User login
2022 Update on pelvic floor dysfunction
Knowledge of the latest evidence on the management of pelvic floor disorders is essential for all practicing ObGyns. In this Update, we review long-term outcomes for a polyacrylamide hydrogel urethral bulking agent for the treatment of stress urinary incontinence (SUI) that presents a viable alternative to the gold standard, midurethral sling. We review the new recommendations from the American Urogynecologic Society (AUGS) regarding the administration of anticholinergics, highlighting a paradigm shift in the management of overactive bladder (OAB). In addition, we present data on a proposed threshold glycosylated hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) level for patients undergoing pelvic organ prolapse (POP) surgery that may help reduce the risk of perioperative complications. Finally, we consider new evidence on the long-term efficacy and safety of transvaginal mesh for repair of POP.
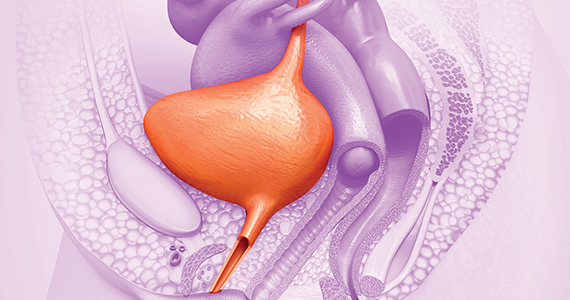
Periurethral injection with polyacrylamide hydrogel is a long-term durable and safe option for women with SUI
Brosche T, Kuhn A, Lobodasch K, et al. Seven-year efficacy and safety outcomes of Bulkamid for the treatment of stress urinary incontinence. Neurourol Urodyn. 2021;40:502-508. doi:10.1002/nau.24589.
Urethral bulking agents are a less invasive management option for women with SUI compared with the gold standard, midurethral sling. Treatment with a polyacrylamide hydrogel (PAHG; Bulkamid)—a nonparticulate hydrogel bulking agent—showed long-term efficacy and a favorable safety profile at 7 years’ follow-up.
Study details
Brosche and colleagues conducted a retrospective cohort study that included women with SUI or stress-predominant mixed urinary incontinence (MUI) who underwent transurethral PAHG injections for primary treatment of their incontinence symptoms. The study objective was to evaluate the long-term efficacy of PAHG based on patient satisfaction. Treatment safety was a secondary outcome.
Pad counts and validated questionnaires were used to determine treatment effectiveness. Additional data on reinjection rates, perioperative complications, and postoperative complications also were collected.
Long-term outcomes favorable
During the study time period, 1,200 patients were treated with PAHG, and 7-year data were available for 553 women. Of the 553 patients, 67% reported improvement or cure of their SUI symptoms when PAHG was performed as a primary procedure, consistent with previously published 12-month data. There were no perioperative complications. Postoperative complications were transient. Short-term subjective prolonged bladder emptying was the most common complication and occurred in 15% of patients.
PAHG injection is a durable and safe alternative for the treatment of stress urinary incontinence in women who are not candidates for or who decline treatment with alternative methods, such as a midurethral sling.
Continue to: New society guidance...
New society guidance on the use of anticholinergic medications for the treatment of OAB
AUGS Clinical Consensus Statement: Association of anticholinergic medication use and cognition in women with overactive bladder. Female Pelvic Med Reconstr Surg. 2021;27:69-71. doi:10.1097/ SPV.0000000000001008.
In 2021, AUGS updated its consensus statement on the use of anticholinergic medications for the treatment of OAB. This action was in response to growing evidence that supports the association of anticholinergic medications with long-term cognitive adverse effects, including cognitive impairment, dementia, and Alzheimer disease.
Here, we summarize the most recent modifications, which differentiate the updated statement from the preceding consensus document published in 2017.
Updated AUGS recommendations
- If considering anticholinergic medications, counsel patients about the risk of cognitive adverse effects and weigh these risks against the potential benefits to their quality of life and overall health.
- Use the lowest possible dose when prescribing anticholinergics and consider alternatives such as β3 agonists (for example, mirabegron or vibegron).
- Avoid using anticholinergic medications in women older than age 70. However, if an anticholinergic must be used, consider a medication that has low potential to cross the blood-brain barrier (for example, trospium).
For patients who are unresponsive to behavioral therapies for OAB, medical management may be considered. However, the risks of anticholinergic medications may outweigh the benefits—especially for older women—and these medications should be prescribed with caution after discussing the potential cognitive adverse effects with patients. β3 agonists should be preferentially prescribed when appropriate. Consider referral to a urogynecologist for discussion of third-line therapies in patients who prefer to forego or may not be candidates for medical management of their OAB symptoms.
HbA1c levels > 8% may increase complications risk in urogyn surgery
Ringel NE, de Winter KL, Siddique M, et al. Surgical outcomes in urogynecology—assessment of perioperative and postoperative complications relative to preoperative hemoglobin A1c—a Fellows Pelvic Research Network study. Female Pelvic Med Reconstr Surg. 2022;28:7-13. doi:10.1097/ SPV.0000000000001057.
Diabetes mellitus is a known risk factor for complications following surgery. Adoption of an HbA1c level threshold for risk stratification before urogynecologic surgery may help improve patient outcomes.
Study details
Ringel and colleagues conducted a multicenter retrospective cohort study that included women with diabetes mellitus who underwent prolapse and/or SUI surgery between 2013 and 2018. The aim of the study was to identify a hemoglobin A1C threshold that would help predict increased risk for perioperative complications in women undergoing pelvic reconstructive surgery. Demographics, preoperative HbA1c levels, and surgical data were collected.
Complication risks correlated with higher HbA1c threshold
The study included 807 women with HbA1c values that ranged from 5% to 12%. The overall complication rate was 44%. Sensitivity analysis was performed to compare complication rates between patients with varying HbA1c levels and determine a threshold HbA1c value with the greatest difference in complication rates.
The authors concluded that women with an HbA1c level ≥ 8% showed the greatest increase of perioperative complications. Patients with an HbA1c ≥ 8%, compared with those who had an HbA1c < 8%, had a statistically significantly increased rate of overall (58% vs 42%, P = .002) and severe (27% vs 13%, P< .001) perioperative complications.
After multivariate logistic regression, the risk of overall complications remained elevated, with a 1.9-times higher risk of perioperative complications for women with an HbA1c ≥ 8%.
Women should be medically optimized before undergoing surgery and, while this study was restricted to urogynecologic surgery patients, it seems reasonable to assume that a similar HbA1c threshold would be beneficial for women undergoing other gynecologic procedures. Appropriately screening patients and referring them for early intervention with their primary care clinician or endocrinologist may improve surgical outcomes, especially in women with an HbA1c level > 8%.
Continue to: Success is similar for TV mesh and native tissue repair...
Success is similar for TV mesh and native tissue repair
Kahn B, Varner RE, Murphy M, et al. Transvaginal mesh compared with native tissue repair for pelvic organ prolapse. Obstet Gynecol. 2022;139:975-985. doi:10.1097/AOG.0000000000004794.
The distribution of vaginal mesh kits for the repair of POP was halted by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in 2019. However, concerns have been raised about the measures used by the FDA to justify pulling these devices from the market. A cohort study compared 36-month outcomes between women who underwent prolapse repair with newer generation transvaginal mesh versus native tissue repair.
Study details
In a nonrandomized prospective multicenter cohort study, Kahn and colleagues compared outcomes in women with POP who underwent native tissue repair or transvaginal mesh repair with the Uphold LITE vaginal support system. The study’s objective was to compare the safety and efficacy of native tissue and transvaginal mesh prolapse repairs at 36 months postoperatively.
Treatment success was measured based on composite and individual measures of anatomic and subjective success, need for retreatment, and the occurrence of adverse events. Quality of life (QoL) measures also were obtained using validated questionnaires. Intention-to-treat and per-protocol analyses were performed.
Composite success rate was higher for mesh repair
A total of 710 patients were screened for eligibility (225 received transvaginal mesh and 485 received native tissue repair). Transvaginal mesh placement was found to be significantly superior to native tissue repair for composite success (84% vs 73%, P = .009) when prolapse within the hymen (that is, Ba and/or C < 0 on the Pelvic Organ Prolapse Quantification System) was used to define anatomic success.
Adverse events were similar between transvaginal mesh and native tissue repair groups, with most adverse events occurring within the first 6 months. The mesh exposure rate was 4.9%. Of the 13 incidents of mesh exposure, 4 patients required surgical intervention and 1 incident was considered a serious adverse event. QoL measures demonstrated improvement without any statistically significant differences between the treatment cohorts. ●
This study established the superiority and safety of newer generation transvaginal mesh used for the treatment of pelvic organ prolapse. Women who received newer generation transvaginal mesh can be reassured that the prolapse recurrence rates are low and that adverse events related to their mesh are rare—even when compared with those of native tissue repair. Patients also may be reassured that most adverse events would have occurred within 6 months of the initial prolapse repair surgery
Knowledge of the latest evidence on the management of pelvic floor disorders is essential for all practicing ObGyns. In this Update, we review long-term outcomes for a polyacrylamide hydrogel urethral bulking agent for the treatment of stress urinary incontinence (SUI) that presents a viable alternative to the gold standard, midurethral sling. We review the new recommendations from the American Urogynecologic Society (AUGS) regarding the administration of anticholinergics, highlighting a paradigm shift in the management of overactive bladder (OAB). In addition, we present data on a proposed threshold glycosylated hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) level for patients undergoing pelvic organ prolapse (POP) surgery that may help reduce the risk of perioperative complications. Finally, we consider new evidence on the long-term efficacy and safety of transvaginal mesh for repair of POP.
