User login
High rates of work-related trauma, PTSD in intern physicians
Work-related posttraumatic stress disorder is three times higher in interns than the general population, new research shows.
Investigators assessed PTSD in more than 1,100 physicians at the end of their internship year and found that a little over half reported work-related trauma exposure, and of these, 20% screened positive for PTSD.
Overall, 10% of participants screened positive for PTSD by the end of the internship year, compared with a 12-month PTSD prevalence of 3.6% in the general population.
“Work-related trauma exposure and PTSD are common and underdiscussed phenomena among intern physicians,” lead author Mary Vance, MD, assistant professor of psychiatry, Uniformed Services University of the Health Sciences, Bethesda, Md., said in an interview.
“I urge medical educators and policy makers to include this topic in their discussions about physician well-being and to implement effective interventions to mitigate the impact of work-related trauma and PTSD among physician trainees,” she said.
The study was published online June 8 in JAMA Network Open.
Burnout, depression, suicide
“Burnout, depression, and suicide are increasingly recognized as occupational mental health hazards among health care professionals, including physicians,” Dr. Vance said.
“However, in my professional experience as a physician and educator, despite observing anecdotal evidence among my peers and trainees that this is also an issue,” she added.
This gap prompted her “to investigate rates of work-related trauma exposure and PTSD among physicians.”
The researchers sent emails to 4,350 individuals during academic year 2018-2019, 2 months prior to starting internships. Of these, 2,129 agreed to participate and 1,134 (58.6% female, 61.6% non-Hispanic White; mean age, 27.52) completed the study.
Prior to beginning internship, participants completed a baseline survey that assessed demographic characteristics as well as medical education and psychological and psychosocial factors.
Participants completed follow-up surveys sent by email at 3, 6, 9, and 12 months of the internship year. The surveys assessed stressful life events, concern over perceived medical errors in the past 3 months, and number of hours worked over the past week.
At month 12, current PTSD and symptoms of depression and anxiety were also assessed using the Primary Care PTSD Screen for DSM-5, the 9-item Patient Health Questionnaire, and the Generalized Anxiety Disorder 7-item scale, respectively.
Participants were asked to self-report whether they ever had an episode of depression and to complete the Risky Families Questionnaire to assess if they had experienced childhood abuse, neglect, and family conflict. Additionally, they completed an 11-item scale developed specifically for the study regarding recent stressful events.
‘Crucible’ year
A total of 56.4% of respondents reported work-related trauma exposure, and among these, 19.0% screened positive for PTSD. One-tenth (10.8%) of the entire sample screened positive for PTSD by the end of internship year, which is three times higher than the 12-month prevalence of PTSD in the general population (3.6%), the authors noted.
Trauma exposure differed by specialty, ranging from 43.1% in anesthesiology to 72.4% in emergency medicine. Of the respondents in internal medicine, surgery, and medicine/pediatrics, 56.6%, 63.3%, and 71%, respectively, reported work-related trauma exposure.
Work-related PTSD also differed by specialty, ranging from 7.5% in ob.gyn. to 30.0% in pediatrics. Of respondents in internal medicine and family practice, 23.9% and 25.9%, respectively, reported work-related PTSD.
Dr. Vance called the intern year “a crucible, during which newly minted doctors receive intensive on-the-job training at the front lines of patient care [and] work long hours in rapidly shifting environments, often caring for critically ill patients.”
Work-related trauma exposure “is more likely to occur during this high-stress internship year than during the same year in the general population,” she said.
She noted that the “issue of workplace trauma and PTSD among health care workers became even more salient during the height of COVID,” adding that she expects it “to remain a pressure issue for healthcare workers in the post-COVID era.”
Call to action
Commenting on the study David A. Marcus, MD, chair, GME Physician Well-Being Committee, Northwell Health, New Hyde Park, N.Y., noted the study’s “relatively low response rate” is a “significant limitation” of the study.
An additional limitation is the lack of a baseline PTSD assessment, said Dr. Marcus, an assistant professor at Hofstra University, Hempstead, N.Y., who was not involved in the research.
Nevertheless, the “overall prevalence [of work-related PTSD] should serve as a call to action for physician leaders and for leaders in academic medicine,” he said.
Additionally, the study “reminds us that trauma-informed care should be an essential part of mental health support services provided to trainees and to physicians in general,” Dr. Marcus stated.
Also commenting on the study, Lotte N. Dyrbye, MD, professor of medicine and medical education, Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minn., agreed.
“Organizational strategies should include system-level interventions to reduce the risk of frightening, horrible, or traumatic events from occurring in the workplace in the first place, as well as faculty development efforts to upskill teaching faculty in their ability to support trainees when such events do occur,” she said.
These approaches “should coincide with organizational efforts to support individual trainees by providing adequate time off after traumatic events, ensuring trainees can access affordable mental healthcare, and reducing other barriers to appropriate help-seeking, such as stigma, and efforts to build a culture of well-being,” suggested Dr. Dyrbye, who is codirector of the Mayo Clinic Program on Physician Wellbeing and was not involved in the study.
The study was supported by grants from the Blue Cross Blue Shield Foundation of Michigan and National Institutes of Health. Dr. Vance and coauthors, Dr. Marcus, and Dr. Dyrbye reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Work-related posttraumatic stress disorder is three times higher in interns than the general population, new research shows.
Investigators assessed PTSD in more than 1,100 physicians at the end of their internship year and found that a little over half reported work-related trauma exposure, and of these, 20% screened positive for PTSD.
Overall, 10% of participants screened positive for PTSD by the end of the internship year, compared with a 12-month PTSD prevalence of 3.6% in the general population.
“Work-related trauma exposure and PTSD are common and underdiscussed phenomena among intern physicians,” lead author Mary Vance, MD, assistant professor of psychiatry, Uniformed Services University of the Health Sciences, Bethesda, Md., said in an interview.
“I urge medical educators and policy makers to include this topic in their discussions about physician well-being and to implement effective interventions to mitigate the impact of work-related trauma and PTSD among physician trainees,” she said.
The study was published online June 8 in JAMA Network Open.
Burnout, depression, suicide
“Burnout, depression, and suicide are increasingly recognized as occupational mental health hazards among health care professionals, including physicians,” Dr. Vance said.
“However, in my professional experience as a physician and educator, despite observing anecdotal evidence among my peers and trainees that this is also an issue,” she added.
This gap prompted her “to investigate rates of work-related trauma exposure and PTSD among physicians.”
The researchers sent emails to 4,350 individuals during academic year 2018-2019, 2 months prior to starting internships. Of these, 2,129 agreed to participate and 1,134 (58.6% female, 61.6% non-Hispanic White; mean age, 27.52) completed the study.
Prior to beginning internship, participants completed a baseline survey that assessed demographic characteristics as well as medical education and psychological and psychosocial factors.
Participants completed follow-up surveys sent by email at 3, 6, 9, and 12 months of the internship year. The surveys assessed stressful life events, concern over perceived medical errors in the past 3 months, and number of hours worked over the past week.
At month 12, current PTSD and symptoms of depression and anxiety were also assessed using the Primary Care PTSD Screen for DSM-5, the 9-item Patient Health Questionnaire, and the Generalized Anxiety Disorder 7-item scale, respectively.
Participants were asked to self-report whether they ever had an episode of depression and to complete the Risky Families Questionnaire to assess if they had experienced childhood abuse, neglect, and family conflict. Additionally, they completed an 11-item scale developed specifically for the study regarding recent stressful events.
‘Crucible’ year
A total of 56.4% of respondents reported work-related trauma exposure, and among these, 19.0% screened positive for PTSD. One-tenth (10.8%) of the entire sample screened positive for PTSD by the end of internship year, which is three times higher than the 12-month prevalence of PTSD in the general population (3.6%), the authors noted.
Trauma exposure differed by specialty, ranging from 43.1% in anesthesiology to 72.4% in emergency medicine. Of the respondents in internal medicine, surgery, and medicine/pediatrics, 56.6%, 63.3%, and 71%, respectively, reported work-related trauma exposure.
Work-related PTSD also differed by specialty, ranging from 7.5% in ob.gyn. to 30.0% in pediatrics. Of respondents in internal medicine and family practice, 23.9% and 25.9%, respectively, reported work-related PTSD.
Dr. Vance called the intern year “a crucible, during which newly minted doctors receive intensive on-the-job training at the front lines of patient care [and] work long hours in rapidly shifting environments, often caring for critically ill patients.”
Work-related trauma exposure “is more likely to occur during this high-stress internship year than during the same year in the general population,” she said.
She noted that the “issue of workplace trauma and PTSD among health care workers became even more salient during the height of COVID,” adding that she expects it “to remain a pressure issue for healthcare workers in the post-COVID era.”
Call to action
Commenting on the study David A. Marcus, MD, chair, GME Physician Well-Being Committee, Northwell Health, New Hyde Park, N.Y., noted the study’s “relatively low response rate” is a “significant limitation” of the study.
An additional limitation is the lack of a baseline PTSD assessment, said Dr. Marcus, an assistant professor at Hofstra University, Hempstead, N.Y., who was not involved in the research.
Nevertheless, the “overall prevalence [of work-related PTSD] should serve as a call to action for physician leaders and for leaders in academic medicine,” he said.
Additionally, the study “reminds us that trauma-informed care should be an essential part of mental health support services provided to trainees and to physicians in general,” Dr. Marcus stated.
Also commenting on the study, Lotte N. Dyrbye, MD, professor of medicine and medical education, Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minn., agreed.
“Organizational strategies should include system-level interventions to reduce the risk of frightening, horrible, or traumatic events from occurring in the workplace in the first place, as well as faculty development efforts to upskill teaching faculty in their ability to support trainees when such events do occur,” she said.
These approaches “should coincide with organizational efforts to support individual trainees by providing adequate time off after traumatic events, ensuring trainees can access affordable mental healthcare, and reducing other barriers to appropriate help-seeking, such as stigma, and efforts to build a culture of well-being,” suggested Dr. Dyrbye, who is codirector of the Mayo Clinic Program on Physician Wellbeing and was not involved in the study.
The study was supported by grants from the Blue Cross Blue Shield Foundation of Michigan and National Institutes of Health. Dr. Vance and coauthors, Dr. Marcus, and Dr. Dyrbye reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Work-related posttraumatic stress disorder is three times higher in interns than the general population, new research shows.
Investigators assessed PTSD in more than 1,100 physicians at the end of their internship year and found that a little over half reported work-related trauma exposure, and of these, 20% screened positive for PTSD.
Overall, 10% of participants screened positive for PTSD by the end of the internship year, compared with a 12-month PTSD prevalence of 3.6% in the general population.
“Work-related trauma exposure and PTSD are common and underdiscussed phenomena among intern physicians,” lead author Mary Vance, MD, assistant professor of psychiatry, Uniformed Services University of the Health Sciences, Bethesda, Md., said in an interview.
“I urge medical educators and policy makers to include this topic in their discussions about physician well-being and to implement effective interventions to mitigate the impact of work-related trauma and PTSD among physician trainees,” she said.
The study was published online June 8 in JAMA Network Open.
Burnout, depression, suicide
“Burnout, depression, and suicide are increasingly recognized as occupational mental health hazards among health care professionals, including physicians,” Dr. Vance said.
“However, in my professional experience as a physician and educator, despite observing anecdotal evidence among my peers and trainees that this is also an issue,” she added.
This gap prompted her “to investigate rates of work-related trauma exposure and PTSD among physicians.”
The researchers sent emails to 4,350 individuals during academic year 2018-2019, 2 months prior to starting internships. Of these, 2,129 agreed to participate and 1,134 (58.6% female, 61.6% non-Hispanic White; mean age, 27.52) completed the study.
Prior to beginning internship, participants completed a baseline survey that assessed demographic characteristics as well as medical education and psychological and psychosocial factors.
Participants completed follow-up surveys sent by email at 3, 6, 9, and 12 months of the internship year. The surveys assessed stressful life events, concern over perceived medical errors in the past 3 months, and number of hours worked over the past week.
At month 12, current PTSD and symptoms of depression and anxiety were also assessed using the Primary Care PTSD Screen for DSM-5, the 9-item Patient Health Questionnaire, and the Generalized Anxiety Disorder 7-item scale, respectively.
Participants were asked to self-report whether they ever had an episode of depression and to complete the Risky Families Questionnaire to assess if they had experienced childhood abuse, neglect, and family conflict. Additionally, they completed an 11-item scale developed specifically for the study regarding recent stressful events.
‘Crucible’ year
A total of 56.4% of respondents reported work-related trauma exposure, and among these, 19.0% screened positive for PTSD. One-tenth (10.8%) of the entire sample screened positive for PTSD by the end of internship year, which is three times higher than the 12-month prevalence of PTSD in the general population (3.6%), the authors noted.
Trauma exposure differed by specialty, ranging from 43.1% in anesthesiology to 72.4% in emergency medicine. Of the respondents in internal medicine, surgery, and medicine/pediatrics, 56.6%, 63.3%, and 71%, respectively, reported work-related trauma exposure.
Work-related PTSD also differed by specialty, ranging from 7.5% in ob.gyn. to 30.0% in pediatrics. Of respondents in internal medicine and family practice, 23.9% and 25.9%, respectively, reported work-related PTSD.
Dr. Vance called the intern year “a crucible, during which newly minted doctors receive intensive on-the-job training at the front lines of patient care [and] work long hours in rapidly shifting environments, often caring for critically ill patients.”
Work-related trauma exposure “is more likely to occur during this high-stress internship year than during the same year in the general population,” she said.
She noted that the “issue of workplace trauma and PTSD among health care workers became even more salient during the height of COVID,” adding that she expects it “to remain a pressure issue for healthcare workers in the post-COVID era.”
Call to action
Commenting on the study David A. Marcus, MD, chair, GME Physician Well-Being Committee, Northwell Health, New Hyde Park, N.Y., noted the study’s “relatively low response rate” is a “significant limitation” of the study.
An additional limitation is the lack of a baseline PTSD assessment, said Dr. Marcus, an assistant professor at Hofstra University, Hempstead, N.Y., who was not involved in the research.
Nevertheless, the “overall prevalence [of work-related PTSD] should serve as a call to action for physician leaders and for leaders in academic medicine,” he said.
Additionally, the study “reminds us that trauma-informed care should be an essential part of mental health support services provided to trainees and to physicians in general,” Dr. Marcus stated.
Also commenting on the study, Lotte N. Dyrbye, MD, professor of medicine and medical education, Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minn., agreed.
“Organizational strategies should include system-level interventions to reduce the risk of frightening, horrible, or traumatic events from occurring in the workplace in the first place, as well as faculty development efforts to upskill teaching faculty in their ability to support trainees when such events do occur,” she said.
These approaches “should coincide with organizational efforts to support individual trainees by providing adequate time off after traumatic events, ensuring trainees can access affordable mental healthcare, and reducing other barriers to appropriate help-seeking, such as stigma, and efforts to build a culture of well-being,” suggested Dr. Dyrbye, who is codirector of the Mayo Clinic Program on Physician Wellbeing and was not involved in the study.
The study was supported by grants from the Blue Cross Blue Shield Foundation of Michigan and National Institutes of Health. Dr. Vance and coauthors, Dr. Marcus, and Dr. Dyrbye reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A Veteran Presenting With Shortness of Breath, Cough, and Leukocytosis
Case Presentation: A 62-year-old male presented with shortness of breath and a cough productive of green sputum. He had a history of hyperlipidemia, posttraumatic stress disorder, bipolar disorder, obstructive sleep apnea, and a 50 pack-year history of smoking. His medications included prazosin, melatonin, lithium, and gabapentin. He also had a significant exposure history including asbestos and chemical paints following his leave from the military. At the initial evaluation, laboratory work revealed a leukocytosis with white blood cell (WBC) count 20 k/cm3and otherwise normal transaminases, albumin, and electrolytes. A chest X-ray revealed a new left hilar mass.
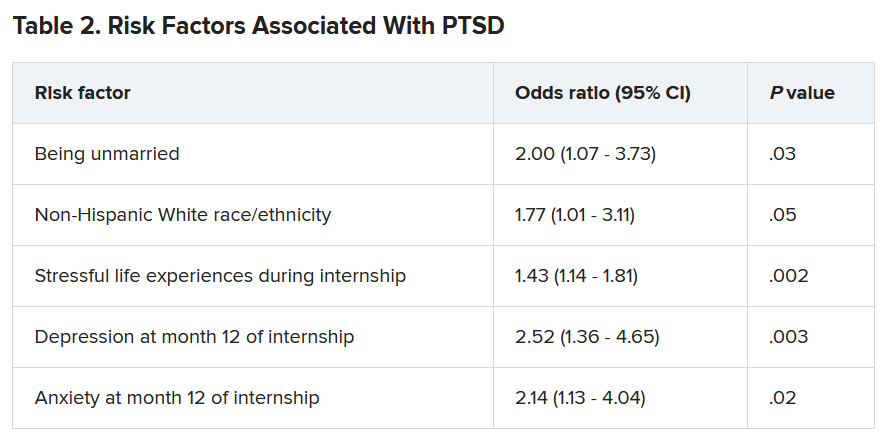
►Manisha Apte, MD, Chief Medical Resident, VA Boston Healthcare System (VABHS) and Boston Medical Center (BMC): To work up his new left hilar mass, a computed tomography (CT) of the chest was ordered (Figure 1), which revealed an apical left lower lobe mass extending into the left hilum encasing part of the ascending aorta. Enlarged mediastinal subcentimeter paratracheal and superior mediastinal lymph nodes also were identified and the pattern raised the concern for lymphangitic carcinomatosis. Dr. Fine, what do you make of the CT findings?
► Alan Fine, MD, Section of Pulmonary and Critical Care, VABHS and Professor of Medicine, Boston University School of Medicine: This mass had irregular edges with septal thickening, which may be why there was a concern for lymphangitic spread. There were no clear tissue planes to see if this process was invading the mediastinum. The mass was irregular, a single lesion, and proximal, making it consistent with a lung cancer. In fact, with his history of smoking, asbestos exposure, the numbers 1 to 10 diagnoses were lung cancer. The lack of demarcation of tissue planes supports this. There are some infections, classically actinomycosis, that do cross and invade anatomical barriers.1 But this looked like a primary lung cancer.
► Dr. Apte: The patient was referred to a pulmonologist where an additional history of night sweats and weight loss were noted. Dr. Fine, we have a patient with a newly identified lung mass, and while we have reason to suspect malignancy as you have already noted, there are many other etiologies to consider, including infections (histoplasmosis, cryptococcosis, bacterial abscess), inflammatory processes (sarcoidosis, rheumatoid nodule) and vasculitis (granulomatosis with polyangiitis). What should be the next step taken to make a diagnosis?
►Dr. Fine: For cancer specifically, we would like to both stage and make a diagnosis with one procedure. That’s part of the utility of a positron emission tomography (PET) scan: We can see lymph node involvement and stage the cancer. We must consider the patient’s comorbidities and the location of the lesion (ie, is it amenable to needle biopsy?). In this case, there are enlarged mediastinal lymph nodes, so one could perform a bronchoscopy with endobronchial ultrasound, which is a relatively noninvasive way to sample the lymph nodes to ideally stage and make a diagnosis as safely as possible. If we are considering infection, needle aspiration is not as sensitive.2
► Dr. Apte: The patient underwent a PET CT, which redemonstrated the lung mass with a loss of aortic fat plane suspicious for aortic involvement as well as lymph nodes in levels 7 and 8 that were concerning for malignancy. Subsequent bronchoscopy with biopsy and endobronchial ultrasound did not show evidence of malignancy; washing and brushing from the mass and lymph node specimens did not identify malignant cells. Benign respiratory mucosa with mild chronic inflammation was noted. Dr. Fine, given the nonspecific findings on the PET scan, negative findings on our bronchoscopy, and a negative biopsy, should we be satisfied that we have ruled out cancer?
► Dr. Fine: No, bronchoscopy has its limitations. It’s highly sensitive to the diagnosis of malignancy if you can see an endobronchial lesion, but we did not see one here. You can only go so far with the scope, and it’s not uncommon for us not to be able to make the diagnosis with bronchoscopy. Malignancy is still the most likely diagnosis, and we need to work this up further. I would perform another biopsy.
►Dr. Apte: Four weeks later, the patient presented with continued shortness of breath, fatigue, and fever. A repeat chest CT showed an opacity suggestive of pneumonia. Given the continued concern for cancer a CT-guided needle biopsy was performed and was once again negative for malignancy. The decision was made to pursue a video-assisted thorascopic surgery (VATS). Following the VATS, the patient developed rigors, fever, and tachycardia with new atrial fibrillation. While being evaluated hypercalcemia was identified, with further workup revealing a low parathyroid hormone (PTH) and low PTH-related peptide. Dr. Fine, the presence of hypercalcemia and a new arrythmia raised the possibility of sarcoidosis. Could this be sarcoidosis?
►Dr. Fine: Sarcoidosis is one of the great masqueraders in medicine. There is a type of sarcoidosis called nodular sarcoidosis where you see masslike distribution in the lung, but generally there are multiple masses and so this presentation would be atypical.3 There is also a phenomenon called sarcoidal reactions usually in the presence of cancer. Again, one tends to see multiple tiny lesions in the lung. It is certainly on the differential, but I would consider it to be less likely than cancer. It is also relatively common to develop atrial fibrillation after manipulation from a lung surgery.4 The other possibility I am concerned about is whether the mass is invading the mediastinum and involving the pericardium.
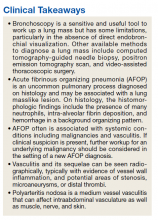
►Dr. Apte: Results from the VATS biopsy once again returned negative for malignancy and instead showed signs of focal micro-abscesses, atypical pneumocytes, and prominent neutrophils. A diagnosis of acute fibrinous organizing pneumonia (AFOP) was offered. Dr. Fine, what is AFOP?
►Dr. Fine: This is the first case of AFOP I had seen and probably the first case many in our department have seen. This is a relatively new entity with limited reported cases in the literature and is a pathological diagnosis originally recorded in autopsies from patients at the National Institutes of Health.5,6 Given the complexity of the lesion, the diagnosis is difficult to make. Most commonly, AFOP is associated with other systemic entities, most commonly hematologic malignancies like lymphomas and leukemias. It has also been associated with vasculitis and certain drugs. The mechanism is poorly understood, and although pneumonia is a part of the term, this just implies there is inflammation of the lung (ie, pneumonitis).
► Dr. Apte: Given the association of AFOP with underlying hematologic malignancies, an emphasis was placed on another finding: the patient’s increasing WBC count. The total WBC count had been 20 k/cm3 at the time of his lung mass discovery but had increased to > 40 k/cm3 with a differential of neutrophils > 80%. Flow cytometry was negative, and his peripheral smear was read as normal. Dr. Gilbert, what might explain this patient’s leukocytosis?
►Gary Gilbert, MD, Section of Hematology and Oncology, VABHS and Associate Professor of Medicine, Harvard Medical School (HMS): This patient had an elevated WBC for 4 months. Initially, the cause was likely lithium as this is known to cause a leukocytosis.7 More recently, the total WBC had increased and there were a couple of other abnormalities: A consistently elevated absolute monocyte count and a markedly elevated mature neutrophil count. These findings are consistent with a leukemoid reaction (ie, a WBC count > 50,000/µL from causes other than leukemia). The question becomes what is this a leukemoid reaction in response to? Once we have excluded a lung malignancy (a well-known common cause of a leukemoid reaction) we must consider a clonal myeloproliferative disorder. This is particularly true because many things that cause a leukemoid reaction (eg, lobar pneumonia) do not cause a persistently elevated neutrophil count. That this patient does have a persistently elevated neutrophil count suggests something abnormal about the neutrophils themselves.
► Dr. Apte: A bone marrow biopsy was performed. Dr. Gilbert, can you comment on this patient’s bone marrow biopsy and whether a myeloproliferative disorder may have played a role in the marked leukocytosis?
► Dr. Gilbert: The bone marrow biopsy was hyperplastic with myeloid predominance and normal maturation in all lineages. A deep sequencing analysis demonstrated the absence of chromosomal abnormalities or genetic mutations that are associated with myeloproliferative disorders. This excludes the possibility of a myeloproliferative disorder.
► Dr. Apte: The patient was started on 60 mg of prednisone daily, which led to marked improvement in his symptoms. He was discharged in stable condition but presented again with abdominal pain. A complete blood count once again showed increased WBC and new thrombocytosis. A CT angiogram (CTA) showed the prior lung mass with new signs of central necrosis. In the abdomen, new splenic and renal infarct were identified, along with signs of multiple arterial thrombi in the abdomen and internal and external iliac vessel wall thickening. These findings were read as concerning for a medium vessel vasculitis. Dr. Kaur, what are some of the imaging findings you would expect to see in vasculitis, and what about this patient’s CT is consistent with a medium vessel vasculitis?
► Maneet Kaur, MD, Section of Rheumatology, VABHS: Vasculitis is inflammation of the vessel wall that can lead to vascular injury and activation of the coagulation cascade. Sometimes these findings can be seen on imaging with evidence of stenosis, microaneurysms, and thrombosis distal to the stenosis. The nomenclature of vasculitis is not simple and has been revised many times. Medium-vessel vasculitis does not just affect the medium vessels (eg, visceral arteries) but can overlap with distal large vessels and smaller cutaneous vessels.
