User login
Cardiology News is an independent news source that provides cardiologists with timely and relevant news and commentary about clinical developments and the impact of health care policy on cardiology and the cardiologist's practice. Cardiology News Digital Network is the online destination and multimedia properties of Cardiology News, the independent news publication for cardiologists. Cardiology news is the leading source of news and commentary about clinical developments in cardiology as well as health care policy and regulations that affect the cardiologist's practice. Cardiology News Digital Network is owned by Frontline Medical Communications.
Patient Navigators for Serious Illnesses Can Now Bill Under New Medicare Codes
In a move that acknowledges the gauntlet the US health system poses for people facing serious and fatal illnesses, Medicare will pay for a new class of workers to help patients manage treatments for conditions like cancer and heart failure.
The 2024 Medicare physician fee schedule includes new billing codes, including G0023, to pay for 60 minutes a month of care coordination by certified or trained auxiliary personnel working under the direction of a clinician.
A diagnosis of cancer or another serious illness takes a toll beyond the physical effects of the disease. Patients often scramble to make adjustments in family and work schedules to manage treatment, said Samyukta Mullangi, MD, MBA, medical director of oncology at Thyme Care, a Nashville, Tennessee–based firm that provides navigation and coordination services to oncology practices and insurers.
“It just really does create a bit of a pressure cooker for patients,” Dr. Mullangi told this news organization.
Medicare has for many years paid for medical professionals to help patients cope with the complexities of disease, such as chronic care management (CCM) provided by physicians, nurses, and physician assistants.
The new principal illness navigation (PIN) payments are intended to pay for work that to date typically has been done by people without medical degrees, including those involved in peer support networks and community health programs. The US Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services(CMS) expects these navigators will undergo training and work under the supervision of clinicians.
The new navigators may coordinate care transitions between medical settings, follow up with patients after emergency department (ED) visits, or communicate with skilled nursing facilities regarding the psychosocial needs and functional deficits of a patient, among other functions.
CMS expects the new navigators may:
- Conduct assessments to understand a patient’s life story, strengths, needs, goals, preferences, and desired outcomes, including understanding cultural and linguistic factors.
- Provide support to accomplish the clinician’s treatment plan.
- Coordinate the receipt of needed services from healthcare facilities, home- and community-based service providers, and caregivers.
Peers as Navigators
The new navigators can be former patients who have undergone similar treatments for serious diseases, CMS said. This approach sets the new program apart from other care management services Medicare already covers, program officials wrote in the 2024 physician fee schedule.
“For some conditions, patients are best able to engage with the healthcare system and access care if they have assistance from a single, dedicated individual who has ‘lived experience,’ ” according to the rule.
The agency has taken a broad initial approach in defining what kinds of illnesses a patient may have to qualify for services. Patients must have a serious condition that is expected to last at least 3 months, such as cancer, heart failure, or substance use disorder.
But those without a definitive diagnosis may also qualify to receive navigator services.
In the rule, CMS cited a case in which a CT scan identified a suspicious mass in a patient’s colon. A clinician might decide this person would benefit from navigation services due to the potential risks for an undiagnosed illness.
“Regardless of the definitive diagnosis of the mass, presence of a colonic mass for that patient may be a serious high-risk condition that could, for example, cause obstruction and lead the patient to present to the emergency department, as well as be potentially indicative of an underlying life-threatening illness such as colon cancer,” CMS wrote in the rule.
Navigators often start their work when cancer patients are screened and guide them through initial diagnosis, potential surgery, radiation, or chemotherapy, said Sharon Gentry, MSN, RN, a former nurse navigator who is now the editor in chief of the Journal of the Academy of Oncology Nurse & Patient Navigators.
The navigators are meant to be a trusted and continual presence for patients, who otherwise might be left to start anew in finding help at each phase of care.
The navigators “see the whole picture. They see the whole journey the patient takes, from pre-diagnosis all the way through diagnosis care out through survival,” Ms. Gentry said.
Gaining a special Medicare payment for these kinds of services will elevate this work, she said.
Many newer drugs can target specific mechanisms and proteins of cancer. Often, oncology treatment involves testing to find out if mutations are allowing the cancer cells to evade a patient’s immune system.
Checking these biomarkers takes time, however. Patients sometimes become frustrated because they are anxious to begin treatment. Patients may receive inaccurate information from friends or family who went through treatment previously. Navigators can provide knowledge on the current state of care for a patient’s disease, helping them better manage anxieties.
“You have to explain to them that things have changed since the guy you drink coffee with was diagnosed with cancer, and there may be a drug that could target that,” Ms. Gentry said.
Potential Challenges
Initial uptake of the new PIN codes may be slow going, however, as clinicians and health systems may already use well-established codes. These include CCM and principal care management services, which may pay higher rates, Mullangi said.
“There might be sensitivity around not wanting to cannibalize existing programs with a new program,” Dr. Mullangi said.
In addition, many patients will have a copay for the services of principal illness navigators, Dr. Mullangi said.
While many patients have additional insurance that would cover the service, not all do. People with traditional Medicare coverage can sometimes pay 20% of the cost of some medical services.
“I think that may give patients pause, particularly if they’re already feeling the financial burden of a cancer treatment journey,” Dr. Mullangi said.
Pay rates for PIN services involve calculations of regional price differences, which are posted publicly by CMS, and potential added fees for services provided by hospital-affiliated organizations.
Consider payments for code G0023, covering 60 minutes of principal navigation services provided in a single month.
A set reimbursement for patients cared for in independent medical practices exists, with variation for local costs. Medicare’s non-facility price for G0023 would be $102.41 in some parts of Silicon Valley in California, including San Jose. In Arkansas, where costs are lower, reimbursement would be $73.14 for this same service.
Patients who get services covered by code G0023 in independent medical practices would have monthly copays of about $15-$20, depending on where they live.
The tab for patients tends to be higher for these same services if delivered through a medical practice owned by a hospital, as this would trigger the addition of facility fees to the payments made to cover the services. Facility fees are difficult for the public to ascertain before getting a treatment or service.
Dr. Mullangi and Ms. Gentry reported no relevant financial disclosures outside of their employers.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
In a move that acknowledges the gauntlet the US health system poses for people facing serious and fatal illnesses, Medicare will pay for a new class of workers to help patients manage treatments for conditions like cancer and heart failure.
The 2024 Medicare physician fee schedule includes new billing codes, including G0023, to pay for 60 minutes a month of care coordination by certified or trained auxiliary personnel working under the direction of a clinician.
A diagnosis of cancer or another serious illness takes a toll beyond the physical effects of the disease. Patients often scramble to make adjustments in family and work schedules to manage treatment, said Samyukta Mullangi, MD, MBA, medical director of oncology at Thyme Care, a Nashville, Tennessee–based firm that provides navigation and coordination services to oncology practices and insurers.
“It just really does create a bit of a pressure cooker for patients,” Dr. Mullangi told this news organization.
Medicare has for many years paid for medical professionals to help patients cope with the complexities of disease, such as chronic care management (CCM) provided by physicians, nurses, and physician assistants.
The new principal illness navigation (PIN) payments are intended to pay for work that to date typically has been done by people without medical degrees, including those involved in peer support networks and community health programs. The US Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services(CMS) expects these navigators will undergo training and work under the supervision of clinicians.
The new navigators may coordinate care transitions between medical settings, follow up with patients after emergency department (ED) visits, or communicate with skilled nursing facilities regarding the psychosocial needs and functional deficits of a patient, among other functions.
CMS expects the new navigators may:
- Conduct assessments to understand a patient’s life story, strengths, needs, goals, preferences, and desired outcomes, including understanding cultural and linguistic factors.
- Provide support to accomplish the clinician’s treatment plan.
- Coordinate the receipt of needed services from healthcare facilities, home- and community-based service providers, and caregivers.
Peers as Navigators
The new navigators can be former patients who have undergone similar treatments for serious diseases, CMS said. This approach sets the new program apart from other care management services Medicare already covers, program officials wrote in the 2024 physician fee schedule.
“For some conditions, patients are best able to engage with the healthcare system and access care if they have assistance from a single, dedicated individual who has ‘lived experience,’ ” according to the rule.
The agency has taken a broad initial approach in defining what kinds of illnesses a patient may have to qualify for services. Patients must have a serious condition that is expected to last at least 3 months, such as cancer, heart failure, or substance use disorder.
But those without a definitive diagnosis may also qualify to receive navigator services.
In the rule, CMS cited a case in which a CT scan identified a suspicious mass in a patient’s colon. A clinician might decide this person would benefit from navigation services due to the potential risks for an undiagnosed illness.
“Regardless of the definitive diagnosis of the mass, presence of a colonic mass for that patient may be a serious high-risk condition that could, for example, cause obstruction and lead the patient to present to the emergency department, as well as be potentially indicative of an underlying life-threatening illness such as colon cancer,” CMS wrote in the rule.
Navigators often start their work when cancer patients are screened and guide them through initial diagnosis, potential surgery, radiation, or chemotherapy, said Sharon Gentry, MSN, RN, a former nurse navigator who is now the editor in chief of the Journal of the Academy of Oncology Nurse & Patient Navigators.
The navigators are meant to be a trusted and continual presence for patients, who otherwise might be left to start anew in finding help at each phase of care.
The navigators “see the whole picture. They see the whole journey the patient takes, from pre-diagnosis all the way through diagnosis care out through survival,” Ms. Gentry said.
Gaining a special Medicare payment for these kinds of services will elevate this work, she said.
Many newer drugs can target specific mechanisms and proteins of cancer. Often, oncology treatment involves testing to find out if mutations are allowing the cancer cells to evade a patient’s immune system.
Checking these biomarkers takes time, however. Patients sometimes become frustrated because they are anxious to begin treatment. Patients may receive inaccurate information from friends or family who went through treatment previously. Navigators can provide knowledge on the current state of care for a patient’s disease, helping them better manage anxieties.
“You have to explain to them that things have changed since the guy you drink coffee with was diagnosed with cancer, and there may be a drug that could target that,” Ms. Gentry said.
Potential Challenges
Initial uptake of the new PIN codes may be slow going, however, as clinicians and health systems may already use well-established codes. These include CCM and principal care management services, which may pay higher rates, Mullangi said.
“There might be sensitivity around not wanting to cannibalize existing programs with a new program,” Dr. Mullangi said.
In addition, many patients will have a copay for the services of principal illness navigators, Dr. Mullangi said.
While many patients have additional insurance that would cover the service, not all do. People with traditional Medicare coverage can sometimes pay 20% of the cost of some medical services.
“I think that may give patients pause, particularly if they’re already feeling the financial burden of a cancer treatment journey,” Dr. Mullangi said.
Pay rates for PIN services involve calculations of regional price differences, which are posted publicly by CMS, and potential added fees for services provided by hospital-affiliated organizations.
Consider payments for code G0023, covering 60 minutes of principal navigation services provided in a single month.
A set reimbursement for patients cared for in independent medical practices exists, with variation for local costs. Medicare’s non-facility price for G0023 would be $102.41 in some parts of Silicon Valley in California, including San Jose. In Arkansas, where costs are lower, reimbursement would be $73.14 for this same service.
Patients who get services covered by code G0023 in independent medical practices would have monthly copays of about $15-$20, depending on where they live.
The tab for patients tends to be higher for these same services if delivered through a medical practice owned by a hospital, as this would trigger the addition of facility fees to the payments made to cover the services. Facility fees are difficult for the public to ascertain before getting a treatment or service.
Dr. Mullangi and Ms. Gentry reported no relevant financial disclosures outside of their employers.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
In a move that acknowledges the gauntlet the US health system poses for people facing serious and fatal illnesses, Medicare will pay for a new class of workers to help patients manage treatments for conditions like cancer and heart failure.
The 2024 Medicare physician fee schedule includes new billing codes, including G0023, to pay for 60 minutes a month of care coordination by certified or trained auxiliary personnel working under the direction of a clinician.
A diagnosis of cancer or another serious illness takes a toll beyond the physical effects of the disease. Patients often scramble to make adjustments in family and work schedules to manage treatment, said Samyukta Mullangi, MD, MBA, medical director of oncology at Thyme Care, a Nashville, Tennessee–based firm that provides navigation and coordination services to oncology practices and insurers.
“It just really does create a bit of a pressure cooker for patients,” Dr. Mullangi told this news organization.
Medicare has for many years paid for medical professionals to help patients cope with the complexities of disease, such as chronic care management (CCM) provided by physicians, nurses, and physician assistants.
The new principal illness navigation (PIN) payments are intended to pay for work that to date typically has been done by people without medical degrees, including those involved in peer support networks and community health programs. The US Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services(CMS) expects these navigators will undergo training and work under the supervision of clinicians.
The new navigators may coordinate care transitions between medical settings, follow up with patients after emergency department (ED) visits, or communicate with skilled nursing facilities regarding the psychosocial needs and functional deficits of a patient, among other functions.
CMS expects the new navigators may:
- Conduct assessments to understand a patient’s life story, strengths, needs, goals, preferences, and desired outcomes, including understanding cultural and linguistic factors.
- Provide support to accomplish the clinician’s treatment plan.
- Coordinate the receipt of needed services from healthcare facilities, home- and community-based service providers, and caregivers.
Peers as Navigators
The new navigators can be former patients who have undergone similar treatments for serious diseases, CMS said. This approach sets the new program apart from other care management services Medicare already covers, program officials wrote in the 2024 physician fee schedule.
“For some conditions, patients are best able to engage with the healthcare system and access care if they have assistance from a single, dedicated individual who has ‘lived experience,’ ” according to the rule.
The agency has taken a broad initial approach in defining what kinds of illnesses a patient may have to qualify for services. Patients must have a serious condition that is expected to last at least 3 months, such as cancer, heart failure, or substance use disorder.
But those without a definitive diagnosis may also qualify to receive navigator services.
In the rule, CMS cited a case in which a CT scan identified a suspicious mass in a patient’s colon. A clinician might decide this person would benefit from navigation services due to the potential risks for an undiagnosed illness.
“Regardless of the definitive diagnosis of the mass, presence of a colonic mass for that patient may be a serious high-risk condition that could, for example, cause obstruction and lead the patient to present to the emergency department, as well as be potentially indicative of an underlying life-threatening illness such as colon cancer,” CMS wrote in the rule.
Navigators often start their work when cancer patients are screened and guide them through initial diagnosis, potential surgery, radiation, or chemotherapy, said Sharon Gentry, MSN, RN, a former nurse navigator who is now the editor in chief of the Journal of the Academy of Oncology Nurse & Patient Navigators.
The navigators are meant to be a trusted and continual presence for patients, who otherwise might be left to start anew in finding help at each phase of care.
The navigators “see the whole picture. They see the whole journey the patient takes, from pre-diagnosis all the way through diagnosis care out through survival,” Ms. Gentry said.
Gaining a special Medicare payment for these kinds of services will elevate this work, she said.
Many newer drugs can target specific mechanisms and proteins of cancer. Often, oncology treatment involves testing to find out if mutations are allowing the cancer cells to evade a patient’s immune system.
Checking these biomarkers takes time, however. Patients sometimes become frustrated because they are anxious to begin treatment. Patients may receive inaccurate information from friends or family who went through treatment previously. Navigators can provide knowledge on the current state of care for a patient’s disease, helping them better manage anxieties.
“You have to explain to them that things have changed since the guy you drink coffee with was diagnosed with cancer, and there may be a drug that could target that,” Ms. Gentry said.
Potential Challenges
Initial uptake of the new PIN codes may be slow going, however, as clinicians and health systems may already use well-established codes. These include CCM and principal care management services, which may pay higher rates, Mullangi said.
“There might be sensitivity around not wanting to cannibalize existing programs with a new program,” Dr. Mullangi said.
In addition, many patients will have a copay for the services of principal illness navigators, Dr. Mullangi said.
While many patients have additional insurance that would cover the service, not all do. People with traditional Medicare coverage can sometimes pay 20% of the cost of some medical services.
“I think that may give patients pause, particularly if they’re already feeling the financial burden of a cancer treatment journey,” Dr. Mullangi said.
Pay rates for PIN services involve calculations of regional price differences, which are posted publicly by CMS, and potential added fees for services provided by hospital-affiliated organizations.
Consider payments for code G0023, covering 60 minutes of principal navigation services provided in a single month.
A set reimbursement for patients cared for in independent medical practices exists, with variation for local costs. Medicare’s non-facility price for G0023 would be $102.41 in some parts of Silicon Valley in California, including San Jose. In Arkansas, where costs are lower, reimbursement would be $73.14 for this same service.
Patients who get services covered by code G0023 in independent medical practices would have monthly copays of about $15-$20, depending on where they live.
The tab for patients tends to be higher for these same services if delivered through a medical practice owned by a hospital, as this would trigger the addition of facility fees to the payments made to cover the services. Facility fees are difficult for the public to ascertain before getting a treatment or service.
Dr. Mullangi and Ms. Gentry reported no relevant financial disclosures outside of their employers.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.

Commission Issues ‘Radical Overhaul’ of Obesity Diagnosis
“We propose a radical overhaul of the actual diagnosis of obesity to improve global healthcare and practices and policies. The specific aims were to facilitate individualized assessment and care of people living with obesity while preserving resources by reducing overdiagnosis and unnecessary or inadequate interventions,” Professor Louise Baur, chair of Child & Adolescent Health at the University of Sydney, Australia, said during a UK Science Media Centre (SMC) news briefing.
The report calls first for a diagnosis of obesity via confirmation of excess adiposity using measures such as waist circumference or waist-to-hip ratio in addition to BMI. Next, a clinical assessment of signs and symptoms of organ dysfunction due to obesity and/or functional limitations determines whether the individual has the disease “clinical obesity,” or “preclinical obesity,” a condition of health risk but not an illness itself.
Published on January 14, 2025, in The Lancet Diabetes & Endocrinology, the document also provides broad guidance on management for the two obesity conditions, emphasizing a personalized and stigma-free approach. The Lancet Commission on Obesity comprised 56 experts in relevant fields including endocrinology, surgery, nutrition, and public health, along with people living with obesity.
The report has been endorsed by more than 75 medical organizations, including the Association of British Clinical Diabetologists, the American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists, the American Diabetes Association, the American Heart Association, the Obesity Society, the World Obesity Federation, and obesity and endocrinology societies from countries in Europe, Latin America, Asia, and South Africa.
In recent years, many in the field have found fault with the current BMI-based definition of obesity (> 30 for people of European descent or other cutoffs for specific ethnic groups), primarily because BMI alone doesn’t reflect a person’s fat vs lean mass, fat distribution, or overall health. The new definition aims to overcome these limitations, as well as settle the debate about whether obesity is a “disease.”
“We now have a clinical diagnosis for obesity, which has been lacking. ... The traditional classification based on BMI ... reflects simply whether or not there is excess adiposity, and sometimes not even precise in that regard, either…It has never been a classification that was meant to diagnose a specific illness with its own clinical characteristics in the same way we diagnose any other illness,” Commission Chair Francesco Rubino, MD, professor and chair of Metabolic and Bariatric Surgery at King’s College London, England, said in an interview.
He added, “The fact that now we have a clinical diagnosis allows recognition of the nuance that obesity is generally a risk and for some can be an illness. There are some who have risk but don’t have the illness here and now. And it’s crucially important for clinical decision-making, but also for policies to have a distinction between those two things because the treatment strategy for one and the other are substantially different.”
Asked to comment, obesity specialist Michael A. Weintraub, MD, clinical assistant professor of endocrinology at New York University Langone Health, said in an interview, “I wholeheartedly agree with modifying the definition of obesity in this more accurate way. ... There has already been a lot of talk about the fallibility of BMI and that BMI over 30 does not equal obesity. ... So a major Commission article like this I think can really move those discussions even more into the forefront and start changing practice.”
However, Weintraub added, “I think there needs to be another step here of more practical guidance on how to actually implement this ... including how to measure waist circumference and to put it into a patient flow.”
