User login
A Group Approach to Clinical Research Mentorship at a Veterans Affairs Medical Center
A Group Approach to Clinical Research Mentorship at a Veterans Affairs Medical Center
Supporting meaningful research that has a positive impact on the health and quality of life of veterans is a priority of the US Department of Veterans Affairs Office of Research and Development.1 For nearly a century, VA researchers have been conducting high quality studies. To continue this trajectory, it is imperative to attract, train, and retain exceptional investigators while nurturing their development throughout their careers.2
Mentorship is defined as guidance provided by an experienced and trusted party to another (usually junior) individual with the intent of helping the person succeed. It benefits the mentee, mentor, and their institutions.3 Mentorship is crucial for personal and professional development as well as productivity, which may help reduce clinician burnout.4-7 Conversely, a lack of mentorship could have negative effects on work satisfaction and stagnate career progression.8
Mentorship is vital for developing and advancing a VA investigator’s research agenda. Funding, grant writing, and research design were among the most discussed topics in a large comprehensive mentorship program for academic faculty.9 However, there are several known barriers to effective research mentorship; among them include a lack of resources, time constraints, and competing clinical priorities.10,11
Finding time for effective one-on-one research mentoring is difficult within the time constraints of clinical duties; a group mentorship model may help overcome this barrier. Group mentorship can aid in personal and professional development because no single mentor can effectively meet every mentoring need of an individual.12 Group mentorship also allows for the exchange of ideas among individuals with different backgrounds and the ability to utilize the strengths of each member of the group. For example, a member may have methodological expertise, while another may be skilled in grantsmanship. A team of mentors may be more beneficial for both the mentors (eg, establish a more manageable workload) and the mentee (eg, gains a broader perspective of expertise) when compared to having a single mentor.3
Peer mentorship within the group setting may also yield additional benefits. For example, having a supportive peer group may help reduce stress levels and burnout, while also improving overall well-being.3,13 Formal mentorship programs do not frequently discuss concerns such as work-life balance, so including peers as mentors may help fill this void.9 Peer mentorship has also been found to be beneficial in providing mentees with pooled resources and shared learning.12,13 This article describes the components, benefits, impacts, and challenges of a group research mentorship program for VA clinicians interested in conducting VA-relevant research.
Program Description
The VA Clinical Research Mentorship Program was initiated at the VA Ann Arbor Healthcare System (VAAAHS) in October 2015 by the Chief of Medicine to assist VA clinician investigators with developing and submitting VA clinical science and health services research grant applications. The program offers group and one-on-one consultation services through the expertise of 2 experienced investigators/faculty mentors who also serve as program directors, each of whom devote about 3 to 5 hours per month to activities associated with the mentorship program (eg, attending the meeting, reviewing materials sent by mentees, and one-on-one discussions with mentees).
The program also fostered peer-led mentorship. This encourages all attendees to provide feedback during group sessions and communication by mentees outside the group sessions. An experienced project manager serves as program coordinator and contributes about 4 hours per month for activities such as attending, scheduling, and sending reminders for each meeting, distributing handouts, reviewing materials, and answering mentee’s questions via email. A statistician and additional research staff (ie, an epidemiologist and research assistant) do not attend the recurring meetings, but are available for offline consultation as needed. The program runs on a 12-month cycle with regular meetings occurring twice monthly during the 9-month academic period. Resources to support the program, primarily program director(s) and project coordinator effort, are provided by the Chief of Medicine and through the VAAAHS affiliated VA Health Systems Research (formerly Health Services Research & Development) Center of Innovation.
Invitations for new mentees are sent annually. Mentees expressing interest in the program outside of its annual recruitment period are evaluated for inclusion on a rolling basis. Recruitment begins with the program coordinator sending email notifications to all VAAAHS Medicine Service faculty, section chiefs, and division chiefs at the VAAAHS academic affiliate. Recipients are encouraged to distribute the announcement to eligible applicants and refer them to the application materials for entry consideration into the program. The application consists of the applicant’s curriculum vitae and a 1-page summary that includes a description of their research area of interest, how it is relevant to the VA, in addition to an idea for a research study, its potential significance, and proposed methodology. Applicant materials are reviewed by the program coordinator and program directors. The applicants are evaluated using a simple scoring approach that focuses on the applicant’s research area and agenda, past research training, past research productivity, potential for obtaining VA funding, and whether they have sufficient research time.
Program eligibility initially required being a physician with ≥ 1/8 VA appointment from the Medicine Service. However, clinicians with clinical appointments from other VA services are also accepted for participation as needed. Applicants must have previous research experience and have a career goal to obtain external funding for conducting and publishing original research. Those who have previously served as a principal investigator on a funded VA grant proposal are not eligible as new applicants but can remain in the program as peer mentors. The number of annual applicants varies and ranges from 1 to 11; on average, about 90% of applicants receive invitations to join the program.
Sessions
The program holds recurring meetings twice monthly for 1 hour during the 9-month academic year. However, program directors are available year-round, and mentees are encouraged to communicate questions or concerns via email during nonacademic months. Prior to the COVID-19 pandemic, all meetings were held in-person. However, the group pivoted to virtual meetings and continues to utilize this format. The dedicated program coordinator is responsible for coordinating meetings and distributing meeting materials.
Each session is informal, flexible, and supportive. Attendance is not enforced, and mentees are allowed to join meetings as their schedules permit; however, program directors and program coordinator attend each meeting. In advance of each session, the program coordinator sends out a call for agenda items to all active members invited to discuss any research related items. Each mentee presents their ideas to lead the discussion for their portion of the meeting with no defined format required.
A variety of topics are covered including, but not limited to: (1) grant-specific concerns (eg, questions related to specific aim pages, grantsmanship, postsubmission comments from reviewers, or postaward logistics); (2) research procedures (eg, questions related to methodological practices or institutional review board concerns); (3) manuscript or presentation preparation; and (4) careerrelated issues. The program coordinator distributes handouts prior to meetings and mentees may record their presentations. These handouts may include, but are not limited to, specific aims pages, analytical plans, grant solicitations, and PowerPoint presentations. If a resource that can benefit the entire group is mentioned during the meeting, the program coordinator is responsible for distribution.
The program follows a group facilitated discussion format. Program directors facilitate each meeting, but input is encouraged from all attendees. This model allows for mentees to learn from the faculty mentors as well as peer mentees in a simultaneous and efficient fashion. Group discussions foster collective problem solving, peer support, and resource sharing that would not be possible through individualized mentorship. Participants have access to varied expertise during each session which reduces the need to seek specialized help elsewhere. Participants are also encouraged to contact the program directors or research staff for consultation as needed. Some one-on-one consultations have transitioned to a more sustained and ongoing mentorship relationship between a program director and mentee, but most are often brief email exchanges or a single meeting.
Participants
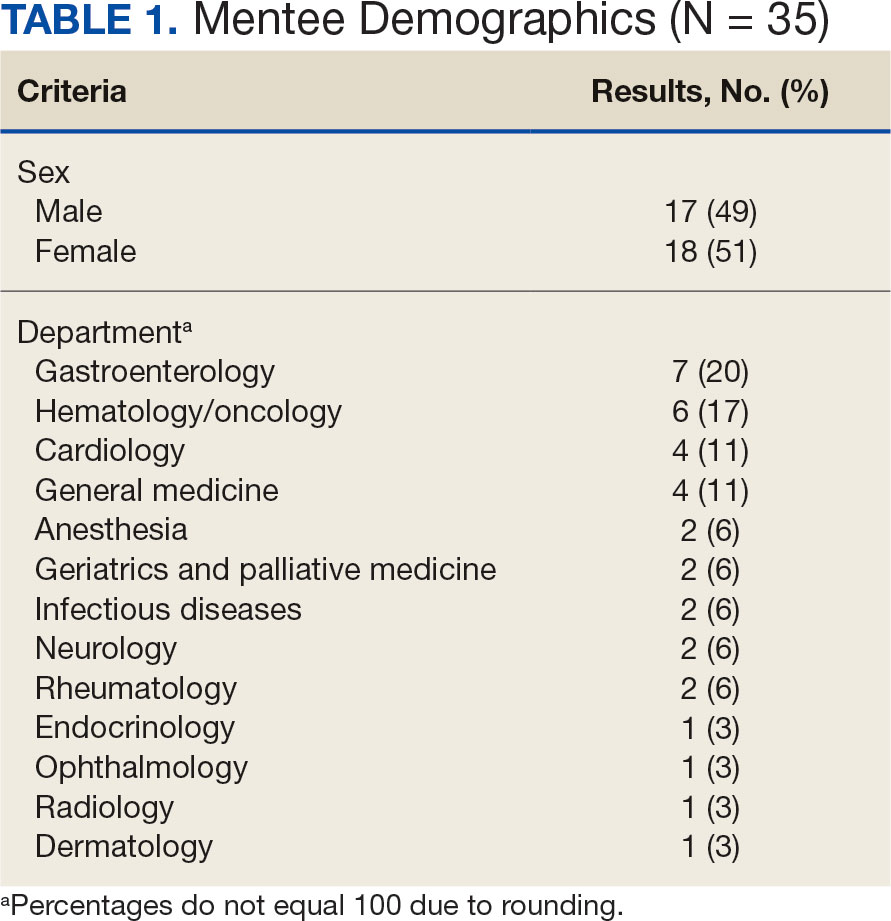
Since its inception in 2015, 35 clinicians have enrolled in the program. The mentees are equally distributed by sex and practice in a variety of disciplines including gastroenterology, hematology/oncology, cardiology, and general medicine (Table 1). Mentees have submitted 33 grant proposals addressing a variety of health care issues to a diverse group of federal and nonfederal funding agencies (Table 2). As of May 15, 2024, 19 (58%) of the submitted applications have been funded.

Many factors contribute to a successfully funded grant application, and several mentees report that participating in the mentorship program was helpful. For example, a mentee became the first lead investigator for a VA Cooperative Studies Program funded at VAAAHS. The VA Cooperative Studies Program, a division of the Office of Research and Development, plans and conducts large multicenter clinical trials and epidemiological studies within the VA via a vast network of clinician investigators, statisticians, and other key research experts.14
Several program mentees have also received VA Clinical Science Research and Development Career Development Awards. The VA Career Development program supports investigators during their early research careers with a goal of retaining talented researchers committed to improving the health and care of veterans.15
Survey Responses
Mentee productivity and updates are tracked through direct mentee input, as requested by the program coordinator. Since 2022, participants could complete an end-of-year survey based on an assessment tool used in a VAAAHS nonresearch mentorship program.16 The survey, distributed to mentees and program directors, requests feedback on logistics (eg, if the meeting was a good use of time and barriers to attendance); perceptions of effectiveness (eg, ability to discuss agenda items, helpfulness with setting and reaching research goals, and quality of mentors’ feedback); and the impact of the mentoring program on work satisfaction and clinician burnout. Respondents are also encouraged to leave open-ended qualitative feedback.
To date the survey has elicited 19 responses. Seventeen (89%) indicated that they agree or strongly agree the meetings were an effective use of their time and 11 (58%) indicated that they were able to discuss all or most of the items they wanted to during the meeting. Sixteen respondents (84%) agreed the program helped them set and achieve their research goals and 14 respondents (74%) agreed the feedback they received during the meeting was specific, actionable, and focused on how to improve their research agenda. Seventeen respondents (89%) agreed the program increased their work satisfaction, while 13 respondents (68%) felt the program reduced levels of clinician burnout.
As attendance was not mandatory, the survey asked participants how often they attended meetings during the past year. Responses were mixed: 4 (21%) respondents attended regularly (12 to 16 times per year) and 8 (42%) attended most sessions (8 to 11 times per year). Noted barriers to attendance included conflicts with patient care activities and conflicts with other high priority meetings.
Mentees also provided qualitive feedback regarding the program. They highlighted the supportive environment, valuable expertise of the mentors, and usefulness of obtaining tailored feedback from the group. “This group is an amazing resource to anyone developing a research career,” a mentee noted, adding that the program directors “fostered an incredibly supportive group where research ideas and methodology can be explored in a nonthreatening and creative environment.”
Conclusions
This mentorship program aims to help aspiring VA clinician investigators develop and submit competitive research grant applications. The addition of the program to the existing robust research environments at VAAAHS and its academic affiliate appears to have contributed to this success, with 58% of applications submitted by program mentees receiving funding.
In addition to funding success, we also found that most participants have a favorable impression of the program. Of the participants who responded to the program evaluation survey, nearly all indicated the program was an effective use of their time. The program also appeared to increase work satisfaction and reduce levels of clinician burnout. Barriers to attendance were also noted, with the most frequent being scheduling conflicts.
This program’s format includes facilitated group discussion as well as peer mentorship. This collaborative structure allows for an efficient and rich learning experience. Feedback from multiple perspectives encourages natural networking and relationship building. Incorporating the collective wisdom of the faculty mentors and peer mentees is beneficial; it not only empowers the mentees but also enriches the experience for the mentors. This program can serve as a model for other VA facilities—or non-VA academic medical centers—to enhance their research programs.