The first thing that comes to mind in this case is polyarteritis nodosa (PAN), an immune complex-mediated medium vessel disease that can involve large and small vessels in muscle, nerve, and skin. It can also present with masses.
►Dr. Apte: To address the arterial thrombi seen on CTA, arterial-brachial indices were obtained and showed bilateral occlusive disease in his distal extremities; findings that could be explained by vasculitis. His VATS biopsy pathology was reviewed for signs of vasculitis. Dr. Huang, can you review these slides for us please?
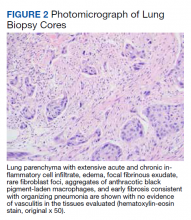
►Qin Huang, MD, Department of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine, VABHS and Assistant Professor of Pathology, HMS: This patient had a history of smoking, and there are many black pigment-laden macrophages present in the lung tissue. There were areas of hemorrhage and fibrin deposition and an overall picture of organizing pneumonia. At a lower power, you can see neutrophils everywhere, some in the form of micro-abscesses. The arterial walls did not show signs of vasculitis (Figure 2). Based on the clinical information and radiology findings, we suspected an acute infection-related pneumonia or a primary lung malignancy causing obstruction pneumonia. We suggested a rebiopsy of the lung mass to rule out a primary lung malignancy.
► Dr. Apte: Given his CT findings, a serologic rheumatologic workup including antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody, antinuclear antibody, and rheumatoid factors were sent and returned negative. The location of arterial wall inflammation on imaging made it unamenable for biopsy. The patient began to experience bilateral temporal pain, which raised the concern for a large vessel vasculitis, specifically giant cell arteritis. Bilateral temporal artery biopsies were obtained and were not suggestive of vasculitis. Dr. Kaur, we still do not have any serologic or biopsy confirmation to support a diagnosis of vasculitis. Can we still call this a vasculitis?
►Dr. Kaur: Few things can cause the picture that was seen radiographically. A few noninflammatory causes like fibromuscular dysplasia can cause both large and small vessel stenosis, but the elevations in erythrocyte sedimentation rate and C-reactive protein along with response to steroids makes these diagnoses unlikely. Sometimes we must make a clinical diagnosis for vasculitis based on the clinical picture, and I would feel comfortable treating this patient for vasculitis.
With that said, I remain concerned that this patient also has a malignancy. His WBC increased to > 70 k/cm3 and his calcium to > 13 mg/dL. These findings are hard to explain by vasculitis alone. There are cancer-associated vasculitis, and I suspect this is the explanation here.8 His temporal pain was pointing to large vessel involvement, so he could have an undifferentiated vasculitis.
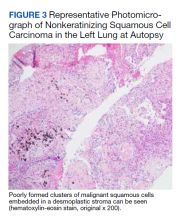
► Dr. Apte: A decision was made to empirically treat with tocilizumab, an IL-6 receptor antagonist, for an undifferentiated autoimmune disease, in addition to tapering steroids. The patient underwent a second VATS, which again revealed AFOP but no signs of malignancy. Unfortunately, he developed multiple complications over the subsequent weeks and passed away. An autopsy was requested by family members and pathology from his lung mass was reviewed. (Figure 3). Dr. Huang, can you review these slides for us?
► Dr. Huang: The left lung mass at autopsy shows nests, poorly formed clusters, and individuals of malignant neoplastic nonkeratinizing squamous cells embedded in a desmoplastic stroma in the mass center, consistent with poorly differentiated squamous cell carcinoma, and a circumscribed area of residual subacute organizing pneumonia with abscess, granulomatous changes, and early fibrosis at the periphery of this mass.
►Dr. Apte: Based on autopsy findings, the final diagnosis was poorly differentiated squamous cell carcinoma associated with subacute organizing pneumonia and medium vessel vasculitis, which presented with a severe leukocytosis ultimately thought to be a leukemoid reaction from his lung cancer.
1. Valour F, Sénéchal A, Dupieux C, et al. Actinomycosis: etiology, clinical features, diagnosis, treatment, and management. Infect Drug Resist. 2014;7:183-197. Published 2014 Jul 5. doi:10.2147/IDR.S39601
2. de Bazelaire C, Coffin A, Cohen-Zarade S, et al. CT-guided biopsies in lung infections in patients with haematological malignancies. Diagn Interv Imaging. 2013;94(2):202-215. doi:10.1016/j.diii.2012.12.008
3. Sweidan AJ, Singh NK, Stein A, Tanios M. Nodular sarcoidosis masquerading as cancer. Clin Med Insights Circ Respir Pulm Med. 2017;11:1179548417703123. Published 2017 Apr 12. doi:10.1177/1179548417703123
4. Bagheri R, Yousefi Y, Rezai R, Azemonfar V, Keshtan FG. Atrial fibrillation after lung surgery: incidence, underlying factors, and predictors. Kardiochir Torakochirurgia Pol. 2019;16(2):53-56. doi:10.5114/kitp.2019.86355
5. Lu J, Yin Q, Zha Y, et al. Acute fibrinous and organizing pneumonia: two case reports and literature review. BMC Pulm Med. 2019;19(1):141. Published 2019 Aug 5. doi:10.1186/s12890-019-0861-3
6. Beasley MB, Franks TJ, Galvin JR, Gochuico B, Travis WD. Acute fibrinous and organizing pneumonia: a histological pattern of lung injury and possible variant of diffuse alveolar damage. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2002;126(9):1064-1070. doi:10.5858/2002-126-1064-AFAOP
7. Murphy DL, Goodwin FK, Bunney WE Jr. Leukocytosis during lithium treatment. Am J Psychiatry. 1971;127(11):1559-1561. doi:10.1176/ajp.127.11.1559
8. Fain O, Hamidou M, Cacoub P, et al. Vasculitides associated with malignancies: analysis of sixty patients. Arthritis Rheum. 2007;57(8):1473-1480. doi:10.1002/art.23085
Case Presentation: A 62-year-old male presented with shortness of breath and a cough productive of green sputum. He had a history of hyperlipidemia, posttraumatic stress disorder, bipolar disorder, obstructive sleep apnea, and a 50 pack-year history of smoking. His medications included prazosin, melatonin, lithium, and gabapentin. He also had a significant exposure history including asbestos and chemical paints following his leave from the military. At the initial evaluation, laboratory work revealed a leukocytosis with white blood cell (WBC) count 20 k/cm3and otherwise normal transaminases, albumin, and electrolytes. A chest X-ray revealed a new left hilar mass.
►Manisha Apte, MD, Chief Medical Resident, VA Boston Healthcare System (VABHS) and Boston Medical Center (BMC): To work up his new left hilar mass, a computed tomography (CT) of the chest was ordered (Figure 1), which revealed an apical left lower lobe mass extending into the left hilum encasing part of the ascending aorta. Enlarged mediastinal subcentimeter paratracheal and superior mediastinal lymph nodes also were identified and the pattern raised the concern for lymphangitic carcinomatosis. Dr. Fine, what do you make of the CT findings?
► Alan Fine, MD, Section of Pulmonary and Critical Care, VABHS and Professor of Medicine, Boston University School of Medicine: This mass had irregular edges with septal thickening, which may be why there was a concern for lymphangitic spread. There were no clear tissue planes to see if this process was invading the mediastinum. The mass was irregular, a single lesion, and proximal, making it consistent with a lung cancer. In fact, with his history of smoking, asbestos exposure, the numbers 1 to 10 diagnoses were lung cancer. The lack of demarcation of tissue planes supports this. There are some infections, classically actinomycosis, that do cross and invade anatomical barriers.1 But this looked like a primary lung cancer.
► Dr. Apte: The patient was referred to a pulmonologist where an additional history of night sweats and weight loss were noted. Dr. Fine, we have a patient with a newly identified lung mass, and while we have reason to suspect malignancy as you have already noted, there are many other etiologies to consider, including infections (histoplasmosis, cryptococcosis, bacterial abscess), inflammatory processes (sarcoidosis, rheumatoid nodule) and vasculitis (granulomatosis with polyangiitis). What should be the next step taken to make a diagnosis?
►Dr. Fine: For cancer specifically, we would like to both stage and make a diagnosis with one procedure. That’s part of the utility of a positron emission tomography (PET) scan: We can see lymph node involvement and stage the cancer. We must consider the patient’s comorbidities and the location of the lesion (ie, is it amenable to needle biopsy?). In this case, there are enlarged mediastinal lymph nodes, so one could perform a bronchoscopy with endobronchial ultrasound, which is a relatively noninvasive way to sample the lymph nodes to ideally stage and make a diagnosis as safely as possible. If we are considering infection, needle aspiration is not as sensitive.2
► Dr. Apte: The patient underwent a PET CT, which redemonstrated the lung mass with a loss of aortic fat plane suspicious for aortic involvement as well as lymph nodes in levels 7 and 8 that were concerning for malignancy. Subsequent bronchoscopy with biopsy and endobronchial ultrasound did not show evidence of malignancy; washing and brushing from the mass and lymph node specimens did not identify malignant cells. Benign respiratory mucosa with mild chronic inflammation was noted. Dr. Fine, given the nonspecific findings on the PET scan, negative findings on our bronchoscopy, and a negative biopsy, should we be satisfied that we have ruled out cancer?
► Dr. Fine: No, bronchoscopy has its limitations. It’s highly sensitive to the diagnosis of malignancy if you can see an endobronchial lesion, but we did not see one here. You can only go so far with the scope, and it’s not uncommon for us not to be able to make the diagnosis with bronchoscopy. Malignancy is still the most likely diagnosis, and we need to work this up further. I would perform another biopsy.
►Dr. Apte: Four weeks later, the patient presented with continued shortness of breath, fatigue, and fever. A repeat chest CT showed an opacity suggestive of pneumonia. Given the continued concern for cancer a CT-guided needle biopsy was performed and was once again negative for malignancy. The decision was made to pursue a video-assisted thorascopic surgery (VATS). Following the VATS, the patient developed rigors, fever, and tachycardia with new atrial fibrillation. While being evaluated hypercalcemia was identified, with further workup revealing a low parathyroid hormone (PTH) and low PTH-related peptide. Dr. Fine, the presence of hypercalcemia and a new arrythmia raised the possibility of sarcoidosis. Could this be sarcoidosis?
►Dr. Fine: Sarcoidosis is one of the great masqueraders in medicine. There is a type of sarcoidosis called nodular sarcoidosis where you see masslike distribution in the lung, but generally there are multiple masses and so this presentation would be atypical.3 There is also a phenomenon called sarcoidal reactions usually in the presence of cancer. Again, one tends to see multiple tiny lesions in the lung. It is certainly on the differential, but I would consider it to be less likely than cancer. It is also relatively common to develop atrial fibrillation after manipulation from a lung surgery.4 The other possibility I am concerned about is whether the mass is invading the mediastinum and involving the pericardium.
►Dr. Apte: Results from the VATS biopsy once again returned negative for malignancy and instead showed signs of focal micro-abscesses, atypical pneumocytes, and prominent neutrophils. A diagnosis of acute fibrinous organizing pneumonia (AFOP) was offered. Dr. Fine, what is AFOP?
►Dr. Fine: This is the first case of AFOP I had seen and probably the first case many in our department have seen. This is a relatively new entity with limited reported cases in the literature and is a pathological diagnosis originally recorded in autopsies from patients at the National Institutes of Health.5,6 Given the complexity of the lesion, the diagnosis is difficult to make. Most commonly, AFOP is associated with other systemic entities, most commonly hematologic malignancies like lymphomas and leukemias. It has also been associated with vasculitis and certain drugs. The mechanism is poorly understood, and although pneumonia is a part of the term, this just implies there is inflammation of the lung (ie, pneumonitis).
► Dr. Apte: Given the association of AFOP with underlying hematologic malignancies, an emphasis was placed on another finding: the patient’s increasing WBC count. The total WBC count had been 20 k/cm3 at the time of his lung mass discovery but had increased to > 40 k/cm3 with a differential of neutrophils > 80%. Flow cytometry was negative, and his peripheral smear was read as normal. Dr. Gilbert, what might explain this patient’s leukocytosis?
►Gary Gilbert, MD, Section of Hematology and Oncology, VABHS and Associate Professor of Medicine, Harvard Medical School (HMS): This patient had an elevated WBC for 4 months. Initially, the cause was likely lithium as this is known to cause a leukocytosis.7 More recently, the total WBC had increased and there were a couple of other abnormalities: A consistently elevated absolute monocyte count and a markedly elevated mature neutrophil count. These findings are consistent with a leukemoid reaction (ie, a WBC count > 50,000/µL from causes other than leukemia). The question becomes what is this a leukemoid reaction in response to? Once we have excluded a lung malignancy (a well-known common cause of a leukemoid reaction) we must consider a clonal myeloproliferative disorder. This is particularly true because many things that cause a leukemoid reaction (eg, lobar pneumonia) do not cause a persistently elevated neutrophil count. That this patient does have a persistently elevated neutrophil count suggests something abnormal about the neutrophils themselves.
► Dr. Apte: A bone marrow biopsy was performed. Dr. Gilbert, can you comment on this patient’s bone marrow biopsy and whether a myeloproliferative disorder may have played a role in the marked leukocytosis?
► Dr. Gilbert: The bone marrow biopsy was hyperplastic with myeloid predominance and normal maturation in all lineages. A deep sequencing analysis demonstrated the absence of chromosomal abnormalities or genetic mutations that are associated with myeloproliferative disorders. This excludes the possibility of a myeloproliferative disorder.
► Dr. Apte: The patient was started on 60 mg of prednisone daily, which led to marked improvement in his symptoms. He was discharged in stable condition but presented again with abdominal pain. A complete blood count once again showed increased WBC and new thrombocytosis. A CT angiogram (CTA) showed the prior lung mass with new signs of central necrosis. In the abdomen, new splenic and renal infarct were identified, along with signs of multiple arterial thrombi in the abdomen and internal and external iliac vessel wall thickening. These findings were read as concerning for a medium vessel vasculitis. Dr. Kaur, what are some of the imaging findings you would expect to see in vasculitis, and what about this patient’s CT is consistent with a medium vessel vasculitis?
► Maneet Kaur, MD, Section of Rheumatology, VABHS: Vasculitis is inflammation of the vessel wall that can lead to vascular injury and activation of the coagulation cascade. Sometimes these findings can be seen on imaging with evidence of stenosis, microaneurysms, and thrombosis distal to the stenosis. The nomenclature of vasculitis is not simple and has been revised many times. Medium-vessel vasculitis does not just affect the medium vessels (eg, visceral arteries) but can overlap with distal large vessels and smaller cutaneous vessels.
The first thing that comes to mind in this case is polyarteritis nodosa (PAN), an immune complex-mediated medium vessel disease that can involve large and small vessels in muscle, nerve, and skin. It can also present with masses.
►Dr. Apte: To address the arterial thrombi seen on CTA, arterial-brachial indices were obtained and showed bilateral occlusive disease in his distal extremities; findings that could be explained by vasculitis. His VATS biopsy pathology was reviewed for signs of vasculitis. Dr. Huang, can you review these slides for us please?
►Qin Huang, MD, Department of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine, VABHS and Assistant Professor of Pathology, HMS: This patient had a history of smoking, and there are many black pigment-laden macrophages present in the lung tissue. There were areas of hemorrhage and fibrin deposition and an overall picture of organizing pneumonia. At a lower power, you can see neutrophils everywhere, some in the form of micro-abscesses. The arterial walls did not show signs of vasculitis (Figure 2). Based on the clinical information and radiology findings, we suspected an acute infection-related pneumonia or a primary lung malignancy causing obstruction pneumonia. We suggested a rebiopsy of the lung mass to rule out a primary lung malignancy.
► Dr. Apte: Given his CT findings, a serologic rheumatologic workup including antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody, antinuclear antibody, and rheumatoid factors were sent and returned negative. The location of arterial wall inflammation on imaging made it unamenable for biopsy. The patient began to experience bilateral temporal pain, which raised the concern for a large vessel vasculitis, specifically giant cell arteritis. Bilateral temporal artery biopsies were obtained and were not suggestive of vasculitis. Dr. Kaur, we still do not have any serologic or biopsy confirmation to support a diagnosis of vasculitis. Can we still call this a vasculitis?
►Dr. Kaur: Few things can cause the picture that was seen radiographically. A few noninflammatory causes like fibromuscular dysplasia can cause both large and small vessel stenosis, but the elevations in erythrocyte sedimentation rate and C-reactive protein along with response to steroids makes these diagnoses unlikely. Sometimes we must make a clinical diagnosis for vasculitis based on the clinical picture, and I would feel comfortable treating this patient for vasculitis.
With that said, I remain concerned that this patient also has a malignancy. His WBC increased to > 70 k/cm3 and his calcium to > 13 mg/dL. These findings are hard to explain by vasculitis alone. There are cancer-associated vasculitis, and I suspect this is the explanation here.8 His temporal pain was pointing to large vessel involvement, so he could have an undifferentiated vasculitis.
► Dr. Apte: A decision was made to empirically treat with tocilizumab, an IL-6 receptor antagonist, for an undifferentiated autoimmune disease, in addition to tapering steroids. The patient underwent a second VATS, which again revealed AFOP but no signs of malignancy. Unfortunately, he developed multiple complications over the subsequent weeks and passed away. An autopsy was requested by family members and pathology from his lung mass was reviewed. (Figure 3). Dr. Huang, can you review these slides for us?
► Dr. Huang: The left lung mass at autopsy shows nests, poorly formed clusters, and individuals of malignant neoplastic nonkeratinizing squamous cells embedded in a desmoplastic stroma in the mass center, consistent with poorly differentiated squamous cell carcinoma, and a circumscribed area of residual subacute organizing pneumonia with abscess, granulomatous changes, and early fibrosis at the periphery of this mass.
►Dr. Apte: Based on autopsy findings, the final diagnosis was poorly differentiated squamous cell carcinoma associated with subacute organizing pneumonia and medium vessel vasculitis, which presented with a severe leukocytosis ultimately thought to be a leukemoid reaction from his lung cancer.
Case Presentation: A 62-year-old male presented with shortness of breath and a cough productive of green sputum. He had a history of hyperlipidemia, posttraumatic stress disorder, bipolar disorder, obstructive sleep apnea, and a 50 pack-year history of smoking. His medications included prazosin, melatonin, lithium, and gabapentin. He also had a significant exposure history including asbestos and chemical paints following his leave from the military. At the initial evaluation, laboratory work revealed a leukocytosis with white blood cell (WBC) count 20 k/cm3and otherwise normal transaminases, albumin, and electrolytes. A chest X-ray revealed a new left hilar mass.
►Manisha Apte, MD, Chief Medical Resident, VA Boston Healthcare System (VABHS) and Boston Medical Center (BMC): To work up his new left hilar mass, a computed tomography (CT) of the chest was ordered (Figure 1), which revealed an apical left lower lobe mass extending into the left hilum encasing part of the ascending aorta. Enlarged mediastinal subcentimeter paratracheal and superior mediastinal lymph nodes also were identified and the pattern raised the concern for lymphangitic carcinomatosis. Dr. Fine, what do you make of the CT findings?
► Alan Fine, MD, Section of Pulmonary and Critical Care, VABHS and Professor of Medicine, Boston University School of Medicine: This mass had irregular edges with septal thickening, which may be why there was a concern for lymphangitic spread. There were no clear tissue planes to see if this process was invading the mediastinum. The mass was irregular, a single lesion, and proximal, making it consistent with a lung cancer. In fact, with his history of smoking, asbestos exposure, the numbers 1 to 10 diagnoses were lung cancer. The lack of demarcation of tissue planes supports this. There are some infections, classically actinomycosis, that do cross and invade anatomical barriers.1 But this looked like a primary lung cancer.
► Dr. Apte: The patient was referred to a pulmonologist where an additional history of night sweats and weight loss were noted. Dr. Fine, we have a patient with a newly identified lung mass, and while we have reason to suspect malignancy as you have already noted, there are many other etiologies to consider, including infections (histoplasmosis, cryptococcosis, bacterial abscess), inflammatory processes (sarcoidosis, rheumatoid nodule) and vasculitis (granulomatosis with polyangiitis). What should be the next step taken to make a diagnosis?
►Dr. Fine: For cancer specifically, we would like to both stage and make a diagnosis with one procedure. That’s part of the utility of a positron emission tomography (PET) scan: We can see lymph node involvement and stage the cancer. We must consider the patient’s comorbidities and the location of the lesion (ie, is it amenable to needle biopsy?). In this case, there are enlarged mediastinal lymph nodes, so one could perform a bronchoscopy with endobronchial ultrasound, which is a relatively noninvasive way to sample the lymph nodes to ideally stage and make a diagnosis as safely as possible. If we are considering infection, needle aspiration is not as sensitive.2
► Dr. Apte: The patient underwent a PET CT, which redemonstrated the lung mass with a loss of aortic fat plane suspicious for aortic involvement as well as lymph nodes in levels 7 and 8 that were concerning for malignancy. Subsequent bronchoscopy with biopsy and endobronchial ultrasound did not show evidence of malignancy; washing and brushing from the mass and lymph node specimens did not identify malignant cells. Benign respiratory mucosa with mild chronic inflammation was noted. Dr. Fine, given the nonspecific findings on the PET scan, negative findings on our bronchoscopy, and a negative biopsy, should we be satisfied that we have ruled out cancer?
► Dr. Fine: No, bronchoscopy has its limitations. It’s highly sensitive to the diagnosis of malignancy if you can see an endobronchial lesion, but we did not see one here. You can only go so far with the scope, and it’s not uncommon for us not to be able to make the diagnosis with bronchoscopy. Malignancy is still the most likely diagnosis, and we need to work this up further. I would perform another biopsy.
►Dr. Apte: Four weeks later, the patient presented with continued shortness of breath, fatigue, and fever. A repeat chest CT showed an opacity suggestive of pneumonia. Given the continued concern for cancer a CT-guided needle biopsy was performed and was once again negative for malignancy. The decision was made to pursue a video-assisted thorascopic surgery (VATS). Following the VATS, the patient developed rigors, fever, and tachycardia with new atrial fibrillation. While being evaluated hypercalcemia was identified, with further workup revealing a low parathyroid hormone (PTH) and low PTH-related peptide. Dr. Fine, the presence of hypercalcemia and a new arrythmia raised the possibility of sarcoidosis. Could this be sarcoidosis?
►Dr. Fine: Sarcoidosis is one of the great masqueraders in medicine. There is a type of sarcoidosis called nodular sarcoidosis where you see masslike distribution in the lung, but generally there are multiple masses and so this presentation would be atypical.3 There is also a phenomenon called sarcoidal reactions usually in the presence of cancer. Again, one tends to see multiple tiny lesions in the lung. It is certainly on the differential, but I would consider it to be less likely than cancer. It is also relatively common to develop atrial fibrillation after manipulation from a lung surgery.4 The other possibility I am concerned about is whether the mass is invading the mediastinum and involving the pericardium.
►Dr. Apte: Results from the VATS biopsy once again returned negative for malignancy and instead showed signs of focal micro-abscesses, atypical pneumocytes, and prominent neutrophils. A diagnosis of acute fibrinous organizing pneumonia (AFOP) was offered. Dr. Fine, what is AFOP?
►Dr. Fine: This is the first case of AFOP I had seen and probably the first case many in our department have seen. This is a relatively new entity with limited reported cases in the literature and is a pathological diagnosis originally recorded in autopsies from patients at the National Institutes of Health.5,6 Given the complexity of the lesion, the diagnosis is difficult to make. Most commonly, AFOP is associated with other systemic entities, most commonly hematologic malignancies like lymphomas and leukemias. It has also been associated with vasculitis and certain drugs. The mechanism is poorly understood, and although pneumonia is a part of the term, this just implies there is inflammation of the lung (ie, pneumonitis).
► Dr. Apte: Given the association of AFOP with underlying hematologic malignancies, an emphasis was placed on another finding: the patient’s increasing WBC count. The total WBC count had been 20 k/cm3 at the time of his lung mass discovery but had increased to > 40 k/cm3 with a differential of neutrophils > 80%. Flow cytometry was negative, and his peripheral smear was read as normal. Dr. Gilbert, what might explain this patient’s leukocytosis?
►Gary Gilbert, MD, Section of Hematology and Oncology, VABHS and Associate Professor of Medicine, Harvard Medical School (HMS): This patient had an elevated WBC for 4 months. Initially, the cause was likely lithium as this is known to cause a leukocytosis.7 More recently, the total WBC had increased and there were a couple of other abnormalities: A consistently elevated absolute monocyte count and a markedly elevated mature neutrophil count. These findings are consistent with a leukemoid reaction (ie, a WBC count > 50,000/µL from causes other than leukemia). The question becomes what is this a leukemoid reaction in response to? Once we have excluded a lung malignancy (a well-known common cause of a leukemoid reaction) we must consider a clonal myeloproliferative disorder. This is particularly true because many things that cause a leukemoid reaction (eg, lobar pneumonia) do not cause a persistently elevated neutrophil count. That this patient does have a persistently elevated neutrophil count suggests something abnormal about the neutrophils themselves.
