User login
2018 Update on abnormal uterine bleeding
Over the past year, a few gems have been published to help us manage and treat abnormal uterine bleeding (AUB). One study suggests an order of performing hysteroscopy and endometrial biopsy, another emphasizes the continued cost-effectiveness of the levonorgestrel-releasing intrauterine system (LNG-IUS), while a third provides more evidence that ulipristal acetate is effective in the management of leiomyomas.
Optimal order of office hysteroscopy and endometrial biopsy?
Sarkar P, Mikhail E, Schickler R, Plosker S, Imudia AN. Optimal order of successive office hysteroscopy and endometrial biopsy for the evaluation of abnormal uterine bleeding: a randomized controlled trial. Obstet Gynecol. 2017;130(3):565-572.
Office hysteroscopy and endometrial biopsy are frequently used in the evaluation of women presenting with AUB. Sarkar and colleagues conducted a study aimed at estimating the optimal order of office hysteroscopy and endometrial biopsy when performed successively among premenopausal women.
Pain perception, procedure duration, and other outcomes
This prospective single-blind randomized trial included 78 consecutive patients. The primary outcome was detection of any difference in patients' global pain perception based on the order of the procedures. Secondary outcome measures included determining whether the procedure order affected the duration of the procedures, the adequacy of the endometrial biopsy sample, the number of attempts to obtain an adequate tissue sample, and optimal visualization of the endometrial cavity during office hysteroscopy.
Order not important, but other factors may be
Not surprisingly, the results showed that the order in which the procedures were performed had no effect on patients' pain perception or on the overall procedure duration. Assessed using a visual analog scale scored from 1 to 10, global pain perception in the hysteroscopy-first patients (group A, n = 40) compared with the biopsy-first patients (group B, n = 38) was similar (7 vs 7, P = .57; 95% confidence interval [CI], 5.8-7.1). Procedure duration also was similar in group A and group B (3 vs 3, P = .32; 95% CI, 3.3-4.1).
However, when hysteroscopy was performed first, the quality of endometrial cavity images was superior compared with images from patients in whom biopsy was performed first. The number of endometrial biopsy curette passes required to obtain an adequate tissue sample was lower in the biopsy-first patients. The endometrial biopsy specimen was adequate for histologic evaluation regardless of whether hysteroscopy or biopsy was performed first.
Sarkar and colleagues suggested that their study findings emphasize the importance of individualizing the order of successive procedures to achieve the most clinically relevant result with maximum ease and comfort. They proposed that patients who have a high index of suspicion for occult malignancy or endometrial hyperplasia should have a biopsy procedure first so that adequate tissue samples can be obtained with fewer attempts. In patients with underlying uterine anatomic defects, performing hysteroscopy first would be clinically relevant to obtain the best images for optimal surgical planning.
Read next: Which treatment for AUB is most cost-effective?
Which treatment for AUB is most cost-effective?
Spencer JC, Louie M, Moulder JK, et al. Cost-effectiveness of treatments for heavy menstrual bleeding. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2017;217(5):574.e1-574e.9.
The costs associated with heavy menstrual bleeding are significant. Spencer and colleagues sought to evaluate the relative cost-effectiveness of 4 treatment options for heavy menstrual bleeding: hysterectomy, resectoscopic endometrial ablation, nonresectoscopic endometrial ablation, and the LNG-IUS in a hypothetical cohort of 100,000 premenopausal women. No previous studies have examined the cost-effectiveness of these options in the context of the US health care setting.
Decision tree used for analysis
The authors formulated a decision tree to evaluate private payer costs and quality-adjusted life-years over a 5-year time horizon for premenopausal women with heavy menstrual bleeding and no suspected malignancy. For each treatment option, the authors used probabilities to estimate frequencies of complications and treatment failure leading to additional therapies. They compared the treatments in terms of total average costs, quality-adjusted life years, and incremental cost-effectiveness ratios.
Comparing costs, quality of life, and complications
Quality of life was fairly high for all treatment options; however, the estimated costs and the complications of each treatment were markedly different between treatment options. The LNG-IUS was superior to all alternatives in terms of both cost and quality, making it the dominant strategy. The 5-year cost for the LNG-IUS was $4,500, about half the cost of endometrial ablation ($9,500) and about one-third the cost of hysterectomy ($13,500). When examined over a range of possible values, the LNG-IUS was cost-effective compared with hysterectomy in the large majority of scenarios (90%).
If the LNG-IUS is removed from consideration because of either patient preference or clinical judgment, the decision between hysterectomy and ablation is more complex. Hysterectomy results in better quality of life in the majority of simulations, but it is cost-effective in just more than half of the simulations compared with either resectoscopic or nonresectoscopic ablation. Therefore, consideration of cost, procedure-specific complications, and patient preferences may guide the therapeutic decision between hysterectomy and endometrial ablation.
The 52-mg LNG-IUS was superior to all treatment alternatives in both cost and quality, making it the dominant strategy for the treatment of heavy menstrual bleeding.
Ulipristal may be useful for managing AUB associated with uterine leiomyomas
Simon JA, Catherino W, Segars JH, et al. Ulipristal acetate for treatment of symptomatic uterine leiomyomas: a randomized controlled trial. Obstet Gynecol. 2018;131(3):431-439.
Managing uterine leiomyomas is a common issue for gynecologists, as up to 70% of white women and more than 80% of black women of reproductive age in the United States have leiomyomas.
Ulipristal acetate is an orally administered selective progesterone-receptor modulator that decreases bleeding and reduces leiomyoma size. Although trials conducted in Europe found ulipristal to be superior to placebo and noninferior to leuprolide acetate in controlling bleeding and reducing leiomyoma size, those initial trials were conducted in a predominantly white population.
Study assessed efficacy and safety
Simon and colleagues recently conducted a randomized double-blind, placebo-controlled trial designed to assess the safety and efficacy of ulipristal in a more diverse population, such as patients in the United States. The 148 participants included in the study were randomly assigned on a 1:1:1 basis to once-daily oral ulipristal 5 mg, ulipristal 10 mg, or placebo for 12 weeks, with a 12-week drug-free follow-up.
Amenorrhea achieved and quality of life improved
The investigators found that ulipristal in 5-mg and 10-mg doses was well tolerated and superior to placebo in both the rate of and the time to amenorrhea (the coprimary end points) in women with symptomatic leiomyomas. In women treated with ulipristal 5 mg, amenorrhea was achieved in 25 of 53 (47.2%; 97.5% CI, 31.6-63.2), and of those treated with the 10-mg dose, 28 of 48 (58.3%; 97.5% CI, 41.2-74.1) achieved amenorrhea (P<.001 for both groups), compared with 1 of 56 (1.8%; 97.5% CI, 0.0-10.9) in the placebo group.
AUB continues to be a significant issue for many women. As women's health care providers, it is important that we deliver care with high value (Quality ÷ Cost). Therefore, consider these takeaway points:
- The LNG-IUS consistently delivers high value by affecting both sides of this equation. We should use it more.
- Although we do not yet know what ulipristal acetate will cost in the United States, effective medical treatments usually affect both sides of the Quality ÷ Cost equation, and new medications on the horizon are worth knowing about.
- Last, efficiency with office-based hysteroscopy is also an opportunity to increase value by improving biopsy and visualization quality.
Ulipristal treatment also was shown to improve health-related quality of life, including physical and social activities. No patient discontinued ulipristal because of lack of efficacy, and 1 patient in the placebo group stopped taking the drug because of an adverse event. Estradiol levels were maintained at midfollicular levels during ulipristal treatment, and endometrial biopsies did not show any atypical or malignant changes. These results are consistent with those of the studies conducted in Europe in a predominantly white, nonobese population.
Results of this study help to define a niche for ulipristal when hysterectomy is not an option for women who wish to preserve fertility. Further, although leuprolide is used for preoperative hematologic improvement of anemia, its use results in hypoestrogenic adverse effects.
The findings from this and other studies suggest that ulipristal may be useful for the medical management of AUB associated with uterine leiomyomas, especially for patients desiring uterine- and fertility-sparing treatment. Hopefully, this treatment will be available soon in the United States.
Share your thoughts! Send your Letter to the Editor to rbarbieri@mdedge.com. Please include your name and the city and state in which you practice.
