User login
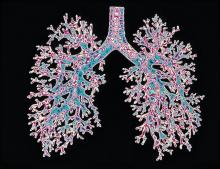
Airway structure in women leads to worse COPD outcomes
A study aimed at determining whether behind some of the sex differences in chronic obstructive airway disease (COPD) prevalence and clinical outcomes lie structural differences in airways found that airway lumen sizes quantified through chest CT were smaller in women than in men.
The findings, published in Radiology, took into account height and lung size. for equivalent changes, compared with men.
Among key findings in a secondary analysis of consecutive participants (9,363 ever-smokers and 420 never-smokers) enrolled in the Genetic Epidemiology of COPD (COPDGene) study, airway lumen dimensions were lower in never-smoker women than in men (segmental lumen diameter, 8.1 mm vs. 9.1 mm; P < .001). Also, ever-smoker women had narrower segmental lumen diameter (7.8 mm ± 0.05 vs. 8.7 mm ± 0.04; P < .001). The investigators found also that a unit change in wall thickness or lumen area resulted in more severe airflow obstruction, more dyspnea, worse respiratory quality of life, lower 6-minute walk distance, and worse survival in women, compared with men.
While COPD is diagnosed more often in men than women, changes in smoking behavior and increasing urbanization have led to COPD prevalence in women fast approaching the rate in men. Although age-adjusted rates for COPD-related deaths have continued to decline in men, in women they have not. Indeed, never-smoking women accounted for two-thirds of COPD in a population-based study.
COPDGene, a prospective, multicenter, observational cohort study, enrolled current and former smokers, as well as never-smokers, aged 45-80 years at 21 clinical centers across the United States from January 2008 to June 2011 with longitudinal follow-up until November 2020. The investigators quantified airway disease through CT imaging using the following metrics: airway wall thickness of segmental airways, wall area percent of segmental airways, the square root of the wall area of a hypothetical airway with 10-mm internal perimeter, total airway count, lumen diameter of segmental airways, airway volume, and airway fractal dimension.
“Not all sex differences in prevalence of COPD have been explained, and structural differences may explain some of these differences. Our findings may have implications for patient selection for clinical trials,” corresponding author Surya P. Bhatt, MD, associate professor of medicine and director of the University of Alabama Imaging Core at Birmingham, said in an interview.
The investigators wrote: “Our findings have implications for airflow limitation and the consequent clinical outcomes. ... We confirmed that men have more emphysema than women with equivalent smoking burden, and our results suggest that the lower reserve conferred by smaller airways predisposes women to develop airflow limitation predominantly through the airway phenotype. All airway remodeling changes were associated with more dyspnea, worse respiratory quality of life, and lower functional capacity in women than in men. The smaller airways in women can result in higher airway resistance and more turbulent airflow, and thus place a higher ventilatory constraint during exertion. Alteration in each airway measure was also associated with worse survival in women than in men, partially explaining the comparable mortality between the sexes for COPD despite the differing degrees of emphysema.”
“I think these findings highlight underappreciated sex differences in the natural history of COPD,” Mohsen Sadatsafavi, MD, PhD, associate professor, faculty of pharmaceutical sciences, at the University of British Columbia, Vancouver, said in an interview. “To me, first and foremost, the Bhatt et al. findings highlight how the ‘one size fits all’ approach to COPD management of using exacerbation history alone to guide preventive therapies is incorrect. These findings have the potential to change the management paradigm of COPD in the long term, but before getting there, I think we need to relate these findings to clinically relevant and patient-reported outcomes.”
Noting study limitations, the authors stated that a higher proportion of men were active smokers, compared with women, and despite adjustments for smoking status, some of the airway wall differences may be from the impact of active cigarette smoking on airway wall thickness.
Five study authors reported receiving support from various government and industry sources and disclosed conflicts of interest based on relationships with industry. The rest reported no conflicts of interest.
A study aimed at determining whether behind some of the sex differences in chronic obstructive airway disease (COPD) prevalence and clinical outcomes lie structural differences in airways found that airway lumen sizes quantified through chest CT were smaller in women than in men.
The findings, published in Radiology, took into account height and lung size. for equivalent changes, compared with men.
Among key findings in a secondary analysis of consecutive participants (9,363 ever-smokers and 420 never-smokers) enrolled in the Genetic Epidemiology of COPD (COPDGene) study, airway lumen dimensions were lower in never-smoker women than in men (segmental lumen diameter, 8.1 mm vs. 9.1 mm; P < .001). Also, ever-smoker women had narrower segmental lumen diameter (7.8 mm ± 0.05 vs. 8.7 mm ± 0.04; P < .001). The investigators found also that a unit change in wall thickness or lumen area resulted in more severe airflow obstruction, more dyspnea, worse respiratory quality of life, lower 6-minute walk distance, and worse survival in women, compared with men.
While COPD is diagnosed more often in men than women, changes in smoking behavior and increasing urbanization have led to COPD prevalence in women fast approaching the rate in men. Although age-adjusted rates for COPD-related deaths have continued to decline in men, in women they have not. Indeed, never-smoking women accounted for two-thirds of COPD in a population-based study.
COPDGene, a prospective, multicenter, observational cohort study, enrolled current and former smokers, as well as never-smokers, aged 45-80 years at 21 clinical centers across the United States from January 2008 to June 2011 with longitudinal follow-up until November 2020. The investigators quantified airway disease through CT imaging using the following metrics: airway wall thickness of segmental airways, wall area percent of segmental airways, the square root of the wall area of a hypothetical airway with 10-mm internal perimeter, total airway count, lumen diameter of segmental airways, airway volume, and airway fractal dimension.
“Not all sex differences in prevalence of COPD have been explained, and structural differences may explain some of these differences. Our findings may have implications for patient selection for clinical trials,” corresponding author Surya P. Bhatt, MD, associate professor of medicine and director of the University of Alabama Imaging Core at Birmingham, said in an interview.
The investigators wrote: “Our findings have implications for airflow limitation and the consequent clinical outcomes. ... We confirmed that men have more emphysema than women with equivalent smoking burden, and our results suggest that the lower reserve conferred by smaller airways predisposes women to develop airflow limitation predominantly through the airway phenotype. All airway remodeling changes were associated with more dyspnea, worse respiratory quality of life, and lower functional capacity in women than in men. The smaller airways in women can result in higher airway resistance and more turbulent airflow, and thus place a higher ventilatory constraint during exertion. Alteration in each airway measure was also associated with worse survival in women than in men, partially explaining the comparable mortality between the sexes for COPD despite the differing degrees of emphysema.”
“I think these findings highlight underappreciated sex differences in the natural history of COPD,” Mohsen Sadatsafavi, MD, PhD, associate professor, faculty of pharmaceutical sciences, at the University of British Columbia, Vancouver, said in an interview. “To me, first and foremost, the Bhatt et al. findings highlight how the ‘one size fits all’ approach to COPD management of using exacerbation history alone to guide preventive therapies is incorrect. These findings have the potential to change the management paradigm of COPD in the long term, but before getting there, I think we need to relate these findings to clinically relevant and patient-reported outcomes.”
Noting study limitations, the authors stated that a higher proportion of men were active smokers, compared with women, and despite adjustments for smoking status, some of the airway wall differences may be from the impact of active cigarette smoking on airway wall thickness.
Five study authors reported receiving support from various government and industry sources and disclosed conflicts of interest based on relationships with industry. The rest reported no conflicts of interest.
A study aimed at determining whether behind some of the sex differences in chronic obstructive airway disease (COPD) prevalence and clinical outcomes lie structural differences in airways found that airway lumen sizes quantified through chest CT were smaller in women than in men.
The findings, published in Radiology, took into account height and lung size. for equivalent changes, compared with men.
Among key findings in a secondary analysis of consecutive participants (9,363 ever-smokers and 420 never-smokers) enrolled in the Genetic Epidemiology of COPD (COPDGene) study, airway lumen dimensions were lower in never-smoker women than in men (segmental lumen diameter, 8.1 mm vs. 9.1 mm; P < .001). Also, ever-smoker women had narrower segmental lumen diameter (7.8 mm ± 0.05 vs. 8.7 mm ± 0.04; P < .001). The investigators found also that a unit change in wall thickness or lumen area resulted in more severe airflow obstruction, more dyspnea, worse respiratory quality of life, lower 6-minute walk distance, and worse survival in women, compared with men.
While COPD is diagnosed more often in men than women, changes in smoking behavior and increasing urbanization have led to COPD prevalence in women fast approaching the rate in men. Although age-adjusted rates for COPD-related deaths have continued to decline in men, in women they have not. Indeed, never-smoking women accounted for two-thirds of COPD in a population-based study.
COPDGene, a prospective, multicenter, observational cohort study, enrolled current and former smokers, as well as never-smokers, aged 45-80 years at 21 clinical centers across the United States from January 2008 to June 2011 with longitudinal follow-up until November 2020. The investigators quantified airway disease through CT imaging using the following metrics: airway wall thickness of segmental airways, wall area percent of segmental airways, the square root of the wall area of a hypothetical airway with 10-mm internal perimeter, total airway count, lumen diameter of segmental airways, airway volume, and airway fractal dimension.
“Not all sex differences in prevalence of COPD have been explained, and structural differences may explain some of these differences. Our findings may have implications for patient selection for clinical trials,” corresponding author Surya P. Bhatt, MD, associate professor of medicine and director of the University of Alabama Imaging Core at Birmingham, said in an interview.
The investigators wrote: “Our findings have implications for airflow limitation and the consequent clinical outcomes. ... We confirmed that men have more emphysema than women with equivalent smoking burden, and our results suggest that the lower reserve conferred by smaller airways predisposes women to develop airflow limitation predominantly through the airway phenotype. All airway remodeling changes were associated with more dyspnea, worse respiratory quality of life, and lower functional capacity in women than in men. The smaller airways in women can result in higher airway resistance and more turbulent airflow, and thus place a higher ventilatory constraint during exertion. Alteration in each airway measure was also associated with worse survival in women than in men, partially explaining the comparable mortality between the sexes for COPD despite the differing degrees of emphysema.”
“I think these findings highlight underappreciated sex differences in the natural history of COPD,” Mohsen Sadatsafavi, MD, PhD, associate professor, faculty of pharmaceutical sciences, at the University of British Columbia, Vancouver, said in an interview. “To me, first and foremost, the Bhatt et al. findings highlight how the ‘one size fits all’ approach to COPD management of using exacerbation history alone to guide preventive therapies is incorrect. These findings have the potential to change the management paradigm of COPD in the long term, but before getting there, I think we need to relate these findings to clinically relevant and patient-reported outcomes.”
Noting study limitations, the authors stated that a higher proportion of men were active smokers, compared with women, and despite adjustments for smoking status, some of the airway wall differences may be from the impact of active cigarette smoking on airway wall thickness.
Five study authors reported receiving support from various government and industry sources and disclosed conflicts of interest based on relationships with industry. The rest reported no conflicts of interest.
FROM RADIOLOGY
Exercise limitations in COPD – not everyone needs more inhalers
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is defined by airway obstruction and alveolar damage caused by exposure to noxious air particles. The physiologic results include varying degrees of gas-exchange abnormality and mechanical respiratory limitation, often in the form of dynamic hyperinflation. There’s a third major contributor, though – skeletal muscle deconditioning. Only one of these abnormalities responds to inhalers.
When your patients with COPD report dyspnea or exercise intolerance, what do you do? Do you attempt to determine its character to pinpoint its origin? Do you quiz them about their baseline activity levels to quantify their conditioning? I bet you get right to the point and order a cardiopulmonary exercise test (CPET). That way you’ll be able to tease out all the contributors. Nah. Most likely you add an inhaler before continuing to rush through your COPD quality metrics: Vaccines? Check. Lung cancer screening? Check. Smoking cessation? Check.
The physiology of dyspnea and exercise limitation in COPD has been extensively studied. Work-of-breathing, dynamic hyperinflation, and gas-exchange inefficiencies interact with each other in complex ways to produce symptoms. The presence of deconditioning simply magnifies the existing abnormalities within the respiratory system by creating more strain at lower work rates. Acute exacerbations (AECOPD) and oral corticosteroids further aggravate skeletal muscle dysfunction.
The Global Strategy for the Diagnosis, Management, and Prevention of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (GOLD) Report directs clinicians to use inhalers to manage dyspnea. If they’re already on one inhaler, they get another. This continues until they’re stabilized on a long-acting beta-agonist (LABA), long-acting muscarinic antagonist (LAMA), and an inhaled corticosteroid (ICS). The GOLD report also advises pulmonary rehabilitation for any patient with grade B through D disease. Unfortunately, the pulmonary rehabilitation recommendation is buried in the text and doesn’t appear within the popularized pharmacologic algorithms in the report’s figures.
The data for adding inhalers on top of each other to reduce AECOPD and improve overall quality of life (QOL) are good. However, although GOLD tells us to keep adding inhalers for the dyspneic patient with COPD, the authors acknowledge that this hasn’t been systematically tested. The difference? A statement doesn’t require the same formal, rigorous scientific analysis known as the GRADE approach. Using this kind of analysis, a recent clinical practice guideline by the American Thoracic Society found no benefit in dyspnea or respiratory QOL with step-up from inhaler monotherapy.
Inhalers won’t do anything for gas-exchange inefficiencies and deconditioning, at least not directly. A recent CPET study from the CanCOLD network found ventilatory inefficiency in 23% of GOLD 1 and 26% of GOLD 2-4 COPD patients. The numbers were higher for those who reported dyspnea. Skeletal muscle dysfunction rates are equally high.
Thus, dyspnea and exercise intolerance are major determinants of QOL in COPD, but inhalers will only get you so far. At a minimum, make sure you get an activity/exercise history from your patients with COPD. For those who are sedentary, provide an exercise prescription (really, it’s not that hard to do). If dyspnea persists despite LABA or LAMA monotherapy, clarify the complaint before doubling down. Finally, try to get the patient into a good pulmonary rehabilitation program. They’ll thank you afterwards.
Dr. Holley is Associate Professor, department of medicine, Uniformed Services University of the Health Sciences and Program Director, Pulmonary and Critical Care Medical Fellowship, department of medicine, Walter Reed National Military Medical Center, both in Bethesda, Md. He reported receiving research grants from Fisher-Paykel and receiving income from the American College of Chest Physicians.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is defined by airway obstruction and alveolar damage caused by exposure to noxious air particles. The physiologic results include varying degrees of gas-exchange abnormality and mechanical respiratory limitation, often in the form of dynamic hyperinflation. There’s a third major contributor, though – skeletal muscle deconditioning. Only one of these abnormalities responds to inhalers.
When your patients with COPD report dyspnea or exercise intolerance, what do you do? Do you attempt to determine its character to pinpoint its origin? Do you quiz them about their baseline activity levels to quantify their conditioning? I bet you get right to the point and order a cardiopulmonary exercise test (CPET). That way you’ll be able to tease out all the contributors. Nah. Most likely you add an inhaler before continuing to rush through your COPD quality metrics: Vaccines? Check. Lung cancer screening? Check. Smoking cessation? Check.
