User login
Transplantation palliative care: The time is ripe
Over 10 years ago, a challenge was made in a surgical publication for increased collaboration between the fields of transplantation and palliative care.1
Since that time not much progress has been made bringing these fields together in a consistent way that would mutually benefit patients and the specialties. However, other progress has been made, particularly in the field of palliative care, which could brighten the prospects and broaden the opportunities to accomplish collaboration between palliative care and transplantation.
Growth of palliative services
During the past decade there has been a robust proliferation of hospital-based palliative care programs in the United States. In all, 67% of U.S. hospitals with 50 or more beds report palliative care teams, up from 63% in 2011 and 53% in 2008.
Only a decade ago, critical care and palliative care were generally considered mutually exclusive. Evidence is trickling in to suggest that this is no longer the case. Although palliative care was not an integral part of critical care at that time, patients, families, and even practitioners began to demand these services. Cook and Rocker have eloquently advocated the rightful place of palliative care in the ICU.2
Studies in recent years have shown that the integration of palliative care into critical care decreases in length of ICU and hospital stay, decreases costs, enhances patient/family satisfaction, and promotes a more rapid consensus about goals of care, without increasing mortality. The ICU experience to date could be considered a reassuring precedent for transplantation palliative care.
Integration of palliative care with transplantation
Early palliative care intervention has been shown to improve symptom burden and depression scores in end-stage liver disease patients awaiting transplant. In addition, early palliative care consultation in conjunction with cancer treatment has been associated with increased survival in non–small-cell lung cancer patients. It has been demonstrated that early integration of palliative care in the surgical ICU alongside disease-directed curative care can be accomplished without change in mortality, while improving end-of-life practice in liver transplant patients.3
What palliative care can do for transplant patients
What does palliative care mean for the person (and family) awaiting transplantation? For the cirrhotic patient with cachexia, ascites, and encephalopathy, it means access to the services of a team trained in the management of these symptoms. Palliative care teams can also provide psychosocial and spiritual support for patients and families who are intimidated by the complex navigation of the health care system and the existential threat that end-stage organ failure presents to them. Skilled palliative care and services can be the difference between failing and extended life with a higher quality of life for these very sick patients
Resuscitation of a patient, whether through restoration of organ function or interdicting the progression of disease, begins with resuscitation of hope. Nothing achieves this more quickly than amelioration of burdensome symptoms for the patient and family.
The barriers for transplant surgeons and teams referring and incorporating palliative care services in their practices are multiple and profound. The unique dilemma facing the transplant team is to balance the treatment of the failing organ, the treatment of the patient (and family and friends), and the best use of the graft, a precious gift of society.
Palliative surgery has been defined as any invasive procedure in which the main intention is to mitigate physical symptoms in patients with noncurable disease without causing premature death. The very success of transplantation over the past 3 decades has obscured our memory of transplantation as a type of palliative surgery. It is a well-known axiom of reconstructive surgery that the reconstructed site should be compared to what was there, not to “normal.” Even in the current era of improved immunosuppression and posttransplant support services, one could hardly describe even a successful transplant patient’s experience as “normal.” These patients’ lives may be extended and/or enhanced but they need palliative care before, during, and after transplantation. The growing availability of trained palliative care clinicians and teams, the increased familiarity of palliative and end-of-life care to surgical residents and fellows, and quality metrics measuring palliative care outcomes will provide reassurance and guidance to address reservations about the convergence of the two seemingly opposite realities.
A modest proposal
We propose that palliative care be presented to the entire spectrum of transplantation care: on the ward, in the ICU, and after transplantation. More specific “triggers” for palliative care for referral of transplant patients should be identified. Wentlandt et al.4 have described a promising model for an ambulatory clinic, which provides early, integrated palliative care to patients awaiting and receiving organ transplantation. In addition, we propose an application for grant funding for a conference and eventual formation of a work group of transplant surgeons and team members, palliative care clinicians, and patient/families who have experienced one of the aspects of the transplant spectrum. We await the subspecialty certification in hospice and palliative medicine of a transplant surgeon. Outside of transplantation, every other surgical specialty in the United States has diplomates certified in hospice and palliative medicine. We await the benefits that will accrue from research about the merging of these fields.
1. Molmenti EP, Dunn GP: Transplantation and palliative care: The convergence of two seemingly opposite realities. Surg Clin North Am. 2005;85:373-82.
2. Cook D, Rocker G. Dying with dignity in the intensive care unit. N Engl J Med. 2014;370:2506-14.
3. Lamba S, Murphy P, McVicker S, Smith JH, and Mosenthal AC. Changing end-of-life care practice for liver transplant patients: structured palliative care intervention in the surgical intensive care unit. J Pain Symptom Manage. 2012; 44(4):508-19.
4. Wentlandt, K., Dall’Osto, A., Freeman, N., Le, L. W., Kaya, E., Ross, H., Singer, L. G., Abbey, S., Clarke, H. and Zimmermann, C. (2016), The Transplant Palliative Care Clinic: An early palliative care model for patients in a transplant program. Clin Transplant. 2016 Nov 4; doi: 10.1111/ctr.12838.
Dr. Azoulay is a transplantation specialist of Assistance Publique – Hôpitaux de Paris, and the University of Paris. Dr. Dunn is medical director of the Palliative Care Consultation Service at the University of Pittsburgh Medical Center Hamot, and vice-chair of the ACS Committee on Surgical Palliative Care.
Over 10 years ago, a challenge was made in a surgical publication for increased collaboration between the fields of transplantation and palliative care.1
Since that time not much progress has been made bringing these fields together in a consistent way that would mutually benefit patients and the specialties. However, other progress has been made, particularly in the field of palliative care, which could brighten the prospects and broaden the opportunities to accomplish collaboration between palliative care and transplantation.
Growth of palliative services
During the past decade there has been a robust proliferation of hospital-based palliative care programs in the United States. In all, 67% of U.S. hospitals with 50 or more beds report palliative care teams, up from 63% in 2011 and 53% in 2008.
Only a decade ago, critical care and palliative care were generally considered mutually exclusive. Evidence is trickling in to suggest that this is no longer the case. Although palliative care was not an integral part of critical care at that time, patients, families, and even practitioners began to demand these services. Cook and Rocker have eloquently advocated the rightful place of palliative care in the ICU.2
Studies in recent years have shown that the integration of palliative care into critical care decreases in length of ICU and hospital stay, decreases costs, enhances patient/family satisfaction, and promotes a more rapid consensus about goals of care, without increasing mortality. The ICU experience to date could be considered a reassuring precedent for transplantation palliative care.
Integration of palliative care with transplantation
Early palliative care intervention has been shown to improve symptom burden and depression scores in end-stage liver disease patients awaiting transplant. In addition, early palliative care consultation in conjunction with cancer treatment has been associated with increased survival in non–small-cell lung cancer patients. It has been demonstrated that early integration of palliative care in the surgical ICU alongside disease-directed curative care can be accomplished without change in mortality, while improving end-of-life practice in liver transplant patients.3
What palliative care can do for transplant patients
What does palliative care mean for the person (and family) awaiting transplantation? For the cirrhotic patient with cachexia, ascites, and encephalopathy, it means access to the services of a team trained in the management of these symptoms. Palliative care teams can also provide psychosocial and spiritual support for patients and families who are intimidated by the complex navigation of the health care system and the existential threat that end-stage organ failure presents to them. Skilled palliative care and services can be the difference between failing and extended life with a higher quality of life for these very sick patients
Resuscitation of a patient, whether through restoration of organ function or interdicting the progression of disease, begins with resuscitation of hope. Nothing achieves this more quickly than amelioration of burdensome symptoms for the patient and family.
The barriers for transplant surgeons and teams referring and incorporating palliative care services in their practices are multiple and profound. The unique dilemma facing the transplant team is to balance the treatment of the failing organ, the treatment of the patient (and family and friends), and the best use of the graft, a precious gift of society.
Palliative surgery has been defined as any invasive procedure in which the main intention is to mitigate physical symptoms in patients with noncurable disease without causing premature death. The very success of transplantation over the past 3 decades has obscured our memory of transplantation as a type of palliative surgery. It is a well-known axiom of reconstructive surgery that the reconstructed site should be compared to what was there, not to “normal.” Even in the current era of improved immunosuppression and posttransplant support services, one could hardly describe even a successful transplant patient’s experience as “normal.” These patients’ lives may be extended and/or enhanced but they need palliative care before, during, and after transplantation. The growing availability of trained palliative care clinicians and teams, the increased familiarity of palliative and end-of-life care to surgical residents and fellows, and quality metrics measuring palliative care outcomes will provide reassurance and guidance to address reservations about the convergence of the two seemingly opposite realities.
A modest proposal
We propose that palliative care be presented to the entire spectrum of transplantation care: on the ward, in the ICU, and after transplantation. More specific “triggers” for palliative care for referral of transplant patients should be identified. Wentlandt et al.4 have described a promising model for an ambulatory clinic, which provides early, integrated palliative care to patients awaiting and receiving organ transplantation. In addition, we propose an application for grant funding for a conference and eventual formation of a work group of transplant surgeons and team members, palliative care clinicians, and patient/families who have experienced one of the aspects of the transplant spectrum. We await the subspecialty certification in hospice and palliative medicine of a transplant surgeon. Outside of transplantation, every other surgical specialty in the United States has diplomates certified in hospice and palliative medicine. We await the benefits that will accrue from research about the merging of these fields.
1. Molmenti EP, Dunn GP: Transplantation and palliative care: The convergence of two seemingly opposite realities. Surg Clin North Am. 2005;85:373-82.
2. Cook D, Rocker G. Dying with dignity in the intensive care unit. N Engl J Med. 2014;370:2506-14.
3. Lamba S, Murphy P, McVicker S, Smith JH, and Mosenthal AC. Changing end-of-life care practice for liver transplant patients: structured palliative care intervention in the surgical intensive care unit. J Pain Symptom Manage. 2012; 44(4):508-19.
4. Wentlandt, K., Dall’Osto, A., Freeman, N., Le, L. W., Kaya, E., Ross, H., Singer, L. G., Abbey, S., Clarke, H. and Zimmermann, C. (2016), The Transplant Palliative Care Clinic: An early palliative care model for patients in a transplant program. Clin Transplant. 2016 Nov 4; doi: 10.1111/ctr.12838.
Dr. Azoulay is a transplantation specialist of Assistance Publique – Hôpitaux de Paris, and the University of Paris. Dr. Dunn is medical director of the Palliative Care Consultation Service at the University of Pittsburgh Medical Center Hamot, and vice-chair of the ACS Committee on Surgical Palliative Care.
Over 10 years ago, a challenge was made in a surgical publication for increased collaboration between the fields of transplantation and palliative care.1
Since that time not much progress has been made bringing these fields together in a consistent way that would mutually benefit patients and the specialties. However, other progress has been made, particularly in the field of palliative care, which could brighten the prospects and broaden the opportunities to accomplish collaboration between palliative care and transplantation.
Growth of palliative services
During the past decade there has been a robust proliferation of hospital-based palliative care programs in the United States. In all, 67% of U.S. hospitals with 50 or more beds report palliative care teams, up from 63% in 2011 and 53% in 2008.
Only a decade ago, critical care and palliative care were generally considered mutually exclusive. Evidence is trickling in to suggest that this is no longer the case. Although palliative care was not an integral part of critical care at that time, patients, families, and even practitioners began to demand these services. Cook and Rocker have eloquently advocated the rightful place of palliative care in the ICU.2
Studies in recent years have shown that the integration of palliative care into critical care decreases in length of ICU and hospital stay, decreases costs, enhances patient/family satisfaction, and promotes a more rapid consensus about goals of care, without increasing mortality. The ICU experience to date could be considered a reassuring precedent for transplantation palliative care.
Integration of palliative care with transplantation
Early palliative care intervention has been shown to improve symptom burden and depression scores in end-stage liver disease patients awaiting transplant. In addition, early palliative care consultation in conjunction with cancer treatment has been associated with increased survival in non–small-cell lung cancer patients. It has been demonstrated that early integration of palliative care in the surgical ICU alongside disease-directed curative care can be accomplished without change in mortality, while improving end-of-life practice in liver transplant patients.3
What palliative care can do for transplant patients
What does palliative care mean for the person (and family) awaiting transplantation? For the cirrhotic patient with cachexia, ascites, and encephalopathy, it means access to the services of a team trained in the management of these symptoms. Palliative care teams can also provide psychosocial and spiritual support for patients and families who are intimidated by the complex navigation of the health care system and the existential threat that end-stage organ failure presents to them. Skilled palliative care and services can be the difference between failing and extended life with a higher quality of life for these very sick patients
Resuscitation of a patient, whether through restoration of organ function or interdicting the progression of disease, begins with resuscitation of hope. Nothing achieves this more quickly than amelioration of burdensome symptoms for the patient and family.
The barriers for transplant surgeons and teams referring and incorporating palliative care services in their practices are multiple and profound. The unique dilemma facing the transplant team is to balance the treatment of the failing organ, the treatment of the patient (and family and friends), and the best use of the graft, a precious gift of society.
Palliative surgery has been defined as any invasive procedure in which the main intention is to mitigate physical symptoms in patients with noncurable disease without causing premature death. The very success of transplantation over the past 3 decades has obscured our memory of transplantation as a type of palliative surgery. It is a well-known axiom of reconstructive surgery that the reconstructed site should be compared to what was there, not to “normal.” Even in the current era of improved immunosuppression and posttransplant support services, one could hardly describe even a successful transplant patient’s experience as “normal.” These patients’ lives may be extended and/or enhanced but they need palliative care before, during, and after transplantation. The growing availability of trained palliative care clinicians and teams, the increased familiarity of palliative and end-of-life care to surgical residents and fellows, and quality metrics measuring palliative care outcomes will provide reassurance and guidance to address reservations about the convergence of the two seemingly opposite realities.
A modest proposal
We propose that palliative care be presented to the entire spectrum of transplantation care: on the ward, in the ICU, and after transplantation. More specific “triggers” for palliative care for referral of transplant patients should be identified. Wentlandt et al.4 have described a promising model for an ambulatory clinic, which provides early, integrated palliative care to patients awaiting and receiving organ transplantation. In addition, we propose an application for grant funding for a conference and eventual formation of a work group of transplant surgeons and team members, palliative care clinicians, and patient/families who have experienced one of the aspects of the transplant spectrum. We await the subspecialty certification in hospice and palliative medicine of a transplant surgeon. Outside of transplantation, every other surgical specialty in the United States has diplomates certified in hospice and palliative medicine. We await the benefits that will accrue from research about the merging of these fields.
1. Molmenti EP, Dunn GP: Transplantation and palliative care: The convergence of two seemingly opposite realities. Surg Clin North Am. 2005;85:373-82.
2. Cook D, Rocker G. Dying with dignity in the intensive care unit. N Engl J Med. 2014;370:2506-14.
3. Lamba S, Murphy P, McVicker S, Smith JH, and Mosenthal AC. Changing end-of-life care practice for liver transplant patients: structured palliative care intervention in the surgical intensive care unit. J Pain Symptom Manage. 2012; 44(4):508-19.
4. Wentlandt, K., Dall’Osto, A., Freeman, N., Le, L. W., Kaya, E., Ross, H., Singer, L. G., Abbey, S., Clarke, H. and Zimmermann, C. (2016), The Transplant Palliative Care Clinic: An early palliative care model for patients in a transplant program. Clin Transplant. 2016 Nov 4; doi: 10.1111/ctr.12838.
Dr. Azoulay is a transplantation specialist of Assistance Publique – Hôpitaux de Paris, and the University of Paris. Dr. Dunn is medical director of the Palliative Care Consultation Service at the University of Pittsburgh Medical Center Hamot, and vice-chair of the ACS Committee on Surgical Palliative Care.
SVS Now Accepting Abstracts for VAM 2017
Abstracts for the 2017 Vascular Annual Meeting are now being accepted. The submission site opened Monday, Nov. 14 for the meeting, to be held May 31 to June 3, 2017, in San Diego. Plenary sessions and exhibits will be June 1 to 3.
Participants may submit abstracts into any of 14 categories and a number of presentation types, including videos. In 2016, organizers selected approximately two-thirds of the submitted abstracts, and this year the VAM Program Committee is seeking additional venues for people to present their work in, including more sessions and other presentation formats.
Click here for abstract guidelines and more information. Abstracts themselves may be submitted here.
Abstracts for the 2017 Vascular Annual Meeting are now being accepted. The submission site opened Monday, Nov. 14 for the meeting, to be held May 31 to June 3, 2017, in San Diego. Plenary sessions and exhibits will be June 1 to 3.
Participants may submit abstracts into any of 14 categories and a number of presentation types, including videos. In 2016, organizers selected approximately two-thirds of the submitted abstracts, and this year the VAM Program Committee is seeking additional venues for people to present their work in, including more sessions and other presentation formats.
Click here for abstract guidelines and more information. Abstracts themselves may be submitted here.
Abstracts for the 2017 Vascular Annual Meeting are now being accepted. The submission site opened Monday, Nov. 14 for the meeting, to be held May 31 to June 3, 2017, in San Diego. Plenary sessions and exhibits will be June 1 to 3.
Participants may submit abstracts into any of 14 categories and a number of presentation types, including videos. In 2016, organizers selected approximately two-thirds of the submitted abstracts, and this year the VAM Program Committee is seeking additional venues for people to present their work in, including more sessions and other presentation formats.
Click here for abstract guidelines and more information. Abstracts themselves may be submitted here.
Best Practices: Protecting Dry Vulnerable Skin with CeraVe® Healing Ointment
A supplement to Dermatology News. This advertising supplement is sponsored by Valeant Pharmaceuticals.
- Reinforcing the Skin Barrier
- NEA Seal of Acceptance
- A Preventative Approach to Dry, Cracked Skin
- CeraVe Ointment in the Clinical Setting
Faculty/Faculty Disclosure
Sheila Fallon Friedlander, MD
Professor of Clinical Dermatology & Pediatrics
Director, Pediatric Dermatology Fellowship Training Program
University of California at San Diego School of Medicine
Rady Children’s Hospital,
San Diego, California
Dr. Friedlander was compensated for her participation in the development of this article.
CeraVe is a registered trademark of Valeant Pharmaceuticals International, Inc. or its affiliates.
A supplement to Dermatology News. This advertising supplement is sponsored by Valeant Pharmaceuticals.
- Reinforcing the Skin Barrier
- NEA Seal of Acceptance
- A Preventative Approach to Dry, Cracked Skin
- CeraVe Ointment in the Clinical Setting
Faculty/Faculty Disclosure
Sheila Fallon Friedlander, MD
Professor of Clinical Dermatology & Pediatrics
Director, Pediatric Dermatology Fellowship Training Program
University of California at San Diego School of Medicine
Rady Children’s Hospital,
San Diego, California
Dr. Friedlander was compensated for her participation in the development of this article.
CeraVe is a registered trademark of Valeant Pharmaceuticals International, Inc. or its affiliates.
A supplement to Dermatology News. This advertising supplement is sponsored by Valeant Pharmaceuticals.
- Reinforcing the Skin Barrier
- NEA Seal of Acceptance
- A Preventative Approach to Dry, Cracked Skin
- CeraVe Ointment in the Clinical Setting
Faculty/Faculty Disclosure
Sheila Fallon Friedlander, MD
Professor of Clinical Dermatology & Pediatrics
Director, Pediatric Dermatology Fellowship Training Program
University of California at San Diego School of Medicine
Rady Children’s Hospital,
San Diego, California
Dr. Friedlander was compensated for her participation in the development of this article.
CeraVe is a registered trademark of Valeant Pharmaceuticals International, Inc. or its affiliates.
