User login
High-dose MTX-based chemo is well tolerated in older PCNSL patients
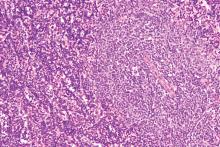
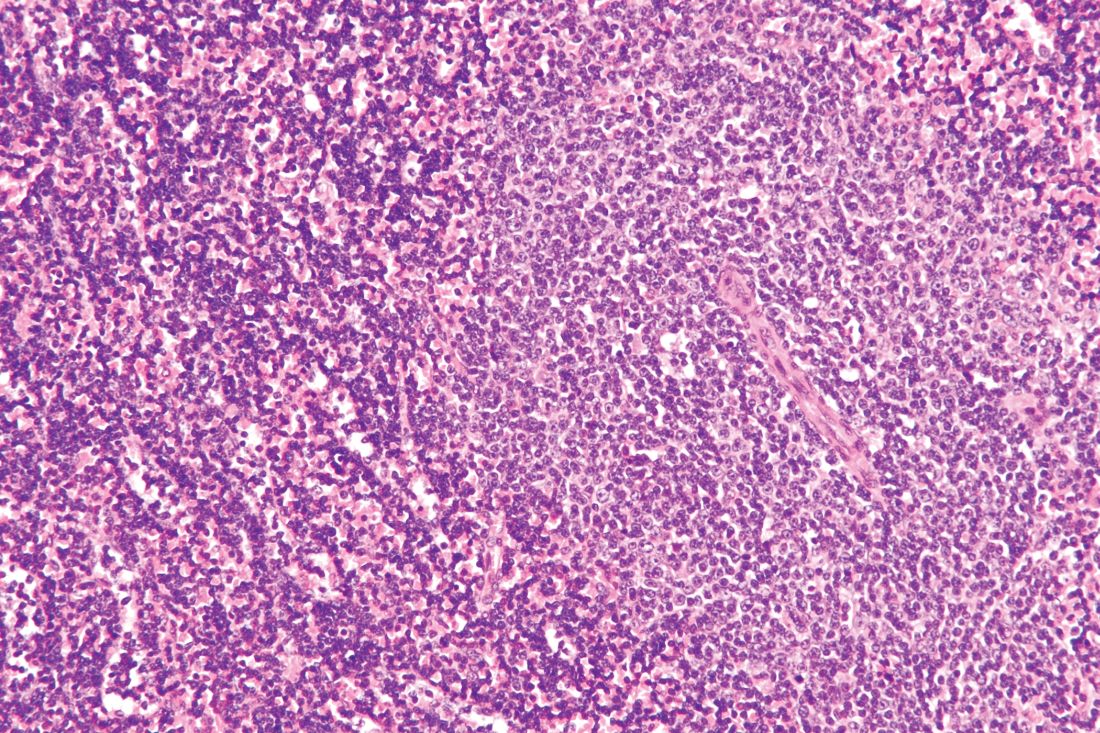
GLASGOW – Most older patients with primary central nervous system lymphoma (PCNSL) can tolerate high-dose methotrexate-based chemotherapy and achieve similar outcomes as younger and fitter patients, according to a retrospective analysis of 244 patients in the United Kingdom.
For older patients – at least 65 years old – who received methotrexate-based regimens, treatment-related mortality was 6.8%, which is comparable with rates seen in trials involving younger patients, reported lead author Edward Poynton, MD, of University College Hospital in London.
Specifically, Dr. Poynton cited the phase 2 IELSG32 trial, which had a treatment-related mortality rate of 6% among patients up to age 70 years. These patients were treated with the established protocol for younger patients: chemotherapy with methotrexate, cytarabine, thiotepa, and rituximab (MATRix) followed by autologous stem cell transplant or whole-brain radiotherapy.
Introducing Dr. Poynton’s presentation at the annual meeting of the British Society for Haematology, Simon Rule, MD, of the University of Plymouth (England), added historical context to the new findings.
“When I started in hematology ... [PCNSL] was a universally fatal disease, pretty much,” Dr. Rule said. “And then we had methotrexate, and it worked occasionally. And then we had a randomized trial, which was randomization of methotrexate plus or minus high-dose cytarabine, showing benefit.”
This combination became the benchmark against which subsequent randomized trials were measured; however, such high-intensity regimens have raised concerns about safety and efficacy in older patients, Dr. Rule said, noting that the present study serves to inform clinicians about real-world outcomes in this population.
The retrospective analysis reviewed 244 patients who were aged at least 65 years when histologically diagnosed with PCNSL at 14 U.K. tertiary centers between 2012 and 2017. All patients received first-line care of any kind, ranging from best supportive care to clinical trial therapy. Patients were grouped into three treatment cohorts divided by level of frailty. Analysis showed that these divisions correlated with age, renal function, Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group performance status, and treatment intensity.
The frail group received palliative treatment consisting of whole-brain radiotherapy, an oral alkylator, or best supportive care. The less-fit group received methotrexate in combination with rituximab, an oral alkylator, or both. The fit group was most intensively treated, receiving high-dose methotrexate and cytarabine – with or without rituximab – or MATRix.
The primary objective was overall response rate, while the secondary objectives were median overall survival and progression-free survival.
The analysis showed that 79% of patients (n = 193) received methotrexate-based therapy of some kind, with 61% receiving three or more cycles of therapy and 30% requiring dose reductions. The overall response rate was 63%.
Dr. Poynton noted that about two-thirds of patients who achieved a partial response in early assessment went on to achieve a complete response. Patients in the fit group more often responded than those who were less fit (87% vs. 65%; P = .01) and more often received consolidation therapy (42% vs. 23%; P = .01).
Fitness level was also associated with median overall survival, which was longest in the fit group at 42 months. The other two groups had dramatically shorter survival times: 8 months in the less-fit group and just 2 months in the frail group.
A closer look at the data revealed some patterns, Dr. Poynton said.
“What we see is that age at diagnosis is significantly correlated with progression-free survival but not with overall survival,” he said, noting that, in contrast, performance status was associated with both survival measures.
Methotrexate dose also impacted both survival measures. Patients who received 75% or more of their induction dose over the course of treatment had better median overall survival and progression-free survival than those who received less than 75%. Similarly, consolidation therapy improved both survival measures.
Patients aged older than 70 years who received intensive chemotherapy had a treatment-related mortality rate of 4.8%, which is lower than the overall treatment-related mortality, Dr. Poynton reported.
Considering the correlation between methotrexate dose and survival, Dr. Poynton suggested that “dose reductions should be carefully considered.”
He also noted that patients in the fit cohort who received intensive chemotherapy had comparable outcomes with younger patients in prospective trials, and yet 44% of patients older than 65 years in the real world who received high-dose methotrexate with cytarabine would have been ineligible for the IELSG32 trial.
“We’ve been able to identify this cohort of patients retrospectively,” Dr. Poynton said. “They definitely exist, and I think we need to work harder at how are going to identify these patients prospectively in the future, so we know which of our patients who are older can benefit from intensive chemotherapy and which patients won’t.”
Dr. Poynton reported having no relevant financial disclosures. His coinvestigators reported relationships with AbbVie, Merck, Takeda, Jazz Pharmaceuticals, and others.
GLASGOW – Most older patients with primary central nervous system lymphoma (PCNSL) can tolerate high-dose methotrexate-based chemotherapy and achieve similar outcomes as younger and fitter patients, according to a retrospective analysis of 244 patients in the United Kingdom.
For older patients – at least 65 years old – who received methotrexate-based regimens, treatment-related mortality was 6.8%, which is comparable with rates seen in trials involving younger patients, reported lead author Edward Poynton, MD, of University College Hospital in London.
Specifically, Dr. Poynton cited the phase 2 IELSG32 trial, which had a treatment-related mortality rate of 6% among patients up to age 70 years. These patients were treated with the established protocol for younger patients: chemotherapy with methotrexate, cytarabine, thiotepa, and rituximab (MATRix) followed by autologous stem cell transplant or whole-brain radiotherapy.
Introducing Dr. Poynton’s presentation at the annual meeting of the British Society for Haematology, Simon Rule, MD, of the University of Plymouth (England), added historical context to the new findings.
“When I started in hematology ... [PCNSL] was a universally fatal disease, pretty much,” Dr. Rule said. “And then we had methotrexate, and it worked occasionally. And then we had a randomized trial, which was randomization of methotrexate plus or minus high-dose cytarabine, showing benefit.”
This combination became the benchmark against which subsequent randomized trials were measured; however, such high-intensity regimens have raised concerns about safety and efficacy in older patients, Dr. Rule said, noting that the present study serves to inform clinicians about real-world outcomes in this population.
The retrospective analysis reviewed 244 patients who were aged at least 65 years when histologically diagnosed with PCNSL at 14 U.K. tertiary centers between 2012 and 2017. All patients received first-line care of any kind, ranging from best supportive care to clinical trial therapy. Patients were grouped into three treatment cohorts divided by level of frailty. Analysis showed that these divisions correlated with age, renal function, Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group performance status, and treatment intensity.
The frail group received palliative treatment consisting of whole-brain radiotherapy, an oral alkylator, or best supportive care. The less-fit group received methotrexate in combination with rituximab, an oral alkylator, or both. The fit group was most intensively treated, receiving high-dose methotrexate and cytarabine – with or without rituximab – or MATRix.
The primary objective was overall response rate, while the secondary objectives were median overall survival and progression-free survival.
The analysis showed that 79% of patients (n = 193) received methotrexate-based therapy of some kind, with 61% receiving three or more cycles of therapy and 30% requiring dose reductions. The overall response rate was 63%.
Dr. Poynton noted that about two-thirds of patients who achieved a partial response in early assessment went on to achieve a complete response. Patients in the fit group more often responded than those who were less fit (87% vs. 65%; P = .01) and more often received consolidation therapy (42% vs. 23%; P = .01).
Fitness level was also associated with median overall survival, which was longest in the fit group at 42 months. The other two groups had dramatically shorter survival times: 8 months in the less-fit group and just 2 months in the frail group.
A closer look at the data revealed some patterns, Dr. Poynton said.
“What we see is that age at diagnosis is significantly correlated with progression-free survival but not with overall survival,” he said, noting that, in contrast, performance status was associated with both survival measures.
Methotrexate dose also impacted both survival measures. Patients who received 75% or more of their induction dose over the course of treatment had better median overall survival and progression-free survival than those who received less than 75%. Similarly, consolidation therapy improved both survival measures.
Patients aged older than 70 years who received intensive chemotherapy had a treatment-related mortality rate of 4.8%, which is lower than the overall treatment-related mortality, Dr. Poynton reported.
Considering the correlation between methotrexate dose and survival, Dr. Poynton suggested that “dose reductions should be carefully considered.”
He also noted that patients in the fit cohort who received intensive chemotherapy had comparable outcomes with younger patients in prospective trials, and yet 44% of patients older than 65 years in the real world who received high-dose methotrexate with cytarabine would have been ineligible for the IELSG32 trial.
“We’ve been able to identify this cohort of patients retrospectively,” Dr. Poynton said. “They definitely exist, and I think we need to work harder at how are going to identify these patients prospectively in the future, so we know which of our patients who are older can benefit from intensive chemotherapy and which patients won’t.”
Dr. Poynton reported having no relevant financial disclosures. His coinvestigators reported relationships with AbbVie, Merck, Takeda, Jazz Pharmaceuticals, and others.
GLASGOW – Most older patients with primary central nervous system lymphoma (PCNSL) can tolerate high-dose methotrexate-based chemotherapy and achieve similar outcomes as younger and fitter patients, according to a retrospective analysis of 244 patients in the United Kingdom.
For older patients – at least 65 years old – who received methotrexate-based regimens, treatment-related mortality was 6.8%, which is comparable with rates seen in trials involving younger patients, reported lead author Edward Poynton, MD, of University College Hospital in London.
Specifically, Dr. Poynton cited the phase 2 IELSG32 trial, which had a treatment-related mortality rate of 6% among patients up to age 70 years. These patients were treated with the established protocol for younger patients: chemotherapy with methotrexate, cytarabine, thiotepa, and rituximab (MATRix) followed by autologous stem cell transplant or whole-brain radiotherapy.
Introducing Dr. Poynton’s presentation at the annual meeting of the British Society for Haematology, Simon Rule, MD, of the University of Plymouth (England), added historical context to the new findings.
“When I started in hematology ... [PCNSL] was a universally fatal disease, pretty much,” Dr. Rule said. “And then we had methotrexate, and it worked occasionally. And then we had a randomized trial, which was randomization of methotrexate plus or minus high-dose cytarabine, showing benefit.”
This combination became the benchmark against which subsequent randomized trials were measured; however, such high-intensity regimens have raised concerns about safety and efficacy in older patients, Dr. Rule said, noting that the present study serves to inform clinicians about real-world outcomes in this population.
The retrospective analysis reviewed 244 patients who were aged at least 65 years when histologically diagnosed with PCNSL at 14 U.K. tertiary centers between 2012 and 2017. All patients received first-line care of any kind, ranging from best supportive care to clinical trial therapy. Patients were grouped into three treatment cohorts divided by level of frailty. Analysis showed that these divisions correlated with age, renal function, Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group performance status, and treatment intensity.
The frail group received palliative treatment consisting of whole-brain radiotherapy, an oral alkylator, or best supportive care. The less-fit group received methotrexate in combination with rituximab, an oral alkylator, or both. The fit group was most intensively treated, receiving high-dose methotrexate and cytarabine – with or without rituximab – or MATRix.
The primary objective was overall response rate, while the secondary objectives were median overall survival and progression-free survival.
The analysis showed that 79% of patients (n = 193) received methotrexate-based therapy of some kind, with 61% receiving three or more cycles of therapy and 30% requiring dose reductions. The overall response rate was 63%.
Dr. Poynton noted that about two-thirds of patients who achieved a partial response in early assessment went on to achieve a complete response. Patients in the fit group more often responded than those who were less fit (87% vs. 65%; P = .01) and more often received consolidation therapy (42% vs. 23%; P = .01).
Fitness level was also associated with median overall survival, which was longest in the fit group at 42 months. The other two groups had dramatically shorter survival times: 8 months in the less-fit group and just 2 months in the frail group.
