User login
TNBC: Adding atezolizumab to paclitaxel does not extend survival
Key clinical point: Atezolizumab in combination with paclitaxel does not improve survival in patients with unresectable locally advanced/metastatic triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) vs paclitaxel plus placebo.
Major finding: The median follow-up was 14.2 months in the atezolizumab group and 14.5 months in the placebo group. Atezolizumab plus paclitaxel did not improve median overall survival vs paclitaxel plus placebo (hazard ratio, 1.11; 95% confidence interval, 0.76-1.64). Compared with placebo plus paclitaxel, atezolizumab plus paclitaxel was associated with a higher incidence of serious (25% vs 18%) and grade 3/4 adverse events (53% vs 46%).
Study details: A global randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase 3 IMpassion131 trial of 651 patients with advanced/metastatic TNBC who were randomly assigned to atezolizumab plus paclitaxel or placebo plus paclitaxel.
Disclosures: The study was supported by F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd. The authors received honoraria, research grants, speaker/advisory/consulting fees, personal fees, and travel/accommodation/expenses from various sources. Some authors were employed by and/or owned stocks in pharmaceutical companies.
Source: Miles D et al. Ann Oncol. 2021 Jul 1. doi: 10.1016/j.annonc.2021.05.801.
Key clinical point: Atezolizumab in combination with paclitaxel does not improve survival in patients with unresectable locally advanced/metastatic triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) vs paclitaxel plus placebo.
Major finding: The median follow-up was 14.2 months in the atezolizumab group and 14.5 months in the placebo group. Atezolizumab plus paclitaxel did not improve median overall survival vs paclitaxel plus placebo (hazard ratio, 1.11; 95% confidence interval, 0.76-1.64). Compared with placebo plus paclitaxel, atezolizumab plus paclitaxel was associated with a higher incidence of serious (25% vs 18%) and grade 3/4 adverse events (53% vs 46%).
Study details: A global randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase 3 IMpassion131 trial of 651 patients with advanced/metastatic TNBC who were randomly assigned to atezolizumab plus paclitaxel or placebo plus paclitaxel.
Disclosures: The study was supported by F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd. The authors received honoraria, research grants, speaker/advisory/consulting fees, personal fees, and travel/accommodation/expenses from various sources. Some authors were employed by and/or owned stocks in pharmaceutical companies.
Source: Miles D et al. Ann Oncol. 2021 Jul 1. doi: 10.1016/j.annonc.2021.05.801.
Key clinical point: Atezolizumab in combination with paclitaxel does not improve survival in patients with unresectable locally advanced/metastatic triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) vs paclitaxel plus placebo.
Major finding: The median follow-up was 14.2 months in the atezolizumab group and 14.5 months in the placebo group. Atezolizumab plus paclitaxel did not improve median overall survival vs paclitaxel plus placebo (hazard ratio, 1.11; 95% confidence interval, 0.76-1.64). Compared with placebo plus paclitaxel, atezolizumab plus paclitaxel was associated with a higher incidence of serious (25% vs 18%) and grade 3/4 adverse events (53% vs 46%).
Study details: A global randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase 3 IMpassion131 trial of 651 patients with advanced/metastatic TNBC who were randomly assigned to atezolizumab plus paclitaxel or placebo plus paclitaxel.
Disclosures: The study was supported by F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd. The authors received honoraria, research grants, speaker/advisory/consulting fees, personal fees, and travel/accommodation/expenses from various sources. Some authors were employed by and/or owned stocks in pharmaceutical companies.
Source: Miles D et al. Ann Oncol. 2021 Jul 1. doi: 10.1016/j.annonc.2021.05.801.
The robot comes to mastectomy, but cancer outcomes data not attached
The FDA warning was issued in February 2019 to both the public and physicians. The FDA cautioned that the safety and effectiveness of robotic surgical devices for mastectomy “have not been established” and robots are not approved for the prevention or treatment of breast cancer.
The agency also noted that “diminished long-term survival” was associated with robotic surgery in another women’s cancer, that of hysterectomy for cervical cancer.
The FDA also made a surprising statement. The agency typically approves the robot for surgical use based on 30-day complication rates (compared with standards of care). But it said that going forward it “anticipates” that any evaluation of new use of robots in cancer “would be supported” by cancer outcomes such as progression-free survival and overall survival, which require much longer follow-up.
In short, the FDA hinted that it would change how it regulated medical devices, or at least robots used in women’s cancers. “The FDA takes women’s health very seriously,” said the organization.
Fast forward to 2021, and there are several prospective clinical trials of robot-assisted nipple-sparing mastectomy underway in the United States, including a five-center study sponsored by Intuitive Surgical, the maker of da Vinci robots, the dominant machine on the market. There are also single-center studies at Ohio State and University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center.
However, in each case, the study design either excludes cancer outcomes or does not primarily focus on those measures.
Instead, the primary outcomes are relatively short term and include safety and efficacy measures such as en bloc (in one piece) removal of the breast tissue, conversions to open mastectomy, and the incidence of adverse events during surgery and up to 6 weeks after surgery.
Importantly, none of the studies is a randomized trial; all have single arms.
That’s not what is needed, says breast surgeon Julie A. Margenthaler, MD of Washington University in St. Louis.
“I firmly believe that robotic-assisted mastectomy should only be considered in the context of a well-designed, randomized trial evaluating patient selection, patient safety, surgical complications, and oncologic outcomes with a concomitant cost analysis,” Dr. Margenthaler wrote in an essay published last year in JAMA Surgery.
As with the FDA warning, she cites worse survival with commonly used minimally invasive radical hysterectomy for cervical cancer, saying it “is a stark reminder that the marketing of robotic surgery has its roots in cosmesis and convenience rather than oncologic outcomes.”
In addition, robotic surgery is prohibitively expensive, said Dr. Margenthaler. In fact, cost is her “main criticism regarding robotic-assisted mastectomy.” It costs an additional $6,000 for robot use per procedure, according to a study conducted at a center in Taiwan. “I simply cannot be convinced that this will ever achieve cost-effective or even cost-neutral status,” Dr. Margenthaler wrote.
Not looking at the right outcomes
“They’re not looking at the right outcomes,” said Hooman Noorchashm, MD, PhD, about the current trials in the United States. He is a former surgeon and faculty member at the University of Pennsylvania in Philadelphia, and is now a patient advocate after his wife, Amy Reed, MD, died of uterine cancer in 2017 following a laparoscopic hysterectomy performed with a power morcellator that resulted in the upstaging of an undetected gynecologic cancer.
“You have to look at oncologic outcomes and do randomized, noninferiority trials to demonstrate that those cancer outcomes are at least equivalent to standard of care,” he said in an interview.
The current U.S. trials are “totally inappropriate,” he said.
Are randomized trials forthcoming after this initial set of single-arm trials? This news organization reached out to Intuitive Surgical, maker of the market leader da Vinci robotic surgical equipment to find out.
“Any plans for use of da Vinci Xi surgical system in nipple-sparing mastectomy will be based on these [single-arm] study results as well as other data and evidence,” said a company spokesperson, who did not confirm use of a randomized trial.
What about the FDA? Will the agency change its current approach to approving robots in surgeries for women’s cancers and require – not just anticipate – cancer-related outcomes data? At press time, the FDA did not respond to a request for comment.
Not having a randomized trial with cancer outcomes in any eventual FDA review opens the door for robotic mastectomy to be cleared for use in some mastectomies with short-term, nononcologic data, said Dr. Noorchashm.
Safety concerns with robotic mastectomy
Proponents of robot-assisted nipple-sparing mastectomy, which is coupled with reconstruction to preserve the shape of both the breast and nipple-areola area, suggest that improved patient cosmesis is a significant advantage with the high-tech intervention, said Dr. Margenthaler.
That’s because most robotic mastectomies performed to date (almost exclusively in Europe and Asia) have employed a 3- to 5-cm vertical incision located behind the lateral breast fold, allowing the scar to be hidden under the patient’s arm.
But therein also lies a safety concern, she asserted.
The “oncologic integrity” of the specimen on extraction is in question in some cases, she wrote, because of “such a small opening.”
Dr. Noorchashm agreed: “It all comes down to trying to get a large specimen out of a small incision.”
Traditional open mastectomy optimally yields the en bloc removal of a tumor – in one whole piece – to avoid fragmenting the cancerous tissue and possibly leaving residual disease behind. These undesirable events are associated with a higher risk for recurrence and treatment failure, he explained.
Thus, there is a need for a randomized trial with longer-term oncologic outcomes that compares the new approach with traditional open mastectomy, argued both Dr. Margenthaler and Dr. Noorchashm.
In defense of single-arm trials
“Oncologic safety is what we are concerned about and what we would like to study,” said Ko Un (Clara) Park, MD, a breast surgeon at The Ohio State University in Columbus.
Dr. Park is leading a single-center, single-arm pilot study of robotic nipple-sparing mastectomy enrolling up to 20 women with early-stage breast cancer or inherited genetic risk factors (but no cancer diagnosis). The trial, sponsored by a Pelotonia Idea Grant and Ohio State, recently enrolled its first patient.
The study’s primary outcomes include the feasibility of removal of the breast tissue en bloc; however, none of the outcomes are classic oncologic metrics such as progression-free survival.
The en bloc removal outcome is in direct response to the FDA’s concerns about minimally invasive cancer surgeries in women, Dr. Park said in an interview. The pilot trial has an investigational device exemption (IDE) granted by the FDA.
“The reason why we can’t just open a randomized controlled study (of robot versus open) and measure oncologic outcomes like recurrence-free survival is because, before we get to that point, we have to make sure” basic safety issues are addressed and established, she explained.
But Dr. Noorchashm said that argument is missing the larger, more important point: “They are still doing an oncologic procedure – you are still obliged to do noninferiority [randomized] testing with respect to cancer outcomes.”
Dr. Park sounded a different note: “We are doing it as safely as we can do it.”
Prophylactic use is also a cancer surgery
Intuitive’s five-center trial does not include en bloc removal of the breast gland as a primary outcome. Instead, the two primary outcomes are conversions to open mastectomy (efficacy measure) and the incidence of adverse events during surgery to 42 days after surgery (safety measure).
The company’s trial does not include any women with breast cancer, but is limited to women at increased risk for breast cancer and seeking prophylactic nipple-sparing mastectomy surgery.
Enrollment in the 145-patient single-arm trial began in the last few months and has a primary completion date of December 2022. It also has an IDE from the FDA.
“I do think that things like this need to be done with caution,” said Katherine Kopkash, MD, an investigator in the Intuitive trial and a breast surgeon at NorthShore University HealthSystem in Evanston, Ill., referring to the trial’s FDA exemption.
Dr. Kopkash said in an interview that the researchers in the multisite, single-arm Intuitive trial will also track oncologic outcomes, but the trial description at clinicaltrials.gov does not indicate that.
Both Dr. Kopkash and Dr. Park cited the high-profile missteps that took place in 2018 at Monmouth County Medical Center in Long Branch, N.J., during what was described as the first-ever use of robotic nipple-sparing mastectomy for invasive cancer in the United States, as reported by Medscape Medical News. However, neither the center or surgeon, Stephen Chagares, MD, requested or received an IDE from the FDA, and use of robotic mastectomy was halted after two cases.
It’s conceivable that Intuitive will seek out FDA clearance for use of its da Vinci system in robotic nipple-sparing mastectomy with data in a prophylactic setting and then expand the pool of patients, argued Dr. Noorchashm.