Thoracic Intramedullary Mass Causing Neurologic Weakness
Thoracic Intramedullary Mass Causing Neurologic Weakness
Discussion
A diagnosis of dural arteriovenous fistula (dAVF) was made. Lesions involving the spinal cord are traditionally classified by location as extradural, intradural/extramedullary, or intramedullary. Intramedullary spinal cord abnormalities pose considerable diagnostic and management challenges because of the risks of biopsy in this location and the added potential for morbidity and mortality from improperly treated lesions. Although MRI is the preferred imaging modality, PET/CT and magnetic resonance angiography (MRA) may also help narrow the differential diagnosis and potentially avoid complications from an invasive biopsy.1 This patient’s intramedullary lesion, which represented a dAVF, posed a diagnostic challenge; after diagnosis, it was successfully managed conservatively with dexamethasone and physical therapy.
Intradural tumors account for 2% to 4% of all primary central nervous system (CNS) tumors.2 Ependymomas account for 50% to 60% of intramedullary tumors in adults, while astrocytomas account for about 60% of all lesions in children and adolescents.3,4 The differential diagnosis for intramedullary tumors also includes hemangioblastoma, metastases, primary CNS lymphoma, germ cell tumors, and gangliogliomas.5,6
Intramedullary metastases remain rare, although the incidence is rising with improvements in oncologic and supportive treatments. Autopsy studies conducted decades ago demonstrated that about 0.9% to 2.1% of patients with systemic cancer have intramedullary metastases at death.7,8 In patients with an established history of malignancy, a metastatic intramedullary tumor should be placed higher on the differential diagnosis. Intramedullary metastases most often occur in the setting of widespread metastatic disease. A systematic review of the literature on patients with lung cancer (small cell and non-small cell lung carcinomas) and ≥ 1 intramedullary spinal cord metastasis demonstrated that 55.8% of patients had concurrent brain metastases, 20.0% had leptomeningeal carcinomatosis, and 19.5% had vertebral metastases.9 While about half of all intramedullary metastases are associated with lung cancer, other common malignancies that metastasize to this area include colorectal, breast, and renal cell carcinoma, as well as lymphoma and melanoma primaries.10,11
On imaging, intramedullary metastases often appear as several short, studded segments with surrounding edema, typically out of proportion to the size of the lesion.1 By contrast, astrocytomas and ependymomas often span multiple segments, and enhancement patterns can vary depending on the subtype and grade. Glioblastoma multiforme, or grade 4 IDH wild-type astrocytomas, demonstrate an irregular, heterogeneous pattern of enhancement. Hemangioblastomas vary in size and are classically hypointense to isointense on T1-weighted sequences, isointense to hyperintense on T2-weighted sequences, and demonstrate avid enhancement on T1- postcontrast images. In large hemangioblastomas, flow voids due to prominent vasculature may be visualized.
Numerous nonneoplastic tumor mimics can obscure the differential diagnosis. Vascular malformations, including cavernomas and dAVFs, can also present with enhancement and edema. dAVFs are the most common type of spinal vascular malformation, accounting for about 70% of cases.12 They are supplied by the radiculomeningeal arteries, whereas pial arteriovenous malformations (AVMs) are supplied by the radiculomedullary and radiculopial arteries. On MRI, dAVFs usually have venous congestion with intramedullary edema, which appears as an ill-defined centromedullary hyperintensity on T2-weighted imaging over multiple segments. The spinal cord may appear swollen with atrophic changes in chronic cases. Spinal cord AVMs are rarer and have an intramedullary nidus. They usually demonstrate mixed heterogeneous signal on T1- and T2-weighted imaging due to blood products, while the nidus demonstrates a variable degree of enhancement. Serpiginous flow voids are seen both within the nidus and at the cord surface.
Demyelinating lesions of the spine may be seen in neuroinflammatory conditions such as multiple sclerosis, neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder, acute transverse myelitis, and acute disseminated encephalomyelitis. In multiple sclerosis, lesions typically extend ≤ 2 vertebral segments in length, cover less than half of the vertebral cross-sectional area, and have a dorsolateral predilection.13 Active lesions may demonstrate enhancement along the rim or in a patchy pattern. In the presence of demyelinating lesions, there may occasionally appear to be an expansile mass with a syrinx.14
Infections such as tuberculosis and neurosarcoidosis should also remain on the differential diagnosis. On MRI, tuberculosis usually involves the thoracic cord and is typically rim-enhancing.15 If there are caseating granulomas, T2-weighted images may also demonstrate rim enhancement.16 Spinal sarcoidosis is unusual without intracranial involvement, and its appearance may include leptomeningeal enhancement, cord expansion, and hyperintense signal on T2- weighted imaging.17
Finally, iatrogenic causes are also possible, including radiation myelopathy and mechanical spinal cord injury. For radiation myelopathy, it is important to ascertain whether a patient has undergone prior radiotherapy in the region and to obtain the pertinent dosimetry. Spinal cord injury may cause a focal signal abnormality within the cord, with T2 hyperintensity; these foci may or may not present with enhancement, edema, or hematoma and therefore may resemble tumors.13
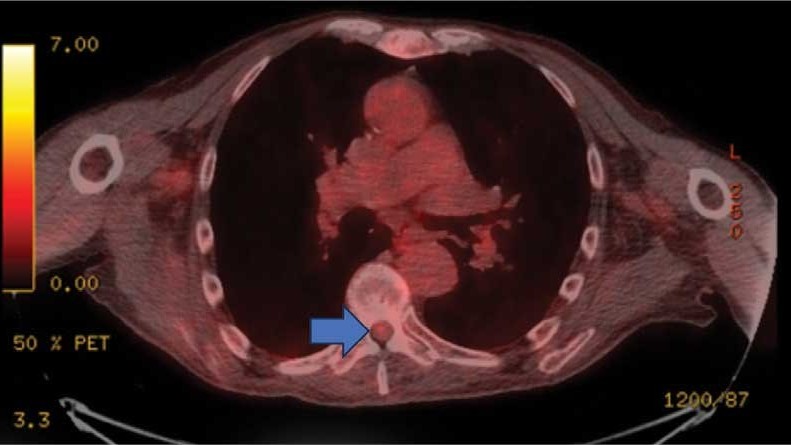
This patient presented with progressive right-sided lower extremity weakness and hypoesthesia and a history of a low-grade right renal/pelvic ureteral tumor. The immediate impression was that the thoracic intramedullary lesion represented a metastatic lesion. However, in the absence of any systemic or intracranial metastases, this progression was much less likely. An extensive interdisciplinary workup was conducted that included medical oncology, neurology, neuroradiology, neuro-oncology, neurosurgery, nuclear medicine, and radiation oncology. Neuroradiology and nuclear medicine identified a slightly hypermetabolic focus on the PET/CT from 1.5 years prior that correlated exactly with the same location as the lesion on the recent spinal MRI. This finding, along with the MRA, confirmed the diagnosis of a dAVF, which was successfully managed conservatively with dexamethasone and physical therapy, rather than through oncologic treatments such as radiotherapy
There remains debate regarding the utility of steroids in treating patients with dAVF. Although there are some case reports documenting that the edema associated with the dAVF responds to steroids, other case series have found that steroids may worsen outcomes in patients with dAVF, possibly due to increased venous hydrostatic pressure.
This case demonstrates the importance of an interdisciplinary workup when evaluating an intramedullary lesion, as well as maintaining a wide differential diagnosis, particularly in the absence of a history of polymetastatic cancer. All the clues (such as the slightly hypermetabolic focus on a PET/CT from 1.5 years prior) need to be obtained to comfortably reach a diagnosis in the absence of pathologic confirmation. These cases can be especially challenging due to the lack of pathologic confirmation, but by understanding the main differentiating features among the various etiologies and obtaining all available information, a correct diagnosis can be made without unnecessary interventions.
- Moghaddam SM, Bhatt AA. Location, length, and enhancement: systematic approach to differentiating intramedullary spinal cord lesions. Insights Imaging. 2018;9:511-526. doi:10.1007/s13244-018-0608-3
- Grimm S, Chamberlain MC. Adult primary spinal cord tumors. Expert Rev Neurother. 2009;9:1487-1495. doi:10.1586/ern.09.101
- Miller DJ, McCutcheon IE. Hemangioblastomas and other uncommon intramedullary tumors. J Neurooncol. 2000;47:253- 270. doi:10.1023/a:1006403500801
- Mottl H, Koutecky J. Treatment of spinal cord tumors in children. Med Pediatr Oncol. 1997;29:293-295.
- Kandemirli SG, Reddy A, Hitchon P, et al. Intramedullary tumours and tumour mimics. Clin Radiol. 2020;75:876.e17-876. e32. doi:10.1016/j.crad.2020.05.010
- Tobin MK, Geraghty JR, Engelhard HH, et al. Intramedullary spinal cord tumors: a review of current and future treatment strategies. Neurosurg Focus. 2015;39:E14. doi:10.3171/2015.5.FOCUS15158
- Chason JL, Walker FB, Landers JW. Metastatic carcinoma in the central nervous system and dorsal root ganglia. A prospective autopsy study. Cancer. 1963;16:781-787.
- Costigan DA, Winkelman MD. Intramedullary spinal cord metastasis. A clinicopathological study of 13 cases. J Neurosurg. 1985;62:227-233.
- Wu L, Wang L, Yang J, et al. Clinical features, treatments, and prognosis of intramedullary spinal cord metastases from lung cancer: a case series and systematic review. Neurospine. 2022;19:65-76. doi:10.14245/ns.2142910.455
- Lv J, Liu B, Quan X, et al. Intramedullary spinal cord metastasis in malignancies: an institutional analysis and review. Onco Targets Ther. 2019;12:4741-4753. doi:10.2147/OTT.S193235
- Goyal A, Yolcu Y, Kerezoudis P, et al. Intramedullary spinal cord metastases: an institutional review of survival and outcomes. J Neurooncol. 2019;142:347-354. doi:10.1007/s11060-019-03105-2
- Krings T. Vascular malformations of the spine and spinal cord: anatomy, classification, treatment. Clin Neuroradiol. 2010;20:5-24. doi:10.1007/s00062-010-9036-6
- Maj E, Wojtowicz K, Aleksandra PP, et al. Intramedullary spinal tumor-like lesions. Acta Radiol. 2019;60:994-1010. doi:10.1177/0284185118809540
- Waziri A, Vonsattel JP, Kaiser MG, et al. Expansile, enhancing cervical cord lesion with an associated syrinx secondary to demyelination. Case report and review of the literature. J Neurosurg Spine. 2007;6:52-56. doi:10.3171/spi.2007.6.1.52
- Nussbaum ES, Rockswold GL, Bergman TA, et al. Spinal tuberculosis: a diagnostic and management challenge. J Neurosurg. 1995;83:243-247. doi:10.3171/jns.1995.83.2.0243
- Lu M. Imaging diagnosis of spinal intramedullary tuberculoma: case reports and literature review. J Spinal Cord Med. 2010;33:159-162. doi:10.1080/10790268.2010.11689691
- Do-Dai DD, Brooks MK, Goldkamp A, et al. Magnetic resonance imaging of intramedullary spinal cord lesions: a pictorial review. Curr Probl Diagn Radiol. 2010;39:160-185. doi:10.1067/j.cpradiol.2009.05.004
Discussion
A diagnosis of dural arteriovenous fistula (dAVF) was made. Lesions involving the spinal cord are traditionally classified by location as extradural, intradural/extramedullary, or intramedullary. Intramedullary spinal cord abnormalities pose considerable diagnostic and management challenges because of the risks of biopsy in this location and the added potential for morbidity and mortality from improperly treated lesions. Although MRI is the preferred imaging modality, PET/CT and magnetic resonance angiography (MRA) may also help narrow the differential diagnosis and potentially avoid complications from an invasive biopsy.1 This patient’s intramedullary lesion, which represented a dAVF, posed a diagnostic challenge; after diagnosis, it was successfully managed conservatively with dexamethasone and physical therapy.
Intradural tumors account for 2% to 4% of all primary central nervous system (CNS) tumors.2 Ependymomas account for 50% to 60% of intramedullary tumors in adults, while astrocytomas account for about 60% of all lesions in children and adolescents.3,4 The differential diagnosis for intramedullary tumors also includes hemangioblastoma, metastases, primary CNS lymphoma, germ cell tumors, and gangliogliomas.5,6
Intramedullary metastases remain rare, although the incidence is rising with improvements in oncologic and supportive treatments. Autopsy studies conducted decades ago demonstrated that about 0.9% to 2.1% of patients with systemic cancer have intramedullary metastases at death.7,8 In patients with an established history of malignancy, a metastatic intramedullary tumor should be placed higher on the differential diagnosis. Intramedullary metastases most often occur in the setting of widespread metastatic disease. A systematic review of the literature on patients with lung cancer (small cell and non-small cell lung carcinomas) and ≥ 1 intramedullary spinal cord metastasis demonstrated that 55.8% of patients had concurrent brain metastases, 20.0% had leptomeningeal carcinomatosis, and 19.5% had vertebral metastases.9 While about half of all intramedullary metastases are associated with lung cancer, other common malignancies that metastasize to this area include colorectal, breast, and renal cell carcinoma, as well as lymphoma and melanoma primaries.10,11
On imaging, intramedullary metastases often appear as several short, studded segments with surrounding edema, typically out of proportion to the size of the lesion.1 By contrast, astrocytomas and ependymomas often span multiple segments, and enhancement patterns can vary depending on the subtype and grade. Glioblastoma multiforme, or grade 4 IDH wild-type astrocytomas, demonstrate an irregular, heterogeneous pattern of enhancement. Hemangioblastomas vary in size and are classically hypointense to isointense on T1-weighted sequences, isointense to hyperintense on T2-weighted sequences, and demonstrate avid enhancement on T1- postcontrast images. In large hemangioblastomas, flow voids due to prominent vasculature may be visualized.
Numerous nonneoplastic tumor mimics can obscure the differential diagnosis. Vascular malformations, including cavernomas and dAVFs, can also present with enhancement and edema. dAVFs are the most common type of spinal vascular malformation, accounting for about 70% of cases.12 They are supplied by the radiculomeningeal arteries, whereas pial arteriovenous malformations (AVMs) are supplied by the radiculomedullary and radiculopial arteries. On MRI, dAVFs usually have venous congestion with intramedullary edema, which appears as an ill-defined centromedullary hyperintensity on T2-weighted imaging over multiple segments. The spinal cord may appear swollen with atrophic changes in chronic cases. Spinal cord AVMs are rarer and have an intramedullary nidus. They usually demonstrate mixed heterogeneous signal on T1- and T2-weighted imaging due to blood products, while the nidus demonstrates a variable degree of enhancement. Serpiginous flow voids are seen both within the nidus and at the cord surface.
Demyelinating lesions of the spine may be seen in neuroinflammatory conditions such as multiple sclerosis, neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder, acute transverse myelitis, and acute disseminated encephalomyelitis. In multiple sclerosis, lesions typically extend ≤ 2 vertebral segments in length, cover less than half of the vertebral cross-sectional area, and have a dorsolateral predilection.13 Active lesions may demonstrate enhancement along the rim or in a patchy pattern. In the presence of demyelinating lesions, there may occasionally appear to be an expansile mass with a syrinx.14
Infections such as tuberculosis and neurosarcoidosis should also remain on the differential diagnosis. On MRI, tuberculosis usually involves the thoracic cord and is typically rim-enhancing.15 If there are caseating granulomas, T2-weighted images may also demonstrate rim enhancement.16 Spinal sarcoidosis is unusual without intracranial involvement, and its appearance may include leptomeningeal enhancement, cord expansion, and hyperintense signal on T2- weighted imaging.17
Finally, iatrogenic causes are also possible, including radiation myelopathy and mechanical spinal cord injury. For radiation myelopathy, it is important to ascertain whether a patient has undergone prior radiotherapy in the region and to obtain the pertinent dosimetry. Spinal cord injury may cause a focal signal abnormality within the cord, with T2 hyperintensity; these foci may or may not present with enhancement, edema, or hematoma and therefore may resemble tumors.13
This patient presented with progressive right-sided lower extremity weakness and hypoesthesia and a history of a low-grade right renal/pelvic ureteral tumor. The immediate impression was that the thoracic intramedullary lesion represented a metastatic lesion. However, in the absence of any systemic or intracranial metastases, this progression was much less likely. An extensive interdisciplinary workup was conducted that included medical oncology, neurology, neuroradiology, neuro-oncology, neurosurgery, nuclear medicine, and radiation oncology. Neuroradiology and nuclear medicine identified a slightly hypermetabolic focus on the PET/CT from 1.5 years prior that correlated exactly with the same location as the lesion on the recent spinal MRI. This finding, along with the MRA, confirmed the diagnosis of a dAVF, which was successfully managed conservatively with dexamethasone and physical therapy, rather than through oncologic treatments such as radiotherapy
There remains debate regarding the utility of steroids in treating patients with dAVF. Although there are some case reports documenting that the edema associated with the dAVF responds to steroids, other case series have found that steroids may worsen outcomes in patients with dAVF, possibly due to increased venous hydrostatic pressure.
This case demonstrates the importance of an interdisciplinary workup when evaluating an intramedullary lesion, as well as maintaining a wide differential diagnosis, particularly in the absence of a history of polymetastatic cancer. All the clues (such as the slightly hypermetabolic focus on a PET/CT from 1.5 years prior) need to be obtained to comfortably reach a diagnosis in the absence of pathologic confirmation. These cases can be especially challenging due to the lack of pathologic confirmation, but by understanding the main differentiating features among the various etiologies and obtaining all available information, a correct diagnosis can be made without unnecessary interventions.
Discussion
A diagnosis of dural arteriovenous fistula (dAVF) was made. Lesions involving the spinal cord are traditionally classified by location as extradural, intradural/extramedullary, or intramedullary. Intramedullary spinal cord abnormalities pose considerable diagnostic and management challenges because of the risks of biopsy in this location and the added potential for morbidity and mortality from improperly treated lesions. Although MRI is the preferred imaging modality, PET/CT and magnetic resonance angiography (MRA) may also help narrow the differential diagnosis and potentially avoid complications from an invasive biopsy.1 This patient’s intramedullary lesion, which represented a dAVF, posed a diagnostic challenge; after diagnosis, it was successfully managed conservatively with dexamethasone and physical therapy.
Intradural tumors account for 2% to 4% of all primary central nervous system (CNS) tumors.2 Ependymomas account for 50% to 60% of intramedullary tumors in adults, while astrocytomas account for about 60% of all lesions in children and adolescents.3,4 The differential diagnosis for intramedullary tumors also includes hemangioblastoma, metastases, primary CNS lymphoma, germ cell tumors, and gangliogliomas.5,6
Intramedullary metastases remain rare, although the incidence is rising with improvements in oncologic and supportive treatments. Autopsy studies conducted decades ago demonstrated that about 0.9% to 2.1% of patients with systemic cancer have intramedullary metastases at death.7,8 In patients with an established history of malignancy, a metastatic intramedullary tumor should be placed higher on the differential diagnosis. Intramedullary metastases most often occur in the setting of widespread metastatic disease. A systematic review of the literature on patients with lung cancer (small cell and non-small cell lung carcinomas) and ≥ 1 intramedullary spinal cord metastasis demonstrated that 55.8% of patients had concurrent brain metastases, 20.0% had leptomeningeal carcinomatosis, and 19.5% had vertebral metastases.9 While about half of all intramedullary metastases are associated with lung cancer, other common malignancies that metastasize to this area include colorectal, breast, and renal cell carcinoma, as well as lymphoma and melanoma primaries.10,11
On imaging, intramedullary metastases often appear as several short, studded segments with surrounding edema, typically out of proportion to the size of the lesion.1 By contrast, astrocytomas and ependymomas often span multiple segments, and enhancement patterns can vary depending on the subtype and grade. Glioblastoma multiforme, or grade 4 IDH wild-type astrocytomas, demonstrate an irregular, heterogeneous pattern of enhancement. Hemangioblastomas vary in size and are classically hypointense to isointense on T1-weighted sequences, isointense to hyperintense on T2-weighted sequences, and demonstrate avid enhancement on T1- postcontrast images. In large hemangioblastomas, flow voids due to prominent vasculature may be visualized.
