User login
FDA approves hydroxyurea for pediatric patients with sickle cell anemia
to reduce the frequency of painful crises and the need for blood transfusions, the Food and Drug Administration announced on Dec. 21.
This is the first FDA approval of hydroxyurea for use in pediatric sickle cell patients. The recommended initial dose is 20 mg/kg once daily but can be changed based on blood count levels, the agency said in a press release.
The most common adverse reactions to hydroxyurea, infections and neutropenia, occurred in less than 10% of patients. Hydroxyurea causes severe myelosuppression and should not be administered to patients with depressed bone marrow function.
Hydroxyurea is manufactured as Siklos by Addmedica. More information concerning hydroxyurea indications, dosing, and precautions can be found here.
SOURCE: FDA press release.
to reduce the frequency of painful crises and the need for blood transfusions, the Food and Drug Administration announced on Dec. 21.
This is the first FDA approval of hydroxyurea for use in pediatric sickle cell patients. The recommended initial dose is 20 mg/kg once daily but can be changed based on blood count levels, the agency said in a press release.
The most common adverse reactions to hydroxyurea, infections and neutropenia, occurred in less than 10% of patients. Hydroxyurea causes severe myelosuppression and should not be administered to patients with depressed bone marrow function.
Hydroxyurea is manufactured as Siklos by Addmedica. More information concerning hydroxyurea indications, dosing, and precautions can be found here.
SOURCE: FDA press release.
to reduce the frequency of painful crises and the need for blood transfusions, the Food and Drug Administration announced on Dec. 21.
This is the first FDA approval of hydroxyurea for use in pediatric sickle cell patients. The recommended initial dose is 20 mg/kg once daily but can be changed based on blood count levels, the agency said in a press release.
The most common adverse reactions to hydroxyurea, infections and neutropenia, occurred in less than 10% of patients. Hydroxyurea causes severe myelosuppression and should not be administered to patients with depressed bone marrow function.
Hydroxyurea is manufactured as Siklos by Addmedica. More information concerning hydroxyurea indications, dosing, and precautions can be found here.
SOURCE: FDA press release.
Drug approved for kids with sickle cell anemia
The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved a hydroxyurea product (Addmedica’s Siklos) for use in pediatric patients with sickle cell anemia.
Siklos is intended to reduce the frequency of painful crises and the need for blood transfusions in pediatric patients age 2 and older who have sickle cell anemia and recurrent moderate to severe painful crises.
The recommended dose of Siklos is 20 mg/kg once daily.
The FDA granted priority review and orphan drug designation to the application for Siklos.
The agency’s approval of Siklos was based on data from the ESCORT HU study (NCT02516579). The trial was an evaluation of Siklos in 405 patients, ages 2 to 18, with sickle cell disease (SCD).
Thirty-five percent of these patients (n=141) had not received hydroxyurea prior to study enrollment and were therefore evaluable for efficacy. The median follow-up was 23 months (range, 12 to 80 months).
The researchers found that Siklos prompted an increase in fetal hemoglobin. Median fetal hemoglobin percentages were 5.6% (range, 1.3 to 15.0) at baseline and 12.8% (range, 2.1 to 37.2) at around 6 months after Siklos initiation (the value closest to 6 months collected between 5 and 14 months).
In addition, the percentage of patients with at least 1 vaso-occlusive episode, 1 episode of acute chest syndrome, 1 hospitalization due to SCD, or 1 blood transfusion decreased after 12 months of Siklos treatment.
The proportion of patients with at least 1 vaso-occlusive episode was 69.2% at baseline and 42.5% at 12 months. The proportion with at least 1 episode of acute chest syndrome was 23.6% and 5.7%, respectively.
The proportion with at least 1 hospitalization due to SCD was 75.5% and 41.8%, respectively. And the proportion with at least 1 blood transfusion was 45.9% and 23.0%, respectively.
The most common adverse events (occurring in at least 10% of patients) were infections (39.8%), gastrointestinal disorders (13.1%), neutropenia (12.6%), nervous system disorders (11.1%), and metabolic and nutrition disorders (10.9%).
Full prescribing information for Siklos is available on the FDA website. ![]()
The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved a hydroxyurea product (Addmedica’s Siklos) for use in pediatric patients with sickle cell anemia.
Siklos is intended to reduce the frequency of painful crises and the need for blood transfusions in pediatric patients age 2 and older who have sickle cell anemia and recurrent moderate to severe painful crises.
The recommended dose of Siklos is 20 mg/kg once daily.
The FDA granted priority review and orphan drug designation to the application for Siklos.
The agency’s approval of Siklos was based on data from the ESCORT HU study (NCT02516579). The trial was an evaluation of Siklos in 405 patients, ages 2 to 18, with sickle cell disease (SCD).
Thirty-five percent of these patients (n=141) had not received hydroxyurea prior to study enrollment and were therefore evaluable for efficacy. The median follow-up was 23 months (range, 12 to 80 months).
The researchers found that Siklos prompted an increase in fetal hemoglobin. Median fetal hemoglobin percentages were 5.6% (range, 1.3 to 15.0) at baseline and 12.8% (range, 2.1 to 37.2) at around 6 months after Siklos initiation (the value closest to 6 months collected between 5 and 14 months).
In addition, the percentage of patients with at least 1 vaso-occlusive episode, 1 episode of acute chest syndrome, 1 hospitalization due to SCD, or 1 blood transfusion decreased after 12 months of Siklos treatment.
The proportion of patients with at least 1 vaso-occlusive episode was 69.2% at baseline and 42.5% at 12 months. The proportion with at least 1 episode of acute chest syndrome was 23.6% and 5.7%, respectively.
The proportion with at least 1 hospitalization due to SCD was 75.5% and 41.8%, respectively. And the proportion with at least 1 blood transfusion was 45.9% and 23.0%, respectively.
The most common adverse events (occurring in at least 10% of patients) were infections (39.8%), gastrointestinal disorders (13.1%), neutropenia (12.6%), nervous system disorders (11.1%), and metabolic and nutrition disorders (10.9%).
Full prescribing information for Siklos is available on the FDA website. ![]()
The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved a hydroxyurea product (Addmedica’s Siklos) for use in pediatric patients with sickle cell anemia.
Siklos is intended to reduce the frequency of painful crises and the need for blood transfusions in pediatric patients age 2 and older who have sickle cell anemia and recurrent moderate to severe painful crises.
The recommended dose of Siklos is 20 mg/kg once daily.
The FDA granted priority review and orphan drug designation to the application for Siklos.
The agency’s approval of Siklos was based on data from the ESCORT HU study (NCT02516579). The trial was an evaluation of Siklos in 405 patients, ages 2 to 18, with sickle cell disease (SCD).
Thirty-five percent of these patients (n=141) had not received hydroxyurea prior to study enrollment and were therefore evaluable for efficacy. The median follow-up was 23 months (range, 12 to 80 months).
The researchers found that Siklos prompted an increase in fetal hemoglobin. Median fetal hemoglobin percentages were 5.6% (range, 1.3 to 15.0) at baseline and 12.8% (range, 2.1 to 37.2) at around 6 months after Siklos initiation (the value closest to 6 months collected between 5 and 14 months).
In addition, the percentage of patients with at least 1 vaso-occlusive episode, 1 episode of acute chest syndrome, 1 hospitalization due to SCD, or 1 blood transfusion decreased after 12 months of Siklos treatment.
The proportion of patients with at least 1 vaso-occlusive episode was 69.2% at baseline and 42.5% at 12 months. The proportion with at least 1 episode of acute chest syndrome was 23.6% and 5.7%, respectively.
The proportion with at least 1 hospitalization due to SCD was 75.5% and 41.8%, respectively. And the proportion with at least 1 blood transfusion was 45.9% and 23.0%, respectively.
The most common adverse events (occurring in at least 10% of patients) were infections (39.8%), gastrointestinal disorders (13.1%), neutropenia (12.6%), nervous system disorders (11.1%), and metabolic and nutrition disorders (10.9%).
Full prescribing information for Siklos is available on the FDA website. ![]()
Rare neurological complication linked to Waldenstrom disease
Bilateral facial nerve palsy has been associated with underlying Waldenstrom disease in only one other known published case report, which was published in 2014. In a more recent case report published in the Journal of Clinical Neuroscience, Gabriel Torrealba-Acosta, MD, and colleagues in the department of neurology at Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, described a second case involving a 67-year-old Hispanic man with a history of Waldenstrom disease who presented with subacute onset of bilateral facial weakness.
The patient, who had longstanding painful neuropathy, had presented to urgent care with a new-onset left facial nerve palsy, was then diagnosed with left Bell’s palsy, and began treatment with valacyclovir and prednisone.
The left-sided facial weakness gradually progressed to total paralysis of the left lower face and inability to close the left eye, and 2 weeks later, he developed right facial weakness that ran a similar course. The patient had a complicated clinical course that included symptomatic acute-on-chronic subdural hematoma, among other complications; eventually the patient’s symptoms stabilized and cranial neuropathies gradually improved, according to the report.
Bilateral facial nerve palsy is an extremely rare condition, occurring in just 0.3%-2% of all facial nerve palsy cases, according to the authors. By contrast, unilateral facial nerve palsy (or Bell’s palsy) is far more common, but it still occurs in only 25 patients per 100,000 population, they said.
Most cases of bilateral facial nerve palsy are caused by underlying Guillain-Barré syndrome, though some are congenital, related to trauma, or caused by etiologies that are metabolic, immunologic, or neoplastic in nature. While various types of neurological disturbances – from ischemic and hemorrhagic events to meningoencephalitis – have been documented to occur in up to a quarter of patients with Waldenstrom disease.
“Given the large differential that comprises the assessment of a bilateral facial nerve palsy, it warrants for an extensive work-up, and Waldenstrom’s macroglobulinemia should be sought as an additional possible etiology,” the authors wrote.
Dr. Torrealba-Acosta and coauthors reported having no financial disclosures.
SOURCE: Torrealba-Acosta G et al. J Clin Neurosci. 2017. doi: 10.1016/j.jocn.2017.10.081.
