User login
Survey: ObGyns’ salaries rose slightly in 2013
The 2014 Medscape Compensation Report surveyed more than 24,000 physicians in 25 specialties. Five percent of respondents were ObGyns, whose mean income rose slightly to $243,000 in 2013 from $242,000 in 2012, up from $220,000 in 2011.1–3 The highest ObGyn earners lived in the Great Lakes and North Central regions.1
Survey findings
Men make more than women. In 2013, male ObGyns reported earning $256,000; female ObGyns reported $229,000 in mean income. However, women felt more satisfied with their salary (47% of women vs 38% of men). Regardless of gender, ObGyns were slightly less happy with their income than all physicians (50% satisfied).1
Among all female physicians, more were employed than self-employed; the opposite was true for male physicians.4 Half of all graduating physicians are now female, and demographics show that 62% of all female physicians are younger than age 45.1
Practice settings are key to income. Sixty percent of ObGyns indicated they would choose medicine again as a career; 43% would choose their own specialty. However, only 25% of ObGyns would make the same decision about practice setting.1
In 2013, employed and self-employed ObGyns reported nearly the same mean income: $243,000 versus $246,000, respectively. However, when broken down by specific practice setting, the highest earners were ObGyns who worked for health-care organizations, at $273,000. Additional 2013 mean earnings ranked by work setting were1:
- multispecialty office-based group practices, $271,000
- single-specialty office-based group practices, $255,000
- hospitals, $228,000
- solo office-based practices, $212,000
- outpatient clinics, $207,000.
In 2013, 49% of employed physicians worked in hospitals or in groups owned by a hospital, while 21% were employed by private groups. Other employment situations included community health centers, corporate laboratories, correction institutions, military bases, and nursing homes.4
ACO participation grows. In 2013, 37% of ObGyns either participated in an Accountable Care Organization (ACO) or planned on joining an ACO within the next year.1 This was an increase from 25% in 2012.2,3
In the most recent report, 2% chose concierge practices (also known as direct primary care) and 5% opted for cash-only practices.1 In 2012, only 1% of ObGyns opted for concierge practices, and 3% for cash-only practices.2,3
Related article: Is private ObGyn practice on its way out? Lucia DiVenere, MA (October 2011)
Employment over private practice? In 2013, physicians were enticed to seek employment by the financial challenges of private practice (38%); not having to be concerned about administrative issues (29%); and working shorter and more regular hours (19%). Other reported benefits of employment were academic opportunities, better life−work balance, more vacation time, and no loss of income during vacation. More than half (53%) of employed physicians who were previously self-employed felt that patient care was superior now that they were employed, and 37% thought it was about the same.4
Related article: Mean income for ObGyns increased in 2012. Deborah Reale (News for your Practice; August 2013)
Career satisfaction
ObGyns were close to the bottom among all physicians (48%) when it came to overall career satisfaction, tied with nephrologists, surgeons, and pulmonologists. The most satisfied physicians were dermatologists (65%); the least satisfied were plastic surgeons (45%).1
What drives you? In 2013, more ObGyns (41%) than all physicians (33%) reported that the most rewarding part of their job was their relationships with patients. Thirty percent of ObGyns chose being good at their jobs; 8% chose making good money; and 2% found nothing rewarding about the job.1
How much patient time do you spend? The majority (58%) of ObGyns reported spending more than 40 hours per week with patients and 16 minutes or less (66%) per patient.1 In 2012, 60% of ObGyn respondents reported spending 16 minutes or less per patient.2,3
Anticipating the effects of the Affordable Care Act
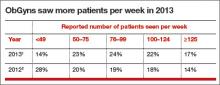
Under the Affordable Care Act (ACA), an organization’s revenue will still be determined largely by the volume generated by physicians. The percentage of ObGyns who saw 50 to 124 patients per week increased from 57% in 2012 to 69% in 2013 (TABLE).1,2
In 2013, 53% of ObGyns still were undecided about health-insurance exchange participation—the same percentage as all survey respondents. Among ObGyns, 30% would participate, and 17% would not participate.1
Related article: As the Affordable Care Act comes of age, a look behind the headlines. Lucia DiVenere, MA (Practice Management; January 2014)
Almost half (49%) of ObGyns expect their income under the ACA to decrease. About 45% of ObGyns did not foresee any change, and 5% believed their incomes would increase (1% didn’t know) under the ACA. ObGyns also anticipated a higher workload, a decline in quality of patient care and access, and reduced ability to make decisions.1
Almost one-third of ObGyns dropped poorly paying insurers. In 2013, 29% of ObGyns said they regularly drop insurers who pay poorly, but 46% said they keep their insurers year after year. In 2012, 26% of ObGyns said they drop insurers who pay the least or create the most trouble; 29% said they keep all insurers.2,3 Private insurance paid for 63% of patient visits to ObGyns in 2013.1
Fewer ObGyns indicated they would see Medicare and Medicaid patients. In 2013, 20% of self-employed and 5% of employed ObGyns said that they plan to stop taking new Medicare or Medicaid patients. More employed (72%) than self-employed (46%) ObGyns reported that they would continue seeing new and current Medicare and Medicaid patients.1
Related article: Medicare and Medicaid are on the brink of insolvency, and you’re not just a bystander. Robert L. Barbieri, MD (Editorial; October 2011)
In 2012, 15% of ObGyn respondents planned to stop taking new Medicare or Medicaid patients, but 53% of ObGyn respondents said they would continue to see current patients and would take on new Medicare or Medicaid patients.2,3
TELL US WHAT YOU THINK! Share your thoughts on this article. Send your Letter to the Editor to: rbarbieri@frontlinemedcom.com
- Peckham C. Medscape OB/GYN Compensation Report 2014. Medscape Web site. http://www.medscape.com/features/slideshow/compensation/2014/womenshealth. Published April 15, 2014. Accessed June 2, 2014.
- Medscape News. Ob/Gyn Compensation Report 2013. Medscape Web site. http://www.medscape.com/features/slideshow/compensation/2013/womenshealth. Accessed June 30, 2013.
- Reale D. Mean income for ObGyns increased in 2012. OBG Manag. 2013;25(8):34–36.
- Kane L. Employed vs self-employed: Who is better off? Medscape Web site. http://www.medscape.com/features/slideshow/public/employed-doctors. Published March 11, 2014. Accessed June 2, 2014.
The 2014 Medscape Compensation Report surveyed more than 24,000 physicians in 25 specialties. Five percent of respondents were ObGyns, whose mean income rose slightly to $243,000 in 2013 from $242,000 in 2012, up from $220,000 in 2011.1–3 The highest ObGyn earners lived in the Great Lakes and North Central regions.1
Survey findings
Men make more than women. In 2013, male ObGyns reported earning $256,000; female ObGyns reported $229,000 in mean income. However, women felt more satisfied with their salary (47% of women vs 38% of men). Regardless of gender, ObGyns were slightly less happy with their income than all physicians (50% satisfied).1
Among all female physicians, more were employed than self-employed; the opposite was true for male physicians.4 Half of all graduating physicians are now female, and demographics show that 62% of all female physicians are younger than age 45.1
Practice settings are key to income. Sixty percent of ObGyns indicated they would choose medicine again as a career; 43% would choose their own specialty. However, only 25% of ObGyns would make the same decision about practice setting.1
In 2013, employed and self-employed ObGyns reported nearly the same mean income: $243,000 versus $246,000, respectively. However, when broken down by specific practice setting, the highest earners were ObGyns who worked for health-care organizations, at $273,000. Additional 2013 mean earnings ranked by work setting were1:
- multispecialty office-based group practices, $271,000
- single-specialty office-based group practices, $255,000
- hospitals, $228,000
- solo office-based practices, $212,000
- outpatient clinics, $207,000.
In 2013, 49% of employed physicians worked in hospitals or in groups owned by a hospital, while 21% were employed by private groups. Other employment situations included community health centers, corporate laboratories, correction institutions, military bases, and nursing homes.4
ACO participation grows. In 2013, 37% of ObGyns either participated in an Accountable Care Organization (ACO) or planned on joining an ACO within the next year.1 This was an increase from 25% in 2012.2,3
In the most recent report, 2% chose concierge practices (also known as direct primary care) and 5% opted for cash-only practices.1 In 2012, only 1% of ObGyns opted for concierge practices, and 3% for cash-only practices.2,3
Related article: Is private ObGyn practice on its way out? Lucia DiVenere, MA (October 2011)
Employment over private practice? In 2013, physicians were enticed to seek employment by the financial challenges of private practice (38%); not having to be concerned about administrative issues (29%); and working shorter and more regular hours (19%). Other reported benefits of employment were academic opportunities, better life−work balance, more vacation time, and no loss of income during vacation. More than half (53%) of employed physicians who were previously self-employed felt that patient care was superior now that they were employed, and 37% thought it was about the same.4
Related article: Mean income for ObGyns increased in 2012. Deborah Reale (News for your Practice; August 2013)
Career satisfaction
ObGyns were close to the bottom among all physicians (48%) when it came to overall career satisfaction, tied with nephrologists, surgeons, and pulmonologists. The most satisfied physicians were dermatologists (65%); the least satisfied were plastic surgeons (45%).1
What drives you? In 2013, more ObGyns (41%) than all physicians (33%) reported that the most rewarding part of their job was their relationships with patients. Thirty percent of ObGyns chose being good at their jobs; 8% chose making good money; and 2% found nothing rewarding about the job.1
How much patient time do you spend? The majority (58%) of ObGyns reported spending more than 40 hours per week with patients and 16 minutes or less (66%) per patient.1 In 2012, 60% of ObGyn respondents reported spending 16 minutes or less per patient.2,3
Anticipating the effects of the Affordable Care Act
Under the Affordable Care Act (ACA), an organization’s revenue will still be determined largely by the volume generated by physicians. The percentage of ObGyns who saw 50 to 124 patients per week increased from 57% in 2012 to 69% in 2013 (TABLE).1,2
In 2013, 53% of ObGyns still were undecided about health-insurance exchange participation—the same percentage as all survey respondents. Among ObGyns, 30% would participate, and 17% would not participate.1
Related article: As the Affordable Care Act comes of age, a look behind the headlines. Lucia DiVenere, MA (Practice Management; January 2014)
Almost half (49%) of ObGyns expect their income under the ACA to decrease. About 45% of ObGyns did not foresee any change, and 5% believed their incomes would increase (1% didn’t know) under the ACA. ObGyns also anticipated a higher workload, a decline in quality of patient care and access, and reduced ability to make decisions.1
Almost one-third of ObGyns dropped poorly paying insurers. In 2013, 29% of ObGyns said they regularly drop insurers who pay poorly, but 46% said they keep their insurers year after year. In 2012, 26% of ObGyns said they drop insurers who pay the least or create the most trouble; 29% said they keep all insurers.2,3 Private insurance paid for 63% of patient visits to ObGyns in 2013.1
Fewer ObGyns indicated they would see Medicare and Medicaid patients. In 2013, 20% of self-employed and 5% of employed ObGyns said that they plan to stop taking new Medicare or Medicaid patients. More employed (72%) than self-employed (46%) ObGyns reported that they would continue seeing new and current Medicare and Medicaid patients.1
Related article: Medicare and Medicaid are on the brink of insolvency, and you’re not just a bystander. Robert L. Barbieri, MD (Editorial; October 2011)
In 2012, 15% of ObGyn respondents planned to stop taking new Medicare or Medicaid patients, but 53% of ObGyn respondents said they would continue to see current patients and would take on new Medicare or Medicaid patients.2,3
TELL US WHAT YOU THINK! Share your thoughts on this article. Send your Letter to the Editor to: rbarbieri@frontlinemedcom.com
The 2014 Medscape Compensation Report surveyed more than 24,000 physicians in 25 specialties. Five percent of respondents were ObGyns, whose mean income rose slightly to $243,000 in 2013 from $242,000 in 2012, up from $220,000 in 2011.1–3 The highest ObGyn earners lived in the Great Lakes and North Central regions.1
Survey findings
Men make more than women. In 2013, male ObGyns reported earning $256,000; female ObGyns reported $229,000 in mean income. However, women felt more satisfied with their salary (47% of women vs 38% of men). Regardless of gender, ObGyns were slightly less happy with their income than all physicians (50% satisfied).1
Among all female physicians, more were employed than self-employed; the opposite was true for male physicians.4 Half of all graduating physicians are now female, and demographics show that 62% of all female physicians are younger than age 45.1
Practice settings are key to income. Sixty percent of ObGyns indicated they would choose medicine again as a career; 43% would choose their own specialty. However, only 25% of ObGyns would make the same decision about practice setting.1
In 2013, employed and self-employed ObGyns reported nearly the same mean income: $243,000 versus $246,000, respectively. However, when broken down by specific practice setting, the highest earners were ObGyns who worked for health-care organizations, at $273,000. Additional 2013 mean earnings ranked by work setting were1:
- multispecialty office-based group practices, $271,000
- single-specialty office-based group practices, $255,000
- hospitals, $228,000
- solo office-based practices, $212,000
- outpatient clinics, $207,000.