Asked to comment, obesity expert Luca Busetto, MD, associate professor of internal medicine at the Department of Medicine of the University of Padova, Italy, said in an interview that he agrees with the general concept of moving beyond BMI in defining obesity. That view was expressed in a proposed “framework” from the European Association for the Study of Obesity (EASO), for which Busetto was the lead author.
Busetto also agrees with the emphasis on the need for a complete clinical evaluation of patients to define their health status. “The precise definition of the symptoms defining clinical obesity in adults and children is extremely important, emphasizing the fact that obesity is a severe and disabling disease by itself, even without or before the occurrence of obesity-related complications,” he said.
However, he takes issue with the Commission’s designation that “preclinical” obesity is not a disease. “The critical point of disagreement for me is the message that obesity is a disease only if it is clinical or only if it presents functional impairment or clinical symptoms. This remains, in my opinion, an oversimplification, not taking into account the fact that the pathophysiological mechanisms that lead to fat accumulation and ‘adipose tissue-based chronic disease’ usually start well before the occurrence of symptoms.”
Busetto pointed to examples such as type 2 diabetes and chronic kidney disease, both of which can be asymptomatic in their early phases yet are still considered diseases at those points. “I have no problem in accepting a distinction between preclinical and clinical stages of the disease, and I like the definition of clinical obesity, but why should this imply the fact that obesity is NOT a disease since its beginning?”
The Commission does state that preclinical obesity should be addressed, mostly with preventive approaches but in some cases with more intensive management. “This is highly relevant, but the risk of an undertreatment of obesity in its asymptomatic state remains in place. This could delay appropriate management for a progressive disease that certainly should not be treated only when presenting symptoms. It would be too late,” Busetto said.
And EASO framework coauthor Gijs Goossens, PhD, professor of cardiometabolic physiology of obesity at Maastricht University Medical Centre, the Netherlands, added a concern that those with excess adiposity but lower BMI might be missed entirely, noting “Since abdominal fat accumulation better predicts chronic cardiometabolic diseases and can also be accompanied by clinical manifestations in individuals with overweight as a consequence of compromised adipose tissue function, the proposed model may lead to underdiagnosis or undertreatment in individuals with BMI 25-30 who have excess abdominal fat.”
Diagnosis and Management Beyond BMI
The Commission advises the use of BMI solely as a marker to screen for potential obesity. Those with a BMI > 40 can be assumed to have excess body fat. For others with a BMI at or near the threshold for obesity in a specific country or ethnic group or for whom there is the clinical judgment of the potential for clinical obesity, confirmation of excess or abnormal adiposity is needed by one of the following:
- At least one measurement of body size and BMI
- At least two measures of body size, regardless of BMI
- Direct body fat measurement, such as a dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry (DEXA) scan
Measurement of body size can be assessed in three ways:
- Waist circumference ≥ 102 cm for men and ≥ 88 cm for women
- Waist-to-hip ratio > 0.90 for men and > 0.50 for women
- Waist-to-height ratio > 0.50 for all.
Weintraub noted, “Telemedicine is a useful tool used by many patients and providers but may also make it challenging to accurately assess someone’s body size. Having technology like an iPhone app to measure body size would circumvent this challenge but this type of tool has not yet been validated.”
If the person does not have excess adiposity, they don’t have obesity. Those with excess adiposity do have obesity. Further assessment is then needed to establish whether the person has an illness, that is, clinical obesity, indicated by signs/symptoms of organ dysfunction, and/or limitations of daily activities. If not, they have “preclinical” obesity.
The document provides a list of 18 obesity-related organ, tissue, and body system criteria for diagnosing “clinical” obesity in adults, including upper airways (eg, apneas/hypopneas), respiratory (breathlessness), cardiovascular (hypertension, heart failure), liver (fatty liver disease with hepatic fibrosis), reproductive (polycystic ovary syndrome, hypogonadism), and metabolism (hyperglycemia, hypertriglyceridemia, low high-density lipoprotein cholesterol). A list of 13 such criteria is also provided for children. “Limitations of day-to-day activities” are included on both lists.
Management Differs by Designation
For preclinical obesity, management should focus on risk reduction and prevention of progression to clinical obesity or other obesity-related diseases. Such approaches include health counseling for weight loss or prevention of weight gain, monitoring over time, and active weight loss interventions in people at higher risk of developing clinical obesity and other obesity-related diseases.
Management for clinical obesity focuses on improvements or reversal of the organ dysfunction. The type of evidence-based treatment and management should be informed by individual risk-benefit assessments and decided via “active discussion” with the patient. Success is determined by improvement in the signs and symptoms rather than measures of weight loss.
In response to a reporter’s question at the SMC briefing about the implications for the use of weight-loss medications, Rubino noted that this wasn’t the focus of the report, but nonetheless said that this new obesity definition could help with their targeted use. “The strategy and intent by which you use the drugs is different in clinical and preclinical obesity. ... Pharmacological interventions could be used for patients with high-risk preclinical obesity, with the intent of reducing risk, but we ... would use the same medication at a different intensity, dose, and maybe in combination therapies.”
As for clinical obesity, “It could be more or less severe and could affect more than one organ, and so clinical obesity might require drugs, might require surgery, or may require, in some cases, a combination of both of them, to achieve the best possible outcomes. ... We want to make sure that the person is restoring health ... with whatever it takes.”
Rubino believes this new definition will convince the remaining clinicians who haven’t yet accepted the concept of obesity as a disease. “When they see clinical obesity, I think it will be much harder to say that a biological process that is capable of causing a dysfunction in the heart or the lungs is less of a disease than another biological process that causes similar dysfunction in the heart of the lungs. ... It’s going to be objective. Obesity is a spectrum of different situations. ... When it’s an illness, clinical obesity, it’s not a matter of if or when. It’s a matter of fact.”
There were no industrial grants or other funding for this initiative. King’s Health Partners hosted the initiative and provided logistical and personnel support to facilitate administrative work and the Delphi-like consensus-development process. Rubino declared receiving research grants from Ethicon (Johnson & Johnson), Novo Nordisk, and Medtronic; consulting fees from Morphic Medical; speaking honoraria from Medtronic, Ethicon, Novo Nordisk, Eli Lilly, and Amgen. Rubino has served (unpaid) as a member of the scientific advisory board for Keyron and a member of the data safety and monitoring board for GI Metabolic Solutions; is president of the Metabolic Health Institute (non-profit); and is the sole director of Metabolic Health International and London Metabolic and Bariatric Surgery (private practice). Baur declared serving on the scientific advisory board for Novo Nordisk (for the ACTION Teens study) and Eli Lilly and receiving speaker fees (paid to the institution) from Novo Nordisk.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
“We propose a radical overhaul of the actual diagnosis of obesity to improve global healthcare and practices and policies. The specific aims were to facilitate individualized assessment and care of people living with obesity while preserving resources by reducing overdiagnosis and unnecessary or inadequate interventions,” Professor Louise Baur, chair of Child & Adolescent Health at the University of Sydney, Australia, said during a UK Science Media Centre (SMC) news briefing.
The report calls first for a diagnosis of obesity via confirmation of excess adiposity using measures such as waist circumference or waist-to-hip ratio in addition to BMI. Next, a clinical assessment of signs and symptoms of organ dysfunction due to obesity and/or functional limitations determines whether the individual has the disease “clinical obesity,” or “preclinical obesity,” a condition of health risk but not an illness itself.
Published on January 14, 2025, in The Lancet Diabetes & Endocrinology, the document also provides broad guidance on management for the two obesity conditions, emphasizing a personalized and stigma-free approach. The Lancet Commission on Obesity comprised 56 experts in relevant fields including endocrinology, surgery, nutrition, and public health, along with people living with obesity.
The report has been endorsed by more than 75 medical organizations, including the Association of British Clinical Diabetologists, the American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists, the American Diabetes Association, the American Heart Association, the Obesity Society, the World Obesity Federation, and obesity and endocrinology societies from countries in Europe, Latin America, Asia, and South Africa.
In recent years, many in the field have found fault with the current BMI-based definition of obesity (> 30 for people of European descent or other cutoffs for specific ethnic groups), primarily because BMI alone doesn’t reflect a person’s fat vs lean mass, fat distribution, or overall health. The new definition aims to overcome these limitations, as well as settle the debate about whether obesity is a “disease.”
“We now have a clinical diagnosis for obesity, which has been lacking. ... The traditional classification based on BMI ... reflects simply whether or not there is excess adiposity, and sometimes not even precise in that regard, either…It has never been a classification that was meant to diagnose a specific illness with its own clinical characteristics in the same way we diagnose any other illness,” Commission Chair Francesco Rubino, MD, professor and chair of Metabolic and Bariatric Surgery at King’s College London, England, said in an interview.
He added, “The fact that now we have a clinical diagnosis allows recognition of the nuance that obesity is generally a risk and for some can be an illness. There are some who have risk but don’t have the illness here and now. And it’s crucially important for clinical decision-making, but also for policies to have a distinction between those two things because the treatment strategy for one and the other are substantially different.”
Asked to comment, obesity specialist Michael A. Weintraub, MD, clinical assistant professor of endocrinology at New York University Langone Health, said in an interview, “I wholeheartedly agree with modifying the definition of obesity in this more accurate way. ... There has already been a lot of talk about the fallibility of BMI and that BMI over 30 does not equal obesity. ... So a major Commission article like this I think can really move those discussions even more into the forefront and start changing practice.”
However, Weintraub added, “I think there needs to be another step here of more practical guidance on how to actually implement this ... including how to measure waist circumference and to put it into a patient flow.”
Asked to comment, obesity expert Luca Busetto, MD, associate professor of internal medicine at the Department of Medicine of the University of Padova, Italy, said in an interview that he agrees with the general concept of moving beyond BMI in defining obesity. That view was expressed in a proposed “framework” from the European Association for the Study of Obesity (EASO), for which Busetto was the lead author.
Busetto also agrees with the emphasis on the need for a complete clinical evaluation of patients to define their health status. “The precise definition of the symptoms defining clinical obesity in adults and children is extremely important, emphasizing the fact that obesity is a severe and disabling disease by itself, even without or before the occurrence of obesity-related complications,” he said.
However, he takes issue with the Commission’s designation that “preclinical” obesity is not a disease. “The critical point of disagreement for me is the message that obesity is a disease only if it is clinical or only if it presents functional impairment or clinical symptoms. This remains, in my opinion, an oversimplification, not taking into account the fact that the pathophysiological mechanisms that lead to fat accumulation and ‘adipose tissue-based chronic disease’ usually start well before the occurrence of symptoms.”
Busetto pointed to examples such as type 2 diabetes and chronic kidney disease, both of which can be asymptomatic in their early phases yet are still considered diseases at those points. “I have no problem in accepting a distinction between preclinical and clinical stages of the disease, and I like the definition of clinical obesity, but why should this imply the fact that obesity is NOT a disease since its beginning?”
The Commission does state that preclinical obesity should be addressed, mostly with preventive approaches but in some cases with more intensive management. “This is highly relevant, but the risk of an undertreatment of obesity in its asymptomatic state remains in place. This could delay appropriate management for a progressive disease that certainly should not be treated only when presenting symptoms. It would be too late,” Busetto said.
And EASO framework coauthor Gijs Goossens, PhD, professor of cardiometabolic physiology of obesity at Maastricht University Medical Centre, the Netherlands, added a concern that those with excess adiposity but lower BMI might be missed entirely, noting “Since abdominal fat accumulation better predicts chronic cardiometabolic diseases and can also be accompanied by clinical manifestations in individuals with overweight as a consequence of compromised adipose tissue function, the proposed model may lead to underdiagnosis or undertreatment in individuals with BMI 25-30 who have excess abdominal fat.”
Diagnosis and Management Beyond BMI
The Commission advises the use of BMI solely as a marker to screen for potential obesity. Those with a BMI > 40 can be assumed to have excess body fat. For others with a BMI at or near the threshold for obesity in a specific country or ethnic group or for whom there is the clinical judgment of the potential for clinical obesity, confirmation of excess or abnormal adiposity is needed by one of the following:
- At least one measurement of body size and BMI
- At least two measures of body size, regardless of BMI
- Direct body fat measurement, such as a dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry (DEXA) scan
Measurement of body size can be assessed in three ways:
- Waist circumference ≥ 102 cm for men and ≥ 88 cm for women
- Waist-to-hip ratio > 0.90 for men and > 0.50 for women
- Waist-to-height ratio > 0.50 for all.
Weintraub noted, “Telemedicine is a useful tool used by many patients and providers but may also make it challenging to accurately assess someone’s body size. Having technology like an iPhone app to measure body size would circumvent this challenge but this type of tool has not yet been validated.”
If the person does not have excess adiposity, they don’t have obesity. Those with excess adiposity do have obesity. Further assessment is then needed to establish whether the person has an illness, that is, clinical obesity, indicated by signs/symptoms of organ dysfunction, and/or limitations of daily activities. If not, they have “preclinical” obesity.
The document provides a list of 18 obesity-related organ, tissue, and body system criteria for diagnosing “clinical” obesity in adults, including upper airways (eg, apneas/hypopneas), respiratory (breathlessness), cardiovascular (hypertension, heart failure), liver (fatty liver disease with hepatic fibrosis), reproductive (polycystic ovary syndrome, hypogonadism), and metabolism (hyperglycemia, hypertriglyceridemia, low high-density lipoprotein cholesterol). A list of 13 such criteria is also provided for children. “Limitations of day-to-day activities” are included on both lists.
Management Differs by Designation
For preclinical obesity, management should focus on risk reduction and prevention of progression to clinical obesity or other obesity-related diseases. Such approaches include health counseling for weight loss or prevention of weight gain, monitoring over time, and active weight loss interventions in people at higher risk of developing clinical obesity and other obesity-related diseases.
Management for clinical obesity focuses on improvements or reversal of the organ dysfunction. The type of evidence-based treatment and management should be informed by individual risk-benefit assessments and decided via “active discussion” with the patient. Success is determined by improvement in the signs and symptoms rather than measures of weight loss.
In response to a reporter’s question at the SMC briefing about the implications for the use of weight-loss medications, Rubino noted that this wasn’t the focus of the report, but nonetheless said that this new obesity definition could help with their targeted use. “The strategy and intent by which you use the drugs is different in clinical and preclinical obesity. ... Pharmacological interventions could be used for patients with high-risk preclinical obesity, with the intent of reducing risk, but we ... would use the same medication at a different intensity, dose, and maybe in combination therapies.”
As for clinical obesity, “It could be more or less severe and could affect more than one organ, and so clinical obesity might require drugs, might require surgery, or may require, in some cases, a combination of both of them, to achieve the best possible outcomes. ... We want to make sure that the person is restoring health ... with whatever it takes.”
Rubino believes this new definition will convince the remaining clinicians who haven’t yet accepted the concept of obesity as a disease. “When they see clinical obesity, I think it will be much harder to say that a biological process that is capable of causing a dysfunction in the heart or the lungs is less of a disease than another biological process that causes similar dysfunction in the heart of the lungs. ... It’s going to be objective. Obesity is a spectrum of different situations. ... When it’s an illness, clinical obesity, it’s not a matter of if or when. It’s a matter of fact.”
There were no industrial grants or other funding for this initiative. King’s Health Partners hosted the initiative and provided logistical and personnel support to facilitate administrative work and the Delphi-like consensus-development process. Rubino declared receiving research grants from Ethicon (Johnson & Johnson), Novo Nordisk, and Medtronic; consulting fees from Morphic Medical; speaking honoraria from Medtronic, Ethicon, Novo Nordisk, Eli Lilly, and Amgen. Rubino has served (unpaid) as a member of the scientific advisory board for Keyron and a member of the data safety and monitoring board for GI Metabolic Solutions; is president of the Metabolic Health Institute (non-profit); and is the sole director of Metabolic Health International and London Metabolic and Bariatric Surgery (private practice). Baur declared serving on the scientific advisory board for Novo Nordisk (for the ACTION Teens study) and Eli Lilly and receiving speaker fees (paid to the institution) from Novo Nordisk.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
“We propose a radical overhaul of the actual diagnosis of obesity to improve global healthcare and practices and policies. The specific aims were to facilitate individualized assessment and care of people living with obesity while preserving resources by reducing overdiagnosis and unnecessary or inadequate interventions,” Professor Louise Baur, chair of Child & Adolescent Health at the University of Sydney, Australia, said during a UK Science Media Centre (SMC) news briefing.
The report calls first for a diagnosis of obesity via confirmation of excess adiposity using measures such as waist circumference or waist-to-hip ratio in addition to BMI. Next, a clinical assessment of signs and symptoms of organ dysfunction due to obesity and/or functional limitations determines whether the individual has the disease “clinical obesity,” or “preclinical obesity,” a condition of health risk but not an illness itself.
Published on January 14, 2025, in The Lancet Diabetes & Endocrinology, the document also provides broad guidance on management for the two obesity conditions, emphasizing a personalized and stigma-free approach. The Lancet Commission on Obesity comprised 56 experts in relevant fields including endocrinology, surgery, nutrition, and public health, along with people living with obesity.
The report has been endorsed by more than 75 medical organizations, including the Association of British Clinical Diabetologists, the American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists, the American Diabetes Association, the American Heart Association, the Obesity Society, the World Obesity Federation, and obesity and endocrinology societies from countries in Europe, Latin America, Asia, and South Africa.
In recent years, many in the field have found fault with the current BMI-based definition of obesity (> 30 for people of European descent or other cutoffs for specific ethnic groups), primarily because BMI alone doesn’t reflect a person’s fat vs lean mass, fat distribution, or overall health. The new definition aims to overcome these limitations, as well as settle the debate about whether obesity is a “disease.”
“We now have a clinical diagnosis for obesity, which has been lacking. ... The traditional classification based on BMI ... reflects simply whether or not there is excess adiposity, and sometimes not even precise in that regard, either…It has never been a classification that was meant to diagnose a specific illness with its own clinical characteristics in the same way we diagnose any other illness,” Commission Chair Francesco Rubino, MD, professor and chair of Metabolic and Bariatric Surgery at King’s College London, England, said in an interview.
He added, “The fact that now we have a clinical diagnosis allows recognition of the nuance that obesity is generally a risk and for some can be an illness. There are some who have risk but don’t have the illness here and now. And it’s crucially important for clinical decision-making, but also for policies to have a distinction between those two things because the treatment strategy for one and the other are substantially different.”
Asked to comment, obesity specialist Michael A. Weintraub, MD, clinical assistant professor of endocrinology at New York University Langone Health, said in an interview, “I wholeheartedly agree with modifying the definition of obesity in this more accurate way. ... There has already been a lot of talk about the fallibility of BMI and that BMI over 30 does not equal obesity. ... So a major Commission article like this I think can really move those discussions even more into the forefront and start changing practice.”
However, Weintraub added, “I think there needs to be another step here of more practical guidance on how to actually implement this ... including how to measure waist circumference and to put it into a patient flow.”
Asked to comment, obesity expert Luca Busetto, MD, associate professor of internal medicine at the Department of Medicine of the University of Padova, Italy, said in an interview that he agrees with the general concept of moving beyond BMI in defining obesity. That view was expressed in a proposed “framework” from the European Association for the Study of Obesity (EASO), for which Busetto was the lead author.
Busetto also agrees with the emphasis on the need for a complete clinical evaluation of patients to define their health status. “The precise definition of the symptoms defining clinical obesity in adults and children is extremely important, emphasizing the fact that obesity is a severe and disabling disease by itself, even without or before the occurrence of obesity-related complications,” he said.
However, he takes issue with the Commission’s designation that “preclinical” obesity is not a disease. “The critical point of disagreement for me is the message that obesity is a disease only if it is clinical or only if it presents functional impairment or clinical symptoms. This remains, in my opinion, an oversimplification, not taking into account the fact that the pathophysiological mechanisms that lead to fat accumulation and ‘adipose tissue-based chronic disease’ usually start well before the occurrence of symptoms.”