Bilateral facial nerve palsy has been associated with underlying Waldenstrom disease in only one other known published case report, which was published in 2014. In a more recent case report published in the Journal of Clinical Neuroscience, Gabriel Torrealba-Acosta, MD, and colleagues in the department of neurology at Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, described a second case involving a 67-year-old Hispanic man with a history of Waldenstrom disease who presented with subacute onset of bilateral facial weakness.
The patient, who had longstanding painful neuropathy, had presented to urgent care with a new-onset left facial nerve palsy, was then diagnosed with left Bell’s palsy, and began treatment with valacyclovir and prednisone.
The left-sided facial weakness gradually progressed to total paralysis of the left lower face and inability to close the left eye, and 2 weeks later, he developed right facial weakness that ran a similar course. The patient had a complicated clinical course that included symptomatic acute-on-chronic subdural hematoma, among other complications; eventually the patient’s symptoms stabilized and cranial neuropathies gradually improved, according to the report.
Bilateral facial nerve palsy is an extremely rare condition, occurring in just 0.3%-2% of all facial nerve palsy cases, according to the authors. By contrast, unilateral facial nerve palsy (or Bell’s palsy) is far more common, but it still occurs in only 25 patients per 100,000 population, they said.
Most cases of bilateral facial nerve palsy are caused by underlying Guillain-Barré syndrome, though some are congenital, related to trauma, or caused by etiologies that are metabolic, immunologic, or neoplastic in nature. While various types of neurological disturbances – from ischemic and hemorrhagic events to meningoencephalitis – have been documented to occur in up to a quarter of patients with Waldenstrom disease.
“Given the large differential that comprises the assessment of a bilateral facial nerve palsy, it warrants for an extensive work-up, and Waldenstrom’s macroglobulinemia should be sought as an additional possible etiology,” the authors wrote.
Dr. Torrealba-Acosta and coauthors reported having no financial disclosures.
SOURCE: Torrealba-Acosta G et al. J Clin Neurosci. 2017. doi: 10.1016/j.jocn.2017.10.081.
Bilateral facial nerve palsy has been associated with underlying Waldenstrom disease in only one other known published case report, which was published in 2014. In a more recent case report published in the Journal of Clinical Neuroscience, Gabriel Torrealba-Acosta, MD, and colleagues in the department of neurology at Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, described a second case involving a 67-year-old Hispanic man with a history of Waldenstrom disease who presented with subacute onset of bilateral facial weakness.
The patient, who had longstanding painful neuropathy, had presented to urgent care with a new-onset left facial nerve palsy, was then diagnosed with left Bell’s palsy, and began treatment with valacyclovir and prednisone.
The left-sided facial weakness gradually progressed to total paralysis of the left lower face and inability to close the left eye, and 2 weeks later, he developed right facial weakness that ran a similar course. The patient had a complicated clinical course that included symptomatic acute-on-chronic subdural hematoma, among other complications; eventually the patient’s symptoms stabilized and cranial neuropathies gradually improved, according to the report.
Bilateral facial nerve palsy is an extremely rare condition, occurring in just 0.3%-2% of all facial nerve palsy cases, according to the authors. By contrast, unilateral facial nerve palsy (or Bell’s palsy) is far more common, but it still occurs in only 25 patients per 100,000 population, they said.
Most cases of bilateral facial nerve palsy are caused by underlying Guillain-Barré syndrome, though some are congenital, related to trauma, or caused by etiologies that are metabolic, immunologic, or neoplastic in nature. While various types of neurological disturbances – from ischemic and hemorrhagic events to meningoencephalitis – have been documented to occur in up to a quarter of patients with Waldenstrom disease.
“Given the large differential that comprises the assessment of a bilateral facial nerve palsy, it warrants for an extensive work-up, and Waldenstrom’s macroglobulinemia should be sought as an additional possible etiology,” the authors wrote.
Dr. Torrealba-Acosta and coauthors reported having no financial disclosures.
SOURCE: Torrealba-Acosta G et al. J Clin Neurosci. 2017. doi: 10.1016/j.jocn.2017.10.081.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF CLINICAL NEUROSCIENCE
Clinic eases pediatric-adult transition in sickle cell disease
CONCORD, N.C. – Teenage sickle cell disease patients transitioning to adulthood can often find the move to adult providers challenging, causing some patients to lose interest in self-care at a critical point in life, but a transitional program can help them develop the skills they need to manage their disease and avoid risky behaviors, according to psychologist Anya Griffin, PhD.
Managing pain in teenagers and young adults with sickle cell disease (SCD) is fraught with challenges, said Dr. Griffin, who led the SCD transition program at Children’s Healthcare of Atlanta and is now the clinical director of the Stanford (Calif.) Children’s Health Pediatric Rehabilitation Program, an intensive pain management program for pediatric chronic pain.
“Think about who you are when you’re a teenager, when you’re a young adult, what’s going on: dating, sex, parties, college, all-night study sessions,” she said at a Sickle Cell Disease Symposium held by Carolinas Health Care System. “But in the world of sickle cell, these are critical choices that have dire consequences.” Those consequences include dehydration from drinking, fatigue from lack of sleep, and pain crises.
Compounding these challenges is the prevalence of depression and other psychological complications in this age group. And among SCD patients, there can be a sense of grief, Dr. Griffin said.
“Grief is something we tend not to talk too much about,” she said. That grief can manifest in excessive absences from school or work. “Sudden academic declines are something we really have to pay attention to,” Dr. Griffin said.
Silent strokes are also of concern in this age group. “I don’t know if we fully understand the impact on each individual unless we do neuropsychological testing,” she said. The intervals for neuropsychological testing should be in childhood to determine a baseline, then again in adolescence and adulthood. For college-bound students, testing may be a requirement for them to receive medical and physical accommodations, Dr. Griffin said.
While in their late teens and early twenties, SCD patients often rely on pediatric care and can get caught between pediatric and adult providers, she said. That prompted Children’s Healthcare of Atlanta to start a program that essentially hands off those patients from pediatric to adult providers and works with patients to reduce their risks.
As teens approach age 18, they come to the clinic to meet with adult providers and tour the facility. The program involves social workers, vocational and school counselors, and mentors and peer support. “It takes an entire village to address the concerns of transition,” Dr. Griffin said.
Support groups and home visits by providers can also play a key role in the transition protocol, as can telemedicine. “The technology is now there; now we have to figure out how we’re going to start using it,” she said.
This full transitional process can involve multiple appointments with a variety of providers. It’s also important that patients – not parents – interact with providers, Dr. Griffin said.
From January 2007 to September 2012, 74 patients participated in the SCD transition at Children’s Healthcare of Atlanta. Participants who attended more than one transition clinic visit in Atlanta (n = 9) had an average baseline score of 60% on an SCD knowledge questionnaire. But 6 months later, those scores improved to 80%, on average. “We found that teenagers who came to that type of clinic more than once improved pretty well,” Dr. Griffin said.
Dr. Griffin reported having no relevant financial disclosures.
CONCORD, N.C. – Teenage sickle cell disease patients transitioning to adulthood can often find the move to adult providers challenging, causing some patients to lose interest in self-care at a critical point in life, but a transitional program can help them develop the skills they need to manage their disease and avoid risky behaviors, according to psychologist Anya Griffin, PhD.
Managing pain in teenagers and young adults with sickle cell disease (SCD) is fraught with challenges, said Dr. Griffin, who led the SCD transition program at Children’s Healthcare of Atlanta and is now the clinical director of the Stanford (Calif.) Children’s Health Pediatric Rehabilitation Program, an intensive pain management program for pediatric chronic pain.
“Think about who you are when you’re a teenager, when you’re a young adult, what’s going on: dating, sex, parties, college, all-night study sessions,” she said at a Sickle Cell Disease Symposium held by Carolinas Health Care System. “But in the world of sickle cell, these are critical choices that have dire consequences.” Those consequences include dehydration from drinking, fatigue from lack of sleep, and pain crises.
Compounding these challenges is the prevalence of depression and other psychological complications in this age group. And among SCD patients, there can be a sense of grief, Dr. Griffin said.
“Grief is something we tend not to talk too much about,” she said. That grief can manifest in excessive absences from school or work. “Sudden academic declines are something we really have to pay attention to,” Dr. Griffin said.
Silent strokes are also of concern in this age group. “I don’t know if we fully understand the impact on each individual unless we do neuropsychological testing,” she said. The intervals for neuropsychological testing should be in childhood to determine a baseline, then again in adolescence and adulthood. For college-bound students, testing may be a requirement for them to receive medical and physical accommodations, Dr. Griffin said.
While in their late teens and early twenties, SCD patients often rely on pediatric care and can get caught between pediatric and adult providers, she said. That prompted Children’s Healthcare of Atlanta to start a program that essentially hands off those patients from pediatric to adult providers and works with patients to reduce their risks.
As teens approach age 18, they come to the clinic to meet with adult providers and tour the facility. The program involves social workers, vocational and school counselors, and mentors and peer support. “It takes an entire village to address the concerns of transition,” Dr. Griffin said.
Support groups and home visits by providers can also play a key role in the transition protocol, as can telemedicine. “The technology is now there; now we have to figure out how we’re going to start using it,” she said.
This full transitional process can involve multiple appointments with a variety of providers. It’s also important that patients – not parents – interact with providers, Dr. Griffin said.
From January 2007 to September 2012, 74 patients participated in the SCD transition at Children’s Healthcare of Atlanta. Participants who attended more than one transition clinic visit in Atlanta (n = 9) had an average baseline score of 60% on an SCD knowledge questionnaire. But 6 months later, those scores improved to 80%, on average. “We found that teenagers who came to that type of clinic more than once improved pretty well,” Dr. Griffin said.
Dr. Griffin reported having no relevant financial disclosures.
CONCORD, N.C. – Teenage sickle cell disease patients transitioning to adulthood can often find the move to adult providers challenging, causing some patients to lose interest in self-care at a critical point in life, but a transitional program can help them develop the skills they need to manage their disease and avoid risky behaviors, according to psychologist Anya Griffin, PhD.