Over the past year, a few gems have been published to help us manage and treat abnormal uterine bleeding (AUB). One study suggests an order of performing hysteroscopy and endometrial biopsy, another emphasizes the continued cost-effectiveness of the levonorgestrel-releasing intrauterine system (LNG-IUS), while a third provides more evidence that ulipristal acetate is effective in the management of leiomyomas.
Optimal order of office hysteroscopy and endometrial biopsy?
Sarkar P, Mikhail E, Schickler R, Plosker S, Imudia AN. Optimal order of successive office hysteroscopy and endometrial biopsy for the evaluation of abnormal uterine bleeding: a randomized controlled trial. Obstet Gynecol. 2017;130(3):565-572.
Office hysteroscopy and endometrial biopsy are frequently used in the evaluation of women presenting with AUB. Sarkar and colleagues conducted a study aimed at estimating the optimal order of office hysteroscopy and endometrial biopsy when performed successively among premenopausal women.
Pain perception, procedure duration, and other outcomes
This prospective single-blind randomized trial included 78 consecutive patients. The primary outcome was detection of any difference in patients' global pain perception based on the order of the procedures. Secondary outcome measures included determining whether the procedure order affected the duration of the procedures, the adequacy of the endometrial biopsy sample, the number of attempts to obtain an adequate tissue sample, and optimal visualization of the endometrial cavity during office hysteroscopy.
Order not important, but other factors may be
Not surprisingly, the results showed that the order in which the procedures were performed had no effect on patients' pain perception or on the overall procedure duration. Assessed using a visual analog scale scored from 1 to 10, global pain perception in the hysteroscopy-first patients (group A, n = 40) compared with the biopsy-first patients (group B, n = 38) was similar (7 vs 7, P = .57; 95% confidence interval [CI], 5.8-7.1). Procedure duration also was similar in group A and group B (3 vs 3, P = .32; 95% CI, 3.3-4.1).
However, when hysteroscopy was performed first, the quality of endometrial cavity images was superior compared with images from patients in whom biopsy was performed first. The number of endometrial biopsy curette passes required to obtain an adequate tissue sample was lower in the biopsy-first patients. The endometrial biopsy specimen was adequate for histologic evaluation regardless of whether hysteroscopy or biopsy was performed first.
Sarkar and colleagues suggested that their study findings emphasize the importance of individualizing the order of successive procedures to achieve the most clinically relevant result with maximum ease and comfort. They proposed that patients who have a high index of suspicion for occult malignancy or endometrial hyperplasia should have a biopsy procedure first so that adequate tissue samples can be obtained with fewer attempts. In patients with underlying uterine anatomic defects, performing hysteroscopy first would be clinically relevant to obtain the best images for optimal surgical planning.
Read next: Which treatment for AUB is most cost-effective?
Which treatment for AUB is most cost-effective?
Spencer JC, Louie M, Moulder JK, et al. Cost-effectiveness of treatments for heavy menstrual bleeding. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2017;217(5):574.e1-574e.9.
The costs associated with heavy menstrual bleeding are significant. Spencer and colleagues sought to evaluate the relative cost-effectiveness of 4 treatment options for heavy menstrual bleeding: hysterectomy, resectoscopic endometrial ablation, nonresectoscopic endometrial ablation, and the LNG-IUS in a hypothetical cohort of 100,000 premenopausal women. No previous studies have examined the cost-effectiveness of these options in the context of the US health care setting.
Decision tree used for analysis
The authors formulated a decision tree to evaluate private payer costs and quality-adjusted life-years over a 5-year time horizon for premenopausal women with heavy menstrual bleeding and no suspected malignancy. For each treatment option, the authors used probabilities to estimate frequencies of complications and treatment failure leading to additional therapies. They compared the treatments in terms of total average costs, quality-adjusted life years, and incremental cost-effectiveness ratios.
Comparing costs, quality of life, and complications
Quality of life was fairly high for all treatment options; however, the estimated costs and the complications of each treatment were markedly different between treatment options. The LNG-IUS was superior to all alternatives in terms of both cost and quality, making it the dominant strategy. The 5-year cost for the LNG-IUS was $4,500, about half the cost of endometrial ablation ($9,500) and about one-third the cost of hysterectomy ($13,500). When examined over a range of possible values, the LNG-IUS was cost-effective compared with hysterectomy in the large majority of scenarios (90%).
If the LNG-IUS is removed from consideration because of either patient preference or clinical judgment, the decision between hysterectomy and ablation is more complex. Hysterectomy results in better quality of life in the majority of simulations, but it is cost-effective in just more than half of the simulations compared with either resectoscopic or nonresectoscopic ablation. Therefore, consideration of cost, procedure-specific complications, and patient preferences may guide the therapeutic decision between hysterectomy and endometrial ablation.
The 52-mg LNG-IUS was superior to all treatment alternatives in both cost and quality, making it the dominant strategy for the treatment of heavy menstrual bleeding.
Ulipristal may be useful for managing AUB associated with uterine leiomyomas
Simon JA, Catherino W, Segars JH, et al. Ulipristal acetate for treatment of symptomatic uterine leiomyomas: a randomized controlled trial. Obstet Gynecol. 2018;131(3):431-439.
Managing uterine leiomyomas is a common issue for gynecologists, as up to 70% of white women and more than 80% of black women of reproductive age in the United States have leiomyomas.
Ulipristal acetate is an orally administered selective progesterone-receptor modulator that decreases bleeding and reduces leiomyoma size. Although trials conducted in Europe found ulipristal to be superior to placebo and noninferior to leuprolide acetate in controlling bleeding and reducing leiomyoma size, those initial trials were conducted in a predominantly white population.
Study assessed efficacy and safety
Simon and colleagues recently conducted a randomized double-blind, placebo-controlled trial designed to assess the safety and efficacy of ulipristal in a more diverse population, such as patients in the United States. The 148 participants included in the study were randomly assigned on a 1:1:1 basis to once-daily oral ulipristal 5 mg, ulipristal 10 mg, or placebo for 12 weeks, with a 12-week drug-free follow-up.
Amenorrhea achieved and quality of life improved
The investigators found that ulipristal in 5-mg and 10-mg doses was well tolerated and superior to placebo in both the rate of and the time to amenorrhea (the coprimary end points) in women with symptomatic leiomyomas. In women treated with ulipristal 5 mg, amenorrhea was achieved in 25 of 53 (47.2%; 97.5% CI, 31.6-63.2), and of those treated with the 10-mg dose, 28 of 48 (58.3%; 97.5% CI, 41.2-74.1) achieved amenorrhea (P<.001 for both groups), compared with 1 of 56 (1.8%; 97.5% CI, 0.0-10.9) in the placebo group.
AUB continues to be a significant issue for many women. As women's health care providers, it is important that we deliver care with high value (Quality ÷ Cost). Therefore, consider these takeaway points:
- The LNG-IUS consistently delivers high value by affecting both sides of this equation. We should use it more.
- Although we do not yet know what ulipristal acetate will cost in the United States, effective medical treatments usually affect both sides of the Quality ÷ Cost equation, and new medications on the horizon are worth knowing about.
- Last, efficiency with office-based hysteroscopy is also an opportunity to increase value by improving biopsy and visualization quality.
Ulipristal treatment also was shown to improve health-related quality of life, including physical and social activities. No patient discontinued ulipristal because of lack of efficacy, and 1 patient in the placebo group stopped taking the drug because of an adverse event. Estradiol levels were maintained at midfollicular levels during ulipristal treatment, and endometrial biopsies did not show any atypical or malignant changes. These results are consistent with those of the studies conducted in Europe in a predominantly white, nonobese population.
Results of this study help to define a niche for ulipristal when hysterectomy is not an option for women who wish to preserve fertility. Further, although leuprolide is used for preoperative hematologic improvement of anemia, its use results in hypoestrogenic adverse effects.
The findings from this and other studies suggest that ulipristal may be useful for the medical management of AUB associated with uterine leiomyomas, especially for patients desiring uterine- and fertility-sparing treatment. Hopefully, this treatment will be available soon in the United States.
Share your thoughts! Send your Letter to the Editor to rbarbieri@mdedge.com. Please include your name and the city and state in which you practice.