Busetto pointed to examples such as type 2 diabetes and chronic kidney disease, both of which can be asymptomatic in their early phases yet are still considered diseases at those points. “I have no problem in accepting a distinction between preclinical and clinical stages of the disease, and I like the definition of clinical obesity, but why should this imply the fact that obesity is NOT a disease since its beginning?”
The Commission does state that preclinical obesity should be addressed, mostly with preventive approaches but in some cases with more intensive management. “This is highly relevant, but the risk of an undertreatment of obesity in its asymptomatic state remains in place. This could delay appropriate management for a progressive disease that certainly should not be treated only when presenting symptoms. It would be too late,” Busetto said.
And EASO framework coauthor Gijs Goossens, PhD, professor of cardiometabolic physiology of obesity at Maastricht University Medical Centre, the Netherlands, added a concern that those with excess adiposity but lower BMI might be missed entirely, noting “Since abdominal fat accumulation better predicts chronic cardiometabolic diseases and can also be accompanied by clinical manifestations in individuals with overweight as a consequence of compromised adipose tissue function, the proposed model may lead to underdiagnosis or undertreatment in individuals with BMI 25-30 who have excess abdominal fat.”
Diagnosis and Management Beyond BMI
The Commission advises the use of BMI solely as a marker to screen for potential obesity. Those with a BMI > 40 can be assumed to have excess body fat. For others with a BMI at or near the threshold for obesity in a specific country or ethnic group or for whom there is the clinical judgment of the potential for clinical obesity, confirmation of excess or abnormal adiposity is needed by one of the following:
- At least one measurement of body size and BMI
- At least two measures of body size, regardless of BMI
- Direct body fat measurement, such as a dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry (DEXA) scan
Measurement of body size can be assessed in three ways:
- Waist circumference ≥ 102 cm for men and ≥ 88 cm for women
- Waist-to-hip ratio > 0.90 for men and > 0.50 for women
- Waist-to-height ratio > 0.50 for all.
Weintraub noted, “Telemedicine is a useful tool used by many patients and providers but may also make it challenging to accurately assess someone’s body size. Having technology like an iPhone app to measure body size would circumvent this challenge but this type of tool has not yet been validated.”
If the person does not have excess adiposity, they don’t have obesity. Those with excess adiposity do have obesity. Further assessment is then needed to establish whether the person has an illness, that is, clinical obesity, indicated by signs/symptoms of organ dysfunction, and/or limitations of daily activities. If not, they have “preclinical” obesity.
The document provides a list of 18 obesity-related organ, tissue, and body system criteria for diagnosing “clinical” obesity in adults, including upper airways (eg, apneas/hypopneas), respiratory (breathlessness), cardiovascular (hypertension, heart failure), liver (fatty liver disease with hepatic fibrosis), reproductive (polycystic ovary syndrome, hypogonadism), and metabolism (hyperglycemia, hypertriglyceridemia, low high-density lipoprotein cholesterol). A list of 13 such criteria is also provided for children. “Limitations of day-to-day activities” are included on both lists.
Management Differs by Designation
For preclinical obesity, management should focus on risk reduction and prevention of progression to clinical obesity or other obesity-related diseases. Such approaches include health counseling for weight loss or prevention of weight gain, monitoring over time, and active weight loss interventions in people at higher risk of developing clinical obesity and other obesity-related diseases.
Management for clinical obesity focuses on improvements or reversal of the organ dysfunction. The type of evidence-based treatment and management should be informed by individual risk-benefit assessments and decided via “active discussion” with the patient. Success is determined by improvement in the signs and symptoms rather than measures of weight loss.
In response to a reporter’s question at the SMC briefing about the implications for the use of weight-loss medications, Rubino noted that this wasn’t the focus of the report, but nonetheless said that this new obesity definition could help with their targeted use. “The strategy and intent by which you use the drugs is different in clinical and preclinical obesity. ... Pharmacological interventions could be used for patients with high-risk preclinical obesity, with the intent of reducing risk, but we ... would use the same medication at a different intensity, dose, and maybe in combination therapies.”
As for clinical obesity, “It could be more or less severe and could affect more than one organ, and so clinical obesity might require drugs, might require surgery, or may require, in some cases, a combination of both of them, to achieve the best possible outcomes. ... We want to make sure that the person is restoring health ... with whatever it takes.”
Rubino believes this new definition will convince the remaining clinicians who haven’t yet accepted the concept of obesity as a disease. “When they see clinical obesity, I think it will be much harder to say that a biological process that is capable of causing a dysfunction in the heart or the lungs is less of a disease than another biological process that causes similar dysfunction in the heart of the lungs. ... It’s going to be objective. Obesity is a spectrum of different situations. ... When it’s an illness, clinical obesity, it’s not a matter of if or when. It’s a matter of fact.”
There were no industrial grants or other funding for this initiative. King’s Health Partners hosted the initiative and provided logistical and personnel support to facilitate administrative work and the Delphi-like consensus-development process. Rubino declared receiving research grants from Ethicon (Johnson & Johnson), Novo Nordisk, and Medtronic; consulting fees from Morphic Medical; speaking honoraria from Medtronic, Ethicon, Novo Nordisk, Eli Lilly, and Amgen. Rubino has served (unpaid) as a member of the scientific advisory board for Keyron and a member of the data safety and monitoring board for GI Metabolic Solutions; is president of the Metabolic Health Institute (non-profit); and is the sole director of Metabolic Health International and London Metabolic and Bariatric Surgery (private practice). Baur declared serving on the scientific advisory board for Novo Nordisk (for the ACTION Teens study) and Eli Lilly and receiving speaker fees (paid to the institution) from Novo Nordisk.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM THE LANCET DIABETES & ENDOCRINOLOGY
Losing Your Mind Trying to Understand the BP-Dementia Link
You could be forgiven if you are confused about how blood pressure (BP) affects dementia. First, you read an article extolling the benefits of BP lowering, then a study about how stopping antihypertensives slows cognitive decline in nursing home residents. It’s enough to make you lose your mind.
The Brain Benefits of BP Lowering
It should be stated unequivocally that you should absolutely treat high BP. It may have once been acceptable to state, “The greatest danger to a man with high blood pressure lies in its discovery, because then some fool is certain to try and reduce it.” But those dark days are long behind us.
In these divided times, at least we can agree that we should treat high BP. The cardiovascular (CV) benefits, in and of themselves, justify the decision. But BP’s relationship with dementia is more complex. There are different types of dementia even though we tend to lump them all into one category. Vascular dementia is driven by the same pathophysiology and risk factors as cardiac disease. It’s intuitive that treating hypertension, diabetes, hypercholesterolemia, and smoking will decrease the risk for stroke and limit the damage to the brain that we see with repeated vascular insults. For Alzheimer’s disease, high BP and other CV risk factors seem to increase the risk even if the mechanism is not fully elucidated.
Estimates suggest that if we could lower the prevalence of hypertension by 25%, there would be 160,000 fewer cases of Alzheimer’s disease. But the data are not as robust as one might hope. A 2021 Cochrane review found that hypertension treatment slowed cognitive decline, but the quality of the evidence was low. Short duration of follow-up, dropouts, crossovers, and other problems with the data precluded any certainty. What’s more, hypertension in midlife is associated with cognitive decline and dementia, but its impact in those over age 70 is less clear. Later in life, or once cognitive impairment has already developed, it may be too late for BP lowering to have any impact.
Potential Harms of Lowering BP
All this needs to be weighed against the potential harms of treating hypertension. I will reiterate that hypertension should be treated and treated aggressively for the prevention of CV events. But overtreatment, especially in older patients, is associated with hypotension, falls, and syncope. Older patients are also at risk for polypharmacy and drug-drug interactions.
A Korean nationwide survey showed a U-shaped association between BP and Alzheimer’s disease risk in adults (mean age, 67 years), with both high and low BPs associated with a higher risk for Alzheimer’s disease. Though not all studies agree. A post hoc analysis of SPRINT MIND did not find any negative impact of intensive BP lowering on cognitive outcomes or cerebral perfusion in older adults (mean age, 68 years). But it didn’t do much good either. Given the heterogeneity of the data, doubts remain on whether aggressive BP lowering might be detrimental in older patients with comorbidities and preexisting dementia. The obvious corollary then is whether deprescribing hypertensive medications could be beneficial.
A recent publication in JAMA Internal Medicine attempted to address this very question. The cohort study used data from Veterans Affairs nursing home residents (mean age, 78 years) to emulate a randomized trial on deprescribing antihypertensives and cognitive decline. Many of the residents’ cognitive scores worsened over the course of follow-up; however, the decline was less pronounced in the deprescribing group (10% vs 12%). The same group did a similar analysis looking at CV outcomes and found no increased risk for heart attack or stroke with deprescribing BP medications. Taken together, these nursing home data suggest that deprescribing may help slow cognitive decline without the expected trade-off of increased CV events.
Deprescribing, Yes or No?
However, randomized data would obviously be preferable, and these are in short supply. One such trial, the DANTE study, found no benefit to deprescribing in terms of cognition in adults aged 75 years or older with mild cognitive impairment. The study follow-up was only 16 weeks, however, which is hardly enough time to demonstrate any effect, positive or negative. The most that can be said is that it didn’t cause many short-term adverse events.
Perhaps the best conclusion to draw from this somewhat underwhelming collection of data is that lowering high BP is important, but less important the closer we get to the end of life. Hypotension is obviously bad, and overly aggressive BP lowering is going to lead to negative outcomes in older adults because gravity is an unforgiving mistress.
Deprescribing antihypertensives in older adults is probably not going to cause major negative outcomes, but whether it will do much good in nonhypotensive patients is debatable. The bigger problem is the millions of people with undiagnosed or undertreated hypertension. We would probably have less dementia if we treated hypertension when it does the most good: as a primary-prevention strategy in midlife.
Dr. Labos is a cardiologist at Hôpital Notre-Dame, Montreal, Quebec, Canada. He disclosed no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
You could be forgiven if you are confused about how blood pressure (BP) affects dementia. First, you read an article extolling the benefits of BP lowering, then a study about how stopping antihypertensives slows cognitive decline in nursing home residents. It’s enough to make you lose your mind.
The Brain Benefits of BP Lowering
It should be stated unequivocally that you should absolutely treat high BP. It may have once been acceptable to state, “The greatest danger to a man with high blood pressure lies in its discovery, because then some fool is certain to try and reduce it.” But those dark days are long behind us.
In these divided times, at least we can agree that we should treat high BP. The cardiovascular (CV) benefits, in and of themselves, justify the decision. But BP’s relationship with dementia is more complex. There are different types of dementia even though we tend to lump them all into one category. Vascular dementia is driven by the same pathophysiology and risk factors as cardiac disease. It’s intuitive that treating hypertension, diabetes, hypercholesterolemia, and smoking will decrease the risk for stroke and limit the damage to the brain that we see with repeated vascular insults. For Alzheimer’s disease, high BP and other CV risk factors seem to increase the risk even if the mechanism is not fully elucidated.
Estimates suggest that if we could lower the prevalence of hypertension by 25%, there would be 160,000 fewer cases of Alzheimer’s disease. But the data are not as robust as one might hope. A 2021 Cochrane review found that hypertension treatment slowed cognitive decline, but the quality of the evidence was low. Short duration of follow-up, dropouts, crossovers, and other problems with the data precluded any certainty. What’s more, hypertension in midlife is associated with cognitive decline and dementia, but its impact in those over age 70 is less clear. Later in life, or once cognitive impairment has already developed, it may be too late for BP lowering to have any impact.
Potential Harms of Lowering BP
All this needs to be weighed against the potential harms of treating hypertension. I will reiterate that hypertension should be treated and treated aggressively for the prevention of CV events. But overtreatment, especially in older patients, is associated with hypotension, falls, and syncope. Older patients are also at risk for polypharmacy and drug-drug interactions.
A Korean nationwide survey showed a U-shaped association between BP and Alzheimer’s disease risk in adults (mean age, 67 years), with both high and low BPs associated with a higher risk for Alzheimer’s disease. Though not all studies agree. A post hoc analysis of SPRINT MIND did not find any negative impact of intensive BP lowering on cognitive outcomes or cerebral perfusion in older adults (mean age, 68 years). But it didn’t do much good either. Given the heterogeneity of the data, doubts remain on whether aggressive BP lowering might be detrimental in older patients with comorbidities and preexisting dementia. The obvious corollary then is whether deprescribing hypertensive medications could be beneficial.
A recent publication in JAMA Internal Medicine attempted to address this very question. The cohort study used data from Veterans Affairs nursing home residents (mean age, 78 years) to emulate a randomized trial on deprescribing antihypertensives and cognitive decline. Many of the residents’ cognitive scores worsened over the course of follow-up; however, the decline was less pronounced in the deprescribing group (10% vs 12%). The same group did a similar analysis looking at CV outcomes and found no increased risk for heart attack or stroke with deprescribing BP medications. Taken together, these nursing home data suggest that deprescribing may help slow cognitive decline without the expected trade-off of increased CV events.
Deprescribing, Yes or No?
However, randomized data would obviously be preferable, and these are in short supply. One such trial, the DANTE study, found no benefit to deprescribing in terms of cognition in adults aged 75 years or older with mild cognitive impairment. The study follow-up was only 16 weeks, however, which is hardly enough time to demonstrate any effect, positive or negative. The most that can be said is that it didn’t cause many short-term adverse events.
Perhaps the best conclusion to draw from this somewhat underwhelming collection of data is that lowering high BP is important, but less important the closer we get to the end of life. Hypotension is obviously bad, and overly aggressive BP lowering is going to lead to negative outcomes in older adults because gravity is an unforgiving mistress.
Deprescribing antihypertensives in older adults is probably not going to cause major negative outcomes, but whether it will do much good in nonhypotensive patients is debatable. The bigger problem is the millions of people with undiagnosed or undertreated hypertension. We would probably have less dementia if we treated hypertension when it does the most good: as a primary-prevention strategy in midlife.
Dr. Labos is a cardiologist at Hôpital Notre-Dame, Montreal, Quebec, Canada. He disclosed no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
You could be forgiven if you are confused about how blood pressure (BP) affects dementia. First, you read an article extolling the benefits of BP lowering, then a study about how stopping antihypertensives slows cognitive decline in nursing home residents. It’s enough to make you lose your mind.
The Brain Benefits of BP Lowering
It should be stated unequivocally that you should absolutely treat high BP. It may have once been acceptable to state, “The greatest danger to a man with high blood pressure lies in its discovery, because then some fool is certain to try and reduce it.” But those dark days are long behind us.
In these divided times, at least we can agree that we should treat high BP. The cardiovascular (CV) benefits, in and of themselves, justify the decision. But BP’s relationship with dementia is more complex. There are different types of dementia even though we tend to lump them all into one category. Vascular dementia is driven by the same pathophysiology and risk factors as cardiac disease. It’s intuitive that treating hypertension, diabetes, hypercholesterolemia, and smoking will decrease the risk for stroke and limit the damage to the brain that we see with repeated vascular insults. For Alzheimer’s disease, high BP and other CV risk factors seem to increase the risk even if the mechanism is not fully elucidated.
Estimates suggest that if we could lower the prevalence of hypertension by 25%, there would be 160,000 fewer cases of Alzheimer’s disease. But the data are not as robust as one might hope. A 2021 Cochrane review found that hypertension treatment slowed cognitive decline, but the quality of the evidence was low. Short duration of follow-up, dropouts, crossovers, and other problems with the data precluded any certainty. What’s more, hypertension in midlife is associated with cognitive decline and dementia, but its impact in those over age 70 is less clear. Later in life, or once cognitive impairment has already developed, it may be too late for BP lowering to have any impact.
Potential Harms of Lowering BP
All this needs to be weighed against the potential harms of treating hypertension. I will reiterate that hypertension should be treated and treated aggressively for the prevention of CV events. But overtreatment, especially in older patients, is associated with hypotension, falls, and syncope. Older patients are also at risk for polypharmacy and drug-drug interactions.
A Korean nationwide survey showed a U-shaped association between BP and Alzheimer’s disease risk in adults (mean age, 67 years), with both high and low BPs associated with a higher risk for Alzheimer’s disease. Though not all studies agree. A post hoc analysis of SPRINT MIND did not find any negative impact of intensive BP lowering on cognitive outcomes or cerebral perfusion in older adults (mean age, 68 years). But it didn’t do much good either. Given the heterogeneity of the data, doubts remain on whether aggressive BP lowering might be detrimental in older patients with comorbidities and preexisting dementia. The obvious corollary then is whether deprescribing hypertensive medications could be beneficial.
A recent publication in JAMA Internal Medicine attempted to address this very question. The cohort study used data from Veterans Affairs nursing home residents (mean age, 78 years) to emulate a randomized trial on deprescribing antihypertensives and cognitive decline. Many of the residents’ cognitive scores worsened over the course of follow-up; however, the decline was less pronounced in the deprescribing group (10% vs 12%). The same group did a similar analysis looking at CV outcomes and found no increased risk for heart attack or stroke with deprescribing BP medications. Taken together, these nursing home data suggest that deprescribing may help slow cognitive decline without the expected trade-off of increased CV events.
Deprescribing, Yes or No?
However, randomized data would obviously be preferable, and these are in short supply. One such trial, the DANTE study, found no benefit to deprescribing in terms of cognition in adults aged 75 years or older with mild cognitive impairment. The study follow-up was only 16 weeks, however, which is hardly enough time to demonstrate any effect, positive or negative. The most that can be said is that it didn’t cause many short-term adverse events.
Perhaps the best conclusion to draw from this somewhat underwhelming collection of data is that lowering high BP is important, but less important the closer we get to the end of life. Hypotension is obviously bad, and overly aggressive BP lowering is going to lead to negative outcomes in older adults because gravity is an unforgiving mistress.
Deprescribing antihypertensives in older adults is probably not going to cause major negative outcomes, but whether it will do much good in nonhypotensive patients is debatable. The bigger problem is the millions of people with undiagnosed or undertreated hypertension. We would probably have less dementia if we treated hypertension when it does the most good: as a primary-prevention strategy in midlife.
Dr. Labos is a cardiologist at Hôpital Notre-Dame, Montreal, Quebec, Canada. He disclosed no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Most Kids With COVID-Linked MIS-C Recover by 6 Months
Children who were severely ill with multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children (MIS-C) related to COVID-19 infection appear to show excellent cardiovascular and noncardiovascular outcomes by 6 months, according to data published in JAMA Pediatrics.
MIS-C is a life-threatening complication of COVID-19 infection and data on outcomes are limited, wrote the authors, led by Dongngan T. Truong, MD, MSSI, with Children’s Healthcare of Atlanta Cardiology, Emory University School of Medicine in Atlanta, Georgia. These 6-month results are from the Long-Term Outcomes After the Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in Children (MUSIC) study, sponsored by the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute.
Researchers found in this cohort study of 1204 participants that by 6 months after hospital discharge, 99% had normalization of left ventricular systolic function, and 92.3% had normalized coronary artery dimensions. More than 95% reported being more than 90% back to baseline health.
Patient-Reported Outcomes Measurement Information Systems (PROMIS) Global Health scores were at least equivalent to prepandemic population normative values. PROMIS Global Health parent/guardian proxy median T scores for fatigue, global health, and pain interference improved significantly from 2 weeks to 6 months: fatigue, 56.1 vs 48.9; global health, 48.8 vs 51.3; pain interference, 53.0 vs 43.3 (P < .001).
The most common symptoms reported at 2 weeks were fatigue (15.9%) and low stamina/energy (9.2%); both decreased to 3.4% and 3.3%, respectively, by 6 months. The most common cardiovascular symptom at 2 weeks was palpitations (1.5%), which decreased to 0.6%.
