User login
Primary care may be inadequate for cancer survivors
Primary care may not meet the healthcare needs of cancer survivors in the US, according to research published in JAMA Internal Medicine.
Researchers examined 12 advanced primary care practices selected from a national registry of “workforce innovators” and found that none of these practices had a comprehensive survivorship care program in place.
In addition, there were 3 main barriers to survivorship care—not treating cancer survivors as a distinct population, limitations of electronic health records, and a lack of information and guidance for clinicians.
“This is troubling because these are highly innovative practices that have a national reputation,” said study author Benjamin Crabtree, PhD, of Rutgers Robert Wood Johnson Medical School in New Brunswick, New Jersey.
Dr Crabtree and his colleagues evaluated survivorship care* at the 12 practices, which were based in Colorado, Illinois, Maine, New York, Pennsylvania, and Washington.
Over nearly 2 years, the team spent 10 to 12 days observing each of the practices and interviewing clinicians and administrators.
In this way, the researchers identified 3 main barriers to integrating survivorship care into primary medicine.
Barrier 1
The first barrier was that clinicians did not treat cancer survivors as a distinct population or clinical category.
“There is no diagnosis code for ‘cancer survivor’ that can be entered into the medical record, which is important if you want physicians to pay attention,” Dr Crabtree said.
Some of the clinicians interviewed said their care was comprehensive enough to address the needs of all patients. Other clinicians did not understand what survivorship care entails.
Barrier 2
The second barrier was that electronic health record systems didn’t support survivorship care.
Clinicians reported an inability to identify patients with a history of cancer. Even if a patient’s cancer history was included in his or her record, it might take searching through multiple screens to find the information.
In addition, medical records were sometimes lost as patients changed clinicians over the years, which left it up to patients to report their cancer histories.
Barrier 3
The third barrier was that clinicians did not receive adequate information or guidance for follow-up care of cancer survivors.
Although some of the practices received cancer-related information about their patients, it was considered “inadequate” or “not actionable.”
Clinicians expressed concerns about their knowledge gaps in cancer care and the need to monitor changing information in oncology.
“There is nothing in the residency curriculum about cancer survivorship,” Dr Crabtree said. “There is also nothing in Continuing Medical Education courses. It’s just not there.”
Dr Crabtree and his colleagues believe these barriers must be addressed so that comprehensive cancer survivorship services can move to the forefront of primary care. ![]()
* Survivorship care includes checking for cancer recurrence, monitoring long-term effects of radiation and chemotherapy, and assessing a patient’s psychological well-being.
Primary care may not meet the healthcare needs of cancer survivors in the US, according to research published in JAMA Internal Medicine.
Researchers examined 12 advanced primary care practices selected from a national registry of “workforce innovators” and found that none of these practices had a comprehensive survivorship care program in place.
In addition, there were 3 main barriers to survivorship care—not treating cancer survivors as a distinct population, limitations of electronic health records, and a lack of information and guidance for clinicians.
“This is troubling because these are highly innovative practices that have a national reputation,” said study author Benjamin Crabtree, PhD, of Rutgers Robert Wood Johnson Medical School in New Brunswick, New Jersey.
Dr Crabtree and his colleagues evaluated survivorship care* at the 12 practices, which were based in Colorado, Illinois, Maine, New York, Pennsylvania, and Washington.
Over nearly 2 years, the team spent 10 to 12 days observing each of the practices and interviewing clinicians and administrators.
In this way, the researchers identified 3 main barriers to integrating survivorship care into primary medicine.
Barrier 1
The first barrier was that clinicians did not treat cancer survivors as a distinct population or clinical category.
“There is no diagnosis code for ‘cancer survivor’ that can be entered into the medical record, which is important if you want physicians to pay attention,” Dr Crabtree said.
Some of the clinicians interviewed said their care was comprehensive enough to address the needs of all patients. Other clinicians did not understand what survivorship care entails.
Barrier 2
The second barrier was that electronic health record systems didn’t support survivorship care.
Clinicians reported an inability to identify patients with a history of cancer. Even if a patient’s cancer history was included in his or her record, it might take searching through multiple screens to find the information.
In addition, medical records were sometimes lost as patients changed clinicians over the years, which left it up to patients to report their cancer histories.
Barrier 3
The third barrier was that clinicians did not receive adequate information or guidance for follow-up care of cancer survivors.
Although some of the practices received cancer-related information about their patients, it was considered “inadequate” or “not actionable.”
Clinicians expressed concerns about their knowledge gaps in cancer care and the need to monitor changing information in oncology.
“There is nothing in the residency curriculum about cancer survivorship,” Dr Crabtree said. “There is also nothing in Continuing Medical Education courses. It’s just not there.”
Dr Crabtree and his colleagues believe these barriers must be addressed so that comprehensive cancer survivorship services can move to the forefront of primary care. ![]()
* Survivorship care includes checking for cancer recurrence, monitoring long-term effects of radiation and chemotherapy, and assessing a patient’s psychological well-being.
Primary care may not meet the healthcare needs of cancer survivors in the US, according to research published in JAMA Internal Medicine.
Researchers examined 12 advanced primary care practices selected from a national registry of “workforce innovators” and found that none of these practices had a comprehensive survivorship care program in place.
In addition, there were 3 main barriers to survivorship care—not treating cancer survivors as a distinct population, limitations of electronic health records, and a lack of information and guidance for clinicians.
“This is troubling because these are highly innovative practices that have a national reputation,” said study author Benjamin Crabtree, PhD, of Rutgers Robert Wood Johnson Medical School in New Brunswick, New Jersey.
Dr Crabtree and his colleagues evaluated survivorship care* at the 12 practices, which were based in Colorado, Illinois, Maine, New York, Pennsylvania, and Washington.
Over nearly 2 years, the team spent 10 to 12 days observing each of the practices and interviewing clinicians and administrators.
In this way, the researchers identified 3 main barriers to integrating survivorship care into primary medicine.
Barrier 1
The first barrier was that clinicians did not treat cancer survivors as a distinct population or clinical category.
“There is no diagnosis code for ‘cancer survivor’ that can be entered into the medical record, which is important if you want physicians to pay attention,” Dr Crabtree said.
Some of the clinicians interviewed said their care was comprehensive enough to address the needs of all patients. Other clinicians did not understand what survivorship care entails.
Barrier 2
The second barrier was that electronic health record systems didn’t support survivorship care.
Clinicians reported an inability to identify patients with a history of cancer. Even if a patient’s cancer history was included in his or her record, it might take searching through multiple screens to find the information.
In addition, medical records were sometimes lost as patients changed clinicians over the years, which left it up to patients to report their cancer histories.
Barrier 3
The third barrier was that clinicians did not receive adequate information or guidance for follow-up care of cancer survivors.
Although some of the practices received cancer-related information about their patients, it was considered “inadequate” or “not actionable.”
Clinicians expressed concerns about their knowledge gaps in cancer care and the need to monitor changing information in oncology.
“There is nothing in the residency curriculum about cancer survivorship,” Dr Crabtree said. “There is also nothing in Continuing Medical Education courses. It’s just not there.”
Dr Crabtree and his colleagues believe these barriers must be addressed so that comprehensive cancer survivorship services can move to the forefront of primary care. ![]()
* Survivorship care includes checking for cancer recurrence, monitoring long-term effects of radiation and chemotherapy, and assessing a patient’s psychological well-being.
Obinutuzumab edges out rituximab for PFS in follicular lymphoma
In a head-to-head trial of anti-CD20 monoclonal antibodies in first-line therapy for follicular lymphoma, obinutuzumab-based chemotherapy was associated with slightly but significantly better progression-free survival than rituximab-based therapy, but at the cost of higher toxicities, including severe adverse events.
Among 1,202 patients with follicular lymphoma followed for a median of 34.5 months, the estimated 3-year rate of progression-free survival (PFS) for patients randomized to obinutuzumab-based chemotherapy and maintenance was 80%, compared with 73.3% for patients randomized to rituximab chemotherapy and maintenance. Response rates and overall survival were similar between the treatment groups, Robert Marcus, MB, BS, of King’s College Hospital, London, and his coinvestigators reported in the GALLIUM trial.
They acknowledged, however, that there were substantial differences between the treatment groups in the cumulative doses of obinutuzumab (Gazyva) and rituximab (Rituxan and others), which could have affected the relative efficacy of each regimen.
In addition, while patients were randomly assigned to one monoclonal antibody or the other, the choice of chemotherapy regimens, while standardized, was left to the discretion of investigators at each treatment site, another factor that might have influenced outcomes.
The investigators reported the results of a preplanned interim efficacy analysis. They compared obinutuzumab or rituximab plus chemotherapy in patients with indolent non-Hodgkin lymphoma, but the trial was powered to detect a PFS difference only in patients with follicular lymphoma. Patients who had a clinical response to induction therapy went on to maintenance therapy with the same monoclonal antibody.
In all, 1,202 patients with follicular lymphoma were enrolled and randomized, 601 in each arm, to receive induction with either intravenous obinutuzumab 1,000 mg on days 1, 8, and 15 of cycle 1 and on day 1 of subsequent cycles, or rituximab 375 mg/m2 on day 1 of each cycle for six or eight cycles, depending on the accompanying chemotherapy regimen. The regimens used were either CHOP (cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone), CVP (cyclophosphamide, vincristine, and prednisone), or bendamustine.
Patients with partial or complete responses were then maintained on the same monoclonal antibody they had received during induction, either obinutuzumab 1,000 mg or rituximab 375 mg/m2 every 2 months for 2 years, or until disease progression. Patients were not allowed to be crossed over to the other maintenance therapy.
Patients with stable disease after induction continued to be followed, but did not receive maintenance therapy.
The interim analysis was performed after 245 of 370 anticipated events (disease progression, relapse, or death) had occurred. At that time, the independent data and safety monitoring committee recommended full analysis of the trial data, and the sponsor agreed.
After a median follow-up of 34.5 months, an intention-to-treat analysis showed that the investigator-assessed, estimated 3-year rate of PFS was 80.0% in the obinutuzumab arm, compared with 73.3%; in the rituximab arm. This translated into a hazard ratio (HR) for progression, relapse, or death of 0.66 (P = .001). An independent review committee calculated a HR favoring obinutuzumab of 0.71 (P = .01).
Estimated 3-year overall survival rates were not significantly different at 94% and 92.1%, respectively.
Overall response rates were similar between the groups, at 88.5% with obinutuzumab group and 86.9% with rituximab, a difference that was not significant.
Obinutuzumab was associated with a higher rate of prespecified events of special interest, including infections, cardiac events, second neoplasms, infusion-related events, neutropenia, and thrombocytopenia.
Adverse events deemed to be related to the antibodies occurred in 59.3% of patients on obinutuzumab, and 48.9% of patients on rituximab.
There were more frequent grade 3 or 4 adverse events and deaths with obinutuzumab, occurring in 74.6% of patients vs. 67.8% on rituximab. Fatal adverse events occurred in 4% and 3.4% of patients, respectively.
A total of 81 patients died during the trial, including 35 in the obinutuzumab group and 46 in the rituximab group.
F. Hoffmann–La Roche supported the trial. Dr. Marcus disclosed consulting fees and lecture fees from Takeda Pharmaceuticals and travel support, consulting fees, and lecture fees from Roche. The majority of coauthors disclosed similar relationships.
Should obinutuzumab replace rituximab as the standard antibody in the treatment of patients receiving chemoimmunotherapy regimens for follicular lymphoma? Results from this trial would suggest that there might be no advantage for an obinutuzumab-containing chemoimmunotherapy regimen if maintenance treatment was not planned. Even with maintenance therapy, there is no evidence from this trial of an overall survival benefit with obinutuzumab. These findings, combined with the higher rate of toxic effects and, presumably, the higher cost of obinutuzumab, raise important questions regarding the advantage of its use. This issue is complicated further because it is possible that giving rituximab at a dose of 1,000 mg might reduce or eliminate any difference in progression-free survival – that is, if the difference is primarily a dose effect.
When the data on minimal residual disease are made available, the case in favor of obinutuzumab may appear to be more compelling if indeed a higher proportion of patients who received obinutuzumab have minimal residual disease status at some point in treatment and remain in remission longer than those who received rituximab. At the moment, the competition between these agents looks too close to call.
These comments are excerpted from an editorial (N Engl J Med. 2017 Oct 5;377;14:1389-90) by James O. Armitage, MD, University of Nebraska, Omaha, and Dan L. Longo, MD, Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, Boston. Dr. Armitage reported personal fees from Conatus, Samus Therapeutics, and Tesaro. Dr. Longo reported no relevant disclosures. He is deputy editor of The New England Journal of Medicine.