In 2013, 49% of employed physicians worked in hospitals or in groups owned by a hospital, while 21% were employed by private groups. Other employment situations included community health centers, corporate laboratories, correction institutions, military bases, and nursing homes.4
ACO participation grows. In 2013, 37% of ObGyns either participated in an Accountable Care Organization (ACO) or planned on joining an ACO within the next year.1 This was an increase from 25% in 2012.2,3
In the most recent report, 2% chose concierge practices (also known as direct primary care) and 5% opted for cash-only practices.1 In 2012, only 1% of ObGyns opted for concierge practices, and 3% for cash-only practices.2,3
Related article: Is private ObGyn practice on its way out? Lucia DiVenere, MA (October 2011)
Employment over private practice? In 2013, physicians were enticed to seek employment by the financial challenges of private practice (38%); not having to be concerned about administrative issues (29%); and working shorter and more regular hours (19%). Other reported benefits of employment were academic opportunities, better life−work balance, more vacation time, and no loss of income during vacation. More than half (53%) of employed physicians who were previously self-employed felt that patient care was superior now that they were employed, and 37% thought it was about the same.4
Related article: Mean income for ObGyns increased in 2012. Deborah Reale (News for your Practice; August 2013)
Career satisfaction
ObGyns were close to the bottom among all physicians (48%) when it came to overall career satisfaction, tied with nephrologists, surgeons, and pulmonologists. The most satisfied physicians were dermatologists (65%); the least satisfied were plastic surgeons (45%).1
What drives you? In 2013, more ObGyns (41%) than all physicians (33%) reported that the most rewarding part of their job was their relationships with patients. Thirty percent of ObGyns chose being good at their jobs; 8% chose making good money; and 2% found nothing rewarding about the job.1
How much patient time do you spend? The majority (58%) of ObGyns reported spending more than 40 hours per week with patients and 16 minutes or less (66%) per patient.1 In 2012, 60% of ObGyn respondents reported spending 16 minutes or less per patient.2,3
Anticipating the effects of the Affordable Care Act
Under the Affordable Care Act (ACA), an organization’s revenue will still be determined largely by the volume generated by physicians. The percentage of ObGyns who saw 50 to 124 patients per week increased from 57% in 2012 to 69% in 2013 (TABLE).1,2
In 2013, 53% of ObGyns still were undecided about health-insurance exchange participation—the same percentage as all survey respondents. Among ObGyns, 30% would participate, and 17% would not participate.1
Related article: As the Affordable Care Act comes of age, a look behind the headlines. Lucia DiVenere, MA (Practice Management; January 2014)
Almost half (49%) of ObGyns expect their income under the ACA to decrease. About 45% of ObGyns did not foresee any change, and 5% believed their incomes would increase (1% didn’t know) under the ACA. ObGyns also anticipated a higher workload, a decline in quality of patient care and access, and reduced ability to make decisions.1
Almost one-third of ObGyns dropped poorly paying insurers. In 2013, 29% of ObGyns said they regularly drop insurers who pay poorly, but 46% said they keep their insurers year after year. In 2012, 26% of ObGyns said they drop insurers who pay the least or create the most trouble; 29% said they keep all insurers.2,3 Private insurance paid for 63% of patient visits to ObGyns in 2013.1
Fewer ObGyns indicated they would see Medicare and Medicaid patients. In 2013, 20% of self-employed and 5% of employed ObGyns said that they plan to stop taking new Medicare or Medicaid patients. More employed (72%) than self-employed (46%) ObGyns reported that they would continue seeing new and current Medicare and Medicaid patients.1
Related article: Medicare and Medicaid are on the brink of insolvency, and you’re not just a bystander. Robert L. Barbieri, MD (Editorial; October 2011)
In 2012, 15% of ObGyn respondents planned to stop taking new Medicare or Medicaid patients, but 53% of ObGyn respondents said they would continue to see current patients and would take on new Medicare or Medicaid patients.2,3
TELL US WHAT YOU THINK! Share your thoughts on this article. Send your Letter to the Editor to: rbarbieri@frontlinemedcom.com
- Peckham C. Medscape OB/GYN Compensation Report 2014. Medscape Web site. http://www.medscape.com/features/slideshow/compensation/2014/womenshealth. Published April 15, 2014. Accessed June 2, 2014.
- Medscape News. Ob/Gyn Compensation Report 2013. Medscape Web site. http://www.medscape.com/features/slideshow/compensation/2013/womenshealth. Accessed June 30, 2013.
- Reale D. Mean income for ObGyns increased in 2012. OBG Manag. 2013;25(8):34–36.
- Kane L. Employed vs self-employed: Who is better off? Medscape Web site. http://www.medscape.com/features/slideshow/public/employed-doctors. Published March 11, 2014. Accessed June 2, 2014.
- Peckham C. Medscape OB/GYN Compensation Report 2014. Medscape Web site. http://www.medscape.com/features/slideshow/compensation/2014/womenshealth. Published April 15, 2014. Accessed June 2, 2014.
- Medscape News. Ob/Gyn Compensation Report 2013. Medscape Web site. http://www.medscape.com/features/slideshow/compensation/2013/womenshealth. Accessed June 30, 2013.
- Reale D. Mean income for ObGyns increased in 2012. OBG Manag. 2013;25(8):34–36.
- Kane L. Employed vs self-employed: Who is better off? Medscape Web site. http://www.medscape.com/features/slideshow/public/employed-doctors. Published March 11, 2014. Accessed June 2, 2014.
HSCT regimen could be ‘transformative’ for SCD

pre-HSCT (top) and post-HSCT
Credit: NIH Molecular and
Clinical Hematology Branch
In a small study, a nonmyeloablative hematopoietic stem cell transplant (HSCT) regimen reversed sickle cell disease (SCD) phenotype in a majority of adult patients, some of whom also had thalassemia.
Half of the patients were able to stop taking immunosuppressants and did not develop graft-vs-host disease (GVHD).
There were adverse events associated with the regimen, but the researchers believe it shows promise and could be “transformative” for patients with severe SCD.
The team described the regimen and its effects in JAMA.
Matthew M. Hsieh, MD, of the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases, Bethesda, Maryland, and his colleagues first explored a nonmyeloablative HSCT approach in a pilot group of 10 adults with severe SCD.
The regimen had few toxic effects, but all patients continued taking immunosuppression medication. The researchers have since revised the protocol to include an option to stop immunosuppression after 1 year in patients with donor CD3 engraftment of greater than 50% and normalization of hemoglobin.
In JAMA, the team described the outcomes for 20 additional patients with severe SCD, with or without thalassemia, along with updated results from the first 10 patients.
All 30 patients (ages 16-65 years) were enrolled in the study from July 2004 to October 2013. Two patients had heterozygous hemoglobin S and C, 1 patient had HbSβ+-thalassemia, 1 patient had HbSβ0- thalassemia, and 1 had transfusion-dependent β-thalassemia intermedia. The remaining patients had homozygous hemoglobin S.
Patients received alemtuzumab (1mg/kg in divided doses), total-body irradiation (300 cGy), sirolimus, and an infusion of unmanipulated, filgrastim-mobilized peripheral blood stem cells (5.5-31.7 × 106 cells/kg) from HLA-matched siblings.
There were 38 serious adverse events. The most common were pain-related (n=15), transplant-related infections (n=6), abdominal events (n=6), and toxic effects associated with sirolimus (n=5).
As of October 25, 2013, 29 patients were still alive, with a median follow-up of 3.4 years. Twenty-six patients (87%) had long-term stable donor engraftment without acute or chronic GVHD.
Hemoglobin levels improved after HSCT. At 1 year, 25 patients (83%) had full donor-type hemoglobin. Fifteen engrafted patients discontinued immunosuppression medication and did not develop GVHD.
“Typically, stem cell recipients must take immunosuppressants all their lives,” Dr Hsieh noted. “That the patients who discontinued this medication were able to do so safely points to the stability of the partial transplant regimen.”
Hospitalization rates also decreased following HSCT. The average annual hospitalization rate was 3.2 the year before HSCT, 0.63 the first year after, 0.19 the second year after, and 0.11 the third year after transplant.
“One of the most debilitating effects of sickle cell disease is the often relentless pain,” Dr Hsieh pointed out. “Following the transplant, we saw a significant decrease in hospitalizations and narcotics to control that pain.”
Eleven patients were taking narcotics long-term at the time of transplant. During the week they were hospitalized and received their HSCT, the average narcotics use per week was 639 mg of intravenous morphine-equivalent dose. The dosage decreased to 140 mg at 6 months after the transplant.
“The devastating complications associated with sickle cell disease can deeply affect quality of life, ability to work, and long-term well-being,” said study author Griffin P. Rodgers, MD, director of the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases.
“This study represents an important advance in our efforts to make a potentially transformative treatment available to a wider range of people, especially those who could not tolerate a standard stem cell transplant or long-term use of immunosuppressants.” ![]()

pre-HSCT (top) and post-HSCT
Credit: NIH Molecular and
Clinical Hematology Branch
In a small study, a nonmyeloablative hematopoietic stem cell transplant (HSCT) regimen reversed sickle cell disease (SCD) phenotype in a majority of adult patients, some of whom also had thalassemia.
Half of the patients were able to stop taking immunosuppressants and did not develop graft-vs-host disease (GVHD).
There were adverse events associated with the regimen, but the researchers believe it shows promise and could be “transformative” for patients with severe SCD.
The team described the regimen and its effects in JAMA.
Matthew M. Hsieh, MD, of the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases, Bethesda, Maryland, and his colleagues first explored a nonmyeloablative HSCT approach in a pilot group of 10 adults with severe SCD.
The regimen had few toxic effects, but all patients continued taking immunosuppression medication. The researchers have since revised the protocol to include an option to stop immunosuppression after 1 year in patients with donor CD3 engraftment of greater than 50% and normalization of hemoglobin.
In JAMA, the team described the outcomes for 20 additional patients with severe SCD, with or without thalassemia, along with updated results from the first 10 patients.
All 30 patients (ages 16-65 years) were enrolled in the study from July 2004 to October 2013. Two patients had heterozygous hemoglobin S and C, 1 patient had HbSβ+-thalassemia, 1 patient had HbSβ0- thalassemia, and 1 had transfusion-dependent β-thalassemia intermedia. The remaining patients had homozygous hemoglobin S.
Patients received alemtuzumab (1mg/kg in divided doses), total-body irradiation (300 cGy), sirolimus, and an infusion of unmanipulated, filgrastim-mobilized peripheral blood stem cells (5.5-31.7 × 106 cells/kg) from HLA-matched siblings.
There were 38 serious adverse events. The most common were pain-related (n=15), transplant-related infections (n=6), abdominal events (n=6), and toxic effects associated with sirolimus (n=5).
As of October 25, 2013, 29 patients were still alive, with a median follow-up of 3.4 years. Twenty-six patients (87%) had long-term stable donor engraftment without acute or chronic GVHD.
Hemoglobin levels improved after HSCT. At 1 year, 25 patients (83%) had full donor-type hemoglobin. Fifteen engrafted patients discontinued immunosuppression medication and did not develop GVHD.
“Typically, stem cell recipients must take immunosuppressants all their lives,” Dr Hsieh noted. “That the patients who discontinued this medication were able to do so safely points to the stability of the partial transplant regimen.”