A closer look at the data revealed some patterns, Dr. Poynton said.
“What we see is that age at diagnosis is significantly correlated with progression-free survival but not with overall survival,” he said, noting that, in contrast, performance status was associated with both survival measures.
Methotrexate dose also impacted both survival measures. Patients who received 75% or more of their induction dose over the course of treatment had better median overall survival and progression-free survival than those who received less than 75%. Similarly, consolidation therapy improved both survival measures.
Patients aged older than 70 years who received intensive chemotherapy had a treatment-related mortality rate of 4.8%, which is lower than the overall treatment-related mortality, Dr. Poynton reported.
Considering the correlation between methotrexate dose and survival, Dr. Poynton suggested that “dose reductions should be carefully considered.”
He also noted that patients in the fit cohort who received intensive chemotherapy had comparable outcomes with younger patients in prospective trials, and yet 44% of patients older than 65 years in the real world who received high-dose methotrexate with cytarabine would have been ineligible for the IELSG32 trial.
“We’ve been able to identify this cohort of patients retrospectively,” Dr. Poynton said. “They definitely exist, and I think we need to work harder at how are going to identify these patients prospectively in the future, so we know which of our patients who are older can benefit from intensive chemotherapy and which patients won’t.”
Dr. Poynton reported having no relevant financial disclosures. His coinvestigators reported relationships with AbbVie, Merck, Takeda, Jazz Pharmaceuticals, and others.
REPORTING FROM BSH 2019
Monitoring, early intervention key to CAR T safety
GLASGOW – Constant patient monitoring and early intervention with tocilizumab and steroids are essential to the safe delivery of chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy in patients with non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL), according to a leading expert.
As a clinical researcher at MD Anderson Cancer Center in Houston, Loretta Nastoupil, MD has played an active role in the evolution of CAR T-cell therapy, from early trials to ongoing development of treatment protocols. During a presentation at the annual meeting of the British Society for Haematology, Dr. Nastoupil discussed leading topics in CAR T-cell therapy, with an emphasis on safe delivery.
“[Toxicity] is something we don’t talk about as much as we should, partly because this therapy works and it’s really exciting,” Dr. Nastoupil said. “But the toxicity is not something that I minimize, and it’s very challenging. It’s led us to restructure our inpatient services. It’s led to a lot of sleepless nights. These patients can do very, very well, or they can do very, very poorly in terms of toxicity and I think the most important strategy is recognition and early intervention.”
Monitoring
Early recognition depends on close monitoring, Dr. Nastoupil said, which is carried out by highly trained nursing staff who follow therapy-specific decision algorithms.
“We have nurses that are on the front line,” Dr. Nastoupil said. “They’re the most important group. We have staff that round on [patients] daily, but the nurses are there 24 hours a day. We have a flow sheet where they grade cytokine release syndrome and neurotoxicity every 8 hours, or if there is an acute change in symptoms or toxicity, they’ll do it in real time.”
Dr. Nastoupil said that if these toxicities are detected, intervention is occurring sooner than it did with some of the first patients to receive CAR-T cell therapy.
“Initially there was a lot of fear surrounding anything that would abort the CAR-T cell therapy,” Dr. Nastoupil said. “There was concern that if you were trying to mitigate some of the toxicity you might have a negative impact on efficacy ... [W]ith the first iteration of studies, generally we were waiting until grade 3 or higher cytokine release syndrome before initiating either tocilizumab and/or steroids. As the studies evolved, it started to move into grade 2 toxicity that we started using therapy, mostly because we started to see that those patients were still responding.”
At MD Anderson, these earlier interventions have decreased severity of adverse events.
“It’s rare nowadays to have grade 3 or 4 cytokine release syndrome because we are generally introducing abortive therapy at grade 2,” Dr. Nastoupil said, citing increased use of steroids and tocilizumab.
Currently, no consensus exists for managing these events, partly because clinicians are still learning about best management practices.
“There will be a consensus on management,” Dr. Nastoupil said. “I think that’s needed. The problem is, it will probably evolve as we get more experience with managing these patients. I think there’s been a little hesitation to put something out on paper knowing that a year from now that might change.”
Grading toxicity
In contrast, Dr. Nastoupil said that a consensus has been reached for grading acute toxicity. Of note, fever is now considered an essential element of cytokine release syndrome.
“The first thing we see [with cytokine release syndrome] is fever, generally speaking,” Dr. Nastoupil said. “That will prompt a workup for infection because these patients are going to be neutropenic. And we initiate broad spectrum antimicrobials.”
She said that some patients treated with CAR T-cell therapy have had disseminated fungal infections, so clinicians need to be on the lookout for septic shock.
To assess neurotoxicity, the team at MD Anderson uses an objective scoring system, called “CARTOX.” This helps maintain consistency when facing broadly different neurological presentations.
“There’s such a wide ranging spectrum of patients that are undergoing neurotoxicity you can’t expect someone, even myself, to be consistent when you are trying to tease out how serious it is,” Dr. Nastoupil said.
With CARTOX, nurses can easily score patients and call clinicians with results. Still, this doesn’t eliminate difficulties inherent to managing neurotoxicity, particularly when it is severe.
“I’d say one of the areas that is still very challenging is when [patients with neurotoxicity] are no longer responding,” Dr. Nastoupil said. “You have to be very mindful of seizure activity. We’ve had a couple of patients with status [epilepticus]. You don’t see seizure activity physically, but when you do an EEG, you pick it up.”
Dr. Nastoupil added that most centers are now giving patients prophylactic levetiracetam (Keppra) to lower seizure risk.
Choosing therapy
When selecting between the two therapies currently approved by the Food and Drug Administration – tisagenlecleucel (Kymriah) and axicabtagene ciloleucel (Yescarta) – based on safety, Dr. Nastoupil said that rates of cytokine release syndrome appear similar, but neurotoxicity rates may differ.
“Cytokine release syndrome in my opinion is probably more similar than different in terms of grade 3 or higher because tocilizumab and steroids work quite well in aborting those toxicities,” Dr. Nastoupil said. “But neurotoxicity still sticks out in my mind as the most striking difference, where with axicabtagene you see more grade 3 or higher neurotoxicity, though very, very few deaths as a result of this. But it’s very challenging in terms of management.”
According to Dr. Nastoupil, comparisons between CAR T-cell therapies have been complicated by differences in clinical trial methodologies. However, she offered a general conclusion regarding efficacy.
“[W]hat I’ll tell you, at the end of the day, is [that existing CAR T-cell therapies] all seem to sort of settle out around 30%-40% in terms of durable responses,” Dr. Nastoupil said.
Dr. Nastoupil concluded her presentation with an overview and look to the future.
“I do think [CAR T-cell therapy] is transformative, particularly for our chemo refractory patients,” she said. “There is nothing else like it. The problem right now is that it is only durable in 40% of patients. So can we be better at selecting out patients that are more likely to respond? Does introducing this in earlier lines of therapy increase that fraction of patients that are potentially cured?”
Considering these questions, she said: “We need more patients. We need more data. We need longer follow-up to understand the nuances of this therapy.”
Dr. Nastoupil previously reported financial relationships with Celgene, Genentech, Gilead, Merck, Novartis, Spectrum, and TG Therapeutics.
GLASGOW – Constant patient monitoring and early intervention with tocilizumab and steroids are essential to the safe delivery of chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy in patients with non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL), according to a leading expert.
As a clinical researcher at MD Anderson Cancer Center in Houston, Loretta Nastoupil, MD has played an active role in the evolution of CAR T-cell therapy, from early trials to ongoing development of treatment protocols. During a presentation at the annual meeting of the British Society for Haematology, Dr. Nastoupil discussed leading topics in CAR T-cell therapy, with an emphasis on safe delivery.
“[Toxicity] is something we don’t talk about as much as we should, partly because this therapy works and it’s really exciting,” Dr. Nastoupil said. “But the toxicity is not something that I minimize, and it’s very challenging. It’s led us to restructure our inpatient services. It’s led to a lot of sleepless nights. These patients can do very, very well, or they can do very, very poorly in terms of toxicity and I think the most important strategy is recognition and early intervention.”
Monitoring
Early recognition depends on close monitoring, Dr. Nastoupil said, which is carried out by highly trained nursing staff who follow therapy-specific decision algorithms.
“We have nurses that are on the front line,” Dr. Nastoupil said. “They’re the most important group. We have staff that round on [patients] daily, but the nurses are there 24 hours a day. We have a flow sheet where they grade cytokine release syndrome and neurotoxicity every 8 hours, or if there is an acute change in symptoms or toxicity, they’ll do it in real time.”
Dr. Nastoupil said that if these toxicities are detected, intervention is occurring sooner than it did with some of the first patients to receive CAR-T cell therapy.
“Initially there was a lot of fear surrounding anything that would abort the CAR-T cell therapy,” Dr. Nastoupil said. “There was concern that if you were trying to mitigate some of the toxicity you might have a negative impact on efficacy ... [W]ith the first iteration of studies, generally we were waiting until grade 3 or higher cytokine release syndrome before initiating either tocilizumab and/or steroids. As the studies evolved, it started to move into grade 2 toxicity that we started using therapy, mostly because we started to see that those patients were still responding.”
At MD Anderson, these earlier interventions have decreased severity of adverse events.
“It’s rare nowadays to have grade 3 or 4 cytokine release syndrome because we are generally introducing abortive therapy at grade 2,” Dr. Nastoupil said, citing increased use of steroids and tocilizumab.
Currently, no consensus exists for managing these events, partly because clinicians are still learning about best management practices.
“There will be a consensus on management,” Dr. Nastoupil said. “I think that’s needed. The problem is, it will probably evolve as we get more experience with managing these patients. I think there’s been a little hesitation to put something out on paper knowing that a year from now that might change.”
Grading toxicity
In contrast, Dr. Nastoupil said that a consensus has been reached for grading acute toxicity. Of note, fever is now considered an essential element of cytokine release syndrome.
“The first thing we see [with cytokine release syndrome] is fever, generally speaking,” Dr. Nastoupil said. “That will prompt a workup for infection because these patients are going to be neutropenic. And we initiate broad spectrum antimicrobials.”
She said that some patients treated with CAR T-cell therapy have had disseminated fungal infections, so clinicians need to be on the lookout for septic shock.
To assess neurotoxicity, the team at MD Anderson uses an objective scoring system, called “CARTOX.” This helps maintain consistency when facing broadly different neurological presentations.
“There’s such a wide ranging spectrum of patients that are undergoing neurotoxicity you can’t expect someone, even myself, to be consistent when you are trying to tease out how serious it is,” Dr. Nastoupil said.
With CARTOX, nurses can easily score patients and call clinicians with results. Still, this doesn’t eliminate difficulties inherent to managing neurotoxicity, particularly when it is severe.
“I’d say one of the areas that is still very challenging is when [patients with neurotoxicity] are no longer responding,” Dr. Nastoupil said. “You have to be very mindful of seizure activity. We’ve had a couple of patients with status [epilepticus]. You don’t see seizure activity physically, but when you do an EEG, you pick it up.”
Dr. Nastoupil added that most centers are now giving patients prophylactic levetiracetam (Keppra) to lower seizure risk.
Choosing therapy
When selecting between the two therapies currently approved by the Food and Drug Administration – tisagenlecleucel (Kymriah) and axicabtagene ciloleucel (Yescarta) – based on safety, Dr. Nastoupil said that rates of cytokine release syndrome appear similar, but neurotoxicity rates may differ.
“Cytokine release syndrome in my opinion is probably more similar than different in terms of grade 3 or higher because tocilizumab and steroids work quite well in aborting those toxicities,” Dr. Nastoupil said. “But neurotoxicity still sticks out in my mind as the most striking difference, where with axicabtagene you see more grade 3 or higher neurotoxicity, though very, very few deaths as a result of this. But it’s very challenging in terms of management.”
According to Dr. Nastoupil, comparisons between CAR T-cell therapies have been complicated by differences in clinical trial methodologies. However, she offered a general conclusion regarding efficacy.
“[W]hat I’ll tell you, at the end of the day, is [that existing CAR T-cell therapies] all seem to sort of settle out around 30%-40% in terms of durable responses,” Dr. Nastoupil said.
Dr. Nastoupil concluded her presentation with an overview and look to the future.
“I do think [CAR T-cell therapy] is transformative, particularly for our chemo refractory patients,” she said. “There is nothing else like it. The problem right now is that it is only durable in 40% of patients. So can we be better at selecting out patients that are more likely to respond? Does introducing this in earlier lines of therapy increase that fraction of patients that are potentially cured?”
Considering these questions, she said: “We need more patients. We need more data. We need longer follow-up to understand the nuances of this therapy.”
Dr. Nastoupil previously reported financial relationships with Celgene, Genentech, Gilead, Merck, Novartis, Spectrum, and TG Therapeutics.
GLASGOW – Constant patient monitoring and early intervention with tocilizumab and steroids are essential to the safe delivery of chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy in patients with non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL), according to a leading expert.
As a clinical researcher at MD Anderson Cancer Center in Houston, Loretta Nastoupil, MD has played an active role in the evolution of CAR T-cell therapy, from early trials to ongoing development of treatment protocols. During a presentation at the annual meeting of the British Society for Haematology, Dr. Nastoupil discussed leading topics in CAR T-cell therapy, with an emphasis on safe delivery.
“[Toxicity] is something we don’t talk about as much as we should, partly because this therapy works and it’s really exciting,” Dr. Nastoupil said. “But the toxicity is not something that I minimize, and it’s very challenging. It’s led us to restructure our inpatient services. It’s led to a lot of sleepless nights. These patients can do very, very well, or they can do very, very poorly in terms of toxicity and I think the most important strategy is recognition and early intervention.”
Monitoring
Early recognition depends on close monitoring, Dr. Nastoupil said, which is carried out by highly trained nursing staff who follow therapy-specific decision algorithms.
“We have nurses that are on the front line,” Dr. Nastoupil said. “They’re the most important group. We have staff that round on [patients] daily, but the nurses are there 24 hours a day. We have a flow sheet where they grade cytokine release syndrome and neurotoxicity every 8 hours, or if there is an acute change in symptoms or toxicity, they’ll do it in real time.”