Should obinutuzumab replace rituximab as the standard antibody in the treatment of patients receiving chemoimmunotherapy regimens for follicular lymphoma? Results from this trial would suggest that there might be no advantage for an obinutuzumab-containing chemoimmunotherapy regimen if maintenance treatment was not planned. Even with maintenance therapy, there is no evidence from this trial of an overall survival benefit with obinutuzumab. These findings, combined with the higher rate of toxic effects and, presumably, the higher cost of obinutuzumab, raise important questions regarding the advantage of its use. This issue is complicated further because it is possible that giving rituximab at a dose of 1,000 mg might reduce or eliminate any difference in progression-free survival – that is, if the difference is primarily a dose effect.
When the data on minimal residual disease are made available, the case in favor of obinutuzumab may appear to be more compelling if indeed a higher proportion of patients who received obinutuzumab have minimal residual disease status at some point in treatment and remain in remission longer than those who received rituximab. At the moment, the competition between these agents looks too close to call.
These comments are excerpted from an editorial (N Engl J Med. 2017 Oct 5;377;14:1389-90) by James O. Armitage, MD, University of Nebraska, Omaha, and Dan L. Longo, MD, Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, Boston. Dr. Armitage reported personal fees from Conatus, Samus Therapeutics, and Tesaro. Dr. Longo reported no relevant disclosures. He is deputy editor of The New England Journal of Medicine.
Should obinutuzumab replace rituximab as the standard antibody in the treatment of patients receiving chemoimmunotherapy regimens for follicular lymphoma? Results from this trial would suggest that there might be no advantage for an obinutuzumab-containing chemoimmunotherapy regimen if maintenance treatment was not planned. Even with maintenance therapy, there is no evidence from this trial of an overall survival benefit with obinutuzumab. These findings, combined with the higher rate of toxic effects and, presumably, the higher cost of obinutuzumab, raise important questions regarding the advantage of its use. This issue is complicated further because it is possible that giving rituximab at a dose of 1,000 mg might reduce or eliminate any difference in progression-free survival – that is, if the difference is primarily a dose effect.
When the data on minimal residual disease are made available, the case in favor of obinutuzumab may appear to be more compelling if indeed a higher proportion of patients who received obinutuzumab have minimal residual disease status at some point in treatment and remain in remission longer than those who received rituximab. At the moment, the competition between these agents looks too close to call.
These comments are excerpted from an editorial (N Engl J Med. 2017 Oct 5;377;14:1389-90) by James O. Armitage, MD, University of Nebraska, Omaha, and Dan L. Longo, MD, Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, Boston. Dr. Armitage reported personal fees from Conatus, Samus Therapeutics, and Tesaro. Dr. Longo reported no relevant disclosures. He is deputy editor of The New England Journal of Medicine.
In a head-to-head trial of anti-CD20 monoclonal antibodies in first-line therapy for follicular lymphoma, obinutuzumab-based chemotherapy was associated with slightly but significantly better progression-free survival than rituximab-based therapy, but at the cost of higher toxicities, including severe adverse events.
Among 1,202 patients with follicular lymphoma followed for a median of 34.5 months, the estimated 3-year rate of progression-free survival (PFS) for patients randomized to obinutuzumab-based chemotherapy and maintenance was 80%, compared with 73.3% for patients randomized to rituximab chemotherapy and maintenance. Response rates and overall survival were similar between the treatment groups, Robert Marcus, MB, BS, of King’s College Hospital, London, and his coinvestigators reported in the GALLIUM trial.
They acknowledged, however, that there were substantial differences between the treatment groups in the cumulative doses of obinutuzumab (Gazyva) and rituximab (Rituxan and others), which could have affected the relative efficacy of each regimen.
In addition, while patients were randomly assigned to one monoclonal antibody or the other, the choice of chemotherapy regimens, while standardized, was left to the discretion of investigators at each treatment site, another factor that might have influenced outcomes.
The investigators reported the results of a preplanned interim efficacy analysis. They compared obinutuzumab or rituximab plus chemotherapy in patients with indolent non-Hodgkin lymphoma, but the trial was powered to detect a PFS difference only in patients with follicular lymphoma. Patients who had a clinical response to induction therapy went on to maintenance therapy with the same monoclonal antibody.
In all, 1,202 patients with follicular lymphoma were enrolled and randomized, 601 in each arm, to receive induction with either intravenous obinutuzumab 1,000 mg on days 1, 8, and 15 of cycle 1 and on day 1 of subsequent cycles, or rituximab 375 mg/m2 on day 1 of each cycle for six or eight cycles, depending on the accompanying chemotherapy regimen. The regimens used were either CHOP (cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone), CVP (cyclophosphamide, vincristine, and prednisone), or bendamustine.
Patients with partial or complete responses were then maintained on the same monoclonal antibody they had received during induction, either obinutuzumab 1,000 mg or rituximab 375 mg/m2 every 2 months for 2 years, or until disease progression. Patients were not allowed to be crossed over to the other maintenance therapy.
Patients with stable disease after induction continued to be followed, but did not receive maintenance therapy.
The interim analysis was performed after 245 of 370 anticipated events (disease progression, relapse, or death) had occurred. At that time, the independent data and safety monitoring committee recommended full analysis of the trial data, and the sponsor agreed.
After a median follow-up of 34.5 months, an intention-to-treat analysis showed that the investigator-assessed, estimated 3-year rate of PFS was 80.0% in the obinutuzumab arm, compared with 73.3%; in the rituximab arm. This translated into a hazard ratio (HR) for progression, relapse, or death of 0.66 (P = .001). An independent review committee calculated a HR favoring obinutuzumab of 0.71 (P = .01).
Estimated 3-year overall survival rates were not significantly different at 94% and 92.1%, respectively.
Overall response rates were similar between the groups, at 88.5% with obinutuzumab group and 86.9% with rituximab, a difference that was not significant.
Obinutuzumab was associated with a higher rate of prespecified events of special interest, including infections, cardiac events, second neoplasms, infusion-related events, neutropenia, and thrombocytopenia.
Adverse events deemed to be related to the antibodies occurred in 59.3% of patients on obinutuzumab, and 48.9% of patients on rituximab.
There were more frequent grade 3 or 4 adverse events and deaths with obinutuzumab, occurring in 74.6% of patients vs. 67.8% on rituximab. Fatal adverse events occurred in 4% and 3.4% of patients, respectively.
A total of 81 patients died during the trial, including 35 in the obinutuzumab group and 46 in the rituximab group.
F. Hoffmann–La Roche supported the trial. Dr. Marcus disclosed consulting fees and lecture fees from Takeda Pharmaceuticals and travel support, consulting fees, and lecture fees from Roche. The majority of coauthors disclosed similar relationships.
In a head-to-head trial of anti-CD20 monoclonal antibodies in first-line therapy for follicular lymphoma, obinutuzumab-based chemotherapy was associated with slightly but significantly better progression-free survival than rituximab-based therapy, but at the cost of higher toxicities, including severe adverse events.
Among 1,202 patients with follicular lymphoma followed for a median of 34.5 months, the estimated 3-year rate of progression-free survival (PFS) for patients randomized to obinutuzumab-based chemotherapy and maintenance was 80%, compared with 73.3% for patients randomized to rituximab chemotherapy and maintenance. Response rates and overall survival were similar between the treatment groups, Robert Marcus, MB, BS, of King’s College Hospital, London, and his coinvestigators reported in the GALLIUM trial.
They acknowledged, however, that there were substantial differences between the treatment groups in the cumulative doses of obinutuzumab (Gazyva) and rituximab (Rituxan and others), which could have affected the relative efficacy of each regimen.
In addition, while patients were randomly assigned to one monoclonal antibody or the other, the choice of chemotherapy regimens, while standardized, was left to the discretion of investigators at each treatment site, another factor that might have influenced outcomes.
The investigators reported the results of a preplanned interim efficacy analysis. They compared obinutuzumab or rituximab plus chemotherapy in patients with indolent non-Hodgkin lymphoma, but the trial was powered to detect a PFS difference only in patients with follicular lymphoma. Patients who had a clinical response to induction therapy went on to maintenance therapy with the same monoclonal antibody.
In all, 1,202 patients with follicular lymphoma were enrolled and randomized, 601 in each arm, to receive induction with either intravenous obinutuzumab 1,000 mg on days 1, 8, and 15 of cycle 1 and on day 1 of subsequent cycles, or rituximab 375 mg/m2 on day 1 of each cycle for six or eight cycles, depending on the accompanying chemotherapy regimen. The regimens used were either CHOP (cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone), CVP (cyclophosphamide, vincristine, and prednisone), or bendamustine.
Patients with partial or complete responses were then maintained on the same monoclonal antibody they had received during induction, either obinutuzumab 1,000 mg or rituximab 375 mg/m2 every 2 months for 2 years, or until disease progression. Patients were not allowed to be crossed over to the other maintenance therapy.
Patients with stable disease after induction continued to be followed, but did not receive maintenance therapy.
The interim analysis was performed after 245 of 370 anticipated events (disease progression, relapse, or death) had occurred. At that time, the independent data and safety monitoring committee recommended full analysis of the trial data, and the sponsor agreed.
After a median follow-up of 34.5 months, an intention-to-treat analysis showed that the investigator-assessed, estimated 3-year rate of PFS was 80.0% in the obinutuzumab arm, compared with 73.3%; in the rituximab arm. This translated into a hazard ratio (HR) for progression, relapse, or death of 0.66 (P = .001). An independent review committee calculated a HR favoring obinutuzumab of 0.71 (P = .01).
Estimated 3-year overall survival rates were not significantly different at 94% and 92.1%, respectively.
Overall response rates were similar between the groups, at 88.5% with obinutuzumab group and 86.9% with rituximab, a difference that was not significant.
Obinutuzumab was associated with a higher rate of prespecified events of special interest, including infections, cardiac events, second neoplasms, infusion-related events, neutropenia, and thrombocytopenia.
Adverse events deemed to be related to the antibodies occurred in 59.3% of patients on obinutuzumab, and 48.9% of patients on rituximab.
There were more frequent grade 3 or 4 adverse events and deaths with obinutuzumab, occurring in 74.6% of patients vs. 67.8% on rituximab. Fatal adverse events occurred in 4% and 3.4% of patients, respectively.
A total of 81 patients died during the trial, including 35 in the obinutuzumab group and 46 in the rituximab group.
F. Hoffmann–La Roche supported the trial. Dr. Marcus disclosed consulting fees and lecture fees from Takeda Pharmaceuticals and travel support, consulting fees, and lecture fees from Roche. The majority of coauthors disclosed similar relationships.
FROM THE NEW ENGLAND JOURNAL OF MEDICINE
Key clinical point: Obinutuzumab-based chemotherapy and maintenance was associated with better progression-free survival, but not overall survival, compared with rituximab-based chemotherapy and maintenance.
Major finding: Three-year progression-free survival was 80% with obinutuzumab, vs. 73.3% with rituximab.
Data source: Interim analysis of a randomized phase 3, open-label trial of 1,202 patients with follicular lymphoma.
Disclosures: F. Hoffmann–La Roche supported the trial. Dr. Marcus disclosed consulting fees and lecture fees from Takeda Pharmaceuticals and travel support, consulting fees, and lecture fees from Roche. The majority of coauthors disclosed similar relationships.