Hospitalization rates also decreased following HSCT. The average annual hospitalization rate was 3.2 the year before HSCT, 0.63 the first year after, 0.19 the second year after, and 0.11 the third year after transplant.
“One of the most debilitating effects of sickle cell disease is the often relentless pain,” Dr Hsieh pointed out. “Following the transplant, we saw a significant decrease in hospitalizations and narcotics to control that pain.”
Eleven patients were taking narcotics long-term at the time of transplant. During the week they were hospitalized and received their HSCT, the average narcotics use per week was 639 mg of intravenous morphine-equivalent dose. The dosage decreased to 140 mg at 6 months after the transplant.
“The devastating complications associated with sickle cell disease can deeply affect quality of life, ability to work, and long-term well-being,” said study author Griffin P. Rodgers, MD, director of the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases.
“This study represents an important advance in our efforts to make a potentially transformative treatment available to a wider range of people, especially those who could not tolerate a standard stem cell transplant or long-term use of immunosuppressants.” ![]()

pre-HSCT (top) and post-HSCT
Credit: NIH Molecular and
Clinical Hematology Branch
In a small study, a nonmyeloablative hematopoietic stem cell transplant (HSCT) regimen reversed sickle cell disease (SCD) phenotype in a majority of adult patients, some of whom also had thalassemia.
Half of the patients were able to stop taking immunosuppressants and did not develop graft-vs-host disease (GVHD).
There were adverse events associated with the regimen, but the researchers believe it shows promise and could be “transformative” for patients with severe SCD.
The team described the regimen and its effects in JAMA.
Matthew M. Hsieh, MD, of the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases, Bethesda, Maryland, and his colleagues first explored a nonmyeloablative HSCT approach in a pilot group of 10 adults with severe SCD.
The regimen had few toxic effects, but all patients continued taking immunosuppression medication. The researchers have since revised the protocol to include an option to stop immunosuppression after 1 year in patients with donor CD3 engraftment of greater than 50% and normalization of hemoglobin.
In JAMA, the team described the outcomes for 20 additional patients with severe SCD, with or without thalassemia, along with updated results from the first 10 patients.
All 30 patients (ages 16-65 years) were enrolled in the study from July 2004 to October 2013. Two patients had heterozygous hemoglobin S and C, 1 patient had HbSβ+-thalassemia, 1 patient had HbSβ0- thalassemia, and 1 had transfusion-dependent β-thalassemia intermedia. The remaining patients had homozygous hemoglobin S.
Patients received alemtuzumab (1mg/kg in divided doses), total-body irradiation (300 cGy), sirolimus, and an infusion of unmanipulated, filgrastim-mobilized peripheral blood stem cells (5.5-31.7 × 106 cells/kg) from HLA-matched siblings.
There were 38 serious adverse events. The most common were pain-related (n=15), transplant-related infections (n=6), abdominal events (n=6), and toxic effects associated with sirolimus (n=5).
As of October 25, 2013, 29 patients were still alive, with a median follow-up of 3.4 years. Twenty-six patients (87%) had long-term stable donor engraftment without acute or chronic GVHD.
Hemoglobin levels improved after HSCT. At 1 year, 25 patients (83%) had full donor-type hemoglobin. Fifteen engrafted patients discontinued immunosuppression medication and did not develop GVHD.
“Typically, stem cell recipients must take immunosuppressants all their lives,” Dr Hsieh noted. “That the patients who discontinued this medication were able to do so safely points to the stability of the partial transplant regimen.”
Hospitalization rates also decreased following HSCT. The average annual hospitalization rate was 3.2 the year before HSCT, 0.63 the first year after, 0.19 the second year after, and 0.11 the third year after transplant.
“One of the most debilitating effects of sickle cell disease is the often relentless pain,” Dr Hsieh pointed out. “Following the transplant, we saw a significant decrease in hospitalizations and narcotics to control that pain.”
Eleven patients were taking narcotics long-term at the time of transplant. During the week they were hospitalized and received their HSCT, the average narcotics use per week was 639 mg of intravenous morphine-equivalent dose. The dosage decreased to 140 mg at 6 months after the transplant.
“The devastating complications associated with sickle cell disease can deeply affect quality of life, ability to work, and long-term well-being,” said study author Griffin P. Rodgers, MD, director of the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases.
“This study represents an important advance in our efforts to make a potentially transformative treatment available to a wider range of people, especially those who could not tolerate a standard stem cell transplant or long-term use of immunosuppressants.” ![]()
Moving forward with ICD-10: Capitalize on this extra time
Yes, we have been here before. Another day, another delay in implementing International Classification of Diseases, Tenth Revision, Clinical Modification (ICD-10-CM). But, do not expect another postponement. If you are already conducting training sessions to move to the new system come next October, continue to do so. If you have not yet started, now is the time to start. ICD-10-CM is coming to your practice, and it will change everything.
“Why the switch?” you ask?
This change in our diagnostic coding system is required to allow coding for increased specificity in the reporting of diseases and recently recognized conditions as well as to maintain our status with respect to the rest of the world (which has been using ICD-10 for years). It also will be essential to use this coding system with the electronic medical record (EMR), so that meaningful use can be demonstrated more easily. Keep in mind that failure to show meaningful use will lead to penalties in the future. This new system offers improvements over ICD-9-CM in coding primary care encounters, external causes of injury, mental disorders, neoplasms, obstetric complications, and preventive health. It also allows physicians to demonstrate severity of illness in a way that is not possible with ICD-9-CM.
There will be 65,000 more codes than currently exist in ICD-9-CM. No physician will be able to keep all of these code numbers handy, but by making changes to clinician documentation and applying diagnostic coding guidelines correctly within the framework of the new system, the transition will not be onerous. And consider that, while the number of new codes is great, the number of codes used in the typical ObGyn practice will be a fraction of that number.
Related article: As ICD-10 conversion nears, keep these factors in mind to ensure proper reimbursements in 2014. Barbara S. Levy, MD (Audiocast, January 2014)
For ICD-10, documentation is paramount
The most important issue when considering overall coding and practice changes will be recognizing that clinician documentation will be the key to coding the highest level of specificity—and this high level of specificity may be required by most payers when deciding to reimburse for treatments rendered. Complete documentation sets the stage for the severity of illness and should in fact result in fewer denials for medical necessity.
For the new process to work efficiently, however, without a lot of delays due to coders and billers having to get more information from clinician offices before sending out claims, your understanding of and “buy-in” to the more clinically specific documentation will be essential.
To explain, under ICD-9-CM coding, simply documenting amenorrhea was acceptable. But when we switch to ICD-10-CM, documentation will need to specify whether the amenorrhea was primary or secondary. This more specific diagnostic coding will make a difference in the health statistics we collect. These data are used for research and to make decisions about allocation of resources—all essential components to excellent quality patient care.
The codes themselves will look different, which may be why some are resisting the change. Instead of the up to five digits required in ICD-9-CM, ICD-10-CM will require up to seven characters. All of the ICD-10-CM codes begin with a letter, may require a placeholder code of “x” as part of the code number, and the seventh character can be either a number or a letter. For instance, with some ICD-10-CM diagnoses reported by ObGyns, a seventh character might require documentation of the encounter as being initial, subsequent, or a sequel; in other cases, that seventh character will be used to identify which fetus has the problem identified by the diagnostic code.
Related article: The economics of surgical gynecology: How we can not only survive, but thrive, in the 21st Century. Q&A with Barbara S. Levy, MD (Practice Management; February 2013)
Your understanding, although not a necessity, is best for all involved
In truth, most clinicians are not familiar with code formats and code numbers within our current ICD-9-CM code set. The expectation that you will suddenly become fluent in ICD-10-CM “code speak” is not realistic. But an understanding of the new codes in relation to documentation expectations will go a long way to making this transition as smooth as possible. For instance, when a patient currently presents reporting vaginal pain that is found to be due to erosion of a previously placed mesh, the code 628.31 (Erosion of implanted vaginal mesh and other prosthetic materials to surrounding organ or tissue) is reported. But in ICD-10-CM, the documentation would need to include whether this was an initial encounter and the code would become T83.711A (Erosion of implanted vaginal mesh and other prosthetic materials to surrounding organ or tissue, initial encounter).
Smart search. The good news is that most EMR products will have a “smart search” program available for clinicians to pick the correct code based on the search criteria. The bad news is that you will have to be a bit more exact in the search terms you use to make the process easy. For instance, the patient has pelvic pain but you search only on the term “pain.” That term by itself will result in about 100 codes to select from, and the order of the codes may mean that the correct code for pelvic pain is 25 codes down the list. However, if you instead search on the term “pelvic pain,” the one and only code for this condition will be listed and you can simply select it and move on.
Develop cheat sheets. Health-care professionals who are not using an EMR or some sort of computerized code search program will have a harder time, but the use of multiple paper “cheat sheets” for general gynecology, family planning, surgical cases, urology, infertility, obstetrics, etc., will ease that burden. Practice management staff can develop these forms, built on the codes that are currently being reported by the clinician. Place all of the options to replace the older code on the sheet so the correct selection can be made.
For instance, if the provider previously had reported vaginitis with one code, when we move to ICD-10-CM the code would expand to four code selections based on documentation of acute vaginitis, subacute and chronic vaginitis, acute vulvitis, or subacute and chronic vulvitis. If you only had documented vaginitis in the medical record, this gives you the opportunity to refine the documentation to something more specific that supports selection of the correct code and supports the medical need for management options.
Related article: Dos, don’ts, and dollars: Making the switch to an HER. Neil H. Baum, MD; Paul Kepper, MS. (Practice Management; November 2013)
Take advantage of the extra time
Now that we have a delay in the rollout, take this time to critically examine your documentation styles, and practice selecting ICD-10-CM codes before it counts toward payment or nonpayment of a claim. When the time comes, your practice will be fluent in the new system and there will be no delays in getting claims out the door or payment due to incorrect diagnostic coding. In other words, practice makes perfect.
In fact, some ObGyn practices that were ready for the new system have decided to switch to ICD-10-CM coding as of October 1, 2014. They will code each encounter by reporting both the ICD-9-CM code and the ICD-10-CM code on the revised CMS claim form or electronic billing format that permits dual diagnostic coding. This type of experience will ensure that all physicians and other health-care professionals in the practice have ample opportunity to improve their documentation and make any adjustments before the 2015 deadline.
Related article: The 2014 CPT and Medicare code changes affecting ObGyn practice. Melanie Witt, RN, CPC, COBGC, MA (Reimbursement Adviser; January 2014)
WE WANT TO HEAR FROM YOU!
Drop us a line and let us know what you think about current articles, which topics you'd like to see covered in future issues, and what challenges you face in daily practice. Tell us what you think by emailing us at: obg@frontlinemedcom.com
Yes, we have been here before. Another day, another delay in implementing International Classification of Diseases, Tenth Revision, Clinical Modification (ICD-10-CM). But, do not expect another postponement. If you are already conducting training sessions to move to the new system come next October, continue to do so. If you have not yet started, now is the time to start. ICD-10-CM is coming to your practice, and it will change everything.
“Why the switch?” you ask?
This change in our diagnostic coding system is required to allow coding for increased specificity in the reporting of diseases and recently recognized conditions as well as to maintain our status with respect to the rest of the world (which has been using ICD-10 for years). It also will be essential to use this coding system with the electronic medical record (EMR), so that meaningful use can be demonstrated more easily. Keep in mind that failure to show meaningful use will lead to penalties in the future. This new system offers improvements over ICD-9-CM in coding primary care encounters, external causes of injury, mental disorders, neoplasms, obstetric complications, and preventive health. It also allows physicians to demonstrate severity of illness in a way that is not possible with ICD-9-CM.
There will be 65,000 more codes than currently exist in ICD-9-CM. No physician will be able to keep all of these code numbers handy, but by making changes to clinician documentation and applying diagnostic coding guidelines correctly within the framework of the new system, the transition will not be onerous. And consider that, while the number of new codes is great, the number of codes used in the typical ObGyn practice will be a fraction of that number.
Related article: As ICD-10 conversion nears, keep these factors in mind to ensure proper reimbursements in 2014. Barbara S. Levy, MD (Audiocast, January 2014)
For ICD-10, documentation is paramount
The most important issue when considering overall coding and practice changes will be recognizing that clinician documentation will be the key to coding the highest level of specificity—and this high level of specificity may be required by most payers when deciding to reimburse for treatments rendered. Complete documentation sets the stage for the severity of illness and should in fact result in fewer denials for medical necessity.
