User login
Interim PET scans identify HL patients with better outcomes
CHICAGO—Interim PET scans can identify a subset of Hodgkin lymphoma (HL) patients with a better outcome suitable for de-escalation treatment after upfront BEACOPP without impairing disease control, according to final results of the AHL2011-LYSA study.
BEACOPP, compared to ABVD, improves progression-free survival (PFS) but not overall survival (OS) and is associated with a higher risk of myelodysplasia, acute leukemia, and infertility.
Investigators evaluated whether some patients might be able to reduce treatment intensity without compromising the effectiveness of their therapy.
Olivier Casasnovas, MD, of CHU Le Bocage Service d'Hématologie Clinique, Dijon, France, presented the final analysis at the 2018 ASCO Annual Meeting (abstract 7503).
AHL2011-LYSA study (NCT01358747)
The randomized phase 3 study compared an early PET-driven treatment de-escalation to a non-PET-monitored strategy in patients with advanced-stage HL.
The study included 823 previously untreated patients, median age 30 years (range 16 – 60), with stage III, IV, or high-risk IIB HL.
The PET-driven strategy consisted of 2 BEACOPP* cycles (PET2), followed by 4 cycles of ABVD** for PET2-negative patients, and 4 cycles of BEACOPP for PET2-positive patients.
The experimental PET-driven strategy (410 patients) was randomly compared to a standard treatment delivering 6 cycles of BEACOPP (413 patients). PFS was the primary endpoint with a hypothesis of non-inferiority of the PET-driven arm compared to the standard arm.
Patients characteristics were well balanced between the arms, Dr Casasnovas said. PET2-positivity rate was similar in both arms (experimental 13%, standard 12%).
Based on PET2 results, 346 (84%) patients received 4 cycles of ABVD and 51 (12%) patients received 4 additional cycles of BEACOPP in the experimental arm.
Results
With a median follow-up of 50 months, the 5-year PFS was similar in the standard (86.2%) and the PET-driven arms (85.7%). The 5-year PFS for PET 2-negative/PET 4-negative patients was 90.9%, for PET 2-positive/PET4-negative patients was 75.4%, and for PET 4-positive patients was 46.5%.
The 5-year OS was similar in both arms (96.4% experimental, 95.2% standard).
The treatment toxicity was significantly higher in patients receiving 6 cycles of BEACOPP as compared to those who received 2 cycles of BEACOPP plus 4 cycles of ABVD.
Those who received more cycles of BEACOPP had more frequent grade 3 or higher adverse events than those with fewer cycles, including anemia (11% vs 2%), leukopenia (85% vs 74%), thrombocytopenia (44% vs 15%), and sepsis (7% vs 3%), as well as in serious adverse events (45% vs 28%).
“After 4 cycles of chemotherapy, it [PET positivity] identifies a subset of patients with a particularly poor outcome,” Dr Casasnovas said, “encouraging researchers to develop new treatment options in these patients.”
“PET performed after 2 cycles of BEACOPP escalation can be safely used to guide subsequent treatment,” he concluded.
“This approach allows clinicians to reduce the treatment-related immediate toxicity in most patients,” he added, “and provides similar patient outcomes compared to standard BEACOPP escalation treatment.”
* Bleomycin, etoposide, doxorubicin, cyclophosphamide, vincristine, procarbazine, prednisone
**Adriamycin (doxorubicin), bleomycin, vinblastine, dacarbazine
CHICAGO—Interim PET scans can identify a subset of Hodgkin lymphoma (HL) patients with a better outcome suitable for de-escalation treatment after upfront BEACOPP without impairing disease control, according to final results of the AHL2011-LYSA study.
BEACOPP, compared to ABVD, improves progression-free survival (PFS) but not overall survival (OS) and is associated with a higher risk of myelodysplasia, acute leukemia, and infertility.
Investigators evaluated whether some patients might be able to reduce treatment intensity without compromising the effectiveness of their therapy.
Olivier Casasnovas, MD, of CHU Le Bocage Service d'Hématologie Clinique, Dijon, France, presented the final analysis at the 2018 ASCO Annual Meeting (abstract 7503).
AHL2011-LYSA study (NCT01358747)
The randomized phase 3 study compared an early PET-driven treatment de-escalation to a non-PET-monitored strategy in patients with advanced-stage HL.
The study included 823 previously untreated patients, median age 30 years (range 16 – 60), with stage III, IV, or high-risk IIB HL.
The PET-driven strategy consisted of 2 BEACOPP* cycles (PET2), followed by 4 cycles of ABVD** for PET2-negative patients, and 4 cycles of BEACOPP for PET2-positive patients.
The experimental PET-driven strategy (410 patients) was randomly compared to a standard treatment delivering 6 cycles of BEACOPP (413 patients). PFS was the primary endpoint with a hypothesis of non-inferiority of the PET-driven arm compared to the standard arm.
Patients characteristics were well balanced between the arms, Dr Casasnovas said. PET2-positivity rate was similar in both arms (experimental 13%, standard 12%).
Based on PET2 results, 346 (84%) patients received 4 cycles of ABVD and 51 (12%) patients received 4 additional cycles of BEACOPP in the experimental arm.
Results
With a median follow-up of 50 months, the 5-year PFS was similar in the standard (86.2%) and the PET-driven arms (85.7%). The 5-year PFS for PET 2-negative/PET 4-negative patients was 90.9%, for PET 2-positive/PET4-negative patients was 75.4%, and for PET 4-positive patients was 46.5%.
The 5-year OS was similar in both arms (96.4% experimental, 95.2% standard).
The treatment toxicity was significantly higher in patients receiving 6 cycles of BEACOPP as compared to those who received 2 cycles of BEACOPP plus 4 cycles of ABVD.
Those who received more cycles of BEACOPP had more frequent grade 3 or higher adverse events than those with fewer cycles, including anemia (11% vs 2%), leukopenia (85% vs 74%), thrombocytopenia (44% vs 15%), and sepsis (7% vs 3%), as well as in serious adverse events (45% vs 28%).
“After 4 cycles of chemotherapy, it [PET positivity] identifies a subset of patients with a particularly poor outcome,” Dr Casasnovas said, “encouraging researchers to develop new treatment options in these patients.”
“PET performed after 2 cycles of BEACOPP escalation can be safely used to guide subsequent treatment,” he concluded.
“This approach allows clinicians to reduce the treatment-related immediate toxicity in most patients,” he added, “and provides similar patient outcomes compared to standard BEACOPP escalation treatment.”
* Bleomycin, etoposide, doxorubicin, cyclophosphamide, vincristine, procarbazine, prednisone
**Adriamycin (doxorubicin), bleomycin, vinblastine, dacarbazine
CHICAGO—Interim PET scans can identify a subset of Hodgkin lymphoma (HL) patients with a better outcome suitable for de-escalation treatment after upfront BEACOPP without impairing disease control, according to final results of the AHL2011-LYSA study.
BEACOPP, compared to ABVD, improves progression-free survival (PFS) but not overall survival (OS) and is associated with a higher risk of myelodysplasia, acute leukemia, and infertility.
Investigators evaluated whether some patients might be able to reduce treatment intensity without compromising the effectiveness of their therapy.
Olivier Casasnovas, MD, of CHU Le Bocage Service d'Hématologie Clinique, Dijon, France, presented the final analysis at the 2018 ASCO Annual Meeting (abstract 7503).
AHL2011-LYSA study (NCT01358747)
The randomized phase 3 study compared an early PET-driven treatment de-escalation to a non-PET-monitored strategy in patients with advanced-stage HL.
The study included 823 previously untreated patients, median age 30 years (range 16 – 60), with stage III, IV, or high-risk IIB HL.
The PET-driven strategy consisted of 2 BEACOPP* cycles (PET2), followed by 4 cycles of ABVD** for PET2-negative patients, and 4 cycles of BEACOPP for PET2-positive patients.
The experimental PET-driven strategy (410 patients) was randomly compared to a standard treatment delivering 6 cycles of BEACOPP (413 patients). PFS was the primary endpoint with a hypothesis of non-inferiority of the PET-driven arm compared to the standard arm.
Patients characteristics were well balanced between the arms, Dr Casasnovas said. PET2-positivity rate was similar in both arms (experimental 13%, standard 12%).
Based on PET2 results, 346 (84%) patients received 4 cycles of ABVD and 51 (12%) patients received 4 additional cycles of BEACOPP in the experimental arm.
Results
With a median follow-up of 50 months, the 5-year PFS was similar in the standard (86.2%) and the PET-driven arms (85.7%). The 5-year PFS for PET 2-negative/PET 4-negative patients was 90.9%, for PET 2-positive/PET4-negative patients was 75.4%, and for PET 4-positive patients was 46.5%.
The 5-year OS was similar in both arms (96.4% experimental, 95.2% standard).
The treatment toxicity was significantly higher in patients receiving 6 cycles of BEACOPP as compared to those who received 2 cycles of BEACOPP plus 4 cycles of ABVD.
Those who received more cycles of BEACOPP had more frequent grade 3 or higher adverse events than those with fewer cycles, including anemia (11% vs 2%), leukopenia (85% vs 74%), thrombocytopenia (44% vs 15%), and sepsis (7% vs 3%), as well as in serious adverse events (45% vs 28%).
“After 4 cycles of chemotherapy, it [PET positivity] identifies a subset of patients with a particularly poor outcome,” Dr Casasnovas said, “encouraging researchers to develop new treatment options in these patients.”
“PET performed after 2 cycles of BEACOPP escalation can be safely used to guide subsequent treatment,” he concluded.
“This approach allows clinicians to reduce the treatment-related immediate toxicity in most patients,” he added, “and provides similar patient outcomes compared to standard BEACOPP escalation treatment.”
