User login
WASHINGTON — A fully automated ultrasound scanning system combined with artificial intelligence–based disease activity scoring performed as well as expert rheumatologists in hand joint assessment of patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA), new research found.
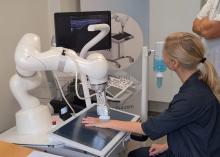
The system, made by a Danish company called ROPCA, comprises an ultrasound scanner called ARTHUR (RA Ultrasound Robot) that interacts directly with the patient and scans 11 joints per hand and a neural network–based software system, DIANA (Diagnosis Aid Network for RA), that evaluates the images and monitors RA activity.
The combined system classifies the degree of RA according to the joint European Alliance of Associations for Rheumatology (EULAR)–Outcome Measures in Rheumatology (OMERACT) standards for RA diagnosis. It received a CE Mark in Europe in 2022 and is currently in use in six rheumatology clinics in Denmark, Germany, Switzerland, and Austria, with more to come, ROPCA Co-founder and Chief Medical Officer Søren A. Just, MD, said in an interview.
“Automated systems could help rheumatologists in the early detection and monitoring of arthritis diseases. Systems can be placed or move in areas with insufficient rheumatological expertise,” Just said during a special late-breaker session presentation at the annual meeting of the American College of Rheumatology (ACR).
He said in an interview: “Currently, there are so many people referred and few and fewer rheumatologists. So we need to think differently. We need good automated assistants.” As a screening tool, the system can determine whether a person with hand pain has RA or just osteoarthritis “and also can give the patient an immediate answer, instead of waiting sometimes up to 6 months to get the information.”
Just, who is also a senior physician in the Department of Internal Medicine at Odense University Hospital in Denmark, said that his department is also using the system to assess flares in patients with established RA. “They can have a blood sample taken. They’re scanned by the robot, and you can see if there is any disease activity. But I think that screening of patients with joint pain is the beginning.”
Asked to comment, session moderator Gregory C. Gardner, MD, Emeritus Professor in the Division of Rheumatology at the University of Washington, Seattle, and a member of the ACR conference program committee, said in an interview “one of the reasons we chose to feature this abstract is because we’re interested in science at the convergence. We really thought this was a potential way to move the field forward for rheumatologists.”
Gardner said it’s an advantage that the patient could potentially have an ARTHUR scan with a DIANA report and get blood tests done prior to a visit with the rheumatologist. “It’s really time-consuming for a human to do these studies, so if you automate it, that’s a step forward in terms of having the data available for the rheumatologist to view and use sequentially to follow how patients are doing.”
When introducing Just’s presentation, Gardner called it “the coolest abstract of the meeting.”
Both DIANA and ARTHUR Performed At Least as Well as Human Rheumatologists
In the study, 30 patients with RA underwent two scans by ARTHUR, followed by a scan from a rheumatologist specialist in musculoskeletal ultrasound. The scans were sent to DIANA, who graded the images according to the Global OMERACT-EULAR Synovitis Score, as did the human rheumatologist.
A “ground truth” was established by another human expert who evaluated both ARTHUR’s and the other rheumatologist’s images, blinded to the scanning method. The image with the highest disease activity was deemed “ground truth,” and agreement with that was assessed for the two individual methods.
Just showed a video of a patient being scanned by ARTHUR. The machine verbally guided her through removing her jewelry, applying the gel, and placing her hand on the screen under the scanner. ARTHUR’s arm moved around on the patient’s hand, locating the best angles to take grayscale images and Doppler images and Doppler video. The scan takes 15-20 minutes, and the images are stored, Just said.
The study patients had a mean age of 65 years, and 23 of the 30 were men. Their average disease duration was 11 years, and mean Disease Activity Score in 28 joints using C-reactive protein was 3.86, indicating moderate disease. A majority (73%) of patients were taking disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs, and about one third were taking biologics. ARTHUR scanned a total of 660 joints, and 564 scans were successful.
For repeatability between the two ARTHUR scans, percent exact agreement was 63% for synovial hypertrophy, 75% for Doppler activity, and 60% combined. Percent close (within a point) agreements were 93%, 94%, and 92%, respectively. Binary agreements as to whether the joint was healthy vs diseased were 88%, 91%, and 85%, respectively.