Periurethral injection with polyacrylamide hydrogel is a long-term durable and safe option for women with SUI
Brosche T, Kuhn A, Lobodasch K, et al. Seven-year efficacy and safety outcomes of Bulkamid for the treatment of stress urinary incontinence. Neurourol Urodyn. 2021;40:502-508. doi:10.1002/nau.24589.
Urethral bulking agents are a less invasive management option for women with SUI compared with the gold standard, midurethral sling. Treatment with a polyacrylamide hydrogel (PAHG; Bulkamid)—a nonparticulate hydrogel bulking agent—showed long-term efficacy and a favorable safety profile at 7 years’ follow-up.
Study details
Brosche and colleagues conducted a retrospective cohort study that included women with SUI or stress-predominant mixed urinary incontinence (MUI) who underwent transurethral PAHG injections for primary treatment of their incontinence symptoms. The study objective was to evaluate the long-term efficacy of PAHG based on patient satisfaction. Treatment safety was a secondary outcome.
Pad counts and validated questionnaires were used to determine treatment effectiveness. Additional data on reinjection rates, perioperative complications, and postoperative complications also were collected.
Long-term outcomes favorable
During the study time period, 1,200 patients were treated with PAHG, and 7-year data were available for 553 women. Of the 553 patients, 67% reported improvement or cure of their SUI symptoms when PAHG was performed as a primary procedure, consistent with previously published 12-month data. There were no perioperative complications. Postoperative complications were transient. Short-term subjective prolonged bladder emptying was the most common complication and occurred in 15% of patients.
PAHG injection is a durable and safe alternative for the treatment of stress urinary incontinence in women who are not candidates for or who decline treatment with alternative methods, such as a midurethral sling.
Continue to: New society guidance...
New society guidance on the use of anticholinergic medications for the treatment of OAB
AUGS Clinical Consensus Statement: Association of anticholinergic medication use and cognition in women with overactive bladder. Female Pelvic Med Reconstr Surg. 2021;27:69-71. doi:10.1097/ SPV.0000000000001008.
In 2021, AUGS updated its consensus statement on the use of anticholinergic medications for the treatment of OAB. This action was in response to growing evidence that supports the association of anticholinergic medications with long-term cognitive adverse effects, including cognitive impairment, dementia, and Alzheimer disease.
Here, we summarize the most recent modifications, which differentiate the updated statement from the preceding consensus document published in 2017.
Updated AUGS recommendations
- If considering anticholinergic medications, counsel patients about the risk of cognitive adverse effects and weigh these risks against the potential benefits to their quality of life and overall health.
- Use the lowest possible dose when prescribing anticholinergics and consider alternatives such as β3 agonists (for example, mirabegron or vibegron).
- Avoid using anticholinergic medications in women older than age 70. However, if an anticholinergic must be used, consider a medication that has low potential to cross the blood-brain barrier (for example, trospium).
For patients who are unresponsive to behavioral therapies for OAB, medical management may be considered. However, the risks of anticholinergic medications may outweigh the benefits—especially for older women—and these medications should be prescribed with caution after discussing the potential cognitive adverse effects with patients. β3 agonists should be preferentially prescribed when appropriate. Consider referral to a urogynecologist for discussion of third-line therapies in patients who prefer to forego or may not be candidates for medical management of their OAB symptoms.
HbA1c levels > 8% may increase complications risk in urogyn surgery
Ringel NE, de Winter KL, Siddique M, et al. Surgical outcomes in urogynecology—assessment of perioperative and postoperative complications relative to preoperative hemoglobin A1c—a Fellows Pelvic Research Network study. Female Pelvic Med Reconstr Surg. 2022;28:7-13. doi:10.1097/ SPV.0000000000001057.
Diabetes mellitus is a known risk factor for complications following surgery. Adoption of an HbA1c level threshold for risk stratification before urogynecologic surgery may help improve patient outcomes.
Study details
Ringel and colleagues conducted a multicenter retrospective cohort study that included women with diabetes mellitus who underwent prolapse and/or SUI surgery between 2013 and 2018. The aim of the study was to identify a hemoglobin A1C threshold that would help predict increased risk for perioperative complications in women undergoing pelvic reconstructive surgery. Demographics, preoperative HbA1c levels, and surgical data were collected.
Complication risks correlated with higher HbA1c threshold
The study included 807 women with HbA1c values that ranged from 5% to 12%. The overall complication rate was 44%. Sensitivity analysis was performed to compare complication rates between patients with varying HbA1c levels and determine a threshold HbA1c value with the greatest difference in complication rates.
The authors concluded that women with an HbA1c level ≥ 8% showed the greatest increase of perioperative complications. Patients with an HbA1c ≥ 8%, compared with those who had an HbA1c < 8%, had a statistically significantly increased rate of overall (58% vs 42%, P = .002) and severe (27% vs 13%, P< .001) perioperative complications.
After multivariate logistic regression, the risk of overall complications remained elevated, with a 1.9-times higher risk of perioperative complications for women with an HbA1c ≥ 8%.
Women should be medically optimized before undergoing surgery and, while this study was restricted to urogynecologic surgery patients, it seems reasonable to assume that a similar HbA1c threshold would be beneficial for women undergoing other gynecologic procedures. Appropriately screening patients and referring them for early intervention with their primary care clinician or endocrinologist may improve surgical outcomes, especially in women with an HbA1c level > 8%.
Continue to: Success is similar for TV mesh and native tissue repair...
Success is similar for TV mesh and native tissue repair
Kahn B, Varner RE, Murphy M, et al. Transvaginal mesh compared with native tissue repair for pelvic organ prolapse. Obstet Gynecol. 2022;139:975-985. doi:10.1097/AOG.0000000000004794.
The distribution of vaginal mesh kits for the repair of POP was halted by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in 2019. However, concerns have been raised about the measures used by the FDA to justify pulling these devices from the market. A cohort study compared 36-month outcomes between women who underwent prolapse repair with newer generation transvaginal mesh versus native tissue repair.
Study details
In a nonrandomized prospective multicenter cohort study, Kahn and colleagues compared outcomes in women with POP who underwent native tissue repair or transvaginal mesh repair with the Uphold LITE vaginal support system. The study’s objective was to compare the safety and efficacy of native tissue and transvaginal mesh prolapse repairs at 36 months postoperatively.
Treatment success was measured based on composite and individual measures of anatomic and subjective success, need for retreatment, and the occurrence of adverse events. Quality of life (QoL) measures also were obtained using validated questionnaires. Intention-to-treat and per-protocol analyses were performed.
Composite success rate was higher for mesh repair
A total of 710 patients were screened for eligibility (225 received transvaginal mesh and 485 received native tissue repair). Transvaginal mesh placement was found to be significantly superior to native tissue repair for composite success (84% vs 73%, P = .009) when prolapse within the hymen (that is, Ba and/or C < 0 on the Pelvic Organ Prolapse Quantification System) was used to define anatomic success.
Adverse events were similar between transvaginal mesh and native tissue repair groups, with most adverse events occurring within the first 6 months. The mesh exposure rate was 4.9%. Of the 13 incidents of mesh exposure, 4 patients required surgical intervention and 1 incident was considered a serious adverse event. QoL measures demonstrated improvement without any statistically significant differences between the treatment cohorts. ●
This study established the superiority and safety of newer generation transvaginal mesh used for the treatment of pelvic organ prolapse. Women who received newer generation transvaginal mesh can be reassured that the prolapse recurrence rates are low and that adverse events related to their mesh are rare—even when compared with those of native tissue repair. Patients also may be reassured that most adverse events would have occurred within 6 months of the initial prolapse repair surgery
Knowledge of the latest evidence on the management of pelvic floor disorders is essential for all practicing ObGyns. In this Update, we review long-term outcomes for a polyacrylamide hydrogel urethral bulking agent for the treatment of stress urinary incontinence (SUI) that presents a viable alternative to the gold standard, midurethral sling. We review the new recommendations from the American Urogynecologic Society (AUGS) regarding the administration of anticholinergics, highlighting a paradigm shift in the management of overactive bladder (OAB). In addition, we present data on a proposed threshold glycosylated hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) level for patients undergoing pelvic organ prolapse (POP) surgery that may help reduce the risk of perioperative complications. Finally, we consider new evidence on the long-term efficacy and safety of transvaginal mesh for repair of POP.
Periurethral injection with polyacrylamide hydrogel is a long-term durable and safe option for women with SUI
Brosche T, Kuhn A, Lobodasch K, et al. Seven-year efficacy and safety outcomes of Bulkamid for the treatment of stress urinary incontinence. Neurourol Urodyn. 2021;40:502-508. doi:10.1002/nau.24589.
Urethral bulking agents are a less invasive management option for women with SUI compared with the gold standard, midurethral sling. Treatment with a polyacrylamide hydrogel (PAHG; Bulkamid)—a nonparticulate hydrogel bulking agent—showed long-term efficacy and a favorable safety profile at 7 years’ follow-up.
