User login
Relationship-Centered Care in the Physician-Patient Interaction: Improving Your Understanding of Metacognitive Interventions
Communication and relationships cannot be taken for granted, particularly in the physician-patient relationship, where life-altering diagnoses may be given. With one diagnosis, someone’s life may be changed, and both physicians and patients need to be cognizant of the importance of a strong relationship and clear communication.
In the current US health care system, both physicians and patients often are not getting their needs met, and studies that include factors of race, ethnicity, and socioeconomic status suggest that physician-patient relationship barriers contribute to racial disparities in health care.1,2 Although patient-centered care is a widely recognized and upheld model, relationship-centered care between physician and patient involves focusing on the patient and the physician-patient relationship through recognizing personhood, affect (being empathic), and reciprocal influence.3,4 Although it is not necessarily intuitive because it can appear to be yet another task for busy physicians, relationship-centered care improves health care delivery for both physicians and patients through decreased physician burnout, reduced medical errors, and better patient outcomes and satisfaction.5,6
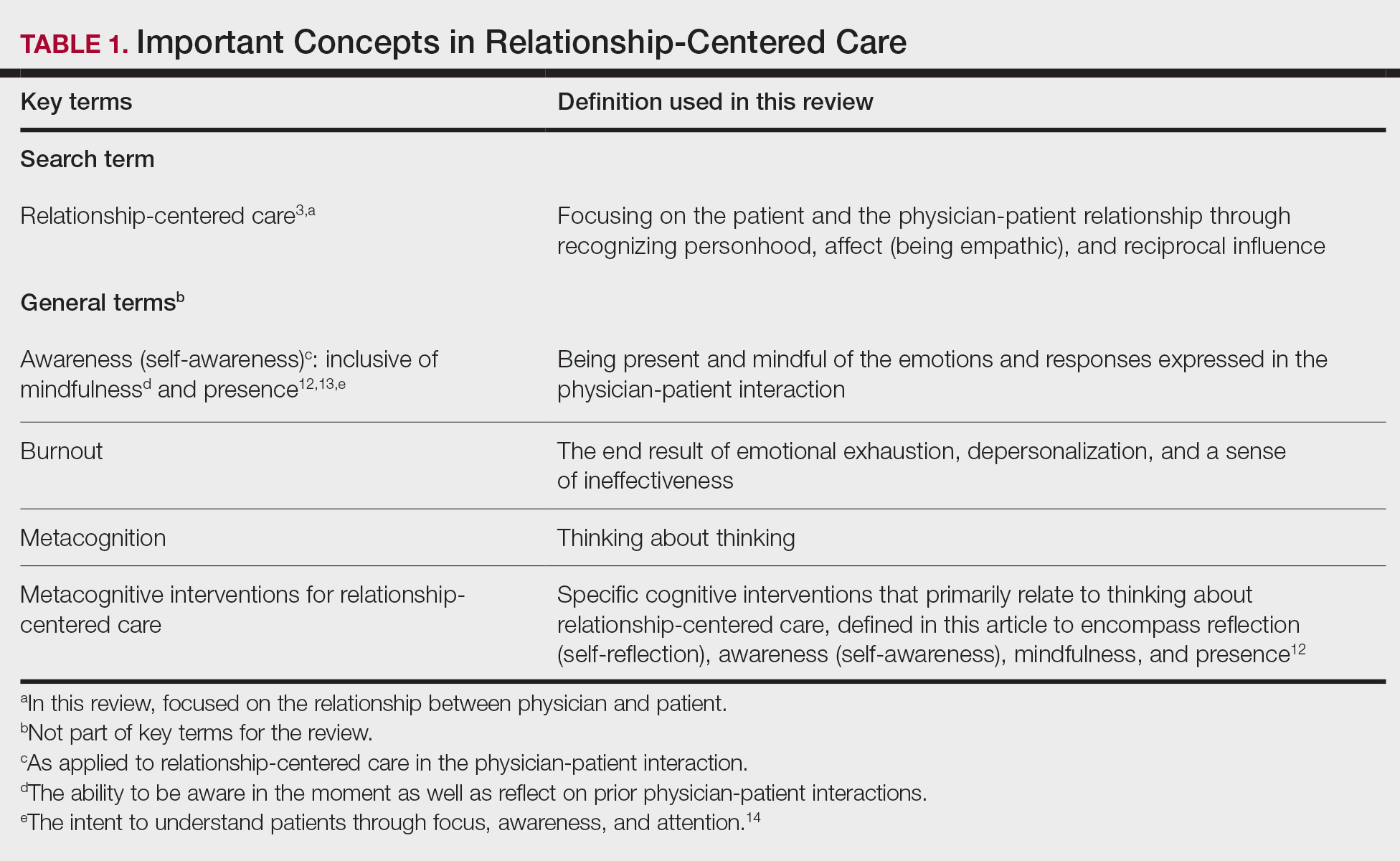
Every physician, patient, and physician-patient relationship is different; unlike the standard questions directed at a routine patient history focused on gathering data, there is no one-size-fits-all relationship-centered conversation.7-10 As with any successful interaction between 2 people, there is a certain amount of necessary self-awareness (Table 1)11 that allows for improvisation and appropriate responsiveness to what is seen, heard, and felt. Rather than attending solely to disease states, the focus of relationship-centered care is on patients, interpersonal interaction, and promoting health and well-being.15
This review summarizes the existing literature on relationship-centered care, introduces the use of metacognition (Table 1), and suggests creating simple habits to promote such care. The following databases were searched from inception through November 23, 2020, using the term relationship-centered care: MEDLINE (Ovid), EMBASE (Ovid), APA PsycInfo (Ovid), Scopus, Web of Science Core Collection, CINAHL Complete (EBSCO), Academic Search Premier (EBSCOhost), and ERIC (ProQuest). A total of 1772 records were retrieved through searches, and after deduplication of 1116 studies, 350 records were screened through a 2-part process. Articles were first screened by title and abstract for relevance to the relationship between physician and patient, with 185 studies deemed irrelevant (eg, pertaining to the relationship of veterinarian to animal). The remaining 165 studies were assessed for eligibility, with 69 further studies excluded for various reasons. The screening process resulted in 96 articles considered in this review.
Definitions/key terms, as used in this article, are listed in Table 1.
Background of Relationship-Centered Care
Given time constraints, the diagnosis and treatment of medical problems often are the focus of physicians. Although proper medical diagnosis and treatment are important, and their delivery is made possible by the physician having the appropriate knowledge, a physician-patient relationship that focuses solely on disease without acknowledging the patient creates a system that ultimately neglects both patients and physicians.15 This prevailing physician-patient relationship paradigm is suboptimal, and a proposed remedy is relationship-centered care, which focuses on relationships among the human beings in health care interactions.3 Relationship-centered care has 4 principles: (1) the personhood of each party must be recognized, (2) emotion is part of relationships, (3) relationships are reciprocal and not just one way, and (4) creating these types of relationships is morally valuable3 and beneficial to patient care.16
Assessment of the Need for Relationship-Centered Care
Relationship-centered care has been studied in physician-patient interactions in various health care settings.17-23 For at least 2 decades, relationship-centered care has been set forth as a model,4,24,25 but there are challenges. Physicians tend to overrate or underrate their communication skills in patient interactions.26,27 A given physician’s preferences often still seem to supersede those of the patient.3,28,29 The impetus to develop relationship-centered care skills generally needs to be internally driven,4,30 as, ultimately, physicians and patients have varying needs.4,31 However, providing physicians with a potential structure is helpful.32
A Solution: Metacognition in the Physician-Patient Interaction
Metacognition is important to integrating basic science knowledge into medical learning and practice,33,34 and it is no less important in translating interpersonal knowledge to the physician-patient interaction. Decreased metacognitive effort35 may underpin the decline in empathy seen with increasing medical training.36,37 Understanding how metacognitive practices foster relationship-centered care is important for teaching, developing, and maintaining that care.