At the joint level, ARTHUR and DIANA’s percent exact agreement with ground truth was 49% for synovial hypertrophy, 63% for Doppler activity, and 48% combined. Binary agreements with disease vs healthy were 80%, 88%, and 78%, respectively.
The human rheumatologists scored very similarly. Percent exact agreement with ground truth was 51% for synovial hypertrophy, 64% for Doppler activity, and 50% combined. Percent close agreements were 94%, 94%, and 92%, respectively. And binary agreements with diseased vs healthy were 83%, 91%, and 80%, respectively.
At the patient level (all joints combined), ARTHUR and DIANA’s binary disease assessment of healthy vs disease showed agreement with the ground truth of 87% for synovial hypertrophy, 83% for Doppler activity, and 87% combined. Here, the rheumatologists scored lower, at 53%, 67%, and 60%, respectively.
“In this study, we think the precision of ARTHUR and DIANA was comparable to that of an experienced rheumatologist, at both the joint and patient level,” Just said.
Gardner pointed out another advantage of the system. “DIANA doesn’t get fatigued. ... With human reading, the precision may change based on the time of day or stress level. ... But with DIANA, you’re going to get consistent information.”
Just said that the Arthritis Foundation in Germany recently put ARTHUR and DIANA on a bus and took it to cities that lacked a rheumatologist. Patients lined up, answered a questionnaire, had blood drawn, and received their scans. A rheumatologist on the bus then interpreted the data and consulted with the individuals about their RA risk. “In the last trip, we screened 800 patients in 6 days. So there are definitely possibilities here.”
Just is co-owner of ROPCA. Gardner had no disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
WASHINGTON — A fully automated ultrasound scanning system combined with artificial intelligence–based disease activity scoring performed as well as expert rheumatologists in hand joint assessment of patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA), new research found.
The system, made by a Danish company called ROPCA, comprises an ultrasound scanner called ARTHUR (RA Ultrasound Robot) that interacts directly with the patient and scans 11 joints per hand and a neural network–based software system, DIANA (Diagnosis Aid Network for RA), that evaluates the images and monitors RA activity.
The combined system classifies the degree of RA according to the joint European Alliance of Associations for Rheumatology (EULAR)–Outcome Measures in Rheumatology (OMERACT) standards for RA diagnosis. It received a CE Mark in Europe in 2022 and is currently in use in six rheumatology clinics in Denmark, Germany, Switzerland, and Austria, with more to come, ROPCA Co-founder and Chief Medical Officer Søren A. Just, MD, said in an interview.
“Automated systems could help rheumatologists in the early detection and monitoring of arthritis diseases. Systems can be placed or move in areas with insufficient rheumatological expertise,” Just said during a special late-breaker session presentation at the annual meeting of the American College of Rheumatology (ACR).
He said in an interview: “Currently, there are so many people referred and few and fewer rheumatologists. So we need to think differently. We need good automated assistants.” As a screening tool, the system can determine whether a person with hand pain has RA or just osteoarthritis “and also can give the patient an immediate answer, instead of waiting sometimes up to 6 months to get the information.”
Just, who is also a senior physician in the Department of Internal Medicine at Odense University Hospital in Denmark, said that his department is also using the system to assess flares in patients with established RA. “They can have a blood sample taken. They’re scanned by the robot, and you can see if there is any disease activity. But I think that screening of patients with joint pain is the beginning.”
Asked to comment, session moderator Gregory C. Gardner, MD, Emeritus Professor in the Division of Rheumatology at the University of Washington, Seattle, and a member of the ACR conference program committee, said in an interview “one of the reasons we chose to feature this abstract is because we’re interested in science at the convergence. We really thought this was a potential way to move the field forward for rheumatologists.”
Gardner said it’s an advantage that the patient could potentially have an ARTHUR scan with a DIANA report and get blood tests done prior to a visit with the rheumatologist. “It’s really time-consuming for a human to do these studies, so if you automate it, that’s a step forward in terms of having the data available for the rheumatologist to view and use sequentially to follow how patients are doing.”
When introducing Just’s presentation, Gardner called it “the coolest abstract of the meeting.”
Both DIANA and ARTHUR Performed At Least as Well as Human Rheumatologists
In the study, 30 patients with RA underwent two scans by ARTHUR, followed by a scan from a rheumatologist specialist in musculoskeletal ultrasound. The scans were sent to DIANA, who graded the images according to the Global OMERACT-EULAR Synovitis Score, as did the human rheumatologist.