“Even if you introduce a new technology ... for a narrow subset of patients, the application of it eventually occurs on a ‘sliding scale,’ ” he said.
The former surgeon gave an example: The first device used in gastric bypass surgery was cleared for use in 2001 by the FDA for adults who were “severely morbidly obese.” But by the late 2000s, the operation was also being performed on people with lower body mass indexes who hadn’t exhausted traditional weight loss procedures. “It was very lucrative,” Dr. Noorchashm said about the surgery.
Surgeons only get one body
Intuitive has been hugely successful in developing and marketing its da Vinci system around the world for general and oncologic surgeries, with more than 1 million surgeries in 2018, a greater than sevenfold increase in 10 years, according to the authors of a new essay published in the June issue of the Annals of Surgery. The authors include breast surgeon Rosa F. Hwang, MD, of MD Anderson Cancer Center in Houston, who is also an investigator for the Intuitive trial.
However, robotic mastectomy is still a new surgery – only about 150 patients have been treated in the world, mostly in Italy, France, Taiwan, and Korea, the authors noted.
Despite such small numbers, “there’s a lot of interest in bringing this to the United States,” said Dr. Park.
One of the arguments in favor of robotic mastectomy for nipple-sparing procedures has nothing to do with patients. Instead, it is improved ergonomics – the robot makes a tough surgery easier on the surgeon.
Even stalwart robot critic Dr. Margenthaler conceded that this was possibly a winning feature.
“Nipple-sparing mastectomy is a very physically demanding procedure for the surgeon, resulting in higher rates of neck and back pain and fatigue compared with a standard skin-sparing approach,” she noted. She suggested, however, that practitioners of traditional mastectomy ought to first experiment with changes to patient positioning and incision placement to alleviate stress before looking to the robot for change.
When this news organization interviewed NorthShore University’s Dr. Kopkash, she had conducted four nipple-sparing mastectomies in the previous week. “It’s a difficult procedure on our bodies. I just turned 40 and I’m considered young for a surgeon. We get one body for our career and we have to figure out ways to make it work and protect it.”
Intuitive Surgical is funding the five-center clinical trial of robot-assisted nipple-sparing mastectomy, and UT Southwestern is funding its own trial. The Ohio State trial is funded by the university and a Pelotonia Idea Grant. Dr. Noorchashm and Dr. Margenthaler have no relevant financial disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The FDA warning was issued in February 2019 to both the public and physicians. The FDA cautioned that the safety and effectiveness of robotic surgical devices for mastectomy “have not been established” and robots are not approved for the prevention or treatment of breast cancer.
The agency also noted that “diminished long-term survival” was associated with robotic surgery in another women’s cancer, that of hysterectomy for cervical cancer.
The FDA also made a surprising statement. The agency typically approves the robot for surgical use based on 30-day complication rates (compared with standards of care). But it said that going forward it “anticipates” that any evaluation of new use of robots in cancer “would be supported” by cancer outcomes such as progression-free survival and overall survival, which require much longer follow-up.
In short, the FDA hinted that it would change how it regulated medical devices, or at least robots used in women’s cancers. “The FDA takes women’s health very seriously,” said the organization.
Fast forward to 2021, and there are several prospective clinical trials of robot-assisted nipple-sparing mastectomy underway in the United States, including a five-center study sponsored by Intuitive Surgical, the maker of da Vinci robots, the dominant machine on the market. There are also single-center studies at Ohio State and University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center.
However, in each case, the study design either excludes cancer outcomes or does not primarily focus on those measures.
Instead, the primary outcomes are relatively short term and include safety and efficacy measures such as en bloc (in one piece) removal of the breast tissue, conversions to open mastectomy, and the incidence of adverse events during surgery and up to 6 weeks after surgery.
Importantly, none of the studies is a randomized trial; all have single arms.
That’s not what is needed, says breast surgeon Julie A. Margenthaler, MD of Washington University in St. Louis.
“I firmly believe that robotic-assisted mastectomy should only be considered in the context of a well-designed, randomized trial evaluating patient selection, patient safety, surgical complications, and oncologic outcomes with a concomitant cost analysis,” Dr. Margenthaler wrote in an essay published last year in JAMA Surgery.
As with the FDA warning, she cites worse survival with commonly used minimally invasive radical hysterectomy for cervical cancer, saying it “is a stark reminder that the marketing of robotic surgery has its roots in cosmesis and convenience rather than oncologic outcomes.”
In addition, robotic surgery is prohibitively expensive, said Dr. Margenthaler. In fact, cost is her “main criticism regarding robotic-assisted mastectomy.” It costs an additional $6,000 for robot use per procedure, according to a study conducted at a center in Taiwan. “I simply cannot be convinced that this will ever achieve cost-effective or even cost-neutral status,” Dr. Margenthaler wrote.
Not looking at the right outcomes
“They’re not looking at the right outcomes,” said Hooman Noorchashm, MD, PhD, about the current trials in the United States. He is a former surgeon and faculty member at the University of Pennsylvania in Philadelphia, and is now a patient advocate after his wife, Amy Reed, MD, died of uterine cancer in 2017 following a laparoscopic hysterectomy performed with a power morcellator that resulted in the upstaging of an undetected gynecologic cancer.
“You have to look at oncologic outcomes and do randomized, noninferiority trials to demonstrate that those cancer outcomes are at least equivalent to standard of care,” he said in an interview.
The current U.S. trials are “totally inappropriate,” he said.
Are randomized trials forthcoming after this initial set of single-arm trials? This news organization reached out to Intuitive Surgical, maker of the market leader da Vinci robotic surgical equipment to find out.
“Any plans for use of da Vinci Xi surgical system in nipple-sparing mastectomy will be based on these [single-arm] study results as well as other data and evidence,” said a company spokesperson, who did not confirm use of a randomized trial.
What about the FDA? Will the agency change its current approach to approving robots in surgeries for women’s cancers and require – not just anticipate – cancer-related outcomes data? At press time, the FDA did not respond to a request for comment.
Not having a randomized trial with cancer outcomes in any eventual FDA review opens the door for robotic mastectomy to be cleared for use in some mastectomies with short-term, nononcologic data, said Dr. Noorchashm.
Safety concerns with robotic mastectomy
Proponents of robot-assisted nipple-sparing mastectomy, which is coupled with reconstruction to preserve the shape of both the breast and nipple-areola area, suggest that improved patient cosmesis is a significant advantage with the high-tech intervention, said Dr. Margenthaler.
That’s because most robotic mastectomies performed to date (almost exclusively in Europe and Asia) have employed a 3- to 5-cm vertical incision located behind the lateral breast fold, allowing the scar to be hidden under the patient’s arm.
But therein also lies a safety concern, she asserted.
The “oncologic integrity” of the specimen on extraction is in question in some cases, she wrote, because of “such a small opening.”
Dr. Noorchashm agreed: “It all comes down to trying to get a large specimen out of a small incision.”
Traditional open mastectomy optimally yields the en bloc removal of a tumor – in one whole piece – to avoid fragmenting the cancerous tissue and possibly leaving residual disease behind. These undesirable events are associated with a higher risk for recurrence and treatment failure, he explained.
Thus, there is a need for a randomized trial with longer-term oncologic outcomes that compares the new approach with traditional open mastectomy, argued both Dr. Margenthaler and Dr. Noorchashm.
In defense of single-arm trials
“Oncologic safety is what we are concerned about and what we would like to study,” said Ko Un (Clara) Park, MD, a breast surgeon at The Ohio State University in Columbus.
Dr. Park is leading a single-center, single-arm pilot study of robotic nipple-sparing mastectomy enrolling up to 20 women with early-stage breast cancer or inherited genetic risk factors (but no cancer diagnosis). The trial, sponsored by a Pelotonia Idea Grant and Ohio State, recently enrolled its first patient.
The study’s primary outcomes include the feasibility of removal of the breast tissue en bloc; however, none of the outcomes are classic oncologic metrics such as progression-free survival.
The en bloc removal outcome is in direct response to the FDA’s concerns about minimally invasive cancer surgeries in women, Dr. Park said in an interview. The pilot trial has an investigational device exemption (IDE) granted by the FDA.
“The reason why we can’t just open a randomized controlled study (of robot versus open) and measure oncologic outcomes like recurrence-free survival is because, before we get to that point, we have to make sure” basic safety issues are addressed and established, she explained.
But Dr. Noorchashm said that argument is missing the larger, more important point: “They are still doing an oncologic procedure – you are still obliged to do noninferiority [randomized] testing with respect to cancer outcomes.”
Dr. Park sounded a different note: “We are doing it as safely as we can do it.”
Prophylactic use is also a cancer surgery
Intuitive’s five-center trial does not include en bloc removal of the breast gland as a primary outcome. Instead, the two primary outcomes are conversions to open mastectomy (efficacy measure) and the incidence of adverse events during surgery to 42 days after surgery (safety measure).
The company’s trial does not include any women with breast cancer, but is limited to women at increased risk for breast cancer and seeking prophylactic nipple-sparing mastectomy surgery.
Enrollment in the 145-patient single-arm trial began in the last few months and has a primary completion date of December 2022. It also has an IDE from the FDA.
“I do think that things like this need to be done with caution,” said Katherine Kopkash, MD, an investigator in the Intuitive trial and a breast surgeon at NorthShore University HealthSystem in Evanston, Ill., referring to the trial’s FDA exemption.
Dr. Kopkash said in an interview that the researchers in the multisite, single-arm Intuitive trial will also track oncologic outcomes, but the trial description at clinicaltrials.gov does not indicate that.
Both Dr. Kopkash and Dr. Park cited the high-profile missteps that took place in 2018 at Monmouth County Medical Center in Long Branch, N.J., during what was described as the first-ever use of robotic nipple-sparing mastectomy for invasive cancer in the United States, as reported by Medscape Medical News. However, neither the center or surgeon, Stephen Chagares, MD, requested or received an IDE from the FDA, and use of robotic mastectomy was halted after two cases.
It’s conceivable that Intuitive will seek out FDA clearance for use of its da Vinci system in robotic nipple-sparing mastectomy with data in a prophylactic setting and then expand the pool of patients, argued Dr. Noorchashm.
“Even if you introduce a new technology ... for a narrow subset of patients, the application of it eventually occurs on a ‘sliding scale,’ ” he said.
The former surgeon gave an example: The first device used in gastric bypass surgery was cleared for use in 2001 by the FDA for adults who were “severely morbidly obese.” But by the late 2000s, the operation was also being performed on people with lower body mass indexes who hadn’t exhausted traditional weight loss procedures. “It was very lucrative,” Dr. Noorchashm said about the surgery.
Surgeons only get one body
Intuitive has been hugely successful in developing and marketing its da Vinci system around the world for general and oncologic surgeries, with more than 1 million surgeries in 2018, a greater than sevenfold increase in 10 years, according to the authors of a new essay published in the June issue of the Annals of Surgery. The authors include breast surgeon Rosa F. Hwang, MD, of MD Anderson Cancer Center in Houston, who is also an investigator for the Intuitive trial.
However, robotic mastectomy is still a new surgery – only about 150 patients have been treated in the world, mostly in Italy, France, Taiwan, and Korea, the authors noted.
Despite such small numbers, “there’s a lot of interest in bringing this to the United States,” said Dr. Park.
One of the arguments in favor of robotic mastectomy for nipple-sparing procedures has nothing to do with patients. Instead, it is improved ergonomics – the robot makes a tough surgery easier on the surgeon.
Even stalwart robot critic Dr. Margenthaler conceded that this was possibly a winning feature.