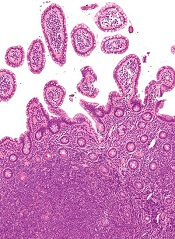
Rare type of MCL mimics Castleman disease
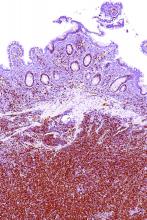
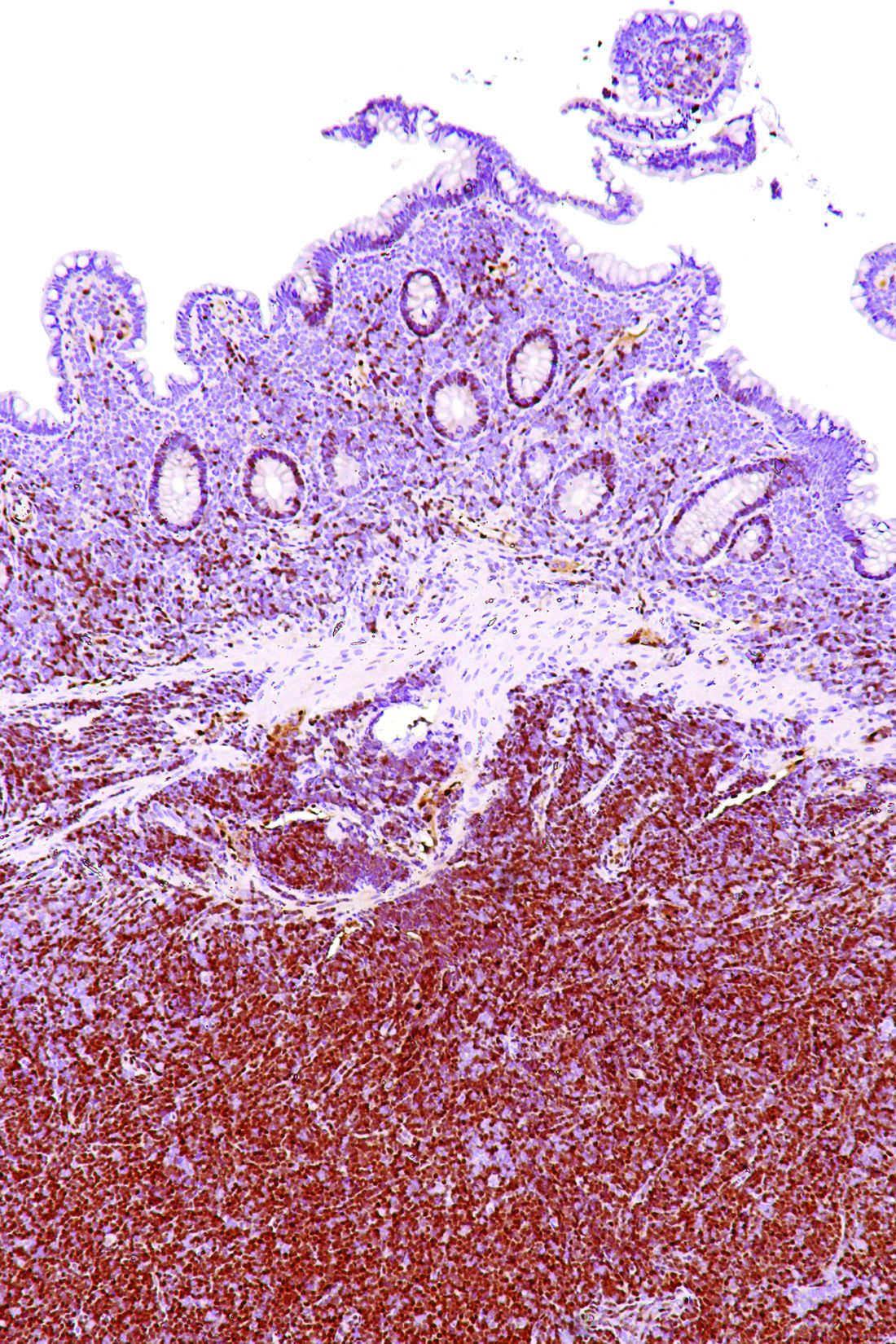
A rare type of mantle cell lymphoma (MCL) has features that are similar to those of Castleman disease, according to a recent report based on three patient cases.
Lymph node biopsies for these patients initially indicated histologic features consistent with those of plasma cell (PC)-type Castleman disease, reported Takuro Igawa, MD, PhD, of Okayama (Japan) University Graduate School of Medicine, Dentistry, and Pharmaceutical Sciences, and his coauthors. Further work-up, including flow cytometric analysis and cyclin D1 immunostaining, showed features consistent with those of MCL.
“This rare type of MCL can mimic Castleman disease in the clinical setting and upon histological examination,” Dr. Igawa and his colleagues wrote (Pathol Res Pract. 2017 Sep 18. pii: S0344-0338[17]30684-2. doi: 10.1016/j.prp.2017.09.015). “These confusing characteristics can make the diagnosis challenging, and careful flow cytometric analysis is recommended when a histopathological diagnosis is made.”
The patients in the study, all male, were 51, 74, and 81 years of age. Each presented with systemic lymphadenopathy, along with abnormal laboratory findings that according to the investigators are not usually associated with B-cell lymphomas such as MCL, including anemia, polyclonal IgG hypergammaglobulinemia, and elevated levels of C-reactive protein.
In lymph node biopsy specimens, the MCL component was “masked by histological features of PC-type Castleman disease” such as interfollicular plasmacytosis and atrophic germinal centers, the researchers wrote.
However, further pathologic investigations revealed features that were “essential to distinguish these 3 cases of MCL from PC-type Castleman disease,” they added.
In particular, an abnormal B-cell population was found using flow cytometric analysis, while subsequent cyclin D1 immunostaining in all three cases showed abnormal B-cells primarily in the mantle zone that were positive for CD20 and CD5, both typically expressed by MCL, along with SOX11, which is an “excellent diagnostic marker for MCL, including atypical MCL,” the investigators wrote.
These case reports also provide some evidence that interleukin-6 (IL-6), which is thought to be a driver of Castleman disease, might also be implicated in the pathogenesis of this rare MCL variant. the researchers found that all three cases had positive IL-6 staining in the interfollicular areas.
If further studies confirm the role of IL-6 in this rare setting, “specific treatments other than chemotherapy could potentially be used for patients with MCL with features of Castleman disease, such as an anti-IL-6 receptor antibody (tocilizumab), which is already used for patients with Castleman disease,” they said.
A rare type of mantle cell lymphoma (MCL) has features that are similar to those of Castleman disease, according to a recent report based on three patient cases.
Lymph node biopsies for these patients initially indicated histologic features consistent with those of plasma cell (PC)-type Castleman disease, reported Takuro Igawa, MD, PhD, of Okayama (Japan) University Graduate School of Medicine, Dentistry, and Pharmaceutical Sciences, and his coauthors. Further work-up, including flow cytometric analysis and cyclin D1 immunostaining, showed features consistent with those of MCL.
“This rare type of MCL can mimic Castleman disease in the clinical setting and upon histological examination,” Dr. Igawa and his colleagues wrote (Pathol Res Pract. 2017 Sep 18. pii: S0344-0338[17]30684-2. doi: 10.1016/j.prp.2017.09.015). “These confusing characteristics can make the diagnosis challenging, and careful flow cytometric analysis is recommended when a histopathological diagnosis is made.”
The patients in the study, all male, were 51, 74, and 81 years of age. Each presented with systemic lymphadenopathy, along with abnormal laboratory findings that according to the investigators are not usually associated with B-cell lymphomas such as MCL, including anemia, polyclonal IgG hypergammaglobulinemia, and elevated levels of C-reactive protein.
In lymph node biopsy specimens, the MCL component was “masked by histological features of PC-type Castleman disease” such as interfollicular plasmacytosis and atrophic germinal centers, the researchers wrote.
However, further pathologic investigations revealed features that were “essential to distinguish these 3 cases of MCL from PC-type Castleman disease,” they added.
In particular, an abnormal B-cell population was found using flow cytometric analysis, while subsequent cyclin D1 immunostaining in all three cases showed abnormal B-cells primarily in the mantle zone that were positive for CD20 and CD5, both typically expressed by MCL, along with SOX11, which is an “excellent diagnostic marker for MCL, including atypical MCL,” the investigators wrote.
These case reports also provide some evidence that interleukin-6 (IL-6), which is thought to be a driver of Castleman disease, might also be implicated in the pathogenesis of this rare MCL variant. the researchers found that all three cases had positive IL-6 staining in the interfollicular areas.
If further studies confirm the role of IL-6 in this rare setting, “specific treatments other than chemotherapy could potentially be used for patients with MCL with features of Castleman disease, such as an anti-IL-6 receptor antibody (tocilizumab), which is already used for patients with Castleman disease,” they said.
A rare type of mantle cell lymphoma (MCL) has features that are similar to those of Castleman disease, according to a recent report based on three patient cases.
Lymph node biopsies for these patients initially indicated histologic features consistent with those of plasma cell (PC)-type Castleman disease, reported Takuro Igawa, MD, PhD, of Okayama (Japan) University Graduate School of Medicine, Dentistry, and Pharmaceutical Sciences, and his coauthors. Further work-up, including flow cytometric analysis and cyclin D1 immunostaining, showed features consistent with those of MCL.
“This rare type of MCL can mimic Castleman disease in the clinical setting and upon histological examination,” Dr. Igawa and his colleagues wrote (Pathol Res Pract. 2017 Sep 18. pii: S0344-0338[17]30684-2. doi: 10.1016/j.prp.2017.09.015). “These confusing characteristics can make the diagnosis challenging, and careful flow cytometric analysis is recommended when a histopathological diagnosis is made.”
The patients in the study, all male, were 51, 74, and 81 years of age. Each presented with systemic lymphadenopathy, along with abnormal laboratory findings that according to the investigators are not usually associated with B-cell lymphomas such as MCL, including anemia, polyclonal IgG hypergammaglobulinemia, and elevated levels of C-reactive protein.
In lymph node biopsy specimens, the MCL component was “masked by histological features of PC-type Castleman disease” such as interfollicular plasmacytosis and atrophic germinal centers, the researchers wrote.
However, further pathologic investigations revealed features that were “essential to distinguish these 3 cases of MCL from PC-type Castleman disease,” they added.
In particular, an abnormal B-cell population was found using flow cytometric analysis, while subsequent cyclin D1 immunostaining in all three cases showed abnormal B-cells primarily in the mantle zone that were positive for CD20 and CD5, both typically expressed by MCL, along with SOX11, which is an “excellent diagnostic marker for MCL, including atypical MCL,” the investigators wrote.
These case reports also provide some evidence that interleukin-6 (IL-6), which is thought to be a driver of Castleman disease, might also be implicated in the pathogenesis of this rare MCL variant. the researchers found that all three cases had positive IL-6 staining in the interfollicular areas.
If further studies confirm the role of IL-6 in this rare setting, “specific treatments other than chemotherapy could potentially be used for patients with MCL with features of Castleman disease, such as an anti-IL-6 receptor antibody (tocilizumab), which is already used for patients with Castleman disease,” they said.
FROM PATHOLOGY – RESEARCH AND PRACTICE
Key clinical point:
Major finding: Lymph node biopsy revealed histologic features consistent with plasma cell (PC)-type Castleman disease, but cyclin D1 immunostaining and flow cytometric analysis showed features consistent with a diagnosis of MCL.
Data source: A report on three patient cases of MCL with features of PC-type Castleman disease retrieved from surgical pathology consultation files.
Disclosures: The authors reported no conflicts of interest.
VCR regimen showed efficacy in mantle cell and indolent lymphomas
The combination of bortezomib, cladribine, and rituximab (VCR) was an effective treatment regimen for patients with CD20-positive mantle cell lymphoma (MCL) and indolent non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma (iNHL), based on results of a recent phase 2, open-label study.
The overall response rate was 92% in the single-center, 24-patient study. The 2-year progression-free survival (PFS) was 82% and 54%, respectively, for MCL and iNHL patients; PFS was 80% for treatment-naive patients and 57% for those with refractory/recalcitrant disease, according to Soham D. Puvvada, MD, of the University of Arizona Cancer Center in Tucson, and her associates.
Two-year overall survival was 91% for MCL and 69% for iNHL patients. Median time to progression was 34.5 months, and median PFS had not been reached at 2 years, according to the researchers.
While the study (NCT00980395) was small and limited by its single-center design, the VCR combination “has encouraging activity in both MCL and iNHL and could be compared to standard therapies in future studies,” the researchers wrote. “For MCL in particular, we believe a noninferiority comparison to standard therapies would be justified by our results.”
Adverse events were most commonly hematologic, and three patients experienced febrile neutropenia, data show.
“Although hematological toxicity can be an issue, the regimen provides an alternative option in transplant ineligible relapsed/refractory MCL and iNHL,” wrote Dr. Puvvada and her colleagues. The study was published in Clinical Lymphoma, Myeloma & Leukemia (doi: 10.1016/j.clml.2017.09.001).
The researchers studied the combination of bortezomib, the proteasome inhibitor initially approved for relapsed/refractory MCL, cladribine, which has shown activity and promising response rates in patients with indolent lymphomas, and rituximab in patients with CD20-positive mantle cell or indolent lymphoma.
Patients with follicular lymphomas were eligible to be included in the study if they had received at least one previous line of therapy. All other participants could be treatment naive or have relapsed after previous treatment.
Of the 24 patients enrolled, 11 had MCL, 5 had follicular lymphoma, 4 had marginal zone lymphoma, 3 had lymphoplasmacytic lymphoma, and 1 had small lymphocytic lymphoma.