Over the past year, a few gems have been published to help us manage and treat abnormal uterine bleeding (AUB). One study suggests an order of performing hysteroscopy and endometrial biopsy, another emphasizes the continued cost-effectiveness of the levonorgestrel-releasing intrauterine system (LNG-IUS), while a third provides more evidence that ulipristal acetate is effective in the management of leiomyomas.
Optimal order of office hysteroscopy and endometrial biopsy?
Sarkar P, Mikhail E, Schickler R, Plosker S, Imudia AN. Optimal order of successive office hysteroscopy and endometrial biopsy for the evaluation of abnormal uterine bleeding: a randomized controlled trial. Obstet Gynecol. 2017;130(3):565-572.
Office hysteroscopy and endometrial biopsy are frequently used in the evaluation of women presenting with AUB. Sarkar and colleagues conducted a study aimed at estimating the optimal order of office hysteroscopy and endometrial biopsy when performed successively among premenopausal women.
Pain perception, procedure duration, and other outcomes
This prospective single-blind randomized trial included 78 consecutive patients. The primary outcome was detection of any difference in patients' global pain perception based on the order of the procedures. Secondary outcome measures included determining whether the procedure order affected the duration of the procedures, the adequacy of the endometrial biopsy sample, the number of attempts to obtain an adequate tissue sample, and optimal visualization of the endometrial cavity during office hysteroscopy.
Order not important, but other factors may be
Not surprisingly, the results showed that the order in which the procedures were performed had no effect on patients' pain perception or on the overall procedure duration. Assessed using a visual analog scale scored from 1 to 10, global pain perception in the hysteroscopy-first patients (group A, n = 40) compared with the biopsy-first patients (group B, n = 38) was similar (7 vs 7, P = .57; 95% confidence interval [CI], 5.8-7.1). Procedure duration also was similar in group A and group B (3 vs 3, P = .32; 95% CI, 3.3-4.1).
However, when hysteroscopy was performed first, the quality of endometrial cavity images was superior compared with images from patients in whom biopsy was performed first. The number of endometrial biopsy curette passes required to obtain an adequate tissue sample was lower in the biopsy-first patients. The endometrial biopsy specimen was adequate for histologic evaluation regardless of whether hysteroscopy or biopsy was performed first.
Sarkar and colleagues suggested that their study findings emphasize the importance of individualizing the order of successive procedures to achieve the most clinically relevant result with maximum ease and comfort. They proposed that patients who have a high index of suspicion for occult malignancy or endometrial hyperplasia should have a biopsy procedure first so that adequate tissue samples can be obtained with fewer attempts. In patients with underlying uterine anatomic defects, performing hysteroscopy first would be clinically relevant to obtain the best images for optimal surgical planning.
Read next: Which treatment for AUB is most cost-effective?
Which treatment for AUB is most cost-effective?
Spencer JC, Louie M, Moulder JK, et al. Cost-effectiveness of treatments for heavy menstrual bleeding. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2017;217(5):574.e1-574e.9.
The costs associated with heavy menstrual bleeding are significant. Spencer and colleagues sought to evaluate the relative cost-effectiveness of 4 treatment options for heavy menstrual bleeding: hysterectomy, resectoscopic endometrial ablation, nonresectoscopic endometrial ablation, and the LNG-IUS in a hypothetical cohort of 100,000 premenopausal women. No previous studies have examined the cost-effectiveness of these options in the context of the US health care setting.
Decision tree used for analysis
The authors formulated a decision tree to evaluate private payer costs and quality-adjusted life-years over a 5-year time horizon for premenopausal women with heavy menstrual bleeding and no suspected malignancy. For each treatment option, the authors used probabilities to estimate frequencies of complications and treatment failure leading to additional therapies. They compared the treatments in terms of total average costs, quality-adjusted life years, and incremental cost-effectiveness ratios.
Comparing costs, quality of life, and complications
Quality of life was fairly high for all treatment options; however, the estimated costs and the complications of each treatment were markedly different between treatment options. The LNG-IUS was superior to all alternatives in terms of both cost and quality, making it the dominant strategy. The 5-year cost for the LNG-IUS was $4,500, about half the cost of endometrial ablation ($9,500) and about one-third the cost of hysterectomy ($13,500). When examined over a range of possible values, the LNG-IUS was cost-effective compared with hysterectomy in the large majority of scenarios (90%).
If the LNG-IUS is removed from consideration because of either patient preference or clinical judgment, the decision between hysterectomy and ablation is more complex. Hysterectomy results in better quality of life in the majority of simulations, but it is cost-effective in just more than half of the simulations compared with either resectoscopic or nonresectoscopic ablation. Therefore, consideration of cost, procedure-specific complications, and patient preferences may guide the therapeutic decision between hysterectomy and endometrial ablation.
The 52-mg LNG-IUS was superior to all treatment alternatives in both cost and quality, making it the dominant strategy for the treatment of heavy menstrual bleeding.
Ulipristal may be useful for managing AUB associated with uterine leiomyomas
Simon JA, Catherino W, Segars JH, et al. Ulipristal acetate for treatment of symptomatic uterine leiomyomas: a randomized controlled trial. Obstet Gynecol. 2018;131(3):431-439.
Managing uterine leiomyomas is a common issue for gynecologists, as up to 70% of white women and more than 80% of black women of reproductive age in the United States have leiomyomas.
Ulipristal acetate is an orally administered selective progesterone-receptor modulator that decreases bleeding and reduces leiomyoma size. Although trials conducted in Europe found ulipristal to be superior to placebo and noninferior to leuprolide acetate in controlling bleeding and reducing leiomyoma size, those initial trials were conducted in a predominantly white population.
Study assessed efficacy and safety
Simon and colleagues recently conducted a randomized double-blind, placebo-controlled trial designed to assess the safety and efficacy of ulipristal in a more diverse population, such as patients in the United States. The 148 participants included in the study were randomly assigned on a 1:1:1 basis to once-daily oral ulipristal 5 mg, ulipristal 10 mg, or placebo for 12 weeks, with a 12-week drug-free follow-up.
Amenorrhea achieved and quality of life improved
The investigators found that ulipristal in 5-mg and 10-mg doses was well tolerated and superior to placebo in both the rate of and the time to amenorrhea (the coprimary end points) in women with symptomatic leiomyomas. In women treated with ulipristal 5 mg, amenorrhea was achieved in 25 of 53 (47.2%; 97.5% CI, 31.6-63.2), and of those treated with the 10-mg dose, 28 of 48 (58.3%; 97.5% CI, 41.2-74.1) achieved amenorrhea (P<.001 for both groups), compared with 1 of 56 (1.8%; 97.5% CI, 0.0-10.9) in the placebo group.
AUB continues to be a significant issue for many women. As women's health care providers, it is important that we deliver care with high value (Quality ÷ Cost). Therefore, consider these takeaway points:
- The LNG-IUS consistently delivers high value by affecting both sides of this equation. We should use it more.
- Although we do not yet know what ulipristal acetate will cost in the United States, effective medical treatments usually affect both sides of the Quality ÷ Cost equation, and new medications on the horizon are worth knowing about.
- Last, efficiency with office-based hysteroscopy is also an opportunity to increase value by improving biopsy and visualization quality.
Ulipristal treatment also was shown to improve health-related quality of life, including physical and social activities. No patient discontinued ulipristal because of lack of efficacy, and 1 patient in the placebo group stopped taking the drug because of an adverse event. Estradiol levels were maintained at midfollicular levels during ulipristal treatment, and endometrial biopsies did not show any atypical or malignant changes. These results are consistent with those of the studies conducted in Europe in a predominantly white, nonobese population.
Results of this study help to define a niche for ulipristal when hysterectomy is not an option for women who wish to preserve fertility. Further, although leuprolide is used for preoperative hematologic improvement of anemia, its use results in hypoestrogenic adverse effects.
The findings from this and other studies suggest that ulipristal may be useful for the medical management of AUB associated with uterine leiomyomas, especially for patients desiring uterine- and fertility-sparing treatment. Hopefully, this treatment will be available soon in the United States.
Share your thoughts! Send your Letter to the Editor to rbarbieri@mdedge.com. Please include your name and the city and state in which you practice.
