User login
Evaluation of Pharmacist-Driven Inhaled Corticosteroid De-escalation in Veterans
Evaluation of Pharmacist-Driven Inhaled Corticosteroid De-escalation in Veterans
Systemic glucocorticoids play an important role in the treatment of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) exacerbations. They are recommended to shorten recovery time and increase forced expiratory volume in 1 second (FEV1) during exacerbations.1 However, the role of the chronic use of inhaled corticosteroids (ICSs) in the treatment of COPD is less clear.
When added to inhaled β-2 agonists and muscarinic antagonists, ICSs can decrease the risk of exacerbations.1 However, not all patients with COPD benefit from ICS therapy. The degree of benefit an ICS can provide has been shown to correlate with eosinophil count—a marker of inflammation. The expected benefit of using an ICS increases as the eosinophil count increases.1 Maximum benefit can be observed with eosinophil counts ≥ 300 cells/µL, and minimal benefit is observed with eosinophil counts < 100 cells/µL. Adverse effects (AEs) of ICSs include a hoarse voice, oral candidiasis, and an increased risk of pneumonia.1 Given the risk of AEs, it is important to limit ICS use in patients who are unlikely to reap any benefits.
The Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease (GOLD) guidelines suggest the use of ICSs in patients who experience exacerbations while using long-acting β agonist (LABA) plus long-acting muscarinic antagonist (LAMA) therapy and have an eosinophil count ≥ 100 cells/µL. Switching from LABA or LAMA monotherapy to triple therapy with LAMA/LABA/ICS may be considered if patients have continued exacerbations and an eosinophil count ≥ 300 cells/µL. De-escalation of ICS therapy should be considered if patients do not meet these criteria or if patients experience ICS AEs, such as pneumonia. The patients most likely to have increased exacerbations or decreased FEV1 with ICS withdrawal are those with eosinophil counts ≥ 300 cells/µL.1,2
Several studies have explored the effects of ICS de-escalation in real-world clinical settings. A systematic review of 11 studies indicated that de-escalation of ICS in COPD does not result in increased exacerbations.3 A prospective study by Rossi et al found that in a 6-month period, 141 of 482 patients on ICS therapy (29%) had an exacerbation. In the opposing arm of the study, 88 of 334 patients (26%) with deprescribed ICS experienced an exacerbation. The difference between these 2 groups was not statistically significant.4 The researchers concluded that in real-world practice, ICS withdrawal can be safe in patients at low risk of exacerbation.
About 25% of veterans (1.25 million) have been diagnosed with COPD.5 To address this, the US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) and US Department of Defense published updated COPD guidelines in 2021 that specify criteria for de-escalation of ICS.6 Guidelines, however, may not be reflected in common clinical practice for several years following publication. The VA Academic Detailing Service (ADS) provides tools to help clinicians identify patients who may benefit from changes in treatment plans. A recent ADS focus was the implementation of a COPD dashboard, which identifies patients with COPD who are candidates for ICS de-escalation based on comorbid diagnoses, exacerbation history, and eosinophil count. VA pharmacists have an expanded role in the management of primary care disease states and are therefore well-positioned to increase adherence to guideline-directed therapy. The objective of this quality improvement project was to determine the impact of pharmacist-driven de-escalation on ICS usage in veterans with COPD.
Methods
This project was conducted in an outpatient clinic at the Robley Rex VA Medical Center beginning September 21, 2023, with a progress note in the Computerized Patient Record System (CPRS). Eligible patients were selected using the COPD Dashboard provided by ADS. The COPD Dashboard defined patients with COPD as those with ≥ 2 outpatient COPD diagnoses in the past 2 years, 1 inpatient discharge COPD diagnosis in the past year, or COPD listed as an active problem. COPD diagnoses were identified using International Statistical Classification of Disease, Tenth Revision (ICD-10) codes
Candidates identified for ICS de-escalation by the dashboard were excluded if they had a history of COPD exacerbation in the previous 2 years. The dashboard identified COPD exacerbations via ICD-10 codes for COPD or acute respiratory failure for inpatient discharges, emergency department (ED) visits, urgent care visits, and community care consults with 1 of the following terms: emergency, inpatient, hospital, urgent, ED (self). The COPD dashboard excluded patients with a diagnosis of asthma.
After patients were selected, they were screened for additional exclusion criteria. Patients were excluded if a pulmonary care practitioner managed their COPD; if identified via an active pulmonary consult in CPRS; if a non-VA clinician prescribed their ICS; or if they were being treated with roflumilast, theophylline, or chronic azithromycin. Individuals taking these 3 drugs were excluded due to potential severe and/or refractory COPD. Patients also were excluded if they: (1) had prior ICS de-escalation failure (defined as a COPD exacerbation following ICS de-escalation that resulted in ICS resumption); (2) had a COPD exacerbation requiring systemic corticosteroids or antibiotics in the previous year; (3) had active lung cancer; (4) did not have any eosinophil levels in CPRS within the previous 2 years; or (5) had any eosinophil levels ≥ 300 cells/µL in the previous year.
Each patient who met the inclusion criteria and was not excluded received a focused medication review by a pharmacist who created a templated progress note, with patient-specific recommendations, that was entered in the CPRS (eAppendix). The recommendations were also attached as an addendum to the patient’s last primary care visit note, and the primary care practitioner (PCP) was alerted via CPRS to consider ICS de-escalation and non-ICS alternatives. Tapering of ICS therapy was offered as an option to de-escalate if abrupt discontinuation was deemed inappropriate. PCPs were also prompted to consider referral to a primary care clinical pharmacy specialist for management and follow-up of ICS de-escalation.
The primary outcome was the number of patients with de-escalated ICS at 3 and 6 months following the recommendation. Secondary outcomes included the number of: patients who were no longer prescribed an ICS or who had a non-ICS alternative initiated at a pharmacist’s recommendation; patients who were referred to a primary care clinical pharmacy specialist for ICS de-escalation; COPD exacerbations requiring systemic steroids or antibiotics, or requiring an ED visit, inpatient admission, or urgent-care clinic visit; and cases of pneumonia or oral candidiasis. Primary and secondary outcomes were evaluated via chart review in CPRS. For secondary outcomes of pneumonia and COPD exacerbation, identification was made by documented diagnosis in CPRS. For continuous data such as age, the mean was calculated.
Results
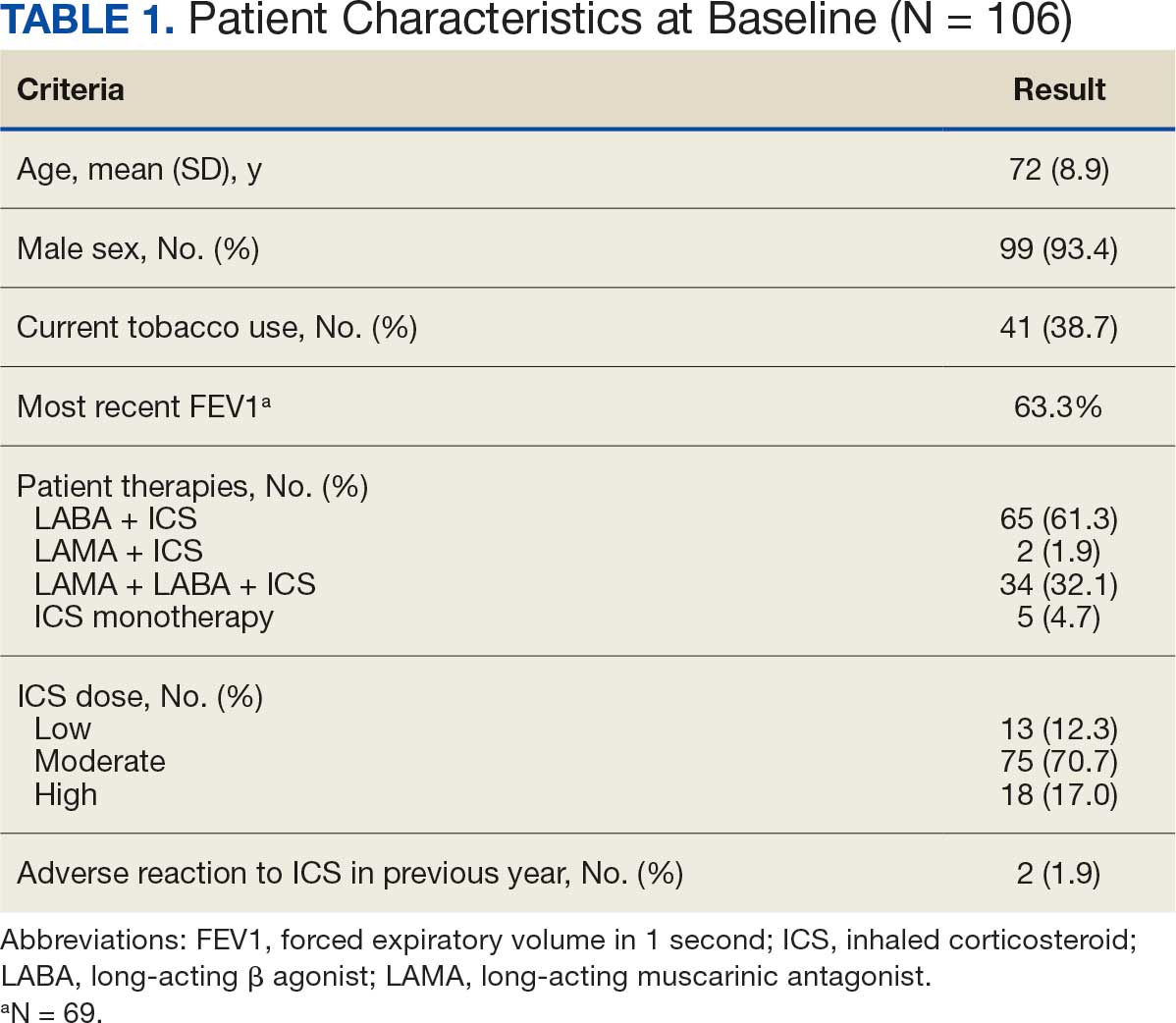
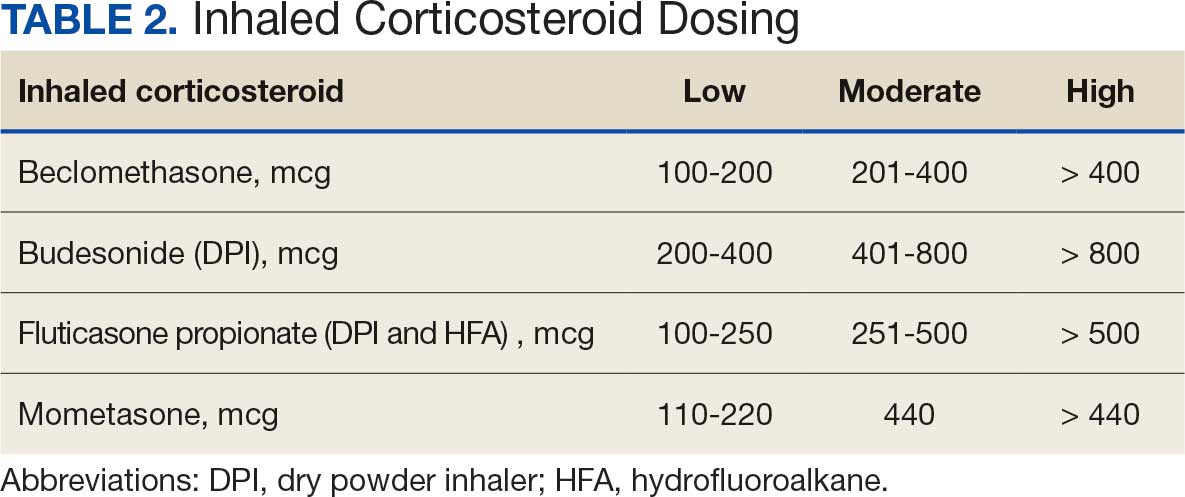
Pharmacist ICS de-escalation recommendations were made between September 21, 2023, and November 19, 2023, for 106 patients. The mean age was 72 years and 99 (93%) patients were male (Table 1). Forty-one (39%) of the patients used tobacco at the time of the study. FEV1 was available for 69 patients with a mean of 63% (GOLD grade 2).1 Based on FEV1 values, 16 patients had mild COPD (GOLD grade 1), 37 patients had moderate COPD (GOLD grade 2), 14 patients had severe COPD (GOLD grade 3), and 2 patients had very severe COPD (GOLD grade 4).1 Thirty-four patients received LABA + LAMA + ICS, 65 received LABA + ICS, 2 received LAMA + ICS, and 5 received ICS monotherapy. The most common dose of ICS was a moderate dose (Table 2). Only 2 patients had an ICS AE in the previous year.
ICS de-escalation recommendations resulted in ICS de-escalation in 50 (47.2%) and 62 (58.5%) patients at 3 and 6 months, respectively. The 6-month ICS de-escalation rate by ICS dose at baseline was 72.2% (high dose), 60.0% (moderate), and 30.8% (low). De-escalation at 6 months by GOLD grade at baseline was 56.3% (9 of 16 patients, GOLD 1), 64.9% (24 of 37 patients, GOLD 2), 50% (7 of 14 patients, GOLD 3), and 50% (1 of 2 patients, GOLD 4). Six months after the ICS de-escalation recommendation appeared in the CPRS, the percentage of patients on LABA + ICS therapy dropped from 65 patients (61.3%) at baseline to 25 patients (23.6%).
Secondary outcomes were assessed at 3 and 6 months following the recommendation. Most patients with de-escalated ICS had their ICS discontinued and a non-ICS alternative initiated per pharmacist recommendations. At 6 months, 39 patients (36.8%) patients were referred to a patient aligned care team (PACT) pharmacist for de-escalation. Of the 39 patients referred to pharmacists, 69.2% (27 patients) were de-escalated; this compared to 52.2% (35 patients) who were not referred to pharmacists (Table 3).
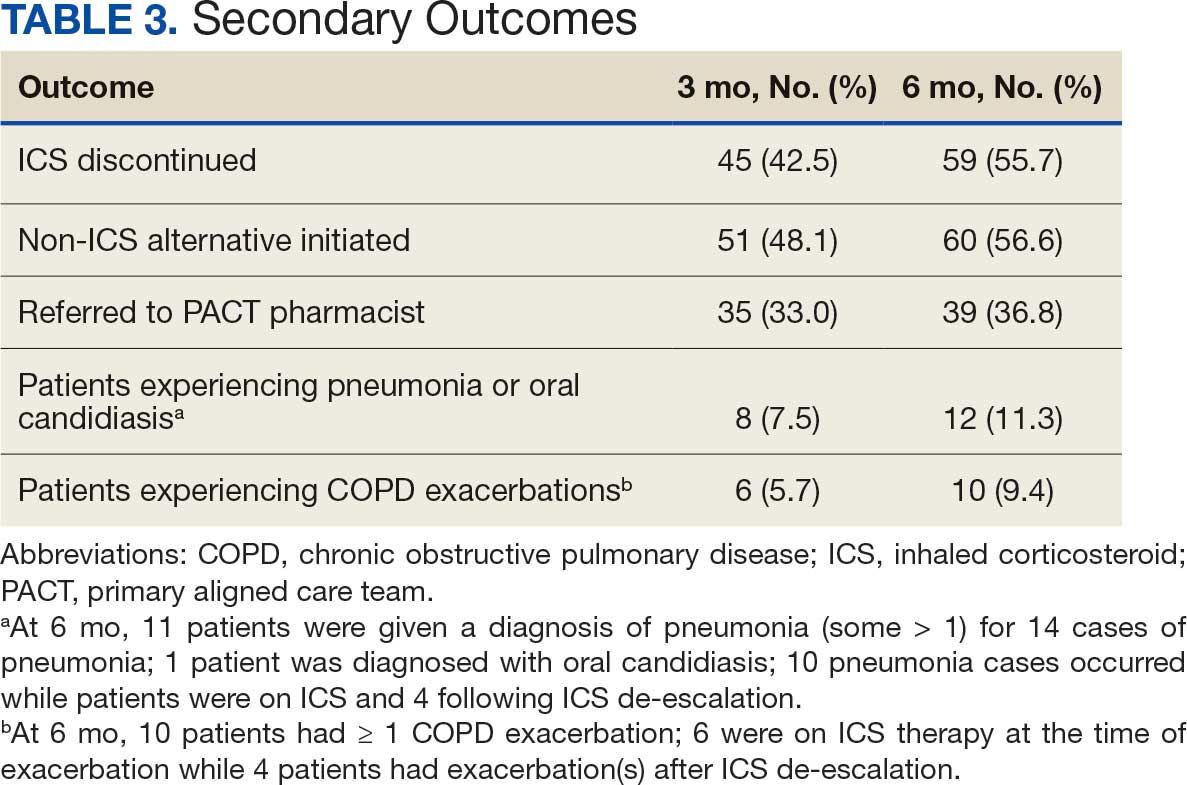
ICS use increases the risk of pneumonia.1 At 6 months, 11 patients were diagnosed with pneumonia; 3 patients were diagnosed with pneumonia twice, resulting in a total of 14 cases. Ten cases occurred while patients were on ICS and 4 cases occurred following ICS de-escalation. One patient had a documented case of oral candidiasis that occurred while on ICS therapy; no patients with discontinued ICS were diagnosed with oral candidiasis. In addition, 10 patients had COPD exacerbations; however no patients had exacerbations both before and after de-escalation. Six patients were on ICS therapy when they experienced an exacerbation, and 4 patients had an exacerbation after ICS de-escalation.
Discussion
More than half of patients receiving the pharmacist intervention achieved the primary outcome of ICS de-escalation at 6 months. Furthermore, a larger percentage of patients referred to pharmacists for the management of ICS de-escalation successfully achieved de-escalation compared to those who were not referred. These outcomes reflect the important role pharmacists can play in identifying appropriate candidates for ICS de-escalation and assisting in the management of ICS de-escalation. Patients referred to pharmacists also received other services such as smoking cessation pharmacotherapy and counseling on inhaler technique and adherence. These interventions can support improved COPD clinical outcomes.
The purpose of de-escalating ICS therapy is to reduce the risk of AEs such as pneumonia and oral candidiasis.1 The secondary outcomes of this study support previous evidence that patients who have de-escalated ICS therapy may have reduced risk of AEs compared to those who remain on ICS therapy.3 Specifically, of the 14 cases of pneumonia that occurred during the study, 10 cases occurred while patients were on ICS and 4 cases occurred following ICS de-escalation.
ICS de-escalation may increase risk of increased COPD exacerbations.1 However, the secondary outcomes of this study do not indicate that those with de-escalated ICS had more COPD exacerbations compared to those who continued on ICS. Pharmacists’ recommendations were more effective for patients with less severe COPD based on baseline FEV1.
The previous GOLD Guidelines for COPD suggested LABA + ICS therapy as an option for patients with a high symptom and exacerbation burden (previously known as GOLD Group D). Guidelines no longer recommend LABA + ICS therapy due to the superiority of triple inhaled therapy for exacerbations and the superiority of LAMA + LABA therapy for dyspnea.7 A majority of identified patients in this project were on LABA + ICS therapy alone at baseline. The ICS de-escalation recommendation resulted in a 61.5% reduction in patients on LABA + ICS therapy at 6 months. By decreasing the number of patients on LABA + ICS without LAMA, recommendations increased the number of patients on guideline-directed therapy.
Limitations
This study lacked a control group, and the rate of ICS de-escalation in patients who did not receive a pharmacist recommendation was not assessed. Therefore, it could not be determined whether the pharmacist recommendation is more effective than no recommendation. Another limitation was our inability to access records from non-VA health care facilities. This may have resulted in missed COPD exacerbations, pneumonia, and oral candidiasis prior to or following the pharmacist recommendation.
In addition, the method used to notify PCPs of the pharmacist recommendation was a CPRS alert. Clinicians often receive multiple daily alerts and may not always pay close attention to them due to alert fatigue. Early in the study, some PCPs were unknowingly omitted from the alert of the pharmacist recommendation for 10 patients due to human error. For 8 of these 10 patients, the PCP was notified of the recommendations during the 3-month follow-up period. However, 2 patients had COPD exacerbations during the 3-month follow-up period. In these cases, the PCP was not alerted to de-escalate ICS. The data for these patients were collected at 3 and 6 months in the same manner as all other patients. Also, 7 of 35 patients who were referred to a pharmacist for ICS de-escalation did not have a scheduled appointment. These patients were considered to be lost to follow-up and this may have resulted in an underestimation of the ability of pharmacists to successfully de-escalate ICS in patients with COPD.
Other studies have evaluated the efficacy of a pharmacy-driven ICS de-escalation.8,9 Hegland et al reported ICS de-escalation for 22% of 141 eligible ambulatory patients with COPD on triple inhaled therapy following pharmacist appointments.8 A study by Hahn et al resulted in 63.8% of 58 patients with COPD being maintained off ICS following a pharmacist de-escalation initiative.9 However, these studies relied upon more time-consuming de-escalation interventions, including at least 1 phone, video, or in-person patient visit.8,9
This project used a single chart review and templated progress note to recommend ICS de-escalation and achieved similar or improved de-escalation rates compared to previous studies.8,9 Previous studies were conducted prior to the updated 2023 GOLD guidelines for COPD which no longer recommend LABA + ICS therapy. This project addressed ICS de-escalation in patients on LABA + ICS therapy in addition to those on triple inhaled therapy. Additionally, previous studies did not address rates of moderate to severe COPD exacerbation and adverse events to ICS following the pharmacist intervention.8,9
This study included COPD exacerbations and cases of pneumonia or oral candidiasis as secondary outcomes to assess the safety and efficacy of the ICS de-escalation. It appeared there were similar or lower rates of COPD exacerbations, pneumonia, and oral candidiasis in those with de-escalated ICS therapy in this study. However, these secondary outcomes are exploratory and would need to be confirmed by larger studies powered to address these outcomes.
CONCLUSIONS
Pharmacist-driven ICS de-escalation may be an effective method for reducing ICS usage in veterans as seen in this study. Additional controlled studies are required to evaluate the efficacy and safety of pharmacist-driven ICS de-escalation.
- Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease (GOLD). Global Strategy for the Diagnosis, Management, and Prevention of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (2024 Report). Accessed October 14, 2025. https://goldcopd.org/2024-gold-report/
- Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease (GOLD). Global Strategy for the Diagnosis, Management, and Prevention of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (2025 Report). Accessed November 14, 2025. https://goldcopd.org/2025-gold-report/
- Rogliani P, Ritondo BL, Gabriele M, et al. Optimizing de-escalation of inhaled corticosteroids in COPD: a systematic review of real-world findings. Expert Rev Clin Pharmacol. 2020;13(9):977-990. doi:10.1080/17512433.2020.1817739
- Rossi A, Guerriero M, Corrado A; OPTIMO/AIPO Study Group. Withdrawal of inhaled corticosteroids can be safe in COPD patients at low risk of exacerbation: a real-life study on the appropriateness of treatment in moderate COPD patients (OPTIMO). Respir Res. 2014;15(1):77. doi:10.1186/1465-9921-15-77
- Anderson E, Wiener RS, Resnick K, et al. Care coordination for veterans with COPD: a positive deviance study. Am J Manag Care. 2020;26(2):63-68. doi:10.37765/ajmc.2020.42394
- US Department of Veterans Affairs, US Department of Defense. VA/DoD Clinical Practice Guideline for the Management of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. 2021. Accessed October 14, 2025. https://www.healthquality.va.gov/guidelines/CD/copd/
- Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease (GOLD). Global Strategy for the Diagnosis, Management, and Prevention of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (2023 Report). Accessed October 14, 2025. https://goldcopd.org/wp-content/uploads/2023/03/GOLD-2023-ver-1.3-17Feb2023_WMV.pdf
- Hegland AJ, Bolduc J, Jones L, Kunisaki KM, Melzer AC. Pharmacist-driven deprescribing of inhaled corticosteroids in patients with stable chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Ann Am Thorac Soc. 2021;18(4):730-733. doi:10.1513/AnnalsATS.202007-871RL
- Hahn NM, Nagy MW. Implementation of a targeted inhaled corticosteroid de-escalation process in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease in the primary care setting. Innov Pharm. 2022;13(1):10.24926/iip.v13i1.4349. doi:10.24926/iip.v13i1.4349
Systemic glucocorticoids play an important role in the treatment of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) exacerbations. They are recommended to shorten recovery time and increase forced expiratory volume in 1 second (FEV1) during exacerbations.1 However, the role of the chronic use of inhaled corticosteroids (ICSs) in the treatment of COPD is less clear.
When added to inhaled β-2 agonists and muscarinic antagonists, ICSs can decrease the risk of exacerbations.1 However, not all patients with COPD benefit from ICS therapy. The degree of benefit an ICS can provide has been shown to correlate with eosinophil count—a marker of inflammation. The expected benefit of using an ICS increases as the eosinophil count increases.1 Maximum benefit can be observed with eosinophil counts ≥ 300 cells/µL, and minimal benefit is observed with eosinophil counts < 100 cells/µL. Adverse effects (AEs) of ICSs include a hoarse voice, oral candidiasis, and an increased risk of pneumonia.1 Given the risk of AEs, it is important to limit ICS use in patients who are unlikely to reap any benefits.
The Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease (GOLD) guidelines suggest the use of ICSs in patients who experience exacerbations while using long-acting β agonist (LABA) plus long-acting muscarinic antagonist (LAMA) therapy and have an eosinophil count ≥ 100 cells/µL. Switching from LABA or LAMA monotherapy to triple therapy with LAMA/LABA/ICS may be considered if patients have continued exacerbations and an eosinophil count ≥ 300 cells/µL. De-escalation of ICS therapy should be considered if patients do not meet these criteria or if patients experience ICS AEs, such as pneumonia. The patients most likely to have increased exacerbations or decreased FEV1 with ICS withdrawal are those with eosinophil counts ≥ 300 cells/µL.1,2
Several studies have explored the effects of ICS de-escalation in real-world clinical settings. A systematic review of 11 studies indicated that de-escalation of ICS in COPD does not result in increased exacerbations.3 A prospective study by Rossi et al found that in a 6-month period, 141 of 482 patients on ICS therapy (29%) had an exacerbation. In the opposing arm of the study, 88 of 334 patients (26%) with deprescribed ICS experienced an exacerbation. The difference between these 2 groups was not statistically significant.4 The researchers concluded that in real-world practice, ICS withdrawal can be safe in patients at low risk of exacerbation.
About 25% of veterans (1.25 million) have been diagnosed with COPD.5 To address this, the US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) and US Department of Defense published updated COPD guidelines in 2021 that specify criteria for de-escalation of ICS.6 Guidelines, however, may not be reflected in common clinical practice for several years following publication. The VA Academic Detailing Service (ADS) provides tools to help clinicians identify patients who may benefit from changes in treatment plans. A recent ADS focus was the implementation of a COPD dashboard, which identifies patients with COPD who are candidates for ICS de-escalation based on comorbid diagnoses, exacerbation history, and eosinophil count. VA pharmacists have an expanded role in the management of primary care disease states and are therefore well-positioned to increase adherence to guideline-directed therapy. The objective of this quality improvement project was to determine the impact of pharmacist-driven de-escalation on ICS usage in veterans with COPD.
Methods
This project was conducted in an outpatient clinic at the Robley Rex VA Medical Center beginning September 21, 2023, with a progress note in the Computerized Patient Record System (CPRS). Eligible patients were selected using the COPD Dashboard provided by ADS. The COPD Dashboard defined patients with COPD as those with ≥ 2 outpatient COPD diagnoses in the past 2 years, 1 inpatient discharge COPD diagnosis in the past year, or COPD listed as an active problem. COPD diagnoses were identified using International Statistical Classification of Disease, Tenth Revision (ICD-10) codes
Candidates identified for ICS de-escalation by the dashboard were excluded if they had a history of COPD exacerbation in the previous 2 years. The dashboard identified COPD exacerbations via ICD-10 codes for COPD or acute respiratory failure for inpatient discharges, emergency department (ED) visits, urgent care visits, and community care consults with 1 of the following terms: emergency, inpatient, hospital, urgent, ED (self). The COPD dashboard excluded patients with a diagnosis of asthma.
After patients were selected, they were screened for additional exclusion criteria. Patients were excluded if a pulmonary care practitioner managed their COPD; if identified via an active pulmonary consult in CPRS; if a non-VA clinician prescribed their ICS; or if they were being treated with roflumilast, theophylline, or chronic azithromycin. Individuals taking these 3 drugs were excluded due to potential severe and/or refractory COPD. Patients also were excluded if they: (1) had prior ICS de-escalation failure (defined as a COPD exacerbation following ICS de-escalation that resulted in ICS resumption); (2) had a COPD exacerbation requiring systemic corticosteroids or antibiotics in the previous year; (3) had active lung cancer; (4) did not have any eosinophil levels in CPRS within the previous 2 years; or (5) had any eosinophil levels ≥ 300 cells/µL in the previous year.
Each patient who met the inclusion criteria and was not excluded received a focused medication review by a pharmacist who created a templated progress note, with patient-specific recommendations, that was entered in the CPRS (eAppendix). The recommendations were also attached as an addendum to the patient’s last primary care visit note, and the primary care practitioner (PCP) was alerted via CPRS to consider ICS de-escalation and non-ICS alternatives. Tapering of ICS therapy was offered as an option to de-escalate if abrupt discontinuation was deemed inappropriate. PCPs were also prompted to consider referral to a primary care clinical pharmacy specialist for management and follow-up of ICS de-escalation.
The primary outcome was the number of patients with de-escalated ICS at 3 and 6 months following the recommendation. Secondary outcomes included the number of: patients who were no longer prescribed an ICS or who had a non-ICS alternative initiated at a pharmacist’s recommendation; patients who were referred to a primary care clinical pharmacy specialist for ICS de-escalation; COPD exacerbations requiring systemic steroids or antibiotics, or requiring an ED visit, inpatient admission, or urgent-care clinic visit; and cases of pneumonia or oral candidiasis. Primary and secondary outcomes were evaluated via chart review in CPRS. For secondary outcomes of pneumonia and COPD exacerbation, identification was made by documented diagnosis in CPRS. For continuous data such as age, the mean was calculated.
Results
Pharmacist ICS de-escalation recommendations were made between September 21, 2023, and November 19, 2023, for 106 patients. The mean age was 72 years and 99 (93%) patients were male (Table 1). Forty-one (39%) of the patients used tobacco at the time of the study. FEV1 was available for 69 patients with a mean of 63% (GOLD grade 2).1 Based on FEV1 values, 16 patients had mild COPD (GOLD grade 1), 37 patients had moderate COPD (GOLD grade 2), 14 patients had severe COPD (GOLD grade 3), and 2 patients had very severe COPD (GOLD grade 4).1 Thirty-four patients received LABA + LAMA + ICS, 65 received LABA + ICS, 2 received LAMA + ICS, and 5 received ICS monotherapy. The most common dose of ICS was a moderate dose (Table 2). Only 2 patients had an ICS AE in the previous year.


ICS de-escalation recommendations resulted in ICS de-escalation in 50 (47.2%) and 62 (58.5%) patients at 3 and 6 months, respectively. The 6-month ICS de-escalation rate by ICS dose at baseline was 72.2% (high dose), 60.0% (moderate), and 30.8% (low). De-escalation at 6 months by GOLD grade at baseline was 56.3% (9 of 16 patients, GOLD 1), 64.9% (24 of 37 patients, GOLD 2), 50% (7 of 14 patients, GOLD 3), and 50% (1 of 2 patients, GOLD 4). Six months after the ICS de-escalation recommendation appeared in the CPRS, the percentage of patients on LABA + ICS therapy dropped from 65 patients (61.3%) at baseline to 25 patients (23.6%).
Secondary outcomes were assessed at 3 and 6 months following the recommendation. Most patients with de-escalated ICS had their ICS discontinued and a non-ICS alternative initiated per pharmacist recommendations. At 6 months, 39 patients (36.8%) patients were referred to a patient aligned care team (PACT) pharmacist for de-escalation. Of the 39 patients referred to pharmacists, 69.2% (27 patients) were de-escalated; this compared to 52.2% (35 patients) who were not referred to pharmacists (Table 3).

ICS use increases the risk of pneumonia.1 At 6 months, 11 patients were diagnosed with pneumonia; 3 patients were diagnosed with pneumonia twice, resulting in a total of 14 cases. Ten cases occurred while patients were on ICS and 4 cases occurred following ICS de-escalation. One patient had a documented case of oral candidiasis that occurred while on ICS therapy; no patients with discontinued ICS were diagnosed with oral candidiasis. In addition, 10 patients had COPD exacerbations; however no patients had exacerbations both before and after de-escalation. Six patients were on ICS therapy when they experienced an exacerbation, and 4 patients had an exacerbation after ICS de-escalation.
Discussion
More than half of patients receiving the pharmacist intervention achieved the primary outcome of ICS de-escalation at 6 months. Furthermore, a larger percentage of patients referred to pharmacists for the management of ICS de-escalation successfully achieved de-escalation compared to those who were not referred. These outcomes reflect the important role pharmacists can play in identifying appropriate candidates for ICS de-escalation and assisting in the management of ICS de-escalation. Patients referred to pharmacists also received other services such as smoking cessation pharmacotherapy and counseling on inhaler technique and adherence. These interventions can support improved COPD clinical outcomes.
The purpose of de-escalating ICS therapy is to reduce the risk of AEs such as pneumonia and oral candidiasis.1 The secondary outcomes of this study support previous evidence that patients who have de-escalated ICS therapy may have reduced risk of AEs compared to those who remain on ICS therapy.3 Specifically, of the 14 cases of pneumonia that occurred during the study, 10 cases occurred while patients were on ICS and 4 cases occurred following ICS de-escalation.
ICS de-escalation may increase risk of increased COPD exacerbations.1 However, the secondary outcomes of this study do not indicate that those with de-escalated ICS had more COPD exacerbations compared to those who continued on ICS. Pharmacists’ recommendations were more effective for patients with less severe COPD based on baseline FEV1.
The previous GOLD Guidelines for COPD suggested LABA + ICS therapy as an option for patients with a high symptom and exacerbation burden (previously known as GOLD Group D). Guidelines no longer recommend LABA + ICS therapy due to the superiority of triple inhaled therapy for exacerbations and the superiority of LAMA + LABA therapy for dyspnea.7 A majority of identified patients in this project were on LABA + ICS therapy alone at baseline. The ICS de-escalation recommendation resulted in a 61.5% reduction in patients on LABA + ICS therapy at 6 months. By decreasing the number of patients on LABA + ICS without LAMA, recommendations increased the number of patients on guideline-directed therapy.
Limitations
This study lacked a control group, and the rate of ICS de-escalation in patients who did not receive a pharmacist recommendation was not assessed. Therefore, it could not be determined whether the pharmacist recommendation is more effective than no recommendation. Another limitation was our inability to access records from non-VA health care facilities. This may have resulted in missed COPD exacerbations, pneumonia, and oral candidiasis prior to or following the pharmacist recommendation.
In addition, the method used to notify PCPs of the pharmacist recommendation was a CPRS alert. Clinicians often receive multiple daily alerts and may not always pay close attention to them due to alert fatigue. Early in the study, some PCPs were unknowingly omitted from the alert of the pharmacist recommendation for 10 patients due to human error. For 8 of these 10 patients, the PCP was notified of the recommendations during the 3-month follow-up period. However, 2 patients had COPD exacerbations during the 3-month follow-up period. In these cases, the PCP was not alerted to de-escalate ICS. The data for these patients were collected at 3 and 6 months in the same manner as all other patients. Also, 7 of 35 patients who were referred to a pharmacist for ICS de-escalation did not have a scheduled appointment. These patients were considered to be lost to follow-up and this may have resulted in an underestimation of the ability of pharmacists to successfully de-escalate ICS in patients with COPD.
Other studies have evaluated the efficacy of a pharmacy-driven ICS de-escalation.8,9 Hegland et al reported ICS de-escalation for 22% of 141 eligible ambulatory patients with COPD on triple inhaled therapy following pharmacist appointments.8 A study by Hahn et al resulted in 63.8% of 58 patients with COPD being maintained off ICS following a pharmacist de-escalation initiative.9 However, these studies relied upon more time-consuming de-escalation interventions, including at least 1 phone, video, or in-person patient visit.8,9
This project used a single chart review and templated progress note to recommend ICS de-escalation and achieved similar or improved de-escalation rates compared to previous studies.8,9 Previous studies were conducted prior to the updated 2023 GOLD guidelines for COPD which no longer recommend LABA + ICS therapy. This project addressed ICS de-escalation in patients on LABA + ICS therapy in addition to those on triple inhaled therapy. Additionally, previous studies did not address rates of moderate to severe COPD exacerbation and adverse events to ICS following the pharmacist intervention.8,9
This study included COPD exacerbations and cases of pneumonia or oral candidiasis as secondary outcomes to assess the safety and efficacy of the ICS de-escalation. It appeared there were similar or lower rates of COPD exacerbations, pneumonia, and oral candidiasis in those with de-escalated ICS therapy in this study. However, these secondary outcomes are exploratory and would need to be confirmed by larger studies powered to address these outcomes.
CONCLUSIONS
Pharmacist-driven ICS de-escalation may be an effective method for reducing ICS usage in veterans as seen in this study. Additional controlled studies are required to evaluate the efficacy and safety of pharmacist-driven ICS de-escalation.

Systemic glucocorticoids play an important role in the treatment of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) exacerbations. They are recommended to shorten recovery time and increase forced expiratory volume in 1 second (FEV1) during exacerbations.1 However, the role of the chronic use of inhaled corticosteroids (ICSs) in the treatment of COPD is less clear.
When added to inhaled β-2 agonists and muscarinic antagonists, ICSs can decrease the risk of exacerbations.1 However, not all patients with COPD benefit from ICS therapy. The degree of benefit an ICS can provide has been shown to correlate with eosinophil count—a marker of inflammation. The expected benefit of using an ICS increases as the eosinophil count increases.1 Maximum benefit can be observed with eosinophil counts ≥ 300 cells/µL, and minimal benefit is observed with eosinophil counts < 100 cells/µL. Adverse effects (AEs) of ICSs include a hoarse voice, oral candidiasis, and an increased risk of pneumonia.1 Given the risk of AEs, it is important to limit ICS use in patients who are unlikely to reap any benefits.
The Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease (GOLD) guidelines suggest the use of ICSs in patients who experience exacerbations while using long-acting β agonist (LABA) plus long-acting muscarinic antagonist (LAMA) therapy and have an eosinophil count ≥ 100 cells/µL. Switching from LABA or LAMA monotherapy to triple therapy with LAMA/LABA/ICS may be considered if patients have continued exacerbations and an eosinophil count ≥ 300 cells/µL. De-escalation of ICS therapy should be considered if patients do not meet these criteria or if patients experience ICS AEs, such as pneumonia. The patients most likely to have increased exacerbations or decreased FEV1 with ICS withdrawal are those with eosinophil counts ≥ 300 cells/µL.1,2
Several studies have explored the effects of ICS de-escalation in real-world clinical settings. A systematic review of 11 studies indicated that de-escalation of ICS in COPD does not result in increased exacerbations.3 A prospective study by Rossi et al found that in a 6-month period, 141 of 482 patients on ICS therapy (29%) had an exacerbation. In the opposing arm of the study, 88 of 334 patients (26%) with deprescribed ICS experienced an exacerbation. The difference between these 2 groups was not statistically significant.4 The researchers concluded that in real-world practice, ICS withdrawal can be safe in patients at low risk of exacerbation.
About 25% of veterans (1.25 million) have been diagnosed with COPD.5 To address this, the US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) and US Department of Defense published updated COPD guidelines in 2021 that specify criteria for de-escalation of ICS.6 Guidelines, however, may not be reflected in common clinical practice for several years following publication. The VA Academic Detailing Service (ADS) provides tools to help clinicians identify patients who may benefit from changes in treatment plans. A recent ADS focus was the implementation of a COPD dashboard, which identifies patients with COPD who are candidates for ICS de-escalation based on comorbid diagnoses, exacerbation history, and eosinophil count. VA pharmacists have an expanded role in the management of primary care disease states and are therefore well-positioned to increase adherence to guideline-directed therapy. The objective of this quality improvement project was to determine the impact of pharmacist-driven de-escalation on ICS usage in veterans with COPD.
Methods
This project was conducted in an outpatient clinic at the Robley Rex VA Medical Center beginning September 21, 2023, with a progress note in the Computerized Patient Record System (CPRS). Eligible patients were selected using the COPD Dashboard provided by ADS. The COPD Dashboard defined patients with COPD as those with ≥ 2 outpatient COPD diagnoses in the past 2 years, 1 inpatient discharge COPD diagnosis in the past year, or COPD listed as an active problem. COPD diagnoses were identified using International Statistical Classification of Disease, Tenth Revision (ICD-10) codes
Candidates identified for ICS de-escalation by the dashboard were excluded if they had a history of COPD exacerbation in the previous 2 years. The dashboard identified COPD exacerbations via ICD-10 codes for COPD or acute respiratory failure for inpatient discharges, emergency department (ED) visits, urgent care visits, and community care consults with 1 of the following terms: emergency, inpatient, hospital, urgent, ED (self). The COPD dashboard excluded patients with a diagnosis of asthma.
After patients were selected, they were screened for additional exclusion criteria. Patients were excluded if a pulmonary care practitioner managed their COPD; if identified via an active pulmonary consult in CPRS; if a non-VA clinician prescribed their ICS; or if they were being treated with roflumilast, theophylline, or chronic azithromycin. Individuals taking these 3 drugs were excluded due to potential severe and/or refractory COPD. Patients also were excluded if they: (1) had prior ICS de-escalation failure (defined as a COPD exacerbation following ICS de-escalation that resulted in ICS resumption); (2) had a COPD exacerbation requiring systemic corticosteroids or antibiotics in the previous year; (3) had active lung cancer; (4) did not have any eosinophil levels in CPRS within the previous 2 years; or (5) had any eosinophil levels ≥ 300 cells/µL in the previous year.
Each patient who met the inclusion criteria and was not excluded received a focused medication review by a pharmacist who created a templated progress note, with patient-specific recommendations, that was entered in the CPRS (eAppendix). The recommendations were also attached as an addendum to the patient’s last primary care visit note, and the primary care practitioner (PCP) was alerted via CPRS to consider ICS de-escalation and non-ICS alternatives. Tapering of ICS therapy was offered as an option to de-escalate if abrupt discontinuation was deemed inappropriate. PCPs were also prompted to consider referral to a primary care clinical pharmacy specialist for management and follow-up of ICS de-escalation.
The primary outcome was the number of patients with de-escalated ICS at 3 and 6 months following the recommendation. Secondary outcomes included the number of: patients who were no longer prescribed an ICS or who had a non-ICS alternative initiated at a pharmacist’s recommendation; patients who were referred to a primary care clinical pharmacy specialist for ICS de-escalation; COPD exacerbations requiring systemic steroids or antibiotics, or requiring an ED visit, inpatient admission, or urgent-care clinic visit; and cases of pneumonia or oral candidiasis. Primary and secondary outcomes were evaluated via chart review in CPRS. For secondary outcomes of pneumonia and COPD exacerbation, identification was made by documented diagnosis in CPRS. For continuous data such as age, the mean was calculated.
Results
Pharmacist ICS de-escalation recommendations were made between September 21, 2023, and November 19, 2023, for 106 patients. The mean age was 72 years and 99 (93%) patients were male (Table 1). Forty-one (39%) of the patients used tobacco at the time of the study. FEV1 was available for 69 patients with a mean of 63% (GOLD grade 2).1 Based on FEV1 values, 16 patients had mild COPD (GOLD grade 1), 37 patients had moderate COPD (GOLD grade 2), 14 patients had severe COPD (GOLD grade 3), and 2 patients had very severe COPD (GOLD grade 4).1 Thirty-four patients received LABA + LAMA + ICS, 65 received LABA + ICS, 2 received LAMA + ICS, and 5 received ICS monotherapy. The most common dose of ICS was a moderate dose (Table 2). Only 2 patients had an ICS AE in the previous year.


ICS de-escalation recommendations resulted in ICS de-escalation in 50 (47.2%) and 62 (58.5%) patients at 3 and 6 months, respectively. The 6-month ICS de-escalation rate by ICS dose at baseline was 72.2% (high dose), 60.0% (moderate), and 30.8% (low). De-escalation at 6 months by GOLD grade at baseline was 56.3% (9 of 16 patients, GOLD 1), 64.9% (24 of 37 patients, GOLD 2), 50% (7 of 14 patients, GOLD 3), and 50% (1 of 2 patients, GOLD 4). Six months after the ICS de-escalation recommendation appeared in the CPRS, the percentage of patients on LABA + ICS therapy dropped from 65 patients (61.3%) at baseline to 25 patients (23.6%).
Secondary outcomes were assessed at 3 and 6 months following the recommendation. Most patients with de-escalated ICS had their ICS discontinued and a non-ICS alternative initiated per pharmacist recommendations. At 6 months, 39 patients (36.8%) patients were referred to a patient aligned care team (PACT) pharmacist for de-escalation. Of the 39 patients referred to pharmacists, 69.2% (27 patients) were de-escalated; this compared to 52.2% (35 patients) who were not referred to pharmacists (Table 3).

ICS use increases the risk of pneumonia.1 At 6 months, 11 patients were diagnosed with pneumonia; 3 patients were diagnosed with pneumonia twice, resulting in a total of 14 cases. Ten cases occurred while patients were on ICS and 4 cases occurred following ICS de-escalation. One patient had a documented case of oral candidiasis that occurred while on ICS therapy; no patients with discontinued ICS were diagnosed with oral candidiasis. In addition, 10 patients had COPD exacerbations; however no patients had exacerbations both before and after de-escalation. Six patients were on ICS therapy when they experienced an exacerbation, and 4 patients had an exacerbation after ICS de-escalation.
Discussion
More than half of patients receiving the pharmacist intervention achieved the primary outcome of ICS de-escalation at 6 months. Furthermore, a larger percentage of patients referred to pharmacists for the management of ICS de-escalation successfully achieved de-escalation compared to those who were not referred. These outcomes reflect the important role pharmacists can play in identifying appropriate candidates for ICS de-escalation and assisting in the management of ICS de-escalation. Patients referred to pharmacists also received other services such as smoking cessation pharmacotherapy and counseling on inhaler technique and adherence. These interventions can support improved COPD clinical outcomes.
The purpose of de-escalating ICS therapy is to reduce the risk of AEs such as pneumonia and oral candidiasis.1 The secondary outcomes of this study support previous evidence that patients who have de-escalated ICS therapy may have reduced risk of AEs compared to those who remain on ICS therapy.3 Specifically, of the 14 cases of pneumonia that occurred during the study, 10 cases occurred while patients were on ICS and 4 cases occurred following ICS de-escalation.
ICS de-escalation may increase risk of increased COPD exacerbations.1 However, the secondary outcomes of this study do not indicate that those with de-escalated ICS had more COPD exacerbations compared to those who continued on ICS. Pharmacists’ recommendations were more effective for patients with less severe COPD based on baseline FEV1.
The previous GOLD Guidelines for COPD suggested LABA + ICS therapy as an option for patients with a high symptom and exacerbation burden (previously known as GOLD Group D). Guidelines no longer recommend LABA + ICS therapy due to the superiority of triple inhaled therapy for exacerbations and the superiority of LAMA + LABA therapy for dyspnea.7 A majority of identified patients in this project were on LABA + ICS therapy alone at baseline. The ICS de-escalation recommendation resulted in a 61.5% reduction in patients on LABA + ICS therapy at 6 months. By decreasing the number of patients on LABA + ICS without LAMA, recommendations increased the number of patients on guideline-directed therapy.
Limitations
This study lacked a control group, and the rate of ICS de-escalation in patients who did not receive a pharmacist recommendation was not assessed. Therefore, it could not be determined whether the pharmacist recommendation is more effective than no recommendation. Another limitation was our inability to access records from non-VA health care facilities. This may have resulted in missed COPD exacerbations, pneumonia, and oral candidiasis prior to or following the pharmacist recommendation.
In addition, the method used to notify PCPs of the pharmacist recommendation was a CPRS alert. Clinicians often receive multiple daily alerts and may not always pay close attention to them due to alert fatigue. Early in the study, some PCPs were unknowingly omitted from the alert of the pharmacist recommendation for 10 patients due to human error. For 8 of these 10 patients, the PCP was notified of the recommendations during the 3-month follow-up period. However, 2 patients had COPD exacerbations during the 3-month follow-up period. In these cases, the PCP was not alerted to de-escalate ICS. The data for these patients were collected at 3 and 6 months in the same manner as all other patients. Also, 7 of 35 patients who were referred to a pharmacist for ICS de-escalation did not have a scheduled appointment. These patients were considered to be lost to follow-up and this may have resulted in an underestimation of the ability of pharmacists to successfully de-escalate ICS in patients with COPD.
Other studies have evaluated the efficacy of a pharmacy-driven ICS de-escalation.8,9 Hegland et al reported ICS de-escalation for 22% of 141 eligible ambulatory patients with COPD on triple inhaled therapy following pharmacist appointments.8 A study by Hahn et al resulted in 63.8% of 58 patients with COPD being maintained off ICS following a pharmacist de-escalation initiative.9 However, these studies relied upon more time-consuming de-escalation interventions, including at least 1 phone, video, or in-person patient visit.8,9
This project used a single chart review and templated progress note to recommend ICS de-escalation and achieved similar or improved de-escalation rates compared to previous studies.8,9 Previous studies were conducted prior to the updated 2023 GOLD guidelines for COPD which no longer recommend LABA + ICS therapy. This project addressed ICS de-escalation in patients on LABA + ICS therapy in addition to those on triple inhaled therapy. Additionally, previous studies did not address rates of moderate to severe COPD exacerbation and adverse events to ICS following the pharmacist intervention.8,9
This study included COPD exacerbations and cases of pneumonia or oral candidiasis as secondary outcomes to assess the safety and efficacy of the ICS de-escalation. It appeared there were similar or lower rates of COPD exacerbations, pneumonia, and oral candidiasis in those with de-escalated ICS therapy in this study. However, these secondary outcomes are exploratory and would need to be confirmed by larger studies powered to address these outcomes.
CONCLUSIONS
Pharmacist-driven ICS de-escalation may be an effective method for reducing ICS usage in veterans as seen in this study. Additional controlled studies are required to evaluate the efficacy and safety of pharmacist-driven ICS de-escalation.

- Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease (GOLD). Global Strategy for the Diagnosis, Management, and Prevention of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (2024 Report). Accessed October 14, 2025. https://goldcopd.org/2024-gold-report/
- Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease (GOLD). Global Strategy for the Diagnosis, Management, and Prevention of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (2025 Report). Accessed November 14, 2025. https://goldcopd.org/2025-gold-report/
- Rogliani P, Ritondo BL, Gabriele M, et al. Optimizing de-escalation of inhaled corticosteroids in COPD: a systematic review of real-world findings. Expert Rev Clin Pharmacol. 2020;13(9):977-990. doi:10.1080/17512433.2020.1817739
- Rossi A, Guerriero M, Corrado A; OPTIMO/AIPO Study Group. Withdrawal of inhaled corticosteroids can be safe in COPD patients at low risk of exacerbation: a real-life study on the appropriateness of treatment in moderate COPD patients (OPTIMO). Respir Res. 2014;15(1):77. doi:10.1186/1465-9921-15-77
- Anderson E, Wiener RS, Resnick K, et al. Care coordination for veterans with COPD: a positive deviance study. Am J Manag Care. 2020;26(2):63-68. doi:10.37765/ajmc.2020.42394
- US Department of Veterans Affairs, US Department of Defense. VA/DoD Clinical Practice Guideline for the Management of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. 2021. Accessed October 14, 2025. https://www.healthquality.va.gov/guidelines/CD/copd/
- Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease (GOLD). Global Strategy for the Diagnosis, Management, and Prevention of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (2023 Report). Accessed October 14, 2025. https://goldcopd.org/wp-content/uploads/2023/03/GOLD-2023-ver-1.3-17Feb2023_WMV.pdf
- Hegland AJ, Bolduc J, Jones L, Kunisaki KM, Melzer AC. Pharmacist-driven deprescribing of inhaled corticosteroids in patients with stable chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Ann Am Thorac Soc. 2021;18(4):730-733. doi:10.1513/AnnalsATS.202007-871RL
- Hahn NM, Nagy MW. Implementation of a targeted inhaled corticosteroid de-escalation process in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease in the primary care setting. Innov Pharm. 2022;13(1):10.24926/iip.v13i1.4349. doi:10.24926/iip.v13i1.4349
- Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease (GOLD). Global Strategy for the Diagnosis, Management, and Prevention of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (2024 Report). Accessed October 14, 2025. https://goldcopd.org/2024-gold-report/
- Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease (GOLD). Global Strategy for the Diagnosis, Management, and Prevention of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (2025 Report). Accessed November 14, 2025. https://goldcopd.org/2025-gold-report/
- Rogliani P, Ritondo BL, Gabriele M, et al. Optimizing de-escalation of inhaled corticosteroids in COPD: a systematic review of real-world findings. Expert Rev Clin Pharmacol. 2020;13(9):977-990. doi:10.1080/17512433.2020.1817739
- Rossi A, Guerriero M, Corrado A; OPTIMO/AIPO Study Group. Withdrawal of inhaled corticosteroids can be safe in COPD patients at low risk of exacerbation: a real-life study on the appropriateness of treatment in moderate COPD patients (OPTIMO). Respir Res. 2014;15(1):77. doi:10.1186/1465-9921-15-77
- Anderson E, Wiener RS, Resnick K, et al. Care coordination for veterans with COPD: a positive deviance study. Am J Manag Care. 2020;26(2):63-68. doi:10.37765/ajmc.2020.42394
- US Department of Veterans Affairs, US Department of Defense. VA/DoD Clinical Practice Guideline for the Management of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. 2021. Accessed October 14, 2025. https://www.healthquality.va.gov/guidelines/CD/copd/
- Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease (GOLD). Global Strategy for the Diagnosis, Management, and Prevention of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (2023 Report). Accessed October 14, 2025. https://goldcopd.org/wp-content/uploads/2023/03/GOLD-2023-ver-1.3-17Feb2023_WMV.pdf
- Hegland AJ, Bolduc J, Jones L, Kunisaki KM, Melzer AC. Pharmacist-driven deprescribing of inhaled corticosteroids in patients with stable chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Ann Am Thorac Soc. 2021;18(4):730-733. doi:10.1513/AnnalsATS.202007-871RL
- Hahn NM, Nagy MW. Implementation of a targeted inhaled corticosteroid de-escalation process in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease in the primary care setting. Innov Pharm. 2022;13(1):10.24926/iip.v13i1.4349. doi:10.24926/iip.v13i1.4349
Evaluation of Pharmacist-Driven Inhaled Corticosteroid De-escalation in Veterans
Evaluation of Pharmacist-Driven Inhaled Corticosteroid De-escalation in Veterans
COPD CARE Academy: Design of Purposeful Training Guided by Implementation Strategies
COPD CARE Academy: Design of Purposeful Training Guided by Implementation Strategies
Quality improvement (QI) initiatives within the US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) play an important role in enhancing health care for veterans.1,2 While effective QI programs are often developed, veterans benefit only if they receive care at sites where the program is offered.3 It is estimated only 1% to 5% of patients receive benefit from evidence-based programs, limiting the opportunity for widespread impact.4,5
The Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) Coordinated Access to Reduce Exacerbations (CARE) Academy is a national training program designed to promote the adoption of a COPD primary care service.6 The Academy was created and iteratively refined by VA staff to include both clinical training emphasizing COPD management and program implementation strategies. Training programs such as COPD CARE are commonly described as a method to support adoption of health care services, but there is no consensus on a universal approach to training design.
This article describes COPD CARE training and implementation strategies (Table). The Academy began as a training program at 1 VA medical center (VAMC) and has expanded to 49 diverse VAMCs. The Academy illustrates how implementation strategies can be leveraged to develop pragmatic and impactful training. Highlights from the Academy's 9-year history are outlined in this article.

COPD CARE
One in 4 veterans have a COPD diagnosis, and the 5-year mortality rate following a COPD flare is ≥ 50%.7,8 In 2015, a pharmacy resident designed and piloted COPD CARE, a program that used evidence-based practice to optimize management of the disease.9,10
The COPD CARE program is delivered by interprofessional team members. It includes a postacute care call completed 48 hours postdischarge, a wellness visit (face-to-face or virtual) 1 month postdischarge, and a follow-up visit scheduled 2 months postdischarge. Clinical pharmacist practitioners (CPPs) prescribe and collaborate with the COPD CARE health care team. Evidence-based practices embedded within COPD CARE include treatment optimization, symptom evaluation, severity staging, vaccination promotion, referrals, tobacco treatment, and comorbidity management.11-16 The initial COPD CARE pilot demonstrated promising results; patients received timely care and high rates of COPD best practices.11
Academy Design and Implementation
Initial COPD CARE training was tailored to the culture, context, and workflow of the William S. Middleton Memorial Veteran’s Hospital in Madison, Wisconsin. Further service expansion required integration of implementation strategies that enable learners to apply and adapt content to fit different processes, staffing, and patient needs.
Formal Implementation Blueprint
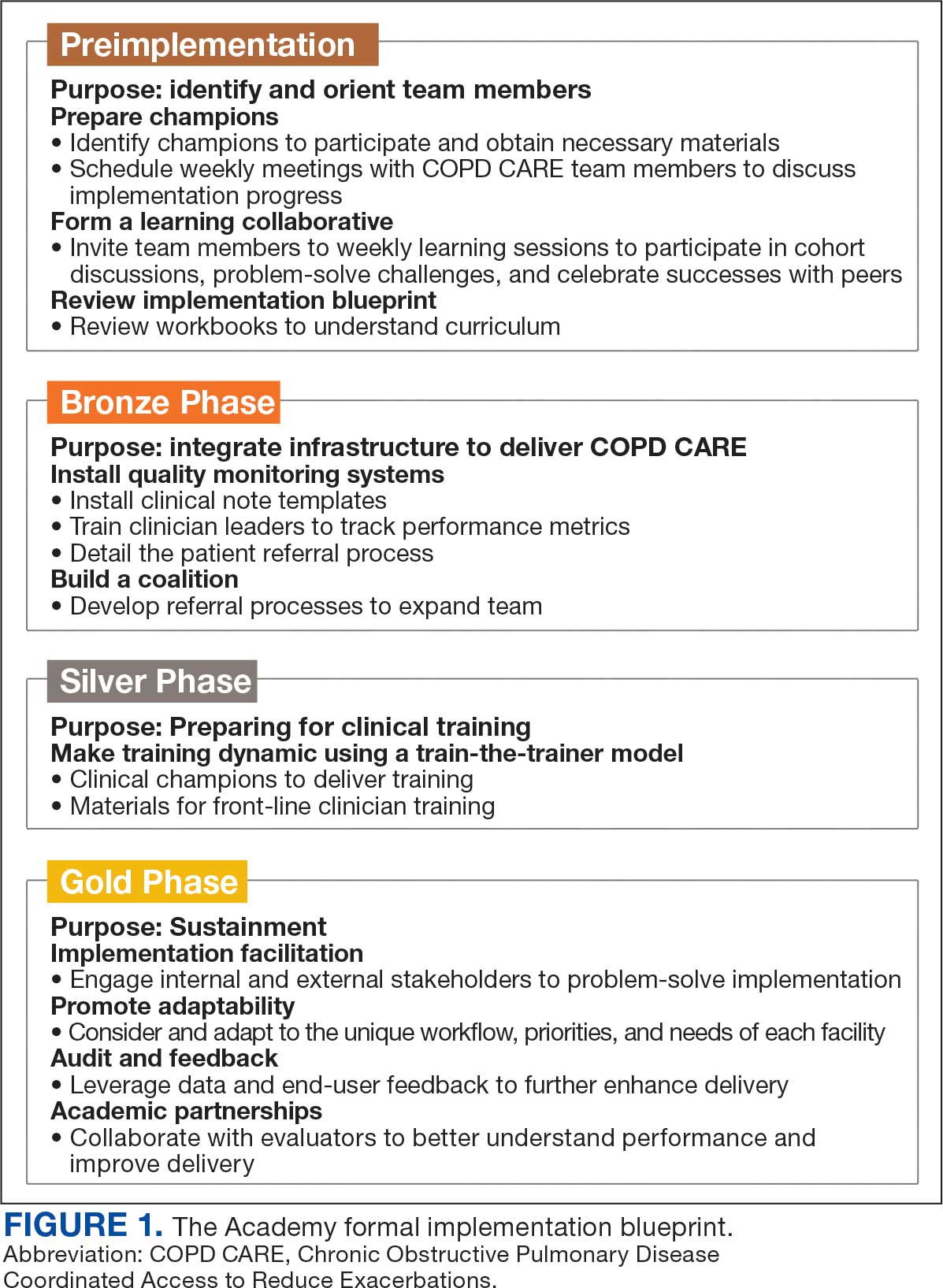
A key aspect of the Academy is the integration of a formal implementation blueprint that includes training goals, scope, and key milestones to guide implementation. The Academy blueprint includes 4 phased training workbooks: (1) preimplementation support from local stakeholders; (2) integration of COPD CARE operational infrastructure into workflows; (3) preparing clinical champions; and (4) leading clinical training (Figure 1). Five weekly 1-hour synchronous virtual discussions are used for learning the workbook content that include learning objectives and opportunities to strategize how to overcome implementation barriers.
Promoting and Facilitating Implementation
As clinicians apply content from the Academy to install informatics tools, coordinate clinical training, and build relationships across service lines, implementation barriers may occur. A learning collaborative allows peer-mentorship and shared problem solving. The Academy learning collaborative includes attendees across multiple VAMCs, allowing for diverse perspectives and cross-site learning. Within the field of dissemination and implementation science, this process of shared problem-solving to support individuals is referred to as implementation facilitation.17 Academy facilitators with prior experience provide a unique perspective and external facilitation from outside local VAMCs. Academy learners form local teams to engage in shared decision-making when applying Academy content. Following Academy completion, learning collaboratives continue to meet monthly to share clinical insights and operational updates.
Local Champions Promote Adaptability
One or more local champions were identified at each VAMC who were focused on the implementation of clinical training content and operational implementation of Academy content.18 Champions have helped develop adaptations of Academy content, such as integrating telehealth nursing within the COPD CARE referral process, which have become new best practices. Champions attend Academy sessions, which provide an opportunity to share adaptations to meet local needs.19
Using a Train-The-Trainer Model
Clinical training was designed to be dynamic and included video modeling, such as recorded examples of CPPs conducting COPD CARE visits and video clips highlighting clinical content. Each learner received a clinical workbook summarizing the content. The champion shares discussion questions to relate training content to the local clinical practice setting. The combination of live training, with videos of clinic visits and case-based discussion was intended to address differing learning styles. Clinical training was delivered using a train-the-trainer model led by the local champion, which allows clinicians with expertise to tailor their training. The use of a train-the-trainer model was intended to promote local buy-in and was often completed by frontline clinicians.
Informatics note templates provide clinicians with information needed to deliver training content during clinic visits. Direct hyperlinks to symptomatic scoring tools, resources to promote evidence-based medication optimization, and patient education resources were embedded within the electronic health record note templates. Direct links to consults for COPD referrals services discussed during clinical training were also included to promote ease of care coordination and awareness of referral opportunities. The integration of clinical training with informatics note template support was intentional to directly relate clinical training to clinical care delivery.
Audit and Feedback
To inform COPD CARE practice, the Academy included informatics infrastructure that allowed for timely local quality monitoring. Electronic health record note templates with embedded data fields track COPD CARE service implementation, including timely completion of patient visits, completion of patient medication reviews, appropriate testing, symptom assessment, and interventions made. Champions can organize template installation and integrate templates into COPD CARE clinical training. Data are included on a COPD CARE implementation dashboard.
An audit and feedback process is allows for the review of performance metrics and development of action plans.20,21 Data reports from note templates are described during the Academy, along with resources to help teams enhance delivery of their program based on performance metrics.
Building a Coalition
Within VA primary care, clinical care delivery is optimized through a team-based coalition of clinicians using the patient aligned care team (PACT) framework. The VA patient-centered team-based care delivery model, patient facilitates coordination of patient referrals, including patient review, scheduling, and completion of patient visits.22
Partnerships with VA Pharmacy Benefits Manager, VA Diffusion of Excellence, VA Quality Enhancement Research Initiative, VA Office of Pulmonary Medicine, and the VA Office of Rural Health have facilitated COPD CARE successes. Collaborations with VA Centers of Innovation helped benchmark the Academy’s impact. An academic partnership with the University of Wisconsin-Madison was established in 2017 and has provided evaluation expertise and leadership as the Academy has been iteratively developed, and revised.
Preliminary Metrics
COPD CARE has delivered > 2000 visits. CPPs have delivered COPD care, with a mean 9.4 of 10 best practices per patient visit. Improvements in veteran COPD symptoms have also been observed following COPD CARE patient visits.
DISCUSSION
The COPD CARE Academy was developed to promote rapid scale-up of a complex, team-based COPD service delivered during veteran care transitions. The implementation blueprint for the Academy is multifaceted and integrates both clinical-focused and implementation-focused infrastructure to apply training content.23 A randomized control trial evaluating the efficacy of training modalities found a need to expand implementation blueprints beyond clinical training alone, as training by itself may not be sufficient to change behavior.24 VA staff designed the Academy using clinical- and implementation-focused content within its implementation blueprint. Key components included leveraging clinical champions, using a train-the-trainer approach, and incorporating facilitation strategies to overcome adoption barriers.
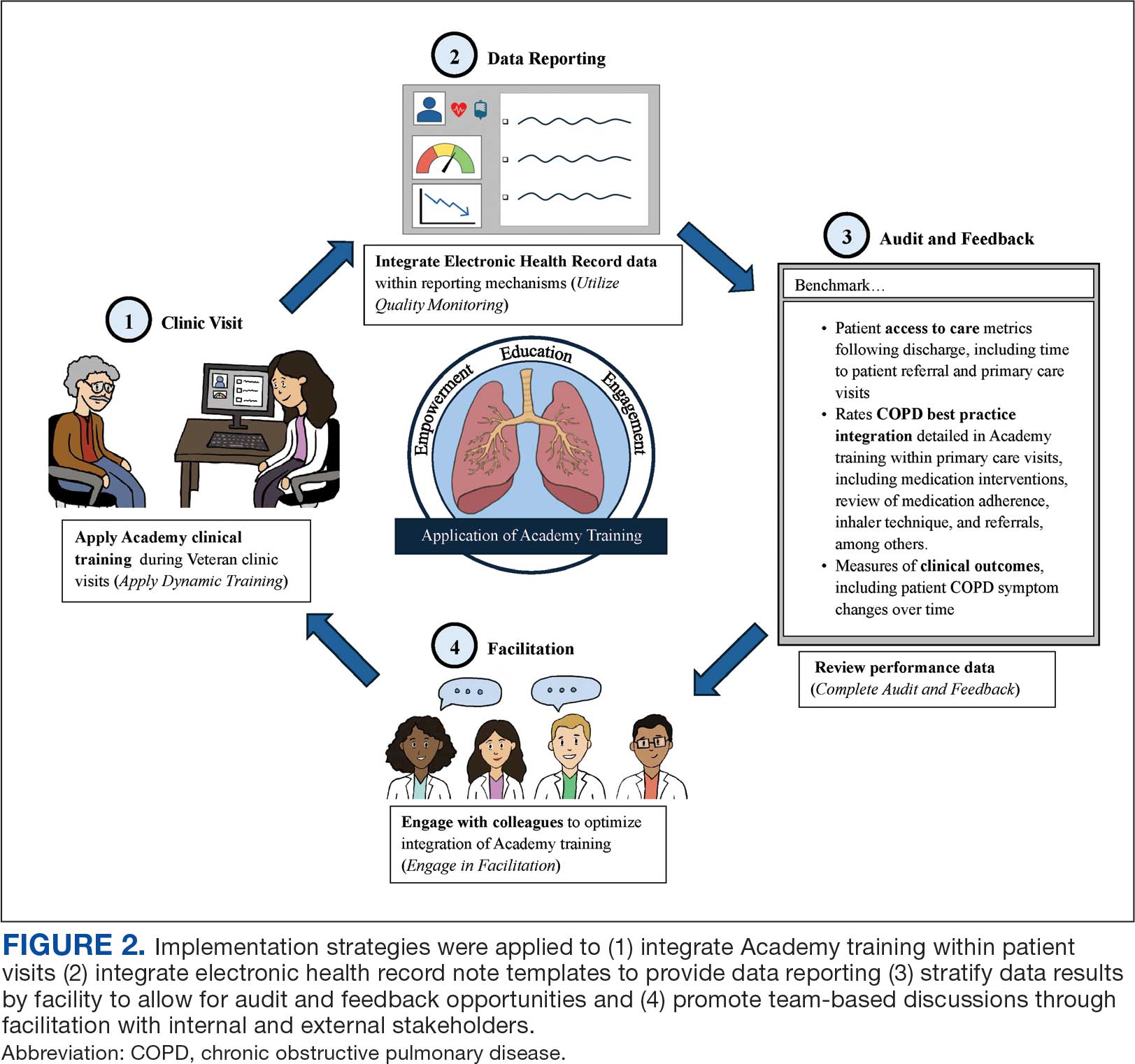
Lewis et al emphasize matching implementation strategies to barriers within VA staff who identify care coordination as a key challenge.23 The informatics infrastructure developed for Academy learners, including standardized note templates, video modeling examples of clinic visits, and data capture for audit and feedback, was designed to complement clinical training and standardize service workflows (Figure 2). There are opportunities to explore how to optimize technology in the Academy.
While Academy clinical training specifically focuses on COPD management, many implementation strategies can be considered to promote care delivery services for other chronic conditions. The Academy blueprint and implementation infrastructure, are strategies that may be considered within and outside the federal health care system. The opportunity for adaptations to Academy training enables clinical champions to promote tailored content to the needs of each unique VAMC. The translation of Academy implementation strategies for new chronic conditions will similarly require adaptations at each VAMC to promote adoption of content.
CONCLUSIONS
COPD CARE Academy is an example of the collaborative spirit within VA, and the opportunity for further advancement of health care programs. The VA is a national leader in Learning Health Systems implementation, in which “science, informatics, incentives and culture are aligned for continuous improvement and innovation.”25,26 There are many opportunities for VA staff to learn from one another to form partnerships between leaders, clinicians, and scientists to optimize health care delivery and further the VA’s work as a learning health system.
- Robinson CH, Thompto AJ, Lima EN, Damschroder LJ. Continuous quality improvement at the frontline: one interdisciplinary clinical team's four-year journey after completing a virtual learning program. Learn Health Syst. 2022;6(4):e10345. doi:10.1002/lrh2.10345
- US Department of Veterans Affairs. Continuous quality improvement (CQI) for clinical teams: a systematic review of reviews. Accessed July 24, 2025. https://www.hsrd.research.va.gov/for_researchers/cyber_seminars/archives/video_archive.cfm?SessionID=4151
- Dondanville KA, Fina BA, Straud CL, et al. Launching a competency-based training program in evidence-based treatments for PTSD: supporting veteran-serving mental health providers in Texas. Community Ment Health J. 2021;57(5):910-919. doi:10.1007/S10597-020-00676-7
- Abildso CG, Zizzi SJ, Reger-Nash B. Evaluating an insurance- sponsored weight management program with the RE-AIM model, West Virginia, 2004-2008. Prev Chronic Dis. 2010;7(3):A46.
- Glasgow RE, Vinson C, Chambers D, Khoury MJ, Kaplan RM, Hunter C. National institutes of health approaches to dissemination and implementation science: current and future directions. Am J Public Health. 2012;102(7):1274- 1281. doi:10.2105/AJPH.2012.300755
- Portillo EC, Maurer MA, Kettner JT, et al. Applying RE-AIM to examine the impact of an implementation facilitation package to scale up a program for veterans with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Implement Sci Commun. 2023;4(1):143. doi:10.1186/S43058-023-00520-5
- McGhan R, Radcliff T, Fish R, Sutherland ER, Welsh C, Make B. Predictors of rehospitalization and death after a severe exacerbation of COPD. Chest. 2007;132(6):1748- 1755. doi:10.1378/chest.06-3018
- Anderson E, Wiener RS, Resnick K, Elwy AR, Rinne ST. Care coordination for veterans with COPD: a positive deviance study. Am J Manag Care. 2020;26(2):63-68. doi:10.37765/AJMC.2020.42394
- 2024 GOLD Report. Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease - GOLD. Accessed July 24, 2025. https://goldcopd.org/2024-gold-report/
- Nici L, Mammen MJ, Charbek E, et al. Pharmacologic management of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. An official American Thoracic Society clinical practice guideline. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2020;201(9):e56-e69. doi:10.1164/rccm.202003-0625ST
- Portillo EC, Wilcox A, Seckel E, et al. Reducing COPD readmission rates: using a COPD care service during care transitions. Fed Pract. 2018;35(11):30-36.
- Portillo EC, Gruber S, Lehmann M, et al. Application of the replicating effective programs framework to design a COPD training program. J Am Pharm Assoc. 2021;61(2):e129-e135. doi:10.1016/J.JAPH.2020.10.023
- Portillo EC, Lehmann MR, Hagen TL, et al. Integration of the patient-centered medical home to deliver a care bundle for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease management. J Am Pharm Assoc. 2023;63(1):212-219. doi:10.1016/j.japh.2022.10.003
- Portillo E, Lehmann M, Hagen T, et al. Evaluation of an implementation package to deliver the COPD CARE service. BMJ Open Qual. 2023;12(1). doi:10.1136/BMJOQ-2022-002074
- Portillo E, Lehmann M, Maurer M, et al. Barriers to implementing a pharmacist-led COPD care bundle in rural settings: A qualitative evaluation. 2025 (under review).
- Population Health Management. American Hospital Association. Accessed July 24, 2025. https://www.aha.org/center/population-health-management
- Ritchie MJ, Dollar KM, Miller CK, et al. Using implementation facilitation to improve healthcare: implementation facilitation training manual. Accessed July 11, 2024. https:// www.queri.research.va.gov/tools/Facilitation-Manual.pdf
- Morena AL, Gaias LM, Larkin C. Understanding the role of clinical champions and their impact on clinician behavior change: the need for causal pathway mechanisms. Front Health Serv. 2022;2:896885. doi:10.3389/FRHS.2022.896885
- Ayele RA, Rabin BA, McCreight M, Battaglia C. Editorial: understanding, assessing, and guiding adaptations in public health and health systems interventions: current and future directions. Front Public Health. 2023;11:1228437. doi:10.3389/fpubh.2023.1228437
- Jamtvedt G, Flottorp S, Ivers N. Audit and feedback as a quality strategy. In: Improving Healthcare Services. World Health Organization; 2019. Accessed July 24, 2025. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK549284/
- Snider MDH, Boyd MR, Walker MR, Powell BJ, Lewis CC. Using audit and feedback to guide tailored implementations of measurement-based care in community mental health: a multiple case study. Implement Sci Commun. 2023;4(1):94. doi:10.1186/s43058-023-00474-8
- Patient Aligned Care Team (PACT) – Patient Care Services. US Department of Veterans Affairs. Accessed July 24, 2025. https://www.patientcare.va.gov/primarycare/PACT.asp
- Lewis CC, Scott K, Marriott BR. A methodology for generating a tailored implementation blueprint: an exemplar from a youth residential setting. Implementat Sci. 2018;13(1):68. doi:10.1186/s13012-018-0761-6
- Beidas RS, Edmunds JM, Marcus SC, Kendall PC. Training and consultation to promote implementation of an empirically supported treatment: a randomized trial. Psychiatr Serv. 2012;63(7):660-665. doi:10.1176/appi.ps.201100401
- Kilbourne AM, Schmidt J, Edmunds M, Vega R, Bowersox N, Atkins D. How the VA is training the next-generation workforce for learning health systems. Learn Health Syst. 2022;6(4):e10333. doi:10.1002/LRH2.10333
- Easterling D, Perry AC, Woodside R, Patel T, Gesell SB. Clarifying the concept of a learning health system for healthcare delivery organizations: implications from a qualitative analysis of the scientific literature. Learn Health Syst. 2021;6(2):e10287. doi:10.1002/LRH2.10287
Quality improvement (QI) initiatives within the US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) play an important role in enhancing health care for veterans.1,2 While effective QI programs are often developed, veterans benefit only if they receive care at sites where the program is offered.3 It is estimated only 1% to 5% of patients receive benefit from evidence-based programs, limiting the opportunity for widespread impact.4,5
The Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) Coordinated Access to Reduce Exacerbations (CARE) Academy is a national training program designed to promote the adoption of a COPD primary care service.6 The Academy was created and iteratively refined by VA staff to include both clinical training emphasizing COPD management and program implementation strategies. Training programs such as COPD CARE are commonly described as a method to support adoption of health care services, but there is no consensus on a universal approach to training design.