Metacognition is already embedded in the fabric of the physician-patient interaction.33,34 The complex interplay of the physician-patient interview, patient examination, and integration of physical as well as ancillary data requires higher-order thinking and the ability to parse out that thinking successfully. As a concrete example, coming to a diagnosis requires thinking about what has been presented during the physician-patient interaction and considering what supports and suggests the disease while a list of potential differential diagnosis alternatives is being generated. Physicians are trained to apply this clinical reasoning approach to their patient care.
Conversely, although communication skills are a key component of doctoring,38 both between physician and patient as well as among other colleagues and staff, many physicians have never received formal training in communication skills,26,32,39 though it is now an integral part of medical school curricula.40 When such training is mandatory, less than 1% of physicians continue to believe that there was no benefit, even from a single 8-hour communications skills training session.41 Communication cannot be taught comprehensively in 8 hours; thus, the benefit of such training may be the end result of metacognition and increased self-awareness (Table 1).42,43
Building Relationship-Centered Care Through Metacognitive Attention
Metacognition as manifested by such self-awareness can build relationship-centered care.4 Self-awareness can be taught through mentorship or role models.44 Journaling,40 meditation, and appreciation of beauty and the arts45 can contribute, as well as more formal training programs,32,38,42 as offered by the Academy of Communication in Healthcare. Creating opportunities for patient empowerment also supports relationship-centered care, as does applying knowledge of implicit bias.46
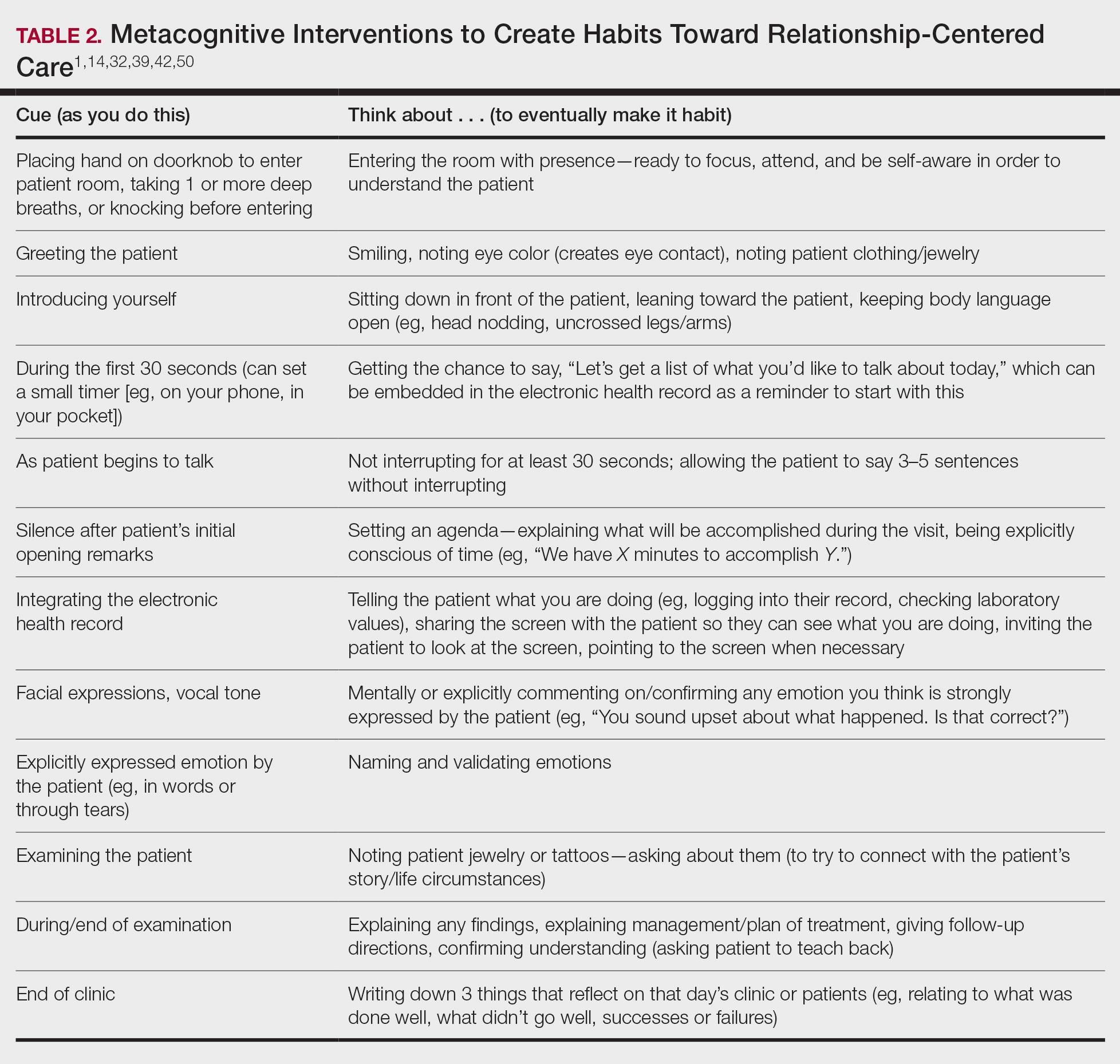
Even without formal training, relationship-centered care can be built through attention to cues9—visual (eg, sitting down, other body language),47,48 auditory (eg, knocking, language, tone, conversational flow),48,49 and emotional (eg, clinical empathy, emotional intelligence)(Table 2). Such attention is familiar to everyone, not just physicians or patients, through interactions outside of health care; inattention may be due to the hidden curriculum or culture of medicine40 as well as real-time changes, such as the introduction of the electronic health record.51 Inattention to these cues also may be a result of context-specific knowledge, in which a physician’s real-life communication skills are not applied to the unique context of patient care.
Although the theoretical foundation of relationship-centered care is relatively complex,9 a simple formula that has improved patient experience is “The Big 3,” which entails (1) simply knocking before entering the examination room, (2) sitting, and (3) asking, “What is your main concern?”30 Another relatively simple technique would be to involve the patient with the electronic health record by sharing the screen with them.52 Learning about narrative medicine and developing skills to appreciate each patient’s story is another method to increase relationship-centered care,40,53 as is emotional intelligence.54 These interventions are simple to implement, and good relationship-centered care will save time, help manage patient visits more effectively, and aid in avoiding the urgent new concern that the patient adds at the end of the visit.55 The positive effect of these different interventions highlights that small changes (Table 2) can shift the prevailing culture of medicine to become more relationship centered.56
Metacognitive Attention Can Generate Habit
Taking metacognition a step further, these small interventions can become habit11,14,39 through self-awareness, deliberate practice, and feedback.43 Habit is generated by linking a given intervention to another defined cue. For example, placing a hand on a doorknob to enter an examination room can be the cue to generate a habit of entering with presence.14 Alternatively, before entering an examination room, taking 3 deep breaths can be the cue to trigger presence.14 Habits can be created in just 3 weeks,57 and other proposed cues to generate habits toward relationship-centered care are listed in Table 2. By creating habit through metacognitive attention, relationship-centered care will become something that happens subconsciously without further burdening physicians with another task. Asking patients for permission to record video of an interaction also can create opportunities for self-awareness and self-evaluation through rewatching the video.58
Final Thoughts
Physicians already have the tools to create relationship-centered care in physician-patient interactions. A critical mental shift is to develop habits and apply thinking patterns toward understanding and responding appropriately to patients of all ethnicities and their emotions in the physician-patient interaction. This shift is aided by metacognitive awareness (Table 1) and the development of useful habits (Table 2).
