User login
To the Editor:
Several mole and skin tag removal products are available online and over the counter (OTC).1 Patients concerned with the cosmetic appearance of nevi may use these products as a do-it-yourself alternative to surgical removal. However, these products have the potential to cause harm.2 Beyond the cosmetic adverse effects of skin necrosis and scar formation, these products can mask premalignant and malignant skin lesions.2 Herein, we describe a patient with a family history of melanoma who developed facial and chest ulcerations with necrosis after applying an OTC mole and skin tag removal product.
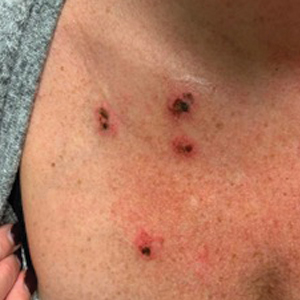
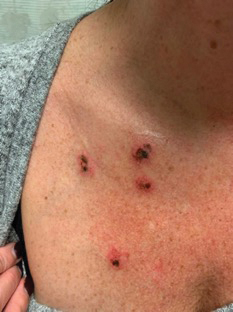
A 45-year-old woman with fair skin presented to a clinic with multiple superficial ulcerations measuring approximately 1 cm in diameter with necrotic black bases and erythematous rims on the face, right side of the upper chest, and left earlobe after using the Ariella Mole Corrector and Skin Tag Remover and Repair Lotion Set, an OTC mole and skin tag removal product. The patient reported using the product 24 hours prior for the cosmetic removal of multiple nevi. After applying the product, she observed that it “immediately melted [her] skin” and the areas where the product was applied “turned black.” She reported that the product was applied to the skin for no longer than 30 seconds, after which she developed the necrotic lesions (Figure). After removing the product, she applied an OTC ointment containing bacitracin, neomycin, and polymyxin B to the lesions.
The patient had no history of nonmelanoma skin cancers or atypical nevi. She had a family history of melanoma in her mother and maternal uncle. The treatment plan was aimed primarily at reducing scar formation. We advised frequent application of petroleum-based ointments for moisture and overlying silicone scar tape to protect the area from photodamage and promote wound healing. We further advocated for sun protection and the use of a physical sunscreen on the lesions as they healed. We discussed potential laser-based scar revision options in the future.
With more than 180 reviews on Amazon and almost 70% of these reviews made within the month prior to compiling this manuscript, the Ariella Mole Corrector and Skin Tag Remover and Repair Lotion Set appeared to be popular; however, the product currently is unavailable on Amazon. Testimonials and before-and-after pictures advertising the product show an all-natural, safe, and effective method as an alternative to surgical removal of skin tags and nevi. The product website claims that skin tags and moles will “fall off naturally within 7 to 10 days” and the product can be used for “almost all skin types.” Users are instructed to apply the removal product and wipe it off when the skin surrounding the mole becomes swollen. The product kit also includes a repair lotion, which claims to help heal the skin after scab formation and scar development.
The ingredients listed on the product packaging are salicylic acid 25%, Melaleuca alternifolia (tea tree) leaf oil, propylene glycol, hydroxyethylcellulose, and alcohol. Salicylic acid 25% is a superficial peeling agent that penetrates the epidermis to the dermoepidermal junction. The potential side effects are mild and include superficial desquamation and epidermolysis.3 The Ariella Mole Corrector and Skin Tag Remover and Repair Lotion Set is not regulated by the US Food and Drug Administration and may contain variable concentrations of salicylic acid and other unknown compounds. Higher concentrations of salicylic acid can penetrate the full thickness of the epidermis into the papillary dermis, which can result in postinflammatory pigmentation, superficial infection, scarring, and deeper desquamation and epidermolysis.3 The product website advertises the use of only natural ingredients and an “advanced blend of concentrated natural ingredients contributing a broad spectrum of healing properties” in the formula. Although these claims are attractive to patients seeking alternatives to surgical approaches to nevi removal, the unfounded claims and unregulated ingredients may pose a threat to unsuspecting consumers.
Other OTC and “all-natural” mole removal products previously have been reported to cause harm.2Sanguinaria canadensis, also known as bloodroot, contains an alkaloid compound (sanguinarine) that has been shown to induce mitochondrial apoptosis and activation of Bcl-2 proteins in keratinocytes.4 Some products, such as Wart & Mole Vanish cream, may claim not to contain bloodroot specifically. However, sanguinarine can be extracted from other plants and may be listed as Argemone mexicana, Chelidonium majus, or Macleaya cordata in the ingredients list.5 The use of alternative medicine products such as black or yellow salve for the removal of suspected skin cancers also is not recommended because these escharotic treatments have not been proven safe or effective, and the manufacturing process for these compounds is unregulated.6,7 Self-treatment with alternative remedies for nevi or suspected skin cancers has been associated with progression of disease and even death due to metastatic spread.2
Self-removal of moles is concerning because the nevi are masked by necrotic lesions and can no longer be assessed by dermoscopy or histopathology. Furthermore, the compounds in the Ariella Mole Corrector and Skin Tag Remover and Repair Lotion Set may have unknown effects on the transformation of premalignant cells. They also may mask an underlying process for which clinically proven and effective treatments such as cryotherapy, prescription topical agents, and surgical excision are warranted. Awareness of this product and similar products is important to educate patients on the harmful effects they may cause.
