User login
American Hunger Games: Food Insecurity Among the Military and Veterans
The requisites of government are that there be sufficiency of food, sufficiency of military equipment, and the confidence of the people in their ruler.
Analects by Confucius1
From ancient festivals to modern holidays, autumn has long been associated with the gathering of the harvest. Friends and families come together around tables laden with delicious food to enjoy the pleasures of peace and plenty. During these celebrations, we must never forget that without the strength of the nation’s military and the service of its veterans, this freedom and abundance would not be possible. Our debt of gratitude to the current and former members of the armed services makes the fact that a substantial minority experiences food insecurity not only a human tragedy, but a travesty of the nation’s promise to support those who wear or have worn the uniform.
The National Defense Authorization Act for Fiscal Year 2020 charged the Secretary of Defense to investigate food insecurity among active-duty service members and their dependents.2 The RAND Corporation conducted the assessment and, based on the results of its analysis, made recommendations to reduce hunger among armed forces members and their families.3
The RAND study found that 10% of active-duty military met US Department of Agriculture (USDA) criteria for very low food security; another 15% were classified as having low food security. The USDA defines food insecurity with hunger as “reports of multiple indications of disrupted eating patterns and reduced food intake.” USDA defines low food security as “reports of reduced quality, variety, or desirability of diet. Little or no indication of reduced food intake.”4
As someone who grew up on an Army base with the commissary a short trip from military housing, I was unpleasantly surprised that food insecurity was more common among in-service members living on post. I was even more dismayed to read that a variety of factors constrained 14% of active-duty military experiencing food insecurity to seek public assistance to feed themselves and their families. As with so many health care and social services, (eg, mental health care), those wearing the uniform were concerned that participating in a food assistance program would damage their career or stigmatize them. Others did not seek help, perhaps because they believed they were not eligible, and in many cases were correct: they did not qualify for food banks or food stamps due to receiving other benefits. A variety of factors contribute to periods of food insecurity among military families, including remote or rural bases that lack access to grocery stores or jobs for partners or other family members, and low base military pay.5
Food insecurity is an even more serious concern among veterans who are frequently older and have more comorbidities, often leading to unemployment and homelessness. Feeding America, the nation’s largest organization of community food banks, estimates that 1 in 9 working-age veterans are food insecure.5 US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) statistics indicate that veterans are 7% more likely to experience food insecurity than other sectors of the population.6 The Veterans Health Administration has recognized that food insecurity is directly related to medical problems already common among veterans, including diabetes, obesity, and depression. Women and minority veterans are the most at risk of food insecurity.7
Recognizing that many veterans are at risk of food insecurity, the US Department of Defense and VA have taken steps to try and reduce hunger among those who serve. In response to the shocking statistic that food insecurity was found in 27% of Iraq and Afghanistan veterans, the VA and Rockefeller Foundation are partnering on the Food as Medicine initiative to improve veteran nutrition as a means of improving nutrition-related health consequences of food insecurity.8
