User login
Ready for post-acute care?
The definition of “hospitalist,” according to the SHM website, is a clinician “dedicated to delivering comprehensive medical care to hospitalized patients.” For years, the hospital setting was the specialties’ identifier. But as hospitalists’ scope has expanded, and post-acute care (PAC) in the United States has grown, more hospitalists are extending their roles into this space.
PAC today is more than the traditional nursing home, according to Manoj K. Mathew, MD, SFHM, national medical director of Agilon Health in Los Angeles.
Many of those expanded settings Dr. Mathew describes emerged as a result of the Affordable Care Act. Since its enactment in 2010, the ACA has heightened providers’ focus on the “Triple Aim” of improving the patient experience (including quality and satisfaction), improving the health of populations, and reducing the per capita cost of healthcare.1 Vishal Kuchaculla, MD, New England regional post-acute medical director of Knoxville,Tenn.-based TeamHealth, says new service lines also developed as Medicare clamped down on long-term inpatient hospital stays by giving financial impetus to discharge patients as soon as possible.
“Over the last few years, there’s been a major shift from fee-for-service to risk-based payment models,” Dr. Kuchaculla says. “The government’s financial incentives are driving outcomes to improve performance initiatives.”
“Today, LTACHs can be used as substitutes for short-term acute care,” says Sean R. Muldoon, MD, MPH, FCCP, chief medical officer of Kindred Healthcare in Louisville, Ky., and former chair of SHM’s Post-Acute Care Committee. “This means that a patient can be directly admitted from their home to an LTACH. In fact, many hospice and home-care patients are referred from physicians’ offices without a preceding hospitalization.”
Hospitalists can fill a need

More hospitalists are working in PACs for a number of reasons. Dr. Mathew says PAC facilities and services have “typically lacked the clinical structure and processes to obtain the results that patients and payors expect.
“These deficits needed to be quickly remedied as patients discharged from hospitals have increased acuity and higher disease burdens,” he adds. “Hospitalists were the natural choice to fill roles requiring their expertise and experience.”
Dr. Muldoon considers the expanded scope of practice into PACs an additional layer to hospital medicine’s value proposition to the healthcare system.
“As experts in the management of inpatient populations, it’s natural for hospitalists to expand to other facilities with inpatient-like populations,” he says, noting SNFs are the most popular choice, with IRFs and LTACHs also being common places to work. Few hospitalists work in home care or hospice.
PAC settings are designed to help patients who are transitioning from an inpatient setting back to their home or other setting.
“Many patients go home after a SNF stay, while others will move to a nursing home or other longer-term care setting for the first time,” says Tiffany Radcliff, PhD, a health economist in the department of health policy and management at Texas A&M University School of Public Health in College Station. “With this in mind, hospitalists working in PAC have the opportunity to address each patient’s ongoing care needs and prepare them for their next setting. Hospitalists can manage medication or other care regimen changes that resulted from an inpatient stay, reinforce discharge instructions to the patient and their caregivers, and identify any other issues with continuing care that need to be addressed before discharge to the next care setting.”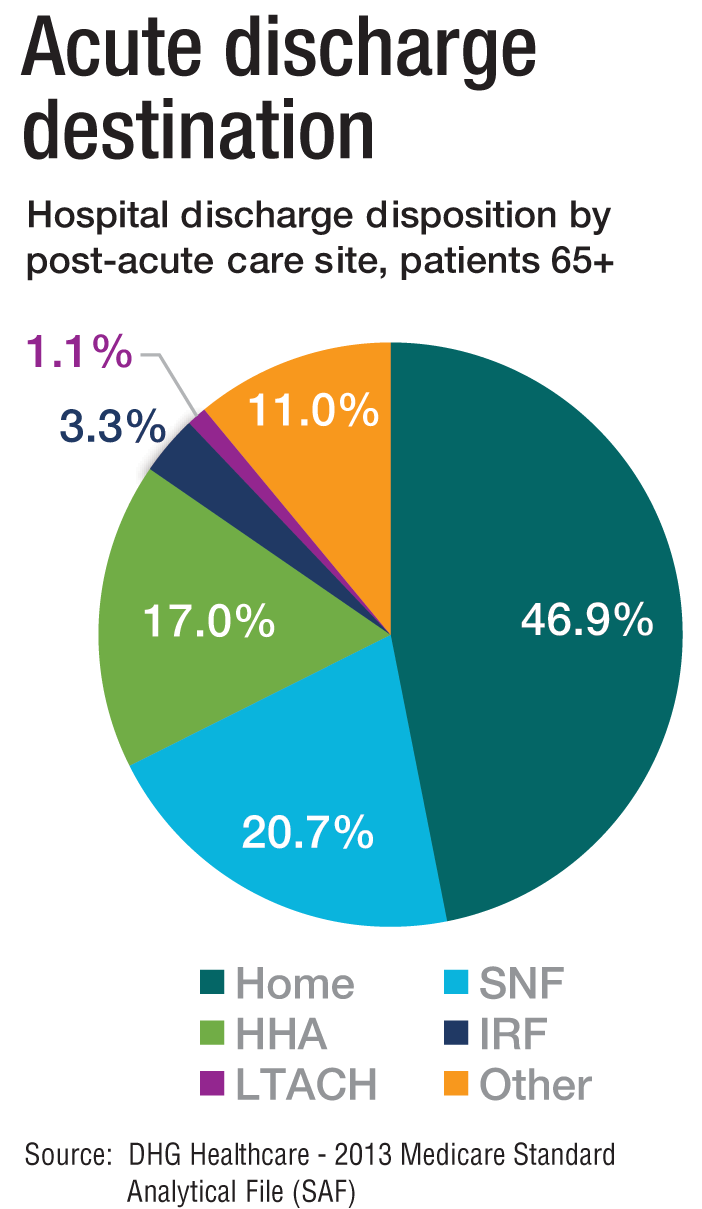
Transitioning Care
Even if a hospitalist is not employed at a PAC, it’s important that they know something about them.
“As patients are moved downstream earlier, hospitalists are being asked to help make a judgment regarding when and where an inpatient is transitioned,” Dr. Muldoon says. As organizations move toward becoming fully risk capable, it is necessary to develop referral networks of high-quality PAC providers to achieve the best clinical outcomes, reduce readmissions, and lower costs.2“Therefore, hospitalists should have a working knowledge of the different sites of service as well as some opinion on the suitability of available options in their community,” Dr. Muldoon says. “The hospitalist can also help to educate the hospitalized patient on what to expect at a PAC.”
If a patient is inappropriately prepared for the PAC setting, it could lead to incomplete management of their condition, which ultimately could lead to readmission.
“When hospitalists know how care is provided in a PAC setting, they are better able to ensure a smoother transition of care between settings,” says Tochi Iroku-Malize, MD, MPH, MBA, FAAFP, SFHM, chair of family medicine at Northwell Health in Long Island, N.Y. “This will ultimately prevent unnecessary readmissions.”
Further, the quality metrics that hospitals and thereby hospitalists are judged by no longer end at the hospital’s exit.
“The ownership of acute-care outcomes requires extending the accountability to outside of the institution’s four walls,” Dr. Mathew says. “The inpatient team needs to place great importance on the transition of care and the subsequent quality of that care when the patient is discharged.”
Robert W. Harrington Jr., MD, SFHM, chief medical officer of Plano, Texas–based Reliant Post-Acute Care Solutions and former SHM president, says the health system landscapes are pushing HM beyond the hospitals’ walls.
How PAC settings differ from hospitals
Practicing in PAC has some important nuances that hospitalists from short-term acute care need to get accustomed to, Dr. Muldoon says. Primarily, the diagnostic capabilities are much more limited, as is the presence of high-level staffing. Further, patients are less resilient to medication changes and interventions, so changes need to be done gradually.
“Hospitalists who try to practice acute-care medicine in a PAC setting may become frustrated by the length of time it takes to do a work-up, get a consultation, and respond to a patient’s change of condition,” Dr. Muldoon says. “Nonetheless, hospitalists can overcome this once recognizing this mind shift.”
According to Dr. Harrington, another challenge hospitalists may face is the inability of the hospital’s and PAC facility’s IT platforms to exchange electronic information.
“The major vendors on both sides need to figure out an interoperability strategy,” he says. “Currently, it often takes 1-3 days to receive a new patient’s discharge summary. The summary may consist of a stack of paper that takes significant time to sort through and requires the PAC facility to perform duplicate data entry. It’s a very highly inefficient process that opens up the doors to mistakes and errors of omission and commission that can result in bad patient outcomes.”
Arif Nazir, MD, CMD, FACP, AGSF, chief medical officer of Signature HealthCARE and president of SHC Medical Partners, both in Louisville, Ky., cites additional reasons the lack of seamless communication between a hospital and PAC facility is problematic. “I see physicians order laboratory tests and investigations that were already done in the hospital because they didn’t know they were already performed or never received the results,” he says. “Similarly, I see patients continue to take medications prescribed in the hospital long term even though they were only supposed to take them short term. I’ve also seen patients come to a PAC setting from a hospital without any formal understanding of their rehabilitative period and expectations for recovery.”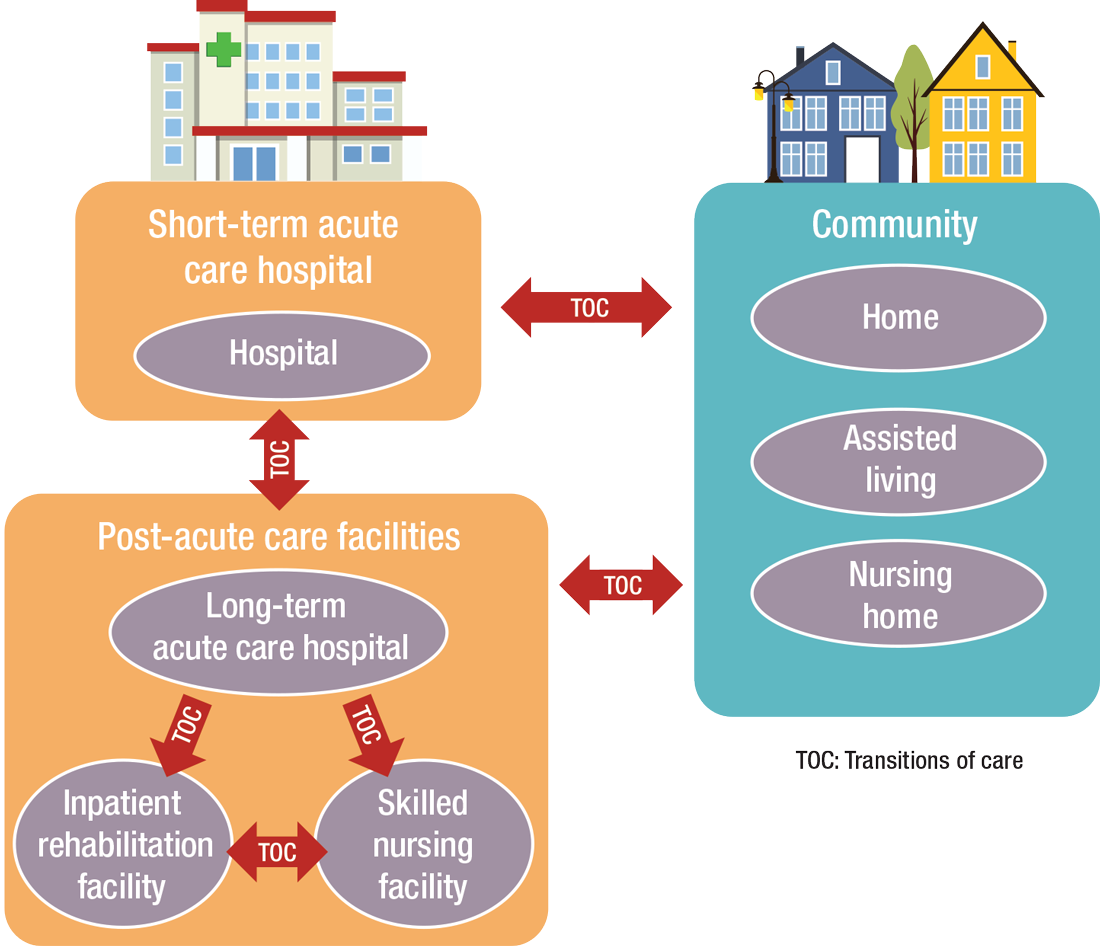
What’s ahead?
Looking to the future, Surafel Tsega, MD, clinical instructor at Mount Sinai Hospital in New York, says he thinks there will be a move toward greater collaboration among inpatient and PAC facilities, particularly in the discharge process, given that hospitals have an added incentive to ensure safe transitions because reimbursement from the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services is tied to readmissions and there are penalties for readmission. This involves more comprehensive planning regarding “warm handoffs” (e.g., real-time discussions with PAC providers about a patient’s hospital course and plan of care upon discharge), transferring of information, and so forth.
And while it can still be challenging to identify high-risk patients or determine the intensity and duration of their care, Dr. Mathew says risk-stratification tools and care pathways are continually being refined to maximize value with the limited resources available. In addition, with an increased emphasis on employing a team approach to care, there will be better integration of non-medical services to address the social determinants of health, which play significant roles in overall health and healing.
“Working with community-based organizations for this purpose will be a valuable tool for any of the population health–based initiatives,” he says.
Dr. Muldoon says he believes healthcare reform will increasingly view an inpatient admission as something to be avoided.
“If hospitalization can’t be avoided, then it should be shortened as much as possible,” he says. “This will shift inpatient care into LTACHs, SNFs, and IRFs. Hospitalists would be wise to follow patients into those settings as traditional inpatient census is reduced. This will take a few years, so hospitalists should start now in preparing for that downstream transition of individuals who were previously inpatients.”
