User login
Early Infantile Hemangioma Diagnosis Is Key in Skin of Color
Early Infantile Hemangioma Diagnosis Is Key in Skin of Color
Richard P. Usatine, MD
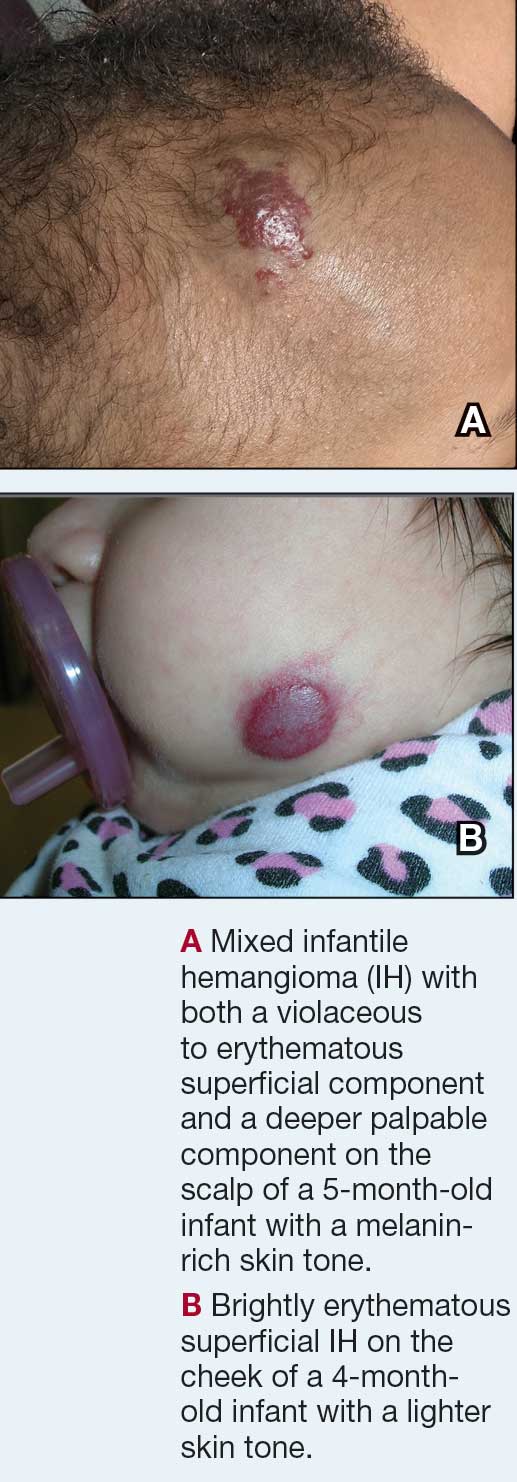
Infantile hemangioma (IH) is the most common vascular tumor of infancy, appearing within the first few weeks of life and typically reaching peak size by age 3 to 5 months.1 It classically manifests as a raised or flat bright-red lesion in the upper dermis of the skin and/or subcutaneous tissue and can vary in number, size, shape, and location.2 It is characterized by a rapid proliferative phase, especially between 5 and 8 weeks of age, followed by gradual spontaneous regression over 1 to 10 years.1-3
Infantile hemangiomas are categorized based on depth (superficial, deep, or mixed) and distribution pattern (focal, multifocal, segmental, or indeterminate).4 In most cases, complete regression occurs by age 4 years, but there can be residual telangiectasia, fibrofatty tissue, and/or scarring.1,4 About 10% to 15% of IHs result in complications that require medical intervention (eg, visual, airway, or auditory compromise; ulceration; disfigurement); ideally, these patients should be referred to a specialist by 5 weeks of age.4 Prompt assessment of IH severity is essential to prevent or mitigate potential complications and ultimately improve outcomes.3 Social drivers of health contribute to delayed diagnosis and management of hemangiomas, leading to increased complications in some patient populations.5-7
Epidemiology
Infantile hemangiomas are estimated to manifest in 4.5% of infants in the United States.1 The most common type is superficial IH, typically found on the head or neck.5 Risk factors in infants include female sex, White race, premature birth, and low birth weight (< 1000 g).1,3 Maternal risk factors include advanced gestational age (ie, > 35 years), multiple gestations, family history of IH, tobacco use, use of progesterone therapy during pregnancy, and pre-eclampsia.1,3
Focal IH typically manifests as a single localized lesion that can occur anywhere on the body.2,3 In contrast, segmental IH manifests in a linear pattern and/or is distributed on a large anatomic area, most commonly on the face and less frequently the extremities and trunk.
Key Clinical Features
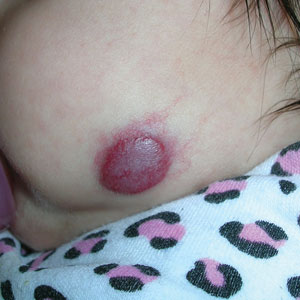
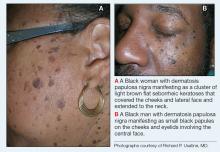
Superficial IH in patients with darker skin tones may appear as a dark-red or violaceous papule or plaque compared to bright red in lighter skin tones.5 Deep IH may appear as a soft, round, flesh-colored or blue-hued subcutaneous mass, the color of which may be harder to appreciate in those with darker skin tones.5
Worth Noting
Complications from IH may require imaging, close follow-up, systemic therapy, multidisciplinary care, and advanced health literacy and patient/family navigation. Multifocal IHs (≥ 5 lesions) are more likely to be associated with infantile hepatic hemangiomas.2,3 Large (> 5 cm) segmental IHs on the face and lumbosacral area require further evaluation for PHACES (posterior fossa malformation, hemangiomas, arterial anomalies, cardiac defects, eye anomalies, and sternal raphe/cleft defects) and LUMBAR (lower-body segmental IH; urogenital anomalies and ulceration; myelopathy; bony deformities; anorectal malformations and arterial anomalies; and renal anomalies) syndromes, which are more common in patients of Hispanic ethnicity.2,3
The Infantile Hemangioma Referral Score is a recently validated tool that can assist primary care physicians in timely referral of IHs requiring early specialist intervention.4,9 It takes into account the location, number, and size of the lesions and the age of the patient; these factors help to determine which IHs may be managed conservatively vs those that may require treatment to prevent life-threatening complications.1-3
Systemic corticosteroids historically have been the primary treatment for IH; however, in the past decade, propranolol oral solution (4.28 mg/mL) has become the first-line therapy for most infants requiring systemic management.10 It is the only medication approved by the US Food and Drug Administration for proliferating IH, with treatment initiation as young as 5 weeks corrected age.11 As a nonselective beta-blocker, propranolol is believed to reduce IHs through vasoconstriction or by inhibition of angiogenesis.1,4,10
For small superficial IHs, treatment options include timolol maleate ophthalmic solution 0.5% (one drop applied twice daily to the IH) or pulsed dye laser therapy.4,10 Surgical excision typically is avoided during infancy due to concerns about anesthetic risks and potential blood loss.4,10 Surgery is reserved for cases involving residual fibrofatty tissue, postinvolution scarring, obstruction of vital structures, or lesions in aesthetically sensitive areas as well as when propranolol is contraindicated.4,10
Health Disparity Highlight
Infants with skin of color and those of lower socioeconomic status (SES) face a heightened risk for delayed diagnosis and more advanced disease at the initial evaluation for IH.5,7 Access barriers such as geographic limitations to specialty services, lack of insurance, underinsurance, and language differences impact timely diagnosis and treatment.5,6 Implementation of telemedicine services in areas with limited access to specialists can facilitate early evaluation and risk stratification for IH.12
A retrospective cohort study of 804 children seen at a large academic hospital found that those of lower SES were more likely to seek care after 3 months of age than their higher-SES counterparts.6 Those who presented after 6 months of age also had higher IH severity scores compared to their counterparts with higher SES.6 Delayed access to care may cause children to miss the critical treatment window during the rapid proliferative growth phase.6,12 However, children insured through Medicaid or the Children’s Health Insurance Program who participated in institutional care management programs (which assist in scheduling specialty care appointments within the institution) sought treatment earlier regardless of their SES, suggesting that such programs may help reduce disparities in timely access for children of lower SES.6
An epidemiologic study analyzing the demographics of children hospitalized across the United States demonstrated that Black infants with IH were more likely to belong to the lowest income quartile compared with White infants or those of other races. They also were 2 times older on average at initial presentation (1.8 vs 1.0 years), experienced longer hospitalizations (16.4 vs 13.8 days), and underwent more IH-related procedures than White infants and infants of other races (2.4, 1.9, and 2.1, respectively).7
These and other factors may contribute to missed windows of opportunity for timely treatment of high-risk IHs in patients with darker skin tones and/or those facing challenges stemming from social drivers of health.
- Léauté-Labrèze C, Harper JI, Hoeger PH. Infantile haemangioma. Lancet. 2017;390:85-94.
- Mitra R, Fitzsimons HL, Hale T, et al. Recent advances in understanding the molecular basis of infantile haemangioma development. Br J Dermatol. 2024;191:661-669.
- Rodríguez Bandera AI, Sebaratnam DF, Wargon O, et al. Infantile hemangioma. Part 1: epidemiology, pathogenesis, clinical presentation and assessment. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2021;85:1379-1392.
- Sebaratnam DF, Rodríguez Bandera AL, Wong LCF, et al. Infantile hemangioma. Part 2: management. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2021;85:1395-1404.
- Taye ME, Shah J, Seiverling EV, et al. Diagnosis of vascular anomalies in patients with skin of color. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2024;17:54-62.
- Lie E, Psoter KJ, Püttgen KB. Lower socioeconomic status is associated with delayed access to care for infantile hemangioma: a cohort study. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2023;88:E221-E230.
- Kumar KD, Desai AD, Shah VP, et al. Racial discrepancies in presentation of hospitalized infantile hemangioma cases using the Kids’ Inpatient Database. Health Sci Rep. 2023;6:E1092.
- Chiller KG, Passaro D, Frieden IJ. Hemangiomas of infancy: clinical characteristics, morphologic subtypes, and their relationship to race, ethnicity, and sex. Arch Dermatol. 2002;138:1567.
- Léauté-Labrèze C, Baselga Torres E, Weibel L, et al. The infantile hemangioma referral score: a validated tool for physicians. Pediatrics. 2020;145:E20191628.
- Macca L, Altavilla D, Di Bartolomeo L, et al. Update on treatment of infantile hemangiomas: what’s new in the last five years? Front Pharmacol. 2022;13:879602.
- Krowchuk DP, Frieden IJ, Mancini AJ, et al. Clinical practice guideline for the management of infantile hemangiomas. Pediatrics. 2019;143:E20183475.
- Frieden IJ, Püttgen KB, Drolet BA, et al. Management of infantile hemangiomas during the COVID pandemic. Pediatr Dermatol. 2020;37:412-418.

Richard P. Usatine, MD
Infantile hemangioma (IH) is the most common vascular tumor of infancy, appearing within the first few weeks of life and typically reaching peak size by age 3 to 5 months.1 It classically manifests as a raised or flat bright-red lesion in the upper dermis of the skin and/or subcutaneous tissue and can vary in number, size, shape, and location.2 It is characterized by a rapid proliferative phase, especially between 5 and 8 weeks of age, followed by gradual spontaneous regression over 1 to 10 years.1-3
Infantile hemangiomas are categorized based on depth (superficial, deep, or mixed) and distribution pattern (focal, multifocal, segmental, or indeterminate).4 In most cases, complete regression occurs by age 4 years, but there can be residual telangiectasia, fibrofatty tissue, and/or scarring.1,4 About 10% to 15% of IHs result in complications that require medical intervention (eg, visual, airway, or auditory compromise; ulceration; disfigurement); ideally, these patients should be referred to a specialist by 5 weeks of age.4 Prompt assessment of IH severity is essential to prevent or mitigate potential complications and ultimately improve outcomes.3 Social drivers of health contribute to delayed diagnosis and management of hemangiomas, leading to increased complications in some patient populations.5-7
Epidemiology
Infantile hemangiomas are estimated to manifest in 4.5% of infants in the United States.1 The most common type is superficial IH, typically found on the head or neck.5 Risk factors in infants include female sex, White race, premature birth, and low birth weight (< 1000 g).1,3 Maternal risk factors include advanced gestational age (ie, > 35 years), multiple gestations, family history of IH, tobacco use, use of progesterone therapy during pregnancy, and pre-eclampsia.1,3
Focal IH typically manifests as a single localized lesion that can occur anywhere on the body.2,3 In contrast, segmental IH manifests in a linear pattern and/or is distributed on a large anatomic area, most commonly on the face and less frequently the extremities and trunk.
Key Clinical Features
Superficial IH in patients with darker skin tones may appear as a dark-red or violaceous papule or plaque compared to bright red in lighter skin tones.5 Deep IH may appear as a soft, round, flesh-colored or blue-hued subcutaneous mass, the color of which may be harder to appreciate in those with darker skin tones.5
Worth Noting
Complications from IH may require imaging, close follow-up, systemic therapy, multidisciplinary care, and advanced health literacy and patient/family navigation. Multifocal IHs (≥ 5 lesions) are more likely to be associated with infantile hepatic hemangiomas.2,3 Large (> 5 cm) segmental IHs on the face and lumbosacral area require further evaluation for PHACES (posterior fossa malformation, hemangiomas, arterial anomalies, cardiac defects, eye anomalies, and sternal raphe/cleft defects) and LUMBAR (lower-body segmental IH; urogenital anomalies and ulceration; myelopathy; bony deformities; anorectal malformations and arterial anomalies; and renal anomalies) syndromes, which are more common in patients of Hispanic ethnicity.2,3
The Infantile Hemangioma Referral Score is a recently validated tool that can assist primary care physicians in timely referral of IHs requiring early specialist intervention.4,9 It takes into account the location, number, and size of the lesions and the age of the patient; these factors help to determine which IHs may be managed conservatively vs those that may require treatment to prevent life-threatening complications.1-3
Systemic corticosteroids historically have been the primary treatment for IH; however, in the past decade, propranolol oral solution (4.28 mg/mL) has become the first-line therapy for most infants requiring systemic management.10 It is the only medication approved by the US Food and Drug Administration for proliferating IH, with treatment initiation as young as 5 weeks corrected age.11 As a nonselective beta-blocker, propranolol is believed to reduce IHs through vasoconstriction or by inhibition of angiogenesis.1,4,10
For small superficial IHs, treatment options include timolol maleate ophthalmic solution 0.5% (one drop applied twice daily to the IH) or pulsed dye laser therapy.4,10 Surgical excision typically is avoided during infancy due to concerns about anesthetic risks and potential blood loss.4,10 Surgery is reserved for cases involving residual fibrofatty tissue, postinvolution scarring, obstruction of vital structures, or lesions in aesthetically sensitive areas as well as when propranolol is contraindicated.4,10
Health Disparity Highlight
Infants with skin of color and those of lower socioeconomic status (SES) face a heightened risk for delayed diagnosis and more advanced disease at the initial evaluation for IH.5,7 Access barriers such as geographic limitations to specialty services, lack of insurance, underinsurance, and language differences impact timely diagnosis and treatment.5,6 Implementation of telemedicine services in areas with limited access to specialists can facilitate early evaluation and risk stratification for IH.12
A retrospective cohort study of 804 children seen at a large academic hospital found that those of lower SES were more likely to seek care after 3 months of age than their higher-SES counterparts.6 Those who presented after 6 months of age also had higher IH severity scores compared to their counterparts with higher SES.6 Delayed access to care may cause children to miss the critical treatment window during the rapid proliferative growth phase.6,12 However, children insured through Medicaid or the Children’s Health Insurance Program who participated in institutional care management programs (which assist in scheduling specialty care appointments within the institution) sought treatment earlier regardless of their SES, suggesting that such programs may help reduce disparities in timely access for children of lower SES.6
An epidemiologic study analyzing the demographics of children hospitalized across the United States demonstrated that Black infants with IH were more likely to belong to the lowest income quartile compared with White infants or those of other races. They also were 2 times older on average at initial presentation (1.8 vs 1.0 years), experienced longer hospitalizations (16.4 vs 13.8 days), and underwent more IH-related procedures than White infants and infants of other races (2.4, 1.9, and 2.1, respectively).7
These and other factors may contribute to missed windows of opportunity for timely treatment of high-risk IHs in patients with darker skin tones and/or those facing challenges stemming from social drivers of health.