“Nipple-sparing mastectomy is a very physically demanding procedure for the surgeon, resulting in higher rates of neck and back pain and fatigue compared with a standard skin-sparing approach,” she noted. She suggested, however, that practitioners of traditional mastectomy ought to first experiment with changes to patient positioning and incision placement to alleviate stress before looking to the robot for change.
When this news organization interviewed NorthShore University’s Dr. Kopkash, she had conducted four nipple-sparing mastectomies in the previous week. “It’s a difficult procedure on our bodies. I just turned 40 and I’m considered young for a surgeon. We get one body for our career and we have to figure out ways to make it work and protect it.”
Intuitive Surgical is funding the five-center clinical trial of robot-assisted nipple-sparing mastectomy, and UT Southwestern is funding its own trial. The Ohio State trial is funded by the university and a Pelotonia Idea Grant. Dr. Noorchashm and Dr. Margenthaler have no relevant financial disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The FDA warning was issued in February 2019 to both the public and physicians. The FDA cautioned that the safety and effectiveness of robotic surgical devices for mastectomy “have not been established” and robots are not approved for the prevention or treatment of breast cancer.
The agency also noted that “diminished long-term survival” was associated with robotic surgery in another women’s cancer, that of hysterectomy for cervical cancer.
The FDA also made a surprising statement. The agency typically approves the robot for surgical use based on 30-day complication rates (compared with standards of care). But it said that going forward it “anticipates” that any evaluation of new use of robots in cancer “would be supported” by cancer outcomes such as progression-free survival and overall survival, which require much longer follow-up.
In short, the FDA hinted that it would change how it regulated medical devices, or at least robots used in women’s cancers. “The FDA takes women’s health very seriously,” said the organization.
Fast forward to 2021, and there are several prospective clinical trials of robot-assisted nipple-sparing mastectomy underway in the United States, including a five-center study sponsored by Intuitive Surgical, the maker of da Vinci robots, the dominant machine on the market. There are also single-center studies at Ohio State and University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center.
However, in each case, the study design either excludes cancer outcomes or does not primarily focus on those measures.
Instead, the primary outcomes are relatively short term and include safety and efficacy measures such as en bloc (in one piece) removal of the breast tissue, conversions to open mastectomy, and the incidence of adverse events during surgery and up to 6 weeks after surgery.
Importantly, none of the studies is a randomized trial; all have single arms.
That’s not what is needed, says breast surgeon Julie A. Margenthaler, MD of Washington University in St. Louis.
“I firmly believe that robotic-assisted mastectomy should only be considered in the context of a well-designed, randomized trial evaluating patient selection, patient safety, surgical complications, and oncologic outcomes with a concomitant cost analysis,” Dr. Margenthaler wrote in an essay published last year in JAMA Surgery.
As with the FDA warning, she cites worse survival with commonly used minimally invasive radical hysterectomy for cervical cancer, saying it “is a stark reminder that the marketing of robotic surgery has its roots in cosmesis and convenience rather than oncologic outcomes.”
In addition, robotic surgery is prohibitively expensive, said Dr. Margenthaler. In fact, cost is her “main criticism regarding robotic-assisted mastectomy.” It costs an additional $6,000 for robot use per procedure, according to a study conducted at a center in Taiwan. “I simply cannot be convinced that this will ever achieve cost-effective or even cost-neutral status,” Dr. Margenthaler wrote.
Not looking at the right outcomes
“They’re not looking at the right outcomes,” said Hooman Noorchashm, MD, PhD, about the current trials in the United States. He is a former surgeon and faculty member at the University of Pennsylvania in Philadelphia, and is now a patient advocate after his wife, Amy Reed, MD, died of uterine cancer in 2017 following a laparoscopic hysterectomy performed with a power morcellator that resulted in the upstaging of an undetected gynecologic cancer.
“You have to look at oncologic outcomes and do randomized, noninferiority trials to demonstrate that those cancer outcomes are at least equivalent to standard of care,” he said in an interview.
The current U.S. trials are “totally inappropriate,” he said.
Are randomized trials forthcoming after this initial set of single-arm trials? This news organization reached out to Intuitive Surgical, maker of the market leader da Vinci robotic surgical equipment to find out.
“Any plans for use of da Vinci Xi surgical system in nipple-sparing mastectomy will be based on these [single-arm] study results as well as other data and evidence,” said a company spokesperson, who did not confirm use of a randomized trial.
What about the FDA? Will the agency change its current approach to approving robots in surgeries for women’s cancers and require – not just anticipate – cancer-related outcomes data? At press time, the FDA did not respond to a request for comment.
Not having a randomized trial with cancer outcomes in any eventual FDA review opens the door for robotic mastectomy to be cleared for use in some mastectomies with short-term, nononcologic data, said Dr. Noorchashm.
Safety concerns with robotic mastectomy
Proponents of robot-assisted nipple-sparing mastectomy, which is coupled with reconstruction to preserve the shape of both the breast and nipple-areola area, suggest that improved patient cosmesis is a significant advantage with the high-tech intervention, said Dr. Margenthaler.
That’s because most robotic mastectomies performed to date (almost exclusively in Europe and Asia) have employed a 3- to 5-cm vertical incision located behind the lateral breast fold, allowing the scar to be hidden under the patient’s arm.
But therein also lies a safety concern, she asserted.
The “oncologic integrity” of the specimen on extraction is in question in some cases, she wrote, because of “such a small opening.”
Dr. Noorchashm agreed: “It all comes down to trying to get a large specimen out of a small incision.”
Traditional open mastectomy optimally yields the en bloc removal of a tumor – in one whole piece – to avoid fragmenting the cancerous tissue and possibly leaving residual disease behind. These undesirable events are associated with a higher risk for recurrence and treatment failure, he explained.
Thus, there is a need for a randomized trial with longer-term oncologic outcomes that compares the new approach with traditional open mastectomy, argued both Dr. Margenthaler and Dr. Noorchashm.
In defense of single-arm trials
“Oncologic safety is what we are concerned about and what we would like to study,” said Ko Un (Clara) Park, MD, a breast surgeon at The Ohio State University in Columbus.
Dr. Park is leading a single-center, single-arm pilot study of robotic nipple-sparing mastectomy enrolling up to 20 women with early-stage breast cancer or inherited genetic risk factors (but no cancer diagnosis). The trial, sponsored by a Pelotonia Idea Grant and Ohio State, recently enrolled its first patient.
The study’s primary outcomes include the feasibility of removal of the breast tissue en bloc; however, none of the outcomes are classic oncologic metrics such as progression-free survival.
The en bloc removal outcome is in direct response to the FDA’s concerns about minimally invasive cancer surgeries in women, Dr. Park said in an interview. The pilot trial has an investigational device exemption (IDE) granted by the FDA.
“The reason why we can’t just open a randomized controlled study (of robot versus open) and measure oncologic outcomes like recurrence-free survival is because, before we get to that point, we have to make sure” basic safety issues are addressed and established, she explained.
But Dr. Noorchashm said that argument is missing the larger, more important point: “They are still doing an oncologic procedure – you are still obliged to do noninferiority [randomized] testing with respect to cancer outcomes.”
Dr. Park sounded a different note: “We are doing it as safely as we can do it.”
Prophylactic use is also a cancer surgery
Intuitive’s five-center trial does not include en bloc removal of the breast gland as a primary outcome. Instead, the two primary outcomes are conversions to open mastectomy (efficacy measure) and the incidence of adverse events during surgery to 42 days after surgery (safety measure).
The company’s trial does not include any women with breast cancer, but is limited to women at increased risk for breast cancer and seeking prophylactic nipple-sparing mastectomy surgery.
Enrollment in the 145-patient single-arm trial began in the last few months and has a primary completion date of December 2022. It also has an IDE from the FDA.
“I do think that things like this need to be done with caution,” said Katherine Kopkash, MD, an investigator in the Intuitive trial and a breast surgeon at NorthShore University HealthSystem in Evanston, Ill., referring to the trial’s FDA exemption.
Dr. Kopkash said in an interview that the researchers in the multisite, single-arm Intuitive trial will also track oncologic outcomes, but the trial description at clinicaltrials.gov does not indicate that.
Both Dr. Kopkash and Dr. Park cited the high-profile missteps that took place in 2018 at Monmouth County Medical Center in Long Branch, N.J., during what was described as the first-ever use of robotic nipple-sparing mastectomy for invasive cancer in the United States, as reported by Medscape Medical News. However, neither the center or surgeon, Stephen Chagares, MD, requested or received an IDE from the FDA, and use of robotic mastectomy was halted after two cases.
It’s conceivable that Intuitive will seek out FDA clearance for use of its da Vinci system in robotic nipple-sparing mastectomy with data in a prophylactic setting and then expand the pool of patients, argued Dr. Noorchashm.
“Even if you introduce a new technology ... for a narrow subset of patients, the application of it eventually occurs on a ‘sliding scale,’ ” he said.
The former surgeon gave an example: The first device used in gastric bypass surgery was cleared for use in 2001 by the FDA for adults who were “severely morbidly obese.” But by the late 2000s, the operation was also being performed on people with lower body mass indexes who hadn’t exhausted traditional weight loss procedures. “It was very lucrative,” Dr. Noorchashm said about the surgery.
Surgeons only get one body
Intuitive has been hugely successful in developing and marketing its da Vinci system around the world for general and oncologic surgeries, with more than 1 million surgeries in 2018, a greater than sevenfold increase in 10 years, according to the authors of a new essay published in the June issue of the Annals of Surgery. The authors include breast surgeon Rosa F. Hwang, MD, of MD Anderson Cancer Center in Houston, who is also an investigator for the Intuitive trial.
However, robotic mastectomy is still a new surgery – only about 150 patients have been treated in the world, mostly in Italy, France, Taiwan, and Korea, the authors noted.
Despite such small numbers, “there’s a lot of interest in bringing this to the United States,” said Dr. Park.
One of the arguments in favor of robotic mastectomy for nipple-sparing procedures has nothing to do with patients. Instead, it is improved ergonomics – the robot makes a tough surgery easier on the surgeon.
Even stalwart robot critic Dr. Margenthaler conceded that this was possibly a winning feature.
“Nipple-sparing mastectomy is a very physically demanding procedure for the surgeon, resulting in higher rates of neck and back pain and fatigue compared with a standard skin-sparing approach,” she noted. She suggested, however, that practitioners of traditional mastectomy ought to first experiment with changes to patient positioning and incision placement to alleviate stress before looking to the robot for change.
When this news organization interviewed NorthShore University’s Dr. Kopkash, she had conducted four nipple-sparing mastectomies in the previous week. “It’s a difficult procedure on our bodies. I just turned 40 and I’m considered young for a surgeon. We get one body for our career and we have to figure out ways to make it work and protect it.”
Intuitive Surgical is funding the five-center clinical trial of robot-assisted nipple-sparing mastectomy, and UT Southwestern is funding its own trial. The Ohio State trial is funded by the university and a Pelotonia Idea Grant. Dr. Noorchashm and Dr. Margenthaler have no relevant financial disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Cancer mortality continues to drop in females as breast cancer reversal looms
Overall cancer mortality in females continues to decrease in the United States, but “previous declining trends in death rates slowed” for breast cancer in recent years, according to an annual report by several national organizations.
The analysis of long-term trends in cancer death rates shows that a decline of 1.4% per year from 2001 to 2016 accelerated to 2.1% per year in 2016-2018, the American Cancer Society, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, National Cancer Institute, and the North American Association of Central Cancer Registries said.