The cost of care, and other PAC facts and figures
The amount of money that Medicare spends on post-acute care (PAC) has been increasing. In 2012, 12.6% of Medicare beneficiaries used some form of PAC, costing $62 billion.2 That amounts to the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services spending close to 25% of Medicare beneficiary expenses on PAC, a 133% increase from 2001 to 2012. Among the different types, $30.4 billion was spent on skilled nursing facilities (SNFs), $18.6 billion on home health, and $13.1 billion on long-term acute care (LTAC) and acute-care rehabilitation.2
It’s also been reported that after short-term acute-care hospitalization, about one in five Medicare beneficiaries requires continued specialized treatment in one of the three typical Medicare PAC settings: inpatient rehabilitation facilities (IRFs), LTAC hospitals, and SNFs.3
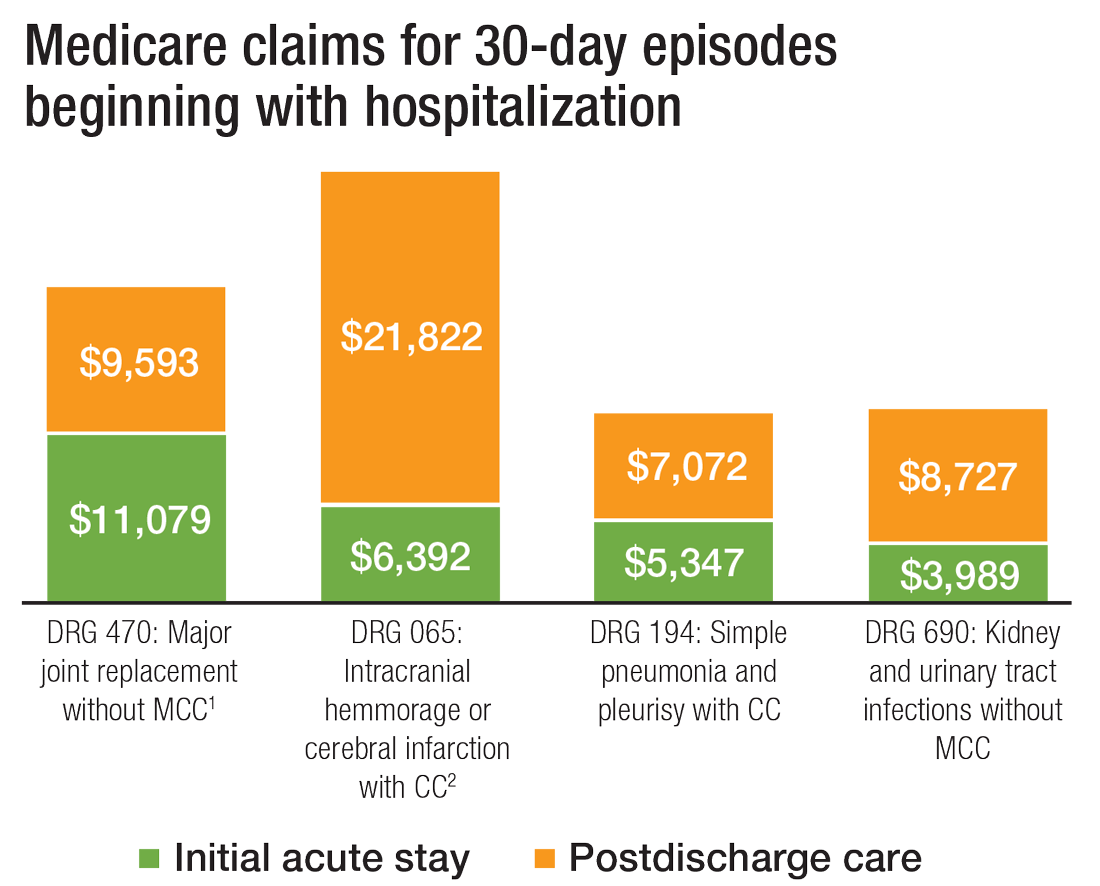
What’s more, hospital readmission nearly doubles the cost of an episode, so the financial implications for organizations operating in risk-bearing arrangements are significant. In 2013, 2,213 hospitals were charged $280 million in readmission penalties.2
References
1. The role of post-acute care in new care delivery models. American Hospital Association website. Available at: http://www.aha.org/research/reports/tw/15dec-tw-postacute.pdf. Accessed Nov. 7, 2016.
2. Post-acute care integration: Today and in the future. DHG Healthcare website. Available at: http://www2.dhgllp.com/res_pubs/HCG-Post-Acute-Care-Integration.pdf. Accessed Nov. 7, 2016.
3. Overview: Post-acute care transitions toolkit. Society for Hospital Medicine website. Available at: http://www.hospitalmedicine.org/Web/Quality___Innovation/Implementation_Toolkit/pact/Overview_PACT.aspx?hkey=dea3da3c-8620-46db-a00f-89f07f021958. Accessed Nov. 10, 2016.
The definition of “hospitalist,” according to the SHM website, is a clinician “dedicated to delivering comprehensive medical care to hospitalized patients.” For years, the hospital setting was the specialties’ identifier. But as hospitalists’ scope has expanded, and post-acute care (PAC) in the United States has grown, more hospitalists are extending their roles into this space.
PAC today is more than the traditional nursing home, according to Manoj K. Mathew, MD, SFHM, national medical director of Agilon Health in Los Angeles.
Many of those expanded settings Dr. Mathew describes emerged as a result of the Affordable Care Act. Since its enactment in 2010, the ACA has heightened providers’ focus on the “Triple Aim” of improving the patient experience (including quality and satisfaction), improving the health of populations, and reducing the per capita cost of healthcare.1 Vishal Kuchaculla, MD, New England regional post-acute medical director of Knoxville,Tenn.-based TeamHealth, says new service lines also developed as Medicare clamped down on long-term inpatient hospital stays by giving financial impetus to discharge patients as soon as possible.
“Over the last few years, there’s been a major shift from fee-for-service to risk-based payment models,” Dr. Kuchaculla says. “The government’s financial incentives are driving outcomes to improve performance initiatives.”
“Today, LTACHs can be used as substitutes for short-term acute care,” says Sean R. Muldoon, MD, MPH, FCCP, chief medical officer of Kindred Healthcare in Louisville, Ky., and former chair of SHM’s Post-Acute Care Committee. “This means that a patient can be directly admitted from their home to an LTACH. In fact, many hospice and home-care patients are referred from physicians’ offices without a preceding hospitalization.”

Hospitalists can fill a need

More hospitalists are working in PACs for a number of reasons. Dr. Mathew says PAC facilities and services have “typically lacked the clinical structure and processes to obtain the results that patients and payors expect.
“These deficits needed to be quickly remedied as patients discharged from hospitals have increased acuity and higher disease burdens,” he adds. “Hospitalists were the natural choice to fill roles requiring their expertise and experience.”
Dr. Muldoon considers the expanded scope of practice into PACs an additional layer to hospital medicine’s value proposition to the healthcare system.
“As experts in the management of inpatient populations, it’s natural for hospitalists to expand to other facilities with inpatient-like populations,” he says, noting SNFs are the most popular choice, with IRFs and LTACHs also being common places to work. Few hospitalists work in home care or hospice.
PAC settings are designed to help patients who are transitioning from an inpatient setting back to their home or other setting.
“Many patients go home after a SNF stay, while others will move to a nursing home or other longer-term care setting for the first time,” says Tiffany Radcliff, PhD, a health economist in the department of health policy and management at Texas A&M University School of Public Health in College Station. “With this in mind, hospitalists working in PAC have the opportunity to address each patient’s ongoing care needs and prepare them for their next setting. Hospitalists can manage medication or other care regimen changes that resulted from an inpatient stay, reinforce discharge instructions to the patient and their caregivers, and identify any other issues with continuing care that need to be addressed before discharge to the next care setting.”
Transitioning Care
Even if a hospitalist is not employed at a PAC, it’s important that they know something about them.
“As patients are moved downstream earlier, hospitalists are being asked to help make a judgment regarding when and where an inpatient is transitioned,” Dr. Muldoon says. As organizations move toward becoming fully risk capable, it is necessary to develop referral networks of high-quality PAC providers to achieve the best clinical outcomes, reduce readmissions, and lower costs.2“Therefore, hospitalists should have a working knowledge of the different sites of service as well as some opinion on the suitability of available options in their community,” Dr. Muldoon says. “The hospitalist can also help to educate the hospitalized patient on what to expect at a PAC.”
If a patient is inappropriately prepared for the PAC setting, it could lead to incomplete management of their condition, which ultimately could lead to readmission.
“When hospitalists know how care is provided in a PAC setting, they are better able to ensure a smoother transition of care between settings,” says Tochi Iroku-Malize, MD, MPH, MBA, FAAFP, SFHM, chair of family medicine at Northwell Health in Long Island, N.Y. “This will ultimately prevent unnecessary readmissions.”
Further, the quality metrics that hospitals and thereby hospitalists are judged by no longer end at the hospital’s exit.
“The ownership of acute-care outcomes requires extending the accountability to outside of the institution’s four walls,” Dr. Mathew says. “The inpatient team needs to place great importance on the transition of care and the subsequent quality of that care when the patient is discharged.”
Robert W. Harrington Jr., MD, SFHM, chief medical officer of Plano, Texas–based Reliant Post-Acute Care Solutions and former SHM president, says the health system landscapes are pushing HM beyond the hospitals’ walls.
How PAC settings differ from hospitals
Practicing in PAC has some important nuances that hospitalists from short-term acute care need to get accustomed to, Dr. Muldoon says. Primarily, the diagnostic capabilities are much more limited, as is the presence of high-level staffing. Further, patients are less resilient to medication changes and interventions, so changes need to be done gradually.
“Hospitalists who try to practice acute-care medicine in a PAC setting may become frustrated by the length of time it takes to do a work-up, get a consultation, and respond to a patient’s change of condition,” Dr. Muldoon says. “Nonetheless, hospitalists can overcome this once recognizing this mind shift.”
According to Dr. Harrington, another challenge hospitalists may face is the inability of the hospital’s and PAC facility’s IT platforms to exchange electronic information.
“The major vendors on both sides need to figure out an interoperability strategy,” he says. “Currently, it often takes 1-3 days to receive a new patient’s discharge summary. The summary may consist of a stack of paper that takes significant time to sort through and requires the PAC facility to perform duplicate data entry. It’s a very highly inefficient process that opens up the doors to mistakes and errors of omission and commission that can result in bad patient outcomes.”
Arif Nazir, MD, CMD, FACP, AGSF, chief medical officer of Signature HealthCARE and president of SHC Medical Partners, both in Louisville, Ky., cites additional reasons the lack of seamless communication between a hospital and PAC facility is problematic. “I see physicians order laboratory tests and investigations that were already done in the hospital because they didn’t know they were already performed or never received the results,” he says. “Similarly, I see patients continue to take medications prescribed in the hospital long term even though they were only supposed to take them short term. I’ve also seen patients come to a PAC setting from a hospital without any formal understanding of their rehabilitative period and expectations for recovery.”
What’s ahead?
Looking to the future, Surafel Tsega, MD, clinical instructor at Mount Sinai Hospital in New York, says he thinks there will be a move toward greater collaboration among inpatient and PAC facilities, particularly in the discharge process, given that hospitals have an added incentive to ensure safe transitions because reimbursement from the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services is tied to readmissions and there are penalties for readmission. This involves more comprehensive planning regarding “warm handoffs” (e.g., real-time discussions with PAC providers about a patient’s hospital course and plan of care upon discharge), transferring of information, and so forth.
And while it can still be challenging to identify high-risk patients or determine the intensity and duration of their care, Dr. Mathew says risk-stratification tools and care pathways are continually being refined to maximize value with the limited resources available. In addition, with an increased emphasis on employing a team approach to care, there will be better integration of non-medical services to address the social determinants of health, which play significant roles in overall health and healing.
“Working with community-based organizations for this purpose will be a valuable tool for any of the population health–based initiatives,” he says.
Dr. Muldoon says he believes healthcare reform will increasingly view an inpatient admission as something to be avoided.
“If hospitalization can’t be avoided, then it should be shortened as much as possible,” he says. “This will shift inpatient care into LTACHs, SNFs, and IRFs. Hospitalists would be wise to follow patients into those settings as traditional inpatient census is reduced. This will take a few years, so hospitalists should start now in preparing for that downstream transition of individuals who were previously inpatients.”
The cost of care, and other PAC facts and figures
The amount of money that Medicare spends on post-acute care (PAC) has been increasing. In 2012, 12.6% of Medicare beneficiaries used some form of PAC, costing $62 billion.2 That amounts to the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services spending close to 25% of Medicare beneficiary expenses on PAC, a 133% increase from 2001 to 2012. Among the different types, $30.4 billion was spent on skilled nursing facilities (SNFs), $18.6 billion on home health, and $13.1 billion on long-term acute care (LTAC) and acute-care rehabilitation.2
It’s also been reported that after short-term acute-care hospitalization, about one in five Medicare beneficiaries requires continued specialized treatment in one of the three typical Medicare PAC settings: inpatient rehabilitation facilities (IRFs), LTAC hospitals, and SNFs.3
What’s more, hospital readmission nearly doubles the cost of an episode, so the financial implications for organizations operating in risk-bearing arrangements are significant. In 2013, 2,213 hospitals were charged $280 million in readmission penalties.2
References
1. The role of post-acute care in new care delivery models. American Hospital Association website. Available at: http://www.aha.org/research/reports/tw/15dec-tw-postacute.pdf. Accessed Nov. 7, 2016.
2. Post-acute care integration: Today and in the future. DHG Healthcare website. Available at: http://www2.dhgllp.com/res_pubs/HCG-Post-Acute-Care-Integration.pdf. Accessed Nov. 7, 2016.
3. Overview: Post-acute care transitions toolkit. Society for Hospital Medicine website. Available at: http://www.hospitalmedicine.org/Web/Quality___Innovation/Implementation_Toolkit/pact/Overview_PACT.aspx?hkey=dea3da3c-8620-46db-a00f-89f07f021958. Accessed Nov. 10, 2016.
The definition of “hospitalist,” according to the SHM website, is a clinician “dedicated to delivering comprehensive medical care to hospitalized patients.” For years, the hospital setting was the specialties’ identifier. But as hospitalists’ scope has expanded, and post-acute care (PAC) in the United States has grown, more hospitalists are extending their roles into this space.
PAC today is more than the traditional nursing home, according to Manoj K. Mathew, MD, SFHM, national medical director of Agilon Health in Los Angeles.
Many of those expanded settings Dr. Mathew describes emerged as a result of the Affordable Care Act. Since its enactment in 2010, the ACA has heightened providers’ focus on the “Triple Aim” of improving the patient experience (including quality and satisfaction), improving the health of populations, and reducing the per capita cost of healthcare.1 Vishal Kuchaculla, MD, New England regional post-acute medical director of Knoxville,Tenn.-based TeamHealth, says new service lines also developed as Medicare clamped down on long-term inpatient hospital stays by giving financial impetus to discharge patients as soon as possible.
“Over the last few years, there’s been a major shift from fee-for-service to risk-based payment models,” Dr. Kuchaculla says. “The government’s financial incentives are driving outcomes to improve performance initiatives.”
“Today, LTACHs can be used as substitutes for short-term acute care,” says Sean R. Muldoon, MD, MPH, FCCP, chief medical officer of Kindred Healthcare in Louisville, Ky., and former chair of SHM’s Post-Acute Care Committee. “This means that a patient can be directly admitted from their home to an LTACH. In fact, many hospice and home-care patients are referred from physicians’ offices without a preceding hospitalization.”

Hospitalists can fill a need

More hospitalists are working in PACs for a number of reasons. Dr. Mathew says PAC facilities and services have “typically lacked the clinical structure and processes to obtain the results that patients and payors expect.
“These deficits needed to be quickly remedied as patients discharged from hospitals have increased acuity and higher disease burdens,” he adds. “Hospitalists were the natural choice to fill roles requiring their expertise and experience.”
Dr. Muldoon considers the expanded scope of practice into PACs an additional layer to hospital medicine’s value proposition to the healthcare system.
“As experts in the management of inpatient populations, it’s natural for hospitalists to expand to other facilities with inpatient-like populations,” he says, noting SNFs are the most popular choice, with IRFs and LTACHs also being common places to work. Few hospitalists work in home care or hospice.
PAC settings are designed to help patients who are transitioning from an inpatient setting back to their home or other setting.
“Many patients go home after a SNF stay, while others will move to a nursing home or other longer-term care setting for the first time,” says Tiffany Radcliff, PhD, a health economist in the department of health policy and management at Texas A&M University School of Public Health in College Station. “With this in mind, hospitalists working in PAC have the opportunity to address each patient’s ongoing care needs and prepare them for their next setting. Hospitalists can manage medication or other care regimen changes that resulted from an inpatient stay, reinforce discharge instructions to the patient and their caregivers, and identify any other issues with continuing care that need to be addressed before discharge to the next care setting.”
Transitioning Care
Even if a hospitalist is not employed at a PAC, it’s important that they know something about them.
“As patients are moved downstream earlier, hospitalists are being asked to help make a judgment regarding when and where an inpatient is transitioned,” Dr. Muldoon says. As organizations move toward becoming fully risk capable, it is necessary to develop referral networks of high-quality PAC providers to achieve the best clinical outcomes, reduce readmissions, and lower costs.2“Therefore, hospitalists should have a working knowledge of the different sites of service as well as some opinion on the suitability of available options in their community,” Dr. Muldoon says. “The hospitalist can also help to educate the hospitalized patient on what to expect at a PAC.”