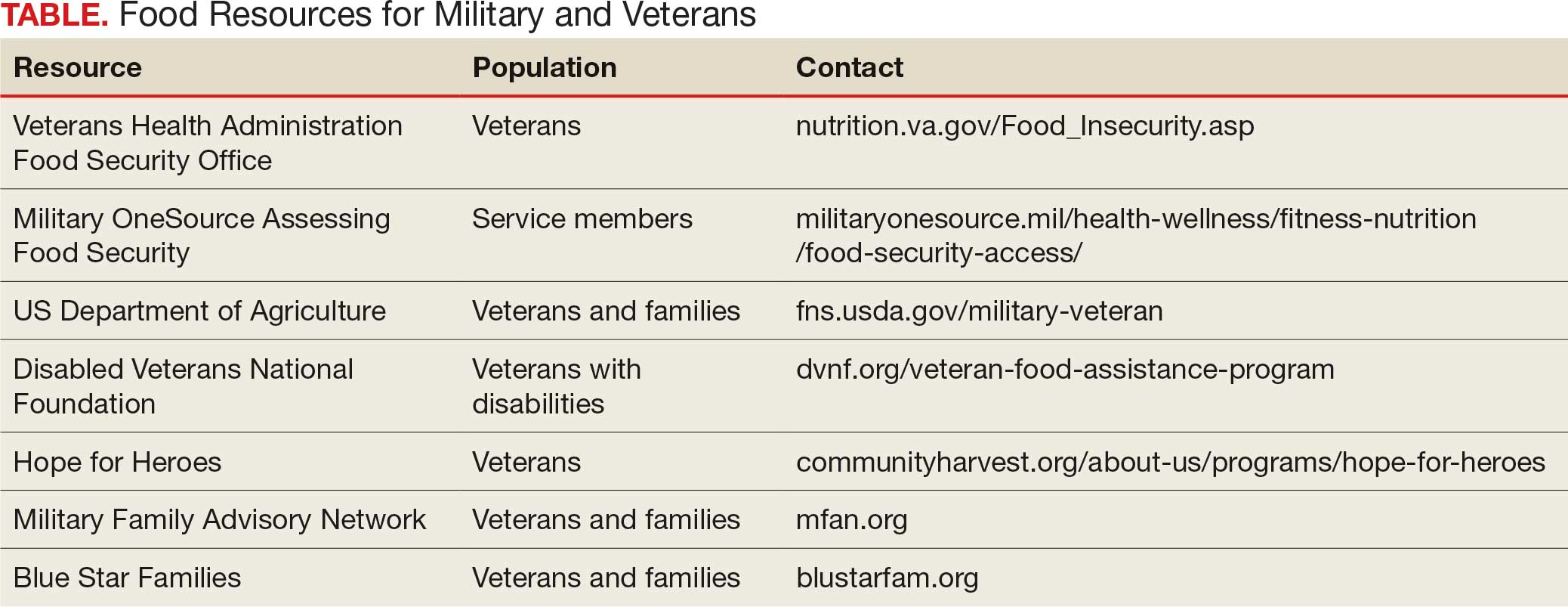
Like many federal practitioners, I was unaware of the food insecurity assistance available to active-duty service members or veterans, or how to help individuals access it. In addition to the resources outlined in the Table, there are many community-based options open to anyone, including veterans and service members.
I have written columns on many difficult issues in my years as the Editor-in-Chief of Federal Practitioner, but personally this is one of the most distressing editorials I have ever published. That individuals dedicated to defending our rights and protecting our safety should be compelled to go hungry or not know if they have enough money at the end of the month to buy food is manifestly unjust. It is challenging when faced with such a large-scale injustice to think we cannot make a difference, but that resignation or abdication only magnifies this inequity. I have a friend who kept giving back even after they retired from federal service: they volunteered at a community garden and brought produce to the local food bank and helped distribute it. That may seem too much for those still working yet almost anyone can pick up a few items on their weekly shopping trip and donate them to a food drive.
As we approach Veterans Day, let’s not just express our gratitude to our military and veterans in words but in deeds like feeding the hungry and urging elected representatives to fulfill their commitment to ensure that service members and veterans and their families do not experience food insecurity. Confucian wisdom written in a very distant time and vastly dissimilar context still rings true: there are direct and critical links between food and trust and between hunger and the military.1
Dawson MM. The Wisdom of Confucius: A Collection of the Ethical Sayings of Confucius and of his disciples. International Pocket Library; 1932.
National Defense Authorization Act for Fiscal Year 2020. 116th Cong (2019), Public Law 116-92. U.S. Government Printing Office. https://www.govinfo.gov/content/pkg/PLAW-116publ92/html/PLAW-116publ92.htm
Asch BJ, Rennane S, Trail TE, et al. Food insecurity among members of the armed forces and their dependents. RAND Corporation. January 3, 2023. Accessed September 22, 2025. https://www.rand.org/pubs/research_reports/RRA1230-1.html
US Department of Agriculture Economic Research Service. Food Security in the U.S.—Definitions of Food Security. US Department of Agriculture Economic Research Service. January 10, 2025. https://www.ers.usda.gov/topics/food-nutrition-assistance/food-security-in-the-us/definitions-of-food-security
Active military and veteran food insecurity. Feeding America. Accessed September 22, 2025. https://www.feedingamerica.org/hunger-in-america/food-insecurity-in-veterans
Pradun S. Find access to stop food insecurity in your community. VA News. September 19, 2025. Accessed September 22, 2025. https://news.va.gov/142733/find-access-stop-food-insecurity-your-community/
Cohen AJ, Dosa DM, Rudolph JL, et al. Risk factors for veteran food insecurity: findings from a National US Department of Veterans Affairs Food Insecurity Screener. Public Health Nutr. 2022;25:819-828. doi:10.1017/S1368980021004584
Chen C. VA and Rockefeller Foundation collaborate to access food for Veterans. VA News. September 5, 2023. Accessed September 22, 2025. https://news.va.gov/123228/va-rockefeller-foundation-expand-access-to-food/
The requisites of government are that there be sufficiency of food, sufficiency of military equipment, and the confidence of the people in their ruler.