Dr. Nastoupil said that if these toxicities are detected, intervention is occurring sooner than it did with some of the first patients to receive CAR-T cell therapy.
“Initially there was a lot of fear surrounding anything that would abort the CAR-T cell therapy,” Dr. Nastoupil said. “There was concern that if you were trying to mitigate some of the toxicity you might have a negative impact on efficacy ... [W]ith the first iteration of studies, generally we were waiting until grade 3 or higher cytokine release syndrome before initiating either tocilizumab and/or steroids. As the studies evolved, it started to move into grade 2 toxicity that we started using therapy, mostly because we started to see that those patients were still responding.”
At MD Anderson, these earlier interventions have decreased severity of adverse events.
“It’s rare nowadays to have grade 3 or 4 cytokine release syndrome because we are generally introducing abortive therapy at grade 2,” Dr. Nastoupil said, citing increased use of steroids and tocilizumab.
Currently, no consensus exists for managing these events, partly because clinicians are still learning about best management practices.
“There will be a consensus on management,” Dr. Nastoupil said. “I think that’s needed. The problem is, it will probably evolve as we get more experience with managing these patients. I think there’s been a little hesitation to put something out on paper knowing that a year from now that might change.”
Grading toxicity
In contrast, Dr. Nastoupil said that a consensus has been reached for grading acute toxicity. Of note, fever is now considered an essential element of cytokine release syndrome.
“The first thing we see [with cytokine release syndrome] is fever, generally speaking,” Dr. Nastoupil said. “That will prompt a workup for infection because these patients are going to be neutropenic. And we initiate broad spectrum antimicrobials.”
She said that some patients treated with CAR T-cell therapy have had disseminated fungal infections, so clinicians need to be on the lookout for septic shock.
To assess neurotoxicity, the team at MD Anderson uses an objective scoring system, called “CARTOX.” This helps maintain consistency when facing broadly different neurological presentations.
“There’s such a wide ranging spectrum of patients that are undergoing neurotoxicity you can’t expect someone, even myself, to be consistent when you are trying to tease out how serious it is,” Dr. Nastoupil said.
With CARTOX, nurses can easily score patients and call clinicians with results. Still, this doesn’t eliminate difficulties inherent to managing neurotoxicity, particularly when it is severe.
“I’d say one of the areas that is still very challenging is when [patients with neurotoxicity] are no longer responding,” Dr. Nastoupil said. “You have to be very mindful of seizure activity. We’ve had a couple of patients with status [epilepticus]. You don’t see seizure activity physically, but when you do an EEG, you pick it up.”
Dr. Nastoupil added that most centers are now giving patients prophylactic levetiracetam (Keppra) to lower seizure risk.
Choosing therapy
When selecting between the two therapies currently approved by the Food and Drug Administration – tisagenlecleucel (Kymriah) and axicabtagene ciloleucel (Yescarta) – based on safety, Dr. Nastoupil said that rates of cytokine release syndrome appear similar, but neurotoxicity rates may differ.
“Cytokine release syndrome in my opinion is probably more similar than different in terms of grade 3 or higher because tocilizumab and steroids work quite well in aborting those toxicities,” Dr. Nastoupil said. “But neurotoxicity still sticks out in my mind as the most striking difference, where with axicabtagene you see more grade 3 or higher neurotoxicity, though very, very few deaths as a result of this. But it’s very challenging in terms of management.”
According to Dr. Nastoupil, comparisons between CAR T-cell therapies have been complicated by differences in clinical trial methodologies. However, she offered a general conclusion regarding efficacy.
“[W]hat I’ll tell you, at the end of the day, is [that existing CAR T-cell therapies] all seem to sort of settle out around 30%-40% in terms of durable responses,” Dr. Nastoupil said.
Dr. Nastoupil concluded her presentation with an overview and look to the future.
“I do think [CAR T-cell therapy] is transformative, particularly for our chemo refractory patients,” she said. “There is nothing else like it. The problem right now is that it is only durable in 40% of patients. So can we be better at selecting out patients that are more likely to respond? Does introducing this in earlier lines of therapy increase that fraction of patients that are potentially cured?”
Considering these questions, she said: “We need more patients. We need more data. We need longer follow-up to understand the nuances of this therapy.”
Dr. Nastoupil previously reported financial relationships with Celgene, Genentech, Gilead, Merck, Novartis, Spectrum, and TG Therapeutics.
EXPERT ANALYSIS FROM BSH 2019
RIT consolidation may be an option for unfit MCL patients
For older, less fit patients with mantle cell lymphoma (MCL) who may not be able to withstand the rigors of autologous stem cell transplants (ASCT), induction chemotherapy followed by radioimmunotherapy (RIT) consolidation with ibritumomab tiuxetan (Zevalin) was associated with good response rates and promising progression-free and overall survival rates, according to results of a phase 2 prospective study.
RIT consolidation improved the complete response rate following first-line therapy from 41% to 91%, reported Wojciech Jurczak, MD, PhD, from the department of hematology at the Uniwersytet Jagiellonski in Krakow, Poland, and colleagues.
In the patients who received RIT following first-line induction, median progression-free survival was 3.3 years, and median overall survival was 6.5 years.
“The achieved responses are durable. Although, several novel agents and targeted therapies alone or in combination are currently being studied and developed in both the upfront and relapsed settings, RIT constitutes a valid and underused option especially in the first-line setting,” they wrote in a study published in Leukemia & Lymphoma.
The investigators enrolled 46 patients with clinical stage III to IV MCL who were either ineligible for, or unwilling to undergo, ASCT. The cohort included 34 patients with newly diagnosed advanced MCL and 12 with chemo-sensitive MCL in first relapse.
Patients were assigned to induction with six cycles of chemotherapy, with or without rituximab. Patients then underwent consolidation with RIT if they had confirmed reductions of the maximal lymph node diameter below 3 cm, their longest spleen measurement was below 15 cm, and bone marrow infiltration was less than 20%.
The chemotherapy regimens included either CVP (cyclophosphamide, vincristine and prednisone), CHOP (cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone), FC (fludarabine and cyclophosphamide), or FCM (FC plus mitoxantrone). Additionally, 27 of the 46 patients received rituximab, which was not considered the standard of care in Poland when the study began in 2005 and was delivered based on availability.
Of the 34 patients who received first-line chemotherapy, 20 received FC or FCM (with or without rituximab), and 14 received CHOP or CVP (with or without rituximab). In this group, 14 patients (41%) had a complete response, and 20 (95%) had a partial response. Of the 12 patients treated after first relapse, two (17%) had a complete response and 10 (83%) had partial response after induction.
RIT consolidation was performed 3-5 weeks after the last chemotherapy cycle. Patients with cytopenias after chemotherapy could wait an additional 3 weeks, during which they would receive a bridging dose of rituximab at the standard 375 mg/m2 dose. The patients received two doses of rituximab 250 mg/m2 administered 7 days then 24 hours prior to intravenous injection of 90Y-labeled ibritumomab tiuxetan. The radiation doses delivered were 0.4 mCi/kg for patients with normal platelet counts and 0.3 mCi/kg for those with platelet counts from 100,000 to 150,000 cells/mm3. The maximum dose was 32.0 mCi.
The longest follow-up was out to slightly more than 8 years.
For the patients who received RIT after first-line induction, the complete response rate was 91%, and the partial response rate was 9%, compared with 41% complete response and 59% partial response after induction. In this group, the median progression-free survival was 3.3 years, and the median overall survival was 6.5 years.
For the patients who received RIT consolidation after first relapse and second chemotherapy regimen, the complete response rate was 75% and the partial response rate was 25%, compared with 17% and 83% at the end of second induction therapy. In this group, the median progression-free survival was 1.8 years (P less than .05, compared with patients treated after first-line responses), and the median overall survival was 2.2 years (P less than .05).
At 8 years of follow-up, 30% of patients who received RIT consolidation following first-line therapy were alive.
Adverse events included cytopenias in the majority of patients (77%), which were grade 1 or 2 in severity in 43% and grade 3 or 4 in 34%. Grade 3 or 4 thrombocytopenia and leukopenia occurred more frequently in patients treated with fludarabine-based regimens, and the thrombocytopenias in these patients lasted longer and required more platelet transfusions than those in CHOP- or CVP-treated patients. Two patients who underwent RIT following FCM induction died from prolonged thrombocytopenia, resulting in hemorrhagic strokes.
Among all patients, 22 patients developed infections following RIT consolidation. Five patients, all of whom had received fludarabine, required hospitalization for the treatment of the infections. There were no infection-related deaths, however.
Five patients developed the myelodysplastic syndrome, with a median onset time of 26 months. Of these patients, four had received fludarabine, and one had undergone a prior ASCT.
The trial was sponsored by Schering AG. Dr. Jurczak reported speakers bureau participation and research funding from multiple companies, not including Schering AG.
SOURCE: Jurczak W et al. Leuk Lymphoma. 2019 Apr 9. doi: 10.1080/10428194.2019.1602261.
For older, less fit patients with mantle cell lymphoma (MCL) who may not be able to withstand the rigors of autologous stem cell transplants (ASCT), induction chemotherapy followed by radioimmunotherapy (RIT) consolidation with ibritumomab tiuxetan (Zevalin) was associated with good response rates and promising progression-free and overall survival rates, according to results of a phase 2 prospective study.
RIT consolidation improved the complete response rate following first-line therapy from 41% to 91%, reported Wojciech Jurczak, MD, PhD, from the department of hematology at the Uniwersytet Jagiellonski in Krakow, Poland, and colleagues.
In the patients who received RIT following first-line induction, median progression-free survival was 3.3 years, and median overall survival was 6.5 years.
“The achieved responses are durable. Although, several novel agents and targeted therapies alone or in combination are currently being studied and developed in both the upfront and relapsed settings, RIT constitutes a valid and underused option especially in the first-line setting,” they wrote in a study published in Leukemia & Lymphoma.
The investigators enrolled 46 patients with clinical stage III to IV MCL who were either ineligible for, or unwilling to undergo, ASCT. The cohort included 34 patients with newly diagnosed advanced MCL and 12 with chemo-sensitive MCL in first relapse.
Patients were assigned to induction with six cycles of chemotherapy, with or without rituximab. Patients then underwent consolidation with RIT if they had confirmed reductions of the maximal lymph node diameter below 3 cm, their longest spleen measurement was below 15 cm, and bone marrow infiltration was less than 20%.
The chemotherapy regimens included either CVP (cyclophosphamide, vincristine and prednisone), CHOP (cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone), FC (fludarabine and cyclophosphamide), or FCM (FC plus mitoxantrone). Additionally, 27 of the 46 patients received rituximab, which was not considered the standard of care in Poland when the study began in 2005 and was delivered based on availability.
Of the 34 patients who received first-line chemotherapy, 20 received FC or FCM (with or without rituximab), and 14 received CHOP or CVP (with or without rituximab). In this group, 14 patients (41%) had a complete response, and 20 (95%) had a partial response. Of the 12 patients treated after first relapse, two (17%) had a complete response and 10 (83%) had partial response after induction.
RIT consolidation was performed 3-5 weeks after the last chemotherapy cycle. Patients with cytopenias after chemotherapy could wait an additional 3 weeks, during which they would receive a bridging dose of rituximab at the standard 375 mg/m2 dose. The patients received two doses of rituximab 250 mg/m2 administered 7 days then 24 hours prior to intravenous injection of 90Y-labeled ibritumomab tiuxetan. The radiation doses delivered were 0.4 mCi/kg for patients with normal platelet counts and 0.3 mCi/kg for those with platelet counts from 100,000 to 150,000 cells/mm3. The maximum dose was 32.0 mCi.
The longest follow-up was out to slightly more than 8 years.
For the patients who received RIT after first-line induction, the complete response rate was 91%, and the partial response rate was 9%, compared with 41% complete response and 59% partial response after induction. In this group, the median progression-free survival was 3.3 years, and the median overall survival was 6.5 years.
For the patients who received RIT consolidation after first relapse and second chemotherapy regimen, the complete response rate was 75% and the partial response rate was 25%, compared with 17% and 83% at the end of second induction therapy. In this group, the median progression-free survival was 1.8 years (P less than .05, compared with patients treated after first-line responses), and the median overall survival was 2.2 years (P less than .05).
At 8 years of follow-up, 30% of patients who received RIT consolidation following first-line therapy were alive.
Adverse events included cytopenias in the majority of patients (77%), which were grade 1 or 2 in severity in 43% and grade 3 or 4 in 34%. Grade 3 or 4 thrombocytopenia and leukopenia occurred more frequently in patients treated with fludarabine-based regimens, and the thrombocytopenias in these patients lasted longer and required more platelet transfusions than those in CHOP- or CVP-treated patients. Two patients who underwent RIT following FCM induction died from prolonged thrombocytopenia, resulting in hemorrhagic strokes.
Among all patients, 22 patients developed infections following RIT consolidation. Five patients, all of whom had received fludarabine, required hospitalization for the treatment of the infections. There were no infection-related deaths, however.
Five patients developed the myelodysplastic syndrome, with a median onset time of 26 months. Of these patients, four had received fludarabine, and one had undergone a prior ASCT.
The trial was sponsored by Schering AG. Dr. Jurczak reported speakers bureau participation and research funding from multiple companies, not including Schering AG.
SOURCE: Jurczak W et al. Leuk Lymphoma. 2019 Apr 9. doi: 10.1080/10428194.2019.1602261.
For older, less fit patients with mantle cell lymphoma (MCL) who may not be able to withstand the rigors of autologous stem cell transplants (ASCT), induction chemotherapy followed by radioimmunotherapy (RIT) consolidation with ibritumomab tiuxetan (Zevalin) was associated with good response rates and promising progression-free and overall survival rates, according to results of a phase 2 prospective study.
RIT consolidation improved the complete response rate following first-line therapy from 41% to 91%, reported Wojciech Jurczak, MD, PhD, from the department of hematology at the Uniwersytet Jagiellonski in Krakow, Poland, and colleagues.
