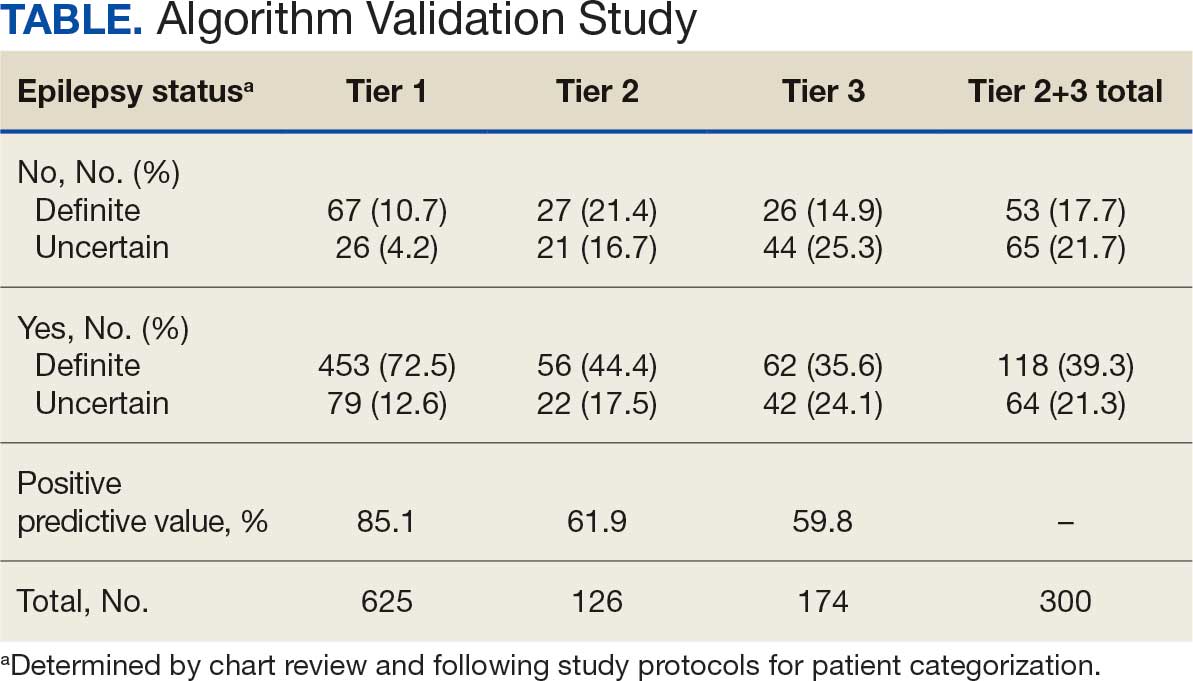
Of 300 patients evaluated, 126 (42.0%) were evaluated for Tier 2 with a PPV of 61.9% (95% CI, 53.4%-70.4%), and 174 (58.0%) patients were evaluated for Tier 3 with a PPV of 59.8% (95% CI, 52.5%-67.1%. The PPV of the algorithm for patients presumed to have epilepsy (definite and uncertain) were combined to calculate the PPV. Estimates of VHA VWE counts were computed for each tier from FY 2014 to FY 2023 using the VSSC Neurology Cube (Figure 2). For all years, > 92% patients were classified using the Tier 1 definition.
Discussion
The development and validation of the 3-tier diagnostic algorithm represents an important advancement in the surveillance and management of epilepsy among veterans within the VHA. The validation of this algorithm also demonstrates its practical utility in a large, integrated health care system.
Specific challenges were encountered when attempting to use pre-existing algorithms; these challenges included differences in the usage patterns of diagnostic codes and the patterns of ASM use within the VHA. These challenges prompted the need for a tailored approach, which led to the development of this algorithm. The inclusion of additional ICD-10 codes led to further revisions and subsequent validation. While many of the basic concepts of the algorithm, including ICD codes and ASMs, could work in other institutions, it would be wise for health care organizations to develop their own algorithms because of certain variables, including organizational size, patient demographics, common comorbidities, and the specific configurations of electronic health records and administrative data systems.
Studies have shown that ICD-10 codes for epilepsy (G40.* and/or R56.9) perform well in identifying epilepsy whether they are assigned by neurologists (sensitivity, 97.7%; specificity, 44.1%; PPV, 96.2%; negative predictive value, 57.7%), or in emergency department or hospital discharges (PPV, 75.5%).13,14 The pilot study of the algorithm’s Tier 1 development (phase 1) evaluated whether the selected ICD-10 diagnostic codes accurately included the VWE population within the VHA and revealed that while most codes (eg, epilepsy [G40.xxx]; posttraumatic seizures [R56.1]; and unspecified convulsions [R56.9]), had a low false positive rate (< 16%), the R40.4 code (transient alteration of awareness) had a higher false positivity of 42%. While this is not surprising given the broad spectrum of conditions that can manifest as transient alteration of awareness, it underscores the inherent challenges in diagnosing epilepsy using diagnosis codes.
In phase 2, the Tier 1 algorithm was validated as effective for identifying VWE in the VHA system, as its PPV was determined to be high (85%). In comparison, Tiers 2 and 3, whose criteria did not require data on VHA prescribed ASM use, had lower tiers of epilepsy predictability (PPV about 60% for both). This was thought to be acceptable because Tiers 2 and 3 represent a smaller population of the identified VWEs (about 8%). These VWEs may otherwise have been missed, partly because veterans are not required to get ASMs from the VHA.
Upon VHA implementation in FY 2021, this diagnostic algorithm exhibited significant clinical utility when integrated within the VSSC Neurology Cube. It facilitated an efficient approach to identifying VWEs using readily available databases. This led to better tracking of real-time epilepsy cases, which facilitated improving current resource allocation and targeted intervention strategies such as identification of drug-resistant epilepsy patients, optimizing strategies for telehealth and patient outreach for awareness of epilepsy care resources within VHA. Meanwhile, data acquired by the algorithm over the decade since its development (FY 2014 to FY 2023) contributed to more accurate epidemiologic information and identification of historic trends. Development of the algorithm represents one of the ways ECoEs have led to improved care for VWEs. ECoEs have been shown to improve health care for veterans in several metrics.15
A strength of this study is the rigorous multitiered validation process to confirm the diagnostic accuracy of ICD-10 codes against the gold standard ILAE definition of epilepsy to identify “definite” epilepsy cases within the VHA. The use of specific ICD codes further enhances the precision of epilepsy diagnoses. The inclusion of ASMs, which are sometimes prescribed for conditions other than epilepsy, could potentially inflate false positive rates.16
This study focused exclusively on the identification and validation of definite epilepsy cases within the VHA VSSC database, employing more stringent diagnostic criteria to ensure the highest level of certainty in ascertaining epilepsy. It is important to note there is a separate category of probable epilepsy, which involves a broader set of diagnostic criteria. While not covered in this study, probable epilepsy would be subject to future research and validation, which could provide insights into a wider spectrum of epilepsy diagnoses. Such future research could help refine the algorithm’s applicability and accuracy and potentially lead to more comprehensive surveillance and management strategies in clinical practice.
This study highlights the inherent challenges in leveraging administrative data for disease identification, particularly for conditions such as epilepsy, where diagnostic clarity can be complex. However, other conditions such as multiple sclerosis have noted similar success with the use of VHA administrative data for categorizing disease.17
Limitations
The algorithm discussed in this article is, in and of itself, generalizable. However, the validation process was unique to the VHA patient population, limiting the generalizability of the findings. Documentation practices and HCP attitudes within the VHA may differ from those in other health care settings. Identifying people with epilepsy can be challenging because of changing definitions of epilepsy over time. In addition to clinical evaluation, EEG and magnetic resonance imaging results, response to ASM treatment, and video-EEG monitoring of habitual events all can help establish the diagnosis. Therefore, studies may vary in how inclusive or exclusive the criteria are. ASMs such as gabapentin, pregabalin, carbamazepine, lamotrigine, topiramate, and valproate are used to treat other conditions, including headaches, generalized pain, and mood disorders. Consequently, including these ASMs in the Tier 1 definition may have increased the false positive rate. Additional research is needed to evaluate whether excluding these ASMs from the algorithm based on specific criteria (eg, dose of ASM used) can further refine the algorithm to identify patients with epilepsy.
Further refinement of this algorithm may also occur as technology changes. Future electronic health records may allow better tracking of different epilepsy factors, the integration of additional diagnostic criteria, and the use of natural language processing or other forms of artificial intelligence.
Conclusions
This study presents a significant step forward in epilepsy surveillance within the VHA. The algorithm offers a robust tool for identifying VWEs with good PPVs, facilitating better resource allocation and targeted care. Despite its limitations, this research lays a foundation for future advancements in the management and understanding of epilepsy within large health care systems. Since this VHA algorithm is based on ASMs and ICD diagnosis codes from patient records, other large managed health care systems also may be able to adapt this algorithm to their data specifications.

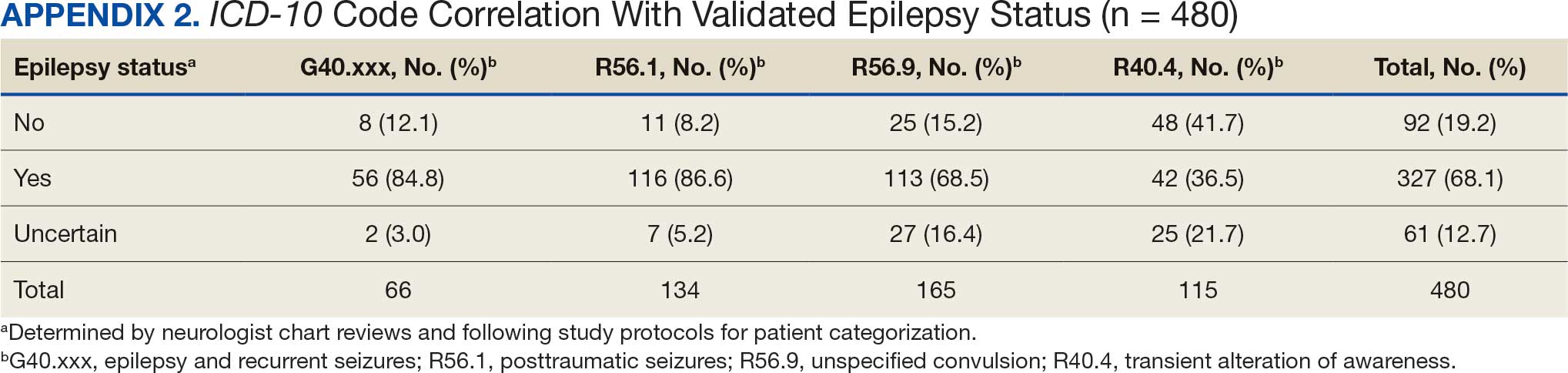
- Kobau R, Luncheon C, Greenlund K. Active epilepsy prevalence among U.S. adults is 1.1% and differs by educational level-National Health Interview Survey, United States, 2021. Epilepsy Behav. 2023;142:109180. doi:10.1016/j.yebeh.2023.109180
- GBD 2017 US Neurological Disorders Collaborators, Feigin VL, Vos T, et al. Burden of neurological disorders across the US from 1990-2017: a global burden of disease study. JAMA Neurol. 2021;78:165-176. doi:10.1001/jamaneurol.2020.4152
- Moura LMVR, Karakis I, Zack MM, et al. Drivers of US health care spending for persons with seizures and/or epilepsies, 2010-2018. Epilepsia. 2022;63:2144-2154. doi:10.1111/epi.17305
- Institute of Medicine. Epilepsy Across the Spectrum: Promoting Health and Understanding. The National Academies Press; 2012. Accessed November 11, 2025. www.nap.edu/catalog/13379
- Mbizvo GK, Bennett KH, Schnier C, Simpson CR, Duncan SE, Chin RFM. The accuracy of using administrative healthcare data to identify epilepsy cases: A systematic review of validation studies. Epilepsia. 2020;61:1319-1335. doi:10.1111/epi.16547
- Montouris GD. How will primary care physicians, specialists, and managed care treat epilepsy in the new millennium? Neurology. 2000;55:S42-S44.
- US Department of Veterans Affairs. Veterans Health Administration: About VHA. Accessed November 11, 2025. https://www.va.gov/health/aboutvha.asp
- Veterans’ Mental Health and Other Care Improvements Act of 2008, S 2162, 110th Cong (2008). Accessed November 11, 2025. https://www.congress.gov/bill/110th-congress/senate-bill/2162
- Rehman R, Kelly PR, Husain AM, Tran TT. Characteristics of Veterans diagnosed with seizures within Veterans Health Administration. J Rehabil Res Dev. 2015;52(7):751-762. doi:10.1682/JRRD.2014.10.0241
- Holden EW, Grossman E, Nguyen HT, et al. Developing a computer algorithm to identify epilepsy cases in managed care organizations. Dis Manag. 2005;8:1-14. doi:10.1089/dis.2005.8.1
- Rehman R, Everhart A, Frontera AT, et al. Implementation of an established algorithm and modifications for the identification of epilepsy patients in the Veterans Health Administration. Epilepsy Res. 2016;127:284-290. doi:10.1016/j.eplepsyres.2016.09.012
- Fisher RS, Acevedo C, Arzimanoglou A, et al. ILAE official report: a practical clinical definition of epilepsy. Epilepsia. 2014;55:475-482. doi:10.1111/epi.12550
- Smith JR, Jones FJS, Fureman BE, et al. Accuracy of ICD-10-CM claims-based definitions for epilepsy and seizure type. Epilepsy Res. 2020;166:106414. doi:10.1016/j.eplepsyres.2020.106414
- Jetté N, Reid AY, Quan H, et al. How accurate is ICD coding for epilepsy? Epilepsia. 2010;51:62-69. doi:10.1111/j.1528-1167.2009.02201.x
- Kelly P, Chinta R, Privitera G. Do centers of excellence reduce health care costs? Evidence from the US Veterans Health Administration Centers for Epilepsy. Glob Bus Organ Excell. 2015;34:18-29.
