User login
Around 5% of US Population Diagnosed With Autoimmune Disease
TOPLINE:
In 2022, autoimmune diseases affected over 15 million individuals in the United States, with women nearly twice as likely to be affected as men and more than one third of affected individuals having more than one autoimmune condition.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers used electronic health record (EHR) data from six healthcare systems in the United States between 2011 and 2022 to estimate the prevalence of autoimmune diseases according to sex and age.
- They selected 105 autoimmune diseases from the textbook The Autoimmune Diseases and estimated their prevalence in more than 10 million individuals from these healthcare systems; these statistics were subsequently extrapolated to an estimated US population of 333.3 million.
- An individual was considered to have a diagnosis of an autoimmune disease if they had at least two diagnosis codes for the condition, with the codes being at least 30 days apart.
- A software program was developed to compute the prevalence of autoimmune diseases alone and in aggregate, enabling other researchers to replicate or modify the analysis over time.
TAKEAWAY:
- More than 15 million people, accounting for 4.6% of the US population, were diagnosed with at least one autoimmune disease from January 2011 to June 2022; 34% were diagnosed with more than one autoimmune disease.
- Sex-stratified analysis revealed that 63% of patients diagnosed with autoimmune disease were women, and only 37% were men, establishing a female-to-male ratio of 1.7:1; age-stratified analysis revealed increasing prevalence of autoimmune conditions with age, peaking in individuals aged ≥ 65 years.
- Among individuals with autoimmune diseases, 65% of patients had one condition, whereas 24% had two, 8% had three, and 2% had four or more autoimmune diseases (does not add to 100% due to rounding).
- Rheumatoid arthritis emerged as the most prevalent autoimmune disease, followed by psoriasis, type 1 diabetes, Grave’s disease, and autoimmune thyroiditis; 19 of the top 20 most prevalent autoimmune diseases occurred more frequently in women.
IN PRACTICE:
“Accurate data on the prevalence of autoimmune diseases as a category of disease and for individual autoimmune diseases are needed to further clinical and basic research to improve diagnosis, biomarkers, and therapies for these diseases, which significantly impact the US population,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Aaron H. Abend, Autoimmune Registry, Guilford, Connecticut, and was published online in The Journal of Clinical Investigation.
LIMITATIONS:
The use of EHR data presented several challenges, including potential inaccuracies in diagnosis codes and the possibility of missing patients with single diagnosis codes because of the two-code requirement. Certain autoimmune diseases evolve over time and involve nonspecific clinical signs and symptoms that can mimic other diseases, potentially resulting in underdiagnosis. Moreover, rare diseases lacking specific diagnosis codes may have been underrepresented.
DISCLOSURES:
The study received support from Autoimmune Registry; the National Institutes of Health National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences; the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute; and other sources. Information on potential conflicts of interest was not disclosed.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including artificial intelligence, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
In 2022, autoimmune diseases affected over 15 million individuals in the United States, with women nearly twice as likely to be affected as men and more than one third of affected individuals having more than one autoimmune condition.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers used electronic health record (EHR) data from six healthcare systems in the United States between 2011 and 2022 to estimate the prevalence of autoimmune diseases according to sex and age.
- They selected 105 autoimmune diseases from the textbook The Autoimmune Diseases and estimated their prevalence in more than 10 million individuals from these healthcare systems; these statistics were subsequently extrapolated to an estimated US population of 333.3 million.
- An individual was considered to have a diagnosis of an autoimmune disease if they had at least two diagnosis codes for the condition, with the codes being at least 30 days apart.
- A software program was developed to compute the prevalence of autoimmune diseases alone and in aggregate, enabling other researchers to replicate or modify the analysis over time.
TAKEAWAY:
- More than 15 million people, accounting for 4.6% of the US population, were diagnosed with at least one autoimmune disease from January 2011 to June 2022; 34% were diagnosed with more than one autoimmune disease.
- Sex-stratified analysis revealed that 63% of patients diagnosed with autoimmune disease were women, and only 37% were men, establishing a female-to-male ratio of 1.7:1; age-stratified analysis revealed increasing prevalence of autoimmune conditions with age, peaking in individuals aged ≥ 65 years.
- Among individuals with autoimmune diseases, 65% of patients had one condition, whereas 24% had two, 8% had three, and 2% had four or more autoimmune diseases (does not add to 100% due to rounding).
- Rheumatoid arthritis emerged as the most prevalent autoimmune disease, followed by psoriasis, type 1 diabetes, Grave’s disease, and autoimmune thyroiditis; 19 of the top 20 most prevalent autoimmune diseases occurred more frequently in women.
IN PRACTICE:
“Accurate data on the prevalence of autoimmune diseases as a category of disease and for individual autoimmune diseases are needed to further clinical and basic research to improve diagnosis, biomarkers, and therapies for these diseases, which significantly impact the US population,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Aaron H. Abend, Autoimmune Registry, Guilford, Connecticut, and was published online in The Journal of Clinical Investigation.
LIMITATIONS:
The use of EHR data presented several challenges, including potential inaccuracies in diagnosis codes and the possibility of missing patients with single diagnosis codes because of the two-code requirement. Certain autoimmune diseases evolve over time and involve nonspecific clinical signs and symptoms that can mimic other diseases, potentially resulting in underdiagnosis. Moreover, rare diseases lacking specific diagnosis codes may have been underrepresented.
DISCLOSURES:
The study received support from Autoimmune Registry; the National Institutes of Health National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences; the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute; and other sources. Information on potential conflicts of interest was not disclosed.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including artificial intelligence, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
In 2022, autoimmune diseases affected over 15 million individuals in the United States, with women nearly twice as likely to be affected as men and more than one third of affected individuals having more than one autoimmune condition.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers used electronic health record (EHR) data from six healthcare systems in the United States between 2011 and 2022 to estimate the prevalence of autoimmune diseases according to sex and age.
- They selected 105 autoimmune diseases from the textbook The Autoimmune Diseases and estimated their prevalence in more than 10 million individuals from these healthcare systems; these statistics were subsequently extrapolated to an estimated US population of 333.3 million.
- An individual was considered to have a diagnosis of an autoimmune disease if they had at least two diagnosis codes for the condition, with the codes being at least 30 days apart.
- A software program was developed to compute the prevalence of autoimmune diseases alone and in aggregate, enabling other researchers to replicate or modify the analysis over time.
TAKEAWAY:
- More than 15 million people, accounting for 4.6% of the US population, were diagnosed with at least one autoimmune disease from January 2011 to June 2022; 34% were diagnosed with more than one autoimmune disease.
- Sex-stratified analysis revealed that 63% of patients diagnosed with autoimmune disease were women, and only 37% were men, establishing a female-to-male ratio of 1.7:1; age-stratified analysis revealed increasing prevalence of autoimmune conditions with age, peaking in individuals aged ≥ 65 years.
- Among individuals with autoimmune diseases, 65% of patients had one condition, whereas 24% had two, 8% had three, and 2% had four or more autoimmune diseases (does not add to 100% due to rounding).
- Rheumatoid arthritis emerged as the most prevalent autoimmune disease, followed by psoriasis, type 1 diabetes, Grave’s disease, and autoimmune thyroiditis; 19 of the top 20 most prevalent autoimmune diseases occurred more frequently in women.
IN PRACTICE:
“Accurate data on the prevalence of autoimmune diseases as a category of disease and for individual autoimmune diseases are needed to further clinical and basic research to improve diagnosis, biomarkers, and therapies for these diseases, which significantly impact the US population,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Aaron H. Abend, Autoimmune Registry, Guilford, Connecticut, and was published online in The Journal of Clinical Investigation.
LIMITATIONS:
The use of EHR data presented several challenges, including potential inaccuracies in diagnosis codes and the possibility of missing patients with single diagnosis codes because of the two-code requirement. Certain autoimmune diseases evolve over time and involve nonspecific clinical signs and symptoms that can mimic other diseases, potentially resulting in underdiagnosis. Moreover, rare diseases lacking specific diagnosis codes may have been underrepresented.
DISCLOSURES:
The study received support from Autoimmune Registry; the National Institutes of Health National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences; the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute; and other sources. Information on potential conflicts of interest was not disclosed.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including artificial intelligence, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Most Kids With COVID-Linked MIS-C Recover by 6 Months
Children who were severely ill with multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children (MIS-C) related to COVID-19 infection appear to show excellent cardiovascular and noncardiovascular outcomes by 6 months, according to data published in JAMA Pediatrics.
MIS-C is a life-threatening complication of COVID-19 infection and data on outcomes are limited, wrote the authors, led by Dongngan T. Truong, MD, MSSI, with Children’s Healthcare of Atlanta Cardiology, Emory University School of Medicine in Atlanta, Georgia. These 6-month results are from the Long-Term Outcomes After the Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in Children (MUSIC) study, sponsored by the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute.
Researchers found in this cohort study of 1204 participants that by 6 months after hospital discharge, 99% had normalization of left ventricular systolic function, and 92.3% had normalized coronary artery dimensions. More than 95% reported being more than 90% back to baseline health.
Patient-Reported Outcomes Measurement Information Systems (PROMIS) Global Health scores were at least equivalent to prepandemic population normative values. PROMIS Global Health parent/guardian proxy median T scores for fatigue, global health, and pain interference improved significantly from 2 weeks to 6 months: fatigue, 56.1 vs 48.9; global health, 48.8 vs 51.3; pain interference, 53.0 vs 43.3 (P < .001).
The most common symptoms reported at 2 weeks were fatigue (15.9%) and low stamina/energy (9.2%); both decreased to 3.4% and 3.3%, respectively, by 6 months. The most common cardiovascular symptom at 2 weeks was palpitations (1.5%), which decreased to 0.6%.
Chest Pain Increased Over Time
Reports of chest pain, however, reportedly increased over time, with 1.3% reporting chest pain at rest at 2 weeks and 2.2% at 6 months. Although gastrointestinal symptoms were common during the acute MIS-C, only 5.3% of respondents reported those symptoms at 2 weeks.
Children in the cohort had a median age of 9 years, and 60% were men. They self-identified with the following races and ethnicities: American Indian or Alaska Native (0.1%), Asian (3.3%), Black (27.0%), Hawaiian Native or Other Pacific Islander (0.2%), Hispanic or Latino (26.9%), multiracial (2.7%), White (31.2%), other (1.0%), and unknown or refused to specify (7.6%). Authors wrote that the cohort was followed-up to 2 years after illness onset and long-term results are not yet known.
Time to Exhale
David J. Goldberg, MD, with the Cardiac Center, Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, and colleagues, wrote in an accompanying editorial that “the decreased frequency of the disease along (with) the reassuring reports on midterm outcomes can allow the pediatric community a moment of collective exhale.”
The editorialists note that of those who initially presented with myocardial dysfunction, all but one patient evaluated had a normal ejection fraction at follow-up. Energy, sleep, appetite, cognition, and mood also normalized by midterm.
“The results of the MUSIC study add to the emerging midterm outcomes data suggesting a near-complete cardiovascular recovery in the overwhelming majority of patients who develop MIS-C,” Goldberg and colleagues wrote. “Despite initial concerns, driven by the severity of acute presentation at diagnosis and longer-term questions that remain (for example, does coronary microvascular dysfunction persist even after normalization of coronary artery z score?), these data suggest an encouraging outlook for the long-term health of affected children.”
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and other agencies have reported a declining overall incidence of MIS-C and highlighted the protective value of vaccination.
The editorialists add, however, that while the drop in MIS-C cases is encouraging, cases are still reported, especially amid high viral activity periods, “and nearly half of affected children continue to require intensive care in the acute phase of illness.”
Truong reported grants from the National Institutes of Health and serving as coprincipal investigator for Pfizer for research on COVID-19 vaccine-associated myocarditis funded by Pfizer and occurring through the framework of the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute’s Pediatric Heart Network outside the submitted work. One coauthor reported grants from Pfizer and Boston Scientific outside the submitted work. One coauthor reported receiving grants from Additional Ventures Foundation outside the submitted work. One coauthor reported receiving consultant fees from Amryt Pharma, Chiesi, Esperion, and Ultragenyx outside the submitted work. A coauthor reported receiving consultant fees from Larimar Therapeutics for mitochondrial therapies outside the submitted work. One coauthor reported being an employee of Takeda Pharmaceuticals since July 2023. One editorialist reported grants from Childhood Arthritis and Rheumatology Research Alliance and the Arthritis Foundation, Academy Health, and the Gordon and Betty Moore Foundation during the conduct of the study.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Children who were severely ill with multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children (MIS-C) related to COVID-19 infection appear to show excellent cardiovascular and noncardiovascular outcomes by 6 months, according to data published in JAMA Pediatrics.
MIS-C is a life-threatening complication of COVID-19 infection and data on outcomes are limited, wrote the authors, led by Dongngan T. Truong, MD, MSSI, with Children’s Healthcare of Atlanta Cardiology, Emory University School of Medicine in Atlanta, Georgia. These 6-month results are from the Long-Term Outcomes After the Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in Children (MUSIC) study, sponsored by the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute.
Researchers found in this cohort study of 1204 participants that by 6 months after hospital discharge, 99% had normalization of left ventricular systolic function, and 92.3% had normalized coronary artery dimensions. More than 95% reported being more than 90% back to baseline health.
Patient-Reported Outcomes Measurement Information Systems (PROMIS) Global Health scores were at least equivalent to prepandemic population normative values. PROMIS Global Health parent/guardian proxy median T scores for fatigue, global health, and pain interference improved significantly from 2 weeks to 6 months: fatigue, 56.1 vs 48.9; global health, 48.8 vs 51.3; pain interference, 53.0 vs 43.3 (P < .001).
The most common symptoms reported at 2 weeks were fatigue (15.9%) and low stamina/energy (9.2%); both decreased to 3.4% and 3.3%, respectively, by 6 months. The most common cardiovascular symptom at 2 weeks was palpitations (1.5%), which decreased to 0.6%.
Chest Pain Increased Over Time
Reports of chest pain, however, reportedly increased over time, with 1.3% reporting chest pain at rest at 2 weeks and 2.2% at 6 months. Although gastrointestinal symptoms were common during the acute MIS-C, only 5.3% of respondents reported those symptoms at 2 weeks.
Children in the cohort had a median age of 9 years, and 60% were men. They self-identified with the following races and ethnicities: American Indian or Alaska Native (0.1%), Asian (3.3%), Black (27.0%), Hawaiian Native or Other Pacific Islander (0.2%), Hispanic or Latino (26.9%), multiracial (2.7%), White (31.2%), other (1.0%), and unknown or refused to specify (7.6%). Authors wrote that the cohort was followed-up to 2 years after illness onset and long-term results are not yet known.
Time to Exhale
David J. Goldberg, MD, with the Cardiac Center, Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, and colleagues, wrote in an accompanying editorial that “the decreased frequency of the disease along (with) the reassuring reports on midterm outcomes can allow the pediatric community a moment of collective exhale.”
The editorialists note that of those who initially presented with myocardial dysfunction, all but one patient evaluated had a normal ejection fraction at follow-up. Energy, sleep, appetite, cognition, and mood also normalized by midterm.
“The results of the MUSIC study add to the emerging midterm outcomes data suggesting a near-complete cardiovascular recovery in the overwhelming majority of patients who develop MIS-C,” Goldberg and colleagues wrote. “Despite initial concerns, driven by the severity of acute presentation at diagnosis and longer-term questions that remain (for example, does coronary microvascular dysfunction persist even after normalization of coronary artery z score?), these data suggest an encouraging outlook for the long-term health of affected children.”
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and other agencies have reported a declining overall incidence of MIS-C and highlighted the protective value of vaccination.
The editorialists add, however, that while the drop in MIS-C cases is encouraging, cases are still reported, especially amid high viral activity periods, “and nearly half of affected children continue to require intensive care in the acute phase of illness.”
Truong reported grants from the National Institutes of Health and serving as coprincipal investigator for Pfizer for research on COVID-19 vaccine-associated myocarditis funded by Pfizer and occurring through the framework of the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute’s Pediatric Heart Network outside the submitted work. One coauthor reported grants from Pfizer and Boston Scientific outside the submitted work. One coauthor reported receiving grants from Additional Ventures Foundation outside the submitted work. One coauthor reported receiving consultant fees from Amryt Pharma, Chiesi, Esperion, and Ultragenyx outside the submitted work. A coauthor reported receiving consultant fees from Larimar Therapeutics for mitochondrial therapies outside the submitted work. One coauthor reported being an employee of Takeda Pharmaceuticals since July 2023. One editorialist reported grants from Childhood Arthritis and Rheumatology Research Alliance and the Arthritis Foundation, Academy Health, and the Gordon and Betty Moore Foundation during the conduct of the study.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Children who were severely ill with multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children (MIS-C) related to COVID-19 infection appear to show excellent cardiovascular and noncardiovascular outcomes by 6 months, according to data published in JAMA Pediatrics.
MIS-C is a life-threatening complication of COVID-19 infection and data on outcomes are limited, wrote the authors, led by Dongngan T. Truong, MD, MSSI, with Children’s Healthcare of Atlanta Cardiology, Emory University School of Medicine in Atlanta, Georgia. These 6-month results are from the Long-Term Outcomes After the Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in Children (MUSIC) study, sponsored by the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute.
Researchers found in this cohort study of 1204 participants that by 6 months after hospital discharge, 99% had normalization of left ventricular systolic function, and 92.3% had normalized coronary artery dimensions. More than 95% reported being more than 90% back to baseline health.
Patient-Reported Outcomes Measurement Information Systems (PROMIS) Global Health scores were at least equivalent to prepandemic population normative values. PROMIS Global Health parent/guardian proxy median T scores for fatigue, global health, and pain interference improved significantly from 2 weeks to 6 months: fatigue, 56.1 vs 48.9; global health, 48.8 vs 51.3; pain interference, 53.0 vs 43.3 (P < .001).
The most common symptoms reported at 2 weeks were fatigue (15.9%) and low stamina/energy (9.2%); both decreased to 3.4% and 3.3%, respectively, by 6 months. The most common cardiovascular symptom at 2 weeks was palpitations (1.5%), which decreased to 0.6%.
Chest Pain Increased Over Time
Reports of chest pain, however, reportedly increased over time, with 1.3% reporting chest pain at rest at 2 weeks and 2.2% at 6 months. Although gastrointestinal symptoms were common during the acute MIS-C, only 5.3% of respondents reported those symptoms at 2 weeks.
Children in the cohort had a median age of 9 years, and 60% were men. They self-identified with the following races and ethnicities: American Indian or Alaska Native (0.1%), Asian (3.3%), Black (27.0%), Hawaiian Native or Other Pacific Islander (0.2%), Hispanic or Latino (26.9%), multiracial (2.7%), White (31.2%), other (1.0%), and unknown or refused to specify (7.6%). Authors wrote that the cohort was followed-up to 2 years after illness onset and long-term results are not yet known.
Time to Exhale
David J. Goldberg, MD, with the Cardiac Center, Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, and colleagues, wrote in an accompanying editorial that “the decreased frequency of the disease along (with) the reassuring reports on midterm outcomes can allow the pediatric community a moment of collective exhale.”
The editorialists note that of those who initially presented with myocardial dysfunction, all but one patient evaluated had a normal ejection fraction at follow-up. Energy, sleep, appetite, cognition, and mood also normalized by midterm.
“The results of the MUSIC study add to the emerging midterm outcomes data suggesting a near-complete cardiovascular recovery in the overwhelming majority of patients who develop MIS-C,” Goldberg and colleagues wrote. “Despite initial concerns, driven by the severity of acute presentation at diagnosis and longer-term questions that remain (for example, does coronary microvascular dysfunction persist even after normalization of coronary artery z score?), these data suggest an encouraging outlook for the long-term health of affected children.”
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and other agencies have reported a declining overall incidence of MIS-C and highlighted the protective value of vaccination.
The editorialists add, however, that while the drop in MIS-C cases is encouraging, cases are still reported, especially amid high viral activity periods, “and nearly half of affected children continue to require intensive care in the acute phase of illness.”
Truong reported grants from the National Institutes of Health and serving as coprincipal investigator for Pfizer for research on COVID-19 vaccine-associated myocarditis funded by Pfizer and occurring through the framework of the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute’s Pediatric Heart Network outside the submitted work. One coauthor reported grants from Pfizer and Boston Scientific outside the submitted work. One coauthor reported receiving grants from Additional Ventures Foundation outside the submitted work. One coauthor reported receiving consultant fees from Amryt Pharma, Chiesi, Esperion, and Ultragenyx outside the submitted work. A coauthor reported receiving consultant fees from Larimar Therapeutics for mitochondrial therapies outside the submitted work. One coauthor reported being an employee of Takeda Pharmaceuticals since July 2023. One editorialist reported grants from Childhood Arthritis and Rheumatology Research Alliance and the Arthritis Foundation, Academy Health, and the Gordon and Betty Moore Foundation during the conduct of the study.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM JAMA PEDIATRICS
Alpha-Gal Syndrome: 5 Things to Know
Alpha-gal syndrome (AGS), a tickborne disease commonly called “red meat allergy,” is a serious, potentially life-threatening allergy to the carbohydrate alpha-gal. The alpha-gal carbohydrate is found in most mammals, though it is not in humans, apes, or old-world monkeys. People with AGS can have allergic reactions when they consume mammalian meat, dairy products, or other products derived from mammals. People often live with this disease for years before receiving a correct diagnosis, greatly impacting their quality of life. The number of suspected cases is also rising.
More than 110,000 suspected AGS cases were identified between 2010 and 2022, according to a Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) report.1 However, because the diagnosis requires a positive test and a clinical exam and some people may not get tested, as many as 450,000 people might be affected by AGS in the United States. Additionally, a CDC survey found that nearly half (42%) of US healthcare providers had never heard of AGS.2 Among those who had, less than one third (29%) knew how to diagnose the condition.
Here are 5 things clinicians need to know about AGS.
1. People can develop AGS after being bitten by a tick, primarily the lone star tick (Amblyomma americanum), in the United States.
In the United States, AGS is primarily associated with the bite of a lone star tick, but other kinds of ticks have not been ruled out. The majority of suspected AGS cases in the United States were reported in parts of Arkansas, Delaware, Illinois, Indiana, Kansas, Kentucky, Maryland, Mississippi, Missouri, North Carolina, Oklahoma, Tennessee, and Virginia. The lone star tick is widely distributed with established populations in Alabama, Arkansas, Connecticut, Delaware, Florida, Georgia, Illinois, Indiana, Iowa, Kansas, Kentucky, Louisiana, Michigan, Minnesota, Mississippi, Missouri, Nebraska, New Hampshire, New Jersey, New York, North Carolina, Ohio, Oklahoma, Pennsylvania, South Carolina, Tennessee, Texas, Virginia, and West Virginia.