- Clayton R, Turner R. Cosmetic surgery: who needs surgeons when you’ve got creams? Br J Dermatol. 2007;156:1383-1384.
- McAllister JC, Petzold CR, Lio PA. Adverse effects of a mole removal cream. Pediatr Dermatol. 2009;26:628-629.
- Soleymani T, Lanoue J, Rahman Z. A practical approach to chemical peels: a review of fundamentals and step-by-step algorithmic protocol for treatment. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2018;11:21-28.
- Adhami VM, Aziz MH, Mukhatar M, et al. Activation of prodeath Bcl-2 family proteins and mitochondrial apoptosis pathway by sanguinarine in immortalized human HaCaT keratinocytes. Clin Cancer Res. 2003;9:3176-3182.
- Santos AC, Adkilen P. The alkaloids of Argemone mexicana. J Am Chem Soc. 1932;54:2923-2924.
- Osswald SS, Elston DM, Farley MF, et al. Self-treatment of a basal cell carcinoma with “black and yellow salve.” J Am Acad Dermatol. 2005;53:509-511.
- McDaniel S, Goldman GD. Consequences of using escharotic agents as primary treatment for nonmelanoma skin cancer. Arch Dermatol. 2002;138:1593-1596.
To the Editor:
Several mole and skin tag removal products are available online and over the counter (OTC).1 Patients concerned with the cosmetic appearance of nevi may use these products as a do-it-yourself alternative to surgical removal. However, these products have the potential to cause harm.2 Beyond the cosmetic adverse effects of skin necrosis and scar formation, these products can mask premalignant and malignant skin lesions.2 Herein, we describe a patient with a family history of melanoma who developed facial and chest ulcerations with necrosis after applying an OTC mole and skin tag removal product.
A 45-year-old woman with fair skin presented to a clinic with multiple superficial ulcerations measuring approximately 1 cm in diameter with necrotic black bases and erythematous rims on the face, right side of the upper chest, and left earlobe after using the Ariella Mole Corrector and Skin Tag Remover and Repair Lotion Set, an OTC mole and skin tag removal product. The patient reported using the product 24 hours prior for the cosmetic removal of multiple nevi. After applying the product, she observed that it “immediately melted [her] skin” and the areas where the product was applied “turned black.” She reported that the product was applied to the skin for no longer than 30 seconds, after which she developed the necrotic lesions (Figure). After removing the product, she applied an OTC ointment containing bacitracin, neomycin, and polymyxin B to the lesions.

The patient had no history of nonmelanoma skin cancers or atypical nevi. She had a family history of melanoma in her mother and maternal uncle. The treatment plan was aimed primarily at reducing scar formation. We advised frequent application of petroleum-based ointments for moisture and overlying silicone scar tape to protect the area from photodamage and promote wound healing. We further advocated for sun protection and the use of a physical sunscreen on the lesions as they healed. We discussed potential laser-based scar revision options in the future.
With more than 180 reviews on Amazon and almost 70% of these reviews made within the month prior to compiling this manuscript, the Ariella Mole Corrector and Skin Tag Remover and Repair Lotion Set appeared to be popular; however, the product currently is unavailable on Amazon. Testimonials and before-and-after pictures advertising the product show an all-natural, safe, and effective method as an alternative to surgical removal of skin tags and nevi. The product website claims that skin tags and moles will “fall off naturally within 7 to 10 days” and the product can be used for “almost all skin types.” Users are instructed to apply the removal product and wipe it off when the skin surrounding the mole becomes swollen. The product kit also includes a repair lotion, which claims to help heal the skin after scab formation and scar development.