- Haneef Z, Rehman R, Husain AM. Association between standardized mortality ratio and utilization of care in US veterans with drug-resistant epilepsy compared with all US veterans and the US general population. JAMA Neurol. 2022;79:879-887. doi:10.1001/jamaneurol.2022.2290
- Culpepper WJ, Marrie RA, Langer-Gould A, et al. Validation of an algorithm for identifying MS cases in administrative health claims datasets. Neurology. 2019;92:e1016-e1028 doi:10.1212/WNL.0000000000007043
Epilepsy affects about 4.5 million people in the United States and 150,000 new individuals are diagnosed each year.1,2 In 2019, epilepsy-attributable health care spending for noninstitutionalized people was around $5.4 billion and total epilepsy-attributable and epilepsy or seizure health care-related costs totaled $54 billion.3
Accurate surveillance of epilepsy in large health care systems can potentially improve health care delivery and resource allocation. A 2012 Institute of Medicine (IOM) report identified 13 recommendations to guide public health action on epilepsy, including validation of standard definitions for case ascertainment, identification of epilepsy through screening programs or protocols, and expansion of surveillance to better understand disease burden.4
A systematic review of validation studies concluded that it is reasonable to use administrative data to identify people with epilepsy in epidemiologic research. Combining The International Classification of Diseases (ICD) codes for epilepsy (ICD-10, G40-41; ICD-9, 345) with antiseizure medications (ASMs) could provide high positive predictive values (PPVs) and combining symptoms codes for convulsions (ICD-10, R56; ICD-9, 780.3, 780.39) with ASMs could lead to high sensitivity.5 However, identifying individuals with epilepsy from administrative data in large managed health care organizations is challenging.6 The IOM report noted that large managed health care organizations presented varying incidence and prevalence estimates due to differing methodology, geographic area, demographics, and definitions of epilepsy.
The Veterans Health Administration (VHA) is the largest integrated US health care system, providing care to > 9.1 million veterans.7 To improve the health and well-being of veterans with epilepsy (VWEs), a network of sites was established in 2008 called the US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) Epilepsy Centers of Excellence (ECoE). Subsequent to the creation of the ECoE, efforts were made to identify VWEs within VHA databases.8,9 Prior to fiscal year (FY) 2016, the ECoE adopted a modified version of a well-established epilepsy diagnostic algorithm developed by Holden et al for large managed care organizations.10 The original algorithm identified patients by cross-matching ASMs with ICD-9 codes for an index year. But it failed to capture a considerable number of stable patients with epilepsy in the VHA due to incomplete documentation, and had false positives due to inclusion of patients identified from diagnostic clinics. The modified algorithm the ECoE used prior to FY 2016 considered additional prior years and excluded encounters from diagnostic clinics. The result was an improvement in the sensitivity and specificity of the algorithm. Researchers evaluating 500 patients with epilepsy estimated that the modified algorithm had a PPV of 82.0% (95% CI, 78.6%-85.4%).11
After implementation of ICD-10 codes in the VHA in FY 2016, the task of reliably and efficiently identifying VWE led to a 3-tier algorithm. This article presents a validation of the different tiers of this algorithm after the implementation of ICD-10 diagnosis codes and summarizes the surveillance data collected over the years within the VHA showing the trends of epilepsy.
Methods
The VHA National Neurology office commissioned a Neurology Cube dashboard in FY 2021 in collaboration with VHA Support Service Center (VSSC) for reporting and surveillance of VWEs as a quality improvement initiative. The Neurology Cube uses a 3-tier system for identifying VWE in the VHA databases. VSSC programmers extract data from the VHA Corporate Data Warehouse (CDW) and utilize Microsoft SQL Server and Microsoft Power BI for Neurology Cube reports. The 3-tier system identifies VWE and divides them into distinct groups. The first tier identifies VWE with the highest degree of confidence; Tiers 2 and 3 represent identification with successively lesser degrees of confidence (Figure 1).

Tier 1
Definition. For a given index year and the preceding 2 years, any of following diagnosis codes on ≥ 1 clinical encounter are considered: 345.xx (epilepsy in ICD-9), 780.3x (other convulsions in ICD-9), G40.xxx (epilepsy in ICD-10), R40.4 (transient alteration of awareness), R56.1 (posttraumatic seizures), or R56.9 (unspecified convulsions). To reduce false positive rates, EEG clinic visits, which may include long-term monitoring, are excluded. Patients identified with ICD codes are then evaluated for an ASM prescription for ≥ 30 days during the index year. ASMs are listed in Appendix 1.
Validation. The development and validation of ICD-9 diagnosis codes crossmatched with an ASM prescription in the VHA has been published elsewhere.11 In FY 2017, after implementation of ICD-10 diagnostic codes, Tier 1 development and validation was performed in 2 phases. Even though Tier 1 study phases were conducted and completed during FY 2017, the patients for Tier 1 were identified from evaluation of FY 2016 data (October 1, 2015, to September 30, 2016). After the pilot analysis, the Tier 1 definition was implemented, and a chart review of 625 randomized patients was conducted at 5 sites for validation. Adequate preliminary data was not available to perform a sample size estimation for this study. Therefore, a practical target of 125 patients was set for Tier 1 from each site to obtain a final sample size of 625 patients. This second phase validated that the crossmatch of ICD-10 diagnosis codes with ASMs had a high PPV for identifying VWE.
Tiers 2 and 3
Definitions. For an index year, Tier 2 includes patients with ≥ 1 inpatient encounter documentation of either ICD-9 345.xx or ICD-10 G40.xxx, excluding EEG clinics. Tier 3 Includes patients who have had ≥ 2 outpatient encounters with diagnosis codes 345.xx or G40.xxx on 2 separate days, excluding EEG clinics. Tiers 2 and 3 do not require ASM prescriptions; this helps to identify VWEs who may be getting their medications outside of VHA or those who have received a new diagnosis.
Validations. Tiers 2 and 3 were included in the epilepsy identification algorithm in FY 2021 after validation was performed on a sample of 8 patients in each tier. Five patients were subsequently identified as having epilepsy in Tier 2 and 6 patients were identified in Tier 3. A more comprehensive validation of Tiers 2 and 3 was performed during FY 2022 that included patients at 5 sites seen during FY 2019 to FY 2022. Since yearly trends showed only about 8% of total patients were identified as having epilepsy through Tiers 2 and 3 we sought ≥ 20 patients per tier for the 5 sites for a total of 200 patients to ensure representation across the VHA. The final count was 126 patients for Tier 2 and 174 patients for Tier 3 (n = 300).
Gold Standard Criteria for Epilepsy Diagnosis
We used the International League Against Epilepsy (ILAE) definition of epilepsy for the validation of the 3 algorithm tiers. ILAE defines epilepsy as ≥ 2 unprovoked (or reflex) seizures occurring > 24 hours apart or 1 unprovoked (or reflex) seizure and a probability of further seizures similar to the general recurrence risk (≥ 60%) after 2 unprovoked seizures, occurring over the next 10 years.12
A standard protocol was provided to evaluators to identify patients using the VHA Computerized Patient Record System (Appendix 1). After review, evaluators categorized each patient in 1 of 4 ways: (1) Yes, definite: The patient’s health care practitioner (HCP) believes the patient has epilepsy and is treating with medication; (2) Yes, uncertain: The HCP has enough suspicion of epilepsy that a medication is prescribed, but uncertainty is expressed of the diagnosis; (3) No, definite: The HCP does not believe the patient has epilepsy and is therefore not treating with medication for seizure; (4) No, uncertain: The HCP is not treating with medication for epilepsy, because the diagnostic suspicion is not high enough, but there is suspicion for epilepsy.
As a quality improvement operational project, the Epilepsy National Program Office approved this validation project and determined that institutional review board approval was not required.
Statistical Analysis
Counts and percentages were computed for categories of epilepsy status. PPV of each tier was estimated with asymptotic 95% CIs.
Results
ICD-10 codes for 480 patients were evaluated in Tier 1 phase 1; 13.8% were documented with G40.xxx, 27.9% with R56.1, 34.4% with R56.9, and 24.0% with R40.4 (Appendix 2). In total, 68.1% fulfilled the criteria of epilepsy, 19.2% did not, and 12.7% were uncertain). From the validation of Tier 1 phase 2 (n = 625), the PPV of the algorithm for patients presumed to have epilepsy (definite and uncertain) was 85.1% (95% CI, 82.1%-87.8%) (Table).

Of 300 patients evaluated, 126 (42.0%) were evaluated for Tier 2 with a PPV of 61.9% (95% CI, 53.4%-70.4%), and 174 (58.0%) patients were evaluated for Tier 3 with a PPV of 59.8% (95% CI, 52.5%-67.1%. The PPV of the algorithm for patients presumed to have epilepsy (definite and uncertain) were combined to calculate the PPV. Estimates of VHA VWE counts were computed for each tier from FY 2014 to FY 2023 using the VSSC Neurology Cube (Figure 2). For all years, > 92% patients were classified using the Tier 1 definition.

Discussion
The development and validation of the 3-tier diagnostic algorithm represents an important advancement in the surveillance and management of epilepsy among veterans within the VHA. The validation of this algorithm also demonstrates its practical utility in a large, integrated health care system.
Specific challenges were encountered when attempting to use pre-existing algorithms; these challenges included differences in the usage patterns of diagnostic codes and the patterns of ASM use within the VHA. These challenges prompted the need for a tailored approach, which led to the development of this algorithm. The inclusion of additional ICD-10 codes led to further revisions and subsequent validation. While many of the basic concepts of the algorithm, including ICD codes and ASMs, could work in other institutions, it would be wise for health care organizations to develop their own algorithms because of certain variables, including organizational size, patient demographics, common comorbidities, and the specific configurations of electronic health records and administrative data systems.
Studies have shown that ICD-10 codes for epilepsy (G40.* and/or R56.9) perform well in identifying epilepsy whether they are assigned by neurologists (sensitivity, 97.7%; specificity, 44.1%; PPV, 96.2%; negative predictive value, 57.7%), or in emergency department or hospital discharges (PPV, 75.5%).13,14 The pilot study of the algorithm’s Tier 1 development (phase 1) evaluated whether the selected ICD-10 diagnostic codes accurately included the VWE population within the VHA and revealed that while most codes (eg, epilepsy [G40.xxx]; posttraumatic seizures [R56.1]; and unspecified convulsions [R56.9]), had a low false positive rate (< 16%), the R40.4 code (transient alteration of awareness) had a higher false positivity of 42%. While this is not surprising given the broad spectrum of conditions that can manifest as transient alteration of awareness, it underscores the inherent challenges in diagnosing epilepsy using diagnosis codes.
In phase 2, the Tier 1 algorithm was validated as effective for identifying VWE in the VHA system, as its PPV was determined to be high (85%). In comparison, Tiers 2 and 3, whose criteria did not require data on VHA prescribed ASM use, had lower tiers of epilepsy predictability (PPV about 60% for both). This was thought to be acceptable because Tiers 2 and 3 represent a smaller population of the identified VWEs (about 8%). These VWEs may otherwise have been missed, partly because veterans are not required to get ASMs from the VHA.
Upon VHA implementation in FY 2021, this diagnostic algorithm exhibited significant clinical utility when integrated within the VSSC Neurology Cube. It facilitated an efficient approach to identifying VWEs using readily available databases. This led to better tracking of real-time epilepsy cases, which facilitated improving current resource allocation and targeted intervention strategies such as identification of drug-resistant epilepsy patients, optimizing strategies for telehealth and patient outreach for awareness of epilepsy care resources within VHA. Meanwhile, data acquired by the algorithm over the decade since its development (FY 2014 to FY 2023) contributed to more accurate epidemiologic information and identification of historic trends. Development of the algorithm represents one of the ways ECoEs have led to improved care for VWEs. ECoEs have been shown to improve health care for veterans in several metrics.15
A strength of this study is the rigorous multitiered validation process to confirm the diagnostic accuracy of ICD-10 codes against the gold standard ILAE definition of epilepsy to identify “definite” epilepsy cases within the VHA. The use of specific ICD codes further enhances the precision of epilepsy diagnoses. The inclusion of ASMs, which are sometimes prescribed for conditions other than epilepsy, could potentially inflate false positive rates.16
This study focused exclusively on the identification and validation of definite epilepsy cases within the VHA VSSC database, employing more stringent diagnostic criteria to ensure the highest level of certainty in ascertaining epilepsy. It is important to note there is a separate category of probable epilepsy, which involves a broader set of diagnostic criteria. While not covered in this study, probable epilepsy would be subject to future research and validation, which could provide insights into a wider spectrum of epilepsy diagnoses. Such future research could help refine the algorithm’s applicability and accuracy and potentially lead to more comprehensive surveillance and management strategies in clinical practice.
This study highlights the inherent challenges in leveraging administrative data for disease identification, particularly for conditions such as epilepsy, where diagnostic clarity can be complex. However, other conditions such as multiple sclerosis have noted similar success with the use of VHA administrative data for categorizing disease.17
Limitations
The algorithm discussed in this article is, in and of itself, generalizable. However, the validation process was unique to the VHA patient population, limiting the generalizability of the findings. Documentation practices and HCP attitudes within the VHA may differ from those in other health care settings. Identifying people with epilepsy can be challenging because of changing definitions of epilepsy over time. In addition to clinical evaluation, EEG and magnetic resonance imaging results, response to ASM treatment, and video-EEG monitoring of habitual events all can help establish the diagnosis. Therefore, studies may vary in how inclusive or exclusive the criteria are. ASMs such as gabapentin, pregabalin, carbamazepine, lamotrigine, topiramate, and valproate are used to treat other conditions, including headaches, generalized pain, and mood disorders. Consequently, including these ASMs in the Tier 1 definition may have increased the false positive rate. Additional research is needed to evaluate whether excluding these ASMs from the algorithm based on specific criteria (eg, dose of ASM used) can further refine the algorithm to identify patients with epilepsy.