A “ground truth” was established by another human expert who evaluated both ARTHUR’s and the other rheumatologist’s images, blinded to the scanning method. The image with the highest disease activity was deemed “ground truth,” and agreement with that was assessed for the two individual methods.
Just showed a video of a patient being scanned by ARTHUR. The machine verbally guided her through removing her jewelry, applying the gel, and placing her hand on the screen under the scanner. ARTHUR’s arm moved around on the patient’s hand, locating the best angles to take grayscale images and Doppler images and Doppler video. The scan takes 15-20 minutes, and the images are stored, Just said.
The study patients had a mean age of 65 years, and 23 of the 30 were men. Their average disease duration was 11 years, and mean Disease Activity Score in 28 joints using C-reactive protein was 3.86, indicating moderate disease. A majority (73%) of patients were taking disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs, and about one third were taking biologics. ARTHUR scanned a total of 660 joints, and 564 scans were successful.
For repeatability between the two ARTHUR scans, percent exact agreement was 63% for synovial hypertrophy, 75% for Doppler activity, and 60% combined. Percent close (within a point) agreements were 93%, 94%, and 92%, respectively. Binary agreements as to whether the joint was healthy vs diseased were 88%, 91%, and 85%, respectively.
At the joint level, ARTHUR and DIANA’s percent exact agreement with ground truth was 49% for synovial hypertrophy, 63% for Doppler activity, and 48% combined. Binary agreements with disease vs healthy were 80%, 88%, and 78%, respectively.
The human rheumatologists scored very similarly. Percent exact agreement with ground truth was 51% for synovial hypertrophy, 64% for Doppler activity, and 50% combined. Percent close agreements were 94%, 94%, and 92%, respectively. And binary agreements with diseased vs healthy were 83%, 91%, and 80%, respectively.
At the patient level (all joints combined), ARTHUR and DIANA’s binary disease assessment of healthy vs disease showed agreement with the ground truth of 87% for synovial hypertrophy, 83% for Doppler activity, and 87% combined. Here, the rheumatologists scored lower, at 53%, 67%, and 60%, respectively.
“In this study, we think the precision of ARTHUR and DIANA was comparable to that of an experienced rheumatologist, at both the joint and patient level,” Just said.
Gardner pointed out another advantage of the system. “DIANA doesn’t get fatigued. ... With human reading, the precision may change based on the time of day or stress level. ... But with DIANA, you’re going to get consistent information.”
Just said that the Arthritis Foundation in Germany recently put ARTHUR and DIANA on a bus and took it to cities that lacked a rheumatologist. Patients lined up, answered a questionnaire, had blood drawn, and received their scans. A rheumatologist on the bus then interpreted the data and consulted with the individuals about their RA risk. “In the last trip, we screened 800 patients in 6 days. So there are definitely possibilities here.”
Just is co-owner of ROPCA. Gardner had no disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
WASHINGTON — A fully automated ultrasound scanning system combined with artificial intelligence–based disease activity scoring performed as well as expert rheumatologists in hand joint assessment of patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA), new research found.
The system, made by a Danish company called ROPCA, comprises an ultrasound scanner called ARTHUR (RA Ultrasound Robot) that interacts directly with the patient and scans 11 joints per hand and a neural network–based software system, DIANA (Diagnosis Aid Network for RA), that evaluates the images and monitors RA activity.
The combined system classifies the degree of RA according to the joint European Alliance of Associations for Rheumatology (EULAR)–Outcome Measures in Rheumatology (OMERACT) standards for RA diagnosis. It received a CE Mark in Europe in 2022 and is currently in use in six rheumatology clinics in Denmark, Germany, Switzerland, and Austria, with more to come, ROPCA Co-founder and Chief Medical Officer Søren A. Just, MD, said in an interview.
“Automated systems could help rheumatologists in the early detection and monitoring of arthritis diseases. Systems can be placed or move in areas with insufficient rheumatological expertise,” Just said during a special late-breaker session presentation at the annual meeting of the American College of Rheumatology (ACR).
He said in an interview: “Currently, there are so many people referred and few and fewer rheumatologists. So we need to think differently. We need good automated assistants.” As a screening tool, the system can determine whether a person with hand pain has RA or just osteoarthritis “and also can give the patient an immediate answer, instead of waiting sometimes up to 6 months to get the information.”