Study details
Brosche and colleagues conducted a retrospective cohort study that included women with SUI or stress-predominant mixed urinary incontinence (MUI) who underwent transurethral PAHG injections for primary treatment of their incontinence symptoms. The study objective was to evaluate the long-term efficacy of PAHG based on patient satisfaction. Treatment safety was a secondary outcome.
Pad counts and validated questionnaires were used to determine treatment effectiveness. Additional data on reinjection rates, perioperative complications, and postoperative complications also were collected.
Long-term outcomes favorable
During the study time period, 1,200 patients were treated with PAHG, and 7-year data were available for 553 women. Of the 553 patients, 67% reported improvement or cure of their SUI symptoms when PAHG was performed as a primary procedure, consistent with previously published 12-month data. There were no perioperative complications. Postoperative complications were transient. Short-term subjective prolonged bladder emptying was the most common complication and occurred in 15% of patients.
PAHG injection is a durable and safe alternative for the treatment of stress urinary incontinence in women who are not candidates for or who decline treatment with alternative methods, such as a midurethral sling.
Continue to: New society guidance...
New society guidance on the use of anticholinergic medications for the treatment of OAB
AUGS Clinical Consensus Statement: Association of anticholinergic medication use and cognition in women with overactive bladder. Female Pelvic Med Reconstr Surg. 2021;27:69-71. doi:10.1097/ SPV.0000000000001008.
In 2021, AUGS updated its consensus statement on the use of anticholinergic medications for the treatment of OAB. This action was in response to growing evidence that supports the association of anticholinergic medications with long-term cognitive adverse effects, including cognitive impairment, dementia, and Alzheimer disease.
Here, we summarize the most recent modifications, which differentiate the updated statement from the preceding consensus document published in 2017.
Updated AUGS recommendations
- If considering anticholinergic medications, counsel patients about the risk of cognitive adverse effects and weigh these risks against the potential benefits to their quality of life and overall health.
- Use the lowest possible dose when prescribing anticholinergics and consider alternatives such as β3 agonists (for example, mirabegron or vibegron).
- Avoid using anticholinergic medications in women older than age 70. However, if an anticholinergic must be used, consider a medication that has low potential to cross the blood-brain barrier (for example, trospium).
For patients who are unresponsive to behavioral therapies for OAB, medical management may be considered. However, the risks of anticholinergic medications may outweigh the benefits—especially for older women—and these medications should be prescribed with caution after discussing the potential cognitive adverse effects with patients. β3 agonists should be preferentially prescribed when appropriate. Consider referral to a urogynecologist for discussion of third-line therapies in patients who prefer to forego or may not be candidates for medical management of their OAB symptoms.
HbA1c levels > 8% may increase complications risk in urogyn surgery
Ringel NE, de Winter KL, Siddique M, et al. Surgical outcomes in urogynecology—assessment of perioperative and postoperative complications relative to preoperative hemoglobin A1c—a Fellows Pelvic Research Network study. Female Pelvic Med Reconstr Surg. 2022;28:7-13. doi:10.1097/ SPV.0000000000001057.
Diabetes mellitus is a known risk factor for complications following surgery. Adoption of an HbA1c level threshold for risk stratification before urogynecologic surgery may help improve patient outcomes.
Study details
Ringel and colleagues conducted a multicenter retrospective cohort study that included women with diabetes mellitus who underwent prolapse and/or SUI surgery between 2013 and 2018. The aim of the study was to identify a hemoglobin A1C threshold that would help predict increased risk for perioperative complications in women undergoing pelvic reconstructive surgery. Demographics, preoperative HbA1c levels, and surgical data were collected.
Complication risks correlated with higher HbA1c threshold
The study included 807 women with HbA1c values that ranged from 5% to 12%. The overall complication rate was 44%. Sensitivity analysis was performed to compare complication rates between patients with varying HbA1c levels and determine a threshold HbA1c value with the greatest difference in complication rates.
The authors concluded that women with an HbA1c level ≥ 8% showed the greatest increase of perioperative complications. Patients with an HbA1c ≥ 8%, compared with those who had an HbA1c < 8%, had a statistically significantly increased rate of overall (58% vs 42%, P = .002) and severe (27% vs 13%, P< .001) perioperative complications.
After multivariate logistic regression, the risk of overall complications remained elevated, with a 1.9-times higher risk of perioperative complications for women with an HbA1c ≥ 8%.
Women should be medically optimized before undergoing surgery and, while this study was restricted to urogynecologic surgery patients, it seems reasonable to assume that a similar HbA1c threshold would be beneficial for women undergoing other gynecologic procedures. Appropriately screening patients and referring them for early intervention with their primary care clinician or endocrinologist may improve surgical outcomes, especially in women with an HbA1c level > 8%.
Continue to: Success is similar for TV mesh and native tissue repair...
Success is similar for TV mesh and native tissue repair
Kahn B, Varner RE, Murphy M, et al. Transvaginal mesh compared with native tissue repair for pelvic organ prolapse. Obstet Gynecol. 2022;139:975-985. doi:10.1097/AOG.0000000000004794.
The distribution of vaginal mesh kits for the repair of POP was halted by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in 2019. However, concerns have been raised about the measures used by the FDA to justify pulling these devices from the market. A cohort study compared 36-month outcomes between women who underwent prolapse repair with newer generation transvaginal mesh versus native tissue repair.
Study details
In a nonrandomized prospective multicenter cohort study, Kahn and colleagues compared outcomes in women with POP who underwent native tissue repair or transvaginal mesh repair with the Uphold LITE vaginal support system. The study’s objective was to compare the safety and efficacy of native tissue and transvaginal mesh prolapse repairs at 36 months postoperatively.
Treatment success was measured based on composite and individual measures of anatomic and subjective success, need for retreatment, and the occurrence of adverse events. Quality of life (QoL) measures also were obtained using validated questionnaires. Intention-to-treat and per-protocol analyses were performed.
Composite success rate was higher for mesh repair
A total of 710 patients were screened for eligibility (225 received transvaginal mesh and 485 received native tissue repair). Transvaginal mesh placement was found to be significantly superior to native tissue repair for composite success (84% vs 73%, P = .009) when prolapse within the hymen (that is, Ba and/or C < 0 on the Pelvic Organ Prolapse Quantification System) was used to define anatomic success.
Adverse events were similar between transvaginal mesh and native tissue repair groups, with most adverse events occurring within the first 6 months. The mesh exposure rate was 4.9%. Of the 13 incidents of mesh exposure, 4 patients required surgical intervention and 1 incident was considered a serious adverse event. QoL measures demonstrated improvement without any statistically significant differences between the treatment cohorts. ●
This study established the superiority and safety of newer generation transvaginal mesh used for the treatment of pelvic organ prolapse. Women who received newer generation transvaginal mesh can be reassured that the prolapse recurrence rates are low and that adverse events related to their mesh are rare—even when compared with those of native tissue repair. Patients also may be reassured that most adverse events would have occurred within 6 months of the initial prolapse repair surgery
Intensive gout treatment meets urate goal, lowers tophi burden
PHILADELPHIA – Patients with gout who underwent an intensive treat-to-target regimen of monthly up-titration of urate-lowering therapy (ULT) to reach a target serum urate level were significantly more likely to reach that goal at 1 year than were patients who received conventional gout management in a randomized, controlled trial.
These results came from the TICOG (Tight Control of Gout) trial, one of a handful of recent trials to test a treat-to-target strategy with ULT in the management of gout. Beyond the primary outcome of reaching target serum urate level of < 5 mg/dL (< 300 micromol/L), the results also showed that the tight-control strategy significantly lowered urate to a greater extent than conventional management, reduced tophus size in the first metatarsophalangeal (MTP) joint, and improved gray scale synovitis on ultrasound significantly more than with conventional management, Sarah Black, MBBS, a rheumatology trainee at Musgrave Park Hospital, Belfast, Northern Ireland, reported at the American College of Rheumatology annual meeting.
“Based on these outcomes, we question whether gout is best managed in primary or secondary care. We think there is an argument for establishing specialist gout clinics with more time to focus on patient education to help improve outcomes. These clinics could be led by allied health care professionals, such as specialist nurses and pharmacists,” Dr. Black said at the meeting.
Gout management guidelines issued by the British Society for Rheumatology in 2017 call for a target serum urate level of < 5 mg/dL, whereas the ACR’s 2020 guideline for the management of gout endorses a treat-to-target management strategy that aims for a serum urate level of < 6 mg/dL.
The single-center, nonblinded trial recruited 110 patients aged 18-85 years over a 3-year period to take ULT with allopurinol as first-line therapy starting at 100 mg/day. Everyone received the same advice regarding ULT up-titration, lifestyle changes, and gout education at baseline. The second-line agent for ULT was febuxostat (Uloric) 80 mg daily, with uricosuric drugs as third-line agents. All patients received colchicine or NSAID prophylaxis for gout flares for the first 6 months, depending on their comorbidities.
The trial excluded patients who had been treated with ULT within the past 6 months or had experienced prior hypersensitivity to ULT, severe renal impairment (creatinine clearance < 30 mL/min as measured by estimated glomerular filtration rate), significant liver impairment, or any other significant medical disease affecting life expectancy shorter than 1 year.
Conventional management consisted of urate level review at 0, 6, and 12 months with up-titration at each visit and primary care management of ULT between reviews until the target serum urate level was reached. In the tight-control group, monthly up-titrations occurred at the Musgrave Park Hospital at visits with the study team that were led by a rheumatologist and a specialist pharmacist.