Further refinement of this algorithm may also occur as technology changes. Future electronic health records may allow better tracking of different epilepsy factors, the integration of additional diagnostic criteria, and the use of natural language processing or other forms of artificial intelligence.
Conclusions
This study presents a significant step forward in epilepsy surveillance within the VHA. The algorithm offers a robust tool for identifying VWEs with good PPVs, facilitating better resource allocation and targeted care. Despite its limitations, this research lays a foundation for future advancements in the management and understanding of epilepsy within large health care systems. Since this VHA algorithm is based on ASMs and ICD diagnosis codes from patient records, other large managed health care systems also may be able to adapt this algorithm to their data specifications.


Epilepsy affects about 4.5 million people in the United States and 150,000 new individuals are diagnosed each year.1,2 In 2019, epilepsy-attributable health care spending for noninstitutionalized people was around $5.4 billion and total epilepsy-attributable and epilepsy or seizure health care-related costs totaled $54 billion.3
Accurate surveillance of epilepsy in large health care systems can potentially improve health care delivery and resource allocation. A 2012 Institute of Medicine (IOM) report identified 13 recommendations to guide public health action on epilepsy, including validation of standard definitions for case ascertainment, identification of epilepsy through screening programs or protocols, and expansion of surveillance to better understand disease burden.4
A systematic review of validation studies concluded that it is reasonable to use administrative data to identify people with epilepsy in epidemiologic research. Combining The International Classification of Diseases (ICD) codes for epilepsy (ICD-10, G40-41; ICD-9, 345) with antiseizure medications (ASMs) could provide high positive predictive values (PPVs) and combining symptoms codes for convulsions (ICD-10, R56; ICD-9, 780.3, 780.39) with ASMs could lead to high sensitivity.5 However, identifying individuals with epilepsy from administrative data in large managed health care organizations is challenging.6 The IOM report noted that large managed health care organizations presented varying incidence and prevalence estimates due to differing methodology, geographic area, demographics, and definitions of epilepsy.
The Veterans Health Administration (VHA) is the largest integrated US health care system, providing care to > 9.1 million veterans.7 To improve the health and well-being of veterans with epilepsy (VWEs), a network of sites was established in 2008 called the US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) Epilepsy Centers of Excellence (ECoE). Subsequent to the creation of the ECoE, efforts were made to identify VWEs within VHA databases.8,9 Prior to fiscal year (FY) 2016, the ECoE adopted a modified version of a well-established epilepsy diagnostic algorithm developed by Holden et al for large managed care organizations.10 The original algorithm identified patients by cross-matching ASMs with ICD-9 codes for an index year. But it failed to capture a considerable number of stable patients with epilepsy in the VHA due to incomplete documentation, and had false positives due to inclusion of patients identified from diagnostic clinics. The modified algorithm the ECoE used prior to FY 2016 considered additional prior years and excluded encounters from diagnostic clinics. The result was an improvement in the sensitivity and specificity of the algorithm. Researchers evaluating 500 patients with epilepsy estimated that the modified algorithm had a PPV of 82.0% (95% CI, 78.6%-85.4%).11
After implementation of ICD-10 codes in the VHA in FY 2016, the task of reliably and efficiently identifying VWE led to a 3-tier algorithm. This article presents a validation of the different tiers of this algorithm after the implementation of ICD-10 diagnosis codes and summarizes the surveillance data collected over the years within the VHA showing the trends of epilepsy.
Methods
The VHA National Neurology office commissioned a Neurology Cube dashboard in FY 2021 in collaboration with VHA Support Service Center (VSSC) for reporting and surveillance of VWEs as a quality improvement initiative. The Neurology Cube uses a 3-tier system for identifying VWE in the VHA databases. VSSC programmers extract data from the VHA Corporate Data Warehouse (CDW) and utilize Microsoft SQL Server and Microsoft Power BI for Neurology Cube reports. The 3-tier system identifies VWE and divides them into distinct groups. The first tier identifies VWE with the highest degree of confidence; Tiers 2 and 3 represent identification with successively lesser degrees of confidence (Figure 1).

Tier 1
Definition. For a given index year and the preceding 2 years, any of following diagnosis codes on ≥ 1 clinical encounter are considered: 345.xx (epilepsy in ICD-9), 780.3x (other convulsions in ICD-9), G40.xxx (epilepsy in ICD-10), R40.4 (transient alteration of awareness), R56.1 (posttraumatic seizures), or R56.9 (unspecified convulsions). To reduce false positive rates, EEG clinic visits, which may include long-term monitoring, are excluded. Patients identified with ICD codes are then evaluated for an ASM prescription for ≥ 30 days during the index year. ASMs are listed in Appendix 1.
Validation. The development and validation of ICD-9 diagnosis codes crossmatched with an ASM prescription in the VHA has been published elsewhere.11 In FY 2017, after implementation of ICD-10 diagnostic codes, Tier 1 development and validation was performed in 2 phases. Even though Tier 1 study phases were conducted and completed during FY 2017, the patients for Tier 1 were identified from evaluation of FY 2016 data (October 1, 2015, to September 30, 2016). After the pilot analysis, the Tier 1 definition was implemented, and a chart review of 625 randomized patients was conducted at 5 sites for validation. Adequate preliminary data was not available to perform a sample size estimation for this study. Therefore, a practical target of 125 patients was set for Tier 1 from each site to obtain a final sample size of 625 patients. This second phase validated that the crossmatch of ICD-10 diagnosis codes with ASMs had a high PPV for identifying VWE.
Tiers 2 and 3
Definitions. For an index year, Tier 2 includes patients with ≥ 1 inpatient encounter documentation of either ICD-9 345.xx or ICD-10 G40.xxx, excluding EEG clinics. Tier 3 Includes patients who have had ≥ 2 outpatient encounters with diagnosis codes 345.xx or G40.xxx on 2 separate days, excluding EEG clinics. Tiers 2 and 3 do not require ASM prescriptions; this helps to identify VWEs who may be getting their medications outside of VHA or those who have received a new diagnosis.
Validations. Tiers 2 and 3 were included in the epilepsy identification algorithm in FY 2021 after validation was performed on a sample of 8 patients in each tier. Five patients were subsequently identified as having epilepsy in Tier 2 and 6 patients were identified in Tier 3. A more comprehensive validation of Tiers 2 and 3 was performed during FY 2022 that included patients at 5 sites seen during FY 2019 to FY 2022. Since yearly trends showed only about 8% of total patients were identified as having epilepsy through Tiers 2 and 3 we sought ≥ 20 patients per tier for the 5 sites for a total of 200 patients to ensure representation across the VHA. The final count was 126 patients for Tier 2 and 174 patients for Tier 3 (n = 300).
Gold Standard Criteria for Epilepsy Diagnosis
We used the International League Against Epilepsy (ILAE) definition of epilepsy for the validation of the 3 algorithm tiers. ILAE defines epilepsy as ≥ 2 unprovoked (or reflex) seizures occurring > 24 hours apart or 1 unprovoked (or reflex) seizure and a probability of further seizures similar to the general recurrence risk (≥ 60%) after 2 unprovoked seizures, occurring over the next 10 years.12
A standard protocol was provided to evaluators to identify patients using the VHA Computerized Patient Record System (Appendix 1). After review, evaluators categorized each patient in 1 of 4 ways: (1) Yes, definite: The patient’s health care practitioner (HCP) believes the patient has epilepsy and is treating with medication; (2) Yes, uncertain: The HCP has enough suspicion of epilepsy that a medication is prescribed, but uncertainty is expressed of the diagnosis; (3) No, definite: The HCP does not believe the patient has epilepsy and is therefore not treating with medication for seizure; (4) No, uncertain: The HCP is not treating with medication for epilepsy, because the diagnostic suspicion is not high enough, but there is suspicion for epilepsy.
As a quality improvement operational project, the Epilepsy National Program Office approved this validation project and determined that institutional review board approval was not required.
Statistical Analysis
Counts and percentages were computed for categories of epilepsy status. PPV of each tier was estimated with asymptotic 95% CIs.
Results
ICD-10 codes for 480 patients were evaluated in Tier 1 phase 1; 13.8% were documented with G40.xxx, 27.9% with R56.1, 34.4% with R56.9, and 24.0% with R40.4 (Appendix 2). In total, 68.1% fulfilled the criteria of epilepsy, 19.2% did not, and 12.7% were uncertain). From the validation of Tier 1 phase 2 (n = 625), the PPV of the algorithm for patients presumed to have epilepsy (definite and uncertain) was 85.1% (95% CI, 82.1%-87.8%) (Table).

Of 300 patients evaluated, 126 (42.0%) were evaluated for Tier 2 with a PPV of 61.9% (95% CI, 53.4%-70.4%), and 174 (58.0%) patients were evaluated for Tier 3 with a PPV of 59.8% (95% CI, 52.5%-67.1%. The PPV of the algorithm for patients presumed to have epilepsy (definite and uncertain) were combined to calculate the PPV. Estimates of VHA VWE counts were computed for each tier from FY 2014 to FY 2023 using the VSSC Neurology Cube (Figure 2). For all years, > 92% patients were classified using the Tier 1 definition.

Discussion
The development and validation of the 3-tier diagnostic algorithm represents an important advancement in the surveillance and management of epilepsy among veterans within the VHA. The validation of this algorithm also demonstrates its practical utility in a large, integrated health care system.
Specific challenges were encountered when attempting to use pre-existing algorithms; these challenges included differences in the usage patterns of diagnostic codes and the patterns of ASM use within the VHA. These challenges prompted the need for a tailored approach, which led to the development of this algorithm. The inclusion of additional ICD-10 codes led to further revisions and subsequent validation. While many of the basic concepts of the algorithm, including ICD codes and ASMs, could work in other institutions, it would be wise for health care organizations to develop their own algorithms because of certain variables, including organizational size, patient demographics, common comorbidities, and the specific configurations of electronic health records and administrative data systems.
Studies have shown that ICD-10 codes for epilepsy (G40.* and/or R56.9) perform well in identifying epilepsy whether they are assigned by neurologists (sensitivity, 97.7%; specificity, 44.1%; PPV, 96.2%; negative predictive value, 57.7%), or in emergency department or hospital discharges (PPV, 75.5%).13,14 The pilot study of the algorithm’s Tier 1 development (phase 1) evaluated whether the selected ICD-10 diagnostic codes accurately included the VWE population within the VHA and revealed that while most codes (eg, epilepsy [G40.xxx]; posttraumatic seizures [R56.1]; and unspecified convulsions [R56.9]), had a low false positive rate (< 16%), the R40.4 code (transient alteration of awareness) had a higher false positivity of 42%. While this is not surprising given the broad spectrum of conditions that can manifest as transient alteration of awareness, it underscores the inherent challenges in diagnosing epilepsy using diagnosis codes.
In phase 2, the Tier 1 algorithm was validated as effective for identifying VWE in the VHA system, as its PPV was determined to be high (85%). In comparison, Tiers 2 and 3, whose criteria did not require data on VHA prescribed ASM use, had lower tiers of epilepsy predictability (PPV about 60% for both). This was thought to be acceptable because Tiers 2 and 3 represent a smaller population of the identified VWEs (about 8%). These VWEs may otherwise have been missed, partly because veterans are not required to get ASMs from the VHA.
Upon VHA implementation in FY 2021, this diagnostic algorithm exhibited significant clinical utility when integrated within the VSSC Neurology Cube. It facilitated an efficient approach to identifying VWEs using readily available databases. This led to better tracking of real-time epilepsy cases, which facilitated improving current resource allocation and targeted intervention strategies such as identification of drug-resistant epilepsy patients, optimizing strategies for telehealth and patient outreach for awareness of epilepsy care resources within VHA. Meanwhile, data acquired by the algorithm over the decade since its development (FY 2014 to FY 2023) contributed to more accurate epidemiologic information and identification of historic trends. Development of the algorithm represents one of the ways ECoEs have led to improved care for VWEs. ECoEs have been shown to improve health care for veterans in several metrics.15
A strength of this study is the rigorous multitiered validation process to confirm the diagnostic accuracy of ICD-10 codes against the gold standard ILAE definition of epilepsy to identify “definite” epilepsy cases within the VHA. The use of specific ICD codes further enhances the precision of epilepsy diagnoses. The inclusion of ASMs, which are sometimes prescribed for conditions other than epilepsy, could potentially inflate false positive rates.16
This study focused exclusively on the identification and validation of definite epilepsy cases within the VHA VSSC database, employing more stringent diagnostic criteria to ensure the highest level of certainty in ascertaining epilepsy. It is important to note there is a separate category of probable epilepsy, which involves a broader set of diagnostic criteria. While not covered in this study, probable epilepsy would be subject to future research and validation, which could provide insights into a wider spectrum of epilepsy diagnoses. Such future research could help refine the algorithm’s applicability and accuracy and potentially lead to more comprehensive surveillance and management strategies in clinical practice.
This study highlights the inherent challenges in leveraging administrative data for disease identification, particularly for conditions such as epilepsy, where diagnostic clarity can be complex. However, other conditions such as multiple sclerosis have noted similar success with the use of VHA administrative data for categorizing disease.17
Limitations
The algorithm discussed in this article is, in and of itself, generalizable. However, the validation process was unique to the VHA patient population, limiting the generalizability of the findings. Documentation practices and HCP attitudes within the VHA may differ from those in other health care settings. Identifying people with epilepsy can be challenging because of changing definitions of epilepsy over time. In addition to clinical evaluation, EEG and magnetic resonance imaging results, response to ASM treatment, and video-EEG monitoring of habitual events all can help establish the diagnosis. Therefore, studies may vary in how inclusive or exclusive the criteria are. ASMs such as gabapentin, pregabalin, carbamazepine, lamotrigine, topiramate, and valproate are used to treat other conditions, including headaches, generalized pain, and mood disorders. Consequently, including these ASMs in the Tier 1 definition may have increased the false positive rate. Additional research is needed to evaluate whether excluding these ASMs from the algorithm based on specific criteria (eg, dose of ASM used) can further refine the algorithm to identify patients with epilepsy.