Chest Pain Increased Over Time
Reports of chest pain, however, reportedly increased over time, with 1.3% reporting chest pain at rest at 2 weeks and 2.2% at 6 months. Although gastrointestinal symptoms were common during the acute MIS-C, only 5.3% of respondents reported those symptoms at 2 weeks.
Children in the cohort had a median age of 9 years, and 60% were men. They self-identified with the following races and ethnicities: American Indian or Alaska Native (0.1%), Asian (3.3%), Black (27.0%), Hawaiian Native or Other Pacific Islander (0.2%), Hispanic or Latino (26.9%), multiracial (2.7%), White (31.2%), other (1.0%), and unknown or refused to specify (7.6%). Authors wrote that the cohort was followed-up to 2 years after illness onset and long-term results are not yet known.
Time to Exhale
David J. Goldberg, MD, with the Cardiac Center, Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, and colleagues, wrote in an accompanying editorial that “the decreased frequency of the disease along (with) the reassuring reports on midterm outcomes can allow the pediatric community a moment of collective exhale.”
The editorialists note that of those who initially presented with myocardial dysfunction, all but one patient evaluated had a normal ejection fraction at follow-up. Energy, sleep, appetite, cognition, and mood also normalized by midterm.
“The results of the MUSIC study add to the emerging midterm outcomes data suggesting a near-complete cardiovascular recovery in the overwhelming majority of patients who develop MIS-C,” Goldberg and colleagues wrote. “Despite initial concerns, driven by the severity of acute presentation at diagnosis and longer-term questions that remain (for example, does coronary microvascular dysfunction persist even after normalization of coronary artery z score?), these data suggest an encouraging outlook for the long-term health of affected children.”
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and other agencies have reported a declining overall incidence of MIS-C and highlighted the protective value of vaccination.
The editorialists add, however, that while the drop in MIS-C cases is encouraging, cases are still reported, especially amid high viral activity periods, “and nearly half of affected children continue to require intensive care in the acute phase of illness.”
Truong reported grants from the National Institutes of Health and serving as coprincipal investigator for Pfizer for research on COVID-19 vaccine-associated myocarditis funded by Pfizer and occurring through the framework of the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute’s Pediatric Heart Network outside the submitted work. One coauthor reported grants from Pfizer and Boston Scientific outside the submitted work. One coauthor reported receiving grants from Additional Ventures Foundation outside the submitted work. One coauthor reported receiving consultant fees from Amryt Pharma, Chiesi, Esperion, and Ultragenyx outside the submitted work. A coauthor reported receiving consultant fees from Larimar Therapeutics for mitochondrial therapies outside the submitted work. One coauthor reported being an employee of Takeda Pharmaceuticals since July 2023. One editorialist reported grants from Childhood Arthritis and Rheumatology Research Alliance and the Arthritis Foundation, Academy Health, and the Gordon and Betty Moore Foundation during the conduct of the study.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Children who were severely ill with multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children (MIS-C) related to COVID-19 infection appear to show excellent cardiovascular and noncardiovascular outcomes by 6 months, according to data published in JAMA Pediatrics.
MIS-C is a life-threatening complication of COVID-19 infection and data on outcomes are limited, wrote the authors, led by Dongngan T. Truong, MD, MSSI, with Children’s Healthcare of Atlanta Cardiology, Emory University School of Medicine in Atlanta, Georgia. These 6-month results are from the Long-Term Outcomes After the Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in Children (MUSIC) study, sponsored by the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute.
Researchers found in this cohort study of 1204 participants that by 6 months after hospital discharge, 99% had normalization of left ventricular systolic function, and 92.3% had normalized coronary artery dimensions. More than 95% reported being more than 90% back to baseline health.
Patient-Reported Outcomes Measurement Information Systems (PROMIS) Global Health scores were at least equivalent to prepandemic population normative values. PROMIS Global Health parent/guardian proxy median T scores for fatigue, global health, and pain interference improved significantly from 2 weeks to 6 months: fatigue, 56.1 vs 48.9; global health, 48.8 vs 51.3; pain interference, 53.0 vs 43.3 (P < .001).
The most common symptoms reported at 2 weeks were fatigue (15.9%) and low stamina/energy (9.2%); both decreased to 3.4% and 3.3%, respectively, by 6 months. The most common cardiovascular symptom at 2 weeks was palpitations (1.5%), which decreased to 0.6%.
Chest Pain Increased Over Time
Reports of chest pain, however, reportedly increased over time, with 1.3% reporting chest pain at rest at 2 weeks and 2.2% at 6 months. Although gastrointestinal symptoms were common during the acute MIS-C, only 5.3% of respondents reported those symptoms at 2 weeks.
Children in the cohort had a median age of 9 years, and 60% were men. They self-identified with the following races and ethnicities: American Indian or Alaska Native (0.1%), Asian (3.3%), Black (27.0%), Hawaiian Native or Other Pacific Islander (0.2%), Hispanic or Latino (26.9%), multiracial (2.7%), White (31.2%), other (1.0%), and unknown or refused to specify (7.6%). Authors wrote that the cohort was followed-up to 2 years after illness onset and long-term results are not yet known.
Time to Exhale
David J. Goldberg, MD, with the Cardiac Center, Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, and colleagues, wrote in an accompanying editorial that “the decreased frequency of the disease along (with) the reassuring reports on midterm outcomes can allow the pediatric community a moment of collective exhale.”
The editorialists note that of those who initially presented with myocardial dysfunction, all but one patient evaluated had a normal ejection fraction at follow-up. Energy, sleep, appetite, cognition, and mood also normalized by midterm.
“The results of the MUSIC study add to the emerging midterm outcomes data suggesting a near-complete cardiovascular recovery in the overwhelming majority of patients who develop MIS-C,” Goldberg and colleagues wrote. “Despite initial concerns, driven by the severity of acute presentation at diagnosis and longer-term questions that remain (for example, does coronary microvascular dysfunction persist even after normalization of coronary artery z score?), these data suggest an encouraging outlook for the long-term health of affected children.”
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and other agencies have reported a declining overall incidence of MIS-C and highlighted the protective value of vaccination.
The editorialists add, however, that while the drop in MIS-C cases is encouraging, cases are still reported, especially amid high viral activity periods, “and nearly half of affected children continue to require intensive care in the acute phase of illness.”
Truong reported grants from the National Institutes of Health and serving as coprincipal investigator for Pfizer for research on COVID-19 vaccine-associated myocarditis funded by Pfizer and occurring through the framework of the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute’s Pediatric Heart Network outside the submitted work. One coauthor reported grants from Pfizer and Boston Scientific outside the submitted work. One coauthor reported receiving grants from Additional Ventures Foundation outside the submitted work. One coauthor reported receiving consultant fees from Amryt Pharma, Chiesi, Esperion, and Ultragenyx outside the submitted work. A coauthor reported receiving consultant fees from Larimar Therapeutics for mitochondrial therapies outside the submitted work. One coauthor reported being an employee of Takeda Pharmaceuticals since July 2023. One editorialist reported grants from Childhood Arthritis and Rheumatology Research Alliance and the Arthritis Foundation, Academy Health, and the Gordon and Betty Moore Foundation during the conduct of the study.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Children who were severely ill with multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children (MIS-C) related to COVID-19 infection appear to show excellent cardiovascular and noncardiovascular outcomes by 6 months, according to data published in JAMA Pediatrics.
MIS-C is a life-threatening complication of COVID-19 infection and data on outcomes are limited, wrote the authors, led by Dongngan T. Truong, MD, MSSI, with Children’s Healthcare of Atlanta Cardiology, Emory University School of Medicine in Atlanta, Georgia. These 6-month results are from the Long-Term Outcomes After the Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in Children (MUSIC) study, sponsored by the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute.
Researchers found in this cohort study of 1204 participants that by 6 months after hospital discharge, 99% had normalization of left ventricular systolic function, and 92.3% had normalized coronary artery dimensions. More than 95% reported being more than 90% back to baseline health.
Patient-Reported Outcomes Measurement Information Systems (PROMIS) Global Health scores were at least equivalent to prepandemic population normative values. PROMIS Global Health parent/guardian proxy median T scores for fatigue, global health, and pain interference improved significantly from 2 weeks to 6 months: fatigue, 56.1 vs 48.9; global health, 48.8 vs 51.3; pain interference, 53.0 vs 43.3 (P < .001).
The most common symptoms reported at 2 weeks were fatigue (15.9%) and low stamina/energy (9.2%); both decreased to 3.4% and 3.3%, respectively, by 6 months. The most common cardiovascular symptom at 2 weeks was palpitations (1.5%), which decreased to 0.6%.
Chest Pain Increased Over Time
Reports of chest pain, however, reportedly increased over time, with 1.3% reporting chest pain at rest at 2 weeks and 2.2% at 6 months. Although gastrointestinal symptoms were common during the acute MIS-C, only 5.3% of respondents reported those symptoms at 2 weeks.
Children in the cohort had a median age of 9 years, and 60% were men. They self-identified with the following races and ethnicities: American Indian or Alaska Native (0.1%), Asian (3.3%), Black (27.0%), Hawaiian Native or Other Pacific Islander (0.2%), Hispanic or Latino (26.9%), multiracial (2.7%), White (31.2%), other (1.0%), and unknown or refused to specify (7.6%). Authors wrote that the cohort was followed-up to 2 years after illness onset and long-term results are not yet known.
Time to Exhale
David J. Goldberg, MD, with the Cardiac Center, Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, and colleagues, wrote in an accompanying editorial that “the decreased frequency of the disease along (with) the reassuring reports on midterm outcomes can allow the pediatric community a moment of collective exhale.”
The editorialists note that of those who initially presented with myocardial dysfunction, all but one patient evaluated had a normal ejection fraction at follow-up. Energy, sleep, appetite, cognition, and mood also normalized by midterm.
“The results of the MUSIC study add to the emerging midterm outcomes data suggesting a near-complete cardiovascular recovery in the overwhelming majority of patients who develop MIS-C,” Goldberg and colleagues wrote. “Despite initial concerns, driven by the severity of acute presentation at diagnosis and longer-term questions that remain (for example, does coronary microvascular dysfunction persist even after normalization of coronary artery z score?), these data suggest an encouraging outlook for the long-term health of affected children.”
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and other agencies have reported a declining overall incidence of MIS-C and highlighted the protective value of vaccination.
The editorialists add, however, that while the drop in MIS-C cases is encouraging, cases are still reported, especially amid high viral activity periods, “and nearly half of affected children continue to require intensive care in the acute phase of illness.”
Truong reported grants from the National Institutes of Health and serving as coprincipal investigator for Pfizer for research on COVID-19 vaccine-associated myocarditis funded by Pfizer and occurring through the framework of the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute’s Pediatric Heart Network outside the submitted work. One coauthor reported grants from Pfizer and Boston Scientific outside the submitted work. One coauthor reported receiving grants from Additional Ventures Foundation outside the submitted work. One coauthor reported receiving consultant fees from Amryt Pharma, Chiesi, Esperion, and Ultragenyx outside the submitted work. A coauthor reported receiving consultant fees from Larimar Therapeutics for mitochondrial therapies outside the submitted work. One coauthor reported being an employee of Takeda Pharmaceuticals since July 2023. One editorialist reported grants from Childhood Arthritis and Rheumatology Research Alliance and the Arthritis Foundation, Academy Health, and the Gordon and Betty Moore Foundation during the conduct of the study.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM JAMA PEDIATRICS
Both High and Low HDL Levels Linked to Increased Risk for Age-Related Macular Degeneration
TOPLINE:
This study also identified a potential novel single-nucleotide polymorphism linked to an elevated risk for the retina condition.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers conducted a cross-sectional retrospective analysis using data from the All of Us research program to assess the association between lipoprotein and the risk for AMD.
- They analyzed data from 2328 patients with AMD (mean age, 75.5 years; 46.7% women; 84.2% White individuals) and 5028 matched controls (mean age, 75.6 years; 52.5% women; 82.9% White individuals).
- Data were extracted for smoking status, history of hyperlipidemia, use of statins (categorized as hepatically and non-hepatically metabolized), and laboratory values for total triglyceride, low-density lipoprotein (LDL), and HDL levels.
- Data for single-nucleotide polymorphisms associated with the dysregulation of LDL and HDL metabolism were extracted using the PLINK toolkit.
TAKEAWAY:
- Both high and low HDL levels were associated with an increased risk for AMD (adjusted odds ratio [aOR], 1.28 for both; both P < .001), whereas low and high levels of triglyceride and LDL did not demonstrate a statistically significant association with the risk for AMD.
- A history of smoking and statin use showed significant associations with an increased risk for AMD (aOR, 1.30 and 1.36, respectively; both P < .001).
- Single-nucleotide polymorphisms in the genes associated with HDL metabolism, ABCA1 and LIPC, were negatively associated with the risk for AMD (aOR, 0.88; P = .04 and aOR, 0.86; P = .001, respectively).
- Lipoprotein(a) or Lp(a) was identified as a novel single nucleotide polymorphism linked to an increased risk for AMD (aOR, 1.37; P = .007).
IN PRACTICE:
“Despite conflicting evidence regarding the relationship with elevated HDL and AMD risk, this is to our knowledge the first time a U-shaped relationship with low and high HDL and AMD has been described. In fact, the presence of a U-shaped relationship may explain inconsistency in prior analyses comparing mean HDL levels in AMD and control populations,” the study authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Jimmy S. Chen, MD, of the Viterbi Family Department of Ophthalmology and Shiley Eye Institute at the University of California, San Diego. It was published online on January 3, 2025, in Ophthalmology.
LIMITATIONS:
The study was limited by the retrospective collection and analysis of data. The use of billing codes for diagnosis extraction may have introduced documentation inaccuracies. The subgroup analysis by severity of AMD was not performed.
DISCLOSURES:
One of the authors was funded by grants from the National Eye Institute (NEI), Research to Prevent Blindness Career Development Award, Robert Machemer MD and International Retinal Research Foundation, and the UC San Diego Academic Senate. Another author reported receiving a grant from the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute, while a third author received funding from the National Institutes of Health (NIH), NEI, and Research to Prevent Blindness. The All of Us Research Program was supported by grants from the NIH and other sources. The authors reported no conflicts of interest.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
This study also identified a potential novel single-nucleotide polymorphism linked to an elevated risk for the retina condition.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers conducted a cross-sectional retrospective analysis using data from the All of Us research program to assess the association between lipoprotein and the risk for AMD.
- They analyzed data from 2328 patients with AMD (mean age, 75.5 years; 46.7% women; 84.2% White individuals) and 5028 matched controls (mean age, 75.6 years; 52.5% women; 82.9% White individuals).
- Data were extracted for smoking status, history of hyperlipidemia, use of statins (categorized as hepatically and non-hepatically metabolized), and laboratory values for total triglyceride, low-density lipoprotein (LDL), and HDL levels.
- Data for single-nucleotide polymorphisms associated with the dysregulation of LDL and HDL metabolism were extracted using the PLINK toolkit.
TAKEAWAY:
- Both high and low HDL levels were associated with an increased risk for AMD (adjusted odds ratio [aOR], 1.28 for both; both P < .001), whereas low and high levels of triglyceride and LDL did not demonstrate a statistically significant association with the risk for AMD.
- A history of smoking and statin use showed significant associations with an increased risk for AMD (aOR, 1.30 and 1.36, respectively; both P < .001).
- Single-nucleotide polymorphisms in the genes associated with HDL metabolism, ABCA1 and LIPC, were negatively associated with the risk for AMD (aOR, 0.88; P = .04 and aOR, 0.86; P = .001, respectively).
- Lipoprotein(a) or Lp(a) was identified as a novel single nucleotide polymorphism linked to an increased risk for AMD (aOR, 1.37; P = .007).
IN PRACTICE:
“Despite conflicting evidence regarding the relationship with elevated HDL and AMD risk, this is to our knowledge the first time a U-shaped relationship with low and high HDL and AMD has been described. In fact, the presence of a U-shaped relationship may explain inconsistency in prior analyses comparing mean HDL levels in AMD and control populations,” the study authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Jimmy S. Chen, MD, of the Viterbi Family Department of Ophthalmology and Shiley Eye Institute at the University of California, San Diego. It was published online on January 3, 2025, in Ophthalmology.
LIMITATIONS:
The study was limited by the retrospective collection and analysis of data. The use of billing codes for diagnosis extraction may have introduced documentation inaccuracies. The subgroup analysis by severity of AMD was not performed.
DISCLOSURES:
One of the authors was funded by grants from the National Eye Institute (NEI), Research to Prevent Blindness Career Development Award, Robert Machemer MD and International Retinal Research Foundation, and the UC San Diego Academic Senate. Another author reported receiving a grant from the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute, while a third author received funding from the National Institutes of Health (NIH), NEI, and Research to Prevent Blindness. The All of Us Research Program was supported by grants from the NIH and other sources. The authors reported no conflicts of interest.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
This study also identified a potential novel single-nucleotide polymorphism linked to an elevated risk for the retina condition.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers conducted a cross-sectional retrospective analysis using data from the All of Us research program to assess the association between lipoprotein and the risk for AMD.
- They analyzed data from 2328 patients with AMD (mean age, 75.5 years; 46.7% women; 84.2% White individuals) and 5028 matched controls (mean age, 75.6 years; 52.5% women; 82.9% White individuals).
- Data were extracted for smoking status, history of hyperlipidemia, use of statins (categorized as hepatically and non-hepatically metabolized), and laboratory values for total triglyceride, low-density lipoprotein (LDL), and HDL levels.
- Data for single-nucleotide polymorphisms associated with the dysregulation of LDL and HDL metabolism were extracted using the PLINK toolkit.
TAKEAWAY:
- Both high and low HDL levels were associated with an increased risk for AMD (adjusted odds ratio [aOR], 1.28 for both; both P < .001), whereas low and high levels of triglyceride and LDL did not demonstrate a statistically significant association with the risk for AMD.
- A history of smoking and statin use showed significant associations with an increased risk for AMD (aOR, 1.30 and 1.36, respectively; both P < .001).
- Single-nucleotide polymorphisms in the genes associated with HDL metabolism, ABCA1 and LIPC, were negatively associated with the risk for AMD (aOR, 0.88; P = .04 and aOR, 0.86; P = .001, respectively).
- Lipoprotein(a) or Lp(a) was identified as a novel single nucleotide polymorphism linked to an increased risk for AMD (aOR, 1.37; P = .007).
IN PRACTICE:
“Despite conflicting evidence regarding the relationship with elevated HDL and AMD risk, this is to our knowledge the first time a U-shaped relationship with low and high HDL and AMD has been described. In fact, the presence of a U-shaped relationship may explain inconsistency in prior analyses comparing mean HDL levels in AMD and control populations,” the study authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Jimmy S. Chen, MD, of the Viterbi Family Department of Ophthalmology and Shiley Eye Institute at the University of California, San Diego. It was published online on January 3, 2025, in Ophthalmology.
LIMITATIONS:
The study was limited by the retrospective collection and analysis of data. The use of billing codes for diagnosis extraction may have introduced documentation inaccuracies. The subgroup analysis by severity of AMD was not performed.
DISCLOSURES:
One of the authors was funded by grants from the National Eye Institute (NEI), Research to Prevent Blindness Career Development Award, Robert Machemer MD and International Retinal Research Foundation, and the UC San Diego Academic Senate. Another author reported receiving a grant from the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute, while a third author received funding from the National Institutes of Health (NIH), NEI, and Research to Prevent Blindness. The All of Us Research Program was supported by grants from the NIH and other sources. The authors reported no conflicts of interest.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Nutrition, Drugs, or Bariatric Surgery: What’s the Best Approach for Sustained Weight Loss?
Given that more than 100 million US adults have obesity, including 22 million with severe obesity, physicians regularly see patients with the condition in their practices.