A total of 48 patients in the conventional arm and 47 in the tight-control arm completed the trial. At baseline, monosodium urate crystals were detected in joint aspirates in 56% of patients receiving tight control and in 58.5% of those receiving conventional management. The mean serum urate level was 490 micromol/L (8.24 mg/dL) for tight-control patients and 470 micromol/L (7.9 mg/dL) for conventionally managed patients.
By 1 year, 89.4% of patients in the tight-control group had achieved the target urate level, compared with 39.6% in the conventional-management group (P < .001). At 6 months, serum urate had declined by 37.6% with tight control vs. 18% with conventional management. By the end of the trial, the median allopurinol dose was 400 mg with tight control (range, 200-900 mg) and 200 mg with conventional management (range, 0-400 mg). A total of 89% of patients were taking allopurinol at the end of the trial.
As expected, tight control led to more flares per month on average (0.35 vs. 0.13) in the 79 patients for whom complete data on flare frequency were available.
On blinded ultrasound evaluations, the median diameter of the first MTP tophus declined significantly more with tight control than with conventional management (–4.65 mm vs. –0.30 mm; P = .003). Gray scale synovitis in the knee improved in 63% of patients undergoing tight control, compared with 14% of conventionally managed patients (P = .043). The researchers observed no difference in resolution of the double-contour sign or in the number of erosions between the groups, although the 1-year time frame may not have been long enough to see resolution and improvement, Dr. Black said.
Dr. Black said that a follow-up study is planned with the same patient cohort at 3 years.
When asked about the feasibility of monthly ULT titration visits for gout management, audience member Tuhina Neogi, MD, professor of epidemiology at Boston University and chief of rheumatology at Boston Medical Center, told this news organization, “We don’t have a lot of data to guide us in that regard, and I also think it depends on what the increment of the dose titration is, but we generally do recognize that therapeutic inertia is bad – keeping someone on a dose for a long time. For me, I don’t think monthly is unreasonable if you have good prophylaxis [against acute flares].”
Dr. Neogi also noted that such monthly assessments don’t have to take place at a hospital. “I think there are many different practice models in which it could be implemented [that are not physician-driven].”
The study had no outside funding. Dr. Black has disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Neogi has received consulting fees from a variety of pharmaceutical companies, including Alnylam, Regeneron, Eli Lilly, EMD Serono, Novartis, Pfizer, and GlaxoSmithKline.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
PHILADELPHIA – Patients with gout who underwent an intensive treat-to-target regimen of monthly up-titration of urate-lowering therapy (ULT) to reach a target serum urate level were significantly more likely to reach that goal at 1 year than were patients who received conventional gout management in a randomized, controlled trial.
These results came from the TICOG (Tight Control of Gout) trial, one of a handful of recent trials to test a treat-to-target strategy with ULT in the management of gout. Beyond the primary outcome of reaching target serum urate level of < 5 mg/dL (< 300 micromol/L), the results also showed that the tight-control strategy significantly lowered urate to a greater extent than conventional management, reduced tophus size in the first metatarsophalangeal (MTP) joint, and improved gray scale synovitis on ultrasound significantly more than with conventional management, Sarah Black, MBBS, a rheumatology trainee at Musgrave Park Hospital, Belfast, Northern Ireland, reported at the American College of Rheumatology annual meeting.
“Based on these outcomes, we question whether gout is best managed in primary or secondary care. We think there is an argument for establishing specialist gout clinics with more time to focus on patient education to help improve outcomes. These clinics could be led by allied health care professionals, such as specialist nurses and pharmacists,” Dr. Black said at the meeting.
Gout management guidelines issued by the British Society for Rheumatology in 2017 call for a target serum urate level of < 5 mg/dL, whereas the ACR’s 2020 guideline for the management of gout endorses a treat-to-target management strategy that aims for a serum urate level of < 6 mg/dL.
The single-center, nonblinded trial recruited 110 patients aged 18-85 years over a 3-year period to take ULT with allopurinol as first-line therapy starting at 100 mg/day. Everyone received the same advice regarding ULT up-titration, lifestyle changes, and gout education at baseline. The second-line agent for ULT was febuxostat (Uloric) 80 mg daily, with uricosuric drugs as third-line agents. All patients received colchicine or NSAID prophylaxis for gout flares for the first 6 months, depending on their comorbidities.
The trial excluded patients who had been treated with ULT within the past 6 months or had experienced prior hypersensitivity to ULT, severe renal impairment (creatinine clearance < 30 mL/min as measured by estimated glomerular filtration rate), significant liver impairment, or any other significant medical disease affecting life expectancy shorter than 1 year.
Conventional management consisted of urate level review at 0, 6, and 12 months with up-titration at each visit and primary care management of ULT between reviews until the target serum urate level was reached. In the tight-control group, monthly up-titrations occurred at the Musgrave Park Hospital at visits with the study team that were led by a rheumatologist and a specialist pharmacist.
A total of 48 patients in the conventional arm and 47 in the tight-control arm completed the trial. At baseline, monosodium urate crystals were detected in joint aspirates in 56% of patients receiving tight control and in 58.5% of those receiving conventional management. The mean serum urate level was 490 micromol/L (8.24 mg/dL) for tight-control patients and 470 micromol/L (7.9 mg/dL) for conventionally managed patients.
By 1 year, 89.4% of patients in the tight-control group had achieved the target urate level, compared with 39.6% in the conventional-management group (P < .001). At 6 months, serum urate had declined by 37.6% with tight control vs. 18% with conventional management. By the end of the trial, the median allopurinol dose was 400 mg with tight control (range, 200-900 mg) and 200 mg with conventional management (range, 0-400 mg). A total of 89% of patients were taking allopurinol at the end of the trial.
As expected, tight control led to more flares per month on average (0.35 vs. 0.13) in the 79 patients for whom complete data on flare frequency were available.
On blinded ultrasound evaluations, the median diameter of the first MTP tophus declined significantly more with tight control than with conventional management (–4.65 mm vs. –0.30 mm; P = .003). Gray scale synovitis in the knee improved in 63% of patients undergoing tight control, compared with 14% of conventionally managed patients (P = .043). The researchers observed no difference in resolution of the double-contour sign or in the number of erosions between the groups, although the 1-year time frame may not have been long enough to see resolution and improvement, Dr. Black said.
Dr. Black said that a follow-up study is planned with the same patient cohort at 3 years.
When asked about the feasibility of monthly ULT titration visits for gout management, audience member Tuhina Neogi, MD, professor of epidemiology at Boston University and chief of rheumatology at Boston Medical Center, told this news organization, “We don’t have a lot of data to guide us in that regard, and I also think it depends on what the increment of the dose titration is, but we generally do recognize that therapeutic inertia is bad – keeping someone on a dose for a long time. For me, I don’t think monthly is unreasonable if you have good prophylaxis [against acute flares].”
Dr. Neogi also noted that such monthly assessments don’t have to take place at a hospital. “I think there are many different practice models in which it could be implemented [that are not physician-driven].”
The study had no outside funding. Dr. Black has disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Neogi has received consulting fees from a variety of pharmaceutical companies, including Alnylam, Regeneron, Eli Lilly, EMD Serono, Novartis, Pfizer, and GlaxoSmithKline.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
PHILADELPHIA – Patients with gout who underwent an intensive treat-to-target regimen of monthly up-titration of urate-lowering therapy (ULT) to reach a target serum urate level were significantly more likely to reach that goal at 1 year than were patients who received conventional gout management in a randomized, controlled trial.
These results came from the TICOG (Tight Control of Gout) trial, one of a handful of recent trials to test a treat-to-target strategy with ULT in the management of gout. Beyond the primary outcome of reaching target serum urate level of < 5 mg/dL (< 300 micromol/L), the results also showed that the tight-control strategy significantly lowered urate to a greater extent than conventional management, reduced tophus size in the first metatarsophalangeal (MTP) joint, and improved gray scale synovitis on ultrasound significantly more than with conventional management, Sarah Black, MBBS, a rheumatology trainee at Musgrave Park Hospital, Belfast, Northern Ireland, reported at the American College of Rheumatology annual meeting.
“Based on these outcomes, we question whether gout is best managed in primary or secondary care. We think there is an argument for establishing specialist gout clinics with more time to focus on patient education to help improve outcomes. These clinics could be led by allied health care professionals, such as specialist nurses and pharmacists,” Dr. Black said at the meeting.
Gout management guidelines issued by the British Society for Rheumatology in 2017 call for a target serum urate level of < 5 mg/dL, whereas the ACR’s 2020 guideline for the management of gout endorses a treat-to-target management strategy that aims for a serum urate level of < 6 mg/dL.
The single-center, nonblinded trial recruited 110 patients aged 18-85 years over a 3-year period to take ULT with allopurinol as first-line therapy starting at 100 mg/day. Everyone received the same advice regarding ULT up-titration, lifestyle changes, and gout education at baseline. The second-line agent for ULT was febuxostat (Uloric) 80 mg daily, with uricosuric drugs as third-line agents. All patients received colchicine or NSAID prophylaxis for gout flares for the first 6 months, depending on their comorbidities.
The trial excluded patients who had been treated with ULT within the past 6 months or had experienced prior hypersensitivity to ULT, severe renal impairment (creatinine clearance < 30 mL/min as measured by estimated glomerular filtration rate), significant liver impairment, or any other significant medical disease affecting life expectancy shorter than 1 year.