- Sanders L, Fortin AH VI, Schiff GD. Connecting with patients—the missing links. JAMA. 2020;323:33-34.
- Peck BM, Denney M. Disparities in the conduct of the medical encounter: the effects of physician and patient race and gender. SAGE Open. 2012;2:1-14.
- Beach MC, Inui T. Relationship-centered care. a constructive reframing. J Gen Intern Med. 2006;21(suppl 1):S3-S8.
- Tresolini CP, Pew-Fetzer Task Force. Health Professions Education and Relationship-Centered Care. Pew Health Professions Commission; 1994.
- Hojat M. Empathy in Health Professions Education and Patient Care. Springer; 2016.
- Wilkinson H, Whittington R, Perry L, et al. Examining the relationship between burnout and empathy in healthcare professionals: a systematic review. Burn Res. 2017;6:18-29.
- Frankel RM, Quill T. Integrating biopsychosocial and relationship-centered care into mainstream medical practice: a challenge that continues to produce positive results. Fam Syst Health. 2005;23:413-421.
- Frankel RM. Relationship-centered care and the patient-physician relationship. J Gen Intern Med. 2004;19:1163-1165.
- Ventres WB, Frankel RM. Shared presence in physician-patient communication: a graphic representation. Fam Syst Health. 2015;33:270-279.
- Cooper LA, Beach MC, Johnson RL, et al. Delving below the surface: understanding how race and ethnicity influence relationships in health care. J Gen Intern Med. 2006;21(suppl 1):S21-S27.
- Epstein RM. Mindful practice. JAMA. 1999;282:833-839.
- Dobie S. Viewpoint: reflections on a well-traveled path: self-awareness, mindful practice, and relationship-centered care as foundations for medical education. Acad Med. 2007;82:422-427.
- Rabow MW. Meaning and relationship-centered care: recommendations for clinicians attending to the spiritual distress of patients at the end of life. Ethics Med Public Health. 2019;9:57-62.
- Zulman DM, Haverfield MC, Shaw JG, et al. Practices to foster physician presence and connection with patients in the clinical encounter. JAMA. 2020;323:70-81.
- Rakel DP, Guerrera MP, Bayles BP, et al. CAM education: promoting a salutogenic focus in health care. J Altern Complement Med. 2008;14:87-93.
- Olaisen RH, Schluchter MD, Flocke SA, et al. Assessing the longitudinal impact of physician-patient relationship on functional health. Ann Fam Med. 2020;18:422-429.
- Berg GM, Ekengren F, Lee FA, et al. Patient satisfaction with surgeons in a trauma population: testing a structural equation model using perceptions of interpersonal and technical care. J Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2012;72:1316-1322.
- Nassar A, Weimer-Elder B, Kline M, et al. Developing an inpatient relationship-centered communication curriculum for surgical teams: pilot study. J Am Coll Surg. 2019;229(4 suppl 2):E48.
- Caldicott CV, Dunn KA, Frankel RM. Can patients tell when they are unwanted? “turfing” in residency training. Patient Educ Couns. 2005;56:104-111.
- Tucker Edmonds B, Mogul M, Shea JA. Understanding low-income African American women’s expectations, preferences, and priorities in prenatal care. Fam Community Health. 2015;38:149-157.
- Sundstrom B, Szabo C, Dempsey A. “My body. my choice:” a qualitative study of the influence of trust and locus of control on postpartum contraceptive choice. J Health Commun. 2018;23:162-169.
- Block S, Billings JA. Nurturing humanism through teaching palliative care. Acad Med. 1998;73:763-765.
- Hebert RS, Schulz R, Copeland VC, et al. Preparing family caregivers for death and bereavement. insights from caregivers of terminally ill patients. J Pain Symptom Manage. 2009;37:3-12.
- Nundy S, Oswald J. Relationship-centered care: a new paradigm for population health management. Healthc (Amst). 2014;2:216-219.
- Sprague S. Relationship centered care. J S C Med Assoc. 2009;105:135-136.
- Roter DL, Frankel RM, Hall JA, et al. The expression of emotion through nonverbal behavior in medical visits. mechanisms and outcomes. J Gen Intern Med. 2006;21(suppl 1):S28-S34.
- Kenny DA, Veldhuijzen W, van der Weijden T, et al. Interpersonal perception in the context of doctor-patient relationships: a dyadic analysis of doctor-patient communication. Soc Sci Med. 2010;70:763-768.
- Tarzian AJ, Neal MT, O’Neil JA. Attitudes, experiences, and beliefs affecting end-of-life decision-making among homeless individuals. J Palliat Med. 2005;8:36-48.
- Roter D. The enduring and evolving nature of the patient-physician relationship. Patient Educ Couns. 2000;39:5-15.
- Sharieff GQ. MD to MD coaching: improving physician-patient experience scores: what works, what doesn’t. J Patient Exp. 2017;4:210-212.
- Duggan AP, Bradshaw YS, Swergold N, et al. When rapport building extends beyond affiliation: communication overaccommodation toward patients with disabilities. Perm J. 2011;15:23-30.
- Hirschmann K, Rosler G, Fortin AH VI. “For me, this has been transforming”: a qualitative analysis of interprofessional relationship-centered communication skills training. J Patient Exp. 2020;7:1007-1014.
- Hennrikus EF, Skolka MP, Hennrikus N. Applying metacognition through patient encounters and illness scripts to create a conceptual framework for basic science integration, storage, and retrieval. J Med Educ Curric Dev. 2018;5:2382120518777770.
- Eichbaum QG. Thinking about thinking and emotion: the metacognitive approach to the medical humanities that integrates the humanities with the basic and clinical sciences. Perm J. 2014;18:64-75.
- Stansfield RB, Schwartz A, O’Brien CL, et al. Development of a metacognitive effort construct of empathy during clinical training: a longitudinal study of the factor structure of the Jefferson Scale of Empathy. Adv Health Sci Educ Theory Pract. 2016;21:5-17.
- Hojat M, Vergare MJ, Maxwell K, et al. The devil is in the third year: a longitudinal study of erosion of empathy in medical school. Acad Med. 2009;84:1182-1191.
- Neumann M, Edelhäuser F, Tauschel D, et al. Empathy decline and its reasons: a systematic review of studies with medical students and residents. Acad Med. 2011;86:996-1009.
- Chou CL, Hirschmann K, Fortin AHT, et al. The impact of a faculty learning community on professional and personal development: the facilitator training program of the American Academy on Communication in Healthcare. Acad Med. 2014;89:1051-1056.
- Rider EA. Advanced communication strategies for relationship-centered care. Pediatr Ann. 2011;40:447-453.
- Reichman JAH. Narrative competence, mindfulness,and relationship-centered care in medical education: an innovative approach to teaching medical interviewing. Dissertation Abstracts International Section A: Humanities and Social Sciences. 2015;75(8-A(E)).
- Boissy A, Windover AK, Bokar D, et al. Communication skills training for physicians improves patient satisfaction. J Gen Intern Med. 2016;31:755-761.
- Hatem DS, Barrett SV, Hewson M, et al. Teaching the medical interview: methods and key learning issues in a faculty development course. J Gen Intern Med. 2007;22:1718-1724.
- Gilligan TD, Baile WF. ASCO patient-clinician communication guideline: fostering relationship-centered care. ASCO Connection. November 20, 2017. Accessed March 5, 2021. https://connection.asco.org/blogs/asco-patient-clinician-communication-guideline-fostering-relationship-centered-care
- Haidet P, Stein HF. The role of the student-teacher relationship in the formation of physicians. The hidden curriculum as process. J Gen Intern Med. 2006;(suppl 1):S16-S20.