► Dr. Apte: A bone marrow biopsy was performed. Dr. Gilbert, can you comment on this patient’s bone marrow biopsy and whether a myeloproliferative disorder may have played a role in the marked leukocytosis?
► Dr. Gilbert: The bone marrow biopsy was hyperplastic with myeloid predominance and normal maturation in all lineages. A deep sequencing analysis demonstrated the absence of chromosomal abnormalities or genetic mutations that are associated with myeloproliferative disorders. This excludes the possibility of a myeloproliferative disorder.
► Dr. Apte: The patient was started on 60 mg of prednisone daily, which led to marked improvement in his symptoms. He was discharged in stable condition but presented again with abdominal pain. A complete blood count once again showed increased WBC and new thrombocytosis. A CT angiogram (CTA) showed the prior lung mass with new signs of central necrosis. In the abdomen, new splenic and renal infarct were identified, along with signs of multiple arterial thrombi in the abdomen and internal and external iliac vessel wall thickening. These findings were read as concerning for a medium vessel vasculitis. Dr. Kaur, what are some of the imaging findings you would expect to see in vasculitis, and what about this patient’s CT is consistent with a medium vessel vasculitis?
► Maneet Kaur, MD, Section of Rheumatology, VABHS: Vasculitis is inflammation of the vessel wall that can lead to vascular injury and activation of the coagulation cascade. Sometimes these findings can be seen on imaging with evidence of stenosis, microaneurysms, and thrombosis distal to the stenosis. The nomenclature of vasculitis is not simple and has been revised many times. Medium-vessel vasculitis does not just affect the medium vessels (eg, visceral arteries) but can overlap with distal large vessels and smaller cutaneous vessels.
The first thing that comes to mind in this case is polyarteritis nodosa (PAN), an immune complex-mediated medium vessel disease that can involve large and small vessels in muscle, nerve, and skin. It can also present with masses.
►Dr. Apte: To address the arterial thrombi seen on CTA, arterial-brachial indices were obtained and showed bilateral occlusive disease in his distal extremities; findings that could be explained by vasculitis. His VATS biopsy pathology was reviewed for signs of vasculitis. Dr. Huang, can you review these slides for us please?
►Qin Huang, MD, Department of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine, VABHS and Assistant Professor of Pathology, HMS: This patient had a history of smoking, and there are many black pigment-laden macrophages present in the lung tissue. There were areas of hemorrhage and fibrin deposition and an overall picture of organizing pneumonia. At a lower power, you can see neutrophils everywhere, some in the form of micro-abscesses. The arterial walls did not show signs of vasculitis (Figure 2). Based on the clinical information and radiology findings, we suspected an acute infection-related pneumonia or a primary lung malignancy causing obstruction pneumonia. We suggested a rebiopsy of the lung mass to rule out a primary lung malignancy.
► Dr. Apte: Given his CT findings, a serologic rheumatologic workup including antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody, antinuclear antibody, and rheumatoid factors were sent and returned negative. The location of arterial wall inflammation on imaging made it unamenable for biopsy. The patient began to experience bilateral temporal pain, which raised the concern for a large vessel vasculitis, specifically giant cell arteritis. Bilateral temporal artery biopsies were obtained and were not suggestive of vasculitis. Dr. Kaur, we still do not have any serologic or biopsy confirmation to support a diagnosis of vasculitis. Can we still call this a vasculitis?
►Dr. Kaur: Few things can cause the picture that was seen radiographically. A few noninflammatory causes like fibromuscular dysplasia can cause both large and small vessel stenosis, but the elevations in erythrocyte sedimentation rate and C-reactive protein along with response to steroids makes these diagnoses unlikely. Sometimes we must make a clinical diagnosis for vasculitis based on the clinical picture, and I would feel comfortable treating this patient for vasculitis.
With that said, I remain concerned that this patient also has a malignancy. His WBC increased to > 70 k/cm3 and his calcium to > 13 mg/dL. These findings are hard to explain by vasculitis alone. There are cancer-associated vasculitis, and I suspect this is the explanation here.8 His temporal pain was pointing to large vessel involvement, so he could have an undifferentiated vasculitis.
► Dr. Apte: A decision was made to empirically treat with tocilizumab, an IL-6 receptor antagonist, for an undifferentiated autoimmune disease, in addition to tapering steroids. The patient underwent a second VATS, which again revealed AFOP but no signs of malignancy. Unfortunately, he developed multiple complications over the subsequent weeks and passed away. An autopsy was requested by family members and pathology from his lung mass was reviewed. (Figure 3). Dr. Huang, can you review these slides for us?
► Dr. Huang: The left lung mass at autopsy shows nests, poorly formed clusters, and individuals of malignant neoplastic nonkeratinizing squamous cells embedded in a desmoplastic stroma in the mass center, consistent with poorly differentiated squamous cell carcinoma, and a circumscribed area of residual subacute organizing pneumonia with abscess, granulomatous changes, and early fibrosis at the periphery of this mass.
►Dr. Apte: Based on autopsy findings, the final diagnosis was poorly differentiated squamous cell carcinoma associated with subacute organizing pneumonia and medium vessel vasculitis, which presented with a severe leukocytosis ultimately thought to be a leukemoid reaction from his lung cancer.
1. Valour F, Sénéchal A, Dupieux C, et al. Actinomycosis: etiology, clinical features, diagnosis, treatment, and management. Infect Drug Resist. 2014;7:183-197. Published 2014 Jul 5. doi:10.2147/IDR.S39601
2. de Bazelaire C, Coffin A, Cohen-Zarade S, et al. CT-guided biopsies in lung infections in patients with haematological malignancies. Diagn Interv Imaging. 2013;94(2):202-215. doi:10.1016/j.diii.2012.12.008
3. Sweidan AJ, Singh NK, Stein A, Tanios M. Nodular sarcoidosis masquerading as cancer. Clin Med Insights Circ Respir Pulm Med. 2017;11:1179548417703123. Published 2017 Apr 12. doi:10.1177/1179548417703123
4. Bagheri R, Yousefi Y, Rezai R, Azemonfar V, Keshtan FG. Atrial fibrillation after lung surgery: incidence, underlying factors, and predictors. Kardiochir Torakochirurgia Pol. 2019;16(2):53-56. doi:10.5114/kitp.2019.86355
5. Lu J, Yin Q, Zha Y, et al. Acute fibrinous and organizing pneumonia: two case reports and literature review. BMC Pulm Med. 2019;19(1):141. Published 2019 Aug 5. doi:10.1186/s12890-019-0861-3
6. Beasley MB, Franks TJ, Galvin JR, Gochuico B, Travis WD. Acute fibrinous and organizing pneumonia: a histological pattern of lung injury and possible variant of diffuse alveolar damage. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2002;126(9):1064-1070. doi:10.5858/2002-126-1064-AFAOP
7. Murphy DL, Goodwin FK, Bunney WE Jr. Leukocytosis during lithium treatment. Am J Psychiatry. 1971;127(11):1559-1561. doi:10.1176/ajp.127.11.1559
8. Fain O, Hamidou M, Cacoub P, et al. Vasculitides associated with malignancies: analysis of sixty patients. Arthritis Rheum. 2007;57(8):1473-1480. doi:10.1002/art.23085
1. Valour F, Sénéchal A, Dupieux C, et al. Actinomycosis: etiology, clinical features, diagnosis, treatment, and management. Infect Drug Resist. 2014;7:183-197. Published 2014 Jul 5. doi:10.2147/IDR.S39601
2. de Bazelaire C, Coffin A, Cohen-Zarade S, et al. CT-guided biopsies in lung infections in patients with haematological malignancies. Diagn Interv Imaging. 2013;94(2):202-215. doi:10.1016/j.diii.2012.12.008
3. Sweidan AJ, Singh NK, Stein A, Tanios M. Nodular sarcoidosis masquerading as cancer. Clin Med Insights Circ Respir Pulm Med. 2017;11:1179548417703123. Published 2017 Apr 12. doi:10.1177/1179548417703123
4. Bagheri R, Yousefi Y, Rezai R, Azemonfar V, Keshtan FG. Atrial fibrillation after lung surgery: incidence, underlying factors, and predictors. Kardiochir Torakochirurgia Pol. 2019;16(2):53-56. doi:10.5114/kitp.2019.86355
5. Lu J, Yin Q, Zha Y, et al. Acute fibrinous and organizing pneumonia: two case reports and literature review. BMC Pulm Med. 2019;19(1):141. Published 2019 Aug 5. doi:10.1186/s12890-019-0861-3
6. Beasley MB, Franks TJ, Galvin JR, Gochuico B, Travis WD. Acute fibrinous and organizing pneumonia: a histological pattern of lung injury and possible variant of diffuse alveolar damage. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2002;126(9):1064-1070. doi:10.5858/2002-126-1064-AFAOP
7. Murphy DL, Goodwin FK, Bunney WE Jr. Leukocytosis during lithium treatment. Am J Psychiatry. 1971;127(11):1559-1561. doi:10.1176/ajp.127.11.1559
8. Fain O, Hamidou M, Cacoub P, et al. Vasculitides associated with malignancies: analysis of sixty patients. Arthritis Rheum. 2007;57(8):1473-1480. doi:10.1002/art.23085
Psychiatric fallout from long-COVID: How to prepare
As mounting evidence points to a significant psychiatric component of COVID-19, experts are concerned about an influx of survivors presenting with persistent mental health problems and how best to prepare.
Clinicians should be aware that patients who have had COVID frequently develop psychiatric symptoms, Silvia S. Martins, MD, PhD, associate professor of epidemiology, Columbia University, New York, said in an interview.
“There should be more screening of all patients recovering from a COVID infection for anxiety, posttraumatic stress disorder, and depression, as well as referral to services, including psychotherapy, and medication as needed,” said Dr. Martins, who, along with colleagues, uncovered a high rate of these symptoms in patients who had the disease.
The COVID-19 pandemic has taken an enormous social, emotional, and public health toll. It has disrupted lives and caused stress, fear, and uncertainty about loss of health and income, not to mention forced isolation.
In addition, a significant number of patients who contract COVID-19 continue to have symptoms after the acute phase of the illness. This post-COVID, or “long-haul,” syndrome isn’t well defined; experts cite a range of symptoms that persist for weeks or months.
These ongoing symptoms can include cough, fatigue, and chronic pain, as well as psychiatric complaints. As reported by this news organization, an observational study of more than 230,000 U.S. patient health records revealed that one in three COVID-19 survivors received a psychiatric or neurologic diagnosis within 6 months of contracting the virus.
The most common psychiatric diagnoses were anxiety disorders, mood disorders, substance misuse disorders, and insomnia.
Significant symptoms even in mild cases
Another study showed that even those with mild COVID-19 may experience psychiatric symptoms independently of previous psychiatric diagnoses. Results revealed that 26% of the sample of almost 900 patients reported depression, 22% reported anxiety, and 17% reported symptoms of posttraumatic stress 2 months after testing positive for the virus. This finding is important because the majority of individuals who contract COVID-19 have a mild case.
“We saw very high levels of clinically significant depression, anxiety, and posttraumatic stress symptoms in people who had mild disease,” study investigator João Mauricio Castaldelli-Maia, MD, PhD, postdoctoral fellow, department of epidemiology, Columbia University, said in an interview.
He attributed these symptoms in part to long periods of isolation, even from relatives in the same household, in cramped spaces typical of large cities such as São Paulo.
Social isolation can have a huge impact on persons who depend on social connections and relationships, Vivian Pender, MD, president of the American Psychiatric Association and clinical professor of psychiatry, Weill Cornell Medical Center, New York, said in an interview.
“The fact that we have not been able to see our colleagues, our friends, our family, and in the case of psychiatrists, even our patients has taken a toll on everyone, and that leads to more stress, more anxiety,” she said.
National surveys show that psychiatric symptoms occur after acute COVID. One survey revealed that over 50% of 3,900 respondents who had COVID reported having at least moderate symptoms of major depression.
Unique depression subtype?
Another survey, slated for publication later this year, shows that lead investigator Roy Perlis, MD, professor of psychiatry, Harvard Medical School, Boston, said in an interview.
This might suggest a neurobiological element. Researchers are speculating as to whether lingering psychiatric problems that occur after having COVID are linked to the psychosocial impact of the disease or to pathological processes, such as inflammation, that affect the brain.
Although rates of post-COVID psychiatric symptoms vary from study to study, “they seem to be pretty enduring,” noted Faith Gunning, PhD, vice chair of research, department of psychology, Weill Cornell Medicine, who specializes in clinical neuropsychology.
“So they’re not just a brief response” to getting sick, a fact that points to the possible need for treatment, she told this news organization. “In some of the work that’s starting to emerge, it does appear that the symptoms persist, at least for a relatively large subset of individuals.”
Although depression typically affects twice as many women as men, these new surveys show that, after COVID, “that difference is not so distinct,” said Dr. Gunning.
It’s unclear why this is, but it could be cause by financial stresses that may affect men to a greater extent, she added. “There is so much we’re still learning.”
Increased suicide risk?
Other researchers, including Leo Sher, MD, professor of psychiatry, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, and director of inpatient psychiatry, James J. Peters Veterans Affairs Medical Center, both in New York, are concerned that higher rates of psychiatric symptoms among patients with long-haul COVID raise the risk for suicidal ideation and behavior.
Studies of suicidality in COVID-19 survivors “are urgently needed,” said Dr. Sher in an article published in the Monthly Journal of the Association of Physicians.
“We need to study what factors may increase suicide risk among the COVID-19 survivors during and after the recovery. We also need to investigate whether there is a long-term increased suicide risk among COVID-19 survivors,” Dr. Sher said.
COVID-19 is not unique among viral respiratory diseases in being associated with long-term mental health problems. Research shows that survivors of the 2003 outbreak of severe acute respiratory syndrome experienced increased psychological distress that persisted for at least a year, as did patients who in 2015 had Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERS-CoV).
Some experts believe clinicians should screen patients for mental health symptoms after the acute phase of COVID and offer early and prolonged care.
“Early mental health intervention such as psychotherapy and supportive groups could play an important role in preventing incident mental health problems for post-COVID sufferers,” said Dr. Castaldelli-Maia.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
As mounting evidence points to a significant psychiatric component of COVID-19, experts are concerned about an influx of survivors presenting with persistent mental health problems and how best to prepare.
Clinicians should be aware that patients who have had COVID frequently develop psychiatric symptoms, Silvia S. Martins, MD, PhD, associate professor of epidemiology, Columbia University, New York, said in an interview.
“There should be more screening of all patients recovering from a COVID infection for anxiety, posttraumatic stress disorder, and depression, as well as referral to services, including psychotherapy, and medication as needed,” said Dr. Martins, who, along with colleagues, uncovered a high rate of these symptoms in patients who had the disease.
The COVID-19 pandemic has taken an enormous social, emotional, and public health toll. It has disrupted lives and caused stress, fear, and uncertainty about loss of health and income, not to mention forced isolation.
In addition, a significant number of patients who contract COVID-19 continue to have symptoms after the acute phase of the illness. This post-COVID, or “long-haul,” syndrome isn’t well defined; experts cite a range of symptoms that persist for weeks or months.
These ongoing symptoms can include cough, fatigue, and chronic pain, as well as psychiatric complaints. As reported by this news organization, an observational study of more than 230,000 U.S. patient health records revealed that one in three COVID-19 survivors received a psychiatric or neurologic diagnosis within 6 months of contracting the virus.
The most common psychiatric diagnoses were anxiety disorders, mood disorders, substance misuse disorders, and insomnia.
Significant symptoms even in mild cases
Another study showed that even those with mild COVID-19 may experience psychiatric symptoms independently of previous psychiatric diagnoses. Results revealed that 26% of the sample of almost 900 patients reported depression, 22% reported anxiety, and 17% reported symptoms of posttraumatic stress 2 months after testing positive for the virus. This finding is important because the majority of individuals who contract COVID-19 have a mild case.
“We saw very high levels of clinically significant depression, anxiety, and posttraumatic stress symptoms in people who had mild disease,” study investigator João Mauricio Castaldelli-Maia, MD, PhD, postdoctoral fellow, department of epidemiology, Columbia University, said in an interview.
He attributed these symptoms in part to long periods of isolation, even from relatives in the same household, in cramped spaces typical of large cities such as São Paulo.
Social isolation can have a huge impact on persons who depend on social connections and relationships, Vivian Pender, MD, president of the American Psychiatric Association and clinical professor of psychiatry, Weill Cornell Medical Center, New York, said in an interview.
“The fact that we have not been able to see our colleagues, our friends, our family, and in the case of psychiatrists, even our patients has taken a toll on everyone, and that leads to more stress, more anxiety,” she said.
National surveys show that psychiatric symptoms occur after acute COVID. One survey revealed that over 50% of 3,900 respondents who had COVID reported having at least moderate symptoms of major depression.
Unique depression subtype?
Another survey, slated for publication later this year, shows that lead investigator Roy Perlis, MD, professor of psychiatry, Harvard Medical School, Boston, said in an interview.
This might suggest a neurobiological element. Researchers are speculating as to whether lingering psychiatric problems that occur after having COVID are linked to the psychosocial impact of the disease or to pathological processes, such as inflammation, that affect the brain.
Although rates of post-COVID psychiatric symptoms vary from study to study, “they seem to be pretty enduring,” noted Faith Gunning, PhD, vice chair of research, department of psychology, Weill Cornell Medicine, who specializes in clinical neuropsychology.
“So they’re not just a brief response” to getting sick, a fact that points to the possible need for treatment, she told this news organization. “In some of the work that’s starting to emerge, it does appear that the symptoms persist, at least for a relatively large subset of individuals.”
Although depression typically affects twice as many women as men, these new surveys show that, after COVID, “that difference is not so distinct,” said Dr. Gunning.
It’s unclear why this is, but it could be cause by financial stresses that may affect men to a greater extent, she added. “There is so much we’re still learning.”
Increased suicide risk?
Other researchers, including Leo Sher, MD, professor of psychiatry, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, and director of inpatient psychiatry, James J. Peters Veterans Affairs Medical Center, both in New York, are concerned that higher rates of psychiatric symptoms among patients with long-haul COVID raise the risk for suicidal ideation and behavior.
Studies of suicidality in COVID-19 survivors “are urgently needed,” said Dr. Sher in an article published in the Monthly Journal of the Association of Physicians.
“We need to study what factors may increase suicide risk among the COVID-19 survivors during and after the recovery. We also need to investigate whether there is a long-term increased suicide risk among COVID-19 survivors,” Dr. Sher said.
COVID-19 is not unique among viral respiratory diseases in being associated with long-term mental health problems. Research shows that survivors of the 2003 outbreak of severe acute respiratory syndrome experienced increased psychological distress that persisted for at least a year, as did patients who in 2015 had Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERS-CoV).
Some experts believe clinicians should screen patients for mental health symptoms after the acute phase of COVID and offer early and prolonged care.
“Early mental health intervention such as psychotherapy and supportive groups could play an important role in preventing incident mental health problems for post-COVID sufferers,” said Dr. Castaldelli-Maia.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
As mounting evidence points to a significant psychiatric component of COVID-19, experts are concerned about an influx of survivors presenting with persistent mental health problems and how best to prepare.
Clinicians should be aware that patients who have had COVID frequently develop psychiatric symptoms, Silvia S. Martins, MD, PhD, associate professor of epidemiology, Columbia University, New York, said in an interview.
“There should be more screening of all patients recovering from a COVID infection for anxiety, posttraumatic stress disorder, and depression, as well as referral to services, including psychotherapy, and medication as needed,” said Dr. Martins, who, along with colleagues, uncovered a high rate of these symptoms in patients who had the disease.
The COVID-19 pandemic has taken an enormous social, emotional, and public health toll. It has disrupted lives and caused stress, fear, and uncertainty about loss of health and income, not to mention forced isolation.
In addition, a significant number of patients who contract COVID-19 continue to have symptoms after the acute phase of the illness. This post-COVID, or “long-haul,” syndrome isn’t well defined; experts cite a range of symptoms that persist for weeks or months.
These ongoing symptoms can include cough, fatigue, and chronic pain, as well as psychiatric complaints. As reported by this news organization, an observational study of more than 230,000 U.S. patient health records revealed that one in three COVID-19 survivors received a psychiatric or neurologic diagnosis within 6 months of contracting the virus.
The most common psychiatric diagnoses were anxiety disorders, mood disorders, substance misuse disorders, and insomnia.
Significant symptoms even in mild cases
Another study showed that even those with mild COVID-19 may experience psychiatric symptoms independently of previous psychiatric diagnoses. Results revealed that 26% of the sample of almost 900 patients reported depression, 22% reported anxiety, and 17% reported symptoms of posttraumatic stress 2 months after testing positive for the virus. This finding is important because the majority of individuals who contract COVID-19 have a mild case.
“We saw very high levels of clinically significant depression, anxiety, and posttraumatic stress symptoms in people who had mild disease,” study investigator João Mauricio Castaldelli-Maia, MD, PhD, postdoctoral fellow, department of epidemiology, Columbia University, said in an interview.
He attributed these symptoms in part to long periods of isolation, even from relatives in the same household, in cramped spaces typical of large cities such as São Paulo.
Social isolation can have a huge impact on persons who depend on social connections and relationships, Vivian Pender, MD, president of the American Psychiatric Association and clinical professor of psychiatry, Weill Cornell Medical Center, New York, said in an interview.
“The fact that we have not been able to see our colleagues, our friends, our family, and in the case of psychiatrists, even our patients has taken a toll on everyone, and that leads to more stress, more anxiety,” she said.
National surveys show that psychiatric symptoms occur after acute COVID. One survey revealed that over 50% of 3,900 respondents who had COVID reported having at least moderate symptoms of major depression.
Unique depression subtype?
Another survey, slated for publication later this year, shows that lead investigator Roy Perlis, MD, professor of psychiatry, Harvard Medical School, Boston, said in an interview.
This might suggest a neurobiological element. Researchers are speculating as to whether lingering psychiatric problems that occur after having COVID are linked to the psychosocial impact of the disease or to pathological processes, such as inflammation, that affect the brain.
Although rates of post-COVID psychiatric symptoms vary from study to study, “they seem to be pretty enduring,” noted Faith Gunning, PhD, vice chair of research, department of psychology, Weill Cornell Medicine, who specializes in clinical neuropsychology.
“So they’re not just a brief response” to getting sick, a fact that points to the possible need for treatment, she told this news organization. “In some of the work that’s starting to emerge, it does appear that the symptoms persist, at least for a relatively large subset of individuals.”
Although depression typically affects twice as many women as men, these new surveys show that, after COVID, “that difference is not so distinct,” said Dr. Gunning.
It’s unclear why this is, but it could be cause by financial stresses that may affect men to a greater extent, she added. “There is so much we’re still learning.”
Increased suicide risk?
Other researchers, including Leo Sher, MD, professor of psychiatry, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, and director of inpatient psychiatry, James J. Peters Veterans Affairs Medical Center, both in New York, are concerned that higher rates of psychiatric symptoms among patients with long-haul COVID raise the risk for suicidal ideation and behavior.
Studies of suicidality in COVID-19 survivors “are urgently needed,” said Dr. Sher in an article published in the Monthly Journal of the Association of Physicians.
“We need to study what factors may increase suicide risk among the COVID-19 survivors during and after the recovery. We also need to investigate whether there is a long-term increased suicide risk among COVID-19 survivors,” Dr. Sher said.
COVID-19 is not unique among viral respiratory diseases in being associated with long-term mental health problems. Research shows that survivors of the 2003 outbreak of severe acute respiratory syndrome experienced increased psychological distress that persisted for at least a year, as did patients who in 2015 had Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERS-CoV).
Some experts believe clinicians should screen patients for mental health symptoms after the acute phase of COVID and offer early and prolonged care.
“Early mental health intervention such as psychotherapy and supportive groups could play an important role in preventing incident mental health problems for post-COVID sufferers,” said Dr. Castaldelli-Maia.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
APA, AMA, others move to stop insurer from overturning mental health claims ruling
The American Psychiatric Association has joined with the American Medical Association and other medical societies to oppose United Behavioral Health’s (UBH) request that a court throw out a ruling that found the insurer unfairly denied tens of thousands of claims for mental health and substance use disorder services.
Wit v. United Behavioral Health, in litigation since 2014, is being closely watched by clinicians, patients, providers, and attorneys.
Reena Kapoor, MD, chair of the APA’s Committee on Judicial Action, said in an interview that the APA is hopeful that “whatever the court says about UBH should be applicable to all insurance companies that are providing employer-sponsored health benefits.”
In a friend of the court (amicus curiae) brief, the APA, AMA, the California Medical Association, Southern California Psychiatric Society, Northern California Psychiatric Society, Orange County Psychiatric Society, Central California Psychiatric Society, and San Diego Psychiatric Society argue that “despite the availability of professionally developed, evidence-based guidelines embodying generally accepted standards of care for mental health and substance use disorders, managed care organizations commonly base coverage decisions on internally developed ‘level of care guidelines’ that are inappropriately restrictive.”
The guidelines “may lead to denial of coverage for treatment that is recommended by a patient’s physician and even cut off coverage when treatment is already being delivered,” said the groups.
The U.S. Department of Labor also filed a brief in support of the plaintiffs who are suing UBH. Those individuals suffered injury when they were denied coverage, said the federal agency, which regulates employer-sponsored insurance plans.