The VCR regimen, given every 28 days for no more than six cycles, included rituximab at 375 mg/m2 given intravenously on day 1 of each cycle, cladribine 4 mg/m2 given intravenously over 2 hours on days 1 through 5, and bortezomib 1.3 mg/m2 given intravenously on days 1 and 4. Patients received a median of five cycles of therapy.
Adverse events of grade 3 or greater occurred in 14 patients (58%); 8 patients had leukopenia, 6 had thrombocytopenia, 5 had fatigue, and 5 had neutropenia, which included febrile neutropenia in 3 patients.
With a median follow-up of 38.5 months, overall response rate for VCR was 96%. Complete responses occurred in 8 of 23 evaluable patients (35%) and partial responses in 14 more patients (61%).
The combination of bortezomib, cladribine, and rituximab (VCR) was an effective treatment regimen for patients with CD20-positive mantle cell lymphoma (MCL) and indolent non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma (iNHL), based on results of a recent phase 2, open-label study.
The overall response rate was 92% in the single-center, 24-patient study. The 2-year progression-free survival (PFS) was 82% and 54%, respectively, for MCL and iNHL patients; PFS was 80% for treatment-naive patients and 57% for those with refractory/recalcitrant disease, according to Soham D. Puvvada, MD, of the University of Arizona Cancer Center in Tucson, and her associates.
Two-year overall survival was 91% for MCL and 69% for iNHL patients. Median time to progression was 34.5 months, and median PFS had not been reached at 2 years, according to the researchers.
While the study (NCT00980395) was small and limited by its single-center design, the VCR combination “has encouraging activity in both MCL and iNHL and could be compared to standard therapies in future studies,” the researchers wrote. “For MCL in particular, we believe a noninferiority comparison to standard therapies would be justified by our results.”
Adverse events were most commonly hematologic, and three patients experienced febrile neutropenia, data show.
“Although hematological toxicity can be an issue, the regimen provides an alternative option in transplant ineligible relapsed/refractory MCL and iNHL,” wrote Dr. Puvvada and her colleagues. The study was published in Clinical Lymphoma, Myeloma & Leukemia (doi: 10.1016/j.clml.2017.09.001).
The researchers studied the combination of bortezomib, the proteasome inhibitor initially approved for relapsed/refractory MCL, cladribine, which has shown activity and promising response rates in patients with indolent lymphomas, and rituximab in patients with CD20-positive mantle cell or indolent lymphoma.
Patients with follicular lymphomas were eligible to be included in the study if they had received at least one previous line of therapy. All other participants could be treatment naive or have relapsed after previous treatment.
Of the 24 patients enrolled, 11 had MCL, 5 had follicular lymphoma, 4 had marginal zone lymphoma, 3 had lymphoplasmacytic lymphoma, and 1 had small lymphocytic lymphoma.
The VCR regimen, given every 28 days for no more than six cycles, included rituximab at 375 mg/m2 given intravenously on day 1 of each cycle, cladribine 4 mg/m2 given intravenously over 2 hours on days 1 through 5, and bortezomib 1.3 mg/m2 given intravenously on days 1 and 4. Patients received a median of five cycles of therapy.
Adverse events of grade 3 or greater occurred in 14 patients (58%); 8 patients had leukopenia, 6 had thrombocytopenia, 5 had fatigue, and 5 had neutropenia, which included febrile neutropenia in 3 patients.
With a median follow-up of 38.5 months, overall response rate for VCR was 96%. Complete responses occurred in 8 of 23 evaluable patients (35%) and partial responses in 14 more patients (61%).
The combination of bortezomib, cladribine, and rituximab (VCR) was an effective treatment regimen for patients with CD20-positive mantle cell lymphoma (MCL) and indolent non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma (iNHL), based on results of a recent phase 2, open-label study.
The overall response rate was 92% in the single-center, 24-patient study. The 2-year progression-free survival (PFS) was 82% and 54%, respectively, for MCL and iNHL patients; PFS was 80% for treatment-naive patients and 57% for those with refractory/recalcitrant disease, according to Soham D. Puvvada, MD, of the University of Arizona Cancer Center in Tucson, and her associates.
Two-year overall survival was 91% for MCL and 69% for iNHL patients. Median time to progression was 34.5 months, and median PFS had not been reached at 2 years, according to the researchers.
While the study (NCT00980395) was small and limited by its single-center design, the VCR combination “has encouraging activity in both MCL and iNHL and could be compared to standard therapies in future studies,” the researchers wrote. “For MCL in particular, we believe a noninferiority comparison to standard therapies would be justified by our results.”
Adverse events were most commonly hematologic, and three patients experienced febrile neutropenia, data show.
“Although hematological toxicity can be an issue, the regimen provides an alternative option in transplant ineligible relapsed/refractory MCL and iNHL,” wrote Dr. Puvvada and her colleagues. The study was published in Clinical Lymphoma, Myeloma & Leukemia (doi: 10.1016/j.clml.2017.09.001).
The researchers studied the combination of bortezomib, the proteasome inhibitor initially approved for relapsed/refractory MCL, cladribine, which has shown activity and promising response rates in patients with indolent lymphomas, and rituximab in patients with CD20-positive mantle cell or indolent lymphoma.
Patients with follicular lymphomas were eligible to be included in the study if they had received at least one previous line of therapy. All other participants could be treatment naive or have relapsed after previous treatment.
Of the 24 patients enrolled, 11 had MCL, 5 had follicular lymphoma, 4 had marginal zone lymphoma, 3 had lymphoplasmacytic lymphoma, and 1 had small lymphocytic lymphoma.
The VCR regimen, given every 28 days for no more than six cycles, included rituximab at 375 mg/m2 given intravenously on day 1 of each cycle, cladribine 4 mg/m2 given intravenously over 2 hours on days 1 through 5, and bortezomib 1.3 mg/m2 given intravenously on days 1 and 4. Patients received a median of five cycles of therapy.
Adverse events of grade 3 or greater occurred in 14 patients (58%); 8 patients had leukopenia, 6 had thrombocytopenia, 5 had fatigue, and 5 had neutropenia, which included febrile neutropenia in 3 patients.
With a median follow-up of 38.5 months, overall response rate for VCR was 96%. Complete responses occurred in 8 of 23 evaluable patients (35%) and partial responses in 14 more patients (61%).
FROM LYMPHOMA, MYELOMA & LEUKEMIA
Key clinical point:
Major finding: The overall response rate was 92%, with a 2-year PFS of 82% and 54% for patients with mantle cell lymphoma (MCL) and indolent non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma (iNHL), respectively. Adverse events were most commonly hematologic, and three patients experienced febrile neutropenia.
Data source: A phase 2, open-label study including 24 patients with mantle cell or indolent lymphomas.
Disclosures: No disclosures were reported in the accepted manuscript.
Newer blood cancer drugs may not improve OS, QOL
A study of cancer drugs approved by the European Commission from 2009 to 2013 showed that few hematology drugs were known to provide a benefit in overall survival (OS) or quality of life (QOL) over existing treatments.
Of 12 drugs approved for 17 hematology indications, 3 drugs had been shown to provide a benefit in OS (for 3 indications) at the time of approval.
None of the other hematology drugs were known to provide an OS benefit even after a median follow-up of 5.4 years.
Two hematology drugs were shown to provide a benefit in QOL (for 2 indications) after approval, but none of the drugs were known to provide a QOL benefit at the time of approval.
These findings were published in The BMJ alongside a related editorial, feature article, and patient commentary.
All cancer drugs
Researchers analyzed reports on all cancer drug approvals by the European Commission from 2009 to 2013.
There were 48 drugs approved for 68 cancer indications during this period. Fifty-one of the indications were for solid tumor malignancies, and 17 were for hematologic malignancies.
For 24 indications (35%), research had demonstrated a significant improvement in OS at the time of the drugs’ approval. For 3 indications, an improvement in OS was demonstrated after approval.
There was a known improvement in QOL for 7 of the indications (10%) at the time of approval and for 5 indications after approval.
The median follow-up was 5.4 years (range, 3.3 years to 8.1 years).
Overall, there was a significant improvement in OS or QOL during the study period for 51% of the indications (35/68). For the other half (49%, n=33), it wasn’t clear if the drugs provide any benefits in OS or QOL.
All cancer trials
The 68 approvals of cancer drugs were supported by 72 clinical trials.
Sixty approvals (88%) were supported by at least 1 randomized, controlled trial. Eight approvals (12%) were based on a single-arm study. This included 6 of 10 conditional marketing authorizations and 2 of 58 regular marketing authorizations.
Eighteen of the approvals (26%) were supported by a pivotal study powered to evaluate OS as the primary endpoint. And 37 of the approvals (54%) had a supporting pivotal trial evaluating QOL, but results were not reported for 2 of these trials.
Hematology trials and drugs
Of the 12 drugs approved for 17 hematology indications, 4 were regular approvals, 5 were conditional approvals, and 8 had orphan drug designation.
The approvals were supported by data from 18 trials—13 randomized and 5 single-arm trials.
The study drug was compared to an active comparator in 9 of the trials. The drug was evaluated as an add-on treatment in 4 trials. And the drug was not compared to anything in 5 trials (the single-arm trials).
OS was the primary endpoint in 1 of the trials, and 17 trials had OS or QOL as a secondary endpoint.
There were 3 drugs that had demonstrated an OS benefit at the time of approval but no QOL benefit at any time:
- Decitabine used for first-line treatment of acute myeloid leukemia in adults 65 and older who are ineligible for chemotherapy
- Pomalidomide in combination with dexamethasone as third-line therapy for relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma (MM)
- Rituximab plus chemotherapy for first-line treatment of chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL).
There were 2 drugs that had demonstrated a QOL benefit, only after approval, but they were not known to provide an OS benefit at any time:
- Nilotinib as a treatment for adults with newly diagnosed, chronic phase, Ph+ chronic myeloid leukemia (CML)
- Ofatumumab for CLL that is refractory to fludarabine and alemtuzumab
For the remaining drugs, there was no evidence of an OS or QOL benefit at any time during the period studied. The drugs included:
- Bortezomib given alone or in combination with doxorubicin or dexamethasone as second-line therapy for MM patients ineligible for hematopoietic stem cell transplant (HSCT)
- Bortezomib plus dexamethasone with or without thalidomide as first-line therapy in MM patients eligible for HSCT
- Bosutinib as second- or third-line treatment of Ph+ CML (any phase)
- Brentuximab vedotin for relapsed or refractory systemic anaplastic large-cell lymphoma
- Brentuximab vedotin for relapsed or refractory, CD30+ Hodgkin lymphoma after autologous HSCT or as third-line treatment for patients ineligible for autologous HSCT
- Dasatinib for first-line treatment of chronic phase, Ph+ CML
- Pixantrone for multiply relapsed or refractory B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma
- Ponatinib for patients with Ph+ acute lymphoblastic leukemia who are ineligible for imatinib or have disease that is resistant or intolerant to dasatinib or characterized by T315I mutation
- Ponatinib for patients with any phase of CML who are ineligible for imatinib or have disease that is resistant or intolerant to dasatinib/nilotinib or characterized by T315I mutation
- Rituximab as maintenance after induction for patients with follicular lymphoma
- Rituximab plus chemotherapy for relapsed or refractory CLL
- Temsirolimus for relapsed or refractory mantle cell lymphoma.
A study of cancer drugs approved by the European Commission from 2009 to 2013 showed that few hematology drugs were known to provide a benefit in overall survival (OS) or quality of life (QOL) over existing treatments.
Of 12 drugs approved for 17 hematology indications, 3 drugs had been shown to provide a benefit in OS (for 3 indications) at the time of approval.
None of the other hematology drugs were known to provide an OS benefit even after a median follow-up of 5.4 years.
Two hematology drugs were shown to provide a benefit in QOL (for 2 indications) after approval, but none of the drugs were known to provide a QOL benefit at the time of approval.
These findings were published in The BMJ alongside a related editorial, feature article, and patient commentary.
All cancer drugs
Researchers analyzed reports on all cancer drug approvals by the European Commission from 2009 to 2013.
There were 48 drugs approved for 68 cancer indications during this period. Fifty-one of the indications were for solid tumor malignancies, and 17 were for hematologic malignancies.
For 24 indications (35%), research had demonstrated a significant improvement in OS at the time of the drugs’ approval. For 3 indications, an improvement in OS was demonstrated after approval.
There was a known improvement in QOL for 7 of the indications (10%) at the time of approval and for 5 indications after approval.
The median follow-up was 5.4 years (range, 3.3 years to 8.1 years).