For the new process to work efficiently, however, without a lot of delays due to coders and billers having to get more information from clinician offices before sending out claims, your understanding of and “buy-in” to the more clinically specific documentation will be essential.
To explain, under ICD-9-CM coding, simply documenting amenorrhea was acceptable. But when we switch to ICD-10-CM, documentation will need to specify whether the amenorrhea was primary or secondary. This more specific diagnostic coding will make a difference in the health statistics we collect. These data are used for research and to make decisions about allocation of resources—all essential components to excellent quality patient care.
The codes themselves will look different, which may be why some are resisting the change. Instead of the up to five digits required in ICD-9-CM, ICD-10-CM will require up to seven characters. All of the ICD-10-CM codes begin with a letter, may require a placeholder code of “x” as part of the code number, and the seventh character can be either a number or a letter. For instance, with some ICD-10-CM diagnoses reported by ObGyns, a seventh character might require documentation of the encounter as being initial, subsequent, or a sequel; in other cases, that seventh character will be used to identify which fetus has the problem identified by the diagnostic code.
Related article: The economics of surgical gynecology: How we can not only survive, but thrive, in the 21st Century. Q&A with Barbara S. Levy, MD (Practice Management; February 2013)
Your understanding, although not a necessity, is best for all involved
In truth, most clinicians are not familiar with code formats and code numbers within our current ICD-9-CM code set. The expectation that you will suddenly become fluent in ICD-10-CM “code speak” is not realistic. But an understanding of the new codes in relation to documentation expectations will go a long way to making this transition as smooth as possible. For instance, when a patient currently presents reporting vaginal pain that is found to be due to erosion of a previously placed mesh, the code 628.31 (Erosion of implanted vaginal mesh and other prosthetic materials to surrounding organ or tissue) is reported. But in ICD-10-CM, the documentation would need to include whether this was an initial encounter and the code would become T83.711A (Erosion of implanted vaginal mesh and other prosthetic materials to surrounding organ or tissue, initial encounter).
Smart search. The good news is that most EMR products will have a “smart search” program available for clinicians to pick the correct code based on the search criteria. The bad news is that you will have to be a bit more exact in the search terms you use to make the process easy. For instance, the patient has pelvic pain but you search only on the term “pain.” That term by itself will result in about 100 codes to select from, and the order of the codes may mean that the correct code for pelvic pain is 25 codes down the list. However, if you instead search on the term “pelvic pain,” the one and only code for this condition will be listed and you can simply select it and move on.
Develop cheat sheets. Health-care professionals who are not using an EMR or some sort of computerized code search program will have a harder time, but the use of multiple paper “cheat sheets” for general gynecology, family planning, surgical cases, urology, infertility, obstetrics, etc., will ease that burden. Practice management staff can develop these forms, built on the codes that are currently being reported by the clinician. Place all of the options to replace the older code on the sheet so the correct selection can be made.
For instance, if the provider previously had reported vaginitis with one code, when we move to ICD-10-CM the code would expand to four code selections based on documentation of acute vaginitis, subacute and chronic vaginitis, acute vulvitis, or subacute and chronic vulvitis. If you only had documented vaginitis in the medical record, this gives you the opportunity to refine the documentation to something more specific that supports selection of the correct code and supports the medical need for management options.
Related article: Dos, don’ts, and dollars: Making the switch to an HER. Neil H. Baum, MD; Paul Kepper, MS. (Practice Management; November 2013)
Take advantage of the extra time
Now that we have a delay in the rollout, take this time to critically examine your documentation styles, and practice selecting ICD-10-CM codes before it counts toward payment or nonpayment of a claim. When the time comes, your practice will be fluent in the new system and there will be no delays in getting claims out the door or payment due to incorrect diagnostic coding. In other words, practice makes perfect.
In fact, some ObGyn practices that were ready for the new system have decided to switch to ICD-10-CM coding as of October 1, 2014. They will code each encounter by reporting both the ICD-9-CM code and the ICD-10-CM code on the revised CMS claim form or electronic billing format that permits dual diagnostic coding. This type of experience will ensure that all physicians and other health-care professionals in the practice have ample opportunity to improve their documentation and make any adjustments before the 2015 deadline.
Related article: The 2014 CPT and Medicare code changes affecting ObGyn practice. Melanie Witt, RN, CPC, COBGC, MA (Reimbursement Adviser; January 2014)
WE WANT TO HEAR FROM YOU!
Drop us a line and let us know what you think about current articles, which topics you'd like to see covered in future issues, and what challenges you face in daily practice. Tell us what you think by emailing us at: obg@frontlinemedcom.com
Yes, we have been here before. Another day, another delay in implementing International Classification of Diseases, Tenth Revision, Clinical Modification (ICD-10-CM). But, do not expect another postponement. If you are already conducting training sessions to move to the new system come next October, continue to do so. If you have not yet started, now is the time to start. ICD-10-CM is coming to your practice, and it will change everything.
“Why the switch?” you ask?
This change in our diagnostic coding system is required to allow coding for increased specificity in the reporting of diseases and recently recognized conditions as well as to maintain our status with respect to the rest of the world (which has been using ICD-10 for years). It also will be essential to use this coding system with the electronic medical record (EMR), so that meaningful use can be demonstrated more easily. Keep in mind that failure to show meaningful use will lead to penalties in the future. This new system offers improvements over ICD-9-CM in coding primary care encounters, external causes of injury, mental disorders, neoplasms, obstetric complications, and preventive health. It also allows physicians to demonstrate severity of illness in a way that is not possible with ICD-9-CM.
There will be 65,000 more codes than currently exist in ICD-9-CM. No physician will be able to keep all of these code numbers handy, but by making changes to clinician documentation and applying diagnostic coding guidelines correctly within the framework of the new system, the transition will not be onerous. And consider that, while the number of new codes is great, the number of codes used in the typical ObGyn practice will be a fraction of that number.
Related article: As ICD-10 conversion nears, keep these factors in mind to ensure proper reimbursements in 2014. Barbara S. Levy, MD (Audiocast, January 2014)
For ICD-10, documentation is paramount
The most important issue when considering overall coding and practice changes will be recognizing that clinician documentation will be the key to coding the highest level of specificity—and this high level of specificity may be required by most payers when deciding to reimburse for treatments rendered. Complete documentation sets the stage for the severity of illness and should in fact result in fewer denials for medical necessity.
For the new process to work efficiently, however, without a lot of delays due to coders and billers having to get more information from clinician offices before sending out claims, your understanding of and “buy-in” to the more clinically specific documentation will be essential.
To explain, under ICD-9-CM coding, simply documenting amenorrhea was acceptable. But when we switch to ICD-10-CM, documentation will need to specify whether the amenorrhea was primary or secondary. This more specific diagnostic coding will make a difference in the health statistics we collect. These data are used for research and to make decisions about allocation of resources—all essential components to excellent quality patient care.
The codes themselves will look different, which may be why some are resisting the change. Instead of the up to five digits required in ICD-9-CM, ICD-10-CM will require up to seven characters. All of the ICD-10-CM codes begin with a letter, may require a placeholder code of “x” as part of the code number, and the seventh character can be either a number or a letter. For instance, with some ICD-10-CM diagnoses reported by ObGyns, a seventh character might require documentation of the encounter as being initial, subsequent, or a sequel; in other cases, that seventh character will be used to identify which fetus has the problem identified by the diagnostic code.
Related article: The economics of surgical gynecology: How we can not only survive, but thrive, in the 21st Century. Q&A with Barbara S. Levy, MD (Practice Management; February 2013)
Your understanding, although not a necessity, is best for all involved
In truth, most clinicians are not familiar with code formats and code numbers within our current ICD-9-CM code set. The expectation that you will suddenly become fluent in ICD-10-CM “code speak” is not realistic. But an understanding of the new codes in relation to documentation expectations will go a long way to making this transition as smooth as possible. For instance, when a patient currently presents reporting vaginal pain that is found to be due to erosion of a previously placed mesh, the code 628.31 (Erosion of implanted vaginal mesh and other prosthetic materials to surrounding organ or tissue) is reported. But in ICD-10-CM, the documentation would need to include whether this was an initial encounter and the code would become T83.711A (Erosion of implanted vaginal mesh and other prosthetic materials to surrounding organ or tissue, initial encounter).
Smart search. The good news is that most EMR products will have a “smart search” program available for clinicians to pick the correct code based on the search criteria. The bad news is that you will have to be a bit more exact in the search terms you use to make the process easy. For instance, the patient has pelvic pain but you search only on the term “pain.” That term by itself will result in about 100 codes to select from, and the order of the codes may mean that the correct code for pelvic pain is 25 codes down the list. However, if you instead search on the term “pelvic pain,” the one and only code for this condition will be listed and you can simply select it and move on.
Develop cheat sheets. Health-care professionals who are not using an EMR or some sort of computerized code search program will have a harder time, but the use of multiple paper “cheat sheets” for general gynecology, family planning, surgical cases, urology, infertility, obstetrics, etc., will ease that burden. Practice management staff can develop these forms, built on the codes that are currently being reported by the clinician. Place all of the options to replace the older code on the sheet so the correct selection can be made.
For instance, if the provider previously had reported vaginitis with one code, when we move to ICD-10-CM the code would expand to four code selections based on documentation of acute vaginitis, subacute and chronic vaginitis, acute vulvitis, or subacute and chronic vulvitis. If you only had documented vaginitis in the medical record, this gives you the opportunity to refine the documentation to something more specific that supports selection of the correct code and supports the medical need for management options.
Related article: Dos, don’ts, and dollars: Making the switch to an HER. Neil H. Baum, MD; Paul Kepper, MS. (Practice Management; November 2013)
Take advantage of the extra time
Now that we have a delay in the rollout, take this time to critically examine your documentation styles, and practice selecting ICD-10-CM codes before it counts toward payment or nonpayment of a claim. When the time comes, your practice will be fluent in the new system and there will be no delays in getting claims out the door or payment due to incorrect diagnostic coding. In other words, practice makes perfect.
In fact, some ObGyn practices that were ready for the new system have decided to switch to ICD-10-CM coding as of October 1, 2014. They will code each encounter by reporting both the ICD-9-CM code and the ICD-10-CM code on the revised CMS claim form or electronic billing format that permits dual diagnostic coding. This type of experience will ensure that all physicians and other health-care professionals in the practice have ample opportunity to improve their documentation and make any adjustments before the 2015 deadline.
Related article: The 2014 CPT and Medicare code changes affecting ObGyn practice. Melanie Witt, RN, CPC, COBGC, MA (Reimbursement Adviser; January 2014)
WE WANT TO HEAR FROM YOU!
Drop us a line and let us know what you think about current articles, which topics you'd like to see covered in future issues, and what challenges you face in daily practice. Tell us what you think by emailing us at: obg@frontlinemedcom.com
Nature retracts STAP cell papers
Credit: Haruko Obokata
The journal Nature has retracted the papers it published several months ago on stimulus-triggered acquisition of pluripotency (STAP) cells.
In January, Nature published an article and a letter in which researchers claimed they could create STAP cells—ie, induce pluripotency in somatic cells by exposing them to a low-pH environment.
Not long after the papers were published, however, members of the scientific community began to question the validity of the research.
They voiced concerns about published images, possible plagiarism, and an inability to replicate the experiments described.
So the Japanese institute RIKEN, where most of the study’s investigators are employed, launched an investigation.
In April, RIKEN’s investigative committee concluded that lead study author Haruko Obokata, PhD, and some of her colleagues were guilty of misconduct and/or negligence.
Dr Obokata appealed the findings, saying the acts of misconduct were simply mistakes and that STAP cells do exist.
But the committee decided another investigation is not warranted, and RIKEN called for a retraction of the Nature papers.
Today, Nature published the retractions, which can be viewed here and here. An editorial on the subject is available here.
As for the future of STAP cells, RIKEN is currently attempting to recreate Dr Obokata’s experiments and determine if the cells do exist. The organization plans to release an interim report on this attempt in late July or early August.