California Attorney General Rob Bonta also made an amicus filing supporting the plaintiffs.
“When insurers limit access to this critical care, they leave Californians who need it feeling as if they have no other option than to try to cope alone,” said Mr. Bonta in a statement.
‘Discrimination must end’
Mr. Bonta said he agreed with a 2019 ruling by the U.S. District Court for the Northern District of California that UBH had violated its fiduciary duties by wrongfully using its internally developed coverage determination guidelines and level of care guidelines to deny care.
The court also found that UBH’s medically necessary criteria meant that only “acute” episodes would be covered. Instead, said the court last November, chronic and comorbid conditions should always be treated, according to Maureen Gammon and Kathleen Rosenow of Willis Towers Watson, a risk advisor.
In November, the same Northern California District Court ruled on the remedies it would require of United, including that the insurer reprocess more than 67,000 claims. UBH was also barred indefinitely from using any of its guidelines to make coverage determinations. Instead, it was ordered to make determinations “consistent with generally accepted standards of care,” and consistent with state laws.
The District Court denied a request by UBH to put a hold on the claims reprocessing until it appealed the overall case. But the Ninth Circuit Court of Appeals in February granted that request.
Then, in March, United appealed the District Court’s overall ruling, claiming that the plaintiffs had not proven harm.
The U.S. Chamber of Commerce has filed a brief in support of United, agreeing with its arguments.
However, the APA and other clinician groups said there is no question of harm.
“Failure to provide appropriate levels of care for treatment of mental illness and substance use disorders leads to relapse, overdose, transmission of infectious diseases, and death,” said APA CEO and Medical Director Saul Levin, MD, MPA, in a statement.
APA President Vivian Pender, MD, said guidelines that “are overly focused on stabilizing acute symptoms of mental health and substance use disorders” are not treating the underlying disease. “When the injury is physical, insurers treat the underlying disease and not just the symptoms. Discrimination against patients with mental illness must end,” she said.
No court has ever recognized the type of claims reprocessing ordered by the District Court judge, said attorneys Nathaniel Cohen and Joseph Laska of Manatt, Phelps & Phillips, in an analysis of the case.
Mr. Cohen and Mr. Laska write. “Practitioners, health plans, and health insurers would be wise to track UBH’s long-awaited appeal to the Ninth Circuit.”
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The American Psychiatric Association has joined with the American Medical Association and other medical societies to oppose United Behavioral Health’s (UBH) request that a court throw out a ruling that found the insurer unfairly denied tens of thousands of claims for mental health and substance use disorder services.
Wit v. United Behavioral Health, in litigation since 2014, is being closely watched by clinicians, patients, providers, and attorneys.
Reena Kapoor, MD, chair of the APA’s Committee on Judicial Action, said in an interview that the APA is hopeful that “whatever the court says about UBH should be applicable to all insurance companies that are providing employer-sponsored health benefits.”
In a friend of the court (amicus curiae) brief, the APA, AMA, the California Medical Association, Southern California Psychiatric Society, Northern California Psychiatric Society, Orange County Psychiatric Society, Central California Psychiatric Society, and San Diego Psychiatric Society argue that “despite the availability of professionally developed, evidence-based guidelines embodying generally accepted standards of care for mental health and substance use disorders, managed care organizations commonly base coverage decisions on internally developed ‘level of care guidelines’ that are inappropriately restrictive.”
The guidelines “may lead to denial of coverage for treatment that is recommended by a patient’s physician and even cut off coverage when treatment is already being delivered,” said the groups.
The U.S. Department of Labor also filed a brief in support of the plaintiffs who are suing UBH. Those individuals suffered injury when they were denied coverage, said the federal agency, which regulates employer-sponsored insurance plans.
California Attorney General Rob Bonta also made an amicus filing supporting the plaintiffs.
“When insurers limit access to this critical care, they leave Californians who need it feeling as if they have no other option than to try to cope alone,” said Mr. Bonta in a statement.
‘Discrimination must end’
Mr. Bonta said he agreed with a 2019 ruling by the U.S. District Court for the Northern District of California that UBH had violated its fiduciary duties by wrongfully using its internally developed coverage determination guidelines and level of care guidelines to deny care.
The court also found that UBH’s medically necessary criteria meant that only “acute” episodes would be covered. Instead, said the court last November, chronic and comorbid conditions should always be treated, according to Maureen Gammon and Kathleen Rosenow of Willis Towers Watson, a risk advisor.
In November, the same Northern California District Court ruled on the remedies it would require of United, including that the insurer reprocess more than 67,000 claims. UBH was also barred indefinitely from using any of its guidelines to make coverage determinations. Instead, it was ordered to make determinations “consistent with generally accepted standards of care,” and consistent with state laws.
The District Court denied a request by UBH to put a hold on the claims reprocessing until it appealed the overall case. But the Ninth Circuit Court of Appeals in February granted that request.
Then, in March, United appealed the District Court’s overall ruling, claiming that the plaintiffs had not proven harm.
The U.S. Chamber of Commerce has filed a brief in support of United, agreeing with its arguments.
However, the APA and other clinician groups said there is no question of harm.
“Failure to provide appropriate levels of care for treatment of mental illness and substance use disorders leads to relapse, overdose, transmission of infectious diseases, and death,” said APA CEO and Medical Director Saul Levin, MD, MPA, in a statement.
APA President Vivian Pender, MD, said guidelines that “are overly focused on stabilizing acute symptoms of mental health and substance use disorders” are not treating the underlying disease. “When the injury is physical, insurers treat the underlying disease and not just the symptoms. Discrimination against patients with mental illness must end,” she said.
No court has ever recognized the type of claims reprocessing ordered by the District Court judge, said attorneys Nathaniel Cohen and Joseph Laska of Manatt, Phelps & Phillips, in an analysis of the case.
Mr. Cohen and Mr. Laska write. “Practitioners, health plans, and health insurers would be wise to track UBH’s long-awaited appeal to the Ninth Circuit.”
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The American Psychiatric Association has joined with the American Medical Association and other medical societies to oppose United Behavioral Health’s (UBH) request that a court throw out a ruling that found the insurer unfairly denied tens of thousands of claims for mental health and substance use disorder services.
Wit v. United Behavioral Health, in litigation since 2014, is being closely watched by clinicians, patients, providers, and attorneys.
Reena Kapoor, MD, chair of the APA’s Committee on Judicial Action, said in an interview that the APA is hopeful that “whatever the court says about UBH should be applicable to all insurance companies that are providing employer-sponsored health benefits.”
In a friend of the court (amicus curiae) brief, the APA, AMA, the California Medical Association, Southern California Psychiatric Society, Northern California Psychiatric Society, Orange County Psychiatric Society, Central California Psychiatric Society, and San Diego Psychiatric Society argue that “despite the availability of professionally developed, evidence-based guidelines embodying generally accepted standards of care for mental health and substance use disorders, managed care organizations commonly base coverage decisions on internally developed ‘level of care guidelines’ that are inappropriately restrictive.”
The guidelines “may lead to denial of coverage for treatment that is recommended by a patient’s physician and even cut off coverage when treatment is already being delivered,” said the groups.
The U.S. Department of Labor also filed a brief in support of the plaintiffs who are suing UBH. Those individuals suffered injury when they were denied coverage, said the federal agency, which regulates employer-sponsored insurance plans.
California Attorney General Rob Bonta also made an amicus filing supporting the plaintiffs.
“When insurers limit access to this critical care, they leave Californians who need it feeling as if they have no other option than to try to cope alone,” said Mr. Bonta in a statement.
‘Discrimination must end’
Mr. Bonta said he agreed with a 2019 ruling by the U.S. District Court for the Northern District of California that UBH had violated its fiduciary duties by wrongfully using its internally developed coverage determination guidelines and level of care guidelines to deny care.
The court also found that UBH’s medically necessary criteria meant that only “acute” episodes would be covered. Instead, said the court last November, chronic and comorbid conditions should always be treated, according to Maureen Gammon and Kathleen Rosenow of Willis Towers Watson, a risk advisor.
In November, the same Northern California District Court ruled on the remedies it would require of United, including that the insurer reprocess more than 67,000 claims. UBH was also barred indefinitely from using any of its guidelines to make coverage determinations. Instead, it was ordered to make determinations “consistent with generally accepted standards of care,” and consistent with state laws.
The District Court denied a request by UBH to put a hold on the claims reprocessing until it appealed the overall case. But the Ninth Circuit Court of Appeals in February granted that request.
Then, in March, United appealed the District Court’s overall ruling, claiming that the plaintiffs had not proven harm.
The U.S. Chamber of Commerce has filed a brief in support of United, agreeing with its arguments.
However, the APA and other clinician groups said there is no question of harm.
“Failure to provide appropriate levels of care for treatment of mental illness and substance use disorders leads to relapse, overdose, transmission of infectious diseases, and death,” said APA CEO and Medical Director Saul Levin, MD, MPA, in a statement.
APA President Vivian Pender, MD, said guidelines that “are overly focused on stabilizing acute symptoms of mental health and substance use disorders” are not treating the underlying disease. “When the injury is physical, insurers treat the underlying disease and not just the symptoms. Discrimination against patients with mental illness must end,” she said.
No court has ever recognized the type of claims reprocessing ordered by the District Court judge, said attorneys Nathaniel Cohen and Joseph Laska of Manatt, Phelps & Phillips, in an analysis of the case.
Mr. Cohen and Mr. Laska write. “Practitioners, health plans, and health insurers would be wise to track UBH’s long-awaited appeal to the Ninth Circuit.”
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Two key suicide risk factors identified in borderline personality disorder
Feelings of chronic emptiness and self-injury have been identified as two key risk factors for suicide attempts (SAs) in patients with borderline personality disorder (BPD), a new cross-sectional, nationally representative study suggests.
The findings also show lifetime and past-year SAs are common among patients with BPD, even when excluding self-injurious behaviors.
The results suggest that in addition to asking patients about self-harm during suicide risk screenings and assessments, clinicians should query them about “longstanding” feelings of emptiness, study investigator Carlos M. Grilo, PhD, professor of psychiatry and psychology, Yale University, New Haven, Conn., said in an interview.
Although related, chronic emptiness “is distinct and goes beyond feelings of sadness, loneliness, and hopelessness,” explained Dr. Grilo. he said.
The study was published online May 11 in JAMA Network Open.
Filling a research gap
While BPD and other psychiatric disorders are associated with suicide, the authors noted there is a “dearth of epidemiological research” examining the link between BPD and suicide.
Criteria for BPD diagnosis requires any five of the following criteria: relationships, affective instability, abandonment fear, anger, identity disturbance, emptiness, disassociation/paranoia, self-injurious behavior, and impulsivity, along with social-occupation dysfunction.
To determine SA risk with specific BPD diagnostic criteria, the investigators examined data on 36,309 individuals who participated in the third wave of the National Epidemiologic Survey on Alcohol and Related Conditions (NESARC-III), conducted from 2012 to 2013.
During computer-assisted, face-to-face interviews, study participants answered questions based on the Alcohol Use Disorder and Associated Disabilities Interview Schedule-5 (AUDADIS-5) of the National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism.
This structured interview assesses a range of DSM-5–defined psychiatric disorders and their criteria. In addition to BPD, the AUDADIS-5 generates diagnoses for mood disorders, anxiety disorders, posttraumatic stress disorder, substance use disorders, antisocial personality disorder, schizotypal disorder, and conduct disorder.
During the interviews, respondents were asked if they had ever attempted suicide. For those who had, interviewers recorded the total number of lifetime attempts.
Participants also answered questions about childhood maltreatment including physical neglect, emotional neglect, physical abuse, emotional abuse, and sexual abuse by parents or caregivers and other adverse events occurring before the age of 18.
Childhood trauma common
Patients with BPD frequently report a history of childhood trauma, noted Dr. Grilo, adding that such trauma is associated with self-harm and suicide attempts. Sociodemographic information, including age, sex, and ethnicity/race, education level, and income, was also gathered.
Investigators examined data on suicide attempts using relatively stringent coding that required serious dysfunction in at least five BPD criteria.
Using this definition, investigators found the lifetime SA prevalence in patients with BPD was 30.4%, and 3.2% for past-year SAs. This compared with a rate of 3.7% for lifetime SAs and 0.2% for past-year SAs in those without a BPD diagnosis.
The authors examined SA rates using diagnostic codes in the NESARC-III that required seriously impaired function in only 1 or 2 BPD criteria. Rates were higher using the 5-criteria definition.
When the researchers excluded the BPD criterion of self-injurious behavior, the prevalence was 28.1% for lifetime and 3.0% for past-year SAs among the BPD group, with corresponding rates of 3.8% and 0.2% in those without a BPD diagnosis.
It’s important to look at this, said Dr. Grilo, as some patients with BPD who engage in self-harm have suicidal intent while others don’t.
“We tested whether BPD had heightened risk for suicide attempts if we eliminated the self-injurious criterion and we found that heightened risk was still there,” he explained.
Looking at individual criteria for BPD, a model that adjusted for sociodemographic characteristics, other psychiatric disorders, age at BPD onset, and history of childhood adverse events uncovered two criteria that were significantly associated with increased odds of SAs.
One was emptiness. For lifetime suicide attempts, the adjusted odds ratio (aOR) was 1.58 (95% confidence interval, 1.16-2.14) and for past-year attempts, the aOR was 1.99 (95% CI, 1.08-3.66).
The second was self-injurious behavior. For lifetime attempts, the aOR was 24.28 (95% CI, 16.83-32.03) and for past-year attempts, the aOR was 19.32 (95% CI, 5.22-71.58).
In a model in which all BPD-specific criteria were entered while excluding self-injurious behavior, the aORs for emptiness were 1.66 (95% CI, 1.23-2.24) for lifetime suicide attempts and 2.45 (95% CI, 1.18-5.08) for past year attempts.
Unlike another recent study that included more than 700 treatment-seeking patients with BPD who were followed for 10 years, the current study did not show significant associations with SAs for two other BPD criteria – identity disturbance and frantic attempts to avoid abandonment.
Dr. Grilo explained this might be because the earlier study included treatment-seeking patients instead of community cases, or because of differences in assessment interviews or other factors.
‘Compelling evidence’
“Our epidemiological sample has much broader generalizability and fewer potential confounds than the clinical treatment-seeking sample,” said Dr. Grilo.
However, he noted that the two studies “converge strongly and provide compelling evidence that BPD is associated with substantially heightened risk for suicide attempts over the lifetime.”
The two studies “also converge in finding that the presence of symptoms such as repeated self-harm and feelings of chronic emptiness are also associated with risk for suicide attempts.”
The new findings highlight the need to ask potentially at-risk patients about feelings of emptiness as well as self-injurious behaviors. Clinicians could, for example, ask: “Have you often felt like your life had no purpose or meaning?” or “Have you often felt empty inside?”
Limitations of the study include reliance on retrospective self-reports and use of lay interviewers, although these interviewers were trained and had an average of 5 years of experience conducting health-related surveys.
Although the study included a representative sample of U.S. adults, the sample did not include groups known to have high rates of suicide and self-harm behaviors, such as institutionalized, incarcerated, or homeless individuals.
In addition, the study did not evaluate severity and duration of BPD, although the authors noted they did adjust for age at BPD onset, this did not alter the findings.
Often misdiagnosed
Commenting on the study, John M. Oldham, MD, Distinguished Emeritus Professor, Menninger Department of Psychiatry and Behavioral Sciences, Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, and past-president, American Psychiatric Association, and an expert on BPD, had high praise for the research.
BPD is often misdiagnosed, Dr. Oldham said in an interview. Many patients seek help from primary care doctors who may label the symptoms as an anxiety disorder or a mood disorder, he said.
Although medications can help treat some BPD symptoms, “the primary, core evidence-based treatment for BPD is psychotherapy,” said Dr. Oldham, who some years ago helped develop evidence-based practice guidelines for BPD.
“It’s a clear and very well-designed study, and I don’t see any major limitations or problems with it,” he said. “The authors kept their focus rigorously on their goals and they used really careful methodology.”
He noted the “huge” numbers of patients included in the data and the relatively large percentage of men (43.7%).
“There’s a general belief that it’s mostly females who have BPD, but that’s not true; it’s females who come to treatment,” said Dr. Oldham.
Requiring that all five criteria lead to seriously impaired functioning “is a much more rigorous diagnostic methodology” than requiring only one or two criteria to lead to such impairment, said Dr. Oldham. “This is really important” and makes it “a much stronger study.”
The finding that self-harm behavior was linked to suicide attempts isn’t that surprising as this association has been well documented, but the finding that chronic emptiness is also predictive of future suicide attempts “is news,” said Dr. Oldham.
“We have not paid enough attention to this criterion in the clinical world or in the research world.”
Dr. Oldham said one patient with BPD gave him an ideal metaphor for emptiness. “She said it’s like there’s just nobody home. Think of it as an empty house that may look fine on the outside but you go inside and nobody lives there; there’s no furniture; no favorite things; no photos; no possessions.”
The authors have “important messages we need to pay attention to, and the main one is to explore this sense of chronic ‘nobody home’ emptiness,” said Dr. Oldham.
Dr. Grilo has reported receiving research grants from the National Institutes of Health; serving as a consultant for Sunovion and Weight Watchers; receiving honoraria for lectures, continuing medical education activities, and presentations at scientific conferences; and receiving royalties from Guilford Press and Taylor & Francis, all outside the submitted work.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Feelings of chronic emptiness and self-injury have been identified as two key risk factors for suicide attempts (SAs) in patients with borderline personality disorder (BPD), a new cross-sectional, nationally representative study suggests.
The findings also show lifetime and past-year SAs are common among patients with BPD, even when excluding self-injurious behaviors.
The results suggest that in addition to asking patients about self-harm during suicide risk screenings and assessments, clinicians should query them about “longstanding” feelings of emptiness, study investigator Carlos M. Grilo, PhD, professor of psychiatry and psychology, Yale University, New Haven, Conn., said in an interview.
Although related, chronic emptiness “is distinct and goes beyond feelings of sadness, loneliness, and hopelessness,” explained Dr. Grilo. he said.
The study was published online May 11 in JAMA Network Open.
Filling a research gap
While BPD and other psychiatric disorders are associated with suicide, the authors noted there is a “dearth of epidemiological research” examining the link between BPD and suicide.
Criteria for BPD diagnosis requires any five of the following criteria: relationships, affective instability, abandonment fear, anger, identity disturbance, emptiness, disassociation/paranoia, self-injurious behavior, and impulsivity, along with social-occupation dysfunction.
To determine SA risk with specific BPD diagnostic criteria, the investigators examined data on 36,309 individuals who participated in the third wave of the National Epidemiologic Survey on Alcohol and Related Conditions (NESARC-III), conducted from 2012 to 2013.
During computer-assisted, face-to-face interviews, study participants answered questions based on the Alcohol Use Disorder and Associated Disabilities Interview Schedule-5 (AUDADIS-5) of the National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism.
This structured interview assesses a range of DSM-5–defined psychiatric disorders and their criteria. In addition to BPD, the AUDADIS-5 generates diagnoses for mood disorders, anxiety disorders, posttraumatic stress disorder, substance use disorders, antisocial personality disorder, schizotypal disorder, and conduct disorder.
During the interviews, respondents were asked if they had ever attempted suicide. For those who had, interviewers recorded the total number of lifetime attempts.
Participants also answered questions about childhood maltreatment including physical neglect, emotional neglect, physical abuse, emotional abuse, and sexual abuse by parents or caregivers and other adverse events occurring before the age of 18.
Childhood trauma common
Patients with BPD frequently report a history of childhood trauma, noted Dr. Grilo, adding that such trauma is associated with self-harm and suicide attempts. Sociodemographic information, including age, sex, and ethnicity/race, education level, and income, was also gathered.
Investigators examined data on suicide attempts using relatively stringent coding that required serious dysfunction in at least five BPD criteria.
Using this definition, investigators found the lifetime SA prevalence in patients with BPD was 30.4%, and 3.2% for past-year SAs. This compared with a rate of 3.7% for lifetime SAs and 0.2% for past-year SAs in those without a BPD diagnosis.
The authors examined SA rates using diagnostic codes in the NESARC-III that required seriously impaired function in only 1 or 2 BPD criteria. Rates were higher using the 5-criteria definition.
When the researchers excluded the BPD criterion of self-injurious behavior, the prevalence was 28.1% for lifetime and 3.0% for past-year SAs among the BPD group, with corresponding rates of 3.8% and 0.2% in those without a BPD diagnosis.
It’s important to look at this, said Dr. Grilo, as some patients with BPD who engage in self-harm have suicidal intent while others don’t.
“We tested whether BPD had heightened risk for suicide attempts if we eliminated the self-injurious criterion and we found that heightened risk was still there,” he explained.
Looking at individual criteria for BPD, a model that adjusted for sociodemographic characteristics, other psychiatric disorders, age at BPD onset, and history of childhood adverse events uncovered two criteria that were significantly associated with increased odds of SAs.
One was emptiness. For lifetime suicide attempts, the adjusted odds ratio (aOR) was 1.58 (95% confidence interval, 1.16-2.14) and for past-year attempts, the aOR was 1.99 (95% CI, 1.08-3.66).
The second was self-injurious behavior. For lifetime attempts, the aOR was 24.28 (95% CI, 16.83-32.03) and for past-year attempts, the aOR was 19.32 (95% CI, 5.22-71.58).
In a model in which all BPD-specific criteria were entered while excluding self-injurious behavior, the aORs for emptiness were 1.66 (95% CI, 1.23-2.24) for lifetime suicide attempts and 2.45 (95% CI, 1.18-5.08) for past year attempts.
Unlike another recent study that included more than 700 treatment-seeking patients with BPD who were followed for 10 years, the current study did not show significant associations with SAs for two other BPD criteria – identity disturbance and frantic attempts to avoid abandonment.
Dr. Grilo explained this might be because the earlier study included treatment-seeking patients instead of community cases, or because of differences in assessment interviews or other factors.
‘Compelling evidence’
“Our epidemiological sample has much broader generalizability and fewer potential confounds than the clinical treatment-seeking sample,” said Dr. Grilo.
However, he noted that the two studies “converge strongly and provide compelling evidence that BPD is associated with substantially heightened risk for suicide attempts over the lifetime.”
The two studies “also converge in finding that the presence of symptoms such as repeated self-harm and feelings of chronic emptiness are also associated with risk for suicide attempts.”
The new findings highlight the need to ask potentially at-risk patients about feelings of emptiness as well as self-injurious behaviors. Clinicians could, for example, ask: “Have you often felt like your life had no purpose or meaning?” or “Have you often felt empty inside?”
Limitations of the study include reliance on retrospective self-reports and use of lay interviewers, although these interviewers were trained and had an average of 5 years of experience conducting health-related surveys.
Although the study included a representative sample of U.S. adults, the sample did not include groups known to have high rates of suicide and self-harm behaviors, such as institutionalized, incarcerated, or homeless individuals.
In addition, the study did not evaluate severity and duration of BPD, although the authors noted they did adjust for age at BPD onset, this did not alter the findings.
Often misdiagnosed
Commenting on the study, John M. Oldham, MD, Distinguished Emeritus Professor, Menninger Department of Psychiatry and Behavioral Sciences, Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, and past-president, American Psychiatric Association, and an expert on BPD, had high praise for the research.
BPD is often misdiagnosed, Dr. Oldham said in an interview. Many patients seek help from primary care doctors who may label the symptoms as an anxiety disorder or a mood disorder, he said.
Although medications can help treat some BPD symptoms, “the primary, core evidence-based treatment for BPD is psychotherapy,” said Dr. Oldham, who some years ago helped develop evidence-based practice guidelines for BPD.
“It’s a clear and very well-designed study, and I don’t see any major limitations or problems with it,” he said. “The authors kept their focus rigorously on their goals and they used really careful methodology.”
He noted the “huge” numbers of patients included in the data and the relatively large percentage of men (43.7%).
“There’s a general belief that it’s mostly females who have BPD, but that’s not true; it’s females who come to treatment,” said Dr. Oldham.
Requiring that all five criteria lead to seriously impaired functioning “is a much more rigorous diagnostic methodology” than requiring only one or two criteria to lead to such impairment, said Dr. Oldham. “This is really important” and makes it “a much stronger study.”
The finding that self-harm behavior was linked to suicide attempts isn’t that surprising as this association has been well documented, but the finding that chronic emptiness is also predictive of future suicide attempts “is news,” said Dr. Oldham.
“We have not paid enough attention to this criterion in the clinical world or in the research world.”
Dr. Oldham said one patient with BPD gave him an ideal metaphor for emptiness. “She said it’s like there’s just nobody home. Think of it as an empty house that may look fine on the outside but you go inside and nobody lives there; there’s no furniture; no favorite things; no photos; no possessions.”
The authors have “important messages we need to pay attention to, and the main one is to explore this sense of chronic ‘nobody home’ emptiness,” said Dr. Oldham.
Dr. Grilo has reported receiving research grants from the National Institutes of Health; serving as a consultant for Sunovion and Weight Watchers; receiving honoraria for lectures, continuing medical education activities, and presentations at scientific conferences; and receiving royalties from Guilford Press and Taylor & Francis, all outside the submitted work.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Feelings of chronic emptiness and self-injury have been identified as two key risk factors for suicide attempts (SAs) in patients with borderline personality disorder (BPD), a new cross-sectional, nationally representative study suggests.