Numerous nonneoplastic tumor mimics can obscure the differential diagnosis. Vascular malformations, including cavernomas and dAVFs, can also present with enhancement and edema. dAVFs are the most common type of spinal vascular malformation, accounting for about 70% of cases.12 They are supplied by the radiculomeningeal arteries, whereas pial arteriovenous malformations (AVMs) are supplied by the radiculomedullary and radiculopial arteries. On MRI, dAVFs usually have venous congestion with intramedullary edema, which appears as an ill-defined centromedullary hyperintensity on T2-weighted imaging over multiple segments. The spinal cord may appear swollen with atrophic changes in chronic cases. Spinal cord AVMs are rarer and have an intramedullary nidus. They usually demonstrate mixed heterogeneous signal on T1- and T2-weighted imaging due to blood products, while the nidus demonstrates a variable degree of enhancement. Serpiginous flow voids are seen both within the nidus and at the cord surface.
Demyelinating lesions of the spine may be seen in neuroinflammatory conditions such as multiple sclerosis, neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder, acute transverse myelitis, and acute disseminated encephalomyelitis. In multiple sclerosis, lesions typically extend ≤ 2 vertebral segments in length, cover less than half of the vertebral cross-sectional area, and have a dorsolateral predilection.13 Active lesions may demonstrate enhancement along the rim or in a patchy pattern. In the presence of demyelinating lesions, there may occasionally appear to be an expansile mass with a syrinx.14
Infections such as tuberculosis and neurosarcoidosis should also remain on the differential diagnosis. On MRI, tuberculosis usually involves the thoracic cord and is typically rim-enhancing.15 If there are caseating granulomas, T2-weighted images may also demonstrate rim enhancement.16 Spinal sarcoidosis is unusual without intracranial involvement, and its appearance may include leptomeningeal enhancement, cord expansion, and hyperintense signal on T2- weighted imaging.17
Finally, iatrogenic causes are also possible, including radiation myelopathy and mechanical spinal cord injury. For radiation myelopathy, it is important to ascertain whether a patient has undergone prior radiotherapy in the region and to obtain the pertinent dosimetry. Spinal cord injury may cause a focal signal abnormality within the cord, with T2 hyperintensity; these foci may or may not present with enhancement, edema, or hematoma and therefore may resemble tumors.13
This patient presented with progressive right-sided lower extremity weakness and hypoesthesia and a history of a low-grade right renal/pelvic ureteral tumor. The immediate impression was that the thoracic intramedullary lesion represented a metastatic lesion. However, in the absence of any systemic or intracranial metastases, this progression was much less likely. An extensive interdisciplinary workup was conducted that included medical oncology, neurology, neuroradiology, neuro-oncology, neurosurgery, nuclear medicine, and radiation oncology. Neuroradiology and nuclear medicine identified a slightly hypermetabolic focus on the PET/CT from 1.5 years prior that correlated exactly with the same location as the lesion on the recent spinal MRI. This finding, along with the MRA, confirmed the diagnosis of a dAVF, which was successfully managed conservatively with dexamethasone and physical therapy, rather than through oncologic treatments such as radiotherapy
There remains debate regarding the utility of steroids in treating patients with dAVF. Although there are some case reports documenting that the edema associated with the dAVF responds to steroids, other case series have found that steroids may worsen outcomes in patients with dAVF, possibly due to increased venous hydrostatic pressure.
This case demonstrates the importance of an interdisciplinary workup when evaluating an intramedullary lesion, as well as maintaining a wide differential diagnosis, particularly in the absence of a history of polymetastatic cancer. All the clues (such as the slightly hypermetabolic focus on a PET/CT from 1.5 years prior) need to be obtained to comfortably reach a diagnosis in the absence of pathologic confirmation. These cases can be especially challenging due to the lack of pathologic confirmation, but by understanding the main differentiating features among the various etiologies and obtaining all available information, a correct diagnosis can be made without unnecessary interventions.
- Moghaddam SM, Bhatt AA. Location, length, and enhancement: systematic approach to differentiating intramedullary spinal cord lesions. Insights Imaging. 2018;9:511-526. doi:10.1007/s13244-018-0608-3
- Grimm S, Chamberlain MC. Adult primary spinal cord tumors. Expert Rev Neurother. 2009;9:1487-1495. doi:10.1586/ern.09.101
- Miller DJ, McCutcheon IE. Hemangioblastomas and other uncommon intramedullary tumors. J Neurooncol. 2000;47:253- 270. doi:10.1023/a:1006403500801
- Mottl H, Koutecky J. Treatment of spinal cord tumors in children. Med Pediatr Oncol. 1997;29:293-295.
- Kandemirli SG, Reddy A, Hitchon P, et al. Intramedullary tumours and tumour mimics. Clin Radiol. 2020;75:876.e17-876. e32. doi:10.1016/j.crad.2020.05.010
- Tobin MK, Geraghty JR, Engelhard HH, et al. Intramedullary spinal cord tumors: a review of current and future treatment strategies. Neurosurg Focus. 2015;39:E14. doi:10.3171/2015.5.FOCUS15158
- Chason JL, Walker FB, Landers JW. Metastatic carcinoma in the central nervous system and dorsal root ganglia. A prospective autopsy study. Cancer. 1963;16:781-787.
- Costigan DA, Winkelman MD. Intramedullary spinal cord metastasis. A clinicopathological study of 13 cases. J Neurosurg. 1985;62:227-233.
- Wu L, Wang L, Yang J, et al. Clinical features, treatments, and prognosis of intramedullary spinal cord metastases from lung cancer: a case series and systematic review. Neurospine. 2022;19:65-76. doi:10.14245/ns.2142910.455
- Lv J, Liu B, Quan X, et al. Intramedullary spinal cord metastasis in malignancies: an institutional analysis and review. Onco Targets Ther. 2019;12:4741-4753. doi:10.2147/OTT.S193235
- Goyal A, Yolcu Y, Kerezoudis P, et al. Intramedullary spinal cord metastases: an institutional review of survival and outcomes. J Neurooncol. 2019;142:347-354. doi:10.1007/s11060-019-03105-2
- Krings T. Vascular malformations of the spine and spinal cord: anatomy, classification, treatment. Clin Neuroradiol. 2010;20:5-24. doi:10.1007/s00062-010-9036-6
- Maj E, Wojtowicz K, Aleksandra PP, et al. Intramedullary spinal tumor-like lesions. Acta Radiol. 2019;60:994-1010. doi:10.1177/0284185118809540
- Waziri A, Vonsattel JP, Kaiser MG, et al. Expansile, enhancing cervical cord lesion with an associated syrinx secondary to demyelination. Case report and review of the literature. J Neurosurg Spine. 2007;6:52-56. doi:10.3171/spi.2007.6.1.52
- Nussbaum ES, Rockswold GL, Bergman TA, et al. Spinal tuberculosis: a diagnostic and management challenge. J Neurosurg. 1995;83:243-247. doi:10.3171/jns.1995.83.2.0243
- Lu M. Imaging diagnosis of spinal intramedullary tuberculoma: case reports and literature review. J Spinal Cord Med. 2010;33:159-162. doi:10.1080/10790268.2010.11689691
- Do-Dai DD, Brooks MK, Goldkamp A, et al. Magnetic resonance imaging of intramedullary spinal cord lesions: a pictorial review. Curr Probl Diagn Radiol. 2010;39:160-185. doi:10.1067/j.cpradiol.2009.05.004
- Moghaddam SM, Bhatt AA. Location, length, and enhancement: systematic approach to differentiating intramedullary spinal cord lesions. Insights Imaging. 2018;9:511-526. doi:10.1007/s13244-018-0608-3
- Grimm S, Chamberlain MC. Adult primary spinal cord tumors. Expert Rev Neurother. 2009;9:1487-1495. doi:10.1586/ern.09.101
- Miller DJ, McCutcheon IE. Hemangioblastomas and other uncommon intramedullary tumors. J Neurooncol. 2000;47:253- 270. doi:10.1023/a:1006403500801
- Mottl H, Koutecky J. Treatment of spinal cord tumors in children. Med Pediatr Oncol. 1997;29:293-295.
- Kandemirli SG, Reddy A, Hitchon P, et al. Intramedullary tumours and tumour mimics. Clin Radiol. 2020;75:876.e17-876. e32. doi:10.1016/j.crad.2020.05.010
- Tobin MK, Geraghty JR, Engelhard HH, et al. Intramedullary spinal cord tumors: a review of current and future treatment strategies. Neurosurg Focus. 2015;39:E14. doi:10.3171/2015.5.FOCUS15158
- Chason JL, Walker FB, Landers JW. Metastatic carcinoma in the central nervous system and dorsal root ganglia. A prospective autopsy study. Cancer. 1963;16:781-787.
- Costigan DA, Winkelman MD. Intramedullary spinal cord metastasis. A clinicopathological study of 13 cases. J Neurosurg. 1985;62:227-233.
- Wu L, Wang L, Yang J, et al. Clinical features, treatments, and prognosis of intramedullary spinal cord metastases from lung cancer: a case series and systematic review. Neurospine. 2022;19:65-76. doi:10.14245/ns.2142910.455
- Lv J, Liu B, Quan X, et al. Intramedullary spinal cord metastasis in malignancies: an institutional analysis and review. Onco Targets Ther. 2019;12:4741-4753. doi:10.2147/OTT.S193235
- Goyal A, Yolcu Y, Kerezoudis P, et al. Intramedullary spinal cord metastases: an institutional review of survival and outcomes. J Neurooncol. 2019;142:347-354. doi:10.1007/s11060-019-03105-2
- Krings T. Vascular malformations of the spine and spinal cord: anatomy, classification, treatment. Clin Neuroradiol. 2010;20:5-24. doi:10.1007/s00062-010-9036-6
- Maj E, Wojtowicz K, Aleksandra PP, et al. Intramedullary spinal tumor-like lesions. Acta Radiol. 2019;60:994-1010. doi:10.1177/0284185118809540
- Waziri A, Vonsattel JP, Kaiser MG, et al. Expansile, enhancing cervical cord lesion with an associated syrinx secondary to demyelination. Case report and review of the literature. J Neurosurg Spine. 2007;6:52-56. doi:10.3171/spi.2007.6.1.52
- Nussbaum ES, Rockswold GL, Bergman TA, et al. Spinal tuberculosis: a diagnostic and management challenge. J Neurosurg. 1995;83:243-247. doi:10.3171/jns.1995.83.2.0243
- Lu M. Imaging diagnosis of spinal intramedullary tuberculoma: case reports and literature review. J Spinal Cord Med. 2010;33:159-162. doi:10.1080/10790268.2010.11689691
- Do-Dai DD, Brooks MK, Goldkamp A, et al. Magnetic resonance imaging of intramedullary spinal cord lesions: a pictorial review. Curr Probl Diagn Radiol. 2010;39:160-185. doi:10.1067/j.cpradiol.2009.05.004
Thoracic Intramedullary Mass Causing Neurologic Weakness
Thoracic Intramedullary Mass Causing Neurologic Weakness
An 87-year-old man presented to the emergency department reporting a 1-month history of right lower extremity weakness, progressing to an inability to ambulate. The patient had a history of hyperlipidemia, hypertension, benign prostatic hyperplasia, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, low-grade right urothelial carcinoma status postbiopsy 2 years earlier, and atrial fibrillation following cardioversion 6 years earlier without anticoagulation therapy. He also reported severe right groin pain and increasing urinary obstruction.
On admission, neurology evaluated the patient’s lower extremity strength as 5/5 on his left, 1/5 on his right hip, and 2/5 on his right knee, with hypoesthesia of his right lower extremity. Computed tomography (CT) with contrast of the chest, abdomen, and pelvis demonstrated moderate to severe right-sided hydronephrosis, possibly due to a proximal right ureteric mass; no evidence of systemic metastases was found. He underwent a gadolinium-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the cervical, thoracic, and lumbar spine, which showed a mass at T7-T8, a mass effect in the central cord, and abnormal spinal cord enhancement from T7 through the conus medullaris. A review of fluorodeoxyglucose- 18 (FDG-18) positron emission tomography (PET)-CT imaging from 1.5 years prior showed a low-grade focus (Figures 1-3). A gadolinium-enhanced brain MRI did not demonstrate any intracranial metastatic disease, acute infarct, hemorrhage, mass effect, or extra-axial fluid collections.


Following the Hyperkalemia Trail: A Case Report of ECG Changes and Treatment Responses
Following the Hyperkalemia Trail: A Case Report of ECG Changes and Treatment Responses
Hyperkalemia involves elevated serum potassium levels (> 5.0 mEq/L) and represents an important electrolyte disturbance due to its potentially severe consequences, including cardiac effects that can lead to dysrhythmia and even asystole and death.1,2 In a US Medicare population, the prevalence of hyperkalemia has been estimated at 2.7% and is associated with substantial health care costs.3 The prevalence is even more marked in patients with preexisting conditions such as chronic kidney disease (CKD) and heart failure.4,5
Hyperkalemia can result from multiple factors, including impaired renal function, adrenal disease, adverse drug reactions of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors (ACEIs) and other medications, and heritable mutations.6 Hyperkalemia poses a considerable clinical risk, associated with adverse outcomes such as myocardial infarction and increased mortality in patients with CKD.5,7,8 Electrocardiographic (ECG) changes associated with hyperkalemia play a vital role in guiding clinical decisions and treatment strategies.9 Understanding the pathophysiology, risk factors, and consequences of hyperkalemia, as well as the significance of ECG changes in its management, is essential for health care practitioners.
Case Presentation
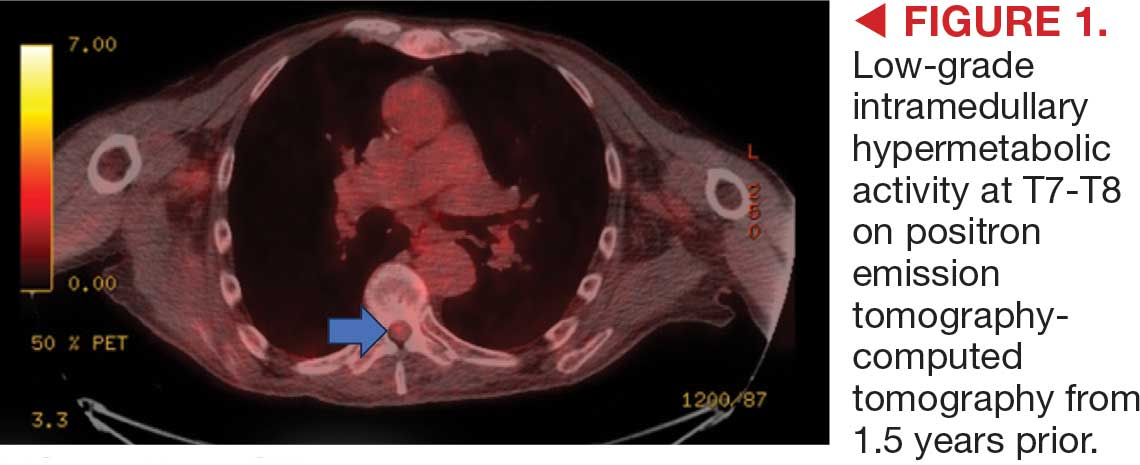
An 81-year-old Hispanic man with a history of hypertension, hypothyroidism, gout, and CKD stage 3B presented to the emergency department with progressive weakness resulting in falls and culminating in an inability to ambulate independently. Additional symptoms included nausea, diarrhea, and myalgia. His vital signs were notable for a pulse of 41 beats/min. The physical examination was remarkable for significant weakness of the bilateral upper extremities, inability to bear his own weight, and bilateral lower extremity edema. His initial ECG upon arrival showed bradycardia with wide QRS, absent P waves, and peaked T waves (Figure 1a). These findings differed from his baseline ECG taken 1 year earlier, which showed sinus rhythm with premature atrial complexes and an old right bundle branch block (Figure 1b).
Medication review revealed that the patient was currently prescribed 100 mg allopurinol daily, 2.5 mg amlodipine daily, 10 mg atorvastatin at bedtime, 4 mg doxazosin daily, 112 mcg levothyroxine daily, 100 mg losartan daily, 25 mg metoprolol daily, and 0.4 mg tamsulosin daily. The patient had also been taking over-the-counter indomethacin for knee pain.
Based on the ECG results, he was treated with 0.083%/6 mL nebulized albuterol, 4.65 Mq/250 mL saline solution intravenous (IV) calcium gluconate, 10 units IV insulin with concomitant 50%/25 mL IV dextrose and 8.4 g of oral patiromer suspension. IV furosemide was held due to concern for renal function. The decision to proceed with hemodialysis was made. Repeat laboratory tests were performed, and an ECG obtained after treatment initiation but prior to hemodialysis demonstrated improvement of rate and T wave shortening (Figure 1c). The serum potassium level dropped from 9.8 mEq/L to 7.9 mEq/L (reference range, 3.5-5.0 mEq/L) (Table 1).
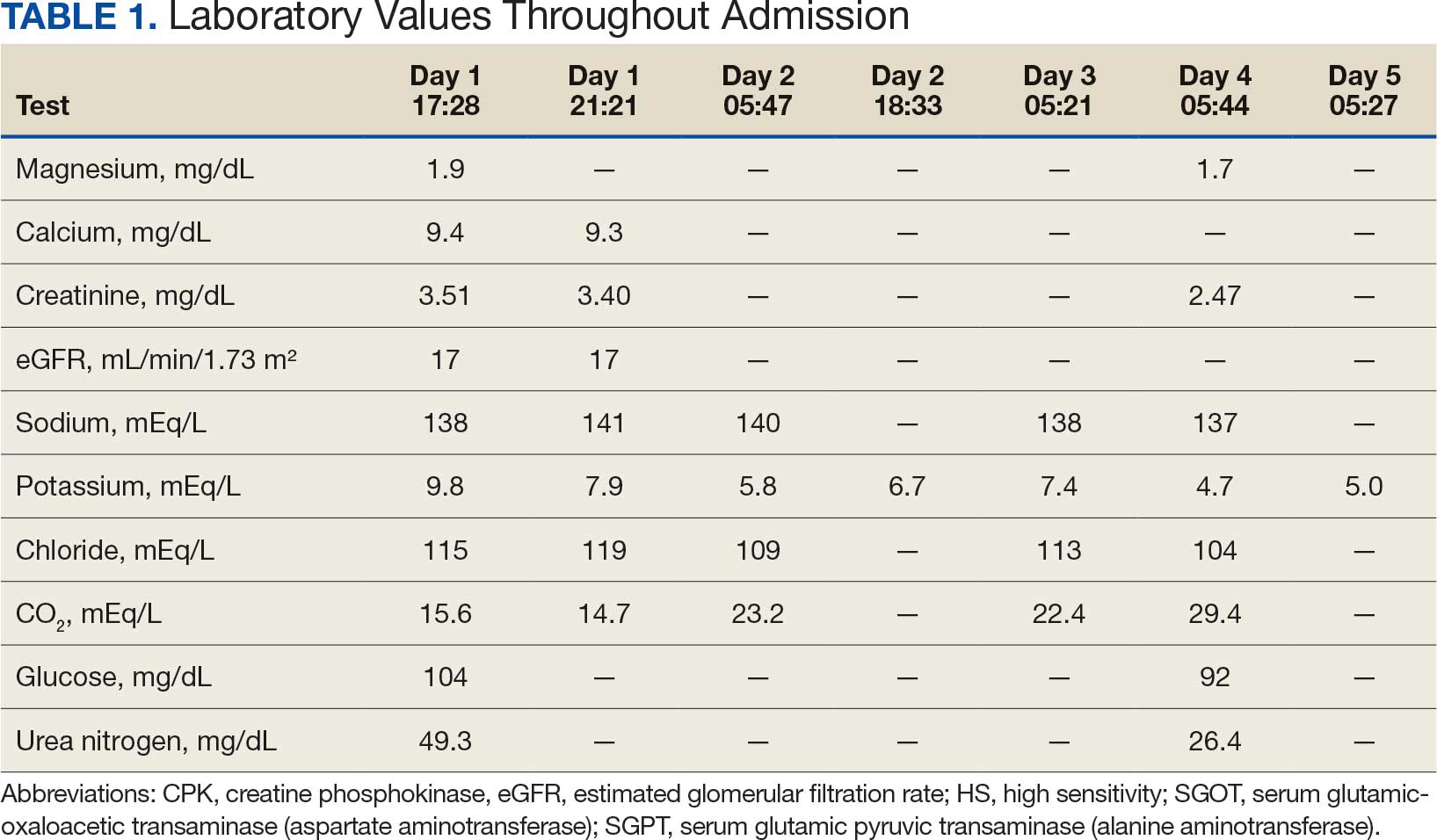
In addition to hemodialysis, sodium zirconium 10 g orally 3 times daily was added. Laboratory test results and an ECG was performed after dialysis continued to demonstrate improvement (Figure 1d). The patient’s potassium level decreased to 5.8 mEq/L, with the ECG demonstrating stability of heart rate and further improvement of the PR interval, QRS complex, and T waves.