Overall, there was a significant improvement in OS or QOL during the study period for 51% of the indications (35/68). For the other half (49%, n=33), it wasn’t clear if the drugs provide any benefits in OS or QOL.
All cancer trials
The 68 approvals of cancer drugs were supported by 72 clinical trials.
Sixty approvals (88%) were supported by at least 1 randomized, controlled trial. Eight approvals (12%) were based on a single-arm study. This included 6 of 10 conditional marketing authorizations and 2 of 58 regular marketing authorizations.
Eighteen of the approvals (26%) were supported by a pivotal study powered to evaluate OS as the primary endpoint. And 37 of the approvals (54%) had a supporting pivotal trial evaluating QOL, but results were not reported for 2 of these trials.
Hematology trials and drugs
Of the 12 drugs approved for 17 hematology indications, 4 were regular approvals, 5 were conditional approvals, and 8 had orphan drug designation.
The approvals were supported by data from 18 trials—13 randomized and 5 single-arm trials.
The study drug was compared to an active comparator in 9 of the trials. The drug was evaluated as an add-on treatment in 4 trials. And the drug was not compared to anything in 5 trials (the single-arm trials).
OS was the primary endpoint in 1 of the trials, and 17 trials had OS or QOL as a secondary endpoint.
There were 3 drugs that had demonstrated an OS benefit at the time of approval but no QOL benefit at any time:
- Decitabine used for first-line treatment of acute myeloid leukemia in adults 65 and older who are ineligible for chemotherapy
- Pomalidomide in combination with dexamethasone as third-line therapy for relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma (MM)
- Rituximab plus chemotherapy for first-line treatment of chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL).
There were 2 drugs that had demonstrated a QOL benefit, only after approval, but they were not known to provide an OS benefit at any time:
- Nilotinib as a treatment for adults with newly diagnosed, chronic phase, Ph+ chronic myeloid leukemia (CML)
- Ofatumumab for CLL that is refractory to fludarabine and alemtuzumab
For the remaining drugs, there was no evidence of an OS or QOL benefit at any time during the period studied. The drugs included:
- Bortezomib given alone or in combination with doxorubicin or dexamethasone as second-line therapy for MM patients ineligible for hematopoietic stem cell transplant (HSCT)
- Bortezomib plus dexamethasone with or without thalidomide as first-line therapy in MM patients eligible for HSCT
- Bosutinib as second- or third-line treatment of Ph+ CML (any phase)
- Brentuximab vedotin for relapsed or refractory systemic anaplastic large-cell lymphoma
- Brentuximab vedotin for relapsed or refractory, CD30+ Hodgkin lymphoma after autologous HSCT or as third-line treatment for patients ineligible for autologous HSCT
- Dasatinib for first-line treatment of chronic phase, Ph+ CML
- Pixantrone for multiply relapsed or refractory B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma
- Ponatinib for patients with Ph+ acute lymphoblastic leukemia who are ineligible for imatinib or have disease that is resistant or intolerant to dasatinib or characterized by T315I mutation
- Ponatinib for patients with any phase of CML who are ineligible for imatinib or have disease that is resistant or intolerant to dasatinib/nilotinib or characterized by T315I mutation
- Rituximab as maintenance after induction for patients with follicular lymphoma
- Rituximab plus chemotherapy for relapsed or refractory CLL
- Temsirolimus for relapsed or refractory mantle cell lymphoma.
A study of cancer drugs approved by the European Commission from 2009 to 2013 showed that few hematology drugs were known to provide a benefit in overall survival (OS) or quality of life (QOL) over existing treatments.
Of 12 drugs approved for 17 hematology indications, 3 drugs had been shown to provide a benefit in OS (for 3 indications) at the time of approval.
None of the other hematology drugs were known to provide an OS benefit even after a median follow-up of 5.4 years.
Two hematology drugs were shown to provide a benefit in QOL (for 2 indications) after approval, but none of the drugs were known to provide a QOL benefit at the time of approval.
These findings were published in The BMJ alongside a related editorial, feature article, and patient commentary.
All cancer drugs
Researchers analyzed reports on all cancer drug approvals by the European Commission from 2009 to 2013.
There were 48 drugs approved for 68 cancer indications during this period. Fifty-one of the indications were for solid tumor malignancies, and 17 were for hematologic malignancies.
For 24 indications (35%), research had demonstrated a significant improvement in OS at the time of the drugs’ approval. For 3 indications, an improvement in OS was demonstrated after approval.
There was a known improvement in QOL for 7 of the indications (10%) at the time of approval and for 5 indications after approval.
The median follow-up was 5.4 years (range, 3.3 years to 8.1 years).
Overall, there was a significant improvement in OS or QOL during the study period for 51% of the indications (35/68). For the other half (49%, n=33), it wasn’t clear if the drugs provide any benefits in OS or QOL.
All cancer trials
The 68 approvals of cancer drugs were supported by 72 clinical trials.
Sixty approvals (88%) were supported by at least 1 randomized, controlled trial. Eight approvals (12%) were based on a single-arm study. This included 6 of 10 conditional marketing authorizations and 2 of 58 regular marketing authorizations.
Eighteen of the approvals (26%) were supported by a pivotal study powered to evaluate OS as the primary endpoint. And 37 of the approvals (54%) had a supporting pivotal trial evaluating QOL, but results were not reported for 2 of these trials.
Hematology trials and drugs
Of the 12 drugs approved for 17 hematology indications, 4 were regular approvals, 5 were conditional approvals, and 8 had orphan drug designation.
The approvals were supported by data from 18 trials—13 randomized and 5 single-arm trials.
The study drug was compared to an active comparator in 9 of the trials. The drug was evaluated as an add-on treatment in 4 trials. And the drug was not compared to anything in 5 trials (the single-arm trials).
OS was the primary endpoint in 1 of the trials, and 17 trials had OS or QOL as a secondary endpoint.
There were 3 drugs that had demonstrated an OS benefit at the time of approval but no QOL benefit at any time:
- Decitabine used for first-line treatment of acute myeloid leukemia in adults 65 and older who are ineligible for chemotherapy
- Pomalidomide in combination with dexamethasone as third-line therapy for relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma (MM)
- Rituximab plus chemotherapy for first-line treatment of chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL).
There were 2 drugs that had demonstrated a QOL benefit, only after approval, but they were not known to provide an OS benefit at any time:
- Nilotinib as a treatment for adults with newly diagnosed, chronic phase, Ph+ chronic myeloid leukemia (CML)
- Ofatumumab for CLL that is refractory to fludarabine and alemtuzumab
For the remaining drugs, there was no evidence of an OS or QOL benefit at any time during the period studied. The drugs included:
- Bortezomib given alone or in combination with doxorubicin or dexamethasone as second-line therapy for MM patients ineligible for hematopoietic stem cell transplant (HSCT)
- Bortezomib plus dexamethasone with or without thalidomide as first-line therapy in MM patients eligible for HSCT
- Bosutinib as second- or third-line treatment of Ph+ CML (any phase)
- Brentuximab vedotin for relapsed or refractory systemic anaplastic large-cell lymphoma
- Brentuximab vedotin for relapsed or refractory, CD30+ Hodgkin lymphoma after autologous HSCT or as third-line treatment for patients ineligible for autologous HSCT
- Dasatinib for first-line treatment of chronic phase, Ph+ CML
- Pixantrone for multiply relapsed or refractory B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma
- Ponatinib for patients with Ph+ acute lymphoblastic leukemia who are ineligible for imatinib or have disease that is resistant or intolerant to dasatinib or characterized by T315I mutation
- Ponatinib for patients with any phase of CML who are ineligible for imatinib or have disease that is resistant or intolerant to dasatinib/nilotinib or characterized by T315I mutation
- Rituximab as maintenance after induction for patients with follicular lymphoma
- Rituximab plus chemotherapy for relapsed or refractory CLL
- Temsirolimus for relapsed or refractory mantle cell lymphoma.
Sperm banking may be underused by young cancer patients
New research suggests sperm banking may be underutilized by adolescent and young adult males with cancer who are at risk of infertility.
However, the study also showed that patients were more likely to attempt sperm banking if they were physically mature, met with fertility specialists, or their parents recommended sperm banking.
These findings were published in the Journal of Clinical Oncology.
“Research has found that the majority of males who survive childhood cancer desire biological children,” said study author James Klosky, PhD, of St. Jude Children’s Research Hospital in Memphis, Tennessee.
“Fertility preservation is also associated with a variety of benefits for survivors, including increased optimism about the future. While sperm banking is not for everyone, it is an effective method for preserving male fertility. Yet this study shows that sperm banking remains underutilized by at-risk patients with cancer.”
Dr Klosky and his colleagues surveyed 146 young males with cancer who were at risk of infertility. The researchers also surveyed 144 parents or guardians and 52 oncologists and other healthcare providers.
The patients’ mean age was 16.49 (range, 13.0-21.99). Diagnoses included leukemia and lymphoma (56.2%), solid tumor malignancies (37.7%), and brain tumors (6.2%).
Slightly more than half of the patients (53.4%, n=78) attempted sperm banking prior to starting treatment. Sixty-two, or 82.1%, of those who attempted sperm banking were successful.
In all, 43.8% of the patients successfully banked sperm.
Of the 68 patients who did not attempt sperm banking, 29 reported discussing the option with their families but deciding against it. Twenty-six patients indicated they did not believe sperm banking was necessary, and 9 patients were unsure what it was.
There were several factors that influenced the likelihood of patients making sperm collection attempts as well as successfully banking sperm.
In a multivariable analysis, the following factors were associated with an increased likelihood of attempting to bank sperm:
- Meeting with a fertility specialist (odds ratio[OR]=29.96; 95% CI, 2.48 to 361.41; P=0.007)
- Parent recommending banking (OR=12.30; 95% CI, 2.01 to 75.94; P=0.007)
- Higher Tanner stage (OR=5.42; 95% CI, 1.75 to 16.78; P=0.003).
In another multivariable analysis, successful sperm banking was associated with:
- Patient history of masturbation (OR=5.99; 95% CI, 1.25 to 28.50; P=0.025)
- Higher self-efficacy for banking coordination (OR=1.23; 95% CI, 1.05 to 1.45; P=0.012)
- Medical team member recommending banking (OR=4.26; 95% CI, 1.45 to 12.43; P=0.008)
- Parent recommending banking (OR=4.62; 95% CI, 1.46 to 14.73; P=0.010).
“These results highlight factors that providers can target to empower adolescents to actively participate in their own healthcare,” Dr Klosky said. “These decisions, which are typically made at the time of diagnosis, have high potential to affect their lives as survivors.” ![]()
New research suggests sperm banking may be underutilized by adolescent and young adult males with cancer who are at risk of infertility.
However, the study also showed that patients were more likely to attempt sperm banking if they were physically mature, met with fertility specialists, or their parents recommended sperm banking.
These findings were published in the Journal of Clinical Oncology.
“Research has found that the majority of males who survive childhood cancer desire biological children,” said study author James Klosky, PhD, of St. Jude Children’s Research Hospital in Memphis, Tennessee.
“Fertility preservation is also associated with a variety of benefits for survivors, including increased optimism about the future. While sperm banking is not for everyone, it is an effective method for preserving male fertility. Yet this study shows that sperm banking remains underutilized by at-risk patients with cancer.”
Dr Klosky and his colleagues surveyed 146 young males with cancer who were at risk of infertility. The researchers also surveyed 144 parents or guardians and 52 oncologists and other healthcare providers.
The patients’ mean age was 16.49 (range, 13.0-21.99). Diagnoses included leukemia and lymphoma (56.2%), solid tumor malignancies (37.7%), and brain tumors (6.2%).
Slightly more than half of the patients (53.4%, n=78) attempted sperm banking prior to starting treatment. Sixty-two, or 82.1%, of those who attempted sperm banking were successful.
In all, 43.8% of the patients successfully banked sperm.
Of the 68 patients who did not attempt sperm banking, 29 reported discussing the option with their families but deciding against it. Twenty-six patients indicated they did not believe sperm banking was necessary, and 9 patients were unsure what it was.
There were several factors that influenced the likelihood of patients making sperm collection attempts as well as successfully banking sperm.
In a multivariable analysis, the following factors were associated with an increased likelihood of attempting to bank sperm:
- Meeting with a fertility specialist (odds ratio[OR]=29.96; 95% CI, 2.48 to 361.41; P=0.007)
- Parent recommending banking (OR=12.30; 95% CI, 2.01 to 75.94; P=0.007)
- Higher Tanner stage (OR=5.42; 95% CI, 1.75 to 16.78; P=0.003).