The findings also show lifetime and past-year SAs are common among patients with BPD, even when excluding self-injurious behaviors.
The results suggest that in addition to asking patients about self-harm during suicide risk screenings and assessments, clinicians should query them about “longstanding” feelings of emptiness, study investigator Carlos M. Grilo, PhD, professor of psychiatry and psychology, Yale University, New Haven, Conn., said in an interview.
Although related, chronic emptiness “is distinct and goes beyond feelings of sadness, loneliness, and hopelessness,” explained Dr. Grilo. he said.
The study was published online May 11 in JAMA Network Open.
Filling a research gap
While BPD and other psychiatric disorders are associated with suicide, the authors noted there is a “dearth of epidemiological research” examining the link between BPD and suicide.
Criteria for BPD diagnosis requires any five of the following criteria: relationships, affective instability, abandonment fear, anger, identity disturbance, emptiness, disassociation/paranoia, self-injurious behavior, and impulsivity, along with social-occupation dysfunction.
To determine SA risk with specific BPD diagnostic criteria, the investigators examined data on 36,309 individuals who participated in the third wave of the National Epidemiologic Survey on Alcohol and Related Conditions (NESARC-III), conducted from 2012 to 2013.
During computer-assisted, face-to-face interviews, study participants answered questions based on the Alcohol Use Disorder and Associated Disabilities Interview Schedule-5 (AUDADIS-5) of the National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism.
This structured interview assesses a range of DSM-5–defined psychiatric disorders and their criteria. In addition to BPD, the AUDADIS-5 generates diagnoses for mood disorders, anxiety disorders, posttraumatic stress disorder, substance use disorders, antisocial personality disorder, schizotypal disorder, and conduct disorder.
During the interviews, respondents were asked if they had ever attempted suicide. For those who had, interviewers recorded the total number of lifetime attempts.
Participants also answered questions about childhood maltreatment including physical neglect, emotional neglect, physical abuse, emotional abuse, and sexual abuse by parents or caregivers and other adverse events occurring before the age of 18.
Childhood trauma common
Patients with BPD frequently report a history of childhood trauma, noted Dr. Grilo, adding that such trauma is associated with self-harm and suicide attempts. Sociodemographic information, including age, sex, and ethnicity/race, education level, and income, was also gathered.
Investigators examined data on suicide attempts using relatively stringent coding that required serious dysfunction in at least five BPD criteria.
Using this definition, investigators found the lifetime SA prevalence in patients with BPD was 30.4%, and 3.2% for past-year SAs. This compared with a rate of 3.7% for lifetime SAs and 0.2% for past-year SAs in those without a BPD diagnosis.
The authors examined SA rates using diagnostic codes in the NESARC-III that required seriously impaired function in only 1 or 2 BPD criteria. Rates were higher using the 5-criteria definition.
When the researchers excluded the BPD criterion of self-injurious behavior, the prevalence was 28.1% for lifetime and 3.0% for past-year SAs among the BPD group, with corresponding rates of 3.8% and 0.2% in those without a BPD diagnosis.
It’s important to look at this, said Dr. Grilo, as some patients with BPD who engage in self-harm have suicidal intent while others don’t.
“We tested whether BPD had heightened risk for suicide attempts if we eliminated the self-injurious criterion and we found that heightened risk was still there,” he explained.
Looking at individual criteria for BPD, a model that adjusted for sociodemographic characteristics, other psychiatric disorders, age at BPD onset, and history of childhood adverse events uncovered two criteria that were significantly associated with increased odds of SAs.
One was emptiness. For lifetime suicide attempts, the adjusted odds ratio (aOR) was 1.58 (95% confidence interval, 1.16-2.14) and for past-year attempts, the aOR was 1.99 (95% CI, 1.08-3.66).
The second was self-injurious behavior. For lifetime attempts, the aOR was 24.28 (95% CI, 16.83-32.03) and for past-year attempts, the aOR was 19.32 (95% CI, 5.22-71.58).
In a model in which all BPD-specific criteria were entered while excluding self-injurious behavior, the aORs for emptiness were 1.66 (95% CI, 1.23-2.24) for lifetime suicide attempts and 2.45 (95% CI, 1.18-5.08) for past year attempts.
Unlike another recent study that included more than 700 treatment-seeking patients with BPD who were followed for 10 years, the current study did not show significant associations with SAs for two other BPD criteria – identity disturbance and frantic attempts to avoid abandonment.
Dr. Grilo explained this might be because the earlier study included treatment-seeking patients instead of community cases, or because of differences in assessment interviews or other factors.
‘Compelling evidence’
“Our epidemiological sample has much broader generalizability and fewer potential confounds than the clinical treatment-seeking sample,” said Dr. Grilo.
However, he noted that the two studies “converge strongly and provide compelling evidence that BPD is associated with substantially heightened risk for suicide attempts over the lifetime.”
The two studies “also converge in finding that the presence of symptoms such as repeated self-harm and feelings of chronic emptiness are also associated with risk for suicide attempts.”
The new findings highlight the need to ask potentially at-risk patients about feelings of emptiness as well as self-injurious behaviors. Clinicians could, for example, ask: “Have you often felt like your life had no purpose or meaning?” or “Have you often felt empty inside?”
Limitations of the study include reliance on retrospective self-reports and use of lay interviewers, although these interviewers were trained and had an average of 5 years of experience conducting health-related surveys.
Although the study included a representative sample of U.S. adults, the sample did not include groups known to have high rates of suicide and self-harm behaviors, such as institutionalized, incarcerated, or homeless individuals.
In addition, the study did not evaluate severity and duration of BPD, although the authors noted they did adjust for age at BPD onset, this did not alter the findings.
Often misdiagnosed
Commenting on the study, John M. Oldham, MD, Distinguished Emeritus Professor, Menninger Department of Psychiatry and Behavioral Sciences, Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, and past-president, American Psychiatric Association, and an expert on BPD, had high praise for the research.
BPD is often misdiagnosed, Dr. Oldham said in an interview. Many patients seek help from primary care doctors who may label the symptoms as an anxiety disorder or a mood disorder, he said.
Although medications can help treat some BPD symptoms, “the primary, core evidence-based treatment for BPD is psychotherapy,” said Dr. Oldham, who some years ago helped develop evidence-based practice guidelines for BPD.
“It’s a clear and very well-designed study, and I don’t see any major limitations or problems with it,” he said. “The authors kept their focus rigorously on their goals and they used really careful methodology.”
He noted the “huge” numbers of patients included in the data and the relatively large percentage of men (43.7%).
“There’s a general belief that it’s mostly females who have BPD, but that’s not true; it’s females who come to treatment,” said Dr. Oldham.
Requiring that all five criteria lead to seriously impaired functioning “is a much more rigorous diagnostic methodology” than requiring only one or two criteria to lead to such impairment, said Dr. Oldham. “This is really important” and makes it “a much stronger study.”
The finding that self-harm behavior was linked to suicide attempts isn’t that surprising as this association has been well documented, but the finding that chronic emptiness is also predictive of future suicide attempts “is news,” said Dr. Oldham.
“We have not paid enough attention to this criterion in the clinical world or in the research world.”
Dr. Oldham said one patient with BPD gave him an ideal metaphor for emptiness. “She said it’s like there’s just nobody home. Think of it as an empty house that may look fine on the outside but you go inside and nobody lives there; there’s no furniture; no favorite things; no photos; no possessions.”
The authors have “important messages we need to pay attention to, and the main one is to explore this sense of chronic ‘nobody home’ emptiness,” said Dr. Oldham.
Dr. Grilo has reported receiving research grants from the National Institutes of Health; serving as a consultant for Sunovion and Weight Watchers; receiving honoraria for lectures, continuing medical education activities, and presentations at scientific conferences; and receiving royalties from Guilford Press and Taylor & Francis, all outside the submitted work.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
How to improve our response to COVID’s mental tolls
We have no way of precisely knowing how many lives might have been saved, and how much grief and loneliness spared and economic ruin contained during COVID-19 if we had risen to its myriad challenges in a timely fashion. However, I feel we can safely say that the United States deserves to be graded with an “F” for its management of the pandemic.
To render this grade, we need only to read the countless verified reports of how critically needed public health measures were not taken soon enough, or sufficiently, to substantially mitigate human and societal suffering.
This began with the failure to protect doctors, nurses, and technicians, who did not have the personal protective equipment needed to prevent infection and spare risk to their loved ones. It soon extended to the country’s failure to adequately protect all its citizens and residents. COVID-19 then rained its grievous consequences disproportionately upon people of color, those living in poverty, and those with housing and food insecurity – those already greatly foreclosed from opportunities to exit from their circumstances.
We all have heard, “Fool me once, shame on you; fool me twice, shame on me.”
Bear witness, colleagues and friends: It will be our shared shame if we too continue to fail in our response to COVID-19. But failure need not happen because protecting ourselves and our country is a solvable problem; complex and demanding for sure, but solvable.
To battle trauma, we must first define it
The sine qua non of a disaster is its psychic and social trauma. I asked Maureen Sayres Van Niel, MD, chair of the American Psychiatric Association’s Minority and Underrepresented Caucus and a former steering committee member of the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force, to define trauma. She said, “It is [the product of] a catastrophic, unexpected event over which we have little control, with grave consequences to the lives and psychological functioning of those individuals and groups affected.”
The COVID-19 pandemic is a massively amplified traumatic event because of the virulence and contagious properties of the virus and its variants; the absence of end date on the horizon; its effect as a proverbial ax that disproportionately falls on the majority of the populace experiencing racial and social inequities; and the ironic yet necessary imperative to distance ourselves from those we care about and who care about us.
Four interdependent factors drive the magnitude of the traumatic impact of a disaster: the degree of exposure to the life-threatening event; the duration and threat of recurrence; an individual’s preexisting (natural and human-made) trauma and mental and addictive disorders; and the adequacy of family and fundamental resources such as housing, food, safety, and access to health care (the social dimensions of health and mental health). These factors underline the “who,” “what,” “where,” and “how” of what should have been (and continue to be) an effective public health response to the COVID-19 pandemic.
Yet existing categories that we have used to predict risk for trauma no longer hold. The gravity, prevalence, and persistence of COVID-19’s horrors erase any differences among victims, witnesses, and bystanders. Dr Sayres Van Niel asserts that we have a “collective, national trauma.” In April, the Kaiser Family Foundation’s Vaccine Monitor reported that 24% of U.S. adults had a close friend or family member who died of COVID-19. That’s 82 million Americans! Our country has eclipsed individual victimization and trauma because we are all in its maw.
Vital lessons from the past
In a previous column, I described my role as New York City’s mental health commissioner after 9/11 and the many lessons we learned during that multiyear process. Our work served as a template for other disasters to follow, such as Hurricane Sandy. Its value to COVID-19 is equally apparent.
We learned that those most at risk of developing symptomatic, functionally impairing mental illness had prior traumatic experiences (for example, from childhood abuse or neglect, violence, war, and forced displacement from their native land) and/or a preexisting mental or substance use disorder.
Once these individuals and communities were identified, we could prioritize their treatment and care. Doing so required mobilizing both inner and external (social) resources, which can be used before disaster strikes or in its wake.
For individuals, adaptive resources include developing any of a number of mind-body activities (for example, meditation, mindfulness, slow breathing, and yoga); sufficient but not necessarily excessive levels of exercise (as has been said, if exercise were a pill, it would be the most potent of medicines); nourishing diets; sleep, nature’s restorative state; and perhaps most important, attachment and human connection to people who care about you and whom you care about and trust.
This does not necessarily mean holding or following an institutional religion or belonging to house of worship (though, of course, that melds and augments faith with community). For a great many, myself included, there is spirituality, the belief in a greater power, which need not be a God yet instills a sense of the vastness, universality, and continuity of life.
For communities, adaptive resources include safe homes and neighborhoods; diminishing housing and food insecurity; education, including pre-K; employment, with a livable wage; ridding human interactions of the endless, so-called microaggressions (which are not micro at all, because they accrue) of race, ethnic, class, and age discrimination and injustice; and ready access to quality and affordable health care, now more than ever for the rising tide of mental and substance use disorders that COVID-19 has unleashed.
Every gain we make to ablate racism, social injustice, discrimination, and widely and deeply spread resource and opportunity inequities means more cohesion among the members of our collective tribe. Greater cohesion, a love for thy neighbor, and equity (in action, not polemics) will fuel the resilience we will need to withstand more of COVID-19’s ongoing trauma; that of other, inescapable disasters and losses; and the wear and tear of everyday life. The rewards of equity are priceless and include the dignity that derives from fairness and justice – given and received.
An unprecedented disaster requires a bold response
My, what a list. But to me, the encompassing nature of what’s needed means that we can make differences anywhere, everywhere, and in countless and continuous ways.
The measure of any society is in how it cares for those who are foreclosed, through no fault of their own, from what we all want: a life safe from violence, secure in housing and food, with loving relationships and the pride that comes of making contributions, each in our own, wonderfully unique way.
Where will we all be in a year, 2, or 3 from now? Prepared, or not? Emotionally inoculated, or not? Better equipped, or not? As divided, or more cohesive?
Well, I imagine that depends on each and every one of us.
Lloyd I. Sederer, MD, is a psychiatrist, public health doctor, and writer. He is an adjunct professor at the Columbia University School of Public Health, director of Columbia Psychiatry Media, chief medical officer of Bongo Media, and chair of the advisory board of Get Help. He has been chief medical officer of McLean Hospital, a Harvard teaching hospital; mental health commissioner of New York City (in the Bloomberg administration); and chief medical officer of the New York State Office of Mental Health, the nation’s largest state mental health agency.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
We have no way of precisely knowing how many lives might have been saved, and how much grief and loneliness spared and economic ruin contained during COVID-19 if we had risen to its myriad challenges in a timely fashion. However, I feel we can safely say that the United States deserves to be graded with an “F” for its management of the pandemic.
To render this grade, we need only to read the countless verified reports of how critically needed public health measures were not taken soon enough, or sufficiently, to substantially mitigate human and societal suffering.
This began with the failure to protect doctors, nurses, and technicians, who did not have the personal protective equipment needed to prevent infection and spare risk to their loved ones. It soon extended to the country’s failure to adequately protect all its citizens and residents. COVID-19 then rained its grievous consequences disproportionately upon people of color, those living in poverty, and those with housing and food insecurity – those already greatly foreclosed from opportunities to exit from their circumstances.
We all have heard, “Fool me once, shame on you; fool me twice, shame on me.”
Bear witness, colleagues and friends: It will be our shared shame if we too continue to fail in our response to COVID-19. But failure need not happen because protecting ourselves and our country is a solvable problem; complex and demanding for sure, but solvable.
To battle trauma, we must first define it
The sine qua non of a disaster is its psychic and social trauma. I asked Maureen Sayres Van Niel, MD, chair of the American Psychiatric Association’s Minority and Underrepresented Caucus and a former steering committee member of the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force, to define trauma. She said, “It is [the product of] a catastrophic, unexpected event over which we have little control, with grave consequences to the lives and psychological functioning of those individuals and groups affected.”
The COVID-19 pandemic is a massively amplified traumatic event because of the virulence and contagious properties of the virus and its variants; the absence of end date on the horizon; its effect as a proverbial ax that disproportionately falls on the majority of the populace experiencing racial and social inequities; and the ironic yet necessary imperative to distance ourselves from those we care about and who care about us.
Four interdependent factors drive the magnitude of the traumatic impact of a disaster: the degree of exposure to the life-threatening event; the duration and threat of recurrence; an individual’s preexisting (natural and human-made) trauma and mental and addictive disorders; and the adequacy of family and fundamental resources such as housing, food, safety, and access to health care (the social dimensions of health and mental health). These factors underline the “who,” “what,” “where,” and “how” of what should have been (and continue to be) an effective public health response to the COVID-19 pandemic.
Yet existing categories that we have used to predict risk for trauma no longer hold. The gravity, prevalence, and persistence of COVID-19’s horrors erase any differences among victims, witnesses, and bystanders. Dr Sayres Van Niel asserts that we have a “collective, national trauma.” In April, the Kaiser Family Foundation’s Vaccine Monitor reported that 24% of U.S. adults had a close friend or family member who died of COVID-19. That’s 82 million Americans! Our country has eclipsed individual victimization and trauma because we are all in its maw.
Vital lessons from the past
In a previous column, I described my role as New York City’s mental health commissioner after 9/11 and the many lessons we learned during that multiyear process. Our work served as a template for other disasters to follow, such as Hurricane Sandy. Its value to COVID-19 is equally apparent.
We learned that those most at risk of developing symptomatic, functionally impairing mental illness had prior traumatic experiences (for example, from childhood abuse or neglect, violence, war, and forced displacement from their native land) and/or a preexisting mental or substance use disorder.
Once these individuals and communities were identified, we could prioritize their treatment and care. Doing so required mobilizing both inner and external (social) resources, which can be used before disaster strikes or in its wake.
For individuals, adaptive resources include developing any of a number of mind-body activities (for example, meditation, mindfulness, slow breathing, and yoga); sufficient but not necessarily excessive levels of exercise (as has been said, if exercise were a pill, it would be the most potent of medicines); nourishing diets; sleep, nature’s restorative state; and perhaps most important, attachment and human connection to people who care about you and whom you care about and trust.
This does not necessarily mean holding or following an institutional religion or belonging to house of worship (though, of course, that melds and augments faith with community). For a great many, myself included, there is spirituality, the belief in a greater power, which need not be a God yet instills a sense of the vastness, universality, and continuity of life.
For communities, adaptive resources include safe homes and neighborhoods; diminishing housing and food insecurity; education, including pre-K; employment, with a livable wage; ridding human interactions of the endless, so-called microaggressions (which are not micro at all, because they accrue) of race, ethnic, class, and age discrimination and injustice; and ready access to quality and affordable health care, now more than ever for the rising tide of mental and substance use disorders that COVID-19 has unleashed.
Every gain we make to ablate racism, social injustice, discrimination, and widely and deeply spread resource and opportunity inequities means more cohesion among the members of our collective tribe. Greater cohesion, a love for thy neighbor, and equity (in action, not polemics) will fuel the resilience we will need to withstand more of COVID-19’s ongoing trauma; that of other, inescapable disasters and losses; and the wear and tear of everyday life. The rewards of equity are priceless and include the dignity that derives from fairness and justice – given and received.
An unprecedented disaster requires a bold response
My, what a list. But to me, the encompassing nature of what’s needed means that we can make differences anywhere, everywhere, and in countless and continuous ways.
The measure of any society is in how it cares for those who are foreclosed, through no fault of their own, from what we all want: a life safe from violence, secure in housing and food, with loving relationships and the pride that comes of making contributions, each in our own, wonderfully unique way.
Where will we all be in a year, 2, or 3 from now? Prepared, or not? Emotionally inoculated, or not? Better equipped, or not? As divided, or more cohesive?
Well, I imagine that depends on each and every one of us.
Lloyd I. Sederer, MD, is a psychiatrist, public health doctor, and writer. He is an adjunct professor at the Columbia University School of Public Health, director of Columbia Psychiatry Media, chief medical officer of Bongo Media, and chair of the advisory board of Get Help. He has been chief medical officer of McLean Hospital, a Harvard teaching hospital; mental health commissioner of New York City (in the Bloomberg administration); and chief medical officer of the New York State Office of Mental Health, the nation’s largest state mental health agency.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
We have no way of precisely knowing how many lives might have been saved, and how much grief and loneliness spared and economic ruin contained during COVID-19 if we had risen to its myriad challenges in a timely fashion. However, I feel we can safely say that the United States deserves to be graded with an “F” for its management of the pandemic.
To render this grade, we need only to read the countless verified reports of how critically needed public health measures were not taken soon enough, or sufficiently, to substantially mitigate human and societal suffering.
This began with the failure to protect doctors, nurses, and technicians, who did not have the personal protective equipment needed to prevent infection and spare risk to their loved ones. It soon extended to the country’s failure to adequately protect all its citizens and residents. COVID-19 then rained its grievous consequences disproportionately upon people of color, those living in poverty, and those with housing and food insecurity – those already greatly foreclosed from opportunities to exit from their circumstances.
We all have heard, “Fool me once, shame on you; fool me twice, shame on me.”
Bear witness, colleagues and friends: It will be our shared shame if we too continue to fail in our response to COVID-19. But failure need not happen because protecting ourselves and our country is a solvable problem; complex and demanding for sure, but solvable.
To battle trauma, we must first define it
The sine qua non of a disaster is its psychic and social trauma. I asked Maureen Sayres Van Niel, MD, chair of the American Psychiatric Association’s Minority and Underrepresented Caucus and a former steering committee member of the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force, to define trauma. She said, “It is [the product of] a catastrophic, unexpected event over which we have little control, with grave consequences to the lives and psychological functioning of those individuals and groups affected.”
The COVID-19 pandemic is a massively amplified traumatic event because of the virulence and contagious properties of the virus and its variants; the absence of end date on the horizon; its effect as a proverbial ax that disproportionately falls on the majority of the populace experiencing racial and social inequities; and the ironic yet necessary imperative to distance ourselves from those we care about and who care about us.
Four interdependent factors drive the magnitude of the traumatic impact of a disaster: the degree of exposure to the life-threatening event; the duration and threat of recurrence; an individual’s preexisting (natural and human-made) trauma and mental and addictive disorders; and the adequacy of family and fundamental resources such as housing, food, safety, and access to health care (the social dimensions of health and mental health). These factors underline the “who,” “what,” “where,” and “how” of what should have been (and continue to be) an effective public health response to the COVID-19 pandemic.
Yet existing categories that we have used to predict risk for trauma no longer hold. The gravity, prevalence, and persistence of COVID-19’s horrors erase any differences among victims, witnesses, and bystanders. Dr Sayres Van Niel asserts that we have a “collective, national trauma.” In April, the Kaiser Family Foundation’s Vaccine Monitor reported that 24% of U.S. adults had a close friend or family member who died of COVID-19. That’s 82 million Americans! Our country has eclipsed individual victimization and trauma because we are all in its maw.
Vital lessons from the past
In a previous column, I described my role as New York City’s mental health commissioner after 9/11 and the many lessons we learned during that multiyear process. Our work served as a template for other disasters to follow, such as Hurricane Sandy. Its value to COVID-19 is equally apparent.
We learned that those most at risk of developing symptomatic, functionally impairing mental illness had prior traumatic experiences (for example, from childhood abuse or neglect, violence, war, and forced displacement from their native land) and/or a preexisting mental or substance use disorder.
Once these individuals and communities were identified, we could prioritize their treatment and care. Doing so required mobilizing both inner and external (social) resources, which can be used before disaster strikes or in its wake.
For individuals, adaptive resources include developing any of a number of mind-body activities (for example, meditation, mindfulness, slow breathing, and yoga); sufficient but not necessarily excessive levels of exercise (as has been said, if exercise were a pill, it would be the most potent of medicines); nourishing diets; sleep, nature’s restorative state; and perhaps most important, attachment and human connection to people who care about you and whom you care about and trust.
This does not necessarily mean holding or following an institutional religion or belonging to house of worship (though, of course, that melds and augments faith with community). For a great many, myself included, there is spirituality, the belief in a greater power, which need not be a God yet instills a sense of the vastness, universality, and continuity of life.
For communities, adaptive resources include safe homes and neighborhoods; diminishing housing and food insecurity; education, including pre-K; employment, with a livable wage; ridding human interactions of the endless, so-called microaggressions (which are not micro at all, because they accrue) of race, ethnic, class, and age discrimination and injustice; and ready access to quality and affordable health care, now more than ever for the rising tide of mental and substance use disorders that COVID-19 has unleashed.
Every gain we make to ablate racism, social injustice, discrimination, and widely and deeply spread resource and opportunity inequities means more cohesion among the members of our collective tribe. Greater cohesion, a love for thy neighbor, and equity (in action, not polemics) will fuel the resilience we will need to withstand more of COVID-19’s ongoing trauma; that of other, inescapable disasters and losses; and the wear and tear of everyday life. The rewards of equity are priceless and include the dignity that derives from fairness and justice – given and received.
An unprecedented disaster requires a bold response
My, what a list. But to me, the encompassing nature of what’s needed means that we can make differences anywhere, everywhere, and in countless and continuous ways.
The measure of any society is in how it cares for those who are foreclosed, through no fault of their own, from what we all want: a life safe from violence, secure in housing and food, with loving relationships and the pride that comes of making contributions, each in our own, wonderfully unique way.
Where will we all be in a year, 2, or 3 from now? Prepared, or not? Emotionally inoculated, or not? Better equipped, or not? As divided, or more cohesive?
Well, I imagine that depends on each and every one of us.