Richard P. Usatine, MD
Infantile hemangioma (IH) is the most common vascular tumor of infancy, appearing within the first few weeks of life and typically reaching peak size by age 3 to 5 months.1 It classically manifests as a raised or flat bright-red lesion in the upper dermis of the skin and/or subcutaneous tissue and can vary in number, size, shape, and location.2 It is characterized by a rapid proliferative phase, especially between 5 and 8 weeks of age, followed by gradual spontaneous regression over 1 to 10 years.1-3
Infantile hemangiomas are categorized based on depth (superficial, deep, or mixed) and distribution pattern (focal, multifocal, segmental, or indeterminate).4 In most cases, complete regression occurs by age 4 years, but there can be residual telangiectasia, fibrofatty tissue, and/or scarring.1,4 About 10% to 15% of IHs result in complications that require medical intervention (eg, visual, airway, or auditory compromise; ulceration; disfigurement); ideally, these patients should be referred to a specialist by 5 weeks of age.4 Prompt assessment of IH severity is essential to prevent or mitigate potential complications and ultimately improve outcomes.3 Social drivers of health contribute to delayed diagnosis and management of hemangiomas, leading to increased complications in some patient populations.5-7
Epidemiology
Infantile hemangiomas are estimated to manifest in 4.5% of infants in the United States.1 The most common type is superficial IH, typically found on the head or neck.5 Risk factors in infants include female sex, White race, premature birth, and low birth weight (< 1000 g).1,3 Maternal risk factors include advanced gestational age (ie, > 35 years), multiple gestations, family history of IH, tobacco use, use of progesterone therapy during pregnancy, and pre-eclampsia.1,3
Focal IH typically manifests as a single localized lesion that can occur anywhere on the body.2,3 In contrast, segmental IH manifests in a linear pattern and/or is distributed on a large anatomic area, most commonly on the face and less frequently the extremities and trunk.
Key Clinical Features
Superficial IH in patients with darker skin tones may appear as a dark-red or violaceous papule or plaque compared to bright red in lighter skin tones.5 Deep IH may appear as a soft, round, flesh-colored or blue-hued subcutaneous mass, the color of which may be harder to appreciate in those with darker skin tones.5
Worth Noting
Complications from IH may require imaging, close follow-up, systemic therapy, multidisciplinary care, and advanced health literacy and patient/family navigation. Multifocal IHs (≥ 5 lesions) are more likely to be associated with infantile hepatic hemangiomas.2,3 Large (> 5 cm) segmental IHs on the face and lumbosacral area require further evaluation for PHACES (posterior fossa malformation, hemangiomas, arterial anomalies, cardiac defects, eye anomalies, and sternal raphe/cleft defects) and LUMBAR (lower-body segmental IH; urogenital anomalies and ulceration; myelopathy; bony deformities; anorectal malformations and arterial anomalies; and renal anomalies) syndromes, which are more common in patients of Hispanic ethnicity.2,3
The Infantile Hemangioma Referral Score is a recently validated tool that can assist primary care physicians in timely referral of IHs requiring early specialist intervention.4,9 It takes into account the location, number, and size of the lesions and the age of the patient; these factors help to determine which IHs may be managed conservatively vs those that may require treatment to prevent life-threatening complications.1-3
Systemic corticosteroids historically have been the primary treatment for IH; however, in the past decade, propranolol oral solution (4.28 mg/mL) has become the first-line therapy for most infants requiring systemic management.10 It is the only medication approved by the US Food and Drug Administration for proliferating IH, with treatment initiation as young as 5 weeks corrected age.11 As a nonselective beta-blocker, propranolol is believed to reduce IHs through vasoconstriction or by inhibition of angiogenesis.1,4,10
For small superficial IHs, treatment options include timolol maleate ophthalmic solution 0.5% (one drop applied twice daily to the IH) or pulsed dye laser therapy.4,10 Surgical excision typically is avoided during infancy due to concerns about anesthetic risks and potential blood loss.4,10 Surgery is reserved for cases involving residual fibrofatty tissue, postinvolution scarring, obstruction of vital structures, or lesions in aesthetically sensitive areas as well as when propranolol is contraindicated.4,10
Health Disparity Highlight
Infants with skin of color and those of lower socioeconomic status (SES) face a heightened risk for delayed diagnosis and more advanced disease at the initial evaluation for IH.5,7 Access barriers such as geographic limitations to specialty services, lack of insurance, underinsurance, and language differences impact timely diagnosis and treatment.5,6 Implementation of telemedicine services in areas with limited access to specialists can facilitate early evaluation and risk stratification for IH.12
A retrospective cohort study of 804 children seen at a large academic hospital found that those of lower SES were more likely to seek care after 3 months of age than their higher-SES counterparts.6 Those who presented after 6 months of age also had higher IH severity scores compared to their counterparts with higher SES.6 Delayed access to care may cause children to miss the critical treatment window during the rapid proliferative growth phase.6,12 However, children insured through Medicaid or the Children’s Health Insurance Program who participated in institutional care management programs (which assist in scheduling specialty care appointments within the institution) sought treatment earlier regardless of their SES, suggesting that such programs may help reduce disparities in timely access for children of lower SES.6
An epidemiologic study analyzing the demographics of children hospitalized across the United States demonstrated that Black infants with IH were more likely to belong to the lowest income quartile compared with White infants or those of other races. They also were 2 times older on average at initial presentation (1.8 vs 1.0 years), experienced longer hospitalizations (16.4 vs 13.8 days), and underwent more IH-related procedures than White infants and infants of other races (2.4, 1.9, and 2.1, respectively).7
These and other factors may contribute to missed windows of opportunity for timely treatment of high-risk IHs in patients with darker skin tones and/or those facing challenges stemming from social drivers of health.
- Léauté-Labrèze C, Harper JI, Hoeger PH. Infantile haemangioma. Lancet. 2017;390:85-94.
- Mitra R, Fitzsimons HL, Hale T, et al. Recent advances in understanding the molecular basis of infantile haemangioma development. Br J Dermatol. 2024;191:661-669.
- Rodríguez Bandera AI, Sebaratnam DF, Wargon O, et al. Infantile hemangioma. Part 1: epidemiology, pathogenesis, clinical presentation and assessment. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2021;85:1379-1392.
- Sebaratnam DF, Rodríguez Bandera AL, Wong LCF, et al. Infantile hemangioma. Part 2: management. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2021;85:1395-1404.
- Taye ME, Shah J, Seiverling EV, et al. Diagnosis of vascular anomalies in patients with skin of color. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2024;17:54-62.
- Lie E, Psoter KJ, Püttgen KB. Lower socioeconomic status is associated with delayed access to care for infantile hemangioma: a cohort study. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2023;88:E221-E230.
- Kumar KD, Desai AD, Shah VP, et al. Racial discrepancies in presentation of hospitalized infantile hemangioma cases using the Kids’ Inpatient Database. Health Sci Rep. 2023;6:E1092.
- Chiller KG, Passaro D, Frieden IJ. Hemangiomas of infancy: clinical characteristics, morphologic subtypes, and their relationship to race, ethnicity, and sex. Arch Dermatol. 2002;138:1567.
- Léauté-Labrèze C, Baselga Torres E, Weibel L, et al. The infantile hemangioma referral score: a validated tool for physicians. Pediatrics. 2020;145:E20191628.
- Macca L, Altavilla D, Di Bartolomeo L, et al. Update on treatment of infantile hemangiomas: what’s new in the last five years? Front Pharmacol. 2022;13:879602.
- Krowchuk DP, Frieden IJ, Mancini AJ, et al. Clinical practice guideline for the management of infantile hemangiomas. Pediatrics. 2019;143:E20183475.
- Frieden IJ, Püttgen KB, Drolet BA, et al. Management of infantile hemangiomas during the COVID pandemic. Pediatr Dermatol. 2020;37:412-418.
- Léauté-Labrèze C, Harper JI, Hoeger PH. Infantile haemangioma. Lancet. 2017;390:85-94.
- Mitra R, Fitzsimons HL, Hale T, et al. Recent advances in understanding the molecular basis of infantile haemangioma development. Br J Dermatol. 2024;191:661-669.
- Rodríguez Bandera AI, Sebaratnam DF, Wargon O, et al. Infantile hemangioma. Part 1: epidemiology, pathogenesis, clinical presentation and assessment. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2021;85:1379-1392.
- Sebaratnam DF, Rodríguez Bandera AL, Wong LCF, et al. Infantile hemangioma. Part 2: management. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2021;85:1395-1404.
- Taye ME, Shah J, Seiverling EV, et al. Diagnosis of vascular anomalies in patients with skin of color. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2024;17:54-62.
- Lie E, Psoter KJ, Püttgen KB. Lower socioeconomic status is associated with delayed access to care for infantile hemangioma: a cohort study. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2023;88:E221-E230.
- Kumar KD, Desai AD, Shah VP, et al. Racial discrepancies in presentation of hospitalized infantile hemangioma cases using the Kids’ Inpatient Database. Health Sci Rep. 2023;6:E1092.
- Chiller KG, Passaro D, Frieden IJ. Hemangiomas of infancy: clinical characteristics, morphologic subtypes, and their relationship to race, ethnicity, and sex. Arch Dermatol. 2002;138:1567.
- Léauté-Labrèze C, Baselga Torres E, Weibel L, et al. The infantile hemangioma referral score: a validated tool for physicians. Pediatrics. 2020;145:E20191628.
- Macca L, Altavilla D, Di Bartolomeo L, et al. Update on treatment of infantile hemangiomas: what’s new in the last five years? Front Pharmacol. 2022;13:879602.
- Krowchuk DP, Frieden IJ, Mancini AJ, et al. Clinical practice guideline for the management of infantile hemangiomas. Pediatrics. 2019;143:E20183475.
- Frieden IJ, Püttgen KB, Drolet BA, et al. Management of infantile hemangiomas during the COVID pandemic. Pediatr Dermatol. 2020;37:412-418.
Early Infantile Hemangioma Diagnosis Is Key in Skin of Color
Early Infantile Hemangioma Diagnosis Is Key in Skin of Color
Early Infantile Hemangioma Diagnosis Is Key in Skin of Color
Early Infantile Hemangioma Diagnosis Is Key in Skin of Color
Infantile hemangioma (IH) is the most common vascular tumor of infancy, appearing within the first few weeks of life and typically reaching peak size by age 3 to 5 months.1 It classically manifests as a raised or flat bright-red lesion in the upper dermis of the skin and/or subcutaneous tissue and can vary in number, size, shape, and location.2 It is characterized by a rapid proliferative phase, especially between 5 and 8 weeks of age, followed by gradual spontaneous regression over 1 to 10 years.1-3
Infantile hemangiomas are categorized based on depth (superficial, deep, or mixed) and distribution pattern (focal, multifocal, segmental, or indeterminate).4 In most cases, complete regression occurs by age 4 years, but there can be residual telangiectasia, fibrofatty tissue, and/or scarring.1,4 About 10% to 15% of IHs result in complications that require medical intervention (eg, visual, airway, or auditory compromise; ulceration; disfigurement); ideally, these patients should be referred to a specialist by 5 weeks of age.4 Prompt assessment of IH severity is essential to prevent or mitigate potential complications and ultimately improve outcomes.3 Social drivers of health contribute to delayed diagnosis and management of hemangiomas, leading to increased complications in some patient populations.5-7
Epidemiology
Infantile hemangiomas are estimated to manifest in 4.5% of infants in the United States.1 The most common type is superficial IH, typically found on the head or neck.5 Risk factors in infants include female sex, White race, premature birth, and low birth weight (<1000 g).1,3 Maternal risk factors include advanced gestational age (ie, >35 years), multiple gestations, family history of IH, tobacco use, use of progesterone therapy during pregnancy, and pre-eclampsia.1,3
Focal IH typically manifests as a single localized lesion that can occur anywhere on the body.2,3 In contrast, segmental IH manifests in a linear pattern and/or is distributed on a large anatomic area, most commonly on the face and less frequently the extremities and trunk.
Key Clinical Features
Superficial IH in patients with darker skin tones may appear as a dark-red or violaceous papule or plaque compared to bright red in lighter skin tones.5 Deep IH may appear as a soft, round, flesh-colored or blue-hued subcutaneous mass, the color of which may be harder to appreciate in those with darker skin tones.5
Worth Noting
Complications from IH may require imaging, close follow-up, systemic therapy, multidisciplinary care, and advanced health literacy and patient/family navigation. Multifocal IHs (≥5 lesions) are more likely to be associated with infantile hepatic hemangiomas.2,3 Large (>5 cm) segmental IHs on the face and lumbosacral area require further evaluation for PHACES (posterior fossa malformation, hemangiomas, arterial anomalies, cardiac defects, eye anomalies, and sternal raphe/cleft defects) and LUMBAR (lower-body segmental IH; urogenital anomalies and ulceration; myelopathy; bony deformities; anorectal malformations and arterial anomalies; and renal anomalies) syndromes, which are more common in patients of Hispanic ethnicity.2,3
The Infantile Hemangioma Referral Score is a recently validated tool that can assist primary care physicians in timely referral of IHs requiring early specialist intervention.4,9 It takes into account the location, number, and size of the lesions and the age of the patient; these factors help to determine which IHs may be managed conservatively vs those that may require treatment to prevent life-threatening complications.1-3
Systemic corticosteroids historically have been the primary treatment for IH; however, in the past decade, propranolol oral solution (4.28 mg/mL) has become the first-line therapy for most infants requiring systemic management.10 It is the only medication approved by the US Food and Drug Administration for proliferating IH, with treatment initiation as young as 5 weeks corrected age.11 As a nonselective beta-blocker, propranolol is believed to reduce IHs through vasoconstriction or by inhibition of angiogenesis.1,4,10
For small superficial IHs, treatment options include timolol maleate ophthalmic solution 0.5% (one drop applied twice daily to the IH) or pulsed dye laser therapy.4,10 Surgical excision typically is avoided during infancy due to concerns about anesthetic risks and potential blood loss.4,10 Surgery is reserved for cases involving residual fibrofatty tissue, postinvolution scarring, obstruction of vital structures, or lesions in aesthetically sensitive areas as well as when propranolol is contraindicated.4,10
Health Disparity Highlight
Infants with skin of color and those of lower socioeconomic status (SES) face a heightened risk for delayed diagnosis and more advanced disease at the initial evaluation for IH.5,7 Access barriers such as geographic limitations to specialty services, lack of insurance, underinsurance, and language differences impact timely diagnosis and treatment.5,6 Implementation of telemedicine services in areas with limited access to specialists can facilitate early evaluation and risk stratification for IH.12
A retrospective cohort study of 804 children seen at a large academic hospital found that those of lower SES were more likely to seek care after 3 months of age than their higher-SES counterparts.6 Those who presented after 6 months of age also had higher IH severity scores compared to their counterparts with higher SES.6 Delayed access to care may cause children to miss the critical treatment window during the rapid proliferative growth phase.6,12 However, children insured through Medicaid or the Children’s Health Insurance Program who participated in institutional care management programs (which assist in scheduling specialty care appointments within the institution) sought treatment earlier regardless of their SES, suggesting that such programs may help reduce disparities in timely access for children of lower SES.6
An epidemiologic study analyzing the demographics of children hospitalized across the United States demonstrated that Black infants with IH were more likely to belong to the lowest income quartile compared with White infants or those of other races. They also were 2 times older on average at initial presentation (1.8 vs 1.0 years), experienced longer hospitalizations (16.4 vs 13.8 days), and underwent more IH-related procedures than White infants and infants of other races (2.4, 1.9, and 2.1, respectively).7
These and other factors may contribute to missed windows of opportunity for timely treatment of high-risk IHs in patients with darker skin tones and/or those facing challenges stemming from social drivers of health.
- Léauté-Labrèze C, Harper JI, Hoeger PH. Infantile haemangioma. Lancet. 2017;390:85-94.
- Mitra R, Fitzsimons HL, Hale T, et al. Recent advances in understanding the molecular basis of infantile haemangioma development. Br J Dermatol. 2024;191:661-669.
- Rodríguez Bandera AI, Sebaratnam DF, Wargon O, et al. Infantile hemangioma. part 1: epidemiology, pathogenesis, clinical presentation and assessment. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2021;85:1379-1392.
- Sebaratnam DF, Rodríguez Bandera AL, Wong LCF, et al. Infantile hemangioma. part 2: management. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2021;85:1395-1404.
- Taye ME, Shah J, Seiverling EV, et al. Diagnosis of vascular anomalies in patients with skin of color. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2024;17:54-62.
- Lie E, Psoter KJ, Püttgen KB. Lower socioeconomic status is associated with delayed access to care for infantile hemangioma: a cohort study. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2023;88:E221-E230.
- Kumar KD, Desai AD, Shah VP, et al. Racial discrepancies in presentation of hospitalized infantile hemangioma cases using the Kids’ Inpatient Database. Health Sci Rep. 2023;6:E1092.
- Chiller KG, Passaro D, Frieden IJ. Hemangiomas of infancy: clinical characteristics, morphologic subtypes, and their relationship to race, ethnicity, and sex. Arch Dermatol. 2002;138:1567.
- Léauté-Labrèze C, Baselga Torres E, Weibel L, et al. The infantile hemangioma referral score: a validated tool for physicians. Pediatrics. 2020;145:E20191628.
- Macca L, Altavilla D, Di Bartolomeo L, et al. Update on treatment of infantile hemangiomas: what’s new in the last five years? Front Pharmacol. 2022;13:879602.
- Krowchuk DP, Frieden IJ, Mancini AJ, et al. Clinical practice guideline for the management of infantile hemangiomas. Pediatrics. 2019;143:E20183475.
- Frieden IJ, Püttgen KB, Drolet BA, et al. Management of infantile hemangiomas during the COVID pandemic. Pediatr Dermatol. 2020;37:412-418.
Infantile hemangioma (IH) is the most common vascular tumor of infancy, appearing within the first few weeks of life and typically reaching peak size by age 3 to 5 months.1 It classically manifests as a raised or flat bright-red lesion in the upper dermis of the skin and/or subcutaneous tissue and can vary in number, size, shape, and location.2 It is characterized by a rapid proliferative phase, especially between 5 and 8 weeks of age, followed by gradual spontaneous regression over 1 to 10 years.1-3
Infantile hemangiomas are categorized based on depth (superficial, deep, or mixed) and distribution pattern (focal, multifocal, segmental, or indeterminate).4 In most cases, complete regression occurs by age 4 years, but there can be residual telangiectasia, fibrofatty tissue, and/or scarring.1,4 About 10% to 15% of IHs result in complications that require medical intervention (eg, visual, airway, or auditory compromise; ulceration; disfigurement); ideally, these patients should be referred to a specialist by 5 weeks of age.4 Prompt assessment of IH severity is essential to prevent or mitigate potential complications and ultimately improve outcomes.3 Social drivers of health contribute to delayed diagnosis and management of hemangiomas, leading to increased complications in some patient populations.5-7
Epidemiology
Infantile hemangiomas are estimated to manifest in 4.5% of infants in the United States.1 The most common type is superficial IH, typically found on the head or neck.5 Risk factors in infants include female sex, White race, premature birth, and low birth weight (<1000 g).1,3 Maternal risk factors include advanced gestational age (ie, >35 years), multiple gestations, family history of IH, tobacco use, use of progesterone therapy during pregnancy, and pre-eclampsia.1,3
Focal IH typically manifests as a single localized lesion that can occur anywhere on the body.2,3 In contrast, segmental IH manifests in a linear pattern and/or is distributed on a large anatomic area, most commonly on the face and less frequently the extremities and trunk.
Key Clinical Features
Superficial IH in patients with darker skin tones may appear as a dark-red or violaceous papule or plaque compared to bright red in lighter skin tones.5 Deep IH may appear as a soft, round, flesh-colored or blue-hued subcutaneous mass, the color of which may be harder to appreciate in those with darker skin tones.5
Worth Noting
Complications from IH may require imaging, close follow-up, systemic therapy, multidisciplinary care, and advanced health literacy and patient/family navigation. Multifocal IHs (≥5 lesions) are more likely to be associated with infantile hepatic hemangiomas.2,3 Large (>5 cm) segmental IHs on the face and lumbosacral area require further evaluation for PHACES (posterior fossa malformation, hemangiomas, arterial anomalies, cardiac defects, eye anomalies, and sternal raphe/cleft defects) and LUMBAR (lower-body segmental IH; urogenital anomalies and ulceration; myelopathy; bony deformities; anorectal malformations and arterial anomalies; and renal anomalies) syndromes, which are more common in patients of Hispanic ethnicity.2,3
The Infantile Hemangioma Referral Score is a recently validated tool that can assist primary care physicians in timely referral of IHs requiring early specialist intervention.4,9 It takes into account the location, number, and size of the lesions and the age of the patient; these factors help to determine which IHs may be managed conservatively vs those that may require treatment to prevent life-threatening complications.1-3
Systemic corticosteroids historically have been the primary treatment for IH; however, in the past decade, propranolol oral solution (4.28 mg/mL) has become the first-line therapy for most infants requiring systemic management.10 It is the only medication approved by the US Food and Drug Administration for proliferating IH, with treatment initiation as young as 5 weeks corrected age.11 As a nonselective beta-blocker, propranolol is believed to reduce IHs through vasoconstriction or by inhibition of angiogenesis.1,4,10
For small superficial IHs, treatment options include timolol maleate ophthalmic solution 0.5% (one drop applied twice daily to the IH) or pulsed dye laser therapy.4,10 Surgical excision typically is avoided during infancy due to concerns about anesthetic risks and potential blood loss.4,10 Surgery is reserved for cases involving residual fibrofatty tissue, postinvolution scarring, obstruction of vital structures, or lesions in aesthetically sensitive areas as well as when propranolol is contraindicated.4,10
Health Disparity Highlight
Infants with skin of color and those of lower socioeconomic status (SES) face a heightened risk for delayed diagnosis and more advanced disease at the initial evaluation for IH.5,7 Access barriers such as geographic limitations to specialty services, lack of insurance, underinsurance, and language differences impact timely diagnosis and treatment.5,6 Implementation of telemedicine services in areas with limited access to specialists can facilitate early evaluation and risk stratification for IH.12
A retrospective cohort study of 804 children seen at a large academic hospital found that those of lower SES were more likely to seek care after 3 months of age than their higher-SES counterparts.6 Those who presented after 6 months of age also had higher IH severity scores compared to their counterparts with higher SES.6 Delayed access to care may cause children to miss the critical treatment window during the rapid proliferative growth phase.6,12 However, children insured through Medicaid or the Children’s Health Insurance Program who participated in institutional care management programs (which assist in scheduling specialty care appointments within the institution) sought treatment earlier regardless of their SES, suggesting that such programs may help reduce disparities in timely access for children of lower SES.6
An epidemiologic study analyzing the demographics of children hospitalized across the United States demonstrated that Black infants with IH were more likely to belong to the lowest income quartile compared with White infants or those of other races. They also were 2 times older on average at initial presentation (1.8 vs 1.0 years), experienced longer hospitalizations (16.4 vs 13.8 days), and underwent more IH-related procedures than White infants and infants of other races (2.4, 1.9, and 2.1, respectively).7
These and other factors may contribute to missed windows of opportunity for timely treatment of high-risk IHs in patients with darker skin tones and/or those facing challenges stemming from social drivers of health.
Infantile hemangioma (IH) is the most common vascular tumor of infancy, appearing within the first few weeks of life and typically reaching peak size by age 3 to 5 months.1 It classically manifests as a raised or flat bright-red lesion in the upper dermis of the skin and/or subcutaneous tissue and can vary in number, size, shape, and location.2 It is characterized by a rapid proliferative phase, especially between 5 and 8 weeks of age, followed by gradual spontaneous regression over 1 to 10 years.1-3
Infantile hemangiomas are categorized based on depth (superficial, deep, or mixed) and distribution pattern (focal, multifocal, segmental, or indeterminate).4 In most cases, complete regression occurs by age 4 years, but there can be residual telangiectasia, fibrofatty tissue, and/or scarring.1,4 About 10% to 15% of IHs result in complications that require medical intervention (eg, visual, airway, or auditory compromise; ulceration; disfigurement); ideally, these patients should be referred to a specialist by 5 weeks of age.4 Prompt assessment of IH severity is essential to prevent or mitigate potential complications and ultimately improve outcomes.3 Social drivers of health contribute to delayed diagnosis and management of hemangiomas, leading to increased complications in some patient populations.5-7
Epidemiology
Infantile hemangiomas are estimated to manifest in 4.5% of infants in the United States.1 The most common type is superficial IH, typically found on the head or neck.5 Risk factors in infants include female sex, White race, premature birth, and low birth weight (<1000 g).1,3 Maternal risk factors include advanced gestational age (ie, >35 years), multiple gestations, family history of IH, tobacco use, use of progesterone therapy during pregnancy, and pre-eclampsia.1,3
Focal IH typically manifests as a single localized lesion that can occur anywhere on the body.2,3 In contrast, segmental IH manifests in a linear pattern and/or is distributed on a large anatomic area, most commonly on the face and less frequently the extremities and trunk.
Key Clinical Features
Superficial IH in patients with darker skin tones may appear as a dark-red or violaceous papule or plaque compared to bright red in lighter skin tones.5 Deep IH may appear as a soft, round, flesh-colored or blue-hued subcutaneous mass, the color of which may be harder to appreciate in those with darker skin tones.5
Worth Noting
Complications from IH may require imaging, close follow-up, systemic therapy, multidisciplinary care, and advanced health literacy and patient/family navigation. Multifocal IHs (≥5 lesions) are more likely to be associated with infantile hepatic hemangiomas.2,3 Large (>5 cm) segmental IHs on the face and lumbosacral area require further evaluation for PHACES (posterior fossa malformation, hemangiomas, arterial anomalies, cardiac defects, eye anomalies, and sternal raphe/cleft defects) and LUMBAR (lower-body segmental IH; urogenital anomalies and ulceration; myelopathy; bony deformities; anorectal malformations and arterial anomalies; and renal anomalies) syndromes, which are more common in patients of Hispanic ethnicity.2,3
The Infantile Hemangioma Referral Score is a recently validated tool that can assist primary care physicians in timely referral of IHs requiring early specialist intervention.4,9 It takes into account the location, number, and size of the lesions and the age of the patient; these factors help to determine which IHs may be managed conservatively vs those that may require treatment to prevent life-threatening complications.1-3
Systemic corticosteroids historically have been the primary treatment for IH; however, in the past decade, propranolol oral solution (4.28 mg/mL) has become the first-line therapy for most infants requiring systemic management.10 It is the only medication approved by the US Food and Drug Administration for proliferating IH, with treatment initiation as young as 5 weeks corrected age.11 As a nonselective beta-blocker, propranolol is believed to reduce IHs through vasoconstriction or by inhibition of angiogenesis.1,4,10
For small superficial IHs, treatment options include timolol maleate ophthalmic solution 0.5% (one drop applied twice daily to the IH) or pulsed dye laser therapy.4,10 Surgical excision typically is avoided during infancy due to concerns about anesthetic risks and potential blood loss.4,10 Surgery is reserved for cases involving residual fibrofatty tissue, postinvolution scarring, obstruction of vital structures, or lesions in aesthetically sensitive areas as well as when propranolol is contraindicated.4,10
Health Disparity Highlight
Infants with skin of color and those of lower socioeconomic status (SES) face a heightened risk for delayed diagnosis and more advanced disease at the initial evaluation for IH.5,7 Access barriers such as geographic limitations to specialty services, lack of insurance, underinsurance, and language differences impact timely diagnosis and treatment.5,6 Implementation of telemedicine services in areas with limited access to specialists can facilitate early evaluation and risk stratification for IH.12
A retrospective cohort study of 804 children seen at a large academic hospital found that those of lower SES were more likely to seek care after 3 months of age than their higher-SES counterparts.6 Those who presented after 6 months of age also had higher IH severity scores compared to their counterparts with higher SES.6 Delayed access to care may cause children to miss the critical treatment window during the rapid proliferative growth phase.6,12 However, children insured through Medicaid or the Children’s Health Insurance Program who participated in institutional care management programs (which assist in scheduling specialty care appointments within the institution) sought treatment earlier regardless of their SES, suggesting that such programs may help reduce disparities in timely access for children of lower SES.6
An epidemiologic study analyzing the demographics of children hospitalized across the United States demonstrated that Black infants with IH were more likely to belong to the lowest income quartile compared with White infants or those of other races. They also were 2 times older on average at initial presentation (1.8 vs 1.0 years), experienced longer hospitalizations (16.4 vs 13.8 days), and underwent more IH-related procedures than White infants and infants of other races (2.4, 1.9, and 2.1, respectively).7
These and other factors may contribute to missed windows of opportunity for timely treatment of high-risk IHs in patients with darker skin tones and/or those facing challenges stemming from social drivers of health.
- Léauté-Labrèze C, Harper JI, Hoeger PH. Infantile haemangioma. Lancet. 2017;390:85-94.
- Mitra R, Fitzsimons HL, Hale T, et al. Recent advances in understanding the molecular basis of infantile haemangioma development. Br J Dermatol. 2024;191:661-669.
- Rodríguez Bandera AI, Sebaratnam DF, Wargon O, et al. Infantile hemangioma. part 1: epidemiology, pathogenesis, clinical presentation and assessment. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2021;85:1379-1392.
- Sebaratnam DF, Rodríguez Bandera AL, Wong LCF, et al. Infantile hemangioma. part 2: management. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2021;85:1395-1404.
- Taye ME, Shah J, Seiverling EV, et al. Diagnosis of vascular anomalies in patients with skin of color. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2024;17:54-62.
- Lie E, Psoter KJ, Püttgen KB. Lower socioeconomic status is associated with delayed access to care for infantile hemangioma: a cohort study. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2023;88:E221-E230.
- Kumar KD, Desai AD, Shah VP, et al. Racial discrepancies in presentation of hospitalized infantile hemangioma cases using the Kids’ Inpatient Database. Health Sci Rep. 2023;6:E1092.
- Chiller KG, Passaro D, Frieden IJ. Hemangiomas of infancy: clinical characteristics, morphologic subtypes, and their relationship to race, ethnicity, and sex. Arch Dermatol. 2002;138:1567.
- Léauté-Labrèze C, Baselga Torres E, Weibel L, et al. The infantile hemangioma referral score: a validated tool for physicians. Pediatrics. 2020;145:E20191628.
- Macca L, Altavilla D, Di Bartolomeo L, et al. Update on treatment of infantile hemangiomas: what’s new in the last five years? Front Pharmacol. 2022;13:879602.
- Krowchuk DP, Frieden IJ, Mancini AJ, et al. Clinical practice guideline for the management of infantile hemangiomas. Pediatrics. 2019;143:E20183475.
- Frieden IJ, Püttgen KB, Drolet BA, et al. Management of infantile hemangiomas during the COVID pandemic. Pediatr Dermatol. 2020;37:412-418.
- Léauté-Labrèze C, Harper JI, Hoeger PH. Infantile haemangioma. Lancet. 2017;390:85-94.
- Mitra R, Fitzsimons HL, Hale T, et al. Recent advances in understanding the molecular basis of infantile haemangioma development. Br J Dermatol. 2024;191:661-669.
- Rodríguez Bandera AI, Sebaratnam DF, Wargon O, et al. Infantile hemangioma. part 1: epidemiology, pathogenesis, clinical presentation and assessment. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2021;85:1379-1392.
- Sebaratnam DF, Rodríguez Bandera AL, Wong LCF, et al. Infantile hemangioma. part 2: management. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2021;85:1395-1404.
- Taye ME, Shah J, Seiverling EV, et al. Diagnosis of vascular anomalies in patients with skin of color. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2024;17:54-62.
- Lie E, Psoter KJ, Püttgen KB. Lower socioeconomic status is associated with delayed access to care for infantile hemangioma: a cohort study. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2023;88:E221-E230.
- Kumar KD, Desai AD, Shah VP, et al. Racial discrepancies in presentation of hospitalized infantile hemangioma cases using the Kids’ Inpatient Database. Health Sci Rep. 2023;6:E1092.
- Chiller KG, Passaro D, Frieden IJ. Hemangiomas of infancy: clinical characteristics, morphologic subtypes, and their relationship to race, ethnicity, and sex. Arch Dermatol. 2002;138:1567.
- Léauté-Labrèze C, Baselga Torres E, Weibel L, et al. The infantile hemangioma referral score: a validated tool for physicians. Pediatrics. 2020;145:E20191628.
- Macca L, Altavilla D, Di Bartolomeo L, et al. Update on treatment of infantile hemangiomas: what’s new in the last five years? Front Pharmacol. 2022;13:879602.
- Krowchuk DP, Frieden IJ, Mancini AJ, et al. Clinical practice guideline for the management of infantile hemangiomas. Pediatrics. 2019;143:E20183475.
- Frieden IJ, Püttgen KB, Drolet BA, et al. Management of infantile hemangiomas during the COVID pandemic. Pediatr Dermatol. 2020;37:412-418.
Early Infantile Hemangioma Diagnosis Is Key in Skin of Color
Early Infantile Hemangioma Diagnosis Is Key in Skin of Color
Pseudofolliculitis Barbae in the Military: Policy, Stigma, and Practical Solutions
Pseudofolliculitis Barbae in the Military: Policy, Stigma, and Practical Solutions
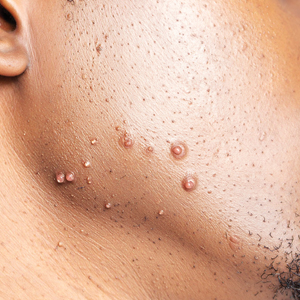
The impact of pseudofolliculitis barbae (PFB) on military service members and other uniformed professionals has been a topic of recent interest due to the announcement of the US Army’s new shaving rule in July 2025.1 The policy prohibits permanent shaving waivers, requires medical re-evaluation of shaving profiles within 90 days, and allows for administrative separation if a service member accumulates shaving exceptions totaling more than 12 months over a 24-month period.2 A common skin condition triggered or worsened by shaving, PFB causes painful bumps, pustules, and hyperpigmentation most often in the beard and cheek areas and negatively impacts quality of life. It disproportionately affects 45% to 83% of men in the United States, particularly those of African, Hispanic, or Middle Eastern descent.3,4 Genetic factors, particularly tightly coiled or coarse curly hair, can predispose individuals to PFB. The most successful treatment for PFB is to stop shaving, but this conflicts with military shaving standards and interferes with the use of protective equipment (eg, masks). Herein, we highlight the adverse impact of PFB on military career progression and provide context for clinicians who treat patients with PFB, especially as policies recently have shifted to allow nonmilitary clinicians to evaluate PFB in service members.5
Shaving Waivers and Advancement
Pseudofolliculitis barbae disproportionately prolongs the time to advancement of many service members, and those with PFB also are overburdened by policy changes related to shaving.6 In the US military, nearly 18% of the active-duty force is Black,7 a population that is more susceptible to PFB. Military personnel may request PFB-related accommodations, including medical shaving waivers that vary by branch. Through a formal documentation process, waivers allow service members to maintain facial hair up to one-quarter inch in length.5 Previously, waivers could be temporary (eg, up to 90 days) or permanent as subjectively determined based on clinician-documented disease severity. Almost 65% of US Air Force medical shaving waivers are held by Black men, and PFB is one of the most common reasons.6 Notably, the US Navy discontinued permanent shaving waivers in October 2019.8 A US Marine Corps policy issued in March 2025 now allows administrative separation of service members with PFB if symptoms do not improve after a 1-year medical shaving waiver due to “incompatibility with service.”9 This change reversed a 2022 policy that protected Marines from separation based on PFB.10 A Marine Corps spokesperson stated that this change aims to clarify how medical conditions can impact uniform compliance and standardize medical condition management while prioritizing compliance and duty readiness.1
Even in the absence of policy changes, obtaining a medical shaving waiver for PFB can be challenging. Service members may have little to no access to military dermatologists who specialize in management of PFB and experience long wait times for civilian network deferment. Service members seen in civilian clinics may have restricted treatment options due to limited insurance coverage for laser hair reduction, even in the most difficult-to-manage areas (eg, neck, jawline). Expanding access to military dermatologists, civilian dermatologists who are experienced with PFB and understand the impact and necessity of military waivers, and teledermatology services could help improve and streamline care. Other challenges include the subjective nature of documenting PFB disease severity, the need for validated assessment tools, a lack of standardized policies across military branches, and stigma. A standardized approach to documentation may reduce variability in how shaving waivers are evaluated across service branches, but at a minimum, clinicians should document the diagnosis, clinical findings, severity of PFB, and the treatment used. Having a waiver would help these service members focus on mastering critical skillsets and performing duties without the time pressures, angst, and expense dedicated to caring for and managing PFB.
Clinical and Policy Barriers
Unfortunately, service members with PFB or shaving waivers often face stigma that can hinder career advancement.6 In a recent analysis of 9339 US Air Force personnel, those with shaving waivers experienced longer times to promotion compared to those without waivers: in the waiver group, 94.47% were enlisted and 5.53% were officers; in the nonwaiver group, 72.11% were enlisted and 27.89% were officers (P=.0003).6 While delays in promotion were consistent across racial groups, most of the waiver holders identified as Black (64.8%), despite this demographic group representing only a small portion of the overall cohort (12.9%).6 Promotion delays may be linked to perceptions of unprofessionalism and exclusion from high-profile assignments, which notably require “the highest standards of military appearance and professional conduct.”11 The burden of career-limiting shaving policies falls disproportionately on military personnel with PFB who self-identify as Black. Perceptions about unprofessional appearance or job readiness often unintentionally introduce bias, unjustly restricting career advancement.6
Safety Equipment and Shaving Standards
Conditions that potentially affect the use of masks and chemical defense equipment extend beyond the military. Firefighters and law enforcement officers generally are required to maintain a clean-shaven face for proper fit of respirator masks; the standard is that no respirator fit test shall be conducted if hair—including stubble, beards, mustaches, or sideburns—grows between the skin and the facepiece sealing surface, and any apparel interfering with a proper seal must be altered or removed.12 This creates challenges for uniformed professionals with PFB who must manage their condition while adhering to safety requirements. Some endure long-term pain and scarring in order to comply, while others seek waivers to treat and prevent symptoms while also facing the stigma of doing so.13 One of the most effective treatments for PFB is to discontinue shaving,14 which may not be feasible for those in uniformed professions with strict grooming standards. Research on mask seal effectiveness in individuals with neatly trimmed beards or PFB remains limited.5 Studies evaluating mask fit across facial hair types and lengths are needed, along with the development of protective equipment that accommodates career-limiting conditions such as PFB, cystic acne, and acne keloidalis nuchae. This also may encourage development of equipment that does not induce such conditions (eg, mechanical acne from friction). These efforts would promote safety, scientific innovation for dermatologic follicular-based disorders, and overall quality of life for service members as well as increase their ability to serve without stigma. These developments also would positively impact other fields that require intermittent or full-time use of masks, including health care and some food service industries.
Final Thoughts
The disproportionate impact of PFB in the military highlights the need for improved access to treatment, culturally informed care, and policies that avoid penalizing service members with tightly coiled hair and a desire to serve. We discussed PFB management strategies, clinical features, and implications across various skin tones in a previous publication.14 It is important to consider insights from individuals with PFB who are serving in the military as well as the medical personnel who care for them. Ensuring or creating effective treatment options drives innovation, and evidence-based accommodation plans can help individuals in uniformed professions avoid choosing between PFB management and their career. Promoting awareness about the impact of PFB beyond the razor is key to reducing disparities and supporting excellence among those who serve and desire to continue to do so.
- Lawrence DF. Marines with skin condition affecting mostly black men could now be booted under new policy. Military.com. March 14, 2025. Accessed May 4, 2025. https://www.military.com/daily-news/2025/03/14/marines-can-now-be-kicked-out-skin-condition-affects-mostly-black-men.html
- Secretary of the Army. Army directive 2025-13 (facial hair grooming standards). Published July 7, 2025. Accessed September 19, 2025. https://lyster.tricare.mil/Portals/61/ARN44307-ARMY_DIR_2025-13-000.pdf
- Alexis A, Heath CR, Halder RM. Folliculitis keloidalis nuchae and pseudofolliculitis barbae: are prevention and effective treatment within reach? Dermatol Clin. 2014;32:183-191. doi:10.1016/j.det.2013.12.001
- Gray J, McMichael AJ. Pseudofolliculitis barbae: understanding the condition and the role of facial grooming. Int J Cosmet Sci. 2016;38:24-27. doi:10.1111/ics.12331
- Jung I, Lannan FM, Weiss A, et al. Treatment and current policies on pseudofolliculitis barbae in the US military. Cutis. 2023;112:299-302. doi:10.12788/cutis.0907
- Ritchie S, Park J, Banta J, et al. Shaving waivers in the United States Air Force and their impact on promotions of Black/African-American members. Mil Med. 2023;188:E242-E247. doi:10.1093/milmed/usab272
- Defense Manpower Data Center. Active-duty military personnel master file and reserve components common personnel data system. Military OneSource. September 2023. Accessed May 3, 2025. https://download.militaryonesource.mil/12038/MOS/Reports/2023-demographics-report.pdf
- Tshudy MT, Cho S. Pseudofolliculitis barbae in the US. Military, a review. Mil Med. 2021;186:E52-E57. doi:10.1093/milmed/usaa243
- US Marine Corps. Uniform and grooming standards for medical conditions (MARADMINS number: 124/25). Published March 13, 2025. Accessed September 19, 2025. https://www.marines.mil/News/Messages/Messages-Display/Article/4119098/uniform-and-grooming-standards-for-medical-conditions/
- US Marine Corps. Advance notification of change to MCO 6310.1C (Pseudofolliculitis Barbae), MCO 1900.16 CH2 (Marine Corps Retirement and Separation Manual), and MCO 1040.31 (Enlisted Retention and Career Development Program). Published January 21, 2022. Accessed September 19, 2025. https://www.marines.mil/News/Messages/Messages-Display/Article/2907104/advance-notification-of-change-to-mco-63101c-pseudofolliculitis-barbae-mco-1900/
- US Department of Defense. Special duty catalog (SPECAT). Published August 15, 2013. Accessed September 19, 2025. https://share.google/iuMrVMIASWx4EFLVN
- Occupational Safety and Health Administration. Appendix A to §1910.134—fit testing procedures (mandatory). Accessed September 19, 2025. https://www.osha.gov/laws-regs/regulations/standardnumber/1910/1910.134AppA
- Jiang YR. Reasonable accommodation and disparate impact: clean shave policy discrimination in today’s workplace. J Law Med Ethics. 2023;51:185-195. doi:10.1017/jme.2023.55
- Welch D, Usatine R, Heath C. Implications of PFB beyond the razor. Cutis. 2025;115:135-136. doi:10.12788/cutis.1194
The impact of pseudofolliculitis barbae (PFB) on military service members and other uniformed professionals has been a topic of recent interest due to the announcement of the US Army’s new shaving rule in July 2025.1 The policy prohibits permanent shaving waivers, requires medical re-evaluation of shaving profiles within 90 days, and allows for administrative separation if a service member accumulates shaving exceptions totaling more than 12 months over a 24-month period.2 A common skin condition triggered or worsened by shaving, PFB causes painful bumps, pustules, and hyperpigmentation most often in the beard and cheek areas and negatively impacts quality of life. It disproportionately affects 45% to 83% of men in the United States, particularly those of African, Hispanic, or Middle Eastern descent.3,4 Genetic factors, particularly tightly coiled or coarse curly hair, can predispose individuals to PFB. The most successful treatment for PFB is to stop shaving, but this conflicts with military shaving standards and interferes with the use of protective equipment (eg, masks). Herein, we highlight the adverse impact of PFB on military career progression and provide context for clinicians who treat patients with PFB, especially as policies recently have shifted to allow nonmilitary clinicians to evaluate PFB in service members.5
Shaving Waivers and Advancement
Pseudofolliculitis barbae disproportionately prolongs the time to advancement of many service members, and those with PFB also are overburdened by policy changes related to shaving.6 In the US military, nearly 18% of the active-duty force is Black,7 a population that is more susceptible to PFB. Military personnel may request PFB-related accommodations, including medical shaving waivers that vary by branch. Through a formal documentation process, waivers allow service members to maintain facial hair up to one-quarter inch in length.5 Previously, waivers could be temporary (eg, up to 90 days) or permanent as subjectively determined based on clinician-documented disease severity. Almost 65% of US Air Force medical shaving waivers are held by Black men, and PFB is one of the most common reasons.6 Notably, the US Navy discontinued permanent shaving waivers in October 2019.8 A US Marine Corps policy issued in March 2025 now allows administrative separation of service members with PFB if symptoms do not improve after a 1-year medical shaving waiver due to “incompatibility with service.”9 This change reversed a 2022 policy that protected Marines from separation based on PFB.10 A Marine Corps spokesperson stated that this change aims to clarify how medical conditions can impact uniform compliance and standardize medical condition management while prioritizing compliance and duty readiness.1
Even in the absence of policy changes, obtaining a medical shaving waiver for PFB can be challenging. Service members may have little to no access to military dermatologists who specialize in management of PFB and experience long wait times for civilian network deferment. Service members seen in civilian clinics may have restricted treatment options due to limited insurance coverage for laser hair reduction, even in the most difficult-to-manage areas (eg, neck, jawline). Expanding access to military dermatologists, civilian dermatologists who are experienced with PFB and understand the impact and necessity of military waivers, and teledermatology services could help improve and streamline care. Other challenges include the subjective nature of documenting PFB disease severity, the need for validated assessment tools, a lack of standardized policies across military branches, and stigma. A standardized approach to documentation may reduce variability in how shaving waivers are evaluated across service branches, but at a minimum, clinicians should document the diagnosis, clinical findings, severity of PFB, and the treatment used. Having a waiver would help these service members focus on mastering critical skillsets and performing duties without the time pressures, angst, and expense dedicated to caring for and managing PFB.
Clinical and Policy Barriers
Unfortunately, service members with PFB or shaving waivers often face stigma that can hinder career advancement.6 In a recent analysis of 9339 US Air Force personnel, those with shaving waivers experienced longer times to promotion compared to those without waivers: in the waiver group, 94.47% were enlisted and 5.53% were officers; in the nonwaiver group, 72.11% were enlisted and 27.89% were officers (P=.0003).6 While delays in promotion were consistent across racial groups, most of the waiver holders identified as Black (64.8%), despite this demographic group representing only a small portion of the overall cohort (12.9%).6 Promotion delays may be linked to perceptions of unprofessionalism and exclusion from high-profile assignments, which notably require “the highest standards of military appearance and professional conduct.”11 The burden of career-limiting shaving policies falls disproportionately on military personnel with PFB who self-identify as Black. Perceptions about unprofessional appearance or job readiness often unintentionally introduce bias, unjustly restricting career advancement.6
Safety Equipment and Shaving Standards
Conditions that potentially affect the use of masks and chemical defense equipment extend beyond the military. Firefighters and law enforcement officers generally are required to maintain a clean-shaven face for proper fit of respirator masks; the standard is that no respirator fit test shall be conducted if hair—including stubble, beards, mustaches, or sideburns—grows between the skin and the facepiece sealing surface, and any apparel interfering with a proper seal must be altered or removed.12 This creates challenges for uniformed professionals with PFB who must manage their condition while adhering to safety requirements. Some endure long-term pain and scarring in order to comply, while others seek waivers to treat and prevent symptoms while also facing the stigma of doing so.13 One of the most effective treatments for PFB is to discontinue shaving,14 which may not be feasible for those in uniformed professions with strict grooming standards. Research on mask seal effectiveness in individuals with neatly trimmed beards or PFB remains limited.5 Studies evaluating mask fit across facial hair types and lengths are needed, along with the development of protective equipment that accommodates career-limiting conditions such as PFB, cystic acne, and acne keloidalis nuchae. This also may encourage development of equipment that does not induce such conditions (eg, mechanical acne from friction). These efforts would promote safety, scientific innovation for dermatologic follicular-based disorders, and overall quality of life for service members as well as increase their ability to serve without stigma. These developments also would positively impact other fields that require intermittent or full-time use of masks, including health care and some food service industries.
Final Thoughts
The disproportionate impact of PFB in the military highlights the need for improved access to treatment, culturally informed care, and policies that avoid penalizing service members with tightly coiled hair and a desire to serve. We discussed PFB management strategies, clinical features, and implications across various skin tones in a previous publication.14 It is important to consider insights from individuals with PFB who are serving in the military as well as the medical personnel who care for them. Ensuring or creating effective treatment options drives innovation, and evidence-based accommodation plans can help individuals in uniformed professions avoid choosing between PFB management and their career. Promoting awareness about the impact of PFB beyond the razor is key to reducing disparities and supporting excellence among those who serve and desire to continue to do so.
The impact of pseudofolliculitis barbae (PFB) on military service members and other uniformed professionals has been a topic of recent interest due to the announcement of the US Army’s new shaving rule in July 2025.1 The policy prohibits permanent shaving waivers, requires medical re-evaluation of shaving profiles within 90 days, and allows for administrative separation if a service member accumulates shaving exceptions totaling more than 12 months over a 24-month period.2 A common skin condition triggered or worsened by shaving, PFB causes painful bumps, pustules, and hyperpigmentation most often in the beard and cheek areas and negatively impacts quality of life. It disproportionately affects 45% to 83% of men in the United States, particularly those of African, Hispanic, or Middle Eastern descent.3,4 Genetic factors, particularly tightly coiled or coarse curly hair, can predispose individuals to PFB. The most successful treatment for PFB is to stop shaving, but this conflicts with military shaving standards and interferes with the use of protective equipment (eg, masks). Herein, we highlight the adverse impact of PFB on military career progression and provide context for clinicians who treat patients with PFB, especially as policies recently have shifted to allow nonmilitary clinicians to evaluate PFB in service members.5
Shaving Waivers and Advancement
Pseudofolliculitis barbae disproportionately prolongs the time to advancement of many service members, and those with PFB also are overburdened by policy changes related to shaving.6 In the US military, nearly 18% of the active-duty force is Black,7 a population that is more susceptible to PFB. Military personnel may request PFB-related accommodations, including medical shaving waivers that vary by branch. Through a formal documentation process, waivers allow service members to maintain facial hair up to one-quarter inch in length.5 Previously, waivers could be temporary (eg, up to 90 days) or permanent as subjectively determined based on clinician-documented disease severity. Almost 65% of US Air Force medical shaving waivers are held by Black men, and PFB is one of the most common reasons.6 Notably, the US Navy discontinued permanent shaving waivers in October 2019.8 A US Marine Corps policy issued in March 2025 now allows administrative separation of service members with PFB if symptoms do not improve after a 1-year medical shaving waiver due to “incompatibility with service.”9 This change reversed a 2022 policy that protected Marines from separation based on PFB.10 A Marine Corps spokesperson stated that this change aims to clarify how medical conditions can impact uniform compliance and standardize medical condition management while prioritizing compliance and duty readiness.1
Even in the absence of policy changes, obtaining a medical shaving waiver for PFB can be challenging. Service members may have little to no access to military dermatologists who specialize in management of PFB and experience long wait times for civilian network deferment. Service members seen in civilian clinics may have restricted treatment options due to limited insurance coverage for laser hair reduction, even in the most difficult-to-manage areas (eg, neck, jawline). Expanding access to military dermatologists, civilian dermatologists who are experienced with PFB and understand the impact and necessity of military waivers, and teledermatology services could help improve and streamline care. Other challenges include the subjective nature of documenting PFB disease severity, the need for validated assessment tools, a lack of standardized policies across military branches, and stigma. A standardized approach to documentation may reduce variability in how shaving waivers are evaluated across service branches, but at a minimum, clinicians should document the diagnosis, clinical findings, severity of PFB, and the treatment used. Having a waiver would help these service members focus on mastering critical skillsets and performing duties without the time pressures, angst, and expense dedicated to caring for and managing PFB.
Clinical and Policy Barriers
Unfortunately, service members with PFB or shaving waivers often face stigma that can hinder career advancement.6 In a recent analysis of 9339 US Air Force personnel, those with shaving waivers experienced longer times to promotion compared to those without waivers: in the waiver group, 94.47% were enlisted and 5.53% were officers; in the nonwaiver group, 72.11% were enlisted and 27.89% were officers (P=.0003).6 While delays in promotion were consistent across racial groups, most of the waiver holders identified as Black (64.8%), despite this demographic group representing only a small portion of the overall cohort (12.9%).6 Promotion delays may be linked to perceptions of unprofessionalism and exclusion from high-profile assignments, which notably require “the highest standards of military appearance and professional conduct.”11 The burden of career-limiting shaving policies falls disproportionately on military personnel with PFB who self-identify as Black. Perceptions about unprofessional appearance or job readiness often unintentionally introduce bias, unjustly restricting career advancement.6
Safety Equipment and Shaving Standards
Conditions that potentially affect the use of masks and chemical defense equipment extend beyond the military. Firefighters and law enforcement officers generally are required to maintain a clean-shaven face for proper fit of respirator masks; the standard is that no respirator fit test shall be conducted if hair—including stubble, beards, mustaches, or sideburns—grows between the skin and the facepiece sealing surface, and any apparel interfering with a proper seal must be altered or removed.12 This creates challenges for uniformed professionals with PFB who must manage their condition while adhering to safety requirements. Some endure long-term pain and scarring in order to comply, while others seek waivers to treat and prevent symptoms while also facing the stigma of doing so.13 One of the most effective treatments for PFB is to discontinue shaving,14 which may not be feasible for those in uniformed professions with strict grooming standards. Research on mask seal effectiveness in individuals with neatly trimmed beards or PFB remains limited.5 Studies evaluating mask fit across facial hair types and lengths are needed, along with the development of protective equipment that accommodates career-limiting conditions such as PFB, cystic acne, and acne keloidalis nuchae. This also may encourage development of equipment that does not induce such conditions (eg, mechanical acne from friction). These efforts would promote safety, scientific innovation for dermatologic follicular-based disorders, and overall quality of life for service members as well as increase their ability to serve without stigma. These developments also would positively impact other fields that require intermittent or full-time use of masks, including health care and some food service industries.
Final Thoughts
The disproportionate impact of PFB in the military highlights the need for improved access to treatment, culturally informed care, and policies that avoid penalizing service members with tightly coiled hair and a desire to serve. We discussed PFB management strategies, clinical features, and implications across various skin tones in a previous publication.14 It is important to consider insights from individuals with PFB who are serving in the military as well as the medical personnel who care for them. Ensuring or creating effective treatment options drives innovation, and evidence-based accommodation plans can help individuals in uniformed professions avoid choosing between PFB management and their career. Promoting awareness about the impact of PFB beyond the razor is key to reducing disparities and supporting excellence among those who serve and desire to continue to do so.
- Lawrence DF. Marines with skin condition affecting mostly black men could now be booted under new policy. Military.com. March 14, 2025. Accessed May 4, 2025. https://www.military.com/daily-news/2025/03/14/marines-can-now-be-kicked-out-skin-condition-affects-mostly-black-men.html
- Secretary of the Army. Army directive 2025-13 (facial hair grooming standards). Published July 7, 2025. Accessed September 19, 2025. https://lyster.tricare.mil/Portals/61/ARN44307-ARMY_DIR_2025-13-000.pdf
- Alexis A, Heath CR, Halder RM. Folliculitis keloidalis nuchae and pseudofolliculitis barbae: are prevention and effective treatment within reach? Dermatol Clin. 2014;32:183-191. doi:10.1016/j.det.2013.12.001
- Gray J, McMichael AJ. Pseudofolliculitis barbae: understanding the condition and the role of facial grooming. Int J Cosmet Sci. 2016;38:24-27. doi:10.1111/ics.12331
- Jung I, Lannan FM, Weiss A, et al. Treatment and current policies on pseudofolliculitis barbae in the US military. Cutis. 2023;112:299-302. doi:10.12788/cutis.0907
- Ritchie S, Park J, Banta J, et al. Shaving waivers in the United States Air Force and their impact on promotions of Black/African-American members. Mil Med. 2023;188:E242-E247. doi:10.1093/milmed/usab272
- Defense Manpower Data Center. Active-duty military personnel master file and reserve components common personnel data system. Military OneSource. September 2023. Accessed May 3, 2025. https://download.militaryonesource.mil/12038/MOS/Reports/2023-demographics-report.pdf
- Tshudy MT, Cho S. Pseudofolliculitis barbae in the US. Military, a review. Mil Med. 2021;186:E52-E57. doi:10.1093/milmed/usaa243
- US Marine Corps. Uniform and grooming standards for medical conditions (MARADMINS number: 124/25). Published March 13, 2025. Accessed September 19, 2025. https://www.marines.mil/News/Messages/Messages-Display/Article/4119098/uniform-and-grooming-standards-for-medical-conditions/
- US Marine Corps. Advance notification of change to MCO 6310.1C (Pseudofolliculitis Barbae), MCO 1900.16 CH2 (Marine Corps Retirement and Separation Manual), and MCO 1040.31 (Enlisted Retention and Career Development Program). Published January 21, 2022. Accessed September 19, 2025. https://www.marines.mil/News/Messages/Messages-Display/Article/2907104/advance-notification-of-change-to-mco-63101c-pseudofolliculitis-barbae-mco-1900/
- US Department of Defense. Special duty catalog (SPECAT). Published August 15, 2013. Accessed September 19, 2025. https://share.google/iuMrVMIASWx4EFLVN
- Occupational Safety and Health Administration. Appendix A to §1910.134—fit testing procedures (mandatory). Accessed September 19, 2025. https://www.osha.gov/laws-regs/regulations/standardnumber/1910/1910.134AppA
- Jiang YR. Reasonable accommodation and disparate impact: clean shave policy discrimination in today’s workplace. J Law Med Ethics. 2023;51:185-195. doi:10.1017/jme.2023.55
- Welch D, Usatine R, Heath C. Implications of PFB beyond the razor. Cutis. 2025;115:135-136. doi:10.12788/cutis.1194
- Lawrence DF. Marines with skin condition affecting mostly black men could now be booted under new policy. Military.com. March 14, 2025. Accessed May 4, 2025. https://www.military.com/daily-news/2025/03/14/marines-can-now-be-kicked-out-skin-condition-affects-mostly-black-men.html
- Secretary of the Army. Army directive 2025-13 (facial hair grooming standards). Published July 7, 2025. Accessed September 19, 2025. https://lyster.tricare.mil/Portals/61/ARN44307-ARMY_DIR_2025-13-000.pdf
- Alexis A, Heath CR, Halder RM. Folliculitis keloidalis nuchae and pseudofolliculitis barbae: are prevention and effective treatment within reach? Dermatol Clin. 2014;32:183-191. doi:10.1016/j.det.2013.12.001
- Gray J, McMichael AJ. Pseudofolliculitis barbae: understanding the condition and the role of facial grooming. Int J Cosmet Sci. 2016;38:24-27. doi:10.1111/ics.12331
- Jung I, Lannan FM, Weiss A, et al. Treatment and current policies on pseudofolliculitis barbae in the US military. Cutis. 2023;112:299-302. doi:10.12788/cutis.0907
- Ritchie S, Park J, Banta J, et al. Shaving waivers in the United States Air Force and their impact on promotions of Black/African-American members. Mil Med. 2023;188:E242-E247. doi:10.1093/milmed/usab272
- Defense Manpower Data Center. Active-duty military personnel master file and reserve components common personnel data system. Military OneSource. September 2023. Accessed May 3, 2025. https://download.militaryonesource.mil/12038/MOS/Reports/2023-demographics-report.pdf
- Tshudy MT, Cho S. Pseudofolliculitis barbae in the US. Military, a review. Mil Med. 2021;186:E52-E57. doi:10.1093/milmed/usaa243
- US Marine Corps. Uniform and grooming standards for medical conditions (MARADMINS number: 124/25). Published March 13, 2025. Accessed September 19, 2025. https://www.marines.mil/News/Messages/Messages-Display/Article/4119098/uniform-and-grooming-standards-for-medical-conditions/
- US Marine Corps. Advance notification of change to MCO 6310.1C (Pseudofolliculitis Barbae), MCO 1900.16 CH2 (Marine Corps Retirement and Separation Manual), and MCO 1040.31 (Enlisted Retention and Career Development Program). Published January 21, 2022. Accessed September 19, 2025. https://www.marines.mil/News/Messages/Messages-Display/Article/2907104/advance-notification-of-change-to-mco-63101c-pseudofolliculitis-barbae-mco-1900/
- US Department of Defense. Special duty catalog (SPECAT). Published August 15, 2013. Accessed September 19, 2025. https://share.google/iuMrVMIASWx4EFLVN
- Occupational Safety and Health Administration. Appendix A to §1910.134—fit testing procedures (mandatory). Accessed September 19, 2025. https://www.osha.gov/laws-regs/regulations/standardnumber/1910/1910.134AppA
- Jiang YR. Reasonable accommodation and disparate impact: clean shave policy discrimination in today’s workplace. J Law Med Ethics. 2023;51:185-195. doi:10.1017/jme.2023.55
- Welch D, Usatine R, Heath C. Implications of PFB beyond the razor. Cutis. 2025;115:135-136. doi:10.12788/cutis.1194
Pseudofolliculitis Barbae in the Military: Policy, Stigma, and Practical Solutions
Pseudofolliculitis Barbae in the Military: Policy, Stigma, and Practical Solutions
Consider Cultural Practices and Barriers to Care When Treating Alopecia Areata
Consider Cultural Practices and Barriers to Care When Treating Alopecia Areata
The Comparison
A. Alopecia areata in a young girl with a lighter skin tone. The fine white vellus hairs are signs of regrowth.
B. Alopecia areata in a 49-year-old man with tightly coiled hair and darker skin tone. Coiled white hairs are noted in the alopecia patches.
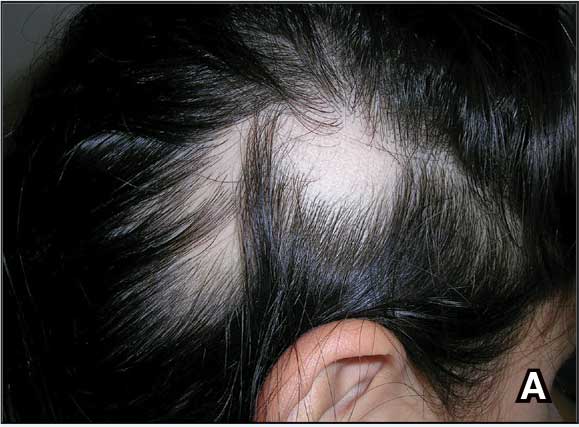
young girl with a lighter skin
tone. The fine white vellus
hairs are signs of regrowth. Photographs courtesy of
Richard P. Usatine, MD.