- US Department of Veterans Affairs, Office of Research and Development. Strategic priorities for VA research. Published March 10, 2021. Accessed September 17, 2024. https://www.research.va.gov/about/strategic_priorities.cfm
- US Department of Veterans Affairs, Office of Research and Development. About the Office of Research & Development. Published November 11, 2023. Accessed September 17, 2024. https://www.research.va.gov/about/default.cfm
- Chopra V, Vaughn V, Saint S. The Mentoring Guide: Helping Mentors and Mentees Succeed. Michigan Publishing Services; 2019.
- Gilster SD, Accorinti KL. Mentoring program yields staff satisfaction. Mentoring through the exchange of information across all organizational levels can help administrators retain valuable staff. Provider. 1999;25(10):99-100.
- Ramanan RA, Phillips RS, Davis RB, Silen W, Reede JY. Mentoring in medicine: keys to satisfaction. Am J Med. 2002;112(4):336-341. doi:10.1016/s0002-9343(02)01032-x
- Sambunjak D, Straus SE, Marusi' A. Mentoring in academic medicine: a systematic review. JAMA. 2006;296(9):1103-1115. doi:10.1001/jama.296.9.1103
- Sambunjak D, Straus SE, Marusi' A. A systematic review of qualitative research on the meaning and characteristics of mentoring in academic medicine. J Gen Intern Med. 2010;25(1):72-78. doi:10.1007/s11606-009-1165-8
- Jackson VA, Palepu A, Szalacha L, Caswell C, Carr PL, Inui T. “Having the right chemistry”: a qualitative study of mentoring in academic medicine. Acad Med. 2003;78(3):328-334. doi:10.1097/00001888-200303000-00020
- Feldman MD, Arean PA, Marshall SJ, Lovett M, O’Sullivan P. Does mentoring matter: results from a survey of faculty mentees at a large health sciences university. Med Educ Online. 2010;15:10.3402/meo.v15i0.5063. doi:10.3402/meo.v15i0.5063
- Leary JC, Schainker EG, Leyenaar JK. The unwritten rules of mentorship: facilitators of and barriers to effective mentorship in pediatric hospital medicine. Hosp Pediatr. 2016;6(4):219-225. doi:10.1542/hpeds.2015-0108
- Rustgi AK, Hecht GA. Mentorship in academic medicine. Gastroenterology. 2011;141(3):789-792. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2011.07.024
- DeCastro R, Sambuco D, Ubel PA, Stewart A, Jagsi R. Mentor networks in academic medicine: moving beyond a dyadic conception of mentoring for junior faculty researchers. Acad Med. 2013;88(4):488-496. doi:10.1097/ACM.0b013e318285d302
- McDaugall M, Beattie RS. Peer mentoring at work: the nature and outcomes of non-hierarchical developmental relationships. Management Learning. 2016;28(4):423-437. doi:10.1177/1350507697284003
- US Department of Veterans Affairs, Office of Rsearch and Development. VA Cooperative Studies Program (CSP). Updated July 2019. Accessed September 17, 2024. https://www.vacsp.research.va.gov
- US Department of Veterans Affairs, Office of Research and Development. Career development program for biomedical laboratory and clinical science R&D services. Published April 17, 2023. Accessed September 17, 2024. https://www.research.va.gov/services/shared_docs/career_dev.cfm
- Houchens N, Kuhn L, Ratz D, Su G, Saint S. Committed to success: a structured mentoring program for clinically-oriented physicians. Mayo Clin Pro Innov Qual Outcomes. 2024;8(4):356-363. doi:10.1016/j.mayocpiqo.2024.05.002
Supporting meaningful research that has a positive impact on the health and quality of life of veterans is a priority of the US Department of Veterans Affairs Office of Research and Development.1 For nearly a century, VA researchers have been conducting high quality studies. To continue this trajectory, it is imperative to attract, train, and retain exceptional investigators while nurturing their development throughout their careers.2
Mentorship is defined as guidance provided by an experienced and trusted party to another (usually junior) individual with the intent of helping the person succeed. It benefits the mentee, mentor, and their institutions.3 Mentorship is crucial for personal and professional development as well as productivity, which may help reduce clinician burnout.4-7 Conversely, a lack of mentorship could have negative effects on work satisfaction and stagnate career progression.8
Mentorship is vital for developing and advancing a VA investigator’s research agenda. Funding, grant writing, and research design were among the most discussed topics in a large comprehensive mentorship program for academic faculty.9 However, there are several known barriers to effective research mentorship; among them include a lack of resources, time constraints, and competing clinical priorities.10,11
Finding time for effective one-on-one research mentoring is difficult within the time constraints of clinical duties; a group mentorship model may help overcome this barrier. Group mentorship can aid in personal and professional development because no single mentor can effectively meet every mentoring need of an individual.12 Group mentorship also allows for the exchange of ideas among individuals with different backgrounds and the ability to utilize the strengths of each member of the group. For example, a member may have methodological expertise, while another may be skilled in grantsmanship. A team of mentors may be more beneficial for both the mentors (eg, establish a more manageable workload) and the mentee (eg, gains a broader perspective of expertise) when compared to having a single mentor.3
Peer mentorship within the group setting may also yield additional benefits. For example, having a supportive peer group may help reduce stress levels and burnout, while also improving overall well-being.3,13 Formal mentorship programs do not frequently discuss concerns such as work-life balance, so including peers as mentors may help fill this void.9 Peer mentorship has also been found to be beneficial in providing mentees with pooled resources and shared learning.12,13 This article describes the components, benefits, impacts, and challenges of a group research mentorship program for VA clinicians interested in conducting VA-relevant research.
Program Description
The VA Clinical Research Mentorship Program was initiated at the VA Ann Arbor Healthcare System (VAAAHS) in October 2015 by the Chief of Medicine to assist VA clinician investigators with developing and submitting VA clinical science and health services research grant applications. The program offers group and one-on-one consultation services through the expertise of 2 experienced investigators/faculty mentors who also serve as program directors, each of whom devote about 3 to 5 hours per month to activities associated with the mentorship program (eg, attending the meeting, reviewing materials sent by mentees, and one-on-one discussions with mentees).
The program also fostered peer-led mentorship. This encourages all attendees to provide feedback during group sessions and communication by mentees outside the group sessions. An experienced project manager serves as program coordinator and contributes about 4 hours per month for activities such as attending, scheduling, and sending reminders for each meeting, distributing handouts, reviewing materials, and answering mentee’s questions via email. A statistician and additional research staff (ie, an epidemiologist and research assistant) do not attend the recurring meetings, but are available for offline consultation as needed. The program runs on a 12-month cycle with regular meetings occurring twice monthly during the 9-month academic period. Resources to support the program, primarily program director(s) and project coordinator effort, are provided by the Chief of Medicine and through the VAAAHS affiliated VA Health Systems Research (formerly Health Services Research & Development) Center of Innovation.
Invitations for new mentees are sent annually. Mentees expressing interest in the program outside of its annual recruitment period are evaluated for inclusion on a rolling basis. Recruitment begins with the program coordinator sending email notifications to all VAAAHS Medicine Service faculty, section chiefs, and division chiefs at the VAAAHS academic affiliate. Recipients are encouraged to distribute the announcement to eligible applicants and refer them to the application materials for entry consideration into the program. The application consists of the applicant’s curriculum vitae and a 1-page summary that includes a description of their research area of interest, how it is relevant to the VA, in addition to an idea for a research study, its potential significance, and proposed methodology. Applicant materials are reviewed by the program coordinator and program directors. The applicants are evaluated using a simple scoring approach that focuses on the applicant’s research area and agenda, past research training, past research productivity, potential for obtaining VA funding, and whether they have sufficient research time.
Program eligibility initially required being a physician with ≥ 1/8 VA appointment from the Medicine Service. However, clinicians with clinical appointments from other VA services are also accepted for participation as needed. Applicants must have previous research experience and have a career goal to obtain external funding for conducting and publishing original research. Those who have previously served as a principal investigator on a funded VA grant proposal are not eligible as new applicants but can remain in the program as peer mentors. The number of annual applicants varies and ranges from 1 to 11; on average, about 90% of applicants receive invitations to join the program.
Sessions
The program holds recurring meetings twice monthly for 1 hour during the 9-month academic year. However, program directors are available year-round, and mentees are encouraged to communicate questions or concerns via email during nonacademic months. Prior to the COVID-19 pandemic, all meetings were held in-person. However, the group pivoted to virtual meetings and continues to utilize this format. The dedicated program coordinator is responsible for coordinating meetings and distributing meeting materials.
Each session is informal, flexible, and supportive. Attendance is not enforced, and mentees are allowed to join meetings as their schedules permit; however, program directors and program coordinator attend each meeting. In advance of each session, the program coordinator sends out a call for agenda items to all active members invited to discuss any research related items. Each mentee presents their ideas to lead the discussion for their portion of the meeting with no defined format required.
A variety of topics are covered including, but not limited to: (1) grant-specific concerns (eg, questions related to specific aim pages, grantsmanship, postsubmission comments from reviewers, or postaward logistics); (2) research procedures (eg, questions related to methodological practices or institutional review board concerns); (3) manuscript or presentation preparation; and (4) careerrelated issues. The program coordinator distributes handouts prior to meetings and mentees may record their presentations. These handouts may include, but are not limited to, specific aims pages, analytical plans, grant solicitations, and PowerPoint presentations. If a resource that can benefit the entire group is mentioned during the meeting, the program coordinator is responsible for distribution.
The program follows a group facilitated discussion format. Program directors facilitate each meeting, but input is encouraged from all attendees. This model allows for mentees to learn from the faculty mentors as well as peer mentees in a simultaneous and efficient fashion. Group discussions foster collective problem solving, peer support, and resource sharing that would not be possible through individualized mentorship. Participants have access to varied expertise during each session which reduces the need to seek specialized help elsewhere. Participants are also encouraged to contact the program directors or research staff for consultation as needed. Some one-on-one consultations have transitioned to a more sustained and ongoing mentorship relationship between a program director and mentee, but most are often brief email exchanges or a single meeting.

Participants
Since its inception in 2015, 35 clinicians have enrolled in the program. The mentees are equally distributed by sex and practice in a variety of disciplines including gastroenterology, hematology/oncology, cardiology, and general medicine (Table 1). Mentees have submitted 33 grant proposals addressing a variety of health care issues to a diverse group of federal and nonfederal funding agencies (Table 2). As of May 15, 2024, 19 (58%) of the submitted applications have been funded.

Many factors contribute to a successfully funded grant application, and several mentees report that participating in the mentorship program was helpful. For example, a mentee became the first lead investigator for a VA Cooperative Studies Program funded at VAAAHS. The VA Cooperative Studies Program, a division of the Office of Research and Development, plans and conducts large multicenter clinical trials and epidemiological studies within the VA via a vast network of clinician investigators, statisticians, and other key research experts.14
Several program mentees have also received VA Clinical Science Research and Development Career Development Awards. The VA Career Development program supports investigators during their early research careers with a goal of retaining talented researchers committed to improving the health and care of veterans.15
Survey Responses
Mentee productivity and updates are tracked through direct mentee input, as requested by the program coordinator. Since 2022, participants could complete an end-of-year survey based on an assessment tool used in a VAAAHS nonresearch mentorship program.16 The survey, distributed to mentees and program directors, requests feedback on logistics (eg, if the meeting was a good use of time and barriers to attendance); perceptions of effectiveness (eg, ability to discuss agenda items, helpfulness with setting and reaching research goals, and quality of mentors’ feedback); and the impact of the mentoring program on work satisfaction and clinician burnout. Respondents are also encouraged to leave open-ended qualitative feedback.
To date the survey has elicited 19 responses. Seventeen (89%) indicated that they agree or strongly agree the meetings were an effective use of their time and 11 (58%) indicated that they were able to discuss all or most of the items they wanted to during the meeting. Sixteen respondents (84%) agreed the program helped them set and achieve their research goals and 14 respondents (74%) agreed the feedback they received during the meeting was specific, actionable, and focused on how to improve their research agenda. Seventeen respondents (89%) agreed the program increased their work satisfaction, while 13 respondents (68%) felt the program reduced levels of clinician burnout.
As attendance was not mandatory, the survey asked participants how often they attended meetings during the past year. Responses were mixed: 4 (21%) respondents attended regularly (12 to 16 times per year) and 8 (42%) attended most sessions (8 to 11 times per year). Noted barriers to attendance included conflicts with patient care activities and conflicts with other high priority meetings.
Mentees also provided qualitive feedback regarding the program. They highlighted the supportive environment, valuable expertise of the mentors, and usefulness of obtaining tailored feedback from the group. “This group is an amazing resource to anyone developing a research career,” a mentee noted, adding that the program directors “fostered an incredibly supportive group where research ideas and methodology can be explored in a nonthreatening and creative environment.”