* Bleomycin, etoposide, doxorubicin, cyclophosphamide, vincristine, procarbazine, prednisone
**Adriamycin (doxorubicin), bleomycin, vinblastine, dacarbazine
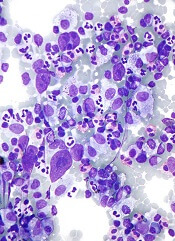
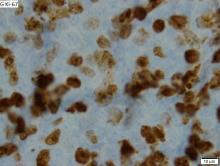
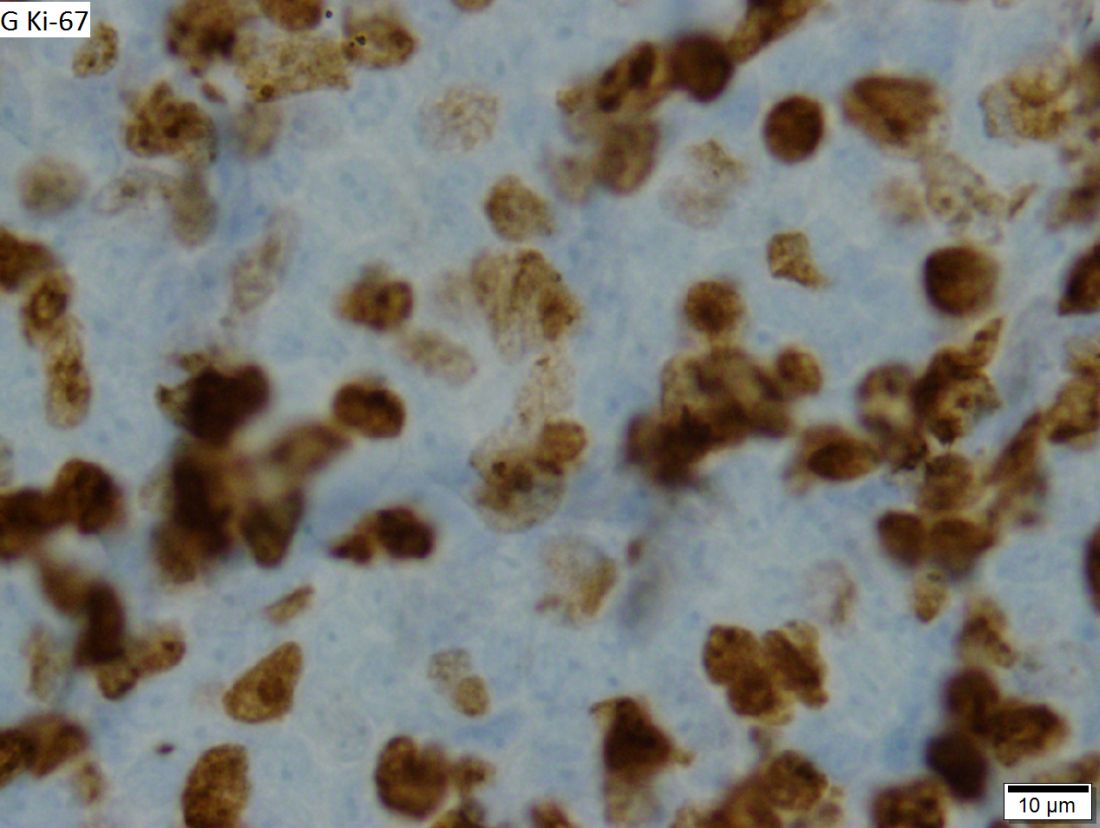
British good practice paper offers MCL diagnosis pearls
Immunohistochemical panels used in the diagnosis of mantle cell lymphoma should include cyclin D1 and SOX11 immunostaining, according to a good practice paper from the British Society of Haematology.
Pamela McKay, MD, of the Beatson West of Scotland Cancer Centre, Glasgow, and her colleagues provided based on a review of literature from 1980 to 2017. The good practice paper aims to offer best practice advice based on consensus where the evidence is limited. Specifically, the paper incorporates new information on molecular pathology and the use of positron emission tomography/computed tomography (PET/CT) scanning in staging of disease.
The top recommendations related to MCL diagnosis include performing lymph node excision or adequate core biopsy for diagnosis of nodal MCL. For non-nodal presentation, a tissue biopsy or peripheral blood can be used. Additionally, immunohistochemical panels should include cyclin D1 and SOX11 immunostaining.
In cases of atypical morphology, aberrant immunophenotype, equivocal cyclin D1 positivity, or unusual clinical presentation, the authors recommended fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) to demonstrate the presence of the t(11;14) translocation. They also recommended recording the Ki67 Proliferation Index at baseline, with an index of greater than 30% being indicative of a poorer outcome.
In terms of staging disease, Dr. McKay and her associates recommended that patients undergo staging with CT of the neck, chest, abdomen, and pelvis. They recommended against routine use of fluorodeoxyglucose PET for MCL staging, but said it could be considered if radical radiotherapy is being proposed for early-stage disease.
For cases with suspicion of central nervous system involvement, lumbar puncture with cytospin and immunophenotyping is recommended.
They recommended that all MCL patients have either their simplified or combined MCL international prognostic index score recorded at baseline.
All the authors made a declaration of interest to the British Society of Haematology and task force chairs, which may be viewed on request.
SOURCE: McKay P et al. Br J Haematol. 2018 Jun 8. doi: 10.1111/bjh.15281.
Immunohistochemical panels used in the diagnosis of mantle cell lymphoma should include cyclin D1 and SOX11 immunostaining, according to a good practice paper from the British Society of Haematology.
Pamela McKay, MD, of the Beatson West of Scotland Cancer Centre, Glasgow, and her colleagues provided based on a review of literature from 1980 to 2017. The good practice paper aims to offer best practice advice based on consensus where the evidence is limited. Specifically, the paper incorporates new information on molecular pathology and the use of positron emission tomography/computed tomography (PET/CT) scanning in staging of disease.
The top recommendations related to MCL diagnosis include performing lymph node excision or adequate core biopsy for diagnosis of nodal MCL. For non-nodal presentation, a tissue biopsy or peripheral blood can be used. Additionally, immunohistochemical panels should include cyclin D1 and SOX11 immunostaining.
In cases of atypical morphology, aberrant immunophenotype, equivocal cyclin D1 positivity, or unusual clinical presentation, the authors recommended fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) to demonstrate the presence of the t(11;14) translocation. They also recommended recording the Ki67 Proliferation Index at baseline, with an index of greater than 30% being indicative of a poorer outcome.
In terms of staging disease, Dr. McKay and her associates recommended that patients undergo staging with CT of the neck, chest, abdomen, and pelvis. They recommended against routine use of fluorodeoxyglucose PET for MCL staging, but said it could be considered if radical radiotherapy is being proposed for early-stage disease.
For cases with suspicion of central nervous system involvement, lumbar puncture with cytospin and immunophenotyping is recommended.
They recommended that all MCL patients have either their simplified or combined MCL international prognostic index score recorded at baseline.
All the authors made a declaration of interest to the British Society of Haematology and task force chairs, which may be viewed on request.
SOURCE: McKay P et al. Br J Haematol. 2018 Jun 8. doi: 10.1111/bjh.15281.
Immunohistochemical panels used in the diagnosis of mantle cell lymphoma should include cyclin D1 and SOX11 immunostaining, according to a good practice paper from the British Society of Haematology.
Pamela McKay, MD, of the Beatson West of Scotland Cancer Centre, Glasgow, and her colleagues provided based on a review of literature from 1980 to 2017. The good practice paper aims to offer best practice advice based on consensus where the evidence is limited. Specifically, the paper incorporates new information on molecular pathology and the use of positron emission tomography/computed tomography (PET/CT) scanning in staging of disease.
The top recommendations related to MCL diagnosis include performing lymph node excision or adequate core biopsy for diagnosis of nodal MCL. For non-nodal presentation, a tissue biopsy or peripheral blood can be used. Additionally, immunohistochemical panels should include cyclin D1 and SOX11 immunostaining.
In cases of atypical morphology, aberrant immunophenotype, equivocal cyclin D1 positivity, or unusual clinical presentation, the authors recommended fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) to demonstrate the presence of the t(11;14) translocation. They also recommended recording the Ki67 Proliferation Index at baseline, with an index of greater than 30% being indicative of a poorer outcome.
In terms of staging disease, Dr. McKay and her associates recommended that patients undergo staging with CT of the neck, chest, abdomen, and pelvis. They recommended against routine use of fluorodeoxyglucose PET for MCL staging, but said it could be considered if radical radiotherapy is being proposed for early-stage disease.
For cases with suspicion of central nervous system involvement, lumbar puncture with cytospin and immunophenotyping is recommended.
They recommended that all MCL patients have either their simplified or combined MCL international prognostic index score recorded at baseline.
All the authors made a declaration of interest to the British Society of Haematology and task force chairs, which may be viewed on request.
SOURCE: McKay P et al. Br J Haematol. 2018 Jun 8. doi: 10.1111/bjh.15281.
FROM THE BRITISH JOURNAL OF HAEMATOLOGY
FDA approves pembrolizumab for relapsed/refractory PMBCL
The immune checkpoint inhibitor in adult and pediatric patients.
The Food and Drug Administration based the accelerated approval on results from 53 patients with relapsed or refractory primary mediastinal large B-cell lymphoma in the KEYNOTE-170 trial. In the phase 2 trial, patients received 200 mg of pembrolizumab intravenously for 3 weeks until unacceptable toxicity or documented disease progression occurred. This continued for up to 24 months in patients who did not display progression. The overall response rate to pembrolizumab was 45% (95% CI, 32-60), which included both complete (11%) and partial (34%) responses. The median duration of response was not met within the follow-up period (median, 9.7 months) and the median time to first objective response was 2.8 months.
The recommended dose for pembrolizumab in adults is 200 mg every 3 weeks. It is recommended that pediatric patients receive 2 mg/kg every 3 weeks, with a maximum dose of 200 mg.
The most common adverse reactions to pembrolizumab were musculoskeletal pain, upper respiratory tract infection, pyrexia, fatigue, cough, dyspnea, diarrhea, nausea, arrhythmia, and headache. In total, a quarter of patients with adverse reactions required systemic treatment with a corticosteroid and 26% of patients had serious adverse reactions.
Pembrolizumab was approved via the FDA’s accelerated approval process, which allows for earlier approval of drugs that treat serious medical conditions and fulfill an unmet medical need. The drug was approved based on tumor response rate and durability of response, the FDA noted.
The immune checkpoint inhibitor in adult and pediatric patients.
The Food and Drug Administration based the accelerated approval on results from 53 patients with relapsed or refractory primary mediastinal large B-cell lymphoma in the KEYNOTE-170 trial. In the phase 2 trial, patients received 200 mg of pembrolizumab intravenously for 3 weeks until unacceptable toxicity or documented disease progression occurred. This continued for up to 24 months in patients who did not display progression. The overall response rate to pembrolizumab was 45% (95% CI, 32-60), which included both complete (11%) and partial (34%) responses. The median duration of response was not met within the follow-up period (median, 9.7 months) and the median time to first objective response was 2.8 months.
The recommended dose for pembrolizumab in adults is 200 mg every 3 weeks. It is recommended that pediatric patients receive 2 mg/kg every 3 weeks, with a maximum dose of 200 mg.
The most common adverse reactions to pembrolizumab were musculoskeletal pain, upper respiratory tract infection, pyrexia, fatigue, cough, dyspnea, diarrhea, nausea, arrhythmia, and headache. In total, a quarter of patients with adverse reactions required systemic treatment with a corticosteroid and 26% of patients had serious adverse reactions.
Pembrolizumab was approved via the FDA’s accelerated approval process, which allows for earlier approval of drugs that treat serious medical conditions and fulfill an unmet medical need. The drug was approved based on tumor response rate and durability of response, the FDA noted.
The immune checkpoint inhibitor in adult and pediatric patients.