Fortunately, doctors have more tools than ever to help their patients. But the question remains: Which method is the safest and most effective? Is it diet and lifestyle changes, one of the recently approved anti-obesity medications (AOMs), bariatric surgery, or a combination approach?
There are no head-to-head trials comparing these three approaches, said Vanita Rahman, MD, clinic director of the Barnard Medical Center, Washington, DC, at the International Conference on Nutrition in Medicine, sponsored by the Physicians Committee for Responsible Medicine.
Instead, doctors must evaluate the merits and drawbacks of each intervention and decide with their patients which treatment is best for them, she told Medscape Medical News. When she sees patients, Rahman shares the pertinent research with them, so they are able to make an informed choice.
Looking at the Options
In her presentation at the conference, Rahman summarized the guidelines issued by the American Heart Association/American College of Cardiology/The Obesity Society for Management of Overweight and Obesity in Adults and the American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists and American College of Endocrinology Comprehensive Clinical Practice Guidelines For Medical Care of Patients with Obesity, including lifestyle changes, AOMs, and bariatric surgery (Table 1).
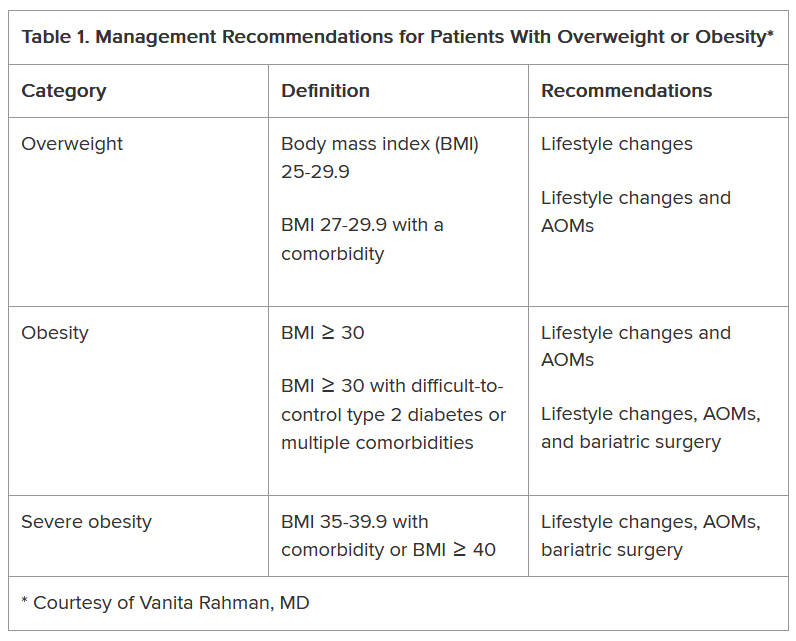
As shown, the current clinical guidelines offer recommendations that consider such factors as the patient’s BMI and presence of one or more comorbidities. Generally, they begin with lifestyle changes for people with overweight, the possibility of an AOM for those with obesity, and bariatric surgery as an option for those with severe obesity-related complications.
“In obesity, we traditionally thought the process was ‘either-or’ — either lifestyle or surgery or medication — and somehow lifestyle is better,” Sheethal Reddy, PhD, a psychologist at the Bariatric Center at Emory University Hospital Midtown, Atlanta, told Medscape Medical News.
Now physicians often use a combination of methods, but lifestyle is foundational to all of them, she said.
“If you don’t make lifestyle changes, none of the approaches will ultimately be effective,” said Reddy, who also is an assistant professor in the Division of General and GI Surgery at Emory School of Medicine, Atlanta.
Lifestyle changes don’t just involve diet and nutrition but include physical exercise.
“Being sedentary affects everything — sleep quality, appetite regulation, and metabolism. Without sufficient exercise, the body isn’t functioning well enough to have a healthy metabolism,” Reddy said.
How Durable Are the Interventions?
Although bariatric surgery has demonstrated effectiveness in helping patients lose weight, many of them regain some or most of it, Rahman said.
A systematic review and meta-analysis found weight regain in 49% of patients who underwent bariatric surgery patients, with the highest prevalence after Roux-en-Y gastric bypass.
Another study of approximately 45,000 patients who underwent bariatric surgery found differences not only in the percentage of total weight loss among Roux-en-Y gastric bypass, sleeve gastrectomy, and adjustable gastric band procedures but also in how much of that weight stayed off between 1 and 5 years following the procedure (Table 2).
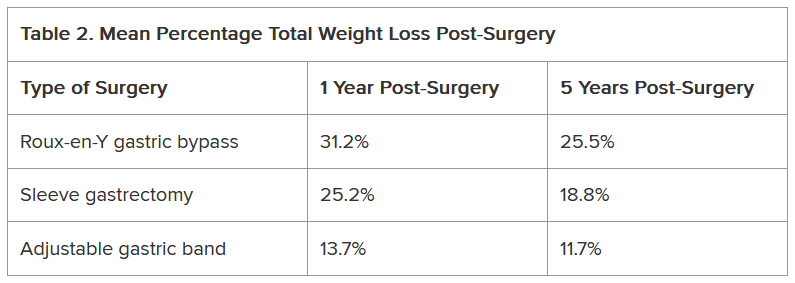
Weight regain also is a risk with AOMs, if they’re discontinued.
The STEP 1 trial tested the effectiveness of semaglutide — a glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) receptor agonist — as an adjunct to lifestyle intervention for weight loss in patients with obesity or with overweight and at least one comorbidity but not diabetes. Mean weight loss with semaglutide was 17.3% but that figure dropped 11.6 percentage points after treatment was discontinued.
Other studies also have found that patients regain weight after GLP-1 discontinuation.
Tirzepatide, a GLP-1 and glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP) combination, has shown efficacy with weight reduction, but patients experienced some weight regain upon discontinuation. In one study, patients experienced a mean weight loss of 20.9% after 36 weeks of tirzepatide. In the study’s subsequent 52-week double-blind, placebo-controlled period, patients who stopped taking the medication experienced a weight regain of 14%, whereas those who remained on the medication lost an additional 5.5% of weight.
GLP-1 and GLP-1/GIP medications do not address the factors that contribute to overweight and obesity, Rahman said. “They simply suppress the appetite; therefore, weight gain occurs after stopping them.”
Patients may stop taking anti-obesity drugs for a variety of reasons, including side effects. Rahman noted that the common side effects include nausea, vomiting, and constipation, whereas rare side effects include gastroparesis, gallbladder and biliary disease, thyroid cancer, and suicidal thoughts. GLP-1 and GLP-1/GIP medications also carry a risk for non-arteritic anterior ischemic optic neuropathy, she said.
Moreover, health insurance does not always cover these medications, which likely affects patient access to the drugs and compliance rates.
“Given the side effects and frequent lack of insurance coverage, significant questions remain about long-term safety and feasibility of these agents,” Rahman said.
What About Nutritional Approaches?
The lifestyle interventions in the semaglutide and tirzepatide studies included 500 kcal/d deficit diets, which is difficult for people to maintain, noted Rahman, who is the author of the book Simply Plant Based: Fabulous Food for a Healthy Life.
Additionally, bariatric surgery has been associated with long-term micronutrient deficiencies, including deficiencies in vitamins A, D, E, K, B1, and B12, as well as folate, iron, zinc, copper, selenium, and calcium, she said.
The best approach to food from a patient compliance standpoint and to avoid nutrient deficiencies is a whole-food, plant-based diet, Rahman said. She advocates this nutritional approach, along with physical activity, for patients regardless of whether they’ve selected lifestyle intervention alone or combined with an AOM or bariatric surgery to address obesity.
Rahman cited a 5-year heart disease study comparing an intensive lifestyle program involving a vegetarian diet, aerobic exercise, stress management training, smoking cessation, and group psychosocial support to treatment as usual. Patients in the lifestyle group lost 10.9 kg at 1 year and sustained weight loss of 5.8 kg at 5 years, whereas weight in the control group remained relatively unchanged from baseline.
She also pointed to the findings of a study of patients with obesity or with overweight and at least one comorbidity that compared standard care with a low-fat, whole-food, plant-based diet with vitamin B12 supplementation. At 6 months, mean BMI reduction was greater in the intervention group than the standard care group (−4.4 vs −0.4).
In her practice, Rahman has seen the benefits of a whole-food, plant-based diet for patients with obesity.
If people are committed to this type of dietary approach and are given the tools and resources to do it effectively, “their thinking changes, their taste buds change, and they grow to enjoy this new way of eating,” she said. “They see results, and it’s a lifestyle that can be sustained long-term.”
Addressing Drivers of Weight Gain
Patients also need help addressing the various factors that may contribute to overweight and obesity, including overconsumption of ultra-processed foods, substandard nutritional quality of restaurant foods, increasing portion sizes, distraction during eating, emotional eating, late-night eating, and cultural/traditional values surrounding food, Rahman noted.
Supatra Tovar, PsyD, RD, a clinical psychologist with a practice in Pasadena, California, agreed that identifying the reasons for weight gain is critical for treatment.
“If you’re not addressing underlying issues, such as a person’s relationship with food, behaviors around food, the tendency to mindlessly eat or emotionally eat or eat to seek comfort, the person’s weight problems won’t ultimately be fully solved by any of the three approaches — dieting, medications, or bariatric surgery,” she said.
Some of her patients “engage in extreme dieting and deprivation, and many who use medications or have had bariatric surgery hardly eat and often develop nutritional deficiencies,” said Tovar, author of the book Deprogram Diet Culture: Rethink Your Relationship with Food, Heal Your Mind, and Live a Diet-Free Life.
The key to healthy and sustained weight loss is to “become attuned to the body’s signals, learn how to honor hunger, stop eating when satisfied, and eat more healthful foods, such as fruits and vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins — especially plant-based proteins — and the body gives signals that this is what it wants,” she said.
Tovar doesn’t give her clients a specific diet or set of portions.
“I teach them to listen to their bodies,” she said. “They’ve lost significant amounts of weight and continued to keep it off because they’ve done this kind of work.”
When Lifestyle Changes Aren’t Enough
For many patients, lifestyle interventions are insufficient to address the degree of overweight and obesity and common comorbidities, said W. Timothy Garvey, MD, associate director and professor, Department of Nutrition Sciences, School of Health Professions, University of Alabama at Birmingham.
“Of course, nutritional approaches are very important, not only for weight but also for general health-related reasons,” said Garvey, lead author of the 2016 American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists obesity guidelines. “We’ve seen that the Mediterranean and some plant-based diets can prevent progression from prediabetes to diabetes and improve other parameters that reflect metabolic health.”
However, it’s “not common that patients can follow these diets, lose weight, and keep it off,” Garvey cautioned. Up to 50% of weight that’s lost through lifestyle changes is typically regained by 1-year follow-up, with almost all remaining lost weight subsequently regained in the majority of individuals because the person “has to fight against pathophysiological process that drive weight regain,” he noted.
Weight-loss medications can address these pathophysiologic processes by “addressing interactions of satiety hormones with feeding centers in the brain, suppressing the appetite, and making it easier for patients to adhere to a reduced-calorie diet.”
Garvey views the weight-loss medications in the same light as drugs for diabetes and hypertension, in that people need to keep taking them to sustain the benefit.
There’s still a role for bariatric surgery because not everyone can tolerate the AOMs or achieve sufficient weight loss.
“Patients with very high BMI who have trouble ambulating might benefit from a combination of bariatric surgery and medication,” Garvey said.
While some side effects are associated with AOMs, being an “alarmist” about them can be detrimental to patients, he warned.
Rahman and Tovar are authors of books about weight loss. Reddy reported no relevant financial relationships. Garvey is a consultant on advisory boards for Boehringer Ingelheim, Eli Lilly, Novo Nordisk, Pfizer, Fractyl Health, Alnylam Pharmaceuticals, Inogen, Zealand, Allurion, Carmot/Roche, Terns Pharmaceuticals, Neurocrine, Keros Therapeutics, and Regeneron. He is the site principal investigator for multi-centered clinical trials sponsored by his university and funded by Novo Nordisk, Eli Lilly, Epitomee, Neurovalens, and Pfizer. He serves as a consultant on the advisory board for the nonprofit Milken Foundation and is a member of the Data Monitoring Committee for phase 3 clinical trials conducted by Boehringer-Ingelheim and Eli Lilly.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Given that more than 100 million US adults have obesity, including 22 million with severe obesity, physicians regularly see patients with the condition in their practices.
Fortunately, doctors have more tools than ever to help their patients. But the question remains: Which method is the safest and most effective? Is it diet and lifestyle changes, one of the recently approved anti-obesity medications (AOMs), bariatric surgery, or a combination approach?
There are no head-to-head trials comparing these three approaches, said Vanita Rahman, MD, clinic director of the Barnard Medical Center, Washington, DC, at the International Conference on Nutrition in Medicine, sponsored by the Physicians Committee for Responsible Medicine.
Instead, doctors must evaluate the merits and drawbacks of each intervention and decide with their patients which treatment is best for them, she told Medscape Medical News. When she sees patients, Rahman shares the pertinent research with them, so they are able to make an informed choice.
Looking at the Options
In her presentation at the conference, Rahman summarized the guidelines issued by the American Heart Association/American College of Cardiology/The Obesity Society for Management of Overweight and Obesity in Adults and the American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists and American College of Endocrinology Comprehensive Clinical Practice Guidelines For Medical Care of Patients with Obesity, including lifestyle changes, AOMs, and bariatric surgery (Table 1).

As shown, the current clinical guidelines offer recommendations that consider such factors as the patient’s BMI and presence of one or more comorbidities. Generally, they begin with lifestyle changes for people with overweight, the possibility of an AOM for those with obesity, and bariatric surgery as an option for those with severe obesity-related complications.
“In obesity, we traditionally thought the process was ‘either-or’ — either lifestyle or surgery or medication — and somehow lifestyle is better,” Sheethal Reddy, PhD, a psychologist at the Bariatric Center at Emory University Hospital Midtown, Atlanta, told Medscape Medical News.
Now physicians often use a combination of methods, but lifestyle is foundational to all of them, she said.
“If you don’t make lifestyle changes, none of the approaches will ultimately be effective,” said Reddy, who also is an assistant professor in the Division of General and GI Surgery at Emory School of Medicine, Atlanta.
Lifestyle changes don’t just involve diet and nutrition but include physical exercise.
“Being sedentary affects everything — sleep quality, appetite regulation, and metabolism. Without sufficient exercise, the body isn’t functioning well enough to have a healthy metabolism,” Reddy said.
How Durable Are the Interventions?
Although bariatric surgery has demonstrated effectiveness in helping patients lose weight, many of them regain some or most of it, Rahman said.
A systematic review and meta-analysis found weight regain in 49% of patients who underwent bariatric surgery patients, with the highest prevalence after Roux-en-Y gastric bypass.
Another study of approximately 45,000 patients who underwent bariatric surgery found differences not only in the percentage of total weight loss among Roux-en-Y gastric bypass, sleeve gastrectomy, and adjustable gastric band procedures but also in how much of that weight stayed off between 1 and 5 years following the procedure (Table 2).

Weight regain also is a risk with AOMs, if they’re discontinued.
The STEP 1 trial tested the effectiveness of semaglutide — a glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) receptor agonist — as an adjunct to lifestyle intervention for weight loss in patients with obesity or with overweight and at least one comorbidity but not diabetes. Mean weight loss with semaglutide was 17.3% but that figure dropped 11.6 percentage points after treatment was discontinued.
Other studies also have found that patients regain weight after GLP-1 discontinuation.
Tirzepatide, a GLP-1 and glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP) combination, has shown efficacy with weight reduction, but patients experienced some weight regain upon discontinuation. In one study, patients experienced a mean weight loss of 20.9% after 36 weeks of tirzepatide. In the study’s subsequent 52-week double-blind, placebo-controlled period, patients who stopped taking the medication experienced a weight regain of 14%, whereas those who remained on the medication lost an additional 5.5% of weight.
GLP-1 and GLP-1/GIP medications do not address the factors that contribute to overweight and obesity, Rahman said. “They simply suppress the appetite; therefore, weight gain occurs after stopping them.”
Patients may stop taking anti-obesity drugs for a variety of reasons, including side effects. Rahman noted that the common side effects include nausea, vomiting, and constipation, whereas rare side effects include gastroparesis, gallbladder and biliary disease, thyroid cancer, and suicidal thoughts. GLP-1 and GLP-1/GIP medications also carry a risk for non-arteritic anterior ischemic optic neuropathy, she said.
Moreover, health insurance does not always cover these medications, which likely affects patient access to the drugs and compliance rates.
“Given the side effects and frequent lack of insurance coverage, significant questions remain about long-term safety and feasibility of these agents,” Rahman said.
What About Nutritional Approaches?
The lifestyle interventions in the semaglutide and tirzepatide studies included 500 kcal/d deficit diets, which is difficult for people to maintain, noted Rahman, who is the author of the book Simply Plant Based: Fabulous Food for a Healthy Life.
Additionally, bariatric surgery has been associated with long-term micronutrient deficiencies, including deficiencies in vitamins A, D, E, K, B1, and B12, as well as folate, iron, zinc, copper, selenium, and calcium, she said.
The best approach to food from a patient compliance standpoint and to avoid nutrient deficiencies is a whole-food, plant-based diet, Rahman said. She advocates this nutritional approach, along with physical activity, for patients regardless of whether they’ve selected lifestyle intervention alone or combined with an AOM or bariatric surgery to address obesity.
Rahman cited a 5-year heart disease study comparing an intensive lifestyle program involving a vegetarian diet, aerobic exercise, stress management training, smoking cessation, and group psychosocial support to treatment as usual. Patients in the lifestyle group lost 10.9 kg at 1 year and sustained weight loss of 5.8 kg at 5 years, whereas weight in the control group remained relatively unchanged from baseline.
She also pointed to the findings of a study of patients with obesity or with overweight and at least one comorbidity that compared standard care with a low-fat, whole-food, plant-based diet with vitamin B12 supplementation. At 6 months, mean BMI reduction was greater in the intervention group than the standard care group (−4.4 vs −0.4).
In her practice, Rahman has seen the benefits of a whole-food, plant-based diet for patients with obesity.
If people are committed to this type of dietary approach and are given the tools and resources to do it effectively, “their thinking changes, their taste buds change, and they grow to enjoy this new way of eating,” she said. “They see results, and it’s a lifestyle that can be sustained long-term.”
Addressing Drivers of Weight Gain
Patients also need help addressing the various factors that may contribute to overweight and obesity, including overconsumption of ultra-processed foods, substandard nutritional quality of restaurant foods, increasing portion sizes, distraction during eating, emotional eating, late-night eating, and cultural/traditional values surrounding food, Rahman noted.
Supatra Tovar, PsyD, RD, a clinical psychologist with a practice in Pasadena, California, agreed that identifying the reasons for weight gain is critical for treatment.
“If you’re not addressing underlying issues, such as a person’s relationship with food, behaviors around food, the tendency to mindlessly eat or emotionally eat or eat to seek comfort, the person’s weight problems won’t ultimately be fully solved by any of the three approaches — dieting, medications, or bariatric surgery,” she said.
Some of her patients “engage in extreme dieting and deprivation, and many who use medications or have had bariatric surgery hardly eat and often develop nutritional deficiencies,” said Tovar, author of the book Deprogram Diet Culture: Rethink Your Relationship with Food, Heal Your Mind, and Live a Diet-Free Life.
The key to healthy and sustained weight loss is to “become attuned to the body’s signals, learn how to honor hunger, stop eating when satisfied, and eat more healthful foods, such as fruits and vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins — especially plant-based proteins — and the body gives signals that this is what it wants,” she said.
Tovar doesn’t give her clients a specific diet or set of portions.
“I teach them to listen to their bodies,” she said. “They’ve lost significant amounts of weight and continued to keep it off because they’ve done this kind of work.”