- Puchalski CM, Guenther M. Restoration and re-creation: spirituality in the lives of healthcare professionals. Curr Opin Support Palliat Care. 2012;6:254-258.
- Williams SW, Hanson LC, Boyd C, et al. Communication, decision making, and cancer: what African Americans want physicians to know. J Palliative Med. 2008;11:1221-1226.
- Lindsley I, Woodhead S, Micallef C, et al. The concept of body language in the medical consultation. Psychiatr Danub. 2015;27(suppl 1):S41-S47.
- Hall JA, Harrigan JA, Rosenthal R. Nonverbal behavior in clinician-patient interaction. Appl Prev Psychol. 1995;4:21-37.
- Ness DE, Kiesling SF. Language and connectedness in the medical and psychiatric interview. Patient Educ Couns. 2007;68:139-144.
- Miller WL. The clinical hand: a curricular map for relationship-centered care. Fam Med. 2004;36:330-335.
- Wald HS, George P, Reis SP, et al. Electronic health record training in undergraduate medical education: bridging theory to practice with curricula for empowering patient- and relationship-centered care in the computerized setting. Acad Med. 2014;89:380-386.
- Silverman H, Ho YX, Kaib S, et al. A novel approach to supporting relationship-centered care through electronic health record ergonomic training in preclerkship medical education. Acad Med. 2014;89:1230-1234.
- Weiss T, Swede MJ. Transforming preprofessional health education through relationship-centered care and narrative medicine. Teach Learn Med. 2019;31:222-233.
- Blanch-Hartigan D. An effective training to increase accurate recognition of patient emotion cues. Patient Educ Couns. 2012;89:274-280.
- White J, Levinson W, Roter D. “Oh, by the way ...”: the closing moments of the medical visit. J Gen Intern Med. 1994;9:24-28.
- Suchman AL, Williamson PR, Litzelman DK, et al. Toward an informal curriculum that teaches professionalism. Transforming the social environment of a medical school. J Gen Intern Med. 2004;19:501-504.
- Lally P, van Jaarsveld CHM, Potts HWW, et al. How are habits formed: modelling habit formation in the real world. Eur J Soc Psychol. 2010;40:998-1009.
- Little P, White P, Kelly J, et al. Randomised controlled trial of a brief intervention targeting predominantly non-verbal communication in general practice consultations. Br J Gen Pract. 2015;65:E351-E356.
Communication and relationships cannot be taken for granted, particularly in the physician-patient relationship, where life-altering diagnoses may be given. With one diagnosis, someone’s life may be changed, and both physicians and patients need to be cognizant of the importance of a strong relationship and clear communication.
In the current US health care system, both physicians and patients often are not getting their needs met, and studies that include factors of race, ethnicity, and socioeconomic status suggest that physician-patient relationship barriers contribute to racial disparities in health care.1,2 Although patient-centered care is a widely recognized and upheld model, relationship-centered care between physician and patient involves focusing on the patient and the physician-patient relationship through recognizing personhood, affect (being empathic), and reciprocal influence.3,4 Although it is not necessarily intuitive because it can appear to be yet another task for busy physicians, relationship-centered care improves health care delivery for both physicians and patients through decreased physician burnout, reduced medical errors, and better patient outcomes and satisfaction.5,6
Every physician, patient, and physician-patient relationship is different; unlike the standard questions directed at a routine patient history focused on gathering data, there is no one-size-fits-all relationship-centered conversation.7-10 As with any successful interaction between 2 people, there is a certain amount of necessary self-awareness (Table 1)11 that allows for improvisation and appropriate responsiveness to what is seen, heard, and felt. Rather than attending solely to disease states, the focus of relationship-centered care is on patients, interpersonal interaction, and promoting health and well-being.15
This review summarizes the existing literature on relationship-centered care, introduces the use of metacognition (Table 1), and suggests creating simple habits to promote such care. The following databases were searched from inception through November 23, 2020, using the term relationship-centered care: MEDLINE (Ovid), EMBASE (Ovid), APA PsycInfo (Ovid), Scopus, Web of Science Core Collection, CINAHL Complete (EBSCO), Academic Search Premier (EBSCOhost), and ERIC (ProQuest). A total of 1772 records were retrieved through searches, and after deduplication of 1116 studies, 350 records were screened through a 2-part process. Articles were first screened by title and abstract for relevance to the relationship between physician and patient, with 185 studies deemed irrelevant (eg, pertaining to the relationship of veterinarian to animal). The remaining 165 studies were assessed for eligibility, with 69 further studies excluded for various reasons. The screening process resulted in 96 articles considered in this review.
Definitions/key terms, as used in this article, are listed in Table 1.
Background of Relationship-Centered Care
Given time constraints, the diagnosis and treatment of medical problems often are the focus of physicians. Although proper medical diagnosis and treatment are important, and their delivery is made possible by the physician having the appropriate knowledge, a physician-patient relationship that focuses solely on disease without acknowledging the patient creates a system that ultimately neglects both patients and physicians.15 This prevailing physician-patient relationship paradigm is suboptimal, and a proposed remedy is relationship-centered care, which focuses on relationships among the human beings in health care interactions.3 Relationship-centered care has 4 principles: (1) the personhood of each party must be recognized, (2) emotion is part of relationships, (3) relationships are reciprocal and not just one way, and (4) creating these types of relationships is morally valuable3 and beneficial to patient care.16
Assessment of the Need for Relationship-Centered Care
Relationship-centered care has been studied in physician-patient interactions in various health care settings.17-23 For at least 2 decades, relationship-centered care has been set forth as a model,4,24,25 but there are challenges. Physicians tend to overrate or underrate their communication skills in patient interactions.26,27 A given physician’s preferences often still seem to supersede those of the patient.3,28,29 The impetus to develop relationship-centered care skills generally needs to be internally driven,4,30 as, ultimately, physicians and patients have varying needs.4,31 However, providing physicians with a potential structure is helpful.32
A Solution: Metacognition in the Physician-Patient Interaction
Metacognition is important to integrating basic science knowledge into medical learning and practice,33,34 and it is no less important in translating interpersonal knowledge to the physician-patient interaction. Decreased metacognitive effort35 may underpin the decline in empathy seen with increasing medical training.36,37 Understanding how metacognitive practices foster relationship-centered care is important for teaching, developing, and maintaining that care.
Metacognition is already embedded in the fabric of the physician-patient interaction.33,34 The complex interplay of the physician-patient interview, patient examination, and integration of physical as well as ancillary data requires higher-order thinking and the ability to parse out that thinking successfully. As a concrete example, coming to a diagnosis requires thinking about what has been presented during the physician-patient interaction and considering what supports and suggests the disease while a list of potential differential diagnosis alternatives is being generated. Physicians are trained to apply this clinical reasoning approach to their patient care.