The Food and Drug Administration based the accelerated approval on results from 53 patients with relapsed or refractory primary mediastinal large B-cell lymphoma in the KEYNOTE-170 trial. In the phase 2 trial, patients received 200 mg of pembrolizumab intravenously for 3 weeks until unacceptable toxicity or documented disease progression occurred. This continued for up to 24 months in patients who did not display progression. The overall response rate to pembrolizumab was 45% (95% CI, 32-60), which included both complete (11%) and partial (34%) responses. The median duration of response was not met within the follow-up period (median, 9.7 months) and the median time to first objective response was 2.8 months.
The recommended dose for pembrolizumab in adults is 200 mg every 3 weeks. It is recommended that pediatric patients receive 2 mg/kg every 3 weeks, with a maximum dose of 200 mg.
The most common adverse reactions to pembrolizumab were musculoskeletal pain, upper respiratory tract infection, pyrexia, fatigue, cough, dyspnea, diarrhea, nausea, arrhythmia, and headache. In total, a quarter of patients with adverse reactions required systemic treatment with a corticosteroid and 26% of patients had serious adverse reactions.
Pembrolizumab was approved via the FDA’s accelerated approval process, which allows for earlier approval of drugs that treat serious medical conditions and fulfill an unmet medical need. The drug was approved based on tumor response rate and durability of response, the FDA noted.
FDA grants pembrolizumab accelerated approval for PMBCL
The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) granted accelerated approval to the anti-PD-1 therapy pembrolizumab (Keytruda) for the treatment of adult and pediatric patients with refractory primary mediastinal large B-cell lymphoma (PMBCL).
The indication also includes patients who have relapsed after 2 or more prior lines of therapy.
Pembrolizumab had received priority review for PMBCL late last year and also has orphan drug designation and breakthrough therapy designation for this indication.
The FDA based its approval on data from the KEYNOTE-170 (NCT02576990 ) trial.
Investigators enrolled 53 patients onto the multicenter, open-label, single-arm trial. Patients received pembrolizumab 200 mg intravenously every 3 weeks until unacceptable toxicity or documented disease progression.
Patients whose disease did not progress received the drug for up to 24 months.
Patient characteristics
Patients were a median age of 33 years (range, 20 – 61), 43% were male, 92% white, 43% had an ECOG performance status of 0, and 57% had an ECOG performance status of 1.
Almost half (49%) had relapsed disease, and 36% had primary refractory disease.
About a quarter (26%) had undergone prior autologous hematopoietic stem cell transplant, and 32% had prior radiation therapy.
All patients had received prior rituximab.
Results
At a median follow-up of 9.7 months, the overall response rate was 45% (24 responders), including 11% complete responses and 34% partial responses.
The median duration of response was not reached during the follow-up period and ranged from a median 1.1 to 19.2 months.
Median time to first objective response was 2.8 months (range, 2.1 – 8.5). Accordingly, investigators do not recommend pembrolizumab for PMBCL patients who require urgent cytoreductive therapy.
Safety
The most common adverse events occurring in 10% or more of patients were musculoskeletal pain (30%), upper respiratory tract infection (28%), pyrexia (28%), fatigue (23%), cough (26%), dyspnea (21%), diarrhea (13%), abdominal pain (13%), nausea (11%), arrhythmia (11%), and headache (11%).
Eight percent of patients discontinued treatment, and 15% interrupted treatment due to adverse reactions.
Adverse events requiring systemic corticosteroid therapy occurred in 25% of patients.
Serious adverse events occurred in 26% and included arrhythmia (4 %), cardiac tamponade (2%), myocardial infarction (2%), pericardial effusion (2%), and pericarditis (2%).
Six (11%) patients died within 30 days of start of treatment.
The recommended pembrolizumab dose for treatment of adults with PMBCL is 200 mg every 3 weeks. The recommended dose in pediatric patients is 2 mg/kg (up to a maximum of 200 mg) every 3 weeks.
Additional indications for pembrolizumab include melanoma, non-small cell lung cancer, head and neck squamous cell cancer, classical Hodgkin lymphoma, urothelial carcinoma, microsatellite instability-high cancer, gastric cancer, and cervical cancer.
The full prescribing information is available on the FDA website.
Pembrolizumab (Keytruda) is a product of Merck & Co, Inc.
The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) granted accelerated approval to the anti-PD-1 therapy pembrolizumab (Keytruda) for the treatment of adult and pediatric patients with refractory primary mediastinal large B-cell lymphoma (PMBCL).
The indication also includes patients who have relapsed after 2 or more prior lines of therapy.
Pembrolizumab had received priority review for PMBCL late last year and also has orphan drug designation and breakthrough therapy designation for this indication.
The FDA based its approval on data from the KEYNOTE-170 (NCT02576990 ) trial.
Investigators enrolled 53 patients onto the multicenter, open-label, single-arm trial. Patients received pembrolizumab 200 mg intravenously every 3 weeks until unacceptable toxicity or documented disease progression.
Patients whose disease did not progress received the drug for up to 24 months.
Patient characteristics
Patients were a median age of 33 years (range, 20 – 61), 43% were male, 92% white, 43% had an ECOG performance status of 0, and 57% had an ECOG performance status of 1.
Almost half (49%) had relapsed disease, and 36% had primary refractory disease.
About a quarter (26%) had undergone prior autologous hematopoietic stem cell transplant, and 32% had prior radiation therapy.
All patients had received prior rituximab.
Results
At a median follow-up of 9.7 months, the overall response rate was 45% (24 responders), including 11% complete responses and 34% partial responses.
The median duration of response was not reached during the follow-up period and ranged from a median 1.1 to 19.2 months.
Median time to first objective response was 2.8 months (range, 2.1 – 8.5). Accordingly, investigators do not recommend pembrolizumab for PMBCL patients who require urgent cytoreductive therapy.
Safety
The most common adverse events occurring in 10% or more of patients were musculoskeletal pain (30%), upper respiratory tract infection (28%), pyrexia (28%), fatigue (23%), cough (26%), dyspnea (21%), diarrhea (13%), abdominal pain (13%), nausea (11%), arrhythmia (11%), and headache (11%).
Eight percent of patients discontinued treatment, and 15% interrupted treatment due to adverse reactions.
Adverse events requiring systemic corticosteroid therapy occurred in 25% of patients.
Serious adverse events occurred in 26% and included arrhythmia (4 %), cardiac tamponade (2%), myocardial infarction (2%), pericardial effusion (2%), and pericarditis (2%).
Six (11%) patients died within 30 days of start of treatment.
The recommended pembrolizumab dose for treatment of adults with PMBCL is 200 mg every 3 weeks. The recommended dose in pediatric patients is 2 mg/kg (up to a maximum of 200 mg) every 3 weeks.
Additional indications for pembrolizumab include melanoma, non-small cell lung cancer, head and neck squamous cell cancer, classical Hodgkin lymphoma, urothelial carcinoma, microsatellite instability-high cancer, gastric cancer, and cervical cancer.
The full prescribing information is available on the FDA website.
Pembrolizumab (Keytruda) is a product of Merck & Co, Inc.
The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) granted accelerated approval to the anti-PD-1 therapy pembrolizumab (Keytruda) for the treatment of adult and pediatric patients with refractory primary mediastinal large B-cell lymphoma (PMBCL).
The indication also includes patients who have relapsed after 2 or more prior lines of therapy.
Pembrolizumab had received priority review for PMBCL late last year and also has orphan drug designation and breakthrough therapy designation for this indication.
The FDA based its approval on data from the KEYNOTE-170 (NCT02576990 ) trial.
Investigators enrolled 53 patients onto the multicenter, open-label, single-arm trial. Patients received pembrolizumab 200 mg intravenously every 3 weeks until unacceptable toxicity or documented disease progression.
Patients whose disease did not progress received the drug for up to 24 months.
Patient characteristics
Patients were a median age of 33 years (range, 20 – 61), 43% were male, 92% white, 43% had an ECOG performance status of 0, and 57% had an ECOG performance status of 1.
Almost half (49%) had relapsed disease, and 36% had primary refractory disease.
About a quarter (26%) had undergone prior autologous hematopoietic stem cell transplant, and 32% had prior radiation therapy.
All patients had received prior rituximab.
Results
At a median follow-up of 9.7 months, the overall response rate was 45% (24 responders), including 11% complete responses and 34% partial responses.
The median duration of response was not reached during the follow-up period and ranged from a median 1.1 to 19.2 months.
Median time to first objective response was 2.8 months (range, 2.1 – 8.5). Accordingly, investigators do not recommend pembrolizumab for PMBCL patients who require urgent cytoreductive therapy.
Safety
The most common adverse events occurring in 10% or more of patients were musculoskeletal pain (30%), upper respiratory tract infection (28%), pyrexia (28%), fatigue (23%), cough (26%), dyspnea (21%), diarrhea (13%), abdominal pain (13%), nausea (11%), arrhythmia (11%), and headache (11%).
Eight percent of patients discontinued treatment, and 15% interrupted treatment due to adverse reactions.
Adverse events requiring systemic corticosteroid therapy occurred in 25% of patients.
Serious adverse events occurred in 26% and included arrhythmia (4 %), cardiac tamponade (2%), myocardial infarction (2%), pericardial effusion (2%), and pericarditis (2%).
Six (11%) patients died within 30 days of start of treatment.
The recommended pembrolizumab dose for treatment of adults with PMBCL is 200 mg every 3 weeks. The recommended dose in pediatric patients is 2 mg/kg (up to a maximum of 200 mg) every 3 weeks.
Additional indications for pembrolizumab include melanoma, non-small cell lung cancer, head and neck squamous cell cancer, classical Hodgkin lymphoma, urothelial carcinoma, microsatellite instability-high cancer, gastric cancer, and cervical cancer.
The full prescribing information is available on the FDA website.
Pembrolizumab (Keytruda) is a product of Merck & Co, Inc.
Ibrutinib and venetoclax combo promising in frontline CLL
CHICAGO—Ibrutinib combined with venetoclax is showing promising clinical activity in the frontline treatment of patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL), according to investigators for the CAPTIVATE study.
In the first 30 patients, 77% of treatment-naïve patients had undetected minimal residual disease (MRD; <10-4 cells) in the blood and 86% showed a similar response in the bone marrow.
The overall response rate (ORR) was 100% in 11 evaluable patients. The investigators reported this initial data at the 2018 Annual Meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology (abstract 7502).
“These early results show a highly active and safe treatment with 12 cycles of combined treatment with ibrutinib and venetoclax,” said William G. Wierda, MD, PhD, of the MD Anderson Cancer Center in Houston, Texas, who presented the findings at ASCO.
Ibrutinib, a Bruton-kinase inhibitor, has already been approved for the treatment of CLL and venetoclax, a Bcl-2 inhibitor, is currently used to treat relapsed del 17p CLL.
Venetoclax in combination with rituximab was recently approved by the US Food and Drug Administration to treat patients with CLL or small lymphocytic lymphoma whether or not patients have del 17p.
With complementary mechanisms of action and preclinical studies suggesting synergy with the combination, CAPTIVATE was designed to test the efficacy of the oral combination given for 12 cycles.