Further refinement of this algorithm may also occur as technology changes. Future electronic health records may allow better tracking of different epilepsy factors, the integration of additional diagnostic criteria, and the use of natural language processing or other forms of artificial intelligence.
Conclusions
This study presents a significant step forward in epilepsy surveillance within the VHA. The algorithm offers a robust tool for identifying VWEs with good PPVs, facilitating better resource allocation and targeted care. Despite its limitations, this research lays a foundation for future advancements in the management and understanding of epilepsy within large health care systems. Since this VHA algorithm is based on ASMs and ICD diagnosis codes from patient records, other large managed health care systems also may be able to adapt this algorithm to their data specifications.


- Kobau R, Luncheon C, Greenlund K. Active epilepsy prevalence among U.S. adults is 1.1% and differs by educational level-National Health Interview Survey, United States, 2021. Epilepsy Behav. 2023;142:109180. doi:10.1016/j.yebeh.2023.109180
- GBD 2017 US Neurological Disorders Collaborators, Feigin VL, Vos T, et al. Burden of neurological disorders across the US from 1990-2017: a global burden of disease study. JAMA Neurol. 2021;78:165-176. doi:10.1001/jamaneurol.2020.4152
- Moura LMVR, Karakis I, Zack MM, et al. Drivers of US health care spending for persons with seizures and/or epilepsies, 2010-2018. Epilepsia. 2022;63:2144-2154. doi:10.1111/epi.17305
- Institute of Medicine. Epilepsy Across the Spectrum: Promoting Health and Understanding. The National Academies Press; 2012. Accessed November 11, 2025. www.nap.edu/catalog/13379
- Mbizvo GK, Bennett KH, Schnier C, Simpson CR, Duncan SE, Chin RFM. The accuracy of using administrative healthcare data to identify epilepsy cases: A systematic review of validation studies. Epilepsia. 2020;61:1319-1335. doi:10.1111/epi.16547
- Montouris GD. How will primary care physicians, specialists, and managed care treat epilepsy in the new millennium? Neurology. 2000;55:S42-S44.
- US Department of Veterans Affairs. Veterans Health Administration: About VHA. Accessed November 11, 2025. https://www.va.gov/health/aboutvha.asp
- Veterans’ Mental Health and Other Care Improvements Act of 2008, S 2162, 110th Cong (2008). Accessed November 11, 2025. https://www.congress.gov/bill/110th-congress/senate-bill/2162
- Rehman R, Kelly PR, Husain AM, Tran TT. Characteristics of Veterans diagnosed with seizures within Veterans Health Administration. J Rehabil Res Dev. 2015;52(7):751-762. doi:10.1682/JRRD.2014.10.0241
- Holden EW, Grossman E, Nguyen HT, et al. Developing a computer algorithm to identify epilepsy cases in managed care organizations. Dis Manag. 2005;8:1-14. doi:10.1089/dis.2005.8.1
- Rehman R, Everhart A, Frontera AT, et al. Implementation of an established algorithm and modifications for the identification of epilepsy patients in the Veterans Health Administration. Epilepsy Res. 2016;127:284-290. doi:10.1016/j.eplepsyres.2016.09.012
- Fisher RS, Acevedo C, Arzimanoglou A, et al. ILAE official report: a practical clinical definition of epilepsy. Epilepsia. 2014;55:475-482. doi:10.1111/epi.12550
- Smith JR, Jones FJS, Fureman BE, et al. Accuracy of ICD-10-CM claims-based definitions for epilepsy and seizure type. Epilepsy Res. 2020;166:106414. doi:10.1016/j.eplepsyres.2020.106414
- Jetté N, Reid AY, Quan H, et al. How accurate is ICD coding for epilepsy? Epilepsia. 2010;51:62-69. doi:10.1111/j.1528-1167.2009.02201.x
- Kelly P, Chinta R, Privitera G. Do centers of excellence reduce health care costs? Evidence from the US Veterans Health Administration Centers for Epilepsy. Glob Bus Organ Excell. 2015;34:18-29.
- Haneef Z, Rehman R, Husain AM. Association between standardized mortality ratio and utilization of care in US veterans with drug-resistant epilepsy compared with all US veterans and the US general population. JAMA Neurol. 2022;79:879-887. doi:10.1001/jamaneurol.2022.2290
- Culpepper WJ, Marrie RA, Langer-Gould A, et al. Validation of an algorithm for identifying MS cases in administrative health claims datasets. Neurology. 2019;92:e1016-e1028 doi:10.1212/WNL.0000000000007043
- Kobau R, Luncheon C, Greenlund K. Active epilepsy prevalence among U.S. adults is 1.1% and differs by educational level-National Health Interview Survey, United States, 2021. Epilepsy Behav. 2023;142:109180. doi:10.1016/j.yebeh.2023.109180
- GBD 2017 US Neurological Disorders Collaborators, Feigin VL, Vos T, et al. Burden of neurological disorders across the US from 1990-2017: a global burden of disease study. JAMA Neurol. 2021;78:165-176. doi:10.1001/jamaneurol.2020.4152
- Moura LMVR, Karakis I, Zack MM, et al. Drivers of US health care spending for persons with seizures and/or epilepsies, 2010-2018. Epilepsia. 2022;63:2144-2154. doi:10.1111/epi.17305
- Institute of Medicine. Epilepsy Across the Spectrum: Promoting Health and Understanding. The National Academies Press; 2012. Accessed November 11, 2025. www.nap.edu/catalog/13379
- Mbizvo GK, Bennett KH, Schnier C, Simpson CR, Duncan SE, Chin RFM. The accuracy of using administrative healthcare data to identify epilepsy cases: A systematic review of validation studies. Epilepsia. 2020;61:1319-1335. doi:10.1111/epi.16547
- Montouris GD. How will primary care physicians, specialists, and managed care treat epilepsy in the new millennium? Neurology. 2000;55:S42-S44.
- US Department of Veterans Affairs. Veterans Health Administration: About VHA. Accessed November 11, 2025. https://www.va.gov/health/aboutvha.asp
- Veterans’ Mental Health and Other Care Improvements Act of 2008, S 2162, 110th Cong (2008). Accessed November 11, 2025. https://www.congress.gov/bill/110th-congress/senate-bill/2162
- Rehman R, Kelly PR, Husain AM, Tran TT. Characteristics of Veterans diagnosed with seizures within Veterans Health Administration. J Rehabil Res Dev. 2015;52(7):751-762. doi:10.1682/JRRD.2014.10.0241
- Holden EW, Grossman E, Nguyen HT, et al. Developing a computer algorithm to identify epilepsy cases in managed care organizations. Dis Manag. 2005;8:1-14. doi:10.1089/dis.2005.8.1
- Rehman R, Everhart A, Frontera AT, et al. Implementation of an established algorithm and modifications for the identification of epilepsy patients in the Veterans Health Administration. Epilepsy Res. 2016;127:284-290. doi:10.1016/j.eplepsyres.2016.09.012
- Fisher RS, Acevedo C, Arzimanoglou A, et al. ILAE official report: a practical clinical definition of epilepsy. Epilepsia. 2014;55:475-482. doi:10.1111/epi.12550
- Smith JR, Jones FJS, Fureman BE, et al. Accuracy of ICD-10-CM claims-based definitions for epilepsy and seizure type. Epilepsy Res. 2020;166:106414. doi:10.1016/j.eplepsyres.2020.106414
- Jetté N, Reid AY, Quan H, et al. How accurate is ICD coding for epilepsy? Epilepsia. 2010;51:62-69. doi:10.1111/j.1528-1167.2009.02201.x
- Kelly P, Chinta R, Privitera G. Do centers of excellence reduce health care costs? Evidence from the US Veterans Health Administration Centers for Epilepsy. Glob Bus Organ Excell. 2015;34:18-29.
- Haneef Z, Rehman R, Husain AM. Association between standardized mortality ratio and utilization of care in US veterans with drug-resistant epilepsy compared with all US veterans and the US general population. JAMA Neurol. 2022;79:879-887. doi:10.1001/jamaneurol.2022.2290
- Culpepper WJ, Marrie RA, Langer-Gould A, et al. Validation of an algorithm for identifying MS cases in administrative health claims datasets. Neurology. 2019;92:e1016-e1028 doi:10.1212/WNL.0000000000007043
Development and Validation of an Administrative Algorithm to Identify Veterans With Epilepsy
Development and Validation of an Administrative Algorithm to Identify Veterans With Epilepsy
Effects of Lumbar Fusion and Dual-Mobility Liners on Dislocation Rates Following Total Hip Arthroplasty in a Veteran Population
Effects of Lumbar Fusion and Dual-Mobility Liners on Dislocation Rates Following Total Hip Arthroplasty in a Veteran Population
Total hip arthroplasty (THA) is among the most common elective orthopedic procedures performed annually in the United States, with an estimated 635,000 to 909,000 THAs expected each year by 2030.1 Consequently, complication rates and revision surgeries related to THA have been increasing, along with the financial burden on the health care system.2-4 Optimizing outcomes for patients undergoing THA and identifying risk factors for treatment failure have become areas of focus.
Over the last decade, there has been a renewed interest in the effect of previous lumbar spine fusion (LSF) surgery on THA outcomes. Studies have explored the rates of complications, postoperative mobility, and THA implant impingement.5-8 However, the outcome receiving the most attention in recent literature is the rate and effect of dislocation in patients with lumbar fusion surgery. Large Medicare database analyses have discovered an association with increased rates of dislocations in patients with lumbar fusion surgeries compared with those without.9,10 Prosthetic hip dislocation is an expensive complication of THA and is projected to have greater impact through 2035 due to a growing number of THA procedures.11 Identifying risk factors associated with hip dislocation is paramount to mitigating its effect on patients who have undergone THA.
Recent research has found increased rates of THA dislocation and revision surgery in patients with LSF, with some studies showing previous LSF as the strongest independent predictor.6-16 However, controversy surrounds this relationship, including the sequence of procedures (LSF before or after THA), the time between procedures, and involvement of the sacrum in LSF. One study found that patients had a 106% increased risk of dislocation when LSF was performed before THA compared with patients who underwent LSF 5 years after undergoing THA, while another study showed no significant difference in dislocations pre- vs post-LSF.16,17 An additional study showed no significant difference in the rate of dislocation in patients without sacral involvement in the LSF, while also showing significantly higher rates of dislocation in LSF with sacral involvement.12 The researchers also found a trend toward more dislocations in longer lumbosacral fusions. Recent studies have also examined dislocation rates with lumbar fusion in patients treated with dual-mobility liners.18-20 The consensus from these studies is that dual-mobility liners significantly decrease the rate of dislocation in primary THAs with lumbar fusion.
The present study sought to determine the rates of hip dislocations in a US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) hospital setting. To the authors’ knowledge, no retrospective study focusing on THAs in the veteran population has been performed. This study benefits from controlling for various surgeon techniques and surgical preferences when compared to large Medicare database studies because the orthopedic surgeon (ABK) only performed the posterior approach for all patients during the study period.
The primary objective of this study was to determine whether the rates of hip dislocation would, in fact, be higher in patients with lumbar fusion surgery, as recent database studies suggest. Secondary objectives included determining whether patient characteristics, comorbidities, number of levels fused, or inclusion of the sacrum in the fusion construct influenced dislocation rates. Furthermore, VA Dayton Healthcare System (VADHS) began routine use of dual-mobility liners for lumbar fusion patients in 2018, allowing for examination of these patients.
Methods
The Wright State University and VADHS Institutional Review Board approved this study design. A retrospective review of all primary THAs at VADHS was performed to investigate the relationship between previous lumbar spine fusion and the incidence of THA revision. Manual chart review was performed for patients who underwent primary THA between January 2003, and December 2022. One surgeon performed all surgeries using only the posterior approach. Patients were not excluded if they had bilateral procedures and all eligible hips were included. Patients with a concomitant diagnosis of fracture of the femoral head or femoral neck at the time of surgery were excluded. Additionally, only patients with ≥ 12 months of follow-up data were included.
The primary outcome was dislocation within 12 months of THA; the primary independent variable was LSF prior to THA. Covariates included patient demographics (age, sex, body mass index [BMI]) and Charlson Comorbidity Index (CCI) score, with additional data collected on the number of levels fused, sacral spine involvement, revision rates, and use of dual-mobility liners. Year of surgery was also included in analyses to account for any changes that may have occurred during the study period.
Statistical Analysis
Statistical analyses were performed in SAS 9.4. Patients were grouped into 2 cohorts, depending on whether they had received LSF prior to THA. Analyses were adjusted for repeated measures to account for the small percentage of patients with bilateral procedures.
Univariate comparisons between cohorts for covariates, as well as rates of dislocation and revision, were performed using the independent samples t test for continuous variables and the Fisher exact test for dichotomous categorical variables. Significant comorbidities, as well as age, sex, BMI, liner type, LSF cohort, and surgery year, were included in a logistic regression model to determine what effect, if any, they had on the likelihood of dislocation. Variables were removed using a backward stepwise approach, starting with the nonsignificant variable effect with the lowest χ2 value, and continuing until reaching a final model where all remaining variable effects were significant. For the variables retained in the final model, odds ratios (ORs) with 95% CIs were derived, with dislocation designated as the event. Individual comorbidity subcomponents of the CCI were also analyzed for their effects on dislocation using backward stepwise logistic regression. A secondary analysis among patients with LSF tested for the influence of the number of vertebral levels fused, the presence or absence of sacral involvement in the fusion, and the use of dual-mobility liners on the likelihood of hip dislocation.