In the patients who received RIT following first-line induction, median progression-free survival was 3.3 years, and median overall survival was 6.5 years.
“The achieved responses are durable. Although, several novel agents and targeted therapies alone or in combination are currently being studied and developed in both the upfront and relapsed settings, RIT constitutes a valid and underused option especially in the first-line setting,” they wrote in a study published in Leukemia & Lymphoma.
The investigators enrolled 46 patients with clinical stage III to IV MCL who were either ineligible for, or unwilling to undergo, ASCT. The cohort included 34 patients with newly diagnosed advanced MCL and 12 with chemo-sensitive MCL in first relapse.
Patients were assigned to induction with six cycles of chemotherapy, with or without rituximab. Patients then underwent consolidation with RIT if they had confirmed reductions of the maximal lymph node diameter below 3 cm, their longest spleen measurement was below 15 cm, and bone marrow infiltration was less than 20%.
The chemotherapy regimens included either CVP (cyclophosphamide, vincristine and prednisone), CHOP (cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone), FC (fludarabine and cyclophosphamide), or FCM (FC plus mitoxantrone). Additionally, 27 of the 46 patients received rituximab, which was not considered the standard of care in Poland when the study began in 2005 and was delivered based on availability.
Of the 34 patients who received first-line chemotherapy, 20 received FC or FCM (with or without rituximab), and 14 received CHOP or CVP (with or without rituximab). In this group, 14 patients (41%) had a complete response, and 20 (95%) had a partial response. Of the 12 patients treated after first relapse, two (17%) had a complete response and 10 (83%) had partial response after induction.
RIT consolidation was performed 3-5 weeks after the last chemotherapy cycle. Patients with cytopenias after chemotherapy could wait an additional 3 weeks, during which they would receive a bridging dose of rituximab at the standard 375 mg/m2 dose. The patients received two doses of rituximab 250 mg/m2 administered 7 days then 24 hours prior to intravenous injection of 90Y-labeled ibritumomab tiuxetan. The radiation doses delivered were 0.4 mCi/kg for patients with normal platelet counts and 0.3 mCi/kg for those with platelet counts from 100,000 to 150,000 cells/mm3. The maximum dose was 32.0 mCi.
The longest follow-up was out to slightly more than 8 years.
For the patients who received RIT after first-line induction, the complete response rate was 91%, and the partial response rate was 9%, compared with 41% complete response and 59% partial response after induction. In this group, the median progression-free survival was 3.3 years, and the median overall survival was 6.5 years.
For the patients who received RIT consolidation after first relapse and second chemotherapy regimen, the complete response rate was 75% and the partial response rate was 25%, compared with 17% and 83% at the end of second induction therapy. In this group, the median progression-free survival was 1.8 years (P less than .05, compared with patients treated after first-line responses), and the median overall survival was 2.2 years (P less than .05).
At 8 years of follow-up, 30% of patients who received RIT consolidation following first-line therapy were alive.
Adverse events included cytopenias in the majority of patients (77%), which were grade 1 or 2 in severity in 43% and grade 3 or 4 in 34%. Grade 3 or 4 thrombocytopenia and leukopenia occurred more frequently in patients treated with fludarabine-based regimens, and the thrombocytopenias in these patients lasted longer and required more platelet transfusions than those in CHOP- or CVP-treated patients. Two patients who underwent RIT following FCM induction died from prolonged thrombocytopenia, resulting in hemorrhagic strokes.
Among all patients, 22 patients developed infections following RIT consolidation. Five patients, all of whom had received fludarabine, required hospitalization for the treatment of the infections. There were no infection-related deaths, however.
Five patients developed the myelodysplastic syndrome, with a median onset time of 26 months. Of these patients, four had received fludarabine, and one had undergone a prior ASCT.
The trial was sponsored by Schering AG. Dr. Jurczak reported speakers bureau participation and research funding from multiple companies, not including Schering AG.
SOURCE: Jurczak W et al. Leuk Lymphoma. 2019 Apr 9. doi: 10.1080/10428194.2019.1602261.
FROM LEUKEMIA & LYMPHOMA
Bendamustine/rituximab combo proves viable for comorbid CLL
A combination of bendamustine and rituximab generated an 88% overall response rate and 96% overall survival rate at 2 years among patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) in a study of 83 patients aged 53-83 years.
Although combined fludarabine, cyclophosphamide, and rituximab has demonstrated success in younger patients with CLL, this therapy is often considered too aggressive for the majority of CLL patients, who tend to be older and have multiple comorbidities, wrote Martin Špacek, MD, of Charles University and General University Hospital in Prague and his colleagues.
The alternative treatment combination of bendamustine and rituximab (BR) has not been well studied in patients with comorbidities, they said.
In a study published in Leukemia Research, the researchers enrolled 83 previously untreated adults with progressive CLL. The average age of the participants was 71 years, and 61% were men. The median creatinine clearance for the study population was 65 mL/min, and all patients had comorbidities, defined as scores greater than 6 on the Cumulative Illness Rating Scale (CIRS).
All patients were prescribed 90 mg/m2 bendamustine on days 1 and 2 combined with 375 mg/m2 rituximab on day 0 of the first course, and 500 mg/m2 rituximab on day 1 during subsequent courses every 28 days for a maximum of six cycles.
The overall response rate to BR was 88.0%, with a complete response rate of 20.5%. At 2 years, progression-free survival and overall survival rates were 69.9% and 96.2%, respectively.
A total of 51 patients (61.4%) experienced at least one grade 3 or 4 adverse event. The most common hematologic effects were neutropenia (40 patients), thrombocytopenia (14 patients), and anemia (8 patients). The most common nonhematologic effects were grade 3– or grade 4–level infections in 12 patients. Six patients developed severe skin rash.
Additionally, one patient developed sepsis during treatment and died after the first course of therapy.
“Age and CIRS failed to predict any severe toxicities or BR dose reduction,” the researchers noted.
The findings support data from previous studies and represent the largest study of CLL patients with significant comorbidities to be treated with BR, the researchers said.
More prospective research is needed, but the results demonstrate that “chemoimmunotherapy with BR is an effective therapeutic option with manageable toxicity for the initial treatment of CLL patients with significant comorbidities,” the investigators wrote.
The study was supported by the Ministry of Health, Czech Republic, the Charles University Progres program, and the Czech CLL Study Group. Researchers reported honoraria and travel grants from Mundipharma and Roche.
SOURCE: Spacek M et al. Leuk Res. 2019;79:17-21.
A combination of bendamustine and rituximab generated an 88% overall response rate and 96% overall survival rate at 2 years among patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) in a study of 83 patients aged 53-83 years.
Although combined fludarabine, cyclophosphamide, and rituximab has demonstrated success in younger patients with CLL, this therapy is often considered too aggressive for the majority of CLL patients, who tend to be older and have multiple comorbidities, wrote Martin Špacek, MD, of Charles University and General University Hospital in Prague and his colleagues.
The alternative treatment combination of bendamustine and rituximab (BR) has not been well studied in patients with comorbidities, they said.
In a study published in Leukemia Research, the researchers enrolled 83 previously untreated adults with progressive CLL. The average age of the participants was 71 years, and 61% were men. The median creatinine clearance for the study population was 65 mL/min, and all patients had comorbidities, defined as scores greater than 6 on the Cumulative Illness Rating Scale (CIRS).
All patients were prescribed 90 mg/m2 bendamustine on days 1 and 2 combined with 375 mg/m2 rituximab on day 0 of the first course, and 500 mg/m2 rituximab on day 1 during subsequent courses every 28 days for a maximum of six cycles.
The overall response rate to BR was 88.0%, with a complete response rate of 20.5%. At 2 years, progression-free survival and overall survival rates were 69.9% and 96.2%, respectively.
A total of 51 patients (61.4%) experienced at least one grade 3 or 4 adverse event. The most common hematologic effects were neutropenia (40 patients), thrombocytopenia (14 patients), and anemia (8 patients). The most common nonhematologic effects were grade 3– or grade 4–level infections in 12 patients. Six patients developed severe skin rash.
Additionally, one patient developed sepsis during treatment and died after the first course of therapy.
“Age and CIRS failed to predict any severe toxicities or BR dose reduction,” the researchers noted.
The findings support data from previous studies and represent the largest study of CLL patients with significant comorbidities to be treated with BR, the researchers said.
More prospective research is needed, but the results demonstrate that “chemoimmunotherapy with BR is an effective therapeutic option with manageable toxicity for the initial treatment of CLL patients with significant comorbidities,” the investigators wrote.
The study was supported by the Ministry of Health, Czech Republic, the Charles University Progres program, and the Czech CLL Study Group. Researchers reported honoraria and travel grants from Mundipharma and Roche.
SOURCE: Spacek M et al. Leuk Res. 2019;79:17-21.
A combination of bendamustine and rituximab generated an 88% overall response rate and 96% overall survival rate at 2 years among patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) in a study of 83 patients aged 53-83 years.
Although combined fludarabine, cyclophosphamide, and rituximab has demonstrated success in younger patients with CLL, this therapy is often considered too aggressive for the majority of CLL patients, who tend to be older and have multiple comorbidities, wrote Martin Špacek, MD, of Charles University and General University Hospital in Prague and his colleagues.
The alternative treatment combination of bendamustine and rituximab (BR) has not been well studied in patients with comorbidities, they said.
In a study published in Leukemia Research, the researchers enrolled 83 previously untreated adults with progressive CLL. The average age of the participants was 71 years, and 61% were men. The median creatinine clearance for the study population was 65 mL/min, and all patients had comorbidities, defined as scores greater than 6 on the Cumulative Illness Rating Scale (CIRS).
All patients were prescribed 90 mg/m2 bendamustine on days 1 and 2 combined with 375 mg/m2 rituximab on day 0 of the first course, and 500 mg/m2 rituximab on day 1 during subsequent courses every 28 days for a maximum of six cycles.
The overall response rate to BR was 88.0%, with a complete response rate of 20.5%. At 2 years, progression-free survival and overall survival rates were 69.9% and 96.2%, respectively.
A total of 51 patients (61.4%) experienced at least one grade 3 or 4 adverse event. The most common hematologic effects were neutropenia (40 patients), thrombocytopenia (14 patients), and anemia (8 patients). The most common nonhematologic effects were grade 3– or grade 4–level infections in 12 patients. Six patients developed severe skin rash.
Additionally, one patient developed sepsis during treatment and died after the first course of therapy.
“Age and CIRS failed to predict any severe toxicities or BR dose reduction,” the researchers noted.
The findings support data from previous studies and represent the largest study of CLL patients with significant comorbidities to be treated with BR, the researchers said.
More prospective research is needed, but the results demonstrate that “chemoimmunotherapy with BR is an effective therapeutic option with manageable toxicity for the initial treatment of CLL patients with significant comorbidities,” the investigators wrote.
The study was supported by the Ministry of Health, Czech Republic, the Charles University Progres program, and the Czech CLL Study Group. Researchers reported honoraria and travel grants from Mundipharma and Roche.
SOURCE: Spacek M et al. Leuk Res. 2019;79:17-21.
FROM LEUKEMIA RESEARCH
Key clinical point:
Major finding: The overall response rate for the combination therapy was 88.0%; complete response was 20.5%.
Study details: A prospective, observational study of 83 patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia.
Disclosures: The study was supported by the Ministry of Health, Czech Republic, the Charles University Progres program, and the Czech CLL Study Group. Researchers reported honoraria and travel grants from Mundipharma and Roche.
Source: Spacek M et al. Leuk Res. 2019;79:17-21.
In situ vaccination produced responses in indolent NHL
A three-pronged treatment approach can produce responses in indolent non-Hodgkin lymphoma (iNHL), according to research published in Nature Medicine.
The approach – “in situ vaccination (ISV)” – involves intratumoral injections of Fms-like tyrosine kinase 3 ligand (Flt3L), local radiotherapy, and intratumoral injections of a TLR3 agonist (poly-ICLC).
ISV produced responses in patients with iNHL, prompting regression of tumors that were directly targeted with ISV, as well as untreated tumors.
In preclinical experiments, ISV induced tumor regression in mice but also overcame resistance to PD1 inhibition. This result led researchers to initiate a trial testing ISV in combination with pembrolizumab in patients with lymphoma and solid tumors.
“We discovered why some tumors do not respond to PD1 blockade: insufficient dendritic cells (DCs) and cross-presentation,” lead study author Joshua Brody, MD, of the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, said in an interview. “We developed a treatment, in situ vaccination (ISV), which brings DCs to the tumor, loads them with tumor antigens, and activates the DCs.”
Specifically, the researchers found that injecting Flt3L into a tumor recruits intratumoral DCs, local radiotherapy loads the DCs with tumor-associated antigens, and poly-ICLC activates DCs. This approach produced responses in mouse models of lymphoma and patients with iNHL.
Preclinical results
Dr. Brody and his colleagues tested ISV in A20 tumor-bearing mice. The mice received intratumoral injections of Flt3L, followed by local radiotherapy and poly-ICLC.
Tumor regression occurred within days of radiotherapy. About 40% of mice experienced tumor-free survival of at least 3 months, although most tumors recurred within 4 weeks of ISV administration.
However, the researchers observed increased PD1 and PD-L1 expression in ISV-treated mice, so the team theorized that an anti-PD1 monoclonal antibody (RMP1-14) could improve the efficacy of ISV.
The researchers found that ISV plus RMP1-14 delayed tumor growth when compared with ISV alone, and the rate of durable remissions increased from about 40% to about 80%.
Clinical results
Dr. Brody and his colleagues also tested ISV in a clinical trial. That trial included 11 iNHL patients – 9 with follicular lymphoma, 1 with marginal zone lymphoma, and 1 with small lymphocytic lymphoma.
The patients received nine daily injections of Flt3L (25 mcg/kg) into a target lesion, then two doses of radiation (2 Gy) to the same lesion, and eight intratumoral injections of poly-ICLC (2 mg).
“We ... have observed dramatic clinical responses; i.e., we administer ISV at one tumor site, and tumors throughout the body regress,” Dr. Brody said.