Conclusions
This mentorship program aims to help aspiring VA clinician investigators develop and submit competitive research grant applications. The addition of the program to the existing robust research environments at VAAAHS and its academic affiliate appears to have contributed to this success, with 58% of applications submitted by program mentees receiving funding.
In addition to funding success, we also found that most participants have a favorable impression of the program. Of the participants who responded to the program evaluation survey, nearly all indicated the program was an effective use of their time. The program also appeared to increase work satisfaction and reduce levels of clinician burnout. Barriers to attendance were also noted, with the most frequent being scheduling conflicts.
This program’s format includes facilitated group discussion as well as peer mentorship. This collaborative structure allows for an efficient and rich learning experience. Feedback from multiple perspectives encourages natural networking and relationship building. Incorporating the collective wisdom of the faculty mentors and peer mentees is beneficial; it not only empowers the mentees but also enriches the experience for the mentors. This program can serve as a model for other VA facilities—or non-VA academic medical centers—to enhance their research programs.
Supporting meaningful research that has a positive impact on the health and quality of life of veterans is a priority of the US Department of Veterans Affairs Office of Research and Development.1 For nearly a century, VA researchers have been conducting high quality studies. To continue this trajectory, it is imperative to attract, train, and retain exceptional investigators while nurturing their development throughout their careers.2
Mentorship is defined as guidance provided by an experienced and trusted party to another (usually junior) individual with the intent of helping the person succeed. It benefits the mentee, mentor, and their institutions.3 Mentorship is crucial for personal and professional development as well as productivity, which may help reduce clinician burnout.4-7 Conversely, a lack of mentorship could have negative effects on work satisfaction and stagnate career progression.8
Mentorship is vital for developing and advancing a VA investigator’s research agenda. Funding, grant writing, and research design were among the most discussed topics in a large comprehensive mentorship program for academic faculty.9 However, there are several known barriers to effective research mentorship; among them include a lack of resources, time constraints, and competing clinical priorities.10,11
Finding time for effective one-on-one research mentoring is difficult within the time constraints of clinical duties; a group mentorship model may help overcome this barrier. Group mentorship can aid in personal and professional development because no single mentor can effectively meet every mentoring need of an individual.12 Group mentorship also allows for the exchange of ideas among individuals with different backgrounds and the ability to utilize the strengths of each member of the group. For example, a member may have methodological expertise, while another may be skilled in grantsmanship. A team of mentors may be more beneficial for both the mentors (eg, establish a more manageable workload) and the mentee (eg, gains a broader perspective of expertise) when compared to having a single mentor.3
Peer mentorship within the group setting may also yield additional benefits. For example, having a supportive peer group may help reduce stress levels and burnout, while also improving overall well-being.3,13 Formal mentorship programs do not frequently discuss concerns such as work-life balance, so including peers as mentors may help fill this void.9 Peer mentorship has also been found to be beneficial in providing mentees with pooled resources and shared learning.12,13 This article describes the components, benefits, impacts, and challenges of a group research mentorship program for VA clinicians interested in conducting VA-relevant research.
Program Description
The VA Clinical Research Mentorship Program was initiated at the VA Ann Arbor Healthcare System (VAAAHS) in October 2015 by the Chief of Medicine to assist VA clinician investigators with developing and submitting VA clinical science and health services research grant applications. The program offers group and one-on-one consultation services through the expertise of 2 experienced investigators/faculty mentors who also serve as program directors, each of whom devote about 3 to 5 hours per month to activities associated with the mentorship program (eg, attending the meeting, reviewing materials sent by mentees, and one-on-one discussions with mentees).
The program also fostered peer-led mentorship. This encourages all attendees to provide feedback during group sessions and communication by mentees outside the group sessions. An experienced project manager serves as program coordinator and contributes about 4 hours per month for activities such as attending, scheduling, and sending reminders for each meeting, distributing handouts, reviewing materials, and answering mentee’s questions via email. A statistician and additional research staff (ie, an epidemiologist and research assistant) do not attend the recurring meetings, but are available for offline consultation as needed. The program runs on a 12-month cycle with regular meetings occurring twice monthly during the 9-month academic period. Resources to support the program, primarily program director(s) and project coordinator effort, are provided by the Chief of Medicine and through the VAAAHS affiliated VA Health Systems Research (formerly Health Services Research & Development) Center of Innovation.
Invitations for new mentees are sent annually. Mentees expressing interest in the program outside of its annual recruitment period are evaluated for inclusion on a rolling basis. Recruitment begins with the program coordinator sending email notifications to all VAAAHS Medicine Service faculty, section chiefs, and division chiefs at the VAAAHS academic affiliate. Recipients are encouraged to distribute the announcement to eligible applicants and refer them to the application materials for entry consideration into the program. The application consists of the applicant’s curriculum vitae and a 1-page summary that includes a description of their research area of interest, how it is relevant to the VA, in addition to an idea for a research study, its potential significance, and proposed methodology. Applicant materials are reviewed by the program coordinator and program directors. The applicants are evaluated using a simple scoring approach that focuses on the applicant’s research area and agenda, past research training, past research productivity, potential for obtaining VA funding, and whether they have sufficient research time.
Program eligibility initially required being a physician with ≥ 1/8 VA appointment from the Medicine Service. However, clinicians with clinical appointments from other VA services are also accepted for participation as needed. Applicants must have previous research experience and have a career goal to obtain external funding for conducting and publishing original research. Those who have previously served as a principal investigator on a funded VA grant proposal are not eligible as new applicants but can remain in the program as peer mentors. The number of annual applicants varies and ranges from 1 to 11; on average, about 90% of applicants receive invitations to join the program.
Sessions
The program holds recurring meetings twice monthly for 1 hour during the 9-month academic year. However, program directors are available year-round, and mentees are encouraged to communicate questions or concerns via email during nonacademic months. Prior to the COVID-19 pandemic, all meetings were held in-person. However, the group pivoted to virtual meetings and continues to utilize this format. The dedicated program coordinator is responsible for coordinating meetings and distributing meeting materials.
Each session is informal, flexible, and supportive. Attendance is not enforced, and mentees are allowed to join meetings as their schedules permit; however, program directors and program coordinator attend each meeting. In advance of each session, the program coordinator sends out a call for agenda items to all active members invited to discuss any research related items. Each mentee presents their ideas to lead the discussion for their portion of the meeting with no defined format required.
A variety of topics are covered including, but not limited to: (1) grant-specific concerns (eg, questions related to specific aim pages, grantsmanship, postsubmission comments from reviewers, or postaward logistics); (2) research procedures (eg, questions related to methodological practices or institutional review board concerns); (3) manuscript or presentation preparation; and (4) careerrelated issues. The program coordinator distributes handouts prior to meetings and mentees may record their presentations. These handouts may include, but are not limited to, specific aims pages, analytical plans, grant solicitations, and PowerPoint presentations. If a resource that can benefit the entire group is mentioned during the meeting, the program coordinator is responsible for distribution.
The program follows a group facilitated discussion format. Program directors facilitate each meeting, but input is encouraged from all attendees. This model allows for mentees to learn from the faculty mentors as well as peer mentees in a simultaneous and efficient fashion. Group discussions foster collective problem solving, peer support, and resource sharing that would not be possible through individualized mentorship. Participants have access to varied expertise during each session which reduces the need to seek specialized help elsewhere. Participants are also encouraged to contact the program directors or research staff for consultation as needed. Some one-on-one consultations have transitioned to a more sustained and ongoing mentorship relationship between a program director and mentee, but most are often brief email exchanges or a single meeting.

Participants
Since its inception in 2015, 35 clinicians have enrolled in the program. The mentees are equally distributed by sex and practice in a variety of disciplines including gastroenterology, hematology/oncology, cardiology, and general medicine (Table 1). Mentees have submitted 33 grant proposals addressing a variety of health care issues to a diverse group of federal and nonfederal funding agencies (Table 2). As of May 15, 2024, 19 (58%) of the submitted applications have been funded.

Many factors contribute to a successfully funded grant application, and several mentees report that participating in the mentorship program was helpful. For example, a mentee became the first lead investigator for a VA Cooperative Studies Program funded at VAAAHS. The VA Cooperative Studies Program, a division of the Office of Research and Development, plans and conducts large multicenter clinical trials and epidemiological studies within the VA via a vast network of clinician investigators, statisticians, and other key research experts.14
Several program mentees have also received VA Clinical Science Research and Development Career Development Awards. The VA Career Development program supports investigators during their early research careers with a goal of retaining talented researchers committed to improving the health and care of veterans.15
Survey Responses
Mentee productivity and updates are tracked through direct mentee input, as requested by the program coordinator. Since 2022, participants could complete an end-of-year survey based on an assessment tool used in a VAAAHS nonresearch mentorship program.16 The survey, distributed to mentees and program directors, requests feedback on logistics (eg, if the meeting was a good use of time and barriers to attendance); perceptions of effectiveness (eg, ability to discuss agenda items, helpfulness with setting and reaching research goals, and quality of mentors’ feedback); and the impact of the mentoring program on work satisfaction and clinician burnout. Respondents are also encouraged to leave open-ended qualitative feedback.
To date the survey has elicited 19 responses. Seventeen (89%) indicated that they agree or strongly agree the meetings were an effective use of their time and 11 (58%) indicated that they were able to discuss all or most of the items they wanted to during the meeting. Sixteen respondents (84%) agreed the program helped them set and achieve their research goals and 14 respondents (74%) agreed the feedback they received during the meeting was specific, actionable, and focused on how to improve their research agenda. Seventeen respondents (89%) agreed the program increased their work satisfaction, while 13 respondents (68%) felt the program reduced levels of clinician burnout.
As attendance was not mandatory, the survey asked participants how often they attended meetings during the past year. Responses were mixed: 4 (21%) respondents attended regularly (12 to 16 times per year) and 8 (42%) attended most sessions (8 to 11 times per year). Noted barriers to attendance included conflicts with patient care activities and conflicts with other high priority meetings.
Mentees also provided qualitive feedback regarding the program. They highlighted the supportive environment, valuable expertise of the mentors, and usefulness of obtaining tailored feedback from the group. “This group is an amazing resource to anyone developing a research career,” a mentee noted, adding that the program directors “fostered an incredibly supportive group where research ideas and methodology can be explored in a nonthreatening and creative environment.”
Conclusions
This mentorship program aims to help aspiring VA clinician investigators develop and submit competitive research grant applications. The addition of the program to the existing robust research environments at VAAAHS and its academic affiliate appears to have contributed to this success, with 58% of applications submitted by program mentees receiving funding.
In addition to funding success, we also found that most participants have a favorable impression of the program. Of the participants who responded to the program evaluation survey, nearly all indicated the program was an effective use of their time. The program also appeared to increase work satisfaction and reduce levels of clinician burnout. Barriers to attendance were also noted, with the most frequent being scheduling conflicts.
This program’s format includes facilitated group discussion as well as peer mentorship. This collaborative structure allows for an efficient and rich learning experience. Feedback from multiple perspectives encourages natural networking and relationship building. Incorporating the collective wisdom of the faculty mentors and peer mentees is beneficial; it not only empowers the mentees but also enriches the experience for the mentors. This program can serve as a model for other VA facilities—or non-VA academic medical centers—to enhance their research programs.
- US Department of Veterans Affairs, Office of Research and Development. Strategic priorities for VA research. Published March 10, 2021. Accessed September 17, 2024. https://www.research.va.gov/about/strategic_priorities.cfm
- US Department of Veterans Affairs, Office of Research and Development. About the Office of Research & Development. Published November 11, 2023. Accessed September 17, 2024. https://www.research.va.gov/about/default.cfm
- Chopra V, Vaughn V, Saint S. The Mentoring Guide: Helping Mentors and Mentees Succeed. Michigan Publishing Services; 2019.
- Gilster SD, Accorinti KL. Mentoring program yields staff satisfaction. Mentoring through the exchange of information across all organizational levels can help administrators retain valuable staff. Provider. 1999;25(10):99-100.