Analects by Confucius1
From ancient festivals to modern holidays, autumn has long been associated with the gathering of the harvest. Friends and families come together around tables laden with delicious food to enjoy the pleasures of peace and plenty. During these celebrations, we must never forget that without the strength of the nation’s military and the service of its veterans, this freedom and abundance would not be possible. Our debt of gratitude to the current and former members of the armed services makes the fact that a substantial minority experiences food insecurity not only a human tragedy, but a travesty of the nation’s promise to support those who wear or have worn the uniform.
The National Defense Authorization Act for Fiscal Year 2020 charged the Secretary of Defense to investigate food insecurity among active-duty service members and their dependents.2 The RAND Corporation conducted the assessment and, based on the results of its analysis, made recommendations to reduce hunger among armed forces members and their families.3
The RAND study found that 10% of active-duty military met US Department of Agriculture (USDA) criteria for very low food security; another 15% were classified as having low food security. The USDA defines food insecurity with hunger as “reports of multiple indications of disrupted eating patterns and reduced food intake.” USDA defines low food security as “reports of reduced quality, variety, or desirability of diet. Little or no indication of reduced food intake.”4
As someone who grew up on an Army base with the commissary a short trip from military housing, I was unpleasantly surprised that food insecurity was more common among in-service members living on post. I was even more dismayed to read that a variety of factors constrained 14% of active-duty military experiencing food insecurity to seek public assistance to feed themselves and their families. As with so many health care and social services, (eg, mental health care), those wearing the uniform were concerned that participating in a food assistance program would damage their career or stigmatize them. Others did not seek help, perhaps because they believed they were not eligible, and in many cases were correct: they did not qualify for food banks or food stamps due to receiving other benefits. A variety of factors contribute to periods of food insecurity among military families, including remote or rural bases that lack access to grocery stores or jobs for partners or other family members, and low base military pay.5
Food insecurity is an even more serious concern among veterans who are frequently older and have more comorbidities, often leading to unemployment and homelessness. Feeding America, the nation’s largest organization of community food banks, estimates that 1 in 9 working-age veterans are food insecure.5 US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) statistics indicate that veterans are 7% more likely to experience food insecurity than other sectors of the population.6 The Veterans Health Administration has recognized that food insecurity is directly related to medical problems already common among veterans, including diabetes, obesity, and depression. Women and minority veterans are the most at risk of food insecurity.7
Recognizing that many veterans are at risk of food insecurity, the US Department of Defense and VA have taken steps to try and reduce hunger among those who serve. In response to the shocking statistic that food insecurity was found in 27% of Iraq and Afghanistan veterans, the VA and Rockefeller Foundation are partnering on the Food as Medicine initiative to improve veteran nutrition as a means of improving nutrition-related health consequences of food insecurity.8

Like many federal practitioners, I was unaware of the food insecurity assistance available to active-duty service members or veterans, or how to help individuals access it. In addition to the resources outlined in the Table, there are many community-based options open to anyone, including veterans and service members.
I have written columns on many difficult issues in my years as the Editor-in-Chief of Federal Practitioner, but personally this is one of the most distressing editorials I have ever published. That individuals dedicated to defending our rights and protecting our safety should be compelled to go hungry or not know if they have enough money at the end of the month to buy food is manifestly unjust. It is challenging when faced with such a large-scale injustice to think we cannot make a difference, but that resignation or abdication only magnifies this inequity. I have a friend who kept giving back even after they retired from federal service: they volunteered at a community garden and brought produce to the local food bank and helped distribute it. That may seem too much for those still working yet almost anyone can pick up a few items on their weekly shopping trip and donate them to a food drive.