While AGS is associated with tick bites, more research is needed to understand the role ticks play in starting this condition, and why certain people develop AGS. Anyone can develop AGS, but most cases have been reported in adults.
Know how to recognize the symptoms of AGS and be prepared to test, diagnose, and manage AGS, particularly in states where lone star ticks are found.
2. Tick bites are only one risk factor for developing AGS.
Many people are bitten by lone star ticks and will never develop AGS. Scientists are exploring the connection between other risk factors and developing AGS. A recent study has shown that people diagnosed with AGS may be more likely to have a family member who was also diagnosed with AGS, have another food allergy, have an allergy to stinging or biting insects, or have A or O blood types.3
Research has also shown that environmental risk factors could contribute to developing AGS,4 like living in an area with lone star ticks, remembering finding a tick on themselves, recalling multiple tick bites, living near a wooded forest, spending more time outside, or living in areas with deer, such as larger properties, wooded forests, and properties with shrubs and brush.
Ask your patient questions about other allergies and history of recent tick bites or outdoor exposure to help determine if testing for AGS is appropriate.
3. Symptoms of AGS are consistently inconsistent.
There is a spectrum of how sensitive AGS patients are to alpha-gal, and reactions are often different from person to person, which can make it difficult to diagnose. The first allergic reaction to AGS typically occurs between 1-6 months after a tick bite. Symptoms commonly appear 2-6 hours after being in contact with products containing alpha-gal, like red meat (beef, pork, lamb, venison, rabbit, or other meat from mammals), dairy, and some medications. Symptoms can range from mild to severe and include hives or itchy rash; swelling of the lips, throat, tongue, or eyelids; gastrointestinal symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, or diarrhea; heartburn or indigestion; cough, shortness of breath, or difficulty breathing; dizziness or a drop in blood pressure; or anaphylaxis.
Consider AGS if a patient reports waking up in the middle of the night with allergic symptoms after eating alpha-gal containing products for dinner, if allergic reactions are delayed, or if a patient has anaphylaxis of unknown cause, adult-onset allergy, or allergic symptoms and reports a recent tick bite.
4. Diagnosing AGS requires a combination of a blood test and a physical exam.
Diagnosing AGS requires a detailed patient history, physical exam, and a blood test to detect specific immunoglobulin E (IgE) antibodies specific to alpha-gal (alpha-gal sIgE). Tests for alpha-gal sIgE antibodies are available at several large commercial laboratories and some academic institutions. Skin tests to identify reactions to allergens like pork or beef may also be used to inform AGS diagnosis. However, a positive alpha-gal sIgE test or skin test does not mean a person has AGS. Many people, particularly those who live in regions with lone star ticks, have positive alpha-gal specific IgE tests without having AGS.
Consider the test results along with your patient’s symptoms and risk factors.
5. There is no treatment for AGS, but people can take prevention steps and AGS can be managed.
People can protect themselves and their family from AGS by preventing tick bites. Encourage your patients to use an Environmental Protection Agency–registered insect repellent outdoors, wear permethrin-treated clothing, and conduct thorough tick checks after outdoor activities.
Once a person is no longer exposed to alpha-gal containing products, they should no longer experience symptoms. People with AGS should also proactively prevent tick bites. Tick bites can trigger or reactivate AGS.
For patients who have AGS, help manage their symptoms and identify alpha-gal containing products to avoid.
Dr. Kersh is Chief of the Rickettsial Zoonoses Branch, Division of Vector-Borne Diseases, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Atlanta, Georgia, and disclosed no relevant conflicts of interest.
CDC resources:
About Alpha-gal Syndrome | Alpha-gal Syndrome | CDC
Clinical Testing and Diagnosis for Alpha-gal Syndrome | Alpha-gal Syndrome | CDC
Clinical Resources | Alpha-gal Syndrome | CDC
References
Thompson JM et al. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2023;72:815-820.
Carpenter A et al. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2023;72:809-814. Taylor ML et al. Ann Allergy, Asthma & Immunol. 2024 Jun;132(6):759.e2-764.e2. Kersh GJ et al. Ann Allergy, Asthma & Immunol. 2023 Apr;130(4):472-478.
Alpha-gal syndrome (AGS), a tickborne disease commonly called “red meat allergy,” is a serious, potentially life-threatening allergy to the carbohydrate alpha-gal. The alpha-gal carbohydrate is found in most mammals, though it is not in humans, apes, or old-world monkeys. People with AGS can have allergic reactions when they consume mammalian meat, dairy products, or other products derived from mammals. People often live with this disease for years before receiving a correct diagnosis, greatly impacting their quality of life. The number of suspected cases is also rising.
More than 110,000 suspected AGS cases were identified between 2010 and 2022, according to a Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) report.1 However, because the diagnosis requires a positive test and a clinical exam and some people may not get tested, as many as 450,000 people might be affected by AGS in the United States. Additionally, a CDC survey found that nearly half (42%) of US healthcare providers had never heard of AGS.2 Among those who had, less than one third (29%) knew how to diagnose the condition.
Here are 5 things clinicians need to know about AGS.
1. People can develop AGS after being bitten by a tick, primarily the lone star tick (Amblyomma americanum), in the United States.
In the United States, AGS is primarily associated with the bite of a lone star tick, but other kinds of ticks have not been ruled out. The majority of suspected AGS cases in the United States were reported in parts of Arkansas, Delaware, Illinois, Indiana, Kansas, Kentucky, Maryland, Mississippi, Missouri, North Carolina, Oklahoma, Tennessee, and Virginia. The lone star tick is widely distributed with established populations in Alabama, Arkansas, Connecticut, Delaware, Florida, Georgia, Illinois, Indiana, Iowa, Kansas, Kentucky, Louisiana, Michigan, Minnesota, Mississippi, Missouri, Nebraska, New Hampshire, New Jersey, New York, North Carolina, Ohio, Oklahoma, Pennsylvania, South Carolina, Tennessee, Texas, Virginia, and West Virginia.
While AGS is associated with tick bites, more research is needed to understand the role ticks play in starting this condition, and why certain people develop AGS. Anyone can develop AGS, but most cases have been reported in adults.
Know how to recognize the symptoms of AGS and be prepared to test, diagnose, and manage AGS, particularly in states where lone star ticks are found.
2. Tick bites are only one risk factor for developing AGS.
Many people are bitten by lone star ticks and will never develop AGS. Scientists are exploring the connection between other risk factors and developing AGS. A recent study has shown that people diagnosed with AGS may be more likely to have a family member who was also diagnosed with AGS, have another food allergy, have an allergy to stinging or biting insects, or have A or O blood types.3
Research has also shown that environmental risk factors could contribute to developing AGS,4 like living in an area with lone star ticks, remembering finding a tick on themselves, recalling multiple tick bites, living near a wooded forest, spending more time outside, or living in areas with deer, such as larger properties, wooded forests, and properties with shrubs and brush.
Ask your patient questions about other allergies and history of recent tick bites or outdoor exposure to help determine if testing for AGS is appropriate.
3. Symptoms of AGS are consistently inconsistent.
There is a spectrum of how sensitive AGS patients are to alpha-gal, and reactions are often different from person to person, which can make it difficult to diagnose. The first allergic reaction to AGS typically occurs between 1-6 months after a tick bite. Symptoms commonly appear 2-6 hours after being in contact with products containing alpha-gal, like red meat (beef, pork, lamb, venison, rabbit, or other meat from mammals), dairy, and some medications. Symptoms can range from mild to severe and include hives or itchy rash; swelling of the lips, throat, tongue, or eyelids; gastrointestinal symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, or diarrhea; heartburn or indigestion; cough, shortness of breath, or difficulty breathing; dizziness or a drop in blood pressure; or anaphylaxis.
Consider AGS if a patient reports waking up in the middle of the night with allergic symptoms after eating alpha-gal containing products for dinner, if allergic reactions are delayed, or if a patient has anaphylaxis of unknown cause, adult-onset allergy, or allergic symptoms and reports a recent tick bite.
4. Diagnosing AGS requires a combination of a blood test and a physical exam.
Diagnosing AGS requires a detailed patient history, physical exam, and a blood test to detect specific immunoglobulin E (IgE) antibodies specific to alpha-gal (alpha-gal sIgE). Tests for alpha-gal sIgE antibodies are available at several large commercial laboratories and some academic institutions. Skin tests to identify reactions to allergens like pork or beef may also be used to inform AGS diagnosis. However, a positive alpha-gal sIgE test or skin test does not mean a person has AGS. Many people, particularly those who live in regions with lone star ticks, have positive alpha-gal specific IgE tests without having AGS.
Consider the test results along with your patient’s symptoms and risk factors.
5. There is no treatment for AGS, but people can take prevention steps and AGS can be managed.
People can protect themselves and their family from AGS by preventing tick bites. Encourage your patients to use an Environmental Protection Agency–registered insect repellent outdoors, wear permethrin-treated clothing, and conduct thorough tick checks after outdoor activities.
Once a person is no longer exposed to alpha-gal containing products, they should no longer experience symptoms. People with AGS should also proactively prevent tick bites. Tick bites can trigger or reactivate AGS.
For patients who have AGS, help manage their symptoms and identify alpha-gal containing products to avoid.
Dr. Kersh is Chief of the Rickettsial Zoonoses Branch, Division of Vector-Borne Diseases, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Atlanta, Georgia, and disclosed no relevant conflicts of interest.
CDC resources:
About Alpha-gal Syndrome | Alpha-gal Syndrome | CDC
Clinical Testing and Diagnosis for Alpha-gal Syndrome | Alpha-gal Syndrome | CDC
Clinical Resources | Alpha-gal Syndrome | CDC
References
Thompson JM et al. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2023;72:815-820.
Carpenter A et al. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2023;72:809-814. Taylor ML et al. Ann Allergy, Asthma & Immunol. 2024 Jun;132(6):759.e2-764.e2. Kersh GJ et al. Ann Allergy, Asthma & Immunol. 2023 Apr;130(4):472-478.
Alpha-gal syndrome (AGS), a tickborne disease commonly called “red meat allergy,” is a serious, potentially life-threatening allergy to the carbohydrate alpha-gal. The alpha-gal carbohydrate is found in most mammals, though it is not in humans, apes, or old-world monkeys. People with AGS can have allergic reactions when they consume mammalian meat, dairy products, or other products derived from mammals. People often live with this disease for years before receiving a correct diagnosis, greatly impacting their quality of life. The number of suspected cases is also rising.
More than 110,000 suspected AGS cases were identified between 2010 and 2022, according to a Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) report.1 However, because the diagnosis requires a positive test and a clinical exam and some people may not get tested, as many as 450,000 people might be affected by AGS in the United States. Additionally, a CDC survey found that nearly half (42%) of US healthcare providers had never heard of AGS.2 Among those who had, less than one third (29%) knew how to diagnose the condition.
Here are 5 things clinicians need to know about AGS.
1. People can develop AGS after being bitten by a tick, primarily the lone star tick (Amblyomma americanum), in the United States.
In the United States, AGS is primarily associated with the bite of a lone star tick, but other kinds of ticks have not been ruled out. The majority of suspected AGS cases in the United States were reported in parts of Arkansas, Delaware, Illinois, Indiana, Kansas, Kentucky, Maryland, Mississippi, Missouri, North Carolina, Oklahoma, Tennessee, and Virginia. The lone star tick is widely distributed with established populations in Alabama, Arkansas, Connecticut, Delaware, Florida, Georgia, Illinois, Indiana, Iowa, Kansas, Kentucky, Louisiana, Michigan, Minnesota, Mississippi, Missouri, Nebraska, New Hampshire, New Jersey, New York, North Carolina, Ohio, Oklahoma, Pennsylvania, South Carolina, Tennessee, Texas, Virginia, and West Virginia.
While AGS is associated with tick bites, more research is needed to understand the role ticks play in starting this condition, and why certain people develop AGS. Anyone can develop AGS, but most cases have been reported in adults.
Know how to recognize the symptoms of AGS and be prepared to test, diagnose, and manage AGS, particularly in states where lone star ticks are found.
2. Tick bites are only one risk factor for developing AGS.
Many people are bitten by lone star ticks and will never develop AGS. Scientists are exploring the connection between other risk factors and developing AGS. A recent study has shown that people diagnosed with AGS may be more likely to have a family member who was also diagnosed with AGS, have another food allergy, have an allergy to stinging or biting insects, or have A or O blood types.3
Research has also shown that environmental risk factors could contribute to developing AGS,4 like living in an area with lone star ticks, remembering finding a tick on themselves, recalling multiple tick bites, living near a wooded forest, spending more time outside, or living in areas with deer, such as larger properties, wooded forests, and properties with shrubs and brush.
Ask your patient questions about other allergies and history of recent tick bites or outdoor exposure to help determine if testing for AGS is appropriate.
3. Symptoms of AGS are consistently inconsistent.
There is a spectrum of how sensitive AGS patients are to alpha-gal, and reactions are often different from person to person, which can make it difficult to diagnose. The first allergic reaction to AGS typically occurs between 1-6 months after a tick bite. Symptoms commonly appear 2-6 hours after being in contact with products containing alpha-gal, like red meat (beef, pork, lamb, venison, rabbit, or other meat from mammals), dairy, and some medications. Symptoms can range from mild to severe and include hives or itchy rash; swelling of the lips, throat, tongue, or eyelids; gastrointestinal symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, or diarrhea; heartburn or indigestion; cough, shortness of breath, or difficulty breathing; dizziness or a drop in blood pressure; or anaphylaxis.
Consider AGS if a patient reports waking up in the middle of the night with allergic symptoms after eating alpha-gal containing products for dinner, if allergic reactions are delayed, or if a patient has anaphylaxis of unknown cause, adult-onset allergy, or allergic symptoms and reports a recent tick bite.
4. Diagnosing AGS requires a combination of a blood test and a physical exam.
Diagnosing AGS requires a detailed patient history, physical exam, and a blood test to detect specific immunoglobulin E (IgE) antibodies specific to alpha-gal (alpha-gal sIgE). Tests for alpha-gal sIgE antibodies are available at several large commercial laboratories and some academic institutions. Skin tests to identify reactions to allergens like pork or beef may also be used to inform AGS diagnosis. However, a positive alpha-gal sIgE test or skin test does not mean a person has AGS. Many people, particularly those who live in regions with lone star ticks, have positive alpha-gal specific IgE tests without having AGS.
Consider the test results along with your patient’s symptoms and risk factors.
5. There is no treatment for AGS, but people can take prevention steps and AGS can be managed.
People can protect themselves and their family from AGS by preventing tick bites. Encourage your patients to use an Environmental Protection Agency–registered insect repellent outdoors, wear permethrin-treated clothing, and conduct thorough tick checks after outdoor activities.
Once a person is no longer exposed to alpha-gal containing products, they should no longer experience symptoms. People with AGS should also proactively prevent tick bites. Tick bites can trigger or reactivate AGS.
For patients who have AGS, help manage their symptoms and identify alpha-gal containing products to avoid.
Dr. Kersh is Chief of the Rickettsial Zoonoses Branch, Division of Vector-Borne Diseases, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Atlanta, Georgia, and disclosed no relevant conflicts of interest.
CDC resources:
About Alpha-gal Syndrome | Alpha-gal Syndrome | CDC
Clinical Testing and Diagnosis for Alpha-gal Syndrome | Alpha-gal Syndrome | CDC
Clinical Resources | Alpha-gal Syndrome | CDC
References
Thompson JM et al. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2023;72:815-820.
Carpenter A et al. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2023;72:809-814. Taylor ML et al. Ann Allergy, Asthma & Immunol. 2024 Jun;132(6):759.e2-764.e2. Kersh GJ et al. Ann Allergy, Asthma & Immunol. 2023 Apr;130(4):472-478.
Health Impacts of Micro- and Nanoplastics
In preparation for a future international treaty aimed at reducing plastic pollution, the French Parliamentary Office for the Evaluation of Scientific and Technological Choices presented the conclusions of a public hearing on the impact of plastics on various aspects of human health.
Increased Global Plastic Production
Philippe Bolo, a member of the French Democratic Party and the rapporteur for the public mission on the health impacts of plastics, spoke about the latest round of treaty negotiations, held from November 25 to December 1 in South Korea, attended by leading French and global experts about the impact of plastics on human health.
The hearing highlighted a sharp increase in plastic production. “It has doubled in the last 20 years and is expected to exceed 500 million tons in 2024,” Bolo said. This is about 60 kg per person. According to projections from the Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development, on its current trajectory, plastic production will reach 750 million tons by 2040 and surpass 1 billion tons before 2050, he said.
Minimal Plastic Waste Recycling
Around one third (32%) of plastics are used for packaging. “Therefore, most plastic production is still intended for single-use purposes,” he said. Plastic waste follows a similar growth trajectory, with volumes expected to rise from 360 million tons in 2020 to 617 million tons by 2040 unless action is taken. Very little of this waste is recycled, even in the most countries that are most advanced in terms of collection, sorting, and processing.
In France, for example, in 2018, only 0.6 million tons of the 3.6 million tons of plastic waste produced was truly recycled. This is less than one fifth (17%). Globally, less than 10% of plastic waste is recycled. In 2020, plastic waste that ended up in the environment represented 81 million tons, or 22% of the total. “Beyond waste, this leads to pollution by microplastics and nanoplastics, resulting from their fragmentation. All environments are affected: Seas, rivers, soils, air, and even living organisms,” Bolo said.
Methodological Challenges
However, measuring the impact of plastics on health faces methodological difficulties due to the wide variety of composition, size, and shape of plastics. Nevertheless, the French Standardization Association (Association Française de Normalisation) has conducted work to establish a characterization standard for microplastics in water, which serves as an international reference.
“It is also very difficult to know what we are ingesting,” Bolo said. “A study conducted in 2019 estimated that the average human absorbs 5 grams of plastics per week, the equivalent of a credit card.» Since then, other studies have revised this estimate downward, but no consensus has been reached.
A recent study across 109 countries, both industrialized and developing, found significant exposure, estimated at 500 mg/d, particularly in Southeast Asian countries, where it was due mainly to seafood consumption.
A study concluded that plastic water bottles contain 240,000 particles per liter, 90% of which are nanoplastics. These nanoparticles can pass through the intestinal barrier to enter the bloodstream and reach several organs including the heart, brain, and placenta, as well as the fetus.
Changes to the Microbiome
Microplastics also accumulate in organs. Thus, the amount of plastic in the lungs increases with age, suggesting that particles may persist in the body without being eliminated. The health consequences of this are still poorly understood, but exposure to plastics appears to cause changes in the composition of the intestinal microbiota. Pathobionts (commensal bacteria with harmful potential) have been found in both adults and children, which could contribute to dysbiosis of the gut microbiome. Furthermore, a decrease in butyrate, a short-chain fatty acid beneficial to health, has been observed in children’s intestines.
Inhaled nanoplastics may disrupt the mucociliary clearance mechanisms of the respiratory system. The toxicity of inhaled plastic particles was demonstrated as early as the 1970s among workers in the flocking industry. Some developed lung function impairments, shortness of breath, inflammation, fibrosis, and even lung cancer. Similar symptoms have been observed in workers in the textile and polyvinyl chloride industries.
A study published recently in The New England Journal of Medicine measured the amount of microplastics collected from carotid plaque of more than 300 patients who had undergone carotid endarterectomy for asymptomatic carotid artery disease. It found a 4.53 times higher risk for the primary endpoint, a composite of myocardial infarction, stroke, and all-cause mortality, among individuals with microplastics and nanoplastics in plaque compared with those without.
Health Affects High
The danger of plastics is also directly linked to the chemical substances they contain. A general scientific review looked at the health impacts of three chemicals used almost exclusively in plastics: Polybromodiphenyl ethers (PBDEs), used as flame retardants in textiles or electronics; bisphenol A (BPA), used in the lining of cans and bottles; and phthalates, particularly diethylhexyl phthalate (DEHP), used to make plastics more flexible.
The review highlighted strong epidemiological evidence linking fetal exposure to PBDEs during pregnancy to low birth weight and later exposure to delayed or impaired cognitive development in children and even a loss of IQ. Statistically significant evidence of disruption of thyroid function in adults was also found.
BPA is linked to genital malformations in female newborns exposed to BPA in utero, type 2 diabetes in adults, insulin resistance, and polycystic ovary syndrome in women. BPA exposure also increases the risk for obesity and hypertension in both children and adults, as well as the risk for cardiovascular disease in adults.
Finally, the review established links between exposure to DEHP and miscarriages, genital malformations in male newborns, delayed or impaired cognitive development in children, loss of IQ, delayed psychomotor development, early puberty in young girls, and endometriosis in young women. DEHP exposure also has multiple effects on cardiometabolic health, including insulin resistance, obesity, and elevated blood pressure.
The economic costs associated with the health impacts of these three substances have been estimated at $675 billion in the United States.
Bolo said that the solution to this plastic pollution is necessarily international. “We need an ambitious and legally binding treaty to reduce plastic production,” he said. “The damage is already done; we need to act to protect human health,” he concluded. The parliamentary office has made nine recommendations to the treaty negotiators.
This story was translated from Medscape’s French edition using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
In preparation for a future international treaty aimed at reducing plastic pollution, the French Parliamentary Office for the Evaluation of Scientific and Technological Choices presented the conclusions of a public hearing on the impact of plastics on various aspects of human health.
Increased Global Plastic Production
Philippe Bolo, a member of the French Democratic Party and the rapporteur for the public mission on the health impacts of plastics, spoke about the latest round of treaty negotiations, held from November 25 to December 1 in South Korea, attended by leading French and global experts about the impact of plastics on human health.
The hearing highlighted a sharp increase in plastic production. “It has doubled in the last 20 years and is expected to exceed 500 million tons in 2024,” Bolo said. This is about 60 kg per person. According to projections from the Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development, on its current trajectory, plastic production will reach 750 million tons by 2040 and surpass 1 billion tons before 2050, he said.