Study design
CAPTIVATE (NCT02910583) is an ongoing phase 2 study that enrolled 164 patients with treatment-naïve CLL. Patients first received 3 cycles of ibrutinib monotherapy at the standard dose. This was intended to debulk the disease and reduce risk for venetoclax-associated tumor lysis syndrome (TLS).
Venetoclax 400 mg was initiated at cycle 4. After 12 cycles of the combination, patients with confirmed MRD negativity were randomized to receive ibrutinib with a placebo or to continue with the combination therapy.
In this initial report, Dr Wierda highlighted safety data for all 164 enrolled patients and efficacy data for the first 30 patients who had 6 cycles of combination therapy (MRD assessment cohort).
Dr Wierda also reported bone marrow data for the first 14 patients, who received a total of 12 cycles of the combination and represent the safety run-in cohort.
Ibrutinib and venetoclax show promising activity
Median age of patients was 58 years; about 2/3 of patients had unmutated IGHV and 1/3 had a creatine clearance of <80 mL/min.
Of 164 patients, 95% remain on therapy, with discontinuations reported for adverse events; one patient had disease progression to Richter’s transformation.
For the MRD evaluation, all 30 patients had 6 months of combination therapy and continue on treatment.
As expected, lead-in with ibrutinib monotherapy debulked the disease.
Investigators observed a reduction in the proportion of patients at high risk for TLS (24% to 3%) and an increase in the proportion of patients at low risk for TLS (12% to 29%).
A similar picture emerged for debulking of lymph node disease. No patient developed clinical TLS.
Other adverse events were consistent with the safety profile of single-agent ibrutinib and venetoclax. No new safety signals were seen.
After 6 cycles of the combination, blood MRD negativity was reported in 77% of the patients in the MRD assessment cohort.
In the safety-run in cohort of 14 patients, blood MRD negativity was reported in 86% of patients after 12 cycles and 93% of patients after 15 cycles of the combination. In these patients, bone marrow MRD negativity was achieved in 86%.
After 12 cycles of combination therapy, the objective response rate was 100% for 11 of the 14 evaluable patients from the safety run-in cohort: 6 patients showed complete remission (CR) or CR with incomplete blood count recovery (CRi) for a CR/CRi of 55%. All patients had confirmed undetectable MRD.
Investigators considered these responses promising and an assessment of the full treatment plan and durability of response are awaited.
The study was sponsored by Pharmacyclics.
CHICAGO—Ibrutinib combined with venetoclax is showing promising clinical activity in the frontline treatment of patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL), according to investigators for the CAPTIVATE study.
In the first 30 patients, 77% of treatment-naïve patients had undetected minimal residual disease (MRD; <10-4 cells) in the blood and 86% showed a similar response in the bone marrow.
The overall response rate (ORR) was 100% in 11 evaluable patients. The investigators reported this initial data at the 2018 Annual Meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology (abstract 7502).
“These early results show a highly active and safe treatment with 12 cycles of combined treatment with ibrutinib and venetoclax,” said William G. Wierda, MD, PhD, of the MD Anderson Cancer Center in Houston, Texas, who presented the findings at ASCO.
Ibrutinib, a Bruton-kinase inhibitor, has already been approved for the treatment of CLL and venetoclax, a Bcl-2 inhibitor, is currently used to treat relapsed del 17p CLL.
Venetoclax in combination with rituximab was recently approved by the US Food and Drug Administration to treat patients with CLL or small lymphocytic lymphoma whether or not patients have del 17p.
With complementary mechanisms of action and preclinical studies suggesting synergy with the combination, CAPTIVATE was designed to test the efficacy of the oral combination given for 12 cycles.
Study design
CAPTIVATE (NCT02910583) is an ongoing phase 2 study that enrolled 164 patients with treatment-naïve CLL. Patients first received 3 cycles of ibrutinib monotherapy at the standard dose. This was intended to debulk the disease and reduce risk for venetoclax-associated tumor lysis syndrome (TLS).
Venetoclax 400 mg was initiated at cycle 4. After 12 cycles of the combination, patients with confirmed MRD negativity were randomized to receive ibrutinib with a placebo or to continue with the combination therapy.
In this initial report, Dr Wierda highlighted safety data for all 164 enrolled patients and efficacy data for the first 30 patients who had 6 cycles of combination therapy (MRD assessment cohort).
Dr Wierda also reported bone marrow data for the first 14 patients, who received a total of 12 cycles of the combination and represent the safety run-in cohort.
Ibrutinib and venetoclax show promising activity
Median age of patients was 58 years; about 2/3 of patients had unmutated IGHV and 1/3 had a creatine clearance of <80 mL/min.
Of 164 patients, 95% remain on therapy, with discontinuations reported for adverse events; one patient had disease progression to Richter’s transformation.
For the MRD evaluation, all 30 patients had 6 months of combination therapy and continue on treatment.
As expected, lead-in with ibrutinib monotherapy debulked the disease.
Investigators observed a reduction in the proportion of patients at high risk for TLS (24% to 3%) and an increase in the proportion of patients at low risk for TLS (12% to 29%).
A similar picture emerged for debulking of lymph node disease. No patient developed clinical TLS.
Other adverse events were consistent with the safety profile of single-agent ibrutinib and venetoclax. No new safety signals were seen.
After 6 cycles of the combination, blood MRD negativity was reported in 77% of the patients in the MRD assessment cohort.
In the safety-run in cohort of 14 patients, blood MRD negativity was reported in 86% of patients after 12 cycles and 93% of patients after 15 cycles of the combination. In these patients, bone marrow MRD negativity was achieved in 86%.
After 12 cycles of combination therapy, the objective response rate was 100% for 11 of the 14 evaluable patients from the safety run-in cohort: 6 patients showed complete remission (CR) or CR with incomplete blood count recovery (CRi) for a CR/CRi of 55%. All patients had confirmed undetectable MRD.
Investigators considered these responses promising and an assessment of the full treatment plan and durability of response are awaited.
The study was sponsored by Pharmacyclics.
CHICAGO—Ibrutinib combined with venetoclax is showing promising clinical activity in the frontline treatment of patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL), according to investigators for the CAPTIVATE study.
In the first 30 patients, 77% of treatment-naïve patients had undetected minimal residual disease (MRD; <10-4 cells) in the blood and 86% showed a similar response in the bone marrow.
The overall response rate (ORR) was 100% in 11 evaluable patients. The investigators reported this initial data at the 2018 Annual Meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology (abstract 7502).
“These early results show a highly active and safe treatment with 12 cycles of combined treatment with ibrutinib and venetoclax,” said William G. Wierda, MD, PhD, of the MD Anderson Cancer Center in Houston, Texas, who presented the findings at ASCO.
Ibrutinib, a Bruton-kinase inhibitor, has already been approved for the treatment of CLL and venetoclax, a Bcl-2 inhibitor, is currently used to treat relapsed del 17p CLL.
Venetoclax in combination with rituximab was recently approved by the US Food and Drug Administration to treat patients with CLL or small lymphocytic lymphoma whether or not patients have del 17p.
With complementary mechanisms of action and preclinical studies suggesting synergy with the combination, CAPTIVATE was designed to test the efficacy of the oral combination given for 12 cycles.
Study design
CAPTIVATE (NCT02910583) is an ongoing phase 2 study that enrolled 164 patients with treatment-naïve CLL. Patients first received 3 cycles of ibrutinib monotherapy at the standard dose. This was intended to debulk the disease and reduce risk for venetoclax-associated tumor lysis syndrome (TLS).
Venetoclax 400 mg was initiated at cycle 4. After 12 cycles of the combination, patients with confirmed MRD negativity were randomized to receive ibrutinib with a placebo or to continue with the combination therapy.
In this initial report, Dr Wierda highlighted safety data for all 164 enrolled patients and efficacy data for the first 30 patients who had 6 cycles of combination therapy (MRD assessment cohort).
Dr Wierda also reported bone marrow data for the first 14 patients, who received a total of 12 cycles of the combination and represent the safety run-in cohort.
Ibrutinib and venetoclax show promising activity
Median age of patients was 58 years; about 2/3 of patients had unmutated IGHV and 1/3 had a creatine clearance of <80 mL/min.
Of 164 patients, 95% remain on therapy, with discontinuations reported for adverse events; one patient had disease progression to Richter’s transformation.
For the MRD evaluation, all 30 patients had 6 months of combination therapy and continue on treatment.
As expected, lead-in with ibrutinib monotherapy debulked the disease.
Investigators observed a reduction in the proportion of patients at high risk for TLS (24% to 3%) and an increase in the proportion of patients at low risk for TLS (12% to 29%).
A similar picture emerged for debulking of lymph node disease. No patient developed clinical TLS.
Other adverse events were consistent with the safety profile of single-agent ibrutinib and venetoclax. No new safety signals were seen.
After 6 cycles of the combination, blood MRD negativity was reported in 77% of the patients in the MRD assessment cohort.
In the safety-run in cohort of 14 patients, blood MRD negativity was reported in 86% of patients after 12 cycles and 93% of patients after 15 cycles of the combination. In these patients, bone marrow MRD negativity was achieved in 86%.
After 12 cycles of combination therapy, the objective response rate was 100% for 11 of the 14 evaluable patients from the safety run-in cohort: 6 patients showed complete remission (CR) or CR with incomplete blood count recovery (CRi) for a CR/CRi of 55%. All patients had confirmed undetectable MRD.
Investigators considered these responses promising and an assessment of the full treatment plan and durability of response are awaited.
The study was sponsored by Pharmacyclics.
Chemo-free combo provides potential first-line option for FL
CHICAGO—A chemotherapy-free combination of lenalidomide plus rituximab shows similar efficacy and a different safety profile to chemotherapy plus rituximab (R-chemo) followed by rituximab maintenance in patients with previously untreated follicular lymphoma (FL).
According to investigators, the multicenter, international phase 3 RELEVANCE trial is the first to evaluate the chemo-free combination against the standard of care, R-chemo with rituximab maintenance.
“These results show that lenalidomide plus rituximab, a novel immunomodulatory approach, is a potential first-line option for patients with FL requiring treatment,” said investigator Nathan H. Fowler, MD, of the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center in Houston.
Dr Fowler presented the results of the study at the 2018 ASCO Annual Meeting (abstract 7500).
The current standard of care in previously untreated symptomatic FL is immunochemotherapy induction followed by rituximab maintenance.
The immunomodulatory agent lenalidomide has complementary mechanisms with rituximab. Phase 2 studies of combined immunotherapy with lenalidomide and rituximab demonstrated 3-year progression-free survival (PFS) of 79%-81% in previously untreated FL, Dr Fowler said.
Phase 3 RELEVANCE trial (NCT01650701)
Investigators evaluated 1030 previously untreated grade 1-3a FL patients who required therapy.