Decreases in overall cancer mortality were seen in females of all races and ethnic groups over the most recent 5-year period included in the report, 2014-2018, varying from –1.6% per year in both non-Hispanic Blacks and Whites to –0.9% for non-Hispanic American Indians/Alaska Natives (AI/ANs), Farhad Islami, MD, PhD, of the American Cancer Society, Atlanta, and associates said in the Journal of the National Cancer Institute.
Over those 5 years, death rates fell for 14 of the 20 most common cancers in females; increased for liver, uterus, brain, pancreas, and soft tissue including heart; and remained stable for cancers of the oral cavity/pharynx, they reported.
Breast cancer was among those that declined, but the rate of that decline has been slowing. Mortality declined by an average of 2.3% per year in 2003-2007, by 1.6% a year in 2007-2014, and by just 1.0% annually during 2014-2018, based on data from the National Center for Health Statistics’ National Vital Statistics System.
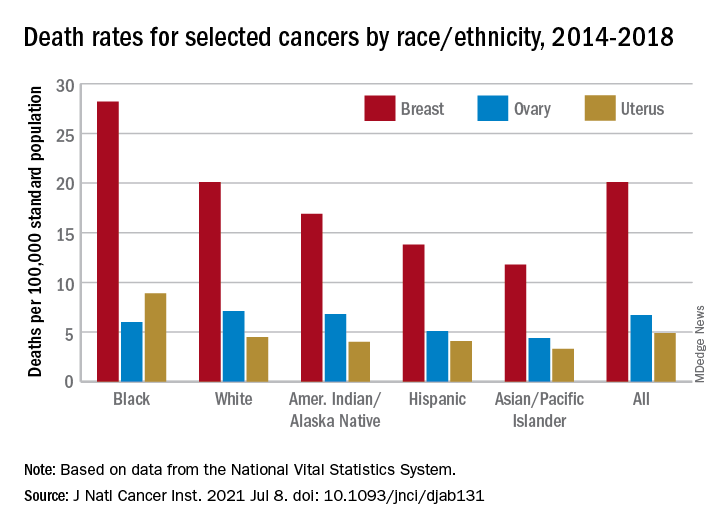
Mortality from all cancers in 2014-2018 was 133.5 deaths per 100,000 standard population, with the racial/ethnic gap ranging from 85.4 per 100,000 (non-Hispanic Asian/Pacific Islander) to 154.9 (non-Hispanic Black), Dr. Islami and associates said.
Melanoma had the largest decline in mortality over that period among the 20 most common cancers in females, falling by an average of 4.4% per year, with lung cancer next at 4.3%. Among those with increased death rates, uterine cancer saw the largest rise at 2.0% a year, the research team said.
The deaths caused by cancer of the uterus were most common in non-Hispanic Black females, 8.9 per 100,000 population, followed by non-Hispanic White (4.5), Hispanic (4.1), non-Hispanic AI/AN (4.0), and non-Hispanic Asian/Pacific Islander (3.3), they reported.
“Long-term increasing trends in uterine cancer death rates parallel trends in incidence, although death rates are increasing at a somewhat faster rate. Increasing uterine cancer incidence has been attributed to increasing obesity prevalence and decreased use of combined hormone replacement therapy,” Dr. Islami and associates pointed out.
Breast cancer deaths also were most common among Blacks in 2014-2018, occurring at a rate of 28.2 per 100,000, as were deaths from cancer of the cervix (3.4 per 100,000), while ovarian cancers deaths were highest in White females (7.1 per 100,000), the researchers noted.
The continuing racial and ethnic disparity “largely reflects a combination of multiple intertwined factors” of tumor biology, diagnosis, treatment, and systemic discrimination, they wrote, adding that Black persons “are more likely to have a higher exposure to some cancer risk factors and limited access to healthy food, safe places for physical activity, and evidence-based cancer preventive services.”
The report was funded by the four participating groups. Six of the 12 investigators are employees of the American Cancer Society whose salaries are solely paid by the society; the other authors had no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Overall cancer mortality in females continues to decrease in the United States, but “previous declining trends in death rates slowed” for breast cancer in recent years, according to an annual report by several national organizations.

The analysis of long-term trends in cancer death rates shows that a decline of 1.4% per year from 2001 to 2016 accelerated to 2.1% per year in 2016-2018, the American Cancer Society, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, National Cancer Institute, and the North American Association of Central Cancer Registries said.
Decreases in overall cancer mortality were seen in females of all races and ethnic groups over the most recent 5-year period included in the report, 2014-2018, varying from –1.6% per year in both non-Hispanic Blacks and Whites to –0.9% for non-Hispanic American Indians/Alaska Natives (AI/ANs), Farhad Islami, MD, PhD, of the American Cancer Society, Atlanta, and associates said in the Journal of the National Cancer Institute.
Over those 5 years, death rates fell for 14 of the 20 most common cancers in females; increased for liver, uterus, brain, pancreas, and soft tissue including heart; and remained stable for cancers of the oral cavity/pharynx, they reported.
Breast cancer was among those that declined, but the rate of that decline has been slowing. Mortality declined by an average of 2.3% per year in 2003-2007, by 1.6% a year in 2007-2014, and by just 1.0% annually during 2014-2018, based on data from the National Center for Health Statistics’ National Vital Statistics System.
Mortality from all cancers in 2014-2018 was 133.5 deaths per 100,000 standard population, with the racial/ethnic gap ranging from 85.4 per 100,000 (non-Hispanic Asian/Pacific Islander) to 154.9 (non-Hispanic Black), Dr. Islami and associates said.
Melanoma had the largest decline in mortality over that period among the 20 most common cancers in females, falling by an average of 4.4% per year, with lung cancer next at 4.3%. Among those with increased death rates, uterine cancer saw the largest rise at 2.0% a year, the research team said.
The deaths caused by cancer of the uterus were most common in non-Hispanic Black females, 8.9 per 100,000 population, followed by non-Hispanic White (4.5), Hispanic (4.1), non-Hispanic AI/AN (4.0), and non-Hispanic Asian/Pacific Islander (3.3), they reported.
“Long-term increasing trends in uterine cancer death rates parallel trends in incidence, although death rates are increasing at a somewhat faster rate. Increasing uterine cancer incidence has been attributed to increasing obesity prevalence and decreased use of combined hormone replacement therapy,” Dr. Islami and associates pointed out.
Breast cancer deaths also were most common among Blacks in 2014-2018, occurring at a rate of 28.2 per 100,000, as were deaths from cancer of the cervix (3.4 per 100,000), while ovarian cancers deaths were highest in White females (7.1 per 100,000), the researchers noted.
The continuing racial and ethnic disparity “largely reflects a combination of multiple intertwined factors” of tumor biology, diagnosis, treatment, and systemic discrimination, they wrote, adding that Black persons “are more likely to have a higher exposure to some cancer risk factors and limited access to healthy food, safe places for physical activity, and evidence-based cancer preventive services.”
The report was funded by the four participating groups. Six of the 12 investigators are employees of the American Cancer Society whose salaries are solely paid by the society; the other authors had no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Overall cancer mortality in females continues to decrease in the United States, but “previous declining trends in death rates slowed” for breast cancer in recent years, according to an annual report by several national organizations.

The analysis of long-term trends in cancer death rates shows that a decline of 1.4% per year from 2001 to 2016 accelerated to 2.1% per year in 2016-2018, the American Cancer Society, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, National Cancer Institute, and the North American Association of Central Cancer Registries said.
Decreases in overall cancer mortality were seen in females of all races and ethnic groups over the most recent 5-year period included in the report, 2014-2018, varying from –1.6% per year in both non-Hispanic Blacks and Whites to –0.9% for non-Hispanic American Indians/Alaska Natives (AI/ANs), Farhad Islami, MD, PhD, of the American Cancer Society, Atlanta, and associates said in the Journal of the National Cancer Institute.
Over those 5 years, death rates fell for 14 of the 20 most common cancers in females; increased for liver, uterus, brain, pancreas, and soft tissue including heart; and remained stable for cancers of the oral cavity/pharynx, they reported.
Breast cancer was among those that declined, but the rate of that decline has been slowing. Mortality declined by an average of 2.3% per year in 2003-2007, by 1.6% a year in 2007-2014, and by just 1.0% annually during 2014-2018, based on data from the National Center for Health Statistics’ National Vital Statistics System.
Mortality from all cancers in 2014-2018 was 133.5 deaths per 100,000 standard population, with the racial/ethnic gap ranging from 85.4 per 100,000 (non-Hispanic Asian/Pacific Islander) to 154.9 (non-Hispanic Black), Dr. Islami and associates said.
Melanoma had the largest decline in mortality over that period among the 20 most common cancers in females, falling by an average of 4.4% per year, with lung cancer next at 4.3%. Among those with increased death rates, uterine cancer saw the largest rise at 2.0% a year, the research team said.
The deaths caused by cancer of the uterus were most common in non-Hispanic Black females, 8.9 per 100,000 population, followed by non-Hispanic White (4.5), Hispanic (4.1), non-Hispanic AI/AN (4.0), and non-Hispanic Asian/Pacific Islander (3.3), they reported.
“Long-term increasing trends in uterine cancer death rates parallel trends in incidence, although death rates are increasing at a somewhat faster rate. Increasing uterine cancer incidence has been attributed to increasing obesity prevalence and decreased use of combined hormone replacement therapy,” Dr. Islami and associates pointed out.
Breast cancer deaths also were most common among Blacks in 2014-2018, occurring at a rate of 28.2 per 100,000, as were deaths from cancer of the cervix (3.4 per 100,000), while ovarian cancers deaths were highest in White females (7.1 per 100,000), the researchers noted.
The continuing racial and ethnic disparity “largely reflects a combination of multiple intertwined factors” of tumor biology, diagnosis, treatment, and systemic discrimination, they wrote, adding that Black persons “are more likely to have a higher exposure to some cancer risk factors and limited access to healthy food, safe places for physical activity, and evidence-based cancer preventive services.”
The report was funded by the four participating groups. Six of the 12 investigators are employees of the American Cancer Society whose salaries are solely paid by the society; the other authors had no conflicts of interest to disclose.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF THE NATIONAL CANCER INSTITUTE
Therapeutic Approaches in Advanced Breast Cancer
More than 280,000 women in the United States will be diagnosed with invasive breast cancer this year. For those with metastatic breast cancer with distant spread, the 5-year survival rate is approximately 28%. Whether advanced disease is discovered at initial diagnosis or in relapsed disease, it is imperative to understand the molecular characteristics of the metastatic tumor.
Dr Susan Domchek, from the University of Pennsylvania, discusses the importance of retesting for estrogen receptor, progesterone receptor, and HER2/neu on a metastatic tumor focus in order to identify potential discordance between the primary cancer and metastatic disease.
Additionally, Dr Domchek discusses the importance of molecular testing for targetable mutations, including P13K and germline BRCA1/2, for which approved therapies have shown survival benefit.
The list of targetable mutations in breast cancer continues to expand. In the tumor-agnostic studies, pembrolizumab has shown survival benefit in tumors that have mismatch repair deficiency and microsatellite instability, and TRK inhibitors have shown efficacy in tumors positive for NTRK fusions. Numerous clinical trials are available looking at additional molecular-based therapies.
--
Susan M. Domchek, MD, Basser Professor, Department of Oncology; Executive Director, Basser Center for BRCA, Abramson Cancer Center, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia.
Susan M. Domchek, MD, has disclosed the following relevant financial relationships: Received income in an amount equal to or greater than $250 from: AstraZeneca; Clovis; Bristol Myers Squibb.