If a patient is inappropriately prepared for the PAC setting, it could lead to incomplete management of their condition, which ultimately could lead to readmission.
“When hospitalists know how care is provided in a PAC setting, they are better able to ensure a smoother transition of care between settings,” says Tochi Iroku-Malize, MD, MPH, MBA, FAAFP, SFHM, chair of family medicine at Northwell Health in Long Island, N.Y. “This will ultimately prevent unnecessary readmissions.”
Further, the quality metrics that hospitals and thereby hospitalists are judged by no longer end at the hospital’s exit.
“The ownership of acute-care outcomes requires extending the accountability to outside of the institution’s four walls,” Dr. Mathew says. “The inpatient team needs to place great importance on the transition of care and the subsequent quality of that care when the patient is discharged.”
Robert W. Harrington Jr., MD, SFHM, chief medical officer of Plano, Texas–based Reliant Post-Acute Care Solutions and former SHM president, says the health system landscapes are pushing HM beyond the hospitals’ walls.
How PAC settings differ from hospitals
Practicing in PAC has some important nuances that hospitalists from short-term acute care need to get accustomed to, Dr. Muldoon says. Primarily, the diagnostic capabilities are much more limited, as is the presence of high-level staffing. Further, patients are less resilient to medication changes and interventions, so changes need to be done gradually.
“Hospitalists who try to practice acute-care medicine in a PAC setting may become frustrated by the length of time it takes to do a work-up, get a consultation, and respond to a patient’s change of condition,” Dr. Muldoon says. “Nonetheless, hospitalists can overcome this once recognizing this mind shift.”
According to Dr. Harrington, another challenge hospitalists may face is the inability of the hospital’s and PAC facility’s IT platforms to exchange electronic information.
“The major vendors on both sides need to figure out an interoperability strategy,” he says. “Currently, it often takes 1-3 days to receive a new patient’s discharge summary. The summary may consist of a stack of paper that takes significant time to sort through and requires the PAC facility to perform duplicate data entry. It’s a very highly inefficient process that opens up the doors to mistakes and errors of omission and commission that can result in bad patient outcomes.”
Arif Nazir, MD, CMD, FACP, AGSF, chief medical officer of Signature HealthCARE and president of SHC Medical Partners, both in Louisville, Ky., cites additional reasons the lack of seamless communication between a hospital and PAC facility is problematic. “I see physicians order laboratory tests and investigations that were already done in the hospital because they didn’t know they were already performed or never received the results,” he says. “Similarly, I see patients continue to take medications prescribed in the hospital long term even though they were only supposed to take them short term. I’ve also seen patients come to a PAC setting from a hospital without any formal understanding of their rehabilitative period and expectations for recovery.”
What’s ahead?
Looking to the future, Surafel Tsega, MD, clinical instructor at Mount Sinai Hospital in New York, says he thinks there will be a move toward greater collaboration among inpatient and PAC facilities, particularly in the discharge process, given that hospitals have an added incentive to ensure safe transitions because reimbursement from the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services is tied to readmissions and there are penalties for readmission. This involves more comprehensive planning regarding “warm handoffs” (e.g., real-time discussions with PAC providers about a patient’s hospital course and plan of care upon discharge), transferring of information, and so forth.
And while it can still be challenging to identify high-risk patients or determine the intensity and duration of their care, Dr. Mathew says risk-stratification tools and care pathways are continually being refined to maximize value with the limited resources available. In addition, with an increased emphasis on employing a team approach to care, there will be better integration of non-medical services to address the social determinants of health, which play significant roles in overall health and healing.
“Working with community-based organizations for this purpose will be a valuable tool for any of the population health–based initiatives,” he says.
Dr. Muldoon says he believes healthcare reform will increasingly view an inpatient admission as something to be avoided.
“If hospitalization can’t be avoided, then it should be shortened as much as possible,” he says. “This will shift inpatient care into LTACHs, SNFs, and IRFs. Hospitalists would be wise to follow patients into those settings as traditional inpatient census is reduced. This will take a few years, so hospitalists should start now in preparing for that downstream transition of individuals who were previously inpatients.”
The cost of care, and other PAC facts and figures
The amount of money that Medicare spends on post-acute care (PAC) has been increasing. In 2012, 12.6% of Medicare beneficiaries used some form of PAC, costing $62 billion.2 That amounts to the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services spending close to 25% of Medicare beneficiary expenses on PAC, a 133% increase from 2001 to 2012. Among the different types, $30.4 billion was spent on skilled nursing facilities (SNFs), $18.6 billion on home health, and $13.1 billion on long-term acute care (LTAC) and acute-care rehabilitation.2
It’s also been reported that after short-term acute-care hospitalization, about one in five Medicare beneficiaries requires continued specialized treatment in one of the three typical Medicare PAC settings: inpatient rehabilitation facilities (IRFs), LTAC hospitals, and SNFs.3
What’s more, hospital readmission nearly doubles the cost of an episode, so the financial implications for organizations operating in risk-bearing arrangements are significant. In 2013, 2,213 hospitals were charged $280 million in readmission penalties.2
References
1. The role of post-acute care in new care delivery models. American Hospital Association website. Available at: http://www.aha.org/research/reports/tw/15dec-tw-postacute.pdf. Accessed Nov. 7, 2016.
2. Post-acute care integration: Today and in the future. DHG Healthcare website. Available at: http://www2.dhgllp.com/res_pubs/HCG-Post-Acute-Care-Integration.pdf. Accessed Nov. 7, 2016.
3. Overview: Post-acute care transitions toolkit. Society for Hospital Medicine website. Available at: http://www.hospitalmedicine.org/Web/Quality___Innovation/Implementation_Toolkit/pact/Overview_PACT.aspx?hkey=dea3da3c-8620-46db-a00f-89f07f021958. Accessed Nov. 10, 2016.
Transplantation palliative care: The time is ripe
Over 10 years ago, a challenge was made in a surgical publication for increased collaboration between the fields of transplantation and palliative care.1
Since that time not much progress has been made bringing these fields together in a consistent way that would mutually benefit patients and the specialties. However, other progress has been made, particularly in the field of palliative care, which could brighten the prospects and broaden the opportunities to accomplish collaboration between palliative care and transplantation.
Growth of palliative services
During the past decade there has been a robust proliferation of hospital-based palliative care programs in the United States. In all, 67% of U.S. hospitals with 50 or more beds report palliative care teams, up from 63% in 2011 and 53% in 2008.
Only a decade ago, critical care and palliative care were generally considered mutually exclusive. Evidence is trickling in to suggest that this is no longer the case. Although palliative care was not an integral part of critical care at that time, patients, families, and even practitioners began to demand these services. Cook and Rocker have eloquently advocated the rightful place of palliative care in the ICU.2
Studies in recent years have shown that the integration of palliative care into critical care decreases in length of ICU and hospital stay, decreases costs, enhances patient/family satisfaction, and promotes a more rapid consensus about goals of care, without increasing mortality. The ICU experience to date could be considered a reassuring precedent for transplantation palliative care.
Integration of palliative care with transplantation
Early palliative care intervention has been shown to improve symptom burden and depression scores in end-stage liver disease patients awaiting transplant. In addition, early palliative care consultation in conjunction with cancer treatment has been associated with increased survival in non–small-cell lung cancer patients. It has been demonstrated that early integration of palliative care in the surgical ICU alongside disease-directed curative care can be accomplished without change in mortality, while improving end-of-life practice in liver transplant patients.3
What palliative care can do for transplant patients
What does palliative care mean for the person (and family) awaiting transplantation? For the cirrhotic patient with cachexia, ascites, and encephalopathy, it means access to the services of a team trained in the management of these symptoms. Palliative care teams can also provide psychosocial and spiritual support for patients and families who are intimidated by the complex navigation of the health care system and the existential threat that end-stage organ failure presents to them. Skilled palliative care and services can be the difference between failing and extended life with a higher quality of life for these very sick patients
Resuscitation of a patient, whether through restoration of organ function or interdicting the progression of disease, begins with resuscitation of hope. Nothing achieves this more quickly than amelioration of burdensome symptoms for the patient and family.
The barriers for transplant surgeons and teams referring and incorporating palliative care services in their practices are multiple and profound. The unique dilemma facing the transplant team is to balance the treatment of the failing organ, the treatment of the patient (and family and friends), and the best use of the graft, a precious gift of society.
Palliative surgery has been defined as any invasive procedure in which the main intention is to mitigate physical symptoms in patients with noncurable disease without causing premature death. The very success of transplantation over the past 3 decades has obscured our memory of transplantation as a type of palliative surgery. It is a well-known axiom of reconstructive surgery that the reconstructed site should be compared to what was there, not to “normal.” Even in the current era of improved immunosuppression and posttransplant support services, one could hardly describe even a successful transplant patient’s experience as “normal.” These patients’ lives may be extended and/or enhanced but they need palliative care before, during, and after transplantation. The growing availability of trained palliative care clinicians and teams, the increased familiarity of palliative and end-of-life care to surgical residents and fellows, and quality metrics measuring palliative care outcomes will provide reassurance and guidance to address reservations about the convergence of the two seemingly opposite realities.
A modest proposal
We propose that palliative care be presented to the entire spectrum of transplantation care: on the ward, in the ICU, and after transplantation. More specific “triggers” for palliative care for referral of transplant patients should be identified. Wentlandt et al.4 have described a promising model for an ambulatory clinic, which provides early, integrated palliative care to patients awaiting and receiving organ transplantation. In addition, we propose an application for grant funding for a conference and eventual formation of a work group of transplant surgeons and team members, palliative care clinicians, and patient/families who have experienced one of the aspects of the transplant spectrum. We await the subspecialty certification in hospice and palliative medicine of a transplant surgeon. Outside of transplantation, every other surgical specialty in the United States has diplomates certified in hospice and palliative medicine. We await the benefits that will accrue from research about the merging of these fields.
1. Molmenti EP, Dunn GP: Transplantation and palliative care: The convergence of two seemingly opposite realities. Surg Clin North Am. 2005;85:373-82.
2. Cook D, Rocker G. Dying with dignity in the intensive care unit. N Engl J Med. 2014;370:2506-14.
3. Lamba S, Murphy P, McVicker S, Smith JH, and Mosenthal AC. Changing end-of-life care practice for liver transplant patients: structured palliative care intervention in the surgical intensive care unit. J Pain Symptom Manage. 2012; 44(4):508-19.
4. Wentlandt, K., Dall’Osto, A., Freeman, N., Le, L. W., Kaya, E., Ross, H., Singer, L. G., Abbey, S., Clarke, H. and Zimmermann, C. (2016), The Transplant Palliative Care Clinic: An early palliative care model for patients in a transplant program. Clin Transplant. 2016 Nov 4; doi: 10.1111/ctr.12838.
Dr. Azoulay is a transplantation specialist of Assistance Publique – Hôpitaux de Paris, and the University of Paris. Dr. Dunn is medical director of the Palliative Care Consultation Service at the University of Pittsburgh Medical Center Hamot, and vice-chair of the ACS Committee on Surgical Palliative Care.
Over 10 years ago, a challenge was made in a surgical publication for increased collaboration between the fields of transplantation and palliative care.1
Since that time not much progress has been made bringing these fields together in a consistent way that would mutually benefit patients and the specialties. However, other progress has been made, particularly in the field of palliative care, which could brighten the prospects and broaden the opportunities to accomplish collaboration between palliative care and transplantation.
Growth of palliative services
During the past decade there has been a robust proliferation of hospital-based palliative care programs in the United States. In all, 67% of U.S. hospitals with 50 or more beds report palliative care teams, up from 63% in 2011 and 53% in 2008.
Only a decade ago, critical care and palliative care were generally considered mutually exclusive. Evidence is trickling in to suggest that this is no longer the case. Although palliative care was not an integral part of critical care at that time, patients, families, and even practitioners began to demand these services. Cook and Rocker have eloquently advocated the rightful place of palliative care in the ICU.2
Studies in recent years have shown that the integration of palliative care into critical care decreases in length of ICU and hospital stay, decreases costs, enhances patient/family satisfaction, and promotes a more rapid consensus about goals of care, without increasing mortality. The ICU experience to date could be considered a reassuring precedent for transplantation palliative care.
Integration of palliative care with transplantation
Early palliative care intervention has been shown to improve symptom burden and depression scores in end-stage liver disease patients awaiting transplant. In addition, early palliative care consultation in conjunction with cancer treatment has been associated with increased survival in non–small-cell lung cancer patients. It has been demonstrated that early integration of palliative care in the surgical ICU alongside disease-directed curative care can be accomplished without change in mortality, while improving end-of-life practice in liver transplant patients.3
What palliative care can do for transplant patients
What does palliative care mean for the person (and family) awaiting transplantation? For the cirrhotic patient with cachexia, ascites, and encephalopathy, it means access to the services of a team trained in the management of these symptoms. Palliative care teams can also provide psychosocial and spiritual support for patients and families who are intimidated by the complex navigation of the health care system and the existential threat that end-stage organ failure presents to them. Skilled palliative care and services can be the difference between failing and extended life with a higher quality of life for these very sick patients
Resuscitation of a patient, whether through restoration of organ function or interdicting the progression of disease, begins with resuscitation of hope. Nothing achieves this more quickly than amelioration of burdensome symptoms for the patient and family.
The barriers for transplant surgeons and teams referring and incorporating palliative care services in their practices are multiple and profound. The unique dilemma facing the transplant team is to balance the treatment of the failing organ, the treatment of the patient (and family and friends), and the best use of the graft, a precious gift of society.
Palliative surgery has been defined as any invasive procedure in which the main intention is to mitigate physical symptoms in patients with noncurable disease without causing premature death. The very success of transplantation over the past 3 decades has obscured our memory of transplantation as a type of palliative surgery. It is a well-known axiom of reconstructive surgery that the reconstructed site should be compared to what was there, not to “normal.” Even in the current era of improved immunosuppression and posttransplant support services, one could hardly describe even a successful transplant patient’s experience as “normal.” These patients’ lives may be extended and/or enhanced but they need palliative care before, during, and after transplantation. The growing availability of trained palliative care clinicians and teams, the increased familiarity of palliative and end-of-life care to surgical residents and fellows, and quality metrics measuring palliative care outcomes will provide reassurance and guidance to address reservations about the convergence of the two seemingly opposite realities.
A modest proposal
We propose that palliative care be presented to the entire spectrum of transplantation care: on the ward, in the ICU, and after transplantation. More specific “triggers” for palliative care for referral of transplant patients should be identified. Wentlandt et al.4 have described a promising model for an ambulatory clinic, which provides early, integrated palliative care to patients awaiting and receiving organ transplantation. In addition, we propose an application for grant funding for a conference and eventual formation of a work group of transplant surgeons and team members, palliative care clinicians, and patient/families who have experienced one of the aspects of the transplant spectrum. We await the subspecialty certification in hospice and palliative medicine of a transplant surgeon. Outside of transplantation, every other surgical specialty in the United States has diplomates certified in hospice and palliative medicine. We await the benefits that will accrue from research about the merging of these fields.
1. Molmenti EP, Dunn GP: Transplantation and palliative care: The convergence of two seemingly opposite realities. Surg Clin North Am. 2005;85:373-82.
2. Cook D, Rocker G. Dying with dignity in the intensive care unit. N Engl J Med. 2014;370:2506-14.
3. Lamba S, Murphy P, McVicker S, Smith JH, and Mosenthal AC. Changing end-of-life care practice for liver transplant patients: structured palliative care intervention in the surgical intensive care unit. J Pain Symptom Manage. 2012; 44(4):508-19.