Patients in the lenalidomide-rituximab group (n=513) received lenalidomide doses of 20 mg per day on days 2 to 22 and 28 for 6 to 12 cycles. Responders continued on therapy at 10 mg per day for a total of 18 cycles.
The rituximab dose was 375 mg/m2 weekly in cycle 1 and day 1 in cycles 2 to 6 and continued in responders for 12 additional cycles.
Patients in the R-chemo arm (n=517) received the investigator’s choice of standard rituximab-CHOP, rituximab-bendamustine, or rituximab-CVP, followed by 12 cycles of rituximab.
Most patients (72%) in the R-chemo arm received R-CHOP.
Baseline characteristics were similar in both groups, Dr Fowler said.
Co-primary endpoints were complete remission/complete remission unconfirmed (CR/Cru) at 120 weeks and PFS.
Results
At a median follow-up of 37.9 months, the superiority for lenalidomide and rituximab over rituximab-chemotherapy was not established.
For the lenalidomide-rituximab patients, the CR/Cru was 48% and 3-year PFS was 77% as compared to 53% and 78%, respectively, for rituximab-chemotherapy patients, as assessed by an independent review committee.
Overall survival was 94% in both groups.
Safety
“Important differences in safety profiles were observed between the arms,” Dr Fowler said.
Rituximab-chemotherapy patients had more frequent neutropenia, febrile neutropenia, growth factor usage, nausea, vomiting, neuropathy, and alopecia.
Lenalidomide and rituximab showed more cutaneous reactions, tumor flare, and diarrhea.
Toxicity profiles differed, with higher grade 4 neutropenia (31% vs 8%) and febrile neutropenia (7% vs 2%) with rituximab-chemotherapy compared with lenalidomide-rituximab, respectively.
More patients experienced grade 3/4 cutaneous events (7% vs 1%) with lenalidomide-rituximab.
Second primary malignancies were slightly higher with rituximab-chemotherapy (10%) than with lenalidomide-rituximab (7%). Grade 5 adverse events were 1% in both groups.
About 70% of patients completed treatment in both groups.
“Lenalidomide and rituximab was not superior to rituximab-chemotherapy based on mature CR/Cru at 120 weeks and interim PFS,” Dr Fowler said. “Both treatments showed similar efficacy results. Treatment effects on PFS were consistent across pre-specified subgroups.”
Dr Fowler presented data as of May 31, 2017. Continued follow-up on PFS and OS is ongoing.
The study is sponsored by Celgene Corporation and the Lymphoma Academic Research Organisation (LYSARC).
CHICAGO—A chemotherapy-free combination of lenalidomide plus rituximab shows similar efficacy and a different safety profile to chemotherapy plus rituximab (R-chemo) followed by rituximab maintenance in patients with previously untreated follicular lymphoma (FL).
According to investigators, the multicenter, international phase 3 RELEVANCE trial is the first to evaluate the chemo-free combination against the standard of care, R-chemo with rituximab maintenance.
“These results show that lenalidomide plus rituximab, a novel immunomodulatory approach, is a potential first-line option for patients with FL requiring treatment,” said investigator Nathan H. Fowler, MD, of the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center in Houston.
Dr Fowler presented the results of the study at the 2018 ASCO Annual Meeting (abstract 7500).
The current standard of care in previously untreated symptomatic FL is immunochemotherapy induction followed by rituximab maintenance.
The immunomodulatory agent lenalidomide has complementary mechanisms with rituximab. Phase 2 studies of combined immunotherapy with lenalidomide and rituximab demonstrated 3-year progression-free survival (PFS) of 79%-81% in previously untreated FL, Dr Fowler said.
Phase 3 RELEVANCE trial (NCT01650701)
Investigators evaluated 1030 previously untreated grade 1-3a FL patients who required therapy.
Patients in the lenalidomide-rituximab group (n=513) received lenalidomide doses of 20 mg per day on days 2 to 22 and 28 for 6 to 12 cycles. Responders continued on therapy at 10 mg per day for a total of 18 cycles.
The rituximab dose was 375 mg/m2 weekly in cycle 1 and day 1 in cycles 2 to 6 and continued in responders for 12 additional cycles.
Patients in the R-chemo arm (n=517) received the investigator’s choice of standard rituximab-CHOP, rituximab-bendamustine, or rituximab-CVP, followed by 12 cycles of rituximab.
Most patients (72%) in the R-chemo arm received R-CHOP.
Baseline characteristics were similar in both groups, Dr Fowler said.
Co-primary endpoints were complete remission/complete remission unconfirmed (CR/Cru) at 120 weeks and PFS.
Results
At a median follow-up of 37.9 months, the superiority for lenalidomide and rituximab over rituximab-chemotherapy was not established.
For the lenalidomide-rituximab patients, the CR/Cru was 48% and 3-year PFS was 77% as compared to 53% and 78%, respectively, for rituximab-chemotherapy patients, as assessed by an independent review committee.
Overall survival was 94% in both groups.
Safety
“Important differences in safety profiles were observed between the arms,” Dr Fowler said.
Rituximab-chemotherapy patients had more frequent neutropenia, febrile neutropenia, growth factor usage, nausea, vomiting, neuropathy, and alopecia.
Lenalidomide and rituximab showed more cutaneous reactions, tumor flare, and diarrhea.
Toxicity profiles differed, with higher grade 4 neutropenia (31% vs 8%) and febrile neutropenia (7% vs 2%) with rituximab-chemotherapy compared with lenalidomide-rituximab, respectively.
More patients experienced grade 3/4 cutaneous events (7% vs 1%) with lenalidomide-rituximab.
Second primary malignancies were slightly higher with rituximab-chemotherapy (10%) than with lenalidomide-rituximab (7%). Grade 5 adverse events were 1% in both groups.
About 70% of patients completed treatment in both groups.
“Lenalidomide and rituximab was not superior to rituximab-chemotherapy based on mature CR/Cru at 120 weeks and interim PFS,” Dr Fowler said. “Both treatments showed similar efficacy results. Treatment effects on PFS were consistent across pre-specified subgroups.”
Dr Fowler presented data as of May 31, 2017. Continued follow-up on PFS and OS is ongoing.
The study is sponsored by Celgene Corporation and the Lymphoma Academic Research Organisation (LYSARC).
CHICAGO—A chemotherapy-free combination of lenalidomide plus rituximab shows similar efficacy and a different safety profile to chemotherapy plus rituximab (R-chemo) followed by rituximab maintenance in patients with previously untreated follicular lymphoma (FL).
According to investigators, the multicenter, international phase 3 RELEVANCE trial is the first to evaluate the chemo-free combination against the standard of care, R-chemo with rituximab maintenance.
“These results show that lenalidomide plus rituximab, a novel immunomodulatory approach, is a potential first-line option for patients with FL requiring treatment,” said investigator Nathan H. Fowler, MD, of the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center in Houston.
Dr Fowler presented the results of the study at the 2018 ASCO Annual Meeting (abstract 7500).
The current standard of care in previously untreated symptomatic FL is immunochemotherapy induction followed by rituximab maintenance.
The immunomodulatory agent lenalidomide has complementary mechanisms with rituximab. Phase 2 studies of combined immunotherapy with lenalidomide and rituximab demonstrated 3-year progression-free survival (PFS) of 79%-81% in previously untreated FL, Dr Fowler said.
Phase 3 RELEVANCE trial (NCT01650701)
Investigators evaluated 1030 previously untreated grade 1-3a FL patients who required therapy.
Patients in the lenalidomide-rituximab group (n=513) received lenalidomide doses of 20 mg per day on days 2 to 22 and 28 for 6 to 12 cycles. Responders continued on therapy at 10 mg per day for a total of 18 cycles.
The rituximab dose was 375 mg/m2 weekly in cycle 1 and day 1 in cycles 2 to 6 and continued in responders for 12 additional cycles.
Patients in the R-chemo arm (n=517) received the investigator’s choice of standard rituximab-CHOP, rituximab-bendamustine, or rituximab-CVP, followed by 12 cycles of rituximab.
Most patients (72%) in the R-chemo arm received R-CHOP.
Baseline characteristics were similar in both groups, Dr Fowler said.
Co-primary endpoints were complete remission/complete remission unconfirmed (CR/Cru) at 120 weeks and PFS.
Results
At a median follow-up of 37.9 months, the superiority for lenalidomide and rituximab over rituximab-chemotherapy was not established.
For the lenalidomide-rituximab patients, the CR/Cru was 48% and 3-year PFS was 77% as compared to 53% and 78%, respectively, for rituximab-chemotherapy patients, as assessed by an independent review committee.
Overall survival was 94% in both groups.
Safety
“Important differences in safety profiles were observed between the arms,” Dr Fowler said.
Rituximab-chemotherapy patients had more frequent neutropenia, febrile neutropenia, growth factor usage, nausea, vomiting, neuropathy, and alopecia.
Lenalidomide and rituximab showed more cutaneous reactions, tumor flare, and diarrhea.
Toxicity profiles differed, with higher grade 4 neutropenia (31% vs 8%) and febrile neutropenia (7% vs 2%) with rituximab-chemotherapy compared with lenalidomide-rituximab, respectively.
More patients experienced grade 3/4 cutaneous events (7% vs 1%) with lenalidomide-rituximab.
Second primary malignancies were slightly higher with rituximab-chemotherapy (10%) than with lenalidomide-rituximab (7%). Grade 5 adverse events were 1% in both groups.
About 70% of patients completed treatment in both groups.
“Lenalidomide and rituximab was not superior to rituximab-chemotherapy based on mature CR/Cru at 120 weeks and interim PFS,” Dr Fowler said. “Both treatments showed similar efficacy results. Treatment effects on PFS were consistent across pre-specified subgroups.”
Dr Fowler presented data as of May 31, 2017. Continued follow-up on PFS and OS is ongoing.
The study is sponsored by Celgene Corporation and the Lymphoma Academic Research Organisation (LYSARC).
FDA approves venetoclax for CLL/SLL with or without del 17p
The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved venetoclax tablets (Venclexta ®) in combination with rituximab to treat patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) or small lymphocytic lymphoma (SLL) who have received 1 prior therapy.
The combination is approved for patients with or without deletion of 17p (del 17p).
The FDA based its approval on the phase 3 MURANO trial, in which venetoclax in combination with rituximab (VEN+R) significantly improved progression-free survival (PFS) in relapsed or refractory CLL patients compared to the chemoimmunotherapy regimen of bendamustine plus rituximab(B+R).
This approval, according to the drug’s developers, makes venetoclax plus rituximab the first oral-based, chemotherapy-free combination with a fixed treatment duration for CLL.
The FDA has also converted venetoclax's accelerated approval to a full approval. The drug was previously granted accelerated approval as a single agent for the treatment of people with CLL with 17p deletion.
Venetoclax is being developed by AbbVie and Roche and jointly commercialized by AbbVie and Genentech in the US and by AbbVie outside the US.