The ingredients listed on the product packaging are salicylic acid 25%, Melaleuca alternifolia (tea tree) leaf oil, propylene glycol, hydroxyethylcellulose, and alcohol. Salicylic acid 25% is a superficial peeling agent that penetrates the epidermis to the dermoepidermal junction. The potential side effects are mild and include superficial desquamation and epidermolysis.3 The Ariella Mole Corrector and Skin Tag Remover and Repair Lotion Set is not regulated by the US Food and Drug Administration and may contain variable concentrations of salicylic acid and other unknown compounds. Higher concentrations of salicylic acid can penetrate the full thickness of the epidermis into the papillary dermis, which can result in postinflammatory pigmentation, superficial infection, scarring, and deeper desquamation and epidermolysis.3 The product website advertises the use of only natural ingredients and an “advanced blend of concentrated natural ingredients contributing a broad spectrum of healing properties” in the formula. Although these claims are attractive to patients seeking alternatives to surgical approaches to nevi removal, the unfounded claims and unregulated ingredients may pose a threat to unsuspecting consumers.
Other OTC and “all-natural” mole removal products previously have been reported to cause harm.2Sanguinaria canadensis, also known as bloodroot, contains an alkaloid compound (sanguinarine) that has been shown to induce mitochondrial apoptosis and activation of Bcl-2 proteins in keratinocytes.4 Some products, such as Wart & Mole Vanish cream, may claim not to contain bloodroot specifically. However, sanguinarine can be extracted from other plants and may be listed as Argemone mexicana, Chelidonium majus, or Macleaya cordata in the ingredients list.5 The use of alternative medicine products such as black or yellow salve for the removal of suspected skin cancers also is not recommended because these escharotic treatments have not been proven safe or effective, and the manufacturing process for these compounds is unregulated.6,7 Self-treatment with alternative remedies for nevi or suspected skin cancers has been associated with progression of disease and even death due to metastatic spread.2
Self-removal of moles is concerning because the nevi are masked by necrotic lesions and can no longer be assessed by dermoscopy or histopathology. Furthermore, the compounds in the Ariella Mole Corrector and Skin Tag Remover and Repair Lotion Set may have unknown effects on the transformation of premalignant cells. They also may mask an underlying process for which clinically proven and effective treatments such as cryotherapy, prescription topical agents, and surgical excision are warranted. Awareness of this product and similar products is important to educate patients on the harmful effects they may cause.
To the Editor:
Several mole and skin tag removal products are available online and over the counter (OTC).1 Patients concerned with the cosmetic appearance of nevi may use these products as a do-it-yourself alternative to surgical removal. However, these products have the potential to cause harm.2 Beyond the cosmetic adverse effects of skin necrosis and scar formation, these products can mask premalignant and malignant skin lesions.2 Herein, we describe a patient with a family history of melanoma who developed facial and chest ulcerations with necrosis after applying an OTC mole and skin tag removal product.
A 45-year-old woman with fair skin presented to a clinic with multiple superficial ulcerations measuring approximately 1 cm in diameter with necrotic black bases and erythematous rims on the face, right side of the upper chest, and left earlobe after using the Ariella Mole Corrector and Skin Tag Remover and Repair Lotion Set, an OTC mole and skin tag removal product. The patient reported using the product 24 hours prior for the cosmetic removal of multiple nevi. After applying the product, she observed that it “immediately melted [her] skin” and the areas where the product was applied “turned black.” She reported that the product was applied to the skin for no longer than 30 seconds, after which she developed the necrotic lesions (Figure). After removing the product, she applied an OTC ointment containing bacitracin, neomycin, and polymyxin B to the lesions.

The patient had no history of nonmelanoma skin cancers or atypical nevi. She had a family history of melanoma in her mother and maternal uncle. The treatment plan was aimed primarily at reducing scar formation. We advised frequent application of petroleum-based ointments for moisture and overlying silicone scar tape to protect the area from photodamage and promote wound healing. We further advocated for sun protection and the use of a physical sunscreen on the lesions as they healed. We discussed potential laser-based scar revision options in the future.
With more than 180 reviews on Amazon and almost 70% of these reviews made within the month prior to compiling this manuscript, the Ariella Mole Corrector and Skin Tag Remover and Repair Lotion Set appeared to be popular; however, the product currently is unavailable on Amazon. Testimonials and before-and-after pictures advertising the product show an all-natural, safe, and effective method as an alternative to surgical removal of skin tags and nevi. The product website claims that skin tags and moles will “fall off naturally within 7 to 10 days” and the product can be used for “almost all skin types.” Users are instructed to apply the removal product and wipe it off when the skin surrounding the mole becomes swollen. The product kit also includes a repair lotion, which claims to help heal the skin after scab formation and scar development.