More than 280,000 women in the United States will be diagnosed with invasive breast cancer this year. For those with metastatic breast cancer with distant spread, the 5-year survival rate is approximately 28%. Whether advanced disease is discovered at initial diagnosis or in relapsed disease, it is imperative to understand the molecular characteristics of the metastatic tumor.
Dr Susan Domchek, from the University of Pennsylvania, discusses the importance of retesting for estrogen receptor, progesterone receptor, and HER2/neu on a metastatic tumor focus in order to identify potential discordance between the primary cancer and metastatic disease.
Additionally, Dr Domchek discusses the importance of molecular testing for targetable mutations, including P13K and germline BRCA1/2, for which approved therapies have shown survival benefit.
The list of targetable mutations in breast cancer continues to expand. In the tumor-agnostic studies, pembrolizumab has shown survival benefit in tumors that have mismatch repair deficiency and microsatellite instability, and TRK inhibitors have shown efficacy in tumors positive for NTRK fusions. Numerous clinical trials are available looking at additional molecular-based therapies.
--
Susan M. Domchek, MD, Basser Professor, Department of Oncology; Executive Director, Basser Center for BRCA, Abramson Cancer Center, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia.
Susan M. Domchek, MD, has disclosed the following relevant financial relationships: Received income in an amount equal to or greater than $250 from: AstraZeneca; Clovis; Bristol Myers Squibb.
More than 280,000 women in the United States will be diagnosed with invasive breast cancer this year. For those with metastatic breast cancer with distant spread, the 5-year survival rate is approximately 28%. Whether advanced disease is discovered at initial diagnosis or in relapsed disease, it is imperative to understand the molecular characteristics of the metastatic tumor.
Dr Susan Domchek, from the University of Pennsylvania, discusses the importance of retesting for estrogen receptor, progesterone receptor, and HER2/neu on a metastatic tumor focus in order to identify potential discordance between the primary cancer and metastatic disease.
Additionally, Dr Domchek discusses the importance of molecular testing for targetable mutations, including P13K and germline BRCA1/2, for which approved therapies have shown survival benefit.
The list of targetable mutations in breast cancer continues to expand. In the tumor-agnostic studies, pembrolizumab has shown survival benefit in tumors that have mismatch repair deficiency and microsatellite instability, and TRK inhibitors have shown efficacy in tumors positive for NTRK fusions. Numerous clinical trials are available looking at additional molecular-based therapies.
--
Susan M. Domchek, MD, Basser Professor, Department of Oncology; Executive Director, Basser Center for BRCA, Abramson Cancer Center, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia.
Susan M. Domchek, MD, has disclosed the following relevant financial relationships: Received income in an amount equal to or greater than $250 from: AstraZeneca; Clovis; Bristol Myers Squibb.

Focus on cancer risk
Hereditary cancer risk assessment is the key to identifying patients and families who are at increased risk for developing cancer. The knowledge generated by cancer risk assessment impacts clinical decisions that obstetricians and gynecologists and their patients make every day. Previvors—patients predisposed to developing cancer, because of their family history or a pathogenic gene variant, who have not had cancer—benefit from counseling, heightened surveillance, and medical and surgical options.
For the last 25 years, this field has been growing dramatically, and although the scientific advances are present, only 15.3% of patients with a personal history of breast or ovarian cancer who meet hereditary cancer testing criteria have been tested.1 As many as 1 in 4 women who present for a gynecologic examination may have a personal history or a family history that qualifies them for genetic testing.2
Cancer risk app considerations
The ability to leverage mobile device applications can provide clinicians and patients with a useful screening tool to identify women who are at increased cancer risk. Only a handful of apps are available today and most are geared to patients. Such apps explore the different testing modalities, including genetic testing, as well as treatment options. When evaluating the best app for patients, using the ACOG-recommended rubric shown on page 35, the qualities to keep in mind and that should score 4 out of 4 include design, authority, usefulness, and accuracy.
A few apps provide reminders for appointments, such as mammograms, magnetic resonance imaging, or breast self-exams, and allow patients to track treatment plans. To date, no app addresses prevention and treatment opportunities that are specific to patients who have a hereditary predisposition. At least one app lists hereditary cancer testing guidelines. Many more apps are geared toward individuals with cancer rather than toward previvors.
As ObGyns, we have an opportunity to educate and identify women and, subsequently, better counsel women identified as at increased risk for developing cancer. We can utilize medical apps to efficiently incorporate this screening into clinical practice. ●
- Childers P, Childers KK, Maggard-Gibbons M, et al. National estimates of genetic testing in women with a history of breast or ovarian cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2017;35:3800-3806.
- DeFrancesco M, Waldman RN, Pearlstone MM, et al. Hereditary cancer risk assessment and genetic testing in a community practice setting. Obstet Gynecol. 2018;132:1121-1129.
Hereditary cancer risk assessment is the key to identifying patients and families who are at increased risk for developing cancer. The knowledge generated by cancer risk assessment impacts clinical decisions that obstetricians and gynecologists and their patients make every day. Previvors—patients predisposed to developing cancer, because of their family history or a pathogenic gene variant, who have not had cancer—benefit from counseling, heightened surveillance, and medical and surgical options.
For the last 25 years, this field has been growing dramatically, and although the scientific advances are present, only 15.3% of patients with a personal history of breast or ovarian cancer who meet hereditary cancer testing criteria have been tested.1 As many as 1 in 4 women who present for a gynecologic examination may have a personal history or a family history that qualifies them for genetic testing.2
Cancer risk app considerations
The ability to leverage mobile device applications can provide clinicians and patients with a useful screening tool to identify women who are at increased cancer risk. Only a handful of apps are available today and most are geared to patients. Such apps explore the different testing modalities, including genetic testing, as well as treatment options. When evaluating the best app for patients, using the ACOG-recommended rubric shown on page 35, the qualities to keep in mind and that should score 4 out of 4 include design, authority, usefulness, and accuracy.
A few apps provide reminders for appointments, such as mammograms, magnetic resonance imaging, or breast self-exams, and allow patients to track treatment plans. To date, no app addresses prevention and treatment opportunities that are specific to patients who have a hereditary predisposition. At least one app lists hereditary cancer testing guidelines. Many more apps are geared toward individuals with cancer rather than toward previvors.
As ObGyns, we have an opportunity to educate and identify women and, subsequently, better counsel women identified as at increased risk for developing cancer. We can utilize medical apps to efficiently incorporate this screening into clinical practice. ●
Hereditary cancer risk assessment is the key to identifying patients and families who are at increased risk for developing cancer. The knowledge generated by cancer risk assessment impacts clinical decisions that obstetricians and gynecologists and their patients make every day. Previvors—patients predisposed to developing cancer, because of their family history or a pathogenic gene variant, who have not had cancer—benefit from counseling, heightened surveillance, and medical and surgical options.
For the last 25 years, this field has been growing dramatically, and although the scientific advances are present, only 15.3% of patients with a personal history of breast or ovarian cancer who meet hereditary cancer testing criteria have been tested.1 As many as 1 in 4 women who present for a gynecologic examination may have a personal history or a family history that qualifies them for genetic testing.2
Cancer risk app considerations
The ability to leverage mobile device applications can provide clinicians and patients with a useful screening tool to identify women who are at increased cancer risk. Only a handful of apps are available today and most are geared to patients. Such apps explore the different testing modalities, including genetic testing, as well as treatment options. When evaluating the best app for patients, using the ACOG-recommended rubric shown on page 35, the qualities to keep in mind and that should score 4 out of 4 include design, authority, usefulness, and accuracy.
A few apps provide reminders for appointments, such as mammograms, magnetic resonance imaging, or breast self-exams, and allow patients to track treatment plans. To date, no app addresses prevention and treatment opportunities that are specific to patients who have a hereditary predisposition. At least one app lists hereditary cancer testing guidelines. Many more apps are geared toward individuals with cancer rather than toward previvors.
As ObGyns, we have an opportunity to educate and identify women and, subsequently, better counsel women identified as at increased risk for developing cancer. We can utilize medical apps to efficiently incorporate this screening into clinical practice. ●
- Childers P, Childers KK, Maggard-Gibbons M, et al. National estimates of genetic testing in women with a history of breast or ovarian cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2017;35:3800-3806.
- DeFrancesco M, Waldman RN, Pearlstone MM, et al. Hereditary cancer risk assessment and genetic testing in a community practice setting. Obstet Gynecol. 2018;132:1121-1129.
- Childers P, Childers KK, Maggard-Gibbons M, et al. National estimates of genetic testing in women with a history of breast or ovarian cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2017;35:3800-3806.
- DeFrancesco M, Waldman RN, Pearlstone MM, et al. Hereditary cancer risk assessment and genetic testing in a community practice setting. Obstet Gynecol. 2018;132:1121-1129.
Huge trial casts doubt on bisphosphonates for breast cancer
say researchers reporting new results from a phase 3 trial with almost 3,000 women.
Current guidelines call for 3-5 years of bisphosphonate therapy on the theory that these drugs might reduce breast cancer recurrence as well as treatment-related bone problems.
However, the new results show no difference in disease-free survival, distant disease-free survival, and overall survival – regardless of menopausal status – between the 1,540 women who received intravenous zoledronate over a 5-year period and 1,447 women who received such therapy over a 2-year period.
What they did find was a substantially higher risk for adverse events with prolonged bisphosphonate treatment, including risks for grade 3/4 events, bone pain, bone fractures, arthralgia, and jaw necrosis, a rare but well- recognized possibility with bisphosphonates.
Lead investigator Thomas Friedl, PhD, a statistician at University Hospital Ulm (Germany), and colleagues concluded that the current duration of treatment can be reduced and that, short of good reason to use bisphosphonates longer, such as decreased bone density, “treatment with zoledronate for 5 years should not be considered in patients with early breast cancer.”
The study was published online on June 24 in JAMA Oncology.
An accompanying editorial went even further, stating not only that “shorter duration of treatment is sufficient” but also that the whole idea of bisphosphonates for breast cancer is in doubt.
With “the modest outcomes of bisphosphonates, compared with no bone-targeted therapy, in historical trials” and the low rates of recurrence with modern treatment – less than 10% in the trial – “what, if any, is the benefit from adjuvant bisphosphonates? It’s time to reevaluate the guidelines,” said the editorialists, led by Alexandra Desnoyers, MD, a breast cancer fellow at the University of Toronto.
“We suggest that zoledronate or other amino-bisphosphonates should not be given as standard adjuvant therapy for unselected women with breast cancer,” they wrote.
Risk for necrosis with 5 years of zoledronate
The women in the trial had primary invasive breast cancer and were at high risk for recurrence. They had either positive nodes or high-risk features, including age (median, 53 years). They were treated at 250 centers in Germany.
The first part of the trial was to see whether use of gemcitabine improved outcomes when added to docetaxel after standard fluorouracil, epirubicin, and cyclophosphamide adjuvant therapy following surgery. It did not, and the authors reported in 2020 that adjuvant gemcitabine should not be used in the treatment of high-risk early breast cancer.
The next phase of the trial involved zoledronate. Women were randomly assigned to receive zoledronate for 2 or 5 years after surgery and after undergoing chemotherapy. Dosing was 4 mg IV every 3 months for 2 years. The women in the 5-year group went on to receive 4 mg IV every 6 months for another 3 years.
At a mean of 5 years’ follow-up after the first zoledronate dose, there was no difference in any of the survival measures between the two dosage groups.