This article describes COPD CARE training and implementation strategies (Table). The Academy began as a training program at 1 VA medical center (VAMC) and has expanded to 49 diverse VAMCs. The Academy illustrates how implementation strategies can be leveraged to develop pragmatic and impactful training. Highlights from the Academy's 9-year history are outlined in this article.

COPD CARE
One in 4 veterans have a COPD diagnosis, and the 5-year mortality rate following a COPD flare is ≥ 50%.7,8 In 2015, a pharmacy resident designed and piloted COPD CARE, a program that used evidence-based practice to optimize management of the disease.9,10
The COPD CARE program is delivered by interprofessional team members. It includes a postacute care call completed 48 hours postdischarge, a wellness visit (face-to-face or virtual) 1 month postdischarge, and a follow-up visit scheduled 2 months postdischarge. Clinical pharmacist practitioners (CPPs) prescribe and collaborate with the COPD CARE health care team. Evidence-based practices embedded within COPD CARE include treatment optimization, symptom evaluation, severity staging, vaccination promotion, referrals, tobacco treatment, and comorbidity management.11-16 The initial COPD CARE pilot demonstrated promising results; patients received timely care and high rates of COPD best practices.11
Academy Design and Implementation
Initial COPD CARE training was tailored to the culture, context, and workflow of the William S. Middleton Memorial Veteran’s Hospital in Madison, Wisconsin. Further service expansion required integration of implementation strategies that enable learners to apply and adapt content to fit different processes, staffing, and patient needs.
Formal Implementation Blueprint
A key aspect of the Academy is the integration of a formal implementation blueprint that includes training goals, scope, and key milestones to guide implementation. The Academy blueprint includes 4 phased training workbooks: (1) preimplementation support from local stakeholders; (2) integration of COPD CARE operational infrastructure into workflows; (3) preparing clinical champions; and (4) leading clinical training (Figure 1). Five weekly 1-hour synchronous virtual discussions are used for learning the workbook content that include learning objectives and opportunities to strategize how to overcome implementation barriers.

Promoting and Facilitating Implementation
As clinicians apply content from the Academy to install informatics tools, coordinate clinical training, and build relationships across service lines, implementation barriers may occur. A learning collaborative allows peer-mentorship and shared problem solving. The Academy learning collaborative includes attendees across multiple VAMCs, allowing for diverse perspectives and cross-site learning. Within the field of dissemination and implementation science, this process of shared problem-solving to support individuals is referred to as implementation facilitation.17 Academy facilitators with prior experience provide a unique perspective and external facilitation from outside local VAMCs. Academy learners form local teams to engage in shared decision-making when applying Academy content. Following Academy completion, learning collaboratives continue to meet monthly to share clinical insights and operational updates.
Local Champions Promote Adaptability
One or more local champions were identified at each VAMC who were focused on the implementation of clinical training content and operational implementation of Academy content.18 Champions have helped develop adaptations of Academy content, such as integrating telehealth nursing within the COPD CARE referral process, which have become new best practices. Champions attend Academy sessions, which provide an opportunity to share adaptations to meet local needs.19
Using a Train-The-Trainer Model
Clinical training was designed to be dynamic and included video modeling, such as recorded examples of CPPs conducting COPD CARE visits and video clips highlighting clinical content. Each learner received a clinical workbook summarizing the content. The champion shares discussion questions to relate training content to the local clinical practice setting. The combination of live training, with videos of clinic visits and case-based discussion was intended to address differing learning styles. Clinical training was delivered using a train-the-trainer model led by the local champion, which allows clinicians with expertise to tailor their training. The use of a train-the-trainer model was intended to promote local buy-in and was often completed by frontline clinicians.
Informatics note templates provide clinicians with information needed to deliver training content during clinic visits. Direct hyperlinks to symptomatic scoring tools, resources to promote evidence-based medication optimization, and patient education resources were embedded within the electronic health record note templates. Direct links to consults for COPD referrals services discussed during clinical training were also included to promote ease of care coordination and awareness of referral opportunities. The integration of clinical training with informatics note template support was intentional to directly relate clinical training to clinical care delivery.
Audit and Feedback
To inform COPD CARE practice, the Academy included informatics infrastructure that allowed for timely local quality monitoring. Electronic health record note templates with embedded data fields track COPD CARE service implementation, including timely completion of patient visits, completion of patient medication reviews, appropriate testing, symptom assessment, and interventions made. Champions can organize template installation and integrate templates into COPD CARE clinical training. Data are included on a COPD CARE implementation dashboard.
An audit and feedback process is allows for the review of performance metrics and development of action plans.20,21 Data reports from note templates are described during the Academy, along with resources to help teams enhance delivery of their program based on performance metrics.
Building a Coalition
Within VA primary care, clinical care delivery is optimized through a team-based coalition of clinicians using the patient aligned care team (PACT) framework. The VA patient-centered team-based care delivery model, patient facilitates coordination of patient referrals, including patient review, scheduling, and completion of patient visits.22
Partnerships with VA Pharmacy Benefits Manager, VA Diffusion of Excellence, VA Quality Enhancement Research Initiative, VA Office of Pulmonary Medicine, and the VA Office of Rural Health have facilitated COPD CARE successes. Collaborations with VA Centers of Innovation helped benchmark the Academy’s impact. An academic partnership with the University of Wisconsin-Madison was established in 2017 and has provided evaluation expertise and leadership as the Academy has been iteratively developed, and revised.
Preliminary Metrics
COPD CARE has delivered > 2000 visits. CPPs have delivered COPD care, with a mean 9.4 of 10 best practices per patient visit. Improvements in veteran COPD symptoms have also been observed following COPD CARE patient visits.
DISCUSSION
The COPD CARE Academy was developed to promote rapid scale-up of a complex, team-based COPD service delivered during veteran care transitions. The implementation blueprint for the Academy is multifaceted and integrates both clinical-focused and implementation-focused infrastructure to apply training content.23 A randomized control trial evaluating the efficacy of training modalities found a need to expand implementation blueprints beyond clinical training alone, as training by itself may not be sufficient to change behavior.24 VA staff designed the Academy using clinical- and implementation-focused content within its implementation blueprint. Key components included leveraging clinical champions, using a train-the-trainer approach, and incorporating facilitation strategies to overcome adoption barriers.
Lewis et al emphasize matching implementation strategies to barriers within VA staff who identify care coordination as a key challenge.23 The informatics infrastructure developed for Academy learners, including standardized note templates, video modeling examples of clinic visits, and data capture for audit and feedback, was designed to complement clinical training and standardize service workflows (Figure 2). There are opportunities to explore how to optimize technology in the Academy.

While Academy clinical training specifically focuses on COPD management, many implementation strategies can be considered to promote care delivery services for other chronic conditions. The Academy blueprint and implementation infrastructure, are strategies that may be considered within and outside the federal health care system. The opportunity for adaptations to Academy training enables clinical champions to promote tailored content to the needs of each unique VAMC. The translation of Academy implementation strategies for new chronic conditions will similarly require adaptations at each VAMC to promote adoption of content.
CONCLUSIONS
COPD CARE Academy is an example of the collaborative spirit within VA, and the opportunity for further advancement of health care programs. The VA is a national leader in Learning Health Systems implementation, in which “science, informatics, incentives and culture are aligned for continuous improvement and innovation.”25,26 There are many opportunities for VA staff to learn from one another to form partnerships between leaders, clinicians, and scientists to optimize health care delivery and further the VA’s work as a learning health system.
Quality improvement (QI) initiatives within the US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) play an important role in enhancing health care for veterans.1,2 While effective QI programs are often developed, veterans benefit only if they receive care at sites where the program is offered.3 It is estimated only 1% to 5% of patients receive benefit from evidence-based programs, limiting the opportunity for widespread impact.4,5
The Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) Coordinated Access to Reduce Exacerbations (CARE) Academy is a national training program designed to promote the adoption of a COPD primary care service.6 The Academy was created and iteratively refined by VA staff to include both clinical training emphasizing COPD management and program implementation strategies. Training programs such as COPD CARE are commonly described as a method to support adoption of health care services, but there is no consensus on a universal approach to training design.
This article describes COPD CARE training and implementation strategies (Table). The Academy began as a training program at 1 VA medical center (VAMC) and has expanded to 49 diverse VAMCs. The Academy illustrates how implementation strategies can be leveraged to develop pragmatic and impactful training. Highlights from the Academy's 9-year history are outlined in this article.

COPD CARE
One in 4 veterans have a COPD diagnosis, and the 5-year mortality rate following a COPD flare is ≥ 50%.7,8 In 2015, a pharmacy resident designed and piloted COPD CARE, a program that used evidence-based practice to optimize management of the disease.9,10
The COPD CARE program is delivered by interprofessional team members. It includes a postacute care call completed 48 hours postdischarge, a wellness visit (face-to-face or virtual) 1 month postdischarge, and a follow-up visit scheduled 2 months postdischarge. Clinical pharmacist practitioners (CPPs) prescribe and collaborate with the COPD CARE health care team. Evidence-based practices embedded within COPD CARE include treatment optimization, symptom evaluation, severity staging, vaccination promotion, referrals, tobacco treatment, and comorbidity management.11-16 The initial COPD CARE pilot demonstrated promising results; patients received timely care and high rates of COPD best practices.11
Academy Design and Implementation
Initial COPD CARE training was tailored to the culture, context, and workflow of the William S. Middleton Memorial Veteran’s Hospital in Madison, Wisconsin. Further service expansion required integration of implementation strategies that enable learners to apply and adapt content to fit different processes, staffing, and patient needs.
Formal Implementation Blueprint
A key aspect of the Academy is the integration of a formal implementation blueprint that includes training goals, scope, and key milestones to guide implementation. The Academy blueprint includes 4 phased training workbooks: (1) preimplementation support from local stakeholders; (2) integration of COPD CARE operational infrastructure into workflows; (3) preparing clinical champions; and (4) leading clinical training (Figure 1). Five weekly 1-hour synchronous virtual discussions are used for learning the workbook content that include learning objectives and opportunities to strategize how to overcome implementation barriers.

Promoting and Facilitating Implementation
As clinicians apply content from the Academy to install informatics tools, coordinate clinical training, and build relationships across service lines, implementation barriers may occur. A learning collaborative allows peer-mentorship and shared problem solving. The Academy learning collaborative includes attendees across multiple VAMCs, allowing for diverse perspectives and cross-site learning. Within the field of dissemination and implementation science, this process of shared problem-solving to support individuals is referred to as implementation facilitation.17 Academy facilitators with prior experience provide a unique perspective and external facilitation from outside local VAMCs. Academy learners form local teams to engage in shared decision-making when applying Academy content. Following Academy completion, learning collaboratives continue to meet monthly to share clinical insights and operational updates.
Local Champions Promote Adaptability
One or more local champions were identified at each VAMC who were focused on the implementation of clinical training content and operational implementation of Academy content.18 Champions have helped develop adaptations of Academy content, such as integrating telehealth nursing within the COPD CARE referral process, which have become new best practices. Champions attend Academy sessions, which provide an opportunity to share adaptations to meet local needs.19
Using a Train-The-Trainer Model
Clinical training was designed to be dynamic and included video modeling, such as recorded examples of CPPs conducting COPD CARE visits and video clips highlighting clinical content. Each learner received a clinical workbook summarizing the content. The champion shares discussion questions to relate training content to the local clinical practice setting. The combination of live training, with videos of clinic visits and case-based discussion was intended to address differing learning styles. Clinical training was delivered using a train-the-trainer model led by the local champion, which allows clinicians with expertise to tailor their training. The use of a train-the-trainer model was intended to promote local buy-in and was often completed by frontline clinicians.
Informatics note templates provide clinicians with information needed to deliver training content during clinic visits. Direct hyperlinks to symptomatic scoring tools, resources to promote evidence-based medication optimization, and patient education resources were embedded within the electronic health record note templates. Direct links to consults for COPD referrals services discussed during clinical training were also included to promote ease of care coordination and awareness of referral opportunities. The integration of clinical training with informatics note template support was intentional to directly relate clinical training to clinical care delivery.
Audit and Feedback
To inform COPD CARE practice, the Academy included informatics infrastructure that allowed for timely local quality monitoring. Electronic health record note templates with embedded data fields track COPD CARE service implementation, including timely completion of patient visits, completion of patient medication reviews, appropriate testing, symptom assessment, and interventions made. Champions can organize template installation and integrate templates into COPD CARE clinical training. Data are included on a COPD CARE implementation dashboard.
An audit and feedback process is allows for the review of performance metrics and development of action plans.20,21 Data reports from note templates are described during the Academy, along with resources to help teams enhance delivery of their program based on performance metrics.
Building a Coalition
Within VA primary care, clinical care delivery is optimized through a team-based coalition of clinicians using the patient aligned care team (PACT) framework. The VA patient-centered team-based care delivery model, patient facilitates coordination of patient referrals, including patient review, scheduling, and completion of patient visits.22
Partnerships with VA Pharmacy Benefits Manager, VA Diffusion of Excellence, VA Quality Enhancement Research Initiative, VA Office of Pulmonary Medicine, and the VA Office of Rural Health have facilitated COPD CARE successes. Collaborations with VA Centers of Innovation helped benchmark the Academy’s impact. An academic partnership with the University of Wisconsin-Madison was established in 2017 and has provided evaluation expertise and leadership as the Academy has been iteratively developed, and revised.
Preliminary Metrics
COPD CARE has delivered > 2000 visits. CPPs have delivered COPD care, with a mean 9.4 of 10 best practices per patient visit. Improvements in veteran COPD symptoms have also been observed following COPD CARE patient visits.
DISCUSSION
The COPD CARE Academy was developed to promote rapid scale-up of a complex, team-based COPD service delivered during veteran care transitions. The implementation blueprint for the Academy is multifaceted and integrates both clinical-focused and implementation-focused infrastructure to apply training content.23 A randomized control trial evaluating the efficacy of training modalities found a need to expand implementation blueprints beyond clinical training alone, as training by itself may not be sufficient to change behavior.24 VA staff designed the Academy using clinical- and implementation-focused content within its implementation blueprint. Key components included leveraging clinical champions, using a train-the-trainer approach, and incorporating facilitation strategies to overcome adoption barriers.
Lewis et al emphasize matching implementation strategies to barriers within VA staff who identify care coordination as a key challenge.23 The informatics infrastructure developed for Academy learners, including standardized note templates, video modeling examples of clinic visits, and data capture for audit and feedback, was designed to complement clinical training and standardize service workflows (Figure 2). There are opportunities to explore how to optimize technology in the Academy.

While Academy clinical training specifically focuses on COPD management, many implementation strategies can be considered to promote care delivery services for other chronic conditions. The Academy blueprint and implementation infrastructure, are strategies that may be considered within and outside the federal health care system. The opportunity for adaptations to Academy training enables clinical champions to promote tailored content to the needs of each unique VAMC. The translation of Academy implementation strategies for new chronic conditions will similarly require adaptations at each VAMC to promote adoption of content.
CONCLUSIONS
COPD CARE Academy is an example of the collaborative spirit within VA, and the opportunity for further advancement of health care programs. The VA is a national leader in Learning Health Systems implementation, in which “science, informatics, incentives and culture are aligned for continuous improvement and innovation.”25,26 There are many opportunities for VA staff to learn from one another to form partnerships between leaders, clinicians, and scientists to optimize health care delivery and further the VA’s work as a learning health system.
- Robinson CH, Thompto AJ, Lima EN, Damschroder LJ. Continuous quality improvement at the frontline: one interdisciplinary clinical team's four-year journey after completing a virtual learning program. Learn Health Syst. 2022;6(4):e10345. doi:10.1002/lrh2.10345
- US Department of Veterans Affairs. Continuous quality improvement (CQI) for clinical teams: a systematic review of reviews. Accessed July 24, 2025. https://www.hsrd.research.va.gov/for_researchers/cyber_seminars/archives/video_archive.cfm?SessionID=4151
- Dondanville KA, Fina BA, Straud CL, et al. Launching a competency-based training program in evidence-based treatments for PTSD: supporting veteran-serving mental health providers in Texas. Community Ment Health J. 2021;57(5):910-919. doi:10.1007/S10597-020-00676-7
- Abildso CG, Zizzi SJ, Reger-Nash B. Evaluating an insurance- sponsored weight management program with the RE-AIM model, West Virginia, 2004-2008. Prev Chronic Dis. 2010;7(3):A46.
- Glasgow RE, Vinson C, Chambers D, Khoury MJ, Kaplan RM, Hunter C. National institutes of health approaches to dissemination and implementation science: current and future directions. Am J Public Health. 2012;102(7):1274- 1281. doi:10.2105/AJPH.2012.300755
- Portillo EC, Maurer MA, Kettner JT, et al. Applying RE-AIM to examine the impact of an implementation facilitation package to scale up a program for veterans with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Implement Sci Commun. 2023;4(1):143. doi:10.1186/S43058-023-00520-5
- McGhan R, Radcliff T, Fish R, Sutherland ER, Welsh C, Make B. Predictors of rehospitalization and death after a severe exacerbation of COPD. Chest. 2007;132(6):1748- 1755. doi:10.1378/chest.06-3018
- Anderson E, Wiener RS, Resnick K, Elwy AR, Rinne ST. Care coordination for veterans with COPD: a positive deviance study. Am J Manag Care. 2020;26(2):63-68. doi:10.37765/AJMC.2020.42394
- 2024 GOLD Report. Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease - GOLD. Accessed July 24, 2025. https://goldcopd.org/2024-gold-report/
- Nici L, Mammen MJ, Charbek E, et al. Pharmacologic management of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. An official American Thoracic Society clinical practice guideline. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2020;201(9):e56-e69. doi:10.1164/rccm.202003-0625ST
- Portillo EC, Wilcox A, Seckel E, et al. Reducing COPD readmission rates: using a COPD care service during care transitions. Fed Pract. 2018;35(11):30-36.
- Portillo EC, Gruber S, Lehmann M, et al. Application of the replicating effective programs framework to design a COPD training program. J Am Pharm Assoc. 2021;61(2):e129-e135. doi:10.1016/J.JAPH.2020.10.023
- Portillo EC, Lehmann MR, Hagen TL, et al. Integration of the patient-centered medical home to deliver a care bundle for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease management. J Am Pharm Assoc. 2023;63(1):212-219. doi:10.1016/j.japh.2022.10.003
- Portillo E, Lehmann M, Hagen T, et al. Evaluation of an implementation package to deliver the COPD CARE service. BMJ Open Qual. 2023;12(1). doi:10.1136/BMJOQ-2022-002074
- Portillo E, Lehmann M, Maurer M, et al. Barriers to implementing a pharmacist-led COPD care bundle in rural settings: A qualitative evaluation. 2025 (under review).
- Population Health Management. American Hospital Association. Accessed July 24, 2025. https://www.aha.org/center/population-health-management
- Ritchie MJ, Dollar KM, Miller CK, et al. Using implementation facilitation to improve healthcare: implementation facilitation training manual. Accessed July 11, 2024. https:// www.queri.research.va.gov/tools/Facilitation-Manual.pdf
- Morena AL, Gaias LM, Larkin C. Understanding the role of clinical champions and their impact on clinician behavior change: the need for causal pathway mechanisms. Front Health Serv. 2022;2:896885. doi:10.3389/FRHS.2022.896885
- Ayele RA, Rabin BA, McCreight M, Battaglia C. Editorial: understanding, assessing, and guiding adaptations in public health and health systems interventions: current and future directions. Front Public Health. 2023;11:1228437. doi:10.3389/fpubh.2023.1228437
- Jamtvedt G, Flottorp S, Ivers N. Audit and feedback as a quality strategy. In: Improving Healthcare Services. World Health Organization; 2019. Accessed July 24, 2025. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK549284/
- Snider MDH, Boyd MR, Walker MR, Powell BJ, Lewis CC. Using audit and feedback to guide tailored implementations of measurement-based care in community mental health: a multiple case study. Implement Sci Commun. 2023;4(1):94. doi:10.1186/s43058-023-00474-8
- Patient Aligned Care Team (PACT) – Patient Care Services. US Department of Veterans Affairs. Accessed July 24, 2025. https://www.patientcare.va.gov/primarycare/PACT.asp
- Lewis CC, Scott K, Marriott BR. A methodology for generating a tailored implementation blueprint: an exemplar from a youth residential setting. Implementat Sci. 2018;13(1):68. doi:10.1186/s13012-018-0761-6
- Beidas RS, Edmunds JM, Marcus SC, Kendall PC. Training and consultation to promote implementation of an empirically supported treatment: a randomized trial. Psychiatr Serv. 2012;63(7):660-665. doi:10.1176/appi.ps.201100401
- Kilbourne AM, Schmidt J, Edmunds M, Vega R, Bowersox N, Atkins D. How the VA is training the next-generation workforce for learning health systems. Learn Health Syst. 2022;6(4):e10333. doi:10.1002/LRH2.10333
- Easterling D, Perry AC, Woodside R, Patel T, Gesell SB. Clarifying the concept of a learning health system for healthcare delivery organizations: implications from a qualitative analysis of the scientific literature. Learn Health Syst. 2021;6(2):e10287. doi:10.1002/LRH2.10287
- Robinson CH, Thompto AJ, Lima EN, Damschroder LJ. Continuous quality improvement at the frontline: one interdisciplinary clinical team's four-year journey after completing a virtual learning program. Learn Health Syst. 2022;6(4):e10345. doi:10.1002/lrh2.10345
- US Department of Veterans Affairs. Continuous quality improvement (CQI) for clinical teams: a systematic review of reviews. Accessed July 24, 2025. https://www.hsrd.research.va.gov/for_researchers/cyber_seminars/archives/video_archive.cfm?SessionID=4151
- Dondanville KA, Fina BA, Straud CL, et al. Launching a competency-based training program in evidence-based treatments for PTSD: supporting veteran-serving mental health providers in Texas. Community Ment Health J. 2021;57(5):910-919. doi:10.1007/S10597-020-00676-7
- Abildso CG, Zizzi SJ, Reger-Nash B. Evaluating an insurance- sponsored weight management program with the RE-AIM model, West Virginia, 2004-2008. Prev Chronic Dis. 2010;7(3):A46.
- Glasgow RE, Vinson C, Chambers D, Khoury MJ, Kaplan RM, Hunter C. National institutes of health approaches to dissemination and implementation science: current and future directions. Am J Public Health. 2012;102(7):1274- 1281. doi:10.2105/AJPH.2012.300755
- Portillo EC, Maurer MA, Kettner JT, et al. Applying RE-AIM to examine the impact of an implementation facilitation package to scale up a program for veterans with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Implement Sci Commun. 2023;4(1):143. doi:10.1186/S43058-023-00520-5
- McGhan R, Radcliff T, Fish R, Sutherland ER, Welsh C, Make B. Predictors of rehospitalization and death after a severe exacerbation of COPD. Chest. 2007;132(6):1748- 1755. doi:10.1378/chest.06-3018
- Anderson E, Wiener RS, Resnick K, Elwy AR, Rinne ST. Care coordination for veterans with COPD: a positive deviance study. Am J Manag Care. 2020;26(2):63-68. doi:10.37765/AJMC.2020.42394
- 2024 GOLD Report. Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease - GOLD. Accessed July 24, 2025. https://goldcopd.org/2024-gold-report/
- Nici L, Mammen MJ, Charbek E, et al. Pharmacologic management of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. An official American Thoracic Society clinical practice guideline. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2020;201(9):e56-e69. doi:10.1164/rccm.202003-0625ST
- Portillo EC, Wilcox A, Seckel E, et al. Reducing COPD readmission rates: using a COPD care service during care transitions. Fed Pract. 2018;35(11):30-36.
- Portillo EC, Gruber S, Lehmann M, et al. Application of the replicating effective programs framework to design a COPD training program. J Am Pharm Assoc. 2021;61(2):e129-e135. doi:10.1016/J.JAPH.2020.10.023
- Portillo EC, Lehmann MR, Hagen TL, et al. Integration of the patient-centered medical home to deliver a care bundle for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease management. J Am Pharm Assoc. 2023;63(1):212-219. doi:10.1016/j.japh.2022.10.003
- Portillo E, Lehmann M, Hagen T, et al. Evaluation of an implementation package to deliver the COPD CARE service. BMJ Open Qual. 2023;12(1). doi:10.1136/BMJOQ-2022-002074
- Portillo E, Lehmann M, Maurer M, et al. Barriers to implementing a pharmacist-led COPD care bundle in rural settings: A qualitative evaluation. 2025 (under review).
- Population Health Management. American Hospital Association. Accessed July 24, 2025. https://www.aha.org/center/population-health-management
- Ritchie MJ, Dollar KM, Miller CK, et al. Using implementation facilitation to improve healthcare: implementation facilitation training manual. Accessed July 11, 2024. https:// www.queri.research.va.gov/tools/Facilitation-Manual.pdf
- Morena AL, Gaias LM, Larkin C. Understanding the role of clinical champions and their impact on clinician behavior change: the need for causal pathway mechanisms. Front Health Serv. 2022;2:896885. doi:10.3389/FRHS.2022.896885
- Ayele RA, Rabin BA, McCreight M, Battaglia C. Editorial: understanding, assessing, and guiding adaptations in public health and health systems interventions: current and future directions. Front Public Health. 2023;11:1228437. doi:10.3389/fpubh.2023.1228437
- Jamtvedt G, Flottorp S, Ivers N. Audit and feedback as a quality strategy. In: Improving Healthcare Services. World Health Organization; 2019. Accessed July 24, 2025. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK549284/
- Snider MDH, Boyd MR, Walker MR, Powell BJ, Lewis CC. Using audit and feedback to guide tailored implementations of measurement-based care in community mental health: a multiple case study. Implement Sci Commun. 2023;4(1):94. doi:10.1186/s43058-023-00474-8
- Patient Aligned Care Team (PACT) – Patient Care Services. US Department of Veterans Affairs. Accessed July 24, 2025. https://www.patientcare.va.gov/primarycare/PACT.asp
- Lewis CC, Scott K, Marriott BR. A methodology for generating a tailored implementation blueprint: an exemplar from a youth residential setting. Implementat Sci. 2018;13(1):68. doi:10.1186/s13012-018-0761-6
- Beidas RS, Edmunds JM, Marcus SC, Kendall PC. Training and consultation to promote implementation of an empirically supported treatment: a randomized trial. Psychiatr Serv. 2012;63(7):660-665. doi:10.1176/appi.ps.201100401
- Kilbourne AM, Schmidt J, Edmunds M, Vega R, Bowersox N, Atkins D. How the VA is training the next-generation workforce for learning health systems. Learn Health Syst. 2022;6(4):e10333. doi:10.1002/LRH2.10333
- Easterling D, Perry AC, Woodside R, Patel T, Gesell SB. Clarifying the concept of a learning health system for healthcare delivery organizations: implications from a qualitative analysis of the scientific literature. Learn Health Syst. 2021;6(2):e10287. doi:10.1002/LRH2.10287
COPD CARE Academy: Design of Purposeful Training Guided by Implementation Strategies
COPD CARE Academy: Design of Purposeful Training Guided by Implementation Strategies
More Biologics May Be Breaking Through for COPD
New biologic drugs for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) are finally here, said Stephen Rennard, MD, in a presentation in a session on new drugs at the 2024 GOLD International COPD Conference.