The ingredients listed on the product packaging are salicylic acid 25%, Melaleuca alternifolia (tea tree) leaf oil, propylene glycol, hydroxyethylcellulose, and alcohol. Salicylic acid 25% is a superficial peeling agent that penetrates the epidermis to the dermoepidermal junction. The potential side effects are mild and include superficial desquamation and epidermolysis.3 The Ariella Mole Corrector and Skin Tag Remover and Repair Lotion Set is not regulated by the US Food and Drug Administration and may contain variable concentrations of salicylic acid and other unknown compounds. Higher concentrations of salicylic acid can penetrate the full thickness of the epidermis into the papillary dermis, which can result in postinflammatory pigmentation, superficial infection, scarring, and deeper desquamation and epidermolysis.3 The product website advertises the use of only natural ingredients and an “advanced blend of concentrated natural ingredients contributing a broad spectrum of healing properties” in the formula. Although these claims are attractive to patients seeking alternatives to surgical approaches to nevi removal, the unfounded claims and unregulated ingredients may pose a threat to unsuspecting consumers.
Other OTC and “all-natural” mole removal products previously have been reported to cause harm.2Sanguinaria canadensis, also known as bloodroot, contains an alkaloid compound (sanguinarine) that has been shown to induce mitochondrial apoptosis and activation of Bcl-2 proteins in keratinocytes.4 Some products, such as Wart & Mole Vanish cream, may claim not to contain bloodroot specifically. However, sanguinarine can be extracted from other plants and may be listed as Argemone mexicana, Chelidonium majus, or Macleaya cordata in the ingredients list.5 The use of alternative medicine products such as black or yellow salve for the removal of suspected skin cancers also is not recommended because these escharotic treatments have not been proven safe or effective, and the manufacturing process for these compounds is unregulated.6,7 Self-treatment with alternative remedies for nevi or suspected skin cancers has been associated with progression of disease and even death due to metastatic spread.2
Self-removal of moles is concerning because the nevi are masked by necrotic lesions and can no longer be assessed by dermoscopy or histopathology. Furthermore, the compounds in the Ariella Mole Corrector and Skin Tag Remover and Repair Lotion Set may have unknown effects on the transformation of premalignant cells. They also may mask an underlying process for which clinically proven and effective treatments such as cryotherapy, prescription topical agents, and surgical excision are warranted. Awareness of this product and similar products is important to educate patients on the harmful effects they may cause.
- Clayton R, Turner R. Cosmetic surgery: who needs surgeons when you’ve got creams? Br J Dermatol. 2007;156:1383-1384.
- McAllister JC, Petzold CR, Lio PA. Adverse effects of a mole removal cream. Pediatr Dermatol. 2009;26:628-629.
- Soleymani T, Lanoue J, Rahman Z. A practical approach to chemical peels: a review of fundamentals and step-by-step algorithmic protocol for treatment. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2018;11:21-28.
- Adhami VM, Aziz MH, Mukhatar M, et al. Activation of prodeath Bcl-2 family proteins and mitochondrial apoptosis pathway by sanguinarine in immortalized human HaCaT keratinocytes. Clin Cancer Res. 2003;9:3176-3182.
- Santos AC, Adkilen P. The alkaloids of Argemone mexicana. J Am Chem Soc. 1932;54:2923-2924.
- Osswald SS, Elston DM, Farley MF, et al. Self-treatment of a basal cell carcinoma with “black and yellow salve.” J Am Acad Dermatol. 2005;53:509-511.
- McDaniel S, Goldman GD. Consequences of using escharotic agents as primary treatment for nonmelanoma skin cancer. Arch Dermatol. 2002;138:1593-1596.
- Clayton R, Turner R. Cosmetic surgery: who needs surgeons when you’ve got creams? Br J Dermatol. 2007;156:1383-1384.
- McAllister JC, Petzold CR, Lio PA. Adverse effects of a mole removal cream. Pediatr Dermatol. 2009;26:628-629.
- Soleymani T, Lanoue J, Rahman Z. A practical approach to chemical peels: a review of fundamentals and step-by-step algorithmic protocol for treatment. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2018;11:21-28.
- Adhami VM, Aziz MH, Mukhatar M, et al. Activation of prodeath Bcl-2 family proteins and mitochondrial apoptosis pathway by sanguinarine in immortalized human HaCaT keratinocytes. Clin Cancer Res. 2003;9:3176-3182.
- Santos AC, Adkilen P. The alkaloids of Argemone mexicana. J Am Chem Soc. 1932;54:2923-2924.
- Osswald SS, Elston DM, Farley MF, et al. Self-treatment of a basal cell carcinoma with “black and yellow salve.” J Am Acad Dermatol. 2005;53:509-511.
- McDaniel S, Goldman GD. Consequences of using escharotic agents as primary treatment for nonmelanoma skin cancer. Arch Dermatol. 2002;138:1593-1596.
Practice Point
- Self-administered mole and skin tag removal products are rising in popularity, but unregulated ingredients in over-the-counter products that are not approved by the US Food and Drug Administration may mask underlying transformation of atypical nevi.