Conversely, although communication skills are a key component of doctoring,38 both between physician and patient as well as among other colleagues and staff, many physicians have never received formal training in communication skills,26,32,39 though it is now an integral part of medical school curricula.40 When such training is mandatory, less than 1% of physicians continue to believe that there was no benefit, even from a single 8-hour communications skills training session.41 Communication cannot be taught comprehensively in 8 hours; thus, the benefit of such training may be the end result of metacognition and increased self-awareness (Table 1).42,43
Building Relationship-Centered Care Through Metacognitive Attention
Metacognition as manifested by such self-awareness can build relationship-centered care.4 Self-awareness can be taught through mentorship or role models.44 Journaling,40 meditation, and appreciation of beauty and the arts45 can contribute, as well as more formal training programs,32,38,42 as offered by the Academy of Communication in Healthcare. Creating opportunities for patient empowerment also supports relationship-centered care, as does applying knowledge of implicit bias.46
Even without formal training, relationship-centered care can be built through attention to cues9—visual (eg, sitting down, other body language),47,48 auditory (eg, knocking, language, tone, conversational flow),48,49 and emotional (eg, clinical empathy, emotional intelligence)(Table 2). Such attention is familiar to everyone, not just physicians or patients, through interactions outside of health care; inattention may be due to the hidden curriculum or culture of medicine40 as well as real-time changes, such as the introduction of the electronic health record.51 Inattention to these cues also may be a result of context-specific knowledge, in which a physician’s real-life communication skills are not applied to the unique context of patient care.
Although the theoretical foundation of relationship-centered care is relatively complex,9 a simple formula that has improved patient experience is “The Big 3,” which entails (1) simply knocking before entering the examination room, (2) sitting, and (3) asking, “What is your main concern?”30 Another relatively simple technique would be to involve the patient with the electronic health record by sharing the screen with them.52 Learning about narrative medicine and developing skills to appreciate each patient’s story is another method to increase relationship-centered care,40,53 as is emotional intelligence.54 These interventions are simple to implement, and good relationship-centered care will save time, help manage patient visits more effectively, and aid in avoiding the urgent new concern that the patient adds at the end of the visit.55 The positive effect of these different interventions highlights that small changes (Table 2) can shift the prevailing culture of medicine to become more relationship centered.56
Metacognitive Attention Can Generate Habit
Taking metacognition a step further, these small interventions can become habit11,14,39 through self-awareness, deliberate practice, and feedback.43 Habit is generated by linking a given intervention to another defined cue. For example, placing a hand on a doorknob to enter an examination room can be the cue to generate a habit of entering with presence.14 Alternatively, before entering an examination room, taking 3 deep breaths can be the cue to trigger presence.14 Habits can be created in just 3 weeks,57 and other proposed cues to generate habits toward relationship-centered care are listed in Table 2. By creating habit through metacognitive attention, relationship-centered care will become something that happens subconsciously without further burdening physicians with another task. Asking patients for permission to record video of an interaction also can create opportunities for self-awareness and self-evaluation through rewatching the video.58
Final Thoughts
Physicians already have the tools to create relationship-centered care in physician-patient interactions. A critical mental shift is to develop habits and apply thinking patterns toward understanding and responding appropriately to patients of all ethnicities and their emotions in the physician-patient interaction. This shift is aided by metacognitive awareness (Table 1) and the development of useful habits (Table 2).
Communication and relationships cannot be taken for granted, particularly in the physician-patient relationship, where life-altering diagnoses may be given. With one diagnosis, someone’s life may be changed, and both physicians and patients need to be cognizant of the importance of a strong relationship and clear communication.
In the current US health care system, both physicians and patients often are not getting their needs met, and studies that include factors of race, ethnicity, and socioeconomic status suggest that physician-patient relationship barriers contribute to racial disparities in health care.1,2 Although patient-centered care is a widely recognized and upheld model, relationship-centered care between physician and patient involves focusing on the patient and the physician-patient relationship through recognizing personhood, affect (being empathic), and reciprocal influence.3,4 Although it is not necessarily intuitive because it can appear to be yet another task for busy physicians, relationship-centered care improves health care delivery for both physicians and patients through decreased physician burnout, reduced medical errors, and better patient outcomes and satisfaction.5,6
Every physician, patient, and physician-patient relationship is different; unlike the standard questions directed at a routine patient history focused on gathering data, there is no one-size-fits-all relationship-centered conversation.7-10 As with any successful interaction between 2 people, there is a certain amount of necessary self-awareness (Table 1)11 that allows for improvisation and appropriate responsiveness to what is seen, heard, and felt. Rather than attending solely to disease states, the focus of relationship-centered care is on patients, interpersonal interaction, and promoting health and well-being.15
This review summarizes the existing literature on relationship-centered care, introduces the use of metacognition (Table 1), and suggests creating simple habits to promote such care. The following databases were searched from inception through November 23, 2020, using the term relationship-centered care: MEDLINE (Ovid), EMBASE (Ovid), APA PsycInfo (Ovid), Scopus, Web of Science Core Collection, CINAHL Complete (EBSCO), Academic Search Premier (EBSCOhost), and ERIC (ProQuest). A total of 1772 records were retrieved through searches, and after deduplication of 1116 studies, 350 records were screened through a 2-part process. Articles were first screened by title and abstract for relevance to the relationship between physician and patient, with 185 studies deemed irrelevant (eg, pertaining to the relationship of veterinarian to animal). The remaining 165 studies were assessed for eligibility, with 69 further studies excluded for various reasons. The screening process resulted in 96 articles considered in this review.
Definitions/key terms, as used in this article, are listed in Table 1.
Background of Relationship-Centered Care
Given time constraints, the diagnosis and treatment of medical problems often are the focus of physicians. Although proper medical diagnosis and treatment are important, and their delivery is made possible by the physician having the appropriate knowledge, a physician-patient relationship that focuses solely on disease without acknowledging the patient creates a system that ultimately neglects both patients and physicians.15 This prevailing physician-patient relationship paradigm is suboptimal, and a proposed remedy is relationship-centered care, which focuses on relationships among the human beings in health care interactions.3 Relationship-centered care has 4 principles: (1) the personhood of each party must be recognized, (2) emotion is part of relationships, (3) relationships are reciprocal and not just one way, and (4) creating these types of relationships is morally valuable3 and beneficial to patient care.16
Assessment of the Need for Relationship-Centered Care
Relationship-centered care has been studied in physician-patient interactions in various health care settings.17-23 For at least 2 decades, relationship-centered care has been set forth as a model,4,24,25 but there are challenges. Physicians tend to overrate or underrate their communication skills in patient interactions.26,27 A given physician’s preferences often still seem to supersede those of the patient.3,28,29 The impetus to develop relationship-centered care skills generally needs to be internally driven,4,30 as, ultimately, physicians and patients have varying needs.4,31 However, providing physicians with a potential structure is helpful.32
A Solution: Metacognition in the Physician-Patient Interaction
Metacognition is important to integrating basic science knowledge into medical learning and practice,33,34 and it is no less important in translating interpersonal knowledge to the physician-patient interaction. Decreased metacognitive effort35 may underpin the decline in empathy seen with increasing medical training.36,37 Understanding how metacognitive practices foster relationship-centered care is important for teaching, developing, and maintaining that care.
Metacognition is already embedded in the fabric of the physician-patient interaction.33,34 The complex interplay of the physician-patient interview, patient examination, and integration of physical as well as ancillary data requires higher-order thinking and the ability to parse out that thinking successfully. As a concrete example, coming to a diagnosis requires thinking about what has been presented during the physician-patient interaction and considering what supports and suggests the disease while a list of potential differential diagnosis alternatives is being generated. Physicians are trained to apply this clinical reasoning approach to their patient care.