When Lifestyle Changes Aren’t Enough
For many patients, lifestyle interventions are insufficient to address the degree of overweight and obesity and common comorbidities, said W. Timothy Garvey, MD, associate director and professor, Department of Nutrition Sciences, School of Health Professions, University of Alabama at Birmingham.
“Of course, nutritional approaches are very important, not only for weight but also for general health-related reasons,” said Garvey, lead author of the 2016 American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists obesity guidelines. “We’ve seen that the Mediterranean and some plant-based diets can prevent progression from prediabetes to diabetes and improve other parameters that reflect metabolic health.”
However, it’s “not common that patients can follow these diets, lose weight, and keep it off,” Garvey cautioned. Up to 50% of weight that’s lost through lifestyle changes is typically regained by 1-year follow-up, with almost all remaining lost weight subsequently regained in the majority of individuals because the person “has to fight against pathophysiological process that drive weight regain,” he noted.
Weight-loss medications can address these pathophysiologic processes by “addressing interactions of satiety hormones with feeding centers in the brain, suppressing the appetite, and making it easier for patients to adhere to a reduced-calorie diet.”
Garvey views the weight-loss medications in the same light as drugs for diabetes and hypertension, in that people need to keep taking them to sustain the benefit.
There’s still a role for bariatric surgery because not everyone can tolerate the AOMs or achieve sufficient weight loss.
“Patients with very high BMI who have trouble ambulating might benefit from a combination of bariatric surgery and medication,” Garvey said.
While some side effects are associated with AOMs, being an “alarmist” about them can be detrimental to patients, he warned.
Rahman and Tovar are authors of books about weight loss. Reddy reported no relevant financial relationships. Garvey is a consultant on advisory boards for Boehringer Ingelheim, Eli Lilly, Novo Nordisk, Pfizer, Fractyl Health, Alnylam Pharmaceuticals, Inogen, Zealand, Allurion, Carmot/Roche, Terns Pharmaceuticals, Neurocrine, Keros Therapeutics, and Regeneron. He is the site principal investigator for multi-centered clinical trials sponsored by his university and funded by Novo Nordisk, Eli Lilly, Epitomee, Neurovalens, and Pfizer. He serves as a consultant on the advisory board for the nonprofit Milken Foundation and is a member of the Data Monitoring Committee for phase 3 clinical trials conducted by Boehringer-Ingelheim and Eli Lilly.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Given that more than 100 million US adults have obesity, including 22 million with severe obesity, physicians regularly see patients with the condition in their practices.
Fortunately, doctors have more tools than ever to help their patients. But the question remains: Which method is the safest and most effective? Is it diet and lifestyle changes, one of the recently approved anti-obesity medications (AOMs), bariatric surgery, or a combination approach?
There are no head-to-head trials comparing these three approaches, said Vanita Rahman, MD, clinic director of the Barnard Medical Center, Washington, DC, at the International Conference on Nutrition in Medicine, sponsored by the Physicians Committee for Responsible Medicine.
Instead, doctors must evaluate the merits and drawbacks of each intervention and decide with their patients which treatment is best for them, she told Medscape Medical News. When she sees patients, Rahman shares the pertinent research with them, so they are able to make an informed choice.
Looking at the Options
In her presentation at the conference, Rahman summarized the guidelines issued by the American Heart Association/American College of Cardiology/The Obesity Society for Management of Overweight and Obesity in Adults and the American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists and American College of Endocrinology Comprehensive Clinical Practice Guidelines For Medical Care of Patients with Obesity, including lifestyle changes, AOMs, and bariatric surgery (Table 1).

As shown, the current clinical guidelines offer recommendations that consider such factors as the patient’s BMI and presence of one or more comorbidities. Generally, they begin with lifestyle changes for people with overweight, the possibility of an AOM for those with obesity, and bariatric surgery as an option for those with severe obesity-related complications.
“In obesity, we traditionally thought the process was ‘either-or’ — either lifestyle or surgery or medication — and somehow lifestyle is better,” Sheethal Reddy, PhD, a psychologist at the Bariatric Center at Emory University Hospital Midtown, Atlanta, told Medscape Medical News.
Now physicians often use a combination of methods, but lifestyle is foundational to all of them, she said.
“If you don’t make lifestyle changes, none of the approaches will ultimately be effective,” said Reddy, who also is an assistant professor in the Division of General and GI Surgery at Emory School of Medicine, Atlanta.
Lifestyle changes don’t just involve diet and nutrition but include physical exercise.
“Being sedentary affects everything — sleep quality, appetite regulation, and metabolism. Without sufficient exercise, the body isn’t functioning well enough to have a healthy metabolism,” Reddy said.
How Durable Are the Interventions?
Although bariatric surgery has demonstrated effectiveness in helping patients lose weight, many of them regain some or most of it, Rahman said.
A systematic review and meta-analysis found weight regain in 49% of patients who underwent bariatric surgery patients, with the highest prevalence after Roux-en-Y gastric bypass.
Another study of approximately 45,000 patients who underwent bariatric surgery found differences not only in the percentage of total weight loss among Roux-en-Y gastric bypass, sleeve gastrectomy, and adjustable gastric band procedures but also in how much of that weight stayed off between 1 and 5 years following the procedure (Table 2).

Weight regain also is a risk with AOMs, if they’re discontinued.
The STEP 1 trial tested the effectiveness of semaglutide — a glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) receptor agonist — as an adjunct to lifestyle intervention for weight loss in patients with obesity or with overweight and at least one comorbidity but not diabetes. Mean weight loss with semaglutide was 17.3% but that figure dropped 11.6 percentage points after treatment was discontinued.
Other studies also have found that patients regain weight after GLP-1 discontinuation.
Tirzepatide, a GLP-1 and glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP) combination, has shown efficacy with weight reduction, but patients experienced some weight regain upon discontinuation. In one study, patients experienced a mean weight loss of 20.9% after 36 weeks of tirzepatide. In the study’s subsequent 52-week double-blind, placebo-controlled period, patients who stopped taking the medication experienced a weight regain of 14%, whereas those who remained on the medication lost an additional 5.5% of weight.
GLP-1 and GLP-1/GIP medications do not address the factors that contribute to overweight and obesity, Rahman said. “They simply suppress the appetite; therefore, weight gain occurs after stopping them.”
Patients may stop taking anti-obesity drugs for a variety of reasons, including side effects. Rahman noted that the common side effects include nausea, vomiting, and constipation, whereas rare side effects include gastroparesis, gallbladder and biliary disease, thyroid cancer, and suicidal thoughts. GLP-1 and GLP-1/GIP medications also carry a risk for non-arteritic anterior ischemic optic neuropathy, she said.
Moreover, health insurance does not always cover these medications, which likely affects patient access to the drugs and compliance rates.
“Given the side effects and frequent lack of insurance coverage, significant questions remain about long-term safety and feasibility of these agents,” Rahman said.
What About Nutritional Approaches?
The lifestyle interventions in the semaglutide and tirzepatide studies included 500 kcal/d deficit diets, which is difficult for people to maintain, noted Rahman, who is the author of the book Simply Plant Based: Fabulous Food for a Healthy Life.
Additionally, bariatric surgery has been associated with long-term micronutrient deficiencies, including deficiencies in vitamins A, D, E, K, B1, and B12, as well as folate, iron, zinc, copper, selenium, and calcium, she said.
The best approach to food from a patient compliance standpoint and to avoid nutrient deficiencies is a whole-food, plant-based diet, Rahman said. She advocates this nutritional approach, along with physical activity, for patients regardless of whether they’ve selected lifestyle intervention alone or combined with an AOM or bariatric surgery to address obesity.
Rahman cited a 5-year heart disease study comparing an intensive lifestyle program involving a vegetarian diet, aerobic exercise, stress management training, smoking cessation, and group psychosocial support to treatment as usual. Patients in the lifestyle group lost 10.9 kg at 1 year and sustained weight loss of 5.8 kg at 5 years, whereas weight in the control group remained relatively unchanged from baseline.
She also pointed to the findings of a study of patients with obesity or with overweight and at least one comorbidity that compared standard care with a low-fat, whole-food, plant-based diet with vitamin B12 supplementation. At 6 months, mean BMI reduction was greater in the intervention group than the standard care group (−4.4 vs −0.4).
In her practice, Rahman has seen the benefits of a whole-food, plant-based diet for patients with obesity.
If people are committed to this type of dietary approach and are given the tools and resources to do it effectively, “their thinking changes, their taste buds change, and they grow to enjoy this new way of eating,” she said. “They see results, and it’s a lifestyle that can be sustained long-term.”
Addressing Drivers of Weight Gain
Patients also need help addressing the various factors that may contribute to overweight and obesity, including overconsumption of ultra-processed foods, substandard nutritional quality of restaurant foods, increasing portion sizes, distraction during eating, emotional eating, late-night eating, and cultural/traditional values surrounding food, Rahman noted.
Supatra Tovar, PsyD, RD, a clinical psychologist with a practice in Pasadena, California, agreed that identifying the reasons for weight gain is critical for treatment.
“If you’re not addressing underlying issues, such as a person’s relationship with food, behaviors around food, the tendency to mindlessly eat or emotionally eat or eat to seek comfort, the person’s weight problems won’t ultimately be fully solved by any of the three approaches — dieting, medications, or bariatric surgery,” she said.
Some of her patients “engage in extreme dieting and deprivation, and many who use medications or have had bariatric surgery hardly eat and often develop nutritional deficiencies,” said Tovar, author of the book Deprogram Diet Culture: Rethink Your Relationship with Food, Heal Your Mind, and Live a Diet-Free Life.
The key to healthy and sustained weight loss is to “become attuned to the body’s signals, learn how to honor hunger, stop eating when satisfied, and eat more healthful foods, such as fruits and vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins — especially plant-based proteins — and the body gives signals that this is what it wants,” she said.
Tovar doesn’t give her clients a specific diet or set of portions.
“I teach them to listen to their bodies,” she said. “They’ve lost significant amounts of weight and continued to keep it off because they’ve done this kind of work.”
When Lifestyle Changes Aren’t Enough
For many patients, lifestyle interventions are insufficient to address the degree of overweight and obesity and common comorbidities, said W. Timothy Garvey, MD, associate director and professor, Department of Nutrition Sciences, School of Health Professions, University of Alabama at Birmingham.
“Of course, nutritional approaches are very important, not only for weight but also for general health-related reasons,” said Garvey, lead author of the 2016 American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists obesity guidelines. “We’ve seen that the Mediterranean and some plant-based diets can prevent progression from prediabetes to diabetes and improve other parameters that reflect metabolic health.”
However, it’s “not common that patients can follow these diets, lose weight, and keep it off,” Garvey cautioned. Up to 50% of weight that’s lost through lifestyle changes is typically regained by 1-year follow-up, with almost all remaining lost weight subsequently regained in the majority of individuals because the person “has to fight against pathophysiological process that drive weight regain,” he noted.
Weight-loss medications can address these pathophysiologic processes by “addressing interactions of satiety hormones with feeding centers in the brain, suppressing the appetite, and making it easier for patients to adhere to a reduced-calorie diet.”
Garvey views the weight-loss medications in the same light as drugs for diabetes and hypertension, in that people need to keep taking them to sustain the benefit.
There’s still a role for bariatric surgery because not everyone can tolerate the AOMs or achieve sufficient weight loss.
“Patients with very high BMI who have trouble ambulating might benefit from a combination of bariatric surgery and medication,” Garvey said.
While some side effects are associated with AOMs, being an “alarmist” about them can be detrimental to patients, he warned.
Rahman and Tovar are authors of books about weight loss. Reddy reported no relevant financial relationships. Garvey is a consultant on advisory boards for Boehringer Ingelheim, Eli Lilly, Novo Nordisk, Pfizer, Fractyl Health, Alnylam Pharmaceuticals, Inogen, Zealand, Allurion, Carmot/Roche, Terns Pharmaceuticals, Neurocrine, Keros Therapeutics, and Regeneron. He is the site principal investigator for multi-centered clinical trials sponsored by his university and funded by Novo Nordisk, Eli Lilly, Epitomee, Neurovalens, and Pfizer. He serves as a consultant on the advisory board for the nonprofit Milken Foundation and is a member of the Data Monitoring Committee for phase 3 clinical trials conducted by Boehringer-Ingelheim and Eli Lilly.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
New Proposed Health Cybersecurity Rule: What Physicians Should Know
A new federal rule could force hospitals and doctors’ groups to boost health cybersecurity measures to better protect patients’ health information and prevent ransomware attacks.
The proposed rule, issued by the US Department of Health & Human Services (HHS) and published on January 6 in the Federal Register, marks the first time in a decade that the federal government has updated regulations governing the security of private health information (PHI) that’s kept or shared online. Comments on the rule are due on March 6.
Because the risks for cyberattacks have increased exponentially, “there is a greater need to invest than ever before in both people and technologies to secure patient information,” Adam Greene, an attorney at Davis Wright Tremaine in Washington, DC, who advises healthcare clients on cybersecurity, said in an interview.
Bad actors continue to evolve and are often far ahead of their targets, added Mark Fox, privacy and research compliance officer for the American College of Cardiology.
In the proposed rule, HHS noted that breaches have risen by more than 50% since 2020. Damages from health data breaches are more expensive than in any other sector, averaging $10 million per incident, said HHS.
The damage can continue for years, as much of the data — such as date of birth — in PHI are “immutable,” unlike a credit card number, the agency said. A review of breach reports made to HHS’ Office for Civil Rights shows near-daily data breaches affecting hundreds to tens of thousands of patients. Since December 1 alone, healthcare providers reported breaches affecting nearly 3 million US patients, according to federal data.
Debi Carr, a Florida-based cybersecurity consultant for small physician and dental practices, welcomed the new proposal. “Many practices are clinging to doing things the way they have always done it, and hackers are taking full advantage of that mindset,” she said in an interview. “We have to change our mindset.”
Among the proposal’s recommendations:
- A shift away from making security specifications “addressable” to required. Fox said that many interpreted addressable to mean optional. The clarification is important. The government will require greater accountability, including a requirement to annually revise the risk analysis, to review policies and procedures and implementation, and to perform penetration testing, said Greene.
- Requiring multifactor authentication (MFA) and encryption of PHI at rest and in transit. “A reasonable person who does security will tell you that should be a requirement,” said Fox. Carr added that the February 2024 Change Healthcare ransomware attack happened because workers at the payment processing company were not using MFA.
- Requiring all entities to verify at least once a year that “business associates” have put into place the required safeguards; the associates would need to provide a written analysis of relevant electronic information systems by a subject matter expert and a written certification that the analysis has been performed and is accurate. In the past, the rule “only required that you sign a business associate agreement” with the associate, which could be a payer, a pharmacy, or another physician practice, said Fox. The rule would require all entities to get certification that the controls are in place.
- Requiring a detailed map of an electronic network. For a physician practice, that means creating an inventory of all the technology assets, including devices, applications, and anything that would touch electronic PHI, and then creating a map of how it comes into the office, flows through it, and departs, said Greene.
- Having a plan of action in the case of a breach. The rule will require written procedures to restore certain relevant systems and data within 72 hours and written incident response plans.
Some physician practices — especially those still relying on passwords instead of more sophisticated MFA or encryption — may have to invest significantly to strengthen their information security, said Greene. Smaller organizations, for example, may need to upgrade systems to ensure that user access is terminated within an hour after someone’s employment ends.
Carr said practices should not view the investments as a burden. The regulation “will force practices to implement best cybersecurity practices,” she said.
Implementing those best practices serves as insurance, said Fox. He suggests that anyone in doubt “talk to someone who’s actually lived through a breach and had to recover.”
Tampa General Hospital in Florida, for instance, recently settled a class action suit, agreeing to pay $6.8 million to patients whose PHI was compromised.
It is not certain whether or when the health cybersecurity rule will be made final.
The incoming Trump administration could cancel or delay the rulemaking process.
Even if it continues, “I would not expect a final rule in 2025,” said Greene. He estimates that the rule would not take effect until at least 2026; healthcare entities would have 180 days to comply. Still, those 180 days can go by fast.
“I would say don’t panic, but don’t ignore it either,” he said.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A new federal rule could force hospitals and doctors’ groups to boost health cybersecurity measures to better protect patients’ health information and prevent ransomware attacks.
The proposed rule, issued by the US Department of Health & Human Services (HHS) and published on January 6 in the Federal Register, marks the first time in a decade that the federal government has updated regulations governing the security of private health information (PHI) that’s kept or shared online. Comments on the rule are due on March 6.
Because the risks for cyberattacks have increased exponentially, “there is a greater need to invest than ever before in both people and technologies to secure patient information,” Adam Greene, an attorney at Davis Wright Tremaine in Washington, DC, who advises healthcare clients on cybersecurity, said in an interview.
Bad actors continue to evolve and are often far ahead of their targets, added Mark Fox, privacy and research compliance officer for the American College of Cardiology.
In the proposed rule, HHS noted that breaches have risen by more than 50% since 2020. Damages from health data breaches are more expensive than in any other sector, averaging $10 million per incident, said HHS.
The damage can continue for years, as much of the data — such as date of birth — in PHI are “immutable,” unlike a credit card number, the agency said. A review of breach reports made to HHS’ Office for Civil Rights shows near-daily data breaches affecting hundreds to tens of thousands of patients. Since December 1 alone, healthcare providers reported breaches affecting nearly 3 million US patients, according to federal data.
Debi Carr, a Florida-based cybersecurity consultant for small physician and dental practices, welcomed the new proposal. “Many practices are clinging to doing things the way they have always done it, and hackers are taking full advantage of that mindset,” she said in an interview. “We have to change our mindset.”
Among the proposal’s recommendations:
- A shift away from making security specifications “addressable” to required. Fox said that many interpreted addressable to mean optional. The clarification is important. The government will require greater accountability, including a requirement to annually revise the risk analysis, to review policies and procedures and implementation, and to perform penetration testing, said Greene.
- Requiring multifactor authentication (MFA) and encryption of PHI at rest and in transit. “A reasonable person who does security will tell you that should be a requirement,” said Fox. Carr added that the February 2024 Change Healthcare ransomware attack happened because workers at the payment processing company were not using MFA.
- Requiring all entities to verify at least once a year that “business associates” have put into place the required safeguards; the associates would need to provide a written analysis of relevant electronic information systems by a subject matter expert and a written certification that the analysis has been performed and is accurate. In the past, the rule “only required that you sign a business associate agreement” with the associate, which could be a payer, a pharmacy, or another physician practice, said Fox. The rule would require all entities to get certification that the controls are in place.
- Requiring a detailed map of an electronic network. For a physician practice, that means creating an inventory of all the technology assets, including devices, applications, and anything that would touch electronic PHI, and then creating a map of how it comes into the office, flows through it, and departs, said Greene.
- Having a plan of action in the case of a breach. The rule will require written procedures to restore certain relevant systems and data within 72 hours and written incident response plans.
Some physician practices — especially those still relying on passwords instead of more sophisticated MFA or encryption — may have to invest significantly to strengthen their information security, said Greene. Smaller organizations, for example, may need to upgrade systems to ensure that user access is terminated within an hour after someone’s employment ends.
Carr said practices should not view the investments as a burden. The regulation “will force practices to implement best cybersecurity practices,” she said.
Implementing those best practices serves as insurance, said Fox. He suggests that anyone in doubt “talk to someone who’s actually lived through a breach and had to recover.”
Tampa General Hospital in Florida, for instance, recently settled a class action suit, agreeing to pay $6.8 million to patients whose PHI was compromised.
It is not certain whether or when the health cybersecurity rule will be made final.
The incoming Trump administration could cancel or delay the rulemaking process.
Even if it continues, “I would not expect a final rule in 2025,” said Greene. He estimates that the rule would not take effect until at least 2026; healthcare entities would have 180 days to comply. Still, those 180 days can go by fast.