The physiology of dyspnea and exercise limitation in COPD has been extensively studied. Work-of-breathing, dynamic hyperinflation, and gas-exchange inefficiencies interact with each other in complex ways to produce symptoms. The presence of deconditioning simply magnifies the existing abnormalities within the respiratory system by creating more strain at lower work rates. Acute exacerbations (AECOPD) and oral corticosteroids further aggravate skeletal muscle dysfunction.
The Global Strategy for the Diagnosis, Management, and Prevention of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (GOLD) Report directs clinicians to use inhalers to manage dyspnea. If they’re already on one inhaler, they get another. This continues until they’re stabilized on a long-acting beta-agonist (LABA), long-acting muscarinic antagonist (LAMA), and an inhaled corticosteroid (ICS). The GOLD report also advises pulmonary rehabilitation for any patient with grade B through D disease. Unfortunately, the pulmonary rehabilitation recommendation is buried in the text and doesn’t appear within the popularized pharmacologic algorithms in the report’s figures.
The data for adding inhalers on top of each other to reduce AECOPD and improve overall quality of life (QOL) are good. However, although GOLD tells us to keep adding inhalers for the dyspneic patient with COPD, the authors acknowledge that this hasn’t been systematically tested. The difference? A statement doesn’t require the same formal, rigorous scientific analysis known as the GRADE approach. Using this kind of analysis, a recent clinical practice guideline by the American Thoracic Society found no benefit in dyspnea or respiratory QOL with step-up from inhaler monotherapy.
Inhalers won’t do anything for gas-exchange inefficiencies and deconditioning, at least not directly. A recent CPET study from the CanCOLD network found ventilatory inefficiency in 23% of GOLD 1 and 26% of GOLD 2-4 COPD patients. The numbers were higher for those who reported dyspnea. Skeletal muscle dysfunction rates are equally high.
Thus, dyspnea and exercise intolerance are major determinants of QOL in COPD, but inhalers will only get you so far. At a minimum, make sure you get an activity/exercise history from your patients with COPD. For those who are sedentary, provide an exercise prescription (really, it’s not that hard to do). If dyspnea persists despite LABA or LAMA monotherapy, clarify the complaint before doubling down. Finally, try to get the patient into a good pulmonary rehabilitation program. They’ll thank you afterwards.
Dr. Holley is Associate Professor, department of medicine, Uniformed Services University of the Health Sciences and Program Director, Pulmonary and Critical Care Medical Fellowship, department of medicine, Walter Reed National Military Medical Center, both in Bethesda, Md. He reported receiving research grants from Fisher-Paykel and receiving income from the American College of Chest Physicians.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is defined by airway obstruction and alveolar damage caused by exposure to noxious air particles. The physiologic results include varying degrees of gas-exchange abnormality and mechanical respiratory limitation, often in the form of dynamic hyperinflation. There’s a third major contributor, though – skeletal muscle deconditioning. Only one of these abnormalities responds to inhalers.
When your patients with COPD report dyspnea or exercise intolerance, what do you do? Do you attempt to determine its character to pinpoint its origin? Do you quiz them about their baseline activity levels to quantify their conditioning? I bet you get right to the point and order a cardiopulmonary exercise test (CPET). That way you’ll be able to tease out all the contributors. Nah. Most likely you add an inhaler before continuing to rush through your COPD quality metrics: Vaccines? Check. Lung cancer screening? Check. Smoking cessation? Check.
The physiology of dyspnea and exercise limitation in COPD has been extensively studied. Work-of-breathing, dynamic hyperinflation, and gas-exchange inefficiencies interact with each other in complex ways to produce symptoms. The presence of deconditioning simply magnifies the existing abnormalities within the respiratory system by creating more strain at lower work rates. Acute exacerbations (AECOPD) and oral corticosteroids further aggravate skeletal muscle dysfunction.
The Global Strategy for the Diagnosis, Management, and Prevention of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (GOLD) Report directs clinicians to use inhalers to manage dyspnea. If they’re already on one inhaler, they get another. This continues until they’re stabilized on a long-acting beta-agonist (LABA), long-acting muscarinic antagonist (LAMA), and an inhaled corticosteroid (ICS). The GOLD report also advises pulmonary rehabilitation for any patient with grade B through D disease. Unfortunately, the pulmonary rehabilitation recommendation is buried in the text and doesn’t appear within the popularized pharmacologic algorithms in the report’s figures.
The data for adding inhalers on top of each other to reduce AECOPD and improve overall quality of life (QOL) are good. However, although GOLD tells us to keep adding inhalers for the dyspneic patient with COPD, the authors acknowledge that this hasn’t been systematically tested. The difference? A statement doesn’t require the same formal, rigorous scientific analysis known as the GRADE approach. Using this kind of analysis, a recent clinical practice guideline by the American Thoracic Society found no benefit in dyspnea or respiratory QOL with step-up from inhaler monotherapy.
Inhalers won’t do anything for gas-exchange inefficiencies and deconditioning, at least not directly. A recent CPET study from the CanCOLD network found ventilatory inefficiency in 23% of GOLD 1 and 26% of GOLD 2-4 COPD patients. The numbers were higher for those who reported dyspnea. Skeletal muscle dysfunction rates are equally high.
Thus, dyspnea and exercise intolerance are major determinants of QOL in COPD, but inhalers will only get you so far. At a minimum, make sure you get an activity/exercise history from your patients with COPD. For those who are sedentary, provide an exercise prescription (really, it’s not that hard to do). If dyspnea persists despite LABA or LAMA monotherapy, clarify the complaint before doubling down. Finally, try to get the patient into a good pulmonary rehabilitation program. They’ll thank you afterwards.
Dr. Holley is Associate Professor, department of medicine, Uniformed Services University of the Health Sciences and Program Director, Pulmonary and Critical Care Medical Fellowship, department of medicine, Walter Reed National Military Medical Center, both in Bethesda, Md. He reported receiving research grants from Fisher-Paykel and receiving income from the American College of Chest Physicians.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Trials data on COPD leave primary care docs in the dark
Primary care clinicians often struggle to care for their patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), thanks to a lack of real-world evidence as to which treatments work best.
As a result, potentially preventable life-threatening exacerbations are common among people with the condition. Central to the problem, some experts believe, is that the average patient bears little resemblance to participants in clinical trials of the medications used to treat COPD.
Indeed, a recent study showed that many COPD patients who were receiving maintenance therapy that should have been controlling their disease experienced severe flare-ups – a finding that caught the researchers by surprise.
“We know the benefit of COPD treatments in the context of clinical trials. However, the kinds of patients in primary care may not completely mimic those in clinical trials,” one of the authors, MeiLan Han, MD, a professor of medicine in the division of pulmonary and critical care at the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, told this news organization. Dr. Han, a volunteer medical spokesperson for the American Lung Association, added that patients “may not be as adherent to medications in real life as they are in clinical trials.”
, who are younger than the average patient with COPD, and who typically are male. Patients are seen in resource-abundant settings designed to maximize adherence to treatment, with supports such as free medication and frequent monitoring – settings far different from those in which most primary care physicians practice.
The authors of the new article said trials conducted with typical patients in primary care settings could help physicians to optimize treatment.
Real-world evidence can shed light on physicians’ intent and on barriers to following guidelines, as well as important patient factors, such as adherence and good inhaler technique, Barbara Yawn, MD, an adjunct professor in the department of family and community health at the University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, and a coauthor of the study, said in an interview.
A window onto patient burden
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, an estimated $15 million Americans have COPD. Annual costs to the health care system approach $50 billion a year. The death rate for COPD has increased since 1969 as death rates of other major killers in the United States, such as heart disease and cancer, declined, according to a 2015 analysis of death records.
The new study, published in the July/August issue of the Annals of Family Medicine, provides a snapshot of COPD’s toll on patients.
Researchers examined electronic health records of 17,192 patients treated at primary care clinics in five states using a dataset maintained by DARTNet Institute, a nonprofit organization that supports research and quality improvement. They also analyzed self-reported assessments from 1,354 patients in the dataset who are in a registry called Advancing the Patient Experience in COPD.
Over half (56%) of patients were female, White (64%), aged 55-84 years (81%), and current or exsmokers (80%). The vast majority had three or more comorbidities, including hypertension, diabetes, and depression.
Serious flare-ups were common; 38% of patients had experienced one or more exacerbations in the previous year. Of registry respondents, half said they had had at least one exacerbation, and 20% said they had been hospitalized for COPD during that period.
Among patients in the registry, 43% reported that COPD had a high or very high impact on their health, and 45% could not walk at a normal pace without losing their breath.
Almost 90% of patients were receiving a maintenance therapy regimen. The number of exacerbations was “somewhat surprising,” the authors say. They write that the findings may indicate that patients were not receiving appropriate treatment or were not complying with their medication regimens and that there may be a need for nonpharmacologic interventions, such as smoking cessation. They also write that physician education is needed to support earlier diagnosis and treatment so as to delay declines in lung function.
The researchers say their findings highlight “the need for more real-life effectiveness trials to better support decision-making at the primary care level.”
Dr. Yawn is a coinvestigator of one such study, called CAPTURE, which is assessing a screening tool for COPD in primary care practices.
At the University of Illinois, Chicago, Jerry Krishnan, MD, PhD, pulmonologist and professor of medicine and public health, is running the RELIANCE study, which is comparing the use of azithromycin and roflumilast in preventing hospitalization and death among patients with COPD who continue to have exacerbations.
Although RELIANCE involves pulmonologists, Dr. Krishnan told this news organization, it offers a model for building real-world evidence on questions relevant to primary care. “We don’t really know if medications used by patients in my clinic are as effective as reported in clinical trials that were used to obtain regulatory approvals by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration,” he said.
Wilson Pace, MD, a family physician and chief medical officer and chief technology officer of DARTNet, said funders of research are becoming aware of the need for real-world studies along with “gold standard” efficacy trials.
Dr. Pace, who helped conduct the new study, said a remaining obstacle to improving care is “a defeatist attitude of clinicians” who are skeptical about the ability of therapy to have an effect.
Real-world evidence could remedy clinician frustrations, he said. When clinicians are shown that they can improve patients’ quality of life and maybe even reduce the cost of care, “then they will hopefully pay attention,” he said.
Some experts who were not involved in the study said the findings offer an illuminating, although incomplete, picture. Nonpharmacologic interventions, the management of other health problems, and access to specialty care are not addressed, and the researchers didn’t have data on treatment adherence, inhaler technique, and patients’ peak inspiratory flow – factors that influence the effectiveness of medications. The study also lacked information on whether patients received pulmonary rehabilitation to help their heart and lungs work better.
Nicola Hanania, MD, a professor of medicine and director of the Airways Clinical Research Center at Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, said the study “adds a lot to what we have known” but pointed out that COPD is grossly underdiagnosed.
According to one analysis of National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys, 72% of individuals with COPD don’t know they have the condition. Such patients were not included in the study, Dr. Hanania noted.
“We need pragmatic studies over multiple years to better understand” the condition, Dr. Yawn said. Real-world evidence “based in an academic setting or specialty practices is not sufficient,” she added. “We need to see results from patients and clinics that look like what we have.”
The registry was established and funded by Optimum Patient Care Global, a nonprofit organization, and Boehringer Ingelheim. Dr. Han has consulted for Boehringer Ingelheim, GlaxoSmithKline, and AstraZeneca and has received research support from Novartis and Sunovion. Dr. Yawn has served on advisory boards for GlaxoSmithKline, Astra-Zeneca, Novartis, and Boehringer Ingelheim and has received research funds from GlaxoSmithKline, Boehringer Ingelheim, AstraZeneca, and Novartis. Dr. Krishnan has disclosed no relevant financial relationshps. Dr. Hanania has received honoraria for serving as consultant or advisory board member for GSK, Boehringer Ingelheim, Novartis, Sanofi, AstraZeneca, Teva, Genentech, and Amgen. His institution has received research grant support on his behalf from GSK, Sanofi, Boehringer Ingelheim, AstraZeneca, Genentech, Teva, and Novartis. Dr. Pace is on the advisory board for Mylan and has received stock from Novo Nordisk, Pfizer, Novartis, Johnson & Johnson, Stryker, Amgen, Gilead, and Sanofi.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Primary care clinicians often struggle to care for their patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), thanks to a lack of real-world evidence as to which treatments work best.
As a result, potentially preventable life-threatening exacerbations are common among people with the condition. Central to the problem, some experts believe, is that the average patient bears little resemblance to participants in clinical trials of the medications used to treat COPD.
Indeed, a recent study showed that many COPD patients who were receiving maintenance therapy that should have been controlling their disease experienced severe flare-ups – a finding that caught the researchers by surprise.
“We know the benefit of COPD treatments in the context of clinical trials. However, the kinds of patients in primary care may not completely mimic those in clinical trials,” one of the authors, MeiLan Han, MD, a professor of medicine in the division of pulmonary and critical care at the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, told this news organization. Dr. Han, a volunteer medical spokesperson for the American Lung Association, added that patients “may not be as adherent to medications in real life as they are in clinical trials.”
, who are younger than the average patient with COPD, and who typically are male. Patients are seen in resource-abundant settings designed to maximize adherence to treatment, with supports such as free medication and frequent monitoring – settings far different from those in which most primary care physicians practice.
The authors of the new article said trials conducted with typical patients in primary care settings could help physicians to optimize treatment.
Real-world evidence can shed light on physicians’ intent and on barriers to following guidelines, as well as important patient factors, such as adherence and good inhaler technique, Barbara Yawn, MD, an adjunct professor in the department of family and community health at the University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, and a coauthor of the study, said in an interview.
A window onto patient burden
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, an estimated $15 million Americans have COPD. Annual costs to the health care system approach $50 billion a year. The death rate for COPD has increased since 1969 as death rates of other major killers in the United States, such as heart disease and cancer, declined, according to a 2015 analysis of death records.
The new study, published in the July/August issue of the Annals of Family Medicine, provides a snapshot of COPD’s toll on patients.
Researchers examined electronic health records of 17,192 patients treated at primary care clinics in five states using a dataset maintained by DARTNet Institute, a nonprofit organization that supports research and quality improvement. They also analyzed self-reported assessments from 1,354 patients in the dataset who are in a registry called Advancing the Patient Experience in COPD.
Over half (56%) of patients were female, White (64%), aged 55-84 years (81%), and current or exsmokers (80%). The vast majority had three or more comorbidities, including hypertension, diabetes, and depression.
Serious flare-ups were common; 38% of patients had experienced one or more exacerbations in the previous year. Of registry respondents, half said they had had at least one exacerbation, and 20% said they had been hospitalized for COPD during that period.
Among patients in the registry, 43% reported that COPD had a high or very high impact on their health, and 45% could not walk at a normal pace without losing their breath.
Almost 90% of patients were receiving a maintenance therapy regimen. The number of exacerbations was “somewhat surprising,” the authors say. They write that the findings may indicate that patients were not receiving appropriate treatment or were not complying with their medication regimens and that there may be a need for nonpharmacologic interventions, such as smoking cessation. They also write that physician education is needed to support earlier diagnosis and treatment so as to delay declines in lung function.