Minimal Plastic Waste Recycling
Around one third (32%) of plastics are used for packaging. “Therefore, most plastic production is still intended for single-use purposes,” he said. Plastic waste follows a similar growth trajectory, with volumes expected to rise from 360 million tons in 2020 to 617 million tons by 2040 unless action is taken. Very little of this waste is recycled, even in the most countries that are most advanced in terms of collection, sorting, and processing.
In France, for example, in 2018, only 0.6 million tons of the 3.6 million tons of plastic waste produced was truly recycled. This is less than one fifth (17%). Globally, less than 10% of plastic waste is recycled. In 2020, plastic waste that ended up in the environment represented 81 million tons, or 22% of the total. “Beyond waste, this leads to pollution by microplastics and nanoplastics, resulting from their fragmentation. All environments are affected: Seas, rivers, soils, air, and even living organisms,” Bolo said.
Methodological Challenges
However, measuring the impact of plastics on health faces methodological difficulties due to the wide variety of composition, size, and shape of plastics. Nevertheless, the French Standardization Association (Association Française de Normalisation) has conducted work to establish a characterization standard for microplastics in water, which serves as an international reference.
“It is also very difficult to know what we are ingesting,” Bolo said. “A study conducted in 2019 estimated that the average human absorbs 5 grams of plastics per week, the equivalent of a credit card.» Since then, other studies have revised this estimate downward, but no consensus has been reached.
A recent study across 109 countries, both industrialized and developing, found significant exposure, estimated at 500 mg/d, particularly in Southeast Asian countries, where it was due mainly to seafood consumption.
A study concluded that plastic water bottles contain 240,000 particles per liter, 90% of which are nanoplastics. These nanoparticles can pass through the intestinal barrier to enter the bloodstream and reach several organs including the heart, brain, and placenta, as well as the fetus.
Changes to the Microbiome
Microplastics also accumulate in organs. Thus, the amount of plastic in the lungs increases with age, suggesting that particles may persist in the body without being eliminated. The health consequences of this are still poorly understood, but exposure to plastics appears to cause changes in the composition of the intestinal microbiota. Pathobionts (commensal bacteria with harmful potential) have been found in both adults and children, which could contribute to dysbiosis of the gut microbiome. Furthermore, a decrease in butyrate, a short-chain fatty acid beneficial to health, has been observed in children’s intestines.
Inhaled nanoplastics may disrupt the mucociliary clearance mechanisms of the respiratory system. The toxicity of inhaled plastic particles was demonstrated as early as the 1970s among workers in the flocking industry. Some developed lung function impairments, shortness of breath, inflammation, fibrosis, and even lung cancer. Similar symptoms have been observed in workers in the textile and polyvinyl chloride industries.
A study published recently in The New England Journal of Medicine measured the amount of microplastics collected from carotid plaque of more than 300 patients who had undergone carotid endarterectomy for asymptomatic carotid artery disease. It found a 4.53 times higher risk for the primary endpoint, a composite of myocardial infarction, stroke, and all-cause mortality, among individuals with microplastics and nanoplastics in plaque compared with those without.
Health Affects High
The danger of plastics is also directly linked to the chemical substances they contain. A general scientific review looked at the health impacts of three chemicals used almost exclusively in plastics: Polybromodiphenyl ethers (PBDEs), used as flame retardants in textiles or electronics; bisphenol A (BPA), used in the lining of cans and bottles; and phthalates, particularly diethylhexyl phthalate (DEHP), used to make plastics more flexible.
The review highlighted strong epidemiological evidence linking fetal exposure to PBDEs during pregnancy to low birth weight and later exposure to delayed or impaired cognitive development in children and even a loss of IQ. Statistically significant evidence of disruption of thyroid function in adults was also found.
BPA is linked to genital malformations in female newborns exposed to BPA in utero, type 2 diabetes in adults, insulin resistance, and polycystic ovary syndrome in women. BPA exposure also increases the risk for obesity and hypertension in both children and adults, as well as the risk for cardiovascular disease in adults.
Finally, the review established links between exposure to DEHP and miscarriages, genital malformations in male newborns, delayed or impaired cognitive development in children, loss of IQ, delayed psychomotor development, early puberty in young girls, and endometriosis in young women. DEHP exposure also has multiple effects on cardiometabolic health, including insulin resistance, obesity, and elevated blood pressure.
The economic costs associated with the health impacts of these three substances have been estimated at $675 billion in the United States.
Bolo said that the solution to this plastic pollution is necessarily international. “We need an ambitious and legally binding treaty to reduce plastic production,” he said. “The damage is already done; we need to act to protect human health,” he concluded. The parliamentary office has made nine recommendations to the treaty negotiators.
This story was translated from Medscape’s French edition using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
In preparation for a future international treaty aimed at reducing plastic pollution, the French Parliamentary Office for the Evaluation of Scientific and Technological Choices presented the conclusions of a public hearing on the impact of plastics on various aspects of human health.
Increased Global Plastic Production
Philippe Bolo, a member of the French Democratic Party and the rapporteur for the public mission on the health impacts of plastics, spoke about the latest round of treaty negotiations, held from November 25 to December 1 in South Korea, attended by leading French and global experts about the impact of plastics on human health.
The hearing highlighted a sharp increase in plastic production. “It has doubled in the last 20 years and is expected to exceed 500 million tons in 2024,” Bolo said. This is about 60 kg per person. According to projections from the Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development, on its current trajectory, plastic production will reach 750 million tons by 2040 and surpass 1 billion tons before 2050, he said.
Minimal Plastic Waste Recycling
Around one third (32%) of plastics are used for packaging. “Therefore, most plastic production is still intended for single-use purposes,” he said. Plastic waste follows a similar growth trajectory, with volumes expected to rise from 360 million tons in 2020 to 617 million tons by 2040 unless action is taken. Very little of this waste is recycled, even in the most countries that are most advanced in terms of collection, sorting, and processing.
In France, for example, in 2018, only 0.6 million tons of the 3.6 million tons of plastic waste produced was truly recycled. This is less than one fifth (17%). Globally, less than 10% of plastic waste is recycled. In 2020, plastic waste that ended up in the environment represented 81 million tons, or 22% of the total. “Beyond waste, this leads to pollution by microplastics and nanoplastics, resulting from their fragmentation. All environments are affected: Seas, rivers, soils, air, and even living organisms,” Bolo said.
Methodological Challenges
However, measuring the impact of plastics on health faces methodological difficulties due to the wide variety of composition, size, and shape of plastics. Nevertheless, the French Standardization Association (Association Française de Normalisation) has conducted work to establish a characterization standard for microplastics in water, which serves as an international reference.
“It is also very difficult to know what we are ingesting,” Bolo said. “A study conducted in 2019 estimated that the average human absorbs 5 grams of plastics per week, the equivalent of a credit card.» Since then, other studies have revised this estimate downward, but no consensus has been reached.
A recent study across 109 countries, both industrialized and developing, found significant exposure, estimated at 500 mg/d, particularly in Southeast Asian countries, where it was due mainly to seafood consumption.
A study concluded that plastic water bottles contain 240,000 particles per liter, 90% of which are nanoplastics. These nanoparticles can pass through the intestinal barrier to enter the bloodstream and reach several organs including the heart, brain, and placenta, as well as the fetus.
Changes to the Microbiome
Microplastics also accumulate in organs. Thus, the amount of plastic in the lungs increases with age, suggesting that particles may persist in the body without being eliminated. The health consequences of this are still poorly understood, but exposure to plastics appears to cause changes in the composition of the intestinal microbiota. Pathobionts (commensal bacteria with harmful potential) have been found in both adults and children, which could contribute to dysbiosis of the gut microbiome. Furthermore, a decrease in butyrate, a short-chain fatty acid beneficial to health, has been observed in children’s intestines.
Inhaled nanoplastics may disrupt the mucociliary clearance mechanisms of the respiratory system. The toxicity of inhaled plastic particles was demonstrated as early as the 1970s among workers in the flocking industry. Some developed lung function impairments, shortness of breath, inflammation, fibrosis, and even lung cancer. Similar symptoms have been observed in workers in the textile and polyvinyl chloride industries.
A study published recently in The New England Journal of Medicine measured the amount of microplastics collected from carotid plaque of more than 300 patients who had undergone carotid endarterectomy for asymptomatic carotid artery disease. It found a 4.53 times higher risk for the primary endpoint, a composite of myocardial infarction, stroke, and all-cause mortality, among individuals with microplastics and nanoplastics in plaque compared with those without.
Health Affects High
The danger of plastics is also directly linked to the chemical substances they contain. A general scientific review looked at the health impacts of three chemicals used almost exclusively in plastics: Polybromodiphenyl ethers (PBDEs), used as flame retardants in textiles or electronics; bisphenol A (BPA), used in the lining of cans and bottles; and phthalates, particularly diethylhexyl phthalate (DEHP), used to make plastics more flexible.
The review highlighted strong epidemiological evidence linking fetal exposure to PBDEs during pregnancy to low birth weight and later exposure to delayed or impaired cognitive development in children and even a loss of IQ. Statistically significant evidence of disruption of thyroid function in adults was also found.
BPA is linked to genital malformations in female newborns exposed to BPA in utero, type 2 diabetes in adults, insulin resistance, and polycystic ovary syndrome in women. BPA exposure also increases the risk for obesity and hypertension in both children and adults, as well as the risk for cardiovascular disease in adults.
Finally, the review established links between exposure to DEHP and miscarriages, genital malformations in male newborns, delayed or impaired cognitive development in children, loss of IQ, delayed psychomotor development, early puberty in young girls, and endometriosis in young women. DEHP exposure also has multiple effects on cardiometabolic health, including insulin resistance, obesity, and elevated blood pressure.
The economic costs associated with the health impacts of these three substances have been estimated at $675 billion in the United States.
Bolo said that the solution to this plastic pollution is necessarily international. “We need an ambitious and legally binding treaty to reduce plastic production,” he said. “The damage is already done; we need to act to protect human health,” he concluded. The parliamentary office has made nine recommendations to the treaty negotiators.
This story was translated from Medscape’s French edition using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Patients With Refractory Systemic Sclerosis Have Early Success With CAR T-Cell Therapy
TOPLINE:
CD19-targeting chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy shows potential to intercept fibrotic organ manifestations and improve disease measures in patients with diffuse cutaneous systemic sclerosis (SSc) who had disease progression despite multiple previous treatments.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers conducted a case series to examine the effect of CD19-targeting CAR T-cell therapy on fibrotic and vascular organ manifestations in six patients with diffuse cutaneous SSc (median age, 42 years; four men and two women) who had an insufficient response to at least two previous treatments.
- Participants received CD19-targeting CAR T-cell treatment at a dose of 1 × 106 CAR T cells per kilogram of body weight after lymphodepletion with fludarabine and cyclophosphamide.
- The primary outcome was event-free time or treatment intensification after study entry, with events defined as the progression of interstitial lung disease, onset of congestive heart or renal failure or arterial hypertension, or initiation of new therapy.
- The secondary outcomes included changes in the modified Rodnan skin score (mRSS), imaging and laboratory assessments, patient-reported outcomes, and the modified American College of Rheumatology Composite Response Index in Systemic Sclerosis (ACR-CRISS), assessed at baseline and 3, 6, 9, and 12 months after treatment.
TAKEAWAY:
- No progression of organ manifestations or new lung, cardiac, or renal events occurred within the median follow-up period of 487 days.
- The probability of improvement in the ACR-CRISS score increased to a median value of 100% within 6 and 12 months of CAR T-cell treatment compared with baseline.
- Skin involvement improved in all the patients after CAR T-cell treatment, with a median mRSS decrease of 8 points within 100 days; the improvements were maintained throughout the 1-year follow-up period.
- This treatment also led to a depletion of antinuclear antibodies and SSc-specific autoantibodies.
IN PRACTICE:
“This case series highlights the potential of CAR T-cell therapy to address a crucial unmet need in refractory systemic sclerosis treatment. The study’s most significant contribution is the demonstration that CD19-targeting CAR T-cell therapy can halt or reverse aspects of fibrosis in systemic sclerosis,” Jérôme Avouac, Service de Rhumatologie, Hôpital Cochin, AP-HP Centre-Université Paris Cité, Paris, France, wrote in an accompanying editorial.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Janina Auth, MD, Deutsches Zentrum Immuntherapie, Friedrich-Alexander-Universität Erlangen-Nürnberg and Universitätsklinikum Erlangen in Germany, and was published online on November 11, 2024, in The Lancet Rheumatology.
LIMITATIONS:
The study lacked a control group, which limited the ability to draw definitive conclusions about the efficacy of CD19-targeting CAR T-cell therapy compared with standard treatments. The unpredictable nature of SSc, in which periods of stability can occur spontaneously, makes it difficult to attribute the improvements merely to the intervention. Moreover, the effect of CAR T-cell therapy on other disease manifestations, such as pulmonary hypertension, myocardial involvement, and scleroderma renal crisis, remains unclear.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was funded by Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft, Deutsche Krebshilfe, ELAN Foundation Erlangen, Interdisziplinäres Zentrum für Klinische Forschung Erlangen, Bundesministerium für Bildung und Forschung, and the European Union. Some authors reported receiving research grants, consulting fees, speaker fees, honoraria, or travel grants from Boehringer Ingelheim, Novartis, Almirall, and other pharmaceutical companies.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
CD19-targeting chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy shows potential to intercept fibrotic organ manifestations and improve disease measures in patients with diffuse cutaneous systemic sclerosis (SSc) who had disease progression despite multiple previous treatments.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers conducted a case series to examine the effect of CD19-targeting CAR T-cell therapy on fibrotic and vascular organ manifestations in six patients with diffuse cutaneous SSc (median age, 42 years; four men and two women) who had an insufficient response to at least two previous treatments.
- Participants received CD19-targeting CAR T-cell treatment at a dose of 1 × 106 CAR T cells per kilogram of body weight after lymphodepletion with fludarabine and cyclophosphamide.
- The primary outcome was event-free time or treatment intensification after study entry, with events defined as the progression of interstitial lung disease, onset of congestive heart or renal failure or arterial hypertension, or initiation of new therapy.
- The secondary outcomes included changes in the modified Rodnan skin score (mRSS), imaging and laboratory assessments, patient-reported outcomes, and the modified American College of Rheumatology Composite Response Index in Systemic Sclerosis (ACR-CRISS), assessed at baseline and 3, 6, 9, and 12 months after treatment.
TAKEAWAY:
- No progression of organ manifestations or new lung, cardiac, or renal events occurred within the median follow-up period of 487 days.
- The probability of improvement in the ACR-CRISS score increased to a median value of 100% within 6 and 12 months of CAR T-cell treatment compared with baseline.
- Skin involvement improved in all the patients after CAR T-cell treatment, with a median mRSS decrease of 8 points within 100 days; the improvements were maintained throughout the 1-year follow-up period.
- This treatment also led to a depletion of antinuclear antibodies and SSc-specific autoantibodies.
IN PRACTICE:
“This case series highlights the potential of CAR T-cell therapy to address a crucial unmet need in refractory systemic sclerosis treatment. The study’s most significant contribution is the demonstration that CD19-targeting CAR T-cell therapy can halt or reverse aspects of fibrosis in systemic sclerosis,” Jérôme Avouac, Service de Rhumatologie, Hôpital Cochin, AP-HP Centre-Université Paris Cité, Paris, France, wrote in an accompanying editorial.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Janina Auth, MD, Deutsches Zentrum Immuntherapie, Friedrich-Alexander-Universität Erlangen-Nürnberg and Universitätsklinikum Erlangen in Germany, and was published online on November 11, 2024, in The Lancet Rheumatology.
LIMITATIONS:
The study lacked a control group, which limited the ability to draw definitive conclusions about the efficacy of CD19-targeting CAR T-cell therapy compared with standard treatments. The unpredictable nature of SSc, in which periods of stability can occur spontaneously, makes it difficult to attribute the improvements merely to the intervention. Moreover, the effect of CAR T-cell therapy on other disease manifestations, such as pulmonary hypertension, myocardial involvement, and scleroderma renal crisis, remains unclear.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was funded by Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft, Deutsche Krebshilfe, ELAN Foundation Erlangen, Interdisziplinäres Zentrum für Klinische Forschung Erlangen, Bundesministerium für Bildung und Forschung, and the European Union. Some authors reported receiving research grants, consulting fees, speaker fees, honoraria, or travel grants from Boehringer Ingelheim, Novartis, Almirall, and other pharmaceutical companies.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
CD19-targeting chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy shows potential to intercept fibrotic organ manifestations and improve disease measures in patients with diffuse cutaneous systemic sclerosis (SSc) who had disease progression despite multiple previous treatments.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers conducted a case series to examine the effect of CD19-targeting CAR T-cell therapy on fibrotic and vascular organ manifestations in six patients with diffuse cutaneous SSc (median age, 42 years; four men and two women) who had an insufficient response to at least two previous treatments.
- Participants received CD19-targeting CAR T-cell treatment at a dose of 1 × 106 CAR T cells per kilogram of body weight after lymphodepletion with fludarabine and cyclophosphamide.
- The primary outcome was event-free time or treatment intensification after study entry, with events defined as the progression of interstitial lung disease, onset of congestive heart or renal failure or arterial hypertension, or initiation of new therapy.
- The secondary outcomes included changes in the modified Rodnan skin score (mRSS), imaging and laboratory assessments, patient-reported outcomes, and the modified American College of Rheumatology Composite Response Index in Systemic Sclerosis (ACR-CRISS), assessed at baseline and 3, 6, 9, and 12 months after treatment.
TAKEAWAY:
- No progression of organ manifestations or new lung, cardiac, or renal events occurred within the median follow-up period of 487 days.
- The probability of improvement in the ACR-CRISS score increased to a median value of 100% within 6 and 12 months of CAR T-cell treatment compared with baseline.
- Skin involvement improved in all the patients after CAR T-cell treatment, with a median mRSS decrease of 8 points within 100 days; the improvements were maintained throughout the 1-year follow-up period.
- This treatment also led to a depletion of antinuclear antibodies and SSc-specific autoantibodies.
IN PRACTICE:
“This case series highlights the potential of CAR T-cell therapy to address a crucial unmet need in refractory systemic sclerosis treatment. The study’s most significant contribution is the demonstration that CD19-targeting CAR T-cell therapy can halt or reverse aspects of fibrosis in systemic sclerosis,” Jérôme Avouac, Service de Rhumatologie, Hôpital Cochin, AP-HP Centre-Université Paris Cité, Paris, France, wrote in an accompanying editorial.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Janina Auth, MD, Deutsches Zentrum Immuntherapie, Friedrich-Alexander-Universität Erlangen-Nürnberg and Universitätsklinikum Erlangen in Germany, and was published online on November 11, 2024, in The Lancet Rheumatology.
LIMITATIONS:
The study lacked a control group, which limited the ability to draw definitive conclusions about the efficacy of CD19-targeting CAR T-cell therapy compared with standard treatments. The unpredictable nature of SSc, in which periods of stability can occur spontaneously, makes it difficult to attribute the improvements merely to the intervention. Moreover, the effect of CAR T-cell therapy on other disease manifestations, such as pulmonary hypertension, myocardial involvement, and scleroderma renal crisis, remains unclear.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was funded by Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft, Deutsche Krebshilfe, ELAN Foundation Erlangen, Interdisziplinäres Zentrum für Klinische Forschung Erlangen, Bundesministerium für Bildung und Forschung, and the European Union. Some authors reported receiving research grants, consulting fees, speaker fees, honoraria, or travel grants from Boehringer Ingelheim, Novartis, Almirall, and other pharmaceutical companies.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Special Considerations Needed in Applying Lupus Nephritis Guideline to Children
WASHINGTON — When the American College of Rheumatology (ACR) released its updated guideline for management of lupus nephritis (LN) at its 2024 Annual Meeting, they included recommendations for managing pediatric LN for the first time.
The pediatric recommendations use the same classification criteria, outcome measures, and treatments as in adults — including the first-line triple therapy recommendation — but there remain important differences between pediatric and adult LN, Mary Beth Son, MD, clinical chief of immunology and section chief of rheumatology at Boston Children’s Hospital in Massachusetts, and an associate professor of pediatrics at Harvard Medical School, also in Boston, told attendees.
“In general, kids and adolescents with lupus are sicker,” Son said. They are more likely to have renal manifestations and neuropsychiatric lupus at diagnosis, compared with adults. Further, “although the disease is the same, it’s happening to kids and adolescents who are undergoing critical periods of growth and development.”
Medication risk profiles also shift for younger patients, Son noted.
“Importantly, they’re at risk for higher cumulative dosing of both glucocorticoids and cyclophosphamide,” Son said. “When we give an adolescent a course of cyclophosphamide, we have to be aware that this might be the first of a few courses over the course of the lifetime disease, and with increasing numbers of cyclophosphamide courses, you have increased risk for infertility and malignancy.”
Son also acknowledged challenges of pediatric literature, including differences in definitions of pediatric lupus, very few randomized controlled trials, and fewer pediatric studies in general, with fewer participants. Given these research gaps, the guideline panels included pediatric rheumatologists and nephrologists, and the patient panel included several patients with childhood-onset disease.
Son also addressed differences in pediatric drug development. Dosing studies also do not always directly translate from adults to children because children have larger drug volume distribution and differences in drug clearance, and they may need different formulations, she said. Children tend to tolerate medications better than adults because they usually have fewer comorbidities, but the assessment of a drug’s safety must take its impact on growth and development into consideration.
During a press conference after the session where the guideline was presented, Linda Hiraki, MD, ScD, a clinician-scientist in rheumatology at the Hospital for Sick Children, Toronto, Ontario, Canada, said the panel took into consideration that pediatric patients receive their diagnosis during a critical time of development, so considerations of medication risks include the fact that children “have much more life to live.”
Triple Therapy Recommended
As with adults, the pediatric LN guideline recommends a triple therapy approach: glucocorticoids plus mycophenolate mofetil and belimumab, in addition to the usual renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system inhibitors and hydroxychloroquine. But Son acknowledged limitations of applying the new guideline to children. For one, voclosporin has not been studied in or approved for pediatric patients, although there exists modest evidence for other calcineurin inhibitors, mainly tacrolimus, in children.
“The other important consideration is that the lower dose of prednisone that’s being offered by the guidelines of 40 mg per day as a starting dose has not been studied in pediatric lupus nephritis patients,” Son said. “However, I would offer that, given that we know that kids get higher doses and longer courses, it’s even more important to consider a lower dose to begin with in the setting of other immunosuppressants.”