Other researchers said they have tried and failed to replicate Dr Obokata’s experiments. One group detailed their failed attempt in F1000Research. ![]()

Credit: Haruko Obokata
The journal Nature has retracted the papers it published several months ago on stimulus-triggered acquisition of pluripotency (STAP) cells.
In January, Nature published an article and a letter in which researchers claimed they could create STAP cells—ie, induce pluripotency in somatic cells by exposing them to a low-pH environment.
Not long after the papers were published, however, members of the scientific community began to question the validity of the research.
They voiced concerns about published images, possible plagiarism, and an inability to replicate the experiments described.
So the Japanese institute RIKEN, where most of the study’s investigators are employed, launched an investigation.
In April, RIKEN’s investigative committee concluded that lead study author Haruko Obokata, PhD, and some of her colleagues were guilty of misconduct and/or negligence.
Dr Obokata appealed the findings, saying the acts of misconduct were simply mistakes and that STAP cells do exist.
But the committee decided another investigation is not warranted, and RIKEN called for a retraction of the Nature papers.
Today, Nature published the retractions, which can be viewed here and here. An editorial on the subject is available here.
As for the future of STAP cells, RIKEN is currently attempting to recreate Dr Obokata’s experiments and determine if the cells do exist. The organization plans to release an interim report on this attempt in late July or early August.
Other researchers said they have tried and failed to replicate Dr Obokata’s experiments. One group detailed their failed attempt in F1000Research. ![]()

Credit: Haruko Obokata
The journal Nature has retracted the papers it published several months ago on stimulus-triggered acquisition of pluripotency (STAP) cells.
In January, Nature published an article and a letter in which researchers claimed they could create STAP cells—ie, induce pluripotency in somatic cells by exposing them to a low-pH environment.
Not long after the papers were published, however, members of the scientific community began to question the validity of the research.
They voiced concerns about published images, possible plagiarism, and an inability to replicate the experiments described.
So the Japanese institute RIKEN, where most of the study’s investigators are employed, launched an investigation.
In April, RIKEN’s investigative committee concluded that lead study author Haruko Obokata, PhD, and some of her colleagues were guilty of misconduct and/or negligence.
Dr Obokata appealed the findings, saying the acts of misconduct were simply mistakes and that STAP cells do exist.
But the committee decided another investigation is not warranted, and RIKEN called for a retraction of the Nature papers.
Today, Nature published the retractions, which can be viewed here and here. An editorial on the subject is available here.
As for the future of STAP cells, RIKEN is currently attempting to recreate Dr Obokata’s experiments and determine if the cells do exist. The organization plans to release an interim report on this attempt in late July or early August.
Other researchers said they have tried and failed to replicate Dr Obokata’s experiments. One group detailed their failed attempt in F1000Research. ![]()
Company recalls lots of warfarin
Bristol-Myers Squibb has announced a recall of 6 lots of the anticoagulant warfarin, sold as Coumadin for Injection in 5 mg single-use vials, in the US.
The company is recalling these lots after discovering visible particulate matter in unreleased samples of the drug.
The company said the safety risk to patients is likely low and is further mitigated by the product’s prescribing information, which advises that intravenous products be inspected visually before administration.
However, injected particulate metallic and non-metallic cellulose material can cause serious and potentially fatal adverse reactions, such as embolization. Allergic reactions to the foreign material could also occur.
To date, there have been no product complaints or adverse events reported to Bristol-Myers Squibb related to particulate matter in Coumadin for Injection.
Coumadin for Injection was discontinued in early April 2014. The oral formulation of Coumadin is not impacted by this recall.
Coumadin for Injection is packaged in cartons of six 5-mg single-use vials. The affected product includes the following 6 lots distributed to hospitals and pharmacies from November 2011 through January 2014:
Lot # Description NDC Expiration
201125 COUMADIN LINJ 5MG (6VL) US 0590-0324-35 Sept. 2014
201126 COUMADIN LINJ 5MG (6VL) US 0590-0324-35 Nov. 2014
201127 COUMADIN LINJ 5MG (6VL) US 0590-0324-35 Dec. 2014
201228 COUMADIN LINJ 5MG (6VL) US 0590-0324-35 June 2015
201229 COUMADIN LINJ 5MG (6VL) US 0590-0324-35 July 2015
201230 COUMADIN LINJ 5MG (6VL) US 0590-0324-35 Sept. 2015
Anyone with the aforementioned lots of Coumadin for Injection should stop using or distributing the product and contact Bristol-Myers Squibb’s recall vendor, GENCO, at 1-855-838-5784 to arrange for the return of remaining stock.
Customers with questions about the recall may contact the Bristol-Myers Squibb Customer Information Center at 1-800-332-2056.
Adverse reactions or quality problems associated with the use of this product can be reported to the FDA’s MedWatch Adverse Event Reporting Program. ![]()

Bristol-Myers Squibb has announced a recall of 6 lots of the anticoagulant warfarin, sold as Coumadin for Injection in 5 mg single-use vials, in the US.
The company is recalling these lots after discovering visible particulate matter in unreleased samples of the drug.
The company said the safety risk to patients is likely low and is further mitigated by the product’s prescribing information, which advises that intravenous products be inspected visually before administration.
However, injected particulate metallic and non-metallic cellulose material can cause serious and potentially fatal adverse reactions, such as embolization. Allergic reactions to the foreign material could also occur.
To date, there have been no product complaints or adverse events reported to Bristol-Myers Squibb related to particulate matter in Coumadin for Injection.
Coumadin for Injection was discontinued in early April 2014. The oral formulation of Coumadin is not impacted by this recall.
Coumadin for Injection is packaged in cartons of six 5-mg single-use vials. The affected product includes the following 6 lots distributed to hospitals and pharmacies from November 2011 through January 2014:
Lot # Description NDC Expiration
201125 COUMADIN LINJ 5MG (6VL) US 0590-0324-35 Sept. 2014
201126 COUMADIN LINJ 5MG (6VL) US 0590-0324-35 Nov. 2014
201127 COUMADIN LINJ 5MG (6VL) US 0590-0324-35 Dec. 2014
201228 COUMADIN LINJ 5MG (6VL) US 0590-0324-35 June 2015
201229 COUMADIN LINJ 5MG (6VL) US 0590-0324-35 July 2015
201230 COUMADIN LINJ 5MG (6VL) US 0590-0324-35 Sept. 2015
Anyone with the aforementioned lots of Coumadin for Injection should stop using or distributing the product and contact Bristol-Myers Squibb’s recall vendor, GENCO, at 1-855-838-5784 to arrange for the return of remaining stock.
Customers with questions about the recall may contact the Bristol-Myers Squibb Customer Information Center at 1-800-332-2056.
Adverse reactions or quality problems associated with the use of this product can be reported to the FDA’s MedWatch Adverse Event Reporting Program. ![]()

Bristol-Myers Squibb has announced a recall of 6 lots of the anticoagulant warfarin, sold as Coumadin for Injection in 5 mg single-use vials, in the US.
The company is recalling these lots after discovering visible particulate matter in unreleased samples of the drug.
The company said the safety risk to patients is likely low and is further mitigated by the product’s prescribing information, which advises that intravenous products be inspected visually before administration.
However, injected particulate metallic and non-metallic cellulose material can cause serious and potentially fatal adverse reactions, such as embolization. Allergic reactions to the foreign material could also occur.
To date, there have been no product complaints or adverse events reported to Bristol-Myers Squibb related to particulate matter in Coumadin for Injection.
Coumadin for Injection was discontinued in early April 2014. The oral formulation of Coumadin is not impacted by this recall.
Coumadin for Injection is packaged in cartons of six 5-mg single-use vials. The affected product includes the following 6 lots distributed to hospitals and pharmacies from November 2011 through January 2014:
Lot # Description NDC Expiration
201125 COUMADIN LINJ 5MG (6VL) US 0590-0324-35 Sept. 2014
201126 COUMADIN LINJ 5MG (6VL) US 0590-0324-35 Nov. 2014
201127 COUMADIN LINJ 5MG (6VL) US 0590-0324-35 Dec. 2014
201228 COUMADIN LINJ 5MG (6VL) US 0590-0324-35 June 2015
201229 COUMADIN LINJ 5MG (6VL) US 0590-0324-35 July 2015
201230 COUMADIN LINJ 5MG (6VL) US 0590-0324-35 Sept. 2015
Anyone with the aforementioned lots of Coumadin for Injection should stop using or distributing the product and contact Bristol-Myers Squibb’s recall vendor, GENCO, at 1-855-838-5784 to arrange for the return of remaining stock.
Customers with questions about the recall may contact the Bristol-Myers Squibb Customer Information Center at 1-800-332-2056.
Adverse reactions or quality problems associated with the use of this product can be reported to the FDA’s MedWatch Adverse Event Reporting Program. ![]()
Phase 2 results lead to breakthrough designation
The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has granted the bispecific antibody blinatumomab breakthrough designation for the treatment of adults with relapsed or refractory B-precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia (B-ALL).
The decision was based on promising results of a phase 2 trial, which were presented at the 50th Annual Meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO) and the 19th Congress of the European Hematology Association (EHA).
According to the FDA, breakthrough designation is intended to expedite the development and review of drugs for serious or life-threatening conditions.
For a treatment to receive this designation, there must be preliminary clinical evidence suggesting the drug may offer substantial improvement over currently available therapy on at least one clinically significant endpoint.
Trial results
Nicola Gökbuget, MD, of Goethe University in Frankfurt, Germany, and Max Topp, MD, of the University of Wuerzberg in Germany, presented phase 2 results with blinatumomab at the EHA Congress as abstracts S1314 and S722. The trial was sponsored by Amgen, the company developing blinatumomab.
“Blinatumomab is a bispecific antibody which has two parts,” Dr Gökbuget noted. “With one part—the CD3 part—it attracts T cells, and with the other part, it binds to CD19. And CD19 is a target available on the vast majority of B-precursor ALL blast cells.”
To test this mechanism, Dr Gökbuget and her colleagues evaluated blinatumomab monotherapy in 189 patients with relapsed or refractory B-ALL and a median age of 39 (range, 18-79).
The patients received blinatumomab by continuous intravenous infusion—4 weeks on and 2 weeks off—for up to 5 cycles.
Safety
Dr Gökbuget noted that major toxicities were related to cytokine release syndrome—for example, fever and headache—but cytopenias were also common.
“Another side effect observed with this compound—and this is something seen often with other T-cell therapies—was [central nervous system] events,” she added.
The most frequent adverse events (AEs) were pyrexia (59%), headache (35%) and febrile neutropenia (29%). The most frequent grade 3 or higher AEs were febrile neutropenia (26%), anemia (15%), and neutropenia (15%). Two percent of patients had grade 3 or higher cytokine release syndrome.
The most common grade 3 or higher nervous system AEs were headache (4%), encephalopathy (3%), and ataxia (2%). Three patients (2%) had grade 5 AEs considered treatment-related—2 with sepsis and 1 with Candida infection.
Efficacy
The study’s primary endpoint was complete remission (CR) or CR with partial hematologic recovery (CRh) within the first 2 cycles.
An exploratory endpoint was minimal residual disease (MRD) response (<10-4) within the first 2 cycles. If a patient was MRD-negative, he was classified as having a complete MRD response.
In all, 43% (81/189) of patients achieved a CR/CRh within 2 cycles of therapy. Thirty-three percent (63/189) achieved a CR, and 9% (18/189) achieved a CRh.
Eighty-two percent (60/73) of patients with a CR/CRh who were evaluable for an MRD assessment achieved an MRD response. This included 86% (50/58) of CR patients and 67% (10/15) of CRh patients. Seventy-one percent (51/73) of patients with CR/CRh had a complete MRD response.
The median relapse-free survival was 5.9 months.
“So to conclude, we have observed considerable antileukemic activity for this single-drug therapy,” Dr Gökbuget said. “We have to keep in mind this is a single drug, and, usually, these patients receive many different chemotherapy compounds.”
“Also, although these patients were poorly selected, this is, so far, the largest trial in adult ALL where standardized PCR-based MRD detection was tested in the relapsed setting. So these data will be very important.” ![]()
The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has granted the bispecific antibody blinatumomab breakthrough designation for the treatment of adults with relapsed or refractory B-precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia (B-ALL).