The researchers say their findings highlight “the need for more real-life effectiveness trials to better support decision-making at the primary care level.”
Dr. Yawn is a coinvestigator of one such study, called CAPTURE, which is assessing a screening tool for COPD in primary care practices.
At the University of Illinois, Chicago, Jerry Krishnan, MD, PhD, pulmonologist and professor of medicine and public health, is running the RELIANCE study, which is comparing the use of azithromycin and roflumilast in preventing hospitalization and death among patients with COPD who continue to have exacerbations.
Although RELIANCE involves pulmonologists, Dr. Krishnan told this news organization, it offers a model for building real-world evidence on questions relevant to primary care. “We don’t really know if medications used by patients in my clinic are as effective as reported in clinical trials that were used to obtain regulatory approvals by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration,” he said.
Wilson Pace, MD, a family physician and chief medical officer and chief technology officer of DARTNet, said funders of research are becoming aware of the need for real-world studies along with “gold standard” efficacy trials.
Dr. Pace, who helped conduct the new study, said a remaining obstacle to improving care is “a defeatist attitude of clinicians” who are skeptical about the ability of therapy to have an effect.
Real-world evidence could remedy clinician frustrations, he said. When clinicians are shown that they can improve patients’ quality of life and maybe even reduce the cost of care, “then they will hopefully pay attention,” he said.
Some experts who were not involved in the study said the findings offer an illuminating, although incomplete, picture. Nonpharmacologic interventions, the management of other health problems, and access to specialty care are not addressed, and the researchers didn’t have data on treatment adherence, inhaler technique, and patients’ peak inspiratory flow – factors that influence the effectiveness of medications. The study also lacked information on whether patients received pulmonary rehabilitation to help their heart and lungs work better.
Nicola Hanania, MD, a professor of medicine and director of the Airways Clinical Research Center at Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, said the study “adds a lot to what we have known” but pointed out that COPD is grossly underdiagnosed.
According to one analysis of National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys, 72% of individuals with COPD don’t know they have the condition. Such patients were not included in the study, Dr. Hanania noted.
“We need pragmatic studies over multiple years to better understand” the condition, Dr. Yawn said. Real-world evidence “based in an academic setting or specialty practices is not sufficient,” she added. “We need to see results from patients and clinics that look like what we have.”
The registry was established and funded by Optimum Patient Care Global, a nonprofit organization, and Boehringer Ingelheim. Dr. Han has consulted for Boehringer Ingelheim, GlaxoSmithKline, and AstraZeneca and has received research support from Novartis and Sunovion. Dr. Yawn has served on advisory boards for GlaxoSmithKline, Astra-Zeneca, Novartis, and Boehringer Ingelheim and has received research funds from GlaxoSmithKline, Boehringer Ingelheim, AstraZeneca, and Novartis. Dr. Krishnan has disclosed no relevant financial relationshps. Dr. Hanania has received honoraria for serving as consultant or advisory board member for GSK, Boehringer Ingelheim, Novartis, Sanofi, AstraZeneca, Teva, Genentech, and Amgen. His institution has received research grant support on his behalf from GSK, Sanofi, Boehringer Ingelheim, AstraZeneca, Genentech, Teva, and Novartis. Dr. Pace is on the advisory board for Mylan and has received stock from Novo Nordisk, Pfizer, Novartis, Johnson & Johnson, Stryker, Amgen, Gilead, and Sanofi.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Primary care clinicians often struggle to care for their patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), thanks to a lack of real-world evidence as to which treatments work best.
As a result, potentially preventable life-threatening exacerbations are common among people with the condition. Central to the problem, some experts believe, is that the average patient bears little resemblance to participants in clinical trials of the medications used to treat COPD.
Indeed, a recent study showed that many COPD patients who were receiving maintenance therapy that should have been controlling their disease experienced severe flare-ups – a finding that caught the researchers by surprise.
“We know the benefit of COPD treatments in the context of clinical trials. However, the kinds of patients in primary care may not completely mimic those in clinical trials,” one of the authors, MeiLan Han, MD, a professor of medicine in the division of pulmonary and critical care at the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, told this news organization. Dr. Han, a volunteer medical spokesperson for the American Lung Association, added that patients “may not be as adherent to medications in real life as they are in clinical trials.”
, who are younger than the average patient with COPD, and who typically are male. Patients are seen in resource-abundant settings designed to maximize adherence to treatment, with supports such as free medication and frequent monitoring – settings far different from those in which most primary care physicians practice.
The authors of the new article said trials conducted with typical patients in primary care settings could help physicians to optimize treatment.
Real-world evidence can shed light on physicians’ intent and on barriers to following guidelines, as well as important patient factors, such as adherence and good inhaler technique, Barbara Yawn, MD, an adjunct professor in the department of family and community health at the University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, and a coauthor of the study, said in an interview.
A window onto patient burden
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, an estimated $15 million Americans have COPD. Annual costs to the health care system approach $50 billion a year. The death rate for COPD has increased since 1969 as death rates of other major killers in the United States, such as heart disease and cancer, declined, according to a 2015 analysis of death records.
The new study, published in the July/August issue of the Annals of Family Medicine, provides a snapshot of COPD’s toll on patients.
Researchers examined electronic health records of 17,192 patients treated at primary care clinics in five states using a dataset maintained by DARTNet Institute, a nonprofit organization that supports research and quality improvement. They also analyzed self-reported assessments from 1,354 patients in the dataset who are in a registry called Advancing the Patient Experience in COPD.
Over half (56%) of patients were female, White (64%), aged 55-84 years (81%), and current or exsmokers (80%). The vast majority had three or more comorbidities, including hypertension, diabetes, and depression.
Serious flare-ups were common; 38% of patients had experienced one or more exacerbations in the previous year. Of registry respondents, half said they had had at least one exacerbation, and 20% said they had been hospitalized for COPD during that period.
Among patients in the registry, 43% reported that COPD had a high or very high impact on their health, and 45% could not walk at a normal pace without losing their breath.
Almost 90% of patients were receiving a maintenance therapy regimen. The number of exacerbations was “somewhat surprising,” the authors say. They write that the findings may indicate that patients were not receiving appropriate treatment or were not complying with their medication regimens and that there may be a need for nonpharmacologic interventions, such as smoking cessation. They also write that physician education is needed to support earlier diagnosis and treatment so as to delay declines in lung function.
The researchers say their findings highlight “the need for more real-life effectiveness trials to better support decision-making at the primary care level.”
Dr. Yawn is a coinvestigator of one such study, called CAPTURE, which is assessing a screening tool for COPD in primary care practices.
At the University of Illinois, Chicago, Jerry Krishnan, MD, PhD, pulmonologist and professor of medicine and public health, is running the RELIANCE study, which is comparing the use of azithromycin and roflumilast in preventing hospitalization and death among patients with COPD who continue to have exacerbations.
Although RELIANCE involves pulmonologists, Dr. Krishnan told this news organization, it offers a model for building real-world evidence on questions relevant to primary care. “We don’t really know if medications used by patients in my clinic are as effective as reported in clinical trials that were used to obtain regulatory approvals by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration,” he said.
Wilson Pace, MD, a family physician and chief medical officer and chief technology officer of DARTNet, said funders of research are becoming aware of the need for real-world studies along with “gold standard” efficacy trials.
Dr. Pace, who helped conduct the new study, said a remaining obstacle to improving care is “a defeatist attitude of clinicians” who are skeptical about the ability of therapy to have an effect.
Real-world evidence could remedy clinician frustrations, he said. When clinicians are shown that they can improve patients’ quality of life and maybe even reduce the cost of care, “then they will hopefully pay attention,” he said.
Some experts who were not involved in the study said the findings offer an illuminating, although incomplete, picture. Nonpharmacologic interventions, the management of other health problems, and access to specialty care are not addressed, and the researchers didn’t have data on treatment adherence, inhaler technique, and patients’ peak inspiratory flow – factors that influence the effectiveness of medications. The study also lacked information on whether patients received pulmonary rehabilitation to help their heart and lungs work better.
Nicola Hanania, MD, a professor of medicine and director of the Airways Clinical Research Center at Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, said the study “adds a lot to what we have known” but pointed out that COPD is grossly underdiagnosed.
According to one analysis of National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys, 72% of individuals with COPD don’t know they have the condition. Such patients were not included in the study, Dr. Hanania noted.
“We need pragmatic studies over multiple years to better understand” the condition, Dr. Yawn said. Real-world evidence “based in an academic setting or specialty practices is not sufficient,” she added. “We need to see results from patients and clinics that look like what we have.”
The registry was established and funded by Optimum Patient Care Global, a nonprofit organization, and Boehringer Ingelheim. Dr. Han has consulted for Boehringer Ingelheim, GlaxoSmithKline, and AstraZeneca and has received research support from Novartis and Sunovion. Dr. Yawn has served on advisory boards for GlaxoSmithKline, Astra-Zeneca, Novartis, and Boehringer Ingelheim and has received research funds from GlaxoSmithKline, Boehringer Ingelheim, AstraZeneca, and Novartis. Dr. Krishnan has disclosed no relevant financial relationshps. Dr. Hanania has received honoraria for serving as consultant or advisory board member for GSK, Boehringer Ingelheim, Novartis, Sanofi, AstraZeneca, Teva, Genentech, and Amgen. His institution has received research grant support on his behalf from GSK, Sanofi, Boehringer Ingelheim, AstraZeneca, Genentech, Teva, and Novartis. Dr. Pace is on the advisory board for Mylan and has received stock from Novo Nordisk, Pfizer, Novartis, Johnson & Johnson, Stryker, Amgen, Gilead, and Sanofi.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
High plasma IgE predicts COPD exacerbation, mortality
COPD patients with high plasma immunoglobulin E are more likely to have exacerbations and die from any cause, based on a Danish population-cohort study.
hinting at different subsets of patients with COPD, lead author Yunus Çolak MD, PhD, of Copenhagen University Hospital, and colleagues reported.
“Additional biomarkers are necessary as blood eosinophils alone seem insufficient for risk stratification in COPD,” the investigators wrote in Annals of Allergy, Asthma & Immunology. “Since asthma and COPD share some pathophysiological mechanisms, a logical approach would be to investigate well-known biomarkers for asthma in COPD and vice versa.”
Dr. Çolak and colleagues cited previous research supporting this perspective. Specifically, IgE-targeting monoclonal antibodies have shown promise in patients with severe asthma and asthma-COPD overlap, whereas COPD with high IgE has been associated with a history of lung function decline and previous exacerbations.
The present study drew from a database of 46,598 adults enrolled in the Copenhagen General Population study. All participants underwent physical examination, completed a questionnaire, and provided blood for analysis. From this population, 1,559 individuals had COPD, among whom 446 had high plasma IgE (at least 76 IU/mL).
Over a median follow-up of 6.9 years in the COPD group, 224 severe exacerbations and 434 deaths of any cause occurred. Compared with COPD patients who had normal plasma IgE, those with high IgE were 43% more likely to have severe exacerbation (hazard ratio, 1.43; 95% confidence interval, 1.07-1.89) and 30% more likely to die of any cause (HR, 1.30; 95% CI, 1.06-1.62). These risks were similar when excluding patients with IgE of 700 IU/mL or higher.
“These findings suggest that plasma IgE concentration may be a potential prognostic biomarker and treatment target for a subset of COPD patient,” wrote Dr. Çolak and colleagues.
The above risks increased moderately when the high IgE group was trimmed to include only those with low eosinophils (less than 300 cells/mcL); in this subgroup, risk of exacerbation was increased 62% (HR, 1.62; 95% CI, 1.17-2.24), while risk of all-cause mortality was increased 47% (HR, 1.47; 95% CI, 1.14-1.88).
“We were not able to show that individuals with higher blood eosinophils further stratified by IgE had higher risk of severe exacerbation or all-cause mortality,” the investigators wrote, although they noted “the relatively low statistical power in stratified analysis,” considering the wide confidence intervals observed.
“Thus, we should be careful with interpreting the results in relation to blood eosinophils and IgE combined,” they suggested. “However, we believe that the mechanisms driving exacerbations through plasma IgE are different from those driving blood eosinophils, and we believe that plasma IgE may be a marker for a subset of COPD patients similar to blood eosinophils, which is compatible with the heterogeneity of patients with COPD.”
According to principal author Shoaib Afzal, MD, PhD, of Copenhagen University Hospital, the findings are “probably no surprise for practitioners that often observe overlap between asthma and COPD pathology.”
As smoking prevalence goes down in many countries, relatively more never-smokers are being diagnosed with COPD, Dr. Afzal said in a written comment, “which means that asthma as a risk factor for COPD is gaining importance.”
While patients with asthma can be treated with IgE-targeting omalizumab, a trial evaluating the same biologic for COPD patients with high IgE was withdrawn because of a lack of recruitment; however, Dr. Afzal suggested that this should not be the end of the story, since these new data imply that more patients could benefit than previously recognized.
“Our observational study has generated a hypothesis that needs to be tested by pulmonologists in randomized interventions trials designed with updated inclusion criteria,” he said.
Such trials are needed, Dr. Afzal went on, because they could help unlock the “huge” potential benefit that may come from characterizing COPD patients beyond “exposures, symptoms, and spirometry.”
“Sadly, the progress in establishing biomarkers in COPD for improving risk stratification and treatment allocation have been rather disappointing in the last decades, with the exception of small successes with eosinophils and perhaps FeNO,” Dr. Afzal said.
Nathaniel Marchetti, DO, professor of thoracic medicine and surgery at Temple University and medical director of the respiratory ICU at Temple University Hospital, both in Philadelphia, said the study by Dr. Afzal and colleagues is noteworthy because “biomarkers for COPD are desperately needed to help risk stratify patients for exacerbation risk and risk of disease progression and even mortality.”
In a written comment, Dr. Marchetti agreed with Dr. Afzal that the findings “open the possibility for interventional trials targeting IgE,” which could one day reshape the way patients with COPD are treated.
“I think that biomarkers will become vital in caring for patients with COPD in the future,” Dr. Marchetti said. “There will be medications that will be used to target different pathways of inflammation that drive disease progression and exacerbations. Biomarkers will be important in driving personalized medicine in COPD. We already know the disease seems to vary greatly from patient to patient.”
The study was supported by The Capital Region of Copenhagen, The Danish Lung Foundation, The Velux Foundation, and others. The investigators disclosed relationships with Boehringer Ingelheim, AstraZeneca, Sanofi Genzyme, and others. Dr. Marchetti disclosed no conflicts of interest.
COPD patients with high plasma immunoglobulin E are more likely to have exacerbations and die from any cause, based on a Danish population-cohort study.
hinting at different subsets of patients with COPD, lead author Yunus Çolak MD, PhD, of Copenhagen University Hospital, and colleagues reported.
“Additional biomarkers are necessary as blood eosinophils alone seem insufficient for risk stratification in COPD,” the investigators wrote in Annals of Allergy, Asthma & Immunology. “Since asthma and COPD share some pathophysiological mechanisms, a logical approach would be to investigate well-known biomarkers for asthma in COPD and vice versa.”