As we approach Veterans Day, let’s not just express our gratitude to our military and veterans in words but in deeds like feeding the hungry and urging elected representatives to fulfill their commitment to ensure that service members and veterans and their families do not experience food insecurity. Confucian wisdom written in a very distant time and vastly dissimilar context still rings true: there are direct and critical links between food and trust and between hunger and the military.1
The requisites of government are that there be sufficiency of food, sufficiency of military equipment, and the confidence of the people in their ruler.
Analects by Confucius1
From ancient festivals to modern holidays, autumn has long been associated with the gathering of the harvest. Friends and families come together around tables laden with delicious food to enjoy the pleasures of peace and plenty. During these celebrations, we must never forget that without the strength of the nation’s military and the service of its veterans, this freedom and abundance would not be possible. Our debt of gratitude to the current and former members of the armed services makes the fact that a substantial minority experiences food insecurity not only a human tragedy, but a travesty of the nation’s promise to support those who wear or have worn the uniform.
The National Defense Authorization Act for Fiscal Year 2020 charged the Secretary of Defense to investigate food insecurity among active-duty service members and their dependents.2 The RAND Corporation conducted the assessment and, based on the results of its analysis, made recommendations to reduce hunger among armed forces members and their families.3
The RAND study found that 10% of active-duty military met US Department of Agriculture (USDA) criteria for very low food security; another 15% were classified as having low food security. The USDA defines food insecurity with hunger as “reports of multiple indications of disrupted eating patterns and reduced food intake.” USDA defines low food security as “reports of reduced quality, variety, or desirability of diet. Little or no indication of reduced food intake.”4
As someone who grew up on an Army base with the commissary a short trip from military housing, I was unpleasantly surprised that food insecurity was more common among in-service members living on post. I was even more dismayed to read that a variety of factors constrained 14% of active-duty military experiencing food insecurity to seek public assistance to feed themselves and their families. As with so many health care and social services, (eg, mental health care), those wearing the uniform were concerned that participating in a food assistance program would damage their career or stigmatize them. Others did not seek help, perhaps because they believed they were not eligible, and in many cases were correct: they did not qualify for food banks or food stamps due to receiving other benefits. A variety of factors contribute to periods of food insecurity among military families, including remote or rural bases that lack access to grocery stores or jobs for partners or other family members, and low base military pay.5
Food insecurity is an even more serious concern among veterans who are frequently older and have more comorbidities, often leading to unemployment and homelessness. Feeding America, the nation’s largest organization of community food banks, estimates that 1 in 9 working-age veterans are food insecure.5 US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) statistics indicate that veterans are 7% more likely to experience food insecurity than other sectors of the population.6 The Veterans Health Administration has recognized that food insecurity is directly related to medical problems already common among veterans, including diabetes, obesity, and depression. Women and minority veterans are the most at risk of food insecurity.7
Recognizing that many veterans are at risk of food insecurity, the US Department of Defense and VA have taken steps to try and reduce hunger among those who serve. In response to the shocking statistic that food insecurity was found in 27% of Iraq and Afghanistan veterans, the VA and Rockefeller Foundation are partnering on the Food as Medicine initiative to improve veteran nutrition as a means of improving nutrition-related health consequences of food insecurity.8

Like many federal practitioners, I was unaware of the food insecurity assistance available to active-duty service members or veterans, or how to help individuals access it. In addition to the resources outlined in the Table, there are many community-based options open to anyone, including veterans and service members.
I have written columns on many difficult issues in my years as the Editor-in-Chief of Federal Practitioner, but personally this is one of the most distressing editorials I have ever published. That individuals dedicated to defending our rights and protecting our safety should be compelled to go hungry or not know if they have enough money at the end of the month to buy food is manifestly unjust. It is challenging when faced with such a large-scale injustice to think we cannot make a difference, but that resignation or abdication only magnifies this inequity. I have a friend who kept giving back even after they retired from federal service: they volunteered at a community garden and brought produce to the local food bank and helped distribute it. That may seem too much for those still working yet almost anyone can pick up a few items on their weekly shopping trip and donate them to a food drive.