Optimize the medical treatment of endometriosis—Use all available medications
CASE Endometriosis pain increases despite hormonal treatment
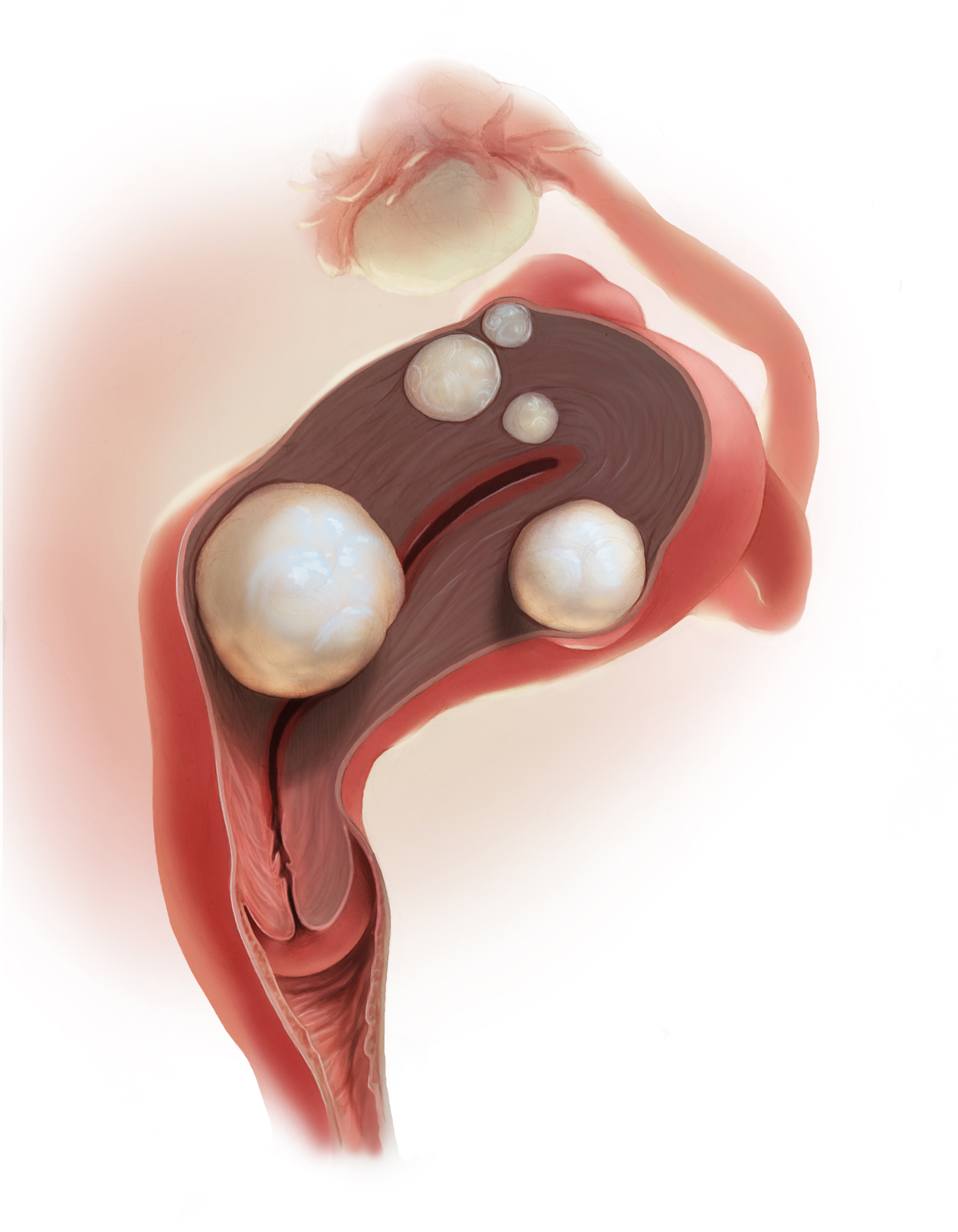
A 25-year-old woman (G0) with severe dysmenorrhea had a laparoscopy showing endometriosis in the cul-de-sac and a peritoneal window near the left uterosacral ligament. Biopsy of a cul-de-sac lesion showed endometriosis on histopathology. The patient was treated with a continuous low-dose estrogen-progestin contraceptive. Initially, the treatment helped relieve her pain symptoms. Over the next year, while on that treatment, her pain gradually increased in severity until it was disabling. At an office visit, the primary clinician renewed the estrogen-progestin contraceptive for another year, even though it was not relieving the patient’s pain. The patient sought a second opinion.
We are the experts in the management of pelvic pain caused by endometriosis
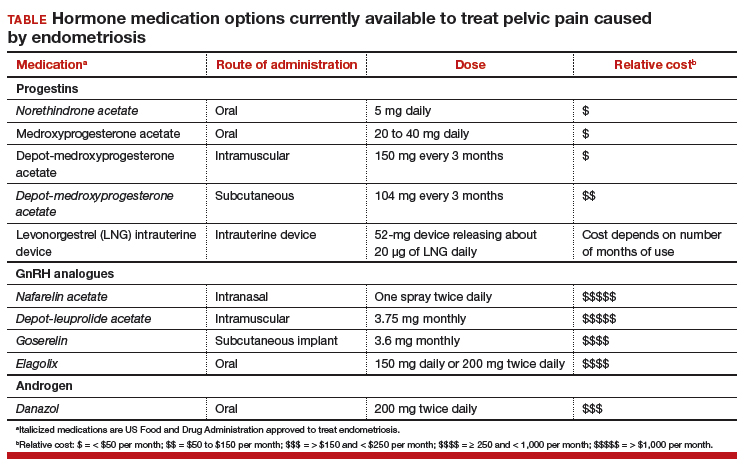
Women’s health clinicians are the specialists best trained to care for patients with severe pain caused by endometriosis. Low-dose continuous estrogen-progestin contraceptives are commonly prescribed as a first-line hormonal treatment for pain caused by endometriosis. My observation is that estrogen-progestincontraceptives are often effective when initially prescribed, but with continued use over years, pain often recurs. Estrogen is known to stimulate endometriosis disease activity. Progestins at high doses suppress endometriosis disease activity. However, endometriosis implants often manifest decreased responsiveness to progestins, permitting the estrogen in the combination contraceptive to exert its disease-stimulating effect.1,2 I frequently see women with pelvic pain caused by endometriosis, who initially had a significant decrease in pain with continuous estrogen-progestin contraceptive treatment but who develop increasing pain with continued use of the medication. In this clinical situation, it is useful to consider stopping the estrogen-progestin therapy and to prescribe a hormone with a different mechanism of action (TABLE).
Progestin-only medications
Progestin-only medications are often effective in the treatment of pain caused by endometriosis. High-dose progestin-only medications suppress pituitary secretion of luteinizing hormone (LH) and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), thereby suppressing ovarian synthesis of estrogen, resulting in low circulating levels of estrogen. This removes the estrogen stimulus that exacerbates endometriosis disease activity. High-dose progestins also directly suppress cellular activity in endometriosis implants. High-dose progestins often overcome the relative resistance of endometriosis lesions to progestin suppression of disease activity. Hence, high-dose progestin-only medications have two mechanisms of action: suppression of estrogen synthesis through pituitary suppression of LH and FSH, and direct inhibition of cellular activity in the endometriosis lesions. High-dose progestin-only treatments include:
- oral norethindrone acetate 5 mg daily
- oral medroxyprogesterone acetate (MPA) 20 to 40 mg daily
- subcutaneous, or depot MPA
- levonorgestrel-releasing intrauterine device (LNG-IUD).
In my practice, I frequently use oral norethindrone acetate 5 mg daily to treat pelvic pain caused by endometriosis. In one randomized trial, 90 women with pelvic pain and rectovaginal endometriosis were randomly assigned to treatment with norethindrone acetate 2.5 mg daily or an estrogen-progestin contraceptive. After 12 months of treatment, satisfaction with treatment was reported by 73% and 62% of the women in the norethindrone acetate and estrogen-progestin groups, respectively.3 The most common adverse effects reported by women taking norethindrone acetate were weight gain (27%) and decreased libido (9%).