Conventional management consisted of urate level review at 0, 6, and 12 months with up-titration at each visit and primary care management of ULT between reviews until the target serum urate level was reached. In the tight-control group, monthly up-titrations occurred at the Musgrave Park Hospital at visits with the study team that were led by a rheumatologist and a specialist pharmacist.
A total of 48 patients in the conventional arm and 47 in the tight-control arm completed the trial. At baseline, monosodium urate crystals were detected in joint aspirates in 56% of patients receiving tight control and in 58.5% of those receiving conventional management. The mean serum urate level was 490 micromol/L (8.24 mg/dL) for tight-control patients and 470 micromol/L (7.9 mg/dL) for conventionally managed patients.
By 1 year, 89.4% of patients in the tight-control group had achieved the target urate level, compared with 39.6% in the conventional-management group (P < .001). At 6 months, serum urate had declined by 37.6% with tight control vs. 18% with conventional management. By the end of the trial, the median allopurinol dose was 400 mg with tight control (range, 200-900 mg) and 200 mg with conventional management (range, 0-400 mg). A total of 89% of patients were taking allopurinol at the end of the trial.
As expected, tight control led to more flares per month on average (0.35 vs. 0.13) in the 79 patients for whom complete data on flare frequency were available.
On blinded ultrasound evaluations, the median diameter of the first MTP tophus declined significantly more with tight control than with conventional management (–4.65 mm vs. –0.30 mm; P = .003). Gray scale synovitis in the knee improved in 63% of patients undergoing tight control, compared with 14% of conventionally managed patients (P = .043). The researchers observed no difference in resolution of the double-contour sign or in the number of erosions between the groups, although the 1-year time frame may not have been long enough to see resolution and improvement, Dr. Black said.
Dr. Black said that a follow-up study is planned with the same patient cohort at 3 years.
When asked about the feasibility of monthly ULT titration visits for gout management, audience member Tuhina Neogi, MD, professor of epidemiology at Boston University and chief of rheumatology at Boston Medical Center, told this news organization, “We don’t have a lot of data to guide us in that regard, and I also think it depends on what the increment of the dose titration is, but we generally do recognize that therapeutic inertia is bad – keeping someone on a dose for a long time. For me, I don’t think monthly is unreasonable if you have good prophylaxis [against acute flares].”
Dr. Neogi also noted that such monthly assessments don’t have to take place at a hospital. “I think there are many different practice models in which it could be implemented [that are not physician-driven].”
The study had no outside funding. Dr. Black has disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Neogi has received consulting fees from a variety of pharmaceutical companies, including Alnylam, Regeneron, Eli Lilly, EMD Serono, Novartis, Pfizer, and GlaxoSmithKline.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
AT ACR 2022
Blame MCL, not transplantation, for late effects?
In patients with mantle cell lymphoma, rates of respiratory disease, blood disorders, and infectious diseases do not vary according to the intensity of treatment given, the results of a large retrospective analysis suggested.
The rate of hospitalization among MCL patients was also high, but again, did not differ between ASCT and non-ASCT subgroups in the study, which included adult patients younger than age 70 with MCL who were treated in Sweden between 2000 and 2014.
Late effects independent of ASCT
These findings may have implications for clinicians tempted to avoid intensive first-line treatment including ASCT because it is “demanding” and may cause late effects, study authors wrote in a research article that appeared in Blood Advances.
In fact, the great majority of long-term health care needs in patients with MCL appear to be related to the lymphoma in itself, according to study senior author Ingrid Glimelius, MD, PhD, senior consultant and professor in oncology in the department of immunology, genetics, and pathology at Uppsala University in Sweden.
“You do have to keep your eyes open for complications like blood disorders, infections, and respiratory (disorders),” Dr. Glimelius said in an interview. “But it’s not the transplant that adds to the extra toxicity. So don’t be afraid of giving that, if you think that can prolong your patient’s remission.”
Whither transplantation?
While these data may advance the discussion over the relative safety of ASCT, she added, the paradigm is changing to ask a different question: Does the patient need a transplant, or not?
Dr. Glimelius said she was looking forward to results of TRIANGLE, a randomized, open-label, three-arm study initiated by the European MCL Network. This study compares standard first-line treatment including ASCT to the kinase inhibitor ibrutinib, which the U.S. Food and Drug Administration approved in 2013 for patients previously treated for MCL.
In the TRIANGLE study, younger patients with MCL were randomized to the standard first-line treatment, standard treatment plus ibrutinib, or ibrutinib alone.
A preliminary report on the study stated that the current standard is “not superior” to the new ibrutinib-containing regimen without ASCT, though more follow-up is needed.
Full results of the study are expected to be presented at the American Society of Hematology meeting on December 11.
“In my opinion, our data will be practice-changing,” said lead investigator Martin Dreyling, MD, PhD, professor of medicine and head of the lymphoma program at the University of Munich Hospital.
Little known about late effects
In the meantime, clinicians may be reassured by the current data from Dr. Glimelius and coauthors, which showed that late effects varied little by treatment choice.
That’s important, Dr. Glimelius said, because even as survival is improving and novel targeted drugs are taking the stage, knowledge about the late effects of MCL remains limited.
Their population-based study included all 620 patients with MCL in the Swedish Lymphoma Register who were 18-69 years of age and diagnosed between 2000 and 2014. Records were found for 620 patients, of whom 247 received high-dose chemotherapy with ASCT.
Compared with healthy individuals with no MCL, the patients with MCL had a high rate of specialist visits and hospital visits, according to the report. The MCL patients also had high risks of infections, respiratory complications, and blood disorders relative to the healthy subjects.
Lack of differences between arms
The key finding of the report, though, is the lack of significant differences in the rate of complications between the ASCT and non–ASCT-treated patients.
Relative to healthy subjects, patients undergoing ASCT and not undergoing ASCT had a higher risk of infections, with hazard ratios of 5.62 (95% confidence interval, 4.20-7.52) and 4.66 (95% CI, 3.62-5.00), respectively.
Relative risks of respiratory complications were also similar, with HRs of 4.38 and 5.26, respectively, and overlapping CIs. Likewise, the risk of blood disorders was not statistically different, with HRs of 9.84 and 5.80, respectively, but again with overlapping CIs.
Outpatient visits, inpatient visits, and bed days were likewise similar between ASCT and non-ASCT arms.
In fact, most patients died of their lymphoma, rather than a treatment complication or another cause of death, the investigators noted in their report.
Dr. Glimelius reported receiving honoraria from Janssen. Coauthors on the paper reported disclosures related to Janssen, Gilead, Celgene, Roche, Acerta. and AbbVie.
Correction, 11/21/22: The photo caption misstated Dr. Ingrid Glimelius' name.
In patients with mantle cell lymphoma, rates of respiratory disease, blood disorders, and infectious diseases do not vary according to the intensity of treatment given, the results of a large retrospective analysis suggested.
The rate of hospitalization among MCL patients was also high, but again, did not differ between ASCT and non-ASCT subgroups in the study, which included adult patients younger than age 70 with MCL who were treated in Sweden between 2000 and 2014.
Late effects independent of ASCT
These findings may have implications for clinicians tempted to avoid intensive first-line treatment including ASCT because it is “demanding” and may cause late effects, study authors wrote in a research article that appeared in Blood Advances.
In fact, the great majority of long-term health care needs in patients with MCL appear to be related to the lymphoma in itself, according to study senior author Ingrid Glimelius, MD, PhD, senior consultant and professor in oncology in the department of immunology, genetics, and pathology at Uppsala University in Sweden.
“You do have to keep your eyes open for complications like blood disorders, infections, and respiratory (disorders),” Dr. Glimelius said in an interview. “But it’s not the transplant that adds to the extra toxicity. So don’t be afraid of giving that, if you think that can prolong your patient’s remission.”
Whither transplantation?
While these data may advance the discussion over the relative safety of ASCT, she added, the paradigm is changing to ask a different question: Does the patient need a transplant, or not?
Dr. Glimelius said she was looking forward to results of TRIANGLE, a randomized, open-label, three-arm study initiated by the European MCL Network. This study compares standard first-line treatment including ASCT to the kinase inhibitor ibrutinib, which the U.S. Food and Drug Administration approved in 2013 for patients previously treated for MCL.
In the TRIANGLE study, younger patients with MCL were randomized to the standard first-line treatment, standard treatment plus ibrutinib, or ibrutinib alone.
A preliminary report on the study stated that the current standard is “not superior” to the new ibrutinib-containing regimen without ASCT, though more follow-up is needed.
Full results of the study are expected to be presented at the American Society of Hematology meeting on December 11.
“In my opinion, our data will be practice-changing,” said lead investigator Martin Dreyling, MD, PhD, professor of medicine and head of the lymphoma program at the University of Munich Hospital.
Little known about late effects
In the meantime, clinicians may be reassured by the current data from Dr. Glimelius and coauthors, which showed that late effects varied little by treatment choice.
That’s important, Dr. Glimelius said, because even as survival is improving and novel targeted drugs are taking the stage, knowledge about the late effects of MCL remains limited.
Their population-based study included all 620 patients with MCL in the Swedish Lymphoma Register who were 18-69 years of age and diagnosed between 2000 and 2014. Records were found for 620 patients, of whom 247 received high-dose chemotherapy with ASCT.