Good Practice Statements for Pediatric LN
Son also reviewed three good practice statements for pediatric LN. First, “glucocorticoid regimens should use pediatric-appropriate doses for children, as reduction of human glucocorticoid dosing is critically important given the early age of pediatric lupus onset and attendant comorbidities,” she said.
That statement is based on both common sense and some literature, including awareness that children are more likely to receive higher doses of steroids and that children’s higher damage scores are driven in part by steroid-related toxicity, such as avascular necrosis and cataracts. In addition, glucocorticoids can have profound effects on body mass index, mood, and height attainment.
“This is during a period of emerging self-identity and struggles with appearance; steroids exacerbate that” as well as mood issues already associated with puberty, Son said.
The second good practice statement recommends that clinicians monitor patients “for delayed pubertal onset and decreased growth velocity that can result from disease activity and glucocorticoid treatment and consider referral to pediatric endocrinology if indicated.” The third states that “a structured, intentional transition from pediatric to adult rheumatology care is indicated to avoid poor outcomes during this vulnerable period.”
During the press conference, Hiraki said that pediatric rheumatologists already recognize the need for discussions about transfer to adult care to begin very early, even years before patients are ready to transfer.
“The transition from being a pediatric patient to being an adult patient is very challenging for a number of reasons,” starting with loss of insurance coverage, added Bonnie Bermas, MD, a professor of internal medicine at UT Southwestern Medical Center in Dallas, Texas. When adult rheumatologists take on these patients, they may not have had care for 2 or 3 years, she said.
Rebecca Sadun, MD, PhD, an associate professor of pediatrics in rheumatology at Duke University School of Medicine, Durham, North Carolina, and vice-chair of the Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Committee for the Childhood Arthritis and Rheumatology Research Alliance, was not involved in the guideline development process but reviewed the new guideline.
“We appreciate that the ACR took care to involve pediatric rheumatologists, pediatric nephrologists, and patients with childhood-onset lupus in the development of the newest lupus nephritis treatment guidelines,” she said in an interview. She also noted, however, that “the dearth of pediatric-specific clinical trial data means that we continue to wonder when it is appropriate to extrapolate from adult data regarding the efficacy, safety, and dosing of certain medications, including steroids and voclosporin.” She also noted that voclosporin use can increase pill burden and therefore be difficult to use in pediatrics.
“Children, adolescents, and young adults are a unique population with unique challenges, including significant struggles with adherence to complex medication regimens,” she said. Sadun drew attention to two themes from the guideline that she found particularly applicable to management of pediatric LN.
“First, we must remain wary of the serious consequences of long-term, high-dose glucocorticoids, and we should continue to look towards steroid-sparing strategies that will reduce reliance on glucocorticoids,” Sadun said. “Second, we are likely to see better outcomes, including better renal response, when we take advantage of combination immunosuppression earlier in the disease course.”
Son, Bermas, and Sadun had no disclosures. Hiraki has consulted for Janssen. The guideline development did not involve outside funding.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
WASHINGTON — When the American College of Rheumatology (ACR) released its updated guideline for management of lupus nephritis (LN) at its 2024 Annual Meeting, they included recommendations for managing pediatric LN for the first time.
The pediatric recommendations use the same classification criteria, outcome measures, and treatments as in adults — including the first-line triple therapy recommendation — but there remain important differences between pediatric and adult LN, Mary Beth Son, MD, clinical chief of immunology and section chief of rheumatology at Boston Children’s Hospital in Massachusetts, and an associate professor of pediatrics at Harvard Medical School, also in Boston, told attendees.
“In general, kids and adolescents with lupus are sicker,” Son said. They are more likely to have renal manifestations and neuropsychiatric lupus at diagnosis, compared with adults. Further, “although the disease is the same, it’s happening to kids and adolescents who are undergoing critical periods of growth and development.”
Medication risk profiles also shift for younger patients, Son noted.
“Importantly, they’re at risk for higher cumulative dosing of both glucocorticoids and cyclophosphamide,” Son said. “When we give an adolescent a course of cyclophosphamide, we have to be aware that this might be the first of a few courses over the course of the lifetime disease, and with increasing numbers of cyclophosphamide courses, you have increased risk for infertility and malignancy.”
Son also acknowledged challenges of pediatric literature, including differences in definitions of pediatric lupus, very few randomized controlled trials, and fewer pediatric studies in general, with fewer participants. Given these research gaps, the guideline panels included pediatric rheumatologists and nephrologists, and the patient panel included several patients with childhood-onset disease.
Son also addressed differences in pediatric drug development. Dosing studies also do not always directly translate from adults to children because children have larger drug volume distribution and differences in drug clearance, and they may need different formulations, she said. Children tend to tolerate medications better than adults because they usually have fewer comorbidities, but the assessment of a drug’s safety must take its impact on growth and development into consideration.
During a press conference after the session where the guideline was presented, Linda Hiraki, MD, ScD, a clinician-scientist in rheumatology at the Hospital for Sick Children, Toronto, Ontario, Canada, said the panel took into consideration that pediatric patients receive their diagnosis during a critical time of development, so considerations of medication risks include the fact that children “have much more life to live.”
Triple Therapy Recommended
As with adults, the pediatric LN guideline recommends a triple therapy approach: glucocorticoids plus mycophenolate mofetil and belimumab, in addition to the usual renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system inhibitors and hydroxychloroquine. But Son acknowledged limitations of applying the new guideline to children. For one, voclosporin has not been studied in or approved for pediatric patients, although there exists modest evidence for other calcineurin inhibitors, mainly tacrolimus, in children.
“The other important consideration is that the lower dose of prednisone that’s being offered by the guidelines of 40 mg per day as a starting dose has not been studied in pediatric lupus nephritis patients,” Son said. “However, I would offer that, given that we know that kids get higher doses and longer courses, it’s even more important to consider a lower dose to begin with in the setting of other immunosuppressants.”
Good Practice Statements for Pediatric LN
Son also reviewed three good practice statements for pediatric LN. First, “glucocorticoid regimens should use pediatric-appropriate doses for children, as reduction of human glucocorticoid dosing is critically important given the early age of pediatric lupus onset and attendant comorbidities,” she said.
That statement is based on both common sense and some literature, including awareness that children are more likely to receive higher doses of steroids and that children’s higher damage scores are driven in part by steroid-related toxicity, such as avascular necrosis and cataracts. In addition, glucocorticoids can have profound effects on body mass index, mood, and height attainment.
“This is during a period of emerging self-identity and struggles with appearance; steroids exacerbate that” as well as mood issues already associated with puberty, Son said.
The second good practice statement recommends that clinicians monitor patients “for delayed pubertal onset and decreased growth velocity that can result from disease activity and glucocorticoid treatment and consider referral to pediatric endocrinology if indicated.” The third states that “a structured, intentional transition from pediatric to adult rheumatology care is indicated to avoid poor outcomes during this vulnerable period.”
During the press conference, Hiraki said that pediatric rheumatologists already recognize the need for discussions about transfer to adult care to begin very early, even years before patients are ready to transfer.
“The transition from being a pediatric patient to being an adult patient is very challenging for a number of reasons,” starting with loss of insurance coverage, added Bonnie Bermas, MD, a professor of internal medicine at UT Southwestern Medical Center in Dallas, Texas. When adult rheumatologists take on these patients, they may not have had care for 2 or 3 years, she said.
Rebecca Sadun, MD, PhD, an associate professor of pediatrics in rheumatology at Duke University School of Medicine, Durham, North Carolina, and vice-chair of the Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Committee for the Childhood Arthritis and Rheumatology Research Alliance, was not involved in the guideline development process but reviewed the new guideline.
“We appreciate that the ACR took care to involve pediatric rheumatologists, pediatric nephrologists, and patients with childhood-onset lupus in the development of the newest lupus nephritis treatment guidelines,” she said in an interview. She also noted, however, that “the dearth of pediatric-specific clinical trial data means that we continue to wonder when it is appropriate to extrapolate from adult data regarding the efficacy, safety, and dosing of certain medications, including steroids and voclosporin.” She also noted that voclosporin use can increase pill burden and therefore be difficult to use in pediatrics.
“Children, adolescents, and young adults are a unique population with unique challenges, including significant struggles with adherence to complex medication regimens,” she said. Sadun drew attention to two themes from the guideline that she found particularly applicable to management of pediatric LN.
“First, we must remain wary of the serious consequences of long-term, high-dose glucocorticoids, and we should continue to look towards steroid-sparing strategies that will reduce reliance on glucocorticoids,” Sadun said. “Second, we are likely to see better outcomes, including better renal response, when we take advantage of combination immunosuppression earlier in the disease course.”
Son, Bermas, and Sadun had no disclosures. Hiraki has consulted for Janssen. The guideline development did not involve outside funding.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
WASHINGTON — When the American College of Rheumatology (ACR) released its updated guideline for management of lupus nephritis (LN) at its 2024 Annual Meeting, they included recommendations for managing pediatric LN for the first time.
The pediatric recommendations use the same classification criteria, outcome measures, and treatments as in adults — including the first-line triple therapy recommendation — but there remain important differences between pediatric and adult LN, Mary Beth Son, MD, clinical chief of immunology and section chief of rheumatology at Boston Children’s Hospital in Massachusetts, and an associate professor of pediatrics at Harvard Medical School, also in Boston, told attendees.
“In general, kids and adolescents with lupus are sicker,” Son said. They are more likely to have renal manifestations and neuropsychiatric lupus at diagnosis, compared with adults. Further, “although the disease is the same, it’s happening to kids and adolescents who are undergoing critical periods of growth and development.”
Medication risk profiles also shift for younger patients, Son noted.
“Importantly, they’re at risk for higher cumulative dosing of both glucocorticoids and cyclophosphamide,” Son said. “When we give an adolescent a course of cyclophosphamide, we have to be aware that this might be the first of a few courses over the course of the lifetime disease, and with increasing numbers of cyclophosphamide courses, you have increased risk for infertility and malignancy.”
Son also acknowledged challenges of pediatric literature, including differences in definitions of pediatric lupus, very few randomized controlled trials, and fewer pediatric studies in general, with fewer participants. Given these research gaps, the guideline panels included pediatric rheumatologists and nephrologists, and the patient panel included several patients with childhood-onset disease.
Son also addressed differences in pediatric drug development. Dosing studies also do not always directly translate from adults to children because children have larger drug volume distribution and differences in drug clearance, and they may need different formulations, she said. Children tend to tolerate medications better than adults because they usually have fewer comorbidities, but the assessment of a drug’s safety must take its impact on growth and development into consideration.
During a press conference after the session where the guideline was presented, Linda Hiraki, MD, ScD, a clinician-scientist in rheumatology at the Hospital for Sick Children, Toronto, Ontario, Canada, said the panel took into consideration that pediatric patients receive their diagnosis during a critical time of development, so considerations of medication risks include the fact that children “have much more life to live.”
Triple Therapy Recommended
As with adults, the pediatric LN guideline recommends a triple therapy approach: glucocorticoids plus mycophenolate mofetil and belimumab, in addition to the usual renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system inhibitors and hydroxychloroquine. But Son acknowledged limitations of applying the new guideline to children. For one, voclosporin has not been studied in or approved for pediatric patients, although there exists modest evidence for other calcineurin inhibitors, mainly tacrolimus, in children.
“The other important consideration is that the lower dose of prednisone that’s being offered by the guidelines of 40 mg per day as a starting dose has not been studied in pediatric lupus nephritis patients,” Son said. “However, I would offer that, given that we know that kids get higher doses and longer courses, it’s even more important to consider a lower dose to begin with in the setting of other immunosuppressants.”
Good Practice Statements for Pediatric LN
Son also reviewed three good practice statements for pediatric LN. First, “glucocorticoid regimens should use pediatric-appropriate doses for children, as reduction of human glucocorticoid dosing is critically important given the early age of pediatric lupus onset and attendant comorbidities,” she said.
That statement is based on both common sense and some literature, including awareness that children are more likely to receive higher doses of steroids and that children’s higher damage scores are driven in part by steroid-related toxicity, such as avascular necrosis and cataracts. In addition, glucocorticoids can have profound effects on body mass index, mood, and height attainment.
“This is during a period of emerging self-identity and struggles with appearance; steroids exacerbate that” as well as mood issues already associated with puberty, Son said.
The second good practice statement recommends that clinicians monitor patients “for delayed pubertal onset and decreased growth velocity that can result from disease activity and glucocorticoid treatment and consider referral to pediatric endocrinology if indicated.” The third states that “a structured, intentional transition from pediatric to adult rheumatology care is indicated to avoid poor outcomes during this vulnerable period.”
During the press conference, Hiraki said that pediatric rheumatologists already recognize the need for discussions about transfer to adult care to begin very early, even years before patients are ready to transfer.
“The transition from being a pediatric patient to being an adult patient is very challenging for a number of reasons,” starting with loss of insurance coverage, added Bonnie Bermas, MD, a professor of internal medicine at UT Southwestern Medical Center in Dallas, Texas. When adult rheumatologists take on these patients, they may not have had care for 2 or 3 years, she said.
Rebecca Sadun, MD, PhD, an associate professor of pediatrics in rheumatology at Duke University School of Medicine, Durham, North Carolina, and vice-chair of the Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Committee for the Childhood Arthritis and Rheumatology Research Alliance, was not involved in the guideline development process but reviewed the new guideline.
“We appreciate that the ACR took care to involve pediatric rheumatologists, pediatric nephrologists, and patients with childhood-onset lupus in the development of the newest lupus nephritis treatment guidelines,” she said in an interview. She also noted, however, that “the dearth of pediatric-specific clinical trial data means that we continue to wonder when it is appropriate to extrapolate from adult data regarding the efficacy, safety, and dosing of certain medications, including steroids and voclosporin.” She also noted that voclosporin use can increase pill burden and therefore be difficult to use in pediatrics.
“Children, adolescents, and young adults are a unique population with unique challenges, including significant struggles with adherence to complex medication regimens,” she said. Sadun drew attention to two themes from the guideline that she found particularly applicable to management of pediatric LN.
“First, we must remain wary of the serious consequences of long-term, high-dose glucocorticoids, and we should continue to look towards steroid-sparing strategies that will reduce reliance on glucocorticoids,” Sadun said. “Second, we are likely to see better outcomes, including better renal response, when we take advantage of combination immunosuppression earlier in the disease course.”
Son, Bermas, and Sadun had no disclosures. Hiraki has consulted for Janssen. The guideline development did not involve outside funding.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM ACR 2024
Advancements in the Treatment of Malignant PEComas with mTOR Inhibitors
Advancements in the Treatment of Malignant PEComas with mTOR Inhibitors
The PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway is an attractive therapeutic target for soft tissue sarcomas, as dysregulation of mechanistic target of rapamycin (mTOR) can lead to the development of various cancer types. Recently, clinical trial data have demonstrated that mTOR inhibitors can significantly improve long-term outcomes in patients with malignant perivascular epithelioid cell tumors, or PEComas—a challenging disease to manage in the advanced stage.
Ultrarare Mesenchymal Tumors
PEComas are ultrarare soft tissue tumors that are mesenchymal in origin and are characterized histologically by distinctive epithelioid cells that express smooth muscle and melanocytic markers.1-3 Malignant PEComas affect fewer than 1/1,000,000 people per year,4,5 and have a predominance in women, as they are commonly found in the uterus.4 PEComas include several histological types, such as angiomyolipoma (the most prevalent type), lymphangioleiomyomatosis, clear cell (“sugar”) tumor, and other tumors with similar features.3
Detecting an Ultrarare Malignant PEComa
Most PEComas are diagnosed incidentally via imaging. Patients may also present with symptoms of abdominal pain, nausea, and unexplained weight loss.6,7 PEComas in the uterus are often detected through an ultrasound, in which they may have the appearance of fibroids.8 Diagnosis must be confirmed by biopsy, and histological analysis can determine the risk classification based on tumor characteristics.6 Many patients with PEComas harbor loss-of-function mutations in the TSC1 and TSC2 genes, resulting in overactivation of the PIK3/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway9; TP53 mutations and TFE3 rearrangements or fusions have also been identified.6,10
Therapeutic Strategies Are Limited
Because PEComas are often resistant to chemotherapy and radiotherapy, resection is considered standard-of-care treatment for localized disease.6 Patients with advanced disease should be considered for systemic therapy. However, there is a substantial unmet need for novel therapies due to the limited efficacy of existing treatment options. Agents that target mTOR have shown important potential in improving long-term outcomes in patients with metastatic PEComas.6 The PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway is a key signaling system that regulates cell proliferation and survival. TSC1 and TSC2 normally negatively regulate the mTOR complex 1 (mTORC1); however, alterations in TSC1 and TSC2 result in increased activity of this pathway, allowing tumors to proliferate (Figure).11,12 Clinical guidelines recommend using mTOR inhibitors for patients with locally advanced, unresectable, or metastatic malignant PEComas, and both on and off-label therapies are often used in the clinical setting.13 nab-Sirolimus, a nanoparticle albumin–bound sirolimus, is one such mTOR (previously known as mammalian target of rapamycin) inhibitor that binds to and blocks activation of the mechanistic target of rapamycin complex 1.11,14
Figure. mTOR Signaling Skin Diseases
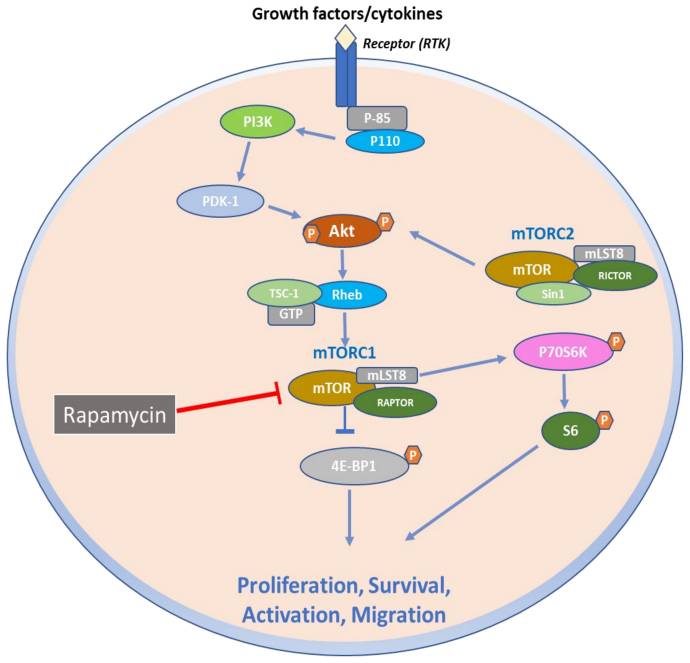
The Promise of mTOR Inhibitors for Malignant PEComas
In 2021, the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved nab-sirolimus to treat patients with locally advanced, unresectable, or metastatic malignant PEComas. This approval was based on results from the phase 2 Advanced Malignant Perivascular Epithelioid Cell Tumors (AMPECT) clinical trial (NCT02494570).14,15 AMPECT was a multicenter, open-label, single-arm trial that evaluated nab-sirolimus in 34 patients with metastatic or locally advanced (ineligible for surgery) malignant PEComa and measurable disease who had not been previously treated with an mTOR inhibitor. Most of the patients were women, and the most common site of disease was the uterus.14 Patients received nab-sirolimus (100 mg/m2 intravenously) on days 1 and 8 of a 21-day cycle. The primary outcome of the study was an overall response rate by 6 months, and secondary endpoints included duration of response, progression-free survival (PFS), PFS at 6 months (PFS6), overall survival (OS), and safety; tumor biomarkers were also evaluated as exploratory measures.14 At 6 months, nab-sirolimus demonstrated an overall response rate of 39%, with rapid and durable responses. The median PFS was 10.6 months, with a PFS6 of 70%; median OS was 40.8 months.
Of the 25 patients for whom tumor profiling was performed, 8 of 9 (89%) patients with a TSC2 mutation achieved a response compared with 2 of 16 (13%) without the mutation. The most common adverse events associated with treatment included mucositis, rash, fatigue, and anemia, which are consistent with the medication class.14 Long-term analysis from the AMPECT trial demonstrated a median OS of 53.1 months, with a median duration of response of 39.7 months. Taken together, these results indicate that nab-sirolimus may provide patients with positive long-term clinical benefits with an acceptable safety profile.15 nab-Sirolimus is currently being evaluated in clinical trials in patients harboring TSC1 and TSC2 mutations and is also being investigated as a therapeutic candidate for other cancer types, such as neuroendocrine tumors, endometrial cancer, and ovarian cancer (NCT05997056; NCT05997017; NCT06494150; NCT05103358).
Case Study Spotlight
A 70-year-old woman presented at a local emergency department with several episodes of tingling in her upper and lower extremities. A chest radiograph revealed multiple bilateral pulmonary nodules, and a computed tomography scan of the chest, abdomen, and pelvis revealed a 21-cm left abdominal mass, innumerable pulmonary nodules, and multiple hepatic lesions. The patient underwent palliative resection of the large left retroperitoneal mass. Pathology revealed malignant PEComa, and a liver biopsy confirmed metastatic disease.
Following referral, the patient was enrolled in the AMPECT clinical trial, during which she received nab-sirolimus treatment. An objective response was confirmed after the initial 6 weeks on therapy and serial imaging revealed continued shrinkage in lung and liver lesions over time; the nab-sirolimus dose was reduced by 25% due to grade 2 pneumonitis after ~18 months of treatment. The patient had a complete response after 4 years on treatment. Unfortunately, the patient died due to complications from an unrelated elective hernia repair. She was 74 at the time of her death, and there was no radiographic evidence of PEComa.
Future Directions
While mTOR inhibitors provide the most favorable outcomes in the advanced disease setting at this time, research is underway to evaluate the utility of additional novel targets to treat malignant PEComa. Anecdotal evidence from case reports indicates that anti-vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) tyrosine kinase inhibitors may be beneficial to patients with malignant PEComa, highlighting the VEGF/VEGF receptor signaling pathway as a potential therapeutic target.16 Some evidence has also suggested that programmed cell death (PD) protein 1/PD ligand 1 (PD-1/PD-L1) inhibitors may be effective for patients with metastatic disease with high PD-L1 levels.17 In addition to more treatment options, diagnostic markers could potentially improve prognosis by facilitating earlier detection, a key challenge in managing malignant PEComas, especially for uterine tumors that are often misdiagnosed.18 Future research may also help guide personalized treatment strategies based on tumor genetic composition.