Dr. Çolak and colleagues cited previous research supporting this perspective. Specifically, IgE-targeting monoclonal antibodies have shown promise in patients with severe asthma and asthma-COPD overlap, whereas COPD with high IgE has been associated with a history of lung function decline and previous exacerbations.
The present study drew from a database of 46,598 adults enrolled in the Copenhagen General Population study. All participants underwent physical examination, completed a questionnaire, and provided blood for analysis. From this population, 1,559 individuals had COPD, among whom 446 had high plasma IgE (at least 76 IU/mL).
Over a median follow-up of 6.9 years in the COPD group, 224 severe exacerbations and 434 deaths of any cause occurred. Compared with COPD patients who had normal plasma IgE, those with high IgE were 43% more likely to have severe exacerbation (hazard ratio, 1.43; 95% confidence interval, 1.07-1.89) and 30% more likely to die of any cause (HR, 1.30; 95% CI, 1.06-1.62). These risks were similar when excluding patients with IgE of 700 IU/mL or higher.
“These findings suggest that plasma IgE concentration may be a potential prognostic biomarker and treatment target for a subset of COPD patient,” wrote Dr. Çolak and colleagues.
The above risks increased moderately when the high IgE group was trimmed to include only those with low eosinophils (less than 300 cells/mcL); in this subgroup, risk of exacerbation was increased 62% (HR, 1.62; 95% CI, 1.17-2.24), while risk of all-cause mortality was increased 47% (HR, 1.47; 95% CI, 1.14-1.88).
“We were not able to show that individuals with higher blood eosinophils further stratified by IgE had higher risk of severe exacerbation or all-cause mortality,” the investigators wrote, although they noted “the relatively low statistical power in stratified analysis,” considering the wide confidence intervals observed.
“Thus, we should be careful with interpreting the results in relation to blood eosinophils and IgE combined,” they suggested. “However, we believe that the mechanisms driving exacerbations through plasma IgE are different from those driving blood eosinophils, and we believe that plasma IgE may be a marker for a subset of COPD patients similar to blood eosinophils, which is compatible with the heterogeneity of patients with COPD.”
According to principal author Shoaib Afzal, MD, PhD, of Copenhagen University Hospital, the findings are “probably no surprise for practitioners that often observe overlap between asthma and COPD pathology.”
As smoking prevalence goes down in many countries, relatively more never-smokers are being diagnosed with COPD, Dr. Afzal said in a written comment, “which means that asthma as a risk factor for COPD is gaining importance.”
While patients with asthma can be treated with IgE-targeting omalizumab, a trial evaluating the same biologic for COPD patients with high IgE was withdrawn because of a lack of recruitment; however, Dr. Afzal suggested that this should not be the end of the story, since these new data imply that more patients could benefit than previously recognized.
“Our observational study has generated a hypothesis that needs to be tested by pulmonologists in randomized interventions trials designed with updated inclusion criteria,” he said.
Such trials are needed, Dr. Afzal went on, because they could help unlock the “huge” potential benefit that may come from characterizing COPD patients beyond “exposures, symptoms, and spirometry.”
“Sadly, the progress in establishing biomarkers in COPD for improving risk stratification and treatment allocation have been rather disappointing in the last decades, with the exception of small successes with eosinophils and perhaps FeNO,” Dr. Afzal said.
Nathaniel Marchetti, DO, professor of thoracic medicine and surgery at Temple University and medical director of the respiratory ICU at Temple University Hospital, both in Philadelphia, said the study by Dr. Afzal and colleagues is noteworthy because “biomarkers for COPD are desperately needed to help risk stratify patients for exacerbation risk and risk of disease progression and even mortality.”
In a written comment, Dr. Marchetti agreed with Dr. Afzal that the findings “open the possibility for interventional trials targeting IgE,” which could one day reshape the way patients with COPD are treated.
“I think that biomarkers will become vital in caring for patients with COPD in the future,” Dr. Marchetti said. “There will be medications that will be used to target different pathways of inflammation that drive disease progression and exacerbations. Biomarkers will be important in driving personalized medicine in COPD. We already know the disease seems to vary greatly from patient to patient.”
The study was supported by The Capital Region of Copenhagen, The Danish Lung Foundation, The Velux Foundation, and others. The investigators disclosed relationships with Boehringer Ingelheim, AstraZeneca, Sanofi Genzyme, and others. Dr. Marchetti disclosed no conflicts of interest.
COPD patients with high plasma immunoglobulin E are more likely to have exacerbations and die from any cause, based on a Danish population-cohort study.
hinting at different subsets of patients with COPD, lead author Yunus Çolak MD, PhD, of Copenhagen University Hospital, and colleagues reported.
“Additional biomarkers are necessary as blood eosinophils alone seem insufficient for risk stratification in COPD,” the investigators wrote in Annals of Allergy, Asthma & Immunology. “Since asthma and COPD share some pathophysiological mechanisms, a logical approach would be to investigate well-known biomarkers for asthma in COPD and vice versa.”
Dr. Çolak and colleagues cited previous research supporting this perspective. Specifically, IgE-targeting monoclonal antibodies have shown promise in patients with severe asthma and asthma-COPD overlap, whereas COPD with high IgE has been associated with a history of lung function decline and previous exacerbations.
The present study drew from a database of 46,598 adults enrolled in the Copenhagen General Population study. All participants underwent physical examination, completed a questionnaire, and provided blood for analysis. From this population, 1,559 individuals had COPD, among whom 446 had high plasma IgE (at least 76 IU/mL).
Over a median follow-up of 6.9 years in the COPD group, 224 severe exacerbations and 434 deaths of any cause occurred. Compared with COPD patients who had normal plasma IgE, those with high IgE were 43% more likely to have severe exacerbation (hazard ratio, 1.43; 95% confidence interval, 1.07-1.89) and 30% more likely to die of any cause (HR, 1.30; 95% CI, 1.06-1.62). These risks were similar when excluding patients with IgE of 700 IU/mL or higher.
“These findings suggest that plasma IgE concentration may be a potential prognostic biomarker and treatment target for a subset of COPD patient,” wrote Dr. Çolak and colleagues.
The above risks increased moderately when the high IgE group was trimmed to include only those with low eosinophils (less than 300 cells/mcL); in this subgroup, risk of exacerbation was increased 62% (HR, 1.62; 95% CI, 1.17-2.24), while risk of all-cause mortality was increased 47% (HR, 1.47; 95% CI, 1.14-1.88).
“We were not able to show that individuals with higher blood eosinophils further stratified by IgE had higher risk of severe exacerbation or all-cause mortality,” the investigators wrote, although they noted “the relatively low statistical power in stratified analysis,” considering the wide confidence intervals observed.
“Thus, we should be careful with interpreting the results in relation to blood eosinophils and IgE combined,” they suggested. “However, we believe that the mechanisms driving exacerbations through plasma IgE are different from those driving blood eosinophils, and we believe that plasma IgE may be a marker for a subset of COPD patients similar to blood eosinophils, which is compatible with the heterogeneity of patients with COPD.”
According to principal author Shoaib Afzal, MD, PhD, of Copenhagen University Hospital, the findings are “probably no surprise for practitioners that often observe overlap between asthma and COPD pathology.”
As smoking prevalence goes down in many countries, relatively more never-smokers are being diagnosed with COPD, Dr. Afzal said in a written comment, “which means that asthma as a risk factor for COPD is gaining importance.”
While patients with asthma can be treated with IgE-targeting omalizumab, a trial evaluating the same biologic for COPD patients with high IgE was withdrawn because of a lack of recruitment; however, Dr. Afzal suggested that this should not be the end of the story, since these new data imply that more patients could benefit than previously recognized.
“Our observational study has generated a hypothesis that needs to be tested by pulmonologists in randomized interventions trials designed with updated inclusion criteria,” he said.
Such trials are needed, Dr. Afzal went on, because they could help unlock the “huge” potential benefit that may come from characterizing COPD patients beyond “exposures, symptoms, and spirometry.”
“Sadly, the progress in establishing biomarkers in COPD for improving risk stratification and treatment allocation have been rather disappointing in the last decades, with the exception of small successes with eosinophils and perhaps FeNO,” Dr. Afzal said.
Nathaniel Marchetti, DO, professor of thoracic medicine and surgery at Temple University and medical director of the respiratory ICU at Temple University Hospital, both in Philadelphia, said the study by Dr. Afzal and colleagues is noteworthy because “biomarkers for COPD are desperately needed to help risk stratify patients for exacerbation risk and risk of disease progression and even mortality.”
In a written comment, Dr. Marchetti agreed with Dr. Afzal that the findings “open the possibility for interventional trials targeting IgE,” which could one day reshape the way patients with COPD are treated.
“I think that biomarkers will become vital in caring for patients with COPD in the future,” Dr. Marchetti said. “There will be medications that will be used to target different pathways of inflammation that drive disease progression and exacerbations. Biomarkers will be important in driving personalized medicine in COPD. We already know the disease seems to vary greatly from patient to patient.”
The study was supported by The Capital Region of Copenhagen, The Danish Lung Foundation, The Velux Foundation, and others. The investigators disclosed relationships with Boehringer Ingelheim, AstraZeneca, Sanofi Genzyme, and others. Dr. Marchetti disclosed no conflicts of interest.
FROM ANNALS OF ALLERGY, ASTHMA & IMMUNOLOGY
Anxiety in COPD: Consequential, but often overlooked
Anand S. Iyer, MD, MSPH, frequently hears his patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) express fear and hopelessness and describe panic and other symptoms of anxiety. He sees anxiety affect the course of COPD, worsening symptoms and outcomes.
“I had questions about what we are doing [to help patients], so I began looking into the role of palliative care to help patients assess and manage these complex emotional and psychological symptoms,” said Dr. Iyer, assistant professor in the division of pulmonology, allergy, and critical care medicine at the University of Alabama at Birmingham.
His research is now focused on the integration of palliative care principles in COPD care. For Dr. Iyer and others engaged in research and/or patient care, finding ways of identifying and managing anxiety in patients with COPD – and other chronic lung diseases – is a calling of growing urgency.
More has been published about anxiety in patients with COPD than in other pulmonary conditions – and . Prevalence rates vary from about 1 in 4, to 1 in 2 or higher, depending on the instruments used and whether clinical DSM-based diagnoses are made, Dr. Iyer said.
A 2013 systematic review of 10 studies that utilized clinical interviews based on DSM criteria, for instance, found a prevalence of clinical anxiety of 10%-55% among inpatients and 13%-46% among outpatients with COPD. The results were similar, investigators said, to studies using self-report screening tools (Respiratory Care 2013;58[5]:858-66).
In the 16 years since an ACCP workshop panel on anxiety and depression in COPD reported higher prevalence rates than for other chronic diseases and detailed a host of problems and research needs (CHEST. 2008;134;43S-56), investigators have more fully documented links to COPD outcomes, showing, for instance, that anxiety predicts exacerbations, hospitalizations, poorer adherence to therapies, poorer quality of life and higher mortality.
Dr. Iyer and other experts say anxiety is still too often a neglected comorbidity. “It’s still underdiagnosed and therefore undertreated,” said Nick Hanania, MD, MS, professor of medicine and director of the Airways Clinical Research Center at Baylor College of Medicine, Houston.
The literature on optimal approaches for management remains limited, and the role of pharmacotherapy for anxiety (and depression) in the context of COPD has not been well investigated. But there have been some advances: Screening tools have been further studied, questionnaires specific to COPD have been developed, and pulmonary rehabilitation (PR) and cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) have both been shown to be effective in decreasing anxiety.
Researchers and academic clinicians are talking, meanwhile, about how to have to important conversations about anxiety with patients who have COPD and other chronic lung conditions, and how improve care in the face of significant health system challenges.
Understanding anxiety in COPD
Anxiety is often intertwined with dyspnea in a bidirectional and complex relationship, but anxiety in COPD is not always acute or limited to times of acute exacerbations.
“There’s not only the acute experience of shortness of breath or a lung change episode, but there’s an anticipation that can occur, psychologically and socially,” said Lauren Garvin, PhD, of the department of psychiatry at the University of Iowa, Iowa City. Patients worry, “what if I’m short of breath in a particular situation? What if my devices fail when I’m out somewhere?”
Patients are often living “in a state of heightened surveillance of the body,” she noted, which can be exhausting and can impact functioning.
It’s also important to appreciate that anxiety is “a continuum of experience,” said Karin Hoth, PhD, associate professor of psychiatry at the medical school, whose research includes projects focusing on psychological adjustment in COPD.
“Research historically categorizes anxiety as ‘have or don’t have.’ But there’s a continuum of experience that we’re moving toward understanding and recognizing in research,” she said. “Anxiety is part of a patient’s whole experience, no matter where one falls on the continuum.”
Female sex, current smoking, greater airflow restrictions – and in some studies, younger age – have all been associated with a greater risk of anxiety in COPD. (It may well be that women receive more attention, leaving men with higher rates of undiagnosed anxiety, Dr. Hoth said.)
Dr. Iyer stresses the complex relationship between smoking – the No. 1 cause of COPD – and anxiety. Smoking has been associated in multiple studies with an increased risk of anxiety (Brain and Behavior. 2013;3[3]:302-26), he said. (A study led by Dr. Iyer found a similar frequency of anxiety symptoms in smokers with and without COPD [Journal of Psychosomatic Research. 2019;118:18-26].)
Some patients with COPD and anxiety may smoke in order to ease their anxiety, he said, making management of anxiety an important part of the smoking cessation desired for COPD improvement.
COPD medications such as bronchodilators may cause transient symptoms of anxiety, but these are rare and short-lived, Dr. Iyer said.
Screening tools and conversations
“It’s not just us not thinking about anxiety that’s the problem, it’s also patients thinking that it’s just the disease [causing their anxiety symptoms],” said Dr. Hanania, a member of the 2006 ACCP panel and an author of numerous papers on COPD and anxiety and depression. “There’s quite a bit of overlap between COPD symptoms and anxiety and depression symptoms, and unless you use structured questionnaires, you may not pick it up,” he said.
Screening tools include the Generalized Anxiety Disorder 7-item (GAD-7) scale, the PHQ-9 for depression and anxiety, and the longer Primary Care Evaluation of Mental Disorders (PRIME-MD). The Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale (HADS), Dr. Iyer noted, has been well validated for use in ambulatory settings.
Validated screening tools specific to anxiety in COPD are also now an option. Abebaw M. Yohannes, PhD, MSc, FCCP, professor in the department of physical therapy at Azuza Pacific University in Orange, Calif., and the author of numerous studies on COPD and anxiety, developed one of these tools – the 10-item Anxiety Inventory for Respiratory Disease (AIR) scale – out of concern that other surveys contain overlapping somatic symptoms (Chest. 2013;144[5]:1587-96).
“We removed the physical symptoms [of anxiety] that often manifest in patients with COPD,” he said.
Dr. Iyer said screening tools can effectively “highlight which person might be dealing with high levels of anxiety symptoms that might meet a threshold of clinical significance and require collaborative or interprofessional management,” including with psychologists and psychiatrists.