Conversely, although communication skills are a key component of doctoring,38 both between physician and patient as well as among other colleagues and staff, many physicians have never received formal training in communication skills,26,32,39 though it is now an integral part of medical school curricula.40 When such training is mandatory, less than 1% of physicians continue to believe that there was no benefit, even from a single 8-hour communications skills training session.41 Communication cannot be taught comprehensively in 8 hours; thus, the benefit of such training may be the end result of metacognition and increased self-awareness (Table 1).42,43
Building Relationship-Centered Care Through Metacognitive Attention
Metacognition as manifested by such self-awareness can build relationship-centered care.4 Self-awareness can be taught through mentorship or role models.44 Journaling,40 meditation, and appreciation of beauty and the arts45 can contribute, as well as more formal training programs,32,38,42 as offered by the Academy of Communication in Healthcare. Creating opportunities for patient empowerment also supports relationship-centered care, as does applying knowledge of implicit bias.46
Even without formal training, relationship-centered care can be built through attention to cues9—visual (eg, sitting down, other body language),47,48 auditory (eg, knocking, language, tone, conversational flow),48,49 and emotional (eg, clinical empathy, emotional intelligence)(Table 2). Such attention is familiar to everyone, not just physicians or patients, through interactions outside of health care; inattention may be due to the hidden curriculum or culture of medicine40 as well as real-time changes, such as the introduction of the electronic health record.51 Inattention to these cues also may be a result of context-specific knowledge, in which a physician’s real-life communication skills are not applied to the unique context of patient care.
Although the theoretical foundation of relationship-centered care is relatively complex,9 a simple formula that has improved patient experience is “The Big 3,” which entails (1) simply knocking before entering the examination room, (2) sitting, and (3) asking, “What is your main concern?”30 Another relatively simple technique would be to involve the patient with the electronic health record by sharing the screen with them.52 Learning about narrative medicine and developing skills to appreciate each patient’s story is another method to increase relationship-centered care,40,53 as is emotional intelligence.54 These interventions are simple to implement, and good relationship-centered care will save time, help manage patient visits more effectively, and aid in avoiding the urgent new concern that the patient adds at the end of the visit.55 The positive effect of these different interventions highlights that small changes (Table 2) can shift the prevailing culture of medicine to become more relationship centered.56
Metacognitive Attention Can Generate Habit
Taking metacognition a step further, these small interventions can become habit11,14,39 through self-awareness, deliberate practice, and feedback.43 Habit is generated by linking a given intervention to another defined cue. For example, placing a hand on a doorknob to enter an examination room can be the cue to generate a habit of entering with presence.14 Alternatively, before entering an examination room, taking 3 deep breaths can be the cue to trigger presence.14 Habits can be created in just 3 weeks,57 and other proposed cues to generate habits toward relationship-centered care are listed in Table 2. By creating habit through metacognitive attention, relationship-centered care will become something that happens subconsciously without further burdening physicians with another task. Asking patients for permission to record video of an interaction also can create opportunities for self-awareness and self-evaluation through rewatching the video.58
Final Thoughts
Physicians already have the tools to create relationship-centered care in physician-patient interactions. A critical mental shift is to develop habits and apply thinking patterns toward understanding and responding appropriately to patients of all ethnicities and their emotions in the physician-patient interaction. This shift is aided by metacognitive awareness (Table 1) and the development of useful habits (Table 2).
- Sanders L, Fortin AH VI, Schiff GD. Connecting with patients—the missing links. JAMA. 2020;323:33-34.
- Peck BM, Denney M. Disparities in the conduct of the medical encounter: the effects of physician and patient race and gender. SAGE Open. 2012;2:1-14.
- Beach MC, Inui T. Relationship-centered care. a constructive reframing. J Gen Intern Med. 2006;21(suppl 1):S3-S8.
- Tresolini CP, Pew-Fetzer Task Force. Health Professions Education and Relationship-Centered Care. Pew Health Professions Commission; 1994.
- Hojat M. Empathy in Health Professions Education and Patient Care. Springer; 2016.
- Wilkinson H, Whittington R, Perry L, et al. Examining the relationship between burnout and empathy in healthcare professionals: a systematic review. Burn Res. 2017;6:18-29.
- Frankel RM, Quill T. Integrating biopsychosocial and relationship-centered care into mainstream medical practice: a challenge that continues to produce positive results. Fam Syst Health. 2005;23:413-421.
- Frankel RM. Relationship-centered care and the patient-physician relationship. J Gen Intern Med. 2004;19:1163-1165.
- Ventres WB, Frankel RM. Shared presence in physician-patient communication: a graphic representation. Fam Syst Health. 2015;33:270-279.
- Cooper LA, Beach MC, Johnson RL, et al. Delving below the surface: understanding how race and ethnicity influence relationships in health care. J Gen Intern Med. 2006;21(suppl 1):S21-S27.
- Epstein RM. Mindful practice. JAMA. 1999;282:833-839.
- Dobie S. Viewpoint: reflections on a well-traveled path: self-awareness, mindful practice, and relationship-centered care as foundations for medical education. Acad Med. 2007;82:422-427.
- Rabow MW. Meaning and relationship-centered care: recommendations for clinicians attending to the spiritual distress of patients at the end of life. Ethics Med Public Health. 2019;9:57-62.
- Zulman DM, Haverfield MC, Shaw JG, et al. Practices to foster physician presence and connection with patients in the clinical encounter. JAMA. 2020;323:70-81.
- Rakel DP, Guerrera MP, Bayles BP, et al. CAM education: promoting a salutogenic focus in health care. J Altern Complement Med. 2008;14:87-93.
- Olaisen RH, Schluchter MD, Flocke SA, et al. Assessing the longitudinal impact of physician-patient relationship on functional health. Ann Fam Med. 2020;18:422-429.
- Berg GM, Ekengren F, Lee FA, et al. Patient satisfaction with surgeons in a trauma population: testing a structural equation model using perceptions of interpersonal and technical care. J Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2012;72:1316-1322.
- Nassar A, Weimer-Elder B, Kline M, et al. Developing an inpatient relationship-centered communication curriculum for surgical teams: pilot study. J Am Coll Surg. 2019;229(4 suppl 2):E48.
- Caldicott CV, Dunn KA, Frankel RM. Can patients tell when they are unwanted? “turfing” in residency training. Patient Educ Couns. 2005;56:104-111.
- Tucker Edmonds B, Mogul M, Shea JA. Understanding low-income African American women’s expectations, preferences, and priorities in prenatal care. Fam Community Health. 2015;38:149-157.
- Sundstrom B, Szabo C, Dempsey A. “My body. my choice:” a qualitative study of the influence of trust and locus of control on postpartum contraceptive choice. J Health Commun. 2018;23:162-169.
- Block S, Billings JA. Nurturing humanism through teaching palliative care. Acad Med. 1998;73:763-765.
- Hebert RS, Schulz R, Copeland VC, et al. Preparing family caregivers for death and bereavement. insights from caregivers of terminally ill patients. J Pain Symptom Manage. 2009;37:3-12.
- Nundy S, Oswald J. Relationship-centered care: a new paradigm for population health management. Healthc (Amst). 2014;2:216-219.
- Sprague S. Relationship centered care. J S C Med Assoc. 2009;105:135-136.
- Roter DL, Frankel RM, Hall JA, et al. The expression of emotion through nonverbal behavior in medical visits. mechanisms and outcomes. J Gen Intern Med. 2006;21(suppl 1):S28-S34.
- Kenny DA, Veldhuijzen W, van der Weijden T, et al. Interpersonal perception in the context of doctor-patient relationships: a dyadic analysis of doctor-patient communication. Soc Sci Med. 2010;70:763-768.
- Tarzian AJ, Neal MT, O’Neil JA. Attitudes, experiences, and beliefs affecting end-of-life decision-making among homeless individuals. J Palliat Med. 2005;8:36-48.
- Roter D. The enduring and evolving nature of the patient-physician relationship. Patient Educ Couns. 2000;39:5-15.
- Sharieff GQ. MD to MD coaching: improving physician-patient experience scores: what works, what doesn’t. J Patient Exp. 2017;4:210-212.
- Duggan AP, Bradshaw YS, Swergold N, et al. When rapport building extends beyond affiliation: communication overaccommodation toward patients with disabilities. Perm J. 2011;15:23-30.