In another multivariable analysis, successful sperm banking was associated with:
- Patient history of masturbation (OR=5.99; 95% CI, 1.25 to 28.50; P=0.025)
- Higher self-efficacy for banking coordination (OR=1.23; 95% CI, 1.05 to 1.45; P=0.012)
- Medical team member recommending banking (OR=4.26; 95% CI, 1.45 to 12.43; P=0.008)
- Parent recommending banking (OR=4.62; 95% CI, 1.46 to 14.73; P=0.010).
“These results highlight factors that providers can target to empower adolescents to actively participate in their own healthcare,” Dr Klosky said. “These decisions, which are typically made at the time of diagnosis, have high potential to affect their lives as survivors.” ![]()
New research suggests sperm banking may be underutilized by adolescent and young adult males with cancer who are at risk of infertility.
However, the study also showed that patients were more likely to attempt sperm banking if they were physically mature, met with fertility specialists, or their parents recommended sperm banking.
These findings were published in the Journal of Clinical Oncology.
“Research has found that the majority of males who survive childhood cancer desire biological children,” said study author James Klosky, PhD, of St. Jude Children’s Research Hospital in Memphis, Tennessee.
“Fertility preservation is also associated with a variety of benefits for survivors, including increased optimism about the future. While sperm banking is not for everyone, it is an effective method for preserving male fertility. Yet this study shows that sperm banking remains underutilized by at-risk patients with cancer.”
Dr Klosky and his colleagues surveyed 146 young males with cancer who were at risk of infertility. The researchers also surveyed 144 parents or guardians and 52 oncologists and other healthcare providers.
The patients’ mean age was 16.49 (range, 13.0-21.99). Diagnoses included leukemia and lymphoma (56.2%), solid tumor malignancies (37.7%), and brain tumors (6.2%).
Slightly more than half of the patients (53.4%, n=78) attempted sperm banking prior to starting treatment. Sixty-two, or 82.1%, of those who attempted sperm banking were successful.
In all, 43.8% of the patients successfully banked sperm.
Of the 68 patients who did not attempt sperm banking, 29 reported discussing the option with their families but deciding against it. Twenty-six patients indicated they did not believe sperm banking was necessary, and 9 patients were unsure what it was.
There were several factors that influenced the likelihood of patients making sperm collection attempts as well as successfully banking sperm.
In a multivariable analysis, the following factors were associated with an increased likelihood of attempting to bank sperm:
- Meeting with a fertility specialist (odds ratio[OR]=29.96; 95% CI, 2.48 to 361.41; P=0.007)
- Parent recommending banking (OR=12.30; 95% CI, 2.01 to 75.94; P=0.007)
- Higher Tanner stage (OR=5.42; 95% CI, 1.75 to 16.78; P=0.003).
In another multivariable analysis, successful sperm banking was associated with:
- Patient history of masturbation (OR=5.99; 95% CI, 1.25 to 28.50; P=0.025)
- Higher self-efficacy for banking coordination (OR=1.23; 95% CI, 1.05 to 1.45; P=0.012)
- Medical team member recommending banking (OR=4.26; 95% CI, 1.45 to 12.43; P=0.008)
- Parent recommending banking (OR=4.62; 95% CI, 1.46 to 14.73; P=0.010).
“These results highlight factors that providers can target to empower adolescents to actively participate in their own healthcare,” Dr Klosky said. “These decisions, which are typically made at the time of diagnosis, have high potential to affect their lives as survivors.” ![]()
Drug receives breakthrough designation for HL
The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has granted breakthrough therapy designation to brentuximab vedotin (BV, Adcetris) for use in combination with chemotherapy as frontline treatment of advanced classical Hodgkin lymphoma (HL).
Seattle Genetics and Takeda plan to submit a supplemental biologics license application seeking approval for BV in this indication before the end of this year.
The breakthrough designation is based on positive topline results from the phase 3 ECHELON-1 trial.
Full results from this trial are expected to be presented at the 2017 ASH Annual Meeting in December.
BV is an antibody-drug conjugate consisting of an anti-CD30 monoclonal antibody attached by a protease-cleavable linker to a microtubule disrupting agent, monomethyl auristatin E.
BV is currently FDA-approved to treat:
- Classical HL after failure of autologous hematopoietic stem cell transplant (auto-HSCT) or after failure of at least 2 prior multi-agent chemotherapy regimens in patients who are not auto-HSCT candidates
- Classical HL patients at high risk of relapse or progression as post-auto-HSCT consolidation.
BV also has accelerated approval from the FDA for the treatment of systemic anaplastic large-cell lymphoma after failure of at least 1 prior multi-agent chemotherapy regimen. This approval is based on overall response rate. Continued approval of BV for this indication may be contingent upon verification and description of clinical benefit in confirmatory trials.
ECHELON-1 trial
In this phase 3 trial, researchers compared BV in combination with doxorubicin, vinblastine, and dacarbazine to a recognized standard of care chemotherapy regimen in patients with previously untreated, advanced classical HL.
The study enrolled 1334 patients who had a histologically confirmed diagnosis of stage III or IV classical HL and had not been previously treated with systemic chemotherapy or radiotherapy.
The study’s primary endpoint is modified progression-free survival (PFS) per an independent review facility. Modified PFS is defined as the time to progression, death, or receipt of additional anticancer therapy for patients who are not in complete response after completion of frontline therapy.
There was a significant improvement in modified PFS in the BV arm compared to the control arm (hazard ratio=0.770; P=0.035). The 2-year modified PFS rate was 82.1% in the BV arm and 77.2% in the control arm.
An interim analysis of overall survival revealed a trend in favor of the BV arm.
The safety profile of BV plus chemotherapy was consistent with the profile known for the single-agent components of the regimen.
About breakthrough designation
The FDA’s breakthrough designation is intended to expedite the development and review of new treatments for serious or life-threatening conditions.
The designation entitles the company developing a therapy to more intensive FDA guidance on an efficient and accelerated development program, as well as eligibility for other actions to expedite FDA review, such as rolling submission and priority review.
To earn breakthrough designation, a treatment must show encouraging early clinical results demonstrating substantial improvement over available therapies with regard to a clinically significant endpoint, or it must fulfill an unmet need. ![]()
The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has granted breakthrough therapy designation to brentuximab vedotin (BV, Adcetris) for use in combination with chemotherapy as frontline treatment of advanced classical Hodgkin lymphoma (HL).
Seattle Genetics and Takeda plan to submit a supplemental biologics license application seeking approval for BV in this indication before the end of this year.
The breakthrough designation is based on positive topline results from the phase 3 ECHELON-1 trial.
Full results from this trial are expected to be presented at the 2017 ASH Annual Meeting in December.
BV is an antibody-drug conjugate consisting of an anti-CD30 monoclonal antibody attached by a protease-cleavable linker to a microtubule disrupting agent, monomethyl auristatin E.
BV is currently FDA-approved to treat:
- Classical HL after failure of autologous hematopoietic stem cell transplant (auto-HSCT) or after failure of at least 2 prior multi-agent chemotherapy regimens in patients who are not auto-HSCT candidates
- Classical HL patients at high risk of relapse or progression as post-auto-HSCT consolidation.
BV also has accelerated approval from the FDA for the treatment of systemic anaplastic large-cell lymphoma after failure of at least 1 prior multi-agent chemotherapy regimen. This approval is based on overall response rate. Continued approval of BV for this indication may be contingent upon verification and description of clinical benefit in confirmatory trials.
ECHELON-1 trial
In this phase 3 trial, researchers compared BV in combination with doxorubicin, vinblastine, and dacarbazine to a recognized standard of care chemotherapy regimen in patients with previously untreated, advanced classical HL.
The study enrolled 1334 patients who had a histologically confirmed diagnosis of stage III or IV classical HL and had not been previously treated with systemic chemotherapy or radiotherapy.
The study’s primary endpoint is modified progression-free survival (PFS) per an independent review facility. Modified PFS is defined as the time to progression, death, or receipt of additional anticancer therapy for patients who are not in complete response after completion of frontline therapy.
There was a significant improvement in modified PFS in the BV arm compared to the control arm (hazard ratio=0.770; P=0.035). The 2-year modified PFS rate was 82.1% in the BV arm and 77.2% in the control arm.
An interim analysis of overall survival revealed a trend in favor of the BV arm.
The safety profile of BV plus chemotherapy was consistent with the profile known for the single-agent components of the regimen.
About breakthrough designation
The FDA’s breakthrough designation is intended to expedite the development and review of new treatments for serious or life-threatening conditions.
The designation entitles the company developing a therapy to more intensive FDA guidance on an efficient and accelerated development program, as well as eligibility for other actions to expedite FDA review, such as rolling submission and priority review.
To earn breakthrough designation, a treatment must show encouraging early clinical results demonstrating substantial improvement over available therapies with regard to a clinically significant endpoint, or it must fulfill an unmet need. ![]()
The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has granted breakthrough therapy designation to brentuximab vedotin (BV, Adcetris) for use in combination with chemotherapy as frontline treatment of advanced classical Hodgkin lymphoma (HL).
Seattle Genetics and Takeda plan to submit a supplemental biologics license application seeking approval for BV in this indication before the end of this year.
The breakthrough designation is based on positive topline results from the phase 3 ECHELON-1 trial.
Full results from this trial are expected to be presented at the 2017 ASH Annual Meeting in December.
BV is an antibody-drug conjugate consisting of an anti-CD30 monoclonal antibody attached by a protease-cleavable linker to a microtubule disrupting agent, monomethyl auristatin E.
BV is currently FDA-approved to treat:
- Classical HL after failure of autologous hematopoietic stem cell transplant (auto-HSCT) or after failure of at least 2 prior multi-agent chemotherapy regimens in patients who are not auto-HSCT candidates
- Classical HL patients at high risk of relapse or progression as post-auto-HSCT consolidation.
BV also has accelerated approval from the FDA for the treatment of systemic anaplastic large-cell lymphoma after failure of at least 1 prior multi-agent chemotherapy regimen. This approval is based on overall response rate. Continued approval of BV for this indication may be contingent upon verification and description of clinical benefit in confirmatory trials.
ECHELON-1 trial
In this phase 3 trial, researchers compared BV in combination with doxorubicin, vinblastine, and dacarbazine to a recognized standard of care chemotherapy regimen in patients with previously untreated, advanced classical HL.
The study enrolled 1334 patients who had a histologically confirmed diagnosis of stage III or IV classical HL and had not been previously treated with systemic chemotherapy or radiotherapy.
The study’s primary endpoint is modified progression-free survival (PFS) per an independent review facility. Modified PFS is defined as the time to progression, death, or receipt of additional anticancer therapy for patients who are not in complete response after completion of frontline therapy.
There was a significant improvement in modified PFS in the BV arm compared to the control arm (hazard ratio=0.770; P=0.035). The 2-year modified PFS rate was 82.1% in the BV arm and 77.2% in the control arm.
An interim analysis of overall survival revealed a trend in favor of the BV arm.
The safety profile of BV plus chemotherapy was consistent with the profile known for the single-agent components of the regimen.
About breakthrough designation
The FDA’s breakthrough designation is intended to expedite the development and review of new treatments for serious or life-threatening conditions.
The designation entitles the company developing a therapy to more intensive FDA guidance on an efficient and accelerated development program, as well as eligibility for other actions to expedite FDA review, such as rolling submission and priority review.
To earn breakthrough designation, a treatment must show encouraging early clinical results demonstrating substantial improvement over available therapies with regard to a clinically significant endpoint, or it must fulfill an unmet need. ![]()
Doc advocates depression screening for cancer patients
SAN DIEGO—New research suggests a need for mental health screening among cancer patients.
The study revealed a 40% rate of depression among patients treated at an urban cancer center over a 3-year period.
Three-quarters of the depressed patients were previously undiagnosed.
Female patients and those who were unable to work due to disability were more likely to be depressed.
Jason Domogauer, PhD, of Rutgers New Jersey Medical School in Newark, New Jersey, presented these findings at ASTRO’s 59th Annual Meeting.
“Depression is widely recognized as an underdiagnosed disorder, particularly among older adults and cancer patients,” Dr Domogauer said. “Our findings point to a clear need for action, including depression screening during initial and continuing patient visits, initiation of mental health treatments for identified patients, and increased collaboration with mental health providers in cancer treatment centers. These efforts are particularly important for patients in urban centers, those who are female, and those who are unable to work because of their disease.”
Dr Domogauer and his colleagues studied 400 cancer patients who received treatment at Rutgers New Jersey Medical School/University Hospital Cancer Center between 2013 and 2016.