The therapeutic goals of biologics remain the same as with other treatments for COPD, namely restoration of normal inflammatory response and alteration of disease progression, as well as restoration of lost structure and function and improvement of systemic effects, Rennard said in his presentation. Most studies of new and up-and-coming drugs have improvement in acute exacerbation of COPD as the primary outcome.
The Biology Behind the Biologics
T2 inflammation is “an inflammatory cascade led by IL [interleukin]-4, IL-13, and IL-5,” Mona Bafadhel, MD, chair of Respiratory Medicine at King’s College London in England, said in her presentation during the session.
Bafadhel, who served as one of the investigators on the BOREAS and NOTUS studies, explained some of the science behind the development of the new biologics.
Eosinophils are powerful regulators of immune response and inflammation by stimulating T-cell production and affecting other immune cell types, she noted.
In the context of COPD and drug development, high blood eosinophil counts have been associated with increased COPD-related exacerbations, Bafadhel said. She cited data from a Dutch study of more than 7000 patients with COPD (with and without clinical diagnoses), in which absolute eosinophil counts ≥ 3.3% were associated with increased risk for severe exacerbations of 32% and 84% across all patients with COPD and clinical COPD, respectively.
Understanding the mechanisms of the eosinophil in COPD is important for research and development, Bafadhel said. Along with standardizing measurement of T2 inflammatory markers (IL-4, IL-13, and IL-5), more research is needed to fully understand the role of eosinophils in immunoregulation and repair.
Fitting the Biologic to the Patient
Several recent studies of up-and-coming biologics have focused on subsets of COPD patients, said Dave Singh, MD, professor of clinical pharmacology and respiratory medicine at The University of Manchester in England, in his presentation at the meeting. In September 2024, the Food and Drug Administration approved dupilumab as the first biologic treatment for patients with uncontrolled COPD and type 2 inflammation on the basis of eosinophil counts. Singh cited data from the BOREAS and NOTUS studies in which dupilumab significantly reduced exacerbations and improved lung function in these patients, compared with a placebo.
Mepolizumab, a biologic approved for asthma, is not currently approved for COPD, but data from a 2017 study showed a trend toward reduced exacerbations, compared with placebo, in a subset of patients with high blood eosinophil counts, Singh said.
In addition, a recent unpublished phase 3 study (MATINEE) showed a reduction in the annualized rate of exacerbations, compared with placebo, on the basis of up to 2 years’ follow-up.
Singh also highlighted data from a phase 2a study of astegolimab, a biologic drug that focuses on the IL-33 receptor, in which COPD exacerbation rates were not significantly different between treatment and placebo groups. However, astegolimab has shown safety and efficacy in adults with severe asthma and is under development in phase 3 trials for COPD.
Tezepelumab, which was approved by the FDA in 2021 as an add-on therapy for severe asthma in patients aged 12 years or older, is also in development as a therapy for COPD exacerbations, Singh said.
In a study presented at the 2024 American Thoracic Society annual meeting, Singh and colleagues found that tezepelumab at a subcutaneous dose of 420 mg every 4 weeks reduced the annualized rate of moderate or severe COPD exacerbations compared with placebo based on data from approximately 300 patients, although the difference was not statistically significant.
Itepekimab, another biologic, showed promise in a phase 2a genetic association study involving current and former smokers with moderate to severe COPD, Singh said.
In that study, published in 2022 in The Lancet Respiratory Medicine, itepekimab failed to meet the primary endpoint in the overall study population of reduced annualized rate of moderate to severe exacerbations; however, a subgroup analysis of former smokers showed a significant (42%) reduction in exacerbations, Singh said in his presentation. Two phase 3 clinical studies (AERIFY-1/2) are ongoing to confirm the safety and efficacy of itepekimab in former smokers with COPD.
Takeaways and Next Steps
“These therapies provide the first new classes of medications approved for COPD in nearly 20 years,” said David M. Mannino, MD, of the University of Kentucky, Lexington, in an interview. “Dupilumab will be available to a subset of patients who are poorly controlled and have evidence of high eosinophils in their blood and is only used once every 2 weeks,” added Mannino, who has served as a consultant to companies developing COPD drugs.
Both dupilumab and ensifentrine, a phosphodiesterase (PDE) 3 and PDE4 inhibitor also recently approved for maintenance treatment of COPD, have been shown in clinical trials to reduce exacerbations and improve symptoms, said Mannino. Both offer additional options for patients who continue to have symptoms and exacerbations in spite of their current therapy.
Some barriers to the use of biologics in practice include the high cost. “Access and overcoming insurance-related issues such as preauthorization and high copays will be a challenge,” he said. Also, because dupilumab is an injectable drug, some patient training will be required.
Newer biologic therapies in development are also injectables, but some studies are examining longer time intervals as long as every 6 months, which could be a major advancement for some patients. The newer therapies in development are similar to dupilumab in that they will be injected therapies. Some in development are looking at longer time intervals as long as every 6 months, which may be a major advancement for some patients. “All of these therapies, however, are currently targeting more advanced or serious disease,” he said.
Looking ahead, more therapies are needed for the treatment of early COPD, as well as therapies that can be administered to a large number of patients at a reasonable cost, Mannino added.
Rennard disclosed serving as a consultant for Verona Pharma, Sanofi, Beyond Air, RS BioTherapeutics, RespirAI, and Roche, as well as speaker fees from Sanofi and temporary ownership interest while employed by AstraZeneca. Rennard is also the founder of Great Plains Biometrix. Bafadhel disclosed funding from the National Institute for Health Research (NIHR), grants from Asthma + Lung UK, Horizon Europe, NIHR, and AstraZeneca to her institution, and honoraria from AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Chiesi, GlaxoSmithKline, Novartis, and Pfizer. Singh disclosed relationships including speaking sponsorships, honoraria, and advisory board memberships for Adovate, Aerogen, Almirall, Apogee, Arrowhead, AstraZeneca, Bial, Boehringer Ingelheim, Chiesi, Cipla, Connect Biopharm, Covis, CSL Behring, DevPro Biopharm, Elpen, Empirico, EpiEndo, Genentech, Generate Biomedicines, GlaxoSmithKline, Glenmark, Kamada, Kinaset Therapeutics, Kymera, Menarini, MicroA, OM Pharma, Orion, Pieris Pharmaceuticals, Pulmatrix, Revolo, Roivant Sciences, Sanofi, Synairgen, Tetherex, Teva, Theravance Biopharma, Upstream, and Verona Pharma. Mannino disclosed serving as a consultant to multiple companies currently developing COPD therapies (AstraZeneca, GlaxoSmithKline, Roche, Regeneron, Sanofi, Genentech, Amgen, and Chiesi).
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
New biologic drugs for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) are finally here, said Stephen Rennard, MD, in a presentation in a session on new drugs at the 2024 GOLD International COPD Conference.
The therapeutic goals of biologics remain the same as with other treatments for COPD, namely restoration of normal inflammatory response and alteration of disease progression, as well as restoration of lost structure and function and improvement of systemic effects, Rennard said in his presentation. Most studies of new and up-and-coming drugs have improvement in acute exacerbation of COPD as the primary outcome.
The Biology Behind the Biologics
T2 inflammation is “an inflammatory cascade led by IL [interleukin]-4, IL-13, and IL-5,” Mona Bafadhel, MD, chair of Respiratory Medicine at King’s College London in England, said in her presentation during the session.
Bafadhel, who served as one of the investigators on the BOREAS and NOTUS studies, explained some of the science behind the development of the new biologics.
Eosinophils are powerful regulators of immune response and inflammation by stimulating T-cell production and affecting other immune cell types, she noted.
In the context of COPD and drug development, high blood eosinophil counts have been associated with increased COPD-related exacerbations, Bafadhel said. She cited data from a Dutch study of more than 7000 patients with COPD (with and without clinical diagnoses), in which absolute eosinophil counts ≥ 3.3% were associated with increased risk for severe exacerbations of 32% and 84% across all patients with COPD and clinical COPD, respectively.
Understanding the mechanisms of the eosinophil in COPD is important for research and development, Bafadhel said. Along with standardizing measurement of T2 inflammatory markers (IL-4, IL-13, and IL-5), more research is needed to fully understand the role of eosinophils in immunoregulation and repair.
Fitting the Biologic to the Patient
Several recent studies of up-and-coming biologics have focused on subsets of COPD patients, said Dave Singh, MD, professor of clinical pharmacology and respiratory medicine at The University of Manchester in England, in his presentation at the meeting. In September 2024, the Food and Drug Administration approved dupilumab as the first biologic treatment for patients with uncontrolled COPD and type 2 inflammation on the basis of eosinophil counts. Singh cited data from the BOREAS and NOTUS studies in which dupilumab significantly reduced exacerbations and improved lung function in these patients, compared with a placebo.
Mepolizumab, a biologic approved for asthma, is not currently approved for COPD, but data from a 2017 study showed a trend toward reduced exacerbations, compared with placebo, in a subset of patients with high blood eosinophil counts, Singh said.
In addition, a recent unpublished phase 3 study (MATINEE) showed a reduction in the annualized rate of exacerbations, compared with placebo, on the basis of up to 2 years’ follow-up.
Singh also highlighted data from a phase 2a study of astegolimab, a biologic drug that focuses on the IL-33 receptor, in which COPD exacerbation rates were not significantly different between treatment and placebo groups. However, astegolimab has shown safety and efficacy in adults with severe asthma and is under development in phase 3 trials for COPD.
Tezepelumab, which was approved by the FDA in 2021 as an add-on therapy for severe asthma in patients aged 12 years or older, is also in development as a therapy for COPD exacerbations, Singh said.
In a study presented at the 2024 American Thoracic Society annual meeting, Singh and colleagues found that tezepelumab at a subcutaneous dose of 420 mg every 4 weeks reduced the annualized rate of moderate or severe COPD exacerbations compared with placebo based on data from approximately 300 patients, although the difference was not statistically significant.
Itepekimab, another biologic, showed promise in a phase 2a genetic association study involving current and former smokers with moderate to severe COPD, Singh said.
In that study, published in 2022 in The Lancet Respiratory Medicine, itepekimab failed to meet the primary endpoint in the overall study population of reduced annualized rate of moderate to severe exacerbations; however, a subgroup analysis of former smokers showed a significant (42%) reduction in exacerbations, Singh said in his presentation. Two phase 3 clinical studies (AERIFY-1/2) are ongoing to confirm the safety and efficacy of itepekimab in former smokers with COPD.
Takeaways and Next Steps
“These therapies provide the first new classes of medications approved for COPD in nearly 20 years,” said David M. Mannino, MD, of the University of Kentucky, Lexington, in an interview. “Dupilumab will be available to a subset of patients who are poorly controlled and have evidence of high eosinophils in their blood and is only used once every 2 weeks,” added Mannino, who has served as a consultant to companies developing COPD drugs.
Both dupilumab and ensifentrine, a phosphodiesterase (PDE) 3 and PDE4 inhibitor also recently approved for maintenance treatment of COPD, have been shown in clinical trials to reduce exacerbations and improve symptoms, said Mannino. Both offer additional options for patients who continue to have symptoms and exacerbations in spite of their current therapy.
Some barriers to the use of biologics in practice include the high cost. “Access and overcoming insurance-related issues such as preauthorization and high copays will be a challenge,” he said. Also, because dupilumab is an injectable drug, some patient training will be required.
Newer biologic therapies in development are also injectables, but some studies are examining longer time intervals as long as every 6 months, which could be a major advancement for some patients. The newer therapies in development are similar to dupilumab in that they will be injected therapies. Some in development are looking at longer time intervals as long as every 6 months, which may be a major advancement for some patients. “All of these therapies, however, are currently targeting more advanced or serious disease,” he said.
Looking ahead, more therapies are needed for the treatment of early COPD, as well as therapies that can be administered to a large number of patients at a reasonable cost, Mannino added.
Rennard disclosed serving as a consultant for Verona Pharma, Sanofi, Beyond Air, RS BioTherapeutics, RespirAI, and Roche, as well as speaker fees from Sanofi and temporary ownership interest while employed by AstraZeneca. Rennard is also the founder of Great Plains Biometrix. Bafadhel disclosed funding from the National Institute for Health Research (NIHR), grants from Asthma + Lung UK, Horizon Europe, NIHR, and AstraZeneca to her institution, and honoraria from AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Chiesi, GlaxoSmithKline, Novartis, and Pfizer. Singh disclosed relationships including speaking sponsorships, honoraria, and advisory board memberships for Adovate, Aerogen, Almirall, Apogee, Arrowhead, AstraZeneca, Bial, Boehringer Ingelheim, Chiesi, Cipla, Connect Biopharm, Covis, CSL Behring, DevPro Biopharm, Elpen, Empirico, EpiEndo, Genentech, Generate Biomedicines, GlaxoSmithKline, Glenmark, Kamada, Kinaset Therapeutics, Kymera, Menarini, MicroA, OM Pharma, Orion, Pieris Pharmaceuticals, Pulmatrix, Revolo, Roivant Sciences, Sanofi, Synairgen, Tetherex, Teva, Theravance Biopharma, Upstream, and Verona Pharma. Mannino disclosed serving as a consultant to multiple companies currently developing COPD therapies (AstraZeneca, GlaxoSmithKline, Roche, Regeneron, Sanofi, Genentech, Amgen, and Chiesi).
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
New biologic drugs for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) are finally here, said Stephen Rennard, MD, in a presentation in a session on new drugs at the 2024 GOLD International COPD Conference.
The therapeutic goals of biologics remain the same as with other treatments for COPD, namely restoration of normal inflammatory response and alteration of disease progression, as well as restoration of lost structure and function and improvement of systemic effects, Rennard said in his presentation. Most studies of new and up-and-coming drugs have improvement in acute exacerbation of COPD as the primary outcome.
The Biology Behind the Biologics
T2 inflammation is “an inflammatory cascade led by IL [interleukin]-4, IL-13, and IL-5,” Mona Bafadhel, MD, chair of Respiratory Medicine at King’s College London in England, said in her presentation during the session.
Bafadhel, who served as one of the investigators on the BOREAS and NOTUS studies, explained some of the science behind the development of the new biologics.
Eosinophils are powerful regulators of immune response and inflammation by stimulating T-cell production and affecting other immune cell types, she noted.
In the context of COPD and drug development, high blood eosinophil counts have been associated with increased COPD-related exacerbations, Bafadhel said. She cited data from a Dutch study of more than 7000 patients with COPD (with and without clinical diagnoses), in which absolute eosinophil counts ≥ 3.3% were associated with increased risk for severe exacerbations of 32% and 84% across all patients with COPD and clinical COPD, respectively.
Understanding the mechanisms of the eosinophil in COPD is important for research and development, Bafadhel said. Along with standardizing measurement of T2 inflammatory markers (IL-4, IL-13, and IL-5), more research is needed to fully understand the role of eosinophils in immunoregulation and repair.
Fitting the Biologic to the Patient
Several recent studies of up-and-coming biologics have focused on subsets of COPD patients, said Dave Singh, MD, professor of clinical pharmacology and respiratory medicine at The University of Manchester in England, in his presentation at the meeting. In September 2024, the Food and Drug Administration approved dupilumab as the first biologic treatment for patients with uncontrolled COPD and type 2 inflammation on the basis of eosinophil counts. Singh cited data from the BOREAS and NOTUS studies in which dupilumab significantly reduced exacerbations and improved lung function in these patients, compared with a placebo.
Mepolizumab, a biologic approved for asthma, is not currently approved for COPD, but data from a 2017 study showed a trend toward reduced exacerbations, compared with placebo, in a subset of patients with high blood eosinophil counts, Singh said.
In addition, a recent unpublished phase 3 study (MATINEE) showed a reduction in the annualized rate of exacerbations, compared with placebo, on the basis of up to 2 years’ follow-up.
Singh also highlighted data from a phase 2a study of astegolimab, a biologic drug that focuses on the IL-33 receptor, in which COPD exacerbation rates were not significantly different between treatment and placebo groups. However, astegolimab has shown safety and efficacy in adults with severe asthma and is under development in phase 3 trials for COPD.
Tezepelumab, which was approved by the FDA in 2021 as an add-on therapy for severe asthma in patients aged 12 years or older, is also in development as a therapy for COPD exacerbations, Singh said.
In a study presented at the 2024 American Thoracic Society annual meeting, Singh and colleagues found that tezepelumab at a subcutaneous dose of 420 mg every 4 weeks reduced the annualized rate of moderate or severe COPD exacerbations compared with placebo based on data from approximately 300 patients, although the difference was not statistically significant.
Itepekimab, another biologic, showed promise in a phase 2a genetic association study involving current and former smokers with moderate to severe COPD, Singh said.
In that study, published in 2022 in The Lancet Respiratory Medicine, itepekimab failed to meet the primary endpoint in the overall study population of reduced annualized rate of moderate to severe exacerbations; however, a subgroup analysis of former smokers showed a significant (42%) reduction in exacerbations, Singh said in his presentation. Two phase 3 clinical studies (AERIFY-1/2) are ongoing to confirm the safety and efficacy of itepekimab in former smokers with COPD.
Takeaways and Next Steps
“These therapies provide the first new classes of medications approved for COPD in nearly 20 years,” said David M. Mannino, MD, of the University of Kentucky, Lexington, in an interview. “Dupilumab will be available to a subset of patients who are poorly controlled and have evidence of high eosinophils in their blood and is only used once every 2 weeks,” added Mannino, who has served as a consultant to companies developing COPD drugs.
Both dupilumab and ensifentrine, a phosphodiesterase (PDE) 3 and PDE4 inhibitor also recently approved for maintenance treatment of COPD, have been shown in clinical trials to reduce exacerbations and improve symptoms, said Mannino. Both offer additional options for patients who continue to have symptoms and exacerbations in spite of their current therapy.
Some barriers to the use of biologics in practice include the high cost. “Access and overcoming insurance-related issues such as preauthorization and high copays will be a challenge,” he said. Also, because dupilumab is an injectable drug, some patient training will be required.
Newer biologic therapies in development are also injectables, but some studies are examining longer time intervals as long as every 6 months, which could be a major advancement for some patients. The newer therapies in development are similar to dupilumab in that they will be injected therapies. Some in development are looking at longer time intervals as long as every 6 months, which may be a major advancement for some patients. “All of these therapies, however, are currently targeting more advanced or serious disease,” he said.
Looking ahead, more therapies are needed for the treatment of early COPD, as well as therapies that can be administered to a large number of patients at a reasonable cost, Mannino added.
Rennard disclosed serving as a consultant for Verona Pharma, Sanofi, Beyond Air, RS BioTherapeutics, RespirAI, and Roche, as well as speaker fees from Sanofi and temporary ownership interest while employed by AstraZeneca. Rennard is also the founder of Great Plains Biometrix. Bafadhel disclosed funding from the National Institute for Health Research (NIHR), grants from Asthma + Lung UK, Horizon Europe, NIHR, and AstraZeneca to her institution, and honoraria from AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Chiesi, GlaxoSmithKline, Novartis, and Pfizer. Singh disclosed relationships including speaking sponsorships, honoraria, and advisory board memberships for Adovate, Aerogen, Almirall, Apogee, Arrowhead, AstraZeneca, Bial, Boehringer Ingelheim, Chiesi, Cipla, Connect Biopharm, Covis, CSL Behring, DevPro Biopharm, Elpen, Empirico, EpiEndo, Genentech, Generate Biomedicines, GlaxoSmithKline, Glenmark, Kamada, Kinaset Therapeutics, Kymera, Menarini, MicroA, OM Pharma, Orion, Pieris Pharmaceuticals, Pulmatrix, Revolo, Roivant Sciences, Sanofi, Synairgen, Tetherex, Teva, Theravance Biopharma, Upstream, and Verona Pharma. Mannino disclosed serving as a consultant to multiple companies currently developing COPD therapies (AstraZeneca, GlaxoSmithKline, Roche, Regeneron, Sanofi, Genentech, Amgen, and Chiesi).
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Lung CT Can Detect Coronary Artery Disease, Predict Death
“The high prevalence of asymptomatic coronary artery disease (83%) was surprising, as was the prevalence of extensive CAC (30%),” principal investigator Gary Small, MBChB, PhD, a cardiologist at the University of Ottawa Heart Institute in Ontario, Canada, said in an interview.
“The size of effect was also surprising, as was the persistence of the effect even in the presence of elevated mortality risk from other causes,” he said. “Extensive coronary disease was associated with a twofold increase in risk for death or cardiovascular events over 4 years of follow-up,” even after adjustment for risk for death from cancer and other comorbidities such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.
“CAC as reported on chest CT exams is often ignored and not factored into clinical practice,” he noted. “The presence of CAC, however, provides a very real and very personal perspective on an individual’s cardiovascular risk. It is a true example of personalized medicine.”
The study was published online in The Canadian Medical Association Journal.
Potential Risk Reduction
In March 2017, Ontario Health launched a pilot low-dose CT lung cancer screening program for high-risk individuals between the ages of 55 and 74 years, Small explained. As CAC, a marker of coronary artery disease, is seen easily during such a scan, the researchers analyzed the lung CTs to determine the prevalence of coronary artery disease and whether CAC was associated with increased risk.
The team quantified CAC using an estimated Agatston score and identified the composite primary outcome of all-cause death and cardiovascular events using linked electronic medical record data from Ottawa Hospital up to December 2023. Among the 1486 people who underwent screening (mean age, 66 years; 52% men; 68% current smokers), CAC was detected in 1232 (82.9%). CAC was mild to moderate in 793 participants (53.4%) and extensive in 439 (29.5%). No CAC was detected in 254 (17.1%) participants.
At follow-up, 78 participants (5.2%) experienced the primary composite outcome, including 39 (8.9%) with extensive CAC, 32 (4.0%) with mild to moderate CAC, and 7 (2.8%) with no CAC.
A total of 49 deaths occurred, including 16 cardiovascular deaths and 19 cancer deaths, of which 10 were from lung cancer. Cardiovascular events included sudden cardiac death (eight participants), fatal stroke (six participants), and one each from heart failure and peripheral vascular disease.
On multivariable analysis, extensive CAC was associated with the composite primary outcome (adjusted hazard ratio [aHR], 2.13), all-cause mortality (aHR, 2.39), and cardiovascular events (aHR, 2.06).
Extensive CAC remained predictive of cardiovascular events even after adjustment for noncardiovascular death as a competing risk (HR, 2.05).
“Our data highlight to lung cancer screening professionals the prevalence of this silent risk factor and re-emphasize the importance of this finding [ie, CAC] as an opportunity for risk reduction,” Small said.
“In terms of next steps, the journey toward cardiovascular risk reduction begins with a clear report of CAC on the lung cancer screening record,” he noted. “Following this step, professionals involved in the lung cancer screening program might consider a local management pathway to ensure that this opportunity for health improvement is not lost or ignored. Preventive medicine of this type would typically involve primary care.”
Managing Other Findings
Commenting on the study, Anna Bader, MD, assistant professor of radiology and biomedical imaging at the Yale School of Medicine in New Haven, Connecticut, said that “low-dose CT for lung cancer screening offers valuable insights beyond nodule detection, with CAC being among the most significant incidental findings.”
However, she added, a “robust mechanism” to effectively manage other findings — such as thoracic aortic disease, low bone density, and abnormalities in the thyroid or upper abdominal organs — without overdiagnosis, is needed. A mechanism also is needed to notify cardiologists or primary care providers about severe CAC findings.
Challenges that need to be overcome before such mechanisms can be put in place, she said, “include ensuring standardized CAC reporting, avoiding overburdening healthcare providers, mitigating the risk of excessive downstream testing, and ensuring equitable access to follow-up care for underserved and rural communities.”
Providers involved in lung cancer screening “must be trained to recognize the importance of CAC findings and act upon them,” she added. “Awareness campaigns or continuing medical education modules could address this.”
Multidisciplinary lung cancer screening programs can help with patient education, she noted. “Clear communication about potential findings, including the significance of incidental CAC, should be prioritized and addressed proactively, ideally before the exam, to enhance patient understanding and engagement.”
Matthew Tomey, MD, assistant professor of medicine at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai in New York City, said that, “as a practicing cardiologist, I find it very helpful to look at my patients’ recent or past CT scans to look for vascular calcification. Whether or not a scan is specifically protocoled as a cardiac study, we can often appreciate vascular calcification when it is present. I would encourage every physician involved in helping their patients to prevent heart disease to take advantage of looking at any prior CT scans for evidence of vascular calcification.