- Ramanan RA, Phillips RS, Davis RB, Silen W, Reede JY. Mentoring in medicine: keys to satisfaction. Am J Med. 2002;112(4):336-341. doi:10.1016/s0002-9343(02)01032-x
- Sambunjak D, Straus SE, Marusi' A. Mentoring in academic medicine: a systematic review. JAMA. 2006;296(9):1103-1115. doi:10.1001/jama.296.9.1103
- Sambunjak D, Straus SE, Marusi' A. A systematic review of qualitative research on the meaning and characteristics of mentoring in academic medicine. J Gen Intern Med. 2010;25(1):72-78. doi:10.1007/s11606-009-1165-8
- Jackson VA, Palepu A, Szalacha L, Caswell C, Carr PL, Inui T. “Having the right chemistry”: a qualitative study of mentoring in academic medicine. Acad Med. 2003;78(3):328-334. doi:10.1097/00001888-200303000-00020
- Feldman MD, Arean PA, Marshall SJ, Lovett M, O’Sullivan P. Does mentoring matter: results from a survey of faculty mentees at a large health sciences university. Med Educ Online. 2010;15:10.3402/meo.v15i0.5063. doi:10.3402/meo.v15i0.5063
- Leary JC, Schainker EG, Leyenaar JK. The unwritten rules of mentorship: facilitators of and barriers to effective mentorship in pediatric hospital medicine. Hosp Pediatr. 2016;6(4):219-225. doi:10.1542/hpeds.2015-0108
- Rustgi AK, Hecht GA. Mentorship in academic medicine. Gastroenterology. 2011;141(3):789-792. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2011.07.024
- DeCastro R, Sambuco D, Ubel PA, Stewart A, Jagsi R. Mentor networks in academic medicine: moving beyond a dyadic conception of mentoring for junior faculty researchers. Acad Med. 2013;88(4):488-496. doi:10.1097/ACM.0b013e318285d302
- McDaugall M, Beattie RS. Peer mentoring at work: the nature and outcomes of non-hierarchical developmental relationships. Management Learning. 2016;28(4):423-437. doi:10.1177/1350507697284003
- US Department of Veterans Affairs, Office of Rsearch and Development. VA Cooperative Studies Program (CSP). Updated July 2019. Accessed September 17, 2024. https://www.vacsp.research.va.gov
- US Department of Veterans Affairs, Office of Research and Development. Career development program for biomedical laboratory and clinical science R&D services. Published April 17, 2023. Accessed September 17, 2024. https://www.research.va.gov/services/shared_docs/career_dev.cfm
- Houchens N, Kuhn L, Ratz D, Su G, Saint S. Committed to success: a structured mentoring program for clinically-oriented physicians. Mayo Clin Pro Innov Qual Outcomes. 2024;8(4):356-363. doi:10.1016/j.mayocpiqo.2024.05.002
- US Department of Veterans Affairs, Office of Research and Development. Strategic priorities for VA research. Published March 10, 2021. Accessed September 17, 2024. https://www.research.va.gov/about/strategic_priorities.cfm
- US Department of Veterans Affairs, Office of Research and Development. About the Office of Research & Development. Published November 11, 2023. Accessed September 17, 2024. https://www.research.va.gov/about/default.cfm
- Chopra V, Vaughn V, Saint S. The Mentoring Guide: Helping Mentors and Mentees Succeed. Michigan Publishing Services; 2019.
- Gilster SD, Accorinti KL. Mentoring program yields staff satisfaction. Mentoring through the exchange of information across all organizational levels can help administrators retain valuable staff. Provider. 1999;25(10):99-100.
- Ramanan RA, Phillips RS, Davis RB, Silen W, Reede JY. Mentoring in medicine: keys to satisfaction. Am J Med. 2002;112(4):336-341. doi:10.1016/s0002-9343(02)01032-x
- Sambunjak D, Straus SE, Marusi' A. Mentoring in academic medicine: a systematic review. JAMA. 2006;296(9):1103-1115. doi:10.1001/jama.296.9.1103
- Sambunjak D, Straus SE, Marusi' A. A systematic review of qualitative research on the meaning and characteristics of mentoring in academic medicine. J Gen Intern Med. 2010;25(1):72-78. doi:10.1007/s11606-009-1165-8
- Jackson VA, Palepu A, Szalacha L, Caswell C, Carr PL, Inui T. “Having the right chemistry”: a qualitative study of mentoring in academic medicine. Acad Med. 2003;78(3):328-334. doi:10.1097/00001888-200303000-00020
- Feldman MD, Arean PA, Marshall SJ, Lovett M, O’Sullivan P. Does mentoring matter: results from a survey of faculty mentees at a large health sciences university. Med Educ Online. 2010;15:10.3402/meo.v15i0.5063. doi:10.3402/meo.v15i0.5063
- Leary JC, Schainker EG, Leyenaar JK. The unwritten rules of mentorship: facilitators of and barriers to effective mentorship in pediatric hospital medicine. Hosp Pediatr. 2016;6(4):219-225. doi:10.1542/hpeds.2015-0108
- Rustgi AK, Hecht GA. Mentorship in academic medicine. Gastroenterology. 2011;141(3):789-792. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2011.07.024
- DeCastro R, Sambuco D, Ubel PA, Stewart A, Jagsi R. Mentor networks in academic medicine: moving beyond a dyadic conception of mentoring for junior faculty researchers. Acad Med. 2013;88(4):488-496. doi:10.1097/ACM.0b013e318285d302
- McDaugall M, Beattie RS. Peer mentoring at work: the nature and outcomes of non-hierarchical developmental relationships. Management Learning. 2016;28(4):423-437. doi:10.1177/1350507697284003
- US Department of Veterans Affairs, Office of Rsearch and Development. VA Cooperative Studies Program (CSP). Updated July 2019. Accessed September 17, 2024. https://www.vacsp.research.va.gov
- US Department of Veterans Affairs, Office of Research and Development. Career development program for biomedical laboratory and clinical science R&D services. Published April 17, 2023. Accessed September 17, 2024. https://www.research.va.gov/services/shared_docs/career_dev.cfm
- Houchens N, Kuhn L, Ratz D, Su G, Saint S. Committed to success: a structured mentoring program for clinically-oriented physicians. Mayo Clin Pro Innov Qual Outcomes. 2024;8(4):356-363. doi:10.1016/j.mayocpiqo.2024.05.002
A Group Approach to Clinical Research Mentorship at a Veterans Affairs Medical Center
A Group Approach to Clinical Research Mentorship at a Veterans Affairs Medical Center
Relationship between Hospital 30-Day Mortality Rates for Heart Failure and Patterns of Early Inpatient Comfort Care
In an effort to improve the quality of care delivered to heart failure (HF) patients, the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) publish hospitals’ 30-day risk-standardized mortality rates (RSMRs) for HF.1 These mortality rates are also used by CMS to determine the financial penalties and bonuses that hospitals receive as part of the national Hospital Value-based Purchasing program.2 Whether or not these efforts effectively direct patients towards high-quality providers or motivate hospitals to provide better care, few would disagree with the overarching goal of decreasing the number of patients who die from HF.
However, for some patients with chronic disease at the end of life, goals of care may change. The quality of days lived may become more important than the quantity of days lived. As a consequence, high-quality care for some patients at the end of life is associated with withdrawing life-sustaining or life-extending therapies. Over time, this therapeutic perspective has become more common, with use of hospice care doubling from 23% to 47% between 2000 and 2012 among Medicare beneficiaries who died.3 For a national cohort of older patients admitted with HF—not just those patients who died in that same year—hospitals’ rates of referral to hospice are considerably lower, averaging 2.9% in 2010 in a national study.4 Nevertheless, it is possible that hospitals that more faithfully follow their dying patients’ wishes and withdraw life-prolonging interventions and provide comfort-focused care at the end of life might be unfairly penalized if such efforts resulted in higher mortality rates than other hospitals.
Therefore, we used Medicare data linked to a national HF registry with information about end-of-life care, to address 3 questions: (1) How much do hospitals vary in their rates of early comfort care and how has this changed over time; (2) What hospital and patient factors are associated with higher early comfort care rates; and (3) Is there a correlation between 30-day risk-adjusted mortality rates for HF with hospital rates of early comfort care?
METHODS
Data Sources
We used data from the American Heart Association’s Get With The Guidelines-Heart Failure (GWTG-HF) registry. GWTG-HF is a voluntary, inpatient, quality improvement registry5-7 that uses web-based tools and standard questionnaires to collect data on patients with HF admitted to participating hospitals nationwide. The data include information from admission (eg, sociodemographic characteristics, symptoms, medical history, and initial laboratory and test results), the inpatient stay (eg, therapies), and discharge (eg, discharge destination, whether and when comfort care was initiated). We linked the GWTG-HF registry data to Medicare claims data in order to obtain information about Medicare eligibility and patient comorbidities. Additionally, we used data from the American Hospital Association (2008) for hospital characteristics. Quintiles Real-World & Late Phase Research (Cambridge, MA) serves as the data coordinating center for GWTG-HF and the Duke Clinical Research Institute (Durham, NC) serves as the statistical analytic center. GWTG-HF participating sites have a waiver of informed consent because the data are de-identified and primarily used for quality improvement. All analyses performed on this data have been approved by the Duke Medical Center Institutional Review Board.
Study Population
Study Outcomes
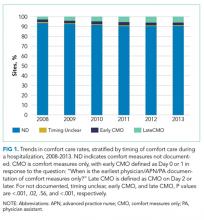
Our outcome of interest was the correlation between a hospital’s rate of initiating early CMO for admitted HF patients and a hospital’s 30-day RSMR for HF. The GWTG-HF questionnaire8 asks “When is the earliest physician/advanced practice nurse/physician assistant documentation of comfort measures only?” and permits 4 responses: day 0 or 1, day 2 or after, timing unclear, or not documented/unable to determine. We defined early CMO as CMO on day 0 or 1, and late/no CMO as any other response. We chose to examine early comfort care because many hospitalized patients transition to comfort care before they die if the death is in any way predictable. Thus, if comfort care is measured at any time during the hospitalization, hospitals that have high mortality rates are likely to have high comfort care rates. Therefore, we chose to use the more precise measure of early comfort care. We created hospital-level, risk-standardized early comfort care rates using the same risk-adjustment model used for RSMRs but with the outcome of early comfort care instead of mortality.9,10
RSMRs were calculated using a validated GWTG-HF 30-day risk-standardized mortality model9 with additional variables identified from other GWTG-HF analyses.10 The 30 days are measured as the 30 days after the index admission date.
Statistical Analyses
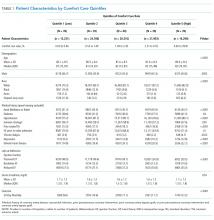
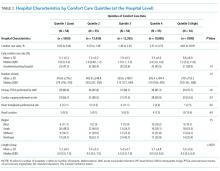
We described trends in early comfort care rates over time, from February 17, 2008, to February 17, 2014, using the Cochran-Armitage test for trend. We then grouped hospitals into quintiles based on their unadjusted early comfort care rates. We described patient and hospital characteristics for each quintile, using χ2 tests to test for differences across quintiles for categorical variables and Wilcoxon rank sum tests to assess for differences across quintiles for continuous variables. We then examined the Spearman’s rank correlation between hospitals’ RSMR and risk-adjusted comfort care rates. Finally, we compared hospital-level RSMRs before and after adjusting for early comfort care.
We performed risk-adjustment for these last 2 analyses as follows. For each patient, covariates were obtained from the GWTG-HF registry. Clinical data captured for the index admission were utilized in the risk-adjustment model (for both RSMRs and risk-adjusted comfort care rates). Included covariates were as follows: age (per 10 years); race (black vs non-black); systolic blood pressure at admission ≤170 (per 10 mm Hg); respiratory rate (per 5 respirations/min); heart rate ≤105 (per 10 beats/min); weight ≤100 (per 5 kg); weight >100 (per 5 kg); blood urea nitrogen (per 10 mg/dl); brain natriuretic peptide ≤2000 (per 500 pg/ml); hemoglobin 10-14 (per 1 g/dl); troponin abnormal (vs normal); creatinine ≤1 (per 1 mg/dl); sodium 130-140 (per 5 mEq/l); and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease or asthma.
Hierarchical logistic regression modeling was used to calculate the hospital-specific RSMR. A predicted/expected ratio similar to an observed/expected (O/E) ratio was calculated using the following modifications: (1) instead of the observed (crude) number of deaths, the numerator is the number of deaths predicted by the hierarchical model among a hospital’s patients given the patients’ risk factors and the hospital-specific effect; (2) the denominator is the expected number of deaths among the hospital’s patients given the patients’ risk factors and the average of all hospital-specific effects overall; and (3) the ratio of the numerator and denominator are then multiplied by the observed overall mortality rate (same as O/E). This calculation is the method used by CMS to derive RSMRs.11 Multiple imputation was used to handle missing data in the models; 25 imputed datasets using the fully conditional specification method were created. Patients with missing prior comorbidities were assumed to not have those conditions. Hospital characteristics were not imputed; therefore, for analyses that required construction of risk-adjusted comfort care rates or RSMRs, we excluded 18,867 patients cared for at 82 hospitals missing hospital characteristics. We ran 2 sets of models for risk-adjusted comfort care rates and RSMRs: the first adjusted only for patient characteristics, and the second adjusted for both patient and hospital characteristics. Results from the 2 models were similar, so we present only results from the latter. Variance inflation factors were all <2, indicating the collinearity between covariates was not an issue.
All statistical analyses were performed by using SAS version 9.4 (SAS Institute, Cary, NC). We tested for statistical significance by using 2-tailed tests and considered P values <.05 to be statistically significant.
RESULTS
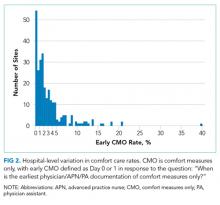
Of the 272 hospitals included in our final study cohort, the observed median overall rate of early comfort care in this study was 1.9% (25th to 75th percentile: 0.9% to 4.0%); hospitals varied widely in unadjusted early comfort care rates (0.00% to 0.46% in the lowest quintile, and 4.60% to 39.91% in the highest quintile; Table 1).