As we approach Veterans Day, let’s not just express our gratitude to our military and veterans in words but in deeds like feeding the hungry and urging elected representatives to fulfill their commitment to ensure that service members and veterans and their families do not experience food insecurity. Confucian wisdom written in a very distant time and vastly dissimilar context still rings true: there are direct and critical links between food and trust and between hunger and the military.1
Dawson MM. The Wisdom of Confucius: A Collection of the Ethical Sayings of Confucius and of his disciples. International Pocket Library; 1932.
National Defense Authorization Act for Fiscal Year 2020. 116th Cong (2019), Public Law 116-92. U.S. Government Printing Office. https://www.govinfo.gov/content/pkg/PLAW-116publ92/html/PLAW-116publ92.htm
Asch BJ, Rennane S, Trail TE, et al. Food insecurity among members of the armed forces and their dependents. RAND Corporation. January 3, 2023. Accessed September 22, 2025. https://www.rand.org/pubs/research_reports/RRA1230-1.html
US Department of Agriculture Economic Research Service. Food Security in the U.S.—Definitions of Food Security. US Department of Agriculture Economic Research Service. January 10, 2025. https://www.ers.usda.gov/topics/food-nutrition-assistance/food-security-in-the-us/definitions-of-food-security
Active military and veteran food insecurity. Feeding America. Accessed September 22, 2025. https://www.feedingamerica.org/hunger-in-america/food-insecurity-in-veterans
Pradun S. Find access to stop food insecurity in your community. VA News. September 19, 2025. Accessed September 22, 2025. https://news.va.gov/142733/find-access-stop-food-insecurity-your-community/
Cohen AJ, Dosa DM, Rudolph JL, et al. Risk factors for veteran food insecurity: findings from a National US Department of Veterans Affairs Food Insecurity Screener. Public Health Nutr. 2022;25:819-828. doi:10.1017/S1368980021004584
Chen C. VA and Rockefeller Foundation collaborate to access food for Veterans. VA News. September 5, 2023. Accessed September 22, 2025. https://news.va.gov/123228/va-rockefeller-foundation-expand-access-to-food/
Dawson MM. The Wisdom of Confucius: A Collection of the Ethical Sayings of Confucius and of his disciples. International Pocket Library; 1932.
National Defense Authorization Act for Fiscal Year 2020. 116th Cong (2019), Public Law 116-92. U.S. Government Printing Office. https://www.govinfo.gov/content/pkg/PLAW-116publ92/html/PLAW-116publ92.htm
Asch BJ, Rennane S, Trail TE, et al. Food insecurity among members of the armed forces and their dependents. RAND Corporation. January 3, 2023. Accessed September 22, 2025. https://www.rand.org/pubs/research_reports/RRA1230-1.html
US Department of Agriculture Economic Research Service. Food Security in the U.S.—Definitions of Food Security. US Department of Agriculture Economic Research Service. January 10, 2025. https://www.ers.usda.gov/topics/food-nutrition-assistance/food-security-in-the-us/definitions-of-food-security
Active military and veteran food insecurity. Feeding America. Accessed September 22, 2025. https://www.feedingamerica.org/hunger-in-america/food-insecurity-in-veterans
Pradun S. Find access to stop food insecurity in your community. VA News. September 19, 2025. Accessed September 22, 2025. https://news.va.gov/142733/find-access-stop-food-insecurity-your-community/
Cohen AJ, Dosa DM, Rudolph JL, et al. Risk factors for veteran food insecurity: findings from a National US Department of Veterans Affairs Food Insecurity Screener. Public Health Nutr. 2022;25:819-828. doi:10.1017/S1368980021004584
Chen C. VA and Rockefeller Foundation collaborate to access food for Veterans. VA News. September 5, 2023. Accessed September 22, 2025. https://news.va.gov/123228/va-rockefeller-foundation-expand-access-to-food/
American Hunger Games: Food Insecurity Among the Military and Veterans
American Hunger Games: Food Insecurity Among the Military and Veterans