Compared with healthy individuals with no MCL, the patients with MCL had a high rate of specialist visits and hospital visits, according to the report. The MCL patients also had high risks of infections, respiratory complications, and blood disorders relative to the healthy subjects.
Lack of differences between arms
The key finding of the report, though, is the lack of significant differences in the rate of complications between the ASCT and non–ASCT-treated patients.
Relative to healthy subjects, patients undergoing ASCT and not undergoing ASCT had a higher risk of infections, with hazard ratios of 5.62 (95% confidence interval, 4.20-7.52) and 4.66 (95% CI, 3.62-5.00), respectively.
Relative risks of respiratory complications were also similar, with HRs of 4.38 and 5.26, respectively, and overlapping CIs. Likewise, the risk of blood disorders was not statistically different, with HRs of 9.84 and 5.80, respectively, but again with overlapping CIs.
Outpatient visits, inpatient visits, and bed days were likewise similar between ASCT and non-ASCT arms.
In fact, most patients died of their lymphoma, rather than a treatment complication or another cause of death, the investigators noted in their report.
Dr. Glimelius reported receiving honoraria from Janssen. Coauthors on the paper reported disclosures related to Janssen, Gilead, Celgene, Roche, Acerta. and AbbVie.
Correction, 11/21/22: The photo caption misstated Dr. Ingrid Glimelius' name.
In patients with mantle cell lymphoma, rates of respiratory disease, blood disorders, and infectious diseases do not vary according to the intensity of treatment given, the results of a large retrospective analysis suggested.
The rate of hospitalization among MCL patients was also high, but again, did not differ between ASCT and non-ASCT subgroups in the study, which included adult patients younger than age 70 with MCL who were treated in Sweden between 2000 and 2014.
Late effects independent of ASCT
These findings may have implications for clinicians tempted to avoid intensive first-line treatment including ASCT because it is “demanding” and may cause late effects, study authors wrote in a research article that appeared in Blood Advances.
In fact, the great majority of long-term health care needs in patients with MCL appear to be related to the lymphoma in itself, according to study senior author Ingrid Glimelius, MD, PhD, senior consultant and professor in oncology in the department of immunology, genetics, and pathology at Uppsala University in Sweden.
“You do have to keep your eyes open for complications like blood disorders, infections, and respiratory (disorders),” Dr. Glimelius said in an interview. “But it’s not the transplant that adds to the extra toxicity. So don’t be afraid of giving that, if you think that can prolong your patient’s remission.”
Whither transplantation?
While these data may advance the discussion over the relative safety of ASCT, she added, the paradigm is changing to ask a different question: Does the patient need a transplant, or not?
Dr. Glimelius said she was looking forward to results of TRIANGLE, a randomized, open-label, three-arm study initiated by the European MCL Network. This study compares standard first-line treatment including ASCT to the kinase inhibitor ibrutinib, which the U.S. Food and Drug Administration approved in 2013 for patients previously treated for MCL.
In the TRIANGLE study, younger patients with MCL were randomized to the standard first-line treatment, standard treatment plus ibrutinib, or ibrutinib alone.
A preliminary report on the study stated that the current standard is “not superior” to the new ibrutinib-containing regimen without ASCT, though more follow-up is needed.
Full results of the study are expected to be presented at the American Society of Hematology meeting on December 11.
“In my opinion, our data will be practice-changing,” said lead investigator Martin Dreyling, MD, PhD, professor of medicine and head of the lymphoma program at the University of Munich Hospital.
Little known about late effects
In the meantime, clinicians may be reassured by the current data from Dr. Glimelius and coauthors, which showed that late effects varied little by treatment choice.
That’s important, Dr. Glimelius said, because even as survival is improving and novel targeted drugs are taking the stage, knowledge about the late effects of MCL remains limited.
Their population-based study included all 620 patients with MCL in the Swedish Lymphoma Register who were 18-69 years of age and diagnosed between 2000 and 2014. Records were found for 620 patients, of whom 247 received high-dose chemotherapy with ASCT.
Compared with healthy individuals with no MCL, the patients with MCL had a high rate of specialist visits and hospital visits, according to the report. The MCL patients also had high risks of infections, respiratory complications, and blood disorders relative to the healthy subjects.
Lack of differences between arms
The key finding of the report, though, is the lack of significant differences in the rate of complications between the ASCT and non–ASCT-treated patients.
Relative to healthy subjects, patients undergoing ASCT and not undergoing ASCT had a higher risk of infections, with hazard ratios of 5.62 (95% confidence interval, 4.20-7.52) and 4.66 (95% CI, 3.62-5.00), respectively.
Relative risks of respiratory complications were also similar, with HRs of 4.38 and 5.26, respectively, and overlapping CIs. Likewise, the risk of blood disorders was not statistically different, with HRs of 9.84 and 5.80, respectively, but again with overlapping CIs.
Outpatient visits, inpatient visits, and bed days were likewise similar between ASCT and non-ASCT arms.
In fact, most patients died of their lymphoma, rather than a treatment complication or another cause of death, the investigators noted in their report.
Dr. Glimelius reported receiving honoraria from Janssen. Coauthors on the paper reported disclosures related to Janssen, Gilead, Celgene, Roche, Acerta. and AbbVie.
Correction, 11/21/22: The photo caption misstated Dr. Ingrid Glimelius' name.
FROM BLOOD ADVANCES
Aspirin use confers multifaceted benefits in HCC
Key clinical point: The use of aspirin is independently associated with a reduced risk for hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) incidence, recurrence, and mortality, but an increased risk for bleeding.
Major finding: Aspirin use was associated with a reduced incidence of HCC (hazard ratio [HR] 0.75; 95% CI 0.71-0.80), recurrence of HCC (HR 0.79; 95% CI 0.65-0.96), and HCC-related mortality (HR 0.64; 95% CI 0.44-0.94), but an increased risk for bleeding (HR 1.10; 95% CI 1.02-1.20).
Study details: This study meta-analyzed the data of 3,273,524 individuals from 30 studies on HCC incidence, HCC recurrence, or mortality.
Disclosures: This study did not report the source of funding. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Source: Ma S, Qu G et al. Does aspirin reduce the incidence, recurrence, and mortality of hepatocellular carcinoma? A GRADE-assessed systematic review and dose-response meta-analysis. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 2022 (Nov 5). Doi: 10.1007/s00228-022-03414-y
Key clinical point: The use of aspirin is independently associated with a reduced risk for hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) incidence, recurrence, and mortality, but an increased risk for bleeding.
Major finding: Aspirin use was associated with a reduced incidence of HCC (hazard ratio [HR] 0.75; 95% CI 0.71-0.80), recurrence of HCC (HR 0.79; 95% CI 0.65-0.96), and HCC-related mortality (HR 0.64; 95% CI 0.44-0.94), but an increased risk for bleeding (HR 1.10; 95% CI 1.02-1.20).
Study details: This study meta-analyzed the data of 3,273,524 individuals from 30 studies on HCC incidence, HCC recurrence, or mortality.
Disclosures: This study did not report the source of funding. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Source: Ma S, Qu G et al. Does aspirin reduce the incidence, recurrence, and mortality of hepatocellular carcinoma? A GRADE-assessed systematic review and dose-response meta-analysis. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 2022 (Nov 5). Doi: 10.1007/s00228-022-03414-y
Key clinical point: The use of aspirin is independently associated with a reduced risk for hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) incidence, recurrence, and mortality, but an increased risk for bleeding.
Major finding: Aspirin use was associated with a reduced incidence of HCC (hazard ratio [HR] 0.75; 95% CI 0.71-0.80), recurrence of HCC (HR 0.79; 95% CI 0.65-0.96), and HCC-related mortality (HR 0.64; 95% CI 0.44-0.94), but an increased risk for bleeding (HR 1.10; 95% CI 1.02-1.20).
Study details: This study meta-analyzed the data of 3,273,524 individuals from 30 studies on HCC incidence, HCC recurrence, or mortality.
Disclosures: This study did not report the source of funding. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Source: Ma S, Qu G et al. Does aspirin reduce the incidence, recurrence, and mortality of hepatocellular carcinoma? A GRADE-assessed systematic review and dose-response meta-analysis. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 2022 (Nov 5). Doi: 10.1007/s00228-022-03414-y
Microwave ablation: An alternative to resection in HCC with BCLC stage 0
Key clinical point: Among patients with hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), an “ideal candidate for ablation” per the Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer (BCLC) staging system may not be ideal for microwave ablation (MWA); however, patients with BCLC-0 disease may comprise the optimal population for MWA.
Major finding: Liver resection (LRE) vs MWA led to a significantly longer recurrence-free survival in the overall population (P = .025) and patients with BCLC-A disease (P = .003) but not in those with BCLC-0 disease (P = .270), in addition to similar overall survival (P = .976) and post-procedure-related complication rates (P = 1.00) in BCLC-0 patients.
Study details: This retrospective study included patients with HCC who met the criteria of “ideal candidates for ablation” per the BCLC staging system and propensity score-matched those receiving MWA and LRE (overall population 140 pairs; BCLC-0 disease 35 pairs; BCLC-A disease 99 pairs).