DISCUSSION
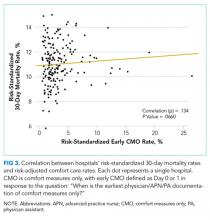
Among a national sample of US hospitals, we found wide variation in how frequently health care providers deliver comfort care within the first 2 days of admission for HF. A minority of hospitals reported no early comfort care on any patients throughout the 6-year study period, but hospitals in the highest quintile initiated early comfort care rates for at least 1 in 20 HF patients. Hospitals that were more likely to initiate early comfort care had a higher proportion of female and white patients and were less likely to have the capacity to deliver aggressive surgical interventions such as heart transplants. Hospital-level 30-day RSMRs were not correlated with rates of early comfort care.
While the appropriate rate of early comfort care for patients hospitalized with HF is unknown, given that the average hospital RSMR is approximately 12% for fee-for-service Medicare patients hospitalized with HF,12 it is surprising that some hospitals initiated early comfort care on none or very few of their HF patients. It is quite possible that many of these hospitals initiated comfort care for some of their patients after 48 hours of hospitalization. We were unable to estimate the average period of time patients received comfort care prior to dying, the degree to which this varies across hospitals or why it might vary, and whether the length of time between comfort care initiation and death is related to satisfaction with end-of-life care. Future research on these topics would help inform providers seeking to deliver better end-of-life care. In this study, we also were unable to estimate how often early comfort care was not initiated because patients had a good prognosis. However, prior studies have suggested low rates of comfort care or hospice referral even among patients at very high estimated mortality risk.4 It is also possible that providers and families had concerns about the ability to accurately prognosticate, although several models have been shown to perform acceptably for patients hospitalized with HF.13
We found that comfort care rates did not increase over time, even though use of hospice care doubled among Medicare beneficiaries between 2000 and 2012. By way of context, cancer—the second leading cause of death in the US—was responsible for 38% of hospice admissions in 2013, whereas heart disease (including but not limited to HF)—the leading cause of death— was responsible for 13% of hospice admissions.14 The 2013 American College of Cardiology Foundation and the American Heart Association guidelines for HF recommend consideration of hospice or palliative care for inpatient and transitional care.15 In future work, it would be important to better understand the drivers behind decisions around comfort care for patients hospitalized with HF.
With regards to the policy implications of our study, we found that on average, adjusting 30-day mortality rates for early comfort care was not associated with a change in hospital mortality rankings. For those hospitals with high comfort care rates, adjusting for comfort care did lower mortality rates, but the change was so small as to be clinically insignificant. CMS’ RSMR for HF excludes patients enrolled in hospice during the 12 months prior to index admission, including the first day of the index admission, acknowledging that death may not be an untoward outcome for such patients.16 Fee-for-service Medicare beneficiaries excluded for hospice enrollment comprised 1.29% of HF admissions from July 2012 to June 201516 and are likely a subset of early comfort care patients in our sample, both because of the inclusiveness of chart review (vs claims-based identification) and because we defined early comfort care as comfort care initiated on day 0 or 1 of hospitalization. Nevertheless, with our data we cannot assess to what degree our findings were due solely to hospice patients excluded from CMS’ current estimates.
Prior research has described the underuse of palliative care among patients with HF17 and the association of palliative care with better patient and family experiences at the end of life.18-20 We add to this literature by describing the epidemiology—prevalence, changes over time, and associated factors—of early comfort care for HF in a national sample of hospitals. This serves as a baseline for future work on end-of-life care among patients hospitalized for HF. Our findings also contribute to ongoing discussion about how best to risk-adjust mortality metrics used to assess hospital quality in pay-for-performance programs. Recent research on stroke and pneumonia based on California data suggests that not accounting for do-not-resuscitate (DNR) status biases hospital mortality rates.21,22 Earlier research examined the impact of adjusting hospital mortality rates for DNR for a broader range of conditions.23,24 We expand this line of inquiry by examining the hospital-level association of early comfort care with mortality rates for HF, utilizing a national, contemporary cohort of inpatient stays. In addition, while studies have found that DNR rates within the first 24 hours of admission are relatively high (median 15.8% for pneumonia; 13.3% for stroke),21,22 comfort care is distinct from DNR.
Our findings should be interpreted in the context of several potential limitations. First, we did not have any information about patient or family wishes regarding end-of-life care, or the exact timing of early comfort care (eg, day 0 or day 1). The initiation of comfort care usually follows conversations about end-of-life care involving a patient, his or her family, and the medical team. Thus, we do not know if low early comfort care rates represent the lack of such a conversation (and thus poor-quality care) or the desire by most patients not to initiate early comfort care (and thus high-quality care). This would be an important area for future research. Second, we included only patients admitted to hospitals that participate in GWTG-HF, a voluntary quality improvement initiative. This may limit the generalizability of our findings, but it is unclear how our sample might bias our findings. Hospitals engaged in quality improvement may be more likely to initiate early comfort care aligned with patients’ wishes; on the other hand, hospitals with advanced surgical capabilities are over-represented in our sample and these hospitals are less likely to initiate early comfort care. Third, we examined associations and cannot make conclusions about causality. Residual measured and unmeasured confounding may influence these findings.
In summary, we found that early comfort care rates for fee-for-service Medicare beneficiaries admitted for HF varies widely among hospitals, but median rates of early comfort care have not changed over time. On average, there was no correlation between hospital-level, 30-day, RSMRs and rates of early comfort care. This suggests that current efforts to lower mortality rates have not had unintended consequences for hospitals that institute early comfort care more commonly than their peers.
Acknowledgments
Dr. Chen and Ms. Cox take responsibility for the integrity of the data and the accuracy of the data analysis. Drs. Chen, Levine, and Hayward are responsible for the study concept and design. Drs. Chen and Fonarow acquired the data. Dr. Chen drafted the manuscript. Drs. Chen, Levin, Hayward, Cox, Fonarow, DeVore, Hernandez, Heidenreich, and Yancy revised the manuscript for important intellectual content. Drs. Chen, Hayward, Cox, and Schulte performed the statistical analysis. Drs. Chen and Fonarow obtained funding for the study. Drs. Hayward and Fonarow supervised the study. The authors thank Bailey Green, MPH, for the research assistance she provided. She was compensated for her work.
Disclosure
Dr. Fonarow reports research support from the National Institutes of Health, and consulting for Amgen, Janssen, Novartis, Medtronic, and St Jude Medical. Dr. DeVore reports research support from the American Heart Association, Amgen, and Novartis, and consulting for Amgen. The other authors have no relevant conflicts of interest. Dr. Chen was supported by a Career Development Grant Award (K08HS020671) from the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality when the manuscript was being prepared. She currently receives support from the Department of Health and Human Services Office of the Assistant Secretary for Planning and Evaluation for her work there. She also receives support from the Blue Cross Blue Shield of Michigan Foundation’s Investigator Initiated Research Program, the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (R01 HS024698), and the National Institute on Aging (P01 AG019783). These funding sources had no role in the preparation, review, or approval of the manuscript. The GWTG-HF program is provided by the American Heart Association. GWTG-HF has been funded in the past through support from Amgen, Medtronic, GlaxoSmithKline, Ortho-McNeil, and the American Heart Association Pharmaceutical Roundtable. These sponsors had no role in the study design, data analysis or manuscript preparation and revision.
1. Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services. Hospital Compare. https://www.medicare.gov/hospitalcompare/. Accessed on November 27, 2016.
2. Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services. Hospital Value-based Purchasing. https://www.medicare.gov/hospitalcompare/data/hospital-vbp.html. Accessed August 30, 2017.
3. Medicare Payment Advisory Comission. Report to the Congress: Medicare payment policy. 2014. http://www.medpac.gov/docs/default-source/reports/mar14_entirereport.pdf. Accessed August 31, 2017.
4. Whellan DJ, Cox M, Hernandez AF, et al. Utilization of hospice and predicted mortality risk among older patients hospitalized with heart failure: findings from GWTG-HF. J Card Fail. 2012;18(6):471-477. PubMed
5. Hong Y, LaBresh KA. Overview of the American Heart Association “Get with the Guidelines” programs: coronary heart disease, stroke, and heart failure. Crit Pathw Cardiol. 2006;5(4):179-186. PubMed
6. LaBresh KA, Gliklich R, Liljestrand J, Peto R, Ellrodt AG. Using “get with the guidelines” to improve cardiovascular secondary prevention. Jt Comm J Qual Saf. 2003;29(10):539-550. PubMed
7. Hernandez AF, Fonarow GC, Liang L, et al. Sex and racial differences in the use of implantable cardioverter-defibrillators among patients hospitalized with heart failure. JAMA. 2007;298(13):1525-1532. PubMed
8. Get With The Guidelines-Heart Failure. HF Patient Management Tool, October 2016.
9. Eapen ZJ, Liang L, Fonarow GC, et al. Validated, electronic health record deployable prediction models for assessing patient risk of 30-day rehospitalization and mortality in older heart failure patients. JACC Heart Fail. 2013;1(3):245-251. PubMed
10. Peterson PN, Rumsfeld JS, Liang L, et al. A validated risk score for in-hospital mortality in patients with heart failure from the American Heart Association get with the guidelines program. Circ Cardiovasc Qual Outcomes. 2010;3(1):25-32. PubMed
11. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs): Implementation and Maintenance of CMS Mortality Measures for AMI & HF. 2007. https://www.cms.gov/Medicare/Quality-Initiatives-Patient-Assessment-Instruments/HospitalQualityInits/downloads/HospitalMortalityAboutAMI_HF.pdf. Accessed August 30, 2017.
12. Suter LG, Li SX, Grady JN, et al. National patterns of risk-standardized mortality and readmission after hospitalization for acute myocardial infarction, heart failure, and pneumonia: update on publicly reported outcomes measures based on the 2013 release. J Gen Intern Med. 2014;29(10):1333-1340. PubMed
13. Lagu T, Pekow PS, Shieh MS, et al. Validation and comparison of seven mortality prediction models for hospitalized patients with acute decompensated heart failure. Circ Heart Fail. Aug 2016;9(8):e002912. PubMed
14. National Hospice and Palliative Care Organization. NHPCO’s facts and figures: hospice care in america. 2015. https://www.nhpco.org/sites/default/files/public/Statistics_Research/2015_Facts_Figures.pdf. Accessed August 30, 2017.
15. Yancy CW, Jessup M, Bozkurt B, et al. 2013 ACCF/AHA guideline for the management of heart failure: executive summary: a report of the American College of Cardiology Foundation/American Heart Association Task Force on practice guidelines. Circulation. 2013;128(16):1810-1852. PubMed
16. Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services. 2016 Condition-Specific Measures Updates and Specifications Report Hospital-Level 30-Day Risk-Standardized Mortality Measures. https://www.qualitynet.org/dcs/ContentServer?c=Page&pagename=QnetPublic%2FPage%2FQnetTier3&cid=1228774398696. Accessed August 30, 2017.
17. Bakitas M, Macmartin M, Trzepkowski K, et al. Palliative care consultations for heart failure patients: how many, when, and why? J Card Fail. 2013;19(3):193-201. PubMed
18. Wachterman MW, Pilver C, Smith D, Ersek M, Lipsitz SR, Keating NL. Quality of End-of-Life Care Provided to Patients With Different Serious Illnesses. JAMA Intern Med. 2016;176(8):1095-1102. PubMed
19. Wright AA, Zhang B, Ray A, et al. Associations between end-of-life discussions, patient mental health, medical care near death, and caregiver bereavement adjustment. JAMA. 2008;300(14):1665-1673. PubMed
20. Rogers JG, Patel CB, Mentz RJ, et al. Palliative care in heart failure: results of a randomized, controlled clinical trial. J Card Fail. 2016;22(11):940. PubMed
21. Kelly AG, Zahuranec DB, Holloway RG, Morgenstern LB, Burke JF. Variation in do-not-resuscitate orders for patients with ischemic stroke: implications for national hospital comparisons. Stroke. 2014;45(3):822-827. PubMed
22. Walkey AJ, Weinberg J, Wiener RS, Cooke CR, Lindenauer PK. Association of Do-Not-Resuscitate Orders and Hospital Mortality Rate Among Patients With Pneumonia. JAMA Intern Med. 2016;176(1):97-104. PubMed
23. Bardach N, Zhao S, Pantilat S, Johnston SC. Adjustment for do-not-resuscitate orders reverses the apparent in-hospital mortality advantage for minorities. Am J Med. 2005;118(4):400-408. PubMed
24. Tabak YP, Johannes RS, Silber JH, Kurtz SG. Should Do-Not-Resuscitate status be included as a mortality risk adjustor? The impact of DNR variations on performance reporting. Med Care. 2005;43(7):658-666. PubMed
In an effort to improve the quality of care delivered to heart failure (HF) patients, the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) publish hospitals’ 30-day risk-standardized mortality rates (RSMRs) for HF.1 These mortality rates are also used by CMS to determine the financial penalties and bonuses that hospitals receive as part of the national Hospital Value-based Purchasing program.2 Whether or not these efforts effectively direct patients towards high-quality providers or motivate hospitals to provide better care, few would disagree with the overarching goal of decreasing the number of patients who die from HF.