49-year-old man with tightly
coiled hair and darker skin
tone. Coiled white hairs
are noted in the alopecia
patches. Photographs courtesy of
Richard P. Usatine, MD.
Alopecia areata (AA) is a common autoimmune condition characterized by hair loss resulting from a T cell–mediated attack on the hair follicles. It manifests as nonscarring patches of hair loss on the scalp, eyebrows, eyelashes, and beard area as well as more extensive complete loss of scalp and body hair. While AA may affect individuals of any age, most patients develop their first patch(es) of hair loss during childhood.1 The treatment landscape for AA has evolved considerably in recent years, but barriers to access to newer treatments persist.
Epidemiology
AA is most prevalent among pediatric and adult individuals of African, Asian, or Hispanic/Latino descent.2-4 In some studies, Black individuals had higher odds and Asian individuals had lower odds of developing AA, while other studies have reported the highest standardized prevalence among Asian individuals.5 In the United States, AA affects about 1.47% of adults and as many as 0.11% of children.6-8 In Black patients, AA often manifests early with a female predominance.5
AA frequently is associated with autoimmune comorbidities, the most common being thyroid disease.3,5 In Black patients, AA is associated with more atopic comorbidities, including asthma, atopic dermatitis, and allergic rhinitis.5
Key Clinical Features
AA clinically manifests similarly across different skin tones; however, in patients with more tightly coiled or curly hair, the extent of scalp hair loss may be underestimated without a full examination. Culturally sensitive approaches to hair and scalp evaluation are essential, especially for Black women, whose hair care practices and scalp conditions may be overlooked or misunderstood during visits to evaluate hair loss. A thoughtful history and gentle examination of the hair and scalp that considers hair texture, cultural practices such as head coverings (eg, headwraps, turbans, hijabs), use of hair adornments (eg, clips, beads, bows), traditional braiding, and use of natural oils or herbal treatments, as well as styling methods including tight hairstyles, use of heat styling tools (eg, flat irons, curling irons), chemical application (eg, straighteners, hair color), and washing or styling frequency can improve diagnostic accuracy and help build trust in the patient-provider relationship.
Classic signs of AA visualized with dermoscopy include yellow and/or black dots on the scalp and exclamation point hairs. The appearance of fine white vellus hairs within the alopecic patches also may indicate early regrowth. On scalp trichoscopy, black dots are more prominent, and yellow dots are less prominent, in individuals with darker skin tones vs lighter skin tones.9
Worth Noting
In addition to a full examination of the scalp, documenting the extent of hair loss using validated severity scales, including the severity of alopecia tool (SALT), AA severity index (AASI), clinician-reported outcome assessment, and patient-reported outcome measures, can standardize disease severity assessment, facilitate timely insurance or medication approvals, and support objective tracking of treatment response, which may ultimately enhance access to care.10
Prompt treatment of AA is essential. Not surprisingly, patients given a diagnosis of AA may experience considerable emotional and psychological distress—regardless of the extent of the loss.11 Treatment options include mid- to high-potency topical or intralesional corticosteroids and newer and more targeted systemic options, including 3 Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitors—baricitinib, ritlecitinib, and deuruxolitinib—for more extensive disease.12 Treatment with intralesional corticosteroids may cause transient hypopigmentation, which may be more noticeable in patients with darker skin tones. Delays in treatment with JAK inhibitors can lead to a less-than-optimal response. Of the 3 JAK inhibitors that are approved by the US Food and Drug Administration for AA, only ritlecitinib is approved for children 12 years and older, leaving a therapeutic gap for younger patients that often leads to uncomfortable scalp injections, delayed or no treatment, off-label use of JAK inhibitors as well as the pairing of off-label dupilumab with oral minoxidil.12
Based on adult data, patients with severe disease and a shorter duration of hair loss (ie, < 4 years) tend to respond better to JAK inhibitors than those experiencing hair loss for longer periods. Also, those with more severe AA tend to have poorer outcomes than those with less severe disease.13 If treatment proves less than optimal, wigs and hair pieces may need to be considered. It is worth noting that some insurance companies will cover the cost of wigs for patients when prescribed as cranial prostheses.
Health Disparity Highlight
Health disparities in AA can be influenced by socioeconomic status and access to care. Patients from lower-income backgrounds often face barriers to accessing dermatologic care and treatments such as JAK inhibitors, which may remain inaccessible due to high costs and insurance limitations.14 These barriers can intersect with other factors such as age, sex, and race, potentially exacerbating disparities. Women with skin of color in underserved communities may experience delayed diagnosis, limited treatment options, and greater psychosocial distress from hair loss.14 Addressing these inequities requires advocacy, education for both patients and clinicians, and improved access to treatment to ensure comprehensive care for all patients.
- Kara T, Topkarcı Z. Interactions between posttraumatic stress disorder and alopecia areata in child with trauma exposure: two case reports. Int J Trichology. 2018;10:131-134. doi:10.4103/ijt.ijt_2_18
- Sy N, Mastacouris N, Strunk A, et al. Overall and racial and ethnic subgroup prevalences of alopecia areata, alopecia totalis, and alopecia universalis. JAMA Dermatol. 2023;159:419-423.
- Lee H, Jung SJ, Patel AB, et al. Racial characteristics of alopecia areata in the United States. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;83:1064-1070.
- Feaster B, McMichael AJ. Epidemiology of alopecia areata in Black patients: a retrospective chart review. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2022;87:1121-1123.
- Lee HH, Gwillim E, Patel KR, et al. Epidemiology of alopecia areata, ophiasis, totalis, and universalis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;82:675-682.
- Mostaghimi A, Gao W, Ray M, et al. Trends in prevalence and incidence of alopecia areata, alopecia totalis, and alopecia universalis among adults and children in a US employer-sponsored insured population. JAMA Dermatol. 2023;159:411-418.
- Adhanom R, Ansbro B, Castelo-Soccio L. Epidemiology of pediatric alopecia areata. Pediatr Dermatol. 2025;42 suppl 1(suppl 1):12-23.
- Karampinis E, Toli O, Georgopoulou KE, et al. Exploring pediatric dermatology in skin of color: focus on dermoscopy. Life (Basel). 2024;14:1604.
- King BA, Senna MM, Ohyama M, et al. Defining severity in alopecia areata: current perspectives and a multidimensional framework. Dermatol Ther (Heidelb). 2022;12:825-834.
- Toussi A, Barton VR, Le ST, et al. Psychosocial and psychiatric comorbidities and health-related quality of life in alopecia areata: a systematic review. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2021;85:162-175.
- Kalil L, Welch D, Heath CR, et al. Systemic therapies for pediatric alopecia areata. Pediatr Dermatol. 2025;42 suppl 1:36-42.
- King BA, Craiglow BG. Janus kinase inhibitors for alopecia areata. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2023;89:S29-S32.
- Klein EJ, Taiwò D, Kakpovbia E, et al. Disparities in Janus kinase inhibitor access for alopecia areata: a retrospective analysis. Int J Womens Dermatol. 2024;10:E155.
- McKenzie PL, Maltenfort M, Bruckner AL, et al. Evaluation of the prevalence and incidence of pediatric alopecia areata using electronic health record data. JAMA Dermatol. 2022;158:547-551. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2022.0351
The Comparison
A. Alopecia areata in a young girl with a lighter skin tone. The fine white vellus hairs are signs of regrowth.
B. Alopecia areata in a 49-year-old man with tightly coiled hair and darker skin tone. Coiled white hairs are noted in the alopecia patches.

young girl with a lighter skin
tone. The fine white vellus
hairs are signs of regrowth. Photographs courtesy of
Richard P. Usatine, MD.

49-year-old man with tightly
coiled hair and darker skin
tone. Coiled white hairs
are noted in the alopecia
patches. Photographs courtesy of
Richard P. Usatine, MD.
Alopecia areata (AA) is a common autoimmune condition characterized by hair loss resulting from a T cell–mediated attack on the hair follicles. It manifests as nonscarring patches of hair loss on the scalp, eyebrows, eyelashes, and beard area as well as more extensive complete loss of scalp and body hair. While AA may affect individuals of any age, most patients develop their first patch(es) of hair loss during childhood.1 The treatment landscape for AA has evolved considerably in recent years, but barriers to access to newer treatments persist.
Epidemiology
AA is most prevalent among pediatric and adult individuals of African, Asian, or Hispanic/Latino descent.2-4 In some studies, Black individuals had higher odds and Asian individuals had lower odds of developing AA, while other studies have reported the highest standardized prevalence among Asian individuals.5 In the United States, AA affects about 1.47% of adults and as many as 0.11% of children.6-8 In Black patients, AA often manifests early with a female predominance.5
AA frequently is associated with autoimmune comorbidities, the most common being thyroid disease.3,5 In Black patients, AA is associated with more atopic comorbidities, including asthma, atopic dermatitis, and allergic rhinitis.5
Key Clinical Features
AA clinically manifests similarly across different skin tones; however, in patients with more tightly coiled or curly hair, the extent of scalp hair loss may be underestimated without a full examination. Culturally sensitive approaches to hair and scalp evaluation are essential, especially for Black women, whose hair care practices and scalp conditions may be overlooked or misunderstood during visits to evaluate hair loss. A thoughtful history and gentle examination of the hair and scalp that considers hair texture, cultural practices such as head coverings (eg, headwraps, turbans, hijabs), use of hair adornments (eg, clips, beads, bows), traditional braiding, and use of natural oils or herbal treatments, as well as styling methods including tight hairstyles, use of heat styling tools (eg, flat irons, curling irons), chemical application (eg, straighteners, hair color), and washing or styling frequency can improve diagnostic accuracy and help build trust in the patient-provider relationship.
Classic signs of AA visualized with dermoscopy include yellow and/or black dots on the scalp and exclamation point hairs. The appearance of fine white vellus hairs within the alopecic patches also may indicate early regrowth. On scalp trichoscopy, black dots are more prominent, and yellow dots are less prominent, in individuals with darker skin tones vs lighter skin tones.9
Worth Noting
In addition to a full examination of the scalp, documenting the extent of hair loss using validated severity scales, including the severity of alopecia tool (SALT), AA severity index (AASI), clinician-reported outcome assessment, and patient-reported outcome measures, can standardize disease severity assessment, facilitate timely insurance or medication approvals, and support objective tracking of treatment response, which may ultimately enhance access to care.10
Prompt treatment of AA is essential. Not surprisingly, patients given a diagnosis of AA may experience considerable emotional and psychological distress—regardless of the extent of the loss.11 Treatment options include mid- to high-potency topical or intralesional corticosteroids and newer and more targeted systemic options, including 3 Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitors—baricitinib, ritlecitinib, and deuruxolitinib—for more extensive disease.12 Treatment with intralesional corticosteroids may cause transient hypopigmentation, which may be more noticeable in patients with darker skin tones. Delays in treatment with JAK inhibitors can lead to a less-than-optimal response. Of the 3 JAK inhibitors that are approved by the US Food and Drug Administration for AA, only ritlecitinib is approved for children 12 years and older, leaving a therapeutic gap for younger patients that often leads to uncomfortable scalp injections, delayed or no treatment, off-label use of JAK inhibitors as well as the pairing of off-label dupilumab with oral minoxidil.12
Based on adult data, patients with severe disease and a shorter duration of hair loss (ie, < 4 years) tend to respond better to JAK inhibitors than those experiencing hair loss for longer periods. Also, those with more severe AA tend to have poorer outcomes than those with less severe disease.13 If treatment proves less than optimal, wigs and hair pieces may need to be considered. It is worth noting that some insurance companies will cover the cost of wigs for patients when prescribed as cranial prostheses.
Health Disparity Highlight
Health disparities in AA can be influenced by socioeconomic status and access to care. Patients from lower-income backgrounds often face barriers to accessing dermatologic care and treatments such as JAK inhibitors, which may remain inaccessible due to high costs and insurance limitations.14 These barriers can intersect with other factors such as age, sex, and race, potentially exacerbating disparities. Women with skin of color in underserved communities may experience delayed diagnosis, limited treatment options, and greater psychosocial distress from hair loss.14 Addressing these inequities requires advocacy, education for both patients and clinicians, and improved access to treatment to ensure comprehensive care for all patients.
The Comparison
A. Alopecia areata in a young girl with a lighter skin tone. The fine white vellus hairs are signs of regrowth.
B. Alopecia areata in a 49-year-old man with tightly coiled hair and darker skin tone. Coiled white hairs are noted in the alopecia patches.

young girl with a lighter skin
tone. The fine white vellus
hairs are signs of regrowth. Photographs courtesy of
Richard P. Usatine, MD.