Phase 3 MURANO trial (NCT02005471)
The multicenter, open-label trial randomized 389 patients to VEN+R (194 patients) or B+R (195 patients). Median age of the patients was 65 years (range, 22 – 85).
Patients in the VEN+R arm completed a 5-week ramp-up of venetoclax followed by venetoclax 400 mg once daily for 24 months measured from the rituximab start date.
Tumor lysis syndrome (TLS), caused by a rapid reduction in tumor volume, is an identified risk with venetoclax treatment. The dose ramp-up was intended to mitigate this risk.
Rituximab was initiated after venetoclax ramp-up and given for 6 cycles (375 mg/m2 intravenously on cycle 1 day 1 and 500 mg/m2 intravenously on day 1 of cycles 2-6, with a 28-day cycle length).
Patients in the B+R arm received 6 cycles of B+R (bendamustine 70 mg/m2 on days 1 and 2 of each 28-day cycle and rituximab at the above described dose and schedule).
Efficacy was based on PFS as assessed by an independent review committee.
After a median follow-up of 23 months, the median PFS was not reached in the VEN+R arm and was 18.1 months in the B+R arm (P<0.0001).
The overall response rate was 92% for patients treated with VEN+R compared to 72% for those treated with B+R.
Safety
The most common adverse events (AEs) in the VEN+R arms that occurred in 20% or more patients were neutropenia (65%), diarrhea (40%), upper respiratory tract infection (39%), fatigue (22%), cough (22%), and nausea (21%).
Grade 3 or 4 neutropenia developed in 64% of patients, and grade 4 neutropenia in 31%.
Serious adverse events (SAEs) developed in 46% of patients and serious infections in 21%, consisting most frequently of pneumonia (9%).
The incidence of TLS was 3%, occurring in 6 of 194 patients.
In the VEN+R arm, discontinuations due to any AEs occurred in 16% of patients, dose reductions in 15%, and dose interruptions in 71%.
Neutropenia led to dose interruptions in 46% of patients and discontinuations in 3%. Thrombocytopenia led to discontinuations in 3% of patients.
Fatal AEs that occurred in the absence of disease progression and within 30 days of the last VEN+R treatment and/or 90 days of the last rituximab infusion were reported in 2% (4/194) of patients.
In the B+R arm, AEs led to treatment discontinuations in 10% of patients, dose reductions in 15%, and dose interruptions in 40 %.
Investigators previously reported data from the phase 3 MURANO study as a late-breaking abstract at the 2017 ASH Annual Meeting and published the findings in NEJM.
John Seymour, MBBS, PhD, lead investigator of the MURANO study, said in the corporate release, the approval "validates the results seen in the phase 3 trial, including the significant improvement in progression-free survival over a standard of care comparator arm."
"Progression-free survival is considered a gold standard for demonstrating clinical benefit in oncology," he added.
Full prescribing information for venetoclax is available here.
The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved venetoclax tablets (Venclexta ®) in combination with rituximab to treat patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) or small lymphocytic lymphoma (SLL) who have received 1 prior therapy.
The combination is approved for patients with or without deletion of 17p (del 17p).
The FDA based its approval on the phase 3 MURANO trial, in which venetoclax in combination with rituximab (VEN+R) significantly improved progression-free survival (PFS) in relapsed or refractory CLL patients compared to the chemoimmunotherapy regimen of bendamustine plus rituximab(B+R).
This approval, according to the drug’s developers, makes venetoclax plus rituximab the first oral-based, chemotherapy-free combination with a fixed treatment duration for CLL.
The FDA has also converted venetoclax's accelerated approval to a full approval. The drug was previously granted accelerated approval as a single agent for the treatment of people with CLL with 17p deletion.
Venetoclax is being developed by AbbVie and Roche and jointly commercialized by AbbVie and Genentech in the US and by AbbVie outside the US.
Phase 3 MURANO trial (NCT02005471)
The multicenter, open-label trial randomized 389 patients to VEN+R (194 patients) or B+R (195 patients). Median age of the patients was 65 years (range, 22 – 85).
Patients in the VEN+R arm completed a 5-week ramp-up of venetoclax followed by venetoclax 400 mg once daily for 24 months measured from the rituximab start date.
Tumor lysis syndrome (TLS), caused by a rapid reduction in tumor volume, is an identified risk with venetoclax treatment. The dose ramp-up was intended to mitigate this risk.
Rituximab was initiated after venetoclax ramp-up and given for 6 cycles (375 mg/m2 intravenously on cycle 1 day 1 and 500 mg/m2 intravenously on day 1 of cycles 2-6, with a 28-day cycle length).
Patients in the B+R arm received 6 cycles of B+R (bendamustine 70 mg/m2 on days 1 and 2 of each 28-day cycle and rituximab at the above described dose and schedule).
Efficacy was based on PFS as assessed by an independent review committee.
After a median follow-up of 23 months, the median PFS was not reached in the VEN+R arm and was 18.1 months in the B+R arm (P<0.0001).
The overall response rate was 92% for patients treated with VEN+R compared to 72% for those treated with B+R.
Safety
The most common adverse events (AEs) in the VEN+R arms that occurred in 20% or more patients were neutropenia (65%), diarrhea (40%), upper respiratory tract infection (39%), fatigue (22%), cough (22%), and nausea (21%).
Grade 3 or 4 neutropenia developed in 64% of patients, and grade 4 neutropenia in 31%.
Serious adverse events (SAEs) developed in 46% of patients and serious infections in 21%, consisting most frequently of pneumonia (9%).
The incidence of TLS was 3%, occurring in 6 of 194 patients.
In the VEN+R arm, discontinuations due to any AEs occurred in 16% of patients, dose reductions in 15%, and dose interruptions in 71%.
Neutropenia led to dose interruptions in 46% of patients and discontinuations in 3%. Thrombocytopenia led to discontinuations in 3% of patients.
Fatal AEs that occurred in the absence of disease progression and within 30 days of the last VEN+R treatment and/or 90 days of the last rituximab infusion were reported in 2% (4/194) of patients.
In the B+R arm, AEs led to treatment discontinuations in 10% of patients, dose reductions in 15%, and dose interruptions in 40 %.
Investigators previously reported data from the phase 3 MURANO study as a late-breaking abstract at the 2017 ASH Annual Meeting and published the findings in NEJM.
John Seymour, MBBS, PhD, lead investigator of the MURANO study, said in the corporate release, the approval "validates the results seen in the phase 3 trial, including the significant improvement in progression-free survival over a standard of care comparator arm."
"Progression-free survival is considered a gold standard for demonstrating clinical benefit in oncology," he added.
Full prescribing information for venetoclax is available here.
The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved venetoclax tablets (Venclexta ®) in combination with rituximab to treat patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) or small lymphocytic lymphoma (SLL) who have received 1 prior therapy.
The combination is approved for patients with or without deletion of 17p (del 17p).
The FDA based its approval on the phase 3 MURANO trial, in which venetoclax in combination with rituximab (VEN+R) significantly improved progression-free survival (PFS) in relapsed or refractory CLL patients compared to the chemoimmunotherapy regimen of bendamustine plus rituximab(B+R).
This approval, according to the drug’s developers, makes venetoclax plus rituximab the first oral-based, chemotherapy-free combination with a fixed treatment duration for CLL.
The FDA has also converted venetoclax's accelerated approval to a full approval. The drug was previously granted accelerated approval as a single agent for the treatment of people with CLL with 17p deletion.
Venetoclax is being developed by AbbVie and Roche and jointly commercialized by AbbVie and Genentech in the US and by AbbVie outside the US.
Phase 3 MURANO trial (NCT02005471)
The multicenter, open-label trial randomized 389 patients to VEN+R (194 patients) or B+R (195 patients). Median age of the patients was 65 years (range, 22 – 85).
Patients in the VEN+R arm completed a 5-week ramp-up of venetoclax followed by venetoclax 400 mg once daily for 24 months measured from the rituximab start date.
Tumor lysis syndrome (TLS), caused by a rapid reduction in tumor volume, is an identified risk with venetoclax treatment. The dose ramp-up was intended to mitigate this risk.
Rituximab was initiated after venetoclax ramp-up and given for 6 cycles (375 mg/m2 intravenously on cycle 1 day 1 and 500 mg/m2 intravenously on day 1 of cycles 2-6, with a 28-day cycle length).
Patients in the B+R arm received 6 cycles of B+R (bendamustine 70 mg/m2 on days 1 and 2 of each 28-day cycle and rituximab at the above described dose and schedule).
Efficacy was based on PFS as assessed by an independent review committee.
After a median follow-up of 23 months, the median PFS was not reached in the VEN+R arm and was 18.1 months in the B+R arm (P<0.0001).
The overall response rate was 92% for patients treated with VEN+R compared to 72% for those treated with B+R.
Safety
The most common adverse events (AEs) in the VEN+R arms that occurred in 20% or more patients were neutropenia (65%), diarrhea (40%), upper respiratory tract infection (39%), fatigue (22%), cough (22%), and nausea (21%).
Grade 3 or 4 neutropenia developed in 64% of patients, and grade 4 neutropenia in 31%.
Serious adverse events (SAEs) developed in 46% of patients and serious infections in 21%, consisting most frequently of pneumonia (9%).
The incidence of TLS was 3%, occurring in 6 of 194 patients.
In the VEN+R arm, discontinuations due to any AEs occurred in 16% of patients, dose reductions in 15%, and dose interruptions in 71%.
Neutropenia led to dose interruptions in 46% of patients and discontinuations in 3%. Thrombocytopenia led to discontinuations in 3% of patients.
Fatal AEs that occurred in the absence of disease progression and within 30 days of the last VEN+R treatment and/or 90 days of the last rituximab infusion were reported in 2% (4/194) of patients.
In the B+R arm, AEs led to treatment discontinuations in 10% of patients, dose reductions in 15%, and dose interruptions in 40 %.
Investigators previously reported data from the phase 3 MURANO study as a late-breaking abstract at the 2017 ASH Annual Meeting and published the findings in NEJM.
John Seymour, MBBS, PhD, lead investigator of the MURANO study, said in the corporate release, the approval "validates the results seen in the phase 3 trial, including the significant improvement in progression-free survival over a standard of care comparator arm."
"Progression-free survival is considered a gold standard for demonstrating clinical benefit in oncology," he added.
Full prescribing information for venetoclax is available here.
FDA grants regular approval to venetoclax for CLL/SLL
Venetoclax (Venclexta) has received regular approval from the Food and Drug Administration for the treatment of patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) or small lymphocytic lymphoma (SLL), with or without 17p deletion, who have received at least one prior therapy.
The approval was based results from the MURANO trial of 389 patients, which was a randomized, multicenter, open-label trial of venetoclax plus rituximab versus bendamustine plus rituximab.