The decision was based on promising results of a phase 2 trial, which were presented at the 50th Annual Meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO) and the 19th Congress of the European Hematology Association (EHA).
According to the FDA, breakthrough designation is intended to expedite the development and review of drugs for serious or life-threatening conditions.
For a treatment to receive this designation, there must be preliminary clinical evidence suggesting the drug may offer substantial improvement over currently available therapy on at least one clinically significant endpoint.
Trial results
Nicola Gökbuget, MD, of Goethe University in Frankfurt, Germany, and Max Topp, MD, of the University of Wuerzberg in Germany, presented phase 2 results with blinatumomab at the EHA Congress as abstracts S1314 and S722. The trial was sponsored by Amgen, the company developing blinatumomab.
“Blinatumomab is a bispecific antibody which has two parts,” Dr Gökbuget noted. “With one part—the CD3 part—it attracts T cells, and with the other part, it binds to CD19. And CD19 is a target available on the vast majority of B-precursor ALL blast cells.”
To test this mechanism, Dr Gökbuget and her colleagues evaluated blinatumomab monotherapy in 189 patients with relapsed or refractory B-ALL and a median age of 39 (range, 18-79).
The patients received blinatumomab by continuous intravenous infusion—4 weeks on and 2 weeks off—for up to 5 cycles.
Safety
Dr Gökbuget noted that major toxicities were related to cytokine release syndrome—for example, fever and headache—but cytopenias were also common.
“Another side effect observed with this compound—and this is something seen often with other T-cell therapies—was [central nervous system] events,” she added.
The most frequent adverse events (AEs) were pyrexia (59%), headache (35%) and febrile neutropenia (29%). The most frequent grade 3 or higher AEs were febrile neutropenia (26%), anemia (15%), and neutropenia (15%). Two percent of patients had grade 3 or higher cytokine release syndrome.
The most common grade 3 or higher nervous system AEs were headache (4%), encephalopathy (3%), and ataxia (2%). Three patients (2%) had grade 5 AEs considered treatment-related—2 with sepsis and 1 with Candida infection.
Efficacy
The study’s primary endpoint was complete remission (CR) or CR with partial hematologic recovery (CRh) within the first 2 cycles.
An exploratory endpoint was minimal residual disease (MRD) response (<10-4) within the first 2 cycles. If a patient was MRD-negative, he was classified as having a complete MRD response.
In all, 43% (81/189) of patients achieved a CR/CRh within 2 cycles of therapy. Thirty-three percent (63/189) achieved a CR, and 9% (18/189) achieved a CRh.
Eighty-two percent (60/73) of patients with a CR/CRh who were evaluable for an MRD assessment achieved an MRD response. This included 86% (50/58) of CR patients and 67% (10/15) of CRh patients. Seventy-one percent (51/73) of patients with CR/CRh had a complete MRD response.
The median relapse-free survival was 5.9 months.
“So to conclude, we have observed considerable antileukemic activity for this single-drug therapy,” Dr Gökbuget said. “We have to keep in mind this is a single drug, and, usually, these patients receive many different chemotherapy compounds.”
“Also, although these patients were poorly selected, this is, so far, the largest trial in adult ALL where standardized PCR-based MRD detection was tested in the relapsed setting. So these data will be very important.” ![]()
The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has granted the bispecific antibody blinatumomab breakthrough designation for the treatment of adults with relapsed or refractory B-precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia (B-ALL).
The decision was based on promising results of a phase 2 trial, which were presented at the 50th Annual Meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO) and the 19th Congress of the European Hematology Association (EHA).
According to the FDA, breakthrough designation is intended to expedite the development and review of drugs for serious or life-threatening conditions.
For a treatment to receive this designation, there must be preliminary clinical evidence suggesting the drug may offer substantial improvement over currently available therapy on at least one clinically significant endpoint.
Trial results
Nicola Gökbuget, MD, of Goethe University in Frankfurt, Germany, and Max Topp, MD, of the University of Wuerzberg in Germany, presented phase 2 results with blinatumomab at the EHA Congress as abstracts S1314 and S722. The trial was sponsored by Amgen, the company developing blinatumomab.
“Blinatumomab is a bispecific antibody which has two parts,” Dr Gökbuget noted. “With one part—the CD3 part—it attracts T cells, and with the other part, it binds to CD19. And CD19 is a target available on the vast majority of B-precursor ALL blast cells.”
To test this mechanism, Dr Gökbuget and her colleagues evaluated blinatumomab monotherapy in 189 patients with relapsed or refractory B-ALL and a median age of 39 (range, 18-79).
The patients received blinatumomab by continuous intravenous infusion—4 weeks on and 2 weeks off—for up to 5 cycles.
Safety
Dr Gökbuget noted that major toxicities were related to cytokine release syndrome—for example, fever and headache—but cytopenias were also common.
“Another side effect observed with this compound—and this is something seen often with other T-cell therapies—was [central nervous system] events,” she added.
The most frequent adverse events (AEs) were pyrexia (59%), headache (35%) and febrile neutropenia (29%). The most frequent grade 3 or higher AEs were febrile neutropenia (26%), anemia (15%), and neutropenia (15%). Two percent of patients had grade 3 or higher cytokine release syndrome.
The most common grade 3 or higher nervous system AEs were headache (4%), encephalopathy (3%), and ataxia (2%). Three patients (2%) had grade 5 AEs considered treatment-related—2 with sepsis and 1 with Candida infection.
Efficacy
The study’s primary endpoint was complete remission (CR) or CR with partial hematologic recovery (CRh) within the first 2 cycles.
An exploratory endpoint was minimal residual disease (MRD) response (<10-4) within the first 2 cycles. If a patient was MRD-negative, he was classified as having a complete MRD response.
In all, 43% (81/189) of patients achieved a CR/CRh within 2 cycles of therapy. Thirty-three percent (63/189) achieved a CR, and 9% (18/189) achieved a CRh.
Eighty-two percent (60/73) of patients with a CR/CRh who were evaluable for an MRD assessment achieved an MRD response. This included 86% (50/58) of CR patients and 67% (10/15) of CRh patients. Seventy-one percent (51/73) of patients with CR/CRh had a complete MRD response.
The median relapse-free survival was 5.9 months.
“So to conclude, we have observed considerable antileukemic activity for this single-drug therapy,” Dr Gökbuget said. “We have to keep in mind this is a single drug, and, usually, these patients receive many different chemotherapy compounds.”
“Also, although these patients were poorly selected, this is, so far, the largest trial in adult ALL where standardized PCR-based MRD detection was tested in the relapsed setting. So these data will be very important.” ![]()
LISTEN NOW: Highlights of the July 2014 issue of The Hospitalist newsmagazine
Highlights from The Hospitalist this month include hospitalist reactions to the once-again delayed implementation of the coding classification system ICD-10. Robert Tennant, senior policy advisor at Medical Group Management Association, shares his organization’s perspective on the postponement. Dr. Amy Boutwell, a hospitalist at Newton-Wellesley Hospital and president of Collaborative Healthcare Strategies, discusses Medicare’s new hospital discharge rules and the opportunity they hold for hospitalists. Elsewhere in this issue, we have an update on SHM’s Leadership Academy scheduled for November 3–6 in Honolulu, Hawaii, and the latest in clinical research, including a review of best practices for end-of-life care and when to suspect Kawasaki disease in infants.
Highlights from The Hospitalist this month include hospitalist reactions to the once-again delayed implementation of the coding classification system ICD-10. Robert Tennant, senior policy advisor at Medical Group Management Association, shares his organization’s perspective on the postponement. Dr. Amy Boutwell, a hospitalist at Newton-Wellesley Hospital and president of Collaborative Healthcare Strategies, discusses Medicare’s new hospital discharge rules and the opportunity they hold for hospitalists. Elsewhere in this issue, we have an update on SHM’s Leadership Academy scheduled for November 3–6 in Honolulu, Hawaii, and the latest in clinical research, including a review of best practices for end-of-life care and when to suspect Kawasaki disease in infants.
Highlights from The Hospitalist this month include hospitalist reactions to the once-again delayed implementation of the coding classification system ICD-10. Robert Tennant, senior policy advisor at Medical Group Management Association, shares his organization’s perspective on the postponement. Dr. Amy Boutwell, a hospitalist at Newton-Wellesley Hospital and president of Collaborative Healthcare Strategies, discusses Medicare’s new hospital discharge rules and the opportunity they hold for hospitalists. Elsewhere in this issue, we have an update on SHM’s Leadership Academy scheduled for November 3–6 in Honolulu, Hawaii, and the latest in clinical research, including a review of best practices for end-of-life care and when to suspect Kawasaki disease in infants.
SHM Fellow in Hospital Medicine Spotlight: Rachel George MD, MBA, SFHM
Dr. George is president of the central business unit for Brentwood, Tenn.-based Cogent Healthcare, the largest privately held hospital medicine company in the United States. She oversees multiple HM programs in the north central region of the U.S. Previously, she was medical director of hospitalist services for OSF St. Anthony Medical Center in Rockford, Ill.
Undergraduate education: Dr. George went straight from high school to a direct medical program and earned her MBA at the University of Tennessee in Knoxville.
Medical school: JJM Medical College in India.
Notable: She began her MBA at the University of Tennessee when she was 34 weeks pregnant, proving wrong the professors who thought she would not be able to finish the program. Actively involved in the SHM Leadership, RIV, and Annual Meeting committees, Dr. George is a frequent annual meeting presenter on women’s workforce issues.
FYI: Dr. George keeps busy with her two children, ages 15 and 9, supporting them in such extra-curricular pursuits as marching band, music lessons, tae kwon do, and chess. In her downtime, she likes to relax by watching movies and spending time with friends.
Quotable: “It is a tremendous honor to be a Fellow in Hospital Medicine; it demonstrates clearly to everyone my accomplishments as a hospitalist, and I am proud to have been a member of the inaugural class of fellows.”
Dr. George is president of the central business unit for Brentwood, Tenn.-based Cogent Healthcare, the largest privately held hospital medicine company in the United States. She oversees multiple HM programs in the north central region of the U.S. Previously, she was medical director of hospitalist services for OSF St. Anthony Medical Center in Rockford, Ill.
Undergraduate education: Dr. George went straight from high school to a direct medical program and earned her MBA at the University of Tennessee in Knoxville.
Medical school: JJM Medical College in India.
Notable: She began her MBA at the University of Tennessee when she was 34 weeks pregnant, proving wrong the professors who thought she would not be able to finish the program. Actively involved in the SHM Leadership, RIV, and Annual Meeting committees, Dr. George is a frequent annual meeting presenter on women’s workforce issues.
FYI: Dr. George keeps busy with her two children, ages 15 and 9, supporting them in such extra-curricular pursuits as marching band, music lessons, tae kwon do, and chess. In her downtime, she likes to relax by watching movies and spending time with friends.
Quotable: “It is a tremendous honor to be a Fellow in Hospital Medicine; it demonstrates clearly to everyone my accomplishments as a hospitalist, and I am proud to have been a member of the inaugural class of fellows.”
Dr. George is president of the central business unit for Brentwood, Tenn.-based Cogent Healthcare, the largest privately held hospital medicine company in the United States. She oversees multiple HM programs in the north central region of the U.S. Previously, she was medical director of hospitalist services for OSF St. Anthony Medical Center in Rockford, Ill.
Undergraduate education: Dr. George went straight from high school to a direct medical program and earned her MBA at the University of Tennessee in Knoxville.
Medical school: JJM Medical College in India.
Notable: She began her MBA at the University of Tennessee when she was 34 weeks pregnant, proving wrong the professors who thought she would not be able to finish the program. Actively involved in the SHM Leadership, RIV, and Annual Meeting committees, Dr. George is a frequent annual meeting presenter on women’s workforce issues.
FYI: Dr. George keeps busy with her two children, ages 15 and 9, supporting them in such extra-curricular pursuits as marching band, music lessons, tae kwon do, and chess. In her downtime, she likes to relax by watching movies and spending time with friends.
Quotable: “It is a tremendous honor to be a Fellow in Hospital Medicine; it demonstrates clearly to everyone my accomplishments as a hospitalist, and I am proud to have been a member of the inaugural class of fellows.”