The average patient age was 55 (range, 20-86), and 53% of patients were female. Forty-eight percent of patients were African-American, 29% were non-Hispanic white, and 16% were Hispanic.
Nearly equal numbers of patients reported being able to work (49%) or unable to work due to disability (51%). Most patients (85%) received radiation as part of their cancer treatment.
The researchers assessed depression in the patients using a minimum score of 16 on the Center for Epidemiologic Studies Depression Scale.
In this way, 40% of the patients were diagnosed with depression. In 75% of these patients, depression was previously undiagnosed. This means roughly 30% of the overall patient population suffered from undiagnosed and untreated depression.
Depression was more common among females than males—47% and 32%, respectively (odds ratio [OR]=1.9, P=0.007).
Depression was also more likely among patients who were unable to work due to disability—48%, compared to 33% of those able to work (OR=1.9, P=0.005).
Depression prevalence did not differ significantly among racial/ethnic groups.
When the researchers looked specifically at patients who were previously not diagnosed with depression, the effects of being female or unable to work persisted.
In this subgroup, depression was more common among women than men—43% and 29%, respectively (OR=1.9, P=0.02)—and patients with disability compared to able patients—43% and 31%, respectively (OR=1.7, P=0.03). ![]()
SAN DIEGO—New research suggests a need for mental health screening among cancer patients.
The study revealed a 40% rate of depression among patients treated at an urban cancer center over a 3-year period.
Three-quarters of the depressed patients were previously undiagnosed.
Female patients and those who were unable to work due to disability were more likely to be depressed.
Jason Domogauer, PhD, of Rutgers New Jersey Medical School in Newark, New Jersey, presented these findings at ASTRO’s 59th Annual Meeting.
“Depression is widely recognized as an underdiagnosed disorder, particularly among older adults and cancer patients,” Dr Domogauer said. “Our findings point to a clear need for action, including depression screening during initial and continuing patient visits, initiation of mental health treatments for identified patients, and increased collaboration with mental health providers in cancer treatment centers. These efforts are particularly important for patients in urban centers, those who are female, and those who are unable to work because of their disease.”
Dr Domogauer and his colleagues studied 400 cancer patients who received treatment at Rutgers New Jersey Medical School/University Hospital Cancer Center between 2013 and 2016.
The average patient age was 55 (range, 20-86), and 53% of patients were female. Forty-eight percent of patients were African-American, 29% were non-Hispanic white, and 16% were Hispanic.
Nearly equal numbers of patients reported being able to work (49%) or unable to work due to disability (51%). Most patients (85%) received radiation as part of their cancer treatment.
The researchers assessed depression in the patients using a minimum score of 16 on the Center for Epidemiologic Studies Depression Scale.
In this way, 40% of the patients were diagnosed with depression. In 75% of these patients, depression was previously undiagnosed. This means roughly 30% of the overall patient population suffered from undiagnosed and untreated depression.
Depression was more common among females than males—47% and 32%, respectively (odds ratio [OR]=1.9, P=0.007).
Depression was also more likely among patients who were unable to work due to disability—48%, compared to 33% of those able to work (OR=1.9, P=0.005).
Depression prevalence did not differ significantly among racial/ethnic groups.
When the researchers looked specifically at patients who were previously not diagnosed with depression, the effects of being female or unable to work persisted.
In this subgroup, depression was more common among women than men—43% and 29%, respectively (OR=1.9, P=0.02)—and patients with disability compared to able patients—43% and 31%, respectively (OR=1.7, P=0.03). ![]()
SAN DIEGO—New research suggests a need for mental health screening among cancer patients.
The study revealed a 40% rate of depression among patients treated at an urban cancer center over a 3-year period.
Three-quarters of the depressed patients were previously undiagnosed.
Female patients and those who were unable to work due to disability were more likely to be depressed.
Jason Domogauer, PhD, of Rutgers New Jersey Medical School in Newark, New Jersey, presented these findings at ASTRO’s 59th Annual Meeting.
“Depression is widely recognized as an underdiagnosed disorder, particularly among older adults and cancer patients,” Dr Domogauer said. “Our findings point to a clear need for action, including depression screening during initial and continuing patient visits, initiation of mental health treatments for identified patients, and increased collaboration with mental health providers in cancer treatment centers. These efforts are particularly important for patients in urban centers, those who are female, and those who are unable to work because of their disease.”
Dr Domogauer and his colleagues studied 400 cancer patients who received treatment at Rutgers New Jersey Medical School/University Hospital Cancer Center between 2013 and 2016.
The average patient age was 55 (range, 20-86), and 53% of patients were female. Forty-eight percent of patients were African-American, 29% were non-Hispanic white, and 16% were Hispanic.
Nearly equal numbers of patients reported being able to work (49%) or unable to work due to disability (51%). Most patients (85%) received radiation as part of their cancer treatment.
The researchers assessed depression in the patients using a minimum score of 16 on the Center for Epidemiologic Studies Depression Scale.
In this way, 40% of the patients were diagnosed with depression. In 75% of these patients, depression was previously undiagnosed. This means roughly 30% of the overall patient population suffered from undiagnosed and untreated depression.
Depression was more common among females than males—47% and 32%, respectively (odds ratio [OR]=1.9, P=0.007).
Depression was also more likely among patients who were unable to work due to disability—48%, compared to 33% of those able to work (OR=1.9, P=0.005).
Depression prevalence did not differ significantly among racial/ethnic groups.
When the researchers looked specifically at patients who were previously not diagnosed with depression, the effects of being female or unable to work persisted.
In this subgroup, depression was more common among women than men—43% and 29%, respectively (OR=1.9, P=0.02)—and patients with disability compared to able patients—43% and 31%, respectively (OR=1.7, P=0.03). ![]()
Adding bortezomib to R-CHOP didn’t improve survival in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma
, findings from the phase-2 PYRAMID trial showed.
When the proteasome inhibitor bortezomib was combined with rituximab, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone (R-CHOP) in patients with previously untreated non–germinal center B-cell–like (non-GCB) DLBCL, a significant improvement in progression-free survival (PFS) was not observed.
There also was no increase in 2-year PFS among patients treated with the combination of bortezomib plus R-CHOP (VR-CHOP), according to findings from the open-label, randomized study published in the Journal of Clinical Oncology (2017 Sep 1. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2017.73.2784).
“A potential reason for the lack of benefit with VR-CHOP was that only two doses of bortezomib were given per 21-day cycle, whereas the standard schedule for bortezomib in multiple myeloma is four doses per cycle on days 1, 4, 8, and 11,” wrote John P. Leonard, MD, of Weill Cornell Medicine and New York Presbyterian Hospital, New York, and his colleagues. “In this study, treatment duration was limited to six 21-day cycles of R-CHOP.”
The authors noted that previous research has demonstrated the feasibility of using VR-CHOP and similar immunochemotherapy regimens in DLBCL. In the current PYRAMID (Personalized Lymphoma Therapy: Randomized Study of Proteasome Inhibition in Non-GCB DLBCL) phase 2 trial, VR-CHOP was compared with R-CHOP in 206 patients with previously untreated non-GCB DLBCL who were selected by real-time subtyping conducted or confirmed at a central laboratory that used the Hans algorithm.
The cohort was randomized to receive six 21-day cycles of standard R-CHOP alone or R-CHOP plus bortezomib 1.3 mg/m2 intravenously on days 1 and 4, and the primary endpoint was PFS.
The hazard ratio (HR) for PFS was 0.73 (90% confidence interval, 0.43-1.24) and favored VR-CHOP (P = .611), while the median PFS was not reached in either group. At 2 years, PFS was 77.6% with R-CHOP, versus 82.0% with VR-CHOP.
Among patients with high-intermediate/high International Prognostic Index (IPI) risk, those rates were 65.1% with R-CHOP, versus 72.4% with VR-CHOP (HR, 0.67; 90% CI, 0.34-1.29; P = .606). For those patients at low/low-intermediate IPI risk, the rates were 90.0% for R-CHOP, versus 88.9% for VR-CHOP (HR, 0.85; 90% CI, 0.35-2.10; P = .958).
The overall response rate was 98% for R-CHOP patients and 96% for VR-CHOP, with complete response rates of 49% and 56%, respectively.
Time to progression rates at 2 years were 79.8% for R-CHOP, versus 83.0% with VR-CHOP (HR, 0.79; 90% CI, 0.45-1.37; P = .767). While median overall survival was not reached in either arm, the HR for the entire cohort was 0.75 (90% CI, 0.38-1.45; P = .763). Two-year overall survival was 88.4% and 93.0%, respectively.
In the high-intermediate/high IPI score group, 2-year overall survival was 79.2% with R-CHOP, versus 92.1% with VR-CHOP (HR, 0.62; 90% CI, 0.25-1.42; P = .638), and for those with low/low-intermediate IPI risk scores, 97.7% versus 93.8% (HR, 1.02; 90% CI, 0.34-3.27; P = .999).
Millennium Pharmaceuticals supported the study. Dr. Leonard and several of the coauthors reported relationships with industry.
, findings from the phase-2 PYRAMID trial showed.
When the proteasome inhibitor bortezomib was combined with rituximab, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone (R-CHOP) in patients with previously untreated non–germinal center B-cell–like (non-GCB) DLBCL, a significant improvement in progression-free survival (PFS) was not observed.
There also was no increase in 2-year PFS among patients treated with the combination of bortezomib plus R-CHOP (VR-CHOP), according to findings from the open-label, randomized study published in the Journal of Clinical Oncology (2017 Sep 1. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2017.73.2784).
“A potential reason for the lack of benefit with VR-CHOP was that only two doses of bortezomib were given per 21-day cycle, whereas the standard schedule for bortezomib in multiple myeloma is four doses per cycle on days 1, 4, 8, and 11,” wrote John P. Leonard, MD, of Weill Cornell Medicine and New York Presbyterian Hospital, New York, and his colleagues. “In this study, treatment duration was limited to six 21-day cycles of R-CHOP.”
The authors noted that previous research has demonstrated the feasibility of using VR-CHOP and similar immunochemotherapy regimens in DLBCL. In the current PYRAMID (Personalized Lymphoma Therapy: Randomized Study of Proteasome Inhibition in Non-GCB DLBCL) phase 2 trial, VR-CHOP was compared with R-CHOP in 206 patients with previously untreated non-GCB DLBCL who were selected by real-time subtyping conducted or confirmed at a central laboratory that used the Hans algorithm.
The cohort was randomized to receive six 21-day cycles of standard R-CHOP alone or R-CHOP plus bortezomib 1.3 mg/m2 intravenously on days 1 and 4, and the primary endpoint was PFS.
The hazard ratio (HR) for PFS was 0.73 (90% confidence interval, 0.43-1.24) and favored VR-CHOP (P = .611), while the median PFS was not reached in either group. At 2 years, PFS was 77.6% with R-CHOP, versus 82.0% with VR-CHOP.
Among patients with high-intermediate/high International Prognostic Index (IPI) risk, those rates were 65.1% with R-CHOP, versus 72.4% with VR-CHOP (HR, 0.67; 90% CI, 0.34-1.29; P = .606). For those patients at low/low-intermediate IPI risk, the rates were 90.0% for R-CHOP, versus 88.9% for VR-CHOP (HR, 0.85; 90% CI, 0.35-2.10; P = .958).
The overall response rate was 98% for R-CHOP patients and 96% for VR-CHOP, with complete response rates of 49% and 56%, respectively.
Time to progression rates at 2 years were 79.8% for R-CHOP, versus 83.0% with VR-CHOP (HR, 0.79; 90% CI, 0.45-1.37; P = .767). While median overall survival was not reached in either arm, the HR for the entire cohort was 0.75 (90% CI, 0.38-1.45; P = .763). Two-year overall survival was 88.4% and 93.0%, respectively.
In the high-intermediate/high IPI score group, 2-year overall survival was 79.2% with R-CHOP, versus 92.1% with VR-CHOP (HR, 0.62; 90% CI, 0.25-1.42; P = .638), and for those with low/low-intermediate IPI risk scores, 97.7% versus 93.8% (HR, 1.02; 90% CI, 0.34-3.27; P = .999).
Millennium Pharmaceuticals supported the study. Dr. Leonard and several of the coauthors reported relationships with industry.
, findings from the phase-2 PYRAMID trial showed.
When the proteasome inhibitor bortezomib was combined with rituximab, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone (R-CHOP) in patients with previously untreated non–germinal center B-cell–like (non-GCB) DLBCL, a significant improvement in progression-free survival (PFS) was not observed.
There also was no increase in 2-year PFS among patients treated with the combination of bortezomib plus R-CHOP (VR-CHOP), according to findings from the open-label, randomized study published in the Journal of Clinical Oncology (2017 Sep 1. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2017.73.2784).