At the target lesion, there were two complete responses, six partial responses, and three cases of stable disease. At nontarget lesions, there was one complete response, two partial responses, six cases of stable disease, and two cases of progression.
ISV was considered well tolerated. One patient had grade 2 fever, three had grade 1 fever, and nine had grade 1 flu-like symptoms. Two patients did not have any adverse events.
This research was supported by Merck, Celldex Therapeutics, Oncovir, and Genentech. The authors reported relationships with Acerta Pharma, Bristol Myers Squibb, Genentech, Gilead Sciences, Seattle Genetics, Pharmacyclics, Celgene, Celldex Therapeutics, and Oncovir.
SOURCE: Hammerich L et al. Nat Med. 2019 Apr 8. doi: 10.1038/s41591-019-0410-x.
A three-pronged treatment approach can produce responses in indolent non-Hodgkin lymphoma (iNHL), according to research published in Nature Medicine.
The approach – “in situ vaccination (ISV)” – involves intratumoral injections of Fms-like tyrosine kinase 3 ligand (Flt3L), local radiotherapy, and intratumoral injections of a TLR3 agonist (poly-ICLC).
ISV produced responses in patients with iNHL, prompting regression of tumors that were directly targeted with ISV, as well as untreated tumors.
In preclinical experiments, ISV induced tumor regression in mice but also overcame resistance to PD1 inhibition. This result led researchers to initiate a trial testing ISV in combination with pembrolizumab in patients with lymphoma and solid tumors.
“We discovered why some tumors do not respond to PD1 blockade: insufficient dendritic cells (DCs) and cross-presentation,” lead study author Joshua Brody, MD, of the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, said in an interview. “We developed a treatment, in situ vaccination (ISV), which brings DCs to the tumor, loads them with tumor antigens, and activates the DCs.”
Specifically, the researchers found that injecting Flt3L into a tumor recruits intratumoral DCs, local radiotherapy loads the DCs with tumor-associated antigens, and poly-ICLC activates DCs. This approach produced responses in mouse models of lymphoma and patients with iNHL.
Preclinical results
Dr. Brody and his colleagues tested ISV in A20 tumor-bearing mice. The mice received intratumoral injections of Flt3L, followed by local radiotherapy and poly-ICLC.
Tumor regression occurred within days of radiotherapy. About 40% of mice experienced tumor-free survival of at least 3 months, although most tumors recurred within 4 weeks of ISV administration.
However, the researchers observed increased PD1 and PD-L1 expression in ISV-treated mice, so the team theorized that an anti-PD1 monoclonal antibody (RMP1-14) could improve the efficacy of ISV.
The researchers found that ISV plus RMP1-14 delayed tumor growth when compared with ISV alone, and the rate of durable remissions increased from about 40% to about 80%.
Clinical results
Dr. Brody and his colleagues also tested ISV in a clinical trial. That trial included 11 iNHL patients – 9 with follicular lymphoma, 1 with marginal zone lymphoma, and 1 with small lymphocytic lymphoma.
The patients received nine daily injections of Flt3L (25 mcg/kg) into a target lesion, then two doses of radiation (2 Gy) to the same lesion, and eight intratumoral injections of poly-ICLC (2 mg).
“We ... have observed dramatic clinical responses; i.e., we administer ISV at one tumor site, and tumors throughout the body regress,” Dr. Brody said.
At the target lesion, there were two complete responses, six partial responses, and three cases of stable disease. At nontarget lesions, there was one complete response, two partial responses, six cases of stable disease, and two cases of progression.
ISV was considered well tolerated. One patient had grade 2 fever, three had grade 1 fever, and nine had grade 1 flu-like symptoms. Two patients did not have any adverse events.
This research was supported by Merck, Celldex Therapeutics, Oncovir, and Genentech. The authors reported relationships with Acerta Pharma, Bristol Myers Squibb, Genentech, Gilead Sciences, Seattle Genetics, Pharmacyclics, Celgene, Celldex Therapeutics, and Oncovir.
SOURCE: Hammerich L et al. Nat Med. 2019 Apr 8. doi: 10.1038/s41591-019-0410-x.
A three-pronged treatment approach can produce responses in indolent non-Hodgkin lymphoma (iNHL), according to research published in Nature Medicine.
The approach – “in situ vaccination (ISV)” – involves intratumoral injections of Fms-like tyrosine kinase 3 ligand (Flt3L), local radiotherapy, and intratumoral injections of a TLR3 agonist (poly-ICLC).
ISV produced responses in patients with iNHL, prompting regression of tumors that were directly targeted with ISV, as well as untreated tumors.
In preclinical experiments, ISV induced tumor regression in mice but also overcame resistance to PD1 inhibition. This result led researchers to initiate a trial testing ISV in combination with pembrolizumab in patients with lymphoma and solid tumors.
“We discovered why some tumors do not respond to PD1 blockade: insufficient dendritic cells (DCs) and cross-presentation,” lead study author Joshua Brody, MD, of the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, said in an interview. “We developed a treatment, in situ vaccination (ISV), which brings DCs to the tumor, loads them with tumor antigens, and activates the DCs.”
Specifically, the researchers found that injecting Flt3L into a tumor recruits intratumoral DCs, local radiotherapy loads the DCs with tumor-associated antigens, and poly-ICLC activates DCs. This approach produced responses in mouse models of lymphoma and patients with iNHL.
Preclinical results
Dr. Brody and his colleagues tested ISV in A20 tumor-bearing mice. The mice received intratumoral injections of Flt3L, followed by local radiotherapy and poly-ICLC.
Tumor regression occurred within days of radiotherapy. About 40% of mice experienced tumor-free survival of at least 3 months, although most tumors recurred within 4 weeks of ISV administration.
However, the researchers observed increased PD1 and PD-L1 expression in ISV-treated mice, so the team theorized that an anti-PD1 monoclonal antibody (RMP1-14) could improve the efficacy of ISV.
The researchers found that ISV plus RMP1-14 delayed tumor growth when compared with ISV alone, and the rate of durable remissions increased from about 40% to about 80%.
Clinical results
Dr. Brody and his colleagues also tested ISV in a clinical trial. That trial included 11 iNHL patients – 9 with follicular lymphoma, 1 with marginal zone lymphoma, and 1 with small lymphocytic lymphoma.
The patients received nine daily injections of Flt3L (25 mcg/kg) into a target lesion, then two doses of radiation (2 Gy) to the same lesion, and eight intratumoral injections of poly-ICLC (2 mg).
“We ... have observed dramatic clinical responses; i.e., we administer ISV at one tumor site, and tumors throughout the body regress,” Dr. Brody said.
At the target lesion, there were two complete responses, six partial responses, and three cases of stable disease. At nontarget lesions, there was one complete response, two partial responses, six cases of stable disease, and two cases of progression.
ISV was considered well tolerated. One patient had grade 2 fever, three had grade 1 fever, and nine had grade 1 flu-like symptoms. Two patients did not have any adverse events.
This research was supported by Merck, Celldex Therapeutics, Oncovir, and Genentech. The authors reported relationships with Acerta Pharma, Bristol Myers Squibb, Genentech, Gilead Sciences, Seattle Genetics, Pharmacyclics, Celgene, Celldex Therapeutics, and Oncovir.
SOURCE: Hammerich L et al. Nat Med. 2019 Apr 8. doi: 10.1038/s41591-019-0410-x.
FROM NATURE MEDICINE
DA-EPOCH-R appears more toxic than standard R-CHOP in DLBCL
The use of dose-adjusted etoposide, prednisone, vincristine, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, and rituximab (DA-EPOCH-R) as upfront treatment in patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) showed greater toxicity and did not improve progression-free survival versus standard rituximab, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone (R-CHOP), according to results from a phase 3 trial.
“Less favorable outcomes for patients with recurrent DLBCL prompted efforts to improve first-line approaches and biomarkers to identify high-risk patients,” wrote Nancy L. Bartlett, MD, of Washington University, St. Louis, and her colleagues wrote in the Journal of Clinical Oncology.
The Alliance/CALGB 50303 study included 491 patients with DLBCL who were randomized in a 1:1 fashion to receive DA-EPOCH-R or R-CHOP every 21 days for a total of six cycles. Dosing for the DA-EPOCH-R regimen was determined using absolute neutrophil and platelet counts.
The primary endpoint measured was progression-free survival (PFS); secondary endpoints included safety, overall survival (OS), and response rate.
After a median follow-up of 5.2 years, the researchers found no significant difference in PFS between the study arms (DA-EPOCH-R hazard ratio, 0.93; 95% confidence interval, 0.68-1.27; P = .65). Additionally, there was no significant difference in OS (HR, 1.09; 95% CI, 0.75-1.59; P = .64).
The overall response rate was 88.0% in the R-CHOP arm versus 86.7% in the DA-EPOCH-R arm (P = .67).
With respect to safety, grade 3 or 4 adverse events were more frequently seen in the DA-EPOCH-R group than in the R-CHOP group (P less than .001). These toxicities included febrile neutropenia, infections, neuropathy, and mucositis.
The researchers did see significantly improved PFS in the DA-EPOCH-R arm in post hoc subset analyses of patients with International Prognostic Index (IPI) 3-5, but the subset analysis “was unplanned and not powered” and the significance “must be tempered in light of multiple comparisons.”
“We now understand DLBCL is even more heterogeneous than appreciated when this trial was designed,” the researchers wrote. “Therefore, the National Clinical Trials Network is planning a precision medicine approach to identify molecular subsets of DLBCL and determine if specific chemotherapy platforms and/or targeted agents offer differential benefit.”
The study was supported by the National Cancer Institute. The authors reported financial relationships with Bristol-Myers Squibb, Celgene, Janssen, Jazz Pharmaceuticals, Morphosys, and other companies.
SOURCE: Bartlett NL et al. J Clin Oncol. 2019 Apr 2. doi: 10.1200/JCO.18.01994.
The use of dose-adjusted etoposide, prednisone, vincristine, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, and rituximab (DA-EPOCH-R) as upfront treatment in patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) showed greater toxicity and did not improve progression-free survival versus standard rituximab, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone (R-CHOP), according to results from a phase 3 trial.
“Less favorable outcomes for patients with recurrent DLBCL prompted efforts to improve first-line approaches and biomarkers to identify high-risk patients,” wrote Nancy L. Bartlett, MD, of Washington University, St. Louis, and her colleagues wrote in the Journal of Clinical Oncology.
The Alliance/CALGB 50303 study included 491 patients with DLBCL who were randomized in a 1:1 fashion to receive DA-EPOCH-R or R-CHOP every 21 days for a total of six cycles. Dosing for the DA-EPOCH-R regimen was determined using absolute neutrophil and platelet counts.
The primary endpoint measured was progression-free survival (PFS); secondary endpoints included safety, overall survival (OS), and response rate.
After a median follow-up of 5.2 years, the researchers found no significant difference in PFS between the study arms (DA-EPOCH-R hazard ratio, 0.93; 95% confidence interval, 0.68-1.27; P = .65). Additionally, there was no significant difference in OS (HR, 1.09; 95% CI, 0.75-1.59; P = .64).
The overall response rate was 88.0% in the R-CHOP arm versus 86.7% in the DA-EPOCH-R arm (P = .67).
With respect to safety, grade 3 or 4 adverse events were more frequently seen in the DA-EPOCH-R group than in the R-CHOP group (P less than .001). These toxicities included febrile neutropenia, infections, neuropathy, and mucositis.
The researchers did see significantly improved PFS in the DA-EPOCH-R arm in post hoc subset analyses of patients with International Prognostic Index (IPI) 3-5, but the subset analysis “was unplanned and not powered” and the significance “must be tempered in light of multiple comparisons.”
“We now understand DLBCL is even more heterogeneous than appreciated when this trial was designed,” the researchers wrote. “Therefore, the National Clinical Trials Network is planning a precision medicine approach to identify molecular subsets of DLBCL and determine if specific chemotherapy platforms and/or targeted agents offer differential benefit.”
The study was supported by the National Cancer Institute. The authors reported financial relationships with Bristol-Myers Squibb, Celgene, Janssen, Jazz Pharmaceuticals, Morphosys, and other companies.
SOURCE: Bartlett NL et al. J Clin Oncol. 2019 Apr 2. doi: 10.1200/JCO.18.01994.
The use of dose-adjusted etoposide, prednisone, vincristine, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, and rituximab (DA-EPOCH-R) as upfront treatment in patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) showed greater toxicity and did not improve progression-free survival versus standard rituximab, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone (R-CHOP), according to results from a phase 3 trial.
“Less favorable outcomes for patients with recurrent DLBCL prompted efforts to improve first-line approaches and biomarkers to identify high-risk patients,” wrote Nancy L. Bartlett, MD, of Washington University, St. Louis, and her colleagues wrote in the Journal of Clinical Oncology.
The Alliance/CALGB 50303 study included 491 patients with DLBCL who were randomized in a 1:1 fashion to receive DA-EPOCH-R or R-CHOP every 21 days for a total of six cycles. Dosing for the DA-EPOCH-R regimen was determined using absolute neutrophil and platelet counts.
The primary endpoint measured was progression-free survival (PFS); secondary endpoints included safety, overall survival (OS), and response rate.
After a median follow-up of 5.2 years, the researchers found no significant difference in PFS between the study arms (DA-EPOCH-R hazard ratio, 0.93; 95% confidence interval, 0.68-1.27; P = .65). Additionally, there was no significant difference in OS (HR, 1.09; 95% CI, 0.75-1.59; P = .64).
The overall response rate was 88.0% in the R-CHOP arm versus 86.7% in the DA-EPOCH-R arm (P = .67).
With respect to safety, grade 3 or 4 adverse events were more frequently seen in the DA-EPOCH-R group than in the R-CHOP group (P less than .001). These toxicities included febrile neutropenia, infections, neuropathy, and mucositis.
The researchers did see significantly improved PFS in the DA-EPOCH-R arm in post hoc subset analyses of patients with International Prognostic Index (IPI) 3-5, but the subset analysis “was unplanned and not powered” and the significance “must be tempered in light of multiple comparisons.”