- Hirschmann K, Rosler G, Fortin AH VI. “For me, this has been transforming”: a qualitative analysis of interprofessional relationship-centered communication skills training. J Patient Exp. 2020;7:1007-1014.
- Hennrikus EF, Skolka MP, Hennrikus N. Applying metacognition through patient encounters and illness scripts to create a conceptual framework for basic science integration, storage, and retrieval. J Med Educ Curric Dev. 2018;5:2382120518777770.
- Eichbaum QG. Thinking about thinking and emotion: the metacognitive approach to the medical humanities that integrates the humanities with the basic and clinical sciences. Perm J. 2014;18:64-75.
- Stansfield RB, Schwartz A, O’Brien CL, et al. Development of a metacognitive effort construct of empathy during clinical training: a longitudinal study of the factor structure of the Jefferson Scale of Empathy. Adv Health Sci Educ Theory Pract. 2016;21:5-17.
- Hojat M, Vergare MJ, Maxwell K, et al. The devil is in the third year: a longitudinal study of erosion of empathy in medical school. Acad Med. 2009;84:1182-1191.
- Neumann M, Edelhäuser F, Tauschel D, et al. Empathy decline and its reasons: a systematic review of studies with medical students and residents. Acad Med. 2011;86:996-1009.
- Chou CL, Hirschmann K, Fortin AHT, et al. The impact of a faculty learning community on professional and personal development: the facilitator training program of the American Academy on Communication in Healthcare. Acad Med. 2014;89:1051-1056.
- Rider EA. Advanced communication strategies for relationship-centered care. Pediatr Ann. 2011;40:447-453.
- Reichman JAH. Narrative competence, mindfulness,and relationship-centered care in medical education: an innovative approach to teaching medical interviewing. Dissertation Abstracts International Section A: Humanities and Social Sciences. 2015;75(8-A(E)).
- Boissy A, Windover AK, Bokar D, et al. Communication skills training for physicians improves patient satisfaction. J Gen Intern Med. 2016;31:755-761.
- Hatem DS, Barrett SV, Hewson M, et al. Teaching the medical interview: methods and key learning issues in a faculty development course. J Gen Intern Med. 2007;22:1718-1724.
- Gilligan TD, Baile WF. ASCO patient-clinician communication guideline: fostering relationship-centered care. ASCO Connection. November 20, 2017. Accessed March 5, 2021. https://connection.asco.org/blogs/asco-patient-clinician-communication-guideline-fostering-relationship-centered-care
- Haidet P, Stein HF. The role of the student-teacher relationship in the formation of physicians. The hidden curriculum as process. J Gen Intern Med. 2006;(suppl 1):S16-S20.
- Puchalski CM, Guenther M. Restoration and re-creation: spirituality in the lives of healthcare professionals. Curr Opin Support Palliat Care. 2012;6:254-258.
- Williams SW, Hanson LC, Boyd C, et al. Communication, decision making, and cancer: what African Americans want physicians to know. J Palliative Med. 2008;11:1221-1226.
- Lindsley I, Woodhead S, Micallef C, et al. The concept of body language in the medical consultation. Psychiatr Danub. 2015;27(suppl 1):S41-S47.
- Hall JA, Harrigan JA, Rosenthal R. Nonverbal behavior in clinician-patient interaction. Appl Prev Psychol. 1995;4:21-37.
- Ness DE, Kiesling SF. Language and connectedness in the medical and psychiatric interview. Patient Educ Couns. 2007;68:139-144.
- Miller WL. The clinical hand: a curricular map for relationship-centered care. Fam Med. 2004;36:330-335.
- Wald HS, George P, Reis SP, et al. Electronic health record training in undergraduate medical education: bridging theory to practice with curricula for empowering patient- and relationship-centered care in the computerized setting. Acad Med. 2014;89:380-386.
- Silverman H, Ho YX, Kaib S, et al. A novel approach to supporting relationship-centered care through electronic health record ergonomic training in preclerkship medical education. Acad Med. 2014;89:1230-1234.
- Weiss T, Swede MJ. Transforming preprofessional health education through relationship-centered care and narrative medicine. Teach Learn Med. 2019;31:222-233.
- Blanch-Hartigan D. An effective training to increase accurate recognition of patient emotion cues. Patient Educ Couns. 2012;89:274-280.
- White J, Levinson W, Roter D. “Oh, by the way ...”: the closing moments of the medical visit. J Gen Intern Med. 1994;9:24-28.
- Suchman AL, Williamson PR, Litzelman DK, et al. Toward an informal curriculum that teaches professionalism. Transforming the social environment of a medical school. J Gen Intern Med. 2004;19:501-504.
- Lally P, van Jaarsveld CHM, Potts HWW, et al. How are habits formed: modelling habit formation in the real world. Eur J Soc Psychol. 2010;40:998-1009.
- Little P, White P, Kelly J, et al. Randomised controlled trial of a brief intervention targeting predominantly non-verbal communication in general practice consultations. Br J Gen Pract. 2015;65:E351-E356.
- Sanders L, Fortin AH VI, Schiff GD. Connecting with patients—the missing links. JAMA. 2020;323:33-34.
- Peck BM, Denney M. Disparities in the conduct of the medical encounter: the effects of physician and patient race and gender. SAGE Open. 2012;2:1-14.
- Beach MC, Inui T. Relationship-centered care. a constructive reframing. J Gen Intern Med. 2006;21(suppl 1):S3-S8.
- Tresolini CP, Pew-Fetzer Task Force. Health Professions Education and Relationship-Centered Care. Pew Health Professions Commission; 1994.
- Hojat M. Empathy in Health Professions Education and Patient Care. Springer; 2016.
- Wilkinson H, Whittington R, Perry L, et al. Examining the relationship between burnout and empathy in healthcare professionals: a systematic review. Burn Res. 2017;6:18-29.
- Frankel RM, Quill T. Integrating biopsychosocial and relationship-centered care into mainstream medical practice: a challenge that continues to produce positive results. Fam Syst Health. 2005;23:413-421.
- Frankel RM. Relationship-centered care and the patient-physician relationship. J Gen Intern Med. 2004;19:1163-1165.
- Ventres WB, Frankel RM. Shared presence in physician-patient communication: a graphic representation. Fam Syst Health. 2015;33:270-279.
- Cooper LA, Beach MC, Johnson RL, et al. Delving below the surface: understanding how race and ethnicity influence relationships in health care. J Gen Intern Med. 2006;21(suppl 1):S21-S27.
- Epstein RM. Mindful practice. JAMA. 1999;282:833-839.
- Dobie S. Viewpoint: reflections on a well-traveled path: self-awareness, mindful practice, and relationship-centered care as foundations for medical education. Acad Med. 2007;82:422-427.
- Rabow MW. Meaning and relationship-centered care: recommendations for clinicians attending to the spiritual distress of patients at the end of life. Ethics Med Public Health. 2019;9:57-62.
- Zulman DM, Haverfield MC, Shaw JG, et al. Practices to foster physician presence and connection with patients in the clinical encounter. JAMA. 2020;323:70-81.
- Rakel DP, Guerrera MP, Bayles BP, et al. CAM education: promoting a salutogenic focus in health care. J Altern Complement Med. 2008;14:87-93.
- Olaisen RH, Schluchter MD, Flocke SA, et al. Assessing the longitudinal impact of physician-patient relationship on functional health. Ann Fam Med. 2020;18:422-429.
- Berg GM, Ekengren F, Lee FA, et al. Patient satisfaction with surgeons in a trauma population: testing a structural equation model using perceptions of interpersonal and technical care. J Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2012;72:1316-1322.