“A potential reason for the lack of benefit with VR-CHOP was that only two doses of bortezomib were given per 21-day cycle, whereas the standard schedule for bortezomib in multiple myeloma is four doses per cycle on days 1, 4, 8, and 11,” wrote John P. Leonard, MD, of Weill Cornell Medicine and New York Presbyterian Hospital, New York, and his colleagues. “In this study, treatment duration was limited to six 21-day cycles of R-CHOP.”
The authors noted that previous research has demonstrated the feasibility of using VR-CHOP and similar immunochemotherapy regimens in DLBCL. In the current PYRAMID (Personalized Lymphoma Therapy: Randomized Study of Proteasome Inhibition in Non-GCB DLBCL) phase 2 trial, VR-CHOP was compared with R-CHOP in 206 patients with previously untreated non-GCB DLBCL who were selected by real-time subtyping conducted or confirmed at a central laboratory that used the Hans algorithm.
The cohort was randomized to receive six 21-day cycles of standard R-CHOP alone or R-CHOP plus bortezomib 1.3 mg/m2 intravenously on days 1 and 4, and the primary endpoint was PFS.
The hazard ratio (HR) for PFS was 0.73 (90% confidence interval, 0.43-1.24) and favored VR-CHOP (P = .611), while the median PFS was not reached in either group. At 2 years, PFS was 77.6% with R-CHOP, versus 82.0% with VR-CHOP.
Among patients with high-intermediate/high International Prognostic Index (IPI) risk, those rates were 65.1% with R-CHOP, versus 72.4% with VR-CHOP (HR, 0.67; 90% CI, 0.34-1.29; P = .606). For those patients at low/low-intermediate IPI risk, the rates were 90.0% for R-CHOP, versus 88.9% for VR-CHOP (HR, 0.85; 90% CI, 0.35-2.10; P = .958).
The overall response rate was 98% for R-CHOP patients and 96% for VR-CHOP, with complete response rates of 49% and 56%, respectively.
Time to progression rates at 2 years were 79.8% for R-CHOP, versus 83.0% with VR-CHOP (HR, 0.79; 90% CI, 0.45-1.37; P = .767). While median overall survival was not reached in either arm, the HR for the entire cohort was 0.75 (90% CI, 0.38-1.45; P = .763). Two-year overall survival was 88.4% and 93.0%, respectively.
In the high-intermediate/high IPI score group, 2-year overall survival was 79.2% with R-CHOP, versus 92.1% with VR-CHOP (HR, 0.62; 90% CI, 0.25-1.42; P = .638), and for those with low/low-intermediate IPI risk scores, 97.7% versus 93.8% (HR, 1.02; 90% CI, 0.34-3.27; P = .999).
Millennium Pharmaceuticals supported the study. Dr. Leonard and several of the coauthors reported relationships with industry.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF CLINICAL ONCOLOGY
Key clinical point: Bortezomib combined with R-CHOP did not improve outcomes significantly in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma.
Major finding: Two-year progression-free survival was 77.6% with R-CHOP, compared with 82.0% with VR-CHOP, a nonsignificant difference.
Data source: An open-label, randomized, phase 2 trial that compared VR-CHOP to R-CHOP in 206 patients with previously untreated non-GCB DLBCL.
Disclosures: Millennium Pharmaceuticals funded the study. Dr. Leonard and several of the coauthors reported relationships with industry.
Maintenance will be a new standard in MCL, doc says
Results of a phase 3 trial suggest rituximab maintenance after transplant can prolong survival in non-elderly patients with mantle cell lymphoma (MCL).
Compared to patients who did not receive maintenance, those who received rituximab every other month for 3 years after autologous transplant had superior event-free survival (EFS), progression-free survival (PFS), and overall survival (OS).
Researchers reported these results in NEJM. The study was funded by Roche and Amgen.
“We demonstrate, with this study, that treatment with immunotherapy can delay the onset of relapse and prolong the survival of patients,” said study author Steven Le Gouill, MD, PhD, of CHU de Nantes in France.*
“It is clear that the use of rituximab maintenance after chemotherapy in this type of lymphoma will become a new standard of treatment.”
Dr Le Gouill and his colleagues began this study with 299 MCL patients. Their median age was 57 (range, 27-65), and 79% were male. Most had Ann Arbor stage IV disease (84%), followed by III (10%), and II (6%).
According to MIPI, 53% of patients had low-risk disease, 27% had intermediate-risk MCL, and 19% had high-risk disease. Ninety-four percent of patients had an ECOG performance status score below 3.
Treatment
Patients first received 4 courses of induction with R-DHAP (rituximab, dexamethasone, cytarabine, and a platinum derivative [carboplatin, oxaliplatin, or cisplatin]).
The overall response rate was 94%, with 41% (n=124) achieving a complete response (CR) and 36% (n=107) achieving an unconfirmed CR.
Twenty patients who had an insufficient response then received 4 courses of R-CHOP (rituximab, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone). Eleven of these patients went on to receive an autologous hematopoietic stem cell transplant (HSCT).
In all, 257 patients (86%) underwent autologous HSCT. The conditioning regimen was R-BEAM (rituximab, carmustine, etoposide, cytarabine, and melphalan).
Sixty-five percent of patients (n=168) achieved a CR after HSCT, and 24% (n=61) had an unconfirmed CR.
Up to 3 months after HSCT, patients were randomized to observation (n=120) or to receive rituximab (375 mg/m2) every 2 months for 3 years (n=120).
The researchers said there were no significant differences between these 2 groups regarding characteristics at study enrollment or the patients’ disease status at randomization.
Results
The median follow-up from randomization was 50.2 months (range, 46.4 to 54.2). The median EFS, PFS, and OS were not reached in either group.
The 4-year EFS was 79% in the rituximab group and 61% in the observation group (P=0.001). The 4-year PFS was 83% and 64%, respectively (P<0.001). And the 4-year OS was 89% and 80%, respectively (P=0.04).
Of the 11 patients who received R-CHOP before randomization, 4 were randomized to the rituximab group and 7 to the observation group.
One patient in the rituximab group relapsed and died. The other 3 were still alive and disease-free at the final analysis.
In the observation group, 4 patients had relapsed but were alive as of the final analysis, while 3 patients had died.
There were 59 patients who did not undergo randomization (due to disease progression, death, HSCT ineligibility, toxic effects, and other reasons).
For these patients, the median PFS was 11.0 months, and the median OS was 30.6 months. ![]()
*Quote has been translated from French.
Results of a phase 3 trial suggest rituximab maintenance after transplant can prolong survival in non-elderly patients with mantle cell lymphoma (MCL).
Compared to patients who did not receive maintenance, those who received rituximab every other month for 3 years after autologous transplant had superior event-free survival (EFS), progression-free survival (PFS), and overall survival (OS).
Researchers reported these results in NEJM. The study was funded by Roche and Amgen.
“We demonstrate, with this study, that treatment with immunotherapy can delay the onset of relapse and prolong the survival of patients,” said study author Steven Le Gouill, MD, PhD, of CHU de Nantes in France.*
“It is clear that the use of rituximab maintenance after chemotherapy in this type of lymphoma will become a new standard of treatment.”
Dr Le Gouill and his colleagues began this study with 299 MCL patients. Their median age was 57 (range, 27-65), and 79% were male. Most had Ann Arbor stage IV disease (84%), followed by III (10%), and II (6%).
According to MIPI, 53% of patients had low-risk disease, 27% had intermediate-risk MCL, and 19% had high-risk disease. Ninety-four percent of patients had an ECOG performance status score below 3.
Treatment
Patients first received 4 courses of induction with R-DHAP (rituximab, dexamethasone, cytarabine, and a platinum derivative [carboplatin, oxaliplatin, or cisplatin]).
The overall response rate was 94%, with 41% (n=124) achieving a complete response (CR) and 36% (n=107) achieving an unconfirmed CR.
Twenty patients who had an insufficient response then received 4 courses of R-CHOP (rituximab, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone). Eleven of these patients went on to receive an autologous hematopoietic stem cell transplant (HSCT).
In all, 257 patients (86%) underwent autologous HSCT. The conditioning regimen was R-BEAM (rituximab, carmustine, etoposide, cytarabine, and melphalan).
Sixty-five percent of patients (n=168) achieved a CR after HSCT, and 24% (n=61) had an unconfirmed CR.
Up to 3 months after HSCT, patients were randomized to observation (n=120) or to receive rituximab (375 mg/m2) every 2 months for 3 years (n=120).
The researchers said there were no significant differences between these 2 groups regarding characteristics at study enrollment or the patients’ disease status at randomization.
Results
The median follow-up from randomization was 50.2 months (range, 46.4 to 54.2). The median EFS, PFS, and OS were not reached in either group.
The 4-year EFS was 79% in the rituximab group and 61% in the observation group (P=0.001). The 4-year PFS was 83% and 64%, respectively (P<0.001). And the 4-year OS was 89% and 80%, respectively (P=0.04).
Of the 11 patients who received R-CHOP before randomization, 4 were randomized to the rituximab group and 7 to the observation group.
One patient in the rituximab group relapsed and died. The other 3 were still alive and disease-free at the final analysis.
In the observation group, 4 patients had relapsed but were alive as of the final analysis, while 3 patients had died.
There were 59 patients who did not undergo randomization (due to disease progression, death, HSCT ineligibility, toxic effects, and other reasons).
For these patients, the median PFS was 11.0 months, and the median OS was 30.6 months. ![]()
*Quote has been translated from French.
Results of a phase 3 trial suggest rituximab maintenance after transplant can prolong survival in non-elderly patients with mantle cell lymphoma (MCL).
Compared to patients who did not receive maintenance, those who received rituximab every other month for 3 years after autologous transplant had superior event-free survival (EFS), progression-free survival (PFS), and overall survival (OS).
Researchers reported these results in NEJM. The study was funded by Roche and Amgen.
“We demonstrate, with this study, that treatment with immunotherapy can delay the onset of relapse and prolong the survival of patients,” said study author Steven Le Gouill, MD, PhD, of CHU de Nantes in France.*
“It is clear that the use of rituximab maintenance after chemotherapy in this type of lymphoma will become a new standard of treatment.”
Dr Le Gouill and his colleagues began this study with 299 MCL patients. Their median age was 57 (range, 27-65), and 79% were male. Most had Ann Arbor stage IV disease (84%), followed by III (10%), and II (6%).
According to MIPI, 53% of patients had low-risk disease, 27% had intermediate-risk MCL, and 19% had high-risk disease. Ninety-four percent of patients had an ECOG performance status score below 3.
Treatment
Patients first received 4 courses of induction with R-DHAP (rituximab, dexamethasone, cytarabine, and a platinum derivative [carboplatin, oxaliplatin, or cisplatin]).
The overall response rate was 94%, with 41% (n=124) achieving a complete response (CR) and 36% (n=107) achieving an unconfirmed CR.
Twenty patients who had an insufficient response then received 4 courses of R-CHOP (rituximab, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone). Eleven of these patients went on to receive an autologous hematopoietic stem cell transplant (HSCT).
In all, 257 patients (86%) underwent autologous HSCT. The conditioning regimen was R-BEAM (rituximab, carmustine, etoposide, cytarabine, and melphalan).
Sixty-five percent of patients (n=168) achieved a CR after HSCT, and 24% (n=61) had an unconfirmed CR.
Up to 3 months after HSCT, patients were randomized to observation (n=120) or to receive rituximab (375 mg/m2) every 2 months for 3 years (n=120).
The researchers said there were no significant differences between these 2 groups regarding characteristics at study enrollment or the patients’ disease status at randomization.
Results
The median follow-up from randomization was 50.2 months (range, 46.4 to 54.2). The median EFS, PFS, and OS were not reached in either group.
The 4-year EFS was 79% in the rituximab group and 61% in the observation group (P=0.001). The 4-year PFS was 83% and 64%, respectively (P<0.001). And the 4-year OS was 89% and 80%, respectively (P=0.04).
Of the 11 patients who received R-CHOP before randomization, 4 were randomized to the rituximab group and 7 to the observation group.
One patient in the rituximab group relapsed and died. The other 3 were still alive and disease-free at the final analysis.
In the observation group, 4 patients had relapsed but were alive as of the final analysis, while 3 patients had died.
There were 59 patients who did not undergo randomization (due to disease progression, death, HSCT ineligibility, toxic effects, and other reasons).
For these patients, the median PFS was 11.0 months, and the median OS was 30.6 months. ![]()
*Quote has been translated from French.