Oral MPA at doses of 30 mg to 100 mg daily has been reported to be effective for the treatment of pelvic pain caused by endometriosis. MPA treatment can induce atrophy and pseudodecidualization in endometrium and endometriosis implants. In my practice I typically prescribe doses in the range of 20 mg to 40 mg daily. With oral MPA treatment, continued uterine bleeding may occur in up to 30% of women, somewhat limiting its efficacy.4–7
Subcutaneous and depot MPA have been reported to be effective in the treatment of pelvic pain caused by endometriosis.4,8 In some resource-limited countries, depot MPA may be the most available progestin for the treatment of pelvic pain caused by endometriosis.
The LNG-IUD, inserted after surgery for endometriosis, has been reported to result in decreased pelvic pain in studies with a modest number of participants.9–11
GnRH analogue medications
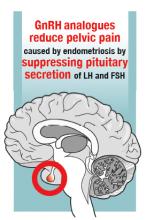
Gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) analogues, including both GnRH agonists (nafarelin, leuprolide, and goserelin) and GnRH antagonists (elagolix) reduce pelvic pain caused by endometriosis by suppressing pituitary secretion of LH and FSH, thereby reducing ovarian synthesis of estradiol. In the absence of estradiol stimulation, cellular activity in endometriosis lesions decreases and pain symptoms improve. In my practice, I frequently use either nafarelin12 or leuprolide acetate depot plus norethindrone add-back.13 I generally avoid the use of leuprolide depot monotherapy because in many women it causes severe vasomotor symptoms.
At standard doses, nafarelin therapy generally results in serum estradiol levels in the range of 20 to 30 pg/mL, a “sweet spot” associated with modest vasomotor symptoms and reduced cellular activity in endometriosis implants.12,14 In many women who become amenorrheic on nafarelin two sprays daily, the dose can be reduced with maintenance of pain control and ovarian suppression.15 Leuprolide acetate depot monotherapy results in serum estradiol levels in the range of 5 to 10 pg/mL, causing severe vasomotor symptoms and reduction in cellular activity in endometriosis lesions. To reduce the adverse effects of leuprolide acetate depot monotherapy, I generally initiate concomitant add-back therapy with norethindrone acetate.13 A little recognized pharmacokinetic observation is that a very small amount of norethindrone acetate, generally less than 1%, is metabolized to ethinyl estradiol.16
The oral GnRH antagonist, elagolix, 150 mg daily for up to 24 months or 200 mg twice daily for 6 months, was approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in July 2018. It is now available in pharmacies. Elagolix treatment results in significant reduction in pain caused by endometriosis, but only moderately bothersome vasomotor symptoms.17,18 Elagolix likely will become a widely used medication because of the simplicity of oral administration, efficacy against endometriosis, and acceptable adverse-effect profile. A major disadvantage of the GnRH analogue-class of medications is that they are more expensive than the progestin medications mentioned above. Among the GnRH analogue class of medications, elagolix and goserelin are the least expensive.
Androgens
Estrogen stimulates cellular activity in endometriosis lesions. Androgen and high-dose progestins inhibit cellular activity in endometriosis lesions. Danazol, an attenuated androgen and a progestin is effectivein treating pelvic pain caused by endometriosis.19,20 However, many women decline to use danazol because it is often associated with weight gain. As an androgen, danazol can permanently change a woman’s voice pitch and should not be used by professional singers or speech therapists.
Aromatase Inhibitors
Estrogen is a critically important stimulus of cell activity in endometriosis lesions. Aromatase inhibitors, which block the synthesis of estrogen, have been explored in the treatment of endometriosis that has proven to be resistant to other therapies. Although the combination of an aromatase inhibitor plus a high-dose progestin or GnRH analogue may be effective, more data are needed before widely using the aromatase inhibitors in clinical practice.21
Don’t get stuck in a rut
When treating pelvic pain caused by endometriosis, if the patient’s hormone regimen is not working, prescribe a medication from another class of hormones. In the case presented above, a woman with pelvic pain and surgically proven endometriosis reported inadequate control of her pain symptoms with a continuous estrogen-progestin medication. Her physician prescribed another year of the same estrogen-progestin medication. Instead of renewing the medication, the physician could have offered the patient a hormone medication from another drug class: 1) progestin only, 2) GnRH analogue, or 3) danazol. By using every available hormonal agent, physicians will improve the treatment of pelvic pain caused by endometriosis. Millions of women in our country have pelvic pain caused by endometriosis. They are counting on us, women’s health specialists, to effectively treat their disease.
Share your thoughts! Send your Letter to the Editor to rbarbieri@mdedge.com. Please include your name and the city and state in which you practice.
- Patel BG, Rudnicki M, Yu J, Shu Y, Taylor RN. Progesterone resistance in endometriosis: origins, consequences and interventions. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand. 2017;96(6):623–632.
- Bulun SE, Cheng YH, Pavone ME, et al. Estrogen receptor-beta, estrogen receptor-alpha, and progesterone resistance in endometriosis. Semin Reprod Med. 2010;28(1):36–43.
- Vercellini P, Pietropaolo G, De Giorgi O, Pasin R, Chiodini A, Crosignani PG. Treatment of symptomatic rectovaginal endometriosis with an estrogen-progestogen combination versus low-dose norethindrone acetate. Fertil Steril. 2005;84(5):1375-1387.
- Brown J, Kives S, Akhtar M. Progestagens and anti-progestagens for pain associated with endometriosis. Cochrane Database of Syst Rev. 2012;(3):CD002122.
- Moghissi KS, Boyce CR. Management of endometriosis with oral medroxyprogesterone acetate. Obstet Gynecol. 1976;47(3):265–267.
- Telimaa S, Puolakka J, Rönnberg L, Kauppila A. Placebo-controlled comparison of danazol and high-dose medroxyprogesterone acetate in the treatment of endometriosis. Gynecol Endocrinol. 1987;1(1):13–23.
- Luciano AA, Turksoy RN, Carleo J. Evaluation of oral medroxyprogesterone acetate in the treatment of endometriosis. Obstet Gynecol. 1988;72(3 pt 1):323–327.
- Schlaff WD, Carson SA, Luciano A, Ross D, Bergqvist A. Subcutaneous injection of depot medroxyprogesterone acetate compared with leu-prolide acetate in the treatment of endometriosis-associated pain. Fertil Steril. 2006;85(2):314–325.
- Abou-Setta AM, Houston B, Al-Inany HG, Farquhar C. Levonorgestrel-releasing intrauterine device (LNG-IUD) for symptomatic endometriosis following surgery. Cochrane Database of Syst Rev. 2013;(1):CD005072.
- Tanmahasamut P, Rattanachaiyanont M, Angsuwathana S, Techatraisak K, Indhavivadhana S, Leerasiri P. Postoperative levonorgestrel-releasing intrauterine system for pelvic endometriosis-pain: a randomized controlled trial. Obstet Gynecol. 2012;119(3):519–526.
- Wong AY, Tang LC, Chin RK. Levonorgestrel-releasing intrauterine system (Mirena) and Depot medroxyprogesterone acetate (Depoprovera) as long-term maintenance therapy for patients with moderate and severe endometriosis: a randomised controlled trial. Aust N Z J Obstet Gynaecol. 2010;50(3):273–279.
- Henzl MR, Corson SL, Moghissi K, Buttram VC, Berqvist C, Jacobsen J. Administration of nasal nafarelin as compared with oral danazol for endo-metriosis. A multicenter double-blind comparative clinical trial. N Engl J Med. 1988;318(8):485–489.
- Hornstein MD, Surrey ES, Weisberg GW, Casino LA. Leuprolide acetate depot and hormonal add-back in endometriosis: a 12-month study. Lupron Add-Back Study Group. Obstet Gynecol. 1998; 91(1):16–24.
- Barbieri RL. Hormone treatment of endometriosis: the estrogen threshold hypothesis. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1992;166(2):740–745.
- Hull ME, Barbieri RL. Nafarelin in the treatment of endometriosis. Dose management. Gynecol Obstet Invest. 1994;37(4):263–264.
- Barbieri RL, Petro Z, Canick JA, Ryan KJ. Aromatization of norethindrone to ethinyl estradiol by human placental microsomes. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1983;57(2):299–303.
- Taylor HS, Giudice LC, Lessey BA, et al. Treatment of endometriosis-associated pain with elagolix, an oral GnRH antagonist. N Engl J Med. 2017;377(1):28–40.
- Surrey E, Taylor HS, Giudice L, et al. Long-term outcomes of elagolix in women with endometriosis: results from two extension studies. Obstet Gynecol. 2018;132(1):147–160.