Lloyd I. Sederer, MD, is a psychiatrist, public health doctor, and writer. He is an adjunct professor at the Columbia University School of Public Health, director of Columbia Psychiatry Media, chief medical officer of Bongo Media, and chair of the advisory board of Get Help. He has been chief medical officer of McLean Hospital, a Harvard teaching hospital; mental health commissioner of New York City (in the Bloomberg administration); and chief medical officer of the New York State Office of Mental Health, the nation’s largest state mental health agency.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
An Anniversary Postponed and a Diagnosis Delayed: Vietnam and PTSD
Many events both personal and public have been deferred during the 15 plus months of the pandemic. Almost everyone has an example of a friend or family member who would have been sitting at what President Biden, during his memorial speech for the 500,000 victims of the virus referred to as the “empty chair” at a holiday gathering sans COVID-19.2 For many in our country, part of the agonizing effort to awaken from the long nightmare of the pandemic is to resume the rhythm of rituals national, local, and personal that mark the year with meaning and offer rest and rejuvenation from the daily toil of duty. There are family dinners now cautiously resumed due to vaccinations; small celebrations of belated birthdays in family pods; socially distanced outdoor gatherings suspended in the cold communicable winter now gingerly possible with the warmth of spring.
As a nation, one of the events that was put on hold was the commemoration of the Vietnam War. On March 16, 2021, following guidance from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, the US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) announced it was postponing commemoration events “until further notice.”3 Annually, the VA partners with the US Department of Defense, state, and local organizations to recognize “the service and sacrifices made by the nearly 3 million service members who served in Vietnam.”4
In 2012, President Barak Obama signed a proclamation establishing a 13-year commemoration of the 50th anniversary of the Vietnam War.5 Five years later, President Donald Trump signed the War Veterans Recognition Act of 2017, designating March 29 annually as National Vietnam War Veterans Day.6 Though many of the events planned for March and April could not take place, the Vietnam War Commemoration (https://www.vietnamwar50th.com) offers information and ideas for honoring and supporting Vietnam War veterans. As Memorial Day approaches in this year of so much loss and heroism, I encourage you to find a way to thank Vietnam veterans who may have received the opposite of gratitude when they initially returned home.
As my small contribution to the commemoration, this editorial will focus on the psychiatric disorder of memory: posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD) and how the Vietnam War brought definition—albeit delayed—to the agonizing diagnosis that too many veterans experience.
The known clinical entity of PTSD is ancient. Narrative descriptions of the disorder are written in the Mesopotamian Epic of Gilgamesh and in Deuteronomy 20:1-9.7 American and European military physicians have given various names to the destructive effects of combat on body and mind from “soldier’s heart” in the American Civil War, to “shell shock” in World War I to “battle fatigue” during World War II.8 These were all descriptive diagnoses field practitioners used to grasp the psychosomatic decompensation they observed in service members who had been exposed to the horrors of war. The VA was the impetus and agent of the earliest attempts at scientific definition. The American Psychiatric Association further developed this nosology in 1952 with the diagnosis of gross stress reaction in the first Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM)-1.9
The combat experience shaped the definition: the stressor had to be extreme, the civilian comparison would be a natural disaster; the reaction could occur only in a previously normal individual, it would be attributed to the extant psychiatric condition in anyone with a premorbid illness; and if it did not remit by 6 months, another primary psychiatric diagnosis must be assigned.
From our vantage point, this set of criteria is obviously woefully inadequate, yet it was at least a beginning of formal recognition of the experience that veterans endured in wartime and real progress compared with what happened next. When DSM-1 was revised in 1968, the diagnosis of gross stress reaction was eliminated without explanation. Researcher Andreasen and others speculate that its disappearance can be attributed to association of the diagnosis with war in a country that had been at peace since the end of the Korean War in 1953.10 Yet military historians among my readers will immediately counter that the Vietnam War began 2 years later and that the year of the revision saw major combat operations.
Many veterans living with the psychological and physical suffering of their service in Vietnam and the organizations that supported them advocated for the psychiatric profession to formally acknowledge post-Vietnam syndrome.11 Five years after the end of the Vietnam War, the experts who authored DSM-III, decided to include a new stress-induced diagnosis.12 Although the manual did not limit the traumatic experience to combat in Vietnam as some veterans wanted, there is no doubt that the criteria reflect the extensive research validating the illness narratives of thousands of service men and women.
The DSM-III criteria clearly had war in mind when it stipulated that the stressor had to be outside the range of usual human experience that would likely trigger significant symptoms in almost anyone as well as specifying chronic symptoms lasting more than 6 months. Despite the controversy about the diagnosis, Vietnam veterans helped bring the PTSD diagnosis to official psychiatric nomenclature and in a more recognizable form that began to capture the intensity of their reexperiencing of the trauma, the psychosocial difficulties numbing caused, and the pervasive interference of hyperarousal and vigilance many aspects and areas of life.13
The National Vietnam Veterans Longitudinal Study examined the course of PTSD over 25 years, using the newly formulated diagnostic criteria for PTSD.14 Results were reported to Congress in 2012 and showed that 11% of men and 7% of women who were in a war theater were still struggling with PTSD 40 years after the war. Of those, 37% met major depressive disorder criteria. Male veterans who in 1987 still met criteria for PTSD were twice as likely to have died than the comparator group of veterans without PTSD. Two-thirds of veterans with PTSD from war zone exposure discussed behavioral health or substance misuse concerns with a health care provider, and 37% of those were receiving VA care.14
Given these disturbing data, perhaps the best way we can pay homage to the aging Vietnam veterans is to support continued research into effective evidence-based treatments for PTSD and funding for the training and recruiting of mental health practitioners to all 3 branches of federal health care who can deliver that care compassionately and competently.
1. The Vietnam War: a new film by Ken Burns and Lynn Novick, to air fall 2017 on PBS. Press release. Updated August 17, 2020. Accessed April 26, 2021. https://www.pbs.org/about/about-pbs/blogs/news/the-vietnam-war-a-new-film-by-ken-burns-and-lynn-novick-to-air-fall-2017-on-pbs
2. The White House Briefing Room. Remarks by President Biden on the more than 500,000 Americans lives lost to COVID-19. Published February 22, 2021. Accessed April 26, 2021.https://www.whitehouse.gov/briefing-room/speeches-remarks/2021/02/22/remarks-by-president-biden-on-the-more-than-500000-american-lives-lost-to-covid-19/
3. US Department of Veterans Affairs. Vantage Point. VA postpones 50th anniversary of the Vietnam War commemoration events. Published March 16, 2021. Accessed April 26, 2021. https://blogs.va.gov/VAntage/72694/va-postpones-50th-anniversary-vietnam-war-commemoration-events
4. US Department of Defense. Nation observes Vietnam War Veterans Day. Published March 29, 2021. Accessed April 26, 2021. https://www.defense.gov/Explore/Features/Story/Article/2545524/nation-observes-vietnam-war-veterans-day
5. The White House. Commemoration of the 50th anniversary of the Vietnam War. Published May 25, 2012. Accessed April 26, 2021. https://obamawhitehouse.archives.gov/the-press-office/2012/05/25/presidential-proclamation-commemoration-50th-anniversary-vietnam-war
6. Vietnam War Veterans Recognition Act. Public Law 115-15. U.S. Government Publishing Office, Washington DC, 2017.
7. Crocq M-A, Crocq L. From shell shock and war neurosis to posttraumatic stress disorder: a history of psychotraumatology. Dialogues Clin Neurosci .2000;2(1):47-55. doi:10.31887/DCNS.2000.2.1/macrocq
8. US Department of Veterans Affairs. History of PTSD in veterans: Civil War to DSM-5. Accessed April 26, 2021. https://www.ptsd.va.gov/understand/what/history_ptsd.asp
9. American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders . Washington, DC: American Psychiatric Association; 1952.
10. Andreasen NC. Posttraumatic stress disorder: a history and a critique. Ann NY Acad Sci. 2010;1208;67-71. doi:10.1111/j.1749-6632.2010.05699.x
11. Shata CF. Post-Vietnam syndrome. The New York Times . Published May 6, 1972. Accessed April 26, 2021. https://www.nytimes.com/1972/05/06/archives/postvietnam-syndrome.html
12. American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders. (DSM-III) . Washington, DC. American Psychiatric Association; 1980.
13. Kinzie JD, Goetz RR. A century of controversy surrounding posttraumatic stress stress: spectrum syndromes: the impact on DSM-III and DSM-IV. J Trauma Stress. 1996;9(2):156-179. doi:10.1007/BF02110653
14. Schlenger WE, Corry NH. Four decades later: Vietnam veterans and PTSD. Published January/February 2015. Accessed April 25, 2021. http://vvaveteran.org/35-1/35-1_longitudinalstudy.html
Many events both personal and public have been deferred during the 15 plus months of the pandemic. Almost everyone has an example of a friend or family member who would have been sitting at what President Biden, during his memorial speech for the 500,000 victims of the virus referred to as the “empty chair” at a holiday gathering sans COVID-19.2 For many in our country, part of the agonizing effort to awaken from the long nightmare of the pandemic is to resume the rhythm of rituals national, local, and personal that mark the year with meaning and offer rest and rejuvenation from the daily toil of duty. There are family dinners now cautiously resumed due to vaccinations; small celebrations of belated birthdays in family pods; socially distanced outdoor gatherings suspended in the cold communicable winter now gingerly possible with the warmth of spring.
As a nation, one of the events that was put on hold was the commemoration of the Vietnam War. On March 16, 2021, following guidance from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, the US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) announced it was postponing commemoration events “until further notice.”3 Annually, the VA partners with the US Department of Defense, state, and local organizations to recognize “the service and sacrifices made by the nearly 3 million service members who served in Vietnam.”4
In 2012, President Barak Obama signed a proclamation establishing a 13-year commemoration of the 50th anniversary of the Vietnam War.5 Five years later, President Donald Trump signed the War Veterans Recognition Act of 2017, designating March 29 annually as National Vietnam War Veterans Day.6 Though many of the events planned for March and April could not take place, the Vietnam War Commemoration (https://www.vietnamwar50th.com) offers information and ideas for honoring and supporting Vietnam War veterans. As Memorial Day approaches in this year of so much loss and heroism, I encourage you to find a way to thank Vietnam veterans who may have received the opposite of gratitude when they initially returned home.
As my small contribution to the commemoration, this editorial will focus on the psychiatric disorder of memory: posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD) and how the Vietnam War brought definition—albeit delayed—to the agonizing diagnosis that too many veterans experience.
The known clinical entity of PTSD is ancient. Narrative descriptions of the disorder are written in the Mesopotamian Epic of Gilgamesh and in Deuteronomy 20:1-9.7 American and European military physicians have given various names to the destructive effects of combat on body and mind from “soldier’s heart” in the American Civil War, to “shell shock” in World War I to “battle fatigue” during World War II.8 These were all descriptive diagnoses field practitioners used to grasp the psychosomatic decompensation they observed in service members who had been exposed to the horrors of war. The VA was the impetus and agent of the earliest attempts at scientific definition. The American Psychiatric Association further developed this nosology in 1952 with the diagnosis of gross stress reaction in the first Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM)-1.9
The combat experience shaped the definition: the stressor had to be extreme, the civilian comparison would be a natural disaster; the reaction could occur only in a previously normal individual, it would be attributed to the extant psychiatric condition in anyone with a premorbid illness; and if it did not remit by 6 months, another primary psychiatric diagnosis must be assigned.
From our vantage point, this set of criteria is obviously woefully inadequate, yet it was at least a beginning of formal recognition of the experience that veterans endured in wartime and real progress compared with what happened next. When DSM-1 was revised in 1968, the diagnosis of gross stress reaction was eliminated without explanation. Researcher Andreasen and others speculate that its disappearance can be attributed to association of the diagnosis with war in a country that had been at peace since the end of the Korean War in 1953.10 Yet military historians among my readers will immediately counter that the Vietnam War began 2 years later and that the year of the revision saw major combat operations.
Many veterans living with the psychological and physical suffering of their service in Vietnam and the organizations that supported them advocated for the psychiatric profession to formally acknowledge post-Vietnam syndrome.11 Five years after the end of the Vietnam War, the experts who authored DSM-III, decided to include a new stress-induced diagnosis.12 Although the manual did not limit the traumatic experience to combat in Vietnam as some veterans wanted, there is no doubt that the criteria reflect the extensive research validating the illness narratives of thousands of service men and women.
The DSM-III criteria clearly had war in mind when it stipulated that the stressor had to be outside the range of usual human experience that would likely trigger significant symptoms in almost anyone as well as specifying chronic symptoms lasting more than 6 months. Despite the controversy about the diagnosis, Vietnam veterans helped bring the PTSD diagnosis to official psychiatric nomenclature and in a more recognizable form that began to capture the intensity of their reexperiencing of the trauma, the psychosocial difficulties numbing caused, and the pervasive interference of hyperarousal and vigilance many aspects and areas of life.13
The National Vietnam Veterans Longitudinal Study examined the course of PTSD over 25 years, using the newly formulated diagnostic criteria for PTSD.14 Results were reported to Congress in 2012 and showed that 11% of men and 7% of women who were in a war theater were still struggling with PTSD 40 years after the war. Of those, 37% met major depressive disorder criteria. Male veterans who in 1987 still met criteria for PTSD were twice as likely to have died than the comparator group of veterans without PTSD. Two-thirds of veterans with PTSD from war zone exposure discussed behavioral health or substance misuse concerns with a health care provider, and 37% of those were receiving VA care.14
Given these disturbing data, perhaps the best way we can pay homage to the aging Vietnam veterans is to support continued research into effective evidence-based treatments for PTSD and funding for the training and recruiting of mental health practitioners to all 3 branches of federal health care who can deliver that care compassionately and competently.
Many events both personal and public have been deferred during the 15 plus months of the pandemic. Almost everyone has an example of a friend or family member who would have been sitting at what President Biden, during his memorial speech for the 500,000 victims of the virus referred to as the “empty chair” at a holiday gathering sans COVID-19.2 For many in our country, part of the agonizing effort to awaken from the long nightmare of the pandemic is to resume the rhythm of rituals national, local, and personal that mark the year with meaning and offer rest and rejuvenation from the daily toil of duty. There are family dinners now cautiously resumed due to vaccinations; small celebrations of belated birthdays in family pods; socially distanced outdoor gatherings suspended in the cold communicable winter now gingerly possible with the warmth of spring.
As a nation, one of the events that was put on hold was the commemoration of the Vietnam War. On March 16, 2021, following guidance from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, the US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) announced it was postponing commemoration events “until further notice.”3 Annually, the VA partners with the US Department of Defense, state, and local organizations to recognize “the service and sacrifices made by the nearly 3 million service members who served in Vietnam.”4
In 2012, President Barak Obama signed a proclamation establishing a 13-year commemoration of the 50th anniversary of the Vietnam War.5 Five years later, President Donald Trump signed the War Veterans Recognition Act of 2017, designating March 29 annually as National Vietnam War Veterans Day.6 Though many of the events planned for March and April could not take place, the Vietnam War Commemoration (https://www.vietnamwar50th.com) offers information and ideas for honoring and supporting Vietnam War veterans. As Memorial Day approaches in this year of so much loss and heroism, I encourage you to find a way to thank Vietnam veterans who may have received the opposite of gratitude when they initially returned home.
As my small contribution to the commemoration, this editorial will focus on the psychiatric disorder of memory: posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD) and how the Vietnam War brought definition—albeit delayed—to the agonizing diagnosis that too many veterans experience.
The known clinical entity of PTSD is ancient. Narrative descriptions of the disorder are written in the Mesopotamian Epic of Gilgamesh and in Deuteronomy 20:1-9.7 American and European military physicians have given various names to the destructive effects of combat on body and mind from “soldier’s heart” in the American Civil War, to “shell shock” in World War I to “battle fatigue” during World War II.8 These were all descriptive diagnoses field practitioners used to grasp the psychosomatic decompensation they observed in service members who had been exposed to the horrors of war. The VA was the impetus and agent of the earliest attempts at scientific definition. The American Psychiatric Association further developed this nosology in 1952 with the diagnosis of gross stress reaction in the first Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM)-1.9
The combat experience shaped the definition: the stressor had to be extreme, the civilian comparison would be a natural disaster; the reaction could occur only in a previously normal individual, it would be attributed to the extant psychiatric condition in anyone with a premorbid illness; and if it did not remit by 6 months, another primary psychiatric diagnosis must be assigned.
From our vantage point, this set of criteria is obviously woefully inadequate, yet it was at least a beginning of formal recognition of the experience that veterans endured in wartime and real progress compared with what happened next. When DSM-1 was revised in 1968, the diagnosis of gross stress reaction was eliminated without explanation. Researcher Andreasen and others speculate that its disappearance can be attributed to association of the diagnosis with war in a country that had been at peace since the end of the Korean War in 1953.10 Yet military historians among my readers will immediately counter that the Vietnam War began 2 years later and that the year of the revision saw major combat operations.
Many veterans living with the psychological and physical suffering of their service in Vietnam and the organizations that supported them advocated for the psychiatric profession to formally acknowledge post-Vietnam syndrome.11 Five years after the end of the Vietnam War, the experts who authored DSM-III, decided to include a new stress-induced diagnosis.12 Although the manual did not limit the traumatic experience to combat in Vietnam as some veterans wanted, there is no doubt that the criteria reflect the extensive research validating the illness narratives of thousands of service men and women.
The DSM-III criteria clearly had war in mind when it stipulated that the stressor had to be outside the range of usual human experience that would likely trigger significant symptoms in almost anyone as well as specifying chronic symptoms lasting more than 6 months. Despite the controversy about the diagnosis, Vietnam veterans helped bring the PTSD diagnosis to official psychiatric nomenclature and in a more recognizable form that began to capture the intensity of their reexperiencing of the trauma, the psychosocial difficulties numbing caused, and the pervasive interference of hyperarousal and vigilance many aspects and areas of life.13
The National Vietnam Veterans Longitudinal Study examined the course of PTSD over 25 years, using the newly formulated diagnostic criteria for PTSD.14 Results were reported to Congress in 2012 and showed that 11% of men and 7% of women who were in a war theater were still struggling with PTSD 40 years after the war. Of those, 37% met major depressive disorder criteria. Male veterans who in 1987 still met criteria for PTSD were twice as likely to have died than the comparator group of veterans without PTSD. Two-thirds of veterans with PTSD from war zone exposure discussed behavioral health or substance misuse concerns with a health care provider, and 37% of those were receiving VA care.14
Given these disturbing data, perhaps the best way we can pay homage to the aging Vietnam veterans is to support continued research into effective evidence-based treatments for PTSD and funding for the training and recruiting of mental health practitioners to all 3 branches of federal health care who can deliver that care compassionately and competently.
1. The Vietnam War: a new film by Ken Burns and Lynn Novick, to air fall 2017 on PBS. Press release. Updated August 17, 2020. Accessed April 26, 2021. https://www.pbs.org/about/about-pbs/blogs/news/the-vietnam-war-a-new-film-by-ken-burns-and-lynn-novick-to-air-fall-2017-on-pbs
2. The White House Briefing Room. Remarks by President Biden on the more than 500,000 Americans lives lost to COVID-19. Published February 22, 2021. Accessed April 26, 2021.https://www.whitehouse.gov/briefing-room/speeches-remarks/2021/02/22/remarks-by-president-biden-on-the-more-than-500000-american-lives-lost-to-covid-19/
3. US Department of Veterans Affairs. Vantage Point. VA postpones 50th anniversary of the Vietnam War commemoration events. Published March 16, 2021. Accessed April 26, 2021. https://blogs.va.gov/VAntage/72694/va-postpones-50th-anniversary-vietnam-war-commemoration-events
4. US Department of Defense. Nation observes Vietnam War Veterans Day. Published March 29, 2021. Accessed April 26, 2021. https://www.defense.gov/Explore/Features/Story/Article/2545524/nation-observes-vietnam-war-veterans-day
5. The White House. Commemoration of the 50th anniversary of the Vietnam War. Published May 25, 2012. Accessed April 26, 2021. https://obamawhitehouse.archives.gov/the-press-office/2012/05/25/presidential-proclamation-commemoration-50th-anniversary-vietnam-war
6. Vietnam War Veterans Recognition Act. Public Law 115-15. U.S. Government Publishing Office, Washington DC, 2017.
7. Crocq M-A, Crocq L. From shell shock and war neurosis to posttraumatic stress disorder: a history of psychotraumatology. Dialogues Clin Neurosci .2000;2(1):47-55. doi:10.31887/DCNS.2000.2.1/macrocq
8. US Department of Veterans Affairs. History of PTSD in veterans: Civil War to DSM-5. Accessed April 26, 2021. https://www.ptsd.va.gov/understand/what/history_ptsd.asp
9. American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders . Washington, DC: American Psychiatric Association; 1952.
10. Andreasen NC. Posttraumatic stress disorder: a history and a critique. Ann NY Acad Sci. 2010;1208;67-71. doi:10.1111/j.1749-6632.2010.05699.x
11. Shata CF. Post-Vietnam syndrome. The New York Times . Published May 6, 1972. Accessed April 26, 2021. https://www.nytimes.com/1972/05/06/archives/postvietnam-syndrome.html
12. American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders. (DSM-III) . Washington, DC. American Psychiatric Association; 1980.
13. Kinzie JD, Goetz RR. A century of controversy surrounding posttraumatic stress stress: spectrum syndromes: the impact on DSM-III and DSM-IV. J Trauma Stress. 1996;9(2):156-179. doi:10.1007/BF02110653
14. Schlenger WE, Corry NH. Four decades later: Vietnam veterans and PTSD. Published January/February 2015. Accessed April 25, 2021. http://vvaveteran.org/35-1/35-1_longitudinalstudy.html
1. The Vietnam War: a new film by Ken Burns and Lynn Novick, to air fall 2017 on PBS. Press release. Updated August 17, 2020. Accessed April 26, 2021. https://www.pbs.org/about/about-pbs/blogs/news/the-vietnam-war-a-new-film-by-ken-burns-and-lynn-novick-to-air-fall-2017-on-pbs
2. The White House Briefing Room. Remarks by President Biden on the more than 500,000 Americans lives lost to COVID-19. Published February 22, 2021. Accessed April 26, 2021.https://www.whitehouse.gov/briefing-room/speeches-remarks/2021/02/22/remarks-by-president-biden-on-the-more-than-500000-american-lives-lost-to-covid-19/
3. US Department of Veterans Affairs. Vantage Point. VA postpones 50th anniversary of the Vietnam War commemoration events. Published March 16, 2021. Accessed April 26, 2021. https://blogs.va.gov/VAntage/72694/va-postpones-50th-anniversary-vietnam-war-commemoration-events
4. US Department of Defense. Nation observes Vietnam War Veterans Day. Published March 29, 2021. Accessed April 26, 2021. https://www.defense.gov/Explore/Features/Story/Article/2545524/nation-observes-vietnam-war-veterans-day
5. The White House. Commemoration of the 50th anniversary of the Vietnam War. Published May 25, 2012. Accessed April 26, 2021. https://obamawhitehouse.archives.gov/the-press-office/2012/05/25/presidential-proclamation-commemoration-50th-anniversary-vietnam-war
6. Vietnam War Veterans Recognition Act. Public Law 115-15. U.S. Government Publishing Office, Washington DC, 2017.
7. Crocq M-A, Crocq L. From shell shock and war neurosis to posttraumatic stress disorder: a history of psychotraumatology. Dialogues Clin Neurosci .2000;2(1):47-55. doi:10.31887/DCNS.2000.2.1/macrocq
8. US Department of Veterans Affairs. History of PTSD in veterans: Civil War to DSM-5. Accessed April 26, 2021. https://www.ptsd.va.gov/understand/what/history_ptsd.asp
9. American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders . Washington, DC: American Psychiatric Association; 1952.
10. Andreasen NC. Posttraumatic stress disorder: a history and a critique. Ann NY Acad Sci. 2010;1208;67-71. doi:10.1111/j.1749-6632.2010.05699.x
11. Shata CF. Post-Vietnam syndrome. The New York Times . Published May 6, 1972. Accessed April 26, 2021. https://www.nytimes.com/1972/05/06/archives/postvietnam-syndrome.html
12. American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders. (DSM-III) . Washington, DC. American Psychiatric Association; 1980.
13. Kinzie JD, Goetz RR. A century of controversy surrounding posttraumatic stress stress: spectrum syndromes: the impact on DSM-III and DSM-IV. J Trauma Stress. 1996;9(2):156-179. doi:10.1007/BF02110653
14. Schlenger WE, Corry NH. Four decades later: Vietnam veterans and PTSD. Published January/February 2015. Accessed April 25, 2021. http://vvaveteran.org/35-1/35-1_longitudinalstudy.html
Is empathy the limit to sociopathy?
Society is having a moment of reflection about the role of law enforcement and correctional facilities in addressing societal problems. During this moment, psychiatry is being asked by courts to arbitrate who qualifies and ultimately deserves certain judgments.
In particular, we are asked to assess how dangerous an individual may be using violent risk assessment tools and measures of antisocial disorders. As such, we are tasked with pointing out the negative factors of defendants. Alternatively, psychiatry is also asked to explain, using biopsychosocial determinants, what led an individual to act in a deviant manner. As such, we are tasked with pointing out mitigating factors of defendants. In this article, we attempt to look at limitations in both paradigms to encourage a more prudent forensic approach.
Negative factors
The criteria in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM) are not composed of rigid rules with validity markers to measure their veracity but leave room for clinical judgment, variance across individuals, and future research and treatment needs.