- Nassar A, Weimer-Elder B, Kline M, et al. Developing an inpatient relationship-centered communication curriculum for surgical teams: pilot study. J Am Coll Surg. 2019;229(4 suppl 2):E48.
- Caldicott CV, Dunn KA, Frankel RM. Can patients tell when they are unwanted? “turfing” in residency training. Patient Educ Couns. 2005;56:104-111.
- Tucker Edmonds B, Mogul M, Shea JA. Understanding low-income African American women’s expectations, preferences, and priorities in prenatal care. Fam Community Health. 2015;38:149-157.
- Sundstrom B, Szabo C, Dempsey A. “My body. my choice:” a qualitative study of the influence of trust and locus of control on postpartum contraceptive choice. J Health Commun. 2018;23:162-169.
- Block S, Billings JA. Nurturing humanism through teaching palliative care. Acad Med. 1998;73:763-765.
- Hebert RS, Schulz R, Copeland VC, et al. Preparing family caregivers for death and bereavement. insights from caregivers of terminally ill patients. J Pain Symptom Manage. 2009;37:3-12.
- Nundy S, Oswald J. Relationship-centered care: a new paradigm for population health management. Healthc (Amst). 2014;2:216-219.
- Sprague S. Relationship centered care. J S C Med Assoc. 2009;105:135-136.
- Roter DL, Frankel RM, Hall JA, et al. The expression of emotion through nonverbal behavior in medical visits. mechanisms and outcomes. J Gen Intern Med. 2006;21(suppl 1):S28-S34.
- Kenny DA, Veldhuijzen W, van der Weijden T, et al. Interpersonal perception in the context of doctor-patient relationships: a dyadic analysis of doctor-patient communication. Soc Sci Med. 2010;70:763-768.
- Tarzian AJ, Neal MT, O’Neil JA. Attitudes, experiences, and beliefs affecting end-of-life decision-making among homeless individuals. J Palliat Med. 2005;8:36-48.
- Roter D. The enduring and evolving nature of the patient-physician relationship. Patient Educ Couns. 2000;39:5-15.
- Sharieff GQ. MD to MD coaching: improving physician-patient experience scores: what works, what doesn’t. J Patient Exp. 2017;4:210-212.
- Duggan AP, Bradshaw YS, Swergold N, et al. When rapport building extends beyond affiliation: communication overaccommodation toward patients with disabilities. Perm J. 2011;15:23-30.
- Hirschmann K, Rosler G, Fortin AH VI. “For me, this has been transforming”: a qualitative analysis of interprofessional relationship-centered communication skills training. J Patient Exp. 2020;7:1007-1014.
- Hennrikus EF, Skolka MP, Hennrikus N. Applying metacognition through patient encounters and illness scripts to create a conceptual framework for basic science integration, storage, and retrieval. J Med Educ Curric Dev. 2018;5:2382120518777770.
- Eichbaum QG. Thinking about thinking and emotion: the metacognitive approach to the medical humanities that integrates the humanities with the basic and clinical sciences. Perm J. 2014;18:64-75.
- Stansfield RB, Schwartz A, O’Brien CL, et al. Development of a metacognitive effort construct of empathy during clinical training: a longitudinal study of the factor structure of the Jefferson Scale of Empathy. Adv Health Sci Educ Theory Pract. 2016;21:5-17.
- Hojat M, Vergare MJ, Maxwell K, et al. The devil is in the third year: a longitudinal study of erosion of empathy in medical school. Acad Med. 2009;84:1182-1191.
- Neumann M, Edelhäuser F, Tauschel D, et al. Empathy decline and its reasons: a systematic review of studies with medical students and residents. Acad Med. 2011;86:996-1009.
- Chou CL, Hirschmann K, Fortin AHT, et al. The impact of a faculty learning community on professional and personal development: the facilitator training program of the American Academy on Communication in Healthcare. Acad Med. 2014;89:1051-1056.
- Rider EA. Advanced communication strategies for relationship-centered care. Pediatr Ann. 2011;40:447-453.
- Reichman JAH. Narrative competence, mindfulness,and relationship-centered care in medical education: an innovative approach to teaching medical interviewing. Dissertation Abstracts International Section A: Humanities and Social Sciences. 2015;75(8-A(E)).
- Boissy A, Windover AK, Bokar D, et al. Communication skills training for physicians improves patient satisfaction. J Gen Intern Med. 2016;31:755-761.
- Hatem DS, Barrett SV, Hewson M, et al. Teaching the medical interview: methods and key learning issues in a faculty development course. J Gen Intern Med. 2007;22:1718-1724.
- Gilligan TD, Baile WF. ASCO patient-clinician communication guideline: fostering relationship-centered care. ASCO Connection. November 20, 2017. Accessed March 5, 2021. https://connection.asco.org/blogs/asco-patient-clinician-communication-guideline-fostering-relationship-centered-care
- Haidet P, Stein HF. The role of the student-teacher relationship in the formation of physicians. The hidden curriculum as process. J Gen Intern Med. 2006;(suppl 1):S16-S20.
- Puchalski CM, Guenther M. Restoration and re-creation: spirituality in the lives of healthcare professionals. Curr Opin Support Palliat Care. 2012;6:254-258.
- Williams SW, Hanson LC, Boyd C, et al. Communication, decision making, and cancer: what African Americans want physicians to know. J Palliative Med. 2008;11:1221-1226.
- Lindsley I, Woodhead S, Micallef C, et al. The concept of body language in the medical consultation. Psychiatr Danub. 2015;27(suppl 1):S41-S47.
- Hall JA, Harrigan JA, Rosenthal R. Nonverbal behavior in clinician-patient interaction. Appl Prev Psychol. 1995;4:21-37.
- Ness DE, Kiesling SF. Language and connectedness in the medical and psychiatric interview. Patient Educ Couns. 2007;68:139-144.
- Miller WL. The clinical hand: a curricular map for relationship-centered care. Fam Med. 2004;36:330-335.
- Wald HS, George P, Reis SP, et al. Electronic health record training in undergraduate medical education: bridging theory to practice with curricula for empowering patient- and relationship-centered care in the computerized setting. Acad Med. 2014;89:380-386.
- Silverman H, Ho YX, Kaib S, et al. A novel approach to supporting relationship-centered care through electronic health record ergonomic training in preclerkship medical education. Acad Med. 2014;89:1230-1234.
- Weiss T, Swede MJ. Transforming preprofessional health education through relationship-centered care and narrative medicine. Teach Learn Med. 2019;31:222-233.
- Blanch-Hartigan D. An effective training to increase accurate recognition of patient emotion cues. Patient Educ Couns. 2012;89:274-280.
- White J, Levinson W, Roter D. “Oh, by the way ...”: the closing moments of the medical visit. J Gen Intern Med. 1994;9:24-28.
- Suchman AL, Williamson PR, Litzelman DK, et al. Toward an informal curriculum that teaches professionalism. Transforming the social environment of a medical school. J Gen Intern Med. 2004;19:501-504.
- Lally P, van Jaarsveld CHM, Potts HWW, et al. How are habits formed: modelling habit formation in the real world. Eur J Soc Psychol. 2010;40:998-1009.
- Little P, White P, Kelly J, et al. Randomised controlled trial of a brief intervention targeting predominantly non-verbal communication in general practice consultations. Br J Gen Pract. 2015;65:E351-E356.
Practice Points
- Relationship-centered care emphasizes that all relationships in health care are important, including not only relationships between physicians and patients but also among physicians and colleagues, staff, students, community, and self.
- The physician-patient relationship can be complex, and metacognition can lead to habitual practice of simple techniques to optimize the interaction