- Selak V, Farquhar C, Prentice A, Singla A. Danazol for pelvic pain associated with endometriosis. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2007;(4):CD000068.
- Barbieri RL, Ryan KJ. Danazol: endocrine pharmacology and therapeutic applications. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1981;141(4):453–463.
- Dunselman GA, Vermeulen N, Becker C, et al; European Society of Human Reproduction and Embryology. ESHRE guideline: management of women with endometriosis. Hum Reprod. 2014;29(3):400–412.
CASE Endometriosis pain increases despite hormonal treatment
A 25-year-old woman (G0) with severe dysmenorrhea had a laparoscopy showing endometriosis in the cul-de-sac and a peritoneal window near the left uterosacral ligament. Biopsy of a cul-de-sac lesion showed endometriosis on histopathology. The patient was treated with a continuous low-dose estrogen-progestin contraceptive. Initially, the treatment helped relieve her pain symptoms. Over the next year, while on that treatment, her pain gradually increased in severity until it was disabling. At an office visit, the primary clinician renewed the estrogen-progestin contraceptive for another year, even though it was not relieving the patient’s pain. The patient sought a second opinion.
We are the experts in the management of pelvic pain caused by endometriosis
Women’s health clinicians are the specialists best trained to care for patients with severe pain caused by endometriosis. Low-dose continuous estrogen-progestin contraceptives are commonly prescribed as a first-line hormonal treatment for pain caused by endometriosis. My observation is that estrogen-progestincontraceptives are often effective when initially prescribed, but with continued use over years, pain often recurs. Estrogen is known to stimulate endometriosis disease activity. Progestins at high doses suppress endometriosis disease activity. However, endometriosis implants often manifest decreased responsiveness to progestins, permitting the estrogen in the combination contraceptive to exert its disease-stimulating effect.1,2 I frequently see women with pelvic pain caused by endometriosis, who initially had a significant decrease in pain with continuous estrogen-progestin contraceptive treatment but who develop increasing pain with continued use of the medication. In this clinical situation, it is useful to consider stopping the estrogen-progestin therapy and to prescribe a hormone with a different mechanism of action (TABLE).
Progestin-only medications
Progestin-only medications are often effective in the treatment of pain caused by endometriosis. High-dose progestin-only medications suppress pituitary secretion of luteinizing hormone (LH) and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), thereby suppressing ovarian synthesis of estrogen, resulting in low circulating levels of estrogen. This removes the estrogen stimulus that exacerbates endometriosis disease activity. High-dose progestins also directly suppress cellular activity in endometriosis implants. High-dose progestins often overcome the relative resistance of endometriosis lesions to progestin suppression of disease activity. Hence, high-dose progestin-only medications have two mechanisms of action: suppression of estrogen synthesis through pituitary suppression of LH and FSH, and direct inhibition of cellular activity in the endometriosis lesions. High-dose progestin-only treatments include:
- oral norethindrone acetate 5 mg daily
- oral medroxyprogesterone acetate (MPA) 20 to 40 mg daily
- subcutaneous, or depot MPA
- levonorgestrel-releasing intrauterine device (LNG-IUD).
In my practice, I frequently use oral norethindrone acetate 5 mg daily to treat pelvic pain caused by endometriosis. In one randomized trial, 90 women with pelvic pain and rectovaginal endometriosis were randomly assigned to treatment with norethindrone acetate 2.5 mg daily or an estrogen-progestin contraceptive. After 12 months of treatment, satisfaction with treatment was reported by 73% and 62% of the women in the norethindrone acetate and estrogen-progestin groups, respectively.3 The most common adverse effects reported by women taking norethindrone acetate were weight gain (27%) and decreased libido (9%).
Oral MPA at doses of 30 mg to 100 mg daily has been reported to be effective for the treatment of pelvic pain caused by endometriosis. MPA treatment can induce atrophy and pseudodecidualization in endometrium and endometriosis implants. In my practice I typically prescribe doses in the range of 20 mg to 40 mg daily. With oral MPA treatment, continued uterine bleeding may occur in up to 30% of women, somewhat limiting its efficacy.4–7
Subcutaneous and depot MPA have been reported to be effective in the treatment of pelvic pain caused by endometriosis.4,8 In some resource-limited countries, depot MPA may be the most available progestin for the treatment of pelvic pain caused by endometriosis.
The LNG-IUD, inserted after surgery for endometriosis, has been reported to result in decreased pelvic pain in studies with a modest number of participants.9–11
GnRH analogue medications
Gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) analogues, including both GnRH agonists (nafarelin, leuprolide, and goserelin) and GnRH antagonists (elagolix) reduce pelvic pain caused by endometriosis by suppressing pituitary secretion of LH and FSH, thereby reducing ovarian synthesis of estradiol. In the absence of estradiol stimulation, cellular activity in endometriosis lesions decreases and pain symptoms improve. In my practice, I frequently use either nafarelin12 or leuprolide acetate depot plus norethindrone add-back.13 I generally avoid the use of leuprolide depot monotherapy because in many women it causes severe vasomotor symptoms.
At standard doses, nafarelin therapy generally results in serum estradiol levels in the range of 20 to 30 pg/mL, a “sweet spot” associated with modest vasomotor symptoms and reduced cellular activity in endometriosis implants.12,14 In many women who become amenorrheic on nafarelin two sprays daily, the dose can be reduced with maintenance of pain control and ovarian suppression.15 Leuprolide acetate depot monotherapy results in serum estradiol levels in the range of 5 to 10 pg/mL, causing severe vasomotor symptoms and reduction in cellular activity in endometriosis lesions. To reduce the adverse effects of leuprolide acetate depot monotherapy, I generally initiate concomitant add-back therapy with norethindrone acetate.13 A little recognized pharmacokinetic observation is that a very small amount of norethindrone acetate, generally less than 1%, is metabolized to ethinyl estradiol.16
The oral GnRH antagonist, elagolix, 150 mg daily for up to 24 months or 200 mg twice daily for 6 months, was approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in July 2018. It is now available in pharmacies. Elagolix treatment results in significant reduction in pain caused by endometriosis, but only moderately bothersome vasomotor symptoms.17,18 Elagolix likely will become a widely used medication because of the simplicity of oral administration, efficacy against endometriosis, and acceptable adverse-effect profile. A major disadvantage of the GnRH analogue-class of medications is that they are more expensive than the progestin medications mentioned above. Among the GnRH analogue class of medications, elagolix and goserelin are the least expensive.
Androgens
Estrogen stimulates cellular activity in endometriosis lesions. Androgen and high-dose progestins inhibit cellular activity in endometriosis lesions. Danazol, an attenuated androgen and a progestin is effectivein treating pelvic pain caused by endometriosis.19,20 However, many women decline to use danazol because it is often associated with weight gain. As an androgen, danazol can permanently change a woman’s voice pitch and should not be used by professional singers or speech therapists.
Aromatase Inhibitors
Estrogen is a critically important stimulus of cell activity in endometriosis lesions. Aromatase inhibitors, which block the synthesis of estrogen, have been explored in the treatment of endometriosis that has proven to be resistant to other therapies. Although the combination of an aromatase inhibitor plus a high-dose progestin or GnRH analogue may be effective, more data are needed before widely using the aromatase inhibitors in clinical practice.21
Don’t get stuck in a rut
When treating pelvic pain caused by endometriosis, if the patient’s hormone regimen is not working, prescribe a medication from another class of hormones. In the case presented above, a woman with pelvic pain and surgically proven endometriosis reported inadequate control of her pain symptoms with a continuous estrogen-progestin medication. Her physician prescribed another year of the same estrogen-progestin medication. Instead of renewing the medication, the physician could have offered the patient a hormone medication from another drug class: 1) progestin only, 2) GnRH analogue, or 3) danazol. By using every available hormonal agent, physicians will improve the treatment of pelvic pain caused by endometriosis. Millions of women in our country have pelvic pain caused by endometriosis. They are counting on us, women’s health specialists, to effectively treat their disease.
Share your thoughts! Send your Letter to the Editor to rbarbieri@mdedge.com. Please include your name and the city and state in which you practice.