Despite the established treatment regimen, potassium levels again rose to 6.7 mEq/L, but there were no significant changes in the ECG, and thus no medication changes were made (Figure 1e). Subsequent monitoring demonstrated a further increase in potassium to 7.4 mEq/L, with an ECG demonstrating a return to the baseline of 1 year prior. The patient underwent hemodialysis again and was given oral furosemide 60 mg every 12 hours. The potassium concentration after dialysis decreased to 4.7 mEq/L and remained stable, not going above 5.0 mEq/L on subsequent monitoring. The patient had resolution of all symptoms and was discharged.
Discussion
We have described in detail the presentation of each pathology and mechanisms of each treatment, starting with the patient’s initial condition that brought him to the emergency room—muscle weakness. Skeletal muscle weakness is a common manifestation of hyperkalemia, occurring in 20% to 40% of cases, and is more prevalent in severe elevations of potassium. Rarely, the weakness can progress to flaccid paralysis of the patient’s extremities and, in extreme cases, the diaphragm.
Muscle weakness progression occurs in a manner that resembles Guillain-Barré syndrome, starting in the lower extremities and ascending toward the upper extremities.10 This is known as secondary hyperkalemic periodic paralysis. Hyperkalemia lowers the transmembrane gradient in neurons, leading to neuronal depolarization independent of the degree of hyperkalemia. If the degree of hyperkalemia is large enough, this depolarization inactivates voltage-gated sodium channels, making neurons refractory to excitation. Electromyographical studies have shown reduction in the compounded muscle action potential.11 The transient nature of this paralysis is reflected by rapid correction of weakness and paralysis when the electrolyte disorder is corrected.
The patient in this case also presented with bradycardia. The ECG manifestations of hyperkalemia can include atrial asystole, intraventricular conduction disturbances, peaked T waves, and widened QRS complexes. However, some patients with renal insufficiency may not exhibit ECG changes despite significantly elevated serum potassium levels.12
The severity of hyperkalemia is crucial in determining the associated ECG changes, with levels > 6.0 mEq/L presenting with abnormalities.13 ECG findings alone may not always accurately reflect the severity of hyperkalemia, as up to 60% of patients with potassium levels > 6.0 mEq/L may not show ECG changes.14 Additionally, extreme hyperkalemia can lead to inconsistent ECG findings, making it challenging to rely solely on ECG for diagnosis and monitoring.8 The level of potassium that causes these effects varies widely through patient populations.
The main mechanism by which hyperkalemia affects the heart’s conduction system is through voltage differences across the conduction fibers and eventual steady-state inactivation of sodium channels. This combination of mechanisms shortens the action potential duration, allowing more cardiomyocytes to undergo synchronized depolarization. This amalgamation of cardiomyocytes repolarizing can be reflected on ECGs as peaked T waves. As the action potential decreases, there is a period during which cardiomyocytes are prone to tachyarrhythmias and ventricular fibrillation.
A reduced action potential may lead to increased rates of depolarization and thus conduction, which in some scenarios may increase heart rate. As the levels of potassium rise, intracellular accumulation impedes the entry of sodium by decreasing the cation gradient across the cell membrane. This effectively slows the sinus nodes and prolongs the QRS by slowing the overall propagation of action potentials. By this mechanism, conduction delays, blocks, or asystole are manifested. The patient in this case showed conduction delays, peaked T waves, and disappearance of P waves when he first arrived.
Hyperkalemia Treatment
Hyperkalemia develops most commonly due to acute or chronic kidney diseases, as was the case with this patient. The patient’s hyperkalemia was also augmented by the use of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), which can directly affect renal function. A properly functioning kidney is responsible for excretion of up to 90% of ingested potassium, while the remainder is excreted through the gastrointestinal (GI) tract. Definitive treatment of hyperkalemia is mitigated primarily through these 2 organ systems. The treatment also includes transitory mechanisms of potassium reduction. The goal of each method is to preserve the action potential of cardiomyocytes and myocytes. This patient presented with acute symptomatic hyperkalemia and received various medications to acutely, transitorily, and definitively treat it.
Initial therapy included calcium gluconate, which functions to stabilize the myocardial cell membrane. Hyperkalemia decreases the resting membrane action potential of excitable cells and predisposes them to early depolarization and thus dysrhythmias. Calcium decreases the threshold potential across cells and offsets the overall gradient back to near normal levels.15 Calcium can be delivered through calcium gluconate or calcium chloride. Calcium chloride is not preferred because extravasation can cause pain, blistering and tissue ischemia. Central venous access is required, potentially delaying prompt treatment. Calcium acts rapidly after administration—within 1 to 3 minutes—but only lasts 30 to 60 minutes.16 Administration of calcium gluconate can be repeated as often as necessary, but patients must be monitored for adverse effects of calcium such as nausea, abdominal pain, polydipsia, polyuria, muscle weakness, and paresthesia. Care must be taken when patients are taking digoxin, because calcium may potentiate toxicity.17 Although calcium provides immediate benefits it does little to correct the underlying cause; other medications are required to remove potassium from the body.
Two medication classes have been proven to shift potassium intracellularly. The first are β-2 agonists, such as albuterol/levalbuterol, and the second is insulin. Both work through sodium-potassium-ATPase in a direct manner. β-2 agonists stimulate sodium-potassium-ATPase to move more potassium intracellularly, but these effects have been seen only with high doses of albuterol, typically 4× the standard dose of 0.5 mg in nebulized solutions to achieve decreases in potassium of 0.3 to 0.6 mEq/L, although some trials have reported decreases of 0.62 to 0.98 mEq/L.15,18 These potassium-lowering effects of β-2 agonist are modest, but can be seen 20 to 30 minutes after administration and persist up to 1 to 2 hours. β-2 agonists are also readily affected by β blockers, which may reduce or negate the desired effect in hyperkalemia. For these reasons, a β-2 agonist should not be given as monotherapy and should be provided as an adjuvant to more independent therapies such as insulin. Insulin binds to receptors on muscle cells and increases the quantity of sodium-potassium-ATPase and glucose transporters. With this increase in influx pumps, surrounding tissues with higher resting membrane potentials can absorb the potassium load, thereby protecting cardiomyocytes.
Potassium Removal
Three methods are currently available to remove potassium from the body: GI excretion, renal excretion, and direct removal from the bloodstream. Under normal physiologic conditions, the kidneys account for about 90% of the body’s ability to remove potassium. Loop diuretics facilitate the removal of potassium by increasing urine production and have an additional potassium-wasting effect. Although the onset of action of loop diuretics is typically 30 to 60 minutes after oral administration, their effect can last for several hours. In this patient, furosemide was introduced later in the treatment plan to manage recurring hyperkalemia by enhancing renal potassium excretion.
Potassium binders such as patiromer act in the GI tract, effectively reducing serum potassium levels although with a slower onset of action than furosemide, generally taking hours to days to exert its effect. Both medications illustrate a tailored approach to managing potassium levels, adapted to the evolving needs and renal function of the patient. The last method is using hemodialysis—by far the most rapid method to remove potassium, but also the most invasive. The different methods of treating hyperkalemia are summarized in Table 2. This patient required multiple days of hemodialysis to completely correct the electrolyte disorder. Upon discharge, the patient continued oral furosemide 40 mg daily and eventually discontinued hemodialysis due to stable renal function.
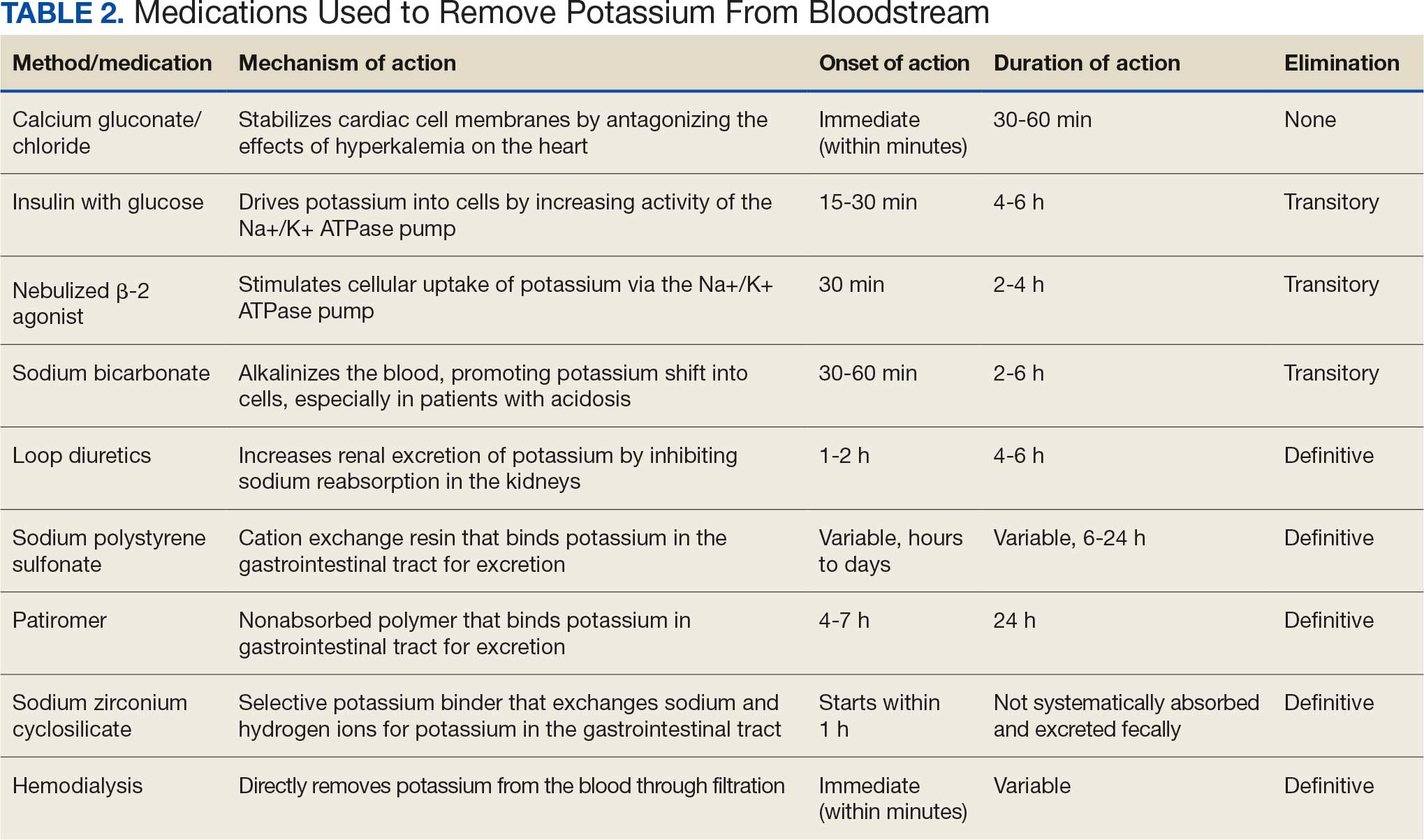
Often, after correcting an inciting event, potassium stores in the body eventually stabilize and do not require additional follow-up. Patients prone to hyperkalemia should be thoroughly educated on medications to avoid (NSAIDs, ACEIs/ARBs, trimethoprim), an adequate low potassium diet, and symptoms that may warrant medical attention.19
Conclusions
This case illustrates the importance of recognizing the spectrum of manifestations of hyperkalemia, which ranged from muscle weakness to cardiac dysrhythmias. Management strategies for the patient included stabilization of cardiac membranes, potassium shifting, and potassium removal, each tailored to the patient’s individual clinical findings.
The case further illustrates the critical role of continuous monitoring and dynamic adjustment of therapeutic strategies in response to evolving clinical and laboratory findings. The initial and subsequent ECGs, alongside laboratory tests, were instrumental in guiding the adjustments needed in the treatment regimen, ensuring both the efficacy and safety of the interventions. This proactive approach can mitigate the risk of recurrent hyperkalemia and its complications.
- Youn JH, McDonough AA. Recent advances in understanding integrative control of potassium homeostasis. Annu Rev Physiol. 2009;71:381-401. doi:10.1146/annurev.physiol.010908.163241 2.
- Simon LV, Hashmi MF, Farrell MW. Hyperkalemia. In: StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing; September 4, 2023. Accessed October 22, 2025.
- Mu F, Betts KA, Woolley JM, et al. Prevalence and economic burden of hyperkalemia in the United States Medicare population. Curr Med Res Opin. 2020;36:1333-1341. doi:10.1080/03007995.2020.1775072
- Loutradis C, Tolika P, Skodra A, et al. Prevalence of hyperkalemia in diabetic and non-diabetic patients with chronic kidney disease: a nested case-control study. Am J Nephrol. 2015;42:351-360. doi:10.1159/000442393
- Grodzinsky A, Goyal A, Gosch K, et al. Prevalence and prognosis of hyperkalemia in patients with acute myocardial infarction. Am J Med. 2016;129:858-865. doi:10.1016/j.amjmed.2016.03.008
- Hunter RW, Bailey MA. Hyperkalemia: pathophysiology, risk factors and consequences. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2019;34(suppl 3):iii2-iii11. doi:10.1093/ndt/gfz206
- Luo J, Brunelli SM, Jensen DE, Yang A. Association between serum potassium and outcomes in patients with reduced kidney function. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2016;11:90-100. doi:10.2215/CJN.01730215
- Montford JR, Linas S. How dangerous is hyperkalemia? J Am Soc Nephrol. 2017;28:3155-3165. doi:10.1681/ASN.2016121344
- Mattu A, Brady WJ, Robinson DA. Electrocardiographic manifestations of hyperkalemia. Am J Emerg Med. 2000;18:721-729. doi:10.1053/ajem.2000.7344
- Kimmons LA, Usery JB. Acute ascending muscle weakness secondary to medication-induced hyperkalemia. Case Rep Med. 2014;2014:789529. doi:10.1155/2014/789529
- Naik KR, Saroja AO, Khanpet MS. Reversible electrophysiological abnormalities in acute secondary hyperkalemic paralysis. Ann Indian Acad Neurol. 2012;15:339-343. doi:10.4103/0972-2327.104354
- Montague BT, Ouellette JR, Buller GK. Retrospective review of the frequency of ECG changes in hyperkalemia. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2008;3:324-330. doi:10.2215/CJN.04611007
- Larivée NL, Michaud JB, More KM, Wilson JA, Tennankore KK. Hyperkalemia: prevalence, predictors and emerging treatments. Cardiol Ther. 2023;12:35-63. doi:10.1007/s40119-022-00289-z
- Shingarev R, Allon M. A physiologic-based approach to the treatment of acute hyperkalemia. Am J Kidney Dis. 2010;56:578-584. doi:10.1053/j.ajkd.2010.03.014
- Parham WA, Mehdirad AA, Biermann KM, Fredman CS. Hyperkalemia revisited. Tex Heart Inst J. 2006;33:40-47.
- Ng KE, Lee CS. Updated treatment options in the management of hyperkalemia. U.S. Pharmacist. February 16, 2017. Accessed October 1, 2025. www.uspharmacist.com/article/updated-treatment-options-in-the-management-of-hyperkalemia
- Quick G, Bastani B. Prolonged asystolic hyperkalemic cardiac arrest with no neurologic sequelae. Ann Emerg Med. 1994;24:305-311. doi:10.1016/s0196-0644(94)70144-x 18.
- Allon M, Dunlay R, Copkney C. Nebulized albuterol for acute hyperkalemia in patients on hemodialysis. Ann Intern Med. 1989;110:426-429. doi:10.7326/0003-4819-110-6-42619.
- Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) CKD Work Group. KDIGO 2024 Clinical Practice Guideline for the Evaluation and Management of Chronic Kidney Disease. Kidney Int. 2024;105(4 suppl):S117-S314. doi:10.1016/j.kint.2023.10.018
Hyperkalemia involves elevated serum potassium levels (> 5.0 mEq/L) and represents an important electrolyte disturbance due to its potentially severe consequences, including cardiac effects that can lead to dysrhythmia and even asystole and death.1,2 In a US Medicare population, the prevalence of hyperkalemia has been estimated at 2.7% and is associated with substantial health care costs.3 The prevalence is even more marked in patients with preexisting conditions such as chronic kidney disease (CKD) and heart failure.4,5
Hyperkalemia can result from multiple factors, including impaired renal function, adrenal disease, adverse drug reactions of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors (ACEIs) and other medications, and heritable mutations.6 Hyperkalemia poses a considerable clinical risk, associated with adverse outcomes such as myocardial infarction and increased mortality in patients with CKD.5,7,8 Electrocardiographic (ECG) changes associated with hyperkalemia play a vital role in guiding clinical decisions and treatment strategies.9 Understanding the pathophysiology, risk factors, and consequences of hyperkalemia, as well as the significance of ECG changes in its management, is essential for health care practitioners.
Case Presentation
An 81-year-old Hispanic man with a history of hypertension, hypothyroidism, gout, and CKD stage 3B presented to the emergency department with progressive weakness resulting in falls and culminating in an inability to ambulate independently. Additional symptoms included nausea, diarrhea, and myalgia. His vital signs were notable for a pulse of 41 beats/min. The physical examination was remarkable for significant weakness of the bilateral upper extremities, inability to bear his own weight, and bilateral lower extremity edema. His initial ECG upon arrival showed bradycardia with wide QRS, absent P waves, and peaked T waves (Figure 1a). These findings differed from his baseline ECG taken 1 year earlier, which showed sinus rhythm with premature atrial complexes and an old right bundle branch block (Figure 1b).

Medication review revealed that the patient was currently prescribed 100 mg allopurinol daily, 2.5 mg amlodipine daily, 10 mg atorvastatin at bedtime, 4 mg doxazosin daily, 112 mcg levothyroxine daily, 100 mg losartan daily, 25 mg metoprolol daily, and 0.4 mg tamsulosin daily. The patient had also been taking over-the-counter indomethacin for knee pain.
Based on the ECG results, he was treated with 0.083%/6 mL nebulized albuterol, 4.65 Mq/250 mL saline solution intravenous (IV) calcium gluconate, 10 units IV insulin with concomitant 50%/25 mL IV dextrose and 8.4 g of oral patiromer suspension. IV furosemide was held due to concern for renal function. The decision to proceed with hemodialysis was made. Repeat laboratory tests were performed, and an ECG obtained after treatment initiation but prior to hemodialysis demonstrated improvement of rate and T wave shortening (Figure 1c). The serum potassium level dropped from 9.8 mEq/L to 7.9 mEq/L (reference range, 3.5-5.0 mEq/L) (Table 1).

In addition to hemodialysis, sodium zirconium 10 g orally 3 times daily was added. Laboratory test results and an ECG was performed after dialysis continued to demonstrate improvement (Figure 1d). The patient’s potassium level decreased to 5.8 mEq/L, with the ECG demonstrating stability of heart rate and further improvement of the PR interval, QRS complex, and T waves.
Despite the established treatment regimen, potassium levels again rose to 6.7 mEq/L, but there were no significant changes in the ECG, and thus no medication changes were made (Figure 1e). Subsequent monitoring demonstrated a further increase in potassium to 7.4 mEq/L, with an ECG demonstrating a return to the baseline of 1 year prior. The patient underwent hemodialysis again and was given oral furosemide 60 mg every 12 hours. The potassium concentration after dialysis decreased to 4.7 mEq/L and remained stable, not going above 5.0 mEq/L on subsequent monitoring. The patient had resolution of all symptoms and was discharged.