“I would say don’t panic, but don’t ignore it either,” he said.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A new federal rule could force hospitals and doctors’ groups to boost health cybersecurity measures to better protect patients’ health information and prevent ransomware attacks.
The proposed rule, issued by the US Department of Health & Human Services (HHS) and published on January 6 in the Federal Register, marks the first time in a decade that the federal government has updated regulations governing the security of private health information (PHI) that’s kept or shared online. Comments on the rule are due on March 6.
Because the risks for cyberattacks have increased exponentially, “there is a greater need to invest than ever before in both people and technologies to secure patient information,” Adam Greene, an attorney at Davis Wright Tremaine in Washington, DC, who advises healthcare clients on cybersecurity, said in an interview.
Bad actors continue to evolve and are often far ahead of their targets, added Mark Fox, privacy and research compliance officer for the American College of Cardiology.
In the proposed rule, HHS noted that breaches have risen by more than 50% since 2020. Damages from health data breaches are more expensive than in any other sector, averaging $10 million per incident, said HHS.
The damage can continue for years, as much of the data — such as date of birth — in PHI are “immutable,” unlike a credit card number, the agency said. A review of breach reports made to HHS’ Office for Civil Rights shows near-daily data breaches affecting hundreds to tens of thousands of patients. Since December 1 alone, healthcare providers reported breaches affecting nearly 3 million US patients, according to federal data.
Debi Carr, a Florida-based cybersecurity consultant for small physician and dental practices, welcomed the new proposal. “Many practices are clinging to doing things the way they have always done it, and hackers are taking full advantage of that mindset,” she said in an interview. “We have to change our mindset.”
Among the proposal’s recommendations:
- A shift away from making security specifications “addressable” to required. Fox said that many interpreted addressable to mean optional. The clarification is important. The government will require greater accountability, including a requirement to annually revise the risk analysis, to review policies and procedures and implementation, and to perform penetration testing, said Greene.
- Requiring multifactor authentication (MFA) and encryption of PHI at rest and in transit. “A reasonable person who does security will tell you that should be a requirement,” said Fox. Carr added that the February 2024 Change Healthcare ransomware attack happened because workers at the payment processing company were not using MFA.
- Requiring all entities to verify at least once a year that “business associates” have put into place the required safeguards; the associates would need to provide a written analysis of relevant electronic information systems by a subject matter expert and a written certification that the analysis has been performed and is accurate. In the past, the rule “only required that you sign a business associate agreement” with the associate, which could be a payer, a pharmacy, or another physician practice, said Fox. The rule would require all entities to get certification that the controls are in place.
- Requiring a detailed map of an electronic network. For a physician practice, that means creating an inventory of all the technology assets, including devices, applications, and anything that would touch electronic PHI, and then creating a map of how it comes into the office, flows through it, and departs, said Greene.
- Having a plan of action in the case of a breach. The rule will require written procedures to restore certain relevant systems and data within 72 hours and written incident response plans.
Some physician practices — especially those still relying on passwords instead of more sophisticated MFA or encryption — may have to invest significantly to strengthen their information security, said Greene. Smaller organizations, for example, may need to upgrade systems to ensure that user access is terminated within an hour after someone’s employment ends.
Carr said practices should not view the investments as a burden. The regulation “will force practices to implement best cybersecurity practices,” she said.
Implementing those best practices serves as insurance, said Fox. He suggests that anyone in doubt “talk to someone who’s actually lived through a breach and had to recover.”
Tampa General Hospital in Florida, for instance, recently settled a class action suit, agreeing to pay $6.8 million to patients whose PHI was compromised.
It is not certain whether or when the health cybersecurity rule will be made final.
The incoming Trump administration could cancel or delay the rulemaking process.
Even if it continues, “I would not expect a final rule in 2025,” said Greene. He estimates that the rule would not take effect until at least 2026; healthcare entities would have 180 days to comply. Still, those 180 days can go by fast.
“I would say don’t panic, but don’t ignore it either,” he said.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Leaving ED Without Being Seen Entails Increasing Risks
Higher rates of leaving the emergency department (ED) without being seen are linked to increased short-term mortality or hospitalization, according to a cohort study in Ontario, Canada.
“We found that after 2020, there was a 14% higher risk for death or hospitalization within 7 days” among patients who left without being seen (LWBS), Candace McNaughton, MD, PhD, associate professor of medicine at the University of Toronto and scientist at Sunnybrook Research Institute, both in Toronto, Ontario, Canada, told this news organization.
“When we looked at death by itself, there was a 46% higher risk after 2020,” she said. “Even 30 days after a LWBS ED visit, there was still a 5% increased risk for death/hospitalization and a 24% increased risk for death.”
The study was published in the Journal of the American College of Emergency Physicians Open.
LWBS Rates Increased
Researchers used linked administrative data to analyze temporal trends in monthly rates of ED and LWBS visits for adults in Ontario from 2014 to 2023.
They compared the composite outcome of 7-day all-cause mortality or hospitalization following an LWBS ED visit in April 2022‒March 2023 (recent period) with that following an LWBS ED visit in April 2014‒March 2020 (baseline period), after adjustment for age, sex, and Charlson Comorbidity Index (CCI).
In the two periods, patient characteristics were similar across age, sex, neighborhood-level income quartile, history of being unhoused, rurality, CCI, day, time, and mode of arrival. The median age was 40 years for the baseline period and 42 years for the recent period.
Temporal trends showed sustained increases in monthly LWBS rates after 2020, despite fewer monthly ED visits. The rate of LWBS ED visits after April 1, 2020, exceeded the baseline period’s single-month LWBS maximum of 4% in 15 of 36 months.
The rate of 7-day all-cause mortality or hospitalization was 3.4% in the recent period vs 2.9% in the baseline period (adjusted risk ratio [aRR], 1.14), despite similar rates of post-ED outpatient visits (7-day recent and baseline, 38.9% and 39.7%, respectively).
Similar trends were seen at 30 days for all-cause mortality or hospitalization (6.2% in the recent period vs 5.8% at baseline; aRR, 1.05) despite similar rates of post-ED outpatient visits (59.4% and 59.7%, respectively).
After April 1, 2020, monthly ED visits and the proportion of patients who LWBS varied widely.
The proportion of LWBS visits categorized as emergent on the Canadian Triage and Acuity Scale was higher during the recent period (12.9% vs 9.2% in the baseline period), and fewer visits were categorized as semiurgent (22.6% vs 31.9%, respectively). This finding suggested a higher acuity of illness among patients who LWBS in the recent period.
LWBS Visits ‘Not Benign’
Results of a preplanned subgroup analysis examining the risk for all-cause mortality after an LWBS visit were “particularly notable,” the authors wrote, with a 46% higher adjusted risk for death at 7 days and 24% higher adjusted risk at 30 days.
The observational study had several limitations, however. The authors could not draw conclusions regarding direct causes of the increased risk for severe short-term adverse health outcomes after an LWBS ED visit, and residual confounding is possible. Cause-of-death information was not available to generate hypotheses for future studies of potential causes. Furthermore, the findings may not be generalizable to systems without universal access to healthcare.
Nevertheless, the findings are a “concerning signal [and] should prompt interventions to address system- and population-level causes,” the authors wrote.
“Unfortunately, because of politics, since 2020, ED closures in Ontario have become more and more common and seem to be affecting more and more Ontarians,” said McNaughton. “It would be surprising if ED closure didn’t play some role in our findings.”
She added, “It is important to note that people in our study were relatively young, with a median age in their 40s; this makes our findings all the more concerning. Clinicians should be aware that LWBS ED visits are not necessarily benign, particularly when rates of LWBS ED visits are high.”
Unanswered Questions
The study raised the following questions that the authors are or will be investigating, according to McNaughton:
- Which patients are at greatest risk for bad outcomes if they leave the ED without being seen, and why?
- How much of the findings might be related to recent ED closures, longer ED wait times, or other factors? Are there geographic variations in risk?
- What can be done in the ED to prevent LWBS ED visits, and what can be changed outside the ED to prevent LWBS ED visits? For example, what can hospitals do to reduce boarding in the ED? If patients leave without being seen, should they be contacted to try to meet their health needs in other ways?
- What worked in terms of maintaining access to outpatient medical care, despite the considerable disruptions starting in 2020, and how can continued success be ensured?
To address the current situation, McNaughton said, “We need consistent, predictable, and sustained investment in our public healthcare system. We need long-term, consistent funding for primary care, ED care, as well as hospital and long-term care.”
“It takes years to recruit and train the teams of people necessary to provide the high-quality medical care that Canadians have a right to. There are no shortcuts,” she concluded.
‘Tragic Situation’
American College of Emergency Physicians (ACEP) spokesperson Jesse Pines, MD, chief of clinical innovation at US Acute Care Solutions; clinical professor of emergency medicine at George Washington University in Washington, DC; and professor of emergency medicine at Drexel University in Philadelphia, commented on the study for this news organization.
“Similar to what the authors found in their report, LWBS and other metrics — specifically boarding — have progressively increased in the United States, in particular, since the early part of 2021,” he said. “The primary factor in the US driving this, and one that ACEP is trying to address on a national scale, is the boarding of admitted patients.”
When the number of boarded patients increases, there is less space in the ED for new patients, and waits increase, Pines explained. Some patients leave without being seen, and a subset of those patients experience poor outcomes. “It’s a tragic situation that is worsening.”
“Emergency physicians like me always worry when patients leave without being seen,” he said. While some of those patients have self-limited conditions that will improve on their own, “some have critical life-threatening conditions that require care and hospitalization. The worry is that these patients experience poorer outcomes,” Pines said. “The authors showed that this is increasingly the case in Canada. The same is likely true in the US.”
The study was funded by the Canadian Institutes of Health Research. McNaughton and Pines declared no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Higher rates of leaving the emergency department (ED) without being seen are linked to increased short-term mortality or hospitalization, according to a cohort study in Ontario, Canada.
“We found that after 2020, there was a 14% higher risk for death or hospitalization within 7 days” among patients who left without being seen (LWBS), Candace McNaughton, MD, PhD, associate professor of medicine at the University of Toronto and scientist at Sunnybrook Research Institute, both in Toronto, Ontario, Canada, told this news organization.
“When we looked at death by itself, there was a 46% higher risk after 2020,” she said. “Even 30 days after a LWBS ED visit, there was still a 5% increased risk for death/hospitalization and a 24% increased risk for death.”
The study was published in the Journal of the American College of Emergency Physicians Open.
LWBS Rates Increased
Researchers used linked administrative data to analyze temporal trends in monthly rates of ED and LWBS visits for adults in Ontario from 2014 to 2023.
They compared the composite outcome of 7-day all-cause mortality or hospitalization following an LWBS ED visit in April 2022‒March 2023 (recent period) with that following an LWBS ED visit in April 2014‒March 2020 (baseline period), after adjustment for age, sex, and Charlson Comorbidity Index (CCI).
In the two periods, patient characteristics were similar across age, sex, neighborhood-level income quartile, history of being unhoused, rurality, CCI, day, time, and mode of arrival. The median age was 40 years for the baseline period and 42 years for the recent period.
Temporal trends showed sustained increases in monthly LWBS rates after 2020, despite fewer monthly ED visits. The rate of LWBS ED visits after April 1, 2020, exceeded the baseline period’s single-month LWBS maximum of 4% in 15 of 36 months.
The rate of 7-day all-cause mortality or hospitalization was 3.4% in the recent period vs 2.9% in the baseline period (adjusted risk ratio [aRR], 1.14), despite similar rates of post-ED outpatient visits (7-day recent and baseline, 38.9% and 39.7%, respectively).
Similar trends were seen at 30 days for all-cause mortality or hospitalization (6.2% in the recent period vs 5.8% at baseline; aRR, 1.05) despite similar rates of post-ED outpatient visits (59.4% and 59.7%, respectively).
After April 1, 2020, monthly ED visits and the proportion of patients who LWBS varied widely.
The proportion of LWBS visits categorized as emergent on the Canadian Triage and Acuity Scale was higher during the recent period (12.9% vs 9.2% in the baseline period), and fewer visits were categorized as semiurgent (22.6% vs 31.9%, respectively). This finding suggested a higher acuity of illness among patients who LWBS in the recent period.
LWBS Visits ‘Not Benign’
Results of a preplanned subgroup analysis examining the risk for all-cause mortality after an LWBS visit were “particularly notable,” the authors wrote, with a 46% higher adjusted risk for death at 7 days and 24% higher adjusted risk at 30 days.
The observational study had several limitations, however. The authors could not draw conclusions regarding direct causes of the increased risk for severe short-term adverse health outcomes after an LWBS ED visit, and residual confounding is possible. Cause-of-death information was not available to generate hypotheses for future studies of potential causes. Furthermore, the findings may not be generalizable to systems without universal access to healthcare.
Nevertheless, the findings are a “concerning signal [and] should prompt interventions to address system- and population-level causes,” the authors wrote.
“Unfortunately, because of politics, since 2020, ED closures in Ontario have become more and more common and seem to be affecting more and more Ontarians,” said McNaughton. “It would be surprising if ED closure didn’t play some role in our findings.”
She added, “It is important to note that people in our study were relatively young, with a median age in their 40s; this makes our findings all the more concerning. Clinicians should be aware that LWBS ED visits are not necessarily benign, particularly when rates of LWBS ED visits are high.”
Unanswered Questions
The study raised the following questions that the authors are or will be investigating, according to McNaughton:
- Which patients are at greatest risk for bad outcomes if they leave the ED without being seen, and why?
- How much of the findings might be related to recent ED closures, longer ED wait times, or other factors? Are there geographic variations in risk?
- What can be done in the ED to prevent LWBS ED visits, and what can be changed outside the ED to prevent LWBS ED visits? For example, what can hospitals do to reduce boarding in the ED? If patients leave without being seen, should they be contacted to try to meet their health needs in other ways?
- What worked in terms of maintaining access to outpatient medical care, despite the considerable disruptions starting in 2020, and how can continued success be ensured?
To address the current situation, McNaughton said, “We need consistent, predictable, and sustained investment in our public healthcare system. We need long-term, consistent funding for primary care, ED care, as well as hospital and long-term care.”
“It takes years to recruit and train the teams of people necessary to provide the high-quality medical care that Canadians have a right to. There are no shortcuts,” she concluded.
‘Tragic Situation’
American College of Emergency Physicians (ACEP) spokesperson Jesse Pines, MD, chief of clinical innovation at US Acute Care Solutions; clinical professor of emergency medicine at George Washington University in Washington, DC; and professor of emergency medicine at Drexel University in Philadelphia, commented on the study for this news organization.
“Similar to what the authors found in their report, LWBS and other metrics — specifically boarding — have progressively increased in the United States, in particular, since the early part of 2021,” he said. “The primary factor in the US driving this, and one that ACEP is trying to address on a national scale, is the boarding of admitted patients.”
When the number of boarded patients increases, there is less space in the ED for new patients, and waits increase, Pines explained. Some patients leave without being seen, and a subset of those patients experience poor outcomes. “It’s a tragic situation that is worsening.”
“Emergency physicians like me always worry when patients leave without being seen,” he said. While some of those patients have self-limited conditions that will improve on their own, “some have critical life-threatening conditions that require care and hospitalization. The worry is that these patients experience poorer outcomes,” Pines said. “The authors showed that this is increasingly the case in Canada. The same is likely true in the US.”
The study was funded by the Canadian Institutes of Health Research. McNaughton and Pines declared no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Higher rates of leaving the emergency department (ED) without being seen are linked to increased short-term mortality or hospitalization, according to a cohort study in Ontario, Canada.
“We found that after 2020, there was a 14% higher risk for death or hospitalization within 7 days” among patients who left without being seen (LWBS), Candace McNaughton, MD, PhD, associate professor of medicine at the University of Toronto and scientist at Sunnybrook Research Institute, both in Toronto, Ontario, Canada, told this news organization.
“When we looked at death by itself, there was a 46% higher risk after 2020,” she said. “Even 30 days after a LWBS ED visit, there was still a 5% increased risk for death/hospitalization and a 24% increased risk for death.”
The study was published in the Journal of the American College of Emergency Physicians Open.
LWBS Rates Increased
Researchers used linked administrative data to analyze temporal trends in monthly rates of ED and LWBS visits for adults in Ontario from 2014 to 2023.
They compared the composite outcome of 7-day all-cause mortality or hospitalization following an LWBS ED visit in April 2022‒March 2023 (recent period) with that following an LWBS ED visit in April 2014‒March 2020 (baseline period), after adjustment for age, sex, and Charlson Comorbidity Index (CCI).
In the two periods, patient characteristics were similar across age, sex, neighborhood-level income quartile, history of being unhoused, rurality, CCI, day, time, and mode of arrival. The median age was 40 years for the baseline period and 42 years for the recent period.
Temporal trends showed sustained increases in monthly LWBS rates after 2020, despite fewer monthly ED visits. The rate of LWBS ED visits after April 1, 2020, exceeded the baseline period’s single-month LWBS maximum of 4% in 15 of 36 months.
The rate of 7-day all-cause mortality or hospitalization was 3.4% in the recent period vs 2.9% in the baseline period (adjusted risk ratio [aRR], 1.14), despite similar rates of post-ED outpatient visits (7-day recent and baseline, 38.9% and 39.7%, respectively).
Similar trends were seen at 30 days for all-cause mortality or hospitalization (6.2% in the recent period vs 5.8% at baseline; aRR, 1.05) despite similar rates of post-ED outpatient visits (59.4% and 59.7%, respectively).
After April 1, 2020, monthly ED visits and the proportion of patients who LWBS varied widely.
The proportion of LWBS visits categorized as emergent on the Canadian Triage and Acuity Scale was higher during the recent period (12.9% vs 9.2% in the baseline period), and fewer visits were categorized as semiurgent (22.6% vs 31.9%, respectively). This finding suggested a higher acuity of illness among patients who LWBS in the recent period.
LWBS Visits ‘Not Benign’
Results of a preplanned subgroup analysis examining the risk for all-cause mortality after an LWBS visit were “particularly notable,” the authors wrote, with a 46% higher adjusted risk for death at 7 days and 24% higher adjusted risk at 30 days.
The observational study had several limitations, however. The authors could not draw conclusions regarding direct causes of the increased risk for severe short-term adverse health outcomes after an LWBS ED visit, and residual confounding is possible. Cause-of-death information was not available to generate hypotheses for future studies of potential causes. Furthermore, the findings may not be generalizable to systems without universal access to healthcare.
Nevertheless, the findings are a “concerning signal [and] should prompt interventions to address system- and population-level causes,” the authors wrote.
“Unfortunately, because of politics, since 2020, ED closures in Ontario have become more and more common and seem to be affecting more and more Ontarians,” said McNaughton. “It would be surprising if ED closure didn’t play some role in our findings.”
She added, “It is important to note that people in our study were relatively young, with a median age in their 40s; this makes our findings all the more concerning. Clinicians should be aware that LWBS ED visits are not necessarily benign, particularly when rates of LWBS ED visits are high.”
Unanswered Questions
The study raised the following questions that the authors are or will be investigating, according to McNaughton:
- Which patients are at greatest risk for bad outcomes if they leave the ED without being seen, and why?
- How much of the findings might be related to recent ED closures, longer ED wait times, or other factors? Are there geographic variations in risk?
- What can be done in the ED to prevent LWBS ED visits, and what can be changed outside the ED to prevent LWBS ED visits? For example, what can hospitals do to reduce boarding in the ED? If patients leave without being seen, should they be contacted to try to meet their health needs in other ways?
- What worked in terms of maintaining access to outpatient medical care, despite the considerable disruptions starting in 2020, and how can continued success be ensured?
To address the current situation, McNaughton said, “We need consistent, predictable, and sustained investment in our public healthcare system. We need long-term, consistent funding for primary care, ED care, as well as hospital and long-term care.”