49-year-old man with tightly
coiled hair and darker skin
tone. Coiled white hairs
are noted in the alopecia
patches. Photographs courtesy of
Richard P. Usatine, MD.
Alopecia areata (AA) is a common autoimmune condition characterized by hair loss resulting from a T cell–mediated attack on the hair follicles. It manifests as nonscarring patches of hair loss on the scalp, eyebrows, eyelashes, and beard area as well as more extensive complete loss of scalp and body hair. While AA may affect individuals of any age, most patients develop their first patch(es) of hair loss during childhood.1 The treatment landscape for AA has evolved considerably in recent years, but barriers to access to newer treatments persist.
Epidemiology
AA is most prevalent among pediatric and adult individuals of African, Asian, or Hispanic/Latino descent.2-4 In some studies, Black individuals had higher odds and Asian individuals had lower odds of developing AA, while other studies have reported the highest standardized prevalence among Asian individuals.5 In the United States, AA affects about 1.47% of adults and as many as 0.11% of children.6-8 In Black patients, AA often manifests early with a female predominance.5
AA frequently is associated with autoimmune comorbidities, the most common being thyroid disease.3,5 In Black patients, AA is associated with more atopic comorbidities, including asthma, atopic dermatitis, and allergic rhinitis.5
Key Clinical Features
AA clinically manifests similarly across different skin tones; however, in patients with more tightly coiled or curly hair, the extent of scalp hair loss may be underestimated without a full examination. Culturally sensitive approaches to hair and scalp evaluation are essential, especially for Black women, whose hair care practices and scalp conditions may be overlooked or misunderstood during visits to evaluate hair loss. A thoughtful history and gentle examination of the hair and scalp that considers hair texture, cultural practices such as head coverings (eg, headwraps, turbans, hijabs), use of hair adornments (eg, clips, beads, bows), traditional braiding, and use of natural oils or herbal treatments, as well as styling methods including tight hairstyles, use of heat styling tools (eg, flat irons, curling irons), chemical application (eg, straighteners, hair color), and washing or styling frequency can improve diagnostic accuracy and help build trust in the patient-provider relationship.
Classic signs of AA visualized with dermoscopy include yellow and/or black dots on the scalp and exclamation point hairs. The appearance of fine white vellus hairs within the alopecic patches also may indicate early regrowth. On scalp trichoscopy, black dots are more prominent, and yellow dots are less prominent, in individuals with darker skin tones vs lighter skin tones.9
Worth Noting
In addition to a full examination of the scalp, documenting the extent of hair loss using validated severity scales, including the severity of alopecia tool (SALT), AA severity index (AASI), clinician-reported outcome assessment, and patient-reported outcome measures, can standardize disease severity assessment, facilitate timely insurance or medication approvals, and support objective tracking of treatment response, which may ultimately enhance access to care.10
Prompt treatment of AA is essential. Not surprisingly, patients given a diagnosis of AA may experience considerable emotional and psychological distress—regardless of the extent of the loss.11 Treatment options include mid- to high-potency topical or intralesional corticosteroids and newer and more targeted systemic options, including 3 Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitors—baricitinib, ritlecitinib, and deuruxolitinib—for more extensive disease.12 Treatment with intralesional corticosteroids may cause transient hypopigmentation, which may be more noticeable in patients with darker skin tones. Delays in treatment with JAK inhibitors can lead to a less-than-optimal response. Of the 3 JAK inhibitors that are approved by the US Food and Drug Administration for AA, only ritlecitinib is approved for children 12 years and older, leaving a therapeutic gap for younger patients that often leads to uncomfortable scalp injections, delayed or no treatment, off-label use of JAK inhibitors as well as the pairing of off-label dupilumab with oral minoxidil.12
Based on adult data, patients with severe disease and a shorter duration of hair loss (ie, < 4 years) tend to respond better to JAK inhibitors than those experiencing hair loss for longer periods. Also, those with more severe AA tend to have poorer outcomes than those with less severe disease.13 If treatment proves less than optimal, wigs and hair pieces may need to be considered. It is worth noting that some insurance companies will cover the cost of wigs for patients when prescribed as cranial prostheses.
Health Disparity Highlight
Health disparities in AA can be influenced by socioeconomic status and access to care. Patients from lower-income backgrounds often face barriers to accessing dermatologic care and treatments such as JAK inhibitors, which may remain inaccessible due to high costs and insurance limitations.14 These barriers can intersect with other factors such as age, sex, and race, potentially exacerbating disparities. Women with skin of color in underserved communities may experience delayed diagnosis, limited treatment options, and greater psychosocial distress from hair loss.14 Addressing these inequities requires advocacy, education for both patients and clinicians, and improved access to treatment to ensure comprehensive care for all patients.
- Kara T, Topkarcı Z. Interactions between posttraumatic stress disorder and alopecia areata in child with trauma exposure: two case reports. Int J Trichology. 2018;10:131-134. doi:10.4103/ijt.ijt_2_18
- Sy N, Mastacouris N, Strunk A, et al. Overall and racial and ethnic subgroup prevalences of alopecia areata, alopecia totalis, and alopecia universalis. JAMA Dermatol. 2023;159:419-423.
- Lee H, Jung SJ, Patel AB, et al. Racial characteristics of alopecia areata in the United States. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;83:1064-1070.
- Feaster B, McMichael AJ. Epidemiology of alopecia areata in Black patients: a retrospective chart review. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2022;87:1121-1123.
- Lee HH, Gwillim E, Patel KR, et al. Epidemiology of alopecia areata, ophiasis, totalis, and universalis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;82:675-682.
- Mostaghimi A, Gao W, Ray M, et al. Trends in prevalence and incidence of alopecia areata, alopecia totalis, and alopecia universalis among adults and children in a US employer-sponsored insured population. JAMA Dermatol. 2023;159:411-418.
- Adhanom R, Ansbro B, Castelo-Soccio L. Epidemiology of pediatric alopecia areata. Pediatr Dermatol. 2025;42 suppl 1(suppl 1):12-23.
- Karampinis E, Toli O, Georgopoulou KE, et al. Exploring pediatric dermatology in skin of color: focus on dermoscopy. Life (Basel). 2024;14:1604.
- King BA, Senna MM, Ohyama M, et al. Defining severity in alopecia areata: current perspectives and a multidimensional framework. Dermatol Ther (Heidelb). 2022;12:825-834.
- Toussi A, Barton VR, Le ST, et al. Psychosocial and psychiatric comorbidities and health-related quality of life in alopecia areata: a systematic review. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2021;85:162-175.
- Kalil L, Welch D, Heath CR, et al. Systemic therapies for pediatric alopecia areata. Pediatr Dermatol. 2025;42 suppl 1:36-42.
- King BA, Craiglow BG. Janus kinase inhibitors for alopecia areata. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2023;89:S29-S32.
- Klein EJ, Taiwò D, Kakpovbia E, et al. Disparities in Janus kinase inhibitor access for alopecia areata: a retrospective analysis. Int J Womens Dermatol. 2024;10:E155.
- McKenzie PL, Maltenfort M, Bruckner AL, et al. Evaluation of the prevalence and incidence of pediatric alopecia areata using electronic health record data. JAMA Dermatol. 2022;158:547-551. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2022.0351
- Kara T, Topkarcı Z. Interactions between posttraumatic stress disorder and alopecia areata in child with trauma exposure: two case reports. Int J Trichology. 2018;10:131-134. doi:10.4103/ijt.ijt_2_18
- Sy N, Mastacouris N, Strunk A, et al. Overall and racial and ethnic subgroup prevalences of alopecia areata, alopecia totalis, and alopecia universalis. JAMA Dermatol. 2023;159:419-423.
- Lee H, Jung SJ, Patel AB, et al. Racial characteristics of alopecia areata in the United States. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;83:1064-1070.
- Feaster B, McMichael AJ. Epidemiology of alopecia areata in Black patients: a retrospective chart review. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2022;87:1121-1123.
- Lee HH, Gwillim E, Patel KR, et al. Epidemiology of alopecia areata, ophiasis, totalis, and universalis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;82:675-682.
- Mostaghimi A, Gao W, Ray M, et al. Trends in prevalence and incidence of alopecia areata, alopecia totalis, and alopecia universalis among adults and children in a US employer-sponsored insured population. JAMA Dermatol. 2023;159:411-418.
- Adhanom R, Ansbro B, Castelo-Soccio L. Epidemiology of pediatric alopecia areata. Pediatr Dermatol. 2025;42 suppl 1(suppl 1):12-23.
- Karampinis E, Toli O, Georgopoulou KE, et al. Exploring pediatric dermatology in skin of color: focus on dermoscopy. Life (Basel). 2024;14:1604.
- King BA, Senna MM, Ohyama M, et al. Defining severity in alopecia areata: current perspectives and a multidimensional framework. Dermatol Ther (Heidelb). 2022;12:825-834.
- Toussi A, Barton VR, Le ST, et al. Psychosocial and psychiatric comorbidities and health-related quality of life in alopecia areata: a systematic review. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2021;85:162-175.
- Kalil L, Welch D, Heath CR, et al. Systemic therapies for pediatric alopecia areata. Pediatr Dermatol. 2025;42 suppl 1:36-42.
- King BA, Craiglow BG. Janus kinase inhibitors for alopecia areata. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2023;89:S29-S32.
- Klein EJ, Taiwò D, Kakpovbia E, et al. Disparities in Janus kinase inhibitor access for alopecia areata: a retrospective analysis. Int J Womens Dermatol. 2024;10:E155.
- McKenzie PL, Maltenfort M, Bruckner AL, et al. Evaluation of the prevalence and incidence of pediatric alopecia areata using electronic health record data. JAMA Dermatol. 2022;158:547-551. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2022.0351
Consider Cultural Practices and Barriers to Care When Treating Alopecia Areata
Consider Cultural Practices and Barriers to Care When Treating Alopecia Areata
Don’t Miss These Signs of Rosacea in Darker Skin Types
Don’t Miss These Signs of Rosacea in Darker Skin Types
THE COMPARISON:
- A. Erythematotelangiectatic rosacea in a polygonal vascular pattern on the cheeks in a Black woman who also has eyelid hypopigmentation due to vitiligo.
- B. Rhinophymatous rosacea in a Hispanic woman who also has papules and pustules on the chin and upper lip region as well as facial scarring from severe inflammatory acne during her teen years.
- C. Papulopustular rosacea in a Hispanic man.
Rosacea is a chronic inflammatory condition characterized by facial flushing and persistent erythema of the central face, typically affecting the cheeks and nose. It also may manifest with papules, pustules, and telangiectasias. The 4 main subtypes of rosacea are erythematotelangiectatic, papulopustular, phymatous (involving thickening of the skin, often of the nose), and ocular (dry, itchy, or irritated eyes).1 Patients also may report stinging, burning, dryness, and edema.2 The etiology of rosacea is unclear but is believed to involve immune dysfunction, neurovascular dysregulation, certain microorganisms, and genetic predisposition.1,2
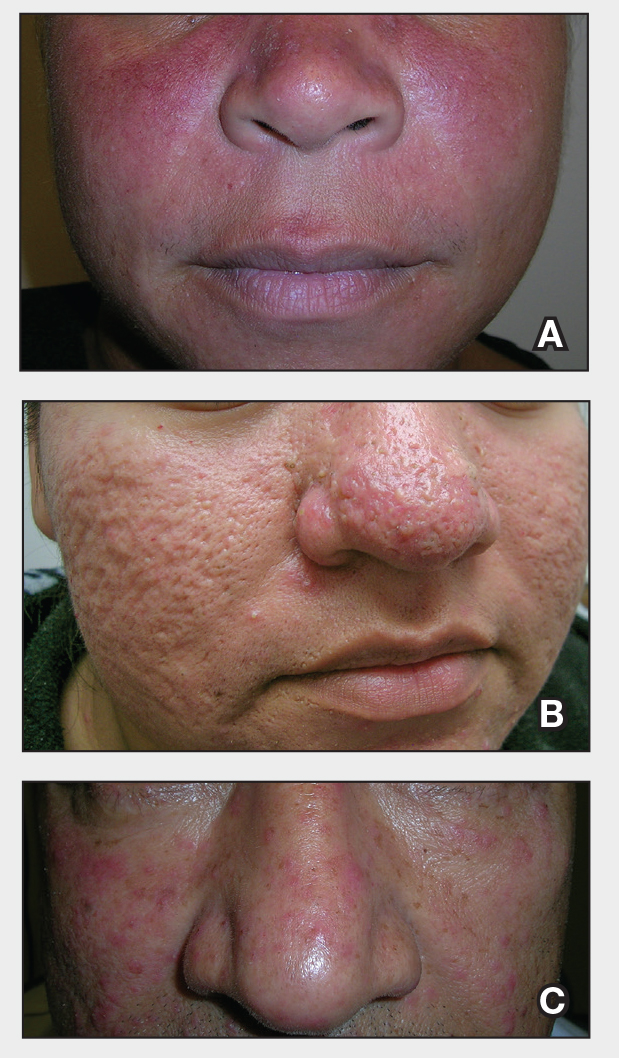
Epidemiology
Rosacea often is associated with fair skin and more frequently is reported in individuals of Northern European descent.1,2 While it may be less common in darker skin types, rosacea is not rare in patients with skin of color (SOC). A review of US outpatient data from 1993 to 2010 found that 2% of patients with rosacea were Black, 2.3% were Asian or Pacific Islander, and 3.9% were Hispanic or Latino.3 Global estimates suggest that up to 40 million individuals with SOC may be affected by rosacea,4 with the reported prevalence as high as 10%.2 Although early research linked rosacea primarily to adults older than 30 years, newer data show peak prevalence between ages 25 to 39 years, suggesting that younger adults may be affected more than previously recognized.5
Key Clinical Features
In addition to the traditional subtypes, updated guidelines recommend a phenotype- based approach to diagnosing rosacea focusing on observable features such as persistent redness in the central face and thickened skin rather than classifying patients into broad categories. A diagnosis can be made when at least one diagnostic feature is present (eg, fixed facial erythema or phymatous changes) or when 2 or more major features are observed (eg, papules, pustules, flushing, visible blood vessels, or ocular findings).6
In individuals with darker skin types, erythema may not be bright red; rather, the skin may appear pink, reddish-brown, violaceous, or dusky brown.7 Postinflammatory hyperpigmentation, which is common in darker skin tones, can further mask erythema.2 Pressing a microscope slide or magnifying glass against the skin can help assess for blanching, which is indicative of erythema. Telangiectasias also may be more challenging to appreciate in patients with SOC and typically require bright, shadow-free lighting or dermoscopy for detection.2
Skin thickening across the cheeks and nose with overlying acneform papules can be diagnostic clues of rosacea in darker skin types and help distinguish it from acne.2 It also is important to distinguish rosacea from systemic lupus erythematosus, which typically manifests as a malar rash that spares the nasolabial folds and is nonpustular. If uncertain, consider serologic testing for antinuclear antibodies, patch testing, or biopsy.8
Worth Noting
Treatment of rosacea is focused on managing symptoms and reducing flares. First-line strategies include behavioral modifications and trigger avoidance, such as minimizing sun exposure and avoiding consumption of alcohol and spicy foods.9 Gentle skin care practices are essential, including the use of light, fragrance-free, nonirritating cleansers and moisturizers at least once daily. Application of sunscreen with an SPF of at least 30 also is routinely recommended.9,10 Additionally, patients should be counseled to avoid harsh cleansers, such as exfoliants, astringents, and chemicals that may further diminish the skin barrier.10
Treatment options approved by the US Food and Drug Administration for rosacea include oral doxycycline, oral minocycline, topical brimonidine, oxymetazoline, ivermectin, metronidazole, azelaic acid, sodium sulfacetamide/sulfur, encapsulated benzoyl peroxide cream, and minocycline.11-13
Topical treatment options commonly used off-label for rosacea include topical clindamycin, topical retinoids, and azithromycin. Oral tetracyclines should be avoided in children and pregnant women; instead, oral erythromycin and topical metronidazole commonly are used.14
Laser or intense pulsed light therapy may be considered, although results have been mixed, and the long-term benefits are uncertain. Given the higher risk for postinflammatory hyperpigmentation in patients with SOC, these modalities should be used cautiously.15 Among the available options, the Nd:YAG laser is preferred in darker skin types due to its safety profile.16 A small case series reported successful CO2 laser treatment for rhinophyma in patients with melanated skin; however, some patients developed localized scarring, suggesting that conservative depth settings should be used to reduce risk for this adverse event.17
Health Disparity Highlight
Rosacea may be underdiagnosed in individuals with darker skin types,2,15,18 likely due in part to reduced contrast between erythema and background skin tone, which can make features such as flushing and telangiectasias harder to appreciate.1,10,15
Although tools to assess erythema exist, they rarely are used in everyday clinical practice.10 In patients with deeply pigmented skin, ensuring adequate examination room lighting and using dermoscopy can help identify any subtle vascular or textural changes localized across the central face. While various imaging techniques are used in clinical trials to monitor treatment response, few have been studied and optimized across a wide range of skin tones.10 There is a need for dermatologic assessment tools that better capture the degree of erythema, inflammation, and vascular features of rosacea in pigmented skin. Emerging research is focused on developing more equitable imaging technologies.19
- Rainer BM, Kang S, Chien AL. Rosacea: epidemiology, pathogenesis, and treatment. Dermatoendocrinol. 2017;9:E1361574.
- Alexis AF, Callender VD, Baldwin HE, et al. Global epidemiology and clinical spectrum of rosacea, highlighting skin of color: review and clinical practice experience. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019;80:1722-1729.e7.
- Al-Dabagh A, Davis SA, McMichael AJ, el al. Rosacea in skin of color: not a rare diagnosis. Dermatol Online J. 2014;20:13030/qt1mv9r0ss.
- Tan J, Berg M. Rosacea: current state of epidemiology. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2013;69(6 suppl 1):S27-S35.
- Saurat JH, Halioua B, Baissac C, et al. Epidemiology of acne and rosacea: a worldwide global study. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2024;90:1016-1018.
- Gallo RL, Granstein RD, Kang S, et al. Standard classification and pathophysiology of rosacea: the 2017 update by the National Rosacea Society Expert Committee. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2018;78:148-155.
- Finlay AY, Griffiths TW, Belmo S, et al. Why we should abandon the misused descriptor ‘erythema’. Br J Dermatol. 2021;185:1240-1241.
- Callender VD, Barbosa V, Burgess CM, et al. Approach to treatment of medical and cosmetic facial concerns in skin of color patients. Cutis. 2017;100:375-380.
- Baldwin H, Alexis A, Andriessen A, et al. Supplement article: skin barrier deficiency in rosacea: an algorithm integrating OTC skincare products into treatment regimens. J Drugs Dermatol. 2022;21:SF3595563-SF35955610.
- Ohanenye C, Taliaferro S, Callender VD. Diagnosing disorders of facial erythema. Dermatol Clin. 2023;41:377-392.
- Thiboutot D, Anderson R, Cook-Bolden F, et al. Standard management options for rosacea: the 2019 update by the National Rosacea Society Expert Committee. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;82:1501-1510.
- Del Rosso JQ, Schlessinger J, Werschler P. Comparison of anti-inflammatory dose doxycycline versus doxycycline 100 mg in the treatment of rosacea. J Drugs Dermatol. 2008;7:573-576.
- van der Linden MMD, van Ratingen AR, van Rappard DC, et al. DOMINO, doxycycline 40 mg vs. minocycline 100 mg in the treatment of rosacea: a randomized, single-blinded, noninferiority trial, comparing efficacy and safety. Br J Dermatol. 2017;176:1465-1474.
- Geng R, Bourkas A, Sibbald RG, et al. Efficacy of treatments for rosacea in the pediatric population: a systematic review. JEADV Clinical Practice. 2024;3:17-48.
- Sarkar R, Podder I, Jagadeesan S. Rosacea in skin of color: a comprehensive review. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2020;86:611-621.
- Chen A, Choi J, Balazic E, et al. Review of laser and energy-based devices to treat rosacea in skin of color. J Cosmet Laser Ther. 2024;26:43-53.
- Nganzeu CG, Lopez A, Brennan TE. Ablative CO2 laser treatment of rhinophyma in people of color: a case series. Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open. 2025;13:E6616.
- Kulthanan K, Andriessen A, Jiang X, et al. A review of the challenges and nuances in treating rosacea in Asian skin types using cleansers and moisturizers as adjuncts. J Drugs Dermatol. 2023;22:45-53.
- Jarang A, McGrath Q, Harunani M, et al. Multispectral SWIR imaging for equitable pigmentation-insensitive assessment of inflammatory acne in darkly pigmented skin. Presented at Photonics in Dermatology and Plastic Surgery 2025; January 25-27, 2025; San Francisco, California.
THE COMPARISON:
- A. Erythematotelangiectatic rosacea in a polygonal vascular pattern on the cheeks in a Black woman who also has eyelid hypopigmentation due to vitiligo.
- B. Rhinophymatous rosacea in a Hispanic woman who also has papules and pustules on the chin and upper lip region as well as facial scarring from severe inflammatory acne during her teen years.
- C. Papulopustular rosacea in a Hispanic man.
Rosacea is a chronic inflammatory condition characterized by facial flushing and persistent erythema of the central face, typically affecting the cheeks and nose. It also may manifest with papules, pustules, and telangiectasias. The 4 main subtypes of rosacea are erythematotelangiectatic, papulopustular, phymatous (involving thickening of the skin, often of the nose), and ocular (dry, itchy, or irritated eyes).1 Patients also may report stinging, burning, dryness, and edema.2 The etiology of rosacea is unclear but is believed to involve immune dysfunction, neurovascular dysregulation, certain microorganisms, and genetic predisposition.1,2

Epidemiology
Rosacea often is associated with fair skin and more frequently is reported in individuals of Northern European descent.1,2 While it may be less common in darker skin types, rosacea is not rare in patients with skin of color (SOC). A review of US outpatient data from 1993 to 2010 found that 2% of patients with rosacea were Black, 2.3% were Asian or Pacific Islander, and 3.9% were Hispanic or Latino.3 Global estimates suggest that up to 40 million individuals with SOC may be affected by rosacea,4 with the reported prevalence as high as 10%.2 Although early research linked rosacea primarily to adults older than 30 years, newer data show peak prevalence between ages 25 to 39 years, suggesting that younger adults may be affected more than previously recognized.5
Key Clinical Features
In addition to the traditional subtypes, updated guidelines recommend a phenotype- based approach to diagnosing rosacea focusing on observable features such as persistent redness in the central face and thickened skin rather than classifying patients into broad categories. A diagnosis can be made when at least one diagnostic feature is present (eg, fixed facial erythema or phymatous changes) or when 2 or more major features are observed (eg, papules, pustules, flushing, visible blood vessels, or ocular findings).6
In individuals with darker skin types, erythema may not be bright red; rather, the skin may appear pink, reddish-brown, violaceous, or dusky brown.7 Postinflammatory hyperpigmentation, which is common in darker skin tones, can further mask erythema.2 Pressing a microscope slide or magnifying glass against the skin can help assess for blanching, which is indicative of erythema. Telangiectasias also may be more challenging to appreciate in patients with SOC and typically require bright, shadow-free lighting or dermoscopy for detection.2
Skin thickening across the cheeks and nose with overlying acneform papules can be diagnostic clues of rosacea in darker skin types and help distinguish it from acne.2 It also is important to distinguish rosacea from systemic lupus erythematosus, which typically manifests as a malar rash that spares the nasolabial folds and is nonpustular. If uncertain, consider serologic testing for antinuclear antibodies, patch testing, or biopsy.8
Worth Noting
Treatment of rosacea is focused on managing symptoms and reducing flares. First-line strategies include behavioral modifications and trigger avoidance, such as minimizing sun exposure and avoiding consumption of alcohol and spicy foods.9 Gentle skin care practices are essential, including the use of light, fragrance-free, nonirritating cleansers and moisturizers at least once daily. Application of sunscreen with an SPF of at least 30 also is routinely recommended.9,10 Additionally, patients should be counseled to avoid harsh cleansers, such as exfoliants, astringents, and chemicals that may further diminish the skin barrier.10
Treatment options approved by the US Food and Drug Administration for rosacea include oral doxycycline, oral minocycline, topical brimonidine, oxymetazoline, ivermectin, metronidazole, azelaic acid, sodium sulfacetamide/sulfur, encapsulated benzoyl peroxide cream, and minocycline.11-13
Topical treatment options commonly used off-label for rosacea include topical clindamycin, topical retinoids, and azithromycin. Oral tetracyclines should be avoided in children and pregnant women; instead, oral erythromycin and topical metronidazole commonly are used.14
Laser or intense pulsed light therapy may be considered, although results have been mixed, and the long-term benefits are uncertain. Given the higher risk for postinflammatory hyperpigmentation in patients with SOC, these modalities should be used cautiously.15 Among the available options, the Nd:YAG laser is preferred in darker skin types due to its safety profile.16 A small case series reported successful CO2 laser treatment for rhinophyma in patients with melanated skin; however, some patients developed localized scarring, suggesting that conservative depth settings should be used to reduce risk for this adverse event.17
Health Disparity Highlight
Rosacea may be underdiagnosed in individuals with darker skin types,2,15,18 likely due in part to reduced contrast between erythema and background skin tone, which can make features such as flushing and telangiectasias harder to appreciate.1,10,15
Although tools to assess erythema exist, they rarely are used in everyday clinical practice.10 In patients with deeply pigmented skin, ensuring adequate examination room lighting and using dermoscopy can help identify any subtle vascular or textural changes localized across the central face. While various imaging techniques are used in clinical trials to monitor treatment response, few have been studied and optimized across a wide range of skin tones.10 There is a need for dermatologic assessment tools that better capture the degree of erythema, inflammation, and vascular features of rosacea in pigmented skin. Emerging research is focused on developing more equitable imaging technologies.19
THE COMPARISON:
- A. Erythematotelangiectatic rosacea in a polygonal vascular pattern on the cheeks in a Black woman who also has eyelid hypopigmentation due to vitiligo.
- B. Rhinophymatous rosacea in a Hispanic woman who also has papules and pustules on the chin and upper lip region as well as facial scarring from severe inflammatory acne during her teen years.
- C. Papulopustular rosacea in a Hispanic man.
Rosacea is a chronic inflammatory condition characterized by facial flushing and persistent erythema of the central face, typically affecting the cheeks and nose. It also may manifest with papules, pustules, and telangiectasias. The 4 main subtypes of rosacea are erythematotelangiectatic, papulopustular, phymatous (involving thickening of the skin, often of the nose), and ocular (dry, itchy, or irritated eyes).1 Patients also may report stinging, burning, dryness, and edema.2 The etiology of rosacea is unclear but is believed to involve immune dysfunction, neurovascular dysregulation, certain microorganisms, and genetic predisposition.1,2

Epidemiology
Rosacea often is associated with fair skin and more frequently is reported in individuals of Northern European descent.1,2 While it may be less common in darker skin types, rosacea is not rare in patients with skin of color (SOC). A review of US outpatient data from 1993 to 2010 found that 2% of patients with rosacea were Black, 2.3% were Asian or Pacific Islander, and 3.9% were Hispanic or Latino.3 Global estimates suggest that up to 40 million individuals with SOC may be affected by rosacea,4 with the reported prevalence as high as 10%.2 Although early research linked rosacea primarily to adults older than 30 years, newer data show peak prevalence between ages 25 to 39 years, suggesting that younger adults may be affected more than previously recognized.5
Key Clinical Features
In addition to the traditional subtypes, updated guidelines recommend a phenotype- based approach to diagnosing rosacea focusing on observable features such as persistent redness in the central face and thickened skin rather than classifying patients into broad categories. A diagnosis can be made when at least one diagnostic feature is present (eg, fixed facial erythema or phymatous changes) or when 2 or more major features are observed (eg, papules, pustules, flushing, visible blood vessels, or ocular findings).6
In individuals with darker skin types, erythema may not be bright red; rather, the skin may appear pink, reddish-brown, violaceous, or dusky brown.7 Postinflammatory hyperpigmentation, which is common in darker skin tones, can further mask erythema.2 Pressing a microscope slide or magnifying glass against the skin can help assess for blanching, which is indicative of erythema. Telangiectasias also may be more challenging to appreciate in patients with SOC and typically require bright, shadow-free lighting or dermoscopy for detection.2
Skin thickening across the cheeks and nose with overlying acneform papules can be diagnostic clues of rosacea in darker skin types and help distinguish it from acne.2 It also is important to distinguish rosacea from systemic lupus erythematosus, which typically manifests as a malar rash that spares the nasolabial folds and is nonpustular. If uncertain, consider serologic testing for antinuclear antibodies, patch testing, or biopsy.8
Worth Noting
Treatment of rosacea is focused on managing symptoms and reducing flares. First-line strategies include behavioral modifications and trigger avoidance, such as minimizing sun exposure and avoiding consumption of alcohol and spicy foods.9 Gentle skin care practices are essential, including the use of light, fragrance-free, nonirritating cleansers and moisturizers at least once daily. Application of sunscreen with an SPF of at least 30 also is routinely recommended.9,10 Additionally, patients should be counseled to avoid harsh cleansers, such as exfoliants, astringents, and chemicals that may further diminish the skin barrier.10
Treatment options approved by the US Food and Drug Administration for rosacea include oral doxycycline, oral minocycline, topical brimonidine, oxymetazoline, ivermectin, metronidazole, azelaic acid, sodium sulfacetamide/sulfur, encapsulated benzoyl peroxide cream, and minocycline.11-13
Topical treatment options commonly used off-label for rosacea include topical clindamycin, topical retinoids, and azithromycin. Oral tetracyclines should be avoided in children and pregnant women; instead, oral erythromycin and topical metronidazole commonly are used.14
Laser or intense pulsed light therapy may be considered, although results have been mixed, and the long-term benefits are uncertain. Given the higher risk for postinflammatory hyperpigmentation in patients with SOC, these modalities should be used cautiously.15 Among the available options, the Nd:YAG laser is preferred in darker skin types due to its safety profile.16 A small case series reported successful CO2 laser treatment for rhinophyma in patients with melanated skin; however, some patients developed localized scarring, suggesting that conservative depth settings should be used to reduce risk for this adverse event.17
Health Disparity Highlight
Rosacea may be underdiagnosed in individuals with darker skin types,2,15,18 likely due in part to reduced contrast between erythema and background skin tone, which can make features such as flushing and telangiectasias harder to appreciate.1,10,15
Although tools to assess erythema exist, they rarely are used in everyday clinical practice.10 In patients with deeply pigmented skin, ensuring adequate examination room lighting and using dermoscopy can help identify any subtle vascular or textural changes localized across the central face. While various imaging techniques are used in clinical trials to monitor treatment response, few have been studied and optimized across a wide range of skin tones.10 There is a need for dermatologic assessment tools that better capture the degree of erythema, inflammation, and vascular features of rosacea in pigmented skin. Emerging research is focused on developing more equitable imaging technologies.19
- Rainer BM, Kang S, Chien AL. Rosacea: epidemiology, pathogenesis, and treatment. Dermatoendocrinol. 2017;9:E1361574.
- Alexis AF, Callender VD, Baldwin HE, et al. Global epidemiology and clinical spectrum of rosacea, highlighting skin of color: review and clinical practice experience. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019;80:1722-1729.e7.
- Al-Dabagh A, Davis SA, McMichael AJ, el al. Rosacea in skin of color: not a rare diagnosis. Dermatol Online J. 2014;20:13030/qt1mv9r0ss.
- Tan J, Berg M. Rosacea: current state of epidemiology. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2013;69(6 suppl 1):S27-S35.
- Saurat JH, Halioua B, Baissac C, et al. Epidemiology of acne and rosacea: a worldwide global study. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2024;90:1016-1018.
- Gallo RL, Granstein RD, Kang S, et al. Standard classification and pathophysiology of rosacea: the 2017 update by the National Rosacea Society Expert Committee. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2018;78:148-155.
- Finlay AY, Griffiths TW, Belmo S, et al. Why we should abandon the misused descriptor ‘erythema’. Br J Dermatol. 2021;185:1240-1241.
- Callender VD, Barbosa V, Burgess CM, et al. Approach to treatment of medical and cosmetic facial concerns in skin of color patients. Cutis. 2017;100:375-380.
- Baldwin H, Alexis A, Andriessen A, et al. Supplement article: skin barrier deficiency in rosacea: an algorithm integrating OTC skincare products into treatment regimens. J Drugs Dermatol. 2022;21:SF3595563-SF35955610.
- Ohanenye C, Taliaferro S, Callender VD. Diagnosing disorders of facial erythema. Dermatol Clin. 2023;41:377-392.
- Thiboutot D, Anderson R, Cook-Bolden F, et al. Standard management options for rosacea: the 2019 update by the National Rosacea Society Expert Committee. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;82:1501-1510.
- Del Rosso JQ, Schlessinger J, Werschler P. Comparison of anti-inflammatory dose doxycycline versus doxycycline 100 mg in the treatment of rosacea. J Drugs Dermatol. 2008;7:573-576.
- van der Linden MMD, van Ratingen AR, van Rappard DC, et al. DOMINO, doxycycline 40 mg vs. minocycline 100 mg in the treatment of rosacea: a randomized, single-blinded, noninferiority trial, comparing efficacy and safety. Br J Dermatol. 2017;176:1465-1474.
- Geng R, Bourkas A, Sibbald RG, et al. Efficacy of treatments for rosacea in the pediatric population: a systematic review. JEADV Clinical Practice. 2024;3:17-48.
- Sarkar R, Podder I, Jagadeesan S. Rosacea in skin of color: a comprehensive review. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2020;86:611-621.
- Chen A, Choi J, Balazic E, et al. Review of laser and energy-based devices to treat rosacea in skin of color. J Cosmet Laser Ther. 2024;26:43-53.
- Nganzeu CG, Lopez A, Brennan TE. Ablative CO2 laser treatment of rhinophyma in people of color: a case series. Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open. 2025;13:E6616.
- Kulthanan K, Andriessen A, Jiang X, et al. A review of the challenges and nuances in treating rosacea in Asian skin types using cleansers and moisturizers as adjuncts. J Drugs Dermatol. 2023;22:45-53.
- Jarang A, McGrath Q, Harunani M, et al. Multispectral SWIR imaging for equitable pigmentation-insensitive assessment of inflammatory acne in darkly pigmented skin. Presented at Photonics in Dermatology and Plastic Surgery 2025; January 25-27, 2025; San Francisco, California.
- Rainer BM, Kang S, Chien AL. Rosacea: epidemiology, pathogenesis, and treatment. Dermatoendocrinol. 2017;9:E1361574.
- Alexis AF, Callender VD, Baldwin HE, et al. Global epidemiology and clinical spectrum of rosacea, highlighting skin of color: review and clinical practice experience. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019;80:1722-1729.e7.
- Al-Dabagh A, Davis SA, McMichael AJ, el al. Rosacea in skin of color: not a rare diagnosis. Dermatol Online J. 2014;20:13030/qt1mv9r0ss.
- Tan J, Berg M. Rosacea: current state of epidemiology. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2013;69(6 suppl 1):S27-S35.
- Saurat JH, Halioua B, Baissac C, et al. Epidemiology of acne and rosacea: a worldwide global study. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2024;90:1016-1018.
- Gallo RL, Granstein RD, Kang S, et al. Standard classification and pathophysiology of rosacea: the 2017 update by the National Rosacea Society Expert Committee. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2018;78:148-155.
- Finlay AY, Griffiths TW, Belmo S, et al. Why we should abandon the misused descriptor ‘erythema’. Br J Dermatol. 2021;185:1240-1241.
- Callender VD, Barbosa V, Burgess CM, et al. Approach to treatment of medical and cosmetic facial concerns in skin of color patients. Cutis. 2017;100:375-380.
- Baldwin H, Alexis A, Andriessen A, et al. Supplement article: skin barrier deficiency in rosacea: an algorithm integrating OTC skincare products into treatment regimens. J Drugs Dermatol. 2022;21:SF3595563-SF35955610.
- Ohanenye C, Taliaferro S, Callender VD. Diagnosing disorders of facial erythema. Dermatol Clin. 2023;41:377-392.
- Thiboutot D, Anderson R, Cook-Bolden F, et al. Standard management options for rosacea: the 2019 update by the National Rosacea Society Expert Committee. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;82:1501-1510.
- Del Rosso JQ, Schlessinger J, Werschler P. Comparison of anti-inflammatory dose doxycycline versus doxycycline 100 mg in the treatment of rosacea. J Drugs Dermatol. 2008;7:573-576.
- van der Linden MMD, van Ratingen AR, van Rappard DC, et al. DOMINO, doxycycline 40 mg vs. minocycline 100 mg in the treatment of rosacea: a randomized, single-blinded, noninferiority trial, comparing efficacy and safety. Br J Dermatol. 2017;176:1465-1474.
- Geng R, Bourkas A, Sibbald RG, et al. Efficacy of treatments for rosacea in the pediatric population: a systematic review. JEADV Clinical Practice. 2024;3:17-48.
- Sarkar R, Podder I, Jagadeesan S. Rosacea in skin of color: a comprehensive review. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2020;86:611-621.
- Chen A, Choi J, Balazic E, et al. Review of laser and energy-based devices to treat rosacea in skin of color. J Cosmet Laser Ther. 2024;26:43-53.
- Nganzeu CG, Lopez A, Brennan TE. Ablative CO2 laser treatment of rhinophyma in people of color: a case series. Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open. 2025;13:E6616.
- Kulthanan K, Andriessen A, Jiang X, et al. A review of the challenges and nuances in treating rosacea in Asian skin types using cleansers and moisturizers as adjuncts. J Drugs Dermatol. 2023;22:45-53.
- Jarang A, McGrath Q, Harunani M, et al. Multispectral SWIR imaging for equitable pigmentation-insensitive assessment of inflammatory acne in darkly pigmented skin. Presented at Photonics in Dermatology and Plastic Surgery 2025; January 25-27, 2025; San Francisco, California.
Don’t Miss These Signs of Rosacea in Darker Skin Types
Don’t Miss These Signs of Rosacea in Darker Skin Types
Beyond the Razor: Managing Pseudofolliculitis Barbae in Skin of Color
Beyond the Razor: Managing Pseudofolliculitis Barbae in Skin of Color
THE COMPARISON
- A. Pustules, erythematous to violaceous nodules, and hyperpigmented patches on the lower cheek and chin.
- B. Brown papules, pink keloidal papules and nodules, pustules, and hyperpigmented papules on the mandibular area and neck.
- C. Coarse hairs, pustules, and pink papules on the mandibular area and neck.
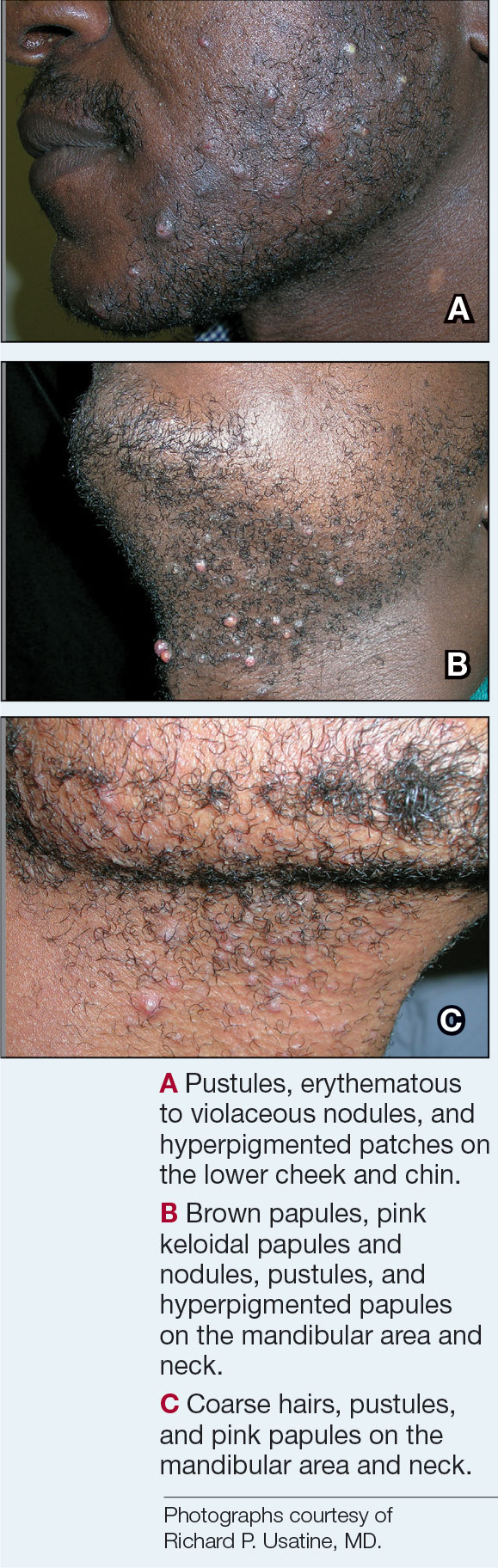
Pseudofolliculitis barbae (PFB), also known as razor bumps, is a common inflammatory condition characterized by papules and pustules that typically appear in the beard and cheek regions. It occurs when shaved hair regrows and penetrates the skin, leading to irritation and inflammation. While anyone who shaves can develop PFB, it is more prevalent and severe in individuals with naturally tightly coiled, coarse-textured hair.1,2 PFB is common in individuals who shave frequently due to personal choice or profession, such as members of the US military3,4 and firefighters, who are required to remain clean shaven for safety (eg, ensuring proper fit of a respirator mask).5 Early diagnosis and treatment of PFB are essential to prevent long-term complications such as scarring or hyperpigmentation, which may be more severe in those with darker skin tones.
Epidemiology
PFB is most common in Black men, affecting 45% to 83% of men of African ancestry.1,2 This condition also can affect individuals of various ethnicities with coarse or curly hair. The spiral shape of the hair increases the likelihood that it will regrow into the skin after shaving.6 Women with hirsutism who shave also can develop PFB.
Key Clinical Features
The papules and pustules seen in PFB may be flesh colored, erythematous, hyperpigmented, brown, or violaceous. Erythema may be less pronounced in darker vs lighter skin tones. Persistent and severe postinflammatory hyperpigmentation may occur, and hypertrophic or keloidal scars may develop in affected areas. Dermoscopy may reveal extrafollicular hair penetration as well as follicular or perifollicular pustules accompanied by hyperkeratosis.
Worth Noting
The most effective management for PFB is to discontinue shaving.1 If shaving is desired or necessary, it is recommended that patients apply lukewarm water to the affected area followed by a generous amount of shaving foam or gel to create a protective antifriction layer that allows the razor to glide more smoothly over the skin and reduces subsequent irritation.2 Using the right razor technology also may help alleviate symptoms. Research has shown that multiblade razors used in conjunction with preshave hair hydration and postshave moisturization do not worsen PFB.2 A recent study found that multiblade razor technology paired with use of a shave foam or gel actually improved skin appearance in patients with PFB.7
It is important to direct patients to shave in the direction of hair growth; however, this may not be possible for individuals with curly or coarse hair, as the hair may grow in many directions.8,9 Patients also should avoid pulling the skin taut while shaving, as doing so allows the hair to be clipped below the surface, where it can repenetrate the skin and cause further irritation. As an alternative to shaving with a razor, patients can use hair clippers to trim beard hair, which leaves behind stubble and interrupts the cycle of retracted hairs under the skin. Nd:YAG laser therapy has demonstrated efficacy in reduction of PFB papules and pustules.9-12 Greater mean improvement in inflammatory papules and reduction in hair density was noted in participants who received Nd:YAG laser plus eflornithine compared with those who received the laser or eflornithine alone.11 Patients should not pluck or dig into the skin to remove any ingrown hairs. If a tweezer is used, the patient should gently lift the tip of the ingrown hair with the tweezer to dislodge it from the skin and prevent plucking out the hair completely.
To help manage inflammation after shaving, topical treatments such as benzoyl peroxide 5%/clindamycin 1% gel can be used.3,13 A low-potency steroid such as topical hydrocortisone 2.5% applied once or twice daily for up to 2 to 3 days may be helpful.1,14 Adjunctive treatments including keratolytics (eg, topical retinoids, hydroxy acids) reduce perifollicular hyperkeratosis.14,15 Agents containing alpha hydroxy acids (eg, glycolic acid) also can decrease the curvature of the hair itself by reducing the sulfhydryl bonds.6 If secondary bacterial infections occur, oral antibiotics (eg, doxycycline) may be necessary.
Health Disparity Highlight
Individuals with darker skin tones are at higher risk for PFB and associated complications. Limited access to dermatology services may further exacerbate these challenges. Individuals with PFB may not seek medical treatment until the condition becomes severe. Clinicians also may underestimate the severity of PFB—particularly in those with darker skin tones—based on erythema alone because it may be less pronounced in darker vs lighter skin tones.16
While permanent hair reduction with laser therapy is a treatment option for PFB, it may be inaccessible to some patients because it can be expensive and is coded as a cosmetic procedure. Additionally, patients may not have access to specialists who are experienced in performing the procedure in those with darker skin tones.9 Some patients also may not want to permanently reduce the amount of hair that grows in the beard area for personal or religious reasons.17
Pseudofolliculitis barbae also has been linked to professional disparities. One study found that members of the US Air Force who had medical shaving waivers experienced longer times to promotion than those with no waiver.18 Delays in promotion may be linked to perceptions of unprofessionalism, exclusion from high-profile duties, and concerns about career progression. While this delay was similar for individuals of all races, the majority of those in the waiver group were Black/African American. In 2021, 4 Black firefighters with PFB were unsuccessful in their bid to get a medical accommodation regarding a New York City Fire Department policy requiring them to be clean shaven where the oxygen mask seals against the skin.5 More research is needed on mask safety and efficiency relative to the length of facial hair. Accommodations or tailored masks for facial hair conditions also are necessary so individuals with PFB can meet job requirements while managing their condition.
- Alexis A, Heath CR, Halder RM. Folliculitis keloidalis nuchae and pseudofolliculitis barbae: are prevention and effective treatment within reach? Dermatol Clin. 2014;32:183-191.
- Gray J, McMichael AJ. Pseudofolliculitis barbae: understanding the condition and the role of facial grooming. Int J Cosmet Sci. 2016;38 (suppl 1):24-27.
- Tshudy MT, Cho S. Pseudofolliculitis barbae in the U.S. military, a review. Mil Med. 2021;186:E52-E57.
- Jung I, Lannan FM, Weiss A, et al. Treatment and current policies on pseudofolliculitis barbae in the US military. Cutis. 2023;112:299-302.
- Jiang YR. Reasonable accommodation and disparate impact: clean shave policy discrimination in today’s workplace. J Law Med Ethics. 2023;51:185-195.
- Taylor SC, Barbosa V, Burgess C, et al. Hair and scalp disorders in adult and pediatric patients with skin of color. Cutis. 2017;100:31-35.
- Moran E, McMichael A, De Souza B, et al. New razor technology improves appearance and quality of life in men with pseudofolliculitis barbae. Cutis. 2022;110:329-334.
- Maurer M, Rietzler M, Burghardt R, et al. The male beard hair and facial skin—challenges for shaving. Int J Cosmet Sci. 2016;38 (suppl 1):3-9.
- Ross EV. How would you treat this patient with lasers & EBDs? casebased panel. Presented at: Skin of Color Update; September 13, 2024; New York, NY.
- Ross EV, Cooke LM, Timko AL, et al. Treatment of pseudofolliculitis barbae in skin types IV, V, and VI with a long-pulsed neodymium:yttrium aluminum garnet laser. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2002;47:263-270.
- Shokeir H, Samy N, Taymour M. Pseudofolliculitis barbae treatment: efficacy of topical eflornithine, long-pulsed Nd-YAG laser versus their combination. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2021;20:3517-3525.
- Amer A, Elsayed A, Gharib K. Evaluation of efficacy and safety of chemical peeling and long-pulse Nd:YAG laser in treatment of pseudofolliculitis barbae. Dermatol Ther. 2021;34:E14859.
- Cook-Bolden FE, Barba A, Halder R, et al. Twice-daily applications of benzoyl peroxide 5%/clindamycin 1% gel versus vehicle in the treatment of pseudofolliculitis barbae. Cutis. 2004;73(6 suppl):18-24.
- Nussbaum D, Friedman A. Pseudofolliculitis barbae: a review of current treatment options. J Drugs Dermatol. 2019;18:246-250.
- Quarles FN, Brody H, Johnson BA, et al. Pseudofolliculitis barbae. Dermatol Ther. 2007;20:133-136.
- McMichael AJ, Frey C. Challenging the tools used to measure cutaneous lupus severity in patients of all skin types. JAMA Dermatol. 2025;161:9-10.
- Okonkwo E, Neal B, Harper HL. Pseudofolliculitis barbae in the military and the need for social awareness. Mil Med. 2021;186:143-144.
- Ritchie S, Park J, Banta J, et al. Shaving waivers in the United States Air Force and their impact on promotions of Black/African-American members. Mil Med. 2023;188:E242-E247.
THE COMPARISON
- A. Pustules, erythematous to violaceous nodules, and hyperpigmented patches on the lower cheek and chin.
- B. Brown papules, pink keloidal papules and nodules, pustules, and hyperpigmented papules on the mandibular area and neck.
- C. Coarse hairs, pustules, and pink papules on the mandibular area and neck.