However, for some patients with chronic disease at the end of life, goals of care may change. The quality of days lived may become more important than the quantity of days lived. As a consequence, high-quality care for some patients at the end of life is associated with withdrawing life-sustaining or life-extending therapies. Over time, this therapeutic perspective has become more common, with use of hospice care doubling from 23% to 47% between 2000 and 2012 among Medicare beneficiaries who died.3 For a national cohort of older patients admitted with HF—not just those patients who died in that same year—hospitals’ rates of referral to hospice are considerably lower, averaging 2.9% in 2010 in a national study.4 Nevertheless, it is possible that hospitals that more faithfully follow their dying patients’ wishes and withdraw life-prolonging interventions and provide comfort-focused care at the end of life might be unfairly penalized if such efforts resulted in higher mortality rates than other hospitals.
Therefore, we used Medicare data linked to a national HF registry with information about end-of-life care, to address 3 questions: (1) How much do hospitals vary in their rates of early comfort care and how has this changed over time; (2) What hospital and patient factors are associated with higher early comfort care rates; and (3) Is there a correlation between 30-day risk-adjusted mortality rates for HF with hospital rates of early comfort care?
METHODS
Data Sources
We used data from the American Heart Association’s Get With The Guidelines-Heart Failure (GWTG-HF) registry. GWTG-HF is a voluntary, inpatient, quality improvement registry5-7 that uses web-based tools and standard questionnaires to collect data on patients with HF admitted to participating hospitals nationwide. The data include information from admission (eg, sociodemographic characteristics, symptoms, medical history, and initial laboratory and test results), the inpatient stay (eg, therapies), and discharge (eg, discharge destination, whether and when comfort care was initiated). We linked the GWTG-HF registry data to Medicare claims data in order to obtain information about Medicare eligibility and patient comorbidities. Additionally, we used data from the American Hospital Association (2008) for hospital characteristics. Quintiles Real-World & Late Phase Research (Cambridge, MA) serves as the data coordinating center for GWTG-HF and the Duke Clinical Research Institute (Durham, NC) serves as the statistical analytic center. GWTG-HF participating sites have a waiver of informed consent because the data are de-identified and primarily used for quality improvement. All analyses performed on this data have been approved by the Duke Medical Center Institutional Review Board.
Study Population
Study Outcomes
Our outcome of interest was the correlation between a hospital’s rate of initiating early CMO for admitted HF patients and a hospital’s 30-day RSMR for HF. The GWTG-HF questionnaire8 asks “When is the earliest physician/advanced practice nurse/physician assistant documentation of comfort measures only?” and permits 4 responses: day 0 or 1, day 2 or after, timing unclear, or not documented/unable to determine. We defined early CMO as CMO on day 0 or 1, and late/no CMO as any other response. We chose to examine early comfort care because many hospitalized patients transition to comfort care before they die if the death is in any way predictable. Thus, if comfort care is measured at any time during the hospitalization, hospitals that have high mortality rates are likely to have high comfort care rates. Therefore, we chose to use the more precise measure of early comfort care. We created hospital-level, risk-standardized early comfort care rates using the same risk-adjustment model used for RSMRs but with the outcome of early comfort care instead of mortality.9,10
RSMRs were calculated using a validated GWTG-HF 30-day risk-standardized mortality model9 with additional variables identified from other GWTG-HF analyses.10 The 30 days are measured as the 30 days after the index admission date.
Statistical Analyses
We described trends in early comfort care rates over time, from February 17, 2008, to February 17, 2014, using the Cochran-Armitage test for trend. We then grouped hospitals into quintiles based on their unadjusted early comfort care rates. We described patient and hospital characteristics for each quintile, using χ2 tests to test for differences across quintiles for categorical variables and Wilcoxon rank sum tests to assess for differences across quintiles for continuous variables. We then examined the Spearman’s rank correlation between hospitals’ RSMR and risk-adjusted comfort care rates. Finally, we compared hospital-level RSMRs before and after adjusting for early comfort care.
We performed risk-adjustment for these last 2 analyses as follows. For each patient, covariates were obtained from the GWTG-HF registry. Clinical data captured for the index admission were utilized in the risk-adjustment model (for both RSMRs and risk-adjusted comfort care rates). Included covariates were as follows: age (per 10 years); race (black vs non-black); systolic blood pressure at admission ≤170 (per 10 mm Hg); respiratory rate (per 5 respirations/min); heart rate ≤105 (per 10 beats/min); weight ≤100 (per 5 kg); weight >100 (per 5 kg); blood urea nitrogen (per 10 mg/dl); brain natriuretic peptide ≤2000 (per 500 pg/ml); hemoglobin 10-14 (per 1 g/dl); troponin abnormal (vs normal); creatinine ≤1 (per 1 mg/dl); sodium 130-140 (per 5 mEq/l); and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease or asthma.
Hierarchical logistic regression modeling was used to calculate the hospital-specific RSMR. A predicted/expected ratio similar to an observed/expected (O/E) ratio was calculated using the following modifications: (1) instead of the observed (crude) number of deaths, the numerator is the number of deaths predicted by the hierarchical model among a hospital’s patients given the patients’ risk factors and the hospital-specific effect; (2) the denominator is the expected number of deaths among the hospital’s patients given the patients’ risk factors and the average of all hospital-specific effects overall; and (3) the ratio of the numerator and denominator are then multiplied by the observed overall mortality rate (same as O/E). This calculation is the method used by CMS to derive RSMRs.11 Multiple imputation was used to handle missing data in the models; 25 imputed datasets using the fully conditional specification method were created. Patients with missing prior comorbidities were assumed to not have those conditions. Hospital characteristics were not imputed; therefore, for analyses that required construction of risk-adjusted comfort care rates or RSMRs, we excluded 18,867 patients cared for at 82 hospitals missing hospital characteristics. We ran 2 sets of models for risk-adjusted comfort care rates and RSMRs: the first adjusted only for patient characteristics, and the second adjusted for both patient and hospital characteristics. Results from the 2 models were similar, so we present only results from the latter. Variance inflation factors were all <2, indicating the collinearity between covariates was not an issue.
All statistical analyses were performed by using SAS version 9.4 (SAS Institute, Cary, NC). We tested for statistical significance by using 2-tailed tests and considered P values <.05 to be statistically significant.
RESULTS
Of the 272 hospitals included in our final study cohort, the observed median overall rate of early comfort care in this study was 1.9% (25th to 75th percentile: 0.9% to 4.0%); hospitals varied widely in unadjusted early comfort care rates (0.00% to 0.46% in the lowest quintile, and 4.60% to 39.91% in the highest quintile; Table 1).
DISCUSSION
Among a national sample of US hospitals, we found wide variation in how frequently health care providers deliver comfort care within the first 2 days of admission for HF. A minority of hospitals reported no early comfort care on any patients throughout the 6-year study period, but hospitals in the highest quintile initiated early comfort care rates for at least 1 in 20 HF patients. Hospitals that were more likely to initiate early comfort care had a higher proportion of female and white patients and were less likely to have the capacity to deliver aggressive surgical interventions such as heart transplants. Hospital-level 30-day RSMRs were not correlated with rates of early comfort care.
While the appropriate rate of early comfort care for patients hospitalized with HF is unknown, given that the average hospital RSMR is approximately 12% for fee-for-service Medicare patients hospitalized with HF,12 it is surprising that some hospitals initiated early comfort care on none or very few of their HF patients. It is quite possible that many of these hospitals initiated comfort care for some of their patients after 48 hours of hospitalization. We were unable to estimate the average period of time patients received comfort care prior to dying, the degree to which this varies across hospitals or why it might vary, and whether the length of time between comfort care initiation and death is related to satisfaction with end-of-life care. Future research on these topics would help inform providers seeking to deliver better end-of-life care. In this study, we also were unable to estimate how often early comfort care was not initiated because patients had a good prognosis. However, prior studies have suggested low rates of comfort care or hospice referral even among patients at very high estimated mortality risk.4 It is also possible that providers and families had concerns about the ability to accurately prognosticate, although several models have been shown to perform acceptably for patients hospitalized with HF.13
We found that comfort care rates did not increase over time, even though use of hospice care doubled among Medicare beneficiaries between 2000 and 2012. By way of context, cancer—the second leading cause of death in the US—was responsible for 38% of hospice admissions in 2013, whereas heart disease (including but not limited to HF)—the leading cause of death— was responsible for 13% of hospice admissions.14 The 2013 American College of Cardiology Foundation and the American Heart Association guidelines for HF recommend consideration of hospice or palliative care for inpatient and transitional care.15 In future work, it would be important to better understand the drivers behind decisions around comfort care for patients hospitalized with HF.
With regards to the policy implications of our study, we found that on average, adjusting 30-day mortality rates for early comfort care was not associated with a change in hospital mortality rankings. For those hospitals with high comfort care rates, adjusting for comfort care did lower mortality rates, but the change was so small as to be clinically insignificant. CMS’ RSMR for HF excludes patients enrolled in hospice during the 12 months prior to index admission, including the first day of the index admission, acknowledging that death may not be an untoward outcome for such patients.16 Fee-for-service Medicare beneficiaries excluded for hospice enrollment comprised 1.29% of HF admissions from July 2012 to June 201516 and are likely a subset of early comfort care patients in our sample, both because of the inclusiveness of chart review (vs claims-based identification) and because we defined early comfort care as comfort care initiated on day 0 or 1 of hospitalization. Nevertheless, with our data we cannot assess to what degree our findings were due solely to hospice patients excluded from CMS’ current estimates.
Prior research has described the underuse of palliative care among patients with HF17 and the association of palliative care with better patient and family experiences at the end of life.18-20 We add to this literature by describing the epidemiology—prevalence, changes over time, and associated factors—of early comfort care for HF in a national sample of hospitals. This serves as a baseline for future work on end-of-life care among patients hospitalized for HF. Our findings also contribute to ongoing discussion about how best to risk-adjust mortality metrics used to assess hospital quality in pay-for-performance programs. Recent research on stroke and pneumonia based on California data suggests that not accounting for do-not-resuscitate (DNR) status biases hospital mortality rates.21,22 Earlier research examined the impact of adjusting hospital mortality rates for DNR for a broader range of conditions.23,24 We expand this line of inquiry by examining the hospital-level association of early comfort care with mortality rates for HF, utilizing a national, contemporary cohort of inpatient stays. In addition, while studies have found that DNR rates within the first 24 hours of admission are relatively high (median 15.8% for pneumonia; 13.3% for stroke),21,22 comfort care is distinct from DNR.
Our findings should be interpreted in the context of several potential limitations. First, we did not have any information about patient or family wishes regarding end-of-life care, or the exact timing of early comfort care (eg, day 0 or day 1). The initiation of comfort care usually follows conversations about end-of-life care involving a patient, his or her family, and the medical team. Thus, we do not know if low early comfort care rates represent the lack of such a conversation (and thus poor-quality care) or the desire by most patients not to initiate early comfort care (and thus high-quality care). This would be an important area for future research. Second, we included only patients admitted to hospitals that participate in GWTG-HF, a voluntary quality improvement initiative. This may limit the generalizability of our findings, but it is unclear how our sample might bias our findings. Hospitals engaged in quality improvement may be more likely to initiate early comfort care aligned with patients’ wishes; on the other hand, hospitals with advanced surgical capabilities are over-represented in our sample and these hospitals are less likely to initiate early comfort care. Third, we examined associations and cannot make conclusions about causality. Residual measured and unmeasured confounding may influence these findings.
In summary, we found that early comfort care rates for fee-for-service Medicare beneficiaries admitted for HF varies widely among hospitals, but median rates of early comfort care have not changed over time. On average, there was no correlation between hospital-level, 30-day, RSMRs and rates of early comfort care. This suggests that current efforts to lower mortality rates have not had unintended consequences for hospitals that institute early comfort care more commonly than their peers.
Acknowledgments
Dr. Chen and Ms. Cox take responsibility for the integrity of the data and the accuracy of the data analysis. Drs. Chen, Levine, and Hayward are responsible for the study concept and design. Drs. Chen and Fonarow acquired the data. Dr. Chen drafted the manuscript. Drs. Chen, Levin, Hayward, Cox, Fonarow, DeVore, Hernandez, Heidenreich, and Yancy revised the manuscript for important intellectual content. Drs. Chen, Hayward, Cox, and Schulte performed the statistical analysis. Drs. Chen and Fonarow obtained funding for the study. Drs. Hayward and Fonarow supervised the study. The authors thank Bailey Green, MPH, for the research assistance she provided. She was compensated for her work.