Managing pain in teenagers and young adults with sickle cell disease (SCD) is fraught with challenges, said Dr. Griffin, who led the SCD transition program at Children’s Healthcare of Atlanta and is now the clinical director of the Stanford (Calif.) Children’s Health Pediatric Rehabilitation Program, an intensive pain management program for pediatric chronic pain.
“Think about who you are when you’re a teenager, when you’re a young adult, what’s going on: dating, sex, parties, college, all-night study sessions,” she said at a Sickle Cell Disease Symposium held by Carolinas Health Care System. “But in the world of sickle cell, these are critical choices that have dire consequences.” Those consequences include dehydration from drinking, fatigue from lack of sleep, and pain crises.
Compounding these challenges is the prevalence of depression and other psychological complications in this age group. And among SCD patients, there can be a sense of grief, Dr. Griffin said.
“Grief is something we tend not to talk too much about,” she said. That grief can manifest in excessive absences from school or work. “Sudden academic declines are something we really have to pay attention to,” Dr. Griffin said.
Silent strokes are also of concern in this age group. “I don’t know if we fully understand the impact on each individual unless we do neuropsychological testing,” she said. The intervals for neuropsychological testing should be in childhood to determine a baseline, then again in adolescence and adulthood. For college-bound students, testing may be a requirement for them to receive medical and physical accommodations, Dr. Griffin said.
While in their late teens and early twenties, SCD patients often rely on pediatric care and can get caught between pediatric and adult providers, she said. That prompted Children’s Healthcare of Atlanta to start a program that essentially hands off those patients from pediatric to adult providers and works with patients to reduce their risks.
As teens approach age 18, they come to the clinic to meet with adult providers and tour the facility. The program involves social workers, vocational and school counselors, and mentors and peer support. “It takes an entire village to address the concerns of transition,” Dr. Griffin said.
Support groups and home visits by providers can also play a key role in the transition protocol, as can telemedicine. “The technology is now there; now we have to figure out how we’re going to start using it,” she said.
This full transitional process can involve multiple appointments with a variety of providers. It’s also important that patients – not parents – interact with providers, Dr. Griffin said.
From January 2007 to September 2012, 74 patients participated in the SCD transition at Children’s Healthcare of Atlanta. Participants who attended more than one transition clinic visit in Atlanta (n = 9) had an average baseline score of 60% on an SCD knowledge questionnaire. But 6 months later, those scores improved to 80%, on average. “We found that teenagers who came to that type of clinic more than once improved pretty well,” Dr. Griffin said.
Dr. Griffin reported having no relevant financial disclosures.
EXPERT ANALYSIS FROM A MEETING ON SICKLE CELL DISEASE
AVP stimulates red blood cell production
Researchers say they have uncovered a new function of arginine vasopressin (AVP).
It seems this hormone does more than maintain fluid balance for the kidneys.
AVP also stimulates the proliferation and differentiation of red blood cell precursors and improves recovery from anemia, according to the researchers.
The group speculates that drugs targeting an AVP receptor could be used to replenish red blood cells lost due to bleeding or treatment toxicity.
Eva Mezey, MD, PhD, of the National Institutes of Health in Bethesda, Maryland, and her colleagues conducted this research and reported the results in Science Translational Medicine.
The team uncovered the unexpected role for AVP by examining clinical data from 92 patients with central diabetes insipidus, a condition that causes AVP deficiency.
Of those individuals, 87% of males and 51% of females had anemia. In comparison, anemia rates in the US general population range from 1.5% to 6% for men and 4.4% to 12% for women.
The researchers also found that all 3 AVP receptors are present on human and murine hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells.
One of these receptors, AVPR1B, plays a predominant role in red blood cell production.
Further experiments revealed that AVP-deficient rats had delayed recovery from anemia, but treatment with AVP or the AVPR1B agonist d(Leu4Lys8)VP was able to speed up anemia recovery in mice.
The researchers tested AVP and the AVPR1B agonist in mouse models of hemorrhage. Compared to vehicle-treated mice, AVP-treated mice had an increase in hematocrit and reticulocyte numbers by day 2. Mice that received d(Leu4Lys8)VP only had an increase in reticulocytes.
The team also tested mice exposed to sublethal irradiation. When the mice received AVP for 2 days, they saw increases in hematocrit and corrected reticulocyte numbers.
The researchers then tested splenectomized mice subjected to hemorrhage. AVP-treated mice had an increase in hematocrit that was similar to that observed in non-splenectomized mice.
Finally, the researchers found that AVP’s effect on hematocrit is independent of erythropoietin. The team said AVP “appears to jump-start peripheral blood cell replenishment,” but later, erythropoietin seems to take over. ![]()
Researchers say they have uncovered a new function of arginine vasopressin (AVP).
It seems this hormone does more than maintain fluid balance for the kidneys.
AVP also stimulates the proliferation and differentiation of red blood cell precursors and improves recovery from anemia, according to the researchers.
The group speculates that drugs targeting an AVP receptor could be used to replenish red blood cells lost due to bleeding or treatment toxicity.
Eva Mezey, MD, PhD, of the National Institutes of Health in Bethesda, Maryland, and her colleagues conducted this research and reported the results in Science Translational Medicine.
The team uncovered the unexpected role for AVP by examining clinical data from 92 patients with central diabetes insipidus, a condition that causes AVP deficiency.
Of those individuals, 87% of males and 51% of females had anemia. In comparison, anemia rates in the US general population range from 1.5% to 6% for men and 4.4% to 12% for women.
The researchers also found that all 3 AVP receptors are present on human and murine hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells.
One of these receptors, AVPR1B, plays a predominant role in red blood cell production.
Further experiments revealed that AVP-deficient rats had delayed recovery from anemia, but treatment with AVP or the AVPR1B agonist d(Leu4Lys8)VP was able to speed up anemia recovery in mice.
The researchers tested AVP and the AVPR1B agonist in mouse models of hemorrhage. Compared to vehicle-treated mice, AVP-treated mice had an increase in hematocrit and reticulocyte numbers by day 2. Mice that received d(Leu4Lys8)VP only had an increase in reticulocytes.
The team also tested mice exposed to sublethal irradiation. When the mice received AVP for 2 days, they saw increases in hematocrit and corrected reticulocyte numbers.
The researchers then tested splenectomized mice subjected to hemorrhage. AVP-treated mice had an increase in hematocrit that was similar to that observed in non-splenectomized mice.
Finally, the researchers found that AVP’s effect on hematocrit is independent of erythropoietin. The team said AVP “appears to jump-start peripheral blood cell replenishment,” but later, erythropoietin seems to take over. ![]()
Researchers say they have uncovered a new function of arginine vasopressin (AVP).
It seems this hormone does more than maintain fluid balance for the kidneys.
AVP also stimulates the proliferation and differentiation of red blood cell precursors and improves recovery from anemia, according to the researchers.
The group speculates that drugs targeting an AVP receptor could be used to replenish red blood cells lost due to bleeding or treatment toxicity.
Eva Mezey, MD, PhD, of the National Institutes of Health in Bethesda, Maryland, and her colleagues conducted this research and reported the results in Science Translational Medicine.
The team uncovered the unexpected role for AVP by examining clinical data from 92 patients with central diabetes insipidus, a condition that causes AVP deficiency.
Of those individuals, 87% of males and 51% of females had anemia. In comparison, anemia rates in the US general population range from 1.5% to 6% for men and 4.4% to 12% for women.
The researchers also found that all 3 AVP receptors are present on human and murine hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells.
One of these receptors, AVPR1B, plays a predominant role in red blood cell production.
Further experiments revealed that AVP-deficient rats had delayed recovery from anemia, but treatment with AVP or the AVPR1B agonist d(Leu4Lys8)VP was able to speed up anemia recovery in mice.
The researchers tested AVP and the AVPR1B agonist in mouse models of hemorrhage. Compared to vehicle-treated mice, AVP-treated mice had an increase in hematocrit and reticulocyte numbers by day 2. Mice that received d(Leu4Lys8)VP only had an increase in reticulocytes.
The team also tested mice exposed to sublethal irradiation. When the mice received AVP for 2 days, they saw increases in hematocrit and corrected reticulocyte numbers.
The researchers then tested splenectomized mice subjected to hemorrhage. AVP-treated mice had an increase in hematocrit that was similar to that observed in non-splenectomized mice.
Finally, the researchers found that AVP’s effect on hematocrit is independent of erythropoietin. The team said AVP “appears to jump-start peripheral blood cell replenishment,” but later, erythropoietin seems to take over. ![]()
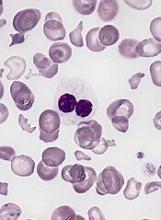
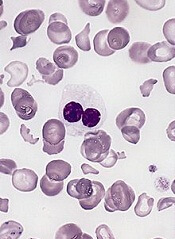
FDA grants drug orphan designation for AML, MDS
The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has granted orphan drug designation to AMV564, a CD33/CD3 bispecific antibody, for the treatment of acute myeloid leukemia (AML) and myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS).
AMV564 is a T-cell engager, derived from human protein sequences, that binds both CD33 and CD3 to mediate T-cell directed lysis of CD33-positive cancer cells.
Amphivena Therapeutics Inc., is currently conducting a phase 1 trial of AMV564 in relapsed or refractory AML. The company plans to launch a phase 1 trial in patients with MDS in early 2018.
According to Amphivena, AMV564 has demonstrated “potent activity” in AML patient samples, and that activity was independent of CD33 expression level, disease stage, and cytogenetic risk.
AMV564 also eliminated nearly all blasts from the bone marrow and spleen in a stringent AML patient-derived xenograft murine model.
In addition, Amphivena established a therapeutic window for AMV564 in cynomolgus monkeys, with rapid and sustained elimination of CD33-expressing cells during AMV564 dosing and rapid hematopoietic recovery following dosing.
About orphan designation
The FDA grants orphan designation to products intended to treat, diagnose, or prevent diseases/disorders that affect fewer than 200,000 people in the US.