Results
The LSF cohort included 39 patients with THA and prior LSF, 3 of whom had bilateral procedures, for a total of 42 hips. The non-LSF cohort included 813 patients with THA, 112 of whom had bilateral procedures, for a total of 925 hips. The LSF and non-LSF cohorts did not differ significantly in age, sex, BMI, CCI, or revision rates (Table). The LSF cohort included a significantly higher percentage of hips receiving dual-mobility liners than did the non-LSF cohort (23.8% vs 0.6%; P < .001) and had more than twice the rate of dislocation (4 of 42 hips [9.5%] vs 35 of 925 hips [3.8%]), although this difference was not statistically significant (P = .08).
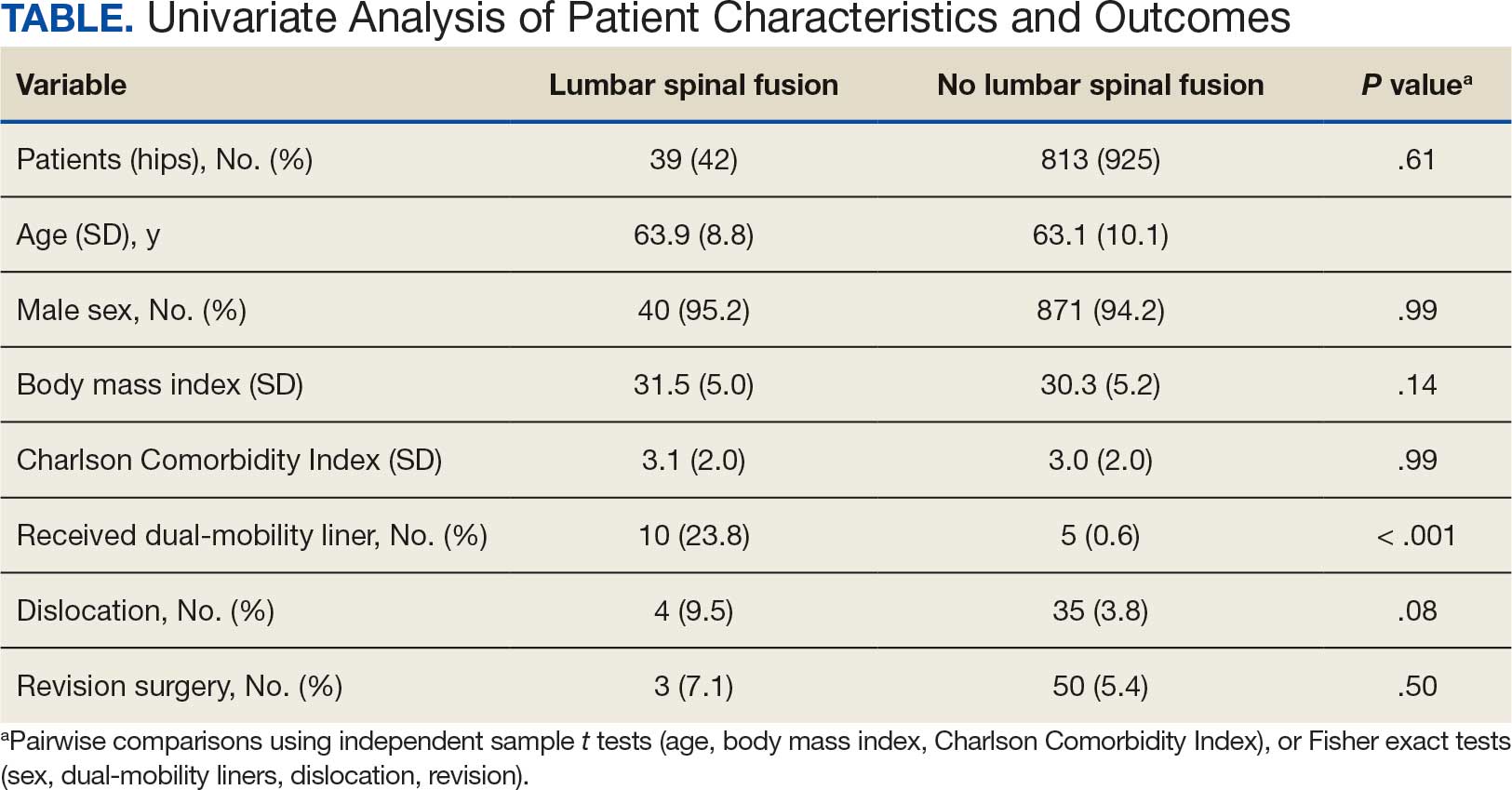
The final logistic regression model with dislocation as the outcome was statistically significant (χ2, 17.47; P < .001) and retained 2 significant predictor variables: LSF cohort (χ2, 4.63; P = .03), and sex (χ2, 18.27; P < .001). Females were more likely than males to experience dislocation (OR, 5.84; 95% CI, 2.60-13.13; P < .001) as were patients who had LSF prior to THA (OR, 3.42; 95% CI, 1.12-10.47; P = .03) (Figure). None of the CCI subcomponent comorbidities significantly affected the probability of dislocation (myocardial infarction, P = .46; congestive heart failure, P = .47; peripheral vascular disease, P = .97; stroke, P = .51; dementia, P = .99; chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, P = .95; connective tissue disease, P = .25; peptic ulcer, P = .41; liver disease, P = .30; diabetes, P = .06; hemiplegia, P = .99; chronic kidney disease, P = .82; solid tumor, P = .90; leukemia, P = .99; lymphoma, P = .99; AIDS, P = .99). Within the LSF cohort, neither the number of levels fused (P = .83) nor sacral involvement (P = .42), significantly affected the probability of hip dislocation. None of the patients in either cohort who received dual-mobility liners subsequently dislocated their hips, nor did any of them require revision surgery.
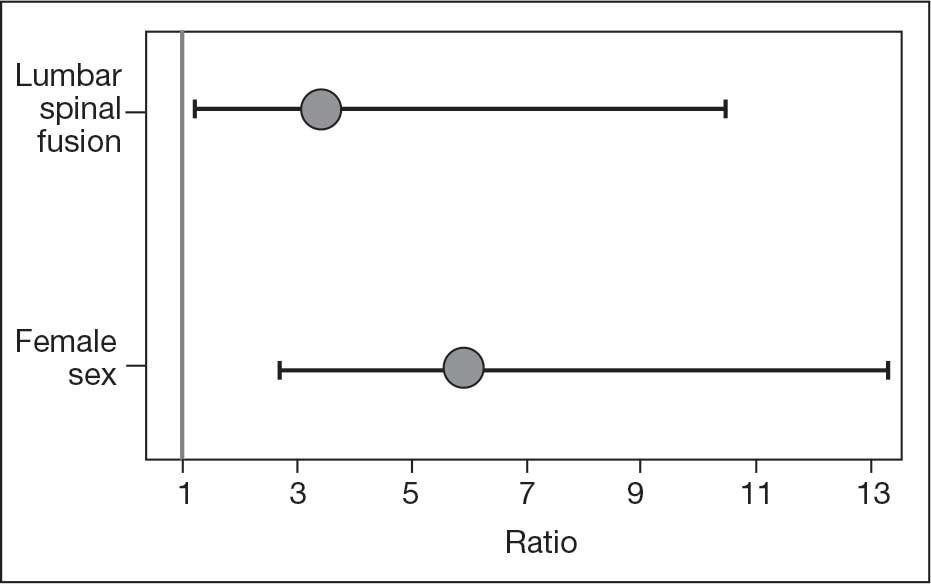
Discussion
Spinopelvic biomechanics have been an area of increasing interest and research. Spinal fusion has been shown to alter the mobility of the pelvis and has been associated with decreased stability of THA implants.21 For example, in the setting of a fused spine, the lack of compensatory changes in pelvic tilt or acetabular anteversion when adjusting to a seated or standing position may predispose patients to impingement because the acetabular component is not properly positioned. Dual-mobility constructs mitigate this risk by providing an additional articulation, which increases jump distance and range of motion prior to impingement, thereby enhancing stability.
The use of dual-mobility liners in patients with LSF has also been examined.18-20 These studies demonstrate a reduced risk of postoperative THA dislocation in patients with previous LSF. The rate of postoperative complications and revisions for LSF patients with dual-mobility liners was also found to be similar to that of THAs without dual-mobility in patients without prior LSF. This study focused on a veteran population to demonstrate the efficacy of dual-mobility liners in patients with LSF. The results indicate that LSF prior to THA and female sex were predictors for prosthetic hip dislocations in the 12-month postoperative period in this patient population, which aligns with the current literature.
The dislocation rate in the LSF-THA group (9.5%) was higher than the dislocation rate in the control group (3.8%). Although not statistically significant in the univariate analysis, LSF was shown to be a significant risk factor after controlling for patient sex. Other studies have found the dislocation rate to be 3% to 7%, which is lower than the dislocation rate observed in this study.8,10,16
The reasons for this higher rate of dislocation are not entirely clear. A veteran population has poorer overall health than the general population, which may contribute to the higher than previously reported dislocation rates.22 These results can be applied to the management of veterans seeking THA.
There have been conflicting reports regarding the impact a patient’s sex has on THA outcomes in the general population.23-26 This study found that female patients had higher rates of dislocation within 1 year of THA than male patients. This difference, which could be due to differences in baseline anatomic hip morphology between the sexes; females tend to have smaller femoral head sizes and less offset compared with males.27,28 However, this finding could have been confounded by the small number of female veterans in the study cohort.
A type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) diagnosis, which is a component of CCI, trended toward increased risk of prosthetic hip dislocation. Multiple studies have also discussed the increased risk of postoperative infections and revisions following THA in patients with T2DM.29-31 One study found T2DM to be an independent risk factor for immediate in-hospital postoperative complications following hip arthroplasty.32
Another factor that may influence postoperative dislocation risk is surgical approach. The posterior approach has historically been associated with higher rates of instability when compared to anterior or lateral THA.33 Researchers have also looked at the role that surgical approach plays in patients with prior LSF. Huebschmann et al confirmed that not only is LSF a significant risk factor for dislocation following THA, but anterior and laterally based surgical approaches may mitigate this risk.34
Limitations
As a retrospective cohort study, the reliability of the data hinges on complete documentation. Documentation of all encounters for dislocations was obtained from the VA Computerized Patient Record System, which may have led to some dislocation events being missed. However, as long as there was adequate postoperative follow-up, it was assumed all events outside the VA were included. Another limitation of this study was that male patients greatly outnumbered female patients, and this fact could limit the generalizability of findings to the population as a whole.
Conclusions
This study in a veteran population found that prior LSF and female sex were significant predictors for postoperative dislocation within 1 year of THA surgery. Additionally, the use of a dual-mobility liner was found to be protective against postoperative dislocation events. These data allow clinicians to better counsel veterans on the risk factors associated with postoperative dislocation and strategies to mitigate this risk.
- Sloan M, Premkumar A, Sheth NP. Projected volume of primary total joint arthroplasty in the U.S., 2014 to 2030. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2018;100:1455-1460. doi:10.2106/JBJS.17.01617
- Bozic KJ, Kurtz SM, Lau E, et al. The epidemiology of revision total hip arthroplasty in the United States. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2009;91:128-133. doi:10.2106/JBJS.H.00155
- Kurtz SM, Ong KL, Schmier J, et al. Future clinical and economic impact of revision total hip and knee arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2007;89:144-151. doi:10.2106/JBJS.G.00587
- Kurtz SM, Ong KL, Schmier J, et al. Primary and revision arthroplasty surgery caseloads in the United States from 1990 to 2004. J Arthroplasty. 2009;24:195-203. doi:10.1016/j.arth.2007.11.015
- Yamato Y, Furuhashi H, Hasegawa T, et al. Simulation of implant impingement after spinal corrective fusion surgery in patients with previous total hip arthroplasty: a retrospective case series. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2021;46:512-519. doi:10.1097/BRS.0000000000003836
- Mudrick CA, Melvin JS, Springer BD. Late posterior hip instability after lumbar spinopelvic fusion. Arthroplast Today. 2015;1:25-29. doi:10.1016/j.artd.2015.05.002
- Diebo BG, Beyer GA, Grieco PW, et al. Complications in patients undergoing spinal fusion after THA. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2018;476:412-417.doi:10.1007/s11999.0000000000000009 8.