Discussion
We have described in detail the presentation of each pathology and mechanisms of each treatment, starting with the patient’s initial condition that brought him to the emergency room—muscle weakness. Skeletal muscle weakness is a common manifestation of hyperkalemia, occurring in 20% to 40% of cases, and is more prevalent in severe elevations of potassium. Rarely, the weakness can progress to flaccid paralysis of the patient’s extremities and, in extreme cases, the diaphragm.
Muscle weakness progression occurs in a manner that resembles Guillain-Barré syndrome, starting in the lower extremities and ascending toward the upper extremities.10 This is known as secondary hyperkalemic periodic paralysis. Hyperkalemia lowers the transmembrane gradient in neurons, leading to neuronal depolarization independent of the degree of hyperkalemia. If the degree of hyperkalemia is large enough, this depolarization inactivates voltage-gated sodium channels, making neurons refractory to excitation. Electromyographical studies have shown reduction in the compounded muscle action potential.11 The transient nature of this paralysis is reflected by rapid correction of weakness and paralysis when the electrolyte disorder is corrected.
The patient in this case also presented with bradycardia. The ECG manifestations of hyperkalemia can include atrial asystole, intraventricular conduction disturbances, peaked T waves, and widened QRS complexes. However, some patients with renal insufficiency may not exhibit ECG changes despite significantly elevated serum potassium levels.12
The severity of hyperkalemia is crucial in determining the associated ECG changes, with levels > 6.0 mEq/L presenting with abnormalities.13 ECG findings alone may not always accurately reflect the severity of hyperkalemia, as up to 60% of patients with potassium levels > 6.0 mEq/L may not show ECG changes.14 Additionally, extreme hyperkalemia can lead to inconsistent ECG findings, making it challenging to rely solely on ECG for diagnosis and monitoring.8 The level of potassium that causes these effects varies widely through patient populations.
The main mechanism by which hyperkalemia affects the heart’s conduction system is through voltage differences across the conduction fibers and eventual steady-state inactivation of sodium channels. This combination of mechanisms shortens the action potential duration, allowing more cardiomyocytes to undergo synchronized depolarization. This amalgamation of cardiomyocytes repolarizing can be reflected on ECGs as peaked T waves. As the action potential decreases, there is a period during which cardiomyocytes are prone to tachyarrhythmias and ventricular fibrillation.
A reduced action potential may lead to increased rates of depolarization and thus conduction, which in some scenarios may increase heart rate. As the levels of potassium rise, intracellular accumulation impedes the entry of sodium by decreasing the cation gradient across the cell membrane. This effectively slows the sinus nodes and prolongs the QRS by slowing the overall propagation of action potentials. By this mechanism, conduction delays, blocks, or asystole are manifested. The patient in this case showed conduction delays, peaked T waves, and disappearance of P waves when he first arrived.
Hyperkalemia Treatment
Hyperkalemia develops most commonly due to acute or chronic kidney diseases, as was the case with this patient. The patient’s hyperkalemia was also augmented by the use of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), which can directly affect renal function. A properly functioning kidney is responsible for excretion of up to 90% of ingested potassium, while the remainder is excreted through the gastrointestinal (GI) tract. Definitive treatment of hyperkalemia is mitigated primarily through these 2 organ systems. The treatment also includes transitory mechanisms of potassium reduction. The goal of each method is to preserve the action potential of cardiomyocytes and myocytes. This patient presented with acute symptomatic hyperkalemia and received various medications to acutely, transitorily, and definitively treat it.
Initial therapy included calcium gluconate, which functions to stabilize the myocardial cell membrane. Hyperkalemia decreases the resting membrane action potential of excitable cells and predisposes them to early depolarization and thus dysrhythmias. Calcium decreases the threshold potential across cells and offsets the overall gradient back to near normal levels.15 Calcium can be delivered through calcium gluconate or calcium chloride. Calcium chloride is not preferred because extravasation can cause pain, blistering and tissue ischemia. Central venous access is required, potentially delaying prompt treatment. Calcium acts rapidly after administration—within 1 to 3 minutes—but only lasts 30 to 60 minutes.16 Administration of calcium gluconate can be repeated as often as necessary, but patients must be monitored for adverse effects of calcium such as nausea, abdominal pain, polydipsia, polyuria, muscle weakness, and paresthesia. Care must be taken when patients are taking digoxin, because calcium may potentiate toxicity.17 Although calcium provides immediate benefits it does little to correct the underlying cause; other medications are required to remove potassium from the body.
Two medication classes have been proven to shift potassium intracellularly. The first are β-2 agonists, such as albuterol/levalbuterol, and the second is insulin. Both work through sodium-potassium-ATPase in a direct manner. β-2 agonists stimulate sodium-potassium-ATPase to move more potassium intracellularly, but these effects have been seen only with high doses of albuterol, typically 4× the standard dose of 0.5 mg in nebulized solutions to achieve decreases in potassium of 0.3 to 0.6 mEq/L, although some trials have reported decreases of 0.62 to 0.98 mEq/L.15,18 These potassium-lowering effects of β-2 agonist are modest, but can be seen 20 to 30 minutes after administration and persist up to 1 to 2 hours. β-2 agonists are also readily affected by β blockers, which may reduce or negate the desired effect in hyperkalemia. For these reasons, a β-2 agonist should not be given as monotherapy and should be provided as an adjuvant to more independent therapies such as insulin. Insulin binds to receptors on muscle cells and increases the quantity of sodium-potassium-ATPase and glucose transporters. With this increase in influx pumps, surrounding tissues with higher resting membrane potentials can absorb the potassium load, thereby protecting cardiomyocytes.
Potassium Removal
Three methods are currently available to remove potassium from the body: GI excretion, renal excretion, and direct removal from the bloodstream. Under normal physiologic conditions, the kidneys account for about 90% of the body’s ability to remove potassium. Loop diuretics facilitate the removal of potassium by increasing urine production and have an additional potassium-wasting effect. Although the onset of action of loop diuretics is typically 30 to 60 minutes after oral administration, their effect can last for several hours. In this patient, furosemide was introduced later in the treatment plan to manage recurring hyperkalemia by enhancing renal potassium excretion.
Potassium binders such as patiromer act in the GI tract, effectively reducing serum potassium levels although with a slower onset of action than furosemide, generally taking hours to days to exert its effect. Both medications illustrate a tailored approach to managing potassium levels, adapted to the evolving needs and renal function of the patient. The last method is using hemodialysis—by far the most rapid method to remove potassium, but also the most invasive. The different methods of treating hyperkalemia are summarized in Table 2. This patient required multiple days of hemodialysis to completely correct the electrolyte disorder. Upon discharge, the patient continued oral furosemide 40 mg daily and eventually discontinued hemodialysis due to stable renal function.

Often, after correcting an inciting event, potassium stores in the body eventually stabilize and do not require additional follow-up. Patients prone to hyperkalemia should be thoroughly educated on medications to avoid (NSAIDs, ACEIs/ARBs, trimethoprim), an adequate low potassium diet, and symptoms that may warrant medical attention.19
Conclusions
This case illustrates the importance of recognizing the spectrum of manifestations of hyperkalemia, which ranged from muscle weakness to cardiac dysrhythmias. Management strategies for the patient included stabilization of cardiac membranes, potassium shifting, and potassium removal, each tailored to the patient’s individual clinical findings.
The case further illustrates the critical role of continuous monitoring and dynamic adjustment of therapeutic strategies in response to evolving clinical and laboratory findings. The initial and subsequent ECGs, alongside laboratory tests, were instrumental in guiding the adjustments needed in the treatment regimen, ensuring both the efficacy and safety of the interventions. This proactive approach can mitigate the risk of recurrent hyperkalemia and its complications.
Hyperkalemia involves elevated serum potassium levels (> 5.0 mEq/L) and represents an important electrolyte disturbance due to its potentially severe consequences, including cardiac effects that can lead to dysrhythmia and even asystole and death.1,2 In a US Medicare population, the prevalence of hyperkalemia has been estimated at 2.7% and is associated with substantial health care costs.3 The prevalence is even more marked in patients with preexisting conditions such as chronic kidney disease (CKD) and heart failure.4,5
Hyperkalemia can result from multiple factors, including impaired renal function, adrenal disease, adverse drug reactions of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors (ACEIs) and other medications, and heritable mutations.6 Hyperkalemia poses a considerable clinical risk, associated with adverse outcomes such as myocardial infarction and increased mortality in patients with CKD.5,7,8 Electrocardiographic (ECG) changes associated with hyperkalemia play a vital role in guiding clinical decisions and treatment strategies.9 Understanding the pathophysiology, risk factors, and consequences of hyperkalemia, as well as the significance of ECG changes in its management, is essential for health care practitioners.
Case Presentation
An 81-year-old Hispanic man with a history of hypertension, hypothyroidism, gout, and CKD stage 3B presented to the emergency department with progressive weakness resulting in falls and culminating in an inability to ambulate independently. Additional symptoms included nausea, diarrhea, and myalgia. His vital signs were notable for a pulse of 41 beats/min. The physical examination was remarkable for significant weakness of the bilateral upper extremities, inability to bear his own weight, and bilateral lower extremity edema. His initial ECG upon arrival showed bradycardia with wide QRS, absent P waves, and peaked T waves (Figure 1a). These findings differed from his baseline ECG taken 1 year earlier, which showed sinus rhythm with premature atrial complexes and an old right bundle branch block (Figure 1b).

Medication review revealed that the patient was currently prescribed 100 mg allopurinol daily, 2.5 mg amlodipine daily, 10 mg atorvastatin at bedtime, 4 mg doxazosin daily, 112 mcg levothyroxine daily, 100 mg losartan daily, 25 mg metoprolol daily, and 0.4 mg tamsulosin daily. The patient had also been taking over-the-counter indomethacin for knee pain.
Based on the ECG results, he was treated with 0.083%/6 mL nebulized albuterol, 4.65 Mq/250 mL saline solution intravenous (IV) calcium gluconate, 10 units IV insulin with concomitant 50%/25 mL IV dextrose and 8.4 g of oral patiromer suspension. IV furosemide was held due to concern for renal function. The decision to proceed with hemodialysis was made. Repeat laboratory tests were performed, and an ECG obtained after treatment initiation but prior to hemodialysis demonstrated improvement of rate and T wave shortening (Figure 1c). The serum potassium level dropped from 9.8 mEq/L to 7.9 mEq/L (reference range, 3.5-5.0 mEq/L) (Table 1).

In addition to hemodialysis, sodium zirconium 10 g orally 3 times daily was added. Laboratory test results and an ECG was performed after dialysis continued to demonstrate improvement (Figure 1d). The patient’s potassium level decreased to 5.8 mEq/L, with the ECG demonstrating stability of heart rate and further improvement of the PR interval, QRS complex, and T waves.
Despite the established treatment regimen, potassium levels again rose to 6.7 mEq/L, but there were no significant changes in the ECG, and thus no medication changes were made (Figure 1e). Subsequent monitoring demonstrated a further increase in potassium to 7.4 mEq/L, with an ECG demonstrating a return to the baseline of 1 year prior. The patient underwent hemodialysis again and was given oral furosemide 60 mg every 12 hours. The potassium concentration after dialysis decreased to 4.7 mEq/L and remained stable, not going above 5.0 mEq/L on subsequent monitoring. The patient had resolution of all symptoms and was discharged.
Discussion
We have described in detail the presentation of each pathology and mechanisms of each treatment, starting with the patient’s initial condition that brought him to the emergency room—muscle weakness. Skeletal muscle weakness is a common manifestation of hyperkalemia, occurring in 20% to 40% of cases, and is more prevalent in severe elevations of potassium. Rarely, the weakness can progress to flaccid paralysis of the patient’s extremities and, in extreme cases, the diaphragm.
Muscle weakness progression occurs in a manner that resembles Guillain-Barré syndrome, starting in the lower extremities and ascending toward the upper extremities.10 This is known as secondary hyperkalemic periodic paralysis. Hyperkalemia lowers the transmembrane gradient in neurons, leading to neuronal depolarization independent of the degree of hyperkalemia. If the degree of hyperkalemia is large enough, this depolarization inactivates voltage-gated sodium channels, making neurons refractory to excitation. Electromyographical studies have shown reduction in the compounded muscle action potential.11 The transient nature of this paralysis is reflected by rapid correction of weakness and paralysis when the electrolyte disorder is corrected.
The patient in this case also presented with bradycardia. The ECG manifestations of hyperkalemia can include atrial asystole, intraventricular conduction disturbances, peaked T waves, and widened QRS complexes. However, some patients with renal insufficiency may not exhibit ECG changes despite significantly elevated serum potassium levels.12
The severity of hyperkalemia is crucial in determining the associated ECG changes, with levels > 6.0 mEq/L presenting with abnormalities.13 ECG findings alone may not always accurately reflect the severity of hyperkalemia, as up to 60% of patients with potassium levels > 6.0 mEq/L may not show ECG changes.14 Additionally, extreme hyperkalemia can lead to inconsistent ECG findings, making it challenging to rely solely on ECG for diagnosis and monitoring.8 The level of potassium that causes these effects varies widely through patient populations.
The main mechanism by which hyperkalemia affects the heart’s conduction system is through voltage differences across the conduction fibers and eventual steady-state inactivation of sodium channels. This combination of mechanisms shortens the action potential duration, allowing more cardiomyocytes to undergo synchronized depolarization. This amalgamation of cardiomyocytes repolarizing can be reflected on ECGs as peaked T waves. As the action potential decreases, there is a period during which cardiomyocytes are prone to tachyarrhythmias and ventricular fibrillation.
A reduced action potential may lead to increased rates of depolarization and thus conduction, which in some scenarios may increase heart rate. As the levels of potassium rise, intracellular accumulation impedes the entry of sodium by decreasing the cation gradient across the cell membrane. This effectively slows the sinus nodes and prolongs the QRS by slowing the overall propagation of action potentials. By this mechanism, conduction delays, blocks, or asystole are manifested. The patient in this case showed conduction delays, peaked T waves, and disappearance of P waves when he first arrived.
Hyperkalemia Treatment
Hyperkalemia develops most commonly due to acute or chronic kidney diseases, as was the case with this patient. The patient’s hyperkalemia was also augmented by the use of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), which can directly affect renal function. A properly functioning kidney is responsible for excretion of up to 90% of ingested potassium, while the remainder is excreted through the gastrointestinal (GI) tract. Definitive treatment of hyperkalemia is mitigated primarily through these 2 organ systems. The treatment also includes transitory mechanisms of potassium reduction. The goal of each method is to preserve the action potential of cardiomyocytes and myocytes. This patient presented with acute symptomatic hyperkalemia and received various medications to acutely, transitorily, and definitively treat it.
Initial therapy included calcium gluconate, which functions to stabilize the myocardial cell membrane. Hyperkalemia decreases the resting membrane action potential of excitable cells and predisposes them to early depolarization and thus dysrhythmias. Calcium decreases the threshold potential across cells and offsets the overall gradient back to near normal levels.15 Calcium can be delivered through calcium gluconate or calcium chloride. Calcium chloride is not preferred because extravasation can cause pain, blistering and tissue ischemia. Central venous access is required, potentially delaying prompt treatment. Calcium acts rapidly after administration—within 1 to 3 minutes—but only lasts 30 to 60 minutes.16 Administration of calcium gluconate can be repeated as often as necessary, but patients must be monitored for adverse effects of calcium such as nausea, abdominal pain, polydipsia, polyuria, muscle weakness, and paresthesia. Care must be taken when patients are taking digoxin, because calcium may potentiate toxicity.17 Although calcium provides immediate benefits it does little to correct the underlying cause; other medications are required to remove potassium from the body.
Two medication classes have been proven to shift potassium intracellularly. The first are β-2 agonists, such as albuterol/levalbuterol, and the second is insulin. Both work through sodium-potassium-ATPase in a direct manner. β-2 agonists stimulate sodium-potassium-ATPase to move more potassium intracellularly, but these effects have been seen only with high doses of albuterol, typically 4× the standard dose of 0.5 mg in nebulized solutions to achieve decreases in potassium of 0.3 to 0.6 mEq/L, although some trials have reported decreases of 0.62 to 0.98 mEq/L.15,18 These potassium-lowering effects of β-2 agonist are modest, but can be seen 20 to 30 minutes after administration and persist up to 1 to 2 hours. β-2 agonists are also readily affected by β blockers, which may reduce or negate the desired effect in hyperkalemia. For these reasons, a β-2 agonist should not be given as monotherapy and should be provided as an adjuvant to more independent therapies such as insulin. Insulin binds to receptors on muscle cells and increases the quantity of sodium-potassium-ATPase and glucose transporters. With this increase in influx pumps, surrounding tissues with higher resting membrane potentials can absorb the potassium load, thereby protecting cardiomyocytes.
Potassium Removal
Three methods are currently available to remove potassium from the body: GI excretion, renal excretion, and direct removal from the bloodstream. Under normal physiologic conditions, the kidneys account for about 90% of the body’s ability to remove potassium. Loop diuretics facilitate the removal of potassium by increasing urine production and have an additional potassium-wasting effect. Although the onset of action of loop diuretics is typically 30 to 60 minutes after oral administration, their effect can last for several hours. In this patient, furosemide was introduced later in the treatment plan to manage recurring hyperkalemia by enhancing renal potassium excretion.
Potassium binders such as patiromer act in the GI tract, effectively reducing serum potassium levels although with a slower onset of action than furosemide, generally taking hours to days to exert its effect. Both medications illustrate a tailored approach to managing potassium levels, adapted to the evolving needs and renal function of the patient. The last method is using hemodialysis—by far the most rapid method to remove potassium, but also the most invasive. The different methods of treating hyperkalemia are summarized in Table 2. This patient required multiple days of hemodialysis to completely correct the electrolyte disorder. Upon discharge, the patient continued oral furosemide 40 mg daily and eventually discontinued hemodialysis due to stable renal function.

Often, after correcting an inciting event, potassium stores in the body eventually stabilize and do not require additional follow-up. Patients prone to hyperkalemia should be thoroughly educated on medications to avoid (NSAIDs, ACEIs/ARBs, trimethoprim), an adequate low potassium diet, and symptoms that may warrant medical attention.19
Conclusions
This case illustrates the importance of recognizing the spectrum of manifestations of hyperkalemia, which ranged from muscle weakness to cardiac dysrhythmias. Management strategies for the patient included stabilization of cardiac membranes, potassium shifting, and potassium removal, each tailored to the patient’s individual clinical findings.
The case further illustrates the critical role of continuous monitoring and dynamic adjustment of therapeutic strategies in response to evolving clinical and laboratory findings. The initial and subsequent ECGs, alongside laboratory tests, were instrumental in guiding the adjustments needed in the treatment regimen, ensuring both the efficacy and safety of the interventions. This proactive approach can mitigate the risk of recurrent hyperkalemia and its complications.
- Youn JH, McDonough AA. Recent advances in understanding integrative control of potassium homeostasis. Annu Rev Physiol. 2009;71:381-401. doi:10.1146/annurev.physiol.010908.163241 2.
- Simon LV, Hashmi MF, Farrell MW. Hyperkalemia. In: StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing; September 4, 2023. Accessed October 22, 2025.