The designation provides incentives for sponsors to develop products for rare diseases. This may include tax credits toward the cost of clinical trials, prescription drug user fee waivers, and 7 years of market exclusivity if the product is approved. ![]()
The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has granted orphan drug designation to AMV564, a CD33/CD3 bispecific antibody, for the treatment of acute myeloid leukemia (AML) and myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS).
AMV564 is a T-cell engager, derived from human protein sequences, that binds both CD33 and CD3 to mediate T-cell directed lysis of CD33-positive cancer cells.
Amphivena Therapeutics Inc., is currently conducting a phase 1 trial of AMV564 in relapsed or refractory AML. The company plans to launch a phase 1 trial in patients with MDS in early 2018.
According to Amphivena, AMV564 has demonstrated “potent activity” in AML patient samples, and that activity was independent of CD33 expression level, disease stage, and cytogenetic risk.
AMV564 also eliminated nearly all blasts from the bone marrow and spleen in a stringent AML patient-derived xenograft murine model.
In addition, Amphivena established a therapeutic window for AMV564 in cynomolgus monkeys, with rapid and sustained elimination of CD33-expressing cells during AMV564 dosing and rapid hematopoietic recovery following dosing.
About orphan designation
The FDA grants orphan designation to products intended to treat, diagnose, or prevent diseases/disorders that affect fewer than 200,000 people in the US.
The designation provides incentives for sponsors to develop products for rare diseases. This may include tax credits toward the cost of clinical trials, prescription drug user fee waivers, and 7 years of market exclusivity if the product is approved. ![]()
The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has granted orphan drug designation to AMV564, a CD33/CD3 bispecific antibody, for the treatment of acute myeloid leukemia (AML) and myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS).
AMV564 is a T-cell engager, derived from human protein sequences, that binds both CD33 and CD3 to mediate T-cell directed lysis of CD33-positive cancer cells.
Amphivena Therapeutics Inc., is currently conducting a phase 1 trial of AMV564 in relapsed or refractory AML. The company plans to launch a phase 1 trial in patients with MDS in early 2018.
According to Amphivena, AMV564 has demonstrated “potent activity” in AML patient samples, and that activity was independent of CD33 expression level, disease stage, and cytogenetic risk.
AMV564 also eliminated nearly all blasts from the bone marrow and spleen in a stringent AML patient-derived xenograft murine model.
In addition, Amphivena established a therapeutic window for AMV564 in cynomolgus monkeys, with rapid and sustained elimination of CD33-expressing cells during AMV564 dosing and rapid hematopoietic recovery following dosing.
About orphan designation
The FDA grants orphan designation to products intended to treat, diagnose, or prevent diseases/disorders that affect fewer than 200,000 people in the US.
The designation provides incentives for sponsors to develop products for rare diseases. This may include tax credits toward the cost of clinical trials, prescription drug user fee waivers, and 7 years of market exclusivity if the product is approved. ![]()
Vasopressin stimulates red blood cell production
The hormone vasopressin, well known for its antidiuretic effects, also appears to stimulate proliferation and differentiation of red blood cell (RBC) precursors, results of a series of preclinical investigations suggest.
Treating anemic mice with an arginine vasopressin (AVP) receptor agonist increased hematocrit and reticulocyte counts significantly, compared with controls, according to the results published in Science Translational Medicine (2017 Nov 29;9:eaao1632).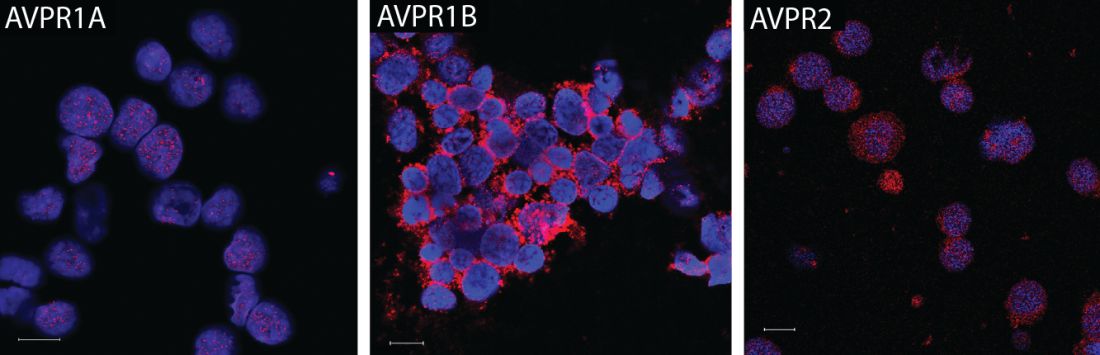
That finding could have implications for the development of new treatments designed to stimulate RBC production after bleeding, chemotherapy, or drug toxicity, according to the investigators.
“Currently, EPO is the only agent that is used clinically to stimulate erythropoiesis, but there are patients who do not respond to EPO or who cannot take the drug because it stimulates tumor growth,” the investigators wrote. “AVP appears to be an EPO-independent, fast-acting agent that increases RBC numbers after anemia.”
Dr. Mayer and his colleagues initially asked whether AVP might play a role in RBC production after observing that patients with central diabetes insipidus (CDI), who lack the antidiuretic hormone, are frequently anemic. A review of patient records from an NIH database revealed that 60% of CDI patients were anemic despite treatment with desmopressin.
They subsequently found that all three AVP receptor subtypes are expressed in human and mouse hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells. In particular, the AVPR1B subtype appeared to play the most important role in regulating erythropoiesis.
Accordingly, they tested the ability of both AVP and a AVPR1B-specific agonist to stimulate production of RBCs in mice that had anemia induced by bleeding or irradiation. They found significant improvements in both hematocrit and reticulocyte numbers as early as 2 days after treatment started.
Subsequent experiments were designed to determine whether the effect of AVP on RBC production was caused by EPO release. In fact, the effects of AVP occurred “long before an effect of EPO was observed,” investigators wrote.
The research was supported by the NIH. Some of the study authors are listed as inventors on a patent application held by the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services covering methods for modulating erythropoiesis with arginine vasopressin receptor 1b molecules.
The hormone vasopressin, well known for its antidiuretic effects, also appears to stimulate proliferation and differentiation of red blood cell (RBC) precursors, results of a series of preclinical investigations suggest.
Treating anemic mice with an arginine vasopressin (AVP) receptor agonist increased hematocrit and reticulocyte counts significantly, compared with controls, according to the results published in Science Translational Medicine (2017 Nov 29;9:eaao1632).
That finding could have implications for the development of new treatments designed to stimulate RBC production after bleeding, chemotherapy, or drug toxicity, according to the investigators.
“Currently, EPO is the only agent that is used clinically to stimulate erythropoiesis, but there are patients who do not respond to EPO or who cannot take the drug because it stimulates tumor growth,” the investigators wrote. “AVP appears to be an EPO-independent, fast-acting agent that increases RBC numbers after anemia.”
Dr. Mayer and his colleagues initially asked whether AVP might play a role in RBC production after observing that patients with central diabetes insipidus (CDI), who lack the antidiuretic hormone, are frequently anemic. A review of patient records from an NIH database revealed that 60% of CDI patients were anemic despite treatment with desmopressin.
They subsequently found that all three AVP receptor subtypes are expressed in human and mouse hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells. In particular, the AVPR1B subtype appeared to play the most important role in regulating erythropoiesis.
Accordingly, they tested the ability of both AVP and a AVPR1B-specific agonist to stimulate production of RBCs in mice that had anemia induced by bleeding or irradiation. They found significant improvements in both hematocrit and reticulocyte numbers as early as 2 days after treatment started.
Subsequent experiments were designed to determine whether the effect of AVP on RBC production was caused by EPO release. In fact, the effects of AVP occurred “long before an effect of EPO was observed,” investigators wrote.
The research was supported by the NIH. Some of the study authors are listed as inventors on a patent application held by the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services covering methods for modulating erythropoiesis with arginine vasopressin receptor 1b molecules.
The hormone vasopressin, well known for its antidiuretic effects, also appears to stimulate proliferation and differentiation of red blood cell (RBC) precursors, results of a series of preclinical investigations suggest.
Treating anemic mice with an arginine vasopressin (AVP) receptor agonist increased hematocrit and reticulocyte counts significantly, compared with controls, according to the results published in Science Translational Medicine (2017 Nov 29;9:eaao1632).
That finding could have implications for the development of new treatments designed to stimulate RBC production after bleeding, chemotherapy, or drug toxicity, according to the investigators.
“Currently, EPO is the only agent that is used clinically to stimulate erythropoiesis, but there are patients who do not respond to EPO or who cannot take the drug because it stimulates tumor growth,” the investigators wrote. “AVP appears to be an EPO-independent, fast-acting agent that increases RBC numbers after anemia.”
Dr. Mayer and his colleagues initially asked whether AVP might play a role in RBC production after observing that patients with central diabetes insipidus (CDI), who lack the antidiuretic hormone, are frequently anemic. A review of patient records from an NIH database revealed that 60% of CDI patients were anemic despite treatment with desmopressin.
They subsequently found that all three AVP receptor subtypes are expressed in human and mouse hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells. In particular, the AVPR1B subtype appeared to play the most important role in regulating erythropoiesis.
Accordingly, they tested the ability of both AVP and a AVPR1B-specific agonist to stimulate production of RBCs in mice that had anemia induced by bleeding or irradiation. They found significant improvements in both hematocrit and reticulocyte numbers as early as 2 days after treatment started.
Subsequent experiments were designed to determine whether the effect of AVP on RBC production was caused by EPO release. In fact, the effects of AVP occurred “long before an effect of EPO was observed,” investigators wrote.
The research was supported by the NIH. Some of the study authors are listed as inventors on a patent application held by the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services covering methods for modulating erythropoiesis with arginine vasopressin receptor 1b molecules.
FROM SCIENCE TRANSLATIONAL MEDICINE
Key clinical point:
Major finding: In anemic mice, treatment with a vasopressin or a vasopressin receptor agonist significantly increased hematocrit and reticulocyte number vs. controls.