They can also open the door to conversation with patients. “I’ll often bluntly ask, do you feel anxious? Do you feel scared, or hopeless about what the future holds for you?,” he said. “Anxiety about the future plays a big role, and helping patients navigate the illness and understand early how it might look … can ease the level of anxiety.”
Asking patients about their experiences in managing their symptoms and about their psychological and emotional well-being can help to normalize anxiety – and it can be therapeutic, said Dr. Hoth and Dr. Garvin. Asking “how it’s going with the things that really matter in [their] life” is often a good question, they said.
Patients “won’t be offended if you ask,” said Dr. Hoth. “They view their mood and [whole] well-being as part of their medical condition.”
Time is a challenge, she said, but “conversation can be done little by little, as part of a philosophy of engaging the patient around their whole functioning, even if there’s not [a need or] a route to refer just then.”
Such early and integrated conversation borrows from the palliative care model. “Palliative care is a specialty, but it can also be an approach to care,” Dr. Iyer said. He is leading a National Institutes of Health–funded study on nurse-coach–led early palliative care for older adults with COPD and wants to see training opportunities for pulmonologists to learn basic palliative care skills that would equip them to better guide management of mild-moderate anxiety and other complex symptoms.
Pulmonary rehabilitation
For many patients with COPD who have anxiety and/or depressive symptoms, referral for nonpharmacologic therapies such as psychotherapy, cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), and pulmonary rehabilitation (PR) is “one of the best things you can do,” Dr. Iyer said.
“If patients haven’t done pulmonary rehabilitation, get them in. And if they have done it before, get them back into it again,” he emphasized. “Accredited programs give a holistic approach to improving your strength, your breathlessness, your mindset and understanding of your breathlessness, and your own levels of security.”
Studies addressing the impact of PR and CBT on anxiety have been mostly small and observational but have yielded encouraging findings. A 2017 review reported that PR and CBT were effective in the treatment of anxiety and dyspnea, in the short term, in the majority of 47 studies (JAMA. 2017;18[12]:1096.e1-1096.e17). And a 2019 systematic review and meta-analysis focused on PR reported that, across 11 studies comprising 734 patients, PR conferred significant benefits for anxiety and depression compared with usual care (CHEST. 2019;156[1]:80-91).
Dr. Yohannes, Dr. Hanania, and colleagues recently reported on 734 patients with clinically stable COPD who completed a community-based 8-week PR program of 2 hours a week: 1 hour of exercise and 1 hour of education, the latter of which covered anxiety, panic management, and relaxation.
Patients who had severe dyspnea and comorbid anxiety and depression prior to PR – one-third of the group compared with 20% having anxiety alone and 5% having depression alone – had the most significant improvements in dyspnea scores and anxiety and depression scores (Respir Med. Apr 9. doi: 10.1016/j.rmed.2022.106850.)
The problem is, pulmonary rehabilitation is under-reimbursed and not widely accessible. It’s logistically challenging for patients to attend therapy 2-3 times a week. And according to a recently published study by Dr. Yohannes, Dr. Hanania, and colleagues, patients with more anxiety and dyspnea may be at higher risk of dropping out (Respir Med. 2022 Jan 20. doi: 10.1016/j.rmed.2022.10674). Moreover, Dr. Iyer said, there is a shortage of programs that are accredited.
Telehealth may help on some of these fronts. The efficacy of real-time video PR for COPD is being investigated in a randomized NIH trial (now in the recruitment phase) led by pulmonologist Surya P. Bhatt, MD, also at the University of Alabama at Birmingham.
Researchers also need to investigate issues of sustainability – to learn what “works best in the long run,” Dr. Iyer said.
Dr. Yohannes and Dr. Hanania are encouraged by a recent finding that patients with COPD who completed 8 weeks of PR maintained improvements in anxiety and quality-of-life scores at 2 years. (Improvements in dyspnea and other outcomes did not persist.) (CHEST. 2021;159[3]:967-74). Prospective studies contrasting maintenance programs with no maintenance following PR, are needed, they wrote.
Understanding psychological interventions
Dr. Hoth and Dr. Garvin advise their pulmonologist colleagues to feel as confident as possible in describing for patients what CBT and other psychological therapies entail.
“A person [with COPD] who is experiencing something on the continuum of anxiety might be really turning inward and [assessing] unwanted internal experiences” and accompanying thoughts, sensations, emotional impacts and behaviors, Dr. Garvin said.
Among the goals, she said, are to “make shifts around those internal experiences that might invoke some more tolerance or that might shift their relationship with the experiences, or even with the diagnosis itself and all the uncertainties it carries.”
Psychological therapies can involve social support, or “breath and grounding work,” she said. “There are lots of different approaches from different providers.”
Dr. Yohannes advocates incorporating principles of CBT into PR. “In the absence of one-on-one or group [stand-alone] CBT … the principles are worth incorporating as part of the education piece [of PR],” he said. “CBT helps patients to refocus their attention. … and gives them self-confidence to engage in exercise and to function a bit more in their daily activities.”
None of those interviewed for this story reported having any relevant conflicts of interest.
Anand S. Iyer, MD, MSPH, frequently hears his patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) express fear and hopelessness and describe panic and other symptoms of anxiety. He sees anxiety affect the course of COPD, worsening symptoms and outcomes.
“I had questions about what we are doing [to help patients], so I began looking into the role of palliative care to help patients assess and manage these complex emotional and psychological symptoms,” said Dr. Iyer, assistant professor in the division of pulmonology, allergy, and critical care medicine at the University of Alabama at Birmingham.
His research is now focused on the integration of palliative care principles in COPD care. For Dr. Iyer and others engaged in research and/or patient care, finding ways of identifying and managing anxiety in patients with COPD – and other chronic lung diseases – is a calling of growing urgency.
More has been published about anxiety in patients with COPD than in other pulmonary conditions – and . Prevalence rates vary from about 1 in 4, to 1 in 2 or higher, depending on the instruments used and whether clinical DSM-based diagnoses are made, Dr. Iyer said.
A 2013 systematic review of 10 studies that utilized clinical interviews based on DSM criteria, for instance, found a prevalence of clinical anxiety of 10%-55% among inpatients and 13%-46% among outpatients with COPD. The results were similar, investigators said, to studies using self-report screening tools (Respiratory Care 2013;58[5]:858-66).
In the 16 years since an ACCP workshop panel on anxiety and depression in COPD reported higher prevalence rates than for other chronic diseases and detailed a host of problems and research needs (CHEST. 2008;134;43S-56), investigators have more fully documented links to COPD outcomes, showing, for instance, that anxiety predicts exacerbations, hospitalizations, poorer adherence to therapies, poorer quality of life and higher mortality.
Dr. Iyer and other experts say anxiety is still too often a neglected comorbidity. “It’s still underdiagnosed and therefore undertreated,” said Nick Hanania, MD, MS, professor of medicine and director of the Airways Clinical Research Center at Baylor College of Medicine, Houston.
The literature on optimal approaches for management remains limited, and the role of pharmacotherapy for anxiety (and depression) in the context of COPD has not been well investigated. But there have been some advances: Screening tools have been further studied, questionnaires specific to COPD have been developed, and pulmonary rehabilitation (PR) and cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) have both been shown to be effective in decreasing anxiety.
Researchers and academic clinicians are talking, meanwhile, about how to have to important conversations about anxiety with patients who have COPD and other chronic lung conditions, and how improve care in the face of significant health system challenges.
Understanding anxiety in COPD
Anxiety is often intertwined with dyspnea in a bidirectional and complex relationship, but anxiety in COPD is not always acute or limited to times of acute exacerbations.
“There’s not only the acute experience of shortness of breath or a lung change episode, but there’s an anticipation that can occur, psychologically and socially,” said Lauren Garvin, PhD, of the department of psychiatry at the University of Iowa, Iowa City. Patients worry, “what if I’m short of breath in a particular situation? What if my devices fail when I’m out somewhere?”
Patients are often living “in a state of heightened surveillance of the body,” she noted, which can be exhausting and can impact functioning.
It’s also important to appreciate that anxiety is “a continuum of experience,” said Karin Hoth, PhD, associate professor of psychiatry at the medical school, whose research includes projects focusing on psychological adjustment in COPD.
“Research historically categorizes anxiety as ‘have or don’t have.’ But there’s a continuum of experience that we’re moving toward understanding and recognizing in research,” she said. “Anxiety is part of a patient’s whole experience, no matter where one falls on the continuum.”
Female sex, current smoking, greater airflow restrictions – and in some studies, younger age – have all been associated with a greater risk of anxiety in COPD. (It may well be that women receive more attention, leaving men with higher rates of undiagnosed anxiety, Dr. Hoth said.)
Dr. Iyer stresses the complex relationship between smoking – the No. 1 cause of COPD – and anxiety. Smoking has been associated in multiple studies with an increased risk of anxiety (Brain and Behavior. 2013;3[3]:302-26), he said. (A study led by Dr. Iyer found a similar frequency of anxiety symptoms in smokers with and without COPD [Journal of Psychosomatic Research. 2019;118:18-26].)
Some patients with COPD and anxiety may smoke in order to ease their anxiety, he said, making management of anxiety an important part of the smoking cessation desired for COPD improvement.
COPD medications such as bronchodilators may cause transient symptoms of anxiety, but these are rare and short-lived, Dr. Iyer said.
Screening tools and conversations
“It’s not just us not thinking about anxiety that’s the problem, it’s also patients thinking that it’s just the disease [causing their anxiety symptoms],” said Dr. Hanania, a member of the 2006 ACCP panel and an author of numerous papers on COPD and anxiety and depression. “There’s quite a bit of overlap between COPD symptoms and anxiety and depression symptoms, and unless you use structured questionnaires, you may not pick it up,” he said.
Screening tools include the Generalized Anxiety Disorder 7-item (GAD-7) scale, the PHQ-9 for depression and anxiety, and the longer Primary Care Evaluation of Mental Disorders (PRIME-MD). The Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale (HADS), Dr. Iyer noted, has been well validated for use in ambulatory settings.
Validated screening tools specific to anxiety in COPD are also now an option. Abebaw M. Yohannes, PhD, MSc, FCCP, professor in the department of physical therapy at Azuza Pacific University in Orange, Calif., and the author of numerous studies on COPD and anxiety, developed one of these tools – the 10-item Anxiety Inventory for Respiratory Disease (AIR) scale – out of concern that other surveys contain overlapping somatic symptoms (Chest. 2013;144[5]:1587-96).
“We removed the physical symptoms [of anxiety] that often manifest in patients with COPD,” he said.
Dr. Iyer said screening tools can effectively “highlight which person might be dealing with high levels of anxiety symptoms that might meet a threshold of clinical significance and require collaborative or interprofessional management,” including with psychologists and psychiatrists.
They can also open the door to conversation with patients. “I’ll often bluntly ask, do you feel anxious? Do you feel scared, or hopeless about what the future holds for you?,” he said. “Anxiety about the future plays a big role, and helping patients navigate the illness and understand early how it might look … can ease the level of anxiety.”
Asking patients about their experiences in managing their symptoms and about their psychological and emotional well-being can help to normalize anxiety – and it can be therapeutic, said Dr. Hoth and Dr. Garvin. Asking “how it’s going with the things that really matter in [their] life” is often a good question, they said.
Patients “won’t be offended if you ask,” said Dr. Hoth. “They view their mood and [whole] well-being as part of their medical condition.”
Time is a challenge, she said, but “conversation can be done little by little, as part of a philosophy of engaging the patient around their whole functioning, even if there’s not [a need or] a route to refer just then.”
Such early and integrated conversation borrows from the palliative care model. “Palliative care is a specialty, but it can also be an approach to care,” Dr. Iyer said. He is leading a National Institutes of Health–funded study on nurse-coach–led early palliative care for older adults with COPD and wants to see training opportunities for pulmonologists to learn basic palliative care skills that would equip them to better guide management of mild-moderate anxiety and other complex symptoms.
Pulmonary rehabilitation
For many patients with COPD who have anxiety and/or depressive symptoms, referral for nonpharmacologic therapies such as psychotherapy, cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), and pulmonary rehabilitation (PR) is “one of the best things you can do,” Dr. Iyer said.
“If patients haven’t done pulmonary rehabilitation, get them in. And if they have done it before, get them back into it again,” he emphasized. “Accredited programs give a holistic approach to improving your strength, your breathlessness, your mindset and understanding of your breathlessness, and your own levels of security.”
Studies addressing the impact of PR and CBT on anxiety have been mostly small and observational but have yielded encouraging findings. A 2017 review reported that PR and CBT were effective in the treatment of anxiety and dyspnea, in the short term, in the majority of 47 studies (JAMA. 2017;18[12]:1096.e1-1096.e17). And a 2019 systematic review and meta-analysis focused on PR reported that, across 11 studies comprising 734 patients, PR conferred significant benefits for anxiety and depression compared with usual care (CHEST. 2019;156[1]:80-91).
Dr. Yohannes, Dr. Hanania, and colleagues recently reported on 734 patients with clinically stable COPD who completed a community-based 8-week PR program of 2 hours a week: 1 hour of exercise and 1 hour of education, the latter of which covered anxiety, panic management, and relaxation.
Patients who had severe dyspnea and comorbid anxiety and depression prior to PR – one-third of the group compared with 20% having anxiety alone and 5% having depression alone – had the most significant improvements in dyspnea scores and anxiety and depression scores (Respir Med. Apr 9. doi: 10.1016/j.rmed.2022.106850.)
The problem is, pulmonary rehabilitation is under-reimbursed and not widely accessible. It’s logistically challenging for patients to attend therapy 2-3 times a week. And according to a recently published study by Dr. Yohannes, Dr. Hanania, and colleagues, patients with more anxiety and dyspnea may be at higher risk of dropping out (Respir Med. 2022 Jan 20. doi: 10.1016/j.rmed.2022.10674). Moreover, Dr. Iyer said, there is a shortage of programs that are accredited.
Telehealth may help on some of these fronts. The efficacy of real-time video PR for COPD is being investigated in a randomized NIH trial (now in the recruitment phase) led by pulmonologist Surya P. Bhatt, MD, also at the University of Alabama at Birmingham.
Researchers also need to investigate issues of sustainability – to learn what “works best in the long run,” Dr. Iyer said.
Dr. Yohannes and Dr. Hanania are encouraged by a recent finding that patients with COPD who completed 8 weeks of PR maintained improvements in anxiety and quality-of-life scores at 2 years. (Improvements in dyspnea and other outcomes did not persist.) (CHEST. 2021;159[3]:967-74). Prospective studies contrasting maintenance programs with no maintenance following PR, are needed, they wrote.
Understanding psychological interventions
Dr. Hoth and Dr. Garvin advise their pulmonologist colleagues to feel as confident as possible in describing for patients what CBT and other psychological therapies entail.
“A person [with COPD] who is experiencing something on the continuum of anxiety might be really turning inward and [assessing] unwanted internal experiences” and accompanying thoughts, sensations, emotional impacts and behaviors, Dr. Garvin said.