There are some benefits to having room for clinical judgment, but it can also lead to overdiagnosis.1 This problem is particularly reflected in the diagnosis of antisocial personality disorder (ASPD), the criteria of which includes failure to conform to social norms, deceitfulness, impulsivity, irritability, recklessness, irresponsibility, and lack of remorse. Each of these criteria is ripe for subjectivity by an inexperienced or biased reviewer.
For example, it is common in our practice to see only two discrete events interpreted as a “pattern of behavior.” Such events could include two lapses in judgment to demonstrate a pattern of behavior meeting the criteria for ASPD. Using this logic, however, most Americans would meet those criteria. According to the National Survey of Drug Use and Health, the majority of Americans have tried illicit substances.2 We presume that many have tried illicit substances at least two times in their lives – in theory creating a pattern – and that subsequently they omitted that information on standard employment application forms. In doing so, they could easily be interpreted in court to have demonstrated failure to follow rules, deceitfulness in wrongfully filing an employment application, impulsivity in deciding to use drugs, recklessness in choosing to use drugs, irresponsibility for using drugs, and a lack of remorse by not acknowledging the use on an employment application, thereby meeting criteria for antisocial personality disorder.
The well-respected Hare Psychopathy Checklist contains similar opportunities for subjective interpretation by a biased evaluator. Conning, glibness, lack of guilt, lack of realistic goals, and irresponsibility are easily diverted to pathologize an individual into an exaggerated sense of menace. Journalist Jon Ronson famously challenged those concepts in his book, “The Psychopath Test: A Journey Through the Madness Industry,” a New York Times bestseller. It is common in our practice to see evaluators list dozens of scales allegedly proving someone’s dangerousness, without realizing the recurrent subjectivity involved in all those assessments.
Forensic evaluators arguing for conviction often rely on violence risk assessments to establish defendants’ propensity for future violence and to predict recidivism. There are numerous violence risk assessment tools, including: the Violence Risk Scale,3 the HCR-20 version 3 (HCR-20 v3),4 and Correctional Offender Management Profiling for Alternative Sanctions (COMPAS). Yet, despite their perceived rigor and reliability from being established assessments, their usefulness continues to be challenged.5Julia Dressel and Hany Farid, PhD, showed in 2018 how people with little to no criminal justice expertise and given only the sex, age, and previous criminal history of defendants were no less accurate than COMPAS.6 Those findings are concerning and should give us pause when we are tempted to rely on seemingly objective measures that can lead us astray. Not only can such reliance result in injudicious court decisions, but it can saddle defendants with a documented report of their perceived elevated risk for violence.
In the forensic setting, ASPD is often treated like a lifelong diagnosis. This is in part because of personality disorders being defined since the DSM-III as “enduring patterns ... [that] continue throughout most of adult life.” Even if a defendant who is diagnosed with ASPD no longer behaves antisocially, a historical ASPD diagnosis is difficult to escape. Historical behavior is part of the diagnosis, and there are no guidelines to determine at what point a person can be rid of it or what redeeming qualities or circumstances make a prior diagnosis inappropriate.
Yet, some evidence suggests that ASPD is one of the least reliable psychiatric diagnoses and that the agreement between providers of such a diagnosis was “questionable.”7Robert D. Hare, PhD, himself has been described as believing that “an awful lot of people misuse his checklist.”8 And a recent study found no “evidence for the claim that [Hare Psychopathy Checklist] psychopaths are untreatable ... on the contrary, there was replicated evidence of positive treatment outcomes.”9 Unfortunately, legal structures often help enshrine an erroneous ASPD diagnosis by imposing more punishing sentences to those diagnosed. Instead, we should recognize that ASPD can also be the culmination of biological as well as changing social and environmental circumstances.
Mitigating factors
On the other side, the defense expert also faces significant challenges, though the tools are different. Contrary to the prosecuting expert who loads an arsenal of subjective assessment tools, the defense expert will point to childhood trauma and mental illness as extenuating explanations for a crime. Having suffered abuse as a child is advanced to justify someone’s subsequent violence. This problem is reflected in the diagnosis of posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD). An unscrupulous expert may simply allow an evaluee to endorse symptoms without clinical correlates or rigorous validation to advance this narrative.
For example, psychiatrists commonly ascribe the DSM criteria A for PTSD, “directly experiencing the traumatic event(s),” to a smaller slight in life. Some experts suggest that a medical diagnosis, even if not life-threatening but perceived as such, could warrant the diagnosis.10 This would expand our understanding of trauma and its consequences significantly. Yet already, a survey of Detroit area residents in 1998 found that 89.6% of the interviewees reported having experienced a significant trauma and that the average number of traumatic experiences was 4.8.11 The meaning of a diagnosis that can be applied to almost 90% of a population has unclear usefulness, especially if meant to diminish guilt and responsibility.
More recently, citing Adverse Childhood Experiences (ACEs) has been a common method of supporting mitigating evaluations. Using the ACEs questionnaires, researchers have supported the idea that social programs are a key player in an improved criminal justice system. The ACEs study identified 10 forms of childhood trauma in 17,000 patients, including abuse, neglect, abandonment, household dysfunction, and exposure to violence, that were strongly associated with negative psychological outcomes, engagement in high-risk behaviors, significant medical consequences, and even early death.12 However, similarly to past trauma, the prevalence of ACEs in the forensic population is the norm, not the exception.
Additional thoughts
Of particular concern is when diagnostic criteria intersect or seemingly contradict one another. For example, acts such as an outburst of anger may be interpreted by one evaluator as a sign of deviance, irritability, or recklessness – and meeting antisocial personality disorder criteria. Whereas another evaluator may interpret the same incident as hypervigilance, exaggerated startle response, or self-destructive behavior in PTSD.
An incident of not assisting someone in need may be interpreted as lack of remorse and glibness from antisocial characteristics or avoidance and detachment from others as a reaction to past trauma. Flashbacks from trauma can be interpreted by some as violent fantasies. Even the experience of trauma can be viewed as a risk factor for future violence. In some ways, our perspectives are influenced by our examination of someone’s history through the lens of sociopathy or empathy.
In summary
Psychiatry is entrusted by courts to comment on negative and mitigating factors. Negative factors hinge in part on our subjective impression of sociopathy, and mitigating factors hinge, in part, on our empathy for a defendant’s trauma. Psychiatry should recognize the limitations of both sides and humble itself in providing balanced evaluations to courts.
Dr. Badre is a clinical and forensic psychiatrist in San Diego. He holds teaching positions at the University of California, San Diego, and the University of San Diego. He teaches medical education, psychopharmacology, ethics in psychiatry, and correctional care. Dr. Badre can be reached at his website, BadreMD.com. Dr. Amendolara is a first-year psychiatry resident at University of California, San Diego. He spent years advocating for survivors of rape and domestic violence at the Crime Victims Treatment Center in New York and conducted public health research at Lourdes Center for Public Health in Camden, N.J. Dr. Amendolara has no disclosures. Dr. Ngo is a second-year child neurology resident at University of California, Los Angeles. She received a master’s degree in narrative medicine from Columbia University, New York. She has no disclosures.
References
1. Frances A. Saving Normal: An Insider’s Revolt Against Out-of-Control Psychiatric Diagnosis, DSM-5, Big Pharma and the Medicalization of Ordinary Life. Harper Collins, 2013.
2. Key Substance Use and Mental Health Indicators in the United States. National Survey on Drug Use and Health. 2018.
3. Wong SCP and Gordon A. Psychol Public Policy Law. 2006;12(3):279-309.
4. Douglas KS et al. Mental Health Law & Policy Institute. About the Historical Clinical Risk Management-20, Version 3.
5. Angwin J et al. ProPublica. 2016 May 23.
6. Dressel J and Farid H. Sci Adv. 2018;4(1). doi: 10.1126/sciady.aao5580.
7. Freedman R et al. Am J Psychiatry. 2013 Jan;170(1):1-5.
8. Lillie B. The complexities of the psychopath test: A Q&A with Ron Jonson. TEDBlog. 2012 Aug 15.
9. Larsen RR et al. Psychol Public Policy Law. 2020;26(3):297-311.
10. Cordova MJ. Psychiatric Times. 2020 Jul 31;37(7).
11. Breslau N et al. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1998;55(7):626-32.
12. Reavis JA et al. Perm J. 2013 Spring;17(2):44-8.
Society is having a moment of reflection about the role of law enforcement and correctional facilities in addressing societal problems. During this moment, psychiatry is being asked by courts to arbitrate who qualifies and ultimately deserves certain judgments.
In particular, we are asked to assess how dangerous an individual may be using violent risk assessment tools and measures of antisocial disorders. As such, we are tasked with pointing out the negative factors of defendants. Alternatively, psychiatry is also asked to explain, using biopsychosocial determinants, what led an individual to act in a deviant manner. As such, we are tasked with pointing out mitigating factors of defendants. In this article, we attempt to look at limitations in both paradigms to encourage a more prudent forensic approach.
Negative factors
The criteria in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM) are not composed of rigid rules with validity markers to measure their veracity but leave room for clinical judgment, variance across individuals, and future research and treatment needs.
There are some benefits to having room for clinical judgment, but it can also lead to overdiagnosis.1 This problem is particularly reflected in the diagnosis of antisocial personality disorder (ASPD), the criteria of which includes failure to conform to social norms, deceitfulness, impulsivity, irritability, recklessness, irresponsibility, and lack of remorse. Each of these criteria is ripe for subjectivity by an inexperienced or biased reviewer.
For example, it is common in our practice to see only two discrete events interpreted as a “pattern of behavior.” Such events could include two lapses in judgment to demonstrate a pattern of behavior meeting the criteria for ASPD. Using this logic, however, most Americans would meet those criteria. According to the National Survey of Drug Use and Health, the majority of Americans have tried illicit substances.2 We presume that many have tried illicit substances at least two times in their lives – in theory creating a pattern – and that subsequently they omitted that information on standard employment application forms. In doing so, they could easily be interpreted in court to have demonstrated failure to follow rules, deceitfulness in wrongfully filing an employment application, impulsivity in deciding to use drugs, recklessness in choosing to use drugs, irresponsibility for using drugs, and a lack of remorse by not acknowledging the use on an employment application, thereby meeting criteria for antisocial personality disorder.
The well-respected Hare Psychopathy Checklist contains similar opportunities for subjective interpretation by a biased evaluator. Conning, glibness, lack of guilt, lack of realistic goals, and irresponsibility are easily diverted to pathologize an individual into an exaggerated sense of menace. Journalist Jon Ronson famously challenged those concepts in his book, “The Psychopath Test: A Journey Through the Madness Industry,” a New York Times bestseller. It is common in our practice to see evaluators list dozens of scales allegedly proving someone’s dangerousness, without realizing the recurrent subjectivity involved in all those assessments.
Forensic evaluators arguing for conviction often rely on violence risk assessments to establish defendants’ propensity for future violence and to predict recidivism. There are numerous violence risk assessment tools, including: the Violence Risk Scale,3 the HCR-20 version 3 (HCR-20 v3),4 and Correctional Offender Management Profiling for Alternative Sanctions (COMPAS). Yet, despite their perceived rigor and reliability from being established assessments, their usefulness continues to be challenged.5Julia Dressel and Hany Farid, PhD, showed in 2018 how people with little to no criminal justice expertise and given only the sex, age, and previous criminal history of defendants were no less accurate than COMPAS.6 Those findings are concerning and should give us pause when we are tempted to rely on seemingly objective measures that can lead us astray. Not only can such reliance result in injudicious court decisions, but it can saddle defendants with a documented report of their perceived elevated risk for violence.
In the forensic setting, ASPD is often treated like a lifelong diagnosis. This is in part because of personality disorders being defined since the DSM-III as “enduring patterns ... [that] continue throughout most of adult life.” Even if a defendant who is diagnosed with ASPD no longer behaves antisocially, a historical ASPD diagnosis is difficult to escape. Historical behavior is part of the diagnosis, and there are no guidelines to determine at what point a person can be rid of it or what redeeming qualities or circumstances make a prior diagnosis inappropriate.
Yet, some evidence suggests that ASPD is one of the least reliable psychiatric diagnoses and that the agreement between providers of such a diagnosis was “questionable.”7Robert D. Hare, PhD, himself has been described as believing that “an awful lot of people misuse his checklist.”8 And a recent study found no “evidence for the claim that [Hare Psychopathy Checklist] psychopaths are untreatable ... on the contrary, there was replicated evidence of positive treatment outcomes.”9 Unfortunately, legal structures often help enshrine an erroneous ASPD diagnosis by imposing more punishing sentences to those diagnosed. Instead, we should recognize that ASPD can also be the culmination of biological as well as changing social and environmental circumstances.
Mitigating factors
On the other side, the defense expert also faces significant challenges, though the tools are different. Contrary to the prosecuting expert who loads an arsenal of subjective assessment tools, the defense expert will point to childhood trauma and mental illness as extenuating explanations for a crime. Having suffered abuse as a child is advanced to justify someone’s subsequent violence. This problem is reflected in the diagnosis of posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD). An unscrupulous expert may simply allow an evaluee to endorse symptoms without clinical correlates or rigorous validation to advance this narrative.
For example, psychiatrists commonly ascribe the DSM criteria A for PTSD, “directly experiencing the traumatic event(s),” to a smaller slight in life. Some experts suggest that a medical diagnosis, even if not life-threatening but perceived as such, could warrant the diagnosis.10 This would expand our understanding of trauma and its consequences significantly. Yet already, a survey of Detroit area residents in 1998 found that 89.6% of the interviewees reported having experienced a significant trauma and that the average number of traumatic experiences was 4.8.11 The meaning of a diagnosis that can be applied to almost 90% of a population has unclear usefulness, especially if meant to diminish guilt and responsibility.
More recently, citing Adverse Childhood Experiences (ACEs) has been a common method of supporting mitigating evaluations. Using the ACEs questionnaires, researchers have supported the idea that social programs are a key player in an improved criminal justice system. The ACEs study identified 10 forms of childhood trauma in 17,000 patients, including abuse, neglect, abandonment, household dysfunction, and exposure to violence, that were strongly associated with negative psychological outcomes, engagement in high-risk behaviors, significant medical consequences, and even early death.12 However, similarly to past trauma, the prevalence of ACEs in the forensic population is the norm, not the exception.
Additional thoughts
Of particular concern is when diagnostic criteria intersect or seemingly contradict one another. For example, acts such as an outburst of anger may be interpreted by one evaluator as a sign of deviance, irritability, or recklessness – and meeting antisocial personality disorder criteria. Whereas another evaluator may interpret the same incident as hypervigilance, exaggerated startle response, or self-destructive behavior in PTSD.
An incident of not assisting someone in need may be interpreted as lack of remorse and glibness from antisocial characteristics or avoidance and detachment from others as a reaction to past trauma. Flashbacks from trauma can be interpreted by some as violent fantasies. Even the experience of trauma can be viewed as a risk factor for future violence. In some ways, our perspectives are influenced by our examination of someone’s history through the lens of sociopathy or empathy.
In summary
Psychiatry is entrusted by courts to comment on negative and mitigating factors. Negative factors hinge in part on our subjective impression of sociopathy, and mitigating factors hinge, in part, on our empathy for a defendant’s trauma. Psychiatry should recognize the limitations of both sides and humble itself in providing balanced evaluations to courts.
Dr. Badre is a clinical and forensic psychiatrist in San Diego. He holds teaching positions at the University of California, San Diego, and the University of San Diego. He teaches medical education, psychopharmacology, ethics in psychiatry, and correctional care. Dr. Badre can be reached at his website, BadreMD.com. Dr. Amendolara is a first-year psychiatry resident at University of California, San Diego. He spent years advocating for survivors of rape and domestic violence at the Crime Victims Treatment Center in New York and conducted public health research at Lourdes Center for Public Health in Camden, N.J. Dr. Amendolara has no disclosures. Dr. Ngo is a second-year child neurology resident at University of California, Los Angeles. She received a master’s degree in narrative medicine from Columbia University, New York. She has no disclosures.
References
1. Frances A. Saving Normal: An Insider’s Revolt Against Out-of-Control Psychiatric Diagnosis, DSM-5, Big Pharma and the Medicalization of Ordinary Life. Harper Collins, 2013.
2. Key Substance Use and Mental Health Indicators in the United States. National Survey on Drug Use and Health. 2018.
3. Wong SCP and Gordon A. Psychol Public Policy Law. 2006;12(3):279-309.
4. Douglas KS et al. Mental Health Law & Policy Institute. About the Historical Clinical Risk Management-20, Version 3.
5. Angwin J et al. ProPublica. 2016 May 23.
6. Dressel J and Farid H. Sci Adv. 2018;4(1). doi: 10.1126/sciady.aao5580.
7. Freedman R et al. Am J Psychiatry. 2013 Jan;170(1):1-5.
8. Lillie B. The complexities of the psychopath test: A Q&A with Ron Jonson. TEDBlog. 2012 Aug 15.
9. Larsen RR et al. Psychol Public Policy Law. 2020;26(3):297-311.
10. Cordova MJ. Psychiatric Times. 2020 Jul 31;37(7).
11. Breslau N et al. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1998;55(7):626-32.
12. Reavis JA et al. Perm J. 2013 Spring;17(2):44-8.
Society is having a moment of reflection about the role of law enforcement and correctional facilities in addressing societal problems. During this moment, psychiatry is being asked by courts to arbitrate who qualifies and ultimately deserves certain judgments.
In particular, we are asked to assess how dangerous an individual may be using violent risk assessment tools and measures of antisocial disorders. As such, we are tasked with pointing out the negative factors of defendants. Alternatively, psychiatry is also asked to explain, using biopsychosocial determinants, what led an individual to act in a deviant manner. As such, we are tasked with pointing out mitigating factors of defendants. In this article, we attempt to look at limitations in both paradigms to encourage a more prudent forensic approach.
Negative factors
The criteria in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM) are not composed of rigid rules with validity markers to measure their veracity but leave room for clinical judgment, variance across individuals, and future research and treatment needs.
There are some benefits to having room for clinical judgment, but it can also lead to overdiagnosis.1 This problem is particularly reflected in the diagnosis of antisocial personality disorder (ASPD), the criteria of which includes failure to conform to social norms, deceitfulness, impulsivity, irritability, recklessness, irresponsibility, and lack of remorse. Each of these criteria is ripe for subjectivity by an inexperienced or biased reviewer.
For example, it is common in our practice to see only two discrete events interpreted as a “pattern of behavior.” Such events could include two lapses in judgment to demonstrate a pattern of behavior meeting the criteria for ASPD. Using this logic, however, most Americans would meet those criteria. According to the National Survey of Drug Use and Health, the majority of Americans have tried illicit substances.2 We presume that many have tried illicit substances at least two times in their lives – in theory creating a pattern – and that subsequently they omitted that information on standard employment application forms. In doing so, they could easily be interpreted in court to have demonstrated failure to follow rules, deceitfulness in wrongfully filing an employment application, impulsivity in deciding to use drugs, recklessness in choosing to use drugs, irresponsibility for using drugs, and a lack of remorse by not acknowledging the use on an employment application, thereby meeting criteria for antisocial personality disorder.
The well-respected Hare Psychopathy Checklist contains similar opportunities for subjective interpretation by a biased evaluator. Conning, glibness, lack of guilt, lack of realistic goals, and irresponsibility are easily diverted to pathologize an individual into an exaggerated sense of menace. Journalist Jon Ronson famously challenged those concepts in his book, “The Psychopath Test: A Journey Through the Madness Industry,” a New York Times bestseller. It is common in our practice to see evaluators list dozens of scales allegedly proving someone’s dangerousness, without realizing the recurrent subjectivity involved in all those assessments.
Forensic evaluators arguing for conviction often rely on violence risk assessments to establish defendants’ propensity for future violence and to predict recidivism. There are numerous violence risk assessment tools, including: the Violence Risk Scale,3 the HCR-20 version 3 (HCR-20 v3),4 and Correctional Offender Management Profiling for Alternative Sanctions (COMPAS). Yet, despite their perceived rigor and reliability from being established assessments, their usefulness continues to be challenged.5Julia Dressel and Hany Farid, PhD, showed in 2018 how people with little to no criminal justice expertise and given only the sex, age, and previous criminal history of defendants were no less accurate than COMPAS.6 Those findings are concerning and should give us pause when we are tempted to rely on seemingly objective measures that can lead us astray. Not only can such reliance result in injudicious court decisions, but it can saddle defendants with a documented report of their perceived elevated risk for violence.
In the forensic setting, ASPD is often treated like a lifelong diagnosis. This is in part because of personality disorders being defined since the DSM-III as “enduring patterns ... [that] continue throughout most of adult life.” Even if a defendant who is diagnosed with ASPD no longer behaves antisocially, a historical ASPD diagnosis is difficult to escape. Historical behavior is part of the diagnosis, and there are no guidelines to determine at what point a person can be rid of it or what redeeming qualities or circumstances make a prior diagnosis inappropriate.
Yet, some evidence suggests that ASPD is one of the least reliable psychiatric diagnoses and that the agreement between providers of such a diagnosis was “questionable.”7Robert D. Hare, PhD, himself has been described as believing that “an awful lot of people misuse his checklist.”8 And a recent study found no “evidence for the claim that [Hare Psychopathy Checklist] psychopaths are untreatable ... on the contrary, there was replicated evidence of positive treatment outcomes.”9 Unfortunately, legal structures often help enshrine an erroneous ASPD diagnosis by imposing more punishing sentences to those diagnosed. Instead, we should recognize that ASPD can also be the culmination of biological as well as changing social and environmental circumstances.
Mitigating factors
On the other side, the defense expert also faces significant challenges, though the tools are different. Contrary to the prosecuting expert who loads an arsenal of subjective assessment tools, the defense expert will point to childhood trauma and mental illness as extenuating explanations for a crime. Having suffered abuse as a child is advanced to justify someone’s subsequent violence. This problem is reflected in the diagnosis of posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD). An unscrupulous expert may simply allow an evaluee to endorse symptoms without clinical correlates or rigorous validation to advance this narrative.
For example, psychiatrists commonly ascribe the DSM criteria A for PTSD, “directly experiencing the traumatic event(s),” to a smaller slight in life. Some experts suggest that a medical diagnosis, even if not life-threatening but perceived as such, could warrant the diagnosis.10 This would expand our understanding of trauma and its consequences significantly. Yet already, a survey of Detroit area residents in 1998 found that 89.6% of the interviewees reported having experienced a significant trauma and that the average number of traumatic experiences was 4.8.11 The meaning of a diagnosis that can be applied to almost 90% of a population has unclear usefulness, especially if meant to diminish guilt and responsibility.
More recently, citing Adverse Childhood Experiences (ACEs) has been a common method of supporting mitigating evaluations. Using the ACEs questionnaires, researchers have supported the idea that social programs are a key player in an improved criminal justice system. The ACEs study identified 10 forms of childhood trauma in 17,000 patients, including abuse, neglect, abandonment, household dysfunction, and exposure to violence, that were strongly associated with negative psychological outcomes, engagement in high-risk behaviors, significant medical consequences, and even early death.12 However, similarly to past trauma, the prevalence of ACEs in the forensic population is the norm, not the exception.
Additional thoughts
Of particular concern is when diagnostic criteria intersect or seemingly contradict one another. For example, acts such as an outburst of anger may be interpreted by one evaluator as a sign of deviance, irritability, or recklessness – and meeting antisocial personality disorder criteria. Whereas another evaluator may interpret the same incident as hypervigilance, exaggerated startle response, or self-destructive behavior in PTSD.
An incident of not assisting someone in need may be interpreted as lack of remorse and glibness from antisocial characteristics or avoidance and detachment from others as a reaction to past trauma. Flashbacks from trauma can be interpreted by some as violent fantasies. Even the experience of trauma can be viewed as a risk factor for future violence. In some ways, our perspectives are influenced by our examination of someone’s history through the lens of sociopathy or empathy.
In summary
Psychiatry is entrusted by courts to comment on negative and mitigating factors. Negative factors hinge in part on our subjective impression of sociopathy, and mitigating factors hinge, in part, on our empathy for a defendant’s trauma. Psychiatry should recognize the limitations of both sides and humble itself in providing balanced evaluations to courts.
Dr. Badre is a clinical and forensic psychiatrist in San Diego. He holds teaching positions at the University of California, San Diego, and the University of San Diego. He teaches medical education, psychopharmacology, ethics in psychiatry, and correctional care. Dr. Badre can be reached at his website, BadreMD.com. Dr. Amendolara is a first-year psychiatry resident at University of California, San Diego. He spent years advocating for survivors of rape and domestic violence at the Crime Victims Treatment Center in New York and conducted public health research at Lourdes Center for Public Health in Camden, N.J. Dr. Amendolara has no disclosures. Dr. Ngo is a second-year child neurology resident at University of California, Los Angeles. She received a master’s degree in narrative medicine from Columbia University, New York. She has no disclosures.
References
1. Frances A. Saving Normal: An Insider’s Revolt Against Out-of-Control Psychiatric Diagnosis, DSM-5, Big Pharma and the Medicalization of Ordinary Life. Harper Collins, 2013.