- Sing DC, Barry JJ, Aguilar TU, et al. Prior lumbar spinal arthrodesis increases risk of prosthetic-related complication in total hip arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2016;31:227-232.e1. doi:10.1016/j.arth.2016.02.069
- King CA, Landy DC, Martell JM, et al. Time to dislocation analysis of lumbar spine fusion following total hip arthroplasty: breaking up a happy home. J Arthroplasty. 2018;33:3768-3772. doi:10.1016/j.arth.2018.08.029
- Buckland AJ, Puvanesarajah V, Vigdorchik J, et al. Dislocation of a primary total hip arthroplasty is more common in patients with a lumbar spinal fusion. Bone Joint J. 2017;99-B:585-591.doi:10.1302/0301-620X.99B5.BJJ-2016-0657.R1
- Pirruccio K, Premkumar A, Sheth NP. The burden of prosthetic hip dislocations in the United States is projected to significantly increase by 2035. Hip Int. 2021;31:714-721. doi:10.1177/1120700020923619
- Salib CG, Reina N, Perry KI, et al. Lumbar fusion involving the sacrum increases dislocation risk in primary total hip arthroplasty. Bone Joint J. 2019;101-B:198-206. doi:10.1302/0301-620X.101B2.BJJ-2018-0754.R1
- An VVG, Phan K, Sivakumar BS, et al. Prior lumbar spinal fusion is associated with an increased risk of dislocation and revision in total hip arthroplasty: a meta-analysis. J Arthroplasty. 2018;33:297-300. doi:10.1016/j.arth.2017.08.040
- Klemt C, Padmanabha A, Tirumala V, et al. Lumbar spine fusion before revision total hip arthroplasty is associated with increased dislocation rates. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2021;29:e860-e868. doi:10.5435/JAAOS-D-20-00824
- Gausden EB, Parhar HS, Popper JE, et al. Risk factors for early dislocation following primary elective total hip arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2018;33:1567-1571. doi:10.1016/j.arth.2017.12.034
- Malkani AL, Himschoot KJ, Ong KL, et al. Does timing of primary total hip arthroplasty prior to or after lumbar spine fusion have an effect on dislocation and revision rates?. J Arthroplasty. 2019;34:907-911. doi:10.1016/j.arth.2019.01.009
- Parilla FW, Shah RR, Gordon AC, et al. Does it matter: total hip arthroplasty or lumbar spinal fusion first? Preoperative sagittal spinopelvic measurements guide patient-specific surgical strategies in patients requiring both. J Arthroplasty. 2019;34:2652-2662. doi:10.1016/j.arth.2019.05.053
- Chalmers BP, Syku M, Sculco TP, et al. Dual-mobility constructs in primary total hip arthroplasty in high-risk patients with spinal fusions: our institutional experience. Arthroplast Today. 2020;6:749-754. doi:10.1016/j.artd.2020.07.024
- Nessler JM, Malkani AL, Sachdeva S, et al. Use of dual mobility cups in patients undergoing primary total hip arthroplasty with prior lumbar spine fusion. Int Orthop. 2020;44:857-862. doi:10.1007/s00264-020-04507-y
- Nessler JM, Malkani AL, Yep PJ, et al. Dislocation rates of primary total hip arthroplasty in patients with prior lumbar spine fusion and lumbar degenerative disk disease with and without utilization of dual mobility cups: an American Joint Replacement Registry study. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2023;31:e271-e277. doi:10.5435/JAAOS-D-22-00767
- Phan D, Bederman SS, Schwarzkopf R. The influence of sagittal spinal deformity on anteversion of the acetabular component in total hip arthroplasty. Bone Joint J. 2015;97-B:1017-1023. doi:10.1302/0301-620X.97B8.35700
- Agha Z, Lofgren RP, VanRuiswyk JV, et al. Are patients at Veterans Affairs medical centers sicker? A comparative analysis of health status and medical resource use. Arch Intern Med. 2000;160:3252-3257. doi:10.1001/archinte.160.21.325223.
- Basques BA, Bell JA, Fillingham YA, et al. Gender differences for hip and knee arthroplasty: complications and healthcare utilization. J Arthroplasty. 2019;34:1593-1597.e1. doi:10.1016/j.arth.2019.03.064
- Kim YH, Choi Y, Kim JS. Influence of patient-, design-, and surgery-related factors on rate of dislocation after primary cementless total hip arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2009;24:1258-1263. doi:10.1016/j.arth.2009.03.017
- Chen A, Paxton L, Zheng X, et al. Association of sex with risk of 2-year revision among patients undergoing total hip arthroplasty. JAMA Netw Open. 2021;4:e2110687. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.10687
- Inacio MCS, Ake CF, Paxton EW, et al. Sex and risk of hip implant failure: assessing total hip arthroplasty outcomes in the United States. JAMA Intern Med. 2013;173:435-441. doi:10.1001/jamainternmed.2013.3271
- Karlson EW, Daltroy LH, Liang MH, et al. Gender differences in patient preferences may underlie differential utilization of elective surgery. Am J Med. 1997;102:524-530. doi:10.1016/s0002-9343(97)00050-8
- Kostamo T, Bourne RB, Whittaker JP, et al. No difference in gender-specific hip replacement outcomes. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2009;467:135-140. doi:10.1007/s11999-008-0466-2
- Papagelopoulos PJ, Idusuyi OB, Wallrichs SL, et al. Long term outcome and survivorship analysis of primary total knee arthroplasty in patients with diabetes mellitus. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1996;(330):124-132. doi:10.1097/00003086-199609000-00015
- Fitzgerald RH Jr, Nolan DR, Ilstrup DM, et al. Deep wound sepsis following total hip arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1977;59:847-855.
- Blom AW, Brown J, Taylor AH, et al. Infection after total knee arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2004;86:688-691. doi:10.1302/0301-620x.86b5.14887
- Jain NB, Guller U, Pietrobon R, et al. Comorbidities increase complication rates in patients having arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2005;435:232-238. doi:10.1097/01.blo.0000156479.97488.a2
- Docter S, Philpott HT, Godkin L, et al. Comparison of intra and post-operative complication rates among surgical approaches in Total Hip Arthroplasty: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J Orthop. 2020;20:310-325. doi:10.1016/j.jor.2020.05.008
- Huebschmann NA, Lawrence KW, Robin JX, et al. Does surgical approach affect dislocation rate after total hip arthroplasty in patients who have prior lumbar spinal fusion? A retrospective analysis of 16,223 cases. J Arthroplasty. 2024;39:S306-S313. doi:10.1016/j.arth.2024.03.068
Total hip arthroplasty (THA) is among the most common elective orthopedic procedures performed annually in the United States, with an estimated 635,000 to 909,000 THAs expected each year by 2030.1 Consequently, complication rates and revision surgeries related to THA have been increasing, along with the financial burden on the health care system.2-4 Optimizing outcomes for patients undergoing THA and identifying risk factors for treatment failure have become areas of focus.
Over the last decade, there has been a renewed interest in the effect of previous lumbar spine fusion (LSF) surgery on THA outcomes. Studies have explored the rates of complications, postoperative mobility, and THA implant impingement.5-8 However, the outcome receiving the most attention in recent literature is the rate and effect of dislocation in patients with lumbar fusion surgery. Large Medicare database analyses have discovered an association with increased rates of dislocations in patients with lumbar fusion surgeries compared with those without.9,10 Prosthetic hip dislocation is an expensive complication of THA and is projected to have greater impact through 2035 due to a growing number of THA procedures.11 Identifying risk factors associated with hip dislocation is paramount to mitigating its effect on patients who have undergone THA.
Recent research has found increased rates of THA dislocation and revision surgery in patients with LSF, with some studies showing previous LSF as the strongest independent predictor.6-16 However, controversy surrounds this relationship, including the sequence of procedures (LSF before or after THA), the time between procedures, and involvement of the sacrum in LSF. One study found that patients had a 106% increased risk of dislocation when LSF was performed before THA compared with patients who underwent LSF 5 years after undergoing THA, while another study showed no significant difference in dislocations pre- vs post-LSF.16,17 An additional study showed no significant difference in the rate of dislocation in patients without sacral involvement in the LSF, while also showing significantly higher rates of dislocation in LSF with sacral involvement.12 The researchers also found a trend toward more dislocations in longer lumbosacral fusions. Recent studies have also examined dislocation rates with lumbar fusion in patients treated with dual-mobility liners.18-20 The consensus from these studies is that dual-mobility liners significantly decrease the rate of dislocation in primary THAs with lumbar fusion.
The present study sought to determine the rates of hip dislocations in a US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) hospital setting. To the authors’ knowledge, no retrospective study focusing on THAs in the veteran population has been performed. This study benefits from controlling for various surgeon techniques and surgical preferences when compared to large Medicare database studies because the orthopedic surgeon (ABK) only performed the posterior approach for all patients during the study period.
The primary objective of this study was to determine whether the rates of hip dislocation would, in fact, be higher in patients with lumbar fusion surgery, as recent database studies suggest. Secondary objectives included determining whether patient characteristics, comorbidities, number of levels fused, or inclusion of the sacrum in the fusion construct influenced dislocation rates. Furthermore, VA Dayton Healthcare System (VADHS) began routine use of dual-mobility liners for lumbar fusion patients in 2018, allowing for examination of these patients.
Methods
The Wright State University and VADHS Institutional Review Board approved this study design. A retrospective review of all primary THAs at VADHS was performed to investigate the relationship between previous lumbar spine fusion and the incidence of THA revision. Manual chart review was performed for patients who underwent primary THA between January 2003, and December 2022. One surgeon performed all surgeries using only the posterior approach. Patients were not excluded if they had bilateral procedures and all eligible hips were included. Patients with a concomitant diagnosis of fracture of the femoral head or femoral neck at the time of surgery were excluded. Additionally, only patients with ≥ 12 months of follow-up data were included.
The primary outcome was dislocation within 12 months of THA; the primary independent variable was LSF prior to THA. Covariates included patient demographics (age, sex, body mass index [BMI]) and Charlson Comorbidity Index (CCI) score, with additional data collected on the number of levels fused, sacral spine involvement, revision rates, and use of dual-mobility liners. Year of surgery was also included in analyses to account for any changes that may have occurred during the study period.
Statistical Analysis
Statistical analyses were performed in SAS 9.4. Patients were grouped into 2 cohorts, depending on whether they had received LSF prior to THA. Analyses were adjusted for repeated measures to account for the small percentage of patients with bilateral procedures.
Univariate comparisons between cohorts for covariates, as well as rates of dislocation and revision, were performed using the independent samples t test for continuous variables and the Fisher exact test for dichotomous categorical variables. Significant comorbidities, as well as age, sex, BMI, liner type, LSF cohort, and surgery year, were included in a logistic regression model to determine what effect, if any, they had on the likelihood of dislocation. Variables were removed using a backward stepwise approach, starting with the nonsignificant variable effect with the lowest χ2 value, and continuing until reaching a final model where all remaining variable effects were significant. For the variables retained in the final model, odds ratios (ORs) with 95% CIs were derived, with dislocation designated as the event. Individual comorbidity subcomponents of the CCI were also analyzed for their effects on dislocation using backward stepwise logistic regression. A secondary analysis among patients with LSF tested for the influence of the number of vertebral levels fused, the presence or absence of sacral involvement in the fusion, and the use of dual-mobility liners on the likelihood of hip dislocation.
Results
The LSF cohort included 39 patients with THA and prior LSF, 3 of whom had bilateral procedures, for a total of 42 hips. The non-LSF cohort included 813 patients with THA, 112 of whom had bilateral procedures, for a total of 925 hips. The LSF and non-LSF cohorts did not differ significantly in age, sex, BMI, CCI, or revision rates (Table). The LSF cohort included a significantly higher percentage of hips receiving dual-mobility liners than did the non-LSF cohort (23.8% vs 0.6%; P < .001) and had more than twice the rate of dislocation (4 of 42 hips [9.5%] vs 35 of 925 hips [3.8%]), although this difference was not statistically significant (P = .08).

The final logistic regression model with dislocation as the outcome was statistically significant (χ2, 17.47; P < .001) and retained 2 significant predictor variables: LSF cohort (χ2, 4.63; P = .03), and sex (χ2, 18.27; P < .001). Females were more likely than males to experience dislocation (OR, 5.84; 95% CI, 2.60-13.13; P < .001) as were patients who had LSF prior to THA (OR, 3.42; 95% CI, 1.12-10.47; P = .03) (Figure). None of the CCI subcomponent comorbidities significantly affected the probability of dislocation (myocardial infarction, P = .46; congestive heart failure, P = .47; peripheral vascular disease, P = .97; stroke, P = .51; dementia, P = .99; chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, P = .95; connective tissue disease, P = .25; peptic ulcer, P = .41; liver disease, P = .30; diabetes, P = .06; hemiplegia, P = .99; chronic kidney disease, P = .82; solid tumor, P = .90; leukemia, P = .99; lymphoma, P = .99; AIDS, P = .99). Within the LSF cohort, neither the number of levels fused (P = .83) nor sacral involvement (P = .42), significantly affected the probability of hip dislocation. None of the patients in either cohort who received dual-mobility liners subsequently dislocated their hips, nor did any of them require revision surgery.

Discussion
Spinopelvic biomechanics have been an area of increasing interest and research. Spinal fusion has been shown to alter the mobility of the pelvis and has been associated with decreased stability of THA implants.21 For example, in the setting of a fused spine, the lack of compensatory changes in pelvic tilt or acetabular anteversion when adjusting to a seated or standing position may predispose patients to impingement because the acetabular component is not properly positioned. Dual-mobility constructs mitigate this risk by providing an additional articulation, which increases jump distance and range of motion prior to impingement, thereby enhancing stability.
The use of dual-mobility liners in patients with LSF has also been examined.18-20 These studies demonstrate a reduced risk of postoperative THA dislocation in patients with previous LSF. The rate of postoperative complications and revisions for LSF patients with dual-mobility liners was also found to be similar to that of THAs without dual-mobility in patients without prior LSF. This study focused on a veteran population to demonstrate the efficacy of dual-mobility liners in patients with LSF. The results indicate that LSF prior to THA and female sex were predictors for prosthetic hip dislocations in the 12-month postoperative period in this patient population, which aligns with the current literature.
The dislocation rate in the LSF-THA group (9.5%) was higher than the dislocation rate in the control group (3.8%). Although not statistically significant in the univariate analysis, LSF was shown to be a significant risk factor after controlling for patient sex. Other studies have found the dislocation rate to be 3% to 7%, which is lower than the dislocation rate observed in this study.8,10,16
The reasons for this higher rate of dislocation are not entirely clear. A veteran population has poorer overall health than the general population, which may contribute to the higher than previously reported dislocation rates.22 These results can be applied to the management of veterans seeking THA.
There have been conflicting reports regarding the impact a patient’s sex has on THA outcomes in the general population.23-26 This study found that female patients had higher rates of dislocation within 1 year of THA than male patients. This difference, which could be due to differences in baseline anatomic hip morphology between the sexes; females tend to have smaller femoral head sizes and less offset compared with males.27,28 However, this finding could have been confounded by the small number of female veterans in the study cohort.