“It takes years to recruit and train the teams of people necessary to provide the high-quality medical care that Canadians have a right to. There are no shortcuts,” she concluded.
‘Tragic Situation’
American College of Emergency Physicians (ACEP) spokesperson Jesse Pines, MD, chief of clinical innovation at US Acute Care Solutions; clinical professor of emergency medicine at George Washington University in Washington, DC; and professor of emergency medicine at Drexel University in Philadelphia, commented on the study for this news organization.
“Similar to what the authors found in their report, LWBS and other metrics — specifically boarding — have progressively increased in the United States, in particular, since the early part of 2021,” he said. “The primary factor in the US driving this, and one that ACEP is trying to address on a national scale, is the boarding of admitted patients.”
When the number of boarded patients increases, there is less space in the ED for new patients, and waits increase, Pines explained. Some patients leave without being seen, and a subset of those patients experience poor outcomes. “It’s a tragic situation that is worsening.”
“Emergency physicians like me always worry when patients leave without being seen,” he said. While some of those patients have self-limited conditions that will improve on their own, “some have critical life-threatening conditions that require care and hospitalization. The worry is that these patients experience poorer outcomes,” Pines said. “The authors showed that this is increasingly the case in Canada. The same is likely true in the US.”
The study was funded by the Canadian Institutes of Health Research. McNaughton and Pines declared no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Scientific Publications Face Credibility Crisis
The quality and credibility of scientific publications have received increasing scrutiny. Findings from studies by Maria Ángeles Oviedo-García, PhD, from the Department of Business and Marketing at the University of Seville in Spain, highlight growing concerns about the integrity of published research. Insights from the journal Science and the US blog Retraction Watch reveal similar concerns regarding research integrity.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) Spurs Low-Quality Submissions
According to a report in Science, journals are inundated with low-quality contributions such as letters and comments generated by AI. Daniel Prevedello, MD, editor in chief of Neurosurgical Review, announced that the journal would temporarily stop accepting these submissions because of their poor quality.
Neurosurgical Review is not the only journal to experience low-quality submissions. In the journal Oral Oncology Reports (Elsevier), comments comprised 70% of the content, whereas in the International Journal of Surgery Open (Wolters Kluwer), they accounted for nearly half. In Neurosurgical Review, letters, comments, and editorials made up 58% of the total content from January to October 2024, compared with only 9% in the previous year.
This trend benefits authors by allowing them to inflate their publication lists with quickly produced contributions that bypass peer review. Publishers may also profit, as many charge fees to publish comments. Additionally, universities and research institutions find this type of content generation useful as more publications can enhance their reputation.
Concerns Over Peer Reviews
The troubling behavior described by Oviedo-García in the journal Scientometrics raises further doubts. An analysis of 263 peer reviews from 37 journals revealed that reviewers often used identical or very similar phrases in their evaluations, regardless of the content. In one case, the reviewer used the same wording in 52 reviews. This suggests that some reviewers read the studies that they are supposed to evaluate only superficially. Such practices can lead to valueless reviews and jeopardize the integrity of scientific literature. “Some other researchers will probably base their future research on these fake reports, which is frightening, especially when it comes to health and medicine,” Oviedo-García stated.
She suspects that the reviewers may have relied on templates to produce their reports quickly. This allowed them to list this work on their resumes for potential career advantages. Some reviewers have reportedly even “requested” the authors of the studies they reviewed to cite their own scientific work.
AI Complicates Peer Review
The process of research and publication has become increasingly challenging in recent years, and more standard and predatory journals allow anyone to publish their work for a fee. Roger W. Byard, MD, PhD, from the University of Adelaide in Australia, explained this trend in the journal Forensic Science, Medicine and Pathology. AI is increasingly being used to generate articles. At international conferences, experts have highlighted claims that AI can complete papers in just a few weeks and dissertations in less than a year. According to the authors of a letter in Critical Care, generative AI is infiltrating the peer review process.
Moreover, the peer review process can be bypassed by publishing research findings on online platforms (eg, preprint servers). Another issue is that some publications have hundreds of authors who can extend their publication list in this manner, even if their contribution to the publication is ambiguous or not substantial.
In a guest article for the Laborjournal, Ulrich Dirnagl, MD, PhD, from the Charité — Universitätsmedizin Berlin in Germany, emphasized that the scientific papers have become so complex that two or three experts often cannot thoroughly assess everything presented. The review process is time-consuming and can take several days for reviewers. Currently, very few people have time, especially because it is an unpaid and anonymous task. Dirnagl stated, “the self-correction of science no longer works as it claims.”
The old Russian saying ‘Dowjerjaj, no prowjerjaj: Trust, but verify’ remains a timeless recommendation that is likely to stay relevant for years to come.
This story was translated from Univadis Germany using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
The quality and credibility of scientific publications have received increasing scrutiny. Findings from studies by Maria Ángeles Oviedo-García, PhD, from the Department of Business and Marketing at the University of Seville in Spain, highlight growing concerns about the integrity of published research. Insights from the journal Science and the US blog Retraction Watch reveal similar concerns regarding research integrity.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) Spurs Low-Quality Submissions
According to a report in Science, journals are inundated with low-quality contributions such as letters and comments generated by AI. Daniel Prevedello, MD, editor in chief of Neurosurgical Review, announced that the journal would temporarily stop accepting these submissions because of their poor quality.
Neurosurgical Review is not the only journal to experience low-quality submissions. In the journal Oral Oncology Reports (Elsevier), comments comprised 70% of the content, whereas in the International Journal of Surgery Open (Wolters Kluwer), they accounted for nearly half. In Neurosurgical Review, letters, comments, and editorials made up 58% of the total content from January to October 2024, compared with only 9% in the previous year.
This trend benefits authors by allowing them to inflate their publication lists with quickly produced contributions that bypass peer review. Publishers may also profit, as many charge fees to publish comments. Additionally, universities and research institutions find this type of content generation useful as more publications can enhance their reputation.
Concerns Over Peer Reviews
The troubling behavior described by Oviedo-García in the journal Scientometrics raises further doubts. An analysis of 263 peer reviews from 37 journals revealed that reviewers often used identical or very similar phrases in their evaluations, regardless of the content. In one case, the reviewer used the same wording in 52 reviews. This suggests that some reviewers read the studies that they are supposed to evaluate only superficially. Such practices can lead to valueless reviews and jeopardize the integrity of scientific literature. “Some other researchers will probably base their future research on these fake reports, which is frightening, especially when it comes to health and medicine,” Oviedo-García stated.
She suspects that the reviewers may have relied on templates to produce their reports quickly. This allowed them to list this work on their resumes for potential career advantages. Some reviewers have reportedly even “requested” the authors of the studies they reviewed to cite their own scientific work.
AI Complicates Peer Review
The process of research and publication has become increasingly challenging in recent years, and more standard and predatory journals allow anyone to publish their work for a fee. Roger W. Byard, MD, PhD, from the University of Adelaide in Australia, explained this trend in the journal Forensic Science, Medicine and Pathology. AI is increasingly being used to generate articles. At international conferences, experts have highlighted claims that AI can complete papers in just a few weeks and dissertations in less than a year. According to the authors of a letter in Critical Care, generative AI is infiltrating the peer review process.
Moreover, the peer review process can be bypassed by publishing research findings on online platforms (eg, preprint servers). Another issue is that some publications have hundreds of authors who can extend their publication list in this manner, even if their contribution to the publication is ambiguous or not substantial.
In a guest article for the Laborjournal, Ulrich Dirnagl, MD, PhD, from the Charité — Universitätsmedizin Berlin in Germany, emphasized that the scientific papers have become so complex that two or three experts often cannot thoroughly assess everything presented. The review process is time-consuming and can take several days for reviewers. Currently, very few people have time, especially because it is an unpaid and anonymous task. Dirnagl stated, “the self-correction of science no longer works as it claims.”
The old Russian saying ‘Dowjerjaj, no prowjerjaj: Trust, but verify’ remains a timeless recommendation that is likely to stay relevant for years to come.
This story was translated from Univadis Germany using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
The quality and credibility of scientific publications have received increasing scrutiny. Findings from studies by Maria Ángeles Oviedo-García, PhD, from the Department of Business and Marketing at the University of Seville in Spain, highlight growing concerns about the integrity of published research. Insights from the journal Science and the US blog Retraction Watch reveal similar concerns regarding research integrity.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) Spurs Low-Quality Submissions
According to a report in Science, journals are inundated with low-quality contributions such as letters and comments generated by AI. Daniel Prevedello, MD, editor in chief of Neurosurgical Review, announced that the journal would temporarily stop accepting these submissions because of their poor quality.
Neurosurgical Review is not the only journal to experience low-quality submissions. In the journal Oral Oncology Reports (Elsevier), comments comprised 70% of the content, whereas in the International Journal of Surgery Open (Wolters Kluwer), they accounted for nearly half. In Neurosurgical Review, letters, comments, and editorials made up 58% of the total content from January to October 2024, compared with only 9% in the previous year.
This trend benefits authors by allowing them to inflate their publication lists with quickly produced contributions that bypass peer review. Publishers may also profit, as many charge fees to publish comments. Additionally, universities and research institutions find this type of content generation useful as more publications can enhance their reputation.
Concerns Over Peer Reviews
The troubling behavior described by Oviedo-García in the journal Scientometrics raises further doubts. An analysis of 263 peer reviews from 37 journals revealed that reviewers often used identical or very similar phrases in their evaluations, regardless of the content. In one case, the reviewer used the same wording in 52 reviews. This suggests that some reviewers read the studies that they are supposed to evaluate only superficially. Such practices can lead to valueless reviews and jeopardize the integrity of scientific literature. “Some other researchers will probably base their future research on these fake reports, which is frightening, especially when it comes to health and medicine,” Oviedo-García stated.
She suspects that the reviewers may have relied on templates to produce their reports quickly. This allowed them to list this work on their resumes for potential career advantages. Some reviewers have reportedly even “requested” the authors of the studies they reviewed to cite their own scientific work.
AI Complicates Peer Review
The process of research and publication has become increasingly challenging in recent years, and more standard and predatory journals allow anyone to publish their work for a fee. Roger W. Byard, MD, PhD, from the University of Adelaide in Australia, explained this trend in the journal Forensic Science, Medicine and Pathology. AI is increasingly being used to generate articles. At international conferences, experts have highlighted claims that AI can complete papers in just a few weeks and dissertations in less than a year. According to the authors of a letter in Critical Care, generative AI is infiltrating the peer review process.
Moreover, the peer review process can be bypassed by publishing research findings on online platforms (eg, preprint servers). Another issue is that some publications have hundreds of authors who can extend their publication list in this manner, even if their contribution to the publication is ambiguous or not substantial.
In a guest article for the Laborjournal, Ulrich Dirnagl, MD, PhD, from the Charité — Universitätsmedizin Berlin in Germany, emphasized that the scientific papers have become so complex that two or three experts often cannot thoroughly assess everything presented. The review process is time-consuming and can take several days for reviewers. Currently, very few people have time, especially because it is an unpaid and anonymous task. Dirnagl stated, “the self-correction of science no longer works as it claims.”
The old Russian saying ‘Dowjerjaj, no prowjerjaj: Trust, but verify’ remains a timeless recommendation that is likely to stay relevant for years to come.
This story was translated from Univadis Germany using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
How Does End of Life Impact Diabetes Care?
TOPLINE:
Among older adults with type 2 diabetes (T2D), the use of antidiabetes medications declined in the last year before death, with notable shifts from metformin and sulfonylureas toward insulin therapy.
METHODOLOGY:
Current recommendations emphasize a more liberal approach to glycemic control in people with a high burden of comorbidities and shorter life expectancy, but little is known about the changes and discontinuation patterns of diabetes medications among older adults near the end of life.
.
All medication classes available during the study period were considered, including short-acting and long-acting insulins, metformin, sulfonylureas, dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors, glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) receptor agonists, sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 (SGLT2) inhibitors, and other medications.
Analysis included temporal trends in prescribing antidiabetes medications, stratified by frailty using a validated claims-based frailty index, with scores ≥ 0.30 indicating higher frailty.
Antidiabetes medication fills were assessed within 1 year before death, examining changes across three time periods: 12 to 8 months, 8 to 4 months, and 4 to 0 months before death.
TAKEAWAY:
The proportion of older patients receiving antidiabetes medications increased slightly from 71.4% in 2015 to 72.9% in 2019, with metformin showing the largest increase from 40.7% to 46.5% (standardized mean difference [SMD], −0.12) and sulfonylureas showing the largest decrease from 37.0% to 31.8% (SMD, 0.11).
The use of newer diabetes medications with cardiovascular benefits, such as GLP-1 receptor agonists and SGLT2 inhibitors, remained less common but showed increasing trends over time.
The use of any antidiabetes medication decreased from 66.1% in the 9 to 12 months before death to 60.8% in the last 4 months of life (P < .01), primarily due to the reduced use of metformin and sulfonylureas.
The use of both short-acting and long-acting insulin agents increased toward the end of life (from 28.0% to 32.9% and from 41.2% to 43.9%, respectively; both P < .001) , particularly among frailer individuals.
IN PRACTICE:
“[The study] findings underscore important implications for diabetes management in patients nearing the end of life. With ~70% of patients with T2D using at least one antidiabetes medication, there is a need to consider further de-escalation or deprescribing in this vulnerable population,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Alexander Kutz, MD, MPH, MSc, Division of Pharmacoepidemiology and Pharmacoeconomics, Department of Medicine, Brigham and Women’s Hospital and Harvard Medical School, Boston, and was published online in Diabetes Care.
LIMITATIONS:
The study lacked details on the reasons for changes in medication patterns, making it unclear whether these changes were due to clinical guidelines or to reduce adverse events. Moreover, the study could not capture transitions or substitutions between medications, information on the dosage data, and causes of death.
DISCLOSURES:
This study was supported by the Division of Pharmacoepidemiology and Pharmacoeconomics, Department of Medicine, Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Harvard Medical School. Some authors reported receiving personal fees or research grants from the National Institutes of Health and other institutions and a few pharmaceutical companies. One author reported acting as a principal investigator and receiving a research grant from Boehringer-Ingelheim, unrelated to the work.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Among older adults with type 2 diabetes (T2D), the use of antidiabetes medications declined in the last year before death, with notable shifts from metformin and sulfonylureas toward insulin therapy.
METHODOLOGY:
Current recommendations emphasize a more liberal approach to glycemic control in people with a high burden of comorbidities and shorter life expectancy, but little is known about the changes and discontinuation patterns of diabetes medications among older adults near the end of life.
.
All medication classes available during the study period were considered, including short-acting and long-acting insulins, metformin, sulfonylureas, dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors, glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) receptor agonists, sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 (SGLT2) inhibitors, and other medications.
Analysis included temporal trends in prescribing antidiabetes medications, stratified by frailty using a validated claims-based frailty index, with scores ≥ 0.30 indicating higher frailty.
Antidiabetes medication fills were assessed within 1 year before death, examining changes across three time periods: 12 to 8 months, 8 to 4 months, and 4 to 0 months before death.
TAKEAWAY:
The proportion of older patients receiving antidiabetes medications increased slightly from 71.4% in 2015 to 72.9% in 2019, with metformin showing the largest increase from 40.7% to 46.5% (standardized mean difference [SMD], −0.12) and sulfonylureas showing the largest decrease from 37.0% to 31.8% (SMD, 0.11).
The use of newer diabetes medications with cardiovascular benefits, such as GLP-1 receptor agonists and SGLT2 inhibitors, remained less common but showed increasing trends over time.
The use of any antidiabetes medication decreased from 66.1% in the 9 to 12 months before death to 60.8% in the last 4 months of life (P < .01), primarily due to the reduced use of metformin and sulfonylureas.
The use of both short-acting and long-acting insulin agents increased toward the end of life (from 28.0% to 32.9% and from 41.2% to 43.9%, respectively; both P < .001) , particularly among frailer individuals.
IN PRACTICE:
“[The study] findings underscore important implications for diabetes management in patients nearing the end of life. With ~70% of patients with T2D using at least one antidiabetes medication, there is a need to consider further de-escalation or deprescribing in this vulnerable population,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Alexander Kutz, MD, MPH, MSc, Division of Pharmacoepidemiology and Pharmacoeconomics, Department of Medicine, Brigham and Women’s Hospital and Harvard Medical School, Boston, and was published online in Diabetes Care.
LIMITATIONS:
The study lacked details on the reasons for changes in medication patterns, making it unclear whether these changes were due to clinical guidelines or to reduce adverse events. Moreover, the study could not capture transitions or substitutions between medications, information on the dosage data, and causes of death.
DISCLOSURES:
This study was supported by the Division of Pharmacoepidemiology and Pharmacoeconomics, Department of Medicine, Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Harvard Medical School. Some authors reported receiving personal fees or research grants from the National Institutes of Health and other institutions and a few pharmaceutical companies. One author reported acting as a principal investigator and receiving a research grant from Boehringer-Ingelheim, unrelated to the work.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Among older adults with type 2 diabetes (T2D), the use of antidiabetes medications declined in the last year before death, with notable shifts from metformin and sulfonylureas toward insulin therapy.
METHODOLOGY:
Current recommendations emphasize a more liberal approach to glycemic control in people with a high burden of comorbidities and shorter life expectancy, but little is known about the changes and discontinuation patterns of diabetes medications among older adults near the end of life.
.
All medication classes available during the study period were considered, including short-acting and long-acting insulins, metformin, sulfonylureas, dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors, glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) receptor agonists, sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 (SGLT2) inhibitors, and other medications.
Analysis included temporal trends in prescribing antidiabetes medications, stratified by frailty using a validated claims-based frailty index, with scores ≥ 0.30 indicating higher frailty.
Antidiabetes medication fills were assessed within 1 year before death, examining changes across three time periods: 12 to 8 months, 8 to 4 months, and 4 to 0 months before death.
TAKEAWAY:
The proportion of older patients receiving antidiabetes medications increased slightly from 71.4% in 2015 to 72.9% in 2019, with metformin showing the largest increase from 40.7% to 46.5% (standardized mean difference [SMD], −0.12) and sulfonylureas showing the largest decrease from 37.0% to 31.8% (SMD, 0.11).
The use of newer diabetes medications with cardiovascular benefits, such as GLP-1 receptor agonists and SGLT2 inhibitors, remained less common but showed increasing trends over time.
The use of any antidiabetes medication decreased from 66.1% in the 9 to 12 months before death to 60.8% in the last 4 months of life (P < .01), primarily due to the reduced use of metformin and sulfonylureas.
The use of both short-acting and long-acting insulin agents increased toward the end of life (from 28.0% to 32.9% and from 41.2% to 43.9%, respectively; both P < .001) , particularly among frailer individuals.
IN PRACTICE:
“[The study] findings underscore important implications for diabetes management in patients nearing the end of life. With ~70% of patients with T2D using at least one antidiabetes medication, there is a need to consider further de-escalation or deprescribing in this vulnerable population,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Alexander Kutz, MD, MPH, MSc, Division of Pharmacoepidemiology and Pharmacoeconomics, Department of Medicine, Brigham and Women’s Hospital and Harvard Medical School, Boston, and was published online in Diabetes Care.
LIMITATIONS:
The study lacked details on the reasons for changes in medication patterns, making it unclear whether these changes were due to clinical guidelines or to reduce adverse events. Moreover, the study could not capture transitions or substitutions between medications, information on the dosage data, and causes of death.
DISCLOSURES:
This study was supported by the Division of Pharmacoepidemiology and Pharmacoeconomics, Department of Medicine, Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Harvard Medical School. Some authors reported receiving personal fees or research grants from the National Institutes of Health and other institutions and a few pharmaceutical companies. One author reported acting as a principal investigator and receiving a research grant from Boehringer-Ingelheim, unrelated to the work.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.