Among the goals, she said, are to “make shifts around those internal experiences that might invoke some more tolerance or that might shift their relationship with the experiences, or even with the diagnosis itself and all the uncertainties it carries.”
Psychological therapies can involve social support, or “breath and grounding work,” she said. “There are lots of different approaches from different providers.”
Dr. Yohannes advocates incorporating principles of CBT into PR. “In the absence of one-on-one or group [stand-alone] CBT … the principles are worth incorporating as part of the education piece [of PR],” he said. “CBT helps patients to refocus their attention. … and gives them self-confidence to engage in exercise and to function a bit more in their daily activities.”
None of those interviewed for this story reported having any relevant conflicts of interest.
Anand S. Iyer, MD, MSPH, frequently hears his patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) express fear and hopelessness and describe panic and other symptoms of anxiety. He sees anxiety affect the course of COPD, worsening symptoms and outcomes.
“I had questions about what we are doing [to help patients], so I began looking into the role of palliative care to help patients assess and manage these complex emotional and psychological symptoms,” said Dr. Iyer, assistant professor in the division of pulmonology, allergy, and critical care medicine at the University of Alabama at Birmingham.
His research is now focused on the integration of palliative care principles in COPD care. For Dr. Iyer and others engaged in research and/or patient care, finding ways of identifying and managing anxiety in patients with COPD – and other chronic lung diseases – is a calling of growing urgency.
More has been published about anxiety in patients with COPD than in other pulmonary conditions – and . Prevalence rates vary from about 1 in 4, to 1 in 2 or higher, depending on the instruments used and whether clinical DSM-based diagnoses are made, Dr. Iyer said.
A 2013 systematic review of 10 studies that utilized clinical interviews based on DSM criteria, for instance, found a prevalence of clinical anxiety of 10%-55% among inpatients and 13%-46% among outpatients with COPD. The results were similar, investigators said, to studies using self-report screening tools (Respiratory Care 2013;58[5]:858-66).
In the 16 years since an ACCP workshop panel on anxiety and depression in COPD reported higher prevalence rates than for other chronic diseases and detailed a host of problems and research needs (CHEST. 2008;134;43S-56), investigators have more fully documented links to COPD outcomes, showing, for instance, that anxiety predicts exacerbations, hospitalizations, poorer adherence to therapies, poorer quality of life and higher mortality.
Dr. Iyer and other experts say anxiety is still too often a neglected comorbidity. “It’s still underdiagnosed and therefore undertreated,” said Nick Hanania, MD, MS, professor of medicine and director of the Airways Clinical Research Center at Baylor College of Medicine, Houston.
The literature on optimal approaches for management remains limited, and the role of pharmacotherapy for anxiety (and depression) in the context of COPD has not been well investigated. But there have been some advances: Screening tools have been further studied, questionnaires specific to COPD have been developed, and pulmonary rehabilitation (PR) and cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) have both been shown to be effective in decreasing anxiety.
Researchers and academic clinicians are talking, meanwhile, about how to have to important conversations about anxiety with patients who have COPD and other chronic lung conditions, and how improve care in the face of significant health system challenges.
Understanding anxiety in COPD
Anxiety is often intertwined with dyspnea in a bidirectional and complex relationship, but anxiety in COPD is not always acute or limited to times of acute exacerbations.
“There’s not only the acute experience of shortness of breath or a lung change episode, but there’s an anticipation that can occur, psychologically and socially,” said Lauren Garvin, PhD, of the department of psychiatry at the University of Iowa, Iowa City. Patients worry, “what if I’m short of breath in a particular situation? What if my devices fail when I’m out somewhere?”
Patients are often living “in a state of heightened surveillance of the body,” she noted, which can be exhausting and can impact functioning.
It’s also important to appreciate that anxiety is “a continuum of experience,” said Karin Hoth, PhD, associate professor of psychiatry at the medical school, whose research includes projects focusing on psychological adjustment in COPD.
“Research historically categorizes anxiety as ‘have or don’t have.’ But there’s a continuum of experience that we’re moving toward understanding and recognizing in research,” she said. “Anxiety is part of a patient’s whole experience, no matter where one falls on the continuum.”
Female sex, current smoking, greater airflow restrictions – and in some studies, younger age – have all been associated with a greater risk of anxiety in COPD. (It may well be that women receive more attention, leaving men with higher rates of undiagnosed anxiety, Dr. Hoth said.)
Dr. Iyer stresses the complex relationship between smoking – the No. 1 cause of COPD – and anxiety. Smoking has been associated in multiple studies with an increased risk of anxiety (Brain and Behavior. 2013;3[3]:302-26), he said. (A study led by Dr. Iyer found a similar frequency of anxiety symptoms in smokers with and without COPD [Journal of Psychosomatic Research. 2019;118:18-26].)
Some patients with COPD and anxiety may smoke in order to ease their anxiety, he said, making management of anxiety an important part of the smoking cessation desired for COPD improvement.
COPD medications such as bronchodilators may cause transient symptoms of anxiety, but these are rare and short-lived, Dr. Iyer said.
Screening tools and conversations
“It’s not just us not thinking about anxiety that’s the problem, it’s also patients thinking that it’s just the disease [causing their anxiety symptoms],” said Dr. Hanania, a member of the 2006 ACCP panel and an author of numerous papers on COPD and anxiety and depression. “There’s quite a bit of overlap between COPD symptoms and anxiety and depression symptoms, and unless you use structured questionnaires, you may not pick it up,” he said.
Screening tools include the Generalized Anxiety Disorder 7-item (GAD-7) scale, the PHQ-9 for depression and anxiety, and the longer Primary Care Evaluation of Mental Disorders (PRIME-MD). The Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale (HADS), Dr. Iyer noted, has been well validated for use in ambulatory settings.
Validated screening tools specific to anxiety in COPD are also now an option. Abebaw M. Yohannes, PhD, MSc, FCCP, professor in the department of physical therapy at Azuza Pacific University in Orange, Calif., and the author of numerous studies on COPD and anxiety, developed one of these tools – the 10-item Anxiety Inventory for Respiratory Disease (AIR) scale – out of concern that other surveys contain overlapping somatic symptoms (Chest. 2013;144[5]:1587-96).
“We removed the physical symptoms [of anxiety] that often manifest in patients with COPD,” he said.
Dr. Iyer said screening tools can effectively “highlight which person might be dealing with high levels of anxiety symptoms that might meet a threshold of clinical significance and require collaborative or interprofessional management,” including with psychologists and psychiatrists.
They can also open the door to conversation with patients. “I’ll often bluntly ask, do you feel anxious? Do you feel scared, or hopeless about what the future holds for you?,” he said. “Anxiety about the future plays a big role, and helping patients navigate the illness and understand early how it might look … can ease the level of anxiety.”
Asking patients about their experiences in managing their symptoms and about their psychological and emotional well-being can help to normalize anxiety – and it can be therapeutic, said Dr. Hoth and Dr. Garvin. Asking “how it’s going with the things that really matter in [their] life” is often a good question, they said.
Patients “won’t be offended if you ask,” said Dr. Hoth. “They view their mood and [whole] well-being as part of their medical condition.”
Time is a challenge, she said, but “conversation can be done little by little, as part of a philosophy of engaging the patient around their whole functioning, even if there’s not [a need or] a route to refer just then.”
Such early and integrated conversation borrows from the palliative care model. “Palliative care is a specialty, but it can also be an approach to care,” Dr. Iyer said. He is leading a National Institutes of Health–funded study on nurse-coach–led early palliative care for older adults with COPD and wants to see training opportunities for pulmonologists to learn basic palliative care skills that would equip them to better guide management of mild-moderate anxiety and other complex symptoms.
Pulmonary rehabilitation
For many patients with COPD who have anxiety and/or depressive symptoms, referral for nonpharmacologic therapies such as psychotherapy, cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), and pulmonary rehabilitation (PR) is “one of the best things you can do,” Dr. Iyer said.
“If patients haven’t done pulmonary rehabilitation, get them in. And if they have done it before, get them back into it again,” he emphasized. “Accredited programs give a holistic approach to improving your strength, your breathlessness, your mindset and understanding of your breathlessness, and your own levels of security.”
Studies addressing the impact of PR and CBT on anxiety have been mostly small and observational but have yielded encouraging findings. A 2017 review reported that PR and CBT were effective in the treatment of anxiety and dyspnea, in the short term, in the majority of 47 studies (JAMA. 2017;18[12]:1096.e1-1096.e17). And a 2019 systematic review and meta-analysis focused on PR reported that, across 11 studies comprising 734 patients, PR conferred significant benefits for anxiety and depression compared with usual care (CHEST. 2019;156[1]:80-91).
Dr. Yohannes, Dr. Hanania, and colleagues recently reported on 734 patients with clinically stable COPD who completed a community-based 8-week PR program of 2 hours a week: 1 hour of exercise and 1 hour of education, the latter of which covered anxiety, panic management, and relaxation.
Patients who had severe dyspnea and comorbid anxiety and depression prior to PR – one-third of the group compared with 20% having anxiety alone and 5% having depression alone – had the most significant improvements in dyspnea scores and anxiety and depression scores (Respir Med. Apr 9. doi: 10.1016/j.rmed.2022.106850.)
The problem is, pulmonary rehabilitation is under-reimbursed and not widely accessible. It’s logistically challenging for patients to attend therapy 2-3 times a week. And according to a recently published study by Dr. Yohannes, Dr. Hanania, and colleagues, patients with more anxiety and dyspnea may be at higher risk of dropping out (Respir Med. 2022 Jan 20. doi: 10.1016/j.rmed.2022.10674). Moreover, Dr. Iyer said, there is a shortage of programs that are accredited.
Telehealth may help on some of these fronts. The efficacy of real-time video PR for COPD is being investigated in a randomized NIH trial (now in the recruitment phase) led by pulmonologist Surya P. Bhatt, MD, also at the University of Alabama at Birmingham.
Researchers also need to investigate issues of sustainability – to learn what “works best in the long run,” Dr. Iyer said.
Dr. Yohannes and Dr. Hanania are encouraged by a recent finding that patients with COPD who completed 8 weeks of PR maintained improvements in anxiety and quality-of-life scores at 2 years. (Improvements in dyspnea and other outcomes did not persist.) (CHEST. 2021;159[3]:967-74). Prospective studies contrasting maintenance programs with no maintenance following PR, are needed, they wrote.
Understanding psychological interventions
Dr. Hoth and Dr. Garvin advise their pulmonologist colleagues to feel as confident as possible in describing for patients what CBT and other psychological therapies entail.
“A person [with COPD] who is experiencing something on the continuum of anxiety might be really turning inward and [assessing] unwanted internal experiences” and accompanying thoughts, sensations, emotional impacts and behaviors, Dr. Garvin said.
Among the goals, she said, are to “make shifts around those internal experiences that might invoke some more tolerance or that might shift their relationship with the experiences, or even with the diagnosis itself and all the uncertainties it carries.”
Psychological therapies can involve social support, or “breath and grounding work,” she said. “There are lots of different approaches from different providers.”
Dr. Yohannes advocates incorporating principles of CBT into PR. “In the absence of one-on-one or group [stand-alone] CBT … the principles are worth incorporating as part of the education piece [of PR],” he said. “CBT helps patients to refocus their attention. … and gives them self-confidence to engage in exercise and to function a bit more in their daily activities.”
None of those interviewed for this story reported having any relevant conflicts of interest.
COPD predicts hospital readmission after fractures
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) was among the significant predictors of hospital readmission in older adults with fractures, based on data from nearly 400 individuals.
Fractures in the elderly remain a major health concern, and readmissions are common; however, Lara Cristina da Cunha Guimarães, MSN, of State School of Public Health Candido Santiago, State Department of Health of Goiás (Brazil), and colleagues wrote.
Previous research suggests that readmissions risk may be greater in patients with preadmission conditions including pulmonary and cardiac disease, history of stroke and other neurological conditions, and other factors associated with aging in general, they said.
In a study published in the journal Injury , the researchers reviewed data from 376 adults aged 60 years and older in a trauma referral hospital in Brazil who had suffered fractures and were hospitalized between Sept. 1, 2016, and Feb. 28, 2017. The primary outcome was readmission up to one year after discharge from the initial hospitalization for fracture.
Approximately half of the patients experienced femur fractures (53.2%), and the most frequent cause was falling from standing height (72.9%). The overall incidence of readmission was 20.7%. A total of 30.5% of readmissions were related to the fracture, and surgical-site infections were the most common cause of fracture-related complications.
More than half (58.3%) of the readmissions were related to clinical complications.
In a multivariate analysis, several clinical factors not related to fractures were independently associated with readmission, including a previous diagnosis of COPD, age between 60 and 69 years, a fracture of the femur, and delirium at the time of the first hospitalization for fracture.
Pneumonia was the most frequent cause of clinical complications, reflecting data from other recent studies, the researchers noted. “Elderly people with COPD are more susceptible to infections, such as pneumonia, which was a cause of frequent readmissions in the population studied. The presence of COPD can contribute to imbalance in the pulmonary microbiome, mucus production and persistent inflammation of the airways, and structural damage, which increases exposure of the pulmonary mucosa to pathogens.” COPD also can be associated with cardiovascular, mental, and musculoskeletal diseases that can further complicate and delay recovery from fractures.
The study findings were limited by the potential for incomplete information in medical records. However, the results indicate a range of causes and conditions associated with hospital readmission after fractures in older adults, they said. Recognizing these factors can guide plans for transitions from hospital to home care to reduce complications and readmissions.
The study received no outside funding. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose.
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) was among the significant predictors of hospital readmission in older adults with fractures, based on data from nearly 400 individuals.
Fractures in the elderly remain a major health concern, and readmissions are common; however, Lara Cristina da Cunha Guimarães, MSN, of State School of Public Health Candido Santiago, State Department of Health of Goiás (Brazil), and colleagues wrote.
Previous research suggests that readmissions risk may be greater in patients with preadmission conditions including pulmonary and cardiac disease, history of stroke and other neurological conditions, and other factors associated with aging in general, they said.
In a study published in the journal Injury , the researchers reviewed data from 376 adults aged 60 years and older in a trauma referral hospital in Brazil who had suffered fractures and were hospitalized between Sept. 1, 2016, and Feb. 28, 2017. The primary outcome was readmission up to one year after discharge from the initial hospitalization for fracture.
Approximately half of the patients experienced femur fractures (53.2%), and the most frequent cause was falling from standing height (72.9%). The overall incidence of readmission was 20.7%. A total of 30.5% of readmissions were related to the fracture, and surgical-site infections were the most common cause of fracture-related complications.
More than half (58.3%) of the readmissions were related to clinical complications.
In a multivariate analysis, several clinical factors not related to fractures were independently associated with readmission, including a previous diagnosis of COPD, age between 60 and 69 years, a fracture of the femur, and delirium at the time of the first hospitalization for fracture.