A type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) diagnosis, which is a component of CCI, trended toward increased risk of prosthetic hip dislocation. Multiple studies have also discussed the increased risk of postoperative infections and revisions following THA in patients with T2DM.29-31 One study found T2DM to be an independent risk factor for immediate in-hospital postoperative complications following hip arthroplasty.32
Another factor that may influence postoperative dislocation risk is surgical approach. The posterior approach has historically been associated with higher rates of instability when compared to anterior or lateral THA.33 Researchers have also looked at the role that surgical approach plays in patients with prior LSF. Huebschmann et al confirmed that not only is LSF a significant risk factor for dislocation following THA, but anterior and laterally based surgical approaches may mitigate this risk.34
Limitations
As a retrospective cohort study, the reliability of the data hinges on complete documentation. Documentation of all encounters for dislocations was obtained from the VA Computerized Patient Record System, which may have led to some dislocation events being missed. However, as long as there was adequate postoperative follow-up, it was assumed all events outside the VA were included. Another limitation of this study was that male patients greatly outnumbered female patients, and this fact could limit the generalizability of findings to the population as a whole.
Conclusions
This study in a veteran population found that prior LSF and female sex were significant predictors for postoperative dislocation within 1 year of THA surgery. Additionally, the use of a dual-mobility liner was found to be protective against postoperative dislocation events. These data allow clinicians to better counsel veterans on the risk factors associated with postoperative dislocation and strategies to mitigate this risk.
Total hip arthroplasty (THA) is among the most common elective orthopedic procedures performed annually in the United States, with an estimated 635,000 to 909,000 THAs expected each year by 2030.1 Consequently, complication rates and revision surgeries related to THA have been increasing, along with the financial burden on the health care system.2-4 Optimizing outcomes for patients undergoing THA and identifying risk factors for treatment failure have become areas of focus.
Over the last decade, there has been a renewed interest in the effect of previous lumbar spine fusion (LSF) surgery on THA outcomes. Studies have explored the rates of complications, postoperative mobility, and THA implant impingement.5-8 However, the outcome receiving the most attention in recent literature is the rate and effect of dislocation in patients with lumbar fusion surgery. Large Medicare database analyses have discovered an association with increased rates of dislocations in patients with lumbar fusion surgeries compared with those without.9,10 Prosthetic hip dislocation is an expensive complication of THA and is projected to have greater impact through 2035 due to a growing number of THA procedures.11 Identifying risk factors associated with hip dislocation is paramount to mitigating its effect on patients who have undergone THA.
Recent research has found increased rates of THA dislocation and revision surgery in patients with LSF, with some studies showing previous LSF as the strongest independent predictor.6-16 However, controversy surrounds this relationship, including the sequence of procedures (LSF before or after THA), the time between procedures, and involvement of the sacrum in LSF. One study found that patients had a 106% increased risk of dislocation when LSF was performed before THA compared with patients who underwent LSF 5 years after undergoing THA, while another study showed no significant difference in dislocations pre- vs post-LSF.16,17 An additional study showed no significant difference in the rate of dislocation in patients without sacral involvement in the LSF, while also showing significantly higher rates of dislocation in LSF with sacral involvement.12 The researchers also found a trend toward more dislocations in longer lumbosacral fusions. Recent studies have also examined dislocation rates with lumbar fusion in patients treated with dual-mobility liners.18-20 The consensus from these studies is that dual-mobility liners significantly decrease the rate of dislocation in primary THAs with lumbar fusion.
The present study sought to determine the rates of hip dislocations in a US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) hospital setting. To the authors’ knowledge, no retrospective study focusing on THAs in the veteran population has been performed. This study benefits from controlling for various surgeon techniques and surgical preferences when compared to large Medicare database studies because the orthopedic surgeon (ABK) only performed the posterior approach for all patients during the study period.
The primary objective of this study was to determine whether the rates of hip dislocation would, in fact, be higher in patients with lumbar fusion surgery, as recent database studies suggest. Secondary objectives included determining whether patient characteristics, comorbidities, number of levels fused, or inclusion of the sacrum in the fusion construct influenced dislocation rates. Furthermore, VA Dayton Healthcare System (VADHS) began routine use of dual-mobility liners for lumbar fusion patients in 2018, allowing for examination of these patients.
Methods
The Wright State University and VADHS Institutional Review Board approved this study design. A retrospective review of all primary THAs at VADHS was performed to investigate the relationship between previous lumbar spine fusion and the incidence of THA revision. Manual chart review was performed for patients who underwent primary THA between January 2003, and December 2022. One surgeon performed all surgeries using only the posterior approach. Patients were not excluded if they had bilateral procedures and all eligible hips were included. Patients with a concomitant diagnosis of fracture of the femoral head or femoral neck at the time of surgery were excluded. Additionally, only patients with ≥ 12 months of follow-up data were included.
The primary outcome was dislocation within 12 months of THA; the primary independent variable was LSF prior to THA. Covariates included patient demographics (age, sex, body mass index [BMI]) and Charlson Comorbidity Index (CCI) score, with additional data collected on the number of levels fused, sacral spine involvement, revision rates, and use of dual-mobility liners. Year of surgery was also included in analyses to account for any changes that may have occurred during the study period.
Statistical Analysis
Statistical analyses were performed in SAS 9.4. Patients were grouped into 2 cohorts, depending on whether they had received LSF prior to THA. Analyses were adjusted for repeated measures to account for the small percentage of patients with bilateral procedures.
Univariate comparisons between cohorts for covariates, as well as rates of dislocation and revision, were performed using the independent samples t test for continuous variables and the Fisher exact test for dichotomous categorical variables. Significant comorbidities, as well as age, sex, BMI, liner type, LSF cohort, and surgery year, were included in a logistic regression model to determine what effect, if any, they had on the likelihood of dislocation. Variables were removed using a backward stepwise approach, starting with the nonsignificant variable effect with the lowest χ2 value, and continuing until reaching a final model where all remaining variable effects were significant. For the variables retained in the final model, odds ratios (ORs) with 95% CIs were derived, with dislocation designated as the event. Individual comorbidity subcomponents of the CCI were also analyzed for their effects on dislocation using backward stepwise logistic regression. A secondary analysis among patients with LSF tested for the influence of the number of vertebral levels fused, the presence or absence of sacral involvement in the fusion, and the use of dual-mobility liners on the likelihood of hip dislocation.
Results
The LSF cohort included 39 patients with THA and prior LSF, 3 of whom had bilateral procedures, for a total of 42 hips. The non-LSF cohort included 813 patients with THA, 112 of whom had bilateral procedures, for a total of 925 hips. The LSF and non-LSF cohorts did not differ significantly in age, sex, BMI, CCI, or revision rates (Table). The LSF cohort included a significantly higher percentage of hips receiving dual-mobility liners than did the non-LSF cohort (23.8% vs 0.6%; P < .001) and had more than twice the rate of dislocation (4 of 42 hips [9.5%] vs 35 of 925 hips [3.8%]), although this difference was not statistically significant (P = .08).

The final logistic regression model with dislocation as the outcome was statistically significant (χ2, 17.47; P < .001) and retained 2 significant predictor variables: LSF cohort (χ2, 4.63; P = .03), and sex (χ2, 18.27; P < .001). Females were more likely than males to experience dislocation (OR, 5.84; 95% CI, 2.60-13.13; P < .001) as were patients who had LSF prior to THA (OR, 3.42; 95% CI, 1.12-10.47; P = .03) (Figure). None of the CCI subcomponent comorbidities significantly affected the probability of dislocation (myocardial infarction, P = .46; congestive heart failure, P = .47; peripheral vascular disease, P = .97; stroke, P = .51; dementia, P = .99; chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, P = .95; connective tissue disease, P = .25; peptic ulcer, P = .41; liver disease, P = .30; diabetes, P = .06; hemiplegia, P = .99; chronic kidney disease, P = .82; solid tumor, P = .90; leukemia, P = .99; lymphoma, P = .99; AIDS, P = .99). Within the LSF cohort, neither the number of levels fused (P = .83) nor sacral involvement (P = .42), significantly affected the probability of hip dislocation. None of the patients in either cohort who received dual-mobility liners subsequently dislocated their hips, nor did any of them require revision surgery.

Discussion
Spinopelvic biomechanics have been an area of increasing interest and research. Spinal fusion has been shown to alter the mobility of the pelvis and has been associated with decreased stability of THA implants.21 For example, in the setting of a fused spine, the lack of compensatory changes in pelvic tilt or acetabular anteversion when adjusting to a seated or standing position may predispose patients to impingement because the acetabular component is not properly positioned. Dual-mobility constructs mitigate this risk by providing an additional articulation, which increases jump distance and range of motion prior to impingement, thereby enhancing stability.
The use of dual-mobility liners in patients with LSF has also been examined.18-20 These studies demonstrate a reduced risk of postoperative THA dislocation in patients with previous LSF. The rate of postoperative complications and revisions for LSF patients with dual-mobility liners was also found to be similar to that of THAs without dual-mobility in patients without prior LSF. This study focused on a veteran population to demonstrate the efficacy of dual-mobility liners in patients with LSF. The results indicate that LSF prior to THA and female sex were predictors for prosthetic hip dislocations in the 12-month postoperative period in this patient population, which aligns with the current literature.
The dislocation rate in the LSF-THA group (9.5%) was higher than the dislocation rate in the control group (3.8%). Although not statistically significant in the univariate analysis, LSF was shown to be a significant risk factor after controlling for patient sex. Other studies have found the dislocation rate to be 3% to 7%, which is lower than the dislocation rate observed in this study.8,10,16
The reasons for this higher rate of dislocation are not entirely clear. A veteran population has poorer overall health than the general population, which may contribute to the higher than previously reported dislocation rates.22 These results can be applied to the management of veterans seeking THA.
There have been conflicting reports regarding the impact a patient’s sex has on THA outcomes in the general population.23-26 This study found that female patients had higher rates of dislocation within 1 year of THA than male patients. This difference, which could be due to differences in baseline anatomic hip morphology between the sexes; females tend to have smaller femoral head sizes and less offset compared with males.27,28 However, this finding could have been confounded by the small number of female veterans in the study cohort.
A type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) diagnosis, which is a component of CCI, trended toward increased risk of prosthetic hip dislocation. Multiple studies have also discussed the increased risk of postoperative infections and revisions following THA in patients with T2DM.29-31 One study found T2DM to be an independent risk factor for immediate in-hospital postoperative complications following hip arthroplasty.32
Another factor that may influence postoperative dislocation risk is surgical approach. The posterior approach has historically been associated with higher rates of instability when compared to anterior or lateral THA.33 Researchers have also looked at the role that surgical approach plays in patients with prior LSF. Huebschmann et al confirmed that not only is LSF a significant risk factor for dislocation following THA, but anterior and laterally based surgical approaches may mitigate this risk.34
Limitations
As a retrospective cohort study, the reliability of the data hinges on complete documentation. Documentation of all encounters for dislocations was obtained from the VA Computerized Patient Record System, which may have led to some dislocation events being missed. However, as long as there was adequate postoperative follow-up, it was assumed all events outside the VA were included. Another limitation of this study was that male patients greatly outnumbered female patients, and this fact could limit the generalizability of findings to the population as a whole.
Conclusions
This study in a veteran population found that prior LSF and female sex were significant predictors for postoperative dislocation within 1 year of THA surgery. Additionally, the use of a dual-mobility liner was found to be protective against postoperative dislocation events. These data allow clinicians to better counsel veterans on the risk factors associated with postoperative dislocation and strategies to mitigate this risk.
- Sloan M, Premkumar A, Sheth NP. Projected volume of primary total joint arthroplasty in the U.S., 2014 to 2030. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2018;100:1455-1460. doi:10.2106/JBJS.17.01617
- Bozic KJ, Kurtz SM, Lau E, et al. The epidemiology of revision total hip arthroplasty in the United States. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2009;91:128-133. doi:10.2106/JBJS.H.00155
- Kurtz SM, Ong KL, Schmier J, et al. Future clinical and economic impact of revision total hip and knee arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2007;89:144-151. doi:10.2106/JBJS.G.00587
- Kurtz SM, Ong KL, Schmier J, et al. Primary and revision arthroplasty surgery caseloads in the United States from 1990 to 2004. J Arthroplasty. 2009;24:195-203. doi:10.1016/j.arth.2007.11.015
- Yamato Y, Furuhashi H, Hasegawa T, et al. Simulation of implant impingement after spinal corrective fusion surgery in patients with previous total hip arthroplasty: a retrospective case series. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2021;46:512-519. doi:10.1097/BRS.0000000000003836
- Mudrick CA, Melvin JS, Springer BD. Late posterior hip instability after lumbar spinopelvic fusion. Arthroplast Today. 2015;1:25-29. doi:10.1016/j.artd.2015.05.002
- Diebo BG, Beyer GA, Grieco PW, et al. Complications in patients undergoing spinal fusion after THA. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2018;476:412-417.doi:10.1007/s11999.0000000000000009 8.