“We now understand DLBCL is even more heterogeneous than appreciated when this trial was designed,” the researchers wrote. “Therefore, the National Clinical Trials Network is planning a precision medicine approach to identify molecular subsets of DLBCL and determine if specific chemotherapy platforms and/or targeted agents offer differential benefit.”
The study was supported by the National Cancer Institute. The authors reported financial relationships with Bristol-Myers Squibb, Celgene, Janssen, Jazz Pharmaceuticals, Morphosys, and other companies.
SOURCE: Bartlett NL et al. J Clin Oncol. 2019 Apr 2. doi: 10.1200/JCO.18.01994.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF CLINICAL ONCOLOGY
Polatuzumab outperforms pinatuzumab in non-Hodgkin lymphoma
Favorable results from a phase 2 trial have prompted further development of polatuzumab vedotin in non-Hodgkin lymphoma.
In the ROMULUS trial, polatuzumab vedotin plus rituximab (R-pola) produced more durable responses than did pinatuzumab vedotin plus rituximab (R-pina) in patients with relapsed or refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) or follicular lymphoma (FL).
Researchers also observed a more favorable benefit-risk profile with R-pola.
Franck Morschhauser, MD, of Centre Hospitalier Régional Universitaire de Lille, France, and his colleagues described these findings in the Lancet Haematology.
The ROMULUS trial included 81 DLBCL patients and 42 FL patients. They were randomized to receive R-pola or R-pina (rituximab at 375 mg/m2 plus either antibody-drug conjugate at 2.4 mg/kg) every 21 days until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity for up to 1 year.
Among DLBCL patients, the median age was 69 years in the R-pina arm and 68 years in the R-pola arm. Among FL patients, the median age was 59 years in the R-pina arm and 67 years in the R-pola arm.
Seventy-six percent of DLBCL patients randomized to R-pina were refractory to their last treatment, as were 80% of DLBCL patients assigned to R-pola, 52% of FL patients assigned to R-pina, and 35% of FL patients assigned to R-pola.
The median number of prior systemic therapies was three in the R-pina DLBCL arm, the R-pola DLBCL arm, and the R-pina FL arm. The median number of prior therapies was two in the R-pola FL arm.
Response and survival
Among the DLBCL patients, R-pina produced an objective response rate (ORR) of 60% and a complete response (CR) rate of 26%. R-pola produced an ORR of 54% and a CR rate of 21%. The median duration of response was 6.2 months in the R-pina arm and 13.4 months in the R-pola arm.
The median progression-free survival in the DLBCL cohort was 5.4 months for the R-pina arm and 5.6 months for the R-pola arm. The median overall survival was 16.5 months and 20.1 months, respectively.
In the FL cohort, R-pina produced an ORR of 62% and a CR rate of 5%. R-pola produced an ORR of 70% and a CR rate of 45%. The median duration of response was 6.5 months in the R-pina arm and 9.4 months in the R-pola arm.
The median progression-free survival in the FL cohort was 12.7 months for the R-pina arm and 15.3 months for the R-pola arm. The 2-year overall survival rate was 90.5% and 87.8%, respectively. The median overall survival was not reached in either arm.
“Patients treated with R-pola tended to have longer durations of response than those receiving R-pina (particularly those with relapsed or refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma), and the results for R-pola compared favorably with other novel antilymphoma agents,” Dr. Morschhauser and his colleagues wrote.
Safety
Among DLBCL patients, serious adverse events (AEs) occurred in 50.0% of those in the R-pina arm and 35.9% of those in the R-pola arm. Among FL patients, serious AEs occurred in 28.6% of those the R-pina arm and 35.0% of those in the R-pola arm.
Ten grade 5 AEs occurred in nine DLBCL patients who received R-pina (21.4%). These events included two cases of sepsis, influenza and pneumonia in the same patient, general physical health deterioration including one death attributed to disease progression, and one case each of Clostridium difficile sepsis, respiratory failure, urosepsis, and sudden death.
There was one grade 5 AE in a FL patient who received R-pola. The 84-year-old patient died of pulmonary congestion 64 days after the last of 12 cycles of treatment.
There were no fatal AEs in the other arms.
“These findings make pola a promising novel candidate for further clinical evaluation in combination regimens in treatment-refractory patients and also in a first-line setting in B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma,” Dr. Morschhauser and his colleagues wrote.
Polatuzumab vedotin was chosen by the study funder for further development in non-Hodgkin lymphoma, partly because of longer durations of response, compared with pinatuzumab vedotin.
Polatuzumab vedotin is currently under investigation in the phase 3 POLARIX study. The drug is being combined with rituximab, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, and prednisone and compared to rituximab-cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone (R-CHOP) in patients with DLBCL.
The ROMULUS study was funded by F Hoffmann-La Roche. The study authors reported relationships with Roche and other companies.
SOURCE: Morschhauser F et al. Lancet Haematol. 2019 Mar 29. doi: 10.1016/S2352-3026(19)30026-2.
Favorable results from a phase 2 trial have prompted further development of polatuzumab vedotin in non-Hodgkin lymphoma.
In the ROMULUS trial, polatuzumab vedotin plus rituximab (R-pola) produced more durable responses than did pinatuzumab vedotin plus rituximab (R-pina) in patients with relapsed or refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) or follicular lymphoma (FL).
Researchers also observed a more favorable benefit-risk profile with R-pola.
Franck Morschhauser, MD, of Centre Hospitalier Régional Universitaire de Lille, France, and his colleagues described these findings in the Lancet Haematology.
The ROMULUS trial included 81 DLBCL patients and 42 FL patients. They were randomized to receive R-pola or R-pina (rituximab at 375 mg/m2 plus either antibody-drug conjugate at 2.4 mg/kg) every 21 days until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity for up to 1 year.
Among DLBCL patients, the median age was 69 years in the R-pina arm and 68 years in the R-pola arm. Among FL patients, the median age was 59 years in the R-pina arm and 67 years in the R-pola arm.
Seventy-six percent of DLBCL patients randomized to R-pina were refractory to their last treatment, as were 80% of DLBCL patients assigned to R-pola, 52% of FL patients assigned to R-pina, and 35% of FL patients assigned to R-pola.
The median number of prior systemic therapies was three in the R-pina DLBCL arm, the R-pola DLBCL arm, and the R-pina FL arm. The median number of prior therapies was two in the R-pola FL arm.
Response and survival
Among the DLBCL patients, R-pina produced an objective response rate (ORR) of 60% and a complete response (CR) rate of 26%. R-pola produced an ORR of 54% and a CR rate of 21%. The median duration of response was 6.2 months in the R-pina arm and 13.4 months in the R-pola arm.
The median progression-free survival in the DLBCL cohort was 5.4 months for the R-pina arm and 5.6 months for the R-pola arm. The median overall survival was 16.5 months and 20.1 months, respectively.
In the FL cohort, R-pina produced an ORR of 62% and a CR rate of 5%. R-pola produced an ORR of 70% and a CR rate of 45%. The median duration of response was 6.5 months in the R-pina arm and 9.4 months in the R-pola arm.
The median progression-free survival in the FL cohort was 12.7 months for the R-pina arm and 15.3 months for the R-pola arm. The 2-year overall survival rate was 90.5% and 87.8%, respectively. The median overall survival was not reached in either arm.
“Patients treated with R-pola tended to have longer durations of response than those receiving R-pina (particularly those with relapsed or refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma), and the results for R-pola compared favorably with other novel antilymphoma agents,” Dr. Morschhauser and his colleagues wrote.
Safety
Among DLBCL patients, serious adverse events (AEs) occurred in 50.0% of those in the R-pina arm and 35.9% of those in the R-pola arm. Among FL patients, serious AEs occurred in 28.6% of those the R-pina arm and 35.0% of those in the R-pola arm.
Ten grade 5 AEs occurred in nine DLBCL patients who received R-pina (21.4%). These events included two cases of sepsis, influenza and pneumonia in the same patient, general physical health deterioration including one death attributed to disease progression, and one case each of Clostridium difficile sepsis, respiratory failure, urosepsis, and sudden death.
There was one grade 5 AE in a FL patient who received R-pola. The 84-year-old patient died of pulmonary congestion 64 days after the last of 12 cycles of treatment.
There were no fatal AEs in the other arms.
“These findings make pola a promising novel candidate for further clinical evaluation in combination regimens in treatment-refractory patients and also in a first-line setting in B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma,” Dr. Morschhauser and his colleagues wrote.
Polatuzumab vedotin was chosen by the study funder for further development in non-Hodgkin lymphoma, partly because of longer durations of response, compared with pinatuzumab vedotin.
Polatuzumab vedotin is currently under investigation in the phase 3 POLARIX study. The drug is being combined with rituximab, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, and prednisone and compared to rituximab-cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone (R-CHOP) in patients with DLBCL.
The ROMULUS study was funded by F Hoffmann-La Roche. The study authors reported relationships with Roche and other companies.
SOURCE: Morschhauser F et al. Lancet Haematol. 2019 Mar 29. doi: 10.1016/S2352-3026(19)30026-2.
Favorable results from a phase 2 trial have prompted further development of polatuzumab vedotin in non-Hodgkin lymphoma.
In the ROMULUS trial, polatuzumab vedotin plus rituximab (R-pola) produced more durable responses than did pinatuzumab vedotin plus rituximab (R-pina) in patients with relapsed or refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) or follicular lymphoma (FL).
Researchers also observed a more favorable benefit-risk profile with R-pola.
Franck Morschhauser, MD, of Centre Hospitalier Régional Universitaire de Lille, France, and his colleagues described these findings in the Lancet Haematology.
The ROMULUS trial included 81 DLBCL patients and 42 FL patients. They were randomized to receive R-pola or R-pina (rituximab at 375 mg/m2 plus either antibody-drug conjugate at 2.4 mg/kg) every 21 days until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity for up to 1 year.
Among DLBCL patients, the median age was 69 years in the R-pina arm and 68 years in the R-pola arm. Among FL patients, the median age was 59 years in the R-pina arm and 67 years in the R-pola arm.
Seventy-six percent of DLBCL patients randomized to R-pina were refractory to their last treatment, as were 80% of DLBCL patients assigned to R-pola, 52% of FL patients assigned to R-pina, and 35% of FL patients assigned to R-pola.
The median number of prior systemic therapies was three in the R-pina DLBCL arm, the R-pola DLBCL arm, and the R-pina FL arm. The median number of prior therapies was two in the R-pola FL arm.
Response and survival
Among the DLBCL patients, R-pina produced an objective response rate (ORR) of 60% and a complete response (CR) rate of 26%. R-pola produced an ORR of 54% and a CR rate of 21%. The median duration of response was 6.2 months in the R-pina arm and 13.4 months in the R-pola arm.
The median progression-free survival in the DLBCL cohort was 5.4 months for the R-pina arm and 5.6 months for the R-pola arm. The median overall survival was 16.5 months and 20.1 months, respectively.
In the FL cohort, R-pina produced an ORR of 62% and a CR rate of 5%. R-pola produced an ORR of 70% and a CR rate of 45%. The median duration of response was 6.5 months in the R-pina arm and 9.4 months in the R-pola arm.
The median progression-free survival in the FL cohort was 12.7 months for the R-pina arm and 15.3 months for the R-pola arm. The 2-year overall survival rate was 90.5% and 87.8%, respectively. The median overall survival was not reached in either arm.
“Patients treated with R-pola tended to have longer durations of response than those receiving R-pina (particularly those with relapsed or refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma), and the results for R-pola compared favorably with other novel antilymphoma agents,” Dr. Morschhauser and his colleagues wrote.
Safety
Among DLBCL patients, serious adverse events (AEs) occurred in 50.0% of those in the R-pina arm and 35.9% of those in the R-pola arm. Among FL patients, serious AEs occurred in 28.6% of those the R-pina arm and 35.0% of those in the R-pola arm.
Ten grade 5 AEs occurred in nine DLBCL patients who received R-pina (21.4%). These events included two cases of sepsis, influenza and pneumonia in the same patient, general physical health deterioration including one death attributed to disease progression, and one case each of Clostridium difficile sepsis, respiratory failure, urosepsis, and sudden death.
There was one grade 5 AE in a FL patient who received R-pola. The 84-year-old patient died of pulmonary congestion 64 days after the last of 12 cycles of treatment.
There were no fatal AEs in the other arms.
“These findings make pola a promising novel candidate for further clinical evaluation in combination regimens in treatment-refractory patients and also in a first-line setting in B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma,” Dr. Morschhauser and his colleagues wrote.
Polatuzumab vedotin was chosen by the study funder for further development in non-Hodgkin lymphoma, partly because of longer durations of response, compared with pinatuzumab vedotin.
Polatuzumab vedotin is currently under investigation in the phase 3 POLARIX study. The drug is being combined with rituximab, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, and prednisone and compared to rituximab-cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone (R-CHOP) in patients with DLBCL.
The ROMULUS study was funded by F Hoffmann-La Roche. The study authors reported relationships with Roche and other companies.
SOURCE: Morschhauser F et al. Lancet Haematol. 2019 Mar 29. doi: 10.1016/S2352-3026(19)30026-2.
FROM LANCET HAEMATOLOGY
Early data support R-BAC for post-BTKi mantle cell lymphoma
GLASGOW – Patients with relapsed or refractory mantle cell lymphoma (MCL) who experience disease progression on a Bruton’s tyrosine kinase inhibitor (BTKi) may respond best to a combination of rituximab, bendamustine, and cytarabine (R-BAC), based on early results from an ongoing retrospective study.
Findings from the study, which were presented at the annual meeting of the British Society for Haematology, showed that R-BAC after BTKi failure had an overall response rate (ORR) of 90.5%.
This is a “remarkable response rate” according to the investigators, who cited previously reported response rates for other treatments ranging from 29% to 53%.
Treatment of relapsed/refractory MCL patients in the post-BTKi setting is an area of unmet clinical need, said senior author Simon Rule, MD, of the University of Plymouth, England. He noted that there is currently no consensus regarding best treatment strategy for this patient population.
Dr. Rule said that he and his colleagues have collected data on 30 patients so far, of which 22 were included in this early data release.