Data source: A series of in vitro and in vivo experiments, plus a retrospective review of anemia incidence data in patients with central diabetes insipidus.
Disclosures: The research was supported by the National Institutes of Health. Some of the study authors are listed as inventors on a patent application held by the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services covering methods for modulating erythropoiesis with arginine vasopressin receptor 1b molecules.
FDA grants priority review to NDA for avatrombopag
The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has granted priority review to the new drug application (NDA) for avatrombopag.
Avatrombopag is a second-generation thrombopoietin receptor agonist that is intended to address the limitations of existing treatments for thrombocytopenia.
With this NDA, Dova Pharmaceuticals, Inc., is seeking approval of avatrombopag for the treatment of thrombocytopenia in patients with chronic liver disease who are scheduled to undergo a procedure.
The FDA expects to make a decision on the NDA by May 21, 2018.
The FDA’s goal is to take action on a priority review application within 6 months of receiving it, rather than the standard 10 months.
The FDA grants priority review to applications for products that may provide significant improvements in the treatment, diagnosis, or prevention of serious conditions.
Phase 3 trials
The NDA submission for avatrombopag is supported by 2 identically designed phase 3 trials, ADAPT 1 and ADAPT 2. Results from these trials were presented at the 2017 American Association for the Study of Liver Disease (AASLD) Meeting last month (abstract 217).
The studies randomized 435 patients with thrombocytopenia and chronic liver disease who were scheduled to undergo a procedure.
Patients with low baseline platelet counts (<40x 109/L) were randomized to receive 60 mg of avatrombopag or placebo daily for 5 days.
Patients with higher baseline platelet counts (40 to <50 x 109/L) were randomized to receive 40 mg of avatrombopag or placebo daily for 5 days.
Patients underwent their procedures 5 to 8 days after their last dose of avatrombopag.
In ADAPT-1, 85 patients completed treatment with avatrombopag at 60 mg, 55 completed treatment with avatrombopag at 40 mg, and 78 controls completed the study.
In ADAPT-2, 68 patients completed treatment with avatrombopag at 60 mg, 55 completed treatment with avatrombopag at 40 mg, and 68 controls completed the study.
Efficacy
The primary efficacy endpoint of these trials was the proportion of patients who did not require any bleeding rescue up to 7 days post-procedure. Bleeding rescue included platelet transfusion, fresh frozen plasma, cryoprecipitate, vitamin K (phytonadione), desmopressin, recombinant activated factor VII, aminocaproicacid, tranexamic acid, whole blood transfusion, packed red cell transfusion, surgical intervention, or interventional radiology.
In ADAPT-1, the primary endpoint was achieved by 66% of patients who received avatrombopag at 60 mg and 23% of those who received placebo in the low-platelet-count cohort (P<0.0001). The endpoint was also achieved by 88% of patients who received avatrombopag at 40 mg and 38% of controls in the higher-platelet-count cohort (P<0.0001).
In ADAPT-2, the primary endpoint was achieved by 69% of patients who received avatrombopag at 60 mg and 35% of those who received placebo in the low-platelet-count cohort (P<0.0006). The endpoint was also achieved by 88% of patients who received avatrombopag at 40 mg and 33% of controls in the higher- platelet-count cohort (P<0.0001).
A secondary efficacy endpoint was the proportion of patients achieving the target platelet count (≥50 x 109/L).
In ADAPT-1, this endpoint was met by 69% of patients who received avatrombopag at 60 mg and 4% of controls in the low-platelet-count cohort (P<0.0001). It was also met by 88% of patients who received avatrombopag at 40 mg and 21% of controls in the higher-platelet-count cohort (P<0.0001)
In ADAPT-2, this endpoint was met by 67% of patients who received avatrombopag at 60 mg and 7% of controls in the low-platelet-count cohort (P<0.0001). It was also met by 93% of patients who received avatrombopag at 40 mg and 39% of controls in the higher-platelet-count cohort (P<0.0001).
Safety
The researchers pooled safety data from the 2 trials.
Treatment-emergent adverse events (AEs) occurred in 58.2% of controls and 56% of avatrombopag-treated patients in the low-platelet-count cohort (60 mg). Treatment-emergent AEs also occurred in 50.8% of controls and 51.3% of avatrombopag-treated patients in the higher-platelet-count cohort (40 mg).
The most frequently reported treatment-emergent AEs were pyrexia, abdominal pain, nausea, headache, diarrhea, and fatigue.
One patient experienced partial portal vein thrombosis that was considered non-serious and potentially related to avatrombopag.
Treatment-related AEs occurred in 17.6% of controls and 11.3% of avatrombopag-treated patients in the low-platelet-count cohort. Treatment-related AEs also occurred in 6.2% of controls and 7% of avatrombopag-treated patients in the higher-platelet-count cohort.
Serious AEs occurred in 13.2%, 6.9%, 3.1%, and 7.8%, respectively.
There were 3 deaths—2 in the 40 mg avatrombopag arm in ADAPT-1 and 1 in the control group in ADAPT-2. None of the deaths was considered treatment-related.
Future directions
Dova Pharmaceuticals, Inc., is planning to explore the potential use of avatrombopag in a broader population of patients with thrombocytopenia. This includes patients undergoing surgical procedures associated with a high risk of bleeding and patients who develop thrombocytopenia after receiving chemotherapy.
In addition, the company is exploring a potential regulatory approval pathway for avatrombopag for the treatment of adults with chronic immune thrombocytopenic purpura based on results from a completed phase 3 trial in this patient population. ![]()
The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has granted priority review to the new drug application (NDA) for avatrombopag.
Avatrombopag is a second-generation thrombopoietin receptor agonist that is intended to address the limitations of existing treatments for thrombocytopenia.
With this NDA, Dova Pharmaceuticals, Inc., is seeking approval of avatrombopag for the treatment of thrombocytopenia in patients with chronic liver disease who are scheduled to undergo a procedure.
The FDA expects to make a decision on the NDA by May 21, 2018.
The FDA’s goal is to take action on a priority review application within 6 months of receiving it, rather than the standard 10 months.
The FDA grants priority review to applications for products that may provide significant improvements in the treatment, diagnosis, or prevention of serious conditions.
Phase 3 trials
The NDA submission for avatrombopag is supported by 2 identically designed phase 3 trials, ADAPT 1 and ADAPT 2. Results from these trials were presented at the 2017 American Association for the Study of Liver Disease (AASLD) Meeting last month (abstract 217).
The studies randomized 435 patients with thrombocytopenia and chronic liver disease who were scheduled to undergo a procedure.
Patients with low baseline platelet counts (<40x 109/L) were randomized to receive 60 mg of avatrombopag or placebo daily for 5 days.
Patients with higher baseline platelet counts (40 to <50 x 109/L) were randomized to receive 40 mg of avatrombopag or placebo daily for 5 days.
Patients underwent their procedures 5 to 8 days after their last dose of avatrombopag.
In ADAPT-1, 85 patients completed treatment with avatrombopag at 60 mg, 55 completed treatment with avatrombopag at 40 mg, and 78 controls completed the study.
In ADAPT-2, 68 patients completed treatment with avatrombopag at 60 mg, 55 completed treatment with avatrombopag at 40 mg, and 68 controls completed the study.
Efficacy
The primary efficacy endpoint of these trials was the proportion of patients who did not require any bleeding rescue up to 7 days post-procedure. Bleeding rescue included platelet transfusion, fresh frozen plasma, cryoprecipitate, vitamin K (phytonadione), desmopressin, recombinant activated factor VII, aminocaproicacid, tranexamic acid, whole blood transfusion, packed red cell transfusion, surgical intervention, or interventional radiology.
In ADAPT-1, the primary endpoint was achieved by 66% of patients who received avatrombopag at 60 mg and 23% of those who received placebo in the low-platelet-count cohort (P<0.0001). The endpoint was also achieved by 88% of patients who received avatrombopag at 40 mg and 38% of controls in the higher-platelet-count cohort (P<0.0001).
In ADAPT-2, the primary endpoint was achieved by 69% of patients who received avatrombopag at 60 mg and 35% of those who received placebo in the low-platelet-count cohort (P<0.0006). The endpoint was also achieved by 88% of patients who received avatrombopag at 40 mg and 33% of controls in the higher- platelet-count cohort (P<0.0001).
A secondary efficacy endpoint was the proportion of patients achieving the target platelet count (≥50 x 109/L).
In ADAPT-1, this endpoint was met by 69% of patients who received avatrombopag at 60 mg and 4% of controls in the low-platelet-count cohort (P<0.0001). It was also met by 88% of patients who received avatrombopag at 40 mg and 21% of controls in the higher-platelet-count cohort (P<0.0001)
In ADAPT-2, this endpoint was met by 67% of patients who received avatrombopag at 60 mg and 7% of controls in the low-platelet-count cohort (P<0.0001). It was also met by 93% of patients who received avatrombopag at 40 mg and 39% of controls in the higher-platelet-count cohort (P<0.0001).
Safety
The researchers pooled safety data from the 2 trials.
Treatment-emergent adverse events (AEs) occurred in 58.2% of controls and 56% of avatrombopag-treated patients in the low-platelet-count cohort (60 mg). Treatment-emergent AEs also occurred in 50.8% of controls and 51.3% of avatrombopag-treated patients in the higher-platelet-count cohort (40 mg).
The most frequently reported treatment-emergent AEs were pyrexia, abdominal pain, nausea, headache, diarrhea, and fatigue.
One patient experienced partial portal vein thrombosis that was considered non-serious and potentially related to avatrombopag.
Treatment-related AEs occurred in 17.6% of controls and 11.3% of avatrombopag-treated patients in the low-platelet-count cohort. Treatment-related AEs also occurred in 6.2% of controls and 7% of avatrombopag-treated patients in the higher-platelet-count cohort.
Serious AEs occurred in 13.2%, 6.9%, 3.1%, and 7.8%, respectively.
There were 3 deaths—2 in the 40 mg avatrombopag arm in ADAPT-1 and 1 in the control group in ADAPT-2. None of the deaths was considered treatment-related.