2. Key Substance Use and Mental Health Indicators in the United States. National Survey on Drug Use and Health. 2018.
3. Wong SCP and Gordon A. Psychol Public Policy Law. 2006;12(3):279-309.
4. Douglas KS et al. Mental Health Law & Policy Institute. About the Historical Clinical Risk Management-20, Version 3.
5. Angwin J et al. ProPublica. 2016 May 23.
6. Dressel J and Farid H. Sci Adv. 2018;4(1). doi: 10.1126/sciady.aao5580.
7. Freedman R et al. Am J Psychiatry. 2013 Jan;170(1):1-5.
8. Lillie B. The complexities of the psychopath test: A Q&A with Ron Jonson. TEDBlog. 2012 Aug 15.
9. Larsen RR et al. Psychol Public Policy Law. 2020;26(3):297-311.
10. Cordova MJ. Psychiatric Times. 2020 Jul 31;37(7).
11. Breslau N et al. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1998;55(7):626-32.
12. Reavis JA et al. Perm J. 2013 Spring;17(2):44-8.
Support group for Asian Americans uses theater to cope with COVID
An online, culturally based peer support group that uses theater and other creative outlets is helping Asian Americans cope with the COVID-19 pandemic, new research shows.
The findings of the qualitative study suggest that the program could be a model to support the mental health of other minority community groups during the COVID pandemic and beyond, say investigators from the Yale University Child Study Center, New Haven, Conn.
The Yale Compassionate Home, Action Together (CHATogether) group was created to promote emotional wellness among Asian American youth, young adults, and their families.
Early in the pandemic, it expanded its purpose to serve as a COVID-19 support group. Through social media outreach, CHATogether encourages members to cope with COVID-19 by using productive and creative outlets.
“We are a community education program serving Asian American families,” said Eunice Yuen, MD, PhD, the program’s founder and director, who is with the Yale University Child Study Center.
“ such as family conflict and xenophobic attacks,” said Dr. Yuen.
She discussed the program at the annual meeting of the American Psychiatric Association, which was held as a virtual live event.
Skits, role playing
CHATogether groups consist of people with similar experiences and challenges who support each other through weekly online group meetings, she explained.
Group members work together to create family conflict scenarios and role-play dialogues on topics amplified during the COVID-19 pandemic, such as cross-cultural challenges among Asian Americans, academic expectations in home schooling, and Black Lives Matter and LGBTQ conflicts within Asian families.
Group members create skits that are based on their personal experiences and that allow them to work through their own internal conflicts and gain a sense of agency, said Dr. Yuen.
“CHATogether is really the interface of mental health, art, and theater, and we’re trying to create a vehicle that can be a lighthearted way for people to talk about mental health, especially for Asian American families,” said Dr. Yuen.
Preliminary results from a focus group with 10 CHATogether members who joined the program since the pandemic started identified four major ways in which the program has had a positive impact on the mental health and well-being of participants:
- It provides a safe and supportive environment, strengthens bonds between members, and increases the sense of belonging, thus encouraging engagement.
- It provides structural consistency/stability through regular meetings and consistent group functions. Weekly meetings provide a sense of control and hope in the midst of uncertainty during periods of sheltering in place.
- Through adapting the group to virtual platforms, group members experience the inherent strengths of a growth mindset and cognitive flexibility when facing challenges.
- It supports healthy coping skills through sublimation and altruism.
Looking ahead, Dr. Yuen said, the team plans to investigate the validity and effectiveness of this model and to expand the group to include other minorities, school educators, and medical education for trainees and medical students.
Commenting on the program, briefing moderator Jeffrey Borenstein, MD, president and CEO of the Brain and Behavior Research Foundation and editor-in-chief of Psychiatric News, described the initiative as a “great project that serves as a model that can be used not only for Asian Americans but for other groups.
“I think the key to it is that cultural sensitivity that we need to really take into account and cultural differences among people in order to best engage them and help support them. I think this program does that beautifully,” said Dr. Borenstein.
The work was supported by the APA’s Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration Minority Fellowship, which provides a 1-year fellowship to psychiatry residents committed to addressing minority psychiatric mental health issues. Dr. Yuen and Dr. Borenstein disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
An online, culturally based peer support group that uses theater and other creative outlets is helping Asian Americans cope with the COVID-19 pandemic, new research shows.
The findings of the qualitative study suggest that the program could be a model to support the mental health of other minority community groups during the COVID pandemic and beyond, say investigators from the Yale University Child Study Center, New Haven, Conn.
The Yale Compassionate Home, Action Together (CHATogether) group was created to promote emotional wellness among Asian American youth, young adults, and their families.
Early in the pandemic, it expanded its purpose to serve as a COVID-19 support group. Through social media outreach, CHATogether encourages members to cope with COVID-19 by using productive and creative outlets.
“We are a community education program serving Asian American families,” said Eunice Yuen, MD, PhD, the program’s founder and director, who is with the Yale University Child Study Center.
“ such as family conflict and xenophobic attacks,” said Dr. Yuen.
She discussed the program at the annual meeting of the American Psychiatric Association, which was held as a virtual live event.
Skits, role playing
CHATogether groups consist of people with similar experiences and challenges who support each other through weekly online group meetings, she explained.
Group members work together to create family conflict scenarios and role-play dialogues on topics amplified during the COVID-19 pandemic, such as cross-cultural challenges among Asian Americans, academic expectations in home schooling, and Black Lives Matter and LGBTQ conflicts within Asian families.
Group members create skits that are based on their personal experiences and that allow them to work through their own internal conflicts and gain a sense of agency, said Dr. Yuen.
“CHATogether is really the interface of mental health, art, and theater, and we’re trying to create a vehicle that can be a lighthearted way for people to talk about mental health, especially for Asian American families,” said Dr. Yuen.
Preliminary results from a focus group with 10 CHATogether members who joined the program since the pandemic started identified four major ways in which the program has had a positive impact on the mental health and well-being of participants:
- It provides a safe and supportive environment, strengthens bonds between members, and increases the sense of belonging, thus encouraging engagement.
- It provides structural consistency/stability through regular meetings and consistent group functions. Weekly meetings provide a sense of control and hope in the midst of uncertainty during periods of sheltering in place.
- Through adapting the group to virtual platforms, group members experience the inherent strengths of a growth mindset and cognitive flexibility when facing challenges.
- It supports healthy coping skills through sublimation and altruism.
Looking ahead, Dr. Yuen said, the team plans to investigate the validity and effectiveness of this model and to expand the group to include other minorities, school educators, and medical education for trainees and medical students.
Commenting on the program, briefing moderator Jeffrey Borenstein, MD, president and CEO of the Brain and Behavior Research Foundation and editor-in-chief of Psychiatric News, described the initiative as a “great project that serves as a model that can be used not only for Asian Americans but for other groups.
“I think the key to it is that cultural sensitivity that we need to really take into account and cultural differences among people in order to best engage them and help support them. I think this program does that beautifully,” said Dr. Borenstein.
The work was supported by the APA’s Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration Minority Fellowship, which provides a 1-year fellowship to psychiatry residents committed to addressing minority psychiatric mental health issues. Dr. Yuen and Dr. Borenstein disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
An online, culturally based peer support group that uses theater and other creative outlets is helping Asian Americans cope with the COVID-19 pandemic, new research shows.
The findings of the qualitative study suggest that the program could be a model to support the mental health of other minority community groups during the COVID pandemic and beyond, say investigators from the Yale University Child Study Center, New Haven, Conn.
The Yale Compassionate Home, Action Together (CHATogether) group was created to promote emotional wellness among Asian American youth, young adults, and their families.
Early in the pandemic, it expanded its purpose to serve as a COVID-19 support group. Through social media outreach, CHATogether encourages members to cope with COVID-19 by using productive and creative outlets.
“We are a community education program serving Asian American families,” said Eunice Yuen, MD, PhD, the program’s founder and director, who is with the Yale University Child Study Center.
“ such as family conflict and xenophobic attacks,” said Dr. Yuen.
She discussed the program at the annual meeting of the American Psychiatric Association, which was held as a virtual live event.
Skits, role playing
CHATogether groups consist of people with similar experiences and challenges who support each other through weekly online group meetings, she explained.
Group members work together to create family conflict scenarios and role-play dialogues on topics amplified during the COVID-19 pandemic, such as cross-cultural challenges among Asian Americans, academic expectations in home schooling, and Black Lives Matter and LGBTQ conflicts within Asian families.
Group members create skits that are based on their personal experiences and that allow them to work through their own internal conflicts and gain a sense of agency, said Dr. Yuen.
“CHATogether is really the interface of mental health, art, and theater, and we’re trying to create a vehicle that can be a lighthearted way for people to talk about mental health, especially for Asian American families,” said Dr. Yuen.
Preliminary results from a focus group with 10 CHATogether members who joined the program since the pandemic started identified four major ways in which the program has had a positive impact on the mental health and well-being of participants:
- It provides a safe and supportive environment, strengthens bonds between members, and increases the sense of belonging, thus encouraging engagement.
- It provides structural consistency/stability through regular meetings and consistent group functions. Weekly meetings provide a sense of control and hope in the midst of uncertainty during periods of sheltering in place.
- Through adapting the group to virtual platforms, group members experience the inherent strengths of a growth mindset and cognitive flexibility when facing challenges.
- It supports healthy coping skills through sublimation and altruism.
Looking ahead, Dr. Yuen said, the team plans to investigate the validity and effectiveness of this model and to expand the group to include other minorities, school educators, and medical education for trainees and medical students.
Commenting on the program, briefing moderator Jeffrey Borenstein, MD, president and CEO of the Brain and Behavior Research Foundation and editor-in-chief of Psychiatric News, described the initiative as a “great project that serves as a model that can be used not only for Asian Americans but for other groups.
“I think the key to it is that cultural sensitivity that we need to really take into account and cultural differences among people in order to best engage them and help support them. I think this program does that beautifully,” said Dr. Borenstein.
The work was supported by the APA’s Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration Minority Fellowship, which provides a 1-year fellowship to psychiatry residents committed to addressing minority psychiatric mental health issues. Dr. Yuen and Dr. Borenstein disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Structural racism tied to psychosis risk in Black people
Social and economic disparities are linked to an increased risk for psychosis in Black and Latino communities, new research shows.
Results of a literature review of social and economic disparities in mental illness suggest that “structural racism” contributes to social and environmental conditions that affect psychosis risk.
“Black and Latino people suffer disproportionately from psychosis risk factors, at the neighborhood level and at the individual level, in large part as a result of structural racism,” study investigator Deidre M. Anglin, PhD, associate professor, department of psychology, City College of New York (N.Y.), told reporters attending a press briefing.
The social environment, which, for minorities, involves disadvantage and discrimination, may account for this increased psychosis risk, perhaps even more so than genetics, she said. Structural racism “is a critical public health threat,” Dr. Anglin added.
The findings were presented at the virtual American Psychiatric Association annual meeting and were simultaneously published online May 3 in The American Journal of Psychiatry.
Perpetual disadvantage
Dr. Anglin and colleagues examined U.S.-based evidence connecting characteristics of social environments with outcomes across the psychosis continuum – from psychotic experiences to schizophrenia.
Citing numerous studies, the researchers highlighted three key areas that reflect social and environmental conditions that may affect psychosis risk, and that disproportionately affect minorities. These were neighborhood factors, trauma in a U.S. context, and racial disparities during the prenatal and perinatal periods.
The data that were related to neighborhoods revealed “just how much racism has historically structured U.S. neighborhoods in ways that generationally perpetuate disadvantage for racially minoritized communities,” said Dr. Anglin.
“This happens through inequitable access to resources, such as health care, clean air, education, [and] employment, but also in terms of disproportionate exposure to environmental toxins and stressors,” she said.
These neighborhood factors are associated with cumulative stress that may be linked to heightened risk for psychosis, the investigators noted.
U.S. studies show that rates of adverse childhood experiences, such as abuse and emotional and physical neglect, are higher among racial and ethnic minorities.
Police victimization and gun violence disproportionately affect racial minorities and create what the investigators call “a unique type of collective trauma” in the United States. They note that Black men have a 1 in 1,000 chance of being victims of lethal force by police over their lifetimes. By comparison, White men have a 39 in 100,000 chance.
One study of a diverse sample from four large U.S. urban centers showed that those who self-reported different types of police victimization were more likely to report psychotic experiences. Another study showed that greater exposure to gun violence fatalities, regardless of police involvement, was positively associated with psychotic experiences.
Obstetric complications
A variety of obstetric complications, including infection, maternal inflammation, and stress, have been associated with increased risk for psychotic disorders in U.S. samples.
“What we saw emerge from the literature is that Black women in the U.S. are at substantially increased risk for many of these obstetrical complications compared to White women, and this is not necessarily explained by socioeconomic status,” said Dr. Anglin.
Neighborhood- and individual-level factors appear to affect the disparity in these outcomes. A recent study revealed that exposure to environmental contaminants such as air pollution is associated with higher rates of preterm birth and low birth weight differentially in Black mothers compared with other mothers, “possibly as a result of an interaction between prenatal stress and contaminants,” the investigators noted.
Research also indicates that Black women are more likely to have lower levels of cortisol during the second trimester of pregnancy compared with women of other racial and ethnic groups. Cortisol is essential for fetal growth. Evidence links lower cortisol levels in later stages of pregnancy with decreased fetal growth in individuals who develop schizophrenia.
, compared with White women of the same socioeconomic status.
Such findings “highlight a complex picture” involving maternal cortisol levels and other stress biomarkers, “potentially leading to poor birth outcomes and subsequent risk for psychotic disorders in adulthood,” the investigators noted.
The researchers call for the dismantling of structural racism and the social policies and norms it shapes. They also recommend changes in health care policy and in the approach to early intervention for psychosis among Black and other racially-minoritized groups.
“Altogether, the current evidence suggests the need to identify, address, and tackle the social determinants deeply ingrained in U.S. society, in tandem with empowering the most marginalized communities,” the researchers wrote.
“We recommend that the field of psychiatry devote considerably more effort to addressing structural racism and social determinants of psychosis in funding priorities, training, and intervention development,” they added.
Dr. Anglin suggests that mental health providers use what she called a “cultural formulation interview” that takes a person’s environmental and social context into consideration. Studies show that incorporating this into clinical practice helps reduce misdiagnosis of mental illness in Black populations, she said.
Call to action
Commenting on the findings in an interview, Ned H. Kalin, MD, editor of The American Journal of Psychiatry and professor and chair of the department of psychiatry, University of Wisconsin, Madison, said the study was well done and serves as a “call to action” to address the impact of structural racism on mental health issues and psychiatric diseases.
The article highlights the need for “collecting better data” on structural racism, said Dr. Kalin. “We know it’s a big issue, but we can’t even quantitate it, so we need some fundamental measures to use as a benchmark as we move forward, as we try to make change.”
He noted that racism “is so embedded in one’s experience and in our society that we sort of don’t even think about it as a trauma.”
In psychiatry, for example, trauma is often thought of as a loss or a traumatic event. “We don’t typically think of trauma as an experience that pervades one’s entire life,” but that needs to change, he said. “At the individual level and in the doctor’s office, being sensitive to and aware of these issues is absolutely critical.”
Dr. Anglin and Dr. Kalin have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Social and economic disparities are linked to an increased risk for psychosis in Black and Latino communities, new research shows.
Results of a literature review of social and economic disparities in mental illness suggest that “structural racism” contributes to social and environmental conditions that affect psychosis risk.
“Black and Latino people suffer disproportionately from psychosis risk factors, at the neighborhood level and at the individual level, in large part as a result of structural racism,” study investigator Deidre M. Anglin, PhD, associate professor, department of psychology, City College of New York (N.Y.), told reporters attending a press briefing.
The social environment, which, for minorities, involves disadvantage and discrimination, may account for this increased psychosis risk, perhaps even more so than genetics, she said. Structural racism “is a critical public health threat,” Dr. Anglin added.
The findings were presented at the virtual American Psychiatric Association annual meeting and were simultaneously published online May 3 in The American Journal of Psychiatry.
Perpetual disadvantage
Dr. Anglin and colleagues examined U.S.-based evidence connecting characteristics of social environments with outcomes across the psychosis continuum – from psychotic experiences to schizophrenia.
Citing numerous studies, the researchers highlighted three key areas that reflect social and environmental conditions that may affect psychosis risk, and that disproportionately affect minorities. These were neighborhood factors, trauma in a U.S. context, and racial disparities during the prenatal and perinatal periods.
The data that were related to neighborhoods revealed “just how much racism has historically structured U.S. neighborhoods in ways that generationally perpetuate disadvantage for racially minoritized communities,” said Dr. Anglin.
“This happens through inequitable access to resources, such as health care, clean air, education, [and] employment, but also in terms of disproportionate exposure to environmental toxins and stressors,” she said.
These neighborhood factors are associated with cumulative stress that may be linked to heightened risk for psychosis, the investigators noted.
U.S. studies show that rates of adverse childhood experiences, such as abuse and emotional and physical neglect, are higher among racial and ethnic minorities.
Police victimization and gun violence disproportionately affect racial minorities and create what the investigators call “a unique type of collective trauma” in the United States. They note that Black men have a 1 in 1,000 chance of being victims of lethal force by police over their lifetimes. By comparison, White men have a 39 in 100,000 chance.
One study of a diverse sample from four large U.S. urban centers showed that those who self-reported different types of police victimization were more likely to report psychotic experiences. Another study showed that greater exposure to gun violence fatalities, regardless of police involvement, was positively associated with psychotic experiences.
Obstetric complications
A variety of obstetric complications, including infection, maternal inflammation, and stress, have been associated with increased risk for psychotic disorders in U.S. samples.
“What we saw emerge from the literature is that Black women in the U.S. are at substantially increased risk for many of these obstetrical complications compared to White women, and this is not necessarily explained by socioeconomic status,” said Dr. Anglin.
Neighborhood- and individual-level factors appear to affect the disparity in these outcomes. A recent study revealed that exposure to environmental contaminants such as air pollution is associated with higher rates of preterm birth and low birth weight differentially in Black mothers compared with other mothers, “possibly as a result of an interaction between prenatal stress and contaminants,” the investigators noted.
Research also indicates that Black women are more likely to have lower levels of cortisol during the second trimester of pregnancy compared with women of other racial and ethnic groups. Cortisol is essential for fetal growth. Evidence links lower cortisol levels in later stages of pregnancy with decreased fetal growth in individuals who develop schizophrenia.
, compared with White women of the same socioeconomic status.
Such findings “highlight a complex picture” involving maternal cortisol levels and other stress biomarkers, “potentially leading to poor birth outcomes and subsequent risk for psychotic disorders in adulthood,” the investigators noted.
The researchers call for the dismantling of structural racism and the social policies and norms it shapes. They also recommend changes in health care policy and in the approach to early intervention for psychosis among Black and other racially-minoritized groups.
“Altogether, the current evidence suggests the need to identify, address, and tackle the social determinants deeply ingrained in U.S. society, in tandem with empowering the most marginalized communities,” the researchers wrote.
“We recommend that the field of psychiatry devote considerably more effort to addressing structural racism and social determinants of psychosis in funding priorities, training, and intervention development,” they added.
Dr. Anglin suggests that mental health providers use what she called a “cultural formulation interview” that takes a person’s environmental and social context into consideration. Studies show that incorporating this into clinical practice helps reduce misdiagnosis of mental illness in Black populations, she said.
Call to action
Commenting on the findings in an interview, Ned H. Kalin, MD, editor of The American Journal of Psychiatry and professor and chair of the department of psychiatry, University of Wisconsin, Madison, said the study was well done and serves as a “call to action” to address the impact of structural racism on mental health issues and psychiatric diseases.
The article highlights the need for “collecting better data” on structural racism, said Dr. Kalin. “We know it’s a big issue, but we can’t even quantitate it, so we need some fundamental measures to use as a benchmark as we move forward, as we try to make change.”
He noted that racism “is so embedded in one’s experience and in our society that we sort of don’t even think about it as a trauma.”
In psychiatry, for example, trauma is often thought of as a loss or a traumatic event. “We don’t typically think of trauma as an experience that pervades one’s entire life,” but that needs to change, he said. “At the individual level and in the doctor’s office, being sensitive to and aware of these issues is absolutely critical.”
Dr. Anglin and Dr. Kalin have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Social and economic disparities are linked to an increased risk for psychosis in Black and Latino communities, new research shows.
Results of a literature review of social and economic disparities in mental illness suggest that “structural racism” contributes to social and environmental conditions that affect psychosis risk.
“Black and Latino people suffer disproportionately from psychosis risk factors, at the neighborhood level and at the individual level, in large part as a result of structural racism,” study investigator Deidre M. Anglin, PhD, associate professor, department of psychology, City College of New York (N.Y.), told reporters attending a press briefing.
The social environment, which, for minorities, involves disadvantage and discrimination, may account for this increased psychosis risk, perhaps even more so than genetics, she said. Structural racism “is a critical public health threat,” Dr. Anglin added.
The findings were presented at the virtual American Psychiatric Association annual meeting and were simultaneously published online May 3 in The American Journal of Psychiatry.
Perpetual disadvantage
Dr. Anglin and colleagues examined U.S.-based evidence connecting characteristics of social environments with outcomes across the psychosis continuum – from psychotic experiences to schizophrenia.
Citing numerous studies, the researchers highlighted three key areas that reflect social and environmental conditions that may affect psychosis risk, and that disproportionately affect minorities. These were neighborhood factors, trauma in a U.S. context, and racial disparities during the prenatal and perinatal periods.
The data that were related to neighborhoods revealed “just how much racism has historically structured U.S. neighborhoods in ways that generationally perpetuate disadvantage for racially minoritized communities,” said Dr. Anglin.
“This happens through inequitable access to resources, such as health care, clean air, education, [and] employment, but also in terms of disproportionate exposure to environmental toxins and stressors,” she said.
These neighborhood factors are associated with cumulative stress that may be linked to heightened risk for psychosis, the investigators noted.
U.S. studies show that rates of adverse childhood experiences, such as abuse and emotional and physical neglect, are higher among racial and ethnic minorities.
Police victimization and gun violence disproportionately affect racial minorities and create what the investigators call “a unique type of collective trauma” in the United States. They note that Black men have a 1 in 1,000 chance of being victims of lethal force by police over their lifetimes. By comparison, White men have a 39 in 100,000 chance.
One study of a diverse sample from four large U.S. urban centers showed that those who self-reported different types of police victimization were more likely to report psychotic experiences. Another study showed that greater exposure to gun violence fatalities, regardless of police involvement, was positively associated with psychotic experiences.
Obstetric complications
A variety of obstetric complications, including infection, maternal inflammation, and stress, have been associated with increased risk for psychotic disorders in U.S. samples.
“What we saw emerge from the literature is that Black women in the U.S. are at substantially increased risk for many of these obstetrical complications compared to White women, and this is not necessarily explained by socioeconomic status,” said Dr. Anglin.
Neighborhood- and individual-level factors appear to affect the disparity in these outcomes. A recent study revealed that exposure to environmental contaminants such as air pollution is associated with higher rates of preterm birth and low birth weight differentially in Black mothers compared with other mothers, “possibly as a result of an interaction between prenatal stress and contaminants,” the investigators noted.
Research also indicates that Black women are more likely to have lower levels of cortisol during the second trimester of pregnancy compared with women of other racial and ethnic groups. Cortisol is essential for fetal growth. Evidence links lower cortisol levels in later stages of pregnancy with decreased fetal growth in individuals who develop schizophrenia.
, compared with White women of the same socioeconomic status.
Such findings “highlight a complex picture” involving maternal cortisol levels and other stress biomarkers, “potentially leading to poor birth outcomes and subsequent risk for psychotic disorders in adulthood,” the investigators noted.
The researchers call for the dismantling of structural racism and the social policies and norms it shapes. They also recommend changes in health care policy and in the approach to early intervention for psychosis among Black and other racially-minoritized groups.
“Altogether, the current evidence suggests the need to identify, address, and tackle the social determinants deeply ingrained in U.S. society, in tandem with empowering the most marginalized communities,” the researchers wrote.
“We recommend that the field of psychiatry devote considerably more effort to addressing structural racism and social determinants of psychosis in funding priorities, training, and intervention development,” they added.
Dr. Anglin suggests that mental health providers use what she called a “cultural formulation interview” that takes a person’s environmental and social context into consideration. Studies show that incorporating this into clinical practice helps reduce misdiagnosis of mental illness in Black populations, she said.
Call to action
Commenting on the findings in an interview, Ned H. Kalin, MD, editor of The American Journal of Psychiatry and professor and chair of the department of psychiatry, University of Wisconsin, Madison, said the study was well done and serves as a “call to action” to address the impact of structural racism on mental health issues and psychiatric diseases.
The article highlights the need for “collecting better data” on structural racism, said Dr. Kalin. “We know it’s a big issue, but we can’t even quantitate it, so we need some fundamental measures to use as a benchmark as we move forward, as we try to make change.”
He noted that racism “is so embedded in one’s experience and in our society that we sort of don’t even think about it as a trauma.”
In psychiatry, for example, trauma is often thought of as a loss or a traumatic event. “We don’t typically think of trauma as an experience that pervades one’s entire life,” but that needs to change, he said. “At the individual level and in the doctor’s office, being sensitive to and aware of these issues is absolutely critical.”
Dr. Anglin and Dr. Kalin have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.