Disclosure
Dr. Fonarow reports research support from the National Institutes of Health, and consulting for Amgen, Janssen, Novartis, Medtronic, and St Jude Medical. Dr. DeVore reports research support from the American Heart Association, Amgen, and Novartis, and consulting for Amgen. The other authors have no relevant conflicts of interest. Dr. Chen was supported by a Career Development Grant Award (K08HS020671) from the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality when the manuscript was being prepared. She currently receives support from the Department of Health and Human Services Office of the Assistant Secretary for Planning and Evaluation for her work there. She also receives support from the Blue Cross Blue Shield of Michigan Foundation’s Investigator Initiated Research Program, the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (R01 HS024698), and the National Institute on Aging (P01 AG019783). These funding sources had no role in the preparation, review, or approval of the manuscript. The GWTG-HF program is provided by the American Heart Association. GWTG-HF has been funded in the past through support from Amgen, Medtronic, GlaxoSmithKline, Ortho-McNeil, and the American Heart Association Pharmaceutical Roundtable. These sponsors had no role in the study design, data analysis or manuscript preparation and revision.
In an effort to improve the quality of care delivered to heart failure (HF) patients, the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) publish hospitals’ 30-day risk-standardized mortality rates (RSMRs) for HF.1 These mortality rates are also used by CMS to determine the financial penalties and bonuses that hospitals receive as part of the national Hospital Value-based Purchasing program.2 Whether or not these efforts effectively direct patients towards high-quality providers or motivate hospitals to provide better care, few would disagree with the overarching goal of decreasing the number of patients who die from HF.
However, for some patients with chronic disease at the end of life, goals of care may change. The quality of days lived may become more important than the quantity of days lived. As a consequence, high-quality care for some patients at the end of life is associated with withdrawing life-sustaining or life-extending therapies. Over time, this therapeutic perspective has become more common, with use of hospice care doubling from 23% to 47% between 2000 and 2012 among Medicare beneficiaries who died.3 For a national cohort of older patients admitted with HF—not just those patients who died in that same year—hospitals’ rates of referral to hospice are considerably lower, averaging 2.9% in 2010 in a national study.4 Nevertheless, it is possible that hospitals that more faithfully follow their dying patients’ wishes and withdraw life-prolonging interventions and provide comfort-focused care at the end of life might be unfairly penalized if such efforts resulted in higher mortality rates than other hospitals.
Therefore, we used Medicare data linked to a national HF registry with information about end-of-life care, to address 3 questions: (1) How much do hospitals vary in their rates of early comfort care and how has this changed over time; (2) What hospital and patient factors are associated with higher early comfort care rates; and (3) Is there a correlation between 30-day risk-adjusted mortality rates for HF with hospital rates of early comfort care?
METHODS
Data Sources
We used data from the American Heart Association’s Get With The Guidelines-Heart Failure (GWTG-HF) registry. GWTG-HF is a voluntary, inpatient, quality improvement registry5-7 that uses web-based tools and standard questionnaires to collect data on patients with HF admitted to participating hospitals nationwide. The data include information from admission (eg, sociodemographic characteristics, symptoms, medical history, and initial laboratory and test results), the inpatient stay (eg, therapies), and discharge (eg, discharge destination, whether and when comfort care was initiated). We linked the GWTG-HF registry data to Medicare claims data in order to obtain information about Medicare eligibility and patient comorbidities. Additionally, we used data from the American Hospital Association (2008) for hospital characteristics. Quintiles Real-World & Late Phase Research (Cambridge, MA) serves as the data coordinating center for GWTG-HF and the Duke Clinical Research Institute (Durham, NC) serves as the statistical analytic center. GWTG-HF participating sites have a waiver of informed consent because the data are de-identified and primarily used for quality improvement. All analyses performed on this data have been approved by the Duke Medical Center Institutional Review Board.
Study Population
Study Outcomes
Our outcome of interest was the correlation between a hospital’s rate of initiating early CMO for admitted HF patients and a hospital’s 30-day RSMR for HF. The GWTG-HF questionnaire8 asks “When is the earliest physician/advanced practice nurse/physician assistant documentation of comfort measures only?” and permits 4 responses: day 0 or 1, day 2 or after, timing unclear, or not documented/unable to determine. We defined early CMO as CMO on day 0 or 1, and late/no CMO as any other response. We chose to examine early comfort care because many hospitalized patients transition to comfort care before they die if the death is in any way predictable. Thus, if comfort care is measured at any time during the hospitalization, hospitals that have high mortality rates are likely to have high comfort care rates. Therefore, we chose to use the more precise measure of early comfort care. We created hospital-level, risk-standardized early comfort care rates using the same risk-adjustment model used for RSMRs but with the outcome of early comfort care instead of mortality.9,10
RSMRs were calculated using a validated GWTG-HF 30-day risk-standardized mortality model9 with additional variables identified from other GWTG-HF analyses.10 The 30 days are measured as the 30 days after the index admission date.
Statistical Analyses
We described trends in early comfort care rates over time, from February 17, 2008, to February 17, 2014, using the Cochran-Armitage test for trend. We then grouped hospitals into quintiles based on their unadjusted early comfort care rates. We described patient and hospital characteristics for each quintile, using χ2 tests to test for differences across quintiles for categorical variables and Wilcoxon rank sum tests to assess for differences across quintiles for continuous variables. We then examined the Spearman’s rank correlation between hospitals’ RSMR and risk-adjusted comfort care rates. Finally, we compared hospital-level RSMRs before and after adjusting for early comfort care.
We performed risk-adjustment for these last 2 analyses as follows. For each patient, covariates were obtained from the GWTG-HF registry. Clinical data captured for the index admission were utilized in the risk-adjustment model (for both RSMRs and risk-adjusted comfort care rates). Included covariates were as follows: age (per 10 years); race (black vs non-black); systolic blood pressure at admission ≤170 (per 10 mm Hg); respiratory rate (per 5 respirations/min); heart rate ≤105 (per 10 beats/min); weight ≤100 (per 5 kg); weight >100 (per 5 kg); blood urea nitrogen (per 10 mg/dl); brain natriuretic peptide ≤2000 (per 500 pg/ml); hemoglobin 10-14 (per 1 g/dl); troponin abnormal (vs normal); creatinine ≤1 (per 1 mg/dl); sodium 130-140 (per 5 mEq/l); and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease or asthma.
Hierarchical logistic regression modeling was used to calculate the hospital-specific RSMR. A predicted/expected ratio similar to an observed/expected (O/E) ratio was calculated using the following modifications: (1) instead of the observed (crude) number of deaths, the numerator is the number of deaths predicted by the hierarchical model among a hospital’s patients given the patients’ risk factors and the hospital-specific effect; (2) the denominator is the expected number of deaths among the hospital’s patients given the patients’ risk factors and the average of all hospital-specific effects overall; and (3) the ratio of the numerator and denominator are then multiplied by the observed overall mortality rate (same as O/E). This calculation is the method used by CMS to derive RSMRs.11 Multiple imputation was used to handle missing data in the models; 25 imputed datasets using the fully conditional specification method were created. Patients with missing prior comorbidities were assumed to not have those conditions. Hospital characteristics were not imputed; therefore, for analyses that required construction of risk-adjusted comfort care rates or RSMRs, we excluded 18,867 patients cared for at 82 hospitals missing hospital characteristics. We ran 2 sets of models for risk-adjusted comfort care rates and RSMRs: the first adjusted only for patient characteristics, and the second adjusted for both patient and hospital characteristics. Results from the 2 models were similar, so we present only results from the latter. Variance inflation factors were all <2, indicating the collinearity between covariates was not an issue.
All statistical analyses were performed by using SAS version 9.4 (SAS Institute, Cary, NC). We tested for statistical significance by using 2-tailed tests and considered P values <.05 to be statistically significant.
RESULTS
Of the 272 hospitals included in our final study cohort, the observed median overall rate of early comfort care in this study was 1.9% (25th to 75th percentile: 0.9% to 4.0%); hospitals varied widely in unadjusted early comfort care rates (0.00% to 0.46% in the lowest quintile, and 4.60% to 39.91% in the highest quintile; Table 1).
DISCUSSION
Among a national sample of US hospitals, we found wide variation in how frequently health care providers deliver comfort care within the first 2 days of admission for HF. A minority of hospitals reported no early comfort care on any patients throughout the 6-year study period, but hospitals in the highest quintile initiated early comfort care rates for at least 1 in 20 HF patients. Hospitals that were more likely to initiate early comfort care had a higher proportion of female and white patients and were less likely to have the capacity to deliver aggressive surgical interventions such as heart transplants. Hospital-level 30-day RSMRs were not correlated with rates of early comfort care.
While the appropriate rate of early comfort care for patients hospitalized with HF is unknown, given that the average hospital RSMR is approximately 12% for fee-for-service Medicare patients hospitalized with HF,12 it is surprising that some hospitals initiated early comfort care on none or very few of their HF patients. It is quite possible that many of these hospitals initiated comfort care for some of their patients after 48 hours of hospitalization. We were unable to estimate the average period of time patients received comfort care prior to dying, the degree to which this varies across hospitals or why it might vary, and whether the length of time between comfort care initiation and death is related to satisfaction with end-of-life care. Future research on these topics would help inform providers seeking to deliver better end-of-life care. In this study, we also were unable to estimate how often early comfort care was not initiated because patients had a good prognosis. However, prior studies have suggested low rates of comfort care or hospice referral even among patients at very high estimated mortality risk.4 It is also possible that providers and families had concerns about the ability to accurately prognosticate, although several models have been shown to perform acceptably for patients hospitalized with HF.13
We found that comfort care rates did not increase over time, even though use of hospice care doubled among Medicare beneficiaries between 2000 and 2012. By way of context, cancer—the second leading cause of death in the US—was responsible for 38% of hospice admissions in 2013, whereas heart disease (including but not limited to HF)—the leading cause of death— was responsible for 13% of hospice admissions.14 The 2013 American College of Cardiology Foundation and the American Heart Association guidelines for HF recommend consideration of hospice or palliative care for inpatient and transitional care.15 In future work, it would be important to better understand the drivers behind decisions around comfort care for patients hospitalized with HF.
With regards to the policy implications of our study, we found that on average, adjusting 30-day mortality rates for early comfort care was not associated with a change in hospital mortality rankings. For those hospitals with high comfort care rates, adjusting for comfort care did lower mortality rates, but the change was so small as to be clinically insignificant. CMS’ RSMR for HF excludes patients enrolled in hospice during the 12 months prior to index admission, including the first day of the index admission, acknowledging that death may not be an untoward outcome for such patients.16 Fee-for-service Medicare beneficiaries excluded for hospice enrollment comprised 1.29% of HF admissions from July 2012 to June 201516 and are likely a subset of early comfort care patients in our sample, both because of the inclusiveness of chart review (vs claims-based identification) and because we defined early comfort care as comfort care initiated on day 0 or 1 of hospitalization. Nevertheless, with our data we cannot assess to what degree our findings were due solely to hospice patients excluded from CMS’ current estimates.
Prior research has described the underuse of palliative care among patients with HF17 and the association of palliative care with better patient and family experiences at the end of life.18-20 We add to this literature by describing the epidemiology—prevalence, changes over time, and associated factors—of early comfort care for HF in a national sample of hospitals. This serves as a baseline for future work on end-of-life care among patients hospitalized for HF. Our findings also contribute to ongoing discussion about how best to risk-adjust mortality metrics used to assess hospital quality in pay-for-performance programs. Recent research on stroke and pneumonia based on California data suggests that not accounting for do-not-resuscitate (DNR) status biases hospital mortality rates.21,22 Earlier research examined the impact of adjusting hospital mortality rates for DNR for a broader range of conditions.23,24 We expand this line of inquiry by examining the hospital-level association of early comfort care with mortality rates for HF, utilizing a national, contemporary cohort of inpatient stays. In addition, while studies have found that DNR rates within the first 24 hours of admission are relatively high (median 15.8% for pneumonia; 13.3% for stroke),21,22 comfort care is distinct from DNR.
Our findings should be interpreted in the context of several potential limitations. First, we did not have any information about patient or family wishes regarding end-of-life care, or the exact timing of early comfort care (eg, day 0 or day 1). The initiation of comfort care usually follows conversations about end-of-life care involving a patient, his or her family, and the medical team. Thus, we do not know if low early comfort care rates represent the lack of such a conversation (and thus poor-quality care) or the desire by most patients not to initiate early comfort care (and thus high-quality care). This would be an important area for future research. Second, we included only patients admitted to hospitals that participate in GWTG-HF, a voluntary quality improvement initiative. This may limit the generalizability of our findings, but it is unclear how our sample might bias our findings. Hospitals engaged in quality improvement may be more likely to initiate early comfort care aligned with patients’ wishes; on the other hand, hospitals with advanced surgical capabilities are over-represented in our sample and these hospitals are less likely to initiate early comfort care. Third, we examined associations and cannot make conclusions about causality. Residual measured and unmeasured confounding may influence these findings.