4. Wentlandt, K., Dall’Osto, A., Freeman, N., Le, L. W., Kaya, E., Ross, H., Singer, L. G., Abbey, S., Clarke, H. and Zimmermann, C. (2016), The Transplant Palliative Care Clinic: An early palliative care model for patients in a transplant program. Clin Transplant. 2016 Nov 4; doi: 10.1111/ctr.12838.
Dr. Azoulay is a transplantation specialist of Assistance Publique – Hôpitaux de Paris, and the University of Paris. Dr. Dunn is medical director of the Palliative Care Consultation Service at the University of Pittsburgh Medical Center Hamot, and vice-chair of the ACS Committee on Surgical Palliative Care.
Over 10 years ago, a challenge was made in a surgical publication for increased collaboration between the fields of transplantation and palliative care.1
Since that time not much progress has been made bringing these fields together in a consistent way that would mutually benefit patients and the specialties. However, other progress has been made, particularly in the field of palliative care, which could brighten the prospects and broaden the opportunities to accomplish collaboration between palliative care and transplantation.
Growth of palliative services
During the past decade there has been a robust proliferation of hospital-based palliative care programs in the United States. In all, 67% of U.S. hospitals with 50 or more beds report palliative care teams, up from 63% in 2011 and 53% in 2008.
Only a decade ago, critical care and palliative care were generally considered mutually exclusive. Evidence is trickling in to suggest that this is no longer the case. Although palliative care was not an integral part of critical care at that time, patients, families, and even practitioners began to demand these services. Cook and Rocker have eloquently advocated the rightful place of palliative care in the ICU.2
Studies in recent years have shown that the integration of palliative care into critical care decreases in length of ICU and hospital stay, decreases costs, enhances patient/family satisfaction, and promotes a more rapid consensus about goals of care, without increasing mortality. The ICU experience to date could be considered a reassuring precedent for transplantation palliative care.
Integration of palliative care with transplantation
Early palliative care intervention has been shown to improve symptom burden and depression scores in end-stage liver disease patients awaiting transplant. In addition, early palliative care consultation in conjunction with cancer treatment has been associated with increased survival in non–small-cell lung cancer patients. It has been demonstrated that early integration of palliative care in the surgical ICU alongside disease-directed curative care can be accomplished without change in mortality, while improving end-of-life practice in liver transplant patients.3
What palliative care can do for transplant patients
What does palliative care mean for the person (and family) awaiting transplantation? For the cirrhotic patient with cachexia, ascites, and encephalopathy, it means access to the services of a team trained in the management of these symptoms. Palliative care teams can also provide psychosocial and spiritual support for patients and families who are intimidated by the complex navigation of the health care system and the existential threat that end-stage organ failure presents to them. Skilled palliative care and services can be the difference between failing and extended life with a higher quality of life for these very sick patients
Resuscitation of a patient, whether through restoration of organ function or interdicting the progression of disease, begins with resuscitation of hope. Nothing achieves this more quickly than amelioration of burdensome symptoms for the patient and family.
The barriers for transplant surgeons and teams referring and incorporating palliative care services in their practices are multiple and profound. The unique dilemma facing the transplant team is to balance the treatment of the failing organ, the treatment of the patient (and family and friends), and the best use of the graft, a precious gift of society.
Palliative surgery has been defined as any invasive procedure in which the main intention is to mitigate physical symptoms in patients with noncurable disease without causing premature death. The very success of transplantation over the past 3 decades has obscured our memory of transplantation as a type of palliative surgery. It is a well-known axiom of reconstructive surgery that the reconstructed site should be compared to what was there, not to “normal.” Even in the current era of improved immunosuppression and posttransplant support services, one could hardly describe even a successful transplant patient’s experience as “normal.” These patients’ lives may be extended and/or enhanced but they need palliative care before, during, and after transplantation. The growing availability of trained palliative care clinicians and teams, the increased familiarity of palliative and end-of-life care to surgical residents and fellows, and quality metrics measuring palliative care outcomes will provide reassurance and guidance to address reservations about the convergence of the two seemingly opposite realities.
A modest proposal
We propose that palliative care be presented to the entire spectrum of transplantation care: on the ward, in the ICU, and after transplantation. More specific “triggers” for palliative care for referral of transplant patients should be identified. Wentlandt et al.4 have described a promising model for an ambulatory clinic, which provides early, integrated palliative care to patients awaiting and receiving organ transplantation. In addition, we propose an application for grant funding for a conference and eventual formation of a work group of transplant surgeons and team members, palliative care clinicians, and patient/families who have experienced one of the aspects of the transplant spectrum. We await the subspecialty certification in hospice and palliative medicine of a transplant surgeon. Outside of transplantation, every other surgical specialty in the United States has diplomates certified in hospice and palliative medicine. We await the benefits that will accrue from research about the merging of these fields.
1. Molmenti EP, Dunn GP: Transplantation and palliative care: The convergence of two seemingly opposite realities. Surg Clin North Am. 2005;85:373-82.
2. Cook D, Rocker G. Dying with dignity in the intensive care unit. N Engl J Med. 2014;370:2506-14.
3. Lamba S, Murphy P, McVicker S, Smith JH, and Mosenthal AC. Changing end-of-life care practice for liver transplant patients: structured palliative care intervention in the surgical intensive care unit. J Pain Symptom Manage. 2012; 44(4):508-19.
4. Wentlandt, K., Dall’Osto, A., Freeman, N., Le, L. W., Kaya, E., Ross, H., Singer, L. G., Abbey, S., Clarke, H. and Zimmermann, C. (2016), The Transplant Palliative Care Clinic: An early palliative care model for patients in a transplant program. Clin Transplant. 2016 Nov 4; doi: 10.1111/ctr.12838.
Dr. Azoulay is a transplantation specialist of Assistance Publique – Hôpitaux de Paris, and the University of Paris. Dr. Dunn is medical director of the Palliative Care Consultation Service at the University of Pittsburgh Medical Center Hamot, and vice-chair of the ACS Committee on Surgical Palliative Care.
Improving Life-Sustaining Treatment Discussions and Order Quality in a Primary Care Clinic
Background
Veterans Health Administration Directive 1004.03(1) (Advance Care Planning) aims to establish a “system-wide, patient-centered and evidence-based approach to Advance Care Planning.”1 Life-sustaining treatment (LST) orders are documents of patient preference regarding interventions such as mechanical ventilation, CPR, dialysis, artificial nutrition and hydration; and are considered part of an Advance Care Plan. From a bioethics perspective, these orders promote patient autonomy by formalizing patient preferences around LSTs in the medical record, particularly for when a patient lacks capacity and/or cannot make decisions on their own.2 Through consensus building, our team defined vague, inactionable, or incorrectly written LST orders as Potentially Problematic Orders (PPO). PPOs which cause confusion at the bedside or lack clarity around preferences can pose serious risks to patient safety and autonomy by exposing patients to inappropriate initiation or withholding of LSTs. Improving the quality of LST orders and reducing the number of PPOs is a crucial element for safe and effective implementation of Directive 1004.03(1).
Aim
The aim of this quality improvement project was to reduce the number of PPOs in a VA Community-Based Outpatient Clinic (CBOC) by 75% by the end of 2025.
Methods
The Model for Improvement was used for this quality improvement project.3 One year of LST orders were audited and thematic analysis identified 7 subtypes of PPO. Some PPO subtypes included clerical errors, potentially mismatched order sets (e.g., Comfort Care order with no associated DNR order) ill-defined or vague orders, and clinically impractical orders (eg, “consents to one shock during CPR”). We defined vague, ill-defined, and impractical orders as the most ethically and clinically challenging given the possibility of confusion or error at the bedside. Initial data were collected from October 2022 to October 2023, and post-intervention data were collected from February 2024 to September 2024. Interventions included process changes (clarifying role responsibility, documentation practices, patient education), regular auditing and feedback from a supervisor, and staff education.
Results
Post-intervention analysis demonstrated that the proportion of PPO remained the same, with 25% of patient charts containing at least one PPO. However, the distribution of PPO in the most ethically and clinically problematic categories (vague, ill-defined, and impractical orders) decreased from 14.7% to <1%.
Conclusions
We successfully reduced the most ethically and clinically challenging PPOs to <1% in our initial intervention. To reduce the overall proportion of PPO, we plan enhancements in process automations, additional physical educational resources, and minor changes in audit criteria. Future projects will aim to address the remaining PPO error types and prepare this project for implementation in other CBOCs.
- US Department of Veterans Affairs, Veterans Health Administration. VHA Directive 1004.03(1): Advance care planning. Published December 12, 2023. Accessed December 11, 2025. https://www.va.gov/vhapublications/ViewPublication.asp?pub_ID=11610
- White DB, Curtis JR, Lo B, Luce JM. Decisions to limit life-sustaining treatment for critically ill patients who lack both decision-making capacity and surrogate decision-makers. Crit Care Med. 2006;34(8):2053-2059. doi:10.1097/01.CCM.0000227654.38708.C1
- Ogrinc GS, Headrick LA, Barton AJ, Dolansky MA, Madigosky WS, Miltner RS, Hall AG. Fundamentals of Health Care Improvement: A Guide to Improving Your Patients’ Care (4th edition). Joint Commission Resources and Institute for Healthcare Improvement; 2022.
Background
Veterans Health Administration Directive 1004.03(1) (Advance Care Planning) aims to establish a “system-wide, patient-centered and evidence-based approach to Advance Care Planning.”1 Life-sustaining treatment (LST) orders are documents of patient preference regarding interventions such as mechanical ventilation, CPR, dialysis, artificial nutrition and hydration; and are considered part of an Advance Care Plan. From a bioethics perspective, these orders promote patient autonomy by formalizing patient preferences around LSTs in the medical record, particularly for when a patient lacks capacity and/or cannot make decisions on their own.2 Through consensus building, our team defined vague, inactionable, or incorrectly written LST orders as Potentially Problematic Orders (PPO). PPOs which cause confusion at the bedside or lack clarity around preferences can pose serious risks to patient safety and autonomy by exposing patients to inappropriate initiation or withholding of LSTs. Improving the quality of LST orders and reducing the number of PPOs is a crucial element for safe and effective implementation of Directive 1004.03(1).
Aim
The aim of this quality improvement project was to reduce the number of PPOs in a VA Community-Based Outpatient Clinic (CBOC) by 75% by the end of 2025.
Methods
The Model for Improvement was used for this quality improvement project.3 One year of LST orders were audited and thematic analysis identified 7 subtypes of PPO. Some PPO subtypes included clerical errors, potentially mismatched order sets (e.g., Comfort Care order with no associated DNR order) ill-defined or vague orders, and clinically impractical orders (eg, “consents to one shock during CPR”). We defined vague, ill-defined, and impractical orders as the most ethically and clinically challenging given the possibility of confusion or error at the bedside. Initial data were collected from October 2022 to October 2023, and post-intervention data were collected from February 2024 to September 2024. Interventions included process changes (clarifying role responsibility, documentation practices, patient education), regular auditing and feedback from a supervisor, and staff education.
Results
Post-intervention analysis demonstrated that the proportion of PPO remained the same, with 25% of patient charts containing at least one PPO. However, the distribution of PPO in the most ethically and clinically problematic categories (vague, ill-defined, and impractical orders) decreased from 14.7% to <1%.
Conclusions
We successfully reduced the most ethically and clinically challenging PPOs to <1% in our initial intervention. To reduce the overall proportion of PPO, we plan enhancements in process automations, additional physical educational resources, and minor changes in audit criteria. Future projects will aim to address the remaining PPO error types and prepare this project for implementation in other CBOCs.
Background
Veterans Health Administration Directive 1004.03(1) (Advance Care Planning) aims to establish a “system-wide, patient-centered and evidence-based approach to Advance Care Planning.”1 Life-sustaining treatment (LST) orders are documents of patient preference regarding interventions such as mechanical ventilation, CPR, dialysis, artificial nutrition and hydration; and are considered part of an Advance Care Plan. From a bioethics perspective, these orders promote patient autonomy by formalizing patient preferences around LSTs in the medical record, particularly for when a patient lacks capacity and/or cannot make decisions on their own.2 Through consensus building, our team defined vague, inactionable, or incorrectly written LST orders as Potentially Problematic Orders (PPO). PPOs which cause confusion at the bedside or lack clarity around preferences can pose serious risks to patient safety and autonomy by exposing patients to inappropriate initiation or withholding of LSTs. Improving the quality of LST orders and reducing the number of PPOs is a crucial element for safe and effective implementation of Directive 1004.03(1).
Aim
The aim of this quality improvement project was to reduce the number of PPOs in a VA Community-Based Outpatient Clinic (CBOC) by 75% by the end of 2025.
Methods
The Model for Improvement was used for this quality improvement project.3 One year of LST orders were audited and thematic analysis identified 7 subtypes of PPO. Some PPO subtypes included clerical errors, potentially mismatched order sets (e.g., Comfort Care order with no associated DNR order) ill-defined or vague orders, and clinically impractical orders (eg, “consents to one shock during CPR”). We defined vague, ill-defined, and impractical orders as the most ethically and clinically challenging given the possibility of confusion or error at the bedside. Initial data were collected from October 2022 to October 2023, and post-intervention data were collected from February 2024 to September 2024. Interventions included process changes (clarifying role responsibility, documentation practices, patient education), regular auditing and feedback from a supervisor, and staff education.
Results
Post-intervention analysis demonstrated that the proportion of PPO remained the same, with 25% of patient charts containing at least one PPO. However, the distribution of PPO in the most ethically and clinically problematic categories (vague, ill-defined, and impractical orders) decreased from 14.7% to <1%.
Conclusions
We successfully reduced the most ethically and clinically challenging PPOs to <1% in our initial intervention. To reduce the overall proportion of PPO, we plan enhancements in process automations, additional physical educational resources, and minor changes in audit criteria. Future projects will aim to address the remaining PPO error types and prepare this project for implementation in other CBOCs.
- US Department of Veterans Affairs, Veterans Health Administration. VHA Directive 1004.03(1): Advance care planning. Published December 12, 2023. Accessed December 11, 2025. https://www.va.gov/vhapublications/ViewPublication.asp?pub_ID=11610
- White DB, Curtis JR, Lo B, Luce JM. Decisions to limit life-sustaining treatment for critically ill patients who lack both decision-making capacity and surrogate decision-makers. Crit Care Med. 2006;34(8):2053-2059. doi:10.1097/01.CCM.0000227654.38708.C1
- Ogrinc GS, Headrick LA, Barton AJ, Dolansky MA, Madigosky WS, Miltner RS, Hall AG. Fundamentals of Health Care Improvement: A Guide to Improving Your Patients’ Care (4th edition). Joint Commission Resources and Institute for Healthcare Improvement; 2022.
- US Department of Veterans Affairs, Veterans Health Administration. VHA Directive 1004.03(1): Advance care planning. Published December 12, 2023. Accessed December 11, 2025. https://www.va.gov/vhapublications/ViewPublication.asp?pub_ID=11610
- White DB, Curtis JR, Lo B, Luce JM. Decisions to limit life-sustaining treatment for critically ill patients who lack both decision-making capacity and surrogate decision-makers. Crit Care Med. 2006;34(8):2053-2059. doi:10.1097/01.CCM.0000227654.38708.C1
- Ogrinc GS, Headrick LA, Barton AJ, Dolansky MA, Madigosky WS, Miltner RS, Hall AG. Fundamentals of Health Care Improvement: A Guide to Improving Your Patients’ Care (4th edition). Joint Commission Resources and Institute for Healthcare Improvement; 2022.
Timeliness of Specialty Palliative Care for Veterans With Cancer: An Analysis of Administrative Data
Background
Studies show that early referral to Specialty Palliative Care (SPC) can improve patient- reported outcomes among Veterans with cancer; quality metrics include referral within 8 weeks of an advanced cancer diagnosis. In this study, we explored timeliness of specialty referrals and compared various factors.