Neutropenia, diarrhea, upper respiratory tract infection, fatigue, cough, and nausea were the most common adverse events seen in the venetoclax arm. Grade 3 or 4 neutropenia developed in 64% of those patients, and grade 4 in 31%. The most common infection in venetoclax patients was pneumonia, but overall, 21% of patients in that arm experienced some kind of infection.
Because of the rapid reduction in tumor size, tumor lysis syndrome is possible with venetoclax treatment, the FDA noted.
In 2016, the FDA granted accelerated approval to venetoclax for treatment of patients with CLL with 17d deletion who had received at least one prior line of therapy.
Venetoclax (Venclexta) has received regular approval from the Food and Drug Administration for the treatment of patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) or small lymphocytic lymphoma (SLL), with or without 17p deletion, who have received at least one prior therapy.
The approval was based results from the MURANO trial of 389 patients, which was a randomized, multicenter, open-label trial of venetoclax plus rituximab versus bendamustine plus rituximab.
Neutropenia, diarrhea, upper respiratory tract infection, fatigue, cough, and nausea were the most common adverse events seen in the venetoclax arm. Grade 3 or 4 neutropenia developed in 64% of those patients, and grade 4 in 31%. The most common infection in venetoclax patients was pneumonia, but overall, 21% of patients in that arm experienced some kind of infection.
Because of the rapid reduction in tumor size, tumor lysis syndrome is possible with venetoclax treatment, the FDA noted.
In 2016, the FDA granted accelerated approval to venetoclax for treatment of patients with CLL with 17d deletion who had received at least one prior line of therapy.
Venetoclax (Venclexta) has received regular approval from the Food and Drug Administration for the treatment of patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) or small lymphocytic lymphoma (SLL), with or without 17p deletion, who have received at least one prior therapy.
The approval was based results from the MURANO trial of 389 patients, which was a randomized, multicenter, open-label trial of venetoclax plus rituximab versus bendamustine plus rituximab.
Neutropenia, diarrhea, upper respiratory tract infection, fatigue, cough, and nausea were the most common adverse events seen in the venetoclax arm. Grade 3 or 4 neutropenia developed in 64% of those patients, and grade 4 in 31%. The most common infection in venetoclax patients was pneumonia, but overall, 21% of patients in that arm experienced some kind of infection.
Because of the rapid reduction in tumor size, tumor lysis syndrome is possible with venetoclax treatment, the FDA noted.
In 2016, the FDA granted accelerated approval to venetoclax for treatment of patients with CLL with 17d deletion who had received at least one prior line of therapy.
Venetoclax plus ibrutinib yields encouraging MRD results in first-line CLL
CHICAGO – The combination of ibrutinib plus venetoclax yielded a high rate of undetectable minimal residual disease (MRD) when used as first-line treatment for chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL), according to preliminary results of the CAPTIVATE trial.
Of the first 30 patients in the trial, 23 (77%) had undetectable blood MRD after just six cycles of combined treatment, said investigator William G. Wierda, MD, PhD, of the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston.
“These early results show a highly active and safe treatment with 12 cycles of combined treatment with ibrutinib and venetoclax,” Dr. Wierda said in a presentation of the CAPTIVATE results at the annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology.
Those MRD results are “at least as good as we can achieve with chemoimmunotherapy,” Bruce D. Cheson, MD, head of hematology at Georgetown University, Washington, said during a discussion of the CAPTIVATE study results.
Dr. Cheson referenced MRD results from a 2016 analysis of the CLL8 and CLL10 trials, which included patients treated with fludarabine, cyclophosphamide, and rituximab (FCR) and bendamustine plus rituximab (BR). In that analysis, 33.6% of patients achieved MRD-negative complete response and 29.1% achieved MRD-negative partial response.
In CAPTIVATE, by contrast, all of the complete remissions were MRD negative, as were a majority of the partial responders, Dr. Cheson noted.
Venetoclax and ibrutinib have “clinically complimentary activity” that provided a rationale for combining the two, Dr. Wierda said at ASCO. Ibrutinib is a BTK inhibitor that has a high rate of response and durable disease control, though continuous treatment is indicated, he said, because most patients achieve partial remissions as best response and continue to have residual disease in blood or bone marrow. Venetoclax, he added, is a BCL-2 inhibitor that produces durable partial remissions, though “residual disease is typically present in the form of persistently enlarged lymph nodes,” he said. “Venetoclax is highly effective at clearing disease from blood and bone marrow.”
The phase 2 CAPTIVATE trial includes a total of 164 patients younger than 70 years of age who receive a 3-cycle ibrutinib lead-in, followed by ibrutinib plus venetoclax for 12 cycles. At that point, patients are randomized according to MRD status. Patients with confirmed undetectable MRD are randomized to further treatment with ibrutinib or placebo, and those with undetectable MRD not confirmed are randomized to ibrutinib versus ibrutinib plus venetoclax.
In addition to early efficacy data, Dr. Wierda also reported some safety data. Compared with the single-agent ibrutinib lead-in period, combined ibrutinib plus venetoclax treatment had more gastrointestinal-associated events and neutropenia. Almost half of patients (45%) have had a treatment-related grade 3-4 adverse event, though just 18 (11%) have had treatment-related adverse events classified as serious, and there have been no adverse event-related deaths on study.
The high activity of ibrutinib plus venetoclax in CAPTIVATE supports further study of the combination, Dr. Wierda said. A randomized, open-label phase 3 trial of ibrutinib plus venetoclax versus chlorambucil plus obinutuzumab as first-line treatment for CLL is currently recruiting.
The study was sponsored by Pharmacyclics, an AbbVie company. Dr. Wierda reported consulting and research funding from Pharmacyclics, AbbVie, and several other companies.
SOURCE: Wierda WG et al. ASCO 2018, Abstract 7502.
CHICAGO – The combination of ibrutinib plus venetoclax yielded a high rate of undetectable minimal residual disease (MRD) when used as first-line treatment for chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL), according to preliminary results of the CAPTIVATE trial.
Of the first 30 patients in the trial, 23 (77%) had undetectable blood MRD after just six cycles of combined treatment, said investigator William G. Wierda, MD, PhD, of the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston.
“These early results show a highly active and safe treatment with 12 cycles of combined treatment with ibrutinib and venetoclax,” Dr. Wierda said in a presentation of the CAPTIVATE results at the annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology.
Those MRD results are “at least as good as we can achieve with chemoimmunotherapy,” Bruce D. Cheson, MD, head of hematology at Georgetown University, Washington, said during a discussion of the CAPTIVATE study results.
Dr. Cheson referenced MRD results from a 2016 analysis of the CLL8 and CLL10 trials, which included patients treated with fludarabine, cyclophosphamide, and rituximab (FCR) and bendamustine plus rituximab (BR). In that analysis, 33.6% of patients achieved MRD-negative complete response and 29.1% achieved MRD-negative partial response.
In CAPTIVATE, by contrast, all of the complete remissions were MRD negative, as were a majority of the partial responders, Dr. Cheson noted.
Venetoclax and ibrutinib have “clinically complimentary activity” that provided a rationale for combining the two, Dr. Wierda said at ASCO. Ibrutinib is a BTK inhibitor that has a high rate of response and durable disease control, though continuous treatment is indicated, he said, because most patients achieve partial remissions as best response and continue to have residual disease in blood or bone marrow. Venetoclax, he added, is a BCL-2 inhibitor that produces durable partial remissions, though “residual disease is typically present in the form of persistently enlarged lymph nodes,” he said. “Venetoclax is highly effective at clearing disease from blood and bone marrow.”
The phase 2 CAPTIVATE trial includes a total of 164 patients younger than 70 years of age who receive a 3-cycle ibrutinib lead-in, followed by ibrutinib plus venetoclax for 12 cycles. At that point, patients are randomized according to MRD status. Patients with confirmed undetectable MRD are randomized to further treatment with ibrutinib or placebo, and those with undetectable MRD not confirmed are randomized to ibrutinib versus ibrutinib plus venetoclax.
In addition to early efficacy data, Dr. Wierda also reported some safety data. Compared with the single-agent ibrutinib lead-in period, combined ibrutinib plus venetoclax treatment had more gastrointestinal-associated events and neutropenia. Almost half of patients (45%) have had a treatment-related grade 3-4 adverse event, though just 18 (11%) have had treatment-related adverse events classified as serious, and there have been no adverse event-related deaths on study.
The high activity of ibrutinib plus venetoclax in CAPTIVATE supports further study of the combination, Dr. Wierda said. A randomized, open-label phase 3 trial of ibrutinib plus venetoclax versus chlorambucil plus obinutuzumab as first-line treatment for CLL is currently recruiting.
The study was sponsored by Pharmacyclics, an AbbVie company. Dr. Wierda reported consulting and research funding from Pharmacyclics, AbbVie, and several other companies.
SOURCE: Wierda WG et al. ASCO 2018, Abstract 7502.
CHICAGO – The combination of ibrutinib plus venetoclax yielded a high rate of undetectable minimal residual disease (MRD) when used as first-line treatment for chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL), according to preliminary results of the CAPTIVATE trial.
Of the first 30 patients in the trial, 23 (77%) had undetectable blood MRD after just six cycles of combined treatment, said investigator William G. Wierda, MD, PhD, of the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston.
“These early results show a highly active and safe treatment with 12 cycles of combined treatment with ibrutinib and venetoclax,” Dr. Wierda said in a presentation of the CAPTIVATE results at the annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology.
Those MRD results are “at least as good as we can achieve with chemoimmunotherapy,” Bruce D. Cheson, MD, head of hematology at Georgetown University, Washington, said during a discussion of the CAPTIVATE study results.
Dr. Cheson referenced MRD results from a 2016 analysis of the CLL8 and CLL10 trials, which included patients treated with fludarabine, cyclophosphamide, and rituximab (FCR) and bendamustine plus rituximab (BR). In that analysis, 33.6% of patients achieved MRD-negative complete response and 29.1% achieved MRD-negative partial response.
In CAPTIVATE, by contrast, all of the complete remissions were MRD negative, as were a majority of the partial responders, Dr. Cheson noted.
Venetoclax and ibrutinib have “clinically complimentary activity” that provided a rationale for combining the two, Dr. Wierda said at ASCO. Ibrutinib is a BTK inhibitor that has a high rate of response and durable disease control, though continuous treatment is indicated, he said, because most patients achieve partial remissions as best response and continue to have residual disease in blood or bone marrow. Venetoclax, he added, is a BCL-2 inhibitor that produces durable partial remissions, though “residual disease is typically present in the form of persistently enlarged lymph nodes,” he said. “Venetoclax is highly effective at clearing disease from blood and bone marrow.”
The phase 2 CAPTIVATE trial includes a total of 164 patients younger than 70 years of age who receive a 3-cycle ibrutinib lead-in, followed by ibrutinib plus venetoclax for 12 cycles. At that point, patients are randomized according to MRD status. Patients with confirmed undetectable MRD are randomized to further treatment with ibrutinib or placebo, and those with undetectable MRD not confirmed are randomized to ibrutinib versus ibrutinib plus venetoclax.