Professional Dress Code Helps Physicians Earn Patient Confidence, Trust
Our large hospitalist group (22 FTEs) just implemented a dress code that requires the men to wear a tie at all times while seeing patients, even on weekends. In this era of many businesses allowing their workers to dress more casually, do you think it is necessary for doctors to always dress so formally?
—Samir in Seattle
Dr. Hospitalist responds:
You bring up an interesting topic, one that causes dissention in most large HM groups and has many roots: age, gender, professionalism, cleanliness, and culture are just a few. After all, it was Hippocrates who said a physician should be “clean in person, well-dressed, and anointed with sweet-smelling unguents.” Of course, Mrs. Smith’s allergies have forced us to get rid of the “unguents.”
Since the late 19th century, traditional (predominantly male) physician attire has been a white coat with formal suit or shirt and tie. The major push for a more professional look was medicine’s movement out of the realm of quackery and into the theatre of science. Once germs were found to be the cause of many of the illnesses responsible for killing people, the white coat and professional look came to represent cleanliness and authority. Who can forget the famous paintings of the late 19th century, such as “The Agnew Clinic,” which depicted surgeons operating with white smocks and the amphitheater full of medical students in three-piece suits?
Still, the physician most people picture (especially in the U.S.) wears the white coat with a shirt and tie if male, or a dress if she is female. More recently, television has anointed scrubs as the official attire of all hospital-based physicians, even though many institutions outlaw them outside of the operating room.
Many businesses in the U.S. allow less formal dress at work (i.e., casual Fridays). And the chorus sings: We are not in business; we are members of a profession! We take an oath to distinguish ourselves and espouse a standard of professionalism that is necessary to earn the trust of patients. As hospitalists, we typically don’t have established relationships with our patients, and those first impressions are priceless.
The U.K. prohibited wristwatches, long sleeves (including white coats), and dangling ties in 2007. Even though there was no epidemiological evidence to support such a move, the public saw physicians as carriers of infectious bugs. As international travel makes our world smaller, vancomycin-resistant enterococci, methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus, Klebsiella pneumoniae Carbapenemase, and Clostridium difficile are increasingly prevalent and virulent in the hospital. Who can blame a suspicious public? I can’t.
Many of our patients grew up in an era when anyone flying by commercial air dressed in their Sunday best. It meant you were important or doing something important, and physicians have traditionally dressed the part. Most of our hospitalized patients today are older and more likely to prefer a physician in professional attire.
But who can forget the uproar in 2004, when an Israeli medical student tested the neckties of doctors and clinical staff at the New York Hospital Medical Center of Queens and found that nearly 50% were infested with potentially pathogenic bacteria. Most of organized medicine didn’t give the study much credence, because there was no evidence that the ties were directly tied to disease and most of the organisms were fairly ubiquitous.
Authors of a study published in The American Journal of Medicine in 2005 explored the impact of physician attire on patient confidence. Four hundred patients and visitors to a VA clinic were shown four sets of photos of doctors in different forms of attire (i.e., business attire, professional attire, scrubs, and T-shirts with jeans). Across all respondents, 76% of people chose the doctor in professional attire, followed by scrubs (10%), and business dress (9%).
I’m historically a very conservative dresser, and my bowties allow me the luxury of being “above” the tie fracas; however, I do like scrubs on the weekends, attire that is allowed in our system-wide dress code. I don’t think jeans and T-shirts are ever appropriate for seeing patients in the hospital.
The most important consideration, one that will evolve with the ages, is how our attire influences patient confidence and trust.
Our large hospitalist group (22 FTEs) just implemented a dress code that requires the men to wear a tie at all times while seeing patients, even on weekends. In this era of many businesses allowing their workers to dress more casually, do you think it is necessary for doctors to always dress so formally?
—Samir in Seattle
Dr. Hospitalist responds:
You bring up an interesting topic, one that causes dissention in most large HM groups and has many roots: age, gender, professionalism, cleanliness, and culture are just a few. After all, it was Hippocrates who said a physician should be “clean in person, well-dressed, and anointed with sweet-smelling unguents.” Of course, Mrs. Smith’s allergies have forced us to get rid of the “unguents.”
Since the late 19th century, traditional (predominantly male) physician attire has been a white coat with formal suit or shirt and tie. The major push for a more professional look was medicine’s movement out of the realm of quackery and into the theatre of science. Once germs were found to be the cause of many of the illnesses responsible for killing people, the white coat and professional look came to represent cleanliness and authority. Who can forget the famous paintings of the late 19th century, such as “The Agnew Clinic,” which depicted surgeons operating with white smocks and the amphitheater full of medical students in three-piece suits?
Still, the physician most people picture (especially in the U.S.) wears the white coat with a shirt and tie if male, or a dress if she is female. More recently, television has anointed scrubs as the official attire of all hospital-based physicians, even though many institutions outlaw them outside of the operating room.
Many businesses in the U.S. allow less formal dress at work (i.e., casual Fridays). And the chorus sings: We are not in business; we are members of a profession! We take an oath to distinguish ourselves and espouse a standard of professionalism that is necessary to earn the trust of patients. As hospitalists, we typically don’t have established relationships with our patients, and those first impressions are priceless.
The U.K. prohibited wristwatches, long sleeves (including white coats), and dangling ties in 2007. Even though there was no epidemiological evidence to support such a move, the public saw physicians as carriers of infectious bugs. As international travel makes our world smaller, vancomycin-resistant enterococci, methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus, Klebsiella pneumoniae Carbapenemase, and Clostridium difficile are increasingly prevalent and virulent in the hospital. Who can blame a suspicious public? I can’t.
Many of our patients grew up in an era when anyone flying by commercial air dressed in their Sunday best. It meant you were important or doing something important, and physicians have traditionally dressed the part. Most of our hospitalized patients today are older and more likely to prefer a physician in professional attire.
But who can forget the uproar in 2004, when an Israeli medical student tested the neckties of doctors and clinical staff at the New York Hospital Medical Center of Queens and found that nearly 50% were infested with potentially pathogenic bacteria. Most of organized medicine didn’t give the study much credence, because there was no evidence that the ties were directly tied to disease and most of the organisms were fairly ubiquitous.
Authors of a study published in The American Journal of Medicine in 2005 explored the impact of physician attire on patient confidence. Four hundred patients and visitors to a VA clinic were shown four sets of photos of doctors in different forms of attire (i.e., business attire, professional attire, scrubs, and T-shirts with jeans). Across all respondents, 76% of people chose the doctor in professional attire, followed by scrubs (10%), and business dress (9%).
I’m historically a very conservative dresser, and my bowties allow me the luxury of being “above” the tie fracas; however, I do like scrubs on the weekends, attire that is allowed in our system-wide dress code. I don’t think jeans and T-shirts are ever appropriate for seeing patients in the hospital.
The most important consideration, one that will evolve with the ages, is how our attire influences patient confidence and trust.
Our large hospitalist group (22 FTEs) just implemented a dress code that requires the men to wear a tie at all times while seeing patients, even on weekends. In this era of many businesses allowing their workers to dress more casually, do you think it is necessary for doctors to always dress so formally?
—Samir in Seattle
Dr. Hospitalist responds:
You bring up an interesting topic, one that causes dissention in most large HM groups and has many roots: age, gender, professionalism, cleanliness, and culture are just a few. After all, it was Hippocrates who said a physician should be “clean in person, well-dressed, and anointed with sweet-smelling unguents.” Of course, Mrs. Smith’s allergies have forced us to get rid of the “unguents.”
Since the late 19th century, traditional (predominantly male) physician attire has been a white coat with formal suit or shirt and tie. The major push for a more professional look was medicine’s movement out of the realm of quackery and into the theatre of science. Once germs were found to be the cause of many of the illnesses responsible for killing people, the white coat and professional look came to represent cleanliness and authority. Who can forget the famous paintings of the late 19th century, such as “The Agnew Clinic,” which depicted surgeons operating with white smocks and the amphitheater full of medical students in three-piece suits?
Still, the physician most people picture (especially in the U.S.) wears the white coat with a shirt and tie if male, or a dress if she is female. More recently, television has anointed scrubs as the official attire of all hospital-based physicians, even though many institutions outlaw them outside of the operating room.
Many businesses in the U.S. allow less formal dress at work (i.e., casual Fridays). And the chorus sings: We are not in business; we are members of a profession! We take an oath to distinguish ourselves and espouse a standard of professionalism that is necessary to earn the trust of patients. As hospitalists, we typically don’t have established relationships with our patients, and those first impressions are priceless.
The U.K. prohibited wristwatches, long sleeves (including white coats), and dangling ties in 2007. Even though there was no epidemiological evidence to support such a move, the public saw physicians as carriers of infectious bugs. As international travel makes our world smaller, vancomycin-resistant enterococci, methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus, Klebsiella pneumoniae Carbapenemase, and Clostridium difficile are increasingly prevalent and virulent in the hospital. Who can blame a suspicious public? I can’t.
Many of our patients grew up in an era when anyone flying by commercial air dressed in their Sunday best. It meant you were important or doing something important, and physicians have traditionally dressed the part. Most of our hospitalized patients today are older and more likely to prefer a physician in professional attire.
But who can forget the uproar in 2004, when an Israeli medical student tested the neckties of doctors and clinical staff at the New York Hospital Medical Center of Queens and found that nearly 50% were infested with potentially pathogenic bacteria. Most of organized medicine didn’t give the study much credence, because there was no evidence that the ties were directly tied to disease and most of the organisms were fairly ubiquitous.
Authors of a study published in The American Journal of Medicine in 2005 explored the impact of physician attire on patient confidence. Four hundred patients and visitors to a VA clinic were shown four sets of photos of doctors in different forms of attire (i.e., business attire, professional attire, scrubs, and T-shirts with jeans). Across all respondents, 76% of people chose the doctor in professional attire, followed by scrubs (10%), and business dress (9%).
I’m historically a very conservative dresser, and my bowties allow me the luxury of being “above” the tie fracas; however, I do like scrubs on the weekends, attire that is allowed in our system-wide dress code. I don’t think jeans and T-shirts are ever appropriate for seeing patients in the hospital.
The most important consideration, one that will evolve with the ages, is how our attire influences patient confidence and trust.
Proper Inpatient Documentation, Coding Essential to Avoid a Medicare Audit
Several years ago we sent a CPT coding auditor 15 chart notes generated by each doctor in our group. Among each doctors’ 15 notes were at least one or two billed as initial hospital care, follow up, discharge, critical care, and so on. This coding expert returned a report showing that, out of all the notes reviewed, a significant portion were not billed at the correct level. Most of the incorrectly billed notes were judged to reflect “up-coding,” and a few were seen as “down-coded.”
This was distressing and hard to believe.
So I took the same set of notes and paid a second coding expert for an independent review. She didn’t know about the first audit but returned a report that showed a nearly identical portion of incorrectly coded notes.
Two independent audits showing nearly the same portion of notes coded incorrectly was alarming. But it was difficult for my partners and me to address, because the auditors didn’t agree on the correct code for many of the notes. In some cases, both flagged a note as incorrectly coded but didn’t agree on the correct code. For a number of the notes, one auditor said the visit was “up-coded,” while the other said it was “down-coded.” There was so little agreement between the two of them that we had a hard time coming up with any firm conclusions about what we should do to improve our performance.
If experts who think about coding all the time can’t agree on the right code for a given note, how can hospitalists be expected to code nearly all of our visits accurately?
RAC: Recovery Audit Contractor
Despite what I believe is poor inter-rater reliability among coding auditors, we need to work diligently to comply with coding guidelines. A 2003 Federal law mandated a program of Recovery Audit Contractors, or RAC for short, to find cases of “up-coding” or other overbilling and require the provider to repay any resulting loss.
A number of companies are in the business of conducting RAC audits (one of them, CGI, is the Canadian company blamed for the failed “Obamacare” exchange websites), and there is a reasonable chance one of these companies has reviewed some of your charges—or those of your hospitalist colleagues.
The RAC auditors review information about your charges, and if they determine that you up-coded or overbilled, they send a “demand letter” summarizing their findings, along with the amount of money they have determined you should pay back. (Theoretically, they could notify you of “under-coding,” so that you can be paid more for past work, but I haven’t yet come across an example of that.)