“Systems of care to facilitate recognition of patients with incidentally discovered vascular calcification would be welcome and, on a large scale, could help prevent cardiovascular events,” he noted. “Such a system might involve facilitating referral to a prevention specialist. It could involve evidence-based guidance for referring physicians who ordered scans.”
Like Bader, he noted the importance of patient education, adding that it could be quite powerful. “We should be doing more to empower our patients to understand the findings of their imaging and to give them actionable, evidence-based guidance on how they can promote their own cardiovascular health,” he concluded.
No funding for the study was reported. Small reported receiving a research grant for amyloid research from Pfizer and honoraria from Pfizer and Alnylam (all paid to the institution, outside the submitted work). Bader and Tomey declared no relevant conflicts.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
“The high prevalence of asymptomatic coronary artery disease (83%) was surprising, as was the prevalence of extensive CAC (30%),” principal investigator Gary Small, MBChB, PhD, a cardiologist at the University of Ottawa Heart Institute in Ontario, Canada, said in an interview.
“The size of effect was also surprising, as was the persistence of the effect even in the presence of elevated mortality risk from other causes,” he said. “Extensive coronary disease was associated with a twofold increase in risk for death or cardiovascular events over 4 years of follow-up,” even after adjustment for risk for death from cancer and other comorbidities such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.
“CAC as reported on chest CT exams is often ignored and not factored into clinical practice,” he noted. “The presence of CAC, however, provides a very real and very personal perspective on an individual’s cardiovascular risk. It is a true example of personalized medicine.”
The study was published online in The Canadian Medical Association Journal.
Potential Risk Reduction
In March 2017, Ontario Health launched a pilot low-dose CT lung cancer screening program for high-risk individuals between the ages of 55 and 74 years, Small explained. As CAC, a marker of coronary artery disease, is seen easily during such a scan, the researchers analyzed the lung CTs to determine the prevalence of coronary artery disease and whether CAC was associated with increased risk.
The team quantified CAC using an estimated Agatston score and identified the composite primary outcome of all-cause death and cardiovascular events using linked electronic medical record data from Ottawa Hospital up to December 2023. Among the 1486 people who underwent screening (mean age, 66 years; 52% men; 68% current smokers), CAC was detected in 1232 (82.9%). CAC was mild to moderate in 793 participants (53.4%) and extensive in 439 (29.5%). No CAC was detected in 254 (17.1%) participants.
At follow-up, 78 participants (5.2%) experienced the primary composite outcome, including 39 (8.9%) with extensive CAC, 32 (4.0%) with mild to moderate CAC, and 7 (2.8%) with no CAC.
A total of 49 deaths occurred, including 16 cardiovascular deaths and 19 cancer deaths, of which 10 were from lung cancer. Cardiovascular events included sudden cardiac death (eight participants), fatal stroke (six participants), and one each from heart failure and peripheral vascular disease.
On multivariable analysis, extensive CAC was associated with the composite primary outcome (adjusted hazard ratio [aHR], 2.13), all-cause mortality (aHR, 2.39), and cardiovascular events (aHR, 2.06).
Extensive CAC remained predictive of cardiovascular events even after adjustment for noncardiovascular death as a competing risk (HR, 2.05).
“Our data highlight to lung cancer screening professionals the prevalence of this silent risk factor and re-emphasize the importance of this finding [ie, CAC] as an opportunity for risk reduction,” Small said.
“In terms of next steps, the journey toward cardiovascular risk reduction begins with a clear report of CAC on the lung cancer screening record,” he noted. “Following this step, professionals involved in the lung cancer screening program might consider a local management pathway to ensure that this opportunity for health improvement is not lost or ignored. Preventive medicine of this type would typically involve primary care.”
Managing Other Findings
Commenting on the study, Anna Bader, MD, assistant professor of radiology and biomedical imaging at the Yale School of Medicine in New Haven, Connecticut, said that “low-dose CT for lung cancer screening offers valuable insights beyond nodule detection, with CAC being among the most significant incidental findings.”
However, she added, a “robust mechanism” to effectively manage other findings — such as thoracic aortic disease, low bone density, and abnormalities in the thyroid or upper abdominal organs — without overdiagnosis, is needed. A mechanism also is needed to notify cardiologists or primary care providers about severe CAC findings.
Challenges that need to be overcome before such mechanisms can be put in place, she said, “include ensuring standardized CAC reporting, avoiding overburdening healthcare providers, mitigating the risk of excessive downstream testing, and ensuring equitable access to follow-up care for underserved and rural communities.”
Providers involved in lung cancer screening “must be trained to recognize the importance of CAC findings and act upon them,” she added. “Awareness campaigns or continuing medical education modules could address this.”
Multidisciplinary lung cancer screening programs can help with patient education, she noted. “Clear communication about potential findings, including the significance of incidental CAC, should be prioritized and addressed proactively, ideally before the exam, to enhance patient understanding and engagement.”
Matthew Tomey, MD, assistant professor of medicine at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai in New York City, said that, “as a practicing cardiologist, I find it very helpful to look at my patients’ recent or past CT scans to look for vascular calcification. Whether or not a scan is specifically protocoled as a cardiac study, we can often appreciate vascular calcification when it is present. I would encourage every physician involved in helping their patients to prevent heart disease to take advantage of looking at any prior CT scans for evidence of vascular calcification.
“Systems of care to facilitate recognition of patients with incidentally discovered vascular calcification would be welcome and, on a large scale, could help prevent cardiovascular events,” he noted. “Such a system might involve facilitating referral to a prevention specialist. It could involve evidence-based guidance for referring physicians who ordered scans.”
Like Bader, he noted the importance of patient education, adding that it could be quite powerful. “We should be doing more to empower our patients to understand the findings of their imaging and to give them actionable, evidence-based guidance on how they can promote their own cardiovascular health,” he concluded.
No funding for the study was reported. Small reported receiving a research grant for amyloid research from Pfizer and honoraria from Pfizer and Alnylam (all paid to the institution, outside the submitted work). Bader and Tomey declared no relevant conflicts.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
“The high prevalence of asymptomatic coronary artery disease (83%) was surprising, as was the prevalence of extensive CAC (30%),” principal investigator Gary Small, MBChB, PhD, a cardiologist at the University of Ottawa Heart Institute in Ontario, Canada, said in an interview.
“The size of effect was also surprising, as was the persistence of the effect even in the presence of elevated mortality risk from other causes,” he said. “Extensive coronary disease was associated with a twofold increase in risk for death or cardiovascular events over 4 years of follow-up,” even after adjustment for risk for death from cancer and other comorbidities such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.
“CAC as reported on chest CT exams is often ignored and not factored into clinical practice,” he noted. “The presence of CAC, however, provides a very real and very personal perspective on an individual’s cardiovascular risk. It is a true example of personalized medicine.”
The study was published online in The Canadian Medical Association Journal.
Potential Risk Reduction
In March 2017, Ontario Health launched a pilot low-dose CT lung cancer screening program for high-risk individuals between the ages of 55 and 74 years, Small explained. As CAC, a marker of coronary artery disease, is seen easily during such a scan, the researchers analyzed the lung CTs to determine the prevalence of coronary artery disease and whether CAC was associated with increased risk.
The team quantified CAC using an estimated Agatston score and identified the composite primary outcome of all-cause death and cardiovascular events using linked electronic medical record data from Ottawa Hospital up to December 2023. Among the 1486 people who underwent screening (mean age, 66 years; 52% men; 68% current smokers), CAC was detected in 1232 (82.9%). CAC was mild to moderate in 793 participants (53.4%) and extensive in 439 (29.5%). No CAC was detected in 254 (17.1%) participants.
At follow-up, 78 participants (5.2%) experienced the primary composite outcome, including 39 (8.9%) with extensive CAC, 32 (4.0%) with mild to moderate CAC, and 7 (2.8%) with no CAC.
A total of 49 deaths occurred, including 16 cardiovascular deaths and 19 cancer deaths, of which 10 were from lung cancer. Cardiovascular events included sudden cardiac death (eight participants), fatal stroke (six participants), and one each from heart failure and peripheral vascular disease.
On multivariable analysis, extensive CAC was associated with the composite primary outcome (adjusted hazard ratio [aHR], 2.13), all-cause mortality (aHR, 2.39), and cardiovascular events (aHR, 2.06).
Extensive CAC remained predictive of cardiovascular events even after adjustment for noncardiovascular death as a competing risk (HR, 2.05).
“Our data highlight to lung cancer screening professionals the prevalence of this silent risk factor and re-emphasize the importance of this finding [ie, CAC] as an opportunity for risk reduction,” Small said.
“In terms of next steps, the journey toward cardiovascular risk reduction begins with a clear report of CAC on the lung cancer screening record,” he noted. “Following this step, professionals involved in the lung cancer screening program might consider a local management pathway to ensure that this opportunity for health improvement is not lost or ignored. Preventive medicine of this type would typically involve primary care.”
Managing Other Findings
Commenting on the study, Anna Bader, MD, assistant professor of radiology and biomedical imaging at the Yale School of Medicine in New Haven, Connecticut, said that “low-dose CT for lung cancer screening offers valuable insights beyond nodule detection, with CAC being among the most significant incidental findings.”
However, she added, a “robust mechanism” to effectively manage other findings — such as thoracic aortic disease, low bone density, and abnormalities in the thyroid or upper abdominal organs — without overdiagnosis, is needed. A mechanism also is needed to notify cardiologists or primary care providers about severe CAC findings.
Challenges that need to be overcome before such mechanisms can be put in place, she said, “include ensuring standardized CAC reporting, avoiding overburdening healthcare providers, mitigating the risk of excessive downstream testing, and ensuring equitable access to follow-up care for underserved and rural communities.”
Providers involved in lung cancer screening “must be trained to recognize the importance of CAC findings and act upon them,” she added. “Awareness campaigns or continuing medical education modules could address this.”
Multidisciplinary lung cancer screening programs can help with patient education, she noted. “Clear communication about potential findings, including the significance of incidental CAC, should be prioritized and addressed proactively, ideally before the exam, to enhance patient understanding and engagement.”
Matthew Tomey, MD, assistant professor of medicine at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai in New York City, said that, “as a practicing cardiologist, I find it very helpful to look at my patients’ recent or past CT scans to look for vascular calcification. Whether or not a scan is specifically protocoled as a cardiac study, we can often appreciate vascular calcification when it is present. I would encourage every physician involved in helping their patients to prevent heart disease to take advantage of looking at any prior CT scans for evidence of vascular calcification.
“Systems of care to facilitate recognition of patients with incidentally discovered vascular calcification would be welcome and, on a large scale, could help prevent cardiovascular events,” he noted. “Such a system might involve facilitating referral to a prevention specialist. It could involve evidence-based guidance for referring physicians who ordered scans.”
Like Bader, he noted the importance of patient education, adding that it could be quite powerful. “We should be doing more to empower our patients to understand the findings of their imaging and to give them actionable, evidence-based guidance on how they can promote their own cardiovascular health,” he concluded.
No funding for the study was reported. Small reported receiving a research grant for amyloid research from Pfizer and honoraria from Pfizer and Alnylam (all paid to the institution, outside the submitted work). Bader and Tomey declared no relevant conflicts.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM THE CANADIAN MEDICAL ASSOCIATION JOURNAL
Older Patients With COPD at Increased Risk for PE-Associated Death
BOSTON — Patients with COPD are at an increased risk for fatal pulmonary embolism (PE) and may require personalized, targeted thromboprophylaxis.
The data suggest that “maybe we should start thinking about if we are admitting a patient with COPD in that specific age group, higher thromboprophylaxis for PE,” said Marwa Oudah, MD, a pulmonary hypertension fellow at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia. She presented her group’s findings in a rapid-fire oral abstract session at the CHEST Annual Meeting.
Known Risk Factor
COPD is a known risk factor for PE. To estimate how the obstructive lung disease may contribute to PE-related deaths among patients of varying ages, Oudah and colleagues drew data on deaths due to an underlying cause of PE from 1999 to 2020 from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s WONDER database.
They stratified the patients into two groups — those with or without COPD — whose data were included in the Multiple Causes of Death dataset, according to age groups ranging from 35 years to over 100 years. The investigators calculated proportional mortality ratios in the non-COPD group and applied these to the COPD-positive group among different age ranges to estimate the observed vs expected number of deaths.
A total of 10,434 persons who died from PE and had COPD listed among causes of death were identified. The sample was evenly divided by sex. The peak range of deaths was among those aged 75-84 years.
The authors saw an increase in PE-related mortality among patients with COPD aged 65-85 years (P < .001).
The ratios of observed-to-expected deaths among patients in this age range were “substantially greater than 1” said Oudah, with patients aged 75-79 years at highest risk for PE-related death, with an observed-to-expected ratio of 1.443.
In contrast, the rate of observed deaths among patients aged 85-89 years was similar to the expected rate, suggesting that the COPD-PE interaction may wane among older patients, she said.
Among patients aged 35-64 years, the risk for death from PE was not significantly higher for any of the 5-year age categories.
The investigators emphasized that “given the observed trend, individualized patient assessments are imperative to optimize preventable measures against PE in the aging COPD population.”
Confounding Comorbidities
In an interview, a pulmonary specialist who was not involved in the study commented that older persons with COPD tend to have multiple comorbidities that may contribute to the risk for PE.
“Older patients have so many comorbidities, and their risk for pulmonary embolism and thromboembolic disease is pretty high, so I’m not surprised that 75 to 79 years olds are having a higher mortality from PE, but it’s a little difficult to say whether that’s due to COPD,” said Krishna Sundar, MBBS, MD, FCCP, a pulmonary, sleep medicine, and critical care medicine specialist at St. John’s Medical Center in Jackson, Wyoming, who moderated the session.
The authors did not report a study funding source. Oudah and Sundar reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
BOSTON — Patients with COPD are at an increased risk for fatal pulmonary embolism (PE) and may require personalized, targeted thromboprophylaxis.
The data suggest that “maybe we should start thinking about if we are admitting a patient with COPD in that specific age group, higher thromboprophylaxis for PE,” said Marwa Oudah, MD, a pulmonary hypertension fellow at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia. She presented her group’s findings in a rapid-fire oral abstract session at the CHEST Annual Meeting.
Known Risk Factor
COPD is a known risk factor for PE. To estimate how the obstructive lung disease may contribute to PE-related deaths among patients of varying ages, Oudah and colleagues drew data on deaths due to an underlying cause of PE from 1999 to 2020 from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s WONDER database.
They stratified the patients into two groups — those with or without COPD — whose data were included in the Multiple Causes of Death dataset, according to age groups ranging from 35 years to over 100 years. The investigators calculated proportional mortality ratios in the non-COPD group and applied these to the COPD-positive group among different age ranges to estimate the observed vs expected number of deaths.
A total of 10,434 persons who died from PE and had COPD listed among causes of death were identified. The sample was evenly divided by sex. The peak range of deaths was among those aged 75-84 years.
The authors saw an increase in PE-related mortality among patients with COPD aged 65-85 years (P < .001).
The ratios of observed-to-expected deaths among patients in this age range were “substantially greater than 1” said Oudah, with patients aged 75-79 years at highest risk for PE-related death, with an observed-to-expected ratio of 1.443.
In contrast, the rate of observed deaths among patients aged 85-89 years was similar to the expected rate, suggesting that the COPD-PE interaction may wane among older patients, she said.
Among patients aged 35-64 years, the risk for death from PE was not significantly higher for any of the 5-year age categories.
The investigators emphasized that “given the observed trend, individualized patient assessments are imperative to optimize preventable measures against PE in the aging COPD population.”
Confounding Comorbidities
In an interview, a pulmonary specialist who was not involved in the study commented that older persons with COPD tend to have multiple comorbidities that may contribute to the risk for PE.
“Older patients have so many comorbidities, and their risk for pulmonary embolism and thromboembolic disease is pretty high, so I’m not surprised that 75 to 79 years olds are having a higher mortality from PE, but it’s a little difficult to say whether that’s due to COPD,” said Krishna Sundar, MBBS, MD, FCCP, a pulmonary, sleep medicine, and critical care medicine specialist at St. John’s Medical Center in Jackson, Wyoming, who moderated the session.
The authors did not report a study funding source. Oudah and Sundar reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
BOSTON — Patients with COPD are at an increased risk for fatal pulmonary embolism (PE) and may require personalized, targeted thromboprophylaxis.
The data suggest that “maybe we should start thinking about if we are admitting a patient with COPD in that specific age group, higher thromboprophylaxis for PE,” said Marwa Oudah, MD, a pulmonary hypertension fellow at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia. She presented her group’s findings in a rapid-fire oral abstract session at the CHEST Annual Meeting.
Known Risk Factor
COPD is a known risk factor for PE. To estimate how the obstructive lung disease may contribute to PE-related deaths among patients of varying ages, Oudah and colleagues drew data on deaths due to an underlying cause of PE from 1999 to 2020 from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s WONDER database.
They stratified the patients into two groups — those with or without COPD — whose data were included in the Multiple Causes of Death dataset, according to age groups ranging from 35 years to over 100 years. The investigators calculated proportional mortality ratios in the non-COPD group and applied these to the COPD-positive group among different age ranges to estimate the observed vs expected number of deaths.
A total of 10,434 persons who died from PE and had COPD listed among causes of death were identified. The sample was evenly divided by sex. The peak range of deaths was among those aged 75-84 years.
The authors saw an increase in PE-related mortality among patients with COPD aged 65-85 years (P < .001).
The ratios of observed-to-expected deaths among patients in this age range were “substantially greater than 1” said Oudah, with patients aged 75-79 years at highest risk for PE-related death, with an observed-to-expected ratio of 1.443.
In contrast, the rate of observed deaths among patients aged 85-89 years was similar to the expected rate, suggesting that the COPD-PE interaction may wane among older patients, she said.
Among patients aged 35-64 years, the risk for death from PE was not significantly higher for any of the 5-year age categories.
The investigators emphasized that “given the observed trend, individualized patient assessments are imperative to optimize preventable measures against PE in the aging COPD population.”
Confounding Comorbidities
In an interview, a pulmonary specialist who was not involved in the study commented that older persons with COPD tend to have multiple comorbidities that may contribute to the risk for PE.
“Older patients have so many comorbidities, and their risk for pulmonary embolism and thromboembolic disease is pretty high, so I’m not surprised that 75 to 79 years olds are having a higher mortality from PE, but it’s a little difficult to say whether that’s due to COPD,” said Krishna Sundar, MBBS, MD, FCCP, a pulmonary, sleep medicine, and critical care medicine specialist at St. John’s Medical Center in Jackson, Wyoming, who moderated the session.
The authors did not report a study funding source. Oudah and Sundar reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM CHEST 2024
AF Burden Increases Around Time of COPD Hospitalizations
BOSTON — Patients with COPD who have exacerbations requiring hospitalization should be monitored for cardiac arrhythmias, investigators said.
This recommendation is based on results of a study of medical records showing that among more than 20,000 hospitalizations for patients with COPD without concurrent heart failure (HF), 40% patients had at least 6 minutes of daily atrial fibrillation (AF) burden, and nearly half of these patients had at least an hour of daily AF burden; patients with COPD and concurrent HF had similar daily AF burdens, reported Trent Fischer, MD, MS, senior principal scientist at Medtronic in Minneapolis.
“We can conclude that AF burden increases in the weeks after a hospitalization for COPD if they don’t have a concurrent diagnosis of heart failure. Also, having concurrent heart failure increases the risk of atrial fibrillation and increases the atrial fibrillation burden around the time of COPD hospitalization,” he said in a rapid-fire oral abstract session at the CHEST Annual Meeting.
The findings indicated a need for increased vigilance for AF around the time of a serious COPD exacerbation and may explain at least some of the increased risks for stroke observed in patients who are hospitalized for COPD exacerbations, he said.
Retrospective Study
They drew data from 2007 through 2021 on patients with implantable cardioverter defibrillators, cardiac resynchronization therapy devices, pacemakers, and implantable cardiac monitors, using the Optum de-identified electronic health record dataset linked with Medtronic’s CareLink database to conduct a retrospective analysis.
They looked at admissions for COPD linked to available device diagnostic parameters between 30 days prior to and 60 days after admission for COPD.
They identified a total of 20,056 COPD hospitalizations for patients with concurrent HF and 3877 for those without HF.
Among patients with HF, 43% had a daily AF burden of at least 6 minutes, and 22% had at least 1 hour of irregular rhythms. Among patients without HF, 40% had at least 6 minutes of irregular rhythms daily, and 18% had at least 1 hour.
Among patients with HF, the daily average AF burden increased from a baseline of 158 min/d 30 days before an admission to 170 min/d at admission, returning to baseline by 20 days after hospitalization.
For patients without HF, the AF burden increased from 107 min/d at baseline to 113 min/d during hospitalization and returned to baseline by 20 days after hospitalization.
Confounding Factor?
In the Q&A, session moderator Krishna Sundar, MBBS, MD, FCCP, a pulmonary, sleep medicine, and critical care medicine specialist at St. John’s Medical Center in Jackson, Wyoming, said that when patients with HF get admitted for COPD exacerbations, their HF typically worsens and asked Dr. Fischer how he could tell the difference.
“I know there’s a lot of interaction between heart failure and COPD. They’re well-know comorbidities, and the exacerbation of one can bring on worsening of the other. At least with this database, we can’t really tease out any sort of differences,” Dr. Fischer replied.
“I think that a diagnosis of COPD exacerbation is pretty well laid out, but it’s sometimes difficult to separate worsening of heart failure in these patients, and often these patients get treated for both problems. It’s clear that it’s the heart failure patients who are having more atrial fibrillation episodes, which is not surprising, but the question is how much is the COPD exacerbation contributing to the atrial fibrillation?” said Dr. Sundar.
The study was supported by Medtronic. Dr. Fischer is employed by the company. Dr. Sundar reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
BOSTON — Patients with COPD who have exacerbations requiring hospitalization should be monitored for cardiac arrhythmias, investigators said.
This recommendation is based on results of a study of medical records showing that among more than 20,000 hospitalizations for patients with COPD without concurrent heart failure (HF), 40% patients had at least 6 minutes of daily atrial fibrillation (AF) burden, and nearly half of these patients had at least an hour of daily AF burden; patients with COPD and concurrent HF had similar daily AF burdens, reported Trent Fischer, MD, MS, senior principal scientist at Medtronic in Minneapolis.
“We can conclude that AF burden increases in the weeks after a hospitalization for COPD if they don’t have a concurrent diagnosis of heart failure. Also, having concurrent heart failure increases the risk of atrial fibrillation and increases the atrial fibrillation burden around the time of COPD hospitalization,” he said in a rapid-fire oral abstract session at the CHEST Annual Meeting.
The findings indicated a need for increased vigilance for AF around the time of a serious COPD exacerbation and may explain at least some of the increased risks for stroke observed in patients who are hospitalized for COPD exacerbations, he said.
Retrospective Study
They drew data from 2007 through 2021 on patients with implantable cardioverter defibrillators, cardiac resynchronization therapy devices, pacemakers, and implantable cardiac monitors, using the Optum de-identified electronic health record dataset linked with Medtronic’s CareLink database to conduct a retrospective analysis.
They looked at admissions for COPD linked to available device diagnostic parameters between 30 days prior to and 60 days after admission for COPD.
They identified a total of 20,056 COPD hospitalizations for patients with concurrent HF and 3877 for those without HF.
Among patients with HF, 43% had a daily AF burden of at least 6 minutes, and 22% had at least 1 hour of irregular rhythms. Among patients without HF, 40% had at least 6 minutes of irregular rhythms daily, and 18% had at least 1 hour.
Among patients with HF, the daily average AF burden increased from a baseline of 158 min/d 30 days before an admission to 170 min/d at admission, returning to baseline by 20 days after hospitalization.
For patients without HF, the AF burden increased from 107 min/d at baseline to 113 min/d during hospitalization and returned to baseline by 20 days after hospitalization.
Confounding Factor?
In the Q&A, session moderator Krishna Sundar, MBBS, MD, FCCP, a pulmonary, sleep medicine, and critical care medicine specialist at St. John’s Medical Center in Jackson, Wyoming, said that when patients with HF get admitted for COPD exacerbations, their HF typically worsens and asked Dr. Fischer how he could tell the difference.
“I know there’s a lot of interaction between heart failure and COPD. They’re well-know comorbidities, and the exacerbation of one can bring on worsening of the other. At least with this database, we can’t really tease out any sort of differences,” Dr. Fischer replied.
“I think that a diagnosis of COPD exacerbation is pretty well laid out, but it’s sometimes difficult to separate worsening of heart failure in these patients, and often these patients get treated for both problems. It’s clear that it’s the heart failure patients who are having more atrial fibrillation episodes, which is not surprising, but the question is how much is the COPD exacerbation contributing to the atrial fibrillation?” said Dr. Sundar.
The study was supported by Medtronic. Dr. Fischer is employed by the company. Dr. Sundar reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
BOSTON — Patients with COPD who have exacerbations requiring hospitalization should be monitored for cardiac arrhythmias, investigators said.
This recommendation is based on results of a study of medical records showing that among more than 20,000 hospitalizations for patients with COPD without concurrent heart failure (HF), 40% patients had at least 6 minutes of daily atrial fibrillation (AF) burden, and nearly half of these patients had at least an hour of daily AF burden; patients with COPD and concurrent HF had similar daily AF burdens, reported Trent Fischer, MD, MS, senior principal scientist at Medtronic in Minneapolis.
“We can conclude that AF burden increases in the weeks after a hospitalization for COPD if they don’t have a concurrent diagnosis of heart failure. Also, having concurrent heart failure increases the risk of atrial fibrillation and increases the atrial fibrillation burden around the time of COPD hospitalization,” he said in a rapid-fire oral abstract session at the CHEST Annual Meeting.
The findings indicated a need for increased vigilance for AF around the time of a serious COPD exacerbation and may explain at least some of the increased risks for stroke observed in patients who are hospitalized for COPD exacerbations, he said.