- Mu F, Betts KA, Woolley JM, et al. Prevalence and economic burden of hyperkalemia in the United States Medicare population. Curr Med Res Opin. 2020;36:1333-1341. doi:10.1080/03007995.2020.1775072
- Loutradis C, Tolika P, Skodra A, et al. Prevalence of hyperkalemia in diabetic and non-diabetic patients with chronic kidney disease: a nested case-control study. Am J Nephrol. 2015;42:351-360. doi:10.1159/000442393
- Grodzinsky A, Goyal A, Gosch K, et al. Prevalence and prognosis of hyperkalemia in patients with acute myocardial infarction. Am J Med. 2016;129:858-865. doi:10.1016/j.amjmed.2016.03.008
- Hunter RW, Bailey MA. Hyperkalemia: pathophysiology, risk factors and consequences. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2019;34(suppl 3):iii2-iii11. doi:10.1093/ndt/gfz206
- Luo J, Brunelli SM, Jensen DE, Yang A. Association between serum potassium and outcomes in patients with reduced kidney function. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2016;11:90-100. doi:10.2215/CJN.01730215
- Montford JR, Linas S. How dangerous is hyperkalemia? J Am Soc Nephrol. 2017;28:3155-3165. doi:10.1681/ASN.2016121344
- Mattu A, Brady WJ, Robinson DA. Electrocardiographic manifestations of hyperkalemia. Am J Emerg Med. 2000;18:721-729. doi:10.1053/ajem.2000.7344
- Kimmons LA, Usery JB. Acute ascending muscle weakness secondary to medication-induced hyperkalemia. Case Rep Med. 2014;2014:789529. doi:10.1155/2014/789529
- Naik KR, Saroja AO, Khanpet MS. Reversible electrophysiological abnormalities in acute secondary hyperkalemic paralysis. Ann Indian Acad Neurol. 2012;15:339-343. doi:10.4103/0972-2327.104354
- Montague BT, Ouellette JR, Buller GK. Retrospective review of the frequency of ECG changes in hyperkalemia. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2008;3:324-330. doi:10.2215/CJN.04611007
- Larivée NL, Michaud JB, More KM, Wilson JA, Tennankore KK. Hyperkalemia: prevalence, predictors and emerging treatments. Cardiol Ther. 2023;12:35-63. doi:10.1007/s40119-022-00289-z
- Shingarev R, Allon M. A physiologic-based approach to the treatment of acute hyperkalemia. Am J Kidney Dis. 2010;56:578-584. doi:10.1053/j.ajkd.2010.03.014
- Parham WA, Mehdirad AA, Biermann KM, Fredman CS. Hyperkalemia revisited. Tex Heart Inst J. 2006;33:40-47.
- Ng KE, Lee CS. Updated treatment options in the management of hyperkalemia. U.S. Pharmacist. February 16, 2017. Accessed October 1, 2025. www.uspharmacist.com/article/updated-treatment-options-in-the-management-of-hyperkalemia
- Quick G, Bastani B. Prolonged asystolic hyperkalemic cardiac arrest with no neurologic sequelae. Ann Emerg Med. 1994;24:305-311. doi:10.1016/s0196-0644(94)70144-x 18.
- Allon M, Dunlay R, Copkney C. Nebulized albuterol for acute hyperkalemia in patients on hemodialysis. Ann Intern Med. 1989;110:426-429. doi:10.7326/0003-4819-110-6-42619.
- Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) CKD Work Group. KDIGO 2024 Clinical Practice Guideline for the Evaluation and Management of Chronic Kidney Disease. Kidney Int. 2024;105(4 suppl):S117-S314. doi:10.1016/j.kint.2023.10.018
- Youn JH, McDonough AA. Recent advances in understanding integrative control of potassium homeostasis. Annu Rev Physiol. 2009;71:381-401. doi:10.1146/annurev.physiol.010908.163241 2.
- Simon LV, Hashmi MF, Farrell MW. Hyperkalemia. In: StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing; September 4, 2023. Accessed October 22, 2025.
- Mu F, Betts KA, Woolley JM, et al. Prevalence and economic burden of hyperkalemia in the United States Medicare population. Curr Med Res Opin. 2020;36:1333-1341. doi:10.1080/03007995.2020.1775072
- Loutradis C, Tolika P, Skodra A, et al. Prevalence of hyperkalemia in diabetic and non-diabetic patients with chronic kidney disease: a nested case-control study. Am J Nephrol. 2015;42:351-360. doi:10.1159/000442393
- Grodzinsky A, Goyal A, Gosch K, et al. Prevalence and prognosis of hyperkalemia in patients with acute myocardial infarction. Am J Med. 2016;129:858-865. doi:10.1016/j.amjmed.2016.03.008
- Hunter RW, Bailey MA. Hyperkalemia: pathophysiology, risk factors and consequences. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2019;34(suppl 3):iii2-iii11. doi:10.1093/ndt/gfz206
- Luo J, Brunelli SM, Jensen DE, Yang A. Association between serum potassium and outcomes in patients with reduced kidney function. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2016;11:90-100. doi:10.2215/CJN.01730215
- Montford JR, Linas S. How dangerous is hyperkalemia? J Am Soc Nephrol. 2017;28:3155-3165. doi:10.1681/ASN.2016121344
- Mattu A, Brady WJ, Robinson DA. Electrocardiographic manifestations of hyperkalemia. Am J Emerg Med. 2000;18:721-729. doi:10.1053/ajem.2000.7344
- Kimmons LA, Usery JB. Acute ascending muscle weakness secondary to medication-induced hyperkalemia. Case Rep Med. 2014;2014:789529. doi:10.1155/2014/789529
- Naik KR, Saroja AO, Khanpet MS. Reversible electrophysiological abnormalities in acute secondary hyperkalemic paralysis. Ann Indian Acad Neurol. 2012;15:339-343. doi:10.4103/0972-2327.104354
- Montague BT, Ouellette JR, Buller GK. Retrospective review of the frequency of ECG changes in hyperkalemia. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2008;3:324-330. doi:10.2215/CJN.04611007
- Larivée NL, Michaud JB, More KM, Wilson JA, Tennankore KK. Hyperkalemia: prevalence, predictors and emerging treatments. Cardiol Ther. 2023;12:35-63. doi:10.1007/s40119-022-00289-z
- Shingarev R, Allon M. A physiologic-based approach to the treatment of acute hyperkalemia. Am J Kidney Dis. 2010;56:578-584. doi:10.1053/j.ajkd.2010.03.014
- Parham WA, Mehdirad AA, Biermann KM, Fredman CS. Hyperkalemia revisited. Tex Heart Inst J. 2006;33:40-47.
- Ng KE, Lee CS. Updated treatment options in the management of hyperkalemia. U.S. Pharmacist. February 16, 2017. Accessed October 1, 2025. www.uspharmacist.com/article/updated-treatment-options-in-the-management-of-hyperkalemia
- Quick G, Bastani B. Prolonged asystolic hyperkalemic cardiac arrest with no neurologic sequelae. Ann Emerg Med. 1994;24:305-311. doi:10.1016/s0196-0644(94)70144-x 18.
- Allon M, Dunlay R, Copkney C. Nebulized albuterol for acute hyperkalemia in patients on hemodialysis. Ann Intern Med. 1989;110:426-429. doi:10.7326/0003-4819-110-6-42619.
- Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) CKD Work Group. KDIGO 2024 Clinical Practice Guideline for the Evaluation and Management of Chronic Kidney Disease. Kidney Int. 2024;105(4 suppl):S117-S314. doi:10.1016/j.kint.2023.10.018
Following the Hyperkalemia Trail: A Case Report of ECG Changes and Treatment Responses
Following the Hyperkalemia Trail: A Case Report of ECG Changes and Treatment Responses
Updated Crohn’s Disease Guideline Stresses Early Use of Advanced Drugs
As the science of Crohn’s disease (CD) rapidly evolves,
The guideline was published in Gastroenterology by an expert panel chaired by Frank I. Scott, MD, MSCE, a gastroenterologist at the Crohn’s and Colitis Center in the Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology at the University of Colorado Anschutz School of Medicine in Aurora, Colorado.
It makes 16 main recommendations in a comprehensive, patient-centered, evidence-based approach to utilizing an array of medical options endorsing early use of advanced therapies such as biologics. Of these, one is a strong recommendation, nine are conditional recommendations, and six are identified as knowledge gaps.
“There’s been a significant increase in the number of therapies available for clinicians and patients when considering treatment options for moderate-to-severe [CD] since the prior guidelines in 2021,” Scott told GI & Hepatology News. “We hope these guidelines will help clinicians determine how to maximize the potential benefit of the full armamentarium of therapies available to treat this disease.”
Guideline co-author Siddharth Singh, MD, MS, of the Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology at the Mayo Clinic Arizona in Scottsdale, Arizona, said the goal of the guideline is to translate evidence into clear, meaningful recommendations for frontline clinicians. “It’s patient centered but also provider centric. We want to help physicians and advanced practice providers make timely, actionable decisions for their patients.”
Among the recommendations:
- Early initiation of high-efficacy advanced therapy to prevent progression is recommended over insurance-driven step therapy.
- For adult patients naive to advanced therapies, the AGA recommends infliximab, adalimumab, ustekinumab, risankizumab, mirikizumab, guselkumab, or upadacitinib over no treatment and suggests the use of certolizumab pegol or vedolizumab over no treatment.
- For adults naive to advanced therapies, the AGA suggests using a higher-efficacy medication (infliximab, adalimumab, vedolizumab, ustekinumab, risankizumab, mirikizumab, or guselkumab) rather than a lower-efficacy option (certolizumab pegol or upadacitinib).
- For those previously exposed to one or more advanced therapies, the AGA suggests a higher-efficacy medication (adalimumab, risankizumab, guselkumab, or upadacitinib) or an intermediate-efficacy medication (ustekinumab or mirikizumab) rather than a lower-efficacy medication (vedolizumab or certolizumab pegol).
- For adult outpatients, the AGA suggests against thiopurine monotherapy for induction of remission but suggests thiopurine monotherapy over no treatment for maintenance of (typically corticosteroid-induced) remission.
- The guideline favors subcutaneous methotrexate for induction and maintenance of remission but suggests against oral methotrexate.
- Combination therapy with infliximab and thiopurines is suggested over infliximab monotherapy, particularly in those naive to thiopurines.
“We identified several critical knowledge gaps, including the role of combination therapy for non-[TNF] biologics, as well as whether targeting endoscopic remission as opposed to clinical remission yields additional benefit,” Scott said.
Most of the panel’s time was spent considering evidence and recommendations in relation to how therapies should be positioned among each other in light of patients’ treatment history. “For those who were advanced therapy-naive, we used two groups, or ‘buckets’: higher and lower efficacy,” Scott said. “For advanced therapy-exposed individuals, we used higher, intermediate, and lower buckets, recommending the use of higher- or intermediate-efficacy medications.” Network meta-analyses were done to determine which therapies belong in which categories.
Perhaps the most unexpected outcome from the panel’s review was the inability to make a recommendation on treating to a target of mucosal healing. “This target conceptually makes sense, but prospective clinical trial data supporting this approach over targeting clinical remission unfortunately are currently limited,” Scott said. Several ongoing clinical trials are assessing this endpoint. “We hope future versions of these guidelines can make a formal recommendation regarding targeting mucosal healing. The benefit of our living guideline approach is that as these data become available, we will be able incorporate them more rapidly.”
Offering a nonparticipant’s perspective on the living, updatable guideline, Ahmed Hassan Gemei, MD, a gastroenterologist at Northwell North Shore University Hospital in Manhasset, New York, said the update was needed because of the shifting therapeutic landscape.
“As great as that is for patient care, it can be daunting for gastroenterologists to keep up with the onslaught of evidence and growing repertoire of advanced therapies,” he told GI & Hepatology News. “For a rapidly evolving field like inflammatory bowel disease, having a guideline come out once every 3-5 years can lag behind the evidence significantly. There is something special and much needed about a living guideline that gets regularly updated as newer data come out, which we have come to appreciate with the AGA living guidelines for ulcerative colitis.”
As to facilitating clinical decision-making, Gemei added, “It does a great job at summarizing the available evidence, making life easier for gastroenterologists who are trying to make evidence-based decisions for their patients. But having a straightforward algorithmic approach to the management of [CD] is ultimately limited by patient-specific differences and patient and payor preferences, as well as gaps in the data such as comparative effectiveness, sequencing of therapy, and advanced dual therapies.”
When it comes to choosing a drug, for example, gastroenterologists are given a general overview of which ones have higher or lower efficacy, but the choice depends on multiple factors, including CD phenotype, previous medications, and patient preference with regard to relative safety, as well as payor preference (although clinicians often try to influence this).
The guidelines align broadly but with some differences with other societal guidelines in the US and Europe. But, said Gemei, the absence of a recommendation for or against treating to a target of endoscopic healing was surprising. “This has been standard practice in recent years based on the updated STRIDE [Selecting Therapeutic Targets in Inflammatory Bowel Disease] consensus statements, as well as recent American College of Gastroenterology guidelines. Though I understand the reason behind this decision, which was simply lack of strong data, it’s still a departure from other society recommendations and current practice. I doubt this will change how we manage our patient, though, and luckily, this is a living guideline, so as more data come out, we should see an update in this area.”
He noted that despite this and other guidelines recommending against the use of 5-aminosalicylic acids in CD, “we still see many of our colleagues using it for their [CD] patients. Hopefully, this guideline can be a helpful resource for everyone trying to update their practice.”
Gemei agreed with the authors that there are persistent knowledge gaps, including insufficient data from head-to-head effectiveness studies, optimal biologic sequencing after failure, advanced combination therapy (such as JAK inhibitors plus anti-interleukin-23), radiologic and endoscopic disease monitoring intervals, and therapy withdrawal strategies after long-term remission. “So there’s a lot we still need to understand better,” he said. “Until we have more data and guidance, we are still practicing all these things based on the available evidence as well as local practice patterns.”
Overall, said Scott, the guidance highlights the options with the best supporting evidence while incorporating the patient’s prior treatment journey. “It’s also important to emphasize that treatment decisions should be individualized and should involve shared decision-making among providers and their patients,” he added. “Patient preferences, age, active comorbidities, and pregnancy should always be considered when selecting the appropriate treatment plan.”
All funding for this guidance was supplied by AGA. The guideline chairs had no conflicts of interest, and fewer than 50% of guideline panel members had conflicts of interest. Gemei had no conflicts of interest.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
As the science of Crohn’s disease (CD) rapidly evolves,
The guideline was published in Gastroenterology by an expert panel chaired by Frank I. Scott, MD, MSCE, a gastroenterologist at the Crohn’s and Colitis Center in the Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology at the University of Colorado Anschutz School of Medicine in Aurora, Colorado.
It makes 16 main recommendations in a comprehensive, patient-centered, evidence-based approach to utilizing an array of medical options endorsing early use of advanced therapies such as biologics. Of these, one is a strong recommendation, nine are conditional recommendations, and six are identified as knowledge gaps.
“There’s been a significant increase in the number of therapies available for clinicians and patients when considering treatment options for moderate-to-severe [CD] since the prior guidelines in 2021,” Scott told GI & Hepatology News. “We hope these guidelines will help clinicians determine how to maximize the potential benefit of the full armamentarium of therapies available to treat this disease.”
Guideline co-author Siddharth Singh, MD, MS, of the Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology at the Mayo Clinic Arizona in Scottsdale, Arizona, said the goal of the guideline is to translate evidence into clear, meaningful recommendations for frontline clinicians. “It’s patient centered but also provider centric. We want to help physicians and advanced practice providers make timely, actionable decisions for their patients.”
Among the recommendations:
- Early initiation of high-efficacy advanced therapy to prevent progression is recommended over insurance-driven step therapy.
- For adult patients naive to advanced therapies, the AGA recommends infliximab, adalimumab, ustekinumab, risankizumab, mirikizumab, guselkumab, or upadacitinib over no treatment and suggests the use of certolizumab pegol or vedolizumab over no treatment.
- For adults naive to advanced therapies, the AGA suggests using a higher-efficacy medication (infliximab, adalimumab, vedolizumab, ustekinumab, risankizumab, mirikizumab, or guselkumab) rather than a lower-efficacy option (certolizumab pegol or upadacitinib).
- For those previously exposed to one or more advanced therapies, the AGA suggests a higher-efficacy medication (adalimumab, risankizumab, guselkumab, or upadacitinib) or an intermediate-efficacy medication (ustekinumab or mirikizumab) rather than a lower-efficacy medication (vedolizumab or certolizumab pegol).
- For adult outpatients, the AGA suggests against thiopurine monotherapy for induction of remission but suggests thiopurine monotherapy over no treatment for maintenance of (typically corticosteroid-induced) remission.
- The guideline favors subcutaneous methotrexate for induction and maintenance of remission but suggests against oral methotrexate.
- Combination therapy with infliximab and thiopurines is suggested over infliximab monotherapy, particularly in those naive to thiopurines.
“We identified several critical knowledge gaps, including the role of combination therapy for non-[TNF] biologics, as well as whether targeting endoscopic remission as opposed to clinical remission yields additional benefit,” Scott said.
Most of the panel’s time was spent considering evidence and recommendations in relation to how therapies should be positioned among each other in light of patients’ treatment history. “For those who were advanced therapy-naive, we used two groups, or ‘buckets’: higher and lower efficacy,” Scott said. “For advanced therapy-exposed individuals, we used higher, intermediate, and lower buckets, recommending the use of higher- or intermediate-efficacy medications.” Network meta-analyses were done to determine which therapies belong in which categories.
Perhaps the most unexpected outcome from the panel’s review was the inability to make a recommendation on treating to a target of mucosal healing. “This target conceptually makes sense, but prospective clinical trial data supporting this approach over targeting clinical remission unfortunately are currently limited,” Scott said. Several ongoing clinical trials are assessing this endpoint. “We hope future versions of these guidelines can make a formal recommendation regarding targeting mucosal healing. The benefit of our living guideline approach is that as these data become available, we will be able incorporate them more rapidly.”
Offering a nonparticipant’s perspective on the living, updatable guideline, Ahmed Hassan Gemei, MD, a gastroenterologist at Northwell North Shore University Hospital in Manhasset, New York, said the update was needed because of the shifting therapeutic landscape.
“As great as that is for patient care, it can be daunting for gastroenterologists to keep up with the onslaught of evidence and growing repertoire of advanced therapies,” he told GI & Hepatology News. “For a rapidly evolving field like inflammatory bowel disease, having a guideline come out once every 3-5 years can lag behind the evidence significantly. There is something special and much needed about a living guideline that gets regularly updated as newer data come out, which we have come to appreciate with the AGA living guidelines for ulcerative colitis.”
As to facilitating clinical decision-making, Gemei added, “It does a great job at summarizing the available evidence, making life easier for gastroenterologists who are trying to make evidence-based decisions for their patients. But having a straightforward algorithmic approach to the management of [CD] is ultimately limited by patient-specific differences and patient and payor preferences, as well as gaps in the data such as comparative effectiveness, sequencing of therapy, and advanced dual therapies.”
When it comes to choosing a drug, for example, gastroenterologists are given a general overview of which ones have higher or lower efficacy, but the choice depends on multiple factors, including CD phenotype, previous medications, and patient preference with regard to relative safety, as well as payor preference (although clinicians often try to influence this).
The guidelines align broadly but with some differences with other societal guidelines in the US and Europe. But, said Gemei, the absence of a recommendation for or against treating to a target of endoscopic healing was surprising. “This has been standard practice in recent years based on the updated STRIDE [Selecting Therapeutic Targets in Inflammatory Bowel Disease] consensus statements, as well as recent American College of Gastroenterology guidelines. Though I understand the reason behind this decision, which was simply lack of strong data, it’s still a departure from other society recommendations and current practice. I doubt this will change how we manage our patient, though, and luckily, this is a living guideline, so as more data come out, we should see an update in this area.”
He noted that despite this and other guidelines recommending against the use of 5-aminosalicylic acids in CD, “we still see many of our colleagues using it for their [CD] patients. Hopefully, this guideline can be a helpful resource for everyone trying to update their practice.”
Gemei agreed with the authors that there are persistent knowledge gaps, including insufficient data from head-to-head effectiveness studies, optimal biologic sequencing after failure, advanced combination therapy (such as JAK inhibitors plus anti-interleukin-23), radiologic and endoscopic disease monitoring intervals, and therapy withdrawal strategies after long-term remission. “So there’s a lot we still need to understand better,” he said. “Until we have more data and guidance, we are still practicing all these things based on the available evidence as well as local practice patterns.”