Future directions
Dova Pharmaceuticals, Inc., is planning to explore the potential use of avatrombopag in a broader population of patients with thrombocytopenia. This includes patients undergoing surgical procedures associated with a high risk of bleeding and patients who develop thrombocytopenia after receiving chemotherapy.
In addition, the company is exploring a potential regulatory approval pathway for avatrombopag for the treatment of adults with chronic immune thrombocytopenic purpura based on results from a completed phase 3 trial in this patient population. ![]()
The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has granted priority review to the new drug application (NDA) for avatrombopag.
Avatrombopag is a second-generation thrombopoietin receptor agonist that is intended to address the limitations of existing treatments for thrombocytopenia.
With this NDA, Dova Pharmaceuticals, Inc., is seeking approval of avatrombopag for the treatment of thrombocytopenia in patients with chronic liver disease who are scheduled to undergo a procedure.
The FDA expects to make a decision on the NDA by May 21, 2018.
The FDA’s goal is to take action on a priority review application within 6 months of receiving it, rather than the standard 10 months.
The FDA grants priority review to applications for products that may provide significant improvements in the treatment, diagnosis, or prevention of serious conditions.
Phase 3 trials
The NDA submission for avatrombopag is supported by 2 identically designed phase 3 trials, ADAPT 1 and ADAPT 2. Results from these trials were presented at the 2017 American Association for the Study of Liver Disease (AASLD) Meeting last month (abstract 217).
The studies randomized 435 patients with thrombocytopenia and chronic liver disease who were scheduled to undergo a procedure.
Patients with low baseline platelet counts (<40x 109/L) were randomized to receive 60 mg of avatrombopag or placebo daily for 5 days.
Patients with higher baseline platelet counts (40 to <50 x 109/L) were randomized to receive 40 mg of avatrombopag or placebo daily for 5 days.
Patients underwent their procedures 5 to 8 days after their last dose of avatrombopag.
In ADAPT-1, 85 patients completed treatment with avatrombopag at 60 mg, 55 completed treatment with avatrombopag at 40 mg, and 78 controls completed the study.
In ADAPT-2, 68 patients completed treatment with avatrombopag at 60 mg, 55 completed treatment with avatrombopag at 40 mg, and 68 controls completed the study.
Efficacy
The primary efficacy endpoint of these trials was the proportion of patients who did not require any bleeding rescue up to 7 days post-procedure. Bleeding rescue included platelet transfusion, fresh frozen plasma, cryoprecipitate, vitamin K (phytonadione), desmopressin, recombinant activated factor VII, aminocaproicacid, tranexamic acid, whole blood transfusion, packed red cell transfusion, surgical intervention, or interventional radiology.
In ADAPT-1, the primary endpoint was achieved by 66% of patients who received avatrombopag at 60 mg and 23% of those who received placebo in the low-platelet-count cohort (P<0.0001). The endpoint was also achieved by 88% of patients who received avatrombopag at 40 mg and 38% of controls in the higher-platelet-count cohort (P<0.0001).
In ADAPT-2, the primary endpoint was achieved by 69% of patients who received avatrombopag at 60 mg and 35% of those who received placebo in the low-platelet-count cohort (P<0.0006). The endpoint was also achieved by 88% of patients who received avatrombopag at 40 mg and 33% of controls in the higher- platelet-count cohort (P<0.0001).
A secondary efficacy endpoint was the proportion of patients achieving the target platelet count (≥50 x 109/L).
In ADAPT-1, this endpoint was met by 69% of patients who received avatrombopag at 60 mg and 4% of controls in the low-platelet-count cohort (P<0.0001). It was also met by 88% of patients who received avatrombopag at 40 mg and 21% of controls in the higher-platelet-count cohort (P<0.0001)
In ADAPT-2, this endpoint was met by 67% of patients who received avatrombopag at 60 mg and 7% of controls in the low-platelet-count cohort (P<0.0001). It was also met by 93% of patients who received avatrombopag at 40 mg and 39% of controls in the higher-platelet-count cohort (P<0.0001).
Safety
The researchers pooled safety data from the 2 trials.
Treatment-emergent adverse events (AEs) occurred in 58.2% of controls and 56% of avatrombopag-treated patients in the low-platelet-count cohort (60 mg). Treatment-emergent AEs also occurred in 50.8% of controls and 51.3% of avatrombopag-treated patients in the higher-platelet-count cohort (40 mg).
The most frequently reported treatment-emergent AEs were pyrexia, abdominal pain, nausea, headache, diarrhea, and fatigue.
One patient experienced partial portal vein thrombosis that was considered non-serious and potentially related to avatrombopag.
Treatment-related AEs occurred in 17.6% of controls and 11.3% of avatrombopag-treated patients in the low-platelet-count cohort. Treatment-related AEs also occurred in 6.2% of controls and 7% of avatrombopag-treated patients in the higher-platelet-count cohort.
Serious AEs occurred in 13.2%, 6.9%, 3.1%, and 7.8%, respectively.
There were 3 deaths—2 in the 40 mg avatrombopag arm in ADAPT-1 and 1 in the control group in ADAPT-2. None of the deaths was considered treatment-related.
Future directions
Dova Pharmaceuticals, Inc., is planning to explore the potential use of avatrombopag in a broader population of patients with thrombocytopenia. This includes patients undergoing surgical procedures associated with a high risk of bleeding and patients who develop thrombocytopenia after receiving chemotherapy.
In addition, the company is exploring a potential regulatory approval pathway for avatrombopag for the treatment of adults with chronic immune thrombocytopenic purpura based on results from a completed phase 3 trial in this patient population. ![]()
Thoughts, emotions linked to opioid use in SCD
Results of a small study suggest that negative thoughts and emotions may increase opioid use in patients with sickle cell disease (SCD).
Researchers analyzed data from daily electronic patient diaries and found that patients were more likely to use short-acting opioids both when they experienced increased pain and “catastrophic” thoughts about that pain.
In fact, pain catastrophizing led to an increased use of short-acting opioids even when patients reported low levels of pain.
In addition, patients were more likely to use long-acting opioids when they experienced negative emotions.
The researchers noted that this study wasn’t designed to show that negative emotions or thinking cause an increase in opioid use. It was only designed to determine if there was an association.
Patrick Finan, PhD, of Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine in Baltimore, Maryland, and his colleagues described this study in The Journal of Pain.
The researchers enrolled 85 adults with SCD in this study. Patients were asked to fill out electronic diaries on a handheld personal computer every evening for 90 days.
The final analysis included only 45 patients, as these were the subjects who filled out the diary more than 25% of the time and had taken opioid pills at least once during the study period.
The patients had an average age of 37, and 71% were female. Most (93%) were African American, and 7% were classified as “other” or did not report their race.
At the start of the study, the patients reported on the dosage and type of opioid pill they were prescribed for long-acting and short-acting use. The daily diary collected data on the number of long-acting and short-acting opioid pills taken per day.
Patients rated their daily pain level on a scale of 0 to 10, with 0 being no pain and 10 being the worst pain imaginable.
Patients also rated positive emotions—including happy, calm, and cheerful—and negative emotions—including lonely, sad, anxious, and tired—on a scale of 0 to 10, with 0 being no emotion and 10 being the most intense emotion. The scores were converted to a 0-to-100 scale for the data analysis.
Separately, the researchers measured negative thinking using a Pain Catastrophizing Scale to rate “rumination,” or focus on pain, helplessness, and magnification of a current pain situation.
Results
Negative emotions were significantly associated with increased levels of long-acting opioids (P=0.001). The opioid dosage increased by 3.4 morphine milligram equivalents for every 10-point increase in negative emotions.
On the other hand, patients’ daily pain level, positive emotions, and negative thinking through catastrophizing did not significantly affect the amount of long-acting opioids taken.
“When someone is prescribed a daily, long-acting opioid, it is typically supposed to be at a fixed dose, and their pain level or emotions shouldn’t dictate whether they take more of this prescription or not,” Dr Finan said.
“Although we can’t prove misuse of the medication in our study, these data suggest that physicians and patients should clearly communicate about how patients should be taking their daily, long-acting opioids in order to minimize the potential for misuse.”
The researchers also found a significant association with short-acting opioid use and daily pain levels (P=0.006) as well as negative thinking by catastrophizing (P<0.001).
For every 10-point increase on the pain scale, the amount of short-acting opioids increased by 1.8 morphine milligram equivalents, and for every 10-point increase on the catastrophizing scale, pain medicine dosage increased by 2.5 morphine milligram equivalents.
Positive and negative emotions had no significant effect on the use of short-acting opioids.
“When pain was reported as low, sickle cell disease patients reported higher opioid use if they catastrophized, or focused their thinking on their pain, than if they didn’t,” Dr Finan said. “When pain levels were higher, negative thinking played less of a role in influencing opioid use.”
Dr Finan cautioned that studies such as this have some weaknesses, including the fact that self-reports are always uncertain, and the study only included 1 time point per day, although a person’s mood may fluctuate throughout the day based on life events and experiences.
For future studies, Dr Finan wants to use smartphone technology that can assess moods randomly throughout the day.
“Once we have a more intensive study to track mood variations throughout the day,” Dr Finan said, “then we can determine when it will be appropriate to send messages through text to intervene and affect patient behavior.” ![]()
Results of a small study suggest that negative thoughts and emotions may increase opioid use in patients with sickle cell disease (SCD).
Researchers analyzed data from daily electronic patient diaries and found that patients were more likely to use short-acting opioids both when they experienced increased pain and “catastrophic” thoughts about that pain.
In fact, pain catastrophizing led to an increased use of short-acting opioids even when patients reported low levels of pain.
In addition, patients were more likely to use long-acting opioids when they experienced negative emotions.
The researchers noted that this study wasn’t designed to show that negative emotions or thinking cause an increase in opioid use. It was only designed to determine if there was an association.
Patrick Finan, PhD, of Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine in Baltimore, Maryland, and his colleagues described this study in The Journal of Pain.