In summary, we found that early comfort care rates for fee-for-service Medicare beneficiaries admitted for HF varies widely among hospitals, but median rates of early comfort care have not changed over time. On average, there was no correlation between hospital-level, 30-day, RSMRs and rates of early comfort care. This suggests that current efforts to lower mortality rates have not had unintended consequences for hospitals that institute early comfort care more commonly than their peers.
Acknowledgments
Dr. Chen and Ms. Cox take responsibility for the integrity of the data and the accuracy of the data analysis. Drs. Chen, Levine, and Hayward are responsible for the study concept and design. Drs. Chen and Fonarow acquired the data. Dr. Chen drafted the manuscript. Drs. Chen, Levin, Hayward, Cox, Fonarow, DeVore, Hernandez, Heidenreich, and Yancy revised the manuscript for important intellectual content. Drs. Chen, Hayward, Cox, and Schulte performed the statistical analysis. Drs. Chen and Fonarow obtained funding for the study. Drs. Hayward and Fonarow supervised the study. The authors thank Bailey Green, MPH, for the research assistance she provided. She was compensated for her work.
Disclosure
Dr. Fonarow reports research support from the National Institutes of Health, and consulting for Amgen, Janssen, Novartis, Medtronic, and St Jude Medical. Dr. DeVore reports research support from the American Heart Association, Amgen, and Novartis, and consulting for Amgen. The other authors have no relevant conflicts of interest. Dr. Chen was supported by a Career Development Grant Award (K08HS020671) from the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality when the manuscript was being prepared. She currently receives support from the Department of Health and Human Services Office of the Assistant Secretary for Planning and Evaluation for her work there. She also receives support from the Blue Cross Blue Shield of Michigan Foundation’s Investigator Initiated Research Program, the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (R01 HS024698), and the National Institute on Aging (P01 AG019783). These funding sources had no role in the preparation, review, or approval of the manuscript. The GWTG-HF program is provided by the American Heart Association. GWTG-HF has been funded in the past through support from Amgen, Medtronic, GlaxoSmithKline, Ortho-McNeil, and the American Heart Association Pharmaceutical Roundtable. These sponsors had no role in the study design, data analysis or manuscript preparation and revision.
1. Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services. Hospital Compare. https://www.medicare.gov/hospitalcompare/. Accessed on November 27, 2016.
2. Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services. Hospital Value-based Purchasing. https://www.medicare.gov/hospitalcompare/data/hospital-vbp.html. Accessed August 30, 2017.
3. Medicare Payment Advisory Comission. Report to the Congress: Medicare payment policy. 2014. http://www.medpac.gov/docs/default-source/reports/mar14_entirereport.pdf. Accessed August 31, 2017.
4. Whellan DJ, Cox M, Hernandez AF, et al. Utilization of hospice and predicted mortality risk among older patients hospitalized with heart failure: findings from GWTG-HF. J Card Fail. 2012;18(6):471-477. PubMed
5. Hong Y, LaBresh KA. Overview of the American Heart Association “Get with the Guidelines” programs: coronary heart disease, stroke, and heart failure. Crit Pathw Cardiol. 2006;5(4):179-186. PubMed
6. LaBresh KA, Gliklich R, Liljestrand J, Peto R, Ellrodt AG. Using “get with the guidelines” to improve cardiovascular secondary prevention. Jt Comm J Qual Saf. 2003;29(10):539-550. PubMed
7. Hernandez AF, Fonarow GC, Liang L, et al. Sex and racial differences in the use of implantable cardioverter-defibrillators among patients hospitalized with heart failure. JAMA. 2007;298(13):1525-1532. PubMed
8. Get With The Guidelines-Heart Failure. HF Patient Management Tool, October 2016.
9. Eapen ZJ, Liang L, Fonarow GC, et al. Validated, electronic health record deployable prediction models for assessing patient risk of 30-day rehospitalization and mortality in older heart failure patients. JACC Heart Fail. 2013;1(3):245-251. PubMed
10. Peterson PN, Rumsfeld JS, Liang L, et al. A validated risk score for in-hospital mortality in patients with heart failure from the American Heart Association get with the guidelines program. Circ Cardiovasc Qual Outcomes. 2010;3(1):25-32. PubMed
11. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs): Implementation and Maintenance of CMS Mortality Measures for AMI & HF. 2007. https://www.cms.gov/Medicare/Quality-Initiatives-Patient-Assessment-Instruments/HospitalQualityInits/downloads/HospitalMortalityAboutAMI_HF.pdf. Accessed August 30, 2017.
12. Suter LG, Li SX, Grady JN, et al. National patterns of risk-standardized mortality and readmission after hospitalization for acute myocardial infarction, heart failure, and pneumonia: update on publicly reported outcomes measures based on the 2013 release. J Gen Intern Med. 2014;29(10):1333-1340. PubMed
13. Lagu T, Pekow PS, Shieh MS, et al. Validation and comparison of seven mortality prediction models for hospitalized patients with acute decompensated heart failure. Circ Heart Fail. Aug 2016;9(8):e002912. PubMed
14. National Hospice and Palliative Care Organization. NHPCO’s facts and figures: hospice care in america. 2015. https://www.nhpco.org/sites/default/files/public/Statistics_Research/2015_Facts_Figures.pdf. Accessed August 30, 2017.
15. Yancy CW, Jessup M, Bozkurt B, et al. 2013 ACCF/AHA guideline for the management of heart failure: executive summary: a report of the American College of Cardiology Foundation/American Heart Association Task Force on practice guidelines. Circulation. 2013;128(16):1810-1852. PubMed
16. Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services. 2016 Condition-Specific Measures Updates and Specifications Report Hospital-Level 30-Day Risk-Standardized Mortality Measures. https://www.qualitynet.org/dcs/ContentServer?c=Page&pagename=QnetPublic%2FPage%2FQnetTier3&cid=1228774398696. Accessed August 30, 2017.
17. Bakitas M, Macmartin M, Trzepkowski K, et al. Palliative care consultations for heart failure patients: how many, when, and why? J Card Fail. 2013;19(3):193-201. PubMed
18. Wachterman MW, Pilver C, Smith D, Ersek M, Lipsitz SR, Keating NL. Quality of End-of-Life Care Provided to Patients With Different Serious Illnesses. JAMA Intern Med. 2016;176(8):1095-1102. PubMed
19. Wright AA, Zhang B, Ray A, et al. Associations between end-of-life discussions, patient mental health, medical care near death, and caregiver bereavement adjustment. JAMA. 2008;300(14):1665-1673. PubMed
20. Rogers JG, Patel CB, Mentz RJ, et al. Palliative care in heart failure: results of a randomized, controlled clinical trial. J Card Fail. 2016;22(11):940. PubMed
21. Kelly AG, Zahuranec DB, Holloway RG, Morgenstern LB, Burke JF. Variation in do-not-resuscitate orders for patients with ischemic stroke: implications for national hospital comparisons. Stroke. 2014;45(3):822-827. PubMed
22. Walkey AJ, Weinberg J, Wiener RS, Cooke CR, Lindenauer PK. Association of Do-Not-Resuscitate Orders and Hospital Mortality Rate Among Patients With Pneumonia. JAMA Intern Med. 2016;176(1):97-104. PubMed
23. Bardach N, Zhao S, Pantilat S, Johnston SC. Adjustment for do-not-resuscitate orders reverses the apparent in-hospital mortality advantage for minorities. Am J Med. 2005;118(4):400-408. PubMed
24. Tabak YP, Johannes RS, Silber JH, Kurtz SG. Should Do-Not-Resuscitate status be included as a mortality risk adjustor? The impact of DNR variations on performance reporting. Med Care. 2005;43(7):658-666. PubMed
1. Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services. Hospital Compare. https://www.medicare.gov/hospitalcompare/. Accessed on November 27, 2016.
2. Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services. Hospital Value-based Purchasing. https://www.medicare.gov/hospitalcompare/data/hospital-vbp.html. Accessed August 30, 2017.
3. Medicare Payment Advisory Comission. Report to the Congress: Medicare payment policy. 2014. http://www.medpac.gov/docs/default-source/reports/mar14_entirereport.pdf. Accessed August 31, 2017.
4. Whellan DJ, Cox M, Hernandez AF, et al. Utilization of hospice and predicted mortality risk among older patients hospitalized with heart failure: findings from GWTG-HF. J Card Fail. 2012;18(6):471-477. PubMed
5. Hong Y, LaBresh KA. Overview of the American Heart Association “Get with the Guidelines” programs: coronary heart disease, stroke, and heart failure. Crit Pathw Cardiol. 2006;5(4):179-186. PubMed
6. LaBresh KA, Gliklich R, Liljestrand J, Peto R, Ellrodt AG. Using “get with the guidelines” to improve cardiovascular secondary prevention. Jt Comm J Qual Saf. 2003;29(10):539-550. PubMed
7. Hernandez AF, Fonarow GC, Liang L, et al. Sex and racial differences in the use of implantable cardioverter-defibrillators among patients hospitalized with heart failure. JAMA. 2007;298(13):1525-1532. PubMed
8. Get With The Guidelines-Heart Failure. HF Patient Management Tool, October 2016.
9. Eapen ZJ, Liang L, Fonarow GC, et al. Validated, electronic health record deployable prediction models for assessing patient risk of 30-day rehospitalization and mortality in older heart failure patients. JACC Heart Fail. 2013;1(3):245-251. PubMed
10. Peterson PN, Rumsfeld JS, Liang L, et al. A validated risk score for in-hospital mortality in patients with heart failure from the American Heart Association get with the guidelines program. Circ Cardiovasc Qual Outcomes. 2010;3(1):25-32. PubMed
11. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs): Implementation and Maintenance of CMS Mortality Measures for AMI & HF. 2007. https://www.cms.gov/Medicare/Quality-Initiatives-Patient-Assessment-Instruments/HospitalQualityInits/downloads/HospitalMortalityAboutAMI_HF.pdf. Accessed August 30, 2017.
12. Suter LG, Li SX, Grady JN, et al. National patterns of risk-standardized mortality and readmission after hospitalization for acute myocardial infarction, heart failure, and pneumonia: update on publicly reported outcomes measures based on the 2013 release. J Gen Intern Med. 2014;29(10):1333-1340. PubMed
13. Lagu T, Pekow PS, Shieh MS, et al. Validation and comparison of seven mortality prediction models for hospitalized patients with acute decompensated heart failure. Circ Heart Fail. Aug 2016;9(8):e002912. PubMed
14. National Hospice and Palliative Care Organization. NHPCO’s facts and figures: hospice care in america. 2015. https://www.nhpco.org/sites/default/files/public/Statistics_Research/2015_Facts_Figures.pdf. Accessed August 30, 2017.
15. Yancy CW, Jessup M, Bozkurt B, et al. 2013 ACCF/AHA guideline for the management of heart failure: executive summary: a report of the American College of Cardiology Foundation/American Heart Association Task Force on practice guidelines. Circulation. 2013;128(16):1810-1852. PubMed
16. Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services. 2016 Condition-Specific Measures Updates and Specifications Report Hospital-Level 30-Day Risk-Standardized Mortality Measures. https://www.qualitynet.org/dcs/ContentServer?c=Page&pagename=QnetPublic%2FPage%2FQnetTier3&cid=1228774398696. Accessed August 30, 2017.
17. Bakitas M, Macmartin M, Trzepkowski K, et al. Palliative care consultations for heart failure patients: how many, when, and why? J Card Fail. 2013;19(3):193-201. PubMed
18. Wachterman MW, Pilver C, Smith D, Ersek M, Lipsitz SR, Keating NL. Quality of End-of-Life Care Provided to Patients With Different Serious Illnesses. JAMA Intern Med. 2016;176(8):1095-1102. PubMed
19. Wright AA, Zhang B, Ray A, et al. Associations between end-of-life discussions, patient mental health, medical care near death, and caregiver bereavement adjustment. JAMA. 2008;300(14):1665-1673. PubMed
20. Rogers JG, Patel CB, Mentz RJ, et al. Palliative care in heart failure: results of a randomized, controlled clinical trial. J Card Fail. 2016;22(11):940. PubMed
21. Kelly AG, Zahuranec DB, Holloway RG, Morgenstern LB, Burke JF. Variation in do-not-resuscitate orders for patients with ischemic stroke: implications for national hospital comparisons. Stroke. 2014;45(3):822-827. PubMed
22. Walkey AJ, Weinberg J, Wiener RS, Cooke CR, Lindenauer PK. Association of Do-Not-Resuscitate Orders and Hospital Mortality Rate Among Patients With Pneumonia. JAMA Intern Med. 2016;176(1):97-104. PubMed
23. Bardach N, Zhao S, Pantilat S, Johnston SC. Adjustment for do-not-resuscitate orders reverses the apparent in-hospital mortality advantage for minorities. Am J Med. 2005;118(4):400-408. PubMed
24. Tabak YP, Johannes RS, Silber JH, Kurtz SG. Should Do-Not-Resuscitate status be included as a mortality risk adjustor? The impact of DNR variations on performance reporting. Med Care. 2005;43(7):658-666. PubMed
© 2018 Society of Hospital Medicine