There was also no difference in rates of bone recurrence or in circulating tumor cells, which the bisphosphonates theory would have predicted. For instance, 10.5% of women in the 5-year group had one or more circulating tumor cells on follow-up versus 7.2% in the 2-year group.
Almost half of the women in the 5-year treatment group experienced adverse events with zoledronate – including 7.6% with grade 3/4 events – versus just over a quarter in the 2-year arm and only 5.1% with grade 3/4 events.
In the 5-year group, 8.3% of patients experienced bone pain and 5.1% experienced arthralgia versus 3.7% and 3.1%, respectively, in the 2-year arm.
Atypical fractures, such as femoral spiral fractures, are another concern with bisphosphonates. Although this trial did not report on fracture type, fractures were reported in 14 women in the 5-year group but in only 3 in the 2-year arm.
Jaw necrosis, another known adverse effect of bisphosphonates, was reported in 11 women in the 5-year group and in 5 in the 2-year group.
The study was funded by several pharmaceutical companies, including Novartis, the maker of zoledronate. The investigators have numerous industry ties. Dr. Friedl has received payments from Novartis.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
say researchers reporting new results from a phase 3 trial with almost 3,000 women.
Current guidelines call for 3-5 years of bisphosphonate therapy on the theory that these drugs might reduce breast cancer recurrence as well as treatment-related bone problems.
However, the new results show no difference in disease-free survival, distant disease-free survival, and overall survival – regardless of menopausal status – between the 1,540 women who received intravenous zoledronate over a 5-year period and 1,447 women who received such therapy over a 2-year period.
What they did find was a substantially higher risk for adverse events with prolonged bisphosphonate treatment, including risks for grade 3/4 events, bone pain, bone fractures, arthralgia, and jaw necrosis, a rare but well- recognized possibility with bisphosphonates.
Lead investigator Thomas Friedl, PhD, a statistician at University Hospital Ulm (Germany), and colleagues concluded that the current duration of treatment can be reduced and that, short of good reason to use bisphosphonates longer, such as decreased bone density, “treatment with zoledronate for 5 years should not be considered in patients with early breast cancer.”
The study was published online on June 24 in JAMA Oncology.
An accompanying editorial went even further, stating not only that “shorter duration of treatment is sufficient” but also that the whole idea of bisphosphonates for breast cancer is in doubt.
With “the modest outcomes of bisphosphonates, compared with no bone-targeted therapy, in historical trials” and the low rates of recurrence with modern treatment – less than 10% in the trial – “what, if any, is the benefit from adjuvant bisphosphonates? It’s time to reevaluate the guidelines,” said the editorialists, led by Alexandra Desnoyers, MD, a breast cancer fellow at the University of Toronto.
“We suggest that zoledronate or other amino-bisphosphonates should not be given as standard adjuvant therapy for unselected women with breast cancer,” they wrote.
Risk for necrosis with 5 years of zoledronate
The women in the trial had primary invasive breast cancer and were at high risk for recurrence. They had either positive nodes or high-risk features, including age (median, 53 years). They were treated at 250 centers in Germany.
The first part of the trial was to see whether use of gemcitabine improved outcomes when added to docetaxel after standard fluorouracil, epirubicin, and cyclophosphamide adjuvant therapy following surgery. It did not, and the authors reported in 2020 that adjuvant gemcitabine should not be used in the treatment of high-risk early breast cancer.
The next phase of the trial involved zoledronate. Women were randomly assigned to receive zoledronate for 2 or 5 years after surgery and after undergoing chemotherapy. Dosing was 4 mg IV every 3 months for 2 years. The women in the 5-year group went on to receive 4 mg IV every 6 months for another 3 years.
At a mean of 5 years’ follow-up after the first zoledronate dose, there was no difference in any of the survival measures between the two dosage groups.
There was also no difference in rates of bone recurrence or in circulating tumor cells, which the bisphosphonates theory would have predicted. For instance, 10.5% of women in the 5-year group had one or more circulating tumor cells on follow-up versus 7.2% in the 2-year group.
Almost half of the women in the 5-year treatment group experienced adverse events with zoledronate – including 7.6% with grade 3/4 events – versus just over a quarter in the 2-year arm and only 5.1% with grade 3/4 events.
In the 5-year group, 8.3% of patients experienced bone pain and 5.1% experienced arthralgia versus 3.7% and 3.1%, respectively, in the 2-year arm.
Atypical fractures, such as femoral spiral fractures, are another concern with bisphosphonates. Although this trial did not report on fracture type, fractures were reported in 14 women in the 5-year group but in only 3 in the 2-year arm.
Jaw necrosis, another known adverse effect of bisphosphonates, was reported in 11 women in the 5-year group and in 5 in the 2-year group.
The study was funded by several pharmaceutical companies, including Novartis, the maker of zoledronate. The investigators have numerous industry ties. Dr. Friedl has received payments from Novartis.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
say researchers reporting new results from a phase 3 trial with almost 3,000 women.
Current guidelines call for 3-5 years of bisphosphonate therapy on the theory that these drugs might reduce breast cancer recurrence as well as treatment-related bone problems.
However, the new results show no difference in disease-free survival, distant disease-free survival, and overall survival – regardless of menopausal status – between the 1,540 women who received intravenous zoledronate over a 5-year period and 1,447 women who received such therapy over a 2-year period.
What they did find was a substantially higher risk for adverse events with prolonged bisphosphonate treatment, including risks for grade 3/4 events, bone pain, bone fractures, arthralgia, and jaw necrosis, a rare but well- recognized possibility with bisphosphonates.
Lead investigator Thomas Friedl, PhD, a statistician at University Hospital Ulm (Germany), and colleagues concluded that the current duration of treatment can be reduced and that, short of good reason to use bisphosphonates longer, such as decreased bone density, “treatment with zoledronate for 5 years should not be considered in patients with early breast cancer.”
The study was published online on June 24 in JAMA Oncology.
An accompanying editorial went even further, stating not only that “shorter duration of treatment is sufficient” but also that the whole idea of bisphosphonates for breast cancer is in doubt.
With “the modest outcomes of bisphosphonates, compared with no bone-targeted therapy, in historical trials” and the low rates of recurrence with modern treatment – less than 10% in the trial – “what, if any, is the benefit from adjuvant bisphosphonates? It’s time to reevaluate the guidelines,” said the editorialists, led by Alexandra Desnoyers, MD, a breast cancer fellow at the University of Toronto.
“We suggest that zoledronate or other amino-bisphosphonates should not be given as standard adjuvant therapy for unselected women with breast cancer,” they wrote.
Risk for necrosis with 5 years of zoledronate
The women in the trial had primary invasive breast cancer and were at high risk for recurrence. They had either positive nodes or high-risk features, including age (median, 53 years). They were treated at 250 centers in Germany.
The first part of the trial was to see whether use of gemcitabine improved outcomes when added to docetaxel after standard fluorouracil, epirubicin, and cyclophosphamide adjuvant therapy following surgery. It did not, and the authors reported in 2020 that adjuvant gemcitabine should not be used in the treatment of high-risk early breast cancer.
The next phase of the trial involved zoledronate. Women were randomly assigned to receive zoledronate for 2 or 5 years after surgery and after undergoing chemotherapy. Dosing was 4 mg IV every 3 months for 2 years. The women in the 5-year group went on to receive 4 mg IV every 6 months for another 3 years.
At a mean of 5 years’ follow-up after the first zoledronate dose, there was no difference in any of the survival measures between the two dosage groups.
There was also no difference in rates of bone recurrence or in circulating tumor cells, which the bisphosphonates theory would have predicted. For instance, 10.5% of women in the 5-year group had one or more circulating tumor cells on follow-up versus 7.2% in the 2-year group.
Almost half of the women in the 5-year treatment group experienced adverse events with zoledronate – including 7.6% with grade 3/4 events – versus just over a quarter in the 2-year arm and only 5.1% with grade 3/4 events.
In the 5-year group, 8.3% of patients experienced bone pain and 5.1% experienced arthralgia versus 3.7% and 3.1%, respectively, in the 2-year arm.
Atypical fractures, such as femoral spiral fractures, are another concern with bisphosphonates. Although this trial did not report on fracture type, fractures were reported in 14 women in the 5-year group but in only 3 in the 2-year arm.
Jaw necrosis, another known adverse effect of bisphosphonates, was reported in 11 women in the 5-year group and in 5 in the 2-year group.
The study was funded by several pharmaceutical companies, including Novartis, the maker of zoledronate. The investigators have numerous industry ties. Dr. Friedl has received payments from Novartis.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
CDC notes sharp declines in breast and cervical cancer screening
The new data come from the National Breast and Cervical Cancer Early Detection Program (NBCCEDP), a program that provides cancer screening services to women with low income and inadequate health insurance.
The data show that the total number of screenings funded by the NBCCEDP declined by 87% for breast cancer screening and by 84% for cervical cancer screening in April 2020 in comparison with the previous 5-year averages for that month.
The declines in breast cancer screening varied from 84% among Hispanic women to 98% among American Indian/Alaskan Native women. The declines in cervical cancer screening varied from 82% among Black women to 92% among Asian Pacific Islander women.
In April 2020, breast cancer screening declined by 86% in metro areas, 88% in urban areas, and 89% in rural areas in comparison with respective 5-year averages. For cervical cancer screenings, the corresponding declines were 85%, 77%, and 82%.
The findings are consistent with those from studies conducted in insured populations, note the authors, led by the Amy DeGroff, PhD, MPH, of the CDC’s National Center for Chronic Disease Prevention and Health Promotion.
“Prolonged delays in screening related to the COVID-19 pandemic may lead to delayed diagnoses, poor health consequences, and an increase in cancer disparities among women already experiencing health inequities,” the CDC states in a press release.
Women from racial and ethnic minority groups already face a disproportionate burden of cervical and breast cancers in the United States: Black women and Hispanic women have the highest rates of cervical cancer incidence (8.3 and 8.9 per 100,000 women, respectively, vs. 7.3 per 100,000 among White women) and the highest rates of cervical cancer deaths. Black women have the highest rate of breast cancer death (26.9 per 100,000 women, vs. 19.4 per 100,000 among White women), the study authors explain.
Although the volume of screening began to recover in May 2020 – test volumes for breast and cervical cancer were 39% and 40% below the 5-year average by June 2020 – breast cancer screening in rural areas remained 52% below the 5-year average, they report.
The findings were published online June 30 in Preventive Medicine.
“This study highlights a decline in cancer screening among women of racial and ethnic minority groups with low incomes when their access to medical services decreased at the beginning of the pandemic,” Dr. DeGroff comments in the CDC press release.
The findings “reinforce the need to safely maintain routine health care services during the pandemic, especially when the health care environment meets COVID-19 safety guidelines,” she adds.
The investigators used NBCCEDP administrative and program data reported to the CDC by awardees – organizations that receive funding to implement the NBCCEDP – to assess the impact of COVID-19 on the number of breast and cervical cancer screening tests administered through the program and the effects of COVID-19 on the availability of screening services and NBCCEDP awardees’ capacity to support partner clinics.
A total of 630,264 breast and 594,566 cervical cancer screening tests were conducted during the review period of January-June 2015-2020.
Despite COVID-related challenges, “a large number of awardees reported flexibility and creative efforts to reach women and support clinics’ resumption of clinical care, including screening, during the COVID-19 pandemic,” the authors write.
“[The] CDC encourages health care professionals to help minimize delays in testing by continuing routine cancer screening for women having symptoms or at high risk for breast or cervical cancer,” Dr. DeGroff commented. “The Early Detection Program can help women overcome barriers to health equity by educating them about the importance of routine screening, addressing their concerns about COVID-19 transmission, and helping them to safely access screening through interventions like patient navigation.”