It is common to appeal the RAC findings, but that can be a long process, and many organizations decide to pay back all the money requested by the RAC as quickly as possible to avoid paying interest on a delayed payment if the appeal is unsuccessful. In the case of a successful appeal, the money previously refunded by the doctor would be returned.
Page 338 of the CMS Fiscal Year 2015 “Justification of Estimates for Appropriations Committees” says that “…about 50 percent of the estimated 43,000 appeals [of adverse RAC audit findings] were fully or partially overturned…” This could mean the RACs are a sort of loose cannon, accusing many providers of overbilling while knowing that some won’t bother to appeal because they don’t understand the process or because the dollar amount involved for a single provider is too small to justify the time and expense of conducting the appeal. In this way, a RAC audit is like the $15 rebate on the last electronic gadget you bought. The seller knows that many people, including me, will fail to do the work required to claim the rebate.
Accuracy Strategies
There are a number of ways to help your group ensure appropriate CPT coding and reduce the chance a RAC will ask for money back.
Education. There are many ways to help providers in your practice understand the elements of documentation and coding. Periodic training classes (e.g. during orientation and annually thereafter) are useful but may not be enough. For me, this is a little like learning a foreign language by going to a couple of classes. Instead, I think “immersion training” is more effective. That might mean a doctor spends a few minutes with a certified coder on most working days for a few weeks. For example, they could meet for 15 minutes near lunchtime and review how the doctor plans to bill visits made that morning. Lastly, consider targeted education for each doctor, based on any problems found in an audit of his/her coding.
Review coding patterns. As I wrote in my August 2007 column, there is value in ensuring that each doctor in the group can see how her coding pattern differs from the group as a whole or any individual in the group. That is, what portion of follow-up visits was billed at the lowest, middle, and highest levels? What about admissions, discharges, and so on? I provided a sample report in that same column.
It also is worth taking the time to compare each doctor’s coding pattern to both the CMS Internal Medicine data and SHM’s State of Hospital Medicine report. The accompanying figure shows the most current data sets available.
Keep in mind that the goal is not to simply ensure that your coding pattern matches these external data sets; knowing where yours differs from these sets can suggest where you might want to investigate further or seek additional education.
Coding audits. Having a certified coder audit your performance at least annually is a good idea. It can help uncover areas in which you’d benefit from further review and training, and if, heaven forbid, questions are ever raised about whether you’re intentionally up-coding (fraud), showing that you’re audited regularly could help demonstrate your efforts to code correctly. In the latter case, it is probably more valuable if the audit is done independently of your employer.
Dr. Nelson has been a practicing hospitalist since 1988. He is co-founder and past president of SHM, and principal in Nelson Flores Hospital Medicine Consultants. He is co-director for SHM’s “Best Practices in Managing a Hospital Medicine Program” course. Write to him at john.nelson@nelsonflores.com.
Several years ago we sent a CPT coding auditor 15 chart notes generated by each doctor in our group. Among each doctors’ 15 notes were at least one or two billed as initial hospital care, follow up, discharge, critical care, and so on. This coding expert returned a report showing that, out of all the notes reviewed, a significant portion were not billed at the correct level. Most of the incorrectly billed notes were judged to reflect “up-coding,” and a few were seen as “down-coded.”
This was distressing and hard to believe.
So I took the same set of notes and paid a second coding expert for an independent review. She didn’t know about the first audit but returned a report that showed a nearly identical portion of incorrectly coded notes.
Two independent audits showing nearly the same portion of notes coded incorrectly was alarming. But it was difficult for my partners and me to address, because the auditors didn’t agree on the correct code for many of the notes. In some cases, both flagged a note as incorrectly coded but didn’t agree on the correct code. For a number of the notes, one auditor said the visit was “up-coded,” while the other said it was “down-coded.” There was so little agreement between the two of them that we had a hard time coming up with any firm conclusions about what we should do to improve our performance.
If experts who think about coding all the time can’t agree on the right code for a given note, how can hospitalists be expected to code nearly all of our visits accurately?
RAC: Recovery Audit Contractor
Despite what I believe is poor inter-rater reliability among coding auditors, we need to work diligently to comply with coding guidelines. A 2003 Federal law mandated a program of Recovery Audit Contractors, or RAC for short, to find cases of “up-coding” or other overbilling and require the provider to repay any resulting loss.
A number of companies are in the business of conducting RAC audits (one of them, CGI, is the Canadian company blamed for the failed “Obamacare” exchange websites), and there is a reasonable chance one of these companies has reviewed some of your charges—or those of your hospitalist colleagues.
The RAC auditors review information about your charges, and if they determine that you up-coded or overbilled, they send a “demand letter” summarizing their findings, along with the amount of money they have determined you should pay back. (Theoretically, they could notify you of “under-coding,” so that you can be paid more for past work, but I haven’t yet come across an example of that.)
It is common to appeal the RAC findings, but that can be a long process, and many organizations decide to pay back all the money requested by the RAC as quickly as possible to avoid paying interest on a delayed payment if the appeal is unsuccessful. In the case of a successful appeal, the money previously refunded by the doctor would be returned.
Page 338 of the CMS Fiscal Year 2015 “Justification of Estimates for Appropriations Committees” says that “…about 50 percent of the estimated 43,000 appeals [of adverse RAC audit findings] were fully or partially overturned…” This could mean the RACs are a sort of loose cannon, accusing many providers of overbilling while knowing that some won’t bother to appeal because they don’t understand the process or because the dollar amount involved for a single provider is too small to justify the time and expense of conducting the appeal. In this way, a RAC audit is like the $15 rebate on the last electronic gadget you bought. The seller knows that many people, including me, will fail to do the work required to claim the rebate.
Accuracy Strategies
There are a number of ways to help your group ensure appropriate CPT coding and reduce the chance a RAC will ask for money back.
Education. There are many ways to help providers in your practice understand the elements of documentation and coding. Periodic training classes (e.g. during orientation and annually thereafter) are useful but may not be enough. For me, this is a little like learning a foreign language by going to a couple of classes. Instead, I think “immersion training” is more effective. That might mean a doctor spends a few minutes with a certified coder on most working days for a few weeks. For example, they could meet for 15 minutes near lunchtime and review how the doctor plans to bill visits made that morning. Lastly, consider targeted education for each doctor, based on any problems found in an audit of his/her coding.
Review coding patterns. As I wrote in my August 2007 column, there is value in ensuring that each doctor in the group can see how her coding pattern differs from the group as a whole or any individual in the group. That is, what portion of follow-up visits was billed at the lowest, middle, and highest levels? What about admissions, discharges, and so on? I provided a sample report in that same column.
It also is worth taking the time to compare each doctor’s coding pattern to both the CMS Internal Medicine data and SHM’s State of Hospital Medicine report. The accompanying figure shows the most current data sets available.
Keep in mind that the goal is not to simply ensure that your coding pattern matches these external data sets; knowing where yours differs from these sets can suggest where you might want to investigate further or seek additional education.
Coding audits. Having a certified coder audit your performance at least annually is a good idea. It can help uncover areas in which you’d benefit from further review and training, and if, heaven forbid, questions are ever raised about whether you’re intentionally up-coding (fraud), showing that you’re audited regularly could help demonstrate your efforts to code correctly. In the latter case, it is probably more valuable if the audit is done independently of your employer.
Dr. Nelson has been a practicing hospitalist since 1988. He is co-founder and past president of SHM, and principal in Nelson Flores Hospital Medicine Consultants. He is co-director for SHM’s “Best Practices in Managing a Hospital Medicine Program” course. Write to him at john.nelson@nelsonflores.com.
Several years ago we sent a CPT coding auditor 15 chart notes generated by each doctor in our group. Among each doctors’ 15 notes were at least one or two billed as initial hospital care, follow up, discharge, critical care, and so on. This coding expert returned a report showing that, out of all the notes reviewed, a significant portion were not billed at the correct level. Most of the incorrectly billed notes were judged to reflect “up-coding,” and a few were seen as “down-coded.”
This was distressing and hard to believe.
So I took the same set of notes and paid a second coding expert for an independent review. She didn’t know about the first audit but returned a report that showed a nearly identical portion of incorrectly coded notes.
Two independent audits showing nearly the same portion of notes coded incorrectly was alarming. But it was difficult for my partners and me to address, because the auditors didn’t agree on the correct code for many of the notes. In some cases, both flagged a note as incorrectly coded but didn’t agree on the correct code. For a number of the notes, one auditor said the visit was “up-coded,” while the other said it was “down-coded.” There was so little agreement between the two of them that we had a hard time coming up with any firm conclusions about what we should do to improve our performance.
If experts who think about coding all the time can’t agree on the right code for a given note, how can hospitalists be expected to code nearly all of our visits accurately?
RAC: Recovery Audit Contractor
Despite what I believe is poor inter-rater reliability among coding auditors, we need to work diligently to comply with coding guidelines. A 2003 Federal law mandated a program of Recovery Audit Contractors, or RAC for short, to find cases of “up-coding” or other overbilling and require the provider to repay any resulting loss.
A number of companies are in the business of conducting RAC audits (one of them, CGI, is the Canadian company blamed for the failed “Obamacare” exchange websites), and there is a reasonable chance one of these companies has reviewed some of your charges—or those of your hospitalist colleagues.
The RAC auditors review information about your charges, and if they determine that you up-coded or overbilled, they send a “demand letter” summarizing their findings, along with the amount of money they have determined you should pay back. (Theoretically, they could notify you of “under-coding,” so that you can be paid more for past work, but I haven’t yet come across an example of that.)
It is common to appeal the RAC findings, but that can be a long process, and many organizations decide to pay back all the money requested by the RAC as quickly as possible to avoid paying interest on a delayed payment if the appeal is unsuccessful. In the case of a successful appeal, the money previously refunded by the doctor would be returned.
Page 338 of the CMS Fiscal Year 2015 “Justification of Estimates for Appropriations Committees” says that “…about 50 percent of the estimated 43,000 appeals [of adverse RAC audit findings] were fully or partially overturned…” This could mean the RACs are a sort of loose cannon, accusing many providers of overbilling while knowing that some won’t bother to appeal because they don’t understand the process or because the dollar amount involved for a single provider is too small to justify the time and expense of conducting the appeal. In this way, a RAC audit is like the $15 rebate on the last electronic gadget you bought. The seller knows that many people, including me, will fail to do the work required to claim the rebate.
Accuracy Strategies
There are a number of ways to help your group ensure appropriate CPT coding and reduce the chance a RAC will ask for money back.
Education. There are many ways to help providers in your practice understand the elements of documentation and coding. Periodic training classes (e.g. during orientation and annually thereafter) are useful but may not be enough. For me, this is a little like learning a foreign language by going to a couple of classes. Instead, I think “immersion training” is more effective. That might mean a doctor spends a few minutes with a certified coder on most working days for a few weeks. For example, they could meet for 15 minutes near lunchtime and review how the doctor plans to bill visits made that morning. Lastly, consider targeted education for each doctor, based on any problems found in an audit of his/her coding.
Review coding patterns. As I wrote in my August 2007 column, there is value in ensuring that each doctor in the group can see how her coding pattern differs from the group as a whole or any individual in the group. That is, what portion of follow-up visits was billed at the lowest, middle, and highest levels? What about admissions, discharges, and so on? I provided a sample report in that same column.
It also is worth taking the time to compare each doctor’s coding pattern to both the CMS Internal Medicine data and SHM’s State of Hospital Medicine report. The accompanying figure shows the most current data sets available.
Keep in mind that the goal is not to simply ensure that your coding pattern matches these external data sets; knowing where yours differs from these sets can suggest where you might want to investigate further or seek additional education.
Coding audits. Having a certified coder audit your performance at least annually is a good idea. It can help uncover areas in which you’d benefit from further review and training, and if, heaven forbid, questions are ever raised about whether you’re intentionally up-coding (fraud), showing that you’re audited regularly could help demonstrate your efforts to code correctly. In the latter case, it is probably more valuable if the audit is done independently of your employer.
Dr. Nelson has been a practicing hospitalist since 1988. He is co-founder and past president of SHM, and principal in Nelson Flores Hospital Medicine Consultants. He is co-director for SHM’s “Best Practices in Managing a Hospital Medicine Program” course. Write to him at john.nelson@nelsonflores.com.