CASE Endometriosis pain increases despite hormonal treatment
A 25-year-old woman (G0) with severe dysmenorrhea had a laparoscopy showing endometriosis in the cul-de-sac and a peritoneal window near the left uterosacral ligament. Biopsy of a cul-de-sac lesion showed endometriosis on histopathology. The patient was treated with a continuous low-dose estrogen-progestin contraceptive. Initially, the treatment helped relieve her pain symptoms. Over the next year, while on that treatment, her pain gradually increased in severity until it was disabling. At an office visit, the primary clinician renewed the estrogen-progestin contraceptive for another year, even though it was not relieving the patient’s pain. The patient sought a second opinion.
We are the experts in the management of pelvic pain caused by endometriosis
Women’s health clinicians are the specialists best trained to care for patients with severe pain caused by endometriosis. Low-dose continuous estrogen-progestin contraceptives are commonly prescribed as a first-line hormonal treatment for pain caused by endometriosis. My observation is that estrogen-progestincontraceptives are often effective when initially prescribed, but with continued use over years, pain often recurs. Estrogen is known to stimulate endometriosis disease activity. Progestins at high doses suppress endometriosis disease activity. However, endometriosis implants often manifest decreased responsiveness to progestins, permitting the estrogen in the combination contraceptive to exert its disease-stimulating effect.1,2 I frequently see women with pelvic pain caused by endometriosis, who initially had a significant decrease in pain with continuous estrogen-progestin contraceptive treatment but who develop increasing pain with continued use of the medication. In this clinical situation, it is useful to consider stopping the estrogen-progestin therapy and to prescribe a hormone with a different mechanism of action (TABLE).
Progestin-only medications
Progestin-only medications are often effective in the treatment of pain caused by endometriosis. High-dose progestin-only medications suppress pituitary secretion of luteinizing hormone (LH) and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), thereby suppressing ovarian synthesis of estrogen, resulting in low circulating levels of estrogen. This removes the estrogen stimulus that exacerbates endometriosis disease activity. High-dose progestins also directly suppress cellular activity in endometriosis implants. High-dose progestins often overcome the relative resistance of endometriosis lesions to progestin suppression of disease activity. Hence, high-dose progestin-only medications have two mechanisms of action: suppression of estrogen synthesis through pituitary suppression of LH and FSH, and direct inhibition of cellular activity in the endometriosis lesions. High-dose progestin-only treatments include:
- oral norethindrone acetate 5 mg daily
- oral medroxyprogesterone acetate (MPA) 20 to 40 mg daily
- subcutaneous, or depot MPA
- levonorgestrel-releasing intrauterine device (LNG-IUD).
In my practice, I frequently use oral norethindrone acetate 5 mg daily to treat pelvic pain caused by endometriosis. In one randomized trial, 90 women with pelvic pain and rectovaginal endometriosis were randomly assigned to treatment with norethindrone acetate 2.5 mg daily or an estrogen-progestin contraceptive. After 12 months of treatment, satisfaction with treatment was reported by 73% and 62% of the women in the norethindrone acetate and estrogen-progestin groups, respectively.3 The most common adverse effects reported by women taking norethindrone acetate were weight gain (27%) and decreased libido (9%).
Oral MPA at doses of 30 mg to 100 mg daily has been reported to be effective for the treatment of pelvic pain caused by endometriosis. MPA treatment can induce atrophy and pseudodecidualization in endometrium and endometriosis implants. In my practice I typically prescribe doses in the range of 20 mg to 40 mg daily. With oral MPA treatment, continued uterine bleeding may occur in up to 30% of women, somewhat limiting its efficacy.4–7
Subcutaneous and depot MPA have been reported to be effective in the treatment of pelvic pain caused by endometriosis.4,8 In some resource-limited countries, depot MPA may be the most available progestin for the treatment of pelvic pain caused by endometriosis.
The LNG-IUD, inserted after surgery for endometriosis, has been reported to result in decreased pelvic pain in studies with a modest number of participants.9–11
GnRH analogue medications
Gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) analogues, including both GnRH agonists (nafarelin, leuprolide, and goserelin) and GnRH antagonists (elagolix) reduce pelvic pain caused by endometriosis by suppressing pituitary secretion of LH and FSH, thereby reducing ovarian synthesis of estradiol. In the absence of estradiol stimulation, cellular activity in endometriosis lesions decreases and pain symptoms improve. In my practice, I frequently use either nafarelin12 or leuprolide acetate depot plus norethindrone add-back.13 I generally avoid the use of leuprolide depot monotherapy because in many women it causes severe vasomotor symptoms.
At standard doses, nafarelin therapy generally results in serum estradiol levels in the range of 20 to 30 pg/mL, a “sweet spot” associated with modest vasomotor symptoms and reduced cellular activity in endometriosis implants.12,14 In many women who become amenorrheic on nafarelin two sprays daily, the dose can be reduced with maintenance of pain control and ovarian suppression.15 Leuprolide acetate depot monotherapy results in serum estradiol levels in the range of 5 to 10 pg/mL, causing severe vasomotor symptoms and reduction in cellular activity in endometriosis lesions. To reduce the adverse effects of leuprolide acetate depot monotherapy, I generally initiate concomitant add-back therapy with norethindrone acetate.13 A little recognized pharmacokinetic observation is that a very small amount of norethindrone acetate, generally less than 1%, is metabolized to ethinyl estradiol.16
The oral GnRH antagonist, elagolix, 150 mg daily for up to 24 months or 200 mg twice daily for 6 months, was approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in July 2018. It is now available in pharmacies. Elagolix treatment results in significant reduction in pain caused by endometriosis, but only moderately bothersome vasomotor symptoms.17,18 Elagolix likely will become a widely used medication because of the simplicity of oral administration, efficacy against endometriosis, and acceptable adverse-effect profile. A major disadvantage of the GnRH analogue-class of medications is that they are more expensive than the progestin medications mentioned above. Among the GnRH analogue class of medications, elagolix and goserelin are the least expensive.
Androgens
Estrogen stimulates cellular activity in endometriosis lesions. Androgen and high-dose progestins inhibit cellular activity in endometriosis lesions. Danazol, an attenuated androgen and a progestin is effectivein treating pelvic pain caused by endometriosis.19,20 However, many women decline to use danazol because it is often associated with weight gain. As an androgen, danazol can permanently change a woman’s voice pitch and should not be used by professional singers or speech therapists.
Aromatase Inhibitors
Estrogen is a critically important stimulus of cell activity in endometriosis lesions. Aromatase inhibitors, which block the synthesis of estrogen, have been explored in the treatment of endometriosis that has proven to be resistant to other therapies. Although the combination of an aromatase inhibitor plus a high-dose progestin or GnRH analogue may be effective, more data are needed before widely using the aromatase inhibitors in clinical practice.21
Don’t get stuck in a rut
When treating pelvic pain caused by endometriosis, if the patient’s hormone regimen is not working, prescribe a medication from another class of hormones. In the case presented above, a woman with pelvic pain and surgically proven endometriosis reported inadequate control of her pain symptoms with a continuous estrogen-progestin medication. Her physician prescribed another year of the same estrogen-progestin medication. Instead of renewing the medication, the physician could have offered the patient a hormone medication from another drug class: 1) progestin only, 2) GnRH analogue, or 3) danazol. By using every available hormonal agent, physicians will improve the treatment of pelvic pain caused by endometriosis. Millions of women in our country have pelvic pain caused by endometriosis. They are counting on us, women’s health specialists, to effectively treat their disease.
Share your thoughts! Send your Letter to the Editor to rbarbieri@mdedge.com. Please include your name and the city and state in which you practice.
- Patel BG, Rudnicki M, Yu J, Shu Y, Taylor RN. Progesterone resistance in endometriosis: origins, consequences and interventions. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand. 2017;96(6):623–632.
- Bulun SE, Cheng YH, Pavone ME, et al. Estrogen receptor-beta, estrogen receptor-alpha, and progesterone resistance in endometriosis. Semin Reprod Med. 2010;28(1):36–43.
- Vercellini P, Pietropaolo G, De Giorgi O, Pasin R, Chiodini A, Crosignani PG. Treatment of symptomatic rectovaginal endometriosis with an estrogen-progestogen combination versus low-dose norethindrone acetate. Fertil Steril. 2005;84(5):1375-1387.