Pseudofolliculitis barbae (PFB), also known as razor bumps, is a common inflammatory condition characterized by papules and pustules that typically appear in the beard and cheek regions. It occurs when shaved hair regrows and penetrates the skin, leading to irritation and inflammation. While anyone who shaves can develop PFB, it is more prevalent and severe in individuals with naturally tightly coiled, coarse-textured hair.1,2 PFB is common in individuals who shave frequently due to personal choice or profession, such as members of the US military3,4 and firefighters, who are required to remain clean shaven for safety (eg, ensuring proper fit of a respirator mask).5 Early diagnosis and treatment of PFB are essential to prevent long-term complications such as scarring or hyperpigmentation, which may be more severe in those with darker skin tones.
Epidemiology
PFB is most common in Black men, affecting 45% to 83% of men of African ancestry.1,2 This condition also can affect individuals of various ethnicities with coarse or curly hair. The spiral shape of the hair increases the likelihood that it will regrow into the skin after shaving.6 Women with hirsutism who shave also can develop PFB.
Key Clinical Features
The papules and pustules seen in PFB may be flesh colored, erythematous, hyperpigmented, brown, or violaceous. Erythema may be less pronounced in darker vs lighter skin tones. Persistent and severe postinflammatory hyperpigmentation may occur, and hypertrophic or keloidal scars may develop in affected areas. Dermoscopy may reveal extrafollicular hair penetration as well as follicular or perifollicular pustules accompanied by hyperkeratosis.
Worth Noting
The most effective management for PFB is to discontinue shaving.1 If shaving is desired or necessary, it is recommended that patients apply lukewarm water to the affected area followed by a generous amount of shaving foam or gel to create a protective antifriction layer that allows the razor to glide more smoothly over the skin and reduces subsequent irritation.2 Using the right razor technology also may help alleviate symptoms. Research has shown that multiblade razors used in conjunction with preshave hair hydration and postshave moisturization do not worsen PFB.2 A recent study found that multiblade razor technology paired with use of a shave foam or gel actually improved skin appearance in patients with PFB.7
It is important to direct patients to shave in the direction of hair growth; however, this may not be possible for individuals with curly or coarse hair, as the hair may grow in many directions.8,9 Patients also should avoid pulling the skin taut while shaving, as doing so allows the hair to be clipped below the surface, where it can repenetrate the skin and cause further irritation. As an alternative to shaving with a razor, patients can use hair clippers to trim beard hair, which leaves behind stubble and interrupts the cycle of retracted hairs under the skin. Nd:YAG laser therapy has demonstrated efficacy in reduction of PFB papules and pustules.9-12 Greater mean improvement in inflammatory papules and reduction in hair density was noted in participants who received Nd:YAG laser plus eflornithine compared with those who received the laser or eflornithine alone.11 Patients should not pluck or dig into the skin to remove any ingrown hairs. If a tweezer is used, the patient should gently lift the tip of the ingrown hair with the tweezer to dislodge it from the skin and prevent plucking out the hair completely.
To help manage inflammation after shaving, topical treatments such as benzoyl peroxide 5%/clindamycin 1% gel can be used.3,13 A low-potency steroid such as topical hydrocortisone 2.5% applied once or twice daily for up to 2 to 3 days may be helpful.1,14 Adjunctive treatments including keratolytics (eg, topical retinoids, hydroxy acids) reduce perifollicular hyperkeratosis.14,15 Agents containing alpha hydroxy acids (eg, glycolic acid) also can decrease the curvature of the hair itself by reducing the sulfhydryl bonds.6 If secondary bacterial infections occur, oral antibiotics (eg, doxycycline) may be necessary.
Health Disparity Highlight
Individuals with darker skin tones are at higher risk for PFB and associated complications. Limited access to dermatology services may further exacerbate these challenges. Individuals with PFB may not seek medical treatment until the condition becomes severe. Clinicians also may underestimate the severity of PFB—particularly in those with darker skin tones—based on erythema alone because it may be less pronounced in darker vs lighter skin tones.16
While permanent hair reduction with laser therapy is a treatment option for PFB, it may be inaccessible to some patients because it can be expensive and is coded as a cosmetic procedure. Additionally, patients may not have access to specialists who are experienced in performing the procedure in those with darker skin tones.9 Some patients also may not want to permanently reduce the amount of hair that grows in the beard area for personal or religious reasons.17
Pseudofolliculitis barbae also has been linked to professional disparities. One study found that members of the US Air Force who had medical shaving waivers experienced longer times to promotion than those with no waiver.18 Delays in promotion may be linked to perceptions of unprofessionalism, exclusion from high-profile duties, and concerns about career progression. While this delay was similar for individuals of all races, the majority of those in the waiver group were Black/African American. In 2021, 4 Black firefighters with PFB were unsuccessful in their bid to get a medical accommodation regarding a New York City Fire Department policy requiring them to be clean shaven where the oxygen mask seals against the skin.5 More research is needed on mask safety and efficiency relative to the length of facial hair. Accommodations or tailored masks for facial hair conditions also are necessary so individuals with PFB can meet job requirements while managing their condition.
THE COMPARISON
- A. Pustules, erythematous to violaceous nodules, and hyperpigmented patches on the lower cheek and chin.
- B. Brown papules, pink keloidal papules and nodules, pustules, and hyperpigmented papules on the mandibular area and neck.
- C. Coarse hairs, pustules, and pink papules on the mandibular area and neck.

Pseudofolliculitis barbae (PFB), also known as razor bumps, is a common inflammatory condition characterized by papules and pustules that typically appear in the beard and cheek regions. It occurs when shaved hair regrows and penetrates the skin, leading to irritation and inflammation. While anyone who shaves can develop PFB, it is more prevalent and severe in individuals with naturally tightly coiled, coarse-textured hair.1,2 PFB is common in individuals who shave frequently due to personal choice or profession, such as members of the US military3,4 and firefighters, who are required to remain clean shaven for safety (eg, ensuring proper fit of a respirator mask).5 Early diagnosis and treatment of PFB are essential to prevent long-term complications such as scarring or hyperpigmentation, which may be more severe in those with darker skin tones.
Epidemiology
PFB is most common in Black men, affecting 45% to 83% of men of African ancestry.1,2 This condition also can affect individuals of various ethnicities with coarse or curly hair. The spiral shape of the hair increases the likelihood that it will regrow into the skin after shaving.6 Women with hirsutism who shave also can develop PFB.
Key Clinical Features
The papules and pustules seen in PFB may be flesh colored, erythematous, hyperpigmented, brown, or violaceous. Erythema may be less pronounced in darker vs lighter skin tones. Persistent and severe postinflammatory hyperpigmentation may occur, and hypertrophic or keloidal scars may develop in affected areas. Dermoscopy may reveal extrafollicular hair penetration as well as follicular or perifollicular pustules accompanied by hyperkeratosis.
Worth Noting
The most effective management for PFB is to discontinue shaving.1 If shaving is desired or necessary, it is recommended that patients apply lukewarm water to the affected area followed by a generous amount of shaving foam or gel to create a protective antifriction layer that allows the razor to glide more smoothly over the skin and reduces subsequent irritation.2 Using the right razor technology also may help alleviate symptoms. Research has shown that multiblade razors used in conjunction with preshave hair hydration and postshave moisturization do not worsen PFB.2 A recent study found that multiblade razor technology paired with use of a shave foam or gel actually improved skin appearance in patients with PFB.7
It is important to direct patients to shave in the direction of hair growth; however, this may not be possible for individuals with curly or coarse hair, as the hair may grow in many directions.8,9 Patients also should avoid pulling the skin taut while shaving, as doing so allows the hair to be clipped below the surface, where it can repenetrate the skin and cause further irritation. As an alternative to shaving with a razor, patients can use hair clippers to trim beard hair, which leaves behind stubble and interrupts the cycle of retracted hairs under the skin. Nd:YAG laser therapy has demonstrated efficacy in reduction of PFB papules and pustules.9-12 Greater mean improvement in inflammatory papules and reduction in hair density was noted in participants who received Nd:YAG laser plus eflornithine compared with those who received the laser or eflornithine alone.11 Patients should not pluck or dig into the skin to remove any ingrown hairs. If a tweezer is used, the patient should gently lift the tip of the ingrown hair with the tweezer to dislodge it from the skin and prevent plucking out the hair completely.
To help manage inflammation after shaving, topical treatments such as benzoyl peroxide 5%/clindamycin 1% gel can be used.3,13 A low-potency steroid such as topical hydrocortisone 2.5% applied once or twice daily for up to 2 to 3 days may be helpful.1,14 Adjunctive treatments including keratolytics (eg, topical retinoids, hydroxy acids) reduce perifollicular hyperkeratosis.14,15 Agents containing alpha hydroxy acids (eg, glycolic acid) also can decrease the curvature of the hair itself by reducing the sulfhydryl bonds.6 If secondary bacterial infections occur, oral antibiotics (eg, doxycycline) may be necessary.
Health Disparity Highlight
Individuals with darker skin tones are at higher risk for PFB and associated complications. Limited access to dermatology services may further exacerbate these challenges. Individuals with PFB may not seek medical treatment until the condition becomes severe. Clinicians also may underestimate the severity of PFB—particularly in those with darker skin tones—based on erythema alone because it may be less pronounced in darker vs lighter skin tones.16
While permanent hair reduction with laser therapy is a treatment option for PFB, it may be inaccessible to some patients because it can be expensive and is coded as a cosmetic procedure. Additionally, patients may not have access to specialists who are experienced in performing the procedure in those with darker skin tones.9 Some patients also may not want to permanently reduce the amount of hair that grows in the beard area for personal or religious reasons.17
Pseudofolliculitis barbae also has been linked to professional disparities. One study found that members of the US Air Force who had medical shaving waivers experienced longer times to promotion than those with no waiver.18 Delays in promotion may be linked to perceptions of unprofessionalism, exclusion from high-profile duties, and concerns about career progression. While this delay was similar for individuals of all races, the majority of those in the waiver group were Black/African American. In 2021, 4 Black firefighters with PFB were unsuccessful in their bid to get a medical accommodation regarding a New York City Fire Department policy requiring them to be clean shaven where the oxygen mask seals against the skin.5 More research is needed on mask safety and efficiency relative to the length of facial hair. Accommodations or tailored masks for facial hair conditions also are necessary so individuals with PFB can meet job requirements while managing their condition.
- Alexis A, Heath CR, Halder RM. Folliculitis keloidalis nuchae and pseudofolliculitis barbae: are prevention and effective treatment within reach? Dermatol Clin. 2014;32:183-191.
- Gray J, McMichael AJ. Pseudofolliculitis barbae: understanding the condition and the role of facial grooming. Int J Cosmet Sci. 2016;38 (suppl 1):24-27.
- Tshudy MT, Cho S. Pseudofolliculitis barbae in the U.S. military, a review. Mil Med. 2021;186:E52-E57.
- Jung I, Lannan FM, Weiss A, et al. Treatment and current policies on pseudofolliculitis barbae in the US military. Cutis. 2023;112:299-302.
- Jiang YR. Reasonable accommodation and disparate impact: clean shave policy discrimination in today’s workplace. J Law Med Ethics. 2023;51:185-195.
- Taylor SC, Barbosa V, Burgess C, et al. Hair and scalp disorders in adult and pediatric patients with skin of color. Cutis. 2017;100:31-35.
- Moran E, McMichael A, De Souza B, et al. New razor technology improves appearance and quality of life in men with pseudofolliculitis barbae. Cutis. 2022;110:329-334.
- Maurer M, Rietzler M, Burghardt R, et al. The male beard hair and facial skin—challenges for shaving. Int J Cosmet Sci. 2016;38 (suppl 1):3-9.
- Ross EV. How would you treat this patient with lasers & EBDs? casebased panel. Presented at: Skin of Color Update; September 13, 2024; New York, NY.
- Ross EV, Cooke LM, Timko AL, et al. Treatment of pseudofolliculitis barbae in skin types IV, V, and VI with a long-pulsed neodymium:yttrium aluminum garnet laser. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2002;47:263-270.
- Shokeir H, Samy N, Taymour M. Pseudofolliculitis barbae treatment: efficacy of topical eflornithine, long-pulsed Nd-YAG laser versus their combination. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2021;20:3517-3525.
- Amer A, Elsayed A, Gharib K. Evaluation of efficacy and safety of chemical peeling and long-pulse Nd:YAG laser in treatment of pseudofolliculitis barbae. Dermatol Ther. 2021;34:E14859.
- Cook-Bolden FE, Barba A, Halder R, et al. Twice-daily applications of benzoyl peroxide 5%/clindamycin 1% gel versus vehicle in the treatment of pseudofolliculitis barbae. Cutis. 2004;73(6 suppl):18-24.
- Nussbaum D, Friedman A. Pseudofolliculitis barbae: a review of current treatment options. J Drugs Dermatol. 2019;18:246-250.
- Quarles FN, Brody H, Johnson BA, et al. Pseudofolliculitis barbae. Dermatol Ther. 2007;20:133-136.
- McMichael AJ, Frey C. Challenging the tools used to measure cutaneous lupus severity in patients of all skin types. JAMA Dermatol. 2025;161:9-10.
- Okonkwo E, Neal B, Harper HL. Pseudofolliculitis barbae in the military and the need for social awareness. Mil Med. 2021;186:143-144.
- Ritchie S, Park J, Banta J, et al. Shaving waivers in the United States Air Force and their impact on promotions of Black/African-American members. Mil Med. 2023;188:E242-E247.
- Alexis A, Heath CR, Halder RM. Folliculitis keloidalis nuchae and pseudofolliculitis barbae: are prevention and effective treatment within reach? Dermatol Clin. 2014;32:183-191.
- Gray J, McMichael AJ. Pseudofolliculitis barbae: understanding the condition and the role of facial grooming. Int J Cosmet Sci. 2016;38 (suppl 1):24-27.
- Tshudy MT, Cho S. Pseudofolliculitis barbae in the U.S. military, a review. Mil Med. 2021;186:E52-E57.
- Jung I, Lannan FM, Weiss A, et al. Treatment and current policies on pseudofolliculitis barbae in the US military. Cutis. 2023;112:299-302.
- Jiang YR. Reasonable accommodation and disparate impact: clean shave policy discrimination in today’s workplace. J Law Med Ethics. 2023;51:185-195.
- Taylor SC, Barbosa V, Burgess C, et al. Hair and scalp disorders in adult and pediatric patients with skin of color. Cutis. 2017;100:31-35.
- Moran E, McMichael A, De Souza B, et al. New razor technology improves appearance and quality of life in men with pseudofolliculitis barbae. Cutis. 2022;110:329-334.
- Maurer M, Rietzler M, Burghardt R, et al. The male beard hair and facial skin—challenges for shaving. Int J Cosmet Sci. 2016;38 (suppl 1):3-9.
- Ross EV. How would you treat this patient with lasers & EBDs? casebased panel. Presented at: Skin of Color Update; September 13, 2024; New York, NY.
- Ross EV, Cooke LM, Timko AL, et al. Treatment of pseudofolliculitis barbae in skin types IV, V, and VI with a long-pulsed neodymium:yttrium aluminum garnet laser. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2002;47:263-270.
- Shokeir H, Samy N, Taymour M. Pseudofolliculitis barbae treatment: efficacy of topical eflornithine, long-pulsed Nd-YAG laser versus their combination. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2021;20:3517-3525.
- Amer A, Elsayed A, Gharib K. Evaluation of efficacy and safety of chemical peeling and long-pulse Nd:YAG laser in treatment of pseudofolliculitis barbae. Dermatol Ther. 2021;34:E14859.
- Cook-Bolden FE, Barba A, Halder R, et al. Twice-daily applications of benzoyl peroxide 5%/clindamycin 1% gel versus vehicle in the treatment of pseudofolliculitis barbae. Cutis. 2004;73(6 suppl):18-24.
- Nussbaum D, Friedman A. Pseudofolliculitis barbae: a review of current treatment options. J Drugs Dermatol. 2019;18:246-250.
- Quarles FN, Brody H, Johnson BA, et al. Pseudofolliculitis barbae. Dermatol Ther. 2007;20:133-136.
- McMichael AJ, Frey C. Challenging the tools used to measure cutaneous lupus severity in patients of all skin types. JAMA Dermatol. 2025;161:9-10.
- Okonkwo E, Neal B, Harper HL. Pseudofolliculitis barbae in the military and the need for social awareness. Mil Med. 2021;186:143-144.
- Ritchie S, Park J, Banta J, et al. Shaving waivers in the United States Air Force and their impact on promotions of Black/African-American members. Mil Med. 2023;188:E242-E247.
Beyond the Razor: Managing Pseudofolliculitis Barbae in Skin of Color
Beyond the Razor: Managing Pseudofolliculitis Barbae in Skin of Color
Consider Cultural Practices and Barriers to Care When Treating Alopecia Areata
The Comparison
A. Alopecia areata in a young girl with a lighter skin tone. The fine white vellus hairs are signs of regrowth.
B. Alopecia areata in a 49-year-old man with tightly coiled hair and darker skin tone. Coiled white hairs are noted in the alopecia patches.
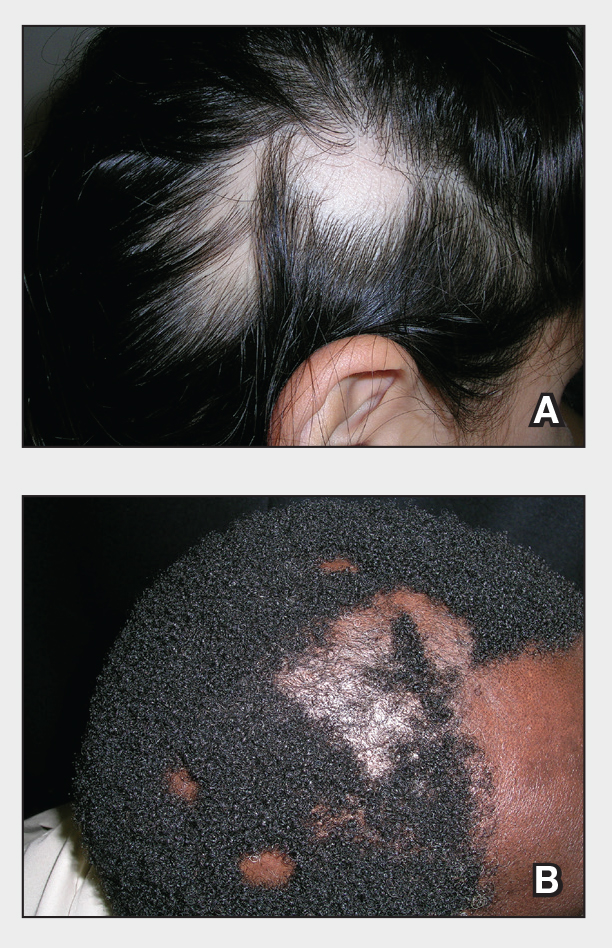
Alopecia areata (AA) is a common autoimmune condition characterized by hair loss resulting from a T cell–mediated attack on the hair follicles. It manifests as nonscarring patches of hair loss on the scalp, eyebrows, eyelashes, and beard area as well as more extensive complete loss of scalp and body hair. While AA may affect individuals of any age, most patients develop their first patch(es) of hair loss during childhood.1 The treatment landscape for AA has evolved considerably in recent years, but barriers to access to newer treatments persist.
Epidemiology
Alopecia areata is most prevalent among pediatric and adult individuals of African, Asian, or Hispanic/Latino descent.2-4 In some studies, Black individuals had higher odds and Asian individuals had lower odds of developing AA, while other studies have reported the highest standardized prevalence among Asian individuals.5 In the United States, AA affects about 1.47% of adults and as many as 0.11% of children.6-8 In Black patients, AA often manifests early with a female predominance.5
Alopecia areata frequently is associated with autoimmune comorbidities, the most common being thyroid disease.3,5 In Black patients, AA is associated with more atopic comorbidities, including asthma, atopic dermatitis, and allergic rhinitis.5
Key Clinical Features
Alopecia areata clinically manifests similarly across different skin tones; however, in patients with more tightly coiled or curly hair, the extent of scalp hair loss may be underestimated without a full examination. Culturally sensitive approaches to hair and scalp evaluation are essential, especially for Black women, whose hair care practices and scalp conditions may be overlooked or misunderstood during visits to evaluate hair loss. A thoughtful history and gentle examination of the hair and scalp that considers hair texture, cultural practices such as head coverings (eg, headwraps, turbans, hijabs), use of hair adornments (eg, clips, beads, bows), traditional braiding, and use of natural oils or herbal treatments, as well as styling methods including tight hairstyles, use of heat styling tools (eg, flat irons, curling irons), chemical application (eg, straighteners, hair color), and washing or styling frequency can improve diagnostic accuracy and help build trust in the patient-provider relationship.
Classic signs of AA visualized with dermoscopy include yellow and/or black dots on the scalp and exclamation point hairs. The appearance of fine white vellus hairs within the alopecic patches also may indicate early regrowth. On scalp trichoscopy, black dots are more prominent, and yellow dots are less prominent, in individuals with darker skin tones vs lighter skin tones.9
Worth Noting
In addition to a full examination of the scalp, documenting the extent of hair loss using validated severity scales, including the severity of alopecia tool (SALT), alopecia areata severity index (AASI), clinician-reported outcome assessment, and patient-reported outcome measures, can standardize disease severity assessment, facilitate timely insurance or medication approvals, and support objective tracking of treatment response, which may ultimately enhance access to care.10
Prompt treatment of AA is essential. Not surprisingly, patients given a diagnosis of AA may experience considerable emotional and psychological distress—regardless of the extent of the loss.11 Treatment options include mid- to high-potency topical or intralesional corticosteroids and newer and more targeted systemic options, including 3 Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitors—baricitinib, ritlecitinib, and deuruxolitinib—for more extensive disease.12 Treatment with intralesional corticosteroids may cause transient hypopigmentation, which may be more noticeable in patients with darker skin tones. Delays in treatment with JAK inhibitors can lead to a less-than-optimal response. Of the 3 JAK inhibitors that are approved by the US Food and Drug Administration for AA, only ritlecitinib is approved for children 12 years and older, leaving a therapeutic gap for younger patients that often leads to uncomfortable scalp injections, delayed or no treatment, off-label use of JAK inhibitors as well as the pairing of off-label dupilumab with oral minoxidil.12
Based on adult data, patients with severe disease and a shorter duration of hair loss (ie, <4 years) tend to respond better to JAK inhibitors than those experiencing hair loss for longer periods. Also, those with more severe AA tend to have poorer outcomes than those with less severe disease.13 If treatment proves less than optimal, wigs and hair pieces may need to be considered. It is worth noting that some insurance companies will cover the cost of wigs for patients when prescribed as cranial prostheses.
Health Disparity Highlight
Health disparities in AA can be influenced by socioeconomic status and access to care. Patients from lower-income backgrounds often face barriers to accessing dermatologic care and treatments such as JAK inhibitors, which may remain inaccessible due to high costs and insurance limitations.14 These barriers can intersect with other factors such as age, sex, and race, potentially exacerbating disparities. Women with skin of color in underserved communities may experience delayed diagnosis, limited treatment options, and greater psychosocial distress from hair loss.14 Addressing these inequities requires advocacy, education for both patients and clinicians, and improved access to treatment to ensure comprehensive care for all patients.
- Kara T, Topkarcı Z. Interactions between posttraumatic stress disorder and alopecia areata in child with trauma exposure: two case reports. Int J Trichology. 2018;10:131-134. doi:10.4103/ijt.ijt_2_18
- Sy N, Mastacouris N, Strunk A, et al. Overall and racial and ethnic subgroup prevalences of alopecia areata, alopecia totalis, and alopecia universalis. JAMA Dermatol. 2023;159:419-423.
- Lee H, Jung SJ, Patel AB, et al. Racial characteristics of alopecia areata in the United States. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;83:1064-1070.
- Feaster B, McMichael AJ. Epidemiology of alopecia areata in Black patients: a retrospective chart review. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2022;87:1121-1123.
- Lee HH, Gwillim E, Patel KR, et al. Epidemiology of alopecia areata, ophiasis, totalis, and universalis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;82:675-682.
- Mostaghimi A, Gao W, Ray M, et al. Trends in prevalence and incidence of alopecia areata, alopecia totalis, and alopecia universalis among adults and children in a US employer-sponsored insured population. JAMA Dermatol. 2023;159:411-418.
- Adhanom R, Ansbro B, Castelo-Soccio L. Epidemiology of pediatric alopecia areata. Pediatr Dermatol. 2025;42 suppl 1(suppl 1):12-23.
- Karampinis E, Toli O, Georgopoulou KE, et al. Exploring pediatric dermatology in skin of color: focus on dermoscopy. Life (Basel). 2024;14:1604.
- King BA, Senna MM, Ohyama M, et al. Defining severity in alopecia areata: current perspectives and a multidimensional framework. Dermatol Ther (Heidelb). 2022;12:825-834.
- Toussi A, Barton VR, Le ST, et al. Psychosocial and psychiatric comorbidities and health-related quality of life in alopecia areata: a systematic review. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2021;85:162-175.
- Kalil L, Welch D, Heath CR, et al. Systemic therapies for pediatric alopecia areata. Pediatr Dermatol. 2025;42 suppl 1:36-42.
- King BA, Craiglow BG. Janus kinase inhibitors for alopecia areata. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2023;89:S29-S32.
- Klein EJ, Taiwò D, Kakpovbia E, et al. Disparities in Janus kinase inhibitor access for alopecia areata: a retrospective analysis. Int J Womens Dermatol. 2024;10:E155.
- McKenzie PL, Maltenfort M, Bruckner AL, et al. Evaluation of the prevalence and incidence of pediatric alopecia areata using electronic health record data. JAMA Dermatol. 2022;158:547-551. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2022.0351
The Comparison
A. Alopecia areata in a young girl with a lighter skin tone. The fine white vellus hairs are signs of regrowth.
B. Alopecia areata in a 49-year-old man with tightly coiled hair and darker skin tone. Coiled white hairs are noted in the alopecia patches.