Retrospective Study
They drew data from 2007 through 2021 on patients with implantable cardioverter defibrillators, cardiac resynchronization therapy devices, pacemakers, and implantable cardiac monitors, using the Optum de-identified electronic health record dataset linked with Medtronic’s CareLink database to conduct a retrospective analysis.
They looked at admissions for COPD linked to available device diagnostic parameters between 30 days prior to and 60 days after admission for COPD.
They identified a total of 20,056 COPD hospitalizations for patients with concurrent HF and 3877 for those without HF.
Among patients with HF, 43% had a daily AF burden of at least 6 minutes, and 22% had at least 1 hour of irregular rhythms. Among patients without HF, 40% had at least 6 minutes of irregular rhythms daily, and 18% had at least 1 hour.
Among patients with HF, the daily average AF burden increased from a baseline of 158 min/d 30 days before an admission to 170 min/d at admission, returning to baseline by 20 days after hospitalization.
For patients without HF, the AF burden increased from 107 min/d at baseline to 113 min/d during hospitalization and returned to baseline by 20 days after hospitalization.
Confounding Factor?
In the Q&A, session moderator Krishna Sundar, MBBS, MD, FCCP, a pulmonary, sleep medicine, and critical care medicine specialist at St. John’s Medical Center in Jackson, Wyoming, said that when patients with HF get admitted for COPD exacerbations, their HF typically worsens and asked Dr. Fischer how he could tell the difference.
“I know there’s a lot of interaction between heart failure and COPD. They’re well-know comorbidities, and the exacerbation of one can bring on worsening of the other. At least with this database, we can’t really tease out any sort of differences,” Dr. Fischer replied.
“I think that a diagnosis of COPD exacerbation is pretty well laid out, but it’s sometimes difficult to separate worsening of heart failure in these patients, and often these patients get treated for both problems. It’s clear that it’s the heart failure patients who are having more atrial fibrillation episodes, which is not surprising, but the question is how much is the COPD exacerbation contributing to the atrial fibrillation?” said Dr. Sundar.
The study was supported by Medtronic. Dr. Fischer is employed by the company. Dr. Sundar reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM CHEST 2024
Hospitalized Patients With COPD and GERD Have Better Short-Term Outcomes
BOSTON — Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) is associated with better in-hospital outcomes for patients hospitalized with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).
“It was a very surprising result. We double-checked the analysis once we got it the first time because the whole expectation was that the outcomes will be worse. But because it’s a retrospective study and it’s based on a national database, there are some limitations,” said ABM Nasibul Alam, MD, who presented the study at the annual meeting of the American College of Chest Physicians (CHEST) . Alam is an internal medicine resident at Northwestern Medicine McHenry Hospital, McHenry, Illinois.
One possible conclusion is that acid reflux therapies received in hospital may be benefitting COPD. The retrospective nature of the study precludes establishing a causal relationship, but there are possible mechanisms that could account for a benefit, according to Alam.
“They might prevent micro-aspirations or silent aspirations in COPD patients. Sometimes you may not have a clinical diagnosis of GERD, but the patient might have silent micro-aspirations, so it might contribute to decreasing that,” said Alam.
The study was conducted to fill a gap in the literature. “Some studies have shown that the lung function in COPD patients gets moderately decreased if they have coexisting GERD, but there aren’t any studies that have looked into how it impacts COPD patients when they’re hospitalized, and especially acute complications,” said Alam.
The researchers retrospectively analyzed data from the Nationwide Readmissions Database from 2017 to 2020, utilizing ICD-10 codes to identify 3,798,952 hospitalized adults with a primary diagnosis of COPD, of which 26.97% also had GERD. Individuals without GERD were more likely to be male (47.72% vs 39.88%).
After multivariate adjustment, the presence of GERD was associated with a lower mortality rate (adjusted odds ratio [aOR], 0.717; P < .001) and reduced risks for acute respiratory failure (aOR, 0.915; P < .001), need for noninvasive mechanical ventilation (aOR, 0.907; P < .001), need for invasive ventilation for 24 hours or more (aOR, 0.727; P < .001), acute kidney injury (aOR, 0.877; P < .001), septic shock (aOR, 0.731; P < .001), and acute heart failure (aOR, 0.762; P < .001).
Despite these improved in-hospital outcomes, the researchers found that patients with GERD were at a higher risk for 30-day readmission (aOR, 1.08; P < .001). They also had slightly longer lengths of stay (+0.09 day; P < .001) and lower total charges (−$2824.5996; P < .001).
There have also been studies suggesting that GERD can directly lead to worse lung function among patients with COPD. “So it will be interesting to see if these medications have some kind of impact on the lung function as well. We need more robust studies [to determine that],” said Alam.
It is also important to keep in mind the long-term risk of proton pump inhibitors, especially in older patients. “We have to have good data before we start recommending this,” said Alam.
He suggested that physicians should begin to think more holistically about COPD management and consider the comorbidities. Alam has studied vitamin B12 deficiency in patients with COPD and found an association with cardiovascular comorbidities. “There are so many comorbidities with COPD. COPD itself puts patients at risk of cardiovascular comorbidity, for example. So when we have patients with COPD, we have to think about all those comorbidities and have to manage the patients comprehensively rather than just focusing on the specific targeted interventions,” said Alam.
The study should encourage further research, according to Kunal Deokar, MD, who moderated the session where the study was presented. “It does give us a signal that probably we should have more studies to look into whether patients hospitalized for COPD with GERD really have lower mortality rates, and what will be the effect of treatment on these patients,” said Deokar, who is an assistant professor of pulmonary medicine at the All India Institute of Medical Sciences, Delhi, India.
Alam and Deokar disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
BOSTON — Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) is associated with better in-hospital outcomes for patients hospitalized with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).
“It was a very surprising result. We double-checked the analysis once we got it the first time because the whole expectation was that the outcomes will be worse. But because it’s a retrospective study and it’s based on a national database, there are some limitations,” said ABM Nasibul Alam, MD, who presented the study at the annual meeting of the American College of Chest Physicians (CHEST) . Alam is an internal medicine resident at Northwestern Medicine McHenry Hospital, McHenry, Illinois.
One possible conclusion is that acid reflux therapies received in hospital may be benefitting COPD. The retrospective nature of the study precludes establishing a causal relationship, but there are possible mechanisms that could account for a benefit, according to Alam.
“They might prevent micro-aspirations or silent aspirations in COPD patients. Sometimes you may not have a clinical diagnosis of GERD, but the patient might have silent micro-aspirations, so it might contribute to decreasing that,” said Alam.
The study was conducted to fill a gap in the literature. “Some studies have shown that the lung function in COPD patients gets moderately decreased if they have coexisting GERD, but there aren’t any studies that have looked into how it impacts COPD patients when they’re hospitalized, and especially acute complications,” said Alam.
The researchers retrospectively analyzed data from the Nationwide Readmissions Database from 2017 to 2020, utilizing ICD-10 codes to identify 3,798,952 hospitalized adults with a primary diagnosis of COPD, of which 26.97% also had GERD. Individuals without GERD were more likely to be male (47.72% vs 39.88%).
After multivariate adjustment, the presence of GERD was associated with a lower mortality rate (adjusted odds ratio [aOR], 0.717; P < .001) and reduced risks for acute respiratory failure (aOR, 0.915; P < .001), need for noninvasive mechanical ventilation (aOR, 0.907; P < .001), need for invasive ventilation for 24 hours or more (aOR, 0.727; P < .001), acute kidney injury (aOR, 0.877; P < .001), septic shock (aOR, 0.731; P < .001), and acute heart failure (aOR, 0.762; P < .001).
Despite these improved in-hospital outcomes, the researchers found that patients with GERD were at a higher risk for 30-day readmission (aOR, 1.08; P < .001). They also had slightly longer lengths of stay (+0.09 day; P < .001) and lower total charges (−$2824.5996; P < .001).
There have also been studies suggesting that GERD can directly lead to worse lung function among patients with COPD. “So it will be interesting to see if these medications have some kind of impact on the lung function as well. We need more robust studies [to determine that],” said Alam.
It is also important to keep in mind the long-term risk of proton pump inhibitors, especially in older patients. “We have to have good data before we start recommending this,” said Alam.
He suggested that physicians should begin to think more holistically about COPD management and consider the comorbidities. Alam has studied vitamin B12 deficiency in patients with COPD and found an association with cardiovascular comorbidities. “There are so many comorbidities with COPD. COPD itself puts patients at risk of cardiovascular comorbidity, for example. So when we have patients with COPD, we have to think about all those comorbidities and have to manage the patients comprehensively rather than just focusing on the specific targeted interventions,” said Alam.
The study should encourage further research, according to Kunal Deokar, MD, who moderated the session where the study was presented. “It does give us a signal that probably we should have more studies to look into whether patients hospitalized for COPD with GERD really have lower mortality rates, and what will be the effect of treatment on these patients,” said Deokar, who is an assistant professor of pulmonary medicine at the All India Institute of Medical Sciences, Delhi, India.
Alam and Deokar disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
BOSTON — Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) is associated with better in-hospital outcomes for patients hospitalized with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).
“It was a very surprising result. We double-checked the analysis once we got it the first time because the whole expectation was that the outcomes will be worse. But because it’s a retrospective study and it’s based on a national database, there are some limitations,” said ABM Nasibul Alam, MD, who presented the study at the annual meeting of the American College of Chest Physicians (CHEST) . Alam is an internal medicine resident at Northwestern Medicine McHenry Hospital, McHenry, Illinois.
One possible conclusion is that acid reflux therapies received in hospital may be benefitting COPD. The retrospective nature of the study precludes establishing a causal relationship, but there are possible mechanisms that could account for a benefit, according to Alam.
“They might prevent micro-aspirations or silent aspirations in COPD patients. Sometimes you may not have a clinical diagnosis of GERD, but the patient might have silent micro-aspirations, so it might contribute to decreasing that,” said Alam.
The study was conducted to fill a gap in the literature. “Some studies have shown that the lung function in COPD patients gets moderately decreased if they have coexisting GERD, but there aren’t any studies that have looked into how it impacts COPD patients when they’re hospitalized, and especially acute complications,” said Alam.
The researchers retrospectively analyzed data from the Nationwide Readmissions Database from 2017 to 2020, utilizing ICD-10 codes to identify 3,798,952 hospitalized adults with a primary diagnosis of COPD, of which 26.97% also had GERD. Individuals without GERD were more likely to be male (47.72% vs 39.88%).
After multivariate adjustment, the presence of GERD was associated with a lower mortality rate (adjusted odds ratio [aOR], 0.717; P < .001) and reduced risks for acute respiratory failure (aOR, 0.915; P < .001), need for noninvasive mechanical ventilation (aOR, 0.907; P < .001), need for invasive ventilation for 24 hours or more (aOR, 0.727; P < .001), acute kidney injury (aOR, 0.877; P < .001), septic shock (aOR, 0.731; P < .001), and acute heart failure (aOR, 0.762; P < .001).
Despite these improved in-hospital outcomes, the researchers found that patients with GERD were at a higher risk for 30-day readmission (aOR, 1.08; P < .001). They also had slightly longer lengths of stay (+0.09 day; P < .001) and lower total charges (−$2824.5996; P < .001).
There have also been studies suggesting that GERD can directly lead to worse lung function among patients with COPD. “So it will be interesting to see if these medications have some kind of impact on the lung function as well. We need more robust studies [to determine that],” said Alam.
It is also important to keep in mind the long-term risk of proton pump inhibitors, especially in older patients. “We have to have good data before we start recommending this,” said Alam.
He suggested that physicians should begin to think more holistically about COPD management and consider the comorbidities. Alam has studied vitamin B12 deficiency in patients with COPD and found an association with cardiovascular comorbidities. “There are so many comorbidities with COPD. COPD itself puts patients at risk of cardiovascular comorbidity, for example. So when we have patients with COPD, we have to think about all those comorbidities and have to manage the patients comprehensively rather than just focusing on the specific targeted interventions,” said Alam.
The study should encourage further research, according to Kunal Deokar, MD, who moderated the session where the study was presented. “It does give us a signal that probably we should have more studies to look into whether patients hospitalized for COPD with GERD really have lower mortality rates, and what will be the effect of treatment on these patients,” said Deokar, who is an assistant professor of pulmonary medicine at the All India Institute of Medical Sciences, Delhi, India.
Alam and Deokar disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM CHEST 2024
Is Wildfire Smoke More Toxic Than General Air Pollution?
Wildfire-related air pollution in Europe kills more than non-wildfire air pollution. As climate change exacerbates the frequency and violence of wildfires, researchers are studying the health implications of mitigation methods such as prescribed fires.
Presenting at the annual congress of the European Respiratory Society (ERS), Cathryn Tonne, PhD, an environmental epidemiologist at the Instituto de Salud Global de Barcelona, Spain, said wildfire-related PM2.5 is more toxic than general PM2.5, leading to significantly higher mortality rates.
Prescribed, controlled fires have been employed worldwide to reduce the chance of uncontrolled, catastrophic fires. However, researchers wonder whether the techniques reduce the overall fire-related PM2.5 or add up to it. “Prescribed fire increases ecosystem resilience and can reduce the risk of catastrophic wildfire,” said Jason Sacks, MPH, an epidemiologist in the Center for Public Health and Environmental Assessment in the Office of Research and Development at the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), at the congress. “But it also leads to poorer air quality and health impacts, and we still don’t know what this means at a regional scale.”
Wildfire Pollution Kills More Than Other Air Pollution
Researchers at the Instituto de Salud Global de Barcelona used a large dataset of daily mortality data from 32 European countries collected through the EARLY-ADAPT project. They utilized the SILAM model to derive daily average concentrations of wildfire-related PM2.5, non-fire PM2.5, and total PM2.5 levels. They also employed GEOSTAT population grids at a 1-km resolution to calculate the attributable number of deaths across different regions, specifically focusing on data from 2006, 2011, and 2018.
The data analysis indicated that the relative risk per unit of PM2.5 is substantially larger for wildfire-related PM2.5, compared with non-fire PM2.5. “We essentially assume that wildfire smoke PM2.5 has the same toxicity as total PM2.5, but it’s increasingly clear that’s likely not the case,” Dr. Tonne said, presenting the study.
When employing exposure-response functions (ERFs) specific to wildfire smoke, researchers found that the attributable deaths from all causes of wildfire PM2.5 were approximately 10 times larger than those calculated using total PM2.5 exposure estimates. Dr. Tonne explained that this stark difference highlights the critical need for tailored ERFs that accurately reflect the unique health risks posed by wildfire smoke.
“Respiratory mortality usually has the strongest relative risks, and we’re seeing that in this study as well,” Dr. Tonne said. “Wildfire smoke seems to operate through quite immediate mechanisms, likely through inflammation and oxidative stress.”
One significant challenge of the study was the lack of uniform spatial resolution across all countries involved in the analysis. This inconsistency may affect how accurately mortality estimates can be attributed to specific PM2.5 sources. Additionally, the study had limited statistical power for generating age- and sex-specific mortality estimates, which could obscure important demographic differences in vulnerability to wildfire smoke exposure. The analysis was also constrained to data available only up to 2020, thereby excluding critical wildfire events from subsequent years, such as those in 2022 and 2023, which may have further elucidated the health impacts of wildfire smoke in Europe.
Fires Prescription
Prescribed fires or controlled burns are intentional fires set by land managers under carefully managed conditions.
Historically, many forested areas have been subjected to fire suppression practices, which allow combustible materials like dry leaves, twigs, and shrubs to accumulate over time. This buildup leads to a higher likelihood of severe, uncontrollable wildfires. Prescribed fires can reduce these fuel loads and improve the health and resilience of ecosystems.
They release fewer pollutants and emissions than the large-scale, unmanageable wildfires they help prevent because they happen at lower temperatures. But they still introduce pollutants in the air that can negatively affect nearby communities’ health.
People with preexisting respiratory conditions, such as asthma or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), are particularly vulnerable to smoke, which can trigger health issues like breathing difficulties, coughing, and eye irritation. The cumulative impact of increased burns raises concerns about long-term air quality, especially in densely populated areas. “We need to understand if we’re actually tipping the scale to having less wildfire smoke or just increasing the total amount of smoke.”
Mitigation strategies include accurately picking the right timing and weather conditions to determine when and where to conduct controlled burns and effective and timely communication to inform local communities about upcoming burns, the potential for smoke exposure, and how to protect themselves.
There is a growing need to improve public messaging around prescribed fires, Mr. Sacks said, because often the message communicated is oversimplified, such as “there will be smoke, but don’t worry. But that’s not the message we want to convey, especially for people with asthma or COPD.”
Instead, he said public health agencies should provide clearer, science-based guidance on the risks for smoke exposure and practical steps people can take to reduce their risk.
What Can Doctors Do?
Chris Carlsten, MD, director of the Centre for Lung Health and professor and head of the Respiratory Medicine Division at the University of British Columbia, Vancouver, Canada, told this news organization that determining whether an exacerbation of a respiratory condition is caused by fire exposure or other factors, such as viral infections, is complex because both can trigger similar responses and may complement each other. “It’s very difficult for any individual to know whether, when they’re having an exacerbation of asthma or COPD, that’s due to the fire,” he said. Fire smoke also increases infection risks, further complicating diagnosis.
Dr. Carlsten suggested that physicians could recommend preventative use of inhalers for at-risk patients when wildfires occur rather than waiting for symptoms to worsen. “That is a really interesting idea that could be practical.” Still, he advises caution, stressing that patients should consult their providers because not all may react well to increased inhaler use.
He also highlighted a significant shift in the healthcare landscape, noting that traditionally, the focus has been on the cardiovascular impacts of pollution, particularly traffic-related pollution. However, as wildfire smoke becomes a growing issue, the focus is shifting back to respiratory problems, with profound implications for healthcare resources, budgets, and drug approvals based on the burden of respiratory disease. “Fire smoke is becoming more of a problem. This swing back to respiratory has huge implications for healthcare systems and respiratory disease burden.”
Mr. Sacks and Dr. Carlsten reported no relevant financial relationships. The study presented by Dr. Tonne received funding from the European Union’s Horizon Europe research and innovation programme under Grant Agreement No. 101057131.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Wildfire-related air pollution in Europe kills more than non-wildfire air pollution. As climate change exacerbates the frequency and violence of wildfires, researchers are studying the health implications of mitigation methods such as prescribed fires.
Presenting at the annual congress of the European Respiratory Society (ERS), Cathryn Tonne, PhD, an environmental epidemiologist at the Instituto de Salud Global de Barcelona, Spain, said wildfire-related PM2.5 is more toxic than general PM2.5, leading to significantly higher mortality rates.
Prescribed, controlled fires have been employed worldwide to reduce the chance of uncontrolled, catastrophic fires. However, researchers wonder whether the techniques reduce the overall fire-related PM2.5 or add up to it. “Prescribed fire increases ecosystem resilience and can reduce the risk of catastrophic wildfire,” said Jason Sacks, MPH, an epidemiologist in the Center for Public Health and Environmental Assessment in the Office of Research and Development at the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), at the congress. “But it also leads to poorer air quality and health impacts, and we still don’t know what this means at a regional scale.”
Wildfire Pollution Kills More Than Other Air Pollution
Researchers at the Instituto de Salud Global de Barcelona used a large dataset of daily mortality data from 32 European countries collected through the EARLY-ADAPT project. They utilized the SILAM model to derive daily average concentrations of wildfire-related PM2.5, non-fire PM2.5, and total PM2.5 levels. They also employed GEOSTAT population grids at a 1-km resolution to calculate the attributable number of deaths across different regions, specifically focusing on data from 2006, 2011, and 2018.
The data analysis indicated that the relative risk per unit of PM2.5 is substantially larger for wildfire-related PM2.5, compared with non-fire PM2.5. “We essentially assume that wildfire smoke PM2.5 has the same toxicity as total PM2.5, but it’s increasingly clear that’s likely not the case,” Dr. Tonne said, presenting the study.
When employing exposure-response functions (ERFs) specific to wildfire smoke, researchers found that the attributable deaths from all causes of wildfire PM2.5 were approximately 10 times larger than those calculated using total PM2.5 exposure estimates. Dr. Tonne explained that this stark difference highlights the critical need for tailored ERFs that accurately reflect the unique health risks posed by wildfire smoke.
“Respiratory mortality usually has the strongest relative risks, and we’re seeing that in this study as well,” Dr. Tonne said. “Wildfire smoke seems to operate through quite immediate mechanisms, likely through inflammation and oxidative stress.”
One significant challenge of the study was the lack of uniform spatial resolution across all countries involved in the analysis. This inconsistency may affect how accurately mortality estimates can be attributed to specific PM2.5 sources. Additionally, the study had limited statistical power for generating age- and sex-specific mortality estimates, which could obscure important demographic differences in vulnerability to wildfire smoke exposure. The analysis was also constrained to data available only up to 2020, thereby excluding critical wildfire events from subsequent years, such as those in 2022 and 2023, which may have further elucidated the health impacts of wildfire smoke in Europe.
Fires Prescription
Prescribed fires or controlled burns are intentional fires set by land managers under carefully managed conditions.
Historically, many forested areas have been subjected to fire suppression practices, which allow combustible materials like dry leaves, twigs, and shrubs to accumulate over time. This buildup leads to a higher likelihood of severe, uncontrollable wildfires. Prescribed fires can reduce these fuel loads and improve the health and resilience of ecosystems.
They release fewer pollutants and emissions than the large-scale, unmanageable wildfires they help prevent because they happen at lower temperatures. But they still introduce pollutants in the air that can negatively affect nearby communities’ health.
People with preexisting respiratory conditions, such as asthma or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), are particularly vulnerable to smoke, which can trigger health issues like breathing difficulties, coughing, and eye irritation. The cumulative impact of increased burns raises concerns about long-term air quality, especially in densely populated areas. “We need to understand if we’re actually tipping the scale to having less wildfire smoke or just increasing the total amount of smoke.”
Mitigation strategies include accurately picking the right timing and weather conditions to determine when and where to conduct controlled burns and effective and timely communication to inform local communities about upcoming burns, the potential for smoke exposure, and how to protect themselves.
There is a growing need to improve public messaging around prescribed fires, Mr. Sacks said, because often the message communicated is oversimplified, such as “there will be smoke, but don’t worry. But that’s not the message we want to convey, especially for people with asthma or COPD.”
Instead, he said public health agencies should provide clearer, science-based guidance on the risks for smoke exposure and practical steps people can take to reduce their risk.
What Can Doctors Do?
Chris Carlsten, MD, director of the Centre for Lung Health and professor and head of the Respiratory Medicine Division at the University of British Columbia, Vancouver, Canada, told this news organization that determining whether an exacerbation of a respiratory condition is caused by fire exposure or other factors, such as viral infections, is complex because both can trigger similar responses and may complement each other. “It’s very difficult for any individual to know whether, when they’re having an exacerbation of asthma or COPD, that’s due to the fire,” he said. Fire smoke also increases infection risks, further complicating diagnosis.
Dr. Carlsten suggested that physicians could recommend preventative use of inhalers for at-risk patients when wildfires occur rather than waiting for symptoms to worsen. “That is a really interesting idea that could be practical.” Still, he advises caution, stressing that patients should consult their providers because not all may react well to increased inhaler use.
He also highlighted a significant shift in the healthcare landscape, noting that traditionally, the focus has been on the cardiovascular impacts of pollution, particularly traffic-related pollution. However, as wildfire smoke becomes a growing issue, the focus is shifting back to respiratory problems, with profound implications for healthcare resources, budgets, and drug approvals based on the burden of respiratory disease. “Fire smoke is becoming more of a problem. This swing back to respiratory has huge implications for healthcare systems and respiratory disease burden.”
Mr. Sacks and Dr. Carlsten reported no relevant financial relationships. The study presented by Dr. Tonne received funding from the European Union’s Horizon Europe research and innovation programme under Grant Agreement No. 101057131.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Wildfire-related air pollution in Europe kills more than non-wildfire air pollution. As climate change exacerbates the frequency and violence of wildfires, researchers are studying the health implications of mitigation methods such as prescribed fires.
Presenting at the annual congress of the European Respiratory Society (ERS), Cathryn Tonne, PhD, an environmental epidemiologist at the Instituto de Salud Global de Barcelona, Spain, said wildfire-related PM2.5 is more toxic than general PM2.5, leading to significantly higher mortality rates.
Prescribed, controlled fires have been employed worldwide to reduce the chance of uncontrolled, catastrophic fires. However, researchers wonder whether the techniques reduce the overall fire-related PM2.5 or add up to it. “Prescribed fire increases ecosystem resilience and can reduce the risk of catastrophic wildfire,” said Jason Sacks, MPH, an epidemiologist in the Center for Public Health and Environmental Assessment in the Office of Research and Development at the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), at the congress. “But it also leads to poorer air quality and health impacts, and we still don’t know what this means at a regional scale.”
Wildfire Pollution Kills More Than Other Air Pollution
Researchers at the Instituto de Salud Global de Barcelona used a large dataset of daily mortality data from 32 European countries collected through the EARLY-ADAPT project. They utilized the SILAM model to derive daily average concentrations of wildfire-related PM2.5, non-fire PM2.5, and total PM2.5 levels. They also employed GEOSTAT population grids at a 1-km resolution to calculate the attributable number of deaths across different regions, specifically focusing on data from 2006, 2011, and 2018.
The data analysis indicated that the relative risk per unit of PM2.5 is substantially larger for wildfire-related PM2.5, compared with non-fire PM2.5. “We essentially assume that wildfire smoke PM2.5 has the same toxicity as total PM2.5, but it’s increasingly clear that’s likely not the case,” Dr. Tonne said, presenting the study.
When employing exposure-response functions (ERFs) specific to wildfire smoke, researchers found that the attributable deaths from all causes of wildfire PM2.5 were approximately 10 times larger than those calculated using total PM2.5 exposure estimates. Dr. Tonne explained that this stark difference highlights the critical need for tailored ERFs that accurately reflect the unique health risks posed by wildfire smoke.