Future studies will examine the effect of the pandemic on screening during the second half of 2020, when surges of COVID-19 and their timing varied geographically, they note.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The new data come from the National Breast and Cervical Cancer Early Detection Program (NBCCEDP), a program that provides cancer screening services to women with low income and inadequate health insurance.
The data show that the total number of screenings funded by the NBCCEDP declined by 87% for breast cancer screening and by 84% for cervical cancer screening in April 2020 in comparison with the previous 5-year averages for that month.
The declines in breast cancer screening varied from 84% among Hispanic women to 98% among American Indian/Alaskan Native women. The declines in cervical cancer screening varied from 82% among Black women to 92% among Asian Pacific Islander women.
In April 2020, breast cancer screening declined by 86% in metro areas, 88% in urban areas, and 89% in rural areas in comparison with respective 5-year averages. For cervical cancer screenings, the corresponding declines were 85%, 77%, and 82%.
The findings are consistent with those from studies conducted in insured populations, note the authors, led by the Amy DeGroff, PhD, MPH, of the CDC’s National Center for Chronic Disease Prevention and Health Promotion.
“Prolonged delays in screening related to the COVID-19 pandemic may lead to delayed diagnoses, poor health consequences, and an increase in cancer disparities among women already experiencing health inequities,” the CDC states in a press release.
Women from racial and ethnic minority groups already face a disproportionate burden of cervical and breast cancers in the United States: Black women and Hispanic women have the highest rates of cervical cancer incidence (8.3 and 8.9 per 100,000 women, respectively, vs. 7.3 per 100,000 among White women) and the highest rates of cervical cancer deaths. Black women have the highest rate of breast cancer death (26.9 per 100,000 women, vs. 19.4 per 100,000 among White women), the study authors explain.
Although the volume of screening began to recover in May 2020 – test volumes for breast and cervical cancer were 39% and 40% below the 5-year average by June 2020 – breast cancer screening in rural areas remained 52% below the 5-year average, they report.
The findings were published online June 30 in Preventive Medicine.
“This study highlights a decline in cancer screening among women of racial and ethnic minority groups with low incomes when their access to medical services decreased at the beginning of the pandemic,” Dr. DeGroff comments in the CDC press release.
The findings “reinforce the need to safely maintain routine health care services during the pandemic, especially when the health care environment meets COVID-19 safety guidelines,” she adds.
The investigators used NBCCEDP administrative and program data reported to the CDC by awardees – organizations that receive funding to implement the NBCCEDP – to assess the impact of COVID-19 on the number of breast and cervical cancer screening tests administered through the program and the effects of COVID-19 on the availability of screening services and NBCCEDP awardees’ capacity to support partner clinics.
A total of 630,264 breast and 594,566 cervical cancer screening tests were conducted during the review period of January-June 2015-2020.
Despite COVID-related challenges, “a large number of awardees reported flexibility and creative efforts to reach women and support clinics’ resumption of clinical care, including screening, during the COVID-19 pandemic,” the authors write.
“[The] CDC encourages health care professionals to help minimize delays in testing by continuing routine cancer screening for women having symptoms or at high risk for breast or cervical cancer,” Dr. DeGroff commented. “The Early Detection Program can help women overcome barriers to health equity by educating them about the importance of routine screening, addressing their concerns about COVID-19 transmission, and helping them to safely access screening through interventions like patient navigation.”
Future studies will examine the effect of the pandemic on screening during the second half of 2020, when surges of COVID-19 and their timing varied geographically, they note.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The new data come from the National Breast and Cervical Cancer Early Detection Program (NBCCEDP), a program that provides cancer screening services to women with low income and inadequate health insurance.
The data show that the total number of screenings funded by the NBCCEDP declined by 87% for breast cancer screening and by 84% for cervical cancer screening in April 2020 in comparison with the previous 5-year averages for that month.
The declines in breast cancer screening varied from 84% among Hispanic women to 98% among American Indian/Alaskan Native women. The declines in cervical cancer screening varied from 82% among Black women to 92% among Asian Pacific Islander women.
In April 2020, breast cancer screening declined by 86% in metro areas, 88% in urban areas, and 89% in rural areas in comparison with respective 5-year averages. For cervical cancer screenings, the corresponding declines were 85%, 77%, and 82%.
The findings are consistent with those from studies conducted in insured populations, note the authors, led by the Amy DeGroff, PhD, MPH, of the CDC’s National Center for Chronic Disease Prevention and Health Promotion.
“Prolonged delays in screening related to the COVID-19 pandemic may lead to delayed diagnoses, poor health consequences, and an increase in cancer disparities among women already experiencing health inequities,” the CDC states in a press release.
Women from racial and ethnic minority groups already face a disproportionate burden of cervical and breast cancers in the United States: Black women and Hispanic women have the highest rates of cervical cancer incidence (8.3 and 8.9 per 100,000 women, respectively, vs. 7.3 per 100,000 among White women) and the highest rates of cervical cancer deaths. Black women have the highest rate of breast cancer death (26.9 per 100,000 women, vs. 19.4 per 100,000 among White women), the study authors explain.
Although the volume of screening began to recover in May 2020 – test volumes for breast and cervical cancer were 39% and 40% below the 5-year average by June 2020 – breast cancer screening in rural areas remained 52% below the 5-year average, they report.
The findings were published online June 30 in Preventive Medicine.
“This study highlights a decline in cancer screening among women of racial and ethnic minority groups with low incomes when their access to medical services decreased at the beginning of the pandemic,” Dr. DeGroff comments in the CDC press release.
The findings “reinforce the need to safely maintain routine health care services during the pandemic, especially when the health care environment meets COVID-19 safety guidelines,” she adds.
The investigators used NBCCEDP administrative and program data reported to the CDC by awardees – organizations that receive funding to implement the NBCCEDP – to assess the impact of COVID-19 on the number of breast and cervical cancer screening tests administered through the program and the effects of COVID-19 on the availability of screening services and NBCCEDP awardees’ capacity to support partner clinics.
A total of 630,264 breast and 594,566 cervical cancer screening tests were conducted during the review period of January-June 2015-2020.
Despite COVID-related challenges, “a large number of awardees reported flexibility and creative efforts to reach women and support clinics’ resumption of clinical care, including screening, during the COVID-19 pandemic,” the authors write.
“[The] CDC encourages health care professionals to help minimize delays in testing by continuing routine cancer screening for women having symptoms or at high risk for breast or cervical cancer,” Dr. DeGroff commented. “The Early Detection Program can help women overcome barriers to health equity by educating them about the importance of routine screening, addressing their concerns about COVID-19 transmission, and helping them to safely access screening through interventions like patient navigation.”
Future studies will examine the effect of the pandemic on screening during the second half of 2020, when surges of COVID-19 and their timing varied geographically, they note.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
No increase in breast cancer risk with fertility treatments
No link between fertility treatment and an increase in the risk for breast cancer was found in the largest study of the issue to date.
This study “provides the evidence needed to reassure women and couples seeking fertility treatments,” commented senior author Sesh Sunkara, MD, a reproductive medicine specialist at King’s College London in a press release.
With an increasing number of women seeking help to become mothers, the question “is a matter of great importance” and a source of considerable concern among patients, the study authors comment.
This is the largest meta-analysis to date, involving 1.8 million women who were followed for an average of 27 years. The investigators found no link with the use of gonadotropins or clomiphene citrate to increase egg production in fertility cycles.
There has been concern over the years that fertility treatment could stimulate estrogen-sensitive precursor breast cancer cells.
More than 4,000 studies of this issue have been conducted since 1990, and results have been conflicting. The investigators analyzed results from the 20 strongest ones.
The new meta-analysis included nine retrospective studies, five case-control studies, five prospective studies, and one comparative study
The team cautioned that the quality of evidence in even these top 20 studies was “very low” but that such an approach is perhaps the best possible on this issue because a randomized trial among women seeking help to have children would be “ethically challenging.”
In the study, the team compared breast cancer incidence among women who underwent ovarian stimulation with the incidence in both age-matched unexposed women in the general population and unexposed infertile women.
There was no significant increase in the risk for breast cancer among women treated with any ovarian stimulation drug (pooled odds ratio, 1.03; 95% confidence interval, 0.86-1.23, but with substantial heterogeneity between study outcomes).
There was also no increased risk when the analysis was limited to the eight studies in which women were treated with both gonadotropins and clomiphene citrate (pooled OR, 0.92; 95% CI, 0.52-1.60, with substantial heterogeneity).
The authors noted that, among the many study limitations, no distinction was made between physiological dosing for anovulation and supraphysiological dosing for in vitro fertilization cycles. In addition, because the treated women were generally young, the follow-up period fell short of the age at which they’d be most at risk for breast cancer.
Individual patient data were also not available, but 14 studies did adjust for confounders, including weight, race, parity, age at first birth, age at menarche, and family history of breast cancer.
Although the findings are reassuring, “further long-term and detailed studies are now needed to confirm” them, Kotryna Temcinaite, PhD, senior research communications manager at the U.K. charity Breast Cancer Now, said in the press release.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
No link between fertility treatment and an increase in the risk for breast cancer was found in the largest study of the issue to date.
This study “provides the evidence needed to reassure women and couples seeking fertility treatments,” commented senior author Sesh Sunkara, MD, a reproductive medicine specialist at King’s College London in a press release.
With an increasing number of women seeking help to become mothers, the question “is a matter of great importance” and a source of considerable concern among patients, the study authors comment.
This is the largest meta-analysis to date, involving 1.8 million women who were followed for an average of 27 years. The investigators found no link with the use of gonadotropins or clomiphene citrate to increase egg production in fertility cycles.
There has been concern over the years that fertility treatment could stimulate estrogen-sensitive precursor breast cancer cells.
More than 4,000 studies of this issue have been conducted since 1990, and results have been conflicting. The investigators analyzed results from the 20 strongest ones.
The new meta-analysis included nine retrospective studies, five case-control studies, five prospective studies, and one comparative study
The team cautioned that the quality of evidence in even these top 20 studies was “very low” but that such an approach is perhaps the best possible on this issue because a randomized trial among women seeking help to have children would be “ethically challenging.”
In the study, the team compared breast cancer incidence among women who underwent ovarian stimulation with the incidence in both age-matched unexposed women in the general population and unexposed infertile women.
There was no significant increase in the risk for breast cancer among women treated with any ovarian stimulation drug (pooled odds ratio, 1.03; 95% confidence interval, 0.86-1.23, but with substantial heterogeneity between study outcomes).
There was also no increased risk when the analysis was limited to the eight studies in which women were treated with both gonadotropins and clomiphene citrate (pooled OR, 0.92; 95% CI, 0.52-1.60, with substantial heterogeneity).
The authors noted that, among the many study limitations, no distinction was made between physiological dosing for anovulation and supraphysiological dosing for in vitro fertilization cycles. In addition, because the treated women were generally young, the follow-up period fell short of the age at which they’d be most at risk for breast cancer.
Individual patient data were also not available, but 14 studies did adjust for confounders, including weight, race, parity, age at first birth, age at menarche, and family history of breast cancer.
Although the findings are reassuring, “further long-term and detailed studies are now needed to confirm” them, Kotryna Temcinaite, PhD, senior research communications manager at the U.K. charity Breast Cancer Now, said in the press release.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
No link between fertility treatment and an increase in the risk for breast cancer was found in the largest study of the issue to date.