Alopecia areata (AA) is a common autoimmune condition characterized by hair loss resulting from a T cell–mediated attack on the hair follicles. It manifests as nonscarring patches of hair loss on the scalp, eyebrows, eyelashes, and beard area as well as more extensive complete loss of scalp and body hair. While AA may affect individuals of any age, most patients develop their first patch(es) of hair loss during childhood.1 The treatment landscape for AA has evolved considerably in recent years, but barriers to access to newer treatments persist.
Epidemiology
Alopecia areata is most prevalent among pediatric and adult individuals of African, Asian, or Hispanic/Latino descent.2-4 In some studies, Black individuals had higher odds and Asian individuals had lower odds of developing AA, while other studies have reported the highest standardized prevalence among Asian individuals.5 In the United States, AA affects about 1.47% of adults and as many as 0.11% of children.6-8 In Black patients, AA often manifests early with a female predominance.5
Alopecia areata frequently is associated with autoimmune comorbidities, the most common being thyroid disease.3,5 In Black patients, AA is associated with more atopic comorbidities, including asthma, atopic dermatitis, and allergic rhinitis.5
Key Clinical Features
Alopecia areata clinically manifests similarly across different skin tones; however, in patients with more tightly coiled or curly hair, the extent of scalp hair loss may be underestimated without a full examination. Culturally sensitive approaches to hair and scalp evaluation are essential, especially for Black women, whose hair care practices and scalp conditions may be overlooked or misunderstood during visits to evaluate hair loss. A thoughtful history and gentle examination of the hair and scalp that considers hair texture, cultural practices such as head coverings (eg, headwraps, turbans, hijabs), use of hair adornments (eg, clips, beads, bows), traditional braiding, and use of natural oils or herbal treatments, as well as styling methods including tight hairstyles, use of heat styling tools (eg, flat irons, curling irons), chemical application (eg, straighteners, hair color), and washing or styling frequency can improve diagnostic accuracy and help build trust in the patient-provider relationship.
Classic signs of AA visualized with dermoscopy include yellow and/or black dots on the scalp and exclamation point hairs. The appearance of fine white vellus hairs within the alopecic patches also may indicate early regrowth. On scalp trichoscopy, black dots are more prominent, and yellow dots are less prominent, in individuals with darker skin tones vs lighter skin tones.9
Worth Noting
In addition to a full examination of the scalp, documenting the extent of hair loss using validated severity scales, including the severity of alopecia tool (SALT), alopecia areata severity index (AASI), clinician-reported outcome assessment, and patient-reported outcome measures, can standardize disease severity assessment, facilitate timely insurance or medication approvals, and support objective tracking of treatment response, which may ultimately enhance access to care.10
Prompt treatment of AA is essential. Not surprisingly, patients given a diagnosis of AA may experience considerable emotional and psychological distress—regardless of the extent of the loss.11 Treatment options include mid- to high-potency topical or intralesional corticosteroids and newer and more targeted systemic options, including 3 Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitors—baricitinib, ritlecitinib, and deuruxolitinib—for more extensive disease.12 Treatment with intralesional corticosteroids may cause transient hypopigmentation, which may be more noticeable in patients with darker skin tones. Delays in treatment with JAK inhibitors can lead to a less-than-optimal response. Of the 3 JAK inhibitors that are approved by the US Food and Drug Administration for AA, only ritlecitinib is approved for children 12 years and older, leaving a therapeutic gap for younger patients that often leads to uncomfortable scalp injections, delayed or no treatment, off-label use of JAK inhibitors as well as the pairing of off-label dupilumab with oral minoxidil.12
Based on adult data, patients with severe disease and a shorter duration of hair loss (ie, <4 years) tend to respond better to JAK inhibitors than those experiencing hair loss for longer periods. Also, those with more severe AA tend to have poorer outcomes than those with less severe disease.13 If treatment proves less than optimal, wigs and hair pieces may need to be considered. It is worth noting that some insurance companies will cover the cost of wigs for patients when prescribed as cranial prostheses.
Health Disparity Highlight
Health disparities in AA can be influenced by socioeconomic status and access to care. Patients from lower-income backgrounds often face barriers to accessing dermatologic care and treatments such as JAK inhibitors, which may remain inaccessible due to high costs and insurance limitations.14 These barriers can intersect with other factors such as age, sex, and race, potentially exacerbating disparities. Women with skin of color in underserved communities may experience delayed diagnosis, limited treatment options, and greater psychosocial distress from hair loss.14 Addressing these inequities requires advocacy, education for both patients and clinicians, and improved access to treatment to ensure comprehensive care for all patients.
The Comparison
A. Alopecia areata in a young girl with a lighter skin tone. The fine white vellus hairs are signs of regrowth.
B. Alopecia areata in a 49-year-old man with tightly coiled hair and darker skin tone. Coiled white hairs are noted in the alopecia patches.

Alopecia areata (AA) is a common autoimmune condition characterized by hair loss resulting from a T cell–mediated attack on the hair follicles. It manifests as nonscarring patches of hair loss on the scalp, eyebrows, eyelashes, and beard area as well as more extensive complete loss of scalp and body hair. While AA may affect individuals of any age, most patients develop their first patch(es) of hair loss during childhood.1 The treatment landscape for AA has evolved considerably in recent years, but barriers to access to newer treatments persist.
Epidemiology
Alopecia areata is most prevalent among pediatric and adult individuals of African, Asian, or Hispanic/Latino descent.2-4 In some studies, Black individuals had higher odds and Asian individuals had lower odds of developing AA, while other studies have reported the highest standardized prevalence among Asian individuals.5 In the United States, AA affects about 1.47% of adults and as many as 0.11% of children.6-8 In Black patients, AA often manifests early with a female predominance.5
Alopecia areata frequently is associated with autoimmune comorbidities, the most common being thyroid disease.3,5 In Black patients, AA is associated with more atopic comorbidities, including asthma, atopic dermatitis, and allergic rhinitis.5
Key Clinical Features
Alopecia areata clinically manifests similarly across different skin tones; however, in patients with more tightly coiled or curly hair, the extent of scalp hair loss may be underestimated without a full examination. Culturally sensitive approaches to hair and scalp evaluation are essential, especially for Black women, whose hair care practices and scalp conditions may be overlooked or misunderstood during visits to evaluate hair loss. A thoughtful history and gentle examination of the hair and scalp that considers hair texture, cultural practices such as head coverings (eg, headwraps, turbans, hijabs), use of hair adornments (eg, clips, beads, bows), traditional braiding, and use of natural oils or herbal treatments, as well as styling methods including tight hairstyles, use of heat styling tools (eg, flat irons, curling irons), chemical application (eg, straighteners, hair color), and washing or styling frequency can improve diagnostic accuracy and help build trust in the patient-provider relationship.
Classic signs of AA visualized with dermoscopy include yellow and/or black dots on the scalp and exclamation point hairs. The appearance of fine white vellus hairs within the alopecic patches also may indicate early regrowth. On scalp trichoscopy, black dots are more prominent, and yellow dots are less prominent, in individuals with darker skin tones vs lighter skin tones.9
Worth Noting
In addition to a full examination of the scalp, documenting the extent of hair loss using validated severity scales, including the severity of alopecia tool (SALT), alopecia areata severity index (AASI), clinician-reported outcome assessment, and patient-reported outcome measures, can standardize disease severity assessment, facilitate timely insurance or medication approvals, and support objective tracking of treatment response, which may ultimately enhance access to care.10
Prompt treatment of AA is essential. Not surprisingly, patients given a diagnosis of AA may experience considerable emotional and psychological distress—regardless of the extent of the loss.11 Treatment options include mid- to high-potency topical or intralesional corticosteroids and newer and more targeted systemic options, including 3 Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitors—baricitinib, ritlecitinib, and deuruxolitinib—for more extensive disease.12 Treatment with intralesional corticosteroids may cause transient hypopigmentation, which may be more noticeable in patients with darker skin tones. Delays in treatment with JAK inhibitors can lead to a less-than-optimal response. Of the 3 JAK inhibitors that are approved by the US Food and Drug Administration for AA, only ritlecitinib is approved for children 12 years and older, leaving a therapeutic gap for younger patients that often leads to uncomfortable scalp injections, delayed or no treatment, off-label use of JAK inhibitors as well as the pairing of off-label dupilumab with oral minoxidil.12
Based on adult data, patients with severe disease and a shorter duration of hair loss (ie, <4 years) tend to respond better to JAK inhibitors than those experiencing hair loss for longer periods. Also, those with more severe AA tend to have poorer outcomes than those with less severe disease.13 If treatment proves less than optimal, wigs and hair pieces may need to be considered. It is worth noting that some insurance companies will cover the cost of wigs for patients when prescribed as cranial prostheses.
Health Disparity Highlight
Health disparities in AA can be influenced by socioeconomic status and access to care. Patients from lower-income backgrounds often face barriers to accessing dermatologic care and treatments such as JAK inhibitors, which may remain inaccessible due to high costs and insurance limitations.14 These barriers can intersect with other factors such as age, sex, and race, potentially exacerbating disparities. Women with skin of color in underserved communities may experience delayed diagnosis, limited treatment options, and greater psychosocial distress from hair loss.14 Addressing these inequities requires advocacy, education for both patients and clinicians, and improved access to treatment to ensure comprehensive care for all patients.
- Kara T, Topkarcı Z. Interactions between posttraumatic stress disorder and alopecia areata in child with trauma exposure: two case reports. Int J Trichology. 2018;10:131-134. doi:10.4103/ijt.ijt_2_18
- Sy N, Mastacouris N, Strunk A, et al. Overall and racial and ethnic subgroup prevalences of alopecia areata, alopecia totalis, and alopecia universalis. JAMA Dermatol. 2023;159:419-423.
- Lee H, Jung SJ, Patel AB, et al. Racial characteristics of alopecia areata in the United States. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;83:1064-1070.
- Feaster B, McMichael AJ. Epidemiology of alopecia areata in Black patients: a retrospective chart review. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2022;87:1121-1123.
- Lee HH, Gwillim E, Patel KR, et al. Epidemiology of alopecia areata, ophiasis, totalis, and universalis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;82:675-682.
- Mostaghimi A, Gao W, Ray M, et al. Trends in prevalence and incidence of alopecia areata, alopecia totalis, and alopecia universalis among adults and children in a US employer-sponsored insured population. JAMA Dermatol. 2023;159:411-418.
- Adhanom R, Ansbro B, Castelo-Soccio L. Epidemiology of pediatric alopecia areata. Pediatr Dermatol. 2025;42 suppl 1(suppl 1):12-23.
- Karampinis E, Toli O, Georgopoulou KE, et al. Exploring pediatric dermatology in skin of color: focus on dermoscopy. Life (Basel). 2024;14:1604.
- King BA, Senna MM, Ohyama M, et al. Defining severity in alopecia areata: current perspectives and a multidimensional framework. Dermatol Ther (Heidelb). 2022;12:825-834.
- Toussi A, Barton VR, Le ST, et al. Psychosocial and psychiatric comorbidities and health-related quality of life in alopecia areata: a systematic review. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2021;85:162-175.
- Kalil L, Welch D, Heath CR, et al. Systemic therapies for pediatric alopecia areata. Pediatr Dermatol. 2025;42 suppl 1:36-42.
- King BA, Craiglow BG. Janus kinase inhibitors for alopecia areata. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2023;89:S29-S32.
- Klein EJ, Taiwò D, Kakpovbia E, et al. Disparities in Janus kinase inhibitor access for alopecia areata: a retrospective analysis. Int J Womens Dermatol. 2024;10:E155.
- McKenzie PL, Maltenfort M, Bruckner AL, et al. Evaluation of the prevalence and incidence of pediatric alopecia areata using electronic health record data. JAMA Dermatol. 2022;158:547-551. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2022.0351
- Kara T, Topkarcı Z. Interactions between posttraumatic stress disorder and alopecia areata in child with trauma exposure: two case reports. Int J Trichology. 2018;10:131-134. doi:10.4103/ijt.ijt_2_18
- Sy N, Mastacouris N, Strunk A, et al. Overall and racial and ethnic subgroup prevalences of alopecia areata, alopecia totalis, and alopecia universalis. JAMA Dermatol. 2023;159:419-423.
- Lee H, Jung SJ, Patel AB, et al. Racial characteristics of alopecia areata in the United States. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;83:1064-1070.
- Feaster B, McMichael AJ. Epidemiology of alopecia areata in Black patients: a retrospective chart review. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2022;87:1121-1123.
- Lee HH, Gwillim E, Patel KR, et al. Epidemiology of alopecia areata, ophiasis, totalis, and universalis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;82:675-682.
- Mostaghimi A, Gao W, Ray M, et al. Trends in prevalence and incidence of alopecia areata, alopecia totalis, and alopecia universalis among adults and children in a US employer-sponsored insured population. JAMA Dermatol. 2023;159:411-418.
- Adhanom R, Ansbro B, Castelo-Soccio L. Epidemiology of pediatric alopecia areata. Pediatr Dermatol. 2025;42 suppl 1(suppl 1):12-23.
- Karampinis E, Toli O, Georgopoulou KE, et al. Exploring pediatric dermatology in skin of color: focus on dermoscopy. Life (Basel). 2024;14:1604.
- King BA, Senna MM, Ohyama M, et al. Defining severity in alopecia areata: current perspectives and a multidimensional framework. Dermatol Ther (Heidelb). 2022;12:825-834.
- Toussi A, Barton VR, Le ST, et al. Psychosocial and psychiatric comorbidities and health-related quality of life in alopecia areata: a systematic review. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2021;85:162-175.
- Kalil L, Welch D, Heath CR, et al. Systemic therapies for pediatric alopecia areata. Pediatr Dermatol. 2025;42 suppl 1:36-42.
- King BA, Craiglow BG. Janus kinase inhibitors for alopecia areata. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2023;89:S29-S32.
- Klein EJ, Taiwò D, Kakpovbia E, et al. Disparities in Janus kinase inhibitor access for alopecia areata: a retrospective analysis. Int J Womens Dermatol. 2024;10:E155.
- McKenzie PL, Maltenfort M, Bruckner AL, et al. Evaluation of the prevalence and incidence of pediatric alopecia areata using electronic health record data. JAMA Dermatol. 2022;158:547-551. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2022.0351
Beyond the Razor: Managing Pseudofolliculitis Barbae in Skin of Color
Beyond the Razor: Managing Pseudofolliculitis Barbae in Skin of Color
THE COMPARISON
- A. Pustules, erythematous to violaceous nodules, and hyperpigmented patches on the lower cheek and chin.
- B. Brown papules, pink keloidal papules and nodules, pustules, and hyperpigmented papules on the mandibular area and neck.
- C. Coarse hairs, pustules, and pink papules on the mandibular area and neck.
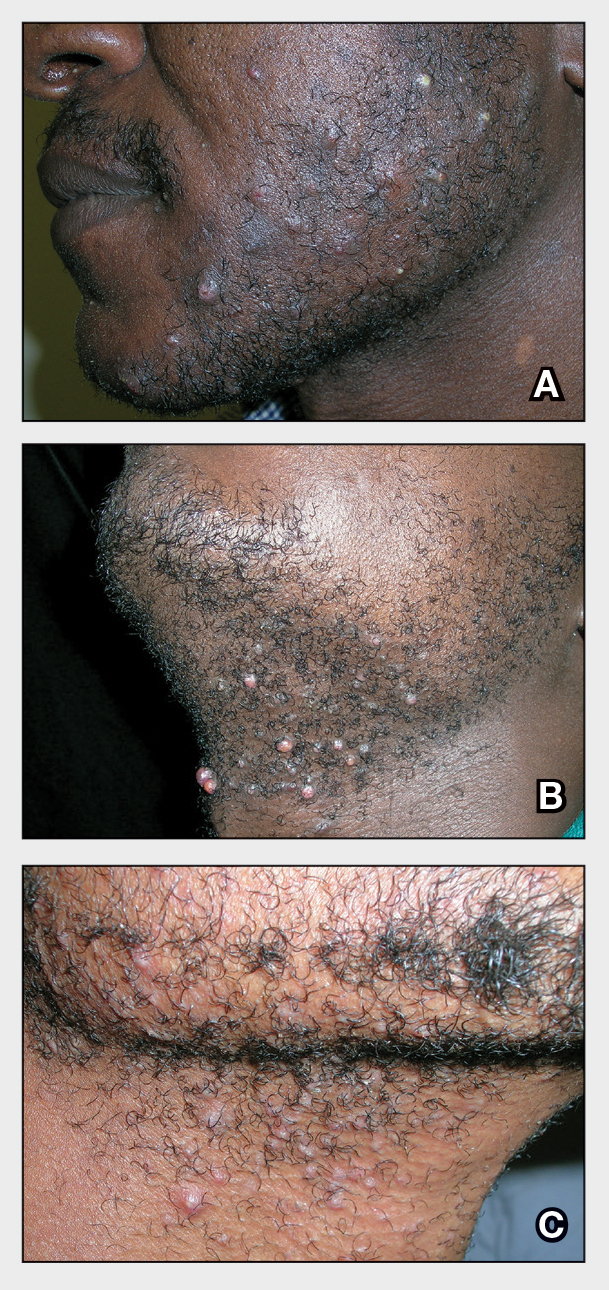
Pseudofolliculitis barbae (PFB), also known as razor bumps, is a common inflammatory condition characterized by papules and pustules that typically appear in the beard and cheek regions. It occurs when shaved hair regrows and penetrates the skin, leading to irritation and inflammation. While anyone who shaves can develop PFB, it is more prevalent and severe in individuals with naturally tightly coiled, coarse-textured hair.1,2 Pseudofolliculitis barbae is common in individuals who shave frequently due to personal choice or profession, such as members of the US military3,4 and firefighters, who are required to remain clean shaven for safety (eg, ensuring proper fit of a respirator mask).5 Early diagnosis and treatment of PFB are essential to prevent long-term complications such as scarring or hyperpigmentation, which may be more severe in those with darker skin tones.
Epidemiology
Pseudofolliculitis barbae is most common in Black men, affecting 45% to 83% of men of African ancestry.1,2 This condition also can affect individuals of various ethnicities with coarse or curly hair. The spiral shape of the hair increases the likelihood that it will regrow into the skin after shaving.6 Women with hirsutism who shave also can develop PFB.
Key Clinical Features
The papules and pustules seen in PFB may be flesh colored, erythematous, hyperpigmented, brown, or violaceous. Erythema may be less pronounced in darker vs lighter skin tones. Persistent and severe postinflammatory hyperpigmentation may occur, and hypertrophic or keloidal scars may develop in affected areas. Dermoscopy may reveal extrafollicular hair penetration as well as follicular or perifollicular pustules accompanied by hyperkeratosis.
Worth Noting
The most effective management for PFB is to discontinue shaving.1 If shaving is desired or necessary, it is recommended that patients apply lukewarm water to the affected area followed by a generous amount of shaving foam or gel to create a protective antifriction layer that allows the razor to glide more smoothly over the skin and reduces subsequent irritation.2 Using the right razor technology also may help alleviate symptoms. Research has shown that multiblade razors used in conjunction with preshave hair hydration and postshave moisturization do not worsen PFB.2 A recent study found that multiblade razor technology paired with use of a shave foam or gel actually improved skin appearance in patients with PFB.7
It is important to direct patients to shave in the direction of hair growth; however, this may not be possible for individuals with curly or coarse hair, as the hair may grow in many directions.8,9 Patients also should avoid pulling the skin taut while shaving, as doing so allows the hair to be clipped below the surface, where it can repenetrate the skin and cause further irritation. As an alternative to shaving with a razor, patients can use hair clippers to trim beard hair, which leaves behind stubble and interrupts the cycle of retracted hairs under the skin. Nd:YAG laser therapy has demonstrated efficacy in reduction of PFB papules and pustules.9-12 Greater mean improvement in inflammatory papules and reduction in hair density was noted in participants who received Nd:YAG laser plus eflornithine compared with those who received the laser or eflornithine alone.11 Patients should not pluck or dig into the skin to remove any ingrown hairs. If a tweezer is used, the patient should gently lift the tip of the ingrown hair with the tweezer to dislodge it from the skin and prevent plucking out the hair completely.
To help manage inflammation after shaving, topical treatments such as benzoyl peroxide 5%/clindamycin 1% gel can be used.3,13 A low-potency steroid such as topical hydrocortisone 2.5% applied once or twice daily for up to 2 to 3 days may be helpful.1,14 Adjunctive treatments including keratolytics (eg, topical retinoids, hydroxy acids) reduce perifollicular hyperkeratosis.14,15 Agents containing alpha hydroxy acids (eg, glycolic acid) also can decrease the curvature of the hair itself by reducing the sulfhydryl bonds.6 If secondary bacterial infections occur, oral antibiotics (eg, doxycycline) may be necessary.
Health Disparity Highlight
Individuals with darker skin tones are at higher risk for PFB and associated complications. Limited access to dermatology services may further exacerbate these challenges. Individuals with PFB may not seek medical treatment until the condition becomes severe. Clinicians also may underestimate the severity of PFB—particularly in those with darker skin tones—based on erythema alone because it may be less pronounced in darker vs lighter skin tones.16
While permanent hair reduction with laser therapy is a treatment option for PFB, it may be inaccessible to some patients because it can be expensive and is coded as a cosmetic procedure. Additionally, patients may not have access to specialists who are experienced in performing the procedure in those with darker skin tones.9 Some patients also may not want to permanently reduce the amount of hair that grows in the beard area for personal or religious reasons.17
Pseudofolliculitis barbae also has been linked to professional disparities. One study found that members of the US Air Force who had medical shaving waivers experienced longer times to promotion than those with no waiver.18 Delays in promotion may be linked to perceptions of unprofessionalism, exclusion from high-profile duties, and concerns about career progression. While this delay was similar for individuals of all races, the majority of those in the waiver group were Black/African American. In 2021, 4 Black firefighters with PFB were unsuccessful in their bid to get a medical accommodation regarding a New York City Fire Department policy requiring them to be clean shaven where the oxygen mask seals against the skin.5 More research is needed on mask safety and efficiency relative to the length of facial hair. Accommodations or tailored masks for facial hair conditions also are necessary so individuals with PFB can meet job requirements while managing their condition.
- Alexis A, Heath CR, Halder RM. Folliculitis keloidalis nuchae and pseudofolliculitis barbae: are prevention and effective treatment within reach? em>Dermatol Clin. 2014;32:183-191.
- Gray J, McMichael AJ. Pseudofolliculitis barbae: understanding the condition and the role of facial grooming. Int J Cosmet Sci. 2016;38 (suppl 1):24-27.
- Tshudy MT, Cho S. Pseudofolliculitis barbae in the U.S. military, a review. Mil Med. 2021;186:E52-E57.
- Jung I, Lannan FM, Weiss A, et al. Treatment and current policies on pseudofolliculitis barbae in the US military. Cutis. 2023;112:299-302.
- Jiang YR. Reasonable accommodation and disparate impact: clean shave policy discrimination in today’s workplace. J Law Med Ethics. 2023;51:185-195.
- Taylor SC, Barbosa V, Burgess C, et al. Hair and scalp disorders in adult and pediatric patients with skin of color. Cutis. 2017;100:31-35.
- Moran E, McMichael A, De Souza B, et al. New razor technology improves appearance and quality of life in men with pseudofolliculitis barbae. Cutis. 2022;110:329-334.
- Maurer M, Rietzler M, Burghardt R, et al. The male beard hair and facial skin—challenges for shaving. Int J Cosmet Sci. 2016;38 (suppl 1):3-9.
- Ross EV. How would you treat this patient with lasers & EBDs? casebased panel. Presented at: Skin of Color Update; September 13, 2024; New York, NY.
- Ross EV, Cooke LM, Timko AL, et al. Treatment of pseudofolliculitis barbae in skin types IV, V, and VI with a long-pulsed neodymium:yttrium aluminum garnet laser. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2002;47:263-270.
- Shokeir H, Samy N, Taymour M. Pseudofolliculitis barbae treatment: efficacy of topical eflornithine, long-pulsed Nd-YAG laser versus their combination. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2021;20:3517-3525.
- Amer A, Elsayed A, Gharib K. Evaluation of efficacy and safety of chemical peeling and long-pulse Nd:YAG laser in treatment of pseudofolliculitis barbae. Dermatol Ther. 2021;34:E14859.
- Cook-Bolden FE, Barba A, Halder R, et al. Twice-daily applications of benzoyl peroxide 5%/clindamycin 1% gel versus vehicle in the treatment of pseudofolliculitis barbae. Cutis. 2004;73(6 suppl):18-24.
- Nussbaum D, Friedman A. Pseudofolliculitis barbae: a review of current treatment options. J Drugs Dermatol. 2019;18:246-250.
- Quarles FN, Brody H, Johnson BA, et al. Pseudofolliculitis barbae. Dermatol Ther. 2007;20:133-136.
- McMichael AJ, Frey C. Challenging the tools used to measure cutaneous lupus severity in patients of all skin types. JAMA Dermatol. 2025;161:9-10.
- Okonkwo E, Neal B, Harper HL. Pseudofolliculitis barbae in the military and the need for social awareness. Mil Med. 2021;186:143-144.
- Ritchie S, Park J, Banta J, et al. Shaving waivers in the United States Air Force and their impact on promotions of Black/African-American members. Mil Med. 2023;188:E242-E247.
THE COMPARISON
- A. Pustules, erythematous to violaceous nodules, and hyperpigmented patches on the lower cheek and chin.
- B. Brown papules, pink keloidal papules and nodules, pustules, and hyperpigmented papules on the mandibular area and neck.
- C. Coarse hairs, pustules, and pink papules on the mandibular area and neck.

Pseudofolliculitis barbae (PFB), also known as razor bumps, is a common inflammatory condition characterized by papules and pustules that typically appear in the beard and cheek regions. It occurs when shaved hair regrows and penetrates the skin, leading to irritation and inflammation. While anyone who shaves can develop PFB, it is more prevalent and severe in individuals with naturally tightly coiled, coarse-textured hair.1,2 Pseudofolliculitis barbae is common in individuals who shave frequently due to personal choice or profession, such as members of the US military3,4 and firefighters, who are required to remain clean shaven for safety (eg, ensuring proper fit of a respirator mask).5 Early diagnosis and treatment of PFB are essential to prevent long-term complications such as scarring or hyperpigmentation, which may be more severe in those with darker skin tones.
Epidemiology
Pseudofolliculitis barbae is most common in Black men, affecting 45% to 83% of men of African ancestry.1,2 This condition also can affect individuals of various ethnicities with coarse or curly hair. The spiral shape of the hair increases the likelihood that it will regrow into the skin after shaving.6 Women with hirsutism who shave also can develop PFB.
Key Clinical Features
The papules and pustules seen in PFB may be flesh colored, erythematous, hyperpigmented, brown, or violaceous. Erythema may be less pronounced in darker vs lighter skin tones. Persistent and severe postinflammatory hyperpigmentation may occur, and hypertrophic or keloidal scars may develop in affected areas. Dermoscopy may reveal extrafollicular hair penetration as well as follicular or perifollicular pustules accompanied by hyperkeratosis.
Worth Noting
The most effective management for PFB is to discontinue shaving.1 If shaving is desired or necessary, it is recommended that patients apply lukewarm water to the affected area followed by a generous amount of shaving foam or gel to create a protective antifriction layer that allows the razor to glide more smoothly over the skin and reduces subsequent irritation.2 Using the right razor technology also may help alleviate symptoms. Research has shown that multiblade razors used in conjunction with preshave hair hydration and postshave moisturization do not worsen PFB.2 A recent study found that multiblade razor technology paired with use of a shave foam or gel actually improved skin appearance in patients with PFB.7
It is important to direct patients to shave in the direction of hair growth; however, this may not be possible for individuals with curly or coarse hair, as the hair may grow in many directions.8,9 Patients also should avoid pulling the skin taut while shaving, as doing so allows the hair to be clipped below the surface, where it can repenetrate the skin and cause further irritation. As an alternative to shaving with a razor, patients can use hair clippers to trim beard hair, which leaves behind stubble and interrupts the cycle of retracted hairs under the skin. Nd:YAG laser therapy has demonstrated efficacy in reduction of PFB papules and pustules.9-12 Greater mean improvement in inflammatory papules and reduction in hair density was noted in participants who received Nd:YAG laser plus eflornithine compared with those who received the laser or eflornithine alone.11 Patients should not pluck or dig into the skin to remove any ingrown hairs. If a tweezer is used, the patient should gently lift the tip of the ingrown hair with the tweezer to dislodge it from the skin and prevent plucking out the hair completely.
To help manage inflammation after shaving, topical treatments such as benzoyl peroxide 5%/clindamycin 1% gel can be used.3,13 A low-potency steroid such as topical hydrocortisone 2.5% applied once or twice daily for up to 2 to 3 days may be helpful.1,14 Adjunctive treatments including keratolytics (eg, topical retinoids, hydroxy acids) reduce perifollicular hyperkeratosis.14,15 Agents containing alpha hydroxy acids (eg, glycolic acid) also can decrease the curvature of the hair itself by reducing the sulfhydryl bonds.6 If secondary bacterial infections occur, oral antibiotics (eg, doxycycline) may be necessary.
Health Disparity Highlight
Individuals with darker skin tones are at higher risk for PFB and associated complications. Limited access to dermatology services may further exacerbate these challenges. Individuals with PFB may not seek medical treatment until the condition becomes severe. Clinicians also may underestimate the severity of PFB—particularly in those with darker skin tones—based on erythema alone because it may be less pronounced in darker vs lighter skin tones.16
While permanent hair reduction with laser therapy is a treatment option for PFB, it may be inaccessible to some patients because it can be expensive and is coded as a cosmetic procedure. Additionally, patients may not have access to specialists who are experienced in performing the procedure in those with darker skin tones.9 Some patients also may not want to permanently reduce the amount of hair that grows in the beard area for personal or religious reasons.17
Pseudofolliculitis barbae also has been linked to professional disparities. One study found that members of the US Air Force who had medical shaving waivers experienced longer times to promotion than those with no waiver.18 Delays in promotion may be linked to perceptions of unprofessionalism, exclusion from high-profile duties, and concerns about career progression. While this delay was similar for individuals of all races, the majority of those in the waiver group were Black/African American. In 2021, 4 Black firefighters with PFB were unsuccessful in their bid to get a medical accommodation regarding a New York City Fire Department policy requiring them to be clean shaven where the oxygen mask seals against the skin.5 More research is needed on mask safety and efficiency relative to the length of facial hair. Accommodations or tailored masks for facial hair conditions also are necessary so individuals with PFB can meet job requirements while managing their condition.
THE COMPARISON
- A. Pustules, erythematous to violaceous nodules, and hyperpigmented patches on the lower cheek and chin.
- B. Brown papules, pink keloidal papules and nodules, pustules, and hyperpigmented papules on the mandibular area and neck.
- C. Coarse hairs, pustules, and pink papules on the mandibular area and neck.