The researchers enrolled 85 adults with SCD in this study. Patients were asked to fill out electronic diaries on a handheld personal computer every evening for 90 days.
The final analysis included only 45 patients, as these were the subjects who filled out the diary more than 25% of the time and had taken opioid pills at least once during the study period.
The patients had an average age of 37, and 71% were female. Most (93%) were African American, and 7% were classified as “other” or did not report their race.
At the start of the study, the patients reported on the dosage and type of opioid pill they were prescribed for long-acting and short-acting use. The daily diary collected data on the number of long-acting and short-acting opioid pills taken per day.
Patients rated their daily pain level on a scale of 0 to 10, with 0 being no pain and 10 being the worst pain imaginable.
Patients also rated positive emotions—including happy, calm, and cheerful—and negative emotions—including lonely, sad, anxious, and tired—on a scale of 0 to 10, with 0 being no emotion and 10 being the most intense emotion. The scores were converted to a 0-to-100 scale for the data analysis.
Separately, the researchers measured negative thinking using a Pain Catastrophizing Scale to rate “rumination,” or focus on pain, helplessness, and magnification of a current pain situation.
Results
Negative emotions were significantly associated with increased levels of long-acting opioids (P=0.001). The opioid dosage increased by 3.4 morphine milligram equivalents for every 10-point increase in negative emotions.
On the other hand, patients’ daily pain level, positive emotions, and negative thinking through catastrophizing did not significantly affect the amount of long-acting opioids taken.
“When someone is prescribed a daily, long-acting opioid, it is typically supposed to be at a fixed dose, and their pain level or emotions shouldn’t dictate whether they take more of this prescription or not,” Dr Finan said.
“Although we can’t prove misuse of the medication in our study, these data suggest that physicians and patients should clearly communicate about how patients should be taking their daily, long-acting opioids in order to minimize the potential for misuse.”
The researchers also found a significant association with short-acting opioid use and daily pain levels (P=0.006) as well as negative thinking by catastrophizing (P<0.001).
For every 10-point increase on the pain scale, the amount of short-acting opioids increased by 1.8 morphine milligram equivalents, and for every 10-point increase on the catastrophizing scale, pain medicine dosage increased by 2.5 morphine milligram equivalents.
Positive and negative emotions had no significant effect on the use of short-acting opioids.
“When pain was reported as low, sickle cell disease patients reported higher opioid use if they catastrophized, or focused their thinking on their pain, than if they didn’t,” Dr Finan said. “When pain levels were higher, negative thinking played less of a role in influencing opioid use.”
Dr Finan cautioned that studies such as this have some weaknesses, including the fact that self-reports are always uncertain, and the study only included 1 time point per day, although a person’s mood may fluctuate throughout the day based on life events and experiences.
For future studies, Dr Finan wants to use smartphone technology that can assess moods randomly throughout the day.
“Once we have a more intensive study to track mood variations throughout the day,” Dr Finan said, “then we can determine when it will be appropriate to send messages through text to intervene and affect patient behavior.” ![]()
Results of a small study suggest that negative thoughts and emotions may increase opioid use in patients with sickle cell disease (SCD).
Researchers analyzed data from daily electronic patient diaries and found that patients were more likely to use short-acting opioids both when they experienced increased pain and “catastrophic” thoughts about that pain.
In fact, pain catastrophizing led to an increased use of short-acting opioids even when patients reported low levels of pain.
In addition, patients were more likely to use long-acting opioids when they experienced negative emotions.
The researchers noted that this study wasn’t designed to show that negative emotions or thinking cause an increase in opioid use. It was only designed to determine if there was an association.
Patrick Finan, PhD, of Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine in Baltimore, Maryland, and his colleagues described this study in The Journal of Pain.
The researchers enrolled 85 adults with SCD in this study. Patients were asked to fill out electronic diaries on a handheld personal computer every evening for 90 days.
The final analysis included only 45 patients, as these were the subjects who filled out the diary more than 25% of the time and had taken opioid pills at least once during the study period.
The patients had an average age of 37, and 71% were female. Most (93%) were African American, and 7% were classified as “other” or did not report their race.
At the start of the study, the patients reported on the dosage and type of opioid pill they were prescribed for long-acting and short-acting use. The daily diary collected data on the number of long-acting and short-acting opioid pills taken per day.
Patients rated their daily pain level on a scale of 0 to 10, with 0 being no pain and 10 being the worst pain imaginable.
Patients also rated positive emotions—including happy, calm, and cheerful—and negative emotions—including lonely, sad, anxious, and tired—on a scale of 0 to 10, with 0 being no emotion and 10 being the most intense emotion. The scores were converted to a 0-to-100 scale for the data analysis.
Separately, the researchers measured negative thinking using a Pain Catastrophizing Scale to rate “rumination,” or focus on pain, helplessness, and magnification of a current pain situation.
Results
Negative emotions were significantly associated with increased levels of long-acting opioids (P=0.001). The opioid dosage increased by 3.4 morphine milligram equivalents for every 10-point increase in negative emotions.
On the other hand, patients’ daily pain level, positive emotions, and negative thinking through catastrophizing did not significantly affect the amount of long-acting opioids taken.
“When someone is prescribed a daily, long-acting opioid, it is typically supposed to be at a fixed dose, and their pain level or emotions shouldn’t dictate whether they take more of this prescription or not,” Dr Finan said.
“Although we can’t prove misuse of the medication in our study, these data suggest that physicians and patients should clearly communicate about how patients should be taking their daily, long-acting opioids in order to minimize the potential for misuse.”
The researchers also found a significant association with short-acting opioid use and daily pain levels (P=0.006) as well as negative thinking by catastrophizing (P<0.001).
For every 10-point increase on the pain scale, the amount of short-acting opioids increased by 1.8 morphine milligram equivalents, and for every 10-point increase on the catastrophizing scale, pain medicine dosage increased by 2.5 morphine milligram equivalents.
Positive and negative emotions had no significant effect on the use of short-acting opioids.
“When pain was reported as low, sickle cell disease patients reported higher opioid use if they catastrophized, or focused their thinking on their pain, than if they didn’t,” Dr Finan said. “When pain levels were higher, negative thinking played less of a role in influencing opioid use.”
Dr Finan cautioned that studies such as this have some weaknesses, including the fact that self-reports are always uncertain, and the study only included 1 time point per day, although a person’s mood may fluctuate throughout the day based on life events and experiences.
For future studies, Dr Finan wants to use smartphone technology that can assess moods randomly throughout the day.
“Once we have a more intensive study to track mood variations throughout the day,” Dr Finan said, “then we can determine when it will be appropriate to send messages through text to intervene and affect patient behavior.” ![]()
Emerging sickle cell agents target new pathways
CONCORD, N.C. – Approved treatments for sickle cell disease have been extremely limited, but there are several therapies in the research pipeline that use new pathways to target the disease.
“We do have much better understanding of the pathophysiology, which is getting us a few more targets to aim at,” Julie Kanter, MD, director of sickle cell research at the Medical University of South Carolina, Charleston, said at Sickle Cell Disease Symposium held by Carolinas Health Care System. These targets include influencing how cells interact with the vascular endothelium, inhibiting platelets, and preventing cell sickling and inflammation.
“I’m waiting to see who’s willing to take it just because it is a lot of powder that the patient has to mix and drink twice a day, but it does look promising to reduce inflammation,” Dr. Kanter said.
SCD pipeline
Deeper in the sickle cell pipeline is a class of antisickling agents known as hemoglobin modifiers. “We’re tying to change the way hemoglobin binds to oxygen, and if we can keep hemoglobin binding to oxygen longer, it actually decreases the risk of hemoglobin sickling and polymerizing in the cell,” Dr. Kanter explained.
One hemoglobin modifier is voxelotor (previously called GBT440), a once-daily oral agent that Global Blood Therapeutics has in development.
Another category of antisickling agents that researchers are looking at is anti-inflammatory moderators, Dr. Kanter said. These include nitric oxide donors like sildenafil, which did not “quite work” in SCD, and arginine and glutamine, which increase the amount of nitric oxide once in the body “and hopefully reduce the risk of sickling,” she said. “If we can improve inflammation, we might be able to improve the risk of crisis.”
Cell adhesion modifiers are a drug class that aims to prevent cells from binding to each other. These include platelet inhibitors and endothelial blockers. “There are several antiplatelet agents that are approved really for stroke prevention or heart attack prevention, and we’re trying to see if we can repurpose these in sickle cell disease in a specific pathway that allows the platelet to stick to the endothelium, but if we only inhibit one pathway it should not increase the risk of bleeding,” Dr. Kanter said.
One platelet inhibition pathway that researchers are focused on is the P2Y12 adenosine diphosphate blockade, which the platelet inhibitor prasugrel (Effient) acts on. A 2016 study of this pathway in SCD “wasn’t successful,” Dr. Kanter said, “but it had some interesting results” – namely that the drug may be most effective in adolescents (N Engl J Med. 2016 Feb 18;374[7]:625-35).
Selectin-blocking medications are a drug class that act on white blood cell adhesion to, and movement through, the endothelium, Dr. Kanter said. “Neutrophils can instigate a sickle cell crisis, so if we can interrupt some of this rolling or sticking, could we decrease the risk of a sickle cell crisis?” The drug GMI-1070 is currently being studied in a phase III trial and so far has shown “a significant decrease in the amount of opioids used by those individuals who received the study drug,” she said.
Crizanlizumab (also known as SelG1) is a humanized monoclonal antibody with an affinity to P-selectin and is the subject of the phase II SUSTAIN trial, which included a cohort that also was taking hydroxyurea. Treatment with high-dose crizanlizumab resulted in an annual rate of sickle cell–related pain crises that was more than 45% lower than with placebo (N Engl J Med. 2017 Feb 2;376[5]:429-39).
Stem cell transplants
Besides drugs, stem cell transplants to treat SCD have advanced in recent years to the point where cure rates are exceeding 90%, Dr. Kanter noted. “However, the real issue with stem cells is that patients still don’t have enough donors,” she said.