This study “provides the evidence needed to reassure women and couples seeking fertility treatments,” commented senior author Sesh Sunkara, MD, a reproductive medicine specialist at King’s College London in a press release.
With an increasing number of women seeking help to become mothers, the question “is a matter of great importance” and a source of considerable concern among patients, the study authors comment.
This is the largest meta-analysis to date, involving 1.8 million women who were followed for an average of 27 years. The investigators found no link with the use of gonadotropins or clomiphene citrate to increase egg production in fertility cycles.
There has been concern over the years that fertility treatment could stimulate estrogen-sensitive precursor breast cancer cells.
More than 4,000 studies of this issue have been conducted since 1990, and results have been conflicting. The investigators analyzed results from the 20 strongest ones.
The new meta-analysis included nine retrospective studies, five case-control studies, five prospective studies, and one comparative study
The team cautioned that the quality of evidence in even these top 20 studies was “very low” but that such an approach is perhaps the best possible on this issue because a randomized trial among women seeking help to have children would be “ethically challenging.”
In the study, the team compared breast cancer incidence among women who underwent ovarian stimulation with the incidence in both age-matched unexposed women in the general population and unexposed infertile women.
There was no significant increase in the risk for breast cancer among women treated with any ovarian stimulation drug (pooled odds ratio, 1.03; 95% confidence interval, 0.86-1.23, but with substantial heterogeneity between study outcomes).
There was also no increased risk when the analysis was limited to the eight studies in which women were treated with both gonadotropins and clomiphene citrate (pooled OR, 0.92; 95% CI, 0.52-1.60, with substantial heterogeneity).
The authors noted that, among the many study limitations, no distinction was made between physiological dosing for anovulation and supraphysiological dosing for in vitro fertilization cycles. In addition, because the treated women were generally young, the follow-up period fell short of the age at which they’d be most at risk for breast cancer.
Individual patient data were also not available, but 14 studies did adjust for confounders, including weight, race, parity, age at first birth, age at menarche, and family history of breast cancer.
Although the findings are reassuring, “further long-term and detailed studies are now needed to confirm” them, Kotryna Temcinaite, PhD, senior research communications manager at the U.K. charity Breast Cancer Now, said in the press release.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Rapid update to ASCO breast cancer guidelines after OlympiA data
The American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO) now recommends offering 1 year of adjuvant olaparib therapy to patients with early-stage HER2-negative, BRCA-mutated breast cancer who have completed chemotherapy and local treatment.
The change in management of hereditary breast cancer is outlined in an update to 2020 guidelines, and it comes as a “rapid recommendation” on the heels of the phase 3 OlympiA trial results, which indicated a 42% improvement in invasive and distant disease-free survival with the PARP inhibitor olaparib (Lynparza) in comparison with placebo.
The OlympiA trial results, as reported by this news organization, were presented during the plenary session of the ASCO 2021 annual meeting and were published June 3 in The New England Journal of Medicine.
“These clear and positive data prompted ASCO to issue a provisional update of the guideline recommendation focused specifically on the role of olaparib in this setting,” states an ASCO press release.
The previous 2020 guidelines stated: “There are insufficient data ... to recommend a PARP inhibitor for patients with nonmetastatic breast cancer.” The OlympiA trial changed that. ASCO now recommends that patients with early-stage, HER2-negative, BRCA-mutated breast cancer at high risk for recurrence be offered olaparib after completion of chemotherapy and local treatment, including radiotherapy.
The update states: “For those who had surgery first, adjuvant olaparib is recommended for patients with TNBC [triple-negative breast cancer] and tumor size greater than 2 cm or any involved axillary nodes. For patients with hormone receptor–positive disease, adjuvant olaparib is recommended for those with at least four involved axillary lymph nodes. For patients who had neoadjuvant chemotherapy, adjuvant olaparib is recommended for patients with TNBC and any residual cancer. Adjuvant olaparib is recommended for patients with residual disease and an estrogen receptor status and tumor grade (CSP+EG) score greater than or equal to 3.”
“The findings from the OlympiA trial – presented just last week – mark a significant improvement in the care of these patients,” Julie Garlow, MD, ASCO’s executive vice president and chief medical officer, states in the ASCO press release.
“ASCO’s Expert Guideline Panel and Evidence-based Medicine Committee noted this and then quickly produced and provisionally approved this guideline update to enable patients to begin to benefit from this research advance as quickly as possible,” she said.
A formal assessment and submission for publication in the Journal of Clinical Oncology will follow the release notes.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO) now recommends offering 1 year of adjuvant olaparib therapy to patients with early-stage HER2-negative, BRCA-mutated breast cancer who have completed chemotherapy and local treatment.
The change in management of hereditary breast cancer is outlined in an update to 2020 guidelines, and it comes as a “rapid recommendation” on the heels of the phase 3 OlympiA trial results, which indicated a 42% improvement in invasive and distant disease-free survival with the PARP inhibitor olaparib (Lynparza) in comparison with placebo.
The OlympiA trial results, as reported by this news organization, were presented during the plenary session of the ASCO 2021 annual meeting and were published June 3 in The New England Journal of Medicine.
“These clear and positive data prompted ASCO to issue a provisional update of the guideline recommendation focused specifically on the role of olaparib in this setting,” states an ASCO press release.
The previous 2020 guidelines stated: “There are insufficient data ... to recommend a PARP inhibitor for patients with nonmetastatic breast cancer.” The OlympiA trial changed that. ASCO now recommends that patients with early-stage, HER2-negative, BRCA-mutated breast cancer at high risk for recurrence be offered olaparib after completion of chemotherapy and local treatment, including radiotherapy.
The update states: “For those who had surgery first, adjuvant olaparib is recommended for patients with TNBC [triple-negative breast cancer] and tumor size greater than 2 cm or any involved axillary nodes. For patients with hormone receptor–positive disease, adjuvant olaparib is recommended for those with at least four involved axillary lymph nodes. For patients who had neoadjuvant chemotherapy, adjuvant olaparib is recommended for patients with TNBC and any residual cancer. Adjuvant olaparib is recommended for patients with residual disease and an estrogen receptor status and tumor grade (CSP+EG) score greater than or equal to 3.”
“The findings from the OlympiA trial – presented just last week – mark a significant improvement in the care of these patients,” Julie Garlow, MD, ASCO’s executive vice president and chief medical officer, states in the ASCO press release.
“ASCO’s Expert Guideline Panel and Evidence-based Medicine Committee noted this and then quickly produced and provisionally approved this guideline update to enable patients to begin to benefit from this research advance as quickly as possible,” she said.
A formal assessment and submission for publication in the Journal of Clinical Oncology will follow the release notes.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO) now recommends offering 1 year of adjuvant olaparib therapy to patients with early-stage HER2-negative, BRCA-mutated breast cancer who have completed chemotherapy and local treatment.
The change in management of hereditary breast cancer is outlined in an update to 2020 guidelines, and it comes as a “rapid recommendation” on the heels of the phase 3 OlympiA trial results, which indicated a 42% improvement in invasive and distant disease-free survival with the PARP inhibitor olaparib (Lynparza) in comparison with placebo.
The OlympiA trial results, as reported by this news organization, were presented during the plenary session of the ASCO 2021 annual meeting and were published June 3 in The New England Journal of Medicine.
“These clear and positive data prompted ASCO to issue a provisional update of the guideline recommendation focused specifically on the role of olaparib in this setting,” states an ASCO press release.
The previous 2020 guidelines stated: “There are insufficient data ... to recommend a PARP inhibitor for patients with nonmetastatic breast cancer.” The OlympiA trial changed that. ASCO now recommends that patients with early-stage, HER2-negative, BRCA-mutated breast cancer at high risk for recurrence be offered olaparib after completion of chemotherapy and local treatment, including radiotherapy.
The update states: “For those who had surgery first, adjuvant olaparib is recommended for patients with TNBC [triple-negative breast cancer] and tumor size greater than 2 cm or any involved axillary nodes. For patients with hormone receptor–positive disease, adjuvant olaparib is recommended for those with at least four involved axillary lymph nodes. For patients who had neoadjuvant chemotherapy, adjuvant olaparib is recommended for patients with TNBC and any residual cancer. Adjuvant olaparib is recommended for patients with residual disease and an estrogen receptor status and tumor grade (CSP+EG) score greater than or equal to 3.”
“The findings from the OlympiA trial – presented just last week – mark a significant improvement in the care of these patients,” Julie Garlow, MD, ASCO’s executive vice president and chief medical officer, states in the ASCO press release.
“ASCO’s Expert Guideline Panel and Evidence-based Medicine Committee noted this and then quickly produced and provisionally approved this guideline update to enable patients to begin to benefit from this research advance as quickly as possible,” she said.
A formal assessment and submission for publication in the Journal of Clinical Oncology will follow the release notes.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Breast cancer: Young women likely to receive guideline-concordant care
Key clinical point: A high number of young women with breast cancer receive guideline-concordant care (GCC).
Major finding: GCC was given to 81.7% of the patients. Patients with stage III vs. stage I or II disease (93.4% vs. 88.4%) received GCC more frequently in hormone receptor (HR)-positive/human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2)-positive or HR-negative/HER-positive subtypes. In women with HR-negative/HER2-negative or HR-positive/HER2-negative tumors, a higher proportion of patients with stage II vs stage I or III disease received GCC (91.8% vs. 83.7%).
Study details: A retrospective study of 1,295 young women with invasive breast cancer diagnosed in 2013.
Disclosures: This study was supported by the National Cancer Institute. Dr. AW Kurian received research funding from Myriad Genetics and served on the board of directors of a patient advocacy group outside this work. The other authors reported no conflicts of interest.
Source: White DP. Cancer. 2021 Jun 1. doi: 10.1002/cncr.33652.
Key clinical point: A high number of young women with breast cancer receive guideline-concordant care (GCC).
Major finding: GCC was given to 81.7% of the patients. Patients with stage III vs. stage I or II disease (93.4% vs. 88.4%) received GCC more frequently in hormone receptor (HR)-positive/human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2)-positive or HR-negative/HER-positive subtypes. In women with HR-negative/HER2-negative or HR-positive/HER2-negative tumors, a higher proportion of patients with stage II vs stage I or III disease received GCC (91.8% vs. 83.7%).
Study details: A retrospective study of 1,295 young women with invasive breast cancer diagnosed in 2013.
Disclosures: This study was supported by the National Cancer Institute. Dr. AW Kurian received research funding from Myriad Genetics and served on the board of directors of a patient advocacy group outside this work. The other authors reported no conflicts of interest.
Source: White DP. Cancer. 2021 Jun 1. doi: 10.1002/cncr.33652.
Key clinical point: A high number of young women with breast cancer receive guideline-concordant care (GCC).
Major finding: GCC was given to 81.7% of the patients. Patients with stage III vs. stage I or II disease (93.4% vs. 88.4%) received GCC more frequently in hormone receptor (HR)-positive/human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2)-positive or HR-negative/HER-positive subtypes. In women with HR-negative/HER2-negative or HR-positive/HER2-negative tumors, a higher proportion of patients with stage II vs stage I or III disease received GCC (91.8% vs. 83.7%).
Study details: A retrospective study of 1,295 young women with invasive breast cancer diagnosed in 2013.
Disclosures: This study was supported by the National Cancer Institute. Dr. AW Kurian received research funding from Myriad Genetics and served on the board of directors of a patient advocacy group outside this work. The other authors reported no conflicts of interest.
Source: White DP. Cancer. 2021 Jun 1. doi: 10.1002/cncr.33652.