Read more from the 2024 Rare Diseases Report: Hematology and Oncology.
- Stacchiotti S, Frezza AM, Blay JY, et al. Ultra-rare sarcomas: a consensus paper from the Connective Tissue Oncology Society community of experts on the incidence threshold and the list of entities. Cancer. 2021;127(16):2934-2942. doi:10.1002/cncr.33618
- Bleeker JS, Quevedo JF, Folpe AL. “Malignant” perivascular epithelioid cell neoplasm: risk stratification and treatment strategies. Sarcoma. 2012;2012:541626. doi:10.1155/2012/541626
- Thway K, Fisher C. PEComa: morphology and genetics of a complex tumor family. Ann Diagn Pathol. 2015;19(5):359-368. doi:10.1016/j.anndiagpath.2015.06.003
- Battistella E, Pomba L, Mirabella M, et al. Metastatic adrenal PEComa: case report and short review of the literature. Medicina (Kaunas). 2023;59(1):149. doi:10.3390/medicina59010149
- Meredith L, Chao T, Nevler A, et al. A rare metastatic mesenteric malignant PEComa with TSC2 mutation treated with palliative surgical resection and nab-sirolimus: a case report. Diagn Pathol. 2023;18(1):45. doi:10.1186/s13000-023-01323-x
- Czarnecka AM, Skoczylas J, Bartnik E, Switaj T, Rutkowski P. Management strategies for adults with locally advanced, unresectable or metastatic malignant perivascular epithelioid cell tumor (PEComa): challenges and solutions. Cancer Manag Res. 2023;15:615-623. doi:10.2147/CMAR.S351284
- Kvietkauskas M, Samuolyte A, Rackauskas R, et al. Primary liver perivascular epithelioid cell tumor (PEComa): case report and literature review. Medicina (Kaunas). 2024;60(3):409. doi:10.3390/medicina60030409
- Giannella L, Delli Carpini G, Montik N, et al. Ultrasound features of a uterine perivascular epithelioid cell tumor (PEComa): case report and literature review. Diagnostic (Basel). 2020;10(8):553. doi:10.3390/diagnostics10080553
- Liu L, Dehner C, Grandhi N, et al. The impact of TSC-1 and -2 mutations on response to therapy in malignant PEComa: a multicenter retrospective analysis. Genes (Basel). 2022;13(11):1932. doi:10.3390/genes13111932
- Schoolmeester JK, Dao LN, Sukov WR, et al. TFE3 translocation-associated perivascular epithelioid cell neoplasm (PEComa) of the gynecologic tract: morphology, immunophenotype, differential diagnosis. Am J Surg Pathol. 2015;39(3):394-404.doi:10.1097/PAS.0000000000000349
- Ali ES, Mitra K, Akter S, et al. Recent advances and limitations of mTOR inhibitors in the treatment of cancer. Cancer Cell Int. 2022;22(1):284. doi:10.1186/s12935-022-02706-8
- Sanfilippo R, Jones RL, Blay JY, et al. Role of chemotherapy, VEGFR inhibitors, and mTOR inhibitors in advanced perivascular epithelioid cell tumors (PEComas). Clin Cancer Res. 2019;25(17):5295-5300. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-19-0288
- National Comprehensive Cancer Network. NCCN clinical practice guidelines in oncology: soft tissue sarcoma. Version 2.2024. July 31, 2024. Accessed September 10, 2024. https://www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/pdf/sarcoma.pdf
- Wagner AJ, Ravi V, Riedel RF, et al. nab-Sirolimus for patients with malignant perivascular epithelioid cell tumors. J Clin Oncol. 2021;39(33):3660-3670. doi:10.1200/JCO.21.01728
- Wagner AJ, Ravi V, Riedel RF, et al. Phase II trial of nab-sirolimus in patients with advanced malignant perivascular epithelioid cell tumors (AMPECT): long-term efficacy and safety update. J Clin Oncol. 2024;42(13):1472-1476. doi:10.1200/JCO.23.02266
- Xu J, Gong XL, Wu H, Zhao L. Case report: gastrointestinal PEComa with TFE3 rearrangement treated with anti-VEGFR TKI apatinib. Front Oncol. 2020;10:582087. doi:10.3389/fonc.2020.582087
- McBride A, Garcia AJ, Sanders LJ, et al. Sustained response to pembrolizumab in recurrent perivascular epithelioid cell tumor with elevated expression of programmed death ligand: a case report. J Med Case Rep. 2021;15(1):400. doi:10.1186/s13256-021-02997-x
- Levin G, Capella MP, Meyer R, Brezinov Y, Gotlieb WH. Gynecologic perivascular epithelioid cell tumors (PEComas): a review of recent evidence. Arch Gynecol Obstet. 2024;309(6):2381-2386. doi:10.1007/s00404-024-07510-5
The PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway is an attractive therapeutic target for soft tissue sarcomas, as dysregulation of mechanistic target of rapamycin (mTOR) can lead to the development of various cancer types. Recently, clinical trial data have demonstrated that mTOR inhibitors can significantly improve long-term outcomes in patients with malignant perivascular epithelioid cell tumors, or PEComas—a challenging disease to manage in the advanced stage.
Ultrarare Mesenchymal Tumors
PEComas are ultrarare soft tissue tumors that are mesenchymal in origin and are characterized histologically by distinctive epithelioid cells that express smooth muscle and melanocytic markers.1-3 Malignant PEComas affect fewer than 1/1,000,000 people per year,4,5 and have a predominance in women, as they are commonly found in the uterus.4 PEComas include several histological types, such as angiomyolipoma (the most prevalent type), lymphangioleiomyomatosis, clear cell (“sugar”) tumor, and other tumors with similar features.3
Detecting an Ultrarare Malignant PEComa
Most PEComas are diagnosed incidentally via imaging. Patients may also present with symptoms of abdominal pain, nausea, and unexplained weight loss.6,7 PEComas in the uterus are often detected through an ultrasound, in which they may have the appearance of fibroids.8 Diagnosis must be confirmed by biopsy, and histological analysis can determine the risk classification based on tumor characteristics.6 Many patients with PEComas harbor loss-of-function mutations in the TSC1 and TSC2 genes, resulting in overactivation of the PIK3/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway9; TP53 mutations and TFE3 rearrangements or fusions have also been identified.6,10
Therapeutic Strategies Are Limited
Because PEComas are often resistant to chemotherapy and radiotherapy, resection is considered standard-of-care treatment for localized disease.6 Patients with advanced disease should be considered for systemic therapy. However, there is a substantial unmet need for novel therapies due to the limited efficacy of existing treatment options. Agents that target mTOR have shown important potential in improving long-term outcomes in patients with metastatic PEComas.6 The PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway is a key signaling system that regulates cell proliferation and survival. TSC1 and TSC2 normally negatively regulate the mTOR complex 1 (mTORC1); however, alterations in TSC1 and TSC2 result in increased activity of this pathway, allowing tumors to proliferate (Figure).11,12 Clinical guidelines recommend using mTOR inhibitors for patients with locally advanced, unresectable, or metastatic malignant PEComas, and both on and off-label therapies are often used in the clinical setting.13 nab-Sirolimus, a nanoparticle albumin–bound sirolimus, is one such mTOR (previously known as mammalian target of rapamycin) inhibitor that binds to and blocks activation of the mechanistic target of rapamycin complex 1.11,14
Figure. mTOR Signaling Skin Diseases

The Promise of mTOR Inhibitors for Malignant PEComas
In 2021, the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved nab-sirolimus to treat patients with locally advanced, unresectable, or metastatic malignant PEComas. This approval was based on results from the phase 2 Advanced Malignant Perivascular Epithelioid Cell Tumors (AMPECT) clinical trial (NCT02494570).14,15 AMPECT was a multicenter, open-label, single-arm trial that evaluated nab-sirolimus in 34 patients with metastatic or locally advanced (ineligible for surgery) malignant PEComa and measurable disease who had not been previously treated with an mTOR inhibitor. Most of the patients were women, and the most common site of disease was the uterus.14 Patients received nab-sirolimus (100 mg/m2 intravenously) on days 1 and 8 of a 21-day cycle. The primary outcome of the study was an overall response rate by 6 months, and secondary endpoints included duration of response, progression-free survival (PFS), PFS at 6 months (PFS6), overall survival (OS), and safety; tumor biomarkers were also evaluated as exploratory measures.14 At 6 months, nab-sirolimus demonstrated an overall response rate of 39%, with rapid and durable responses. The median PFS was 10.6 months, with a PFS6 of 70%; median OS was 40.8 months.
Of the 25 patients for whom tumor profiling was performed, 8 of 9 (89%) patients with a TSC2 mutation achieved a response compared with 2 of 16 (13%) without the mutation. The most common adverse events associated with treatment included mucositis, rash, fatigue, and anemia, which are consistent with the medication class.14 Long-term analysis from the AMPECT trial demonstrated a median OS of 53.1 months, with a median duration of response of 39.7 months. Taken together, these results indicate that nab-sirolimus may provide patients with positive long-term clinical benefits with an acceptable safety profile.15 nab-Sirolimus is currently being evaluated in clinical trials in patients harboring TSC1 and TSC2 mutations and is also being investigated as a therapeutic candidate for other cancer types, such as neuroendocrine tumors, endometrial cancer, and ovarian cancer (NCT05997056; NCT05997017; NCT06494150; NCT05103358).
Case Study Spotlight
A 70-year-old woman presented at a local emergency department with several episodes of tingling in her upper and lower extremities. A chest radiograph revealed multiple bilateral pulmonary nodules, and a computed tomography scan of the chest, abdomen, and pelvis revealed a 21-cm left abdominal mass, innumerable pulmonary nodules, and multiple hepatic lesions. The patient underwent palliative resection of the large left retroperitoneal mass. Pathology revealed malignant PEComa, and a liver biopsy confirmed metastatic disease.
Following referral, the patient was enrolled in the AMPECT clinical trial, during which she received nab-sirolimus treatment. An objective response was confirmed after the initial 6 weeks on therapy and serial imaging revealed continued shrinkage in lung and liver lesions over time; the nab-sirolimus dose was reduced by 25% due to grade 2 pneumonitis after ~18 months of treatment. The patient had a complete response after 4 years on treatment. Unfortunately, the patient died due to complications from an unrelated elective hernia repair. She was 74 at the time of her death, and there was no radiographic evidence of PEComa.
Future Directions
While mTOR inhibitors provide the most favorable outcomes in the advanced disease setting at this time, research is underway to evaluate the utility of additional novel targets to treat malignant PEComa. Anecdotal evidence from case reports indicates that anti-vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) tyrosine kinase inhibitors may be beneficial to patients with malignant PEComa, highlighting the VEGF/VEGF receptor signaling pathway as a potential therapeutic target.16 Some evidence has also suggested that programmed cell death (PD) protein 1/PD ligand 1 (PD-1/PD-L1) inhibitors may be effective for patients with metastatic disease with high PD-L1 levels.17 In addition to more treatment options, diagnostic markers could potentially improve prognosis by facilitating earlier detection, a key challenge in managing malignant PEComas, especially for uterine tumors that are often misdiagnosed.18 Future research may also help guide personalized treatment strategies based on tumor genetic composition.
Read more from the 2024 Rare Diseases Report: Hematology and Oncology.
The PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway is an attractive therapeutic target for soft tissue sarcomas, as dysregulation of mechanistic target of rapamycin (mTOR) can lead to the development of various cancer types. Recently, clinical trial data have demonstrated that mTOR inhibitors can significantly improve long-term outcomes in patients with malignant perivascular epithelioid cell tumors, or PEComas—a challenging disease to manage in the advanced stage.
Ultrarare Mesenchymal Tumors
PEComas are ultrarare soft tissue tumors that are mesenchymal in origin and are characterized histologically by distinctive epithelioid cells that express smooth muscle and melanocytic markers.1-3 Malignant PEComas affect fewer than 1/1,000,000 people per year,4,5 and have a predominance in women, as they are commonly found in the uterus.4 PEComas include several histological types, such as angiomyolipoma (the most prevalent type), lymphangioleiomyomatosis, clear cell (“sugar”) tumor, and other tumors with similar features.3
Detecting an Ultrarare Malignant PEComa
Most PEComas are diagnosed incidentally via imaging. Patients may also present with symptoms of abdominal pain, nausea, and unexplained weight loss.6,7 PEComas in the uterus are often detected through an ultrasound, in which they may have the appearance of fibroids.8 Diagnosis must be confirmed by biopsy, and histological analysis can determine the risk classification based on tumor characteristics.6 Many patients with PEComas harbor loss-of-function mutations in the TSC1 and TSC2 genes, resulting in overactivation of the PIK3/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway9; TP53 mutations and TFE3 rearrangements or fusions have also been identified.6,10
Therapeutic Strategies Are Limited
Because PEComas are often resistant to chemotherapy and radiotherapy, resection is considered standard-of-care treatment for localized disease.6 Patients with advanced disease should be considered for systemic therapy. However, there is a substantial unmet need for novel therapies due to the limited efficacy of existing treatment options. Agents that target mTOR have shown important potential in improving long-term outcomes in patients with metastatic PEComas.6 The PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway is a key signaling system that regulates cell proliferation and survival. TSC1 and TSC2 normally negatively regulate the mTOR complex 1 (mTORC1); however, alterations in TSC1 and TSC2 result in increased activity of this pathway, allowing tumors to proliferate (Figure).11,12 Clinical guidelines recommend using mTOR inhibitors for patients with locally advanced, unresectable, or metastatic malignant PEComas, and both on and off-label therapies are often used in the clinical setting.13 nab-Sirolimus, a nanoparticle albumin–bound sirolimus, is one such mTOR (previously known as mammalian target of rapamycin) inhibitor that binds to and blocks activation of the mechanistic target of rapamycin complex 1.11,14
Figure. mTOR Signaling Skin Diseases

The Promise of mTOR Inhibitors for Malignant PEComas
In 2021, the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved nab-sirolimus to treat patients with locally advanced, unresectable, or metastatic malignant PEComas. This approval was based on results from the phase 2 Advanced Malignant Perivascular Epithelioid Cell Tumors (AMPECT) clinical trial (NCT02494570).14,15 AMPECT was a multicenter, open-label, single-arm trial that evaluated nab-sirolimus in 34 patients with metastatic or locally advanced (ineligible for surgery) malignant PEComa and measurable disease who had not been previously treated with an mTOR inhibitor. Most of the patients were women, and the most common site of disease was the uterus.14 Patients received nab-sirolimus (100 mg/m2 intravenously) on days 1 and 8 of a 21-day cycle. The primary outcome of the study was an overall response rate by 6 months, and secondary endpoints included duration of response, progression-free survival (PFS), PFS at 6 months (PFS6), overall survival (OS), and safety; tumor biomarkers were also evaluated as exploratory measures.14 At 6 months, nab-sirolimus demonstrated an overall response rate of 39%, with rapid and durable responses. The median PFS was 10.6 months, with a PFS6 of 70%; median OS was 40.8 months.
Of the 25 patients for whom tumor profiling was performed, 8 of 9 (89%) patients with a TSC2 mutation achieved a response compared with 2 of 16 (13%) without the mutation. The most common adverse events associated with treatment included mucositis, rash, fatigue, and anemia, which are consistent with the medication class.14 Long-term analysis from the AMPECT trial demonstrated a median OS of 53.1 months, with a median duration of response of 39.7 months. Taken together, these results indicate that nab-sirolimus may provide patients with positive long-term clinical benefits with an acceptable safety profile.15 nab-Sirolimus is currently being evaluated in clinical trials in patients harboring TSC1 and TSC2 mutations and is also being investigated as a therapeutic candidate for other cancer types, such as neuroendocrine tumors, endometrial cancer, and ovarian cancer (NCT05997056; NCT05997017; NCT06494150; NCT05103358).
Case Study Spotlight
A 70-year-old woman presented at a local emergency department with several episodes of tingling in her upper and lower extremities. A chest radiograph revealed multiple bilateral pulmonary nodules, and a computed tomography scan of the chest, abdomen, and pelvis revealed a 21-cm left abdominal mass, innumerable pulmonary nodules, and multiple hepatic lesions. The patient underwent palliative resection of the large left retroperitoneal mass. Pathology revealed malignant PEComa, and a liver biopsy confirmed metastatic disease.
Following referral, the patient was enrolled in the AMPECT clinical trial, during which she received nab-sirolimus treatment. An objective response was confirmed after the initial 6 weeks on therapy and serial imaging revealed continued shrinkage in lung and liver lesions over time; the nab-sirolimus dose was reduced by 25% due to grade 2 pneumonitis after ~18 months of treatment. The patient had a complete response after 4 years on treatment. Unfortunately, the patient died due to complications from an unrelated elective hernia repair. She was 74 at the time of her death, and there was no radiographic evidence of PEComa.
Future Directions
While mTOR inhibitors provide the most favorable outcomes in the advanced disease setting at this time, research is underway to evaluate the utility of additional novel targets to treat malignant PEComa. Anecdotal evidence from case reports indicates that anti-vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) tyrosine kinase inhibitors may be beneficial to patients with malignant PEComa, highlighting the VEGF/VEGF receptor signaling pathway as a potential therapeutic target.16 Some evidence has also suggested that programmed cell death (PD) protein 1/PD ligand 1 (PD-1/PD-L1) inhibitors may be effective for patients with metastatic disease with high PD-L1 levels.17 In addition to more treatment options, diagnostic markers could potentially improve prognosis by facilitating earlier detection, a key challenge in managing malignant PEComas, especially for uterine tumors that are often misdiagnosed.18 Future research may also help guide personalized treatment strategies based on tumor genetic composition.
Read more from the 2024 Rare Diseases Report: Hematology and Oncology.