Overall, said Scott, the guidance highlights the options with the best supporting evidence while incorporating the patient’s prior treatment journey. “It’s also important to emphasize that treatment decisions should be individualized and should involve shared decision-making among providers and their patients,” he added. “Patient preferences, age, active comorbidities, and pregnancy should always be considered when selecting the appropriate treatment plan.”
All funding for this guidance was supplied by AGA. The guideline chairs had no conflicts of interest, and fewer than 50% of guideline panel members had conflicts of interest. Gemei had no conflicts of interest.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
As the science of Crohn’s disease (CD) rapidly evolves,
The guideline was published in Gastroenterology by an expert panel chaired by Frank I. Scott, MD, MSCE, a gastroenterologist at the Crohn’s and Colitis Center in the Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology at the University of Colorado Anschutz School of Medicine in Aurora, Colorado.
It makes 16 main recommendations in a comprehensive, patient-centered, evidence-based approach to utilizing an array of medical options endorsing early use of advanced therapies such as biologics. Of these, one is a strong recommendation, nine are conditional recommendations, and six are identified as knowledge gaps.
“There’s been a significant increase in the number of therapies available for clinicians and patients when considering treatment options for moderate-to-severe [CD] since the prior guidelines in 2021,” Scott told GI & Hepatology News. “We hope these guidelines will help clinicians determine how to maximize the potential benefit of the full armamentarium of therapies available to treat this disease.”
Guideline co-author Siddharth Singh, MD, MS, of the Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology at the Mayo Clinic Arizona in Scottsdale, Arizona, said the goal of the guideline is to translate evidence into clear, meaningful recommendations for frontline clinicians. “It’s patient centered but also provider centric. We want to help physicians and advanced practice providers make timely, actionable decisions for their patients.”
Among the recommendations:
- Early initiation of high-efficacy advanced therapy to prevent progression is recommended over insurance-driven step therapy.
- For adult patients naive to advanced therapies, the AGA recommends infliximab, adalimumab, ustekinumab, risankizumab, mirikizumab, guselkumab, or upadacitinib over no treatment and suggests the use of certolizumab pegol or vedolizumab over no treatment.
- For adults naive to advanced therapies, the AGA suggests using a higher-efficacy medication (infliximab, adalimumab, vedolizumab, ustekinumab, risankizumab, mirikizumab, or guselkumab) rather than a lower-efficacy option (certolizumab pegol or upadacitinib).
- For those previously exposed to one or more advanced therapies, the AGA suggests a higher-efficacy medication (adalimumab, risankizumab, guselkumab, or upadacitinib) or an intermediate-efficacy medication (ustekinumab or mirikizumab) rather than a lower-efficacy medication (vedolizumab or certolizumab pegol).
- For adult outpatients, the AGA suggests against thiopurine monotherapy for induction of remission but suggests thiopurine monotherapy over no treatment for maintenance of (typically corticosteroid-induced) remission.
- The guideline favors subcutaneous methotrexate for induction and maintenance of remission but suggests against oral methotrexate.
- Combination therapy with infliximab and thiopurines is suggested over infliximab monotherapy, particularly in those naive to thiopurines.
“We identified several critical knowledge gaps, including the role of combination therapy for non-[TNF] biologics, as well as whether targeting endoscopic remission as opposed to clinical remission yields additional benefit,” Scott said.
Most of the panel’s time was spent considering evidence and recommendations in relation to how therapies should be positioned among each other in light of patients’ treatment history. “For those who were advanced therapy-naive, we used two groups, or ‘buckets’: higher and lower efficacy,” Scott said. “For advanced therapy-exposed individuals, we used higher, intermediate, and lower buckets, recommending the use of higher- or intermediate-efficacy medications.” Network meta-analyses were done to determine which therapies belong in which categories.
Perhaps the most unexpected outcome from the panel’s review was the inability to make a recommendation on treating to a target of mucosal healing. “This target conceptually makes sense, but prospective clinical trial data supporting this approach over targeting clinical remission unfortunately are currently limited,” Scott said. Several ongoing clinical trials are assessing this endpoint. “We hope future versions of these guidelines can make a formal recommendation regarding targeting mucosal healing. The benefit of our living guideline approach is that as these data become available, we will be able incorporate them more rapidly.”
Offering a nonparticipant’s perspective on the living, updatable guideline, Ahmed Hassan Gemei, MD, a gastroenterologist at Northwell North Shore University Hospital in Manhasset, New York, said the update was needed because of the shifting therapeutic landscape.
“As great as that is for patient care, it can be daunting for gastroenterologists to keep up with the onslaught of evidence and growing repertoire of advanced therapies,” he told GI & Hepatology News. “For a rapidly evolving field like inflammatory bowel disease, having a guideline come out once every 3-5 years can lag behind the evidence significantly. There is something special and much needed about a living guideline that gets regularly updated as newer data come out, which we have come to appreciate with the AGA living guidelines for ulcerative colitis.”
As to facilitating clinical decision-making, Gemei added, “It does a great job at summarizing the available evidence, making life easier for gastroenterologists who are trying to make evidence-based decisions for their patients. But having a straightforward algorithmic approach to the management of [CD] is ultimately limited by patient-specific differences and patient and payor preferences, as well as gaps in the data such as comparative effectiveness, sequencing of therapy, and advanced dual therapies.”
When it comes to choosing a drug, for example, gastroenterologists are given a general overview of which ones have higher or lower efficacy, but the choice depends on multiple factors, including CD phenotype, previous medications, and patient preference with regard to relative safety, as well as payor preference (although clinicians often try to influence this).
The guidelines align broadly but with some differences with other societal guidelines in the US and Europe. But, said Gemei, the absence of a recommendation for or against treating to a target of endoscopic healing was surprising. “This has been standard practice in recent years based on the updated STRIDE [Selecting Therapeutic Targets in Inflammatory Bowel Disease] consensus statements, as well as recent American College of Gastroenterology guidelines. Though I understand the reason behind this decision, which was simply lack of strong data, it’s still a departure from other society recommendations and current practice. I doubt this will change how we manage our patient, though, and luckily, this is a living guideline, so as more data come out, we should see an update in this area.”
He noted that despite this and other guidelines recommending against the use of 5-aminosalicylic acids in CD, “we still see many of our colleagues using it for their [CD] patients. Hopefully, this guideline can be a helpful resource for everyone trying to update their practice.”
Gemei agreed with the authors that there are persistent knowledge gaps, including insufficient data from head-to-head effectiveness studies, optimal biologic sequencing after failure, advanced combination therapy (such as JAK inhibitors plus anti-interleukin-23), radiologic and endoscopic disease monitoring intervals, and therapy withdrawal strategies after long-term remission. “So there’s a lot we still need to understand better,” he said. “Until we have more data and guidance, we are still practicing all these things based on the available evidence as well as local practice patterns.”
Overall, said Scott, the guidance highlights the options with the best supporting evidence while incorporating the patient’s prior treatment journey. “It’s also important to emphasize that treatment decisions should be individualized and should involve shared decision-making among providers and their patients,” he added. “Patient preferences, age, active comorbidities, and pregnancy should always be considered when selecting the appropriate treatment plan.”
All funding for this guidance was supplied by AGA. The guideline chairs had no conflicts of interest, and fewer than 50% of guideline panel members had conflicts of interest. Gemei had no conflicts of interest.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM GASTROENTEROLOGY
Dr. David Lieberman: A Groundbreaking Career in Gastroenterology
David Lieberman, MD, AGAF, spent much of his long career asking questions about everyday clinical practice in GI medicine and then researching ways to answer those questions.
“The answer to one question often leads to further questions. And I think that’s what makes this research so exciting and dynamic,” said Lieberman, professor emeritus with Oregon Health and Science University, where he served as chief of the Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology for 24 years.
He was also instrumental in creating a blood and tissue repository for colorectal cancer (CRC) research, and a national endoscopic database.
His groundbreaking GI research in colorectal cancer screening earned him AGA’s Julius Friedenwald Medal, a top career honor. “We started off with some questions about the role of specific screening tests like colonoscopy and stool-based tests for screening,” he said. This led to the first large study about the value of screening with colonoscopy, which set the stage for current screening guidelines. Assessing more than 3,000 asymptomatic adults, Lieberman and colleagues determined that colonoscopy was more effective than sigmoidoscopy in detecting advanced colonic neoplasms.
The next phase of research focused on how well GI doctors were performing colonoscopy, asking questions about the quality of the colonoscopies being performed, and what course of action to take in polyp discovery. “We did some work related to polyp surveillance, what happens after we take out polyps and some recommendations for the appropriate length of follow up afterwards,” he summarized.
Most recently, Lieberman has centered his research on program effectiveness. “If you’re doing high quality colonoscopy and you’re doing appropriate surveillance, how effective is that? And what are the potential problems that might impair effectiveness?”
Adherence and participation remain significant challenges, he said. “If people don’t get the tests done, then they’re not going to be effective. Or if they get part of it done, there can be issues.”
In an interview, Lieberman discussed the reasons why people resist CRC screening, and the new technologies and research underway to make screening options more palatable for reluctant patients.
What do you think are the biggest deterrents to getting screened for CRC?
Dr. Lieberman: The whole idea of dealing with a stool sample is not appealing to patients. The second issue, and this has been shown in many studies, is patients who are referred for colonoscopy may resist because they have heard stories about bowel preps and about colonoscopy itself. But there are many other reasons. I mean, there are issues with access to care that are important. What if you have a positive stool test and you need to get a colonoscopy? How do you get a colonoscopy? There are barriers in moving from one test to the other in a different setting. There are issues with having to take a day off work that’s potentially a financial hardship for some patients. If you’re taking care of elderly relatives or children or if you need transportation, that’s an issue for people.
So, there are many potential barriers, and we’ve been trying to work at a national level to try to understand these barriers and then develop tools to mitigate these problems and improve the overall participation in screening.
How has the field of GI changed since you started practicing medicine?
Dr. Lieberman: I think there have been many exciting changes in technology. The endoscopes we used when I started my career were called fiberoptic scopes. These were scopes that contained tiny glass fibers that ran the length of the scope, and they were good, but not great in terms of imaging, and sometimes they would break down. We now have digital imaging that far surpasses the quality there. We’ve come a long way in terms of things like CT scans, for example, and MRI imaging. The other big technology change has been the development of minimally invasive treatments. For example, if you have a gallstone that’s in your bile duct, we now have ways to remove that without sending the patient to surgery.
The second big change has been the assessment of quality. When I started my career in gastroenterology, we were doing a lot of things, but we didn’t necessarily know if we were doing them well. Most of us thought we were doing them well, of course, but nobody was really measuring quality. There were no quality benchmarks. And so if you don’t measure it, you don’t know. Where we are today in gastroenterology is we’re intensively concerned about quality and measuring quality in various aspects of what we do. And I think that’s a positive development.
What key achievements came out of the U.S. Multi-Society Task Force on Colorectal Cancer?
Dr. Lieberman: This panel evolved because back in the early 2000s, each of the GI organizations were producing guidelines related to colon cancer screening and follow-up. And they were slightly different. This was an attempt to bring all the relevant groups together and try to align the guidelines and recommendations among the GI organizations so that there wouldn’t be a confusing message.
Over the history of this task force, which started around 2002, it’s been remarkably productive. The task force has really examined all aspects of colorectal cancer, including things like the bowel prep, quality of exams, high risk management, hereditary syndromes that can lead to the higher likelihood of developing colon cancer, polypectomy and polypectomy techniques, and screening and surveillance recommendations, which have evolved over time. It’s been, in my opinion, a remarkably productive task force and continues to this day. I’m so very proud of that group.
Could you give a status update on the blood and tissue repository you created for CRC research?
Dr. Lieberman: Our initial studies were part of a Veterans Affairs cooperative study, which is a mechanism of funding within the VA that allows us to work with multiple VA centers to collect data and information. At the very outset of this study, we were performing screening colonoscopies in individuals, and we decided to create a bio-repository that included blood samples, polyp tissue, and normal rectal tissue. The thinking was at some point we might be able to do some genomic studies that might help us predict which patients are most likely to develop colon polyps and colon cancer. All that happened in the 1990s. It was supported by the National Cancer Institute. We created this repository, which sat for a long period of time while we were waiting for the technology to develop and so that we could perform genomic studies in a cost-effective way.
We’re now at that point, which is really exciting. We’re beginning to look at this tissue and perform some genomic studies. Some of this data has been presented at national meetings. This was a precursor to creating a similar type of bio-repository in a larger VA cooperative study. CSP #577 Colonoscopy vs. Fecal Immunochemical Test in Reducing Mortality from Colorectal Cancer (CONFIRM) is a randomized study comparing two forms of screening, a fecal immunochemical test versus a colonoscopy. We’re in the process of enrolling 50,000 patients in that study. We have also created a blood and tissue repository, which we hope will be useful for future studies.
You lead the AGA CRC Task Force, which advances research and policy initiatives to improve screening rates and patient outcomes. What would you like to see in future GI research, particularly in colorectal cancer?
Dr. Lieberman: We have new blood tests coming along that are going to be very attractive to both patients and physicians. You can obtain a blood sample at a point of service and patients won’t have to deal with stool samples. We need to understand how those tests perform in clinical practice. If the test is abnormal, indicating a patient has a higher risk of colon cancer and should get a colonoscopy, are they getting that colonoscopy or not? And what are the barriers? And if it’s normal, then that patient should have a repeat test at an appropriate interval.
We know that the effectiveness of screening really depends on the participation of individuals in terms of completing the steps. We’ve published some work already on trying to understand the role of these blood tests. We expect that these tests will continue to improve over time.
We’re also working on trying to develop these risk stratification tools that could be used in clinical practice to help figure out the most appropriate test for a particular individual.
Let’s say you go to your doctor for colon cancer screening, and if we could determine that you are a low-risk individual, you may benefit best from having a non-invasive test, like a blood test or a stool test. Whereas if you’re a higher risk individual, you may need to have a more invasive screening test like colonoscopy.
This falls into a concept of personalized medicine where we’re trying to use all the information we have from the medical history, and maybe genomic information that I mentioned earlier, to try to determine who needs the most intensive screening and who might benefit from less intensive screening.
I think the most recent work is really focused on these gaps in screening. And the biggest gap are patients that get a non-invasive test, like a stool test, but do not get a colonoscopy that renders the program ineffective if they don’t get the colonoscopy. We’re trying to highlight that for primary care providers and make sure that everyone understands the importance of this follow-up. And then, trying to develop tools to help the primary care provider navigate that patient to a colonoscopy.
What do you think is the biggest misconception about your specialty?
Dr. Lieberman: If there’s a misconception, it’s that GI physicians are focused on procedures. I think a good GI provider should be holistic, and I think many are. What I mean by holistic is that many GI symptoms could be due to stress, medications, diet, or other aspects of behavior, and the remedy is not necessarily a procedure. I think that many GI physicians are really skilled at obtaining this information and trying to help guide the patient through some uncomfortable symptoms.
It means being more like an internist, spending time with the patient to take a detailed history and delve into many different possibilities that might be going on.
David Lieberman, MD, AGAF, spent much of his long career asking questions about everyday clinical practice in GI medicine and then researching ways to answer those questions.
“The answer to one question often leads to further questions. And I think that’s what makes this research so exciting and dynamic,” said Lieberman, professor emeritus with Oregon Health and Science University, where he served as chief of the Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology for 24 years.
He was also instrumental in creating a blood and tissue repository for colorectal cancer (CRC) research, and a national endoscopic database.
His groundbreaking GI research in colorectal cancer screening earned him AGA’s Julius Friedenwald Medal, a top career honor. “We started off with some questions about the role of specific screening tests like colonoscopy and stool-based tests for screening,” he said. This led to the first large study about the value of screening with colonoscopy, which set the stage for current screening guidelines. Assessing more than 3,000 asymptomatic adults, Lieberman and colleagues determined that colonoscopy was more effective than sigmoidoscopy in detecting advanced colonic neoplasms.
The next phase of research focused on how well GI doctors were performing colonoscopy, asking questions about the quality of the colonoscopies being performed, and what course of action to take in polyp discovery. “We did some work related to polyp surveillance, what happens after we take out polyps and some recommendations for the appropriate length of follow up afterwards,” he summarized.
Most recently, Lieberman has centered his research on program effectiveness. “If you’re doing high quality colonoscopy and you’re doing appropriate surveillance, how effective is that? And what are the potential problems that might impair effectiveness?”
Adherence and participation remain significant challenges, he said. “If people don’t get the tests done, then they’re not going to be effective. Or if they get part of it done, there can be issues.”
In an interview, Lieberman discussed the reasons why people resist CRC screening, and the new technologies and research underway to make screening options more palatable for reluctant patients.
What do you think are the biggest deterrents to getting screened for CRC?
Dr. Lieberman: The whole idea of dealing with a stool sample is not appealing to patients. The second issue, and this has been shown in many studies, is patients who are referred for colonoscopy may resist because they have heard stories about bowel preps and about colonoscopy itself. But there are many other reasons. I mean, there are issues with access to care that are important. What if you have a positive stool test and you need to get a colonoscopy? How do you get a colonoscopy? There are barriers in moving from one test to the other in a different setting. There are issues with having to take a day off work that’s potentially a financial hardship for some patients. If you’re taking care of elderly relatives or children or if you need transportation, that’s an issue for people.
So, there are many potential barriers, and we’ve been trying to work at a national level to try to understand these barriers and then develop tools to mitigate these problems and improve the overall participation in screening.
How has the field of GI changed since you started practicing medicine?
Dr. Lieberman: I think there have been many exciting changes in technology. The endoscopes we used when I started my career were called fiberoptic scopes. These were scopes that contained tiny glass fibers that ran the length of the scope, and they were good, but not great in terms of imaging, and sometimes they would break down. We now have digital imaging that far surpasses the quality there. We’ve come a long way in terms of things like CT scans, for example, and MRI imaging. The other big technology change has been the development of minimally invasive treatments. For example, if you have a gallstone that’s in your bile duct, we now have ways to remove that without sending the patient to surgery.
The second big change has been the assessment of quality. When I started my career in gastroenterology, we were doing a lot of things, but we didn’t necessarily know if we were doing them well. Most of us thought we were doing them well, of course, but nobody was really measuring quality. There were no quality benchmarks. And so if you don’t measure it, you don’t know. Where we are today in gastroenterology is we’re intensively concerned about quality and measuring quality in various aspects of what we do. And I think that’s a positive development.
What key achievements came out of the U.S. Multi-Society Task Force on Colorectal Cancer?
Dr. Lieberman: This panel evolved because back in the early 2000s, each of the GI organizations were producing guidelines related to colon cancer screening and follow-up. And they were slightly different. This was an attempt to bring all the relevant groups together and try to align the guidelines and recommendations among the GI organizations so that there wouldn’t be a confusing message.
Over the history of this task force, which started around 2002, it’s been remarkably productive. The task force has really examined all aspects of colorectal cancer, including things like the bowel prep, quality of exams, high risk management, hereditary syndromes that can lead to the higher likelihood of developing colon cancer, polypectomy and polypectomy techniques, and screening and surveillance recommendations, which have evolved over time. It’s been, in my opinion, a remarkably productive task force and continues to this day. I’m so very proud of that group.
Could you give a status update on the blood and tissue repository you created for CRC research?
Dr. Lieberman: Our initial studies were part of a Veterans Affairs cooperative study, which is a mechanism of funding within the VA that allows us to work with multiple VA centers to collect data and information. At the very outset of this study, we were performing screening colonoscopies in individuals, and we decided to create a bio-repository that included blood samples, polyp tissue, and normal rectal tissue. The thinking was at some point we might be able to do some genomic studies that might help us predict which patients are most likely to develop colon polyps and colon cancer. All that happened in the 1990s. It was supported by the National Cancer Institute. We created this repository, which sat for a long period of time while we were waiting for the technology to develop and so that we could perform genomic studies in a cost-effective way.