All patients received R-BAC between 2016 and 2018 at treatment centers in Italy and the United Kingdom. Treatment consisted of rituximab (375 mg/m2 or 500 mg) on day 1, bendamustine 70 mg/m2 on days 1 and 2, and cytarabine 500 mg/m2 on days 1 through 3, given in a 28-day cycle.
Patients received R-BAC immediately after BTKi failure. Data were drawn from hospital records.
Analysis showed that the median patient age was 65 years, with a range from 43 to 79 years. Most patients were men (81.8%), 55.0% were high risk based on the Mantle Cell Lymphoma International Prognostic Index, and 22.7% had blastoid morphology.
Patients had a median of two prior systemic therapies, with a range from one to six lines. First-line therapies included rituximab in combination with HDAC (high-dose cytarabine containing regimen), CHOP, CVP, or ibrutinib. Nine patients (42.9%) had allogeneic stem cell transplantation (ASCT) after induction treatment.
For BTKi therapy, most patients received ibrutinib (n = 18), while the remainder received acalabrutinib, tirabrutinib or M7583. Most patients discontinued BTKi therapy because of disease progression (90.9%); two patients stopped because of a lack of response (9.1%).
The median number of R-BAC cycles received was four. Two patients started with attenuated doses and seven patients reduced doses after the first cycle. More than 70% of patients completed R-BAC treatment.
The estimated median progression-free survival was 7.3 months and estimated median overall survival was 11.2 months.
Although the investigators reported a complete response rate of 57.1%, they noted that this figure “may be exaggerated” because of a lack of bone marrow biopsy; however, they suggested that the overall response rate (90.5%) “should be accurate.”
During the course of treatment, 31.8% of patients required inpatient admission, 22.7% developed neutropenic fever, and 77.8% required transfusion support. No treatment-related deaths occurred.
“This population, enriched for patients with high risk features, showed remarkable response rates to R-BAC,” the investigators wrote. “The treatment had acceptable toxicity, maintained efficacy at attenuated doses, and was used successfully as a bridge to ASCT in over 20% of patients.”
The investigators suggested that R-BAC should be considered a new standard of care in the United Kingdom for bendamustine-naive patients who are unable to be enrolled in clinical trials. “The high response rate makes it particularly appealing for patients considered candidates for consolidation ASCT,” they wrote.
In an interview, Dr. Rule added perspective to these findings.
“There’s been an obsession with venetoclax, that that’s the answer, but it really isn’t,” Dr. Rule said. “So people are looking for a new drug. I guess what I do differently to most people is I use CHOP frontline rather than bendamustine. To me, that’s the best way of sequencing the therapies, whereas if you use [bendamustine and rituximab] up front, which a lot of people do, particularly in the [United] States, your R-BAC might not be so effective.”
However, Dr. Rule said that first-line therapies appear to have minimal impact on R-BAC efficacy. “Even if you’ve had bendamustine, even if you’ve had high-dose cytarabine, even if you’ve had an allogeneic stem cell transplant, [R-BAC] still works,” he said.
Where patients have issues with tolerability, Dr. Rule noted that dose reductions are possible without sacrificing efficacy.
He offered an example of such a scenario. “My oldest patient was about 80 with blastoid disease, relapsing,” Dr. Rule said. “After ibrutinib, I gave him just a single dose of bendamustine at 70 mg, a single dose of cytarabine at 500 mg, just 1 day, and he had that six times, probably 3 weeks apart. He’s been in complete remission for over a year.”
With data on 30 patients collected, Dr. Rule said that he and his colleagues plan to present more extensive findings at the European Hematology Association Congress, held June 13-16 in Amsterdam.
The investigators reported having no conflicts of interest.
GLASGOW – Patients with relapsed or refractory mantle cell lymphoma (MCL) who experience disease progression on a Bruton’s tyrosine kinase inhibitor (BTKi) may respond best to a combination of rituximab, bendamustine, and cytarabine (R-BAC), based on early results from an ongoing retrospective study.
Findings from the study, which were presented at the annual meeting of the British Society for Haematology, showed that R-BAC after BTKi failure had an overall response rate (ORR) of 90.5%.
This is a “remarkable response rate” according to the investigators, who cited previously reported response rates for other treatments ranging from 29% to 53%.
Treatment of relapsed/refractory MCL patients in the post-BTKi setting is an area of unmet clinical need, said senior author Simon Rule, MD, of the University of Plymouth, England. He noted that there is currently no consensus regarding best treatment strategy for this patient population.
Dr. Rule said that he and his colleagues have collected data on 30 patients so far, of which 22 were included in this early data release.
All patients received R-BAC between 2016 and 2018 at treatment centers in Italy and the United Kingdom. Treatment consisted of rituximab (375 mg/m2 or 500 mg) on day 1, bendamustine 70 mg/m2 on days 1 and 2, and cytarabine 500 mg/m2 on days 1 through 3, given in a 28-day cycle.
Patients received R-BAC immediately after BTKi failure. Data were drawn from hospital records.
Analysis showed that the median patient age was 65 years, with a range from 43 to 79 years. Most patients were men (81.8%), 55.0% were high risk based on the Mantle Cell Lymphoma International Prognostic Index, and 22.7% had blastoid morphology.
Patients had a median of two prior systemic therapies, with a range from one to six lines. First-line therapies included rituximab in combination with HDAC (high-dose cytarabine containing regimen), CHOP, CVP, or ibrutinib. Nine patients (42.9%) had allogeneic stem cell transplantation (ASCT) after induction treatment.
For BTKi therapy, most patients received ibrutinib (n = 18), while the remainder received acalabrutinib, tirabrutinib or M7583. Most patients discontinued BTKi therapy because of disease progression (90.9%); two patients stopped because of a lack of response (9.1%).
The median number of R-BAC cycles received was four. Two patients started with attenuated doses and seven patients reduced doses after the first cycle. More than 70% of patients completed R-BAC treatment.
The estimated median progression-free survival was 7.3 months and estimated median overall survival was 11.2 months.
Although the investigators reported a complete response rate of 57.1%, they noted that this figure “may be exaggerated” because of a lack of bone marrow biopsy; however, they suggested that the overall response rate (90.5%) “should be accurate.”
During the course of treatment, 31.8% of patients required inpatient admission, 22.7% developed neutropenic fever, and 77.8% required transfusion support. No treatment-related deaths occurred.
“This population, enriched for patients with high risk features, showed remarkable response rates to R-BAC,” the investigators wrote. “The treatment had acceptable toxicity, maintained efficacy at attenuated doses, and was used successfully as a bridge to ASCT in over 20% of patients.”
The investigators suggested that R-BAC should be considered a new standard of care in the United Kingdom for bendamustine-naive patients who are unable to be enrolled in clinical trials. “The high response rate makes it particularly appealing for patients considered candidates for consolidation ASCT,” they wrote.
In an interview, Dr. Rule added perspective to these findings.
“There’s been an obsession with venetoclax, that that’s the answer, but it really isn’t,” Dr. Rule said. “So people are looking for a new drug. I guess what I do differently to most people is I use CHOP frontline rather than bendamustine. To me, that’s the best way of sequencing the therapies, whereas if you use [bendamustine and rituximab] up front, which a lot of people do, particularly in the [United] States, your R-BAC might not be so effective.”
However, Dr. Rule said that first-line therapies appear to have minimal impact on R-BAC efficacy. “Even if you’ve had bendamustine, even if you’ve had high-dose cytarabine, even if you’ve had an allogeneic stem cell transplant, [R-BAC] still works,” he said.
Where patients have issues with tolerability, Dr. Rule noted that dose reductions are possible without sacrificing efficacy.
He offered an example of such a scenario. “My oldest patient was about 80 with blastoid disease, relapsing,” Dr. Rule said. “After ibrutinib, I gave him just a single dose of bendamustine at 70 mg, a single dose of cytarabine at 500 mg, just 1 day, and he had that six times, probably 3 weeks apart. He’s been in complete remission for over a year.”
With data on 30 patients collected, Dr. Rule said that he and his colleagues plan to present more extensive findings at the European Hematology Association Congress, held June 13-16 in Amsterdam.
The investigators reported having no conflicts of interest.
GLASGOW – Patients with relapsed or refractory mantle cell lymphoma (MCL) who experience disease progression on a Bruton’s tyrosine kinase inhibitor (BTKi) may respond best to a combination of rituximab, bendamustine, and cytarabine (R-BAC), based on early results from an ongoing retrospective study.
Findings from the study, which were presented at the annual meeting of the British Society for Haematology, showed that R-BAC after BTKi failure had an overall response rate (ORR) of 90.5%.
This is a “remarkable response rate” according to the investigators, who cited previously reported response rates for other treatments ranging from 29% to 53%.
Treatment of relapsed/refractory MCL patients in the post-BTKi setting is an area of unmet clinical need, said senior author Simon Rule, MD, of the University of Plymouth, England. He noted that there is currently no consensus regarding best treatment strategy for this patient population.
Dr. Rule said that he and his colleagues have collected data on 30 patients so far, of which 22 were included in this early data release.
All patients received R-BAC between 2016 and 2018 at treatment centers in Italy and the United Kingdom. Treatment consisted of rituximab (375 mg/m2 or 500 mg) on day 1, bendamustine 70 mg/m2 on days 1 and 2, and cytarabine 500 mg/m2 on days 1 through 3, given in a 28-day cycle.
Patients received R-BAC immediately after BTKi failure. Data were drawn from hospital records.
Analysis showed that the median patient age was 65 years, with a range from 43 to 79 years. Most patients were men (81.8%), 55.0% were high risk based on the Mantle Cell Lymphoma International Prognostic Index, and 22.7% had blastoid morphology.
Patients had a median of two prior systemic therapies, with a range from one to six lines. First-line therapies included rituximab in combination with HDAC (high-dose cytarabine containing regimen), CHOP, CVP, or ibrutinib. Nine patients (42.9%) had allogeneic stem cell transplantation (ASCT) after induction treatment.
For BTKi therapy, most patients received ibrutinib (n = 18), while the remainder received acalabrutinib, tirabrutinib or M7583. Most patients discontinued BTKi therapy because of disease progression (90.9%); two patients stopped because of a lack of response (9.1%).
The median number of R-BAC cycles received was four. Two patients started with attenuated doses and seven patients reduced doses after the first cycle. More than 70% of patients completed R-BAC treatment.
The estimated median progression-free survival was 7.3 months and estimated median overall survival was 11.2 months.
Although the investigators reported a complete response rate of 57.1%, they noted that this figure “may be exaggerated” because of a lack of bone marrow biopsy; however, they suggested that the overall response rate (90.5%) “should be accurate.”
During the course of treatment, 31.8% of patients required inpatient admission, 22.7% developed neutropenic fever, and 77.8% required transfusion support. No treatment-related deaths occurred.
“This population, enriched for patients with high risk features, showed remarkable response rates to R-BAC,” the investigators wrote. “The treatment had acceptable toxicity, maintained efficacy at attenuated doses, and was used successfully as a bridge to ASCT in over 20% of patients.”
The investigators suggested that R-BAC should be considered a new standard of care in the United Kingdom for bendamustine-naive patients who are unable to be enrolled in clinical trials. “The high response rate makes it particularly appealing for patients considered candidates for consolidation ASCT,” they wrote.
In an interview, Dr. Rule added perspective to these findings.
“There’s been an obsession with venetoclax, that that’s the answer, but it really isn’t,” Dr. Rule said. “So people are looking for a new drug. I guess what I do differently to most people is I use CHOP frontline rather than bendamustine. To me, that’s the best way of sequencing the therapies, whereas if you use [bendamustine and rituximab] up front, which a lot of people do, particularly in the [United] States, your R-BAC might not be so effective.”
However, Dr. Rule said that first-line therapies appear to have minimal impact on R-BAC efficacy. “Even if you’ve had bendamustine, even if you’ve had high-dose cytarabine, even if you’ve had an allogeneic stem cell transplant, [R-BAC] still works,” he said.
Where patients have issues with tolerability, Dr. Rule noted that dose reductions are possible without sacrificing efficacy.
He offered an example of such a scenario. “My oldest patient was about 80 with blastoid disease, relapsing,” Dr. Rule said. “After ibrutinib, I gave him just a single dose of bendamustine at 70 mg, a single dose of cytarabine at 500 mg, just 1 day, and he had that six times, probably 3 weeks apart. He’s been in complete remission for over a year.”
With data on 30 patients collected, Dr. Rule said that he and his colleagues plan to present more extensive findings at the European Hematology Association Congress, held June 13-16 in Amsterdam.
The investigators reported having no conflicts of interest.
REPORTING FROM BSH 2019
Ibrutinib sustained responses in refractory CLL in long-term follow-up
Prolonged exposure to ibrutinib showed sustained progression-free and overall survival and had tolerable safety outcomes in patients with relapsed or refractory chronic lymphocytic leukemia, according to a post hoc analysis of the phase 3 RESONATE trial.
“This study ... provides further evidence for efficacy and safety with prolonged treatment across multiple high-risk genomic and clinical disease features and with increasing depth of response,” John C. Byrd, MD, of the Ohio State University, Columbus, and his colleagues wrote in Blood.
RESONATE included 391 high-risk patients with relapsed or refractory chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL). Study participants were randomized in a 1:1 fashion to receive ibrutinib 420 mg daily or ofatumumab (initial infusion of 300 mg followed by seven weekly infusions and four monthly infusions of 2,000 mg) for a maximum of 24 weeks. Drug therapy was continued until cancer progression or intolerable toxicity of either agent was seen.
“Primary analysis at median follow-up of 9.7 months demonstrated superiority of ibrutinib over ofatumumab in PFS [progression-free survival], OS [overall survival], and overall response,” the researchers wrote. “With extended follow-up of median 44 months, these same results persist; a plateau of PFS has not yet been reached in this long-term follow-up. We also observe very durable remissions among patients of all genomic groups, including those with del(17)(p13.1), del(11)(q22.3), or unmutated IgHV [immunoglobulin heavy chain gene], who are traditionally considered high-risk populations.”