Methods
We identified our cohort using Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) Corporate Data Warehouse (CDW). Eligibility criteria included active or history of cancer—using a peer-reviewed, in-house list of ICD-9 and ICD-10 codes—between 2013-2023. We stratified our cohort of Veterans using factors including cancer stage, rurality, and care assessment needs (CAN) scores. We performed survival analyses to look at time to SPC from initial diagnosis and peak CAN score. Predictors of utilization were evaluated using multinomial regression and Cox proportional hazards models through R.
Results
Using CDW’s oncology domain, we identified 475,775 Veterans. 28% received SPC. Most received it near the end of their life as evidenced by the mortality rates (79.5%) in the early period following SPC consultation. Median time to SPC was 515 days. There was a significant difference in utilization rates between urban and rural Veterans (Wilcoxon W-statistic = 2.31E+10, p < 0.001). Peak CAN scores ranged from 0 to 0.81, median peak of 0.057 and interquartile range of 0.1. Multinomial regression model indicated statistically significant associations of advanced cancer (Stages 3 and 4) with timing of SPC. Stage 4 cancer showed the strongest association with receipt of palliative care within 60 days of initial diagnosis (OR 4.8, 95% CI: 4.69-4.93, p < 0.001), suggesting higher stage disease increases the likelihood of palliative care referral and accelerates the timing of these referrals.
Conclusions
We found Veterans received SPC from a broad range of peak CAN scores (0 to 0.81), suggesting that absolute CAN scores may not be clinically actionable indicators but perhaps indicative of changes in condition warranting referral. Stage IV cancer at diagnosis was associated with early SPC. The significant differences in utilization rates between urban and rural patients highlight potential access barriers that should be addressed.
Background
Studies show that early referral to Specialty Palliative Care (SPC) can improve patient- reported outcomes among Veterans with cancer; quality metrics include referral within 8 weeks of an advanced cancer diagnosis. In this study, we explored timeliness of specialty referrals and compared various factors.
Methods
We identified our cohort using Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) Corporate Data Warehouse (CDW). Eligibility criteria included active or history of cancer—using a peer-reviewed, in-house list of ICD-9 and ICD-10 codes—between 2013-2023. We stratified our cohort of Veterans using factors including cancer stage, rurality, and care assessment needs (CAN) scores. We performed survival analyses to look at time to SPC from initial diagnosis and peak CAN score. Predictors of utilization were evaluated using multinomial regression and Cox proportional hazards models through R.
Results
Using CDW’s oncology domain, we identified 475,775 Veterans. 28% received SPC. Most received it near the end of their life as evidenced by the mortality rates (79.5%) in the early period following SPC consultation. Median time to SPC was 515 days. There was a significant difference in utilization rates between urban and rural Veterans (Wilcoxon W-statistic = 2.31E+10, p < 0.001). Peak CAN scores ranged from 0 to 0.81, median peak of 0.057 and interquartile range of 0.1. Multinomial regression model indicated statistically significant associations of advanced cancer (Stages 3 and 4) with timing of SPC. Stage 4 cancer showed the strongest association with receipt of palliative care within 60 days of initial diagnosis (OR 4.8, 95% CI: 4.69-4.93, p < 0.001), suggesting higher stage disease increases the likelihood of palliative care referral and accelerates the timing of these referrals.
Conclusions
We found Veterans received SPC from a broad range of peak CAN scores (0 to 0.81), suggesting that absolute CAN scores may not be clinically actionable indicators but perhaps indicative of changes in condition warranting referral. Stage IV cancer at diagnosis was associated with early SPC. The significant differences in utilization rates between urban and rural patients highlight potential access barriers that should be addressed.
Background
Studies show that early referral to Specialty Palliative Care (SPC) can improve patient- reported outcomes among Veterans with cancer; quality metrics include referral within 8 weeks of an advanced cancer diagnosis. In this study, we explored timeliness of specialty referrals and compared various factors.
Methods
We identified our cohort using Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) Corporate Data Warehouse (CDW). Eligibility criteria included active or history of cancer—using a peer-reviewed, in-house list of ICD-9 and ICD-10 codes—between 2013-2023. We stratified our cohort of Veterans using factors including cancer stage, rurality, and care assessment needs (CAN) scores. We performed survival analyses to look at time to SPC from initial diagnosis and peak CAN score. Predictors of utilization were evaluated using multinomial regression and Cox proportional hazards models through R.
Results
Using CDW’s oncology domain, we identified 475,775 Veterans. 28% received SPC. Most received it near the end of their life as evidenced by the mortality rates (79.5%) in the early period following SPC consultation. Median time to SPC was 515 days. There was a significant difference in utilization rates between urban and rural Veterans (Wilcoxon W-statistic = 2.31E+10, p < 0.001). Peak CAN scores ranged from 0 to 0.81, median peak of 0.057 and interquartile range of 0.1. Multinomial regression model indicated statistically significant associations of advanced cancer (Stages 3 and 4) with timing of SPC. Stage 4 cancer showed the strongest association with receipt of palliative care within 60 days of initial diagnosis (OR 4.8, 95% CI: 4.69-4.93, p < 0.001), suggesting higher stage disease increases the likelihood of palliative care referral and accelerates the timing of these referrals.
Conclusions
We found Veterans received SPC from a broad range of peak CAN scores (0 to 0.81), suggesting that absolute CAN scores may not be clinically actionable indicators but perhaps indicative of changes in condition warranting referral. Stage IV cancer at diagnosis was associated with early SPC. The significant differences in utilization rates between urban and rural patients highlight potential access barriers that should be addressed.
Improving Palliative Care Referrals through Education of Hematology/Oncology Fellows: A QI Initiative
Purpose/Background
Palliative care referrals are recommended for patients with advanced or metastatic cancer to enhance patient and caregiver outcomes. However, challenges like delays or lack of referrals hinder implementation. This study identified rate of palliative care referrals at James A. Haley Veterans’ Hospital in Tampa, Florida; explored potential barriers to referral, and implemented targeted interventions to improve referral rates and patient outcomes.
Methods
A Plan-Do-Study-Act (PDSA) cycle was used for this quality improvement project. Data was collected from electronic medical record, focusing on consult dates, patient demographics, and reasons for seeking palliative care. Pre-intervention surveys were administered to Hematology-Oncology fellows at the institution to identify barriers to referral. Following a root cause analysis, a targeted intervention was developed, focusing on educational programs for fellows for streamlined referral processes.
Results
Before the intervention, monthly average for palliative care consults was low (3-8, typically 5). Pre-intervention surveys revealed that fellows lacked knowledge about palliative care resources, which contributed to low referral rates. To address this issue, a didactic session led by a palliative care specialist was conducted for the fellows in the fellowship program. This session provided education on the role of palliative care, how to initiate referrals, and the benefits of early involvement of palliative care teams in oncology patient management. Post-intervention surveys showed a marked improvement in fellows’ confidence regarding identification of patients suitable for palliative care. Following the session, 90% (9/10) of fellows reported being “very likely” to consult palliative care more often and 80% (8/10) indicated they were “very likely” to initiate palliative care discussions earlier in patient’s disease trajectory, with the remaining 20% (2/10) reporting a neutral stance. All fellows (100%) agreed that earlier palliative care involvement improves patient outcomes.
Implications/Significance
This PDSA cycle demonstrated that targeted education for fellows can increase awareness of palliative care resources and improve referral rates. Future work will focus on reassessing usage of palliative care consults post-intervention to evaluate effects of fellows’ education of appropriate palliative care consultation, make necessary interventions based on data and further evaluate the long-term impact on patient outcomes at James A. Haley Veterans’ Hospital.
Purpose/Background
Palliative care referrals are recommended for patients with advanced or metastatic cancer to enhance patient and caregiver outcomes. However, challenges like delays or lack of referrals hinder implementation. This study identified rate of palliative care referrals at James A. Haley Veterans’ Hospital in Tampa, Florida; explored potential barriers to referral, and implemented targeted interventions to improve referral rates and patient outcomes.
Methods
A Plan-Do-Study-Act (PDSA) cycle was used for this quality improvement project. Data was collected from electronic medical record, focusing on consult dates, patient demographics, and reasons for seeking palliative care. Pre-intervention surveys were administered to Hematology-Oncology fellows at the institution to identify barriers to referral. Following a root cause analysis, a targeted intervention was developed, focusing on educational programs for fellows for streamlined referral processes.
Results
Before the intervention, monthly average for palliative care consults was low (3-8, typically 5). Pre-intervention surveys revealed that fellows lacked knowledge about palliative care resources, which contributed to low referral rates. To address this issue, a didactic session led by a palliative care specialist was conducted for the fellows in the fellowship program. This session provided education on the role of palliative care, how to initiate referrals, and the benefits of early involvement of palliative care teams in oncology patient management. Post-intervention surveys showed a marked improvement in fellows’ confidence regarding identification of patients suitable for palliative care. Following the session, 90% (9/10) of fellows reported being “very likely” to consult palliative care more often and 80% (8/10) indicated they were “very likely” to initiate palliative care discussions earlier in patient’s disease trajectory, with the remaining 20% (2/10) reporting a neutral stance. All fellows (100%) agreed that earlier palliative care involvement improves patient outcomes.
Implications/Significance
This PDSA cycle demonstrated that targeted education for fellows can increase awareness of palliative care resources and improve referral rates. Future work will focus on reassessing usage of palliative care consults post-intervention to evaluate effects of fellows’ education of appropriate palliative care consultation, make necessary interventions based on data and further evaluate the long-term impact on patient outcomes at James A. Haley Veterans’ Hospital.
Purpose/Background
Palliative care referrals are recommended for patients with advanced or metastatic cancer to enhance patient and caregiver outcomes. However, challenges like delays or lack of referrals hinder implementation. This study identified rate of palliative care referrals at James A. Haley Veterans’ Hospital in Tampa, Florida; explored potential barriers to referral, and implemented targeted interventions to improve referral rates and patient outcomes.
Methods
A Plan-Do-Study-Act (PDSA) cycle was used for this quality improvement project. Data was collected from electronic medical record, focusing on consult dates, patient demographics, and reasons for seeking palliative care. Pre-intervention surveys were administered to Hematology-Oncology fellows at the institution to identify barriers to referral. Following a root cause analysis, a targeted intervention was developed, focusing on educational programs for fellows for streamlined referral processes.
Results
Before the intervention, monthly average for palliative care consults was low (3-8, typically 5). Pre-intervention surveys revealed that fellows lacked knowledge about palliative care resources, which contributed to low referral rates. To address this issue, a didactic session led by a palliative care specialist was conducted for the fellows in the fellowship program. This session provided education on the role of palliative care, how to initiate referrals, and the benefits of early involvement of palliative care teams in oncology patient management. Post-intervention surveys showed a marked improvement in fellows’ confidence regarding identification of patients suitable for palliative care. Following the session, 90% (9/10) of fellows reported being “very likely” to consult palliative care more often and 80% (8/10) indicated they were “very likely” to initiate palliative care discussions earlier in patient’s disease trajectory, with the remaining 20% (2/10) reporting a neutral stance. All fellows (100%) agreed that earlier palliative care involvement improves patient outcomes.
Implications/Significance
This PDSA cycle demonstrated that targeted education for fellows can increase awareness of palliative care resources and improve referral rates. Future work will focus on reassessing usage of palliative care consults post-intervention to evaluate effects of fellows’ education of appropriate palliative care consultation, make necessary interventions based on data and further evaluate the long-term impact on patient outcomes at James A. Haley Veterans’ Hospital.
A Workflow Initiative to Increase the Early Palliative Care Referral Rate in Patients With Advanced Cancer
Background
Early palliative care (PC) has been shown to improve cancer patients’ quality of life, symptom control, disease knowledge, psychological and spiritual health, end-of-life care, and survival, as well as reduce hospital admissions and emergency visits. The American Society of Clinical Oncology and the World Health Organization recommend that every patient with advanced cancer should be treated by a multidisciplinary palliative care team early in the course of the disease and in conjunction with anticancer treatment. Despite the documented benefits and the recommendations, early PC is still not often offered in clinical practice.
Results
Through a retrospective data review from July, August, and September 2023, a low percentage of early PC referrals were identified among Veterans with pancreatic, head and neck, and stage IV lung cancer in the Infusion Clinic. Only 48.5% had an early PC referral, which is a referral made within 8 weeks from the time of diagnosis and 3 or more months before death. A survey conducted among oncology providers suggests that the lack of provider knowledge about the scope of PC, the lack of set criteria/protocol to initiate a referral, and provider discomfort in referring patients were thought to hinder early referrals or cause late or/lack of referrals.
Discussion
This quality improvement project aimed to increase the early PC referral rate among advanced cancer patients in the infusion clinic to improve patient outcomes. An early PC referral toolkit was implemented consisting of (a) provider education about the scope of PC, (b) a script to help providers introduce PC as part of the comprehensive care team, (c) a PC brochure for reference, and (d) an Evidence-Based Five-item Screening Checklist to identify patients needing PC.
Conclusions
Nine months of data monitoring and analysis post-implementation revealed a 100% (n=12) early PC referral rate, and 80% (n=12) of providers reported feeling comfortable referring their patients. The project fostered a culture of comprehensive cancer care while empowering providers to make early referrals that improve patients’ multidimensional outcomes. The toolkit remains available to oncology providers and is shared upon request with other VA centers, as it is replicable in most VA settings that offer PC.
Background
Early palliative care (PC) has been shown to improve cancer patients’ quality of life, symptom control, disease knowledge, psychological and spiritual health, end-of-life care, and survival, as well as reduce hospital admissions and emergency visits. The American Society of Clinical Oncology and the World Health Organization recommend that every patient with advanced cancer should be treated by a multidisciplinary palliative care team early in the course of the disease and in conjunction with anticancer treatment. Despite the documented benefits and the recommendations, early PC is still not often offered in clinical practice.
Results
Through a retrospective data review from July, August, and September 2023, a low percentage of early PC referrals were identified among Veterans with pancreatic, head and neck, and stage IV lung cancer in the Infusion Clinic. Only 48.5% had an early PC referral, which is a referral made within 8 weeks from the time of diagnosis and 3 or more months before death. A survey conducted among oncology providers suggests that the lack of provider knowledge about the scope of PC, the lack of set criteria/protocol to initiate a referral, and provider discomfort in referring patients were thought to hinder early referrals or cause late or/lack of referrals.
Discussion
This quality improvement project aimed to increase the early PC referral rate among advanced cancer patients in the infusion clinic to improve patient outcomes. An early PC referral toolkit was implemented consisting of (a) provider education about the scope of PC, (b) a script to help providers introduce PC as part of the comprehensive care team, (c) a PC brochure for reference, and (d) an Evidence-Based Five-item Screening Checklist to identify patients needing PC.
Conclusions
Nine months of data monitoring and analysis post-implementation revealed a 100% (n=12) early PC referral rate, and 80% (n=12) of providers reported feeling comfortable referring their patients. The project fostered a culture of comprehensive cancer care while empowering providers to make early referrals that improve patients’ multidimensional outcomes. The toolkit remains available to oncology providers and is shared upon request with other VA centers, as it is replicable in most VA settings that offer PC.
Background
Early palliative care (PC) has been shown to improve cancer patients’ quality of life, symptom control, disease knowledge, psychological and spiritual health, end-of-life care, and survival, as well as reduce hospital admissions and emergency visits. The American Society of Clinical Oncology and the World Health Organization recommend that every patient with advanced cancer should be treated by a multidisciplinary palliative care team early in the course of the disease and in conjunction with anticancer treatment. Despite the documented benefits and the recommendations, early PC is still not often offered in clinical practice.