Disclosures: This study did not receive any funding. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Source: Tong Y, Cai R et al. Liver resection versus microwave ablation for hepatocellular carcinoma in ideal candidates for ablation per Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer staging: A propensity score matching and inverse probability of treatment weighting analysis. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2022;56(11-12):1602-1614 (Oct 26). Doi: 10.1111/apt.17263
Key clinical point: Among patients with hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), an “ideal candidate for ablation” per the Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer (BCLC) staging system may not be ideal for microwave ablation (MWA); however, patients with BCLC-0 disease may comprise the optimal population for MWA.
Major finding: Liver resection (LRE) vs MWA led to a significantly longer recurrence-free survival in the overall population (P = .025) and patients with BCLC-A disease (P = .003) but not in those with BCLC-0 disease (P = .270), in addition to similar overall survival (P = .976) and post-procedure-related complication rates (P = 1.00) in BCLC-0 patients.
Study details: This retrospective study included patients with HCC who met the criteria of “ideal candidates for ablation” per the BCLC staging system and propensity score-matched those receiving MWA and LRE (overall population 140 pairs; BCLC-0 disease 35 pairs; BCLC-A disease 99 pairs).
Disclosures: This study did not receive any funding. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Source: Tong Y, Cai R et al. Liver resection versus microwave ablation for hepatocellular carcinoma in ideal candidates for ablation per Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer staging: A propensity score matching and inverse probability of treatment weighting analysis. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2022;56(11-12):1602-1614 (Oct 26). Doi: 10.1111/apt.17263
Key clinical point: Among patients with hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), an “ideal candidate for ablation” per the Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer (BCLC) staging system may not be ideal for microwave ablation (MWA); however, patients with BCLC-0 disease may comprise the optimal population for MWA.
Major finding: Liver resection (LRE) vs MWA led to a significantly longer recurrence-free survival in the overall population (P = .025) and patients with BCLC-A disease (P = .003) but not in those with BCLC-0 disease (P = .270), in addition to similar overall survival (P = .976) and post-procedure-related complication rates (P = 1.00) in BCLC-0 patients.
Study details: This retrospective study included patients with HCC who met the criteria of “ideal candidates for ablation” per the BCLC staging system and propensity score-matched those receiving MWA and LRE (overall population 140 pairs; BCLC-0 disease 35 pairs; BCLC-A disease 99 pairs).
Disclosures: This study did not receive any funding. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Source: Tong Y, Cai R et al. Liver resection versus microwave ablation for hepatocellular carcinoma in ideal candidates for ablation per Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer staging: A propensity score matching and inverse probability of treatment weighting analysis. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2022;56(11-12):1602-1614 (Oct 26). Doi: 10.1111/apt.17263
Sequence of radiotherapy and TACE affects the prognosis of HCC with portal vein tumor thrombus
Key clinical point: Compared with transcatheter arterial chemoembolization (TACE) followed by radiotherapy (RT), administering RT before TACE leads to better survival outcomes in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) and portal vein tumor thrombus (PVTT).
Major finding: Patients who received RT+TACE vs TACE+RT had significantly longer median progression-free survival (6.6 vs 4.2 months; hazard ratio [HR] 0.66; P = .030), with the prolongation of median overall survival being marginally significant (15.4 vs 11.5 months; HR 0.68; P = .054).
Study details: Findings are from a randomized controlled study including 120 patients with unresectable HCC and PVTT who were randomly assigned (1:1) to receive RT+TACE or TACE+RT.
Disclosures: This study was supported by the Clinical Research Plan of Shanghai Shenkang Hospital Development Center, China, among others. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Source: Guo L et al. Radiotherapy prior to or after transcatheter arterial chemoembolization for the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma with portal vein tumor thrombus: A randomized controlled trial. Hepatol Int. 2022 (Oct 21). Doi: 10.1007/s12072-022-10423-7
Key clinical point: Compared with transcatheter arterial chemoembolization (TACE) followed by radiotherapy (RT), administering RT before TACE leads to better survival outcomes in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) and portal vein tumor thrombus (PVTT).
Major finding: Patients who received RT+TACE vs TACE+RT had significantly longer median progression-free survival (6.6 vs 4.2 months; hazard ratio [HR] 0.66; P = .030), with the prolongation of median overall survival being marginally significant (15.4 vs 11.5 months; HR 0.68; P = .054).
Study details: Findings are from a randomized controlled study including 120 patients with unresectable HCC and PVTT who were randomly assigned (1:1) to receive RT+TACE or TACE+RT.
Disclosures: This study was supported by the Clinical Research Plan of Shanghai Shenkang Hospital Development Center, China, among others. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Source: Guo L et al. Radiotherapy prior to or after transcatheter arterial chemoembolization for the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma with portal vein tumor thrombus: A randomized controlled trial. Hepatol Int. 2022 (Oct 21). Doi: 10.1007/s12072-022-10423-7
Key clinical point: Compared with transcatheter arterial chemoembolization (TACE) followed by radiotherapy (RT), administering RT before TACE leads to better survival outcomes in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) and portal vein tumor thrombus (PVTT).
Major finding: Patients who received RT+TACE vs TACE+RT had significantly longer median progression-free survival (6.6 vs 4.2 months; hazard ratio [HR] 0.66; P = .030), with the prolongation of median overall survival being marginally significant (15.4 vs 11.5 months; HR 0.68; P = .054).
Study details: Findings are from a randomized controlled study including 120 patients with unresectable HCC and PVTT who were randomly assigned (1:1) to receive RT+TACE or TACE+RT.
Disclosures: This study was supported by the Clinical Research Plan of Shanghai Shenkang Hospital Development Center, China, among others. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Source: Guo L et al. Radiotherapy prior to or after transcatheter arterial chemoembolization for the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma with portal vein tumor thrombus: A randomized controlled trial. Hepatol Int. 2022 (Oct 21). Doi: 10.1007/s12072-022-10423-7
Atezolizumab+bevacizumab: A better first-line treatment option for unresectable HCC than lenvatinib
Key clinical point: Atezolizumab plus bevacizumab (Atezo/Bev) is a more effective and safe first-line therapy than lenvatinib in patients with unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC).
Major finding: Patients who received Atezo/Bev vs lenvatinib had a significantly longer progression-free survival (8.3 vs 6.0 months; P = .005) and overall survival (median survival time not reached vs 20.2 months; P = .039) and lower prevalence of grade ≥3 adverse events, such as hypertension (P = .004) and proteinuria (P = .046).
Study details: This retrospective study propensity score-matched patients with unresectable HCC who received Atezo/Bev (n = 152) with those who received lenvatinib (n = 152) as first-line systemic therapies.
Disclosures: This study did not receive any funding. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Source: Niizeki T et al. Comparison of efficacy and safety of atezolizumab plus bevacizumab and lenvatinib as first-line therapy for unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: A propensity score matching analysis. Target Oncol. 2022 (Oct 22). Doi: 10.1007/s11523-022-00921-x
Key clinical point: Atezolizumab plus bevacizumab (Atezo/Bev) is a more effective and safe first-line therapy than lenvatinib in patients with unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC).
Major finding: Patients who received Atezo/Bev vs lenvatinib had a significantly longer progression-free survival (8.3 vs 6.0 months; P = .005) and overall survival (median survival time not reached vs 20.2 months; P = .039) and lower prevalence of grade ≥3 adverse events, such as hypertension (P = .004) and proteinuria (P = .046).
Study details: This retrospective study propensity score-matched patients with unresectable HCC who received Atezo/Bev (n = 152) with those who received lenvatinib (n = 152) as first-line systemic therapies.
Disclosures: This study did not receive any funding. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Source: Niizeki T et al. Comparison of efficacy and safety of atezolizumab plus bevacizumab and lenvatinib as first-line therapy for unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: A propensity score matching analysis. Target Oncol. 2022 (Oct 22). Doi: 10.1007/s11523-022-00921-x
Key clinical point: Atezolizumab plus bevacizumab (Atezo/Bev) is a more effective and safe first-line therapy than lenvatinib in patients with unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC).
Major finding: Patients who received Atezo/Bev vs lenvatinib had a significantly longer progression-free survival (8.3 vs 6.0 months; P = .005) and overall survival (median survival time not reached vs 20.2 months; P = .039) and lower prevalence of grade ≥3 adverse events, such as hypertension (P = .004) and proteinuria (P = .046).
Study details: This retrospective study propensity score-matched patients with unresectable HCC who received Atezo/Bev (n = 152) with those who received lenvatinib (n = 152) as first-line systemic therapies.
Disclosures: This study did not receive any funding. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Source: Niizeki T et al. Comparison of efficacy and safety of atezolizumab plus bevacizumab and lenvatinib as first-line therapy for unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: A propensity score matching analysis. Target Oncol. 2022 (Oct 22). Doi: 10.1007/s11523-022-00921-x
Alpha-fetoprotein and carbohydrate antigen 19-9: Prognostic markers in HCC after hepatectomy
Key clinical point: The combination of alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) and carbohydrate antigen 19-9 (CA19-9) may effectively predict the prognosis of patients with hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) after radical hepatectomy.
Major finding: The 5-year overall and recurrence-free survival rates were significantly lower among patients with high preoperative serum AFP and CA19-9 levels than among those with high serum AFP or CA19-9 levels (P = .022 and P = .004, respectively) and those with low serum AFP and CA19-9 levels (both P < .001).