- Stacchiotti S, Frezza AM, Blay JY, et al. Ultra-rare sarcomas: a consensus paper from the Connective Tissue Oncology Society community of experts on the incidence threshold and the list of entities. Cancer. 2021;127(16):2934-2942. doi:10.1002/cncr.33618
- Bleeker JS, Quevedo JF, Folpe AL. “Malignant” perivascular epithelioid cell neoplasm: risk stratification and treatment strategies. Sarcoma. 2012;2012:541626. doi:10.1155/2012/541626
- Thway K, Fisher C. PEComa: morphology and genetics of a complex tumor family. Ann Diagn Pathol. 2015;19(5):359-368. doi:10.1016/j.anndiagpath.2015.06.003
- Battistella E, Pomba L, Mirabella M, et al. Metastatic adrenal PEComa: case report and short review of the literature. Medicina (Kaunas). 2023;59(1):149. doi:10.3390/medicina59010149
- Meredith L, Chao T, Nevler A, et al. A rare metastatic mesenteric malignant PEComa with TSC2 mutation treated with palliative surgical resection and nab-sirolimus: a case report. Diagn Pathol. 2023;18(1):45. doi:10.1186/s13000-023-01323-x
- Czarnecka AM, Skoczylas J, Bartnik E, Switaj T, Rutkowski P. Management strategies for adults with locally advanced, unresectable or metastatic malignant perivascular epithelioid cell tumor (PEComa): challenges and solutions. Cancer Manag Res. 2023;15:615-623. doi:10.2147/CMAR.S351284
- Kvietkauskas M, Samuolyte A, Rackauskas R, et al. Primary liver perivascular epithelioid cell tumor (PEComa): case report and literature review. Medicina (Kaunas). 2024;60(3):409. doi:10.3390/medicina60030409
- Giannella L, Delli Carpini G, Montik N, et al. Ultrasound features of a uterine perivascular epithelioid cell tumor (PEComa): case report and literature review. Diagnostic (Basel). 2020;10(8):553. doi:10.3390/diagnostics10080553
- Liu L, Dehner C, Grandhi N, et al. The impact of TSC-1 and -2 mutations on response to therapy in malignant PEComa: a multicenter retrospective analysis. Genes (Basel). 2022;13(11):1932. doi:10.3390/genes13111932
- Schoolmeester JK, Dao LN, Sukov WR, et al. TFE3 translocation-associated perivascular epithelioid cell neoplasm (PEComa) of the gynecologic tract: morphology, immunophenotype, differential diagnosis. Am J Surg Pathol. 2015;39(3):394-404.doi:10.1097/PAS.0000000000000349
- Ali ES, Mitra K, Akter S, et al. Recent advances and limitations of mTOR inhibitors in the treatment of cancer. Cancer Cell Int. 2022;22(1):284. doi:10.1186/s12935-022-02706-8
- Sanfilippo R, Jones RL, Blay JY, et al. Role of chemotherapy, VEGFR inhibitors, and mTOR inhibitors in advanced perivascular epithelioid cell tumors (PEComas). Clin Cancer Res. 2019;25(17):5295-5300. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-19-0288
- National Comprehensive Cancer Network. NCCN clinical practice guidelines in oncology: soft tissue sarcoma. Version 2.2024. July 31, 2024. Accessed September 10, 2024. https://www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/pdf/sarcoma.pdf
- Wagner AJ, Ravi V, Riedel RF, et al. nab-Sirolimus for patients with malignant perivascular epithelioid cell tumors. J Clin Oncol. 2021;39(33):3660-3670. doi:10.1200/JCO.21.01728
- Wagner AJ, Ravi V, Riedel RF, et al. Phase II trial of nab-sirolimus in patients with advanced malignant perivascular epithelioid cell tumors (AMPECT): long-term efficacy and safety update. J Clin Oncol. 2024;42(13):1472-1476. doi:10.1200/JCO.23.02266
- Xu J, Gong XL, Wu H, Zhao L. Case report: gastrointestinal PEComa with TFE3 rearrangement treated with anti-VEGFR TKI apatinib. Front Oncol. 2020;10:582087. doi:10.3389/fonc.2020.582087
- McBride A, Garcia AJ, Sanders LJ, et al. Sustained response to pembrolizumab in recurrent perivascular epithelioid cell tumor with elevated expression of programmed death ligand: a case report. J Med Case Rep. 2021;15(1):400. doi:10.1186/s13256-021-02997-x
- Levin G, Capella MP, Meyer R, Brezinov Y, Gotlieb WH. Gynecologic perivascular epithelioid cell tumors (PEComas): a review of recent evidence. Arch Gynecol Obstet. 2024;309(6):2381-2386. doi:10.1007/s00404-024-07510-5
- Stacchiotti S, Frezza AM, Blay JY, et al. Ultra-rare sarcomas: a consensus paper from the Connective Tissue Oncology Society community of experts on the incidence threshold and the list of entities. Cancer. 2021;127(16):2934-2942. doi:10.1002/cncr.33618
- Bleeker JS, Quevedo JF, Folpe AL. “Malignant” perivascular epithelioid cell neoplasm: risk stratification and treatment strategies. Sarcoma. 2012;2012:541626. doi:10.1155/2012/541626
- Thway K, Fisher C. PEComa: morphology and genetics of a complex tumor family. Ann Diagn Pathol. 2015;19(5):359-368. doi:10.1016/j.anndiagpath.2015.06.003
- Battistella E, Pomba L, Mirabella M, et al. Metastatic adrenal PEComa: case report and short review of the literature. Medicina (Kaunas). 2023;59(1):149. doi:10.3390/medicina59010149
- Meredith L, Chao T, Nevler A, et al. A rare metastatic mesenteric malignant PEComa with TSC2 mutation treated with palliative surgical resection and nab-sirolimus: a case report. Diagn Pathol. 2023;18(1):45. doi:10.1186/s13000-023-01323-x
- Czarnecka AM, Skoczylas J, Bartnik E, Switaj T, Rutkowski P. Management strategies for adults with locally advanced, unresectable or metastatic malignant perivascular epithelioid cell tumor (PEComa): challenges and solutions. Cancer Manag Res. 2023;15:615-623. doi:10.2147/CMAR.S351284
- Kvietkauskas M, Samuolyte A, Rackauskas R, et al. Primary liver perivascular epithelioid cell tumor (PEComa): case report and literature review. Medicina (Kaunas). 2024;60(3):409. doi:10.3390/medicina60030409
- Giannella L, Delli Carpini G, Montik N, et al. Ultrasound features of a uterine perivascular epithelioid cell tumor (PEComa): case report and literature review. Diagnostic (Basel). 2020;10(8):553. doi:10.3390/diagnostics10080553
- Liu L, Dehner C, Grandhi N, et al. The impact of TSC-1 and -2 mutations on response to therapy in malignant PEComa: a multicenter retrospective analysis. Genes (Basel). 2022;13(11):1932. doi:10.3390/genes13111932
- Schoolmeester JK, Dao LN, Sukov WR, et al. TFE3 translocation-associated perivascular epithelioid cell neoplasm (PEComa) of the gynecologic tract: morphology, immunophenotype, differential diagnosis. Am J Surg Pathol. 2015;39(3):394-404.doi:10.1097/PAS.0000000000000349
- Ali ES, Mitra K, Akter S, et al. Recent advances and limitations of mTOR inhibitors in the treatment of cancer. Cancer Cell Int. 2022;22(1):284. doi:10.1186/s12935-022-02706-8
- Sanfilippo R, Jones RL, Blay JY, et al. Role of chemotherapy, VEGFR inhibitors, and mTOR inhibitors in advanced perivascular epithelioid cell tumors (PEComas). Clin Cancer Res. 2019;25(17):5295-5300. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-19-0288
- National Comprehensive Cancer Network. NCCN clinical practice guidelines in oncology: soft tissue sarcoma. Version 2.2024. July 31, 2024. Accessed September 10, 2024. https://www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/pdf/sarcoma.pdf
- Wagner AJ, Ravi V, Riedel RF, et al. nab-Sirolimus for patients with malignant perivascular epithelioid cell tumors. J Clin Oncol. 2021;39(33):3660-3670. doi:10.1200/JCO.21.01728
- Wagner AJ, Ravi V, Riedel RF, et al. Phase II trial of nab-sirolimus in patients with advanced malignant perivascular epithelioid cell tumors (AMPECT): long-term efficacy and safety update. J Clin Oncol. 2024;42(13):1472-1476. doi:10.1200/JCO.23.02266
- Xu J, Gong XL, Wu H, Zhao L. Case report: gastrointestinal PEComa with TFE3 rearrangement treated with anti-VEGFR TKI apatinib. Front Oncol. 2020;10:582087. doi:10.3389/fonc.2020.582087
- McBride A, Garcia AJ, Sanders LJ, et al. Sustained response to pembrolizumab in recurrent perivascular epithelioid cell tumor with elevated expression of programmed death ligand: a case report. J Med Case Rep. 2021;15(1):400. doi:10.1186/s13256-021-02997-x
- Levin G, Capella MP, Meyer R, Brezinov Y, Gotlieb WH. Gynecologic perivascular epithelioid cell tumors (PEComas): a review of recent evidence. Arch Gynecol Obstet. 2024;309(6):2381-2386. doi:10.1007/s00404-024-07510-5
Advancements in the Treatment of Malignant PEComas with mTOR Inhibitors
Advancements in the Treatment of Malignant PEComas with mTOR Inhibitors
National Organization for Rare Disorders: Strengthening Rare Cancer Advocacy
National Organization for Rare Disorders: Strengthening Rare Cancer Advocacy
Rare cancers account for 25% to 30% of all cancer diagnoses and approximately 25% of all cancer deaths, thereby posing a significant public health burden.1 Recognizing the need for action to address this health crisis, the National Organization for Rare Disorders (NORD) established the Rare Cancer Coalition in 2017 to alleviate the challenges faced by people living with rare cancers. Since its inception, the Rare Cancer Coalition has reached millions of people through patient and caregiver education sessions, healthcare provider education, and public awareness campaigns. Since its inception, the Rare Cancer Coalition has reached millions of people through patient and caregiver education sessions, healthcare provider education, and public awareness campaigns. The Coalition Members have had an impact on other rare cancer advocacy groups, contributed to medical publications, and provided collaborative networking opportunities among patients, advocates and researchers.
Thanks to successful advocacy by the Rare Cancer Coalition, the United States Congress established “Rare Cancer Day.” This event takes place annually on September 30 and brings global awareness to rare cancers through mass media and public events. In recognition of Rare Cancer Day 2024, NORD focused its public education on the importance of patient participation in rare cancer research.
NORD and the Rare Cancer Coalition are deeply committed to addressing the unique challenges faced by the rare cancer community. Moving forward, we will focus on promoting the development of innovative and effective treatments, enhancing access to diagnostic testing, advancing new technologies, and fostering research that leads to improved medical approaches for patients with rare cancers.
To that end, we are pleased to present the 2024 Rare Disease Report: Hematology and Oncology in collaboration with our partners at MDedge. This issue will highlight some of the latest advances in rare cancer research, diagnosis, and treatments that are providing new hope for improved outcomes. In this issue, you will find articles that cover recent discoveries on specific rare cancers, including:
- The promise of mTOR inhibitors in improving malignant PEComas
- How novel immunotherapies are demonstrating the potential for improved outcomes for large cell neuroendocrine carcinoma of the lung
- Potential paradigm shifts in the treatment of glioblastoma leveraging CAR T-cell therapies and targeted inhibitors
- Future directions in the treatment of gallbladder cancer with molecular profiling, immunotherapies, and targeted treatments
- The benefits of a multidisciplinary approach in addressing cutaneous T-cell lymphomas
- The evolving role of JAK inhibitors in managing symptoms of myelofibrosis
- Advancements in staging and tailored treatments for hepatoblastoma
- And more!
We hope these articles will enhance your knowledge and enrich your day-to-day clinical practices. We invite you to explore NORD resources including digital CME sessions and disease-specific reports written in accessible language for patients and families. Additionally, you can sign up for our quarterly Caring for Rare newsletter, for timely updates on rare diseases.
Thank you for your commitment to advancing care for rare cancer patients. Your dedication to staying informed is vital for improving patient outcomes.
Read more from the 2024 Rare Diseases Report: Hematology and Oncology.
- International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC). Rare Disease Day 2022: IARC Highlights the Burden of Rare Cancers. Published February 28, 2022. Accessed October 2, 2024. https://www.iarc.who.int/news-events/rare-disease-day-2022-iarc-highlights-the-burden-of-rare-cancers/
Rare cancers account for 25% to 30% of all cancer diagnoses and approximately 25% of all cancer deaths, thereby posing a significant public health burden.1 Recognizing the need for action to address this health crisis, the National Organization for Rare Disorders (NORD) established the Rare Cancer Coalition in 2017 to alleviate the challenges faced by people living with rare cancers. Since its inception, the Rare Cancer Coalition has reached millions of people through patient and caregiver education sessions, healthcare provider education, and public awareness campaigns. Since its inception, the Rare Cancer Coalition has reached millions of people through patient and caregiver education sessions, healthcare provider education, and public awareness campaigns. The Coalition Members have had an impact on other rare cancer advocacy groups, contributed to medical publications, and provided collaborative networking opportunities among patients, advocates and researchers.
Thanks to successful advocacy by the Rare Cancer Coalition, the United States Congress established “Rare Cancer Day.” This event takes place annually on September 30 and brings global awareness to rare cancers through mass media and public events. In recognition of Rare Cancer Day 2024, NORD focused its public education on the importance of patient participation in rare cancer research.
NORD and the Rare Cancer Coalition are deeply committed to addressing the unique challenges faced by the rare cancer community. Moving forward, we will focus on promoting the development of innovative and effective treatments, enhancing access to diagnostic testing, advancing new technologies, and fostering research that leads to improved medical approaches for patients with rare cancers.
To that end, we are pleased to present the 2024 Rare Disease Report: Hematology and Oncology in collaboration with our partners at MDedge. This issue will highlight some of the latest advances in rare cancer research, diagnosis, and treatments that are providing new hope for improved outcomes. In this issue, you will find articles that cover recent discoveries on specific rare cancers, including:
- The promise of mTOR inhibitors in improving malignant PEComas
- How novel immunotherapies are demonstrating the potential for improved outcomes for large cell neuroendocrine carcinoma of the lung
- Potential paradigm shifts in the treatment of glioblastoma leveraging CAR T-cell therapies and targeted inhibitors
- Future directions in the treatment of gallbladder cancer with molecular profiling, immunotherapies, and targeted treatments
- The benefits of a multidisciplinary approach in addressing cutaneous T-cell lymphomas
- The evolving role of JAK inhibitors in managing symptoms of myelofibrosis
- Advancements in staging and tailored treatments for hepatoblastoma
- And more!
We hope these articles will enhance your knowledge and enrich your day-to-day clinical practices. We invite you to explore NORD resources including digital CME sessions and disease-specific reports written in accessible language for patients and families. Additionally, you can sign up for our quarterly Caring for Rare newsletter, for timely updates on rare diseases.
Thank you for your commitment to advancing care for rare cancer patients. Your dedication to staying informed is vital for improving patient outcomes.
Read more from the 2024 Rare Diseases Report: Hematology and Oncology.
Rare cancers account for 25% to 30% of all cancer diagnoses and approximately 25% of all cancer deaths, thereby posing a significant public health burden.1 Recognizing the need for action to address this health crisis, the National Organization for Rare Disorders (NORD) established the Rare Cancer Coalition in 2017 to alleviate the challenges faced by people living with rare cancers. Since its inception, the Rare Cancer Coalition has reached millions of people through patient and caregiver education sessions, healthcare provider education, and public awareness campaigns. Since its inception, the Rare Cancer Coalition has reached millions of people through patient and caregiver education sessions, healthcare provider education, and public awareness campaigns. The Coalition Members have had an impact on other rare cancer advocacy groups, contributed to medical publications, and provided collaborative networking opportunities among patients, advocates and researchers.
Thanks to successful advocacy by the Rare Cancer Coalition, the United States Congress established “Rare Cancer Day.” This event takes place annually on September 30 and brings global awareness to rare cancers through mass media and public events. In recognition of Rare Cancer Day 2024, NORD focused its public education on the importance of patient participation in rare cancer research.
NORD and the Rare Cancer Coalition are deeply committed to addressing the unique challenges faced by the rare cancer community. Moving forward, we will focus on promoting the development of innovative and effective treatments, enhancing access to diagnostic testing, advancing new technologies, and fostering research that leads to improved medical approaches for patients with rare cancers.
To that end, we are pleased to present the 2024 Rare Disease Report: Hematology and Oncology in collaboration with our partners at MDedge. This issue will highlight some of the latest advances in rare cancer research, diagnosis, and treatments that are providing new hope for improved outcomes. In this issue, you will find articles that cover recent discoveries on specific rare cancers, including:
- The promise of mTOR inhibitors in improving malignant PEComas
- How novel immunotherapies are demonstrating the potential for improved outcomes for large cell neuroendocrine carcinoma of the lung
- Potential paradigm shifts in the treatment of glioblastoma leveraging CAR T-cell therapies and targeted inhibitors
- Future directions in the treatment of gallbladder cancer with molecular profiling, immunotherapies, and targeted treatments
- The benefits of a multidisciplinary approach in addressing cutaneous T-cell lymphomas
- The evolving role of JAK inhibitors in managing symptoms of myelofibrosis
- Advancements in staging and tailored treatments for hepatoblastoma
- And more!
We hope these articles will enhance your knowledge and enrich your day-to-day clinical practices. We invite you to explore NORD resources including digital CME sessions and disease-specific reports written in accessible language for patients and families. Additionally, you can sign up for our quarterly Caring for Rare newsletter, for timely updates on rare diseases.
Thank you for your commitment to advancing care for rare cancer patients. Your dedication to staying informed is vital for improving patient outcomes.
Read more from the 2024 Rare Diseases Report: Hematology and Oncology.
- International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC). Rare Disease Day 2022: IARC Highlights the Burden of Rare Cancers. Published February 28, 2022. Accessed October 2, 2024. https://www.iarc.who.int/news-events/rare-disease-day-2022-iarc-highlights-the-burden-of-rare-cancers/
- International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC). Rare Disease Day 2022: IARC Highlights the Burden of Rare Cancers. Published February 28, 2022. Accessed October 2, 2024. https://www.iarc.who.int/news-events/rare-disease-day-2022-iarc-highlights-the-burden-of-rare-cancers/
National Organization for Rare Disorders: Strengthening Rare Cancer Advocacy
National Organization for Rare Disorders: Strengthening Rare Cancer Advocacy
2024 Rare Diseases Report: Hematology and Oncology
2024 Rare Diseases Report: Hematology and Oncology
National Organization for Rare Disorders: Strengthening Rare Cancer Advocacy
By Alli Ward
NORD's Rare Cancer Coalition has transformed advocacy and awareness efforts, offering education and fostering research to address the challenges of rare cancers.
Treatment of Glioblastoma: A Potential Shift in Paradigm
By Jeffrey N. Bruce, MD
Immunotherapies and molecular profiling are paving the way for more targeted approaches in treating glioblastoma.
Emerging Insights and Therapeutic Strategies for Large Cell Neuroendocrine Carcinoma of the Lung
By Robert A. Ramirez, DO, FACP, and Aman Chauhan, MD
New diagnostic tools and precision medicine approaches are addressing the unique challenges of this aggressive neuroendocrine cancer.
Advancements in the Treatment of Malignant PEComas with mTOR Inhibitors
By Richard F. Riedel, MD
The use of mTOR inhibitors marks significant progress in managing advanced malignant PEComas, offering new hope for patients.
Cutaneous T-Cell Lymphomas Update: Benefits of a Multidisciplinary Care Approach
By Jina Chung, MD, and Eric Mou, MD
A multidisciplinary care model ensures optimal outcomes for patients with cutaneous T-cell lymphomas, addressing both medical and emotional needs.
Optimizing Myelofibrosis Care in the Age of JAK Inhibitors
By Douglas Tremblay, MD
JAK inhibitors are central to myelofibrosis management, with personalized strategies helping to navigate resistance and improve quality of life.
Current Management and Future Directions in the Treatment of Gallbladder Cancer
By Ghassan K. Abou-Alfa, MD, MBA, JD, FASCO
Molecular profiling and immunotherapy are reshaping the treatment paradigm for gallbladder cancer, improving survival outcomes.
Improving Prognosis in Hepatoblastoma: Evolving Risk Stratification and Treatment Strategies
By Greg M. Tiao, MD
Risk stratification and individualized therapies are driving progress in treating hepatoblastoma, with promising advancements on the horizon.
National Organization for Rare Disorders: Strengthening Rare Cancer Advocacy
By Alli Ward
NORD's Rare Cancer Coalition has transformed advocacy and awareness efforts, offering education and fostering research to address the challenges of rare cancers.
Treatment of Glioblastoma: A Potential Shift in Paradigm
By Jeffrey N. Bruce, MD
Immunotherapies and molecular profiling are paving the way for more targeted approaches in treating glioblastoma.
Emerging Insights and Therapeutic Strategies for Large Cell Neuroendocrine Carcinoma of the Lung
By Robert A. Ramirez, DO, FACP, and Aman Chauhan, MD
New diagnostic tools and precision medicine approaches are addressing the unique challenges of this aggressive neuroendocrine cancer.
Advancements in the Treatment of Malignant PEComas with mTOR Inhibitors
By Richard F. Riedel, MD
The use of mTOR inhibitors marks significant progress in managing advanced malignant PEComas, offering new hope for patients.
Cutaneous T-Cell Lymphomas Update: Benefits of a Multidisciplinary Care Approach
By Jina Chung, MD, and Eric Mou, MD
A multidisciplinary care model ensures optimal outcomes for patients with cutaneous T-cell lymphomas, addressing both medical and emotional needs.
Optimizing Myelofibrosis Care in the Age of JAK Inhibitors
By Douglas Tremblay, MD
JAK inhibitors are central to myelofibrosis management, with personalized strategies helping to navigate resistance and improve quality of life.
Current Management and Future Directions in the Treatment of Gallbladder Cancer
By Ghassan K. Abou-Alfa, MD, MBA, JD, FASCO
Molecular profiling and immunotherapy are reshaping the treatment paradigm for gallbladder cancer, improving survival outcomes.
Improving Prognosis in Hepatoblastoma: Evolving Risk Stratification and Treatment Strategies
By Greg M. Tiao, MD
Risk stratification and individualized therapies are driving progress in treating hepatoblastoma, with promising advancements on the horizon.
National Organization for Rare Disorders: Strengthening Rare Cancer Advocacy
By Alli Ward
NORD's Rare Cancer Coalition has transformed advocacy and awareness efforts, offering education and fostering research to address the challenges of rare cancers.
Treatment of Glioblastoma: A Potential Shift in Paradigm
By Jeffrey N. Bruce, MD
Immunotherapies and molecular profiling are paving the way for more targeted approaches in treating glioblastoma.
Emerging Insights and Therapeutic Strategies for Large Cell Neuroendocrine Carcinoma of the Lung
By Robert A. Ramirez, DO, FACP, and Aman Chauhan, MD
New diagnostic tools and precision medicine approaches are addressing the unique challenges of this aggressive neuroendocrine cancer.
Advancements in the Treatment of Malignant PEComas with mTOR Inhibitors
By Richard F. Riedel, MD
The use of mTOR inhibitors marks significant progress in managing advanced malignant PEComas, offering new hope for patients.
Cutaneous T-Cell Lymphomas Update: Benefits of a Multidisciplinary Care Approach
By Jina Chung, MD, and Eric Mou, MD
A multidisciplinary care model ensures optimal outcomes for patients with cutaneous T-cell lymphomas, addressing both medical and emotional needs.
Optimizing Myelofibrosis Care in the Age of JAK Inhibitors
By Douglas Tremblay, MD
JAK inhibitors are central to myelofibrosis management, with personalized strategies helping to navigate resistance and improve quality of life.
Current Management and Future Directions in the Treatment of Gallbladder Cancer
By Ghassan K. Abou-Alfa, MD, MBA, JD, FASCO
Molecular profiling and immunotherapy are reshaping the treatment paradigm for gallbladder cancer, improving survival outcomes.
Improving Prognosis in Hepatoblastoma: Evolving Risk Stratification and Treatment Strategies
By Greg M. Tiao, MD
Risk stratification and individualized therapies are driving progress in treating hepatoblastoma, with promising advancements on the horizon.
2024 Rare Diseases Report: Hematology and Oncology
2024 Rare Diseases Report: Hematology and Oncology
Current Management and Future Directions in the Treatment of Gallbladder Cancer
Current Management and Future Directions in the Treatment of Gallbladder Cancer
Clinical outcomes of patients with gallbladder cancer have improved considerably with the advent of immunotherapy and targeted therapies. While specialists have gained tremendous insights into the disease over the last 10 years, significant knowledge gaps remain, as relapse rates remain high. Early referral to specialized treatment centers and timely molecular profiling can help guide therapeutic regimen choice and potentially improve patient outcomes.