Results
Through a retrospective data review from July, August, and September 2023, a low percentage of early PC referrals were identified among Veterans with pancreatic, head and neck, and stage IV lung cancer in the Infusion Clinic. Only 48.5% had an early PC referral, which is a referral made within 8 weeks from the time of diagnosis and 3 or more months before death. A survey conducted among oncology providers suggests that the lack of provider knowledge about the scope of PC, the lack of set criteria/protocol to initiate a referral, and provider discomfort in referring patients were thought to hinder early referrals or cause late or/lack of referrals.
Discussion
This quality improvement project aimed to increase the early PC referral rate among advanced cancer patients in the infusion clinic to improve patient outcomes. An early PC referral toolkit was implemented consisting of (a) provider education about the scope of PC, (b) a script to help providers introduce PC as part of the comprehensive care team, (c) a PC brochure for reference, and (d) an Evidence-Based Five-item Screening Checklist to identify patients needing PC.
Conclusions
Nine months of data monitoring and analysis post-implementation revealed a 100% (n=12) early PC referral rate, and 80% (n=12) of providers reported feeling comfortable referring their patients. The project fostered a culture of comprehensive cancer care while empowering providers to make early referrals that improve patients’ multidimensional outcomes. The toolkit remains available to oncology providers and is shared upon request with other VA centers, as it is replicable in most VA settings that offer PC.
Walking the Line: Balancing Autonomy and Safety at End-of-Life
Background
The goal of hospice and palliative care is to provide comfort and dignity for individuals by honoring autonomy and patient preferences at endof- life. These standards can be difficult to balance when concerns around decision-making capacity and safety arise. The Veteran’s Health Administration has numerous resources to support interdisciplinary teams. We present a case study highlighting conflict between these ethical principles
Case Presentation
Veteran is a 66-year-old male with metastatic neuroendocrine cancer to brain and co-occurring polysubstance use disorder. Veteran agreed to VA inpatient hospice due to functional decline and limited social support at home. Day passes were initially allowed but later restricted due to multiple safety concerns surrounding mental status, smoking on campus and unauthorized passes. Behaviors escalated and veteran removed secure care monitor, left the unit without notifying staff, and erratically drove off campus prompting local police involvement.
Discussion
Patient demonstrated a preference to attend Alcoholics Anonymous meetings in person, to use his vehicle and to live at home. Given the complexity of this case, we turned to the National Center for Ethics in Health Care for input. This included guidance about legal and ethical limitations and recommendations for ongoing assessment and documentation of decisionmaking capacity and use of a surrogate.
Results
As veteran’s mental status declined, veteran no longer demonstrated the capacity to understand the safety risks of driving or living at home. His sister served as his health care agent and was opposed to home discharge due to safety concerns. The interdisciplinary team attempted to focus on respecting veteran’s dignity and autonomy as veteran approached end-oflife. Conflicts arose between the ethical pillars of autonomy, non-maleficence, community safety, and legal risks to institution. Lessons learned included the importance of daily safety huddles, ensuring secure care system functions properly, performing ongoing capacity assessments, and improving pre-admission screening.
Conclusions
Balancing autonomy and patient prefpreferences in VA hospice care demands continuous evaluation and adjustment of care plans. Legal and institutional ethics can be consulted to assist providers in formulating optimal plans and to guide use of ethical pillars within the VA framework.
Background
The goal of hospice and palliative care is to provide comfort and dignity for individuals by honoring autonomy and patient preferences at endof- life. These standards can be difficult to balance when concerns around decision-making capacity and safety arise. The Veteran’s Health Administration has numerous resources to support interdisciplinary teams. We present a case study highlighting conflict between these ethical principles
Case Presentation
Veteran is a 66-year-old male with metastatic neuroendocrine cancer to brain and co-occurring polysubstance use disorder. Veteran agreed to VA inpatient hospice due to functional decline and limited social support at home. Day passes were initially allowed but later restricted due to multiple safety concerns surrounding mental status, smoking on campus and unauthorized passes. Behaviors escalated and veteran removed secure care monitor, left the unit without notifying staff, and erratically drove off campus prompting local police involvement.
Discussion
Patient demonstrated a preference to attend Alcoholics Anonymous meetings in person, to use his vehicle and to live at home. Given the complexity of this case, we turned to the National Center for Ethics in Health Care for input. This included guidance about legal and ethical limitations and recommendations for ongoing assessment and documentation of decisionmaking capacity and use of a surrogate.
Results
As veteran’s mental status declined, veteran no longer demonstrated the capacity to understand the safety risks of driving or living at home. His sister served as his health care agent and was opposed to home discharge due to safety concerns. The interdisciplinary team attempted to focus on respecting veteran’s dignity and autonomy as veteran approached end-oflife. Conflicts arose between the ethical pillars of autonomy, non-maleficence, community safety, and legal risks to institution. Lessons learned included the importance of daily safety huddles, ensuring secure care system functions properly, performing ongoing capacity assessments, and improving pre-admission screening.
Conclusions
Balancing autonomy and patient prefpreferences in VA hospice care demands continuous evaluation and adjustment of care plans. Legal and institutional ethics can be consulted to assist providers in formulating optimal plans and to guide use of ethical pillars within the VA framework.
Background
The goal of hospice and palliative care is to provide comfort and dignity for individuals by honoring autonomy and patient preferences at endof- life. These standards can be difficult to balance when concerns around decision-making capacity and safety arise. The Veteran’s Health Administration has numerous resources to support interdisciplinary teams. We present a case study highlighting conflict between these ethical principles
Case Presentation
Veteran is a 66-year-old male with metastatic neuroendocrine cancer to brain and co-occurring polysubstance use disorder. Veteran agreed to VA inpatient hospice due to functional decline and limited social support at home. Day passes were initially allowed but later restricted due to multiple safety concerns surrounding mental status, smoking on campus and unauthorized passes. Behaviors escalated and veteran removed secure care monitor, left the unit without notifying staff, and erratically drove off campus prompting local police involvement.
Discussion
Patient demonstrated a preference to attend Alcoholics Anonymous meetings in person, to use his vehicle and to live at home. Given the complexity of this case, we turned to the National Center for Ethics in Health Care for input. This included guidance about legal and ethical limitations and recommendations for ongoing assessment and documentation of decisionmaking capacity and use of a surrogate.
Results
As veteran’s mental status declined, veteran no longer demonstrated the capacity to understand the safety risks of driving or living at home. His sister served as his health care agent and was opposed to home discharge due to safety concerns. The interdisciplinary team attempted to focus on respecting veteran’s dignity and autonomy as veteran approached end-oflife. Conflicts arose between the ethical pillars of autonomy, non-maleficence, community safety, and legal risks to institution. Lessons learned included the importance of daily safety huddles, ensuring secure care system functions properly, performing ongoing capacity assessments, and improving pre-admission screening.
Conclusions
Balancing autonomy and patient prefpreferences in VA hospice care demands continuous evaluation and adjustment of care plans. Legal and institutional ethics can be consulted to assist providers in formulating optimal plans and to guide use of ethical pillars within the VA framework.
Dying in the Hospital: A Necessary Choice?
More than a third of all patients with cancer die in hospitals, a figure that has increased slightly in recent years, while deaths at home have decreased. These findings come from a recent study published in Cancer Epidemiology, which analyzed data on the different places in Italy where end of life occurs.
“Place of death is relevant both for individuals and for the society. Home is universally considered the optimal place of death, while dying in a hospital may be a signal of inappropriate end-of-life care,” wrote the authors, led by Gianmauro Numico, MD, head of the Oncology Department at the Santa Croce e Carle General Hospital in Cuneo, Italy.
“Despite the general trend toward strengthening community-based networks and the increasing number of hospice and long-term care facilities, we oncologists are facing an opposite trend, with many patients spending their last days in the hospital,” Numico explained to Univadis Italy. This observation led to the questions that prompted the study: Is this only a perception among doctors, or is it a real phenomenon? If the latter, why is it happening?
What’s Preferable
For their analysis, Numico and colleagues relied on death certificates published by the Italian National Institute of Statistics from 2015 to 2019, excluding data from the pandemic years to avoid potential biases.
The analysis of data pertaining to cancer deaths revealed that approximately 35% of Italian patients with cancer die in hospitals, with a slight increase over the study period. Of the patients who die elsewhere, 40% die at home and 20% die in hospice or other long-term care facilities. Home deaths have decreased by 3.09%, while those in hospices and long-term care facilities have increased by 2.71%, and hospital deaths have risen by 0.3%.
The study also highlighted notable geographical differences: Hospital deaths are more frequent in the north, while in the south, home deaths remain predominant, although hospital admissions are on the rise. “These differences reflect not only access to facilities but also cultural and social variables,” explained Numico. “Some end-of-life issues with cancer patients are more straightforward, while others are difficult to manage outside the hospital,” he said, recalling that many family members and caregivers are afraid they won’t be able to care for their loved ones properly without the support of an appropriate facility and skilled personnel.
Social factors also contribute to the increased use of hospitals for end-of-life care: Without a social and family network, it is often impossible to manage the final stages of life at home. “We cannot guarantee that dying at home is better for everyone; in some cases, the home cannot provide the necessary care and emotional support,” Numico added.
Attitudes Need Change
Looking beyond Italy, it is clear that this trend exists in other countries as well. For example, in the Netherlands — where community-based care is highly developed and includes practices such as euthanasia — hospital death rates are higher than those in Italy. In the United States, the trend is different, but this is largely due to the structure of the US healthcare system, where patients bear much of the financial burden of hospital admissions.
“The basic requests of patients and families are clear: They want a safe place that is adequately staffed and where the patient won’t suffer,” said Numico, questioning whether the home is truly the best place to die. “In reality, this is not always the case, and it’s important to focus on the quality of care in the final days rather than just the place of care,” he added.
Ruling out hospitals a priori as a place to die is not a winning strategy, according to the expert. Instead of trying to reverse the trend, he suggests integrating the hospital into a care network that prioritizes the patient’s well-being, regardless of the setting. “Our goal should not be to eliminate hospital deaths — a common request from hospital administrations — but rather to ensure that end-of-life care in hospitals is a dignified experience that respects the needs of the dying and their loved ones,” Numico said. “We must ensure that, wherever the end-of-life process occurs, it should happen in the best way possible, and the hospital must be a part of this overall framework,” he concluded.
This story was translated from Univadis Italy using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
More than a third of all patients with cancer die in hospitals, a figure that has increased slightly in recent years, while deaths at home have decreased. These findings come from a recent study published in Cancer Epidemiology, which analyzed data on the different places in Italy where end of life occurs.
“Place of death is relevant both for individuals and for the society. Home is universally considered the optimal place of death, while dying in a hospital may be a signal of inappropriate end-of-life care,” wrote the authors, led by Gianmauro Numico, MD, head of the Oncology Department at the Santa Croce e Carle General Hospital in Cuneo, Italy.
“Despite the general trend toward strengthening community-based networks and the increasing number of hospice and long-term care facilities, we oncologists are facing an opposite trend, with many patients spending their last days in the hospital,” Numico explained to Univadis Italy. This observation led to the questions that prompted the study: Is this only a perception among doctors, or is it a real phenomenon? If the latter, why is it happening?
What’s Preferable
For their analysis, Numico and colleagues relied on death certificates published by the Italian National Institute of Statistics from 2015 to 2019, excluding data from the pandemic years to avoid potential biases.
The analysis of data pertaining to cancer deaths revealed that approximately 35% of Italian patients with cancer die in hospitals, with a slight increase over the study period. Of the patients who die elsewhere, 40% die at home and 20% die in hospice or other long-term care facilities. Home deaths have decreased by 3.09%, while those in hospices and long-term care facilities have increased by 2.71%, and hospital deaths have risen by 0.3%.
The study also highlighted notable geographical differences: Hospital deaths are more frequent in the north, while in the south, home deaths remain predominant, although hospital admissions are on the rise. “These differences reflect not only access to facilities but also cultural and social variables,” explained Numico. “Some end-of-life issues with cancer patients are more straightforward, while others are difficult to manage outside the hospital,” he said, recalling that many family members and caregivers are afraid they won’t be able to care for their loved ones properly without the support of an appropriate facility and skilled personnel.
Social factors also contribute to the increased use of hospitals for end-of-life care: Without a social and family network, it is often impossible to manage the final stages of life at home. “We cannot guarantee that dying at home is better for everyone; in some cases, the home cannot provide the necessary care and emotional support,” Numico added.
Attitudes Need Change
Looking beyond Italy, it is clear that this trend exists in other countries as well. For example, in the Netherlands — where community-based care is highly developed and includes practices such as euthanasia — hospital death rates are higher than those in Italy. In the United States, the trend is different, but this is largely due to the structure of the US healthcare system, where patients bear much of the financial burden of hospital admissions.
“The basic requests of patients and families are clear: They want a safe place that is adequately staffed and where the patient won’t suffer,” said Numico, questioning whether the home is truly the best place to die. “In reality, this is not always the case, and it’s important to focus on the quality of care in the final days rather than just the place of care,” he added.
Ruling out hospitals a priori as a place to die is not a winning strategy, according to the expert. Instead of trying to reverse the trend, he suggests integrating the hospital into a care network that prioritizes the patient’s well-being, regardless of the setting. “Our goal should not be to eliminate hospital deaths — a common request from hospital administrations — but rather to ensure that end-of-life care in hospitals is a dignified experience that respects the needs of the dying and their loved ones,” Numico said. “We must ensure that, wherever the end-of-life process occurs, it should happen in the best way possible, and the hospital must be a part of this overall framework,” he concluded.
This story was translated from Univadis Italy using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
More than a third of all patients with cancer die in hospitals, a figure that has increased slightly in recent years, while deaths at home have decreased. These findings come from a recent study published in Cancer Epidemiology, which analyzed data on the different places in Italy where end of life occurs.
“Place of death is relevant both for individuals and for the society. Home is universally considered the optimal place of death, while dying in a hospital may be a signal of inappropriate end-of-life care,” wrote the authors, led by Gianmauro Numico, MD, head of the Oncology Department at the Santa Croce e Carle General Hospital in Cuneo, Italy.
“Despite the general trend toward strengthening community-based networks and the increasing number of hospice and long-term care facilities, we oncologists are facing an opposite trend, with many patients spending their last days in the hospital,” Numico explained to Univadis Italy. This observation led to the questions that prompted the study: Is this only a perception among doctors, or is it a real phenomenon? If the latter, why is it happening?
What’s Preferable
For their analysis, Numico and colleagues relied on death certificates published by the Italian National Institute of Statistics from 2015 to 2019, excluding data from the pandemic years to avoid potential biases.
The analysis of data pertaining to cancer deaths revealed that approximately 35% of Italian patients with cancer die in hospitals, with a slight increase over the study period. Of the patients who die elsewhere, 40% die at home and 20% die in hospice or other long-term care facilities. Home deaths have decreased by 3.09%, while those in hospices and long-term care facilities have increased by 2.71%, and hospital deaths have risen by 0.3%.
The study also highlighted notable geographical differences: Hospital deaths are more frequent in the north, while in the south, home deaths remain predominant, although hospital admissions are on the rise. “These differences reflect not only access to facilities but also cultural and social variables,” explained Numico. “Some end-of-life issues with cancer patients are more straightforward, while others are difficult to manage outside the hospital,” he said, recalling that many family members and caregivers are afraid they won’t be able to care for their loved ones properly without the support of an appropriate facility and skilled personnel.
Social factors also contribute to the increased use of hospitals for end-of-life care: Without a social and family network, it is often impossible to manage the final stages of life at home. “We cannot guarantee that dying at home is better for everyone; in some cases, the home cannot provide the necessary care and emotional support,” Numico added.