Pneumonia was the most frequent cause of clinical complications, reflecting data from other recent studies, the researchers noted. “Elderly people with COPD are more susceptible to infections, such as pneumonia, which was a cause of frequent readmissions in the population studied. The presence of COPD can contribute to imbalance in the pulmonary microbiome, mucus production and persistent inflammation of the airways, and structural damage, which increases exposure of the pulmonary mucosa to pathogens.” COPD also can be associated with cardiovascular, mental, and musculoskeletal diseases that can further complicate and delay recovery from fractures.
The study findings were limited by the potential for incomplete information in medical records. However, the results indicate a range of causes and conditions associated with hospital readmission after fractures in older adults, they said. Recognizing these factors can guide plans for transitions from hospital to home care to reduce complications and readmissions.
The study received no outside funding. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose.
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) was among the significant predictors of hospital readmission in older adults with fractures, based on data from nearly 400 individuals.
Fractures in the elderly remain a major health concern, and readmissions are common; however, Lara Cristina da Cunha Guimarães, MSN, of State School of Public Health Candido Santiago, State Department of Health of Goiás (Brazil), and colleagues wrote.
Previous research suggests that readmissions risk may be greater in patients with preadmission conditions including pulmonary and cardiac disease, history of stroke and other neurological conditions, and other factors associated with aging in general, they said.
In a study published in the journal Injury , the researchers reviewed data from 376 adults aged 60 years and older in a trauma referral hospital in Brazil who had suffered fractures and were hospitalized between Sept. 1, 2016, and Feb. 28, 2017. The primary outcome was readmission up to one year after discharge from the initial hospitalization for fracture.
Approximately half of the patients experienced femur fractures (53.2%), and the most frequent cause was falling from standing height (72.9%). The overall incidence of readmission was 20.7%. A total of 30.5% of readmissions were related to the fracture, and surgical-site infections were the most common cause of fracture-related complications.
More than half (58.3%) of the readmissions were related to clinical complications.
In a multivariate analysis, several clinical factors not related to fractures were independently associated with readmission, including a previous diagnosis of COPD, age between 60 and 69 years, a fracture of the femur, and delirium at the time of the first hospitalization for fracture.
Pneumonia was the most frequent cause of clinical complications, reflecting data from other recent studies, the researchers noted. “Elderly people with COPD are more susceptible to infections, such as pneumonia, which was a cause of frequent readmissions in the population studied. The presence of COPD can contribute to imbalance in the pulmonary microbiome, mucus production and persistent inflammation of the airways, and structural damage, which increases exposure of the pulmonary mucosa to pathogens.” COPD also can be associated with cardiovascular, mental, and musculoskeletal diseases that can further complicate and delay recovery from fractures.
The study findings were limited by the potential for incomplete information in medical records. However, the results indicate a range of causes and conditions associated with hospital readmission after fractures in older adults, they said. Recognizing these factors can guide plans for transitions from hospital to home care to reduce complications and readmissions.
The study received no outside funding. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose.
FROM INJURY
Air pollution mediates temperature’s impact on COPD
in adults with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) based on data from 117 individuals.
COPD is attributed to environmental factors including air pollution, and air pollution has been linked to increased risk of hospitalization and mortality because of acute COPD exacerbation, wrote Huan Minh Tran, PhD, of Taipei (Taiwan) Medical University and colleagues. However, the effects of air pollution on climate-associated health outcomes in COPD have not been explored, they said.
In a study published in Science of The Total Environment the researchers identified 117 adult COPD patients at a single center in Taiwan. They measured lung function, 6-minute walking distance, oxygen desaturation, white blood cell count, and percent emphysema (defined as low attenuation area [LAA]) and linked them to 0- to 1-year, 0- to 3-year, and 0- to 5-year lags in exposures to relative humidity (RH), temperature, and air pollution. The mean age of the participants was 72.9 years; 93% were men.
Pollution was defined in terms of fine particulate matter (PM2.5).
Overall, an increase in RH by 1% was associated with increases in forced expiratory volume in 1 second (FEV1), eosinophils, and lymphocytes.
A 1% increase in RH also was associated with a decrease in the total-lobe LAA.
As for temperature, an increase of 1° C was associated with decreased oxygen desaturation and with decreases in right-, left-, and upper-lobe LAA values.
When the researchers examined the impact of pollution, they found that a 1 mcg/m3 increase in PM2.5 was associated with a decrease in the FEV1 as well as with an increase in oxygen desaturation. A 1 mcg/m3 increase in PM10 and PM2.5 was associated with increases in the total-, right-, left, and upper-lobe LAA; increases in lower-lobe LAA were associated with an increase in PM2.5 only.
“This is reasonable because PM2.5 can travel and deposit in distal parts of the lung, while PM10 is preferably deposited in the larger airways of the upper lung regions,” the researchers wrote in their discussion.
A one part per billion increase in nitrogen dioxide (NO2) was associated with decreased FEV1 and increased upper-lobe LAA.
“We observed that NO2 fully mediated the association between RH and FEV1, while PM2.5 fully mediated associations of temperature with oxygen saturation and emphysema severity in COPD patients,” the researchers added.
The study findings were limited by several factors including the relatively small and homogeneous male, Taiwanese population, which may limit generalizability, the researchers noted. Other limitations included the lack of control for factors such as body mass index, occupational exposure, comorbidities, medication use, and indoor air pollution, they said.
However, the results suggest that air pollution could have an effect on the established associations between climate and adverse health outcomes in COPD, and more research is needed. Climate change–related air pollution is an important public health issue, especially with regards to respiratory disease,” they concluded.
The study was supported by the Ministry of Science and Technology of Taiwan. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose.
in adults with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) based on data from 117 individuals.
COPD is attributed to environmental factors including air pollution, and air pollution has been linked to increased risk of hospitalization and mortality because of acute COPD exacerbation, wrote Huan Minh Tran, PhD, of Taipei (Taiwan) Medical University and colleagues. However, the effects of air pollution on climate-associated health outcomes in COPD have not been explored, they said.
In a study published in Science of The Total Environment the researchers identified 117 adult COPD patients at a single center in Taiwan. They measured lung function, 6-minute walking distance, oxygen desaturation, white blood cell count, and percent emphysema (defined as low attenuation area [LAA]) and linked them to 0- to 1-year, 0- to 3-year, and 0- to 5-year lags in exposures to relative humidity (RH), temperature, and air pollution. The mean age of the participants was 72.9 years; 93% were men.
Pollution was defined in terms of fine particulate matter (PM2.5).
Overall, an increase in RH by 1% was associated with increases in forced expiratory volume in 1 second (FEV1), eosinophils, and lymphocytes.
A 1% increase in RH also was associated with a decrease in the total-lobe LAA.
As for temperature, an increase of 1° C was associated with decreased oxygen desaturation and with decreases in right-, left-, and upper-lobe LAA values.
When the researchers examined the impact of pollution, they found that a 1 mcg/m3 increase in PM2.5 was associated with a decrease in the FEV1 as well as with an increase in oxygen desaturation. A 1 mcg/m3 increase in PM10 and PM2.5 was associated with increases in the total-, right-, left, and upper-lobe LAA; increases in lower-lobe LAA were associated with an increase in PM2.5 only.
“This is reasonable because PM2.5 can travel and deposit in distal parts of the lung, while PM10 is preferably deposited in the larger airways of the upper lung regions,” the researchers wrote in their discussion.
A one part per billion increase in nitrogen dioxide (NO2) was associated with decreased FEV1 and increased upper-lobe LAA.
“We observed that NO2 fully mediated the association between RH and FEV1, while PM2.5 fully mediated associations of temperature with oxygen saturation and emphysema severity in COPD patients,” the researchers added.
The study findings were limited by several factors including the relatively small and homogeneous male, Taiwanese population, which may limit generalizability, the researchers noted. Other limitations included the lack of control for factors such as body mass index, occupational exposure, comorbidities, medication use, and indoor air pollution, they said.
However, the results suggest that air pollution could have an effect on the established associations between climate and adverse health outcomes in COPD, and more research is needed. Climate change–related air pollution is an important public health issue, especially with regards to respiratory disease,” they concluded.
The study was supported by the Ministry of Science and Technology of Taiwan. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose.
in adults with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) based on data from 117 individuals.
COPD is attributed to environmental factors including air pollution, and air pollution has been linked to increased risk of hospitalization and mortality because of acute COPD exacerbation, wrote Huan Minh Tran, PhD, of Taipei (Taiwan) Medical University and colleagues. However, the effects of air pollution on climate-associated health outcomes in COPD have not been explored, they said.
In a study published in Science of The Total Environment the researchers identified 117 adult COPD patients at a single center in Taiwan. They measured lung function, 6-minute walking distance, oxygen desaturation, white blood cell count, and percent emphysema (defined as low attenuation area [LAA]) and linked them to 0- to 1-year, 0- to 3-year, and 0- to 5-year lags in exposures to relative humidity (RH), temperature, and air pollution. The mean age of the participants was 72.9 years; 93% were men.
Pollution was defined in terms of fine particulate matter (PM2.5).
Overall, an increase in RH by 1% was associated with increases in forced expiratory volume in 1 second (FEV1), eosinophils, and lymphocytes.
A 1% increase in RH also was associated with a decrease in the total-lobe LAA.
As for temperature, an increase of 1° C was associated with decreased oxygen desaturation and with decreases in right-, left-, and upper-lobe LAA values.
When the researchers examined the impact of pollution, they found that a 1 mcg/m3 increase in PM2.5 was associated with a decrease in the FEV1 as well as with an increase in oxygen desaturation. A 1 mcg/m3 increase in PM10 and PM2.5 was associated with increases in the total-, right-, left, and upper-lobe LAA; increases in lower-lobe LAA were associated with an increase in PM2.5 only.
“This is reasonable because PM2.5 can travel and deposit in distal parts of the lung, while PM10 is preferably deposited in the larger airways of the upper lung regions,” the researchers wrote in their discussion.
A one part per billion increase in nitrogen dioxide (NO2) was associated with decreased FEV1 and increased upper-lobe LAA.
“We observed that NO2 fully mediated the association between RH and FEV1, while PM2.5 fully mediated associations of temperature with oxygen saturation and emphysema severity in COPD patients,” the researchers added.
The study findings were limited by several factors including the relatively small and homogeneous male, Taiwanese population, which may limit generalizability, the researchers noted. Other limitations included the lack of control for factors such as body mass index, occupational exposure, comorbidities, medication use, and indoor air pollution, they said.
However, the results suggest that air pollution could have an effect on the established associations between climate and adverse health outcomes in COPD, and more research is needed. Climate change–related air pollution is an important public health issue, especially with regards to respiratory disease,” they concluded.
The study was supported by the Ministry of Science and Technology of Taiwan. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose.
FROM SCIENCE OF THE TOTAL ENVIRONMENT
The Role of Bronchoscopic Lung Volume Reduction in COPD
Patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) typically have emphysema, which involves destruction of alveoli and reduction of elasticity leading to airflow obstruction, air trapping, and hyperinflation. Over time, these changes cause low respiratory reserve volume and increased residual volume, which cause dyspnea.
One of the newest treatment options for patients who have advanced COPD with severe emphysema is a minimally invasive procedure called bronchoscopic lung volume reduction (BLVR). Most recently, the FDA approved the use of endobronchial valves for this procedure, which are implanted in the airways of the lungs to reduce air trapping and hyperinflation.
In certain patients, BLVR has been shown to improve lung function, facilitate easier breathing, enhance exercise tolerance, and lead to better quality of life.
In this ReCAP, Dr. Javier Diaz-Mendoza, program director of the Interventional Pulmonology Fellowship at Henry Ford Health System in Detroit, discusses the benefits of BLVR in patients who have advanced COPD with emphysema. He discusses the procedure, patient outcomes, and which patients should be considered for BLVR.
--
Associate Professor of Medicine, Henry Ford Hospital, Wayne State University; Program Director, Interventional Pulmonology Fellowship, Henry Ford Health System, Detroit, MI
Javier Diaz-Mendoza, MD, FCCP, has disclosed the following relevant financial relationships: Serve(d) as a director, officer, partner, employee, advisor, consultant, or trustee for: Ion Intuitive Serve(d) as a speaker or a member of a speakers bureau for: Association of Interventional Pulmonology Program Directors
Patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) typically have emphysema, which involves destruction of alveoli and reduction of elasticity leading to airflow obstruction, air trapping, and hyperinflation. Over time, these changes cause low respiratory reserve volume and increased residual volume, which cause dyspnea.
One of the newest treatment options for patients who have advanced COPD with severe emphysema is a minimally invasive procedure called bronchoscopic lung volume reduction (BLVR). Most recently, the FDA approved the use of endobronchial valves for this procedure, which are implanted in the airways of the lungs to reduce air trapping and hyperinflation.
In certain patients, BLVR has been shown to improve lung function, facilitate easier breathing, enhance exercise tolerance, and lead to better quality of life.
In this ReCAP, Dr. Javier Diaz-Mendoza, program director of the Interventional Pulmonology Fellowship at Henry Ford Health System in Detroit, discusses the benefits of BLVR in patients who have advanced COPD with emphysema. He discusses the procedure, patient outcomes, and which patients should be considered for BLVR.
--
Associate Professor of Medicine, Henry Ford Hospital, Wayne State University; Program Director, Interventional Pulmonology Fellowship, Henry Ford Health System, Detroit, MI
Javier Diaz-Mendoza, MD, FCCP, has disclosed the following relevant financial relationships: Serve(d) as a director, officer, partner, employee, advisor, consultant, or trustee for: Ion Intuitive Serve(d) as a speaker or a member of a speakers bureau for: Association of Interventional Pulmonology Program Directors
Patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) typically have emphysema, which involves destruction of alveoli and reduction of elasticity leading to airflow obstruction, air trapping, and hyperinflation. Over time, these changes cause low respiratory reserve volume and increased residual volume, which cause dyspnea.
One of the newest treatment options for patients who have advanced COPD with severe emphysema is a minimally invasive procedure called bronchoscopic lung volume reduction (BLVR). Most recently, the FDA approved the use of endobronchial valves for this procedure, which are implanted in the airways of the lungs to reduce air trapping and hyperinflation.
In certain patients, BLVR has been shown to improve lung function, facilitate easier breathing, enhance exercise tolerance, and lead to better quality of life.
In this ReCAP, Dr. Javier Diaz-Mendoza, program director of the Interventional Pulmonology Fellowship at Henry Ford Health System in Detroit, discusses the benefits of BLVR in patients who have advanced COPD with emphysema. He discusses the procedure, patient outcomes, and which patients should be considered for BLVR.
--
Associate Professor of Medicine, Henry Ford Hospital, Wayne State University; Program Director, Interventional Pulmonology Fellowship, Henry Ford Health System, Detroit, MI
Javier Diaz-Mendoza, MD, FCCP, has disclosed the following relevant financial relationships: Serve(d) as a director, officer, partner, employee, advisor, consultant, or trustee for: Ion Intuitive Serve(d) as a speaker or a member of a speakers bureau for: Association of Interventional Pulmonology Program Directors

IL-6 antibody mitigates mucus hypersecretion in COPD
Treatment with an interleukin-6 neutralizing antibody significantly reduced airway mucus hypersecretion (AMH) in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), based on data from human and mouse cells in a human organoid model.