Insights Into Disease Prevalence and Development
Gallbladder cancer is a rare malignancy with an aggressive course. Most gallbladder cancers are of epithelial origin, with adenocarcinoma being the most common type.1 Approximately 12,350 new cases of gallbladder cancer and nearby large bile duct cancers are anticipated in 2024 in the United States,2 predominantly affecting Southwestern Native Americans.3 The prevalence of gallbladder cancer varies greatly worldwide; rates are highest in South America (mainly in Chile) and Southeast Asia, including Eastern India.3,4
Multiple factors, including environment and genetics, contribute to the development of gallbladder cancer, which is driven primarily by chronic inflammation.5 While there are no defined risk factors, this malignancy is mostly associated with female sex, chronic gallbladder infections, and gallstones.4 Some evidence also suggests a dietary association with consuming mustard seed oil.6 Exposure to certain environmental toxins or heavy metals may also contribute to disease risk.1,4
Several genetic alterations have been identified in patients with gallbladder cancer that may be related to disease etiology; these include somatic mutations in the human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2), Kirsten rat sarcoma viral oncogene homolog (KRAS), and tumor protein p53 (TP53) genes, and many others.7,8 In addition to somatic mutations, gene overexpression, epigenetic changes, and microRNA-associated changes have also been linked to the disease.3
Challenges in Uncovering a “Hidden” Disease
While most gallbladder cancers are usually detected incidentally, patients may present with symptoms of abdominal pain, discomfort, and biliary obstruction–related symptoms like jaundice, itching, and dark urine.3,9,10 Cases may initially be misdiagnosed as inflammatory conditions such as cholecystitis or gallbladder stones; as a result, patients may be rushed into an inappropriate or incorrect surgical intervention.11 For these reasons, as well as the tight anatomical location of the gallbladder, cases are often not detected until advanced-stage disease.3,4
Patients diagnosed in stage 4 with distant metastases have an expected survival rate of less than 1 year,12 and low referral rates are associated with poor outcomes.13 Patients with suspected disease should therefore be referred to a specialized treatment center as soon as possible to confirm a diagnosis and initiate appropriate treatment. Core biopsies can provide histological confirmation, where feasible and safe, followed by imaging to determine extent of the disease.14
Evolving Management of Localized and Advanced Disease
Localized disease
Surgery with curative intent is the standard of care in patients with localized disease (Figure).14,15 Contraindications for resection include distant metastases and occlusion of blood vessels.4 Depending on tumor stage, eligible patients may undergo radical cholecystectomy and portal lymphadenectomy, as well as potential liver resection (segments 4b and 5).5
Figure. Biliary Tract Cancers (BTCs): Diagnosis and Management Algorithm14
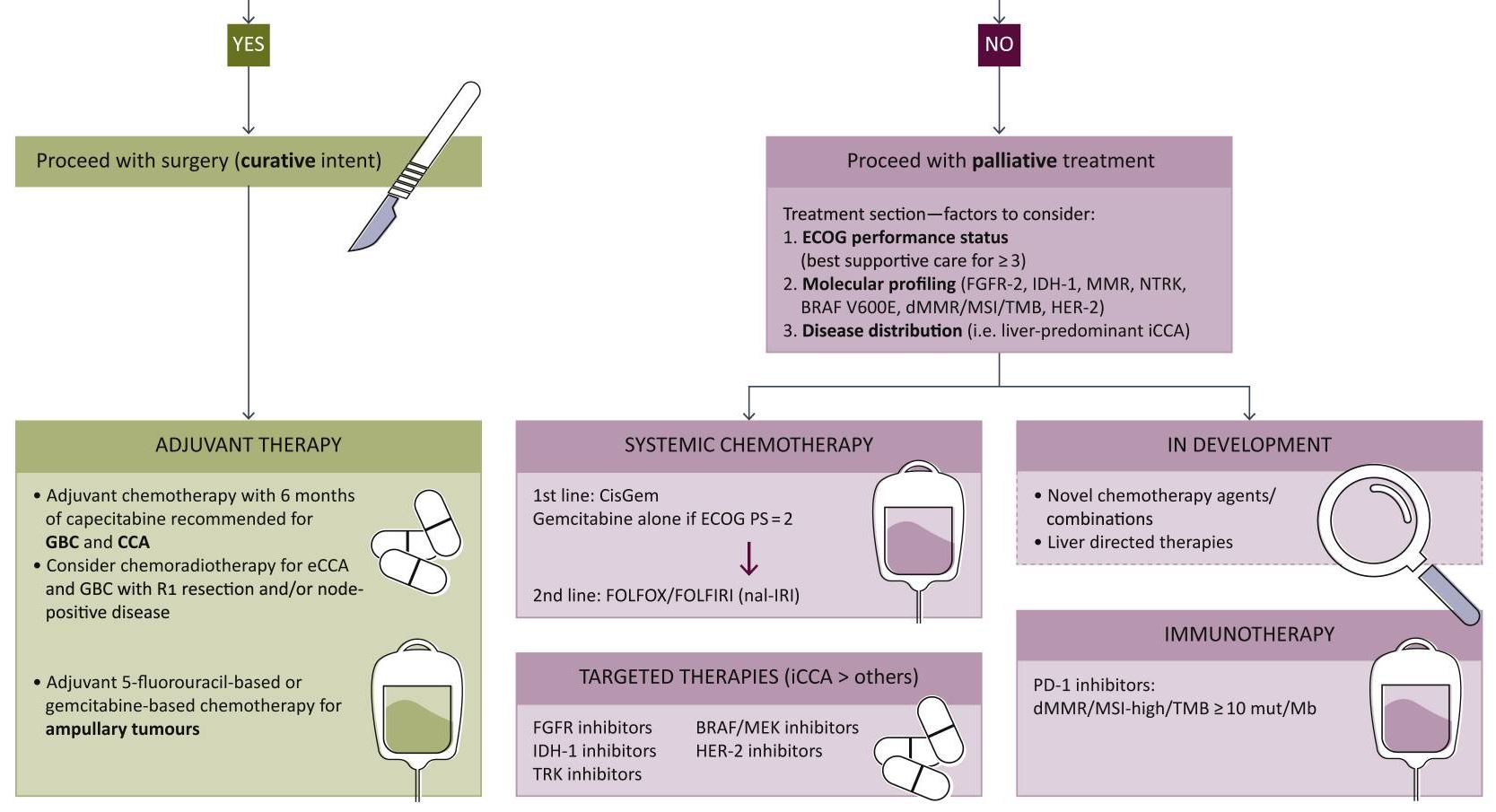
From Lamarca A, Edeline J, Goyal L. How I treat biliary tract cancer. ESMO Open. 2022;7(1):100378. doi:10.1016/j.esmoop.2021.100378. [Open access].
As the nonencapsulated nature of the gallbladder renders local extension very likely, a peri-adjuvant approach including neoadjuvant and adjuvant arms should be initiated. Standard chemotherapy regimens may include capecitabine or gemcitabine + cisplatin/capecitabine.16,17
Advanced disease
Systemic therapy remains key in the setting of locally advanced or metastatic disease. In August 2024, the National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN) updated its guidelines to strongly recommend durvalumab + gemcitabine + cisplatin or pembrolizumab + gemcitabine + cisplatin as the preferred regimens for primary treatment of these patients.17 Other regimens to consider based on both NCCN and European Society of Medical Oncology (ESMO) guidelines include gemcitabine + cisplatin or capecitabine + oxaliplatin.17,18 In addition, gemcitabine + S-1 (tegafur, gimeracil, and oteracil) may also be considered as part of first-line treatment based on data from clinical trials conducted in Japan.19 FOLFOX (folinic acid, fluorouracil, and oxaliplatin) is recommended for second-line treatment.16
While the American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO) guidelines are yet to be published, they have previously reviewed data on several potential novel agents and targeted therapies for first-line treatment.20
The addition of immunotherapies such as checkpoint inhibitors to the treatment algorithm has been monumental for the treatment of advanced gallbladder cancer. Durvalumab and pembrolizumab, programmed cell death protein 1 (PD-1)/programmed death-ligand 1 (PDL-1) receptor inhibitors, in combination with gemcitabine + cisplatin, significantly improve overall survival compared to gemcitabine + cisplatin alone.17,21,22 These regimens are strongly recommended as first-line therapy in eligible patients who have not previously been treated with a checkpoint inhibitor.
Biopsies should be performed as early as possible in all patients with unresectable or metastatic disease for genomic profiling. Next-generation sequencing can help inform response to targeted therapies in testing by identifying genetic mutations, potentially improving treatment response.1,23
In certain circumstances, patients with genetic mutations are eligible for molecularly targeted therapies17:
Unresectable or metastatic disease:
- Neurotrophic tyrosine receptor kinase (NTRK) gene fusion-positive tumors: entrectinib, larotrectinib, or repotrectinib
- High mutational burden (TMB-H) tumors: nivolumab + ipilimumab
Following disease progression:
- B-Raf Proto-Oncogene, Serine/Threonine Kinase (BRAF) V600E-mutated tumors: dabrafenib + trametinib
- Cholangiocarcinoma with fibroblast growth factor receptor 2 (FGFR2) fusions: futibatinib + pemigatinib
- Cholangiocarcinoma with rearrangements or isocitrate dehydrogenase 1 (IDH1) mutations: ivosidenib
It is important to note that further development of adjuvant strategies is greatly needed to better guide management across disease stages.16
Therapeutic candidates in testing
Despite the advancements achieved with immunotherapies and targeted treatments, therapeutic options have remained comparable to those of other biliary tumors such as intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. However, some novel candidates currently being evaluated in clinical trials have shown promise24-26:
HER2: Overexpression of the HER2 protein in gallbladder cancer causes abnormal cell survival and proliferation. Initial clinical trial data have suggested that agents targeting HER2 may improve outcomes in patients with advanced gallbladder cancer who harbor somatic HER2 mutations. In fact, the anti-HER2 agent zanidatamab provided clinical benefit and was well tolerated in patients with treatment-refractory, HER2-positive biliary tract cancer in a phase 2 single-arm trial.
Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF): The VEGF/ VEGF receptor pathway may also be a promising target due to its role in regulating epithelial cell differentiation and migration. Phase 2 studies of VEGF antibodies, such as bevacizumab, in combination with standard chemotherapy have demonstrated improved response rates; however, some of these studies have shown mixed results.
Phosphoinositide 3-kinases (PI3K)/protein kinase B (AKT)/mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR): This key signaling pathway plays an important role in driving cancer growth and metastases. Early trials of an mTOR inhibitor in combination with standard chemotherapy have demonstrated an acceptable tolerability profile with potential signs of clinical benefit.
The immunotherapy landscape for gallbladder cancer may evolve beyond currently approved PD-1/PDL-1 receptor inhibitors with the development of agonist antibodies and chimeric antigen receptor T cell (CAR-T) candidates.27 Novel treatment approaches like vaccines and nanoparticle delivery systems are also under investigation.
Looking Toward the Future
Gallbladder cancer is challenging to detect, and earlier diagnosis is key to improving outcomes. It is critical to refer patients to specialized treatment centers as soon as the disease is suspected. Rapid development in advanced genetic testing and other analytical methods may lead to identification of diagnostic biomarkers to aid in detecting cases sooner.24
Despite the fast-evolving pipeline for therapeutic candidates, greater research is also needed to inform sequencing of chemotherapy regimens with immunotherapy and targeted therapy to achieve favorable long-term outcomes.27 As new candidates are approved, management may become remain less than ideal without this crucial guidance.
We hope the future will bring the opportunity to provide more tailored treatments to patients with novel candidates that can further engage the immune system beyond currently identified targets.
Read more from the 2024 Rare Diseases Report: Hematology and Oncology.
- Okumura K, Gogna S, Gachabayov M, et al. Gallbladder cancer: historical treatment and new management options. World J Gastrointest Oncol. 2021;13(10):1317-1335. doi:10.4251/wjgo.v13.i10.1317
- Key statistics for gallbladder cancer. American Cancer Society. Updated May 22, 2024. Accessed August 26, 2024. https://www.cancer.org/cancer/types/gallbladder-cancer/about/key-statistics.html
- Nemunaitis JM, Brown-Glabeman U, Soares H, et al. Gallbladder cancer: review of a rare orphan gastrointestinal cancer with a focus on populations of New Mexico. BMC Cancer. 2018;18(1):665. doi:10.1186/s12885-018-4575-3
- Halaseh SA, Halaseh S, Shakman R. A review of the etiology and epidemiology of gallbladder cancer: what you need to know. Cureus. 2022;14(8):e28260. doi:10.7759/cureus.28260
- Menon G, Babiker HM. Gallbladder carcinoma. StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island, FL: StatPearls Publishing; 2024. Updated August 17, 2024. Accessed September 30, 2024. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK442002/
- Mhatre S, Rajaraman P, Chatterjee N, et al. Mustard oil consumption, cooking method, diet and gallbladder cancer risk in high- and low-risk regions of India. Int J Cancer. 2020;147(6):1621-1628. doi:10.1002/ijc.32952
- Sharma A, Sharma KL, Gupta A, Yadav A, Kumar A. Gallbladder cancer epidemiology, pathogenesis and molecular genetics: recent update. World J Gastroenterol. 2017;23(22):3978-3998. doi:10.3748/wjg.v23.i22.3978
- Kuipers H, de Bitter TJJ, de Boer MT, et al. Gallbladder cancer: current insights in genetic alterations and their possible therapeutic implications. Cancers (Basel). 2021;13(21):5257. doi:10.3390/cancers13215257
- Larson VA, Tang O, Ständer S, Kang S, Kwatra SG. Association between itch and cancer in 16,925 patients with pruritus: experience at a tertiary care center. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019;80(4):931-937. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2018.08.044
- Neculoiu D, Neculoiu LC, Popa RM, Manea RM. The many hidden faces of gallbladder carcinoma on CT and MRI imaging—from A to Z. Diagnostics (Basel). 2024;14(5):475. doi:10.3390/diagnostics14050475
- Deo KB, Avudaiappan M, Shenvi S, et al. Misdiagnosis of carcinoma gallbladder in endemic regions. BMC Surg. 2022;22(1):343. doi:10.1186/s12893-022-01793-8
- Prieto M, Gastaca M, Ruiz P, et al. Long term recurrence free survival in a stage IV gallbladder cancer treated with chemotherapy plus trastuzumab and salvage liver resection. Ann Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg. 2019;23(4):403-407. doi:10.14701/ahbps.2019.23.4.403
- van Dooren M, de Savornin Lohman EAJ, van der Post RS, et al. Referral rate of patients with incidental gallbladder cancer and survival: outcomes of a multicentre retrospective study. BJS Open. 2024;8(2):zrae013. doi:10.1093/bjsopen/zrae013
- Lamarca A, Edeline J, Goyal L. How I treat biliary tract cancer. ESMO Open. 2022;7(1):100378. doi:10.1016/j.esmoop.2021.100378
- Zhou Y, Yuan K, Yang Y, et al. Gallbladder cancer: current and future treatment options. Front Pharmacol. 2023;14:1183619. doi:10.3389/fphar.2023.1183619
- Banales JM, Marin JJG, Lamarca A, et al. Cholangiocarcinoma 2020: the next horizon in mechanisms and management. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2020;17(9):557-588. doi:10.1038/s41575-020-0310-z
- National Comprehensive Cancer Network. NCCN clinical practice guidelines in oncology: biliary tract cancers. Version 4.2024. August 29, 2024. Accessed September 30, 2024. https://www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/pdf/btc.pdf
- Vogel A, Bridgewater J, Edeline J, et al. Biliary tract cancer: ESMO clinical practice guideline for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann Oncol. 2023;34(2):127-140. doi:10.1016/j.annonc.2022.10.506
- Nagino M, Hirano S, Yoshitomi H, et al. Clinical practice guidelines for the management of biliary tract cancers 2019: the 3rd English edition. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Sci. 2021;28(1):26-54. doi:10.1002/jhbp.870
- Müller BG, De Aretxabala X, González Domingo M. A review of recent data in the treatment of gallbladder cancer: what we know, what we do, and what should be done. Am Soc Clin Oncol Educ Book. 2014;e165-e170. doi:10.14694/EdBook_AM.2014.34.e165
- Kelley RK, Ueno M, Yoo C, et al; for the KEYNOTE-966 investigators. Pembrolizumab in combination with gemcitabine and cisplatin compared with gemcitabine and cisplatin alone for patients with advanced biliary tract cancer (KEYNOTE-966): a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet. 2023;401(10391):1853-1865. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(23)00727-4
- Oh DY, Ruth He A, Qin S, et al. Durvalumab plus gemcitabine and cisplatin in advanced biliary tract cancer. NEJM Evid. 2022;1(8):EVIDoa2200015. doi:10.1056/EVIDoa2200015
- DiPeri TP, Javle MM, Meric-Bernstam F. Next generation sequencing for biliary tract cancers. Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2021;15(5):471-474. doi:10.1080/17474124.2021.1896967
- Song X, Hu Y, Li Y, Shao R, Liu F, Liu Y. Overview of current targeted therapy in gallbladder cancer. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2020;5(1):230. doi:10.1038/s41392-020-00324-2
- LaPelusa M, Heumann T, Goff L, Agarwal R. Targeted therapies in advanced biliary tract cancers—a narrative review. Chin Clin Oncol. 2023;12(2):14. doi:10.21037/cco-22-93
- Harding JJ, Fan J, Oh DY, et al; for the HERIZON-BTC-01 study group. Zanidatamab for HER2-amplified, unresectable, locally advanced or metastatic biliary tract cancer (HERIZON-BTC-01): a multicentre, single-arm, phase 2b study. Lancet Oncol. 2023;24(7):772-782. doi:10.1016/S1470-2045(23)00242-5
- Lo JH, Agarwal R, Goff LW, Heumann TR. Immunotherapy in biliary tract cancers: current standard-of-care and emerging strategies. Cancers (Basel). 2023;15(13):3312. doi:10.3390/cancers15133312
Clinical outcomes of patients with gallbladder cancer have improved considerably with the advent of immunotherapy and targeted therapies. While specialists have gained tremendous insights into the disease over the last 10 years, significant knowledge gaps remain, as relapse rates remain high. Early referral to specialized treatment centers and timely molecular profiling can help guide therapeutic regimen choice and potentially improve patient outcomes.
Insights Into Disease Prevalence and Development
Gallbladder cancer is a rare malignancy with an aggressive course. Most gallbladder cancers are of epithelial origin, with adenocarcinoma being the most common type.1 Approximately 12,350 new cases of gallbladder cancer and nearby large bile duct cancers are anticipated in 2024 in the United States,2 predominantly affecting Southwestern Native Americans.3 The prevalence of gallbladder cancer varies greatly worldwide; rates are highest in South America (mainly in Chile) and Southeast Asia, including Eastern India.3,4
Multiple factors, including environment and genetics, contribute to the development of gallbladder cancer, which is driven primarily by chronic inflammation.5 While there are no defined risk factors, this malignancy is mostly associated with female sex, chronic gallbladder infections, and gallstones.4 Some evidence also suggests a dietary association with consuming mustard seed oil.6 Exposure to certain environmental toxins or heavy metals may also contribute to disease risk.1,4
Several genetic alterations have been identified in patients with gallbladder cancer that may be related to disease etiology; these include somatic mutations in the human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2), Kirsten rat sarcoma viral oncogene homolog (KRAS), and tumor protein p53 (TP53) genes, and many others.7,8 In addition to somatic mutations, gene overexpression, epigenetic changes, and microRNA-associated changes have also been linked to the disease.3
Challenges in Uncovering a “Hidden” Disease
While most gallbladder cancers are usually detected incidentally, patients may present with symptoms of abdominal pain, discomfort, and biliary obstruction–related symptoms like jaundice, itching, and dark urine.3,9,10 Cases may initially be misdiagnosed as inflammatory conditions such as cholecystitis or gallbladder stones; as a result, patients may be rushed into an inappropriate or incorrect surgical intervention.11 For these reasons, as well as the tight anatomical location of the gallbladder, cases are often not detected until advanced-stage disease.3,4
Patients diagnosed in stage 4 with distant metastases have an expected survival rate of less than 1 year,12 and low referral rates are associated with poor outcomes.13 Patients with suspected disease should therefore be referred to a specialized treatment center as soon as possible to confirm a diagnosis and initiate appropriate treatment. Core biopsies can provide histological confirmation, where feasible and safe, followed by imaging to determine extent of the disease.14
Evolving Management of Localized and Advanced Disease
Localized disease
Surgery with curative intent is the standard of care in patients with localized disease (Figure).14,15 Contraindications for resection include distant metastases and occlusion of blood vessels.4 Depending on tumor stage, eligible patients may undergo radical cholecystectomy and portal lymphadenectomy, as well as potential liver resection (segments 4b and 5).5
Figure. Biliary Tract Cancers (BTCs): Diagnosis and Management Algorithm14

From Lamarca A, Edeline J, Goyal L. How I treat biliary tract cancer. ESMO Open. 2022;7(1):100378. doi:10.1016/j.esmoop.2021.100378. [Open access].
As the nonencapsulated nature of the gallbladder renders local extension very likely, a peri-adjuvant approach including neoadjuvant and adjuvant arms should be initiated. Standard chemotherapy regimens may include capecitabine or gemcitabine + cisplatin/capecitabine.16,17
Advanced disease
Systemic therapy remains key in the setting of locally advanced or metastatic disease. In August 2024, the National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN) updated its guidelines to strongly recommend durvalumab + gemcitabine + cisplatin or pembrolizumab + gemcitabine + cisplatin as the preferred regimens for primary treatment of these patients.17 Other regimens to consider based on both NCCN and European Society of Medical Oncology (ESMO) guidelines include gemcitabine + cisplatin or capecitabine + oxaliplatin.17,18 In addition, gemcitabine + S-1 (tegafur, gimeracil, and oteracil) may also be considered as part of first-line treatment based on data from clinical trials conducted in Japan.19 FOLFOX (folinic acid, fluorouracil, and oxaliplatin) is recommended for second-line treatment.16
While the American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO) guidelines are yet to be published, they have previously reviewed data on several potential novel agents and targeted therapies for first-line treatment.20
The addition of immunotherapies such as checkpoint inhibitors to the treatment algorithm has been monumental for the treatment of advanced gallbladder cancer. Durvalumab and pembrolizumab, programmed cell death protein 1 (PD-1)/programmed death-ligand 1 (PDL-1) receptor inhibitors, in combination with gemcitabine + cisplatin, significantly improve overall survival compared to gemcitabine + cisplatin alone.17,21,22 These regimens are strongly recommended as first-line therapy in eligible patients who have not previously been treated with a checkpoint inhibitor.
Biopsies should be performed as early as possible in all patients with unresectable or metastatic disease for genomic profiling. Next-generation sequencing can help inform response to targeted therapies in testing by identifying genetic mutations, potentially improving treatment response.1,23
In certain circumstances, patients with genetic mutations are eligible for molecularly targeted therapies17:
Unresectable or metastatic disease:
- Neurotrophic tyrosine receptor kinase (NTRK) gene fusion-positive tumors: entrectinib, larotrectinib, or repotrectinib
- High mutational burden (TMB-H) tumors: nivolumab + ipilimumab
Following disease progression:
- B-Raf Proto-Oncogene, Serine/Threonine Kinase (BRAF) V600E-mutated tumors: dabrafenib + trametinib
- Cholangiocarcinoma with fibroblast growth factor receptor 2 (FGFR2) fusions: futibatinib + pemigatinib
- Cholangiocarcinoma with rearrangements or isocitrate dehydrogenase 1 (IDH1) mutations: ivosidenib
It is important to note that further development of adjuvant strategies is greatly needed to better guide management across disease stages.16
Therapeutic candidates in testing
Despite the advancements achieved with immunotherapies and targeted treatments, therapeutic options have remained comparable to those of other biliary tumors such as intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. However, some novel candidates currently being evaluated in clinical trials have shown promise24-26:
HER2: Overexpression of the HER2 protein in gallbladder cancer causes abnormal cell survival and proliferation. Initial clinical trial data have suggested that agents targeting HER2 may improve outcomes in patients with advanced gallbladder cancer who harbor somatic HER2 mutations. In fact, the anti-HER2 agent zanidatamab provided clinical benefit and was well tolerated in patients with treatment-refractory, HER2-positive biliary tract cancer in a phase 2 single-arm trial.
Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF): The VEGF/ VEGF receptor pathway may also be a promising target due to its role in regulating epithelial cell differentiation and migration. Phase 2 studies of VEGF antibodies, such as bevacizumab, in combination with standard chemotherapy have demonstrated improved response rates; however, some of these studies have shown mixed results.
Phosphoinositide 3-kinases (PI3K)/protein kinase B (AKT)/mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR): This key signaling pathway plays an important role in driving cancer growth and metastases. Early trials of an mTOR inhibitor in combination with standard chemotherapy have demonstrated an acceptable tolerability profile with potential signs of clinical benefit.
The immunotherapy landscape for gallbladder cancer may evolve beyond currently approved PD-1/PDL-1 receptor inhibitors with the development of agonist antibodies and chimeric antigen receptor T cell (CAR-T) candidates.27 Novel treatment approaches like vaccines and nanoparticle delivery systems are also under investigation.
Looking Toward the Future
Gallbladder cancer is challenging to detect, and earlier diagnosis is key to improving outcomes. It is critical to refer patients to specialized treatment centers as soon as the disease is suspected. Rapid development in advanced genetic testing and other analytical methods may lead to identification of diagnostic biomarkers to aid in detecting cases sooner.24
Despite the fast-evolving pipeline for therapeutic candidates, greater research is also needed to inform sequencing of chemotherapy regimens with immunotherapy and targeted therapy to achieve favorable long-term outcomes.27 As new candidates are approved, management may become remain less than ideal without this crucial guidance.
We hope the future will bring the opportunity to provide more tailored treatments to patients with novel candidates that can further engage the immune system beyond currently identified targets.
Read more from the 2024 Rare Diseases Report: Hematology and Oncology.
Clinical outcomes of patients with gallbladder cancer have improved considerably with the advent of immunotherapy and targeted therapies. While specialists have gained tremendous insights into the disease over the last 10 years, significant knowledge gaps remain, as relapse rates remain high. Early referral to specialized treatment centers and timely molecular profiling can help guide therapeutic regimen choice and potentially improve patient outcomes.
Insights Into Disease Prevalence and Development
Gallbladder cancer is a rare malignancy with an aggressive course. Most gallbladder cancers are of epithelial origin, with adenocarcinoma being the most common type.1 Approximately 12,350 new cases of gallbladder cancer and nearby large bile duct cancers are anticipated in 2024 in the United States,2 predominantly affecting Southwestern Native Americans.3 The prevalence of gallbladder cancer varies greatly worldwide; rates are highest in South America (mainly in Chile) and Southeast Asia, including Eastern India.3,4
Multiple factors, including environment and genetics, contribute to the development of gallbladder cancer, which is driven primarily by chronic inflammation.5 While there are no defined risk factors, this malignancy is mostly associated with female sex, chronic gallbladder infections, and gallstones.4 Some evidence also suggests a dietary association with consuming mustard seed oil.6 Exposure to certain environmental toxins or heavy metals may also contribute to disease risk.1,4
Several genetic alterations have been identified in patients with gallbladder cancer that may be related to disease etiology; these include somatic mutations in the human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2), Kirsten rat sarcoma viral oncogene homolog (KRAS), and tumor protein p53 (TP53) genes, and many others.7,8 In addition to somatic mutations, gene overexpression, epigenetic changes, and microRNA-associated changes have also been linked to the disease.3
Challenges in Uncovering a “Hidden” Disease
While most gallbladder cancers are usually detected incidentally, patients may present with symptoms of abdominal pain, discomfort, and biliary obstruction–related symptoms like jaundice, itching, and dark urine.3,9,10 Cases may initially be misdiagnosed as inflammatory conditions such as cholecystitis or gallbladder stones; as a result, patients may be rushed into an inappropriate or incorrect surgical intervention.11 For these reasons, as well as the tight anatomical location of the gallbladder, cases are often not detected until advanced-stage disease.3,4
Patients diagnosed in stage 4 with distant metastases have an expected survival rate of less than 1 year,12 and low referral rates are associated with poor outcomes.13 Patients with suspected disease should therefore be referred to a specialized treatment center as soon as possible to confirm a diagnosis and initiate appropriate treatment. Core biopsies can provide histological confirmation, where feasible and safe, followed by imaging to determine extent of the disease.14
Evolving Management of Localized and Advanced Disease
Localized disease
Surgery with curative intent is the standard of care in patients with localized disease (Figure).14,15 Contraindications for resection include distant metastases and occlusion of blood vessels.4 Depending on tumor stage, eligible patients may undergo radical cholecystectomy and portal lymphadenectomy, as well as potential liver resection (segments 4b and 5).5
Figure. Biliary Tract Cancers (BTCs): Diagnosis and Management Algorithm14

From Lamarca A, Edeline J, Goyal L. How I treat biliary tract cancer. ESMO Open. 2022;7(1):100378. doi:10.1016/j.esmoop.2021.100378. [Open access].
As the nonencapsulated nature of the gallbladder renders local extension very likely, a peri-adjuvant approach including neoadjuvant and adjuvant arms should be initiated. Standard chemotherapy regimens may include capecitabine or gemcitabine + cisplatin/capecitabine.16,17
Advanced disease
Systemic therapy remains key in the setting of locally advanced or metastatic disease. In August 2024, the National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN) updated its guidelines to strongly recommend durvalumab + gemcitabine + cisplatin or pembrolizumab + gemcitabine + cisplatin as the preferred regimens for primary treatment of these patients.17 Other regimens to consider based on both NCCN and European Society of Medical Oncology (ESMO) guidelines include gemcitabine + cisplatin or capecitabine + oxaliplatin.17,18 In addition, gemcitabine + S-1 (tegafur, gimeracil, and oteracil) may also be considered as part of first-line treatment based on data from clinical trials conducted in Japan.19 FOLFOX (folinic acid, fluorouracil, and oxaliplatin) is recommended for second-line treatment.16
While the American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO) guidelines are yet to be published, they have previously reviewed data on several potential novel agents and targeted therapies for first-line treatment.20
The addition of immunotherapies such as checkpoint inhibitors to the treatment algorithm has been monumental for the treatment of advanced gallbladder cancer. Durvalumab and pembrolizumab, programmed cell death protein 1 (PD-1)/programmed death-ligand 1 (PDL-1) receptor inhibitors, in combination with gemcitabine + cisplatin, significantly improve overall survival compared to gemcitabine + cisplatin alone.17,21,22 These regimens are strongly recommended as first-line therapy in eligible patients who have not previously been treated with a checkpoint inhibitor.
Biopsies should be performed as early as possible in all patients with unresectable or metastatic disease for genomic profiling. Next-generation sequencing can help inform response to targeted therapies in testing by identifying genetic mutations, potentially improving treatment response.1,23
In certain circumstances, patients with genetic mutations are eligible for molecularly targeted therapies17:
Unresectable or metastatic disease:
- Neurotrophic tyrosine receptor kinase (NTRK) gene fusion-positive tumors: entrectinib, larotrectinib, or repotrectinib
- High mutational burden (TMB-H) tumors: nivolumab + ipilimumab
Following disease progression:
- B-Raf Proto-Oncogene, Serine/Threonine Kinase (BRAF) V600E-mutated tumors: dabrafenib + trametinib
- Cholangiocarcinoma with fibroblast growth factor receptor 2 (FGFR2) fusions: futibatinib + pemigatinib
- Cholangiocarcinoma with rearrangements or isocitrate dehydrogenase 1 (IDH1) mutations: ivosidenib
It is important to note that further development of adjuvant strategies is greatly needed to better guide management across disease stages.16
Therapeutic candidates in testing
Despite the advancements achieved with immunotherapies and targeted treatments, therapeutic options have remained comparable to those of other biliary tumors such as intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. However, some novel candidates currently being evaluated in clinical trials have shown promise24-26:
HER2: Overexpression of the HER2 protein in gallbladder cancer causes abnormal cell survival and proliferation. Initial clinical trial data have suggested that agents targeting HER2 may improve outcomes in patients with advanced gallbladder cancer who harbor somatic HER2 mutations. In fact, the anti-HER2 agent zanidatamab provided clinical benefit and was well tolerated in patients with treatment-refractory, HER2-positive biliary tract cancer in a phase 2 single-arm trial.
Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF): The VEGF/ VEGF receptor pathway may also be a promising target due to its role in regulating epithelial cell differentiation and migration. Phase 2 studies of VEGF antibodies, such as bevacizumab, in combination with standard chemotherapy have demonstrated improved response rates; however, some of these studies have shown mixed results.
Phosphoinositide 3-kinases (PI3K)/protein kinase B (AKT)/mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR): This key signaling pathway plays an important role in driving cancer growth and metastases. Early trials of an mTOR inhibitor in combination with standard chemotherapy have demonstrated an acceptable tolerability profile with potential signs of clinical benefit.
The immunotherapy landscape for gallbladder cancer may evolve beyond currently approved PD-1/PDL-1 receptor inhibitors with the development of agonist antibodies and chimeric antigen receptor T cell (CAR-T) candidates.27 Novel treatment approaches like vaccines and nanoparticle delivery systems are also under investigation.
Looking Toward the Future
Gallbladder cancer is challenging to detect, and earlier diagnosis is key to improving outcomes. It is critical to refer patients to specialized treatment centers as soon as the disease is suspected. Rapid development in advanced genetic testing and other analytical methods may lead to identification of diagnostic biomarkers to aid in detecting cases sooner.24
Despite the fast-evolving pipeline for therapeutic candidates, greater research is also needed to inform sequencing of chemotherapy regimens with immunotherapy and targeted therapy to achieve favorable long-term outcomes.27 As new candidates are approved, management may become remain less than ideal without this crucial guidance.
We hope the future will bring the opportunity to provide more tailored treatments to patients with novel candidates that can further engage the immune system beyond currently identified targets.
Read more from the 2024 Rare Diseases Report: Hematology and Oncology.
- Okumura K, Gogna S, Gachabayov M, et al. Gallbladder cancer: historical treatment and new management options. World J Gastrointest Oncol. 2021;13(10):1317-1335. doi:10.4251/wjgo.v13.i10.1317
- Key statistics for gallbladder cancer. American Cancer Society. Updated May 22, 2024. Accessed August 26, 2024. https://www.cancer.org/cancer/types/gallbladder-cancer/about/key-statistics.html
- Nemunaitis JM, Brown-Glabeman U, Soares H, et al. Gallbladder cancer: review of a rare orphan gastrointestinal cancer with a focus on populations of New Mexico. BMC Cancer. 2018;18(1):665. doi:10.1186/s12885-018-4575-3
- Halaseh SA, Halaseh S, Shakman R. A review of the etiology and epidemiology of gallbladder cancer: what you need to know. Cureus. 2022;14(8):e28260. doi:10.7759/cureus.28260
- Menon G, Babiker HM. Gallbladder carcinoma. StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island, FL: StatPearls Publishing; 2024. Updated August 17, 2024. Accessed September 30, 2024. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK442002/
- Mhatre S, Rajaraman P, Chatterjee N, et al. Mustard oil consumption, cooking method, diet and gallbladder cancer risk in high- and low-risk regions of India. Int J Cancer. 2020;147(6):1621-1628. doi:10.1002/ijc.32952
- Sharma A, Sharma KL, Gupta A, Yadav A, Kumar A. Gallbladder cancer epidemiology, pathogenesis and molecular genetics: recent update. World J Gastroenterol. 2017;23(22):3978-3998. doi:10.3748/wjg.v23.i22.3978
- Kuipers H, de Bitter TJJ, de Boer MT, et al. Gallbladder cancer: current insights in genetic alterations and their possible therapeutic implications. Cancers (Basel). 2021;13(21):5257. doi:10.3390/cancers13215257
- Larson VA, Tang O, Ständer S, Kang S, Kwatra SG. Association between itch and cancer in 16,925 patients with pruritus: experience at a tertiary care center. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019;80(4):931-937. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2018.08.044
- Neculoiu D, Neculoiu LC, Popa RM, Manea RM. The many hidden faces of gallbladder carcinoma on CT and MRI imaging—from A to Z. Diagnostics (Basel). 2024;14(5):475. doi:10.3390/diagnostics14050475
- Deo KB, Avudaiappan M, Shenvi S, et al. Misdiagnosis of carcinoma gallbladder in endemic regions. BMC Surg. 2022;22(1):343. doi:10.1186/s12893-022-01793-8
- Prieto M, Gastaca M, Ruiz P, et al. Long term recurrence free survival in a stage IV gallbladder cancer treated with chemotherapy plus trastuzumab and salvage liver resection. Ann Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg. 2019;23(4):403-407. doi:10.14701/ahbps.2019.23.4.403
- van Dooren M, de Savornin Lohman EAJ, van der Post RS, et al. Referral rate of patients with incidental gallbladder cancer and survival: outcomes of a multicentre retrospective study. BJS Open. 2024;8(2):zrae013. doi:10.1093/bjsopen/zrae013
- Lamarca A, Edeline J, Goyal L. How I treat biliary tract cancer. ESMO Open. 2022;7(1):100378. doi:10.1016/j.esmoop.2021.100378
- Zhou Y, Yuan K, Yang Y, et al. Gallbladder cancer: current and future treatment options. Front Pharmacol. 2023;14:1183619. doi:10.3389/fphar.2023.1183619
- Banales JM, Marin JJG, Lamarca A, et al. Cholangiocarcinoma 2020: the next horizon in mechanisms and management. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2020;17(9):557-588. doi:10.1038/s41575-020-0310-z
- National Comprehensive Cancer Network. NCCN clinical practice guidelines in oncology: biliary tract cancers. Version 4.2024. August 29, 2024. Accessed September 30, 2024. https://www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/pdf/btc.pdf
- Vogel A, Bridgewater J, Edeline J, et al. Biliary tract cancer: ESMO clinical practice guideline for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann Oncol. 2023;34(2):127-140. doi:10.1016/j.annonc.2022.10.506
- Nagino M, Hirano S, Yoshitomi H, et al. Clinical practice guidelines for the management of biliary tract cancers 2019: the 3rd English edition. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Sci. 2021;28(1):26-54. doi:10.1002/jhbp.870
- Müller BG, De Aretxabala X, González Domingo M. A review of recent data in the treatment of gallbladder cancer: what we know, what we do, and what should be done. Am Soc Clin Oncol Educ Book. 2014;e165-e170. doi:10.14694/EdBook_AM.2014.34.e165
- Kelley RK, Ueno M, Yoo C, et al; for the KEYNOTE-966 investigators. Pembrolizumab in combination with gemcitabine and cisplatin compared with gemcitabine and cisplatin alone for patients with advanced biliary tract cancer (KEYNOTE-966): a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet. 2023;401(10391):1853-1865. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(23)00727-4
- Oh DY, Ruth He A, Qin S, et al. Durvalumab plus gemcitabine and cisplatin in advanced biliary tract cancer. NEJM Evid. 2022;1(8):EVIDoa2200015. doi:10.1056/EVIDoa2200015
- DiPeri TP, Javle MM, Meric-Bernstam F. Next generation sequencing for biliary tract cancers. Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2021;15(5):471-474. doi:10.1080/17474124.2021.1896967
- Song X, Hu Y, Li Y, Shao R, Liu F, Liu Y. Overview of current targeted therapy in gallbladder cancer. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2020;5(1):230. doi:10.1038/s41392-020-00324-2
- LaPelusa M, Heumann T, Goff L, Agarwal R. Targeted therapies in advanced biliary tract cancers—a narrative review. Chin Clin Oncol. 2023;12(2):14. doi:10.21037/cco-22-93
- Harding JJ, Fan J, Oh DY, et al; for the HERIZON-BTC-01 study group. Zanidatamab for HER2-amplified, unresectable, locally advanced or metastatic biliary tract cancer (HERIZON-BTC-01): a multicentre, single-arm, phase 2b study. Lancet Oncol. 2023;24(7):772-782. doi:10.1016/S1470-2045(23)00242-5
- Lo JH, Agarwal R, Goff LW, Heumann TR. Immunotherapy in biliary tract cancers: current standard-of-care and emerging strategies. Cancers (Basel). 2023;15(13):3312. doi:10.3390/cancers15133312
- Okumura K, Gogna S, Gachabayov M, et al. Gallbladder cancer: historical treatment and new management options. World J Gastrointest Oncol. 2021;13(10):1317-1335. doi:10.4251/wjgo.v13.i10.1317
- Key statistics for gallbladder cancer. American Cancer Society. Updated May 22, 2024. Accessed August 26, 2024. https://www.cancer.org/cancer/types/gallbladder-cancer/about/key-statistics.html
- Nemunaitis JM, Brown-Glabeman U, Soares H, et al. Gallbladder cancer: review of a rare orphan gastrointestinal cancer with a focus on populations of New Mexico. BMC Cancer. 2018;18(1):665. doi:10.1186/s12885-018-4575-3
- Halaseh SA, Halaseh S, Shakman R. A review of the etiology and epidemiology of gallbladder cancer: what you need to know. Cureus. 2022;14(8):e28260. doi:10.7759/cureus.28260
- Menon G, Babiker HM. Gallbladder carcinoma. StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island, FL: StatPearls Publishing; 2024. Updated August 17, 2024. Accessed September 30, 2024. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK442002/
- Mhatre S, Rajaraman P, Chatterjee N, et al. Mustard oil consumption, cooking method, diet and gallbladder cancer risk in high- and low-risk regions of India. Int J Cancer. 2020;147(6):1621-1628. doi:10.1002/ijc.32952
- Sharma A, Sharma KL, Gupta A, Yadav A, Kumar A. Gallbladder cancer epidemiology, pathogenesis and molecular genetics: recent update. World J Gastroenterol. 2017;23(22):3978-3998. doi:10.3748/wjg.v23.i22.3978
- Kuipers H, de Bitter TJJ, de Boer MT, et al. Gallbladder cancer: current insights in genetic alterations and their possible therapeutic implications. Cancers (Basel). 2021;13(21):5257. doi:10.3390/cancers13215257
- Larson VA, Tang O, Ständer S, Kang S, Kwatra SG. Association between itch and cancer in 16,925 patients with pruritus: experience at a tertiary care center. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019;80(4):931-937. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2018.08.044
- Neculoiu D, Neculoiu LC, Popa RM, Manea RM. The many hidden faces of gallbladder carcinoma on CT and MRI imaging—from A to Z. Diagnostics (Basel). 2024;14(5):475. doi:10.3390/diagnostics14050475
- Deo KB, Avudaiappan M, Shenvi S, et al. Misdiagnosis of carcinoma gallbladder in endemic regions. BMC Surg. 2022;22(1):343. doi:10.1186/s12893-022-01793-8
- Prieto M, Gastaca M, Ruiz P, et al. Long term recurrence free survival in a stage IV gallbladder cancer treated with chemotherapy plus trastuzumab and salvage liver resection. Ann Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg. 2019;23(4):403-407. doi:10.14701/ahbps.2019.23.4.403
- van Dooren M, de Savornin Lohman EAJ, van der Post RS, et al. Referral rate of patients with incidental gallbladder cancer and survival: outcomes of a multicentre retrospective study. BJS Open. 2024;8(2):zrae013. doi:10.1093/bjsopen/zrae013
- Lamarca A, Edeline J, Goyal L. How I treat biliary tract cancer. ESMO Open. 2022;7(1):100378. doi:10.1016/j.esmoop.2021.100378
- Zhou Y, Yuan K, Yang Y, et al. Gallbladder cancer: current and future treatment options. Front Pharmacol. 2023;14:1183619. doi:10.3389/fphar.2023.1183619
- Banales JM, Marin JJG, Lamarca A, et al. Cholangiocarcinoma 2020: the next horizon in mechanisms and management. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2020;17(9):557-588. doi:10.1038/s41575-020-0310-z
- National Comprehensive Cancer Network. NCCN clinical practice guidelines in oncology: biliary tract cancers. Version 4.2024. August 29, 2024. Accessed September 30, 2024. https://www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/pdf/btc.pdf
- Vogel A, Bridgewater J, Edeline J, et al. Biliary tract cancer: ESMO clinical practice guideline for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann Oncol. 2023;34(2):127-140. doi:10.1016/j.annonc.2022.10.506
- Nagino M, Hirano S, Yoshitomi H, et al. Clinical practice guidelines for the management of biliary tract cancers 2019: the 3rd English edition. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Sci. 2021;28(1):26-54. doi:10.1002/jhbp.870
- Müller BG, De Aretxabala X, González Domingo M. A review of recent data in the treatment of gallbladder cancer: what we know, what we do, and what should be done. Am Soc Clin Oncol Educ Book. 2014;e165-e170. doi:10.14694/EdBook_AM.2014.34.e165
- Kelley RK, Ueno M, Yoo C, et al; for the KEYNOTE-966 investigators. Pembrolizumab in combination with gemcitabine and cisplatin compared with gemcitabine and cisplatin alone for patients with advanced biliary tract cancer (KEYNOTE-966): a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet. 2023;401(10391):1853-1865. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(23)00727-4
- Oh DY, Ruth He A, Qin S, et al. Durvalumab plus gemcitabine and cisplatin in advanced biliary tract cancer. NEJM Evid. 2022;1(8):EVIDoa2200015. doi:10.1056/EVIDoa2200015
- DiPeri TP, Javle MM, Meric-Bernstam F. Next generation sequencing for biliary tract cancers. Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2021;15(5):471-474. doi:10.1080/17474124.2021.1896967
- Song X, Hu Y, Li Y, Shao R, Liu F, Liu Y. Overview of current targeted therapy in gallbladder cancer. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2020;5(1):230. doi:10.1038/s41392-020-00324-2
- LaPelusa M, Heumann T, Goff L, Agarwal R. Targeted therapies in advanced biliary tract cancers—a narrative review. Chin Clin Oncol. 2023;12(2):14. doi:10.21037/cco-22-93
- Harding JJ, Fan J, Oh DY, et al; for the HERIZON-BTC-01 study group. Zanidatamab for HER2-amplified, unresectable, locally advanced or metastatic biliary tract cancer (HERIZON-BTC-01): a multicentre, single-arm, phase 2b study. Lancet Oncol. 2023;24(7):772-782. doi:10.1016/S1470-2045(23)00242-5
- Lo JH, Agarwal R, Goff LW, Heumann TR. Immunotherapy in biliary tract cancers: current standard-of-care and emerging strategies. Cancers (Basel). 2023;15(13):3312. doi:10.3390/cancers15133312
Current Management and Future Directions in the Treatment of Gallbladder Cancer
Current Management and Future Directions in the Treatment of Gallbladder Cancer