Pseudofolliculitis barbae (PFB), also known as razor bumps, is a common inflammatory condition characterized by papules and pustules that typically appear in the beard and cheek regions. It occurs when shaved hair regrows and penetrates the skin, leading to irritation and inflammation. While anyone who shaves can develop PFB, it is more prevalent and severe in individuals with naturally tightly coiled, coarse-textured hair.1,2 Pseudofolliculitis barbae is common in individuals who shave frequently due to personal choice or profession, such as members of the US military3,4 and firefighters, who are required to remain clean shaven for safety (eg, ensuring proper fit of a respirator mask).5 Early diagnosis and treatment of PFB are essential to prevent long-term complications such as scarring or hyperpigmentation, which may be more severe in those with darker skin tones.
Epidemiology
Pseudofolliculitis barbae is most common in Black men, affecting 45% to 83% of men of African ancestry.1,2 This condition also can affect individuals of various ethnicities with coarse or curly hair. The spiral shape of the hair increases the likelihood that it will regrow into the skin after shaving.6 Women with hirsutism who shave also can develop PFB.
Key Clinical Features
The papules and pustules seen in PFB may be flesh colored, erythematous, hyperpigmented, brown, or violaceous. Erythema may be less pronounced in darker vs lighter skin tones. Persistent and severe postinflammatory hyperpigmentation may occur, and hypertrophic or keloidal scars may develop in affected areas. Dermoscopy may reveal extrafollicular hair penetration as well as follicular or perifollicular pustules accompanied by hyperkeratosis.
Worth Noting
The most effective management for PFB is to discontinue shaving.1 If shaving is desired or necessary, it is recommended that patients apply lukewarm water to the affected area followed by a generous amount of shaving foam or gel to create a protective antifriction layer that allows the razor to glide more smoothly over the skin and reduces subsequent irritation.2 Using the right razor technology also may help alleviate symptoms. Research has shown that multiblade razors used in conjunction with preshave hair hydration and postshave moisturization do not worsen PFB.2 A recent study found that multiblade razor technology paired with use of a shave foam or gel actually improved skin appearance in patients with PFB.7
It is important to direct patients to shave in the direction of hair growth; however, this may not be possible for individuals with curly or coarse hair, as the hair may grow in many directions.8,9 Patients also should avoid pulling the skin taut while shaving, as doing so allows the hair to be clipped below the surface, where it can repenetrate the skin and cause further irritation. As an alternative to shaving with a razor, patients can use hair clippers to trim beard hair, which leaves behind stubble and interrupts the cycle of retracted hairs under the skin. Nd:YAG laser therapy has demonstrated efficacy in reduction of PFB papules and pustules.9-12 Greater mean improvement in inflammatory papules and reduction in hair density was noted in participants who received Nd:YAG laser plus eflornithine compared with those who received the laser or eflornithine alone.11 Patients should not pluck or dig into the skin to remove any ingrown hairs. If a tweezer is used, the patient should gently lift the tip of the ingrown hair with the tweezer to dislodge it from the skin and prevent plucking out the hair completely.
To help manage inflammation after shaving, topical treatments such as benzoyl peroxide 5%/clindamycin 1% gel can be used.3,13 A low-potency steroid such as topical hydrocortisone 2.5% applied once or twice daily for up to 2 to 3 days may be helpful.1,14 Adjunctive treatments including keratolytics (eg, topical retinoids, hydroxy acids) reduce perifollicular hyperkeratosis.14,15 Agents containing alpha hydroxy acids (eg, glycolic acid) also can decrease the curvature of the hair itself by reducing the sulfhydryl bonds.6 If secondary bacterial infections occur, oral antibiotics (eg, doxycycline) may be necessary.
Health Disparity Highlight
Individuals with darker skin tones are at higher risk for PFB and associated complications. Limited access to dermatology services may further exacerbate these challenges. Individuals with PFB may not seek medical treatment until the condition becomes severe. Clinicians also may underestimate the severity of PFB—particularly in those with darker skin tones—based on erythema alone because it may be less pronounced in darker vs lighter skin tones.16
While permanent hair reduction with laser therapy is a treatment option for PFB, it may be inaccessible to some patients because it can be expensive and is coded as a cosmetic procedure. Additionally, patients may not have access to specialists who are experienced in performing the procedure in those with darker skin tones.9 Some patients also may not want to permanently reduce the amount of hair that grows in the beard area for personal or religious reasons.17
Pseudofolliculitis barbae also has been linked to professional disparities. One study found that members of the US Air Force who had medical shaving waivers experienced longer times to promotion than those with no waiver.18 Delays in promotion may be linked to perceptions of unprofessionalism, exclusion from high-profile duties, and concerns about career progression. While this delay was similar for individuals of all races, the majority of those in the waiver group were Black/African American. In 2021, 4 Black firefighters with PFB were unsuccessful in their bid to get a medical accommodation regarding a New York City Fire Department policy requiring them to be clean shaven where the oxygen mask seals against the skin.5 More research is needed on mask safety and efficiency relative to the length of facial hair. Accommodations or tailored masks for facial hair conditions also are necessary so individuals with PFB can meet job requirements while managing their condition.
- Alexis A, Heath CR, Halder RM. Folliculitis keloidalis nuchae and pseudofolliculitis barbae: are prevention and effective treatment within reach? em>Dermatol Clin. 2014;32:183-191.
- Gray J, McMichael AJ. Pseudofolliculitis barbae: understanding the condition and the role of facial grooming. Int J Cosmet Sci. 2016;38 (suppl 1):24-27.
- Tshudy MT, Cho S. Pseudofolliculitis barbae in the U.S. military, a review. Mil Med. 2021;186:E52-E57.
- Jung I, Lannan FM, Weiss A, et al. Treatment and current policies on pseudofolliculitis barbae in the US military. Cutis. 2023;112:299-302.
- Jiang YR. Reasonable accommodation and disparate impact: clean shave policy discrimination in today’s workplace. J Law Med Ethics. 2023;51:185-195.
- Taylor SC, Barbosa V, Burgess C, et al. Hair and scalp disorders in adult and pediatric patients with skin of color. Cutis. 2017;100:31-35.
- Moran E, McMichael A, De Souza B, et al. New razor technology improves appearance and quality of life in men with pseudofolliculitis barbae. Cutis. 2022;110:329-334.
- Maurer M, Rietzler M, Burghardt R, et al. The male beard hair and facial skin—challenges for shaving. Int J Cosmet Sci. 2016;38 (suppl 1):3-9.
- Ross EV. How would you treat this patient with lasers & EBDs? casebased panel. Presented at: Skin of Color Update; September 13, 2024; New York, NY.
- Ross EV, Cooke LM, Timko AL, et al. Treatment of pseudofolliculitis barbae in skin types IV, V, and VI with a long-pulsed neodymium:yttrium aluminum garnet laser. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2002;47:263-270.
- Shokeir H, Samy N, Taymour M. Pseudofolliculitis barbae treatment: efficacy of topical eflornithine, long-pulsed Nd-YAG laser versus their combination. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2021;20:3517-3525.
- Amer A, Elsayed A, Gharib K. Evaluation of efficacy and safety of chemical peeling and long-pulse Nd:YAG laser in treatment of pseudofolliculitis barbae. Dermatol Ther. 2021;34:E14859.
- Cook-Bolden FE, Barba A, Halder R, et al. Twice-daily applications of benzoyl peroxide 5%/clindamycin 1% gel versus vehicle in the treatment of pseudofolliculitis barbae. Cutis. 2004;73(6 suppl):18-24.
- Nussbaum D, Friedman A. Pseudofolliculitis barbae: a review of current treatment options. J Drugs Dermatol. 2019;18:246-250.
- Quarles FN, Brody H, Johnson BA, et al. Pseudofolliculitis barbae. Dermatol Ther. 2007;20:133-136.
- McMichael AJ, Frey C. Challenging the tools used to measure cutaneous lupus severity in patients of all skin types. JAMA Dermatol. 2025;161:9-10.
- Okonkwo E, Neal B, Harper HL. Pseudofolliculitis barbae in the military and the need for social awareness. Mil Med. 2021;186:143-144.
- Ritchie S, Park J, Banta J, et al. Shaving waivers in the United States Air Force and their impact on promotions of Black/African-American members. Mil Med. 2023;188:E242-E247.
- Alexis A, Heath CR, Halder RM. Folliculitis keloidalis nuchae and pseudofolliculitis barbae: are prevention and effective treatment within reach? em>Dermatol Clin. 2014;32:183-191.
- Gray J, McMichael AJ. Pseudofolliculitis barbae: understanding the condition and the role of facial grooming. Int J Cosmet Sci. 2016;38 (suppl 1):24-27.
- Tshudy MT, Cho S. Pseudofolliculitis barbae in the U.S. military, a review. Mil Med. 2021;186:E52-E57.
- Jung I, Lannan FM, Weiss A, et al. Treatment and current policies on pseudofolliculitis barbae in the US military. Cutis. 2023;112:299-302.
- Jiang YR. Reasonable accommodation and disparate impact: clean shave policy discrimination in today’s workplace. J Law Med Ethics. 2023;51:185-195.
- Taylor SC, Barbosa V, Burgess C, et al. Hair and scalp disorders in adult and pediatric patients with skin of color. Cutis. 2017;100:31-35.
- Moran E, McMichael A, De Souza B, et al. New razor technology improves appearance and quality of life in men with pseudofolliculitis barbae. Cutis. 2022;110:329-334.
- Maurer M, Rietzler M, Burghardt R, et al. The male beard hair and facial skin—challenges for shaving. Int J Cosmet Sci. 2016;38 (suppl 1):3-9.
- Ross EV. How would you treat this patient with lasers & EBDs? casebased panel. Presented at: Skin of Color Update; September 13, 2024; New York, NY.
- Ross EV, Cooke LM, Timko AL, et al. Treatment of pseudofolliculitis barbae in skin types IV, V, and VI with a long-pulsed neodymium:yttrium aluminum garnet laser. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2002;47:263-270.
- Shokeir H, Samy N, Taymour M. Pseudofolliculitis barbae treatment: efficacy of topical eflornithine, long-pulsed Nd-YAG laser versus their combination. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2021;20:3517-3525.
- Amer A, Elsayed A, Gharib K. Evaluation of efficacy and safety of chemical peeling and long-pulse Nd:YAG laser in treatment of pseudofolliculitis barbae. Dermatol Ther. 2021;34:E14859.
- Cook-Bolden FE, Barba A, Halder R, et al. Twice-daily applications of benzoyl peroxide 5%/clindamycin 1% gel versus vehicle in the treatment of pseudofolliculitis barbae. Cutis. 2004;73(6 suppl):18-24.
- Nussbaum D, Friedman A. Pseudofolliculitis barbae: a review of current treatment options. J Drugs Dermatol. 2019;18:246-250.
- Quarles FN, Brody H, Johnson BA, et al. Pseudofolliculitis barbae. Dermatol Ther. 2007;20:133-136.
- McMichael AJ, Frey C. Challenging the tools used to measure cutaneous lupus severity in patients of all skin types. JAMA Dermatol. 2025;161:9-10.
- Okonkwo E, Neal B, Harper HL. Pseudofolliculitis barbae in the military and the need for social awareness. Mil Med. 2021;186:143-144.
- Ritchie S, Park J, Banta J, et al. Shaving waivers in the United States Air Force and their impact on promotions of Black/African-American members. Mil Med. 2023;188:E242-E247.
Beyond the Razor: Managing Pseudofolliculitis Barbae in Skin of Color
Beyond the Razor: Managing Pseudofolliculitis Barbae in Skin of Color
Key Features of Dermatosis Papulosa Nigra vs Seborrheic Keratosis
Key Features of Dermatosis Papulosa Nigra vs Seborrheic Keratosis
Dermatosis papulosa nigra (DPN), a subvariant of seborrheic keratosis (SK), is characterized by benign pigmented epidermal neoplasms that typically manifest on the face, neck, and trunk in individuals with darker skin tones (Figure).1,2 While DPN meets the diagnostic criteria for SK, certain characteristics can help distinguish these lesions from other SK types. Treatment of DPN in patients with skin of color requires caution, particularly regarding the use of abrasive methods as well as cryotherapy, which generally should be avoided.
EPIDEMIOLOGY
The incidence of SKs increases with age.3,4 Although it can occur in patients of all skin tones, SK is more common in lighter skin tones, while DPN predominantly is diagnosed in darker skin types.1,4 The prevalence of DPN in Black patients ranges from 10% to 30%, and Black women are twice as likely to be diagnosed with DPN as men.2 One study reported a first-degree relative with DPN in 84% (42/50) of patients.5 The number and size of DPN papules increase with age.1
KEY CLINICAL FEATURES
Dermatosis papulosa nigra and SK have distinctive morphologies: DPN typically manifests as raised, round or filiform, sessile, brown to black, 1- to 5-mm papules. 2 Seborrheic keratoses tend to be larger with a “stuck on” appearance and manifest as well-demarcated, pink to black papules or plaques that can range in size from millimeters to a few centimeters. 3,4 In DPN, the lesions usually are asymptomatic but may be tender, pruritic, dry, or scaly and may become irritated.1,2 They develop symmetrically in sun-exposed areas, and the most common sites are the malar face, temporal region, neck, and trunk.1,2,6,7 Seborrheic keratoses can appear throughout the body, including in sun-exposed areas, but have varying textures (eg, greasy, waxy, verrucous).3,4
WORTH NOTING
Dermatosis papulosa nigra and SK can resemble each other histologically: DPN demonstrates a fibrous stroma, papillomatosis, hyperkeratosis, and acanthosis at the intraepidermal layer, which are diagnostic criteria for SK.2,4,8 However, other histologic features characteristic of SK that are not seen in DPN include pseudohorn cysts, spindle tumor cells, and basaloid cell nests.8
Dermoscopy can be useful in ruling out malignant skin cancers when evaluating pigmented lesions. The most common dermoscopic features of SK are cerebriform patterns such as fissures and ridges, comedolike openings, and pigmented fingerprintlike structures.3,4 To a lesser degree, milialike cysts, sharp demarcation, and hairpin-shaped vascular structures also may be present.4 The dermoscopic findings of DPN have not been well evaluated, but one study revealed that DPN had similar dermoscopic features to SK with some predominant features.6 Ridges and fissures were seen in 59% of patients diagnosed with DPN followed by comedolike openings seen in 27% of patients. The coexistence of a cerebriform pattern with comedolike openings was infrequent, and milialike cysts were rare.6
While DPN and SK are benign, patients often seek treatment for cosmetic reasons. Factors to consider when choosing a treatment modality include location of the lesions, the patient’s skin tone, and postprocedural outcomes (eg, depigmentation, wound healing). In general, treatments for SK include cryotherapy, electrodesiccation and curettage, and topical therapeutics such as hydrogen peroxide 40%, topical vitamin D3, and nitric-zinc 30%-50% solutions. 4,8 Well-established treatment options for DPN include electrodesiccation, laser therapies, scissor excision, and cryotherapy, but topical options such as tazarotene also have been reported.1,9 Of the treatments for DPN, electrodesiccation and laser therapy routinely are used.10
The efficacy of electrodessication and potassium titanyl phosphate (KTP) laser were assessed in a randomized, investigatorblinded split-face study.11 Both modalities received high improvement ratings, with the results favoring the KTP laser. The patients (most of whom were Black) reported that KTP laser was more effective but more painful than electrodessication (P =.002).11 In another randomized study, patients received 3 treatments—electrodessication, pulsed dye laser, and curettage—for select DPN papules.10 There was no difference in the degree of clearance, cosmetic outcome, or postinflammatory hyperpigmentation between the 3 modalities, but patients found the laser to be the most painful.
It is important to exercise caution when using abrasive methods (eg, laser therapy, electrodesiccation, curettage) in patients with darker skin tones because of the increased risk for postinflammatory pigment alteration.1,2,12 Adverse effects of treatment are a top concern in the management of DPN.5,13 While cryotherapy is a preferred treatment of SK in lighter skin tones, it generally is avoided for DPN in darker skin types because melanocyte destruction can lead to cosmetically unsatisfactory and easily visible depigmentation.9
To mitigate postprocedural adverse effects, proper aftercare can promote wound healing and minimize postinflammatory pigment alteration. In one split-face study of Black patients, 2 DPN papules were removed from each side of the face using fine-curved surgical scissors.14 Next, a petrolatum-based ointment and an antibiotic ointment with polymyxin B sulfate/bacitracin zinc was applied twice daily for 21 days to opposite sides of the face. Patients did not develop infection, tolerated both treatments well, and demonstrated improved general wound appearance according to investigator- rated clinical assessment.14 Other reported postprocedural approaches include using topical agents with ingredients shown to improve hyperpigmentation (eg, niacinamide, azelaic acid) as well as photoprotection.12
HEALTH DISPARITY HIGHLIGHT
While DPN is benign, it can have adverse psychosocial effects on patients. A study in Senegal revealed that 60% (19/30) of patients with DPN experienced anxiety related to their condition, while others noted that DPN hindered their social relationships.13 In one US study of 50 Black patients with DPN, there was a moderate effect on quality of life, and 36% (18/50) of patients had the lesions removed. However, of the treated patients, 67% (12/18) reported few—if any—symptoms prior to removal.5 Although treatment of DPN is widely considered a cosmetic procedure, therapeutic management can address— and may improve—mental health in patients with skin of color.1,5,13 Despite the high prevalence of DPN in patients with darker skin tones, data on treatment frequency and insurance coverage are not widely available, thus limiting our understanding of treatment accessibility and economic burden.
- Frazier WT, Proddutur S, Swope K. Common dermatologic conditions in skin of color. Am Fam Physician. 2023;107:26-34.
- Metin SA, Lee BW, Lambert WC, et al. Dermatosis papulosa nigra: a clinically and histopathologically distinct entity. Clin Dermatol. 2017;35:491-496.
- Braun RP, Ludwig S, Marghoob AA. Differential diagnosis of seborrheic keratosis: clinical and dermoscopic features. J Drugs Dermatol. 2017;16:835-842.
- Sun MD, Halpern AC. Advances in the etiology, detection, and clinical management of seborrheic keratoses. Dermatology. 2022;238:205-217.
- Uwakwe LN, De Souza B, Subash J, et al. Dermatosis papulosa nigra: a quality of life survey study. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2020;13:17-19.
- Bhat RM, Patrao N, Monteiro R, et al. A clinical, dermoscopic, and histopathological study of dermatosis papulosa nigra (DPN)—an Indian perspective. Int J Dermatol. 2017;56:957-960.
- Karampinis E, Georgopoulou KE, Kampra E, et al. Clinical and dermoscopic patterns of basal cell carcinoma and its mimickers in skin of color: a practical summary. Medicina (Kaunas). 2024;60:1386.
- Gorai S, Ahmad S, Raza SSM, et al. Update of pathophysiology and treatment options of seborrheic keratosis. Dermatol Ther. 2022;35:E15934.
- Jain S, Caire H, Haas CJ. Management of dermatosis papulosa nigra: a systematic review. Int J Dermatol. Published online October 4, 2024.
- Garcia MS, Azari R, Eisen DB. Treatment of dermatosis papulosa nigra in 10 patients: a comparison trial of electrodesiccation, pulsed dye laser, and curettage. Dermatol Surg. 2010;36:1968-1972.
- Kundu RV, Joshi SS, Suh KY, et al. Comparison of electrodesiccation and potassium-titanyl-phosphate laser for treatment of dermatosis papulosa nigra. Dermatol Surg. 2009;35:1079-1083.
- Markiewicz E, Karaman-Jurukovska N, Mammone T, et al. Post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation in dark skin: molecular mechanism and skincare implications. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2022;15:2555-2565.
- Niang SO, Kane A, Diallo M, et al. Dermatosis papulosa nigra in Dakar, Senegal. Int J Dermatol. 2007;46(suppl 1):45-47.
- Taylor SC, Averyhart AN, Heath CR. Postprocedural wound-healing efficacy following removal of dermatosis papulosa nigra lesions in an African American population: a comparison of a skin protectant ointment and a topical antibiotic. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2011;64(suppl 3):S30-S35.
Dermatosis papulosa nigra (DPN), a subvariant of seborrheic keratosis (SK), is characterized by benign pigmented epidermal neoplasms that typically manifest on the face, neck, and trunk in individuals with darker skin tones (Figure).1,2 While DPN meets the diagnostic criteria for SK, certain characteristics can help distinguish these lesions from other SK types. Treatment of DPN in patients with skin of color requires caution, particularly regarding the use of abrasive methods as well as cryotherapy, which generally should be avoided.
EPIDEMIOLOGY
The incidence of SKs increases with age.3,4 Although it can occur in patients of all skin tones, SK is more common in lighter skin tones, while DPN predominantly is diagnosed in darker skin types.1,4 The prevalence of DPN in Black patients ranges from 10% to 30%, and Black women are twice as likely to be diagnosed with DPN as men.2 One study reported a first-degree relative with DPN in 84% (42/50) of patients.5 The number and size of DPN papules increase with age.1
KEY CLINICAL FEATURES
Dermatosis papulosa nigra and SK have distinctive morphologies: DPN typically manifests as raised, round or filiform, sessile, brown to black, 1- to 5-mm papules. 2 Seborrheic keratoses tend to be larger with a “stuck on” appearance and manifest as well-demarcated, pink to black papules or plaques that can range in size from millimeters to a few centimeters. 3,4 In DPN, the lesions usually are asymptomatic but may be tender, pruritic, dry, or scaly and may become irritated.1,2 They develop symmetrically in sun-exposed areas, and the most common sites are the malar face, temporal region, neck, and trunk.1,2,6,7 Seborrheic keratoses can appear throughout the body, including in sun-exposed areas, but have varying textures (eg, greasy, waxy, verrucous).3,4
WORTH NOTING
Dermatosis papulosa nigra and SK can resemble each other histologically: DPN demonstrates a fibrous stroma, papillomatosis, hyperkeratosis, and acanthosis at the intraepidermal layer, which are diagnostic criteria for SK.2,4,8 However, other histologic features characteristic of SK that are not seen in DPN include pseudohorn cysts, spindle tumor cells, and basaloid cell nests.8
Dermoscopy can be useful in ruling out malignant skin cancers when evaluating pigmented lesions. The most common dermoscopic features of SK are cerebriform patterns such as fissures and ridges, comedolike openings, and pigmented fingerprintlike structures.3,4 To a lesser degree, milialike cysts, sharp demarcation, and hairpin-shaped vascular structures also may be present.4 The dermoscopic findings of DPN have not been well evaluated, but one study revealed that DPN had similar dermoscopic features to SK with some predominant features.6 Ridges and fissures were seen in 59% of patients diagnosed with DPN followed by comedolike openings seen in 27% of patients. The coexistence of a cerebriform pattern with comedolike openings was infrequent, and milialike cysts were rare.6
While DPN and SK are benign, patients often seek treatment for cosmetic reasons. Factors to consider when choosing a treatment modality include location of the lesions, the patient’s skin tone, and postprocedural outcomes (eg, depigmentation, wound healing). In general, treatments for SK include cryotherapy, electrodesiccation and curettage, and topical therapeutics such as hydrogen peroxide 40%, topical vitamin D3, and nitric-zinc 30%-50% solutions. 4,8 Well-established treatment options for DPN include electrodesiccation, laser therapies, scissor excision, and cryotherapy, but topical options such as tazarotene also have been reported.1,9 Of the treatments for DPN, electrodesiccation and laser therapy routinely are used.10
The efficacy of electrodessication and potassium titanyl phosphate (KTP) laser were assessed in a randomized, investigatorblinded split-face study.11 Both modalities received high improvement ratings, with the results favoring the KTP laser. The patients (most of whom were Black) reported that KTP laser was more effective but more painful than electrodessication (P =.002).11 In another randomized study, patients received 3 treatments—electrodessication, pulsed dye laser, and curettage—for select DPN papules.10 There was no difference in the degree of clearance, cosmetic outcome, or postinflammatory hyperpigmentation between the 3 modalities, but patients found the laser to be the most painful.
It is important to exercise caution when using abrasive methods (eg, laser therapy, electrodesiccation, curettage) in patients with darker skin tones because of the increased risk for postinflammatory pigment alteration.1,2,12 Adverse effects of treatment are a top concern in the management of DPN.5,13 While cryotherapy is a preferred treatment of SK in lighter skin tones, it generally is avoided for DPN in darker skin types because melanocyte destruction can lead to cosmetically unsatisfactory and easily visible depigmentation.9
To mitigate postprocedural adverse effects, proper aftercare can promote wound healing and minimize postinflammatory pigment alteration. In one split-face study of Black patients, 2 DPN papules were removed from each side of the face using fine-curved surgical scissors.14 Next, a petrolatum-based ointment and an antibiotic ointment with polymyxin B sulfate/bacitracin zinc was applied twice daily for 21 days to opposite sides of the face. Patients did not develop infection, tolerated both treatments well, and demonstrated improved general wound appearance according to investigator- rated clinical assessment.14 Other reported postprocedural approaches include using topical agents with ingredients shown to improve hyperpigmentation (eg, niacinamide, azelaic acid) as well as photoprotection.12
HEALTH DISPARITY HIGHLIGHT
While DPN is benign, it can have adverse psychosocial effects on patients. A study in Senegal revealed that 60% (19/30) of patients with DPN experienced anxiety related to their condition, while others noted that DPN hindered their social relationships.13 In one US study of 50 Black patients with DPN, there was a moderate effect on quality of life, and 36% (18/50) of patients had the lesions removed. However, of the treated patients, 67% (12/18) reported few—if any—symptoms prior to removal.5 Although treatment of DPN is widely considered a cosmetic procedure, therapeutic management can address— and may improve—mental health in patients with skin of color.1,5,13 Despite the high prevalence of DPN in patients with darker skin tones, data on treatment frequency and insurance coverage are not widely available, thus limiting our understanding of treatment accessibility and economic burden.
Dermatosis papulosa nigra (DPN), a subvariant of seborrheic keratosis (SK), is characterized by benign pigmented epidermal neoplasms that typically manifest on the face, neck, and trunk in individuals with darker skin tones (Figure).1,2 While DPN meets the diagnostic criteria for SK, certain characteristics can help distinguish these lesions from other SK types. Treatment of DPN in patients with skin of color requires caution, particularly regarding the use of abrasive methods as well as cryotherapy, which generally should be avoided.
EPIDEMIOLOGY
The incidence of SKs increases with age.3,4 Although it can occur in patients of all skin tones, SK is more common in lighter skin tones, while DPN predominantly is diagnosed in darker skin types.1,4 The prevalence of DPN in Black patients ranges from 10% to 30%, and Black women are twice as likely to be diagnosed with DPN as men.2 One study reported a first-degree relative with DPN in 84% (42/50) of patients.5 The number and size of DPN papules increase with age.1
KEY CLINICAL FEATURES
Dermatosis papulosa nigra and SK have distinctive morphologies: DPN typically manifests as raised, round or filiform, sessile, brown to black, 1- to 5-mm papules. 2 Seborrheic keratoses tend to be larger with a “stuck on” appearance and manifest as well-demarcated, pink to black papules or plaques that can range in size from millimeters to a few centimeters. 3,4 In DPN, the lesions usually are asymptomatic but may be tender, pruritic, dry, or scaly and may become irritated.1,2 They develop symmetrically in sun-exposed areas, and the most common sites are the malar face, temporal region, neck, and trunk.1,2,6,7 Seborrheic keratoses can appear throughout the body, including in sun-exposed areas, but have varying textures (eg, greasy, waxy, verrucous).3,4
WORTH NOTING
Dermatosis papulosa nigra and SK can resemble each other histologically: DPN demonstrates a fibrous stroma, papillomatosis, hyperkeratosis, and acanthosis at the intraepidermal layer, which are diagnostic criteria for SK.2,4,8 However, other histologic features characteristic of SK that are not seen in DPN include pseudohorn cysts, spindle tumor cells, and basaloid cell nests.8
Dermoscopy can be useful in ruling out malignant skin cancers when evaluating pigmented lesions. The most common dermoscopic features of SK are cerebriform patterns such as fissures and ridges, comedolike openings, and pigmented fingerprintlike structures.3,4 To a lesser degree, milialike cysts, sharp demarcation, and hairpin-shaped vascular structures also may be present.4 The dermoscopic findings of DPN have not been well evaluated, but one study revealed that DPN had similar dermoscopic features to SK with some predominant features.6 Ridges and fissures were seen in 59% of patients diagnosed with DPN followed by comedolike openings seen in 27% of patients. The coexistence of a cerebriform pattern with comedolike openings was infrequent, and milialike cysts were rare.6
While DPN and SK are benign, patients often seek treatment for cosmetic reasons. Factors to consider when choosing a treatment modality include location of the lesions, the patient’s skin tone, and postprocedural outcomes (eg, depigmentation, wound healing). In general, treatments for SK include cryotherapy, electrodesiccation and curettage, and topical therapeutics such as hydrogen peroxide 40%, topical vitamin D3, and nitric-zinc 30%-50% solutions. 4,8 Well-established treatment options for DPN include electrodesiccation, laser therapies, scissor excision, and cryotherapy, but topical options such as tazarotene also have been reported.1,9 Of the treatments for DPN, electrodesiccation and laser therapy routinely are used.10
The efficacy of electrodessication and potassium titanyl phosphate (KTP) laser were assessed in a randomized, investigatorblinded split-face study.11 Both modalities received high improvement ratings, with the results favoring the KTP laser. The patients (most of whom were Black) reported that KTP laser was more effective but more painful than electrodessication (P =.002).11 In another randomized study, patients received 3 treatments—electrodessication, pulsed dye laser, and curettage—for select DPN papules.10 There was no difference in the degree of clearance, cosmetic outcome, or postinflammatory hyperpigmentation between the 3 modalities, but patients found the laser to be the most painful.
It is important to exercise caution when using abrasive methods (eg, laser therapy, electrodesiccation, curettage) in patients with darker skin tones because of the increased risk for postinflammatory pigment alteration.1,2,12 Adverse effects of treatment are a top concern in the management of DPN.5,13 While cryotherapy is a preferred treatment of SK in lighter skin tones, it generally is avoided for DPN in darker skin types because melanocyte destruction can lead to cosmetically unsatisfactory and easily visible depigmentation.9
To mitigate postprocedural adverse effects, proper aftercare can promote wound healing and minimize postinflammatory pigment alteration. In one split-face study of Black patients, 2 DPN papules were removed from each side of the face using fine-curved surgical scissors.14 Next, a petrolatum-based ointment and an antibiotic ointment with polymyxin B sulfate/bacitracin zinc was applied twice daily for 21 days to opposite sides of the face. Patients did not develop infection, tolerated both treatments well, and demonstrated improved general wound appearance according to investigator- rated clinical assessment.14 Other reported postprocedural approaches include using topical agents with ingredients shown to improve hyperpigmentation (eg, niacinamide, azelaic acid) as well as photoprotection.12
HEALTH DISPARITY HIGHLIGHT
While DPN is benign, it can have adverse psychosocial effects on patients. A study in Senegal revealed that 60% (19/30) of patients with DPN experienced anxiety related to their condition, while others noted that DPN hindered their social relationships.13 In one US study of 50 Black patients with DPN, there was a moderate effect on quality of life, and 36% (18/50) of patients had the lesions removed. However, of the treated patients, 67% (12/18) reported few—if any—symptoms prior to removal.5 Although treatment of DPN is widely considered a cosmetic procedure, therapeutic management can address— and may improve—mental health in patients with skin of color.1,5,13 Despite the high prevalence of DPN in patients with darker skin tones, data on treatment frequency and insurance coverage are not widely available, thus limiting our understanding of treatment accessibility and economic burden.
- Frazier WT, Proddutur S, Swope K. Common dermatologic conditions in skin of color. Am Fam Physician. 2023;107:26-34.
- Metin SA, Lee BW, Lambert WC, et al. Dermatosis papulosa nigra: a clinically and histopathologically distinct entity. Clin Dermatol. 2017;35:491-496.
- Braun RP, Ludwig S, Marghoob AA. Differential diagnosis of seborrheic keratosis: clinical and dermoscopic features. J Drugs Dermatol. 2017;16:835-842.
- Sun MD, Halpern AC. Advances in the etiology, detection, and clinical management of seborrheic keratoses. Dermatology. 2022;238:205-217.
- Uwakwe LN, De Souza B, Subash J, et al. Dermatosis papulosa nigra: a quality of life survey study. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2020;13:17-19.
- Bhat RM, Patrao N, Monteiro R, et al. A clinical, dermoscopic, and histopathological study of dermatosis papulosa nigra (DPN)—an Indian perspective. Int J Dermatol. 2017;56:957-960.
- Karampinis E, Georgopoulou KE, Kampra E, et al. Clinical and dermoscopic patterns of basal cell carcinoma and its mimickers in skin of color: a practical summary. Medicina (Kaunas). 2024;60:1386.
- Gorai S, Ahmad S, Raza SSM, et al. Update of pathophysiology and treatment options of seborrheic keratosis. Dermatol Ther. 2022;35:E15934.
- Jain S, Caire H, Haas CJ. Management of dermatosis papulosa nigra: a systematic review. Int J Dermatol. Published online October 4, 2024.
- Garcia MS, Azari R, Eisen DB. Treatment of dermatosis papulosa nigra in 10 patients: a comparison trial of electrodesiccation, pulsed dye laser, and curettage. Dermatol Surg. 2010;36:1968-1972.
- Kundu RV, Joshi SS, Suh KY, et al. Comparison of electrodesiccation and potassium-titanyl-phosphate laser for treatment of dermatosis papulosa nigra. Dermatol Surg. 2009;35:1079-1083.
- Markiewicz E, Karaman-Jurukovska N, Mammone T, et al. Post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation in dark skin: molecular mechanism and skincare implications. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2022;15:2555-2565.
- Niang SO, Kane A, Diallo M, et al. Dermatosis papulosa nigra in Dakar, Senegal. Int J Dermatol. 2007;46(suppl 1):45-47.
- Taylor SC, Averyhart AN, Heath CR. Postprocedural wound-healing efficacy following removal of dermatosis papulosa nigra lesions in an African American population: a comparison of a skin protectant ointment and a topical antibiotic. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2011;64(suppl 3):S30-S35.
- Frazier WT, Proddutur S, Swope K. Common dermatologic conditions in skin of color. Am Fam Physician. 2023;107:26-34.
- Metin SA, Lee BW, Lambert WC, et al. Dermatosis papulosa nigra: a clinically and histopathologically distinct entity. Clin Dermatol. 2017;35:491-496.
- Braun RP, Ludwig S, Marghoob AA. Differential diagnosis of seborrheic keratosis: clinical and dermoscopic features. J Drugs Dermatol. 2017;16:835-842.
- Sun MD, Halpern AC. Advances in the etiology, detection, and clinical management of seborrheic keratoses. Dermatology. 2022;238:205-217.
- Uwakwe LN, De Souza B, Subash J, et al. Dermatosis papulosa nigra: a quality of life survey study. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2020;13:17-19.
- Bhat RM, Patrao N, Monteiro R, et al. A clinical, dermoscopic, and histopathological study of dermatosis papulosa nigra (DPN)—an Indian perspective. Int J Dermatol. 2017;56:957-960.
- Karampinis E, Georgopoulou KE, Kampra E, et al. Clinical and dermoscopic patterns of basal cell carcinoma and its mimickers in skin of color: a practical summary. Medicina (Kaunas). 2024;60:1386.
- Gorai S, Ahmad S, Raza SSM, et al. Update of pathophysiology and treatment options of seborrheic keratosis. Dermatol Ther. 2022;35:E15934.
- Jain S, Caire H, Haas CJ. Management of dermatosis papulosa nigra: a systematic review. Int J Dermatol. Published online October 4, 2024.
- Garcia MS, Azari R, Eisen DB. Treatment of dermatosis papulosa nigra in 10 patients: a comparison trial of electrodesiccation, pulsed dye laser, and curettage. Dermatol Surg. 2010;36:1968-1972.
- Kundu RV, Joshi SS, Suh KY, et al. Comparison of electrodesiccation and potassium-titanyl-phosphate laser for treatment of dermatosis papulosa nigra. Dermatol Surg. 2009;35:1079-1083.
- Markiewicz E, Karaman-Jurukovska N, Mammone T, et al. Post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation in dark skin: molecular mechanism and skincare implications. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2022;15:2555-2565.
- Niang SO, Kane A, Diallo M, et al. Dermatosis papulosa nigra in Dakar, Senegal. Int J Dermatol. 2007;46(suppl 1):45-47.
- Taylor SC, Averyhart AN, Heath CR. Postprocedural wound-healing efficacy following removal of dermatosis papulosa nigra lesions in an African American population: a comparison of a skin protectant ointment and a topical antibiotic. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2011;64(suppl 3):S30-S35.
Key Features of Dermatosis Papulosa Nigra vs Seborrheic Keratosis
Key Features of Dermatosis Papulosa Nigra vs Seborrheic Keratosis
Key Features of Dermatosis Papulosa Nigra vs Seborrheic Keratosis
Key Features of Dermatosis Papulosa Nigra vs Seborrheic Keratosis
THE COMPARISON
- A A Black woman with dermatosis papulosa nigra manifesting as a cluster of light brown flat seborrheic keratoses that covered the cheeks and lateral face and extended to the neck.
- B A Black man with dermatosis papulosa nigra manifesting as small black papules on the cheeks and eyelids involving the central face.
Dermatosis papulosa nigra (DPN), a subvariant of seborrheic keratosis (SK), is characterized by benign pigmented epidermal neoplasms that typically manifest on the face, neck, and trunk in individuals with darker skin tones.1,2 While DPN meets the diagnostic criteria for SK, certain characteristics can help distinguish these lesions from other SK types. Treatment of DPN in patients with skin of color requires caution, particularly regarding the use of abrasive methods as well as cryotherapy, which generally should be avoided.
Epidemiology
The incidence of SKs increases with age.3,4 Although it can occur in patients of all skin tones, SK is more common in lighter skin tones, while DPN predominantly is diagnosed in darker skin types.1,4 The prevalence of DPN in Black patients ranges from 10% to 30%, and Black women are twice as likely to be diagnosed with DPN as men.2 One study reported a first-degree relative with DPN in 84% (42/50) of patients.5 The number and size of DPN papules increase with age.1
Key Clinical Features
Dermatosis papulosa nigra and SK have distinctive morphologies: DPN typically manifests as raised, round or filiform, sessile, brown to black, 1- to 5-mm papules.2 Seborrheic keratoses tend to be larger with a “stuck on” appearance and manifest as well-demarcated, pink to black papules or plaques that can range in size from millimeters to a few centimeters.3,4 In DPN, the lesions usually are asymptomatic but may be tender, pruritic, dry, or scaly and may become irritated.1,2 They develop symmetrically in sun-exposed areas, and the most common sites are the malar face, temporal region, neck, and trunk.1,2,6,7 Seborrheic keratoses can appear throughout the body, including in sun-exposed areas, but have varying textures (eg, greasy, waxy, verrucous).3,4
Worth Noting
Dermatosis papulosa nigra and SK can resemble each other histologically: DPN demonstrates a fibrous stroma, papillomatosis, hyperkeratosis, and acanthosis at the intraepidermal layer, which are diagnostic criteria for SK.2,4,8 However, other histologic features characteristic of SK that are not seen in DPN include pseudohorn cysts, spindle tumor cells, and basaloid cell nests.8
Dermoscopy can be useful in ruling out malignant skin cancers when evaluating pigmented lesions. The most common dermoscopic features of SK are cerebriform patterns such as fissures and ridges, comedolike openings, and pigmented fingerprintlike structures.3,4 To a lesser degree, milialike cysts, sharp demarcation, and hairpin-shaped vascular structures also may be present.4 The dermoscopic findings of DPN have not been well evaluated, but one study revealed that DPN had similar dermoscopic features to SK with some predominant features.6 Ridges and fissures were seen in 59% of patients diagnosed with DPN followed by comedolike openings seen in 27% of patients. The coexistence of a cerebriform pattern with comedolike openings was infrequent, and milialike cysts were rare.6
While DPN and SK are benign, patients often seek treatment for cosmetic reasons. Factors to consider when choosing a treatment modality include location of the lesions, the patient’s skin tone, and postprocedural outcomes (eg, depigmentation, wound healing). In general, treatments for SK include cryotherapy, electrodesiccation and curettage, and topical therapeutics such as hydrogen peroxide 40%, topical vitamin D3, and nitric-zinc 30%-50% solutions.4,8 Well-established treatment options for DPN include electrodesiccation, laser therapies, scissor excision, and cryotherapy, but topical options such as tazarotene also have been reported.1,9 Of the treatments for DPN, electrodesiccation and laser therapy routinely are used.10
The efficacy of electrodessication and potassium titanyl phosphate (KTP) laser were assessed in a randomized, investigator-blinded split-face study.11 Both modalities received high improvement ratings, with the results favoring the KTP laser. The patients (most of whom were Black) reported that KTP laser was more effective but more painful than electrodessication (P=.002).11 In another randomized study, patients received 3 treatments—electrodessication, pulsed dye laser, and curettage—for select DPN papules.10 There was no difference in the degree of clearance, cosmetic outcome, or postinflammatory hyperpigmentation between the 3 modalities, but patients found the laser to be the most painful.
It is important to exercise caution when using abrasive methods (eg, laser therapy, electrodesiccation, curettage) in patients with darker skin tones because of the increased risk for postinflammatory pigment alteration.1,2,12 Adverse effects of treatment are a top concern in the management of DPN.5,13 While cryotherapy is a preferred treatment of SK in lighter skin tones, it generally is avoided for DPN in darker skin types because melanocyte destruction can lead to cosmetically unsatisfactory and easily visible depigmentation.9
To mitigate postprocedural adverse effects, proper aftercare can promote wound healing and minimize postinflammatory pigment alteration. In one split-face study of Black patients, 2 DPN papules were removed from each side of the face using fine-curved surgical scissors.14 Next, a petrolatum-based ointment and an antibiotic ointment with polymyxin B sulfate/bacitracin zinc was applied twice daily for 21 days to opposite sides of the face. Patients did not develop infection, tolerated both treatments well, and demonstrated improved general wound appearance according to investigator- rated clinical assessment.14 Other reported postprocedural approaches include using topical agents with ingredients shown to improve hyperpigmentation (eg, niacinamide, azelaic acid) as well as photoprotection.12
Health Disparity Highlight
While DPN is benign, it can have adverse psychosocial effects on patients. A study in Senegal revealed that 60% (19/30) of patients with DPN experienced anxiety related to their condition, while others noted that DPN hindered their social relationships.13 In one US study of 50 Black patients with DPN, there was a moderate effect on quality of life, and 36% (18/50) of patients had the lesions removed. However, of the treated patients, 67% (12/18) reported few—if any—symptoms prior to removal.5 Although treatment of DPN is widely considered a cosmetic procedure, therapeutic management can address—and may improve—mental health in patients with skin of color.1,5,13 Despite the high prevalence of DPN in patients with darker skin tones, data on treatment frequency and insurance coverage are not widely available, thus limiting our understanding of treatment accessibility and economic burden.
- Frazier WT, Proddutur S, Swope K. Common dermatologic conditions in skin of color. Am Fam Physician.2023;107:26-34.
- Metin SA, Lee BW, Lambert WC, et al. Dermatosis papulosa nigra: a clinically and histopathologically distinct entity. Clin Dermatol. 2017;35:491-496.
- Braun RP, Ludwig S, Marghoob AA. Differential diagnosis of seborrheic keratosis: clinical and dermoscopic features. J Drugs Dermatol. 2017; 16: 835-842.
- Sun MD, Halpern AC. Advances in the etiology, detection, and clinical management of seborrheic keratoses. Dermatology. 2022;238:205-217.
- Uwakwe LN, De Souza B, Subash J, et al. Dermatosis papulosa nigra: a quality of life survey study. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2020;13:17-19.
- Bhat RM, Patrao N, Monteiro R, et al. A clinical, dermoscopic, and histopathological study of dermatosis papulosa nigra (DPN)—an Indian perspective. Int J Dermatol. 2017;56:957-960.
- Karampinis E, Georgopoulou KE, Kampra E, et al. Clinical and dermoscopic patterns of basal cell carcinoma and its mimickers in skin of color: a practical summary. Medicina (Kaunas). 2024;60:1386.
- Gorai S, Ahmad S, Raza SSM, et al. Update of pathophysiology and treatment options of seborrheic keratosis. Dermatol Ther. 2022;35:E15934.
- Jain S, Caire H, Haas CJ. Management of dermatosis papulosa nigra: a systematic review. Int J Dermatol. Published online October 4, 2024.
- Garcia MS, Azari R, Eisen DB. Treatment of dermatosis papulosa nigra in 10 patients: a comparison trial of electrodesiccation, pulsed dye laser, and curettage. Dermatol Surg. 2010;36:1968-1972.
- Kundu RV, Joshi SS, Suh KY, et al. Comparison of electrodesiccation and potassium-titanyl-phosphate laser for treatment of dermatosis papulosa nigra. Dermatol Surg. 2009;35:1079-1083.
- Markiewicz E, Karaman-Jurukovska N, Mammone T, et al. Postinflammatory hyperpigmentation in dark skin: molecular mechanism and skincare implications. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2022;15: 2555-2565.
- Niang SO, Kane A, Diallo M, et al. Dermatosis papulosa nigra in Dakar, Senegal. Int J Dermatol. 2007;46(suppl 1):45-47.
- Taylor SC, Averyhart AN, Heath CR. Postprocedural wound-healing efficacy following removal of dermatosis papulosa nigra lesions in an African American population: a comparison of a skin protectant ointment and a topical antibiotic. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2011;64(suppl 3):S30-S35.