Attitudes Need Change
Looking beyond Italy, it is clear that this trend exists in other countries as well. For example, in the Netherlands — where community-based care is highly developed and includes practices such as euthanasia — hospital death rates are higher than those in Italy. In the United States, the trend is different, but this is largely due to the structure of the US healthcare system, where patients bear much of the financial burden of hospital admissions.
“The basic requests of patients and families are clear: They want a safe place that is adequately staffed and where the patient won’t suffer,” said Numico, questioning whether the home is truly the best place to die. “In reality, this is not always the case, and it’s important to focus on the quality of care in the final days rather than just the place of care,” he added.
Ruling out hospitals a priori as a place to die is not a winning strategy, according to the expert. Instead of trying to reverse the trend, he suggests integrating the hospital into a care network that prioritizes the patient’s well-being, regardless of the setting. “Our goal should not be to eliminate hospital deaths — a common request from hospital administrations — but rather to ensure that end-of-life care in hospitals is a dignified experience that respects the needs of the dying and their loved ones,” Numico said. “We must ensure that, wherever the end-of-life process occurs, it should happen in the best way possible, and the hospital must be a part of this overall framework,” he concluded.
This story was translated from Univadis Italy using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Cancer Treatment 101: A Primer for Non-Oncologists
The remaining 700,000 or so often proceed to chemotherapy either immediately or upon cancer recurrence, spread, or newly recognized metastases. “Cures” after that point are rare.
I’m speaking in generalities, understanding that each cancer and each patient is unique.
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy alone can cure a small number of cancer types. When added to radiation or surgery, chemotherapy can help to cure a wider range of cancer types. As an add-on, chemotherapy can extend the length and quality of life for many patients with cancer. Since chemotherapy is by definition “toxic,” it can also shorten the duration or harm the quality of life and provide false hope. The Table summarizes what chemotherapy can and cannot achieve in selected cancer types.
Careful, compassionate communication between patient and physician is key. Goals and expectations must be clearly understood.
Organized chemotherapeutic efforts are further categorized as first line, second line, and third line.
First-line treatment. The initial round of recommended chemotherapy for a specific cancer. It is typically considered the most effective treatment for that type and stage of cancer on the basis of current research and clinical trials.
Second-line treatment. This is the treatment used if the first-line chemotherapy doesn’t work as desired. Reasons to switch to second-line chemo include:
- Lack of response (the tumor failed to shrink).
- Progression (the cancer may have grown or spread further).
- Adverse side effects were too severe to continue.
The drugs used in second-line chemo will typically be different from those used in first line, sometimes because cancer cells can develop resistance to chemotherapy drugs over time. Moreover, the goal of second-line chemo may differ from that of first-line therapy. Rather than chiefly aiming for a cure, second-line treatment might focus on slowing cancer growth, managing symptoms, or improving quality of life. Unfortunately, not every type of cancer has a readily available second-line option.
Third-line treatment. Third-line options come into play when both the initial course of chemo (first line) and the subsequent treatment (second line) have failed to achieve remission or control the cancer’s spread. Owing to the progressive nature of advanced cancers, patients might not be eligible or healthy enough for third-line therapy. Depending on cancer type, the patient’s general health, and response to previous treatments, third-line options could include:
- New or different chemotherapy drugs compared with prior lines.
- Surgery to debulk the tumor.
- Radiation for symptom control.
- Targeted therapy: drugs designed to target specific vulnerabilities in cancer cells.
- Immunotherapy: agents that help the body’s immune system fight cancer cells.
- Clinical trials testing new or investigational treatments, which may be applicable at any time, depending on the questions being addressed.
The goals of third-line therapy may shift from aiming for a cure to managing symptoms, improving quality of life, and potentially slowing cancer growth. The decision to pursue third-line therapy involves careful consideration by the doctor and patient, weighing the potential benefits and risks of treatment considering the individual’s overall health and specific situation.
It’s important to have realistic expectations about the potential outcomes of third-line therapy. Although remission may be unlikely, third-line therapy can still play a role in managing the disease.
Navigating advanced cancer treatment is very complex. The patient and physician must together consider detailed explanations and clarifications to set expectations and make informed decisions about care.
Interventions to Consider Earlier
In traditional clinical oncology practice, other interventions are possible, but these may not be offered until treatment has reached the third line:
- Molecular testing.
- Palliation.
- Clinical trials.
- Innovative testing to guide targeted therapy by ascertaining which agents are most likely (or not likely at all) to be effective.
I would argue that the patient’s interests are better served by considering and offering these other interventions much earlier, even before starting first-line chemotherapy.
Molecular testing. The best time for molecular testing of a new malignant tumor is typically at the time of diagnosis. Here’s why:
- Molecular testing helps identify specific genetic mutations in the cancer cells. This information can be crucial for selecting targeted therapies that are most effective against those specific mutations. Early detection allows for the most treatment options. For example, for non–small cell lung cancer, early is best because treatment and outcomes may well be changed by test results.
- Knowing the tumor’s molecular makeup can help determine whether a patient qualifies for clinical trials of new drugs designed for specific mutations.
- Some molecular markers can offer information about the tumor’s aggressiveness and potential for metastasis so that prognosis can be informed.
Molecular testing can be a valuable tool throughout a cancer patient’s journey. With genetically diverse tumors, the initial biopsy might not capture the full picture. Molecular testing of circulating tumor DNA can be used to monitor a patient’s response to treatment and detect potential mutations that might arise during treatment resistance. Retesting after metastasis can provide additional information that can aid in treatment decisions.
Palliative care. The ideal time to discuss palliative care with a patient with cancer is early in the diagnosis and treatment process. Palliative care is not the same as hospice care; it isn’t just about end-of-life. Palliative care focuses on improving a patient’s quality of life throughout cancer treatment. Palliative care specialists can address a wide range of symptoms a patient might experience from cancer or its treatment, including pain, fatigue, nausea, and anxiety.
Early discussions allow for a more comprehensive care plan. Open communication about all treatment options, including palliative care, empowers patients to make informed decisions about their care goals and preferences.
Specific situations where discussing palliative care might be appropriate are:
- Soon after a cancer diagnosis.
- If the patient experiences significant side effects from cancer treatment.
- When considering different treatment options, palliative care can complement those treatments.
- In advanced stages of cancer, to focus on comfort and quality of life.
Clinical trials. Participation in a clinical trial to explore new or investigational treatments should always be considered.
In theory, clinical trials should be an option at any time in the patient’s course. But the organized clinical trial experience may not be available or appropriate. Then, the individual becomes a de facto “clinical trial with an n of 1.” Read this brief open-access blog post at Cancer Commons to learn more about that circumstance.
Innovative testing. The best choice of chemotherapeutic or targeted therapies is often unclear. The clinician is likely to follow published guidelines, often from the National Comprehensive Cancer Network.
These are evidence based and driven by consensus of experts. But guideline-recommended therapy is not always effective, and weeks or months can pass before this ineffectiveness becomes apparent. Thus, many researchers and companies are seeking methods of testing each patient’s specific cancer to determine in advance, or very quickly, whether a particular drug is likely to be effective.
Read more about these leading innovations:
SAGE Oncotest: Entering the Next Generation of Tailored Cancer Treatment
Alibrex: A New Blood Test to Reveal Whether a Cancer Treatment is Working
PARIS Test Uses Lab-Grown Mini-Tumors to Find a Patient’s Best Treatment
Using Live Cells from Patients to Find the Right Cancer Drug
Other innovative therapies under investigation could even be agnostic to cancer type:
Treating Pancreatic Cancer: Could Metabolism — Not Genomics — Be the Key?
High-Energy Blue Light Powers a Promising New Treatment to Destroy Cancer Cells
All-Clear Follow-Up: Hydrogen Peroxide Appears to Treat Oral and Skin Lesions
Cancer is a tough nut to crack. Many people and organizations are trying very hard. So much is being learned. Some approaches will be effective. We can all hope.
Dr. Lundberg, editor in chief, Cancer Commons, has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
The remaining 700,000 or so often proceed to chemotherapy either immediately or upon cancer recurrence, spread, or newly recognized metastases. “Cures” after that point are rare.
I’m speaking in generalities, understanding that each cancer and each patient is unique.
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy alone can cure a small number of cancer types. When added to radiation or surgery, chemotherapy can help to cure a wider range of cancer types. As an add-on, chemotherapy can extend the length and quality of life for many patients with cancer. Since chemotherapy is by definition “toxic,” it can also shorten the duration or harm the quality of life and provide false hope. The Table summarizes what chemotherapy can and cannot achieve in selected cancer types.
Careful, compassionate communication between patient and physician is key. Goals and expectations must be clearly understood.
Organized chemotherapeutic efforts are further categorized as first line, second line, and third line.
First-line treatment. The initial round of recommended chemotherapy for a specific cancer. It is typically considered the most effective treatment for that type and stage of cancer on the basis of current research and clinical trials.
Second-line treatment. This is the treatment used if the first-line chemotherapy doesn’t work as desired. Reasons to switch to second-line chemo include:
- Lack of response (the tumor failed to shrink).
- Progression (the cancer may have grown or spread further).
- Adverse side effects were too severe to continue.
The drugs used in second-line chemo will typically be different from those used in first line, sometimes because cancer cells can develop resistance to chemotherapy drugs over time. Moreover, the goal of second-line chemo may differ from that of first-line therapy. Rather than chiefly aiming for a cure, second-line treatment might focus on slowing cancer growth, managing symptoms, or improving quality of life. Unfortunately, not every type of cancer has a readily available second-line option.
Third-line treatment. Third-line options come into play when both the initial course of chemo (first line) and the subsequent treatment (second line) have failed to achieve remission or control the cancer’s spread. Owing to the progressive nature of advanced cancers, patients might not be eligible or healthy enough for third-line therapy. Depending on cancer type, the patient’s general health, and response to previous treatments, third-line options could include:
- New or different chemotherapy drugs compared with prior lines.
- Surgery to debulk the tumor.
- Radiation for symptom control.
- Targeted therapy: drugs designed to target specific vulnerabilities in cancer cells.
- Immunotherapy: agents that help the body’s immune system fight cancer cells.
- Clinical trials testing new or investigational treatments, which may be applicable at any time, depending on the questions being addressed.
The goals of third-line therapy may shift from aiming for a cure to managing symptoms, improving quality of life, and potentially slowing cancer growth. The decision to pursue third-line therapy involves careful consideration by the doctor and patient, weighing the potential benefits and risks of treatment considering the individual’s overall health and specific situation.
It’s important to have realistic expectations about the potential outcomes of third-line therapy. Although remission may be unlikely, third-line therapy can still play a role in managing the disease.
Navigating advanced cancer treatment is very complex. The patient and physician must together consider detailed explanations and clarifications to set expectations and make informed decisions about care.
Interventions to Consider Earlier
In traditional clinical oncology practice, other interventions are possible, but these may not be offered until treatment has reached the third line:
- Molecular testing.
- Palliation.
- Clinical trials.
- Innovative testing to guide targeted therapy by ascertaining which agents are most likely (or not likely at all) to be effective.
I would argue that the patient’s interests are better served by considering and offering these other interventions much earlier, even before starting first-line chemotherapy.
Molecular testing. The best time for molecular testing of a new malignant tumor is typically at the time of diagnosis. Here’s why:
- Molecular testing helps identify specific genetic mutations in the cancer cells. This information can be crucial for selecting targeted therapies that are most effective against those specific mutations. Early detection allows for the most treatment options. For example, for non–small cell lung cancer, early is best because treatment and outcomes may well be changed by test results.
- Knowing the tumor’s molecular makeup can help determine whether a patient qualifies for clinical trials of new drugs designed for specific mutations.
- Some molecular markers can offer information about the tumor’s aggressiveness and potential for metastasis so that prognosis can be informed.
Molecular testing can be a valuable tool throughout a cancer patient’s journey. With genetically diverse tumors, the initial biopsy might not capture the full picture. Molecular testing of circulating tumor DNA can be used to monitor a patient’s response to treatment and detect potential mutations that might arise during treatment resistance. Retesting after metastasis can provide additional information that can aid in treatment decisions.
Palliative care. The ideal time to discuss palliative care with a patient with cancer is early in the diagnosis and treatment process. Palliative care is not the same as hospice care; it isn’t just about end-of-life. Palliative care focuses on improving a patient’s quality of life throughout cancer treatment. Palliative care specialists can address a wide range of symptoms a patient might experience from cancer or its treatment, including pain, fatigue, nausea, and anxiety.
Early discussions allow for a more comprehensive care plan. Open communication about all treatment options, including palliative care, empowers patients to make informed decisions about their care goals and preferences.
Specific situations where discussing palliative care might be appropriate are:
- Soon after a cancer diagnosis.
- If the patient experiences significant side effects from cancer treatment.
- When considering different treatment options, palliative care can complement those treatments.
- In advanced stages of cancer, to focus on comfort and quality of life.
Clinical trials. Participation in a clinical trial to explore new or investigational treatments should always be considered.
In theory, clinical trials should be an option at any time in the patient’s course. But the organized clinical trial experience may not be available or appropriate. Then, the individual becomes a de facto “clinical trial with an n of 1.” Read this brief open-access blog post at Cancer Commons to learn more about that circumstance.
Innovative testing. The best choice of chemotherapeutic or targeted therapies is often unclear. The clinician is likely to follow published guidelines, often from the National Comprehensive Cancer Network.
These are evidence based and driven by consensus of experts. But guideline-recommended therapy is not always effective, and weeks or months can pass before this ineffectiveness becomes apparent. Thus, many researchers and companies are seeking methods of testing each patient’s specific cancer to determine in advance, or very quickly, whether a particular drug is likely to be effective.
Read more about these leading innovations:
SAGE Oncotest: Entering the Next Generation of Tailored Cancer Treatment
Alibrex: A New Blood Test to Reveal Whether a Cancer Treatment is Working
PARIS Test Uses Lab-Grown Mini-Tumors to Find a Patient’s Best Treatment
Using Live Cells from Patients to Find the Right Cancer Drug
Other innovative therapies under investigation could even be agnostic to cancer type:
Treating Pancreatic Cancer: Could Metabolism — Not Genomics — Be the Key?
High-Energy Blue Light Powers a Promising New Treatment to Destroy Cancer Cells
All-Clear Follow-Up: Hydrogen Peroxide Appears to Treat Oral and Skin Lesions
Cancer is a tough nut to crack. Many people and organizations are trying very hard. So much is being learned. Some approaches will be effective. We can all hope.
Dr. Lundberg, editor in chief, Cancer Commons, has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
The remaining 700,000 or so often proceed to chemotherapy either immediately or upon cancer recurrence, spread, or newly recognized metastases. “Cures” after that point are rare.
I’m speaking in generalities, understanding that each cancer and each patient is unique.
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy alone can cure a small number of cancer types. When added to radiation or surgery, chemotherapy can help to cure a wider range of cancer types. As an add-on, chemotherapy can extend the length and quality of life for many patients with cancer. Since chemotherapy is by definition “toxic,” it can also shorten the duration or harm the quality of life and provide false hope. The Table summarizes what chemotherapy can and cannot achieve in selected cancer types.
Careful, compassionate communication between patient and physician is key. Goals and expectations must be clearly understood.
Organized chemotherapeutic efforts are further categorized as first line, second line, and third line.
First-line treatment. The initial round of recommended chemotherapy for a specific cancer. It is typically considered the most effective treatment for that type and stage of cancer on the basis of current research and clinical trials.
Second-line treatment. This is the treatment used if the first-line chemotherapy doesn’t work as desired. Reasons to switch to second-line chemo include:
- Lack of response (the tumor failed to shrink).