We’re now at that point, which is really exciting. We’re beginning to look at this tissue and perform some genomic studies. Some of this data has been presented at national meetings. This was a precursor to creating a similar type of bio-repository in a larger VA cooperative study. CSP #577 Colonoscopy vs. Fecal Immunochemical Test in Reducing Mortality from Colorectal Cancer (CONFIRM) is a randomized study comparing two forms of screening, a fecal immunochemical test versus a colonoscopy. We’re in the process of enrolling 50,000 patients in that study. We have also created a blood and tissue repository, which we hope will be useful for future studies.
You lead the AGA CRC Task Force, which advances research and policy initiatives to improve screening rates and patient outcomes. What would you like to see in future GI research, particularly in colorectal cancer?
Dr. Lieberman: We have new blood tests coming along that are going to be very attractive to both patients and physicians. You can obtain a blood sample at a point of service and patients won’t have to deal with stool samples. We need to understand how those tests perform in clinical practice. If the test is abnormal, indicating a patient has a higher risk of colon cancer and should get a colonoscopy, are they getting that colonoscopy or not? And what are the barriers? And if it’s normal, then that patient should have a repeat test at an appropriate interval.
We know that the effectiveness of screening really depends on the participation of individuals in terms of completing the steps. We’ve published some work already on trying to understand the role of these blood tests. We expect that these tests will continue to improve over time.
We’re also working on trying to develop these risk stratification tools that could be used in clinical practice to help figure out the most appropriate test for a particular individual.
Let’s say you go to your doctor for colon cancer screening, and if we could determine that you are a low-risk individual, you may benefit best from having a non-invasive test, like a blood test or a stool test. Whereas if you’re a higher risk individual, you may need to have a more invasive screening test like colonoscopy.
This falls into a concept of personalized medicine where we’re trying to use all the information we have from the medical history, and maybe genomic information that I mentioned earlier, to try to determine who needs the most intensive screening and who might benefit from less intensive screening.
I think the most recent work is really focused on these gaps in screening. And the biggest gap are patients that get a non-invasive test, like a stool test, but do not get a colonoscopy that renders the program ineffective if they don’t get the colonoscopy. We’re trying to highlight that for primary care providers and make sure that everyone understands the importance of this follow-up. And then, trying to develop tools to help the primary care provider navigate that patient to a colonoscopy.
What do you think is the biggest misconception about your specialty?
Dr. Lieberman: If there’s a misconception, it’s that GI physicians are focused on procedures. I think a good GI provider should be holistic, and I think many are. What I mean by holistic is that many GI symptoms could be due to stress, medications, diet, or other aspects of behavior, and the remedy is not necessarily a procedure. I think that many GI physicians are really skilled at obtaining this information and trying to help guide the patient through some uncomfortable symptoms.
It means being more like an internist, spending time with the patient to take a detailed history and delve into many different possibilities that might be going on.
David Lieberman, MD, AGAF, spent much of his long career asking questions about everyday clinical practice in GI medicine and then researching ways to answer those questions.
“The answer to one question often leads to further questions. And I think that’s what makes this research so exciting and dynamic,” said Lieberman, professor emeritus with Oregon Health and Science University, where he served as chief of the Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology for 24 years.
He was also instrumental in creating a blood and tissue repository for colorectal cancer (CRC) research, and a national endoscopic database.
His groundbreaking GI research in colorectal cancer screening earned him AGA’s Julius Friedenwald Medal, a top career honor. “We started off with some questions about the role of specific screening tests like colonoscopy and stool-based tests for screening,” he said. This led to the first large study about the value of screening with colonoscopy, which set the stage for current screening guidelines. Assessing more than 3,000 asymptomatic adults, Lieberman and colleagues determined that colonoscopy was more effective than sigmoidoscopy in detecting advanced colonic neoplasms.
The next phase of research focused on how well GI doctors were performing colonoscopy, asking questions about the quality of the colonoscopies being performed, and what course of action to take in polyp discovery. “We did some work related to polyp surveillance, what happens after we take out polyps and some recommendations for the appropriate length of follow up afterwards,” he summarized.
Most recently, Lieberman has centered his research on program effectiveness. “If you’re doing high quality colonoscopy and you’re doing appropriate surveillance, how effective is that? And what are the potential problems that might impair effectiveness?”
Adherence and participation remain significant challenges, he said. “If people don’t get the tests done, then they’re not going to be effective. Or if they get part of it done, there can be issues.”
In an interview, Lieberman discussed the reasons why people resist CRC screening, and the new technologies and research underway to make screening options more palatable for reluctant patients.
What do you think are the biggest deterrents to getting screened for CRC?
Dr. Lieberman: The whole idea of dealing with a stool sample is not appealing to patients. The second issue, and this has been shown in many studies, is patients who are referred for colonoscopy may resist because they have heard stories about bowel preps and about colonoscopy itself. But there are many other reasons. I mean, there are issues with access to care that are important. What if you have a positive stool test and you need to get a colonoscopy? How do you get a colonoscopy? There are barriers in moving from one test to the other in a different setting. There are issues with having to take a day off work that’s potentially a financial hardship for some patients. If you’re taking care of elderly relatives or children or if you need transportation, that’s an issue for people.
So, there are many potential barriers, and we’ve been trying to work at a national level to try to understand these barriers and then develop tools to mitigate these problems and improve the overall participation in screening.
How has the field of GI changed since you started practicing medicine?
Dr. Lieberman: I think there have been many exciting changes in technology. The endoscopes we used when I started my career were called fiberoptic scopes. These were scopes that contained tiny glass fibers that ran the length of the scope, and they were good, but not great in terms of imaging, and sometimes they would break down. We now have digital imaging that far surpasses the quality there. We’ve come a long way in terms of things like CT scans, for example, and MRI imaging. The other big technology change has been the development of minimally invasive treatments. For example, if you have a gallstone that’s in your bile duct, we now have ways to remove that without sending the patient to surgery.
The second big change has been the assessment of quality. When I started my career in gastroenterology, we were doing a lot of things, but we didn’t necessarily know if we were doing them well. Most of us thought we were doing them well, of course, but nobody was really measuring quality. There were no quality benchmarks. And so if you don’t measure it, you don’t know. Where we are today in gastroenterology is we’re intensively concerned about quality and measuring quality in various aspects of what we do. And I think that’s a positive development.
What key achievements came out of the U.S. Multi-Society Task Force on Colorectal Cancer?
Dr. Lieberman: This panel evolved because back in the early 2000s, each of the GI organizations were producing guidelines related to colon cancer screening and follow-up. And they were slightly different. This was an attempt to bring all the relevant groups together and try to align the guidelines and recommendations among the GI organizations so that there wouldn’t be a confusing message.
Over the history of this task force, which started around 2002, it’s been remarkably productive. The task force has really examined all aspects of colorectal cancer, including things like the bowel prep, quality of exams, high risk management, hereditary syndromes that can lead to the higher likelihood of developing colon cancer, polypectomy and polypectomy techniques, and screening and surveillance recommendations, which have evolved over time. It’s been, in my opinion, a remarkably productive task force and continues to this day. I’m so very proud of that group.
Could you give a status update on the blood and tissue repository you created for CRC research?
Dr. Lieberman: Our initial studies were part of a Veterans Affairs cooperative study, which is a mechanism of funding within the VA that allows us to work with multiple VA centers to collect data and information. At the very outset of this study, we were performing screening colonoscopies in individuals, and we decided to create a bio-repository that included blood samples, polyp tissue, and normal rectal tissue. The thinking was at some point we might be able to do some genomic studies that might help us predict which patients are most likely to develop colon polyps and colon cancer. All that happened in the 1990s. It was supported by the National Cancer Institute. We created this repository, which sat for a long period of time while we were waiting for the technology to develop and so that we could perform genomic studies in a cost-effective way.
We’re now at that point, which is really exciting. We’re beginning to look at this tissue and perform some genomic studies. Some of this data has been presented at national meetings. This was a precursor to creating a similar type of bio-repository in a larger VA cooperative study. CSP #577 Colonoscopy vs. Fecal Immunochemical Test in Reducing Mortality from Colorectal Cancer (CONFIRM) is a randomized study comparing two forms of screening, a fecal immunochemical test versus a colonoscopy. We’re in the process of enrolling 50,000 patients in that study. We have also created a blood and tissue repository, which we hope will be useful for future studies.
You lead the AGA CRC Task Force, which advances research and policy initiatives to improve screening rates and patient outcomes. What would you like to see in future GI research, particularly in colorectal cancer?
Dr. Lieberman: We have new blood tests coming along that are going to be very attractive to both patients and physicians. You can obtain a blood sample at a point of service and patients won’t have to deal with stool samples. We need to understand how those tests perform in clinical practice. If the test is abnormal, indicating a patient has a higher risk of colon cancer and should get a colonoscopy, are they getting that colonoscopy or not? And what are the barriers? And if it’s normal, then that patient should have a repeat test at an appropriate interval.
We know that the effectiveness of screening really depends on the participation of individuals in terms of completing the steps. We’ve published some work already on trying to understand the role of these blood tests. We expect that these tests will continue to improve over time.
We’re also working on trying to develop these risk stratification tools that could be used in clinical practice to help figure out the most appropriate test for a particular individual.
Let’s say you go to your doctor for colon cancer screening, and if we could determine that you are a low-risk individual, you may benefit best from having a non-invasive test, like a blood test or a stool test. Whereas if you’re a higher risk individual, you may need to have a more invasive screening test like colonoscopy.
This falls into a concept of personalized medicine where we’re trying to use all the information we have from the medical history, and maybe genomic information that I mentioned earlier, to try to determine who needs the most intensive screening and who might benefit from less intensive screening.
I think the most recent work is really focused on these gaps in screening. And the biggest gap are patients that get a non-invasive test, like a stool test, but do not get a colonoscopy that renders the program ineffective if they don’t get the colonoscopy. We’re trying to highlight that for primary care providers and make sure that everyone understands the importance of this follow-up. And then, trying to develop tools to help the primary care provider navigate that patient to a colonoscopy.
What do you think is the biggest misconception about your specialty?
Dr. Lieberman: If there’s a misconception, it’s that GI physicians are focused on procedures. I think a good GI provider should be holistic, and I think many are. What I mean by holistic is that many GI symptoms could be due to stress, medications, diet, or other aspects of behavior, and the remedy is not necessarily a procedure. I think that many GI physicians are really skilled at obtaining this information and trying to help guide the patient through some uncomfortable symptoms.
It means being more like an internist, spending time with the patient to take a detailed history and delve into many different possibilities that might be going on.
Beta-Blockers May Reduce Mortality in Patients with Gastric Varices
, according to investigators.
In a real-world dataset of patients with gastric varices, NSBBs were associated with a 38% reduced mortality rate, supporting the common belief that protective effects extend across different types of varices, lead author Rebecca H. Moon, MD, of Kaiser Permanente Los Angeles Medical Center, and colleagues, reported.
“Overall, numerous randomized trials have established NSBB efficacy in primary and secondary prevention of esophageal variceal hemorrhage,” the investigators wrote in Gastro Hep Advances. “While these benefits are presumed to extend to gastric varices, empirical data on NSBB efficacy in gastric varices management remain scarce.”
To address this knowledge gap, Moon and colleagues conducted a retrospective cohort study of 1,276 adults (aged 18-75 years) diagnosed with gastric varices between 2015 and 2021 within the Kaiser Permanente Southern California system.
Patients were followed through February 2022. Those with splenectomy, transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt (TIPS) performed outside the system, or use of more than one type of NSBB were excluded. NSBB exposure was defined as therapy initiated within 1 year before or after variceal diagnosis.
Outcomes included gastric and esophageal variceal hemorrhage, TIPS, liver transplantation, and mortality. Multivariable logistic regression was used to compare NSBB users with nonusers and to assess individual effects of different NSBBs while adjusting for baseline characteristics.
The study population had a mean age of 58 years with a male predominance (63%). Approximately half (48%) of the patients were Hispanic. Common comorbidities included hypertension (66%), obesity (49%), and type 2 diabetes (45%). More than half of the patients (52.6%) had coexisting esophageal varices, 38% had ascites, and 22% had a history of hepatic encephalopathy.
In total, 767 patients (62%) received an NSBB. Propranolol and nadolol were most commonly prescribed, while carvedilol use was rare. Median follow-up was 1.1 years.
Overall, 40% of patients died during the study period. Mortality was significantly lower among NSBB users compared with nonusers (39.2% vs 50.9%), corresponding to a 38% reduced risk (odds ratio [OR], 0.62; 95% CI, 0.46–0.84). Nadolol was associated with the lowest mortality risk (OR, 0.55; 95% CI, 0.38–0.79), followed by propranolol (OR, 0.71; 95% CI, 0.50–1.00). Carvedilol use was too infrequent for meaningful analysis.
Rates of gastric variceal hemorrhage (7%), esophageal variceal hemorrhage (22%), TIPS (4%), and liver transplantation (5%) did not differ significantly between NSBB and non-NSBB groups.
“The observed reduction in mortality among NSBB users, particularly those on nadolol, suggests a potential survival benefit,” the investigators wrote. “However, the lack of statistically significant differences in other clinical outcomes, including gastric variceal hemorrhage, esophageal variceal hemorrhage, TIPS, and liver transplantation, indicates that the primary benefit of NSBBs in gastric varices management may be limited to mortality reduction rather than prevention of other complications.”
Moon and colleagues went on to call for additional research.
“Further prospective studies are needed to elucidate the effects of NSBBs on gastric varices and to refine treatment strategies for this high-risk population,” they wrote. “Given the substantial mortality associated with gastric variceal hemorrhage, continued research into novel therapeutic approaches is essential to improving outcomes for patients with gastric varices.”
Publication costs were covered by Kaiser Permanente Los Angeles Medical Education and Research. The investigators disclosed no conflicts of interest.
, according to investigators.
In a real-world dataset of patients with gastric varices, NSBBs were associated with a 38% reduced mortality rate, supporting the common belief that protective effects extend across different types of varices, lead author Rebecca H. Moon, MD, of Kaiser Permanente Los Angeles Medical Center, and colleagues, reported.
“Overall, numerous randomized trials have established NSBB efficacy in primary and secondary prevention of esophageal variceal hemorrhage,” the investigators wrote in Gastro Hep Advances. “While these benefits are presumed to extend to gastric varices, empirical data on NSBB efficacy in gastric varices management remain scarce.”
To address this knowledge gap, Moon and colleagues conducted a retrospective cohort study of 1,276 adults (aged 18-75 years) diagnosed with gastric varices between 2015 and 2021 within the Kaiser Permanente Southern California system.
Patients were followed through February 2022. Those with splenectomy, transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt (TIPS) performed outside the system, or use of more than one type of NSBB were excluded. NSBB exposure was defined as therapy initiated within 1 year before or after variceal diagnosis.
Outcomes included gastric and esophageal variceal hemorrhage, TIPS, liver transplantation, and mortality. Multivariable logistic regression was used to compare NSBB users with nonusers and to assess individual effects of different NSBBs while adjusting for baseline characteristics.
The study population had a mean age of 58 years with a male predominance (63%). Approximately half (48%) of the patients were Hispanic. Common comorbidities included hypertension (66%), obesity (49%), and type 2 diabetes (45%). More than half of the patients (52.6%) had coexisting esophageal varices, 38% had ascites, and 22% had a history of hepatic encephalopathy.
In total, 767 patients (62%) received an NSBB. Propranolol and nadolol were most commonly prescribed, while carvedilol use was rare. Median follow-up was 1.1 years.
Overall, 40% of patients died during the study period. Mortality was significantly lower among NSBB users compared with nonusers (39.2% vs 50.9%), corresponding to a 38% reduced risk (odds ratio [OR], 0.62; 95% CI, 0.46–0.84). Nadolol was associated with the lowest mortality risk (OR, 0.55; 95% CI, 0.38–0.79), followed by propranolol (OR, 0.71; 95% CI, 0.50–1.00). Carvedilol use was too infrequent for meaningful analysis.
Rates of gastric variceal hemorrhage (7%), esophageal variceal hemorrhage (22%), TIPS (4%), and liver transplantation (5%) did not differ significantly between NSBB and non-NSBB groups.
“The observed reduction in mortality among NSBB users, particularly those on nadolol, suggests a potential survival benefit,” the investigators wrote. “However, the lack of statistically significant differences in other clinical outcomes, including gastric variceal hemorrhage, esophageal variceal hemorrhage, TIPS, and liver transplantation, indicates that the primary benefit of NSBBs in gastric varices management may be limited to mortality reduction rather than prevention of other complications.”
Moon and colleagues went on to call for additional research.
“Further prospective studies are needed to elucidate the effects of NSBBs on gastric varices and to refine treatment strategies for this high-risk population,” they wrote. “Given the substantial mortality associated with gastric variceal hemorrhage, continued research into novel therapeutic approaches is essential to improving outcomes for patients with gastric varices.”
Publication costs were covered by Kaiser Permanente Los Angeles Medical Education and Research. The investigators disclosed no conflicts of interest.
, according to investigators.
In a real-world dataset of patients with gastric varices, NSBBs were associated with a 38% reduced mortality rate, supporting the common belief that protective effects extend across different types of varices, lead author Rebecca H. Moon, MD, of Kaiser Permanente Los Angeles Medical Center, and colleagues, reported.
“Overall, numerous randomized trials have established NSBB efficacy in primary and secondary prevention of esophageal variceal hemorrhage,” the investigators wrote in Gastro Hep Advances. “While these benefits are presumed to extend to gastric varices, empirical data on NSBB efficacy in gastric varices management remain scarce.”
To address this knowledge gap, Moon and colleagues conducted a retrospective cohort study of 1,276 adults (aged 18-75 years) diagnosed with gastric varices between 2015 and 2021 within the Kaiser Permanente Southern California system.
Patients were followed through February 2022. Those with splenectomy, transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt (TIPS) performed outside the system, or use of more than one type of NSBB were excluded. NSBB exposure was defined as therapy initiated within 1 year before or after variceal diagnosis.
Outcomes included gastric and esophageal variceal hemorrhage, TIPS, liver transplantation, and mortality. Multivariable logistic regression was used to compare NSBB users with nonusers and to assess individual effects of different NSBBs while adjusting for baseline characteristics.
The study population had a mean age of 58 years with a male predominance (63%). Approximately half (48%) of the patients were Hispanic. Common comorbidities included hypertension (66%), obesity (49%), and type 2 diabetes (45%). More than half of the patients (52.6%) had coexisting esophageal varices, 38% had ascites, and 22% had a history of hepatic encephalopathy.
In total, 767 patients (62%) received an NSBB. Propranolol and nadolol were most commonly prescribed, while carvedilol use was rare. Median follow-up was 1.1 years.
Overall, 40% of patients died during the study period. Mortality was significantly lower among NSBB users compared with nonusers (39.2% vs 50.9%), corresponding to a 38% reduced risk (odds ratio [OR], 0.62; 95% CI, 0.46–0.84). Nadolol was associated with the lowest mortality risk (OR, 0.55; 95% CI, 0.38–0.79), followed by propranolol (OR, 0.71; 95% CI, 0.50–1.00). Carvedilol use was too infrequent for meaningful analysis.
Rates of gastric variceal hemorrhage (7%), esophageal variceal hemorrhage (22%), TIPS (4%), and liver transplantation (5%) did not differ significantly between NSBB and non-NSBB groups.
“The observed reduction in mortality among NSBB users, particularly those on nadolol, suggests a potential survival benefit,” the investigators wrote. “However, the lack of statistically significant differences in other clinical outcomes, including gastric variceal hemorrhage, esophageal variceal hemorrhage, TIPS, and liver transplantation, indicates that the primary benefit of NSBBs in gastric varices management may be limited to mortality reduction rather than prevention of other complications.”
Moon and colleagues went on to call for additional research.
“Further prospective studies are needed to elucidate the effects of NSBBs on gastric varices and to refine treatment strategies for this high-risk population,” they wrote. “Given the substantial mortality associated with gastric variceal hemorrhage, continued research into novel therapeutic approaches is essential to improving outcomes for patients with gastric varices.”
Publication costs were covered by Kaiser Permanente Los Angeles Medical Education and Research. The investigators disclosed no conflicts of interest.
FROM GASTRO HEP ADVANCES