SCD is also potentially amenable to gene therapy, Dr. Kanter said, noting that SCD gene therapy trials in progress are looking at harvesting patients’ own bone marrow, using the lentivirus viral vector, inserting a gene to increase production of nonsickle hemoglobin, and using myeloablative chemotherapy to remove old marrow and replace it with new, manipulated bone marrow.
Several programs are investigating using a gene editing technique, known as CRISPR/Cas9, to alter the BCL11A gene to maintain fetal hemoglobin production.
“We all make fetal hemoglobin at birth, and then over 6 months to 1 year of life, our bodies convert fetal hemoglobin to adult hemoglobin,” she said. “In sickle cell disease, it converts to sickle hemoglobin. What if we could prevent that conversion and keep the fetal hemoglobin turned on?” That could potentially eradicate the complications of SCD starting at an early age, Dr. Kanter said.
Dr. Kanter, who has been involved in several of the SCD trials, reported relationships with Pfizer, AstraZeneca, Bluebird Bio, Global Blood Therapeutics, Novartis, Guidepoint, GLG, ApoPharma, and Purdue Pharma.
CONCORD, N.C. – Approved treatments for sickle cell disease have been extremely limited, but there are several therapies in the research pipeline that use new pathways to target the disease.
“We do have much better understanding of the pathophysiology, which is getting us a few more targets to aim at,” Julie Kanter, MD, director of sickle cell research at the Medical University of South Carolina, Charleston, said at Sickle Cell Disease Symposium held by Carolinas Health Care System. These targets include influencing how cells interact with the vascular endothelium, inhibiting platelets, and preventing cell sickling and inflammation.
“I’m waiting to see who’s willing to take it just because it is a lot of powder that the patient has to mix and drink twice a day, but it does look promising to reduce inflammation,” Dr. Kanter said.
SCD pipeline
Deeper in the sickle cell pipeline is a class of antisickling agents known as hemoglobin modifiers. “We’re tying to change the way hemoglobin binds to oxygen, and if we can keep hemoglobin binding to oxygen longer, it actually decreases the risk of hemoglobin sickling and polymerizing in the cell,” Dr. Kanter explained.
One hemoglobin modifier is voxelotor (previously called GBT440), a once-daily oral agent that Global Blood Therapeutics has in development.
Another category of antisickling agents that researchers are looking at is anti-inflammatory moderators, Dr. Kanter said. These include nitric oxide donors like sildenafil, which did not “quite work” in SCD, and arginine and glutamine, which increase the amount of nitric oxide once in the body “and hopefully reduce the risk of sickling,” she said. “If we can improve inflammation, we might be able to improve the risk of crisis.”
Cell adhesion modifiers are a drug class that aims to prevent cells from binding to each other. These include platelet inhibitors and endothelial blockers. “There are several antiplatelet agents that are approved really for stroke prevention or heart attack prevention, and we’re trying to see if we can repurpose these in sickle cell disease in a specific pathway that allows the platelet to stick to the endothelium, but if we only inhibit one pathway it should not increase the risk of bleeding,” Dr. Kanter said.
One platelet inhibition pathway that researchers are focused on is the P2Y12 adenosine diphosphate blockade, which the platelet inhibitor prasugrel (Effient) acts on. A 2016 study of this pathway in SCD “wasn’t successful,” Dr. Kanter said, “but it had some interesting results” – namely that the drug may be most effective in adolescents (N Engl J Med. 2016 Feb 18;374[7]:625-35).
Selectin-blocking medications are a drug class that act on white blood cell adhesion to, and movement through, the endothelium, Dr. Kanter said. “Neutrophils can instigate a sickle cell crisis, so if we can interrupt some of this rolling or sticking, could we decrease the risk of a sickle cell crisis?” The drug GMI-1070 is currently being studied in a phase III trial and so far has shown “a significant decrease in the amount of opioids used by those individuals who received the study drug,” she said.
Crizanlizumab (also known as SelG1) is a humanized monoclonal antibody with an affinity to P-selectin and is the subject of the phase II SUSTAIN trial, which included a cohort that also was taking hydroxyurea. Treatment with high-dose crizanlizumab resulted in an annual rate of sickle cell–related pain crises that was more than 45% lower than with placebo (N Engl J Med. 2017 Feb 2;376[5]:429-39).
Stem cell transplants
Besides drugs, stem cell transplants to treat SCD have advanced in recent years to the point where cure rates are exceeding 90%, Dr. Kanter noted. “However, the real issue with stem cells is that patients still don’t have enough donors,” she said.
SCD is also potentially amenable to gene therapy, Dr. Kanter said, noting that SCD gene therapy trials in progress are looking at harvesting patients’ own bone marrow, using the lentivirus viral vector, inserting a gene to increase production of nonsickle hemoglobin, and using myeloablative chemotherapy to remove old marrow and replace it with new, manipulated bone marrow.
Several programs are investigating using a gene editing technique, known as CRISPR/Cas9, to alter the BCL11A gene to maintain fetal hemoglobin production.
“We all make fetal hemoglobin at birth, and then over 6 months to 1 year of life, our bodies convert fetal hemoglobin to adult hemoglobin,” she said. “In sickle cell disease, it converts to sickle hemoglobin. What if we could prevent that conversion and keep the fetal hemoglobin turned on?” That could potentially eradicate the complications of SCD starting at an early age, Dr. Kanter said.
Dr. Kanter, who has been involved in several of the SCD trials, reported relationships with Pfizer, AstraZeneca, Bluebird Bio, Global Blood Therapeutics, Novartis, Guidepoint, GLG, ApoPharma, and Purdue Pharma.
CONCORD, N.C. – Approved treatments for sickle cell disease have been extremely limited, but there are several therapies in the research pipeline that use new pathways to target the disease.
“We do have much better understanding of the pathophysiology, which is getting us a few more targets to aim at,” Julie Kanter, MD, director of sickle cell research at the Medical University of South Carolina, Charleston, said at Sickle Cell Disease Symposium held by Carolinas Health Care System. These targets include influencing how cells interact with the vascular endothelium, inhibiting platelets, and preventing cell sickling and inflammation.
“I’m waiting to see who’s willing to take it just because it is a lot of powder that the patient has to mix and drink twice a day, but it does look promising to reduce inflammation,” Dr. Kanter said.
SCD pipeline
Deeper in the sickle cell pipeline is a class of antisickling agents known as hemoglobin modifiers. “We’re tying to change the way hemoglobin binds to oxygen, and if we can keep hemoglobin binding to oxygen longer, it actually decreases the risk of hemoglobin sickling and polymerizing in the cell,” Dr. Kanter explained.
One hemoglobin modifier is voxelotor (previously called GBT440), a once-daily oral agent that Global Blood Therapeutics has in development.
Another category of antisickling agents that researchers are looking at is anti-inflammatory moderators, Dr. Kanter said. These include nitric oxide donors like sildenafil, which did not “quite work” in SCD, and arginine and glutamine, which increase the amount of nitric oxide once in the body “and hopefully reduce the risk of sickling,” she said. “If we can improve inflammation, we might be able to improve the risk of crisis.”
Cell adhesion modifiers are a drug class that aims to prevent cells from binding to each other. These include platelet inhibitors and endothelial blockers. “There are several antiplatelet agents that are approved really for stroke prevention or heart attack prevention, and we’re trying to see if we can repurpose these in sickle cell disease in a specific pathway that allows the platelet to stick to the endothelium, but if we only inhibit one pathway it should not increase the risk of bleeding,” Dr. Kanter said.
One platelet inhibition pathway that researchers are focused on is the P2Y12 adenosine diphosphate blockade, which the platelet inhibitor prasugrel (Effient) acts on. A 2016 study of this pathway in SCD “wasn’t successful,” Dr. Kanter said, “but it had some interesting results” – namely that the drug may be most effective in adolescents (N Engl J Med. 2016 Feb 18;374[7]:625-35).
Selectin-blocking medications are a drug class that act on white blood cell adhesion to, and movement through, the endothelium, Dr. Kanter said. “Neutrophils can instigate a sickle cell crisis, so if we can interrupt some of this rolling or sticking, could we decrease the risk of a sickle cell crisis?” The drug GMI-1070 is currently being studied in a phase III trial and so far has shown “a significant decrease in the amount of opioids used by those individuals who received the study drug,” she said.
Crizanlizumab (also known as SelG1) is a humanized monoclonal antibody with an affinity to P-selectin and is the subject of the phase II SUSTAIN trial, which included a cohort that also was taking hydroxyurea. Treatment with high-dose crizanlizumab resulted in an annual rate of sickle cell–related pain crises that was more than 45% lower than with placebo (N Engl J Med. 2017 Feb 2;376[5]:429-39).
Stem cell transplants
Besides drugs, stem cell transplants to treat SCD have advanced in recent years to the point where cure rates are exceeding 90%, Dr. Kanter noted. “However, the real issue with stem cells is that patients still don’t have enough donors,” she said.
SCD is also potentially amenable to gene therapy, Dr. Kanter said, noting that SCD gene therapy trials in progress are looking at harvesting patients’ own bone marrow, using the lentivirus viral vector, inserting a gene to increase production of nonsickle hemoglobin, and using myeloablative chemotherapy to remove old marrow and replace it with new, manipulated bone marrow.
Several programs are investigating using a gene editing technique, known as CRISPR/Cas9, to alter the BCL11A gene to maintain fetal hemoglobin production.
“We all make fetal hemoglobin at birth, and then over 6 months to 1 year of life, our bodies convert fetal hemoglobin to adult hemoglobin,” she said. “In sickle cell disease, it converts to sickle hemoglobin. What if we could prevent that conversion and keep the fetal hemoglobin turned on?” That could potentially eradicate the complications of SCD starting at an early age, Dr. Kanter said.
Dr. Kanter, who has been involved in several of the SCD trials, reported relationships with Pfizer, AstraZeneca, Bluebird Bio, Global Blood Therapeutics, Novartis, Guidepoint, GLG, ApoPharma, and Purdue Pharma.
EXPERT ANALYSIS FROM A MEETING ON SICKLE CELL DISEASE