AMH plays a large part in aggravating airway obstruction in patients with COPD, Yuan-Yuan Wei, MD, of First Affiliated Hospital of Anhui Medical University, Hefei, China, and colleagues wrote.
Current pharmacotherapies relieve COPD symptoms and improve exercise tolerance, but have not proven effective for relieving the airflow limitations caused by mucus accumulation that “leads to irreversible structural damage and an unfavorable prognosis,” the researchers said. Although reducing AMH could help manage COPD, the molecular mechanisms of action have not been fully explored.
In a study published in Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy , the researchers examined the relationship between IL-6 and AMH. Since IL-6 has been shown to cause overexpression of the mucin-type protein known as Muc5ac, they hypothesized that IL-6 antibodies (IL-6Ab) might block this protein elevation.
The researchers recruited 30 adults with COPD and 30 controls from a single center. Bronchial epithelial cells were isolated from the participants and measured the levels of Muc5ac protein and mRNA in the lung tissue. Compared with controls, COPD patients had elevated Muc5ac positively correlated with IL-6.
The researchers then created an organoid model of a trachea for COPD patients and controls. In the model, Muc5ac was similarly elevated in COPD patients, compared with controls. “Furthermore, IL-6 significantly induced excessive secretion of mucus in the organoid model of trachea in COPD patients as observed under electron microscope, and IL-6Ab attenuated these effects,” they noted.
IL-6 significantly increased both Muc5ac mRNA and protein expression in the organoid model of trachea (P < .0001 and P < .005, respectively), but both of these significantly decreased when treated with IL-6Ab (P < .0001 and P < .05, respectively).
The researchers also examined human and mouse cells to explore the mechanism of action of IL-6Ab. Using high-throughput sequencing, they found that the IL-6Ab induced nuclear translocation of the Nrt2 gene in COPD patients, and that this action promoted the effect of IL-6Ab on excessive mucus secretion.
The study findings were limited by the relatively small study population from a single center, the researchers noted.
However, the results support the potential of IL-6Ab as “a novel therapeutic strategy in the treatment of IL-6–induced hypersecretion of airway mucus so as to improve airflow limitations in COPD,” they concluded.
The study was supported by supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China and the Scientific Research Project of Education Department of Anhui Province. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose.
Treatment with an interleukin-6 neutralizing antibody significantly reduced airway mucus hypersecretion (AMH) in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), based on data from human and mouse cells in a human organoid model.
AMH plays a large part in aggravating airway obstruction in patients with COPD, Yuan-Yuan Wei, MD, of First Affiliated Hospital of Anhui Medical University, Hefei, China, and colleagues wrote.
Current pharmacotherapies relieve COPD symptoms and improve exercise tolerance, but have not proven effective for relieving the airflow limitations caused by mucus accumulation that “leads to irreversible structural damage and an unfavorable prognosis,” the researchers said. Although reducing AMH could help manage COPD, the molecular mechanisms of action have not been fully explored.
In a study published in Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy , the researchers examined the relationship between IL-6 and AMH. Since IL-6 has been shown to cause overexpression of the mucin-type protein known as Muc5ac, they hypothesized that IL-6 antibodies (IL-6Ab) might block this protein elevation.
The researchers recruited 30 adults with COPD and 30 controls from a single center. Bronchial epithelial cells were isolated from the participants and measured the levels of Muc5ac protein and mRNA in the lung tissue. Compared with controls, COPD patients had elevated Muc5ac positively correlated with IL-6.
The researchers then created an organoid model of a trachea for COPD patients and controls. In the model, Muc5ac was similarly elevated in COPD patients, compared with controls. “Furthermore, IL-6 significantly induced excessive secretion of mucus in the organoid model of trachea in COPD patients as observed under electron microscope, and IL-6Ab attenuated these effects,” they noted.
IL-6 significantly increased both Muc5ac mRNA and protein expression in the organoid model of trachea (P < .0001 and P < .005, respectively), but both of these significantly decreased when treated with IL-6Ab (P < .0001 and P < .05, respectively).
The researchers also examined human and mouse cells to explore the mechanism of action of IL-6Ab. Using high-throughput sequencing, they found that the IL-6Ab induced nuclear translocation of the Nrt2 gene in COPD patients, and that this action promoted the effect of IL-6Ab on excessive mucus secretion.
The study findings were limited by the relatively small study population from a single center, the researchers noted.
However, the results support the potential of IL-6Ab as “a novel therapeutic strategy in the treatment of IL-6–induced hypersecretion of airway mucus so as to improve airflow limitations in COPD,” they concluded.
The study was supported by supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China and the Scientific Research Project of Education Department of Anhui Province. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose.
Treatment with an interleukin-6 neutralizing antibody significantly reduced airway mucus hypersecretion (AMH) in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), based on data from human and mouse cells in a human organoid model.
AMH plays a large part in aggravating airway obstruction in patients with COPD, Yuan-Yuan Wei, MD, of First Affiliated Hospital of Anhui Medical University, Hefei, China, and colleagues wrote.
Current pharmacotherapies relieve COPD symptoms and improve exercise tolerance, but have not proven effective for relieving the airflow limitations caused by mucus accumulation that “leads to irreversible structural damage and an unfavorable prognosis,” the researchers said. Although reducing AMH could help manage COPD, the molecular mechanisms of action have not been fully explored.
In a study published in Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy , the researchers examined the relationship between IL-6 and AMH. Since IL-6 has been shown to cause overexpression of the mucin-type protein known as Muc5ac, they hypothesized that IL-6 antibodies (IL-6Ab) might block this protein elevation.
The researchers recruited 30 adults with COPD and 30 controls from a single center. Bronchial epithelial cells were isolated from the participants and measured the levels of Muc5ac protein and mRNA in the lung tissue. Compared with controls, COPD patients had elevated Muc5ac positively correlated with IL-6.
The researchers then created an organoid model of a trachea for COPD patients and controls. In the model, Muc5ac was similarly elevated in COPD patients, compared with controls. “Furthermore, IL-6 significantly induced excessive secretion of mucus in the organoid model of trachea in COPD patients as observed under electron microscope, and IL-6Ab attenuated these effects,” they noted.
IL-6 significantly increased both Muc5ac mRNA and protein expression in the organoid model of trachea (P < .0001 and P < .005, respectively), but both of these significantly decreased when treated with IL-6Ab (P < .0001 and P < .05, respectively).
The researchers also examined human and mouse cells to explore the mechanism of action of IL-6Ab. Using high-throughput sequencing, they found that the IL-6Ab induced nuclear translocation of the Nrt2 gene in COPD patients, and that this action promoted the effect of IL-6Ab on excessive mucus secretion.
The study findings were limited by the relatively small study population from a single center, the researchers noted.
However, the results support the potential of IL-6Ab as “a novel therapeutic strategy in the treatment of IL-6–induced hypersecretion of airway mucus so as to improve airflow limitations in COPD,” they concluded.
The study was supported by supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China and the Scientific Research Project of Education Department of Anhui Province. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose.
FROM BIOMEDICINE & PHARMACOTHERAPY
Eosinophils may predict outcomes in acute COPD exacerbations
High levels of eosinophils had a protective effect for individuals who experienced acute exacerbations of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, based on data from nearly 1,000 patients.
Several blood biomarkers are under investigation for links to acute exacerbation of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (AECOPD), which remains one of the top three causes of death worldwide, wrote Riuying Wang, MD, of Third Hospital of Shanxi Medical University, Taiyuan, China, and colleagues.
“Numerous studies have shown the relationship between eosinophilia and clinical outcomes of patients with AECOPD. However, the evidence lacks consensus, and the research thresholds are controversial,” they said.
In a study published in Heart & Lung, the researchers reviewed data from 984 adults with AECOPD over a 3-year follow-up period. The mean age of the patients was 71 years, and 78% were men. The patients’ blood eosinophil levels were grouped into three categories: EOS < 2%, EOS from 2% to < 3%, and 3% or higher. The researchers examined the association between eosinophilia and various comorbidities, treatment, and mortality.
Eosinophilia occurred in 477 cases. The prevalence of eosinophilia in the three groups was 36.48%, 22.87%, and 48.48% respectively, with eosinophilia defined as eosinophil counts of at least 100 cells per microliter, according to the report in Heart & Lung.
An EOS of 2% or higher was associated with significantly fewer cases of complicated pulmonary heart disease and atrial fibrillation than the lower EOS group. Similarly, patients in the EOS group of 2% or higher were less likely to use ventilators and systemic glucocorticoids and those in the EOS less than 2% group had significantly heavier airflow limitation, higher D-dimer, higher burden of infectious inflammation, and higher prevalence of respiratory failure than the other groups.
In addition, significantly fewer deaths occurred during the study period among patients with EOS of 2% or higher, compared with the lower EOS group (P < .01). The findings suggest that “Eosinophils can be used as a prognostic indicator of mortality in AECOPD,” the researchers said.
The researchers also used the area under the curve to examine the predictive value of EOS. The ROC curve showed that the indicators of AUC 0.5 included chest CT imaging, osteoporosis, mental illness, dust exposure, and being a former smoker; however, “the predictive value of EOS by the ROC curve was unstable. Further validation in large samples is needed,” the researchers wrote in their discussion.
The study findings were limited by several factors including the retrospective design and use of data from a single center, the researchers noted. Other limitations included the relatively small sample size and a lack of data on some clinical features and performance metrics, as well as lack of evaluation of chest CT subtypes.
However, the results are consistent with previous studies on infection and antibiotics and reviewed the optimal threshold of AECOPD, the researchers wrote. Based on their findings, “Eosinophils can not only guide clinical treatment but also be used as an index to predict the clinical outcome and prognosis of AECOPD patients,” they concluded.
The study received no outside funding. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose.
High levels of eosinophils had a protective effect for individuals who experienced acute exacerbations of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, based on data from nearly 1,000 patients.
Several blood biomarkers are under investigation for links to acute exacerbation of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (AECOPD), which remains one of the top three causes of death worldwide, wrote Riuying Wang, MD, of Third Hospital of Shanxi Medical University, Taiyuan, China, and colleagues.
“Numerous studies have shown the relationship between eosinophilia and clinical outcomes of patients with AECOPD. However, the evidence lacks consensus, and the research thresholds are controversial,” they said.
In a study published in Heart & Lung, the researchers reviewed data from 984 adults with AECOPD over a 3-year follow-up period. The mean age of the patients was 71 years, and 78% were men. The patients’ blood eosinophil levels were grouped into three categories: EOS < 2%, EOS from 2% to < 3%, and 3% or higher. The researchers examined the association between eosinophilia and various comorbidities, treatment, and mortality.
Eosinophilia occurred in 477 cases. The prevalence of eosinophilia in the three groups was 36.48%, 22.87%, and 48.48% respectively, with eosinophilia defined as eosinophil counts of at least 100 cells per microliter, according to the report in Heart & Lung.
An EOS of 2% or higher was associated with significantly fewer cases of complicated pulmonary heart disease and atrial fibrillation than the lower EOS group. Similarly, patients in the EOS group of 2% or higher were less likely to use ventilators and systemic glucocorticoids and those in the EOS less than 2% group had significantly heavier airflow limitation, higher D-dimer, higher burden of infectious inflammation, and higher prevalence of respiratory failure than the other groups.
In addition, significantly fewer deaths occurred during the study period among patients with EOS of 2% or higher, compared with the lower EOS group (P < .01). The findings suggest that “Eosinophils can be used as a prognostic indicator of mortality in AECOPD,” the researchers said.
The researchers also used the area under the curve to examine the predictive value of EOS. The ROC curve showed that the indicators of AUC 0.5 included chest CT imaging, osteoporosis, mental illness, dust exposure, and being a former smoker; however, “the predictive value of EOS by the ROC curve was unstable. Further validation in large samples is needed,” the researchers wrote in their discussion.
The study findings were limited by several factors including the retrospective design and use of data from a single center, the researchers noted. Other limitations included the relatively small sample size and a lack of data on some clinical features and performance metrics, as well as lack of evaluation of chest CT subtypes.
However, the results are consistent with previous studies on infection and antibiotics and reviewed the optimal threshold of AECOPD, the researchers wrote. Based on their findings, “Eosinophils can not only guide clinical treatment but also be used as an index to predict the clinical outcome and prognosis of AECOPD patients,” they concluded.
The study received no outside funding. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose.
High levels of eosinophils had a protective effect for individuals who experienced acute exacerbations of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, based on data from nearly 1,000 patients.
Several blood biomarkers are under investigation for links to acute exacerbation of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (AECOPD), which remains one of the top three causes of death worldwide, wrote Riuying Wang, MD, of Third Hospital of Shanxi Medical University, Taiyuan, China, and colleagues.
“Numerous studies have shown the relationship between eosinophilia and clinical outcomes of patients with AECOPD. However, the evidence lacks consensus, and the research thresholds are controversial,” they said.
In a study published in Heart & Lung, the researchers reviewed data from 984 adults with AECOPD over a 3-year follow-up period. The mean age of the patients was 71 years, and 78% were men. The patients’ blood eosinophil levels were grouped into three categories: EOS < 2%, EOS from 2% to < 3%, and 3% or higher. The researchers examined the association between eosinophilia and various comorbidities, treatment, and mortality.
Eosinophilia occurred in 477 cases. The prevalence of eosinophilia in the three groups was 36.48%, 22.87%, and 48.48% respectively, with eosinophilia defined as eosinophil counts of at least 100 cells per microliter, according to the report in Heart & Lung.
An EOS of 2% or higher was associated with significantly fewer cases of complicated pulmonary heart disease and atrial fibrillation than the lower EOS group. Similarly, patients in the EOS group of 2% or higher were less likely to use ventilators and systemic glucocorticoids and those in the EOS less than 2% group had significantly heavier airflow limitation, higher D-dimer, higher burden of infectious inflammation, and higher prevalence of respiratory failure than the other groups.
In addition, significantly fewer deaths occurred during the study period among patients with EOS of 2% or higher, compared with the lower EOS group (P < .01). The findings suggest that “Eosinophils can be used as a prognostic indicator of mortality in AECOPD,” the researchers said.
The researchers also used the area under the curve to examine the predictive value of EOS. The ROC curve showed that the indicators of AUC 0.5 included chest CT imaging, osteoporosis, mental illness, dust exposure, and being a former smoker; however, “the predictive value of EOS by the ROC curve was unstable. Further validation in large samples is needed,” the researchers wrote in their discussion.
The study findings were limited by several factors including the retrospective design and use of data from a single center, the researchers noted. Other limitations included the relatively small sample size and a lack of data on some clinical features and performance metrics, as well as lack of evaluation of chest CT subtypes.
However, the results are consistent with previous studies on infection and antibiotics and reviewed the optimal threshold of AECOPD, the researchers wrote. Based on their findings, “Eosinophils can not only guide clinical treatment but also be used as an index to predict the clinical outcome and prognosis of AECOPD patients,” they concluded.
The study received no outside funding. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose.
FROM HEART & LUNG