In addition to early efficacy data, Dr. Wierda also reported some safety data. Compared with the single-agent ibrutinib lead-in period, combined ibrutinib plus venetoclax treatment had more gastrointestinal-associated events and neutropenia. Almost half of patients (45%) have had a treatment-related grade 3-4 adverse event, though just 18 (11%) have had treatment-related adverse events classified as serious, and there have been no adverse event-related deaths on study.
The high activity of ibrutinib plus venetoclax in CAPTIVATE supports further study of the combination, Dr. Wierda said. A randomized, open-label phase 3 trial of ibrutinib plus venetoclax versus chlorambucil plus obinutuzumab as first-line treatment for CLL is currently recruiting.
The study was sponsored by Pharmacyclics, an AbbVie company. Dr. Wierda reported consulting and research funding from Pharmacyclics, AbbVie, and several other companies.
SOURCE: Wierda WG et al. ASCO 2018, Abstract 7502.
REPORTING FROM ASCO 2018
Key clinical point:
Major finding: Of 14 patients, 12 (86%) who completed 12 cycles of treatment had undetectable bone marrow MRD.
Study details: Early results of the phase 2 CAPTIVATE trial including 164 patients younger than 70 years of age with previously untreated CLL.
Disclosures: The study was sponsored by Pharmacyclics, an Abbvie company. Dr. Wierda reported consulting and research funding from Pharmacyclics, AbbVie, and several other companies.
Source: Wierda WG et al. ASCO 2018, Abstract 7502.
Polatuzumab plus BR improves efficacy in DLBCL
CHICAGO—Polatuzumab vedotin, when added to bendamustine (B) and rituximab (R), significantly improved response and survival rates in a cohort of patients with relapsed/refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL), according to a phase 2 study.
By contrast, there were no such improvements in a cohort of follicular lymphoma (FL) patients, at least in short-term follow-up, investigator Laurie Helen Sehn, MD, of the BC Cancer Agency in Vancouver, Canada, said at the 2018 ASCO Annual Meeting.
However, the improvement in overall survival in DLBCL patients is “remarkable,” Dr Sehn affirmed in an oral presentation (abstract 7507).
“Based on these encouraging results, polatuzumab vedotin has received breakthrough therapy designation and priority medicines designation by the FDA and EMA for patients with relapsed or refractory DLBCL,” she said.
Polatuzumab-BR study (NCT02257567)
The study by Dr Sehn and colleagues included a cohort of 80 DLBCL patients randomized to BR or polatuzumab-BR for 6 planned 21-day cycles.
Investigators randomized another cohort of 80 FL patients to BR or polatuzumab-BR for 6 planned 28-day cycles.
The primary endpoint was complete response (CR) assessed by fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography (FDG-PET) at 6 to 8 weeks after the end of treatment.
DLBCL patients
A total of 40% of polatuzumab-BR-treated DLBCL patients achieved CR at the end of treatment, versus 15% of BR-treated patients (P=0.012).
That CR improvement translated into a significantly higher progression-free survival (PFS) (6.7 months for polatuzumab-BR vs 2.0 months for BR, P<0.0001) and overall survival (11.8 months versus 4.7 months, P=0.0008), according to Dr Sehn.
The FDG-PET CR rates were higher in the polatuzumab-BR arm regardless of the number of prior lines of treatment for DLBCL, and regardless of relapsed versus refractory status, Dr. Sehn added.
FL patients
By contrast, in the FL cohort, the FDG-PET CR rate was high for both arms, at 69% for polatuzumab-BR and 63% for BR.
And there was no significant difference in progression-free survival (P=0.58) with “relatively short-term follow-up,” she said.
Adverse events
The most common grades 3 – 5 adverse events for both DLBCL and FL patients were higher in the polatuzumab-BR arm than the BR arm and included cytopenias, febrile neutropenia, and infections.
Serious AEs were also higher in the polatuzumab-BR arm and included febrile neutropenia for both FL and DLBCL patients and infection for FL patients.
Five percent of FL patients and 18% of DLBCL had a grade 5 event.
Commentary
Whether polatuzumab vedotin will change treatment paradigms for DLBCL patients may be answered by the ongoing POLARIX study, according to Alison Moskowitz, MD, of Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center in New York, NY.
The randomized phase 3 POLARIX study (abstract TPS7589) is comparing polatuzumab plus R-CHP to R-CHOP in patients with previously untreated DLBCL.
“Certainly, there are patients who do very well with R-CHOP chemotherapy alone, and so we need to learn whether this is necessary for all patients, or only the high-risk patients,” Dr Moskowitz said in a talk at ASCO commenting on the results of the polatuzumab-BR study.
Hoffman-LaRoche is the sponsor of the study.
CHICAGO—Polatuzumab vedotin, when added to bendamustine (B) and rituximab (R), significantly improved response and survival rates in a cohort of patients with relapsed/refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL), according to a phase 2 study.
By contrast, there were no such improvements in a cohort of follicular lymphoma (FL) patients, at least in short-term follow-up, investigator Laurie Helen Sehn, MD, of the BC Cancer Agency in Vancouver, Canada, said at the 2018 ASCO Annual Meeting.
However, the improvement in overall survival in DLBCL patients is “remarkable,” Dr Sehn affirmed in an oral presentation (abstract 7507).
“Based on these encouraging results, polatuzumab vedotin has received breakthrough therapy designation and priority medicines designation by the FDA and EMA for patients with relapsed or refractory DLBCL,” she said.
Polatuzumab-BR study (NCT02257567)
The study by Dr Sehn and colleagues included a cohort of 80 DLBCL patients randomized to BR or polatuzumab-BR for 6 planned 21-day cycles.
Investigators randomized another cohort of 80 FL patients to BR or polatuzumab-BR for 6 planned 28-day cycles.
The primary endpoint was complete response (CR) assessed by fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography (FDG-PET) at 6 to 8 weeks after the end of treatment.
DLBCL patients
A total of 40% of polatuzumab-BR-treated DLBCL patients achieved CR at the end of treatment, versus 15% of BR-treated patients (P=0.012).
That CR improvement translated into a significantly higher progression-free survival (PFS) (6.7 months for polatuzumab-BR vs 2.0 months for BR, P<0.0001) and overall survival (11.8 months versus 4.7 months, P=0.0008), according to Dr Sehn.
The FDG-PET CR rates were higher in the polatuzumab-BR arm regardless of the number of prior lines of treatment for DLBCL, and regardless of relapsed versus refractory status, Dr. Sehn added.
FL patients
By contrast, in the FL cohort, the FDG-PET CR rate was high for both arms, at 69% for polatuzumab-BR and 63% for BR.
And there was no significant difference in progression-free survival (P=0.58) with “relatively short-term follow-up,” she said.
Adverse events
The most common grades 3 – 5 adverse events for both DLBCL and FL patients were higher in the polatuzumab-BR arm than the BR arm and included cytopenias, febrile neutropenia, and infections.
Serious AEs were also higher in the polatuzumab-BR arm and included febrile neutropenia for both FL and DLBCL patients and infection for FL patients.
Five percent of FL patients and 18% of DLBCL had a grade 5 event.
Commentary
Whether polatuzumab vedotin will change treatment paradigms for DLBCL patients may be answered by the ongoing POLARIX study, according to Alison Moskowitz, MD, of Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center in New York, NY.
The randomized phase 3 POLARIX study (abstract TPS7589) is comparing polatuzumab plus R-CHP to R-CHOP in patients with previously untreated DLBCL.
“Certainly, there are patients who do very well with R-CHOP chemotherapy alone, and so we need to learn whether this is necessary for all patients, or only the high-risk patients,” Dr Moskowitz said in a talk at ASCO commenting on the results of the polatuzumab-BR study.
Hoffman-LaRoche is the sponsor of the study.
CHICAGO—Polatuzumab vedotin, when added to bendamustine (B) and rituximab (R), significantly improved response and survival rates in a cohort of patients with relapsed/refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL), according to a phase 2 study.
By contrast, there were no such improvements in a cohort of follicular lymphoma (FL) patients, at least in short-term follow-up, investigator Laurie Helen Sehn, MD, of the BC Cancer Agency in Vancouver, Canada, said at the 2018 ASCO Annual Meeting.
However, the improvement in overall survival in DLBCL patients is “remarkable,” Dr Sehn affirmed in an oral presentation (abstract 7507).
“Based on these encouraging results, polatuzumab vedotin has received breakthrough therapy designation and priority medicines designation by the FDA and EMA for patients with relapsed or refractory DLBCL,” she said.
Polatuzumab-BR study (NCT02257567)
The study by Dr Sehn and colleagues included a cohort of 80 DLBCL patients randomized to BR or polatuzumab-BR for 6 planned 21-day cycles.
Investigators randomized another cohort of 80 FL patients to BR or polatuzumab-BR for 6 planned 28-day cycles.
The primary endpoint was complete response (CR) assessed by fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography (FDG-PET) at 6 to 8 weeks after the end of treatment.
DLBCL patients
A total of 40% of polatuzumab-BR-treated DLBCL patients achieved CR at the end of treatment, versus 15% of BR-treated patients (P=0.012).
That CR improvement translated into a significantly higher progression-free survival (PFS) (6.7 months for polatuzumab-BR vs 2.0 months for BR, P<0.0001) and overall survival (11.8 months versus 4.7 months, P=0.0008), according to Dr Sehn.
The FDG-PET CR rates were higher in the polatuzumab-BR arm regardless of the number of prior lines of treatment for DLBCL, and regardless of relapsed versus refractory status, Dr. Sehn added.
FL patients
By contrast, in the FL cohort, the FDG-PET CR rate was high for both arms, at 69% for polatuzumab-BR and 63% for BR.
And there was no significant difference in progression-free survival (P=0.58) with “relatively short-term follow-up,” she said.
Adverse events
The most common grades 3 – 5 adverse events for both DLBCL and FL patients were higher in the polatuzumab-BR arm than the BR arm and included cytopenias, febrile neutropenia, and infections.
Serious AEs were also higher in the polatuzumab-BR arm and included febrile neutropenia for both FL and DLBCL patients and infection for FL patients.
Five percent of FL patients and 18% of DLBCL had a grade 5 event.
Commentary
Whether polatuzumab vedotin will change treatment paradigms for DLBCL patients may be answered by the ongoing POLARIX study, according to Alison Moskowitz, MD, of Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center in New York, NY.
The randomized phase 3 POLARIX study (abstract TPS7589) is comparing polatuzumab plus R-CHP to R-CHOP in patients with previously untreated DLBCL.
“Certainly, there are patients who do very well with R-CHOP chemotherapy alone, and so we need to learn whether this is necessary for all patients, or only the high-risk patients,” Dr Moskowitz said in a talk at ASCO commenting on the results of the polatuzumab-BR study.
Hoffman-LaRoche is the sponsor of the study.