- Brown J, Kives S, Akhtar M. Progestagens and anti-progestagens for pain associated with endometriosis. Cochrane Database of Syst Rev. 2012;(3):CD002122.
- Moghissi KS, Boyce CR. Management of endometriosis with oral medroxyprogesterone acetate. Obstet Gynecol. 1976;47(3):265–267.
- Telimaa S, Puolakka J, Rönnberg L, Kauppila A. Placebo-controlled comparison of danazol and high-dose medroxyprogesterone acetate in the treatment of endometriosis. Gynecol Endocrinol. 1987;1(1):13–23.
- Luciano AA, Turksoy RN, Carleo J. Evaluation of oral medroxyprogesterone acetate in the treatment of endometriosis. Obstet Gynecol. 1988;72(3 pt 1):323–327.
- Schlaff WD, Carson SA, Luciano A, Ross D, Bergqvist A. Subcutaneous injection of depot medroxyprogesterone acetate compared with leu-prolide acetate in the treatment of endometriosis-associated pain. Fertil Steril. 2006;85(2):314–325.
- Abou-Setta AM, Houston B, Al-Inany HG, Farquhar C. Levonorgestrel-releasing intrauterine device (LNG-IUD) for symptomatic endometriosis following surgery. Cochrane Database of Syst Rev. 2013;(1):CD005072.
- Tanmahasamut P, Rattanachaiyanont M, Angsuwathana S, Techatraisak K, Indhavivadhana S, Leerasiri P. Postoperative levonorgestrel-releasing intrauterine system for pelvic endometriosis-pain: a randomized controlled trial. Obstet Gynecol. 2012;119(3):519–526.
- Wong AY, Tang LC, Chin RK. Levonorgestrel-releasing intrauterine system (Mirena) and Depot medroxyprogesterone acetate (Depoprovera) as long-term maintenance therapy for patients with moderate and severe endometriosis: a randomised controlled trial. Aust N Z J Obstet Gynaecol. 2010;50(3):273–279.
- Henzl MR, Corson SL, Moghissi K, Buttram VC, Berqvist C, Jacobsen J. Administration of nasal nafarelin as compared with oral danazol for endo-metriosis. A multicenter double-blind comparative clinical trial. N Engl J Med. 1988;318(8):485–489.
- Hornstein MD, Surrey ES, Weisberg GW, Casino LA. Leuprolide acetate depot and hormonal add-back in endometriosis: a 12-month study. Lupron Add-Back Study Group. Obstet Gynecol. 1998; 91(1):16–24.
- Barbieri RL. Hormone treatment of endometriosis: the estrogen threshold hypothesis. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1992;166(2):740–745.
- Hull ME, Barbieri RL. Nafarelin in the treatment of endometriosis. Dose management. Gynecol Obstet Invest. 1994;37(4):263–264.
- Barbieri RL, Petro Z, Canick JA, Ryan KJ. Aromatization of norethindrone to ethinyl estradiol by human placental microsomes. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1983;57(2):299–303.
- Taylor HS, Giudice LC, Lessey BA, et al. Treatment of endometriosis-associated pain with elagolix, an oral GnRH antagonist. N Engl J Med. 2017;377(1):28–40.
- Surrey E, Taylor HS, Giudice L, et al. Long-term outcomes of elagolix in women with endometriosis: results from two extension studies. Obstet Gynecol. 2018;132(1):147–160.
- Selak V, Farquhar C, Prentice A, Singla A. Danazol for pelvic pain associated with endometriosis. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2007;(4):CD000068.
- Barbieri RL, Ryan KJ. Danazol: endocrine pharmacology and therapeutic applications. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1981;141(4):453–463.
- Dunselman GA, Vermeulen N, Becker C, et al; European Society of Human Reproduction and Embryology. ESHRE guideline: management of women with endometriosis. Hum Reprod. 2014;29(3):400–412.
- Patel BG, Rudnicki M, Yu J, Shu Y, Taylor RN. Progesterone resistance in endometriosis: origins, consequences and interventions. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand. 2017;96(6):623–632.
- Bulun SE, Cheng YH, Pavone ME, et al. Estrogen receptor-beta, estrogen receptor-alpha, and progesterone resistance in endometriosis. Semin Reprod Med. 2010;28(1):36–43.
- Vercellini P, Pietropaolo G, De Giorgi O, Pasin R, Chiodini A, Crosignani PG. Treatment of symptomatic rectovaginal endometriosis with an estrogen-progestogen combination versus low-dose norethindrone acetate. Fertil Steril. 2005;84(5):1375-1387.
- Brown J, Kives S, Akhtar M. Progestagens and anti-progestagens for pain associated with endometriosis. Cochrane Database of Syst Rev. 2012;(3):CD002122.
- Moghissi KS, Boyce CR. Management of endometriosis with oral medroxyprogesterone acetate. Obstet Gynecol. 1976;47(3):265–267.
- Telimaa S, Puolakka J, Rönnberg L, Kauppila A. Placebo-controlled comparison of danazol and high-dose medroxyprogesterone acetate in the treatment of endometriosis. Gynecol Endocrinol. 1987;1(1):13–23.
- Luciano AA, Turksoy RN, Carleo J. Evaluation of oral medroxyprogesterone acetate in the treatment of endometriosis. Obstet Gynecol. 1988;72(3 pt 1):323–327.
- Schlaff WD, Carson SA, Luciano A, Ross D, Bergqvist A. Subcutaneous injection of depot medroxyprogesterone acetate compared with leu-prolide acetate in the treatment of endometriosis-associated pain. Fertil Steril. 2006;85(2):314–325.
- Abou-Setta AM, Houston B, Al-Inany HG, Farquhar C. Levonorgestrel-releasing intrauterine device (LNG-IUD) for symptomatic endometriosis following surgery. Cochrane Database of Syst Rev. 2013;(1):CD005072.
- Tanmahasamut P, Rattanachaiyanont M, Angsuwathana S, Techatraisak K, Indhavivadhana S, Leerasiri P. Postoperative levonorgestrel-releasing intrauterine system for pelvic endometriosis-pain: a randomized controlled trial. Obstet Gynecol. 2012;119(3):519–526.
- Wong AY, Tang LC, Chin RK. Levonorgestrel-releasing intrauterine system (Mirena) and Depot medroxyprogesterone acetate (Depoprovera) as long-term maintenance therapy for patients with moderate and severe endometriosis: a randomised controlled trial. Aust N Z J Obstet Gynaecol. 2010;50(3):273–279.
- Henzl MR, Corson SL, Moghissi K, Buttram VC, Berqvist C, Jacobsen J. Administration of nasal nafarelin as compared with oral danazol for endo-metriosis. A multicenter double-blind comparative clinical trial. N Engl J Med. 1988;318(8):485–489.
- Hornstein MD, Surrey ES, Weisberg GW, Casino LA. Leuprolide acetate depot and hormonal add-back in endometriosis: a 12-month study. Lupron Add-Back Study Group. Obstet Gynecol. 1998; 91(1):16–24.
- Barbieri RL. Hormone treatment of endometriosis: the estrogen threshold hypothesis. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1992;166(2):740–745.
- Hull ME, Barbieri RL. Nafarelin in the treatment of endometriosis. Dose management. Gynecol Obstet Invest. 1994;37(4):263–264.
- Barbieri RL, Petro Z, Canick JA, Ryan KJ. Aromatization of norethindrone to ethinyl estradiol by human placental microsomes. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1983;57(2):299–303.
- Taylor HS, Giudice LC, Lessey BA, et al. Treatment of endometriosis-associated pain with elagolix, an oral GnRH antagonist. N Engl J Med. 2017;377(1):28–40.
- Surrey E, Taylor HS, Giudice L, et al. Long-term outcomes of elagolix in women with endometriosis: results from two extension studies. Obstet Gynecol. 2018;132(1):147–160.
- Selak V, Farquhar C, Prentice A, Singla A. Danazol for pelvic pain associated with endometriosis. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2007;(4):CD000068.
- Barbieri RL, Ryan KJ. Danazol: endocrine pharmacology and therapeutic applications. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1981;141(4):453–463.
- Dunselman GA, Vermeulen N, Becker C, et al; European Society of Human Reproduction and Embryology. ESHRE guideline: management of women with endometriosis. Hum Reprod. 2014;29(3):400–412.