Just, who is also a senior physician in the Department of Internal Medicine at Odense University Hospital in Denmark, said that his department is also using the system to assess flares in patients with established RA. “They can have a blood sample taken. They’re scanned by the robot, and you can see if there is any disease activity. But I think that screening of patients with joint pain is the beginning.”
Asked to comment, session moderator Gregory C. Gardner, MD, Emeritus Professor in the Division of Rheumatology at the University of Washington, Seattle, and a member of the ACR conference program committee, said in an interview “one of the reasons we chose to feature this abstract is because we’re interested in science at the convergence. We really thought this was a potential way to move the field forward for rheumatologists.”
Gardner said it’s an advantage that the patient could potentially have an ARTHUR scan with a DIANA report and get blood tests done prior to a visit with the rheumatologist. “It’s really time-consuming for a human to do these studies, so if you automate it, that’s a step forward in terms of having the data available for the rheumatologist to view and use sequentially to follow how patients are doing.”
When introducing Just’s presentation, Gardner called it “the coolest abstract of the meeting.”
Both DIANA and ARTHUR Performed At Least as Well as Human Rheumatologists
In the study, 30 patients with RA underwent two scans by ARTHUR, followed by a scan from a rheumatologist specialist in musculoskeletal ultrasound. The scans were sent to DIANA, who graded the images according to the Global OMERACT-EULAR Synovitis Score, as did the human rheumatologist.
A “ground truth” was established by another human expert who evaluated both ARTHUR’s and the other rheumatologist’s images, blinded to the scanning method. The image with the highest disease activity was deemed “ground truth,” and agreement with that was assessed for the two individual methods.
Just showed a video of a patient being scanned by ARTHUR. The machine verbally guided her through removing her jewelry, applying the gel, and placing her hand on the screen under the scanner. ARTHUR’s arm moved around on the patient’s hand, locating the best angles to take grayscale images and Doppler images and Doppler video. The scan takes 15-20 minutes, and the images are stored, Just said.
The study patients had a mean age of 65 years, and 23 of the 30 were men. Their average disease duration was 11 years, and mean Disease Activity Score in 28 joints using C-reactive protein was 3.86, indicating moderate disease. A majority (73%) of patients were taking disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs, and about one third were taking biologics. ARTHUR scanned a total of 660 joints, and 564 scans were successful.
For repeatability between the two ARTHUR scans, percent exact agreement was 63% for synovial hypertrophy, 75% for Doppler activity, and 60% combined. Percent close (within a point) agreements were 93%, 94%, and 92%, respectively. Binary agreements as to whether the joint was healthy vs diseased were 88%, 91%, and 85%, respectively.
At the joint level, ARTHUR and DIANA’s percent exact agreement with ground truth was 49% for synovial hypertrophy, 63% for Doppler activity, and 48% combined. Binary agreements with disease vs healthy were 80%, 88%, and 78%, respectively.
The human rheumatologists scored very similarly. Percent exact agreement with ground truth was 51% for synovial hypertrophy, 64% for Doppler activity, and 50% combined. Percent close agreements were 94%, 94%, and 92%, respectively. And binary agreements with diseased vs healthy were 83%, 91%, and 80%, respectively.
At the patient level (all joints combined), ARTHUR and DIANA’s binary disease assessment of healthy vs disease showed agreement with the ground truth of 87% for synovial hypertrophy, 83% for Doppler activity, and 87% combined. Here, the rheumatologists scored lower, at 53%, 67%, and 60%, respectively.
“In this study, we think the precision of ARTHUR and DIANA was comparable to that of an experienced rheumatologist, at both the joint and patient level,” Just said.
Gardner pointed out another advantage of the system. “DIANA doesn’t get fatigued. ... With human reading, the precision may change based on the time of day or stress level. ... But with DIANA, you’re going to get consistent information.”
Just said that the Arthritis Foundation in Germany recently put ARTHUR and DIANA on a bus and took it to cities that lacked a rheumatologist. Patients lined up, answered a questionnaire, had blood drawn, and received their scans. A rheumatologist on the bus then interpreted the data and consulted with the individuals about their RA risk. “In the last trip, we screened 800 patients in 6 days. So there are definitely possibilities here.”
Just is co-owner of ROPCA. Gardner had no disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM ACR 2024