- Progression (the cancer may have grown or spread further).
- Adverse side effects were too severe to continue.
The drugs used in second-line chemo will typically be different from those used in first line, sometimes because cancer cells can develop resistance to chemotherapy drugs over time. Moreover, the goal of second-line chemo may differ from that of first-line therapy. Rather than chiefly aiming for a cure, second-line treatment might focus on slowing cancer growth, managing symptoms, or improving quality of life. Unfortunately, not every type of cancer has a readily available second-line option.
Third-line treatment. Third-line options come into play when both the initial course of chemo (first line) and the subsequent treatment (second line) have failed to achieve remission or control the cancer’s spread. Owing to the progressive nature of advanced cancers, patients might not be eligible or healthy enough for third-line therapy. Depending on cancer type, the patient’s general health, and response to previous treatments, third-line options could include:
- New or different chemotherapy drugs compared with prior lines.
- Surgery to debulk the tumor.
- Radiation for symptom control.
- Targeted therapy: drugs designed to target specific vulnerabilities in cancer cells.
- Immunotherapy: agents that help the body’s immune system fight cancer cells.
- Clinical trials testing new or investigational treatments, which may be applicable at any time, depending on the questions being addressed.
The goals of third-line therapy may shift from aiming for a cure to managing symptoms, improving quality of life, and potentially slowing cancer growth. The decision to pursue third-line therapy involves careful consideration by the doctor and patient, weighing the potential benefits and risks of treatment considering the individual’s overall health and specific situation.
It’s important to have realistic expectations about the potential outcomes of third-line therapy. Although remission may be unlikely, third-line therapy can still play a role in managing the disease.
Navigating advanced cancer treatment is very complex. The patient and physician must together consider detailed explanations and clarifications to set expectations and make informed decisions about care.
Interventions to Consider Earlier
In traditional clinical oncology practice, other interventions are possible, but these may not be offered until treatment has reached the third line:
- Molecular testing.
- Palliation.
- Clinical trials.
- Innovative testing to guide targeted therapy by ascertaining which agents are most likely (or not likely at all) to be effective.
I would argue that the patient’s interests are better served by considering and offering these other interventions much earlier, even before starting first-line chemotherapy.
Molecular testing. The best time for molecular testing of a new malignant tumor is typically at the time of diagnosis. Here’s why:
- Molecular testing helps identify specific genetic mutations in the cancer cells. This information can be crucial for selecting targeted therapies that are most effective against those specific mutations. Early detection allows for the most treatment options. For example, for non–small cell lung cancer, early is best because treatment and outcomes may well be changed by test results.
- Knowing the tumor’s molecular makeup can help determine whether a patient qualifies for clinical trials of new drugs designed for specific mutations.
- Some molecular markers can offer information about the tumor’s aggressiveness and potential for metastasis so that prognosis can be informed.
Molecular testing can be a valuable tool throughout a cancer patient’s journey. With genetically diverse tumors, the initial biopsy might not capture the full picture. Molecular testing of circulating tumor DNA can be used to monitor a patient’s response to treatment and detect potential mutations that might arise during treatment resistance. Retesting after metastasis can provide additional information that can aid in treatment decisions.
Palliative care. The ideal time to discuss palliative care with a patient with cancer is early in the diagnosis and treatment process. Palliative care is not the same as hospice care; it isn’t just about end-of-life. Palliative care focuses on improving a patient’s quality of life throughout cancer treatment. Palliative care specialists can address a wide range of symptoms a patient might experience from cancer or its treatment, including pain, fatigue, nausea, and anxiety.
Early discussions allow for a more comprehensive care plan. Open communication about all treatment options, including palliative care, empowers patients to make informed decisions about their care goals and preferences.
Specific situations where discussing palliative care might be appropriate are:
- Soon after a cancer diagnosis.
- If the patient experiences significant side effects from cancer treatment.
- When considering different treatment options, palliative care can complement those treatments.
- In advanced stages of cancer, to focus on comfort and quality of life.
Clinical trials. Participation in a clinical trial to explore new or investigational treatments should always be considered.
In theory, clinical trials should be an option at any time in the patient’s course. But the organized clinical trial experience may not be available or appropriate. Then, the individual becomes a de facto “clinical trial with an n of 1.” Read this brief open-access blog post at Cancer Commons to learn more about that circumstance.
Innovative testing. The best choice of chemotherapeutic or targeted therapies is often unclear. The clinician is likely to follow published guidelines, often from the National Comprehensive Cancer Network.
These are evidence based and driven by consensus of experts. But guideline-recommended therapy is not always effective, and weeks or months can pass before this ineffectiveness becomes apparent. Thus, many researchers and companies are seeking methods of testing each patient’s specific cancer to determine in advance, or very quickly, whether a particular drug is likely to be effective.
Read more about these leading innovations:
SAGE Oncotest: Entering the Next Generation of Tailored Cancer Treatment
Alibrex: A New Blood Test to Reveal Whether a Cancer Treatment is Working
PARIS Test Uses Lab-Grown Mini-Tumors to Find a Patient’s Best Treatment
Using Live Cells from Patients to Find the Right Cancer Drug
Other innovative therapies under investigation could even be agnostic to cancer type:
Treating Pancreatic Cancer: Could Metabolism — Not Genomics — Be the Key?
High-Energy Blue Light Powers a Promising New Treatment to Destroy Cancer Cells
All-Clear Follow-Up: Hydrogen Peroxide Appears to Treat Oral and Skin Lesions
Cancer is a tough nut to crack. Many people and organizations are trying very hard. So much is being learned. Some approaches will be effective. We can all hope.
Dr. Lundberg, editor in chief, Cancer Commons, has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Leaving Your Legacy Via Death Bots? Ethicist Shares Concerns
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
I heard recently about a fascinating, important development in artificial intelligence (AI). All kinds of things are happening in AI. Clearly, it’s being used in the background to trace and keep track of medical information inside hospitals.
There are AI bots out there that are starting to talk to patients about, say, mental health issues. Plenty of people are using AI to get information about their medical condition, seeing it supplement search engines, and on and on AI goes.
It has entered into a space where I think patients may raise questions about whether they should use it or seek opinions from doctors and nurses, particularly those involved with seriously ill people. That space is grieving, and what might be called “death bots.”
Here’s what’s going on. There’s a gentleman I read about online, who was dying of end-stage colon cancer. His wife and he were talking, knowing his death was coming, about what it would be like after his death. She said she would really miss being able to ask him questions about a variety of topics that he was expert at and that he knew very well.
He thought about it and decided, well, maybe he could record his voice and then use AI to search information that he would record and have available, which could really address questions that his wife might put to “him” once he was gone.
It turns out that a company was formed shortly thereafter, which is now offering the service both in the US and Europe, and in fact, I think perhaps even worldwide, basically saying we’ll record a dying person’s voice. We will help people grieve by allowing people to interact with the AI version of the departed when they’re gone.
It will be able to, if you will, search not just recorded information but anything they might have online — diaries, things they may have written, earlier videos, and information from earlier parts of their life — to generate plausible answers to questions that might be put to the artificial version of the deceased.
Obviously, this would allow not only spouses but grandchildren and people in future generations to have some way to interact with an ancestor who’s gone. It may allow people to feel comfort when they miss a loved one, to hear their voice, and not just in a prerecorded way but creatively interacting with them.
On the other hand, Is it all right if people wander from the truth in trying to interact with someone who’s died?
There are other ways to leave memories behind. You certainly can record messages so that you can control the content. Many people video themselves and so on. There are obviously people who would say that they have a diary or have written information they can leave behind.
Is there a place in terms of accuracy for a kind of artificial version of ourselves to go on forever? Another interesting issue is who controls that. Can you add to it after your death? Can information be shared about you with third parties who don’t sign up for the service? Maybe the police take an interest in how you died. You can imagine many scenarios where questions might come up about wanting to access these data that the artificial agent is providing.
Some people might say that it’s just not the way to grieve. Maybe the best way to grieve is to accept death and not try to interact with a constructed version of yourself once you’ve passed. That isn’t really accepting death. It’s a form, perhaps, of denial of death, and maybe that isn’t going to be good for the mental health of survivors who really have not come to terms with the fact that someone has passed on.
I’m not against these death bots or AI versions of trying to leave a legacy. There are all kinds of legacies that people might want to leave. While perhaps not 100% accurate, I can see how this technology has a use.
I do think one has to go in with their eyes open. We need consent before anything like this is really purchased by or sold to surviving people. They really have to understand it may not be an accurate version of what the deceased might have said in response to questions, conversations, or interactions.
I think we need to know who controls the information, who can erase it, and who can say, “I’m done with it, and I don’t want my husband’s AI to go on anymore.”
All that said, it’s an interesting development in a world in which I think those who are very ill might start to plan to leave a legacy that is more than just a diary or a video message. It becomes a kind of ongoing, artificial, interactive version of themselves that may provide some people with comfort.
Dr. Caplan, director of the Division of Medical Ethics at New York University Langone Medical Center, New York City, reported conflicts of interest with Johnson & Johnson and Medscape.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
I heard recently about a fascinating, important development in artificial intelligence (AI). All kinds of things are happening in AI. Clearly, it’s being used in the background to trace and keep track of medical information inside hospitals.
There are AI bots out there that are starting to talk to patients about, say, mental health issues. Plenty of people are using AI to get information about their medical condition, seeing it supplement search engines, and on and on AI goes.
It has entered into a space where I think patients may raise questions about whether they should use it or seek opinions from doctors and nurses, particularly those involved with seriously ill people. That space is grieving, and what might be called “death bots.”
Here’s what’s going on. There’s a gentleman I read about online, who was dying of end-stage colon cancer. His wife and he were talking, knowing his death was coming, about what it would be like after his death. She said she would really miss being able to ask him questions about a variety of topics that he was expert at and that he knew very well.
He thought about it and decided, well, maybe he could record his voice and then use AI to search information that he would record and have available, which could really address questions that his wife might put to “him” once he was gone.
It turns out that a company was formed shortly thereafter, which is now offering the service both in the US and Europe, and in fact, I think perhaps even worldwide, basically saying we’ll record a dying person’s voice. We will help people grieve by allowing people to interact with the AI version of the departed when they’re gone.
It will be able to, if you will, search not just recorded information but anything they might have online — diaries, things they may have written, earlier videos, and information from earlier parts of their life — to generate plausible answers to questions that might be put to the artificial version of the deceased.
Obviously, this would allow not only spouses but grandchildren and people in future generations to have some way to interact with an ancestor who’s gone. It may allow people to feel comfort when they miss a loved one, to hear their voice, and not just in a prerecorded way but creatively interacting with them.
On the other hand, Is it all right if people wander from the truth in trying to interact with someone who’s died?
There are other ways to leave memories behind. You certainly can record messages so that you can control the content. Many people video themselves and so on. There are obviously people who would say that they have a diary or have written information they can leave behind.
Is there a place in terms of accuracy for a kind of artificial version of ourselves to go on forever? Another interesting issue is who controls that. Can you add to it after your death? Can information be shared about you with third parties who don’t sign up for the service? Maybe the police take an interest in how you died. You can imagine many scenarios where questions might come up about wanting to access these data that the artificial agent is providing.
Some people might say that it’s just not the way to grieve. Maybe the best way to grieve is to accept death and not try to interact with a constructed version of yourself once you’ve passed. That isn’t really accepting death. It’s a form, perhaps, of denial of death, and maybe that isn’t going to be good for the mental health of survivors who really have not come to terms with the fact that someone has passed on.
I’m not against these death bots or AI versions of trying to leave a legacy. There are all kinds of legacies that people might want to leave. While perhaps not 100% accurate, I can see how this technology has a use.
I do think one has to go in with their eyes open. We need consent before anything like this is really purchased by or sold to surviving people. They really have to understand it may not be an accurate version of what the deceased might have said in response to questions, conversations, or interactions.
I think we need to know who controls the information, who can erase it, and who can say, “I’m done with it, and I don’t want my husband’s AI to go on anymore.”
All that said, it’s an interesting development in a world in which I think those who are very ill might start to plan to leave a legacy that is more than just a diary or a video message. It becomes a kind of ongoing, artificial, interactive version of themselves that may provide some people with comfort.
Dr. Caplan, director of the Division of Medical Ethics at New York University Langone Medical Center, New York City, reported conflicts of interest with Johnson & Johnson and Medscape.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
I heard recently about a fascinating, important development in artificial intelligence (AI). All kinds of things are happening in AI. Clearly, it’s being used in the background to trace and keep track of medical information inside hospitals.
There are AI bots out there that are starting to talk to patients about, say, mental health issues. Plenty of people are using AI to get information about their medical condition, seeing it supplement search engines, and on and on AI goes.
It has entered into a space where I think patients may raise questions about whether they should use it or seek opinions from doctors and nurses, particularly those involved with seriously ill people. That space is grieving, and what might be called “death bots.”
Here’s what’s going on. There’s a gentleman I read about online, who was dying of end-stage colon cancer. His wife and he were talking, knowing his death was coming, about what it would be like after his death. She said she would really miss being able to ask him questions about a variety of topics that he was expert at and that he knew very well.
He thought about it and decided, well, maybe he could record his voice and then use AI to search information that he would record and have available, which could really address questions that his wife might put to “him” once he was gone.
It turns out that a company was formed shortly thereafter, which is now offering the service both in the US and Europe, and in fact, I think perhaps even worldwide, basically saying we’ll record a dying person’s voice. We will help people grieve by allowing people to interact with the AI version of the departed when they’re gone.
It will be able to, if you will, search not just recorded information but anything they might have online — diaries, things they may have written, earlier videos, and information from earlier parts of their life — to generate plausible answers to questions that might be put to the artificial version of the deceased.
Obviously, this would allow not only spouses but grandchildren and people in future generations to have some way to interact with an ancestor who’s gone. It may allow people to feel comfort when they miss a loved one, to hear their voice, and not just in a prerecorded way but creatively interacting with them.
On the other hand, Is it all right if people wander from the truth in trying to interact with someone who’s died?
There are other ways to leave memories behind. You certainly can record messages so that you can control the content. Many people video themselves and so on. There are obviously people who would say that they have a diary or have written information they can leave behind.
Is there a place in terms of accuracy for a kind of artificial version of ourselves to go on forever? Another interesting issue is who controls that. Can you add to it after your death? Can information be shared about you with third parties who don’t sign up for the service? Maybe the police take an interest in how you died. You can imagine many scenarios where questions might come up about wanting to access these data that the artificial agent is providing.
Some people might say that it’s just not the way to grieve. Maybe the best way to grieve is to accept death and not try to interact with a constructed version of yourself once you’ve passed. That isn’t really accepting death. It’s a form, perhaps, of denial of death, and maybe that isn’t going to be good for the mental health of survivors who really have not come to terms with the fact that someone has passed on.
I’m not against these death bots or AI versions of trying to leave a legacy. There are all kinds of legacies that people might want to leave. While perhaps not 100% accurate, I can see how this technology has a use.
I do think one has to go in with their eyes open. We need consent before anything like this is really purchased by or sold to surviving people. They really have to understand it may not be an accurate version of what the deceased might have said in response to questions, conversations, or interactions.
I think we need to know who controls the information, who can erase it, and who can say, “I’m done with it, and I don’t want my husband’s AI to go on anymore.”
All that said, it’s an interesting development in a world in which I think those who are very ill might start to plan to leave a legacy that is more than just a diary or a video message. It becomes a kind of ongoing, artificial, interactive version of themselves that may provide some people with comfort.
Dr. Caplan, director of the Division of Medical Ethics at New York University Langone Medical Center, New York City, reported conflicts of interest with Johnson & Johnson and Medscape.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.