“Respiratory mortality usually has the strongest relative risks, and we’re seeing that in this study as well,” Dr. Tonne said. “Wildfire smoke seems to operate through quite immediate mechanisms, likely through inflammation and oxidative stress.”
One significant challenge of the study was the lack of uniform spatial resolution across all countries involved in the analysis. This inconsistency may affect how accurately mortality estimates can be attributed to specific PM2.5 sources. Additionally, the study had limited statistical power for generating age- and sex-specific mortality estimates, which could obscure important demographic differences in vulnerability to wildfire smoke exposure. The analysis was also constrained to data available only up to 2020, thereby excluding critical wildfire events from subsequent years, such as those in 2022 and 2023, which may have further elucidated the health impacts of wildfire smoke in Europe.
Fires Prescription
Prescribed fires or controlled burns are intentional fires set by land managers under carefully managed conditions.
Historically, many forested areas have been subjected to fire suppression practices, which allow combustible materials like dry leaves, twigs, and shrubs to accumulate over time. This buildup leads to a higher likelihood of severe, uncontrollable wildfires. Prescribed fires can reduce these fuel loads and improve the health and resilience of ecosystems.
They release fewer pollutants and emissions than the large-scale, unmanageable wildfires they help prevent because they happen at lower temperatures. But they still introduce pollutants in the air that can negatively affect nearby communities’ health.
People with preexisting respiratory conditions, such as asthma or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), are particularly vulnerable to smoke, which can trigger health issues like breathing difficulties, coughing, and eye irritation. The cumulative impact of increased burns raises concerns about long-term air quality, especially in densely populated areas. “We need to understand if we’re actually tipping the scale to having less wildfire smoke or just increasing the total amount of smoke.”
Mitigation strategies include accurately picking the right timing and weather conditions to determine when and where to conduct controlled burns and effective and timely communication to inform local communities about upcoming burns, the potential for smoke exposure, and how to protect themselves.
There is a growing need to improve public messaging around prescribed fires, Mr. Sacks said, because often the message communicated is oversimplified, such as “there will be smoke, but don’t worry. But that’s not the message we want to convey, especially for people with asthma or COPD.”
Instead, he said public health agencies should provide clearer, science-based guidance on the risks for smoke exposure and practical steps people can take to reduce their risk.
What Can Doctors Do?
Chris Carlsten, MD, director of the Centre for Lung Health and professor and head of the Respiratory Medicine Division at the University of British Columbia, Vancouver, Canada, told this news organization that determining whether an exacerbation of a respiratory condition is caused by fire exposure or other factors, such as viral infections, is complex because both can trigger similar responses and may complement each other. “It’s very difficult for any individual to know whether, when they’re having an exacerbation of asthma or COPD, that’s due to the fire,” he said. Fire smoke also increases infection risks, further complicating diagnosis.
Dr. Carlsten suggested that physicians could recommend preventative use of inhalers for at-risk patients when wildfires occur rather than waiting for symptoms to worsen. “That is a really interesting idea that could be practical.” Still, he advises caution, stressing that patients should consult their providers because not all may react well to increased inhaler use.
He also highlighted a significant shift in the healthcare landscape, noting that traditionally, the focus has been on the cardiovascular impacts of pollution, particularly traffic-related pollution. However, as wildfire smoke becomes a growing issue, the focus is shifting back to respiratory problems, with profound implications for healthcare resources, budgets, and drug approvals based on the burden of respiratory disease. “Fire smoke is becoming more of a problem. This swing back to respiratory has huge implications for healthcare systems and respiratory disease burden.”
Mr. Sacks and Dr. Carlsten reported no relevant financial relationships. The study presented by Dr. Tonne received funding from the European Union’s Horizon Europe research and innovation programme under Grant Agreement No. 101057131.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM ERS 2024
Majority of Hospitalized Patients With COPD Misuse Inhalers
Approximately two thirds of hospitalized adults with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) received suboptimal treatment with inhalers, mainly resulting from errors, based on data from 96 individuals.
“Numerous studies have highlighted the significant issue of improper inhaler use in outpatient settings, but the extent of this problem within hospital settings remains poorly documented,” said lead author Gaël Grandmaison, MD, of the University of Fribourg in Switzerland, in an interview.
“This gap in knowledge is concerning, especially considering that several factors associated with suboptimal inhaler use, such as improper inhalation techniques, insufficient inspiratory flow, or the use of inhalers that are not suited to the patient’s specific characteristics, are associated with poorer disease control, more frequent exacerbations, and increased costs,” Dr. Grandmaison said.
To better characterize the prevalence of and factors associated with inhaler misuse in hospitalized patients with COPD, the researchers reviewed data from consecutive patients with COPD who were hospitalized in the general internal medicine department of a single institution between August 2022 and April 2023. Patients were assessed for peak inspiratory flow (PIF) and inhaler technique.
The primary outcome was the proportion of misused inhalers, which was defined as any inhaler used with either insufficient PIF and/or a critical error. The mean age of the patients was 71.6 years, 63% were men, and 67% were hospitalized for COPD exacerbations. Patients used 3.0 inhalers on average.
The study included 96 patients and 160 inhalers that were assessed at hospital admission. Overall, 111 were misused. Of those misused, 105 were associated with a critical error in the inhalation technique, and 22 were used with an insufficient PIF. After an episode of misuse, patients received targeted teaching on correct use that was repeated until they performed the technique without errors.
The percentage of inhaler misuse decreased over the course of the teaching sessions. The proportion of inhaler misuse decreased to 20.6%, 9.4%, and 5.6% after one, two, and three sessions, respectively.
“The inhalation technique was classified as ‘non-teachable’ if the patient continued to exhibit critical errors despite receiving three repetitions of the instructions,” the researchers wrote. Factors associated with inhaler misuse included cognitive disorders, fine motor disorders, poor coordination between inhaler activation and aspiration, and the inability to hold one’s breath.
Overall, the proportion of misused inhalers did not vary by age or gender. In an analysis at the patient level, 79 patients used at least one misused inhaler, 78 used at least one inhaler with a critical error, and 21 used inhalers with insufficient PIF.
“This study is particularly timely because reasons for hospitalization, such as COPD exacerbations or confusional states, could exacerbate the problem, leading to a potentially higher prevalence of suboptimal inhaler use compared to outpatient settings,” Dr. Grandmaison said.
The researchers also examined secondary outcomes including the prevalence of inhalers that were not suited to them and the number of patients using at least one misused inhaler.
The study findings confirm that suboptimal inhaler use is a significant problem in the hospital setting and provide new insights into the specific reasons behind this suboptimal usage, Dr. Grandmaison said.
“In the majority of cases, poor inhalation technique is the primary cause, which can generally be corrected through targeted therapeutic education,” she said. However, the study also revealed that 20% of patients are unable to use at least one of their inhalers correctly because of insufficient inspiratory force. Another 10% struggle despite receiving proper instruction, often because of cognitive impairments or difficulty with fine motor skills.
The results underscore the need for a comprehensive approach to inhaler use in hospitalized patients that combines continuous therapeutic education with personalized assessment in order to improve technique and subsequently enhance patient outcomes, she said.
Changing Clinical Practice
“As hospital physicians, these findings have led us to systematically evaluate the inhalers used by COPD patients, regardless of their reason for hospitalization,” Dr. Grandmaison said. Consequently, the hospital has implemented an assessment of inhaler use among patients that includes a review of techniques, an evaluation of the appropriateness of the inhaler prescribed, and an algorithm to help clinicians choose the most appropriate inhaler. Since its inception, the targeted intervention has significantly reduced improper inhaler use at discharge.
Limitations and Next Steps
The findings were limited by several factors including the possible underreporting of misuse caused by inadequate PIF, a lack of consensus on what constitutes a critical error, and the small sample of patients from a single center.
Despite these limitations, the study adds to the understanding of improper inhaler use in the hospital setting, Dr. Grandmaison said. “Our subsequent research demonstrated that a systematic evaluation of inhalers, combined with therapeutic education and an algorithm to select an inhaler suited to the patient’s characteristics, significantly reduces the number of improperly used inhalers at hospital discharge.”
However, several areas require further investigation, said Dr. Grandmaison. The most effective methods and frequency for teaching inhalation techniques must be defined, and more research is needed to understand the factors influencing PIF and its progression over the course of disease. The next steps for the current research are to evaluate the impact of the intervention on long-term symptom control and disease progression.
“Moreover, adapting the strategy developed in our institution for use in outpatient care is a priority, and multicenter studies would be valuable in validating these findings across different hospital settings,” she added.
In-Hospital Inhaler Education Falls Short
“Poor inhaler technique can lead to ineffective inhaler use and suboptimal treatment of COPD,” said Arianne K. Baldomero, MD, a pulmonologist and assistant professor of medicine at the University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, in an interview.
“The results from this study are consistent with prior studies showing a high prevalence of suboptimal inhaler use,” said Dr. Baldomero, who was not involved in the current study.
“The investigators also found that therapeutic education led to a significant reduction in the number of critical errors,” she said.
“What is surprising is that it can take up to three lessons to reduce this critical error down to 3.8%,” Dr. Baldomero said. “In most real-world clinic settings, many patients are not taught how to properly use inhalers, and many patients who receive inhaler technique education only receive instructions once.”
Dr. Baldomero’s takeaway from the study is that teaching patients to properly use their inhalers is critical, but that this education may need to be repeated multiple times. The findings also remind clinicians that some types of inhaler delivery are not suited for patients who cannot generate adequate respiratory flow.
Looking ahead, a larger sample size is needed to better identify which patients need additional teaching, Dr. Baldomero said. Also, the current study is limited by the focus on hospitalized patients. “I am interested in learning about the characteristics of patients in the outpatient settings who would benefit from additional inhaler teaching,” she noted.
The study was supported by a grant from the Hospital of Fribourg in Switzerland. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose. Dr. Baldomero had no financial conflicts to disclose.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Approximately two thirds of hospitalized adults with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) received suboptimal treatment with inhalers, mainly resulting from errors, based on data from 96 individuals.
“Numerous studies have highlighted the significant issue of improper inhaler use in outpatient settings, but the extent of this problem within hospital settings remains poorly documented,” said lead author Gaël Grandmaison, MD, of the University of Fribourg in Switzerland, in an interview.
“This gap in knowledge is concerning, especially considering that several factors associated with suboptimal inhaler use, such as improper inhalation techniques, insufficient inspiratory flow, or the use of inhalers that are not suited to the patient’s specific characteristics, are associated with poorer disease control, more frequent exacerbations, and increased costs,” Dr. Grandmaison said.
To better characterize the prevalence of and factors associated with inhaler misuse in hospitalized patients with COPD, the researchers reviewed data from consecutive patients with COPD who were hospitalized in the general internal medicine department of a single institution between August 2022 and April 2023. Patients were assessed for peak inspiratory flow (PIF) and inhaler technique.
The primary outcome was the proportion of misused inhalers, which was defined as any inhaler used with either insufficient PIF and/or a critical error. The mean age of the patients was 71.6 years, 63% were men, and 67% were hospitalized for COPD exacerbations. Patients used 3.0 inhalers on average.
The study included 96 patients and 160 inhalers that were assessed at hospital admission. Overall, 111 were misused. Of those misused, 105 were associated with a critical error in the inhalation technique, and 22 were used with an insufficient PIF. After an episode of misuse, patients received targeted teaching on correct use that was repeated until they performed the technique without errors.
The percentage of inhaler misuse decreased over the course of the teaching sessions. The proportion of inhaler misuse decreased to 20.6%, 9.4%, and 5.6% after one, two, and three sessions, respectively.
“The inhalation technique was classified as ‘non-teachable’ if the patient continued to exhibit critical errors despite receiving three repetitions of the instructions,” the researchers wrote. Factors associated with inhaler misuse included cognitive disorders, fine motor disorders, poor coordination between inhaler activation and aspiration, and the inability to hold one’s breath.
Overall, the proportion of misused inhalers did not vary by age or gender. In an analysis at the patient level, 79 patients used at least one misused inhaler, 78 used at least one inhaler with a critical error, and 21 used inhalers with insufficient PIF.
“This study is particularly timely because reasons for hospitalization, such as COPD exacerbations or confusional states, could exacerbate the problem, leading to a potentially higher prevalence of suboptimal inhaler use compared to outpatient settings,” Dr. Grandmaison said.
The researchers also examined secondary outcomes including the prevalence of inhalers that were not suited to them and the number of patients using at least one misused inhaler.
The study findings confirm that suboptimal inhaler use is a significant problem in the hospital setting and provide new insights into the specific reasons behind this suboptimal usage, Dr. Grandmaison said.
“In the majority of cases, poor inhalation technique is the primary cause, which can generally be corrected through targeted therapeutic education,” she said. However, the study also revealed that 20% of patients are unable to use at least one of their inhalers correctly because of insufficient inspiratory force. Another 10% struggle despite receiving proper instruction, often because of cognitive impairments or difficulty with fine motor skills.
The results underscore the need for a comprehensive approach to inhaler use in hospitalized patients that combines continuous therapeutic education with personalized assessment in order to improve technique and subsequently enhance patient outcomes, she said.
Changing Clinical Practice
“As hospital physicians, these findings have led us to systematically evaluate the inhalers used by COPD patients, regardless of their reason for hospitalization,” Dr. Grandmaison said. Consequently, the hospital has implemented an assessment of inhaler use among patients that includes a review of techniques, an evaluation of the appropriateness of the inhaler prescribed, and an algorithm to help clinicians choose the most appropriate inhaler. Since its inception, the targeted intervention has significantly reduced improper inhaler use at discharge.
Limitations and Next Steps
The findings were limited by several factors including the possible underreporting of misuse caused by inadequate PIF, a lack of consensus on what constitutes a critical error, and the small sample of patients from a single center.
Despite these limitations, the study adds to the understanding of improper inhaler use in the hospital setting, Dr. Grandmaison said. “Our subsequent research demonstrated that a systematic evaluation of inhalers, combined with therapeutic education and an algorithm to select an inhaler suited to the patient’s characteristics, significantly reduces the number of improperly used inhalers at hospital discharge.”
However, several areas require further investigation, said Dr. Grandmaison. The most effective methods and frequency for teaching inhalation techniques must be defined, and more research is needed to understand the factors influencing PIF and its progression over the course of disease. The next steps for the current research are to evaluate the impact of the intervention on long-term symptom control and disease progression.
“Moreover, adapting the strategy developed in our institution for use in outpatient care is a priority, and multicenter studies would be valuable in validating these findings across different hospital settings,” she added.
In-Hospital Inhaler Education Falls Short
“Poor inhaler technique can lead to ineffective inhaler use and suboptimal treatment of COPD,” said Arianne K. Baldomero, MD, a pulmonologist and assistant professor of medicine at the University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, in an interview.
“The results from this study are consistent with prior studies showing a high prevalence of suboptimal inhaler use,” said Dr. Baldomero, who was not involved in the current study.
“The investigators also found that therapeutic education led to a significant reduction in the number of critical errors,” she said.
“What is surprising is that it can take up to three lessons to reduce this critical error down to 3.8%,” Dr. Baldomero said. “In most real-world clinic settings, many patients are not taught how to properly use inhalers, and many patients who receive inhaler technique education only receive instructions once.”
Dr. Baldomero’s takeaway from the study is that teaching patients to properly use their inhalers is critical, but that this education may need to be repeated multiple times. The findings also remind clinicians that some types of inhaler delivery are not suited for patients who cannot generate adequate respiratory flow.
Looking ahead, a larger sample size is needed to better identify which patients need additional teaching, Dr. Baldomero said. Also, the current study is limited by the focus on hospitalized patients. “I am interested in learning about the characteristics of patients in the outpatient settings who would benefit from additional inhaler teaching,” she noted.
The study was supported by a grant from the Hospital of Fribourg in Switzerland. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose. Dr. Baldomero had no financial conflicts to disclose.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Approximately two thirds of hospitalized adults with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) received suboptimal treatment with inhalers, mainly resulting from errors, based on data from 96 individuals.
“Numerous studies have highlighted the significant issue of improper inhaler use in outpatient settings, but the extent of this problem within hospital settings remains poorly documented,” said lead author Gaël Grandmaison, MD, of the University of Fribourg in Switzerland, in an interview.
“This gap in knowledge is concerning, especially considering that several factors associated with suboptimal inhaler use, such as improper inhalation techniques, insufficient inspiratory flow, or the use of inhalers that are not suited to the patient’s specific characteristics, are associated with poorer disease control, more frequent exacerbations, and increased costs,” Dr. Grandmaison said.
To better characterize the prevalence of and factors associated with inhaler misuse in hospitalized patients with COPD, the researchers reviewed data from consecutive patients with COPD who were hospitalized in the general internal medicine department of a single institution between August 2022 and April 2023. Patients were assessed for peak inspiratory flow (PIF) and inhaler technique.
The primary outcome was the proportion of misused inhalers, which was defined as any inhaler used with either insufficient PIF and/or a critical error. The mean age of the patients was 71.6 years, 63% were men, and 67% were hospitalized for COPD exacerbations. Patients used 3.0 inhalers on average.
The study included 96 patients and 160 inhalers that were assessed at hospital admission. Overall, 111 were misused. Of those misused, 105 were associated with a critical error in the inhalation technique, and 22 were used with an insufficient PIF. After an episode of misuse, patients received targeted teaching on correct use that was repeated until they performed the technique without errors.
The percentage of inhaler misuse decreased over the course of the teaching sessions. The proportion of inhaler misuse decreased to 20.6%, 9.4%, and 5.6% after one, two, and three sessions, respectively.
“The inhalation technique was classified as ‘non-teachable’ if the patient continued to exhibit critical errors despite receiving three repetitions of the instructions,” the researchers wrote. Factors associated with inhaler misuse included cognitive disorders, fine motor disorders, poor coordination between inhaler activation and aspiration, and the inability to hold one’s breath.
Overall, the proportion of misused inhalers did not vary by age or gender. In an analysis at the patient level, 79 patients used at least one misused inhaler, 78 used at least one inhaler with a critical error, and 21 used inhalers with insufficient PIF.
“This study is particularly timely because reasons for hospitalization, such as COPD exacerbations or confusional states, could exacerbate the problem, leading to a potentially higher prevalence of suboptimal inhaler use compared to outpatient settings,” Dr. Grandmaison said.
The researchers also examined secondary outcomes including the prevalence of inhalers that were not suited to them and the number of patients using at least one misused inhaler.
The study findings confirm that suboptimal inhaler use is a significant problem in the hospital setting and provide new insights into the specific reasons behind this suboptimal usage, Dr. Grandmaison said.
“In the majority of cases, poor inhalation technique is the primary cause, which can generally be corrected through targeted therapeutic education,” she said. However, the study also revealed that 20% of patients are unable to use at least one of their inhalers correctly because of insufficient inspiratory force. Another 10% struggle despite receiving proper instruction, often because of cognitive impairments or difficulty with fine motor skills.
The results underscore the need for a comprehensive approach to inhaler use in hospitalized patients that combines continuous therapeutic education with personalized assessment in order to improve technique and subsequently enhance patient outcomes, she said.
Changing Clinical Practice
“As hospital physicians, these findings have led us to systematically evaluate the inhalers used by COPD patients, regardless of their reason for hospitalization,” Dr. Grandmaison said. Consequently, the hospital has implemented an assessment of inhaler use among patients that includes a review of techniques, an evaluation of the appropriateness of the inhaler prescribed, and an algorithm to help clinicians choose the most appropriate inhaler. Since its inception, the targeted intervention has significantly reduced improper inhaler use at discharge.
Limitations and Next Steps
The findings were limited by several factors including the possible underreporting of misuse caused by inadequate PIF, a lack of consensus on what constitutes a critical error, and the small sample of patients from a single center.
Despite these limitations, the study adds to the understanding of improper inhaler use in the hospital setting, Dr. Grandmaison said. “Our subsequent research demonstrated that a systematic evaluation of inhalers, combined with therapeutic education and an algorithm to select an inhaler suited to the patient’s characteristics, significantly reduces the number of improperly used inhalers at hospital discharge.”
However, several areas require further investigation, said Dr. Grandmaison. The most effective methods and frequency for teaching inhalation techniques must be defined, and more research is needed to understand the factors influencing PIF and its progression over the course of disease. The next steps for the current research are to evaluate the impact of the intervention on long-term symptom control and disease progression.
“Moreover, adapting the strategy developed in our institution for use in outpatient care is a priority, and multicenter studies would be valuable in validating these findings across different hospital settings,” she added.
In-Hospital Inhaler Education Falls Short
“Poor inhaler technique can lead to ineffective inhaler use and suboptimal treatment of COPD,” said Arianne K. Baldomero, MD, a pulmonologist and assistant professor of medicine at the University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, in an interview.
“The results from this study are consistent with prior studies showing a high prevalence of suboptimal inhaler use,” said Dr. Baldomero, who was not involved in the current study.
“The investigators also found that therapeutic education led to a significant reduction in the number of critical errors,” she said.
“What is surprising is that it can take up to three lessons to reduce this critical error down to 3.8%,” Dr. Baldomero said. “In most real-world clinic settings, many patients are not taught how to properly use inhalers, and many patients who receive inhaler technique education only receive instructions once.”
Dr. Baldomero’s takeaway from the study is that teaching patients to properly use their inhalers is critical, but that this education may need to be repeated multiple times. The findings also remind clinicians that some types of inhaler delivery are not suited for patients who cannot generate adequate respiratory flow.
Looking ahead, a larger sample size is needed to better identify which patients need additional teaching, Dr. Baldomero said. Also, the current study is limited by the focus on hospitalized patients. “I am interested in learning about the characteristics of patients in the outpatient settings who would benefit from additional inhaler teaching,” she noted.
The study was supported by a grant from the Hospital of Fribourg in Switzerland. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose. Dr. Baldomero had no financial conflicts to disclose.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM CHRONIC OBSTRUCTIVE PULMONARY DISEASES
Pulmonology Data Trends 2024
Pulmonology Data Trends 2024 is a supplement to CHEST Physician highlighting the latest breakthroughs in pulmonology research and treatments through a series of infographics.
Read more:
Artificial Intelligence in Sleep Apnea
Ritwick Agrawal, MD, MS, FCCP
RSV Updates: Prophylaxis Approval and Hospitalization for Severe RSV
Riddhi Upadhyay, MD
Biologics in Asthma: Changing the Severe Asthma Paradigm
Shyam Subramanian, MD, FCCP
Updates in COPD Guidelines and Treatment
Dharani K. Narendra, MD, FCCP
Targeted Therapies and Surgical Resection for Lung Cancer: Evolving Treatment Options
Saadia A. Faiz, MD, FCCP
Closing the GAP in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis
Humayun Anjum, MD, FCCP
Severe Community-Acquired Pneumonia: Diagnostic Criteria, Treatment, and COVID-19
Sujith V. Cherian, MD, FCCP
Pulmonary Hypertension: Comorbidities and Novel Therapies
Mary Jo S. Farmer, MD, PhD, FCCP
The Genetic Side of Interstitial Lung Disease
Priya Balakrishnan, MD, MS, FCCP
Noninvasive Ventilation in Neuromuscular Disease
Sreelatha Naik, MD, FCCP, and Kelly Lobrutto, CRNP
Pulmonology Data Trends 2024 is a supplement to CHEST Physician highlighting the latest breakthroughs in pulmonology research and treatments through a series of infographics.
Read more:
Artificial Intelligence in Sleep Apnea
Ritwick Agrawal, MD, MS, FCCP
RSV Updates: Prophylaxis Approval and Hospitalization for Severe RSV
Riddhi Upadhyay, MD
Biologics in Asthma: Changing the Severe Asthma Paradigm
Shyam Subramanian, MD, FCCP
Updates in COPD Guidelines and Treatment
Dharani K. Narendra, MD, FCCP
Targeted Therapies and Surgical Resection for Lung Cancer: Evolving Treatment Options
Saadia A. Faiz, MD, FCCP
Closing the GAP in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis
Humayun Anjum, MD, FCCP
Severe Community-Acquired Pneumonia: Diagnostic Criteria, Treatment, and COVID-19
Sujith V. Cherian, MD, FCCP
Pulmonary Hypertension: Comorbidities and Novel Therapies
Mary Jo S. Farmer, MD, PhD, FCCP
The Genetic Side of Interstitial Lung Disease
Priya Balakrishnan, MD, MS, FCCP
Noninvasive Ventilation in Neuromuscular Disease
Sreelatha Naik, MD, FCCP, and Kelly Lobrutto, CRNP
Pulmonology Data Trends 2024 is a supplement to CHEST Physician highlighting the latest breakthroughs in pulmonology research and treatments through a series of infographics.
Read more:
Artificial Intelligence in Sleep Apnea
Ritwick Agrawal, MD, MS, FCCP
RSV Updates: Prophylaxis Approval and Hospitalization for Severe RSV
Riddhi Upadhyay, MD
Biologics in Asthma: Changing the Severe Asthma Paradigm
Shyam Subramanian, MD, FCCP
Updates in COPD Guidelines and Treatment
Dharani K. Narendra, MD, FCCP
Targeted Therapies and Surgical Resection for Lung Cancer: Evolving Treatment Options
Saadia A. Faiz, MD, FCCP
Closing the GAP in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis
Humayun Anjum, MD, FCCP
Severe Community-Acquired Pneumonia: Diagnostic Criteria, Treatment, and COVID-19
Sujith V. Cherian, MD, FCCP
Pulmonary Hypertension: Comorbidities and Novel Therapies
Mary Jo S. Farmer, MD, PhD, FCCP
The Genetic Side of Interstitial Lung Disease
Priya Balakrishnan, MD, MS, FCCP
Noninvasive Ventilation in Neuromuscular Disease
Sreelatha Naik, MD, FCCP, and Kelly Lobrutto, CRNP