Study details: This retrospective study included 711 patients with HCC who were categorized as having low (≤400 ng/mL; n = 381) or high (>400 ng/mL; n = 330) preoperative serum AFP levels and as having low (≤37 U/mL; n = 552) or high (>37 U/mL; n = 159) preoperative serum CA19-9 levels.
Disclosures: This study was sponsored by the Youth Program of Scientific Research Foundation of Guangxi Medical University Cancer Hospital, China, among others. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Source: Zhang J et al. Prognostic significance of combined α-fetoprotein and CA19-9 for hepatocellular carcinoma after hepatectomy. World J Surg Oncol. 2022;20:346 (Oct 19). Doi: 10.1186/s12957-022-02806-9
Key clinical point: The combination of alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) and carbohydrate antigen 19-9 (CA19-9) may effectively predict the prognosis of patients with hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) after radical hepatectomy.
Major finding: The 5-year overall and recurrence-free survival rates were significantly lower among patients with high preoperative serum AFP and CA19-9 levels than among those with high serum AFP or CA19-9 levels (P = .022 and P = .004, respectively) and those with low serum AFP and CA19-9 levels (both P < .001).
Study details: This retrospective study included 711 patients with HCC who were categorized as having low (≤400 ng/mL; n = 381) or high (>400 ng/mL; n = 330) preoperative serum AFP levels and as having low (≤37 U/mL; n = 552) or high (>37 U/mL; n = 159) preoperative serum CA19-9 levels.
Disclosures: This study was sponsored by the Youth Program of Scientific Research Foundation of Guangxi Medical University Cancer Hospital, China, among others. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Source: Zhang J et al. Prognostic significance of combined α-fetoprotein and CA19-9 for hepatocellular carcinoma after hepatectomy. World J Surg Oncol. 2022;20:346 (Oct 19). Doi: 10.1186/s12957-022-02806-9
Key clinical point: The combination of alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) and carbohydrate antigen 19-9 (CA19-9) may effectively predict the prognosis of patients with hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) after radical hepatectomy.
Major finding: The 5-year overall and recurrence-free survival rates were significantly lower among patients with high preoperative serum AFP and CA19-9 levels than among those with high serum AFP or CA19-9 levels (P = .022 and P = .004, respectively) and those with low serum AFP and CA19-9 levels (both P < .001).
Study details: This retrospective study included 711 patients with HCC who were categorized as having low (≤400 ng/mL; n = 381) or high (>400 ng/mL; n = 330) preoperative serum AFP levels and as having low (≤37 U/mL; n = 552) or high (>37 U/mL; n = 159) preoperative serum CA19-9 levels.
Disclosures: This study was sponsored by the Youth Program of Scientific Research Foundation of Guangxi Medical University Cancer Hospital, China, among others. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Source: Zhang J et al. Prognostic significance of combined α-fetoprotein and CA19-9 for hepatocellular carcinoma after hepatectomy. World J Surg Oncol. 2022;20:346 (Oct 19). Doi: 10.1186/s12957-022-02806-9
HAIC+lenvatinib+sequential ablation: An effective and safe treatment option for advanced HCC
Key clinical point: Compared with hepatic arterial infusion chemotherapy (HAIC)+lenvatinib, the triple therapeutic regimen HAIC+lenvatinib+sequential ablation significantly improved the survival of patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) without compromising safety.
Major finding: Patients who received HAIC+lenvatinib+sequential ablation vs HAIC+lenvatinib had a significantly longer median overall survival (>30 vs 13.6 months; P = .010), progression-free survival (PFS; 12.8 vs 5.6 months; P = .001), and intrahepatic PFS (14.6 vs 6.4 months; P = .002) and similar incidence of grade 1-2 (P = .404) and 3-4 (P = .333) adverse events.
Study details: This multicenter retrospective study included 150 patients with advanced HCC who received HAIC+lenvatinib (n = 97) or HAIC+lenvatinib+sequential ablation (n = 53).
Disclosures: This study did not receive any funding. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Source: Liu Y et al. Efficacy and safety of hepatic arterial infusion chemotherapy combined with lenvatinib and sequential ablation in the treatment of advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Med. 2022 (Oct 17). Doi: 10.1002/cam4.5366
Key clinical point: Compared with hepatic arterial infusion chemotherapy (HAIC)+lenvatinib, the triple therapeutic regimen HAIC+lenvatinib+sequential ablation significantly improved the survival of patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) without compromising safety.
Major finding: Patients who received HAIC+lenvatinib+sequential ablation vs HAIC+lenvatinib had a significantly longer median overall survival (>30 vs 13.6 months; P = .010), progression-free survival (PFS; 12.8 vs 5.6 months; P = .001), and intrahepatic PFS (14.6 vs 6.4 months; P = .002) and similar incidence of grade 1-2 (P = .404) and 3-4 (P = .333) adverse events.
Study details: This multicenter retrospective study included 150 patients with advanced HCC who received HAIC+lenvatinib (n = 97) or HAIC+lenvatinib+sequential ablation (n = 53).
Disclosures: This study did not receive any funding. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Source: Liu Y et al. Efficacy and safety of hepatic arterial infusion chemotherapy combined with lenvatinib and sequential ablation in the treatment of advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Med. 2022 (Oct 17). Doi: 10.1002/cam4.5366
Key clinical point: Compared with hepatic arterial infusion chemotherapy (HAIC)+lenvatinib, the triple therapeutic regimen HAIC+lenvatinib+sequential ablation significantly improved the survival of patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) without compromising safety.
Major finding: Patients who received HAIC+lenvatinib+sequential ablation vs HAIC+lenvatinib had a significantly longer median overall survival (>30 vs 13.6 months; P = .010), progression-free survival (PFS; 12.8 vs 5.6 months; P = .001), and intrahepatic PFS (14.6 vs 6.4 months; P = .002) and similar incidence of grade 1-2 (P = .404) and 3-4 (P = .333) adverse events.
Study details: This multicenter retrospective study included 150 patients with advanced HCC who received HAIC+lenvatinib (n = 97) or HAIC+lenvatinib+sequential ablation (n = 53).
Disclosures: This study did not receive any funding. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Source: Liu Y et al. Efficacy and safety of hepatic arterial infusion chemotherapy combined with lenvatinib and sequential ablation in the treatment of advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Med. 2022 (Oct 17). Doi: 10.1002/cam4.5366
HCC: Atezolizumab+bevacizumab treatment outcome unaffected by the underlying liver etiology
Key clinical point: Atezolizumab plus bevacizumab (Atez/Bev) is effective and safe against both virus-related and non-viral hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC).
Major finding: The objective response rate (20.6% and 24.6%, respectively; P = .55), median progression-free survival (7.0 and 6.2 months, respectively; hazard ratio 0.96; P = .33), and incidence and severity of adverse events, including diarrhea and liver injury, were comparable between patients with virus-related and non-viral HCC.
Study details: Findings are from a retrospective cohort study including 126 propensity score-matched pairs of patients with virus-related and non-viral HCC who had Child-Pugh class A, Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer stage B or C, and performance status ≤1 and received Atez/Bev.
Disclosures: No source of funding was reported. Some authors declared receiving honoraria and research grants from various sources.
Source: Hatanaka T et al. Comparative efficacy and safety of atezolizumab and bevacizumab between hepatocellular carcinoma patients with viral and non-viral infection: A Japanese multicenter observational study. Cancer Med. 2022 (Oct 13). Doi: 10.1002/cam4.5337
Key clinical point: Atezolizumab plus bevacizumab (Atez/Bev) is effective and safe against both virus-related and non-viral hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC).
Major finding: The objective response rate (20.6% and 24.6%, respectively; P = .55), median progression-free survival (7.0 and 6.2 months, respectively; hazard ratio 0.96; P = .33), and incidence and severity of adverse events, including diarrhea and liver injury, were comparable between patients with virus-related and non-viral HCC.
Study details: Findings are from a retrospective cohort study including 126 propensity score-matched pairs of patients with virus-related and non-viral HCC who had Child-Pugh class A, Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer stage B or C, and performance status ≤1 and received Atez/Bev.
Disclosures: No source of funding was reported. Some authors declared receiving honoraria and research grants from various sources.
Source: Hatanaka T et al. Comparative efficacy and safety of atezolizumab and bevacizumab between hepatocellular carcinoma patients with viral and non-viral infection: A Japanese multicenter observational study. Cancer Med. 2022 (Oct 13). Doi: 10.1002/cam4.5337
Key clinical point: Atezolizumab plus bevacizumab (Atez/Bev) is effective and safe against both virus-related and non-viral hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC).
Major finding: The objective response rate (20.6% and 24.6%, respectively; P = .55), median progression-free survival (7.0 and 6.2 months, respectively; hazard ratio 0.96; P = .33), and incidence and severity of adverse events, including diarrhea and liver injury, were comparable between patients with virus-related and non-viral HCC.
Study details: Findings are from a retrospective cohort study including 126 propensity score-matched pairs of patients with virus-related and non-viral HCC who had Child-Pugh class A, Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer stage B or C, and performance status ≤1 and received Atez/Bev.
Disclosures: No source of funding was reported. Some authors declared receiving honoraria and research grants from various sources.
Source: Hatanaka T et al. Comparative efficacy and safety of atezolizumab and bevacizumab between hepatocellular carcinoma patients with viral and non-viral infection: A Japanese multicenter observational study. Cancer Med. 2022 (Oct 13). Doi: 10.1002/cam4.5337