- Sing DC, Barry JJ, Aguilar TU, et al. Prior lumbar spinal arthrodesis increases risk of prosthetic-related complication in total hip arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2016;31:227-232.e1. doi:10.1016/j.arth.2016.02.069
- King CA, Landy DC, Martell JM, et al. Time to dislocation analysis of lumbar spine fusion following total hip arthroplasty: breaking up a happy home. J Arthroplasty. 2018;33:3768-3772. doi:10.1016/j.arth.2018.08.029
- Buckland AJ, Puvanesarajah V, Vigdorchik J, et al. Dislocation of a primary total hip arthroplasty is more common in patients with a lumbar spinal fusion. Bone Joint J. 2017;99-B:585-591.doi:10.1302/0301-620X.99B5.BJJ-2016-0657.R1
- Pirruccio K, Premkumar A, Sheth NP. The burden of prosthetic hip dislocations in the United States is projected to significantly increase by 2035. Hip Int. 2021;31:714-721. doi:10.1177/1120700020923619
- Salib CG, Reina N, Perry KI, et al. Lumbar fusion involving the sacrum increases dislocation risk in primary total hip arthroplasty. Bone Joint J. 2019;101-B:198-206. doi:10.1302/0301-620X.101B2.BJJ-2018-0754.R1
- An VVG, Phan K, Sivakumar BS, et al. Prior lumbar spinal fusion is associated with an increased risk of dislocation and revision in total hip arthroplasty: a meta-analysis. J Arthroplasty. 2018;33:297-300. doi:10.1016/j.arth.2017.08.040
- Klemt C, Padmanabha A, Tirumala V, et al. Lumbar spine fusion before revision total hip arthroplasty is associated with increased dislocation rates. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2021;29:e860-e868. doi:10.5435/JAAOS-D-20-00824
- Gausden EB, Parhar HS, Popper JE, et al. Risk factors for early dislocation following primary elective total hip arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2018;33:1567-1571. doi:10.1016/j.arth.2017.12.034
- Malkani AL, Himschoot KJ, Ong KL, et al. Does timing of primary total hip arthroplasty prior to or after lumbar spine fusion have an effect on dislocation and revision rates?. J Arthroplasty. 2019;34:907-911. doi:10.1016/j.arth.2019.01.009
- Parilla FW, Shah RR, Gordon AC, et al. Does it matter: total hip arthroplasty or lumbar spinal fusion first? Preoperative sagittal spinopelvic measurements guide patient-specific surgical strategies in patients requiring both. J Arthroplasty. 2019;34:2652-2662. doi:10.1016/j.arth.2019.05.053
- Chalmers BP, Syku M, Sculco TP, et al. Dual-mobility constructs in primary total hip arthroplasty in high-risk patients with spinal fusions: our institutional experience. Arthroplast Today. 2020;6:749-754. doi:10.1016/j.artd.2020.07.024
- Nessler JM, Malkani AL, Sachdeva S, et al. Use of dual mobility cups in patients undergoing primary total hip arthroplasty with prior lumbar spine fusion. Int Orthop. 2020;44:857-862. doi:10.1007/s00264-020-04507-y
- Nessler JM, Malkani AL, Yep PJ, et al. Dislocation rates of primary total hip arthroplasty in patients with prior lumbar spine fusion and lumbar degenerative disk disease with and without utilization of dual mobility cups: an American Joint Replacement Registry study. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2023;31:e271-e277. doi:10.5435/JAAOS-D-22-00767
- Phan D, Bederman SS, Schwarzkopf R. The influence of sagittal spinal deformity on anteversion of the acetabular component in total hip arthroplasty. Bone Joint J. 2015;97-B:1017-1023. doi:10.1302/0301-620X.97B8.35700
- Agha Z, Lofgren RP, VanRuiswyk JV, et al. Are patients at Veterans Affairs medical centers sicker? A comparative analysis of health status and medical resource use. Arch Intern Med. 2000;160:3252-3257. doi:10.1001/archinte.160.21.325223.
- Basques BA, Bell JA, Fillingham YA, et al. Gender differences for hip and knee arthroplasty: complications and healthcare utilization. J Arthroplasty. 2019;34:1593-1597.e1. doi:10.1016/j.arth.2019.03.064
- Kim YH, Choi Y, Kim JS. Influence of patient-, design-, and surgery-related factors on rate of dislocation after primary cementless total hip arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2009;24:1258-1263. doi:10.1016/j.arth.2009.03.017
- Chen A, Paxton L, Zheng X, et al. Association of sex with risk of 2-year revision among patients undergoing total hip arthroplasty. JAMA Netw Open. 2021;4:e2110687. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.10687
- Inacio MCS, Ake CF, Paxton EW, et al. Sex and risk of hip implant failure: assessing total hip arthroplasty outcomes in the United States. JAMA Intern Med. 2013;173:435-441. doi:10.1001/jamainternmed.2013.3271
- Karlson EW, Daltroy LH, Liang MH, et al. Gender differences in patient preferences may underlie differential utilization of elective surgery. Am J Med. 1997;102:524-530. doi:10.1016/s0002-9343(97)00050-8
- Kostamo T, Bourne RB, Whittaker JP, et al. No difference in gender-specific hip replacement outcomes. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2009;467:135-140. doi:10.1007/s11999-008-0466-2
- Papagelopoulos PJ, Idusuyi OB, Wallrichs SL, et al. Long term outcome and survivorship analysis of primary total knee arthroplasty in patients with diabetes mellitus. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1996;(330):124-132. doi:10.1097/00003086-199609000-00015
- Fitzgerald RH Jr, Nolan DR, Ilstrup DM, et al. Deep wound sepsis following total hip arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1977;59:847-855.
- Blom AW, Brown J, Taylor AH, et al. Infection after total knee arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2004;86:688-691. doi:10.1302/0301-620x.86b5.14887
- Jain NB, Guller U, Pietrobon R, et al. Comorbidities increase complication rates in patients having arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2005;435:232-238. doi:10.1097/01.blo.0000156479.97488.a2
- Docter S, Philpott HT, Godkin L, et al. Comparison of intra and post-operative complication rates among surgical approaches in Total Hip Arthroplasty: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J Orthop. 2020;20:310-325. doi:10.1016/j.jor.2020.05.008
- Huebschmann NA, Lawrence KW, Robin JX, et al. Does surgical approach affect dislocation rate after total hip arthroplasty in patients who have prior lumbar spinal fusion? A retrospective analysis of 16,223 cases. J Arthroplasty. 2024;39:S306-S313. doi:10.1016/j.arth.2024.03.068
- Sloan M, Premkumar A, Sheth NP. Projected volume of primary total joint arthroplasty in the U.S., 2014 to 2030. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2018;100:1455-1460. doi:10.2106/JBJS.17.01617
- Bozic KJ, Kurtz SM, Lau E, et al. The epidemiology of revision total hip arthroplasty in the United States. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2009;91:128-133. doi:10.2106/JBJS.H.00155
- Kurtz SM, Ong KL, Schmier J, et al. Future clinical and economic impact of revision total hip and knee arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2007;89:144-151. doi:10.2106/JBJS.G.00587
- Kurtz SM, Ong KL, Schmier J, et al. Primary and revision arthroplasty surgery caseloads in the United States from 1990 to 2004. J Arthroplasty. 2009;24:195-203. doi:10.1016/j.arth.2007.11.015
- Yamato Y, Furuhashi H, Hasegawa T, et al. Simulation of implant impingement after spinal corrective fusion surgery in patients with previous total hip arthroplasty: a retrospective case series. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2021;46:512-519. doi:10.1097/BRS.0000000000003836
- Mudrick CA, Melvin JS, Springer BD. Late posterior hip instability after lumbar spinopelvic fusion. Arthroplast Today. 2015;1:25-29. doi:10.1016/j.artd.2015.05.002
- Diebo BG, Beyer GA, Grieco PW, et al. Complications in patients undergoing spinal fusion after THA. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2018;476:412-417.doi:10.1007/s11999.0000000000000009 8.
- Sing DC, Barry JJ, Aguilar TU, et al. Prior lumbar spinal arthrodesis increases risk of prosthetic-related complication in total hip arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2016;31:227-232.e1. doi:10.1016/j.arth.2016.02.069
- King CA, Landy DC, Martell JM, et al. Time to dislocation analysis of lumbar spine fusion following total hip arthroplasty: breaking up a happy home. J Arthroplasty. 2018;33:3768-3772. doi:10.1016/j.arth.2018.08.029
- Buckland AJ, Puvanesarajah V, Vigdorchik J, et al. Dislocation of a primary total hip arthroplasty is more common in patients with a lumbar spinal fusion. Bone Joint J. 2017;99-B:585-591.doi:10.1302/0301-620X.99B5.BJJ-2016-0657.R1
- Pirruccio K, Premkumar A, Sheth NP. The burden of prosthetic hip dislocations in the United States is projected to significantly increase by 2035. Hip Int. 2021;31:714-721. doi:10.1177/1120700020923619
- Salib CG, Reina N, Perry KI, et al. Lumbar fusion involving the sacrum increases dislocation risk in primary total hip arthroplasty. Bone Joint J. 2019;101-B:198-206. doi:10.1302/0301-620X.101B2.BJJ-2018-0754.R1
- An VVG, Phan K, Sivakumar BS, et al. Prior lumbar spinal fusion is associated with an increased risk of dislocation and revision in total hip arthroplasty: a meta-analysis. J Arthroplasty. 2018;33:297-300. doi:10.1016/j.arth.2017.08.040
- Klemt C, Padmanabha A, Tirumala V, et al. Lumbar spine fusion before revision total hip arthroplasty is associated with increased dislocation rates. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2021;29:e860-e868. doi:10.5435/JAAOS-D-20-00824
- Gausden EB, Parhar HS, Popper JE, et al. Risk factors for early dislocation following primary elective total hip arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2018;33:1567-1571. doi:10.1016/j.arth.2017.12.034
- Malkani AL, Himschoot KJ, Ong KL, et al. Does timing of primary total hip arthroplasty prior to or after lumbar spine fusion have an effect on dislocation and revision rates?. J Arthroplasty. 2019;34:907-911. doi:10.1016/j.arth.2019.01.009
- Parilla FW, Shah RR, Gordon AC, et al. Does it matter: total hip arthroplasty or lumbar spinal fusion first? Preoperative sagittal spinopelvic measurements guide patient-specific surgical strategies in patients requiring both. J Arthroplasty. 2019;34:2652-2662. doi:10.1016/j.arth.2019.05.053
- Chalmers BP, Syku M, Sculco TP, et al. Dual-mobility constructs in primary total hip arthroplasty in high-risk patients with spinal fusions: our institutional experience. Arthroplast Today. 2020;6:749-754. doi:10.1016/j.artd.2020.07.024
- Nessler JM, Malkani AL, Sachdeva S, et al. Use of dual mobility cups in patients undergoing primary total hip arthroplasty with prior lumbar spine fusion. Int Orthop. 2020;44:857-862. doi:10.1007/s00264-020-04507-y
- Nessler JM, Malkani AL, Yep PJ, et al. Dislocation rates of primary total hip arthroplasty in patients with prior lumbar spine fusion and lumbar degenerative disk disease with and without utilization of dual mobility cups: an American Joint Replacement Registry study. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2023;31:e271-e277. doi:10.5435/JAAOS-D-22-00767
- Phan D, Bederman SS, Schwarzkopf R. The influence of sagittal spinal deformity on anteversion of the acetabular component in total hip arthroplasty. Bone Joint J. 2015;97-B:1017-1023. doi:10.1302/0301-620X.97B8.35700
- Agha Z, Lofgren RP, VanRuiswyk JV, et al. Are patients at Veterans Affairs medical centers sicker? A comparative analysis of health status and medical resource use. Arch Intern Med. 2000;160:3252-3257. doi:10.1001/archinte.160.21.325223.
- Basques BA, Bell JA, Fillingham YA, et al. Gender differences for hip and knee arthroplasty: complications and healthcare utilization. J Arthroplasty. 2019;34:1593-1597.e1. doi:10.1016/j.arth.2019.03.064
- Kim YH, Choi Y, Kim JS. Influence of patient-, design-, and surgery-related factors on rate of dislocation after primary cementless total hip arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2009;24:1258-1263. doi:10.1016/j.arth.2009.03.017
- Chen A, Paxton L, Zheng X, et al. Association of sex with risk of 2-year revision among patients undergoing total hip arthroplasty. JAMA Netw Open. 2021;4:e2110687. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.10687
- Inacio MCS, Ake CF, Paxton EW, et al. Sex and risk of hip implant failure: assessing total hip arthroplasty outcomes in the United States. JAMA Intern Med. 2013;173:435-441. doi:10.1001/jamainternmed.2013.3271
- Karlson EW, Daltroy LH, Liang MH, et al. Gender differences in patient preferences may underlie differential utilization of elective surgery. Am J Med. 1997;102:524-530. doi:10.1016/s0002-9343(97)00050-8
- Kostamo T, Bourne RB, Whittaker JP, et al. No difference in gender-specific hip replacement outcomes. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2009;467:135-140. doi:10.1007/s11999-008-0466-2
- Papagelopoulos PJ, Idusuyi OB, Wallrichs SL, et al. Long term outcome and survivorship analysis of primary total knee arthroplasty in patients with diabetes mellitus. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1996;(330):124-132. doi:10.1097/00003086-199609000-00015
- Fitzgerald RH Jr, Nolan DR, Ilstrup DM, et al. Deep wound sepsis following total hip arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1977;59:847-855.
- Blom AW, Brown J, Taylor AH, et al. Infection after total knee arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2004;86:688-691. doi:10.1302/0301-620x.86b5.14887
- Jain NB, Guller U, Pietrobon R, et al. Comorbidities increase complication rates in patients having arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2005;435:232-238. doi:10.1097/01.blo.0000156479.97488.a2
- Docter S, Philpott HT, Godkin L, et al. Comparison of intra and post-operative complication rates among surgical approaches in Total Hip Arthroplasty: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J Orthop. 2020;20:310-325. doi:10.1016/j.jor.2020.05.008
- Huebschmann NA, Lawrence KW, Robin JX, et al. Does surgical approach affect dislocation rate after total hip arthroplasty in patients who have prior lumbar spinal fusion? A retrospective analysis of 16,223 cases. J Arthroplasty. 2024;39:S306-S313. doi:10.1016/j.arth.2024.03.068
Effects of Lumbar Fusion and Dual-Mobility Liners on Dislocation Rates Following Total Hip Arthroplasty in a Veteran Population
Effects of Lumbar Fusion and Dual-Mobility Liners on Dislocation Rates Following Total Hip Arthroplasty in a Veteran Population