After an extended follow-up (median, 44 months), the team found that the PFS benefit with ibrutinib was sustained, compared with ofatumumab (hazard ratio, 0.133; 95% confidence interval, 0.099-0.178; P less than .0001). The 3-year PFS rate was 59% for ibrutinib, compared with 3% for ofatumumab. Similar PFS benefits were seen among subgroups of high- and very high–risk patients, based on their scores on the International Prognostic Index for CLL.
The OS benefit was also sustained in those randomized to ibrutinib (HR, 0.591; 95% CI, 0.378-0.926; P = .0208). The continued OS benefit with ibrutinib versus ofatumumab continued even after a sensitivity analysis adjusted for crossover of patients to ibrutinib.
With respect to safety, adverse events of any grade were similar to previous reports of ibrutinib. In fact, the prevalence of adverse events (grade 3 or higher) decreased over time for participants that continued on ibrutinib.
“Multiple studies are ongoing to investigate ibrutinib earlier in the course of CLL therapy, including phase 3 studies of first-line ibrutinib [or ibrutinib combined with anti-CD20 therapy], compared with standard chemoimmunotherapy regimens,” they wrote.
The study was sponsored by Pharmacyclics and Janssen. The authors reported financial disclosures related to the sponsors and several other companies.
SOURCE: Byrd JC et al. Blood. 2019 Mar 6. doi: 10.1182/blood-2018-08-870238.
Prolonged exposure to ibrutinib showed sustained progression-free and overall survival and had tolerable safety outcomes in patients with relapsed or refractory chronic lymphocytic leukemia, according to a post hoc analysis of the phase 3 RESONATE trial.
“This study ... provides further evidence for efficacy and safety with prolonged treatment across multiple high-risk genomic and clinical disease features and with increasing depth of response,” John C. Byrd, MD, of the Ohio State University, Columbus, and his colleagues wrote in Blood.
RESONATE included 391 high-risk patients with relapsed or refractory chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL). Study participants were randomized in a 1:1 fashion to receive ibrutinib 420 mg daily or ofatumumab (initial infusion of 300 mg followed by seven weekly infusions and four monthly infusions of 2,000 mg) for a maximum of 24 weeks. Drug therapy was continued until cancer progression or intolerable toxicity of either agent was seen.
“Primary analysis at median follow-up of 9.7 months demonstrated superiority of ibrutinib over ofatumumab in PFS [progression-free survival], OS [overall survival], and overall response,” the researchers wrote. “With extended follow-up of median 44 months, these same results persist; a plateau of PFS has not yet been reached in this long-term follow-up. We also observe very durable remissions among patients of all genomic groups, including those with del(17)(p13.1), del(11)(q22.3), or unmutated IgHV [immunoglobulin heavy chain gene], who are traditionally considered high-risk populations.”
After an extended follow-up (median, 44 months), the team found that the PFS benefit with ibrutinib was sustained, compared with ofatumumab (hazard ratio, 0.133; 95% confidence interval, 0.099-0.178; P less than .0001). The 3-year PFS rate was 59% for ibrutinib, compared with 3% for ofatumumab. Similar PFS benefits were seen among subgroups of high- and very high–risk patients, based on their scores on the International Prognostic Index for CLL.
The OS benefit was also sustained in those randomized to ibrutinib (HR, 0.591; 95% CI, 0.378-0.926; P = .0208). The continued OS benefit with ibrutinib versus ofatumumab continued even after a sensitivity analysis adjusted for crossover of patients to ibrutinib.
With respect to safety, adverse events of any grade were similar to previous reports of ibrutinib. In fact, the prevalence of adverse events (grade 3 or higher) decreased over time for participants that continued on ibrutinib.
“Multiple studies are ongoing to investigate ibrutinib earlier in the course of CLL therapy, including phase 3 studies of first-line ibrutinib [or ibrutinib combined with anti-CD20 therapy], compared with standard chemoimmunotherapy regimens,” they wrote.
The study was sponsored by Pharmacyclics and Janssen. The authors reported financial disclosures related to the sponsors and several other companies.
SOURCE: Byrd JC et al. Blood. 2019 Mar 6. doi: 10.1182/blood-2018-08-870238.
Prolonged exposure to ibrutinib showed sustained progression-free and overall survival and had tolerable safety outcomes in patients with relapsed or refractory chronic lymphocytic leukemia, according to a post hoc analysis of the phase 3 RESONATE trial.
“This study ... provides further evidence for efficacy and safety with prolonged treatment across multiple high-risk genomic and clinical disease features and with increasing depth of response,” John C. Byrd, MD, of the Ohio State University, Columbus, and his colleagues wrote in Blood.
RESONATE included 391 high-risk patients with relapsed or refractory chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL). Study participants were randomized in a 1:1 fashion to receive ibrutinib 420 mg daily or ofatumumab (initial infusion of 300 mg followed by seven weekly infusions and four monthly infusions of 2,000 mg) for a maximum of 24 weeks. Drug therapy was continued until cancer progression or intolerable toxicity of either agent was seen.
“Primary analysis at median follow-up of 9.7 months demonstrated superiority of ibrutinib over ofatumumab in PFS [progression-free survival], OS [overall survival], and overall response,” the researchers wrote. “With extended follow-up of median 44 months, these same results persist; a plateau of PFS has not yet been reached in this long-term follow-up. We also observe very durable remissions among patients of all genomic groups, including those with del(17)(p13.1), del(11)(q22.3), or unmutated IgHV [immunoglobulin heavy chain gene], who are traditionally considered high-risk populations.”
After an extended follow-up (median, 44 months), the team found that the PFS benefit with ibrutinib was sustained, compared with ofatumumab (hazard ratio, 0.133; 95% confidence interval, 0.099-0.178; P less than .0001). The 3-year PFS rate was 59% for ibrutinib, compared with 3% for ofatumumab. Similar PFS benefits were seen among subgroups of high- and very high–risk patients, based on their scores on the International Prognostic Index for CLL.
The OS benefit was also sustained in those randomized to ibrutinib (HR, 0.591; 95% CI, 0.378-0.926; P = .0208). The continued OS benefit with ibrutinib versus ofatumumab continued even after a sensitivity analysis adjusted for crossover of patients to ibrutinib.
With respect to safety, adverse events of any grade were similar to previous reports of ibrutinib. In fact, the prevalence of adverse events (grade 3 or higher) decreased over time for participants that continued on ibrutinib.
“Multiple studies are ongoing to investigate ibrutinib earlier in the course of CLL therapy, including phase 3 studies of first-line ibrutinib [or ibrutinib combined with anti-CD20 therapy], compared with standard chemoimmunotherapy regimens,” they wrote.
The study was sponsored by Pharmacyclics and Janssen. The authors reported financial disclosures related to the sponsors and several other companies.
SOURCE: Byrd JC et al. Blood. 2019 Mar 6. doi: 10.1182/blood-2018-08-870238.
FROM BLOOD
Rituximab boosts survival in primary CNS lymphoma
For patients with primary central nervous system lymphoma (PCNSL), adding rituximab to combination high-dose methotrexate and temozolomide significantly boosted the 5-year overall survival rate, according to a retrospective study.
The triplet combination could be a safe and effective first-line option for patients with PCNSL, particularly the frail and elderly, who may have issues with toxicity when receiving current standard care, reported lead author Cui Chen, MD, of Sun Yat-Sen University Cancer Center in Guangzhou, China, and his colleagues.
“An increasing number of studies and meta‐analyses have investigated the effect of rituximab in PCNSL, indicating that rituximab can robustly enhance the response rate and possibly improve survival,” the investigators wrote in Cancer Medicine. “However, data regarding the addition of rituximab to [methotrexate and temozolomide] for PCNSL are limited, and no study has directly compared the efficacy of [rituximab/high-dose methotrexate/temozolomide] to that of [high-dose methotrexate/temozolomide].”
The study involved 62 patients with untreated PCNSL who were diagnosed between 2005 and 2015. Out of the 62 patients, 32 received rituximab/high-dose methotrexate/temozolomide (RMT) and 30 received high-dose methotrexate/temozolomide (MT). Patients received up to eight cycles of therapy, with discontinuation upon disease progression or toxicity.
The results showed that patients treated with RMT had significantly better outcomes than those who received MT, first marked by objective response rates, which were 93.7% for RMT and 69.0% for MT.
Survival rates also showed the advantage of rituximab. For the RMT group, 2-year and 5-year progression-free survival rates were 81.3% and 53.3%, respectively, compared with 46.5% and 29.1% for patients receiving MT.
Most importantly, rituximab boosted overall survival to a significant and notable extent, with higher rates at 2 years (82.3% vs. 65.7%) and 5 years (82.3% vs. 50.0%).
Efficacy did not diminish safety, as no significant differences in toxicity were found between treatment types. The most common grade 3-4 toxicities were hematologic; most commonly, this entailed neutropenia, which occurred in about one-quarter of patients.
“Given its outstanding efficacy and favorable toxicity, we consider RMT to be a feasible and safe therapeutic approach as a first‐line treatment for PCNSL. Moreover, RMT is an ideal regimen for elderly patients and frail populations who may not tolerate [whole‐brain radiation therapy] or [autologous stem‐cell transplantation],” the researchers wrote.
The study was funded by the Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province. The researchers reported having no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Chen C et al. Cancer Med. 2019 Mar 1. doi: 10.1002/cam4.1906.
For patients with primary central nervous system lymphoma (PCNSL), adding rituximab to combination high-dose methotrexate and temozolomide significantly boosted the 5-year overall survival rate, according to a retrospective study.
The triplet combination could be a safe and effective first-line option for patients with PCNSL, particularly the frail and elderly, who may have issues with toxicity when receiving current standard care, reported lead author Cui Chen, MD, of Sun Yat-Sen University Cancer Center in Guangzhou, China, and his colleagues.
“An increasing number of studies and meta‐analyses have investigated the effect of rituximab in PCNSL, indicating that rituximab can robustly enhance the response rate and possibly improve survival,” the investigators wrote in Cancer Medicine. “However, data regarding the addition of rituximab to [methotrexate and temozolomide] for PCNSL are limited, and no study has directly compared the efficacy of [rituximab/high-dose methotrexate/temozolomide] to that of [high-dose methotrexate/temozolomide].”
The study involved 62 patients with untreated PCNSL who were diagnosed between 2005 and 2015. Out of the 62 patients, 32 received rituximab/high-dose methotrexate/temozolomide (RMT) and 30 received high-dose methotrexate/temozolomide (MT). Patients received up to eight cycles of therapy, with discontinuation upon disease progression or toxicity.
The results showed that patients treated with RMT had significantly better outcomes than those who received MT, first marked by objective response rates, which were 93.7% for RMT and 69.0% for MT.
Survival rates also showed the advantage of rituximab. For the RMT group, 2-year and 5-year progression-free survival rates were 81.3% and 53.3%, respectively, compared with 46.5% and 29.1% for patients receiving MT.
Most importantly, rituximab boosted overall survival to a significant and notable extent, with higher rates at 2 years (82.3% vs. 65.7%) and 5 years (82.3% vs. 50.0%).
Efficacy did not diminish safety, as no significant differences in toxicity were found between treatment types. The most common grade 3-4 toxicities were hematologic; most commonly, this entailed neutropenia, which occurred in about one-quarter of patients.
“Given its outstanding efficacy and favorable toxicity, we consider RMT to be a feasible and safe therapeutic approach as a first‐line treatment for PCNSL. Moreover, RMT is an ideal regimen for elderly patients and frail populations who may not tolerate [whole‐brain radiation therapy] or [autologous stem‐cell transplantation],” the researchers wrote.
The study was funded by the Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province. The researchers reported having no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Chen C et al. Cancer Med. 2019 Mar 1. doi: 10.1002/cam4.1906.
For patients with primary central nervous system lymphoma (PCNSL), adding rituximab to combination high-dose methotrexate and temozolomide significantly boosted the 5-year overall survival rate, according to a retrospective study.
The triplet combination could be a safe and effective first-line option for patients with PCNSL, particularly the frail and elderly, who may have issues with toxicity when receiving current standard care, reported lead author Cui Chen, MD, of Sun Yat-Sen University Cancer Center in Guangzhou, China, and his colleagues.
“An increasing number of studies and meta‐analyses have investigated the effect of rituximab in PCNSL, indicating that rituximab can robustly enhance the response rate and possibly improve survival,” the investigators wrote in Cancer Medicine. “However, data regarding the addition of rituximab to [methotrexate and temozolomide] for PCNSL are limited, and no study has directly compared the efficacy of [rituximab/high-dose methotrexate/temozolomide] to that of [high-dose methotrexate/temozolomide].”
The study involved 62 patients with untreated PCNSL who were diagnosed between 2005 and 2015. Out of the 62 patients, 32 received rituximab/high-dose methotrexate/temozolomide (RMT) and 30 received high-dose methotrexate/temozolomide (MT). Patients received up to eight cycles of therapy, with discontinuation upon disease progression or toxicity.
The results showed that patients treated with RMT had significantly better outcomes than those who received MT, first marked by objective response rates, which were 93.7% for RMT and 69.0% for MT.
Survival rates also showed the advantage of rituximab. For the RMT group, 2-year and 5-year progression-free survival rates were 81.3% and 53.3%, respectively, compared with 46.5% and 29.1% for patients receiving MT.
Most importantly, rituximab boosted overall survival to a significant and notable extent, with higher rates at 2 years (82.3% vs. 65.7%) and 5 years (82.3% vs. 50.0%).
Efficacy did not diminish safety, as no significant differences in toxicity were found between treatment types. The most common grade 3-4 toxicities were hematologic; most commonly, this entailed neutropenia, which occurred in about one-quarter of patients.
“Given its outstanding efficacy and favorable toxicity, we consider RMT to be a feasible and safe therapeutic approach as a first‐line treatment for PCNSL. Moreover, RMT is an ideal regimen for elderly patients and frail populations who may not tolerate [whole‐brain radiation therapy] or [autologous stem‐cell transplantation],” the researchers wrote.
The study was funded by the Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province. The researchers reported having no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Chen C et al. Cancer Med. 2019 Mar 1. doi: 10.1002/cam4.1906.
FROM CANCER MEDICINE