THE COMPARISON
- A A Black woman with dermatosis papulosa nigra manifesting as a cluster of light brown flat seborrheic keratoses that covered the cheeks and lateral face and extended to the neck.
- B A Black man with dermatosis papulosa nigra manifesting as small black papules on the cheeks and eyelids involving the central face.
Dermatosis papulosa nigra (DPN), a subvariant of seborrheic keratosis (SK), is characterized by benign pigmented epidermal neoplasms that typically manifest on the face, neck, and trunk in individuals with darker skin tones.1,2 While DPN meets the diagnostic criteria for SK, certain characteristics can help distinguish these lesions from other SK types. Treatment of DPN in patients with skin of color requires caution, particularly regarding the use of abrasive methods as well as cryotherapy, which generally should be avoided.
Epidemiology
The incidence of SKs increases with age.3,4 Although it can occur in patients of all skin tones, SK is more common in lighter skin tones, while DPN predominantly is diagnosed in darker skin types.1,4 The prevalence of DPN in Black patients ranges from 10% to 30%, and Black women are twice as likely to be diagnosed with DPN as men.2 One study reported a first-degree relative with DPN in 84% (42/50) of patients.5 The number and size of DPN papules increase with age.1
Key Clinical Features
Dermatosis papulosa nigra and SK have distinctive morphologies: DPN typically manifests as raised, round or filiform, sessile, brown to black, 1- to 5-mm papules.2 Seborrheic keratoses tend to be larger with a “stuck on” appearance and manifest as well-demarcated, pink to black papules or plaques that can range in size from millimeters to a few centimeters.3,4 In DPN, the lesions usually are asymptomatic but may be tender, pruritic, dry, or scaly and may become irritated.1,2 They develop symmetrically in sun-exposed areas, and the most common sites are the malar face, temporal region, neck, and trunk.1,2,6,7 Seborrheic keratoses can appear throughout the body, including in sun-exposed areas, but have varying textures (eg, greasy, waxy, verrucous).3,4
Worth Noting
Dermatosis papulosa nigra and SK can resemble each other histologically: DPN demonstrates a fibrous stroma, papillomatosis, hyperkeratosis, and acanthosis at the intraepidermal layer, which are diagnostic criteria for SK.2,4,8 However, other histologic features characteristic of SK that are not seen in DPN include pseudohorn cysts, spindle tumor cells, and basaloid cell nests.8
Dermoscopy can be useful in ruling out malignant skin cancers when evaluating pigmented lesions. The most common dermoscopic features of SK are cerebriform patterns such as fissures and ridges, comedolike openings, and pigmented fingerprintlike structures.3,4 To a lesser degree, milialike cysts, sharp demarcation, and hairpin-shaped vascular structures also may be present.4 The dermoscopic findings of DPN have not been well evaluated, but one study revealed that DPN had similar dermoscopic features to SK with some predominant features.6 Ridges and fissures were seen in 59% of patients diagnosed with DPN followed by comedolike openings seen in 27% of patients. The coexistence of a cerebriform pattern with comedolike openings was infrequent, and milialike cysts were rare.6
While DPN and SK are benign, patients often seek treatment for cosmetic reasons. Factors to consider when choosing a treatment modality include location of the lesions, the patient’s skin tone, and postprocedural outcomes (eg, depigmentation, wound healing). In general, treatments for SK include cryotherapy, electrodesiccation and curettage, and topical therapeutics such as hydrogen peroxide 40%, topical vitamin D3, and nitric-zinc 30%-50% solutions.4,8 Well-established treatment options for DPN include electrodesiccation, laser therapies, scissor excision, and cryotherapy, but topical options such as tazarotene also have been reported.1,9 Of the treatments for DPN, electrodesiccation and laser therapy routinely are used.10
The efficacy of electrodessication and potassium titanyl phosphate (KTP) laser were assessed in a randomized, investigator-blinded split-face study.11 Both modalities received high improvement ratings, with the results favoring the KTP laser. The patients (most of whom were Black) reported that KTP laser was more effective but more painful than electrodessication (P=.002).11 In another randomized study, patients received 3 treatments—electrodessication, pulsed dye laser, and curettage—for select DPN papules.10 There was no difference in the degree of clearance, cosmetic outcome, or postinflammatory hyperpigmentation between the 3 modalities, but patients found the laser to be the most painful.
It is important to exercise caution when using abrasive methods (eg, laser therapy, electrodesiccation, curettage) in patients with darker skin tones because of the increased risk for postinflammatory pigment alteration.1,2,12 Adverse effects of treatment are a top concern in the management of DPN.5,13 While cryotherapy is a preferred treatment of SK in lighter skin tones, it generally is avoided for DPN in darker skin types because melanocyte destruction can lead to cosmetically unsatisfactory and easily visible depigmentation.9
To mitigate postprocedural adverse effects, proper aftercare can promote wound healing and minimize postinflammatory pigment alteration. In one split-face study of Black patients, 2 DPN papules were removed from each side of the face using fine-curved surgical scissors.14 Next, a petrolatum-based ointment and an antibiotic ointment with polymyxin B sulfate/bacitracin zinc was applied twice daily for 21 days to opposite sides of the face. Patients did not develop infection, tolerated both treatments well, and demonstrated improved general wound appearance according to investigator- rated clinical assessment.14 Other reported postprocedural approaches include using topical agents with ingredients shown to improve hyperpigmentation (eg, niacinamide, azelaic acid) as well as photoprotection.12
Health Disparity Highlight
While DPN is benign, it can have adverse psychosocial effects on patients. A study in Senegal revealed that 60% (19/30) of patients with DPN experienced anxiety related to their condition, while others noted that DPN hindered their social relationships.13 In one US study of 50 Black patients with DPN, there was a moderate effect on quality of life, and 36% (18/50) of patients had the lesions removed. However, of the treated patients, 67% (12/18) reported few—if any—symptoms prior to removal.5 Although treatment of DPN is widely considered a cosmetic procedure, therapeutic management can address—and may improve—mental health in patients with skin of color.1,5,13 Despite the high prevalence of DPN in patients with darker skin tones, data on treatment frequency and insurance coverage are not widely available, thus limiting our understanding of treatment accessibility and economic burden.

THE COMPARISON
- A A Black woman with dermatosis papulosa nigra manifesting as a cluster of light brown flat seborrheic keratoses that covered the cheeks and lateral face and extended to the neck.
- B A Black man with dermatosis papulosa nigra manifesting as small black papules on the cheeks and eyelids involving the central face.
Dermatosis papulosa nigra (DPN), a subvariant of seborrheic keratosis (SK), is characterized by benign pigmented epidermal neoplasms that typically manifest on the face, neck, and trunk in individuals with darker skin tones.1,2 While DPN meets the diagnostic criteria for SK, certain characteristics can help distinguish these lesions from other SK types. Treatment of DPN in patients with skin of color requires caution, particularly regarding the use of abrasive methods as well as cryotherapy, which generally should be avoided.
Epidemiology
The incidence of SKs increases with age.3,4 Although it can occur in patients of all skin tones, SK is more common in lighter skin tones, while DPN predominantly is diagnosed in darker skin types.1,4 The prevalence of DPN in Black patients ranges from 10% to 30%, and Black women are twice as likely to be diagnosed with DPN as men.2 One study reported a first-degree relative with DPN in 84% (42/50) of patients.5 The number and size of DPN papules increase with age.1
Key Clinical Features
Dermatosis papulosa nigra and SK have distinctive morphologies: DPN typically manifests as raised, round or filiform, sessile, brown to black, 1- to 5-mm papules.2 Seborrheic keratoses tend to be larger with a “stuck on” appearance and manifest as well-demarcated, pink to black papules or plaques that can range in size from millimeters to a few centimeters.3,4 In DPN, the lesions usually are asymptomatic but may be tender, pruritic, dry, or scaly and may become irritated.1,2 They develop symmetrically in sun-exposed areas, and the most common sites are the malar face, temporal region, neck, and trunk.1,2,6,7 Seborrheic keratoses can appear throughout the body, including in sun-exposed areas, but have varying textures (eg, greasy, waxy, verrucous).3,4
Worth Noting
Dermatosis papulosa nigra and SK can resemble each other histologically: DPN demonstrates a fibrous stroma, papillomatosis, hyperkeratosis, and acanthosis at the intraepidermal layer, which are diagnostic criteria for SK.2,4,8 However, other histologic features characteristic of SK that are not seen in DPN include pseudohorn cysts, spindle tumor cells, and basaloid cell nests.8
Dermoscopy can be useful in ruling out malignant skin cancers when evaluating pigmented lesions. The most common dermoscopic features of SK are cerebriform patterns such as fissures and ridges, comedolike openings, and pigmented fingerprintlike structures.3,4 To a lesser degree, milialike cysts, sharp demarcation, and hairpin-shaped vascular structures also may be present.4 The dermoscopic findings of DPN have not been well evaluated, but one study revealed that DPN had similar dermoscopic features to SK with some predominant features.6 Ridges and fissures were seen in 59% of patients diagnosed with DPN followed by comedolike openings seen in 27% of patients. The coexistence of a cerebriform pattern with comedolike openings was infrequent, and milialike cysts were rare.6
While DPN and SK are benign, patients often seek treatment for cosmetic reasons. Factors to consider when choosing a treatment modality include location of the lesions, the patient’s skin tone, and postprocedural outcomes (eg, depigmentation, wound healing). In general, treatments for SK include cryotherapy, electrodesiccation and curettage, and topical therapeutics such as hydrogen peroxide 40%, topical vitamin D3, and nitric-zinc 30%-50% solutions.4,8 Well-established treatment options for DPN include electrodesiccation, laser therapies, scissor excision, and cryotherapy, but topical options such as tazarotene also have been reported.1,9 Of the treatments for DPN, electrodesiccation and laser therapy routinely are used.10
The efficacy of electrodessication and potassium titanyl phosphate (KTP) laser were assessed in a randomized, investigator-blinded split-face study.11 Both modalities received high improvement ratings, with the results favoring the KTP laser. The patients (most of whom were Black) reported that KTP laser was more effective but more painful than electrodessication (P=.002).11 In another randomized study, patients received 3 treatments—electrodessication, pulsed dye laser, and curettage—for select DPN papules.10 There was no difference in the degree of clearance, cosmetic outcome, or postinflammatory hyperpigmentation between the 3 modalities, but patients found the laser to be the most painful.
It is important to exercise caution when using abrasive methods (eg, laser therapy, electrodesiccation, curettage) in patients with darker skin tones because of the increased risk for postinflammatory pigment alteration.1,2,12 Adverse effects of treatment are a top concern in the management of DPN.5,13 While cryotherapy is a preferred treatment of SK in lighter skin tones, it generally is avoided for DPN in darker skin types because melanocyte destruction can lead to cosmetically unsatisfactory and easily visible depigmentation.9
To mitigate postprocedural adverse effects, proper aftercare can promote wound healing and minimize postinflammatory pigment alteration. In one split-face study of Black patients, 2 DPN papules were removed from each side of the face using fine-curved surgical scissors.14 Next, a petrolatum-based ointment and an antibiotic ointment with polymyxin B sulfate/bacitracin zinc was applied twice daily for 21 days to opposite sides of the face. Patients did not develop infection, tolerated both treatments well, and demonstrated improved general wound appearance according to investigator- rated clinical assessment.14 Other reported postprocedural approaches include using topical agents with ingredients shown to improve hyperpigmentation (eg, niacinamide, azelaic acid) as well as photoprotection.12
Health Disparity Highlight
While DPN is benign, it can have adverse psychosocial effects on patients. A study in Senegal revealed that 60% (19/30) of patients with DPN experienced anxiety related to their condition, while others noted that DPN hindered their social relationships.13 In one US study of 50 Black patients with DPN, there was a moderate effect on quality of life, and 36% (18/50) of patients had the lesions removed. However, of the treated patients, 67% (12/18) reported few—if any—symptoms prior to removal.5 Although treatment of DPN is widely considered a cosmetic procedure, therapeutic management can address—and may improve—mental health in patients with skin of color.1,5,13 Despite the high prevalence of DPN in patients with darker skin tones, data on treatment frequency and insurance coverage are not widely available, thus limiting our understanding of treatment accessibility and economic burden.
- Frazier WT, Proddutur S, Swope K. Common dermatologic conditions in skin of color. Am Fam Physician.2023;107:26-34.
- Metin SA, Lee BW, Lambert WC, et al. Dermatosis papulosa nigra: a clinically and histopathologically distinct entity. Clin Dermatol. 2017;35:491-496.
- Braun RP, Ludwig S, Marghoob AA. Differential diagnosis of seborrheic keratosis: clinical and dermoscopic features. J Drugs Dermatol. 2017; 16: 835-842.
- Sun MD, Halpern AC. Advances in the etiology, detection, and clinical management of seborrheic keratoses. Dermatology. 2022;238:205-217.
- Uwakwe LN, De Souza B, Subash J, et al. Dermatosis papulosa nigra: a quality of life survey study. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2020;13:17-19.
- Bhat RM, Patrao N, Monteiro R, et al. A clinical, dermoscopic, and histopathological study of dermatosis papulosa nigra (DPN)—an Indian perspective. Int J Dermatol. 2017;56:957-960.
- Karampinis E, Georgopoulou KE, Kampra E, et al. Clinical and dermoscopic patterns of basal cell carcinoma and its mimickers in skin of color: a practical summary. Medicina (Kaunas). 2024;60:1386.
- Gorai S, Ahmad S, Raza SSM, et al. Update of pathophysiology and treatment options of seborrheic keratosis. Dermatol Ther. 2022;35:E15934.
- Jain S, Caire H, Haas CJ. Management of dermatosis papulosa nigra: a systematic review. Int J Dermatol. Published online October 4, 2024.
- Garcia MS, Azari R, Eisen DB. Treatment of dermatosis papulosa nigra in 10 patients: a comparison trial of electrodesiccation, pulsed dye laser, and curettage. Dermatol Surg. 2010;36:1968-1972.
- Kundu RV, Joshi SS, Suh KY, et al. Comparison of electrodesiccation and potassium-titanyl-phosphate laser for treatment of dermatosis papulosa nigra. Dermatol Surg. 2009;35:1079-1083.
- Markiewicz E, Karaman-Jurukovska N, Mammone T, et al. Postinflammatory hyperpigmentation in dark skin: molecular mechanism and skincare implications. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2022;15: 2555-2565.
- Niang SO, Kane A, Diallo M, et al. Dermatosis papulosa nigra in Dakar, Senegal. Int J Dermatol. 2007;46(suppl 1):45-47.
- Taylor SC, Averyhart AN, Heath CR. Postprocedural wound-healing efficacy following removal of dermatosis papulosa nigra lesions in an African American population: a comparison of a skin protectant ointment and a topical antibiotic. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2011;64(suppl 3):S30-S35.
- Frazier WT, Proddutur S, Swope K. Common dermatologic conditions in skin of color. Am Fam Physician.2023;107:26-34.
- Metin SA, Lee BW, Lambert WC, et al. Dermatosis papulosa nigra: a clinically and histopathologically distinct entity. Clin Dermatol. 2017;35:491-496.
- Braun RP, Ludwig S, Marghoob AA. Differential diagnosis of seborrheic keratosis: clinical and dermoscopic features. J Drugs Dermatol. 2017; 16: 835-842.
- Sun MD, Halpern AC. Advances in the etiology, detection, and clinical management of seborrheic keratoses. Dermatology. 2022;238:205-217.
- Uwakwe LN, De Souza B, Subash J, et al. Dermatosis papulosa nigra: a quality of life survey study. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2020;13:17-19.
- Bhat RM, Patrao N, Monteiro R, et al. A clinical, dermoscopic, and histopathological study of dermatosis papulosa nigra (DPN)—an Indian perspective. Int J Dermatol. 2017;56:957-960.
- Karampinis E, Georgopoulou KE, Kampra E, et al. Clinical and dermoscopic patterns of basal cell carcinoma and its mimickers in skin of color: a practical summary. Medicina (Kaunas). 2024;60:1386.
- Gorai S, Ahmad S, Raza SSM, et al. Update of pathophysiology and treatment options of seborrheic keratosis. Dermatol Ther. 2022;35:E15934.
- Jain S, Caire H, Haas CJ. Management of dermatosis papulosa nigra: a systematic review. Int J Dermatol. Published online October 4, 2024.
- Garcia MS, Azari R, Eisen DB. Treatment of dermatosis papulosa nigra in 10 patients: a comparison trial of electrodesiccation, pulsed dye laser, and curettage. Dermatol Surg. 2010;36:1968-1972.
- Kundu RV, Joshi SS, Suh KY, et al. Comparison of electrodesiccation and potassium-titanyl-phosphate laser for treatment of dermatosis papulosa nigra. Dermatol Surg. 2009;35:1079-1083.
- Markiewicz E, Karaman-Jurukovska N, Mammone T, et al. Postinflammatory hyperpigmentation in dark skin: molecular mechanism and skincare implications. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2022;15: 2555-2565.
- Niang SO, Kane A, Diallo M, et al. Dermatosis papulosa nigra in Dakar, Senegal. Int J Dermatol. 2007;46(suppl 1):45-47.
- Taylor SC, Averyhart AN, Heath CR. Postprocedural wound-healing efficacy following removal of dermatosis papulosa nigra lesions in an African American population: a comparison of a skin protectant ointment and a topical antibiotic. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2011;64(suppl 3):S30-S35.
Key Features of Dermatosis Papulosa Nigra vs Seborrheic Keratosis
Key Features of Dermatosis Papulosa Nigra vs Seborrheic Keratosis