User login
Red-Blue Nodule on the Scalp
Metastatic Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma
The differential diagnosis of cutaneous neoplasms with clear cells is broad. Clear cell features can be seen in primary tumors arising from the epidermis and cutaneous adnexa as well as in mesenchymal and melanocytic neoplasms. Furthermore, metastatic disease should be considered in the histologic differential diagnosis, as many visceral malignancies have clear cell features. This patient was subsequently found to have a large renal mass with metastasis to the lungs, spleen, and bone. The histologic findings support the diagnosis of metastatic clear cell renal cell carcinoma (RCC) to the skin.
Approximately 30% of patients with clear cell RCC present with metastatic disease with approximately 8% of those involving the skin.1,2 Cutaneous RCC metastases show a predilection for the head, especially the scalp. The clinical presentation is variable, but there often is a history of a rapidly growing brown, black, or purple nodule or plaque. A thorough review of the patient's history should be conducted if metastatic RCC is in the differential diagnosis, as it has been reported to occur up to 20 years after initial diagnosis.3
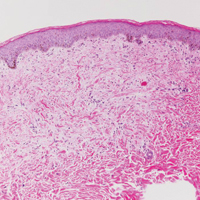
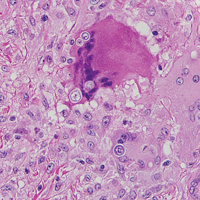
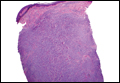
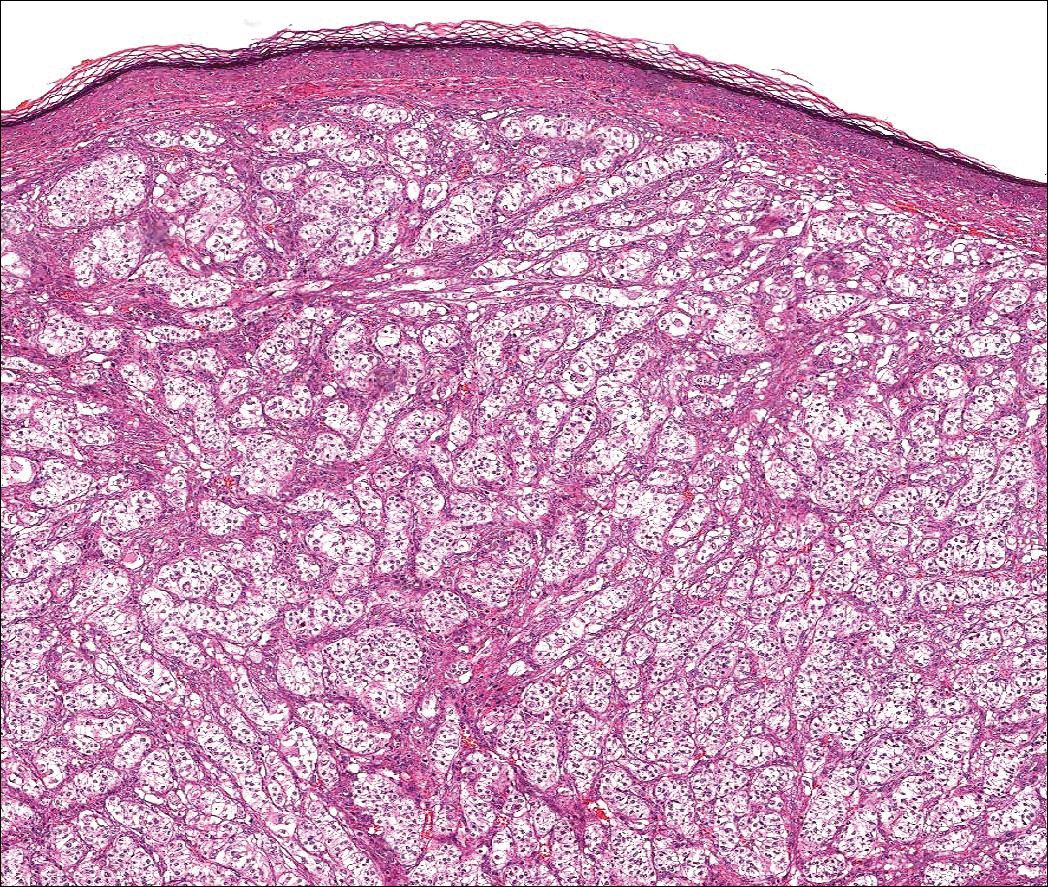
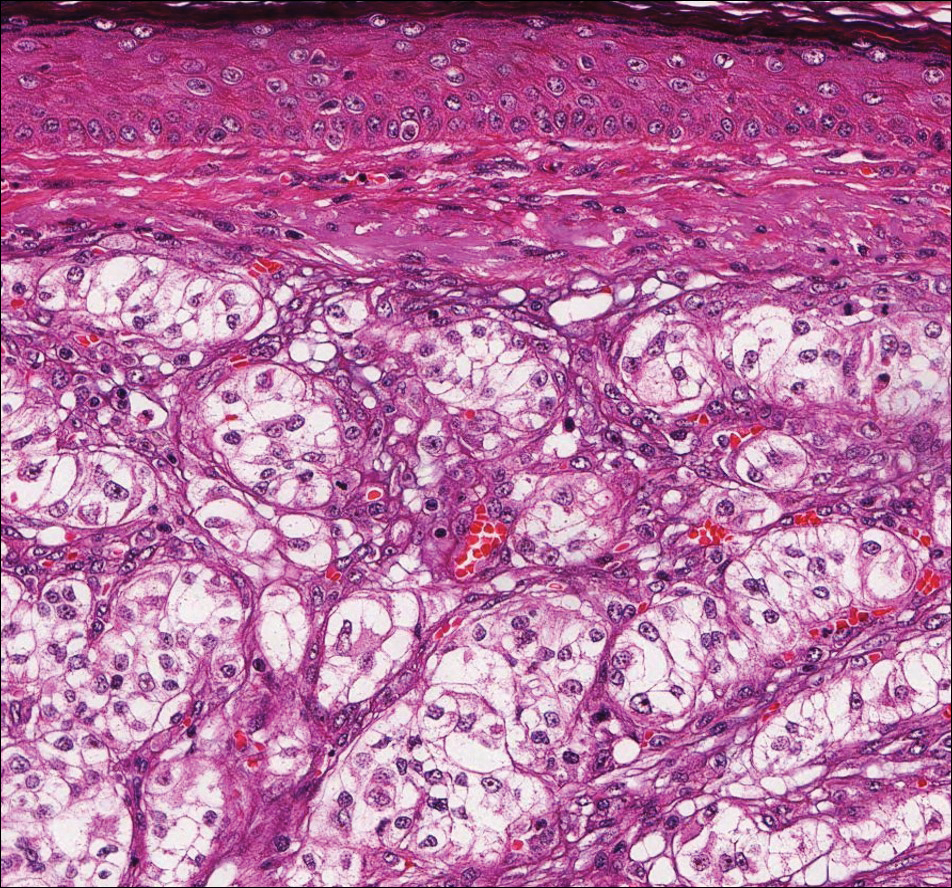
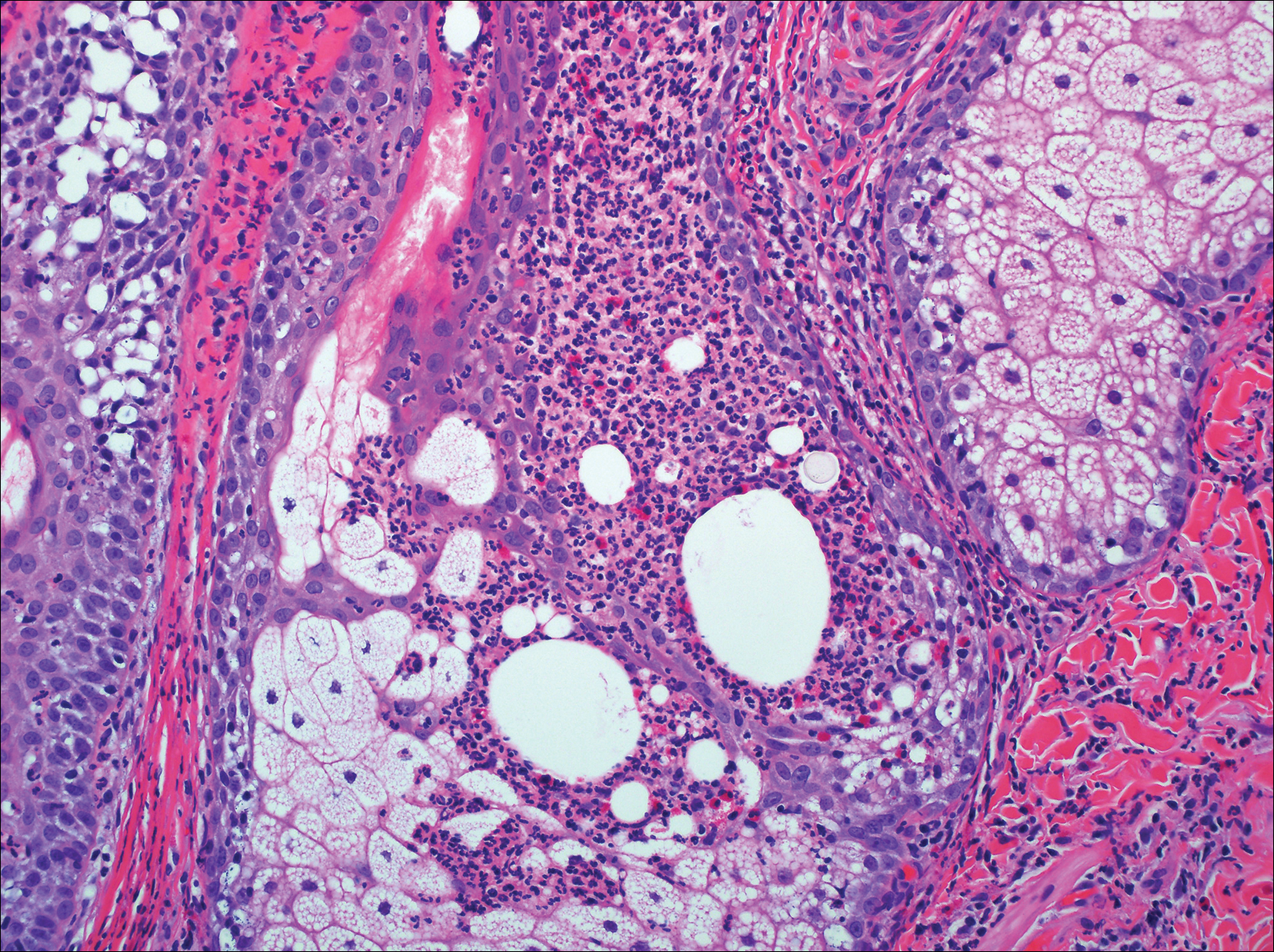
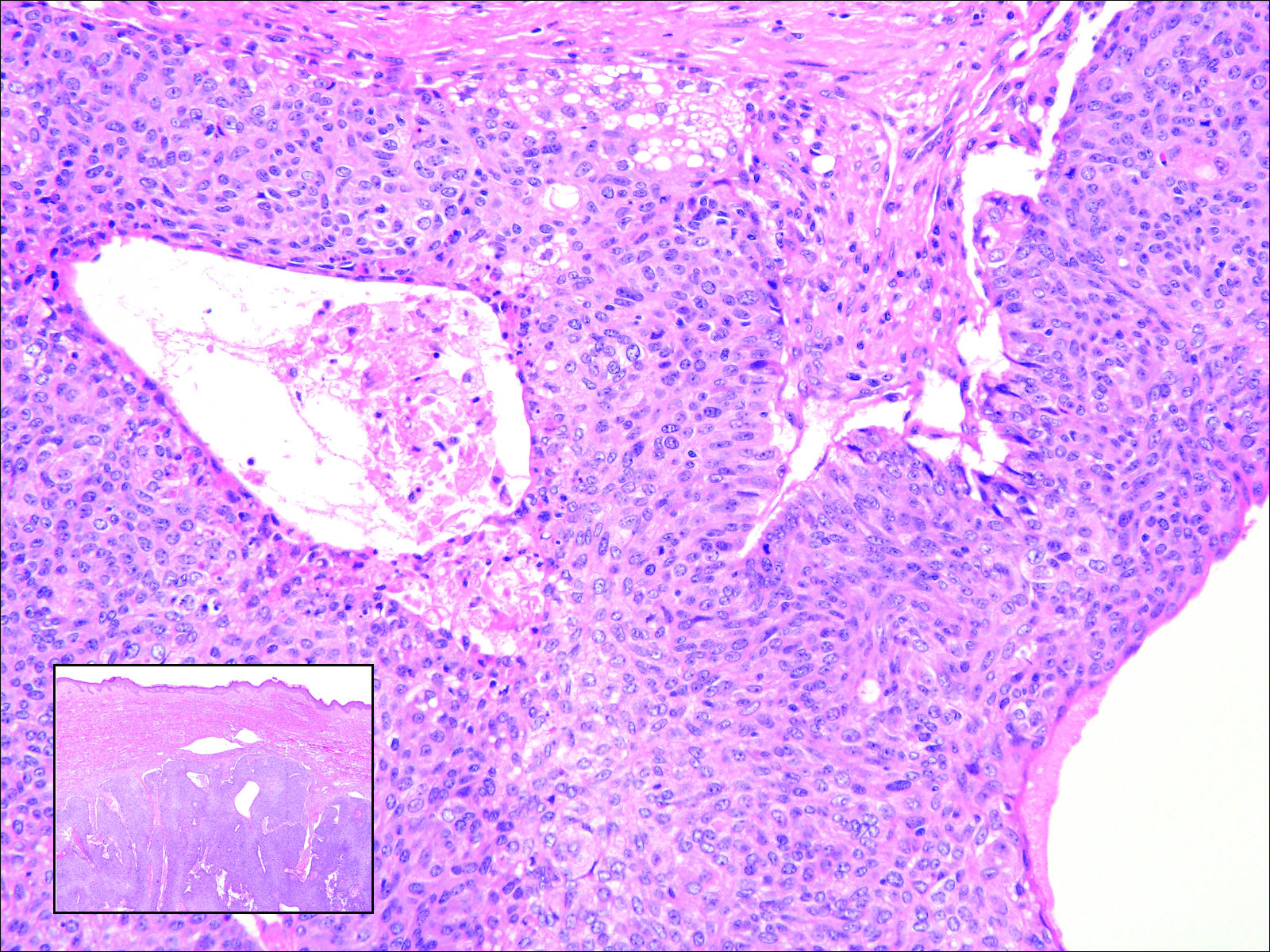
Histologically, clear cell RCC (quiz image) is composed of nests of tumor cells with clear cytoplasm and centrally located nuclei with prominent nucleoli. The clear cell features result from abundant cytoplasmic glycogen and lipid but may not be present in every case. One of the most important histologic features is the presence of delicate branching blood vessels (Figure 1). Numerous extravasated red blood cells also may be present. Positive immunohistochemical staining for PAX8, CD10, and RCC antigens support the diagnosis.4
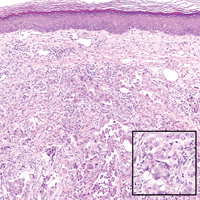
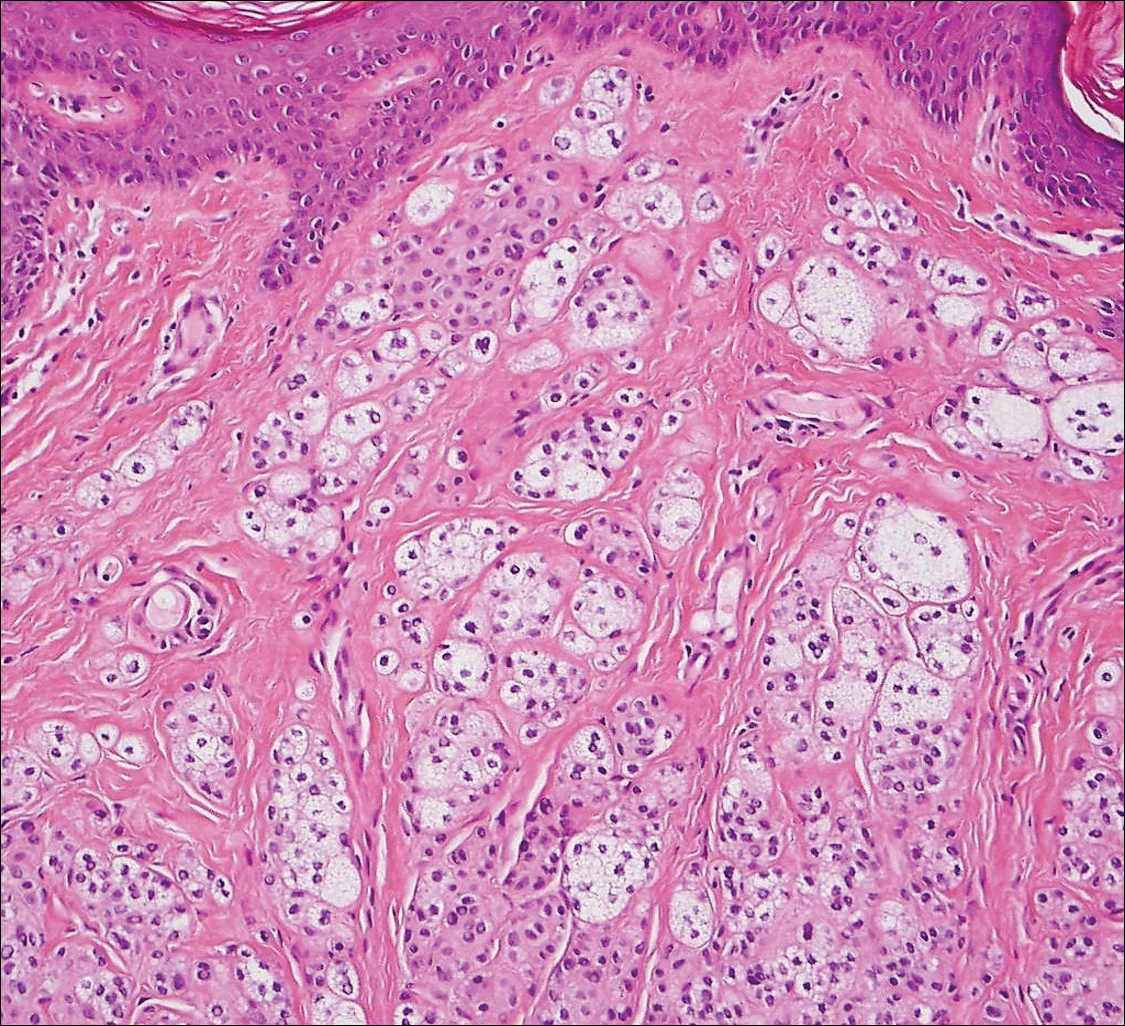
Balloon cell nevi (Figure 2) most commonly occur on the head and neck in adolescents and young adults but clinically are indistinguishable from other banal nevi. The nevus cells are large with foamy to finely vacuolated cytoplasm and lack atypia. The clear cell change is the result of melanosome degeneration and may be extensive. The presence of melanin pigment, nests of typical nevus cells, and positive staining with MART-1 can help distinguish the tumor from xanthomas and RCC.5
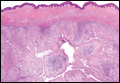
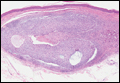
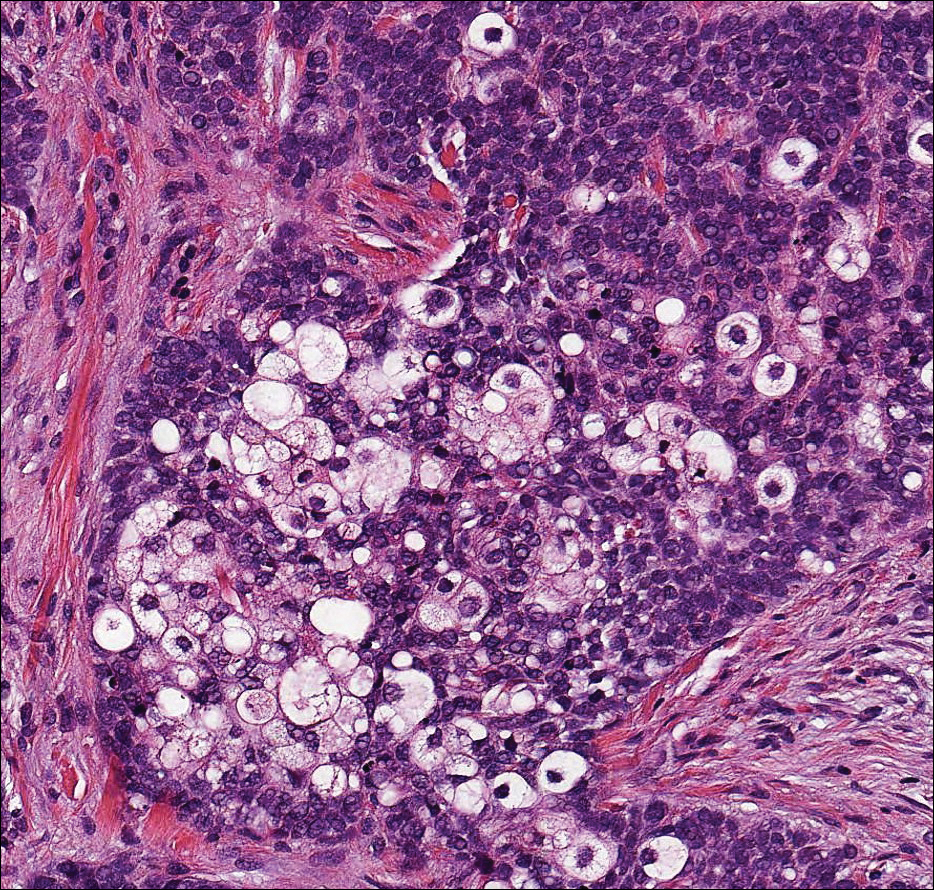
Clear cell hidradenoma (Figure 3) is a well-circumscribed tumor of sweat gland origin that arises in the dermis. The architecture usually is solid, cystic, or a combination of both. The cytology is classically bland with poroid, squamoid, or clear cell morphology. Clear cells that are positive on periodic acid-Schiff staining predominate in up to one-third of cases. Carcinoembryonic antigen and epithelial membrane antigen can be used to highlight the eosinophilic cuticles of ducts within solid areas.6

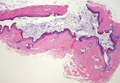
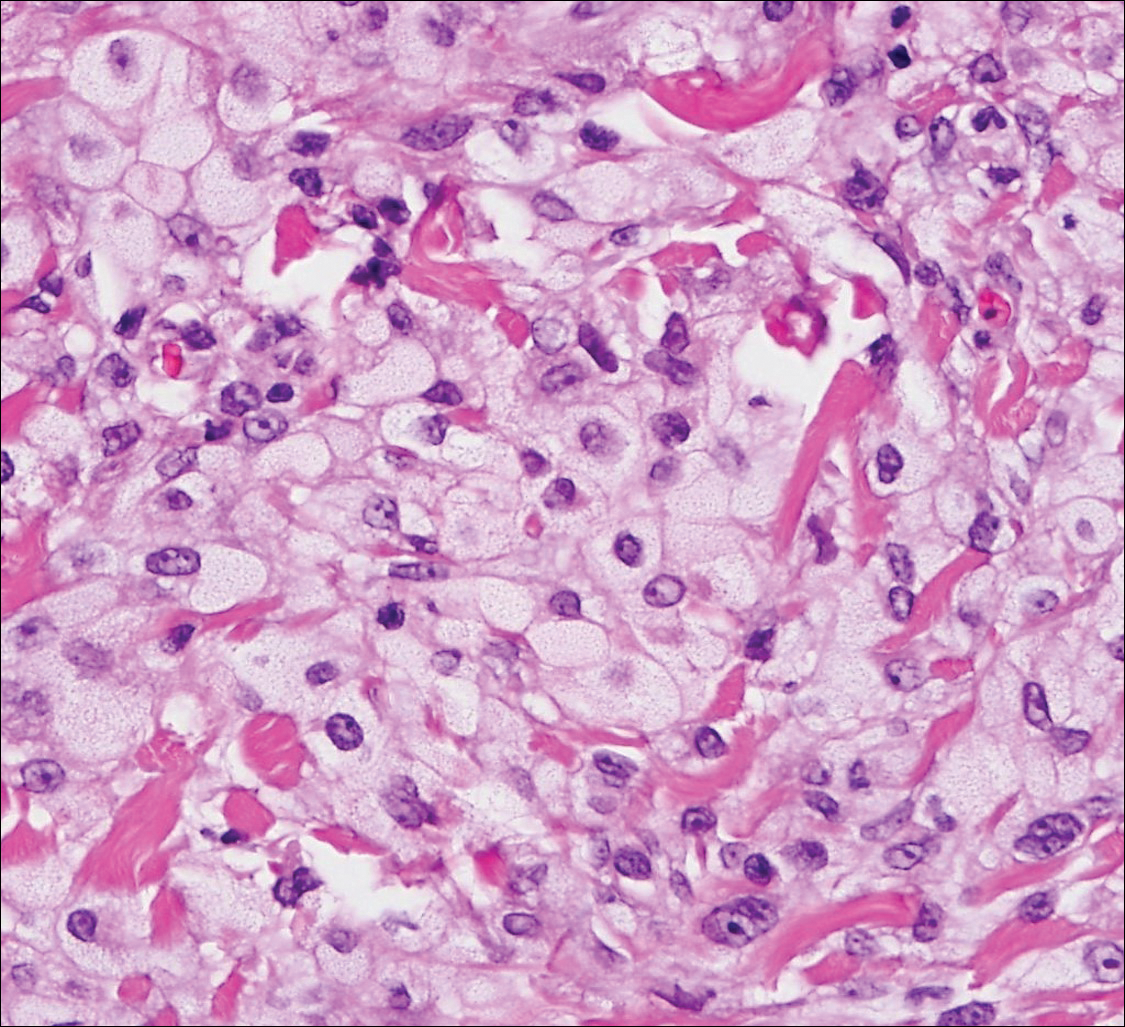
Sebaceous carcinoma (Figure 4) most frequently arises in a periorbital distribution, although extraocular lesions are known to occur. Histologically, there is a proliferation of both mature sebocytes and basaloid cells in the dermis, occasionally involving the epidermis. The mature sebocytes demonstrate clear cell features with foamy to vacuolated cytoplasm and large nuclei with scalloped borders. The clear cells may vary greatly in number and often are sparse in poorly differentiated tumors in which pleomorphic basaloid cells may predominate. The basaloid cells may resemble those of squamous or basal cell carcinoma, leading to a diagnostic dilemma in some cases. Special staining with Sudan black B and oil red O highlights the cytoplasmic lipid but must be performed on frozen section specimens. Although not entirely specific, immunohistochemical expression of epithelial membrane antigen, androgen receptor, and membranous vesicular adipophilin staining in sebaceous carcinoma can assist in the diagnosis.7
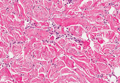
Cutaneous xanthomas (Figure 5) may arise in patients of any age and represent deposition of lipid-laden macrophages. Classification often is dependent on the clinical presentation; however, some subtypes demonstrate unique morphologic features (eg, verruciform xanthomas). Xanthomas classically arise in association with elevated serum lipids, but they also may occur in normolipemic patients. Individuals with Erdheim-Chester disease have an increased propensity to develop xanthelasma. Similarly, plane xanthomas have been associated with monoclonal gammopathy. Histologically, xanthomas are characterized by sheets of foamy macrophages within the dermis and subcutis. Positive immunohistochemical staining for CD68 highlighting the histiocytic nature of the cells and the absence of a delicate vascular network aid in the differentiation from RCC.
- Patterson JW, Hosler GA. Weedon's Skin Pathology. 4th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Churchill Livingstone/Elsevier; 2016.
- Alcaraz I, Cerroni L, Rutten A, et al. Cutaneous metastases from internal malignancies: a clinicopathologic and immunohistochemical review. Am J Dermatopathol. 2012;34:347-393.
- Calonje E, McKee PH. McKee's Pathology of the Skin. 4th ed. Edinburgh, Scotland: Elsevier/Saunders; 2012.
- Lin F, Prichard J. Handbook of Practical Immunohistochemistry: Frequently Asked Questions. 2nd ed. New York, NY: Springer; 2015.
- McKee PH, Calonje E. Diagnostic Atlas of Melanocytic Pathology. Edinburgh, Scotland: Mosby/Elsevier; 2009.
- Elston DM, Ferringer T, Ko CJ. Dermatopathology. 2nd ed. Philadelphia, PA: Saunders Elsevier; 2014.
- Ansai S, Takeichi H, Arase S, et al. Sebaceous carcinoma: an immunohistochemical reappraisal. Am J Dermatopathol. 2011;33:579-587.
Metastatic Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma
The differential diagnosis of cutaneous neoplasms with clear cells is broad. Clear cell features can be seen in primary tumors arising from the epidermis and cutaneous adnexa as well as in mesenchymal and melanocytic neoplasms. Furthermore, metastatic disease should be considered in the histologic differential diagnosis, as many visceral malignancies have clear cell features. This patient was subsequently found to have a large renal mass with metastasis to the lungs, spleen, and bone. The histologic findings support the diagnosis of metastatic clear cell renal cell carcinoma (RCC) to the skin.
Approximately 30% of patients with clear cell RCC present with metastatic disease with approximately 8% of those involving the skin.1,2 Cutaneous RCC metastases show a predilection for the head, especially the scalp. The clinical presentation is variable, but there often is a history of a rapidly growing brown, black, or purple nodule or plaque. A thorough review of the patient's history should be conducted if metastatic RCC is in the differential diagnosis, as it has been reported to occur up to 20 years after initial diagnosis.3
Histologically, clear cell RCC (quiz image) is composed of nests of tumor cells with clear cytoplasm and centrally located nuclei with prominent nucleoli. The clear cell features result from abundant cytoplasmic glycogen and lipid but may not be present in every case. One of the most important histologic features is the presence of delicate branching blood vessels (Figure 1). Numerous extravasated red blood cells also may be present. Positive immunohistochemical staining for PAX8, CD10, and RCC antigens support the diagnosis.4

Balloon cell nevi (Figure 2) most commonly occur on the head and neck in adolescents and young adults but clinically are indistinguishable from other banal nevi. The nevus cells are large with foamy to finely vacuolated cytoplasm and lack atypia. The clear cell change is the result of melanosome degeneration and may be extensive. The presence of melanin pigment, nests of typical nevus cells, and positive staining with MART-1 can help distinguish the tumor from xanthomas and RCC.5

Clear cell hidradenoma (Figure 3) is a well-circumscribed tumor of sweat gland origin that arises in the dermis. The architecture usually is solid, cystic, or a combination of both. The cytology is classically bland with poroid, squamoid, or clear cell morphology. Clear cells that are positive on periodic acid-Schiff staining predominate in up to one-third of cases. Carcinoembryonic antigen and epithelial membrane antigen can be used to highlight the eosinophilic cuticles of ducts within solid areas.6

Sebaceous carcinoma (Figure 4) most frequently arises in a periorbital distribution, although extraocular lesions are known to occur. Histologically, there is a proliferation of both mature sebocytes and basaloid cells in the dermis, occasionally involving the epidermis. The mature sebocytes demonstrate clear cell features with foamy to vacuolated cytoplasm and large nuclei with scalloped borders. The clear cells may vary greatly in number and often are sparse in poorly differentiated tumors in which pleomorphic basaloid cells may predominate. The basaloid cells may resemble those of squamous or basal cell carcinoma, leading to a diagnostic dilemma in some cases. Special staining with Sudan black B and oil red O highlights the cytoplasmic lipid but must be performed on frozen section specimens. Although not entirely specific, immunohistochemical expression of epithelial membrane antigen, androgen receptor, and membranous vesicular adipophilin staining in sebaceous carcinoma can assist in the diagnosis.7

Cutaneous xanthomas (Figure 5) may arise in patients of any age and represent deposition of lipid-laden macrophages. Classification often is dependent on the clinical presentation; however, some subtypes demonstrate unique morphologic features (eg, verruciform xanthomas). Xanthomas classically arise in association with elevated serum lipids, but they also may occur in normolipemic patients. Individuals with Erdheim-Chester disease have an increased propensity to develop xanthelasma. Similarly, plane xanthomas have been associated with monoclonal gammopathy. Histologically, xanthomas are characterized by sheets of foamy macrophages within the dermis and subcutis. Positive immunohistochemical staining for CD68 highlighting the histiocytic nature of the cells and the absence of a delicate vascular network aid in the differentiation from RCC.

Metastatic Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma
The differential diagnosis of cutaneous neoplasms with clear cells is broad. Clear cell features can be seen in primary tumors arising from the epidermis and cutaneous adnexa as well as in mesenchymal and melanocytic neoplasms. Furthermore, metastatic disease should be considered in the histologic differential diagnosis, as many visceral malignancies have clear cell features. This patient was subsequently found to have a large renal mass with metastasis to the lungs, spleen, and bone. The histologic findings support the diagnosis of metastatic clear cell renal cell carcinoma (RCC) to the skin.
Approximately 30% of patients with clear cell RCC present with metastatic disease with approximately 8% of those involving the skin.1,2 Cutaneous RCC metastases show a predilection for the head, especially the scalp. The clinical presentation is variable, but there often is a history of a rapidly growing brown, black, or purple nodule or plaque. A thorough review of the patient's history should be conducted if metastatic RCC is in the differential diagnosis, as it has been reported to occur up to 20 years after initial diagnosis.3
Histologically, clear cell RCC (quiz image) is composed of nests of tumor cells with clear cytoplasm and centrally located nuclei with prominent nucleoli. The clear cell features result from abundant cytoplasmic glycogen and lipid but may not be present in every case. One of the most important histologic features is the presence of delicate branching blood vessels (Figure 1). Numerous extravasated red blood cells also may be present. Positive immunohistochemical staining for PAX8, CD10, and RCC antigens support the diagnosis.4

Balloon cell nevi (Figure 2) most commonly occur on the head and neck in adolescents and young adults but clinically are indistinguishable from other banal nevi. The nevus cells are large with foamy to finely vacuolated cytoplasm and lack atypia. The clear cell change is the result of melanosome degeneration and may be extensive. The presence of melanin pigment, nests of typical nevus cells, and positive staining with MART-1 can help distinguish the tumor from xanthomas and RCC.5

Clear cell hidradenoma (Figure 3) is a well-circumscribed tumor of sweat gland origin that arises in the dermis. The architecture usually is solid, cystic, or a combination of both. The cytology is classically bland with poroid, squamoid, or clear cell morphology. Clear cells that are positive on periodic acid-Schiff staining predominate in up to one-third of cases. Carcinoembryonic antigen and epithelial membrane antigen can be used to highlight the eosinophilic cuticles of ducts within solid areas.6

Sebaceous carcinoma (Figure 4) most frequently arises in a periorbital distribution, although extraocular lesions are known to occur. Histologically, there is a proliferation of both mature sebocytes and basaloid cells in the dermis, occasionally involving the epidermis. The mature sebocytes demonstrate clear cell features with foamy to vacuolated cytoplasm and large nuclei with scalloped borders. The clear cells may vary greatly in number and often are sparse in poorly differentiated tumors in which pleomorphic basaloid cells may predominate. The basaloid cells may resemble those of squamous or basal cell carcinoma, leading to a diagnostic dilemma in some cases. Special staining with Sudan black B and oil red O highlights the cytoplasmic lipid but must be performed on frozen section specimens. Although not entirely specific, immunohistochemical expression of epithelial membrane antigen, androgen receptor, and membranous vesicular adipophilin staining in sebaceous carcinoma can assist in the diagnosis.7

Cutaneous xanthomas (Figure 5) may arise in patients of any age and represent deposition of lipid-laden macrophages. Classification often is dependent on the clinical presentation; however, some subtypes demonstrate unique morphologic features (eg, verruciform xanthomas). Xanthomas classically arise in association with elevated serum lipids, but they also may occur in normolipemic patients. Individuals with Erdheim-Chester disease have an increased propensity to develop xanthelasma. Similarly, plane xanthomas have been associated with monoclonal gammopathy. Histologically, xanthomas are characterized by sheets of foamy macrophages within the dermis and subcutis. Positive immunohistochemical staining for CD68 highlighting the histiocytic nature of the cells and the absence of a delicate vascular network aid in the differentiation from RCC.

- Patterson JW, Hosler GA. Weedon's Skin Pathology. 4th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Churchill Livingstone/Elsevier; 2016.
- Alcaraz I, Cerroni L, Rutten A, et al. Cutaneous metastases from internal malignancies: a clinicopathologic and immunohistochemical review. Am J Dermatopathol. 2012;34:347-393.
- Calonje E, McKee PH. McKee's Pathology of the Skin. 4th ed. Edinburgh, Scotland: Elsevier/Saunders; 2012.
- Lin F, Prichard J. Handbook of Practical Immunohistochemistry: Frequently Asked Questions. 2nd ed. New York, NY: Springer; 2015.
- McKee PH, Calonje E. Diagnostic Atlas of Melanocytic Pathology. Edinburgh, Scotland: Mosby/Elsevier; 2009.
- Elston DM, Ferringer T, Ko CJ. Dermatopathology. 2nd ed. Philadelphia, PA: Saunders Elsevier; 2014.
- Ansai S, Takeichi H, Arase S, et al. Sebaceous carcinoma: an immunohistochemical reappraisal. Am J Dermatopathol. 2011;33:579-587.
- Patterson JW, Hosler GA. Weedon's Skin Pathology. 4th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Churchill Livingstone/Elsevier; 2016.
- Alcaraz I, Cerroni L, Rutten A, et al. Cutaneous metastases from internal malignancies: a clinicopathologic and immunohistochemical review. Am J Dermatopathol. 2012;34:347-393.
- Calonje E, McKee PH. McKee's Pathology of the Skin. 4th ed. Edinburgh, Scotland: Elsevier/Saunders; 2012.
- Lin F, Prichard J. Handbook of Practical Immunohistochemistry: Frequently Asked Questions. 2nd ed. New York, NY: Springer; 2015.
- McKee PH, Calonje E. Diagnostic Atlas of Melanocytic Pathology. Edinburgh, Scotland: Mosby/Elsevier; 2009.
- Elston DM, Ferringer T, Ko CJ. Dermatopathology. 2nd ed. Philadelphia, PA: Saunders Elsevier; 2014.
- Ansai S, Takeichi H, Arase S, et al. Sebaceous carcinoma: an immunohistochemical reappraisal. Am J Dermatopathol. 2011;33:579-587.
A 59-year-old man presented with a 1.5×1.0-cm asymptomatic, smooth, red-blue nodule on the left parietal scalp. The nodule had been rapidly enlarging over the last 3 weeks. After resection, the cut surface was golden yellow and focally hemorrhagic.
Flesh-Colored Papular Eruption
Papular Mucinosis/Scleromyxedema
Papular mucinosis/scleromyxedema, also known as generalized lichen myxedematosus, is a rare dermal mucinosis characterized by a papular eruption that can have an associated IgG λ paraproteinemia. The clinical presentation is gradual with the development of firm, flesh-colored, 2- to 3-mm papules often involving the hands, face, and neck that can progress to plaques that cover the entire body. Skin stiffening also can be seen.1 Extracutaneous symptoms are common and include dysphagia, arthralgia, myopathy, and cardiac dysfunction.2 Occasionally, central nervous system involvement can lead to the often fatal dermato-neuro syndrome.3,4
Histologically, papular mucinosis/scleromyxedema demonstrates increased, irregularly arranged fibroblasts in the reticular dermis with increased dermal mucin deposition (quiz image and Figure 1). The epidermis is normal or slightly thinned due to pressure from dermal changes. There may be a mild superficial perivascular lymphocytic infiltrate and atrophy of hair follicles.5 In this case, the clinical and histologic findings best supported a diagnosis of papular mucinosis/scleromyxedema.

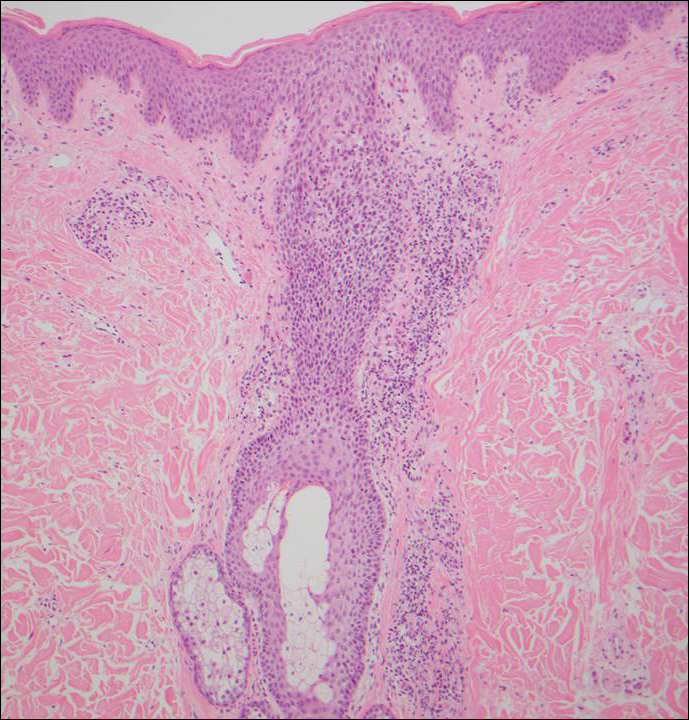
Infundibulofolliculitis is a pruritic follicular papular eruption typically involving the neck, trunk, and proximal upper arms and shoulders. It is most common in black men who reside in hot and humid climates. Although infundibulofolliculitis would be included in the clinical differential diagnosis for the current patient, the histopathologic findings were quite distinct for the correct diagnosis of papular mucinosis/scleromyxedema. Infundibulofolliculitis shows widening of the upper part of the hair follicle (infundibulum) and infundibular inflammatory infiltrate with follicular spongiosis (Figure 2). Neither mucin deposition nor fibroblast proliferation is appreciated in infundibulofolliculitis.6,7
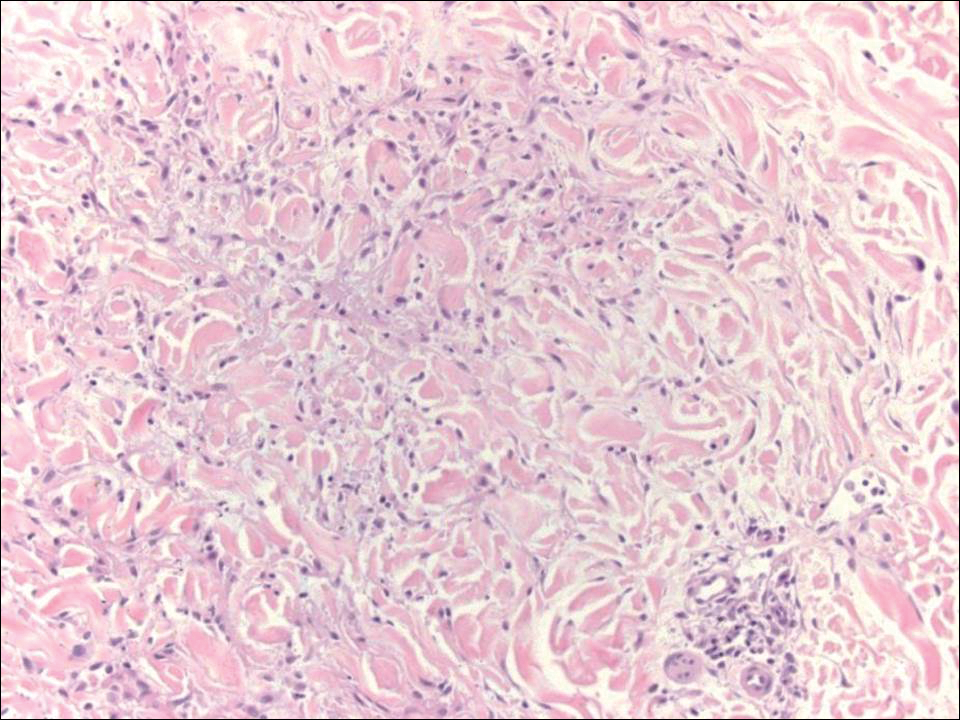
Granuloma annulare (GA) often can be distinguished clinically from papular mucinosis/scleromyxedema due to the annular appearance of papules and plaques in GA and the lack of stiffness of underlying skin. Interstitial granuloma annulare is a histologic variant of GA that can be included in the histologic differential diagnosis of papular mucinosis/scleromyxedema. Histologically, there is an interstitial infiltrate of cytologically bland histiocytes dissecting between collagen bundles in interstitial GA (Figure 3). Necrobiosis and collections of mucin often are inconspicuous. Occasionally, the presence of eosinophils can be a helpful clue.8 A fibroblast proliferation is not a feature of GA.
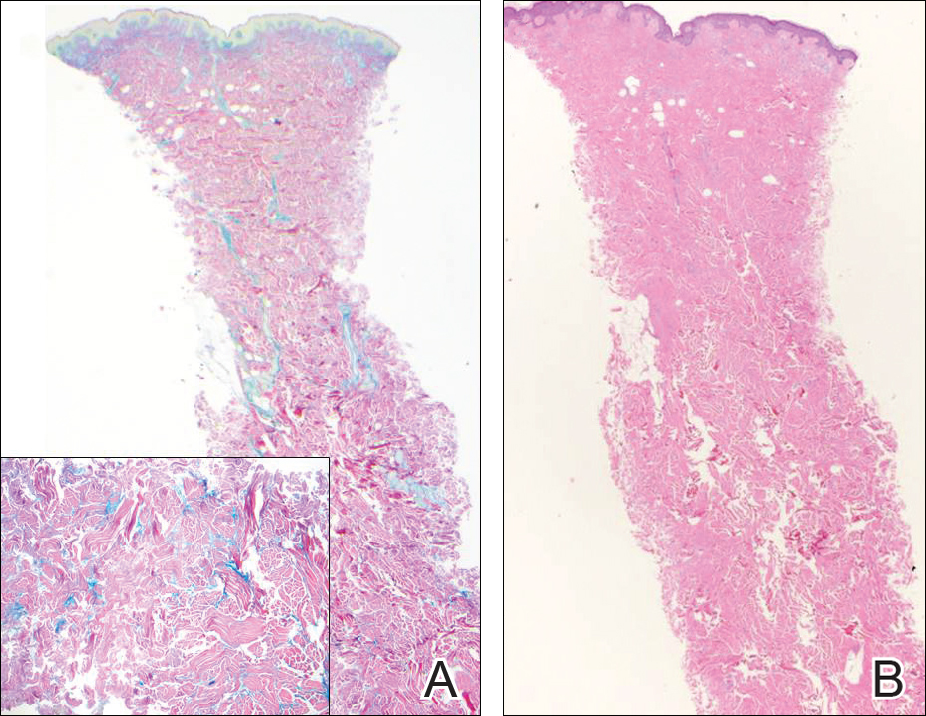
Reticular erythematous mucinosis also is a type of cutaneous mucinosis but with a classic clinical appearance of a reticulated erythematous plaque on the chest or back, making it clinically distinct from papular mucinosis/scleromyxedema and the presentation described in the current patient. Reticular erythematous mucinosis can be histologically distinguished from papular mucinosis/scleromyxedema by the presence of a superficial and deep perivascular lymphocytic infiltrate with increased dermal mucin deposition (Figure 4). It often shows a positive IgM deposition on the basement membrane on direct immunofluorescence.9

Similar to papular mucinosis/scleromyxedema, scleredema shows thickening of the skin with decreased movement of involved areas. Scleredema often involves the upper back, shoulders, and neck where affected areas often have a peau d'orange appearance. Scleredema is classified into 3 clinical forms based on clinical associations. Type 1 often is preceded by an infection, classically Streptococcus pyogenes. Type 2 is associated with a hematologic dyscrasia such as multiple myeloma, or it can have an associated paraproteinemia that is typically of the IgA κ type, which is distinct from papular mucinosis/scleromyxedema where IgG λ paraproteinemia typically is seen. Type 3 is associated with diabetes mellitus. Histologically, scleredema also is distinct from papular mucinosis/scleromyxedema. Although increased mucin is seen in the dermis, the mucin is classically more prominent in the deep reticular dermis as compared with papular mucinosis/scleromyxedema (Figure 5). Additionally, collagen bundles are thickened with clear separation between them. Hyperplasia of fibroblasts in the dermis that is a characteristic feature of papular mucinosis/scleromyxedema is not observed in scleredema.10
- Georgakis CD, Falasca G, Georgakis A, et al. Scleromyxedema. Clin Dermatol. 2006;24:493-497.
- Rongioletti F, Merlo G, Cinotti E, et al. Scleromyxedema: a multicenter study of characteristics, comorbidities, course, and therapy in 30 patients. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2013;69:66-72.
- Fleming KE, Virmani D, Sutton E, et al. Scleromyxedema and the dermato-neuro syndrome: case report and review of the literature. J Cutan Pathol. 2012;39:508-517.
- Hummers LK. Scleromyxedema. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2014;26:658-662.
- Rongioleti F, Rebora A. Updated classification of papular mucinosis, lichen myxedematosus, and scleromyxedema. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2001;44:273-281.
- Owen WR, Wood C. Disseminate and recurrent infundibulofolliculitis. Arch Dermatol. 1979;5:174-175.
- Soyinka F. Recurrent disseminated infundibulofolliculitis. Int J Dermatol. 1973;12:314-317.
- Keimig EL. Granuloma annulare. Dermatol Clin. 2015;33:315-329.
- Thareja S, Paghdal K, Lein MH, et al. Reticular erythematous mucinosis--a review. Int J Dermatol. 2012;51:903-909.
- Beers WH, Ince AI, Moore TL. Scleredema adultorum of Buschke: a case report and review of the literature. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2006;35:355-359.
Papular Mucinosis/Scleromyxedema
Papular mucinosis/scleromyxedema, also known as generalized lichen myxedematosus, is a rare dermal mucinosis characterized by a papular eruption that can have an associated IgG λ paraproteinemia. The clinical presentation is gradual with the development of firm, flesh-colored, 2- to 3-mm papules often involving the hands, face, and neck that can progress to plaques that cover the entire body. Skin stiffening also can be seen.1 Extracutaneous symptoms are common and include dysphagia, arthralgia, myopathy, and cardiac dysfunction.2 Occasionally, central nervous system involvement can lead to the often fatal dermato-neuro syndrome.3,4
Histologically, papular mucinosis/scleromyxedema demonstrates increased, irregularly arranged fibroblasts in the reticular dermis with increased dermal mucin deposition (quiz image and Figure 1). The epidermis is normal or slightly thinned due to pressure from dermal changes. There may be a mild superficial perivascular lymphocytic infiltrate and atrophy of hair follicles.5 In this case, the clinical and histologic findings best supported a diagnosis of papular mucinosis/scleromyxedema.

Infundibulofolliculitis is a pruritic follicular papular eruption typically involving the neck, trunk, and proximal upper arms and shoulders. It is most common in black men who reside in hot and humid climates. Although infundibulofolliculitis would be included in the clinical differential diagnosis for the current patient, the histopathologic findings were quite distinct for the correct diagnosis of papular mucinosis/scleromyxedema. Infundibulofolliculitis shows widening of the upper part of the hair follicle (infundibulum) and infundibular inflammatory infiltrate with follicular spongiosis (Figure 2). Neither mucin deposition nor fibroblast proliferation is appreciated in infundibulofolliculitis.6,7

Granuloma annulare (GA) often can be distinguished clinically from papular mucinosis/scleromyxedema due to the annular appearance of papules and plaques in GA and the lack of stiffness of underlying skin. Interstitial granuloma annulare is a histologic variant of GA that can be included in the histologic differential diagnosis of papular mucinosis/scleromyxedema. Histologically, there is an interstitial infiltrate of cytologically bland histiocytes dissecting between collagen bundles in interstitial GA (Figure 3). Necrobiosis and collections of mucin often are inconspicuous. Occasionally, the presence of eosinophils can be a helpful clue.8 A fibroblast proliferation is not a feature of GA.

Reticular erythematous mucinosis also is a type of cutaneous mucinosis but with a classic clinical appearance of a reticulated erythematous plaque on the chest or back, making it clinically distinct from papular mucinosis/scleromyxedema and the presentation described in the current patient. Reticular erythematous mucinosis can be histologically distinguished from papular mucinosis/scleromyxedema by the presence of a superficial and deep perivascular lymphocytic infiltrate with increased dermal mucin deposition (Figure 4). It often shows a positive IgM deposition on the basement membrane on direct immunofluorescence.9

Similar to papular mucinosis/scleromyxedema, scleredema shows thickening of the skin with decreased movement of involved areas. Scleredema often involves the upper back, shoulders, and neck where affected areas often have a peau d'orange appearance. Scleredema is classified into 3 clinical forms based on clinical associations. Type 1 often is preceded by an infection, classically Streptococcus pyogenes. Type 2 is associated with a hematologic dyscrasia such as multiple myeloma, or it can have an associated paraproteinemia that is typically of the IgA κ type, which is distinct from papular mucinosis/scleromyxedema where IgG λ paraproteinemia typically is seen. Type 3 is associated with diabetes mellitus. Histologically, scleredema also is distinct from papular mucinosis/scleromyxedema. Although increased mucin is seen in the dermis, the mucin is classically more prominent in the deep reticular dermis as compared with papular mucinosis/scleromyxedema (Figure 5). Additionally, collagen bundles are thickened with clear separation between them. Hyperplasia of fibroblasts in the dermis that is a characteristic feature of papular mucinosis/scleromyxedema is not observed in scleredema.10

Papular Mucinosis/Scleromyxedema
Papular mucinosis/scleromyxedema, also known as generalized lichen myxedematosus, is a rare dermal mucinosis characterized by a papular eruption that can have an associated IgG λ paraproteinemia. The clinical presentation is gradual with the development of firm, flesh-colored, 2- to 3-mm papules often involving the hands, face, and neck that can progress to plaques that cover the entire body. Skin stiffening also can be seen.1 Extracutaneous symptoms are common and include dysphagia, arthralgia, myopathy, and cardiac dysfunction.2 Occasionally, central nervous system involvement can lead to the often fatal dermato-neuro syndrome.3,4
Histologically, papular mucinosis/scleromyxedema demonstrates increased, irregularly arranged fibroblasts in the reticular dermis with increased dermal mucin deposition (quiz image and Figure 1). The epidermis is normal or slightly thinned due to pressure from dermal changes. There may be a mild superficial perivascular lymphocytic infiltrate and atrophy of hair follicles.5 In this case, the clinical and histologic findings best supported a diagnosis of papular mucinosis/scleromyxedema.

Infundibulofolliculitis is a pruritic follicular papular eruption typically involving the neck, trunk, and proximal upper arms and shoulders. It is most common in black men who reside in hot and humid climates. Although infundibulofolliculitis would be included in the clinical differential diagnosis for the current patient, the histopathologic findings were quite distinct for the correct diagnosis of papular mucinosis/scleromyxedema. Infundibulofolliculitis shows widening of the upper part of the hair follicle (infundibulum) and infundibular inflammatory infiltrate with follicular spongiosis (Figure 2). Neither mucin deposition nor fibroblast proliferation is appreciated in infundibulofolliculitis.6,7

Granuloma annulare (GA) often can be distinguished clinically from papular mucinosis/scleromyxedema due to the annular appearance of papules and plaques in GA and the lack of stiffness of underlying skin. Interstitial granuloma annulare is a histologic variant of GA that can be included in the histologic differential diagnosis of papular mucinosis/scleromyxedema. Histologically, there is an interstitial infiltrate of cytologically bland histiocytes dissecting between collagen bundles in interstitial GA (Figure 3). Necrobiosis and collections of mucin often are inconspicuous. Occasionally, the presence of eosinophils can be a helpful clue.8 A fibroblast proliferation is not a feature of GA.

Reticular erythematous mucinosis also is a type of cutaneous mucinosis but with a classic clinical appearance of a reticulated erythematous plaque on the chest or back, making it clinically distinct from papular mucinosis/scleromyxedema and the presentation described in the current patient. Reticular erythematous mucinosis can be histologically distinguished from papular mucinosis/scleromyxedema by the presence of a superficial and deep perivascular lymphocytic infiltrate with increased dermal mucin deposition (Figure 4). It often shows a positive IgM deposition on the basement membrane on direct immunofluorescence.9

Similar to papular mucinosis/scleromyxedema, scleredema shows thickening of the skin with decreased movement of involved areas. Scleredema often involves the upper back, shoulders, and neck where affected areas often have a peau d'orange appearance. Scleredema is classified into 3 clinical forms based on clinical associations. Type 1 often is preceded by an infection, classically Streptococcus pyogenes. Type 2 is associated with a hematologic dyscrasia such as multiple myeloma, or it can have an associated paraproteinemia that is typically of the IgA κ type, which is distinct from papular mucinosis/scleromyxedema where IgG λ paraproteinemia typically is seen. Type 3 is associated with diabetes mellitus. Histologically, scleredema also is distinct from papular mucinosis/scleromyxedema. Although increased mucin is seen in the dermis, the mucin is classically more prominent in the deep reticular dermis as compared with papular mucinosis/scleromyxedema (Figure 5). Additionally, collagen bundles are thickened with clear separation between them. Hyperplasia of fibroblasts in the dermis that is a characteristic feature of papular mucinosis/scleromyxedema is not observed in scleredema.10

- Georgakis CD, Falasca G, Georgakis A, et al. Scleromyxedema. Clin Dermatol. 2006;24:493-497.
- Rongioletti F, Merlo G, Cinotti E, et al. Scleromyxedema: a multicenter study of characteristics, comorbidities, course, and therapy in 30 patients. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2013;69:66-72.
- Fleming KE, Virmani D, Sutton E, et al. Scleromyxedema and the dermato-neuro syndrome: case report and review of the literature. J Cutan Pathol. 2012;39:508-517.
- Hummers LK. Scleromyxedema. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2014;26:658-662.
- Rongioleti F, Rebora A. Updated classification of papular mucinosis, lichen myxedematosus, and scleromyxedema. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2001;44:273-281.
- Owen WR, Wood C. Disseminate and recurrent infundibulofolliculitis. Arch Dermatol. 1979;5:174-175.
- Soyinka F. Recurrent disseminated infundibulofolliculitis. Int J Dermatol. 1973;12:314-317.
- Keimig EL. Granuloma annulare. Dermatol Clin. 2015;33:315-329.
- Thareja S, Paghdal K, Lein MH, et al. Reticular erythematous mucinosis--a review. Int J Dermatol. 2012;51:903-909.
- Beers WH, Ince AI, Moore TL. Scleredema adultorum of Buschke: a case report and review of the literature. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2006;35:355-359.
- Georgakis CD, Falasca G, Georgakis A, et al. Scleromyxedema. Clin Dermatol. 2006;24:493-497.
- Rongioletti F, Merlo G, Cinotti E, et al. Scleromyxedema: a multicenter study of characteristics, comorbidities, course, and therapy in 30 patients. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2013;69:66-72.
- Fleming KE, Virmani D, Sutton E, et al. Scleromyxedema and the dermato-neuro syndrome: case report and review of the literature. J Cutan Pathol. 2012;39:508-517.
- Hummers LK. Scleromyxedema. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2014;26:658-662.
- Rongioleti F, Rebora A. Updated classification of papular mucinosis, lichen myxedematosus, and scleromyxedema. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2001;44:273-281.
- Owen WR, Wood C. Disseminate and recurrent infundibulofolliculitis. Arch Dermatol. 1979;5:174-175.
- Soyinka F. Recurrent disseminated infundibulofolliculitis. Int J Dermatol. 1973;12:314-317.
- Keimig EL. Granuloma annulare. Dermatol Clin. 2015;33:315-329.
- Thareja S, Paghdal K, Lein MH, et al. Reticular erythematous mucinosis--a review. Int J Dermatol. 2012;51:903-909.
- Beers WH, Ince AI, Moore TL. Scleredema adultorum of Buschke: a case report and review of the literature. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2006;35:355-359.
A 48-year-old black man presented with a rash of 7 months' duration that started on the face and spread to the body. He had extreme pruritus, increased stiffness in the hands and joints, and paresthesia. Physical examination revealed an eruption of 2- to 4-mm, flesh-colored papules with follicular accentuation on the face, neck, bilateral upper extremities, back, and thighs.
Verrucous Plaque on the Leg
Blastomycosis
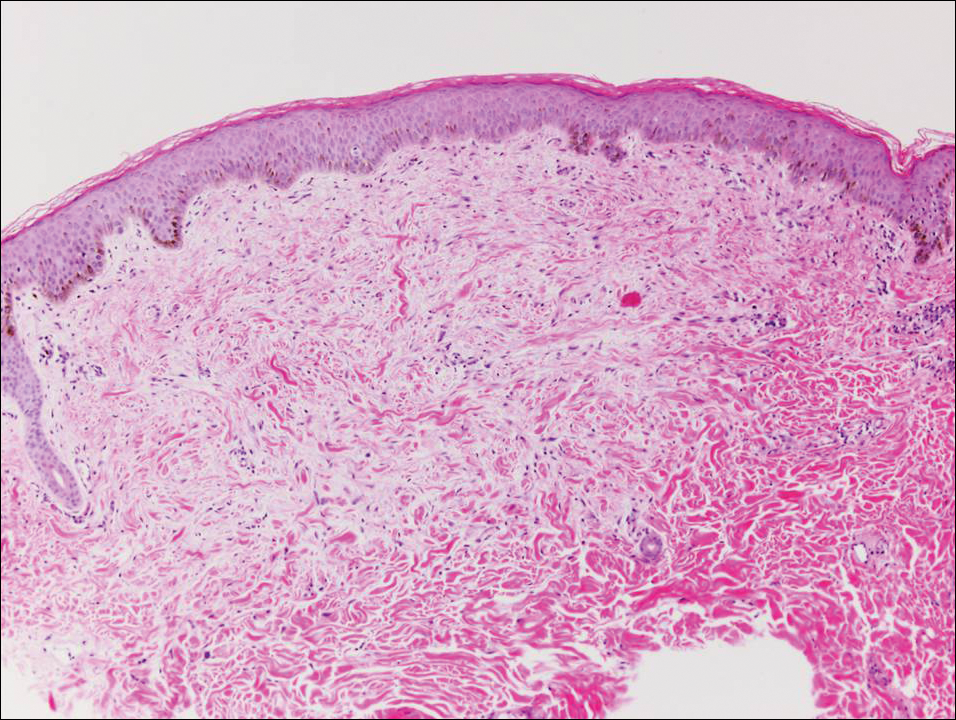
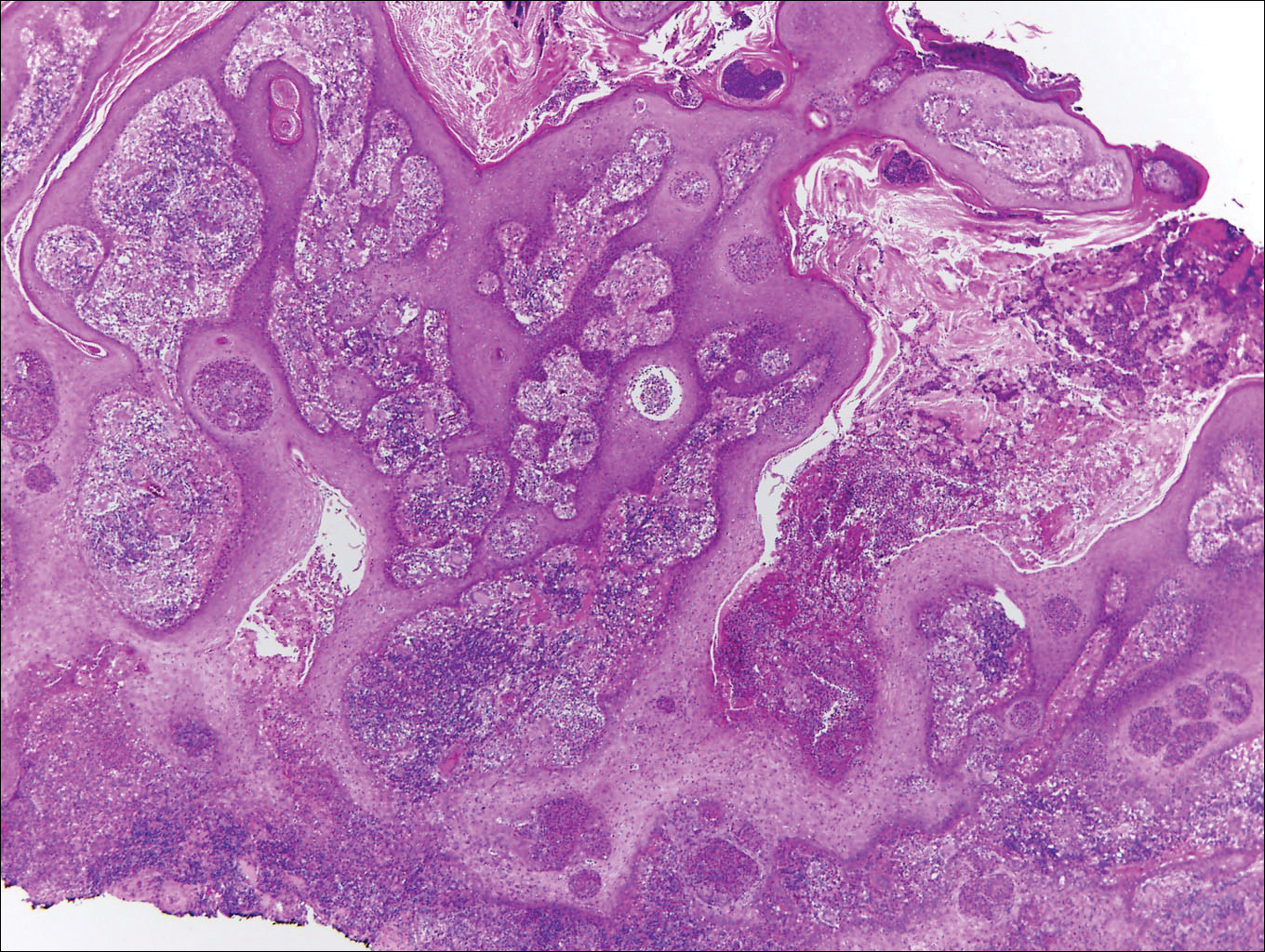
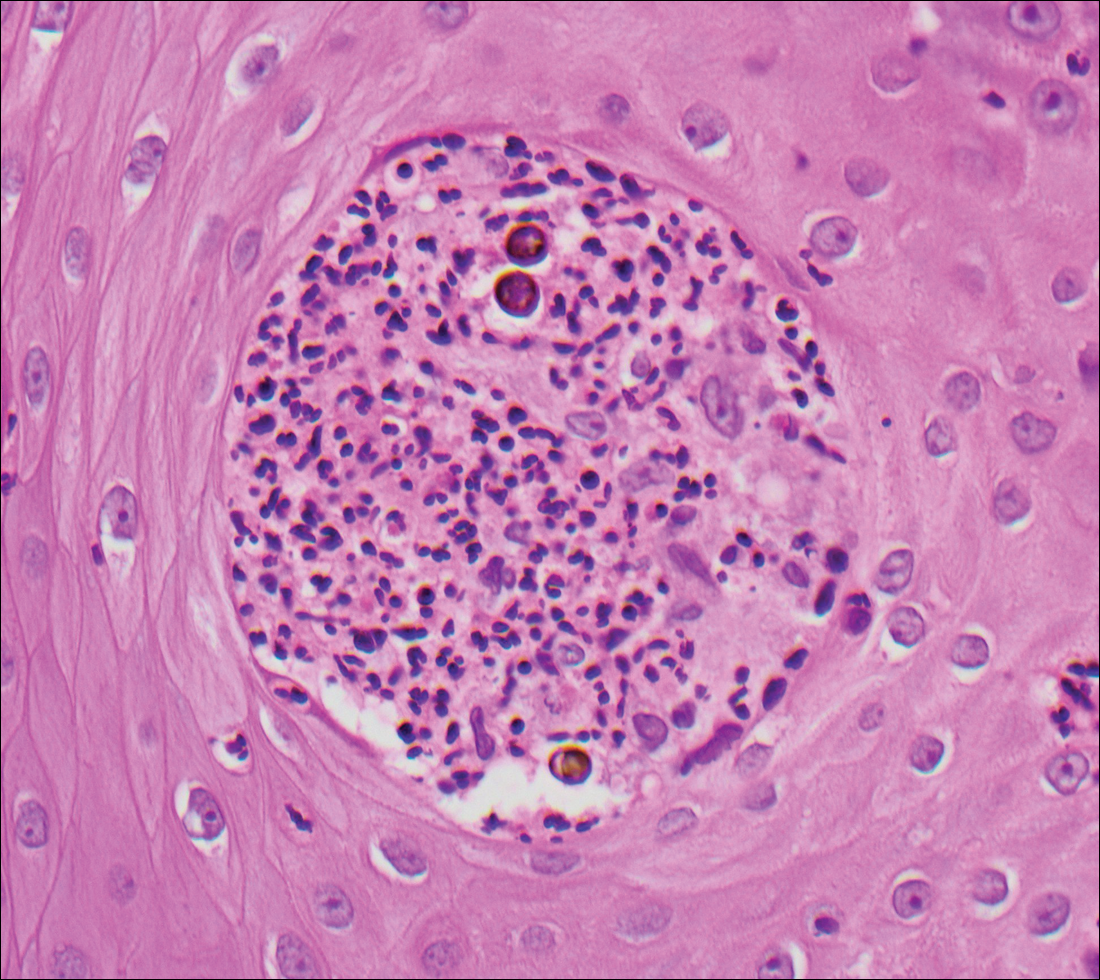
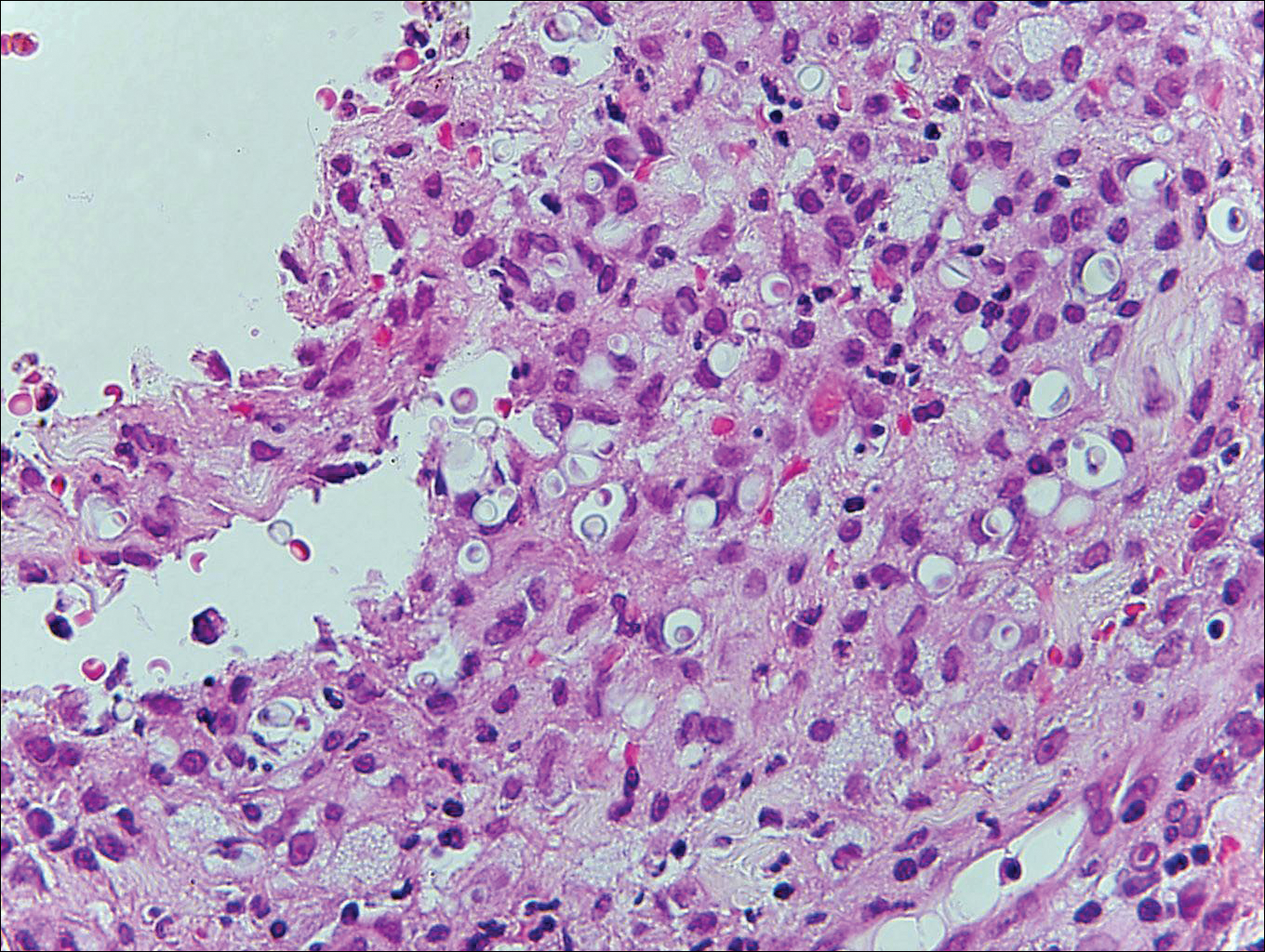
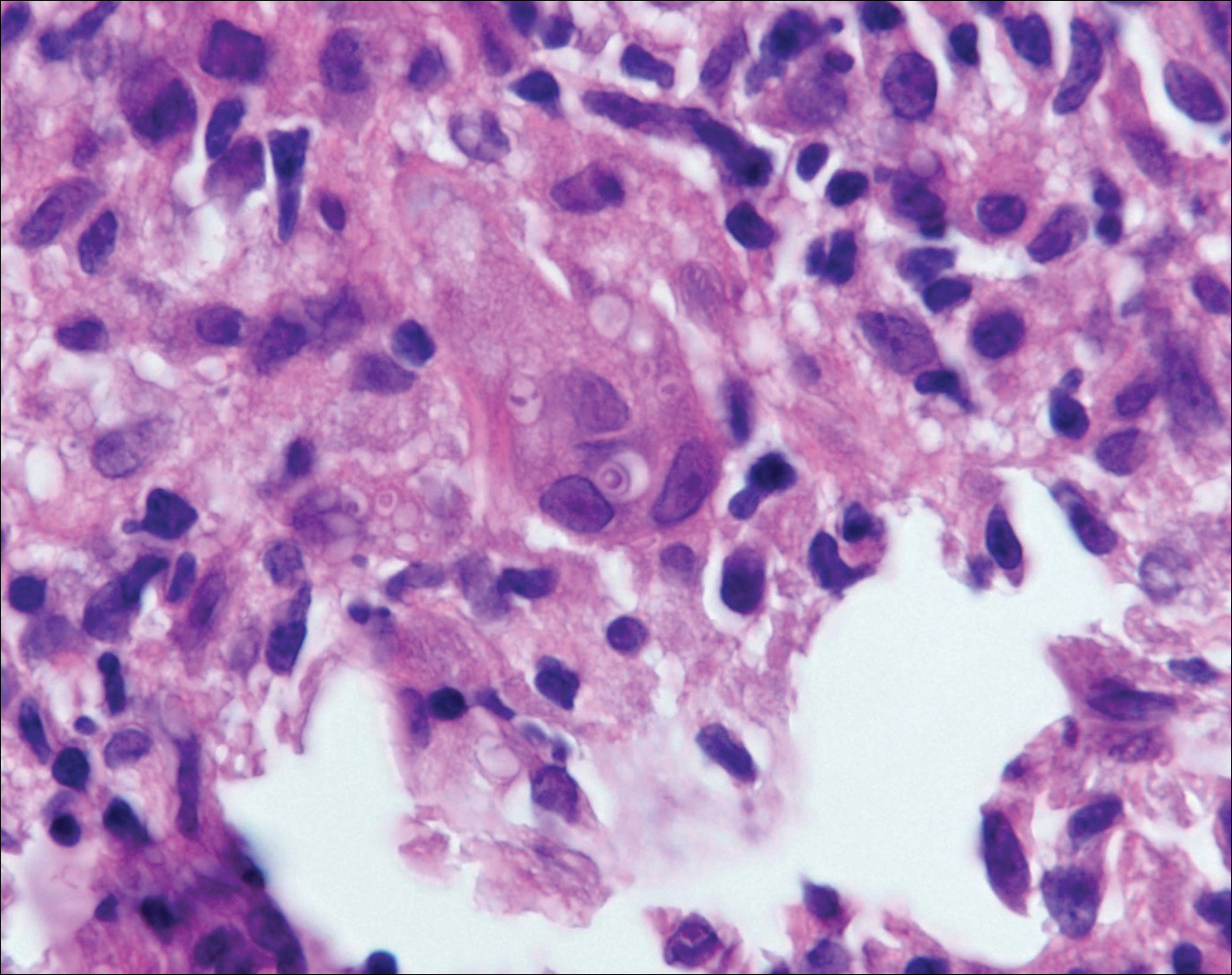
Blastomycosis is caused by Blastomyces dermatitidis, which is endemic in the Midwestern and southeastern United States where it occurs environmentally in wood and soil. Unlike many fungal infections, blastomycosis most often develops in immunocompetent hosts. Infection is usually acquired via inhalation,1 and cutaneous disease typically is secondary to pulmonary infection. Although not common, traumatic inoculation also can cause cutaneous blastomycosis. Skin lesions include crusted verrucous nodules and plaques with elevated borders.1,2 Histologic features include pseudoepitheliomatous hyperplasia with intraepidermal neutrophilic microabscesses (Figure 1), and a neutrophilic and granulomatous dermal infiltrate. Organisms often are found within histiocytes (quiz image) or small abscesses. The yeasts usually are 8 to 15 µm in diameter with a thick cell wall and occasionally display broad-based budding.
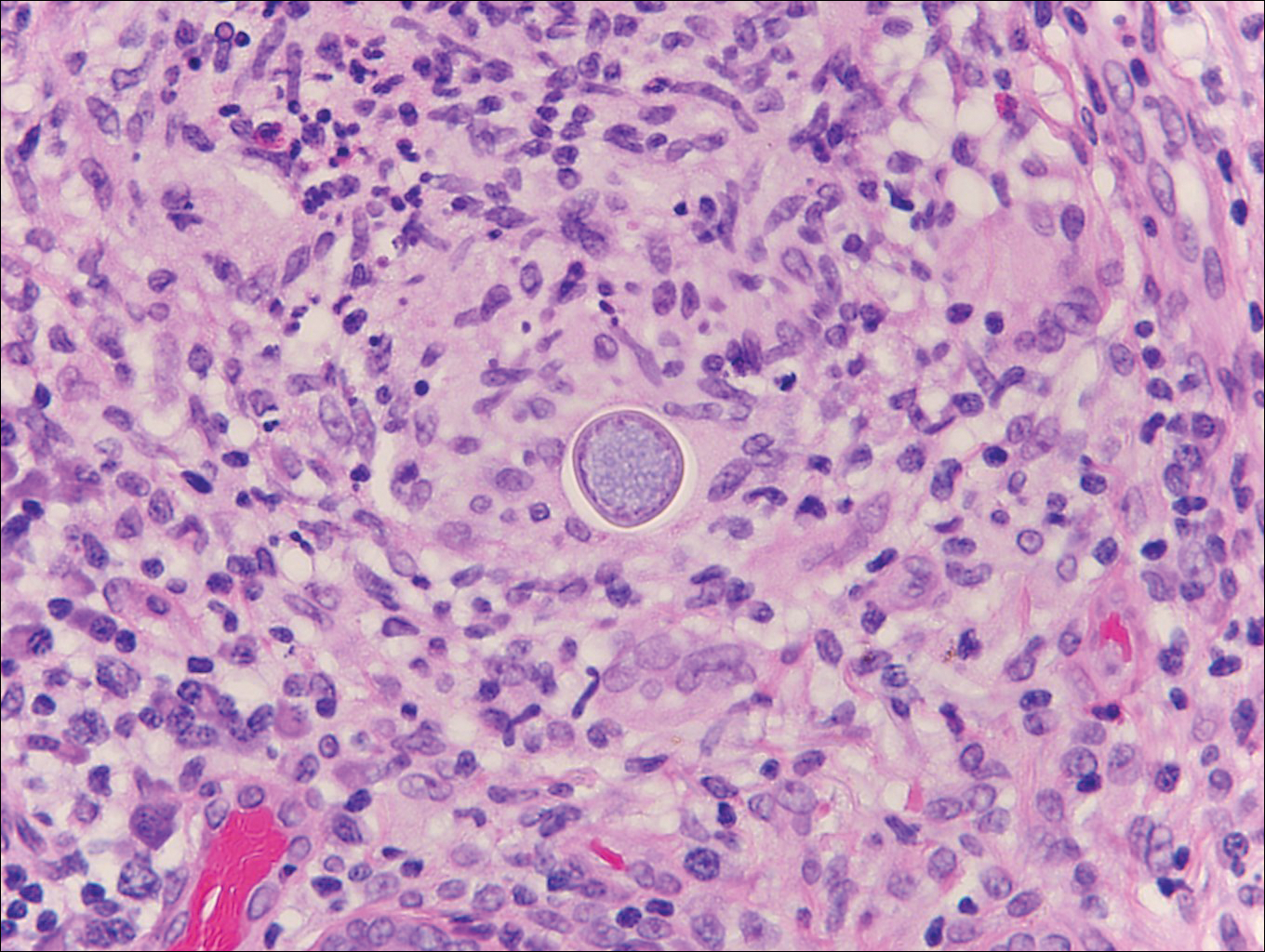
Chromoblastomycosis is caused by dematiaceous (pigmented) fungi, including Fonsecaea, Phialophora, Cladophialophora, and Rhinocladiella species,3 which are present in soil and vegetable debris in tropical and subtropical regions. Infection typically occurs in the foot or lower leg from traumatic inoculation, such as a thorn or splinter injury.2 Histologically, chromoblastomycosis is characterized by pseudoepitheliomatous hyperplasia; suppurative and granulomatous dermatitis; and sclerotic (Medlar) bodies, which are 5 to 12 µm in diameter, round, brown, sometimes septate cells resembling copper pennies (Figure 2).2
Coccidioidomycosis is caused by Coccidioides immitis, which is found in soil in the southwestern United States. Infection most often occurs via inhalation of airborne arthrospores.2 Cutaneous lesions occasionally are observed following dissemination or rarely following primary inoculation injury. They may present as papules, nodules, pustules, plaques, and ulcers, with the face being the most commonly affected site.1 Histologically, coccidioidomycosis is characterized by pseudoepitheliomatous hyperplasia, suppurative and granulomatous dermatitis, and large spherules (up to 100 µm in diameter) containing numerous small endospores (Figure 3).
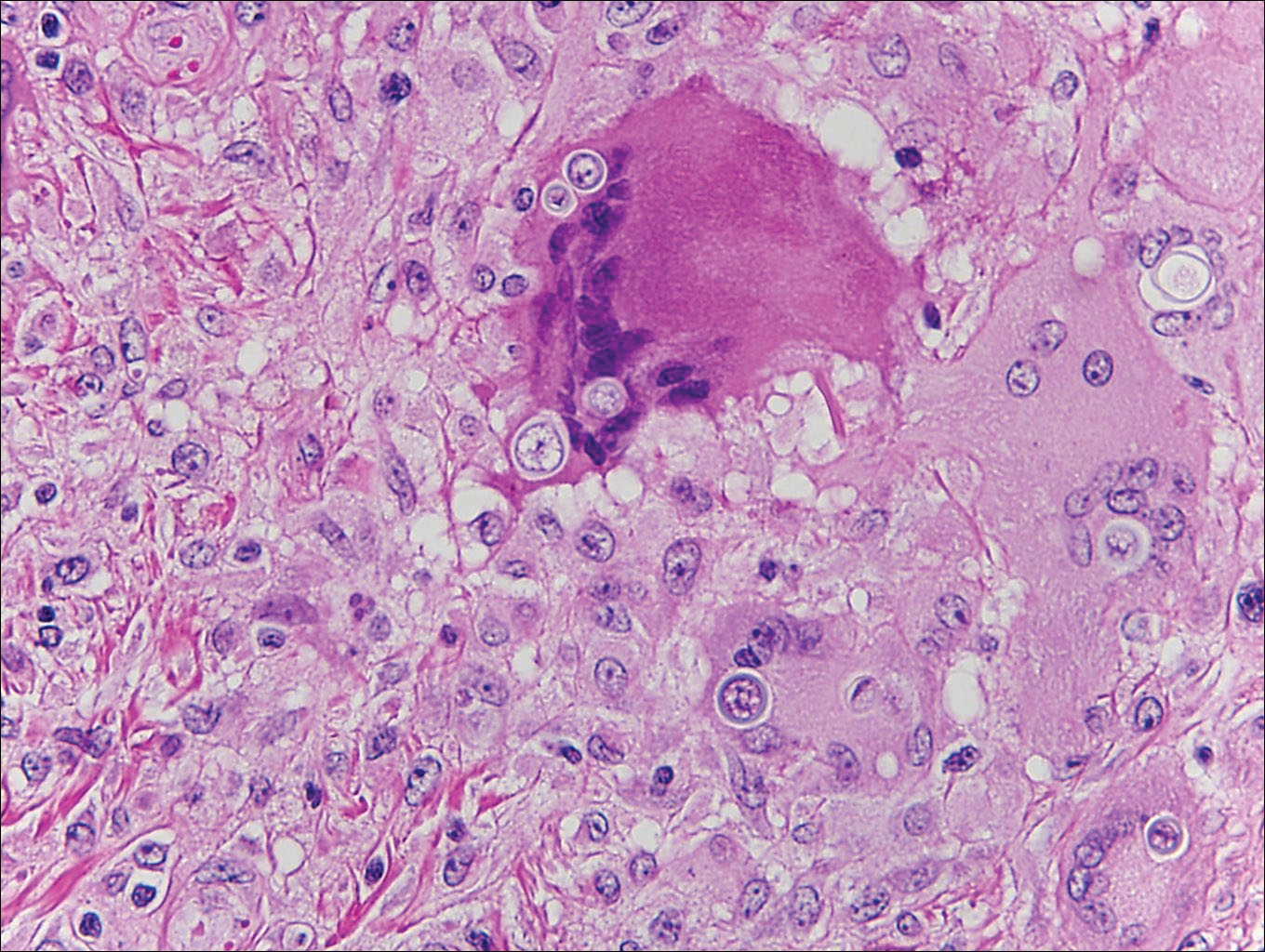
Cryptococcosis is caused by Cryptococcus neoformans, a fungus found in soil, fruit, and pigeon droppings throughout the world.2,3 The most common route of infection is via the respiratory tract. Systemic spread and central nervous system involvement may occur in immunocompromised hosts.2 Skin involvement is uncommon and may present on the head and neck with umbilicated papules, pustules, nodules, plaques, or ulcers. Histologically, Cryptococcus is a spherical yeast, often 4 to 20 µm in diameter. Replication is by narrow-based budding. A characteristic feature is a mucoid capsule, which retracts during processing, leaving a clear space around the yeast (Figure 4). When present, the mucoid capsule can be highlighted on mucicarmine or Alcian blue staining. Histologic variants of cryptococcosis include granulomatous (high host immune response), gelatinous (low host immune response), and suppurative types.3
Histoplasmosis is caused by Histoplasma capsulatum, which occurs in soil and bird and bat droppings, with exposure primarily via inhalation. Cutaneous histoplasmosis is almost always a feature of disseminated disease, which occurs most commonly in immunosuppressed individuals.1 Skin lesions may present as macules, papules, indurated plaques, ulcers, purpura, panniculitis, and subcutaneous nodules.2 Histologically, there is a granulomatous and neutrophilic infiltrate within the dermis and subcutis. Yeasts are small (2-4 µm in diameter) and are observed within the cytoplasm of macrophages (Figure 5) where they appear as basophilic dots, sometimes surrounded by an artifactual clear space (pseudocapsule).2
- Bolognia JL, Jorizzo JL, Shaffer JV. Dermatology. 3rd ed. Vol 2. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier/Saunders; 2012.
- Calonje JE, Brenn T, Lazar AJ, et al. McKee's Pathology of the Skin. 4th ed. St. Louis, MO: Elsevier/Saunders; 2012.
- Schwarzenberger K, Werchniak A, Ko C. Requisites in Dermatology: General Dermatology. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier/Saunders; 2009.
Blastomycosis
Blastomycosis is caused by Blastomyces dermatitidis, which is endemic in the Midwestern and southeastern United States where it occurs environmentally in wood and soil. Unlike many fungal infections, blastomycosis most often develops in immunocompetent hosts. Infection is usually acquired via inhalation,1 and cutaneous disease typically is secondary to pulmonary infection. Although not common, traumatic inoculation also can cause cutaneous blastomycosis. Skin lesions include crusted verrucous nodules and plaques with elevated borders.1,2 Histologic features include pseudoepitheliomatous hyperplasia with intraepidermal neutrophilic microabscesses (Figure 1), and a neutrophilic and granulomatous dermal infiltrate. Organisms often are found within histiocytes (quiz image) or small abscesses. The yeasts usually are 8 to 15 µm in diameter with a thick cell wall and occasionally display broad-based budding.

Chromoblastomycosis is caused by dematiaceous (pigmented) fungi, including Fonsecaea, Phialophora, Cladophialophora, and Rhinocladiella species,3 which are present in soil and vegetable debris in tropical and subtropical regions. Infection typically occurs in the foot or lower leg from traumatic inoculation, such as a thorn or splinter injury.2 Histologically, chromoblastomycosis is characterized by pseudoepitheliomatous hyperplasia; suppurative and granulomatous dermatitis; and sclerotic (Medlar) bodies, which are 5 to 12 µm in diameter, round, brown, sometimes septate cells resembling copper pennies (Figure 2).2

Coccidioidomycosis is caused by Coccidioides immitis, which is found in soil in the southwestern United States. Infection most often occurs via inhalation of airborne arthrospores.2 Cutaneous lesions occasionally are observed following dissemination or rarely following primary inoculation injury. They may present as papules, nodules, pustules, plaques, and ulcers, with the face being the most commonly affected site.1 Histologically, coccidioidomycosis is characterized by pseudoepitheliomatous hyperplasia, suppurative and granulomatous dermatitis, and large spherules (up to 100 µm in diameter) containing numerous small endospores (Figure 3).

Cryptococcosis is caused by Cryptococcus neoformans, a fungus found in soil, fruit, and pigeon droppings throughout the world.2,3 The most common route of infection is via the respiratory tract. Systemic spread and central nervous system involvement may occur in immunocompromised hosts.2 Skin involvement is uncommon and may present on the head and neck with umbilicated papules, pustules, nodules, plaques, or ulcers. Histologically, Cryptococcus is a spherical yeast, often 4 to 20 µm in diameter. Replication is by narrow-based budding. A characteristic feature is a mucoid capsule, which retracts during processing, leaving a clear space around the yeast (Figure 4). When present, the mucoid capsule can be highlighted on mucicarmine or Alcian blue staining. Histologic variants of cryptococcosis include granulomatous (high host immune response), gelatinous (low host immune response), and suppurative types.3

Histoplasmosis is caused by Histoplasma capsulatum, which occurs in soil and bird and bat droppings, with exposure primarily via inhalation. Cutaneous histoplasmosis is almost always a feature of disseminated disease, which occurs most commonly in immunosuppressed individuals.1 Skin lesions may present as macules, papules, indurated plaques, ulcers, purpura, panniculitis, and subcutaneous nodules.2 Histologically, there is a granulomatous and neutrophilic infiltrate within the dermis and subcutis. Yeasts are small (2-4 µm in diameter) and are observed within the cytoplasm of macrophages (Figure 5) where they appear as basophilic dots, sometimes surrounded by an artifactual clear space (pseudocapsule).2

Blastomycosis
Blastomycosis is caused by Blastomyces dermatitidis, which is endemic in the Midwestern and southeastern United States where it occurs environmentally in wood and soil. Unlike many fungal infections, blastomycosis most often develops in immunocompetent hosts. Infection is usually acquired via inhalation,1 and cutaneous disease typically is secondary to pulmonary infection. Although not common, traumatic inoculation also can cause cutaneous blastomycosis. Skin lesions include crusted verrucous nodules and plaques with elevated borders.1,2 Histologic features include pseudoepitheliomatous hyperplasia with intraepidermal neutrophilic microabscesses (Figure 1), and a neutrophilic and granulomatous dermal infiltrate. Organisms often are found within histiocytes (quiz image) or small abscesses. The yeasts usually are 8 to 15 µm in diameter with a thick cell wall and occasionally display broad-based budding.

Chromoblastomycosis is caused by dematiaceous (pigmented) fungi, including Fonsecaea, Phialophora, Cladophialophora, and Rhinocladiella species,3 which are present in soil and vegetable debris in tropical and subtropical regions. Infection typically occurs in the foot or lower leg from traumatic inoculation, such as a thorn or splinter injury.2 Histologically, chromoblastomycosis is characterized by pseudoepitheliomatous hyperplasia; suppurative and granulomatous dermatitis; and sclerotic (Medlar) bodies, which are 5 to 12 µm in diameter, round, brown, sometimes septate cells resembling copper pennies (Figure 2).2

Coccidioidomycosis is caused by Coccidioides immitis, which is found in soil in the southwestern United States. Infection most often occurs via inhalation of airborne arthrospores.2 Cutaneous lesions occasionally are observed following dissemination or rarely following primary inoculation injury. They may present as papules, nodules, pustules, plaques, and ulcers, with the face being the most commonly affected site.1 Histologically, coccidioidomycosis is characterized by pseudoepitheliomatous hyperplasia, suppurative and granulomatous dermatitis, and large spherules (up to 100 µm in diameter) containing numerous small endospores (Figure 3).

Cryptococcosis is caused by Cryptococcus neoformans, a fungus found in soil, fruit, and pigeon droppings throughout the world.2,3 The most common route of infection is via the respiratory tract. Systemic spread and central nervous system involvement may occur in immunocompromised hosts.2 Skin involvement is uncommon and may present on the head and neck with umbilicated papules, pustules, nodules, plaques, or ulcers. Histologically, Cryptococcus is a spherical yeast, often 4 to 20 µm in diameter. Replication is by narrow-based budding. A characteristic feature is a mucoid capsule, which retracts during processing, leaving a clear space around the yeast (Figure 4). When present, the mucoid capsule can be highlighted on mucicarmine or Alcian blue staining. Histologic variants of cryptococcosis include granulomatous (high host immune response), gelatinous (low host immune response), and suppurative types.3

Histoplasmosis is caused by Histoplasma capsulatum, which occurs in soil and bird and bat droppings, with exposure primarily via inhalation. Cutaneous histoplasmosis is almost always a feature of disseminated disease, which occurs most commonly in immunosuppressed individuals.1 Skin lesions may present as macules, papules, indurated plaques, ulcers, purpura, panniculitis, and subcutaneous nodules.2 Histologically, there is a granulomatous and neutrophilic infiltrate within the dermis and subcutis. Yeasts are small (2-4 µm in diameter) and are observed within the cytoplasm of macrophages (Figure 5) where they appear as basophilic dots, sometimes surrounded by an artifactual clear space (pseudocapsule).2

- Bolognia JL, Jorizzo JL, Shaffer JV. Dermatology. 3rd ed. Vol 2. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier/Saunders; 2012.
- Calonje JE, Brenn T, Lazar AJ, et al. McKee's Pathology of the Skin. 4th ed. St. Louis, MO: Elsevier/Saunders; 2012.
- Schwarzenberger K, Werchniak A, Ko C. Requisites in Dermatology: General Dermatology. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier/Saunders; 2009.
- Bolognia JL, Jorizzo JL, Shaffer JV. Dermatology. 3rd ed. Vol 2. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier/Saunders; 2012.
- Calonje JE, Brenn T, Lazar AJ, et al. McKee's Pathology of the Skin. 4th ed. St. Louis, MO: Elsevier/Saunders; 2012.
- Schwarzenberger K, Werchniak A, Ko C. Requisites in Dermatology: General Dermatology. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier/Saunders; 2009.
Pruritic Papules on the Scalp and Arms
Folliculotropic Mycosis Fungoides
Folliculotropic mycosis fungoides (FMF) is a variant of mycosis fungoides (MF) that occurs mostly in adults with a male predilection. The disease clinically favors the head and neck. Patients commonly present with pruritic papules that often are grouped, alopecia, and frequent secondary bacterial infections. Less commonly patients present with acneiform lesions and mucinorrhea. Patients often experience more pruritus in FMF than in classic MF, which can provide a good means of assessing disease activity. Disease-specific 5-year survival is approximately 70% to 80%, which is worse than classic plaque-stage MF and similar to tumor-stage MF.1
Treatment of FMF differs from classic MF in that the lesions are less responsive to skin-targeted therapies due to the perifollicular nature of dermal infiltrates. Superficial skin lesions can be treated with psoralen plus UVA (PUVA) therapy. Other options include PUVA in combination with interferon alfa or retinoids and local radiotherapy for solitary thick tumors; however, in patients who have more infiltrative skin lesions or had PUVA therapy that failed, total skin electron beam therapy may be required.2
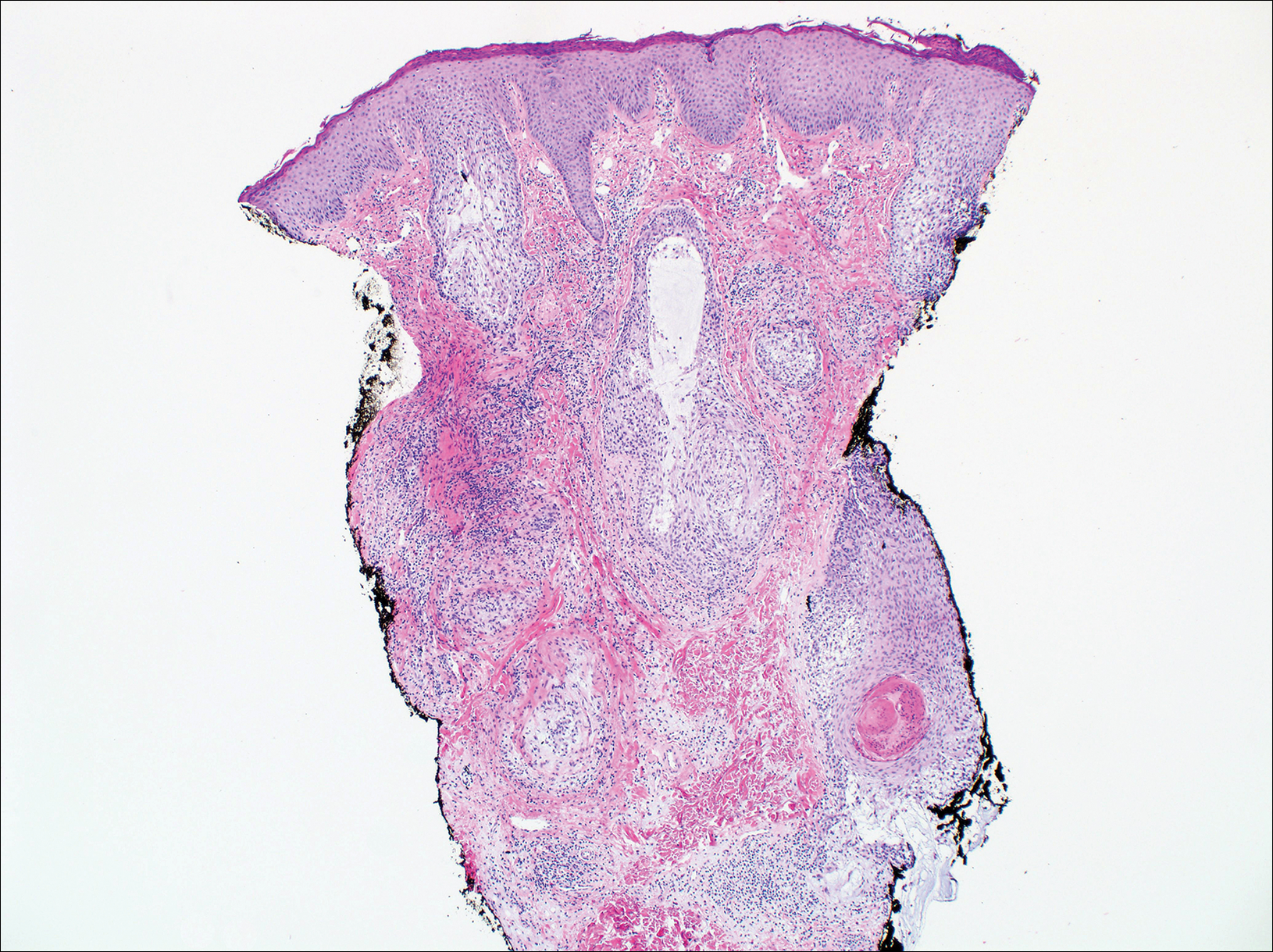
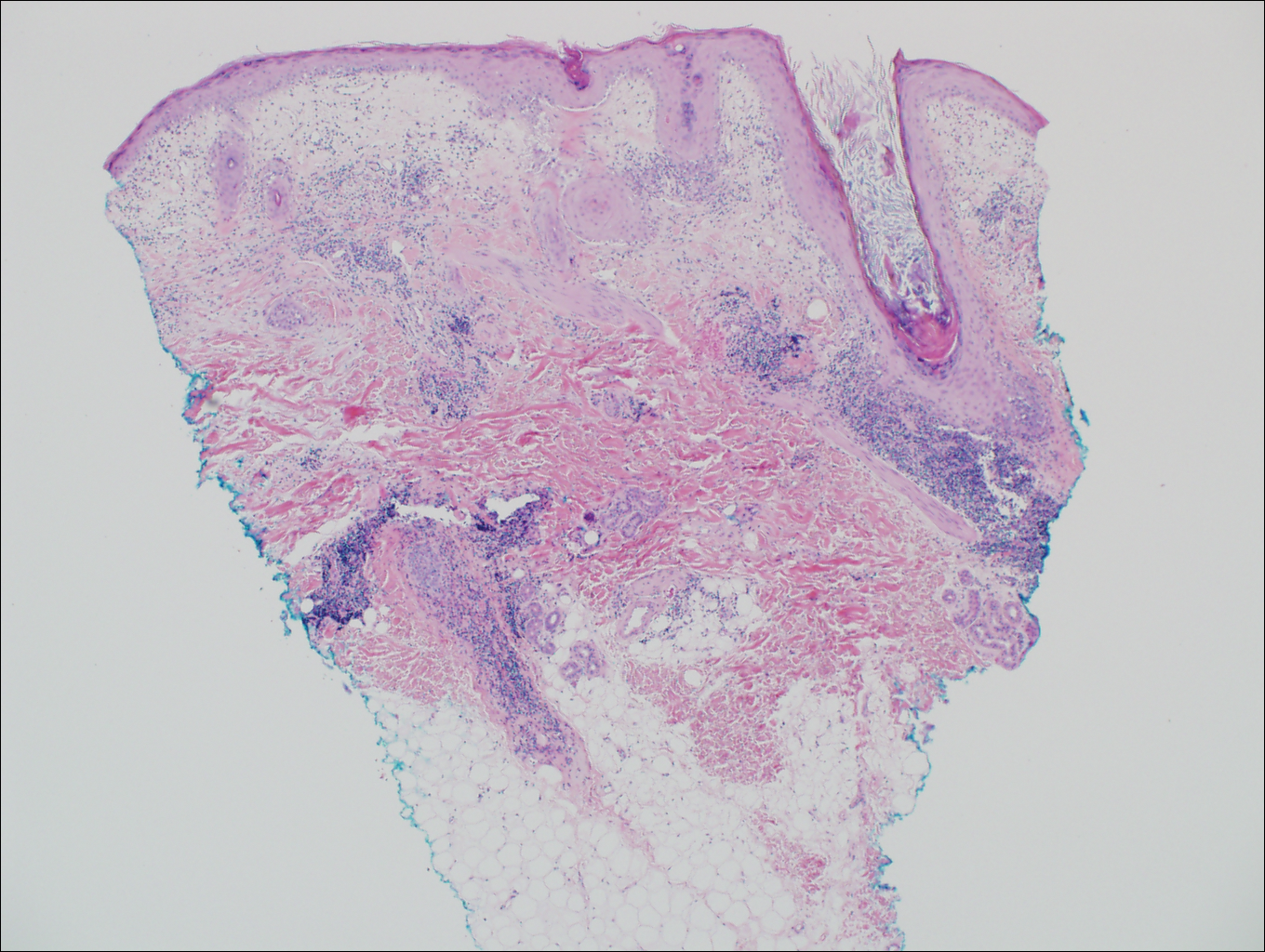
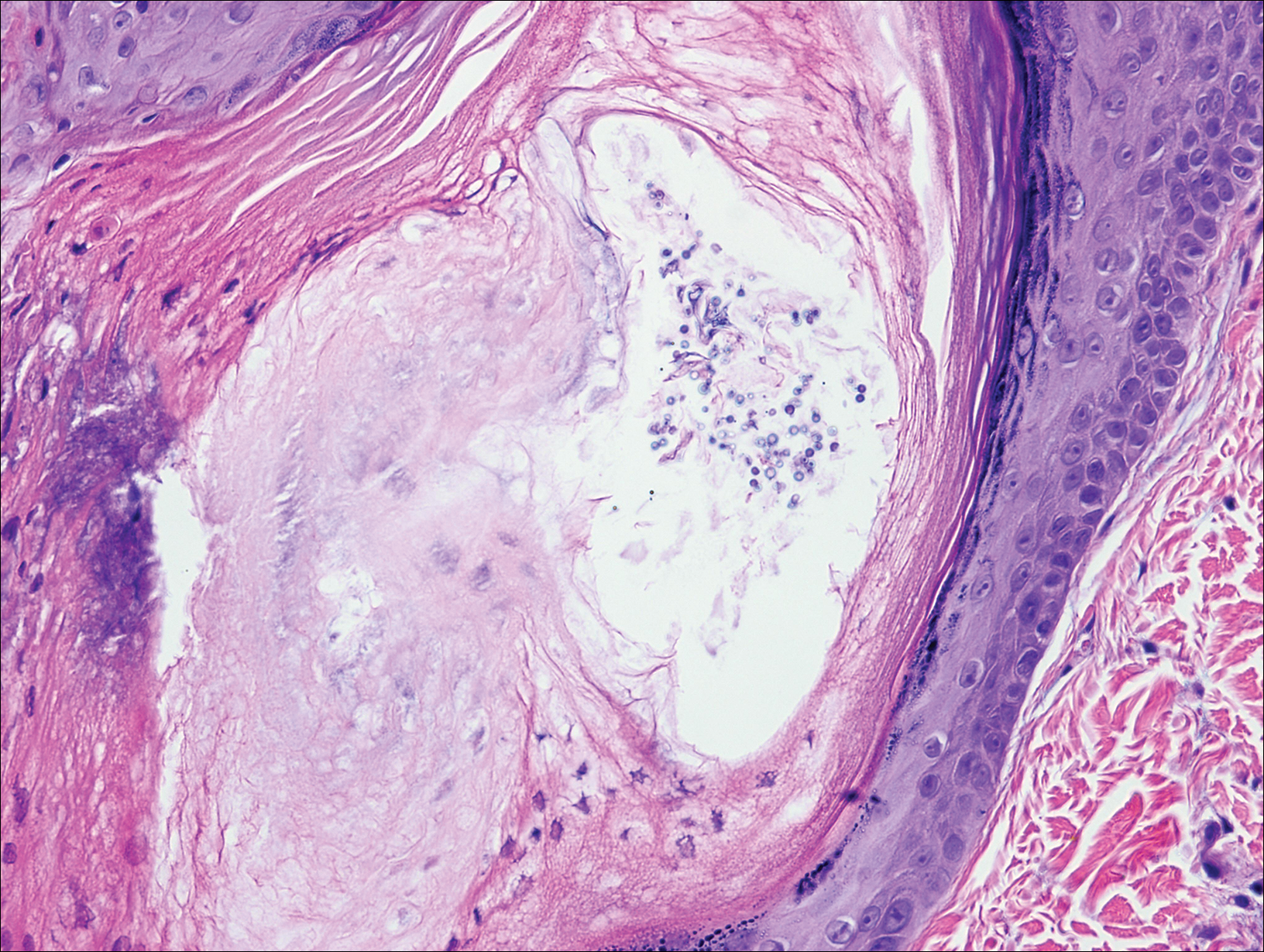
On histologic examination, there typically is perivascular and periadnexal localization of dermal infiltrates with varied involvement of the follicular epithelium and damage to hair follicles by atypical small, medium, and large hyperchromatic lymphocytes with cerebriform nuclei. Mucinous degeneration of the follicular epithelium can be seen, as highlighted on Alcian blue staining, and a mixed infiltrate of eosinophils and plasma cells often is present (quiz image and Figure 1). Frequent sparing of the epidermis is noteworthy.2-4 In most cases, the neoplastic T lymphocytes are characterized by a CD3+CD4+CD8-immunophenotype as is seen in classic MF. Sometimes an admixture of CD30+ blast cells is seen.1
Histologic differential considerations for FMF include eosinophilic pustular folliculitis (EPF), primary follicular mucinosis, lupus erythematosus, and pityrosporum folliculitis.
Eosinophilic pustular folliculitis has several clinical subtypes, such as classic Ofuji disease and immunosuppression-associated EPF secondary to human immunodeficiency virus. Histologically, EPF is characterized by spongiosis of the hair follicle epithelium with exocytosis of a mixed infiltrate of lymphocytes and eosinophils extending from the sebaceous gland and its duct to the infundibulum with formation of hallmark eosinophilic pustules (Figure 2). Infiltration of neutrophils in inflamed lesions generally is seen. Eosinophilic pustular folliculitis is an important differential for FMF, as follicular mucinosis has been observed in lesions of EPF.5 Both EPF and FMF can exhibit eosinophils and lymphocytes in the upper dermis, spongiosis of the hair follicle epithelium, and mucinous degeneration of follicles,6 though lymphocytic atypia and relatively fewer eosinophils are suggestive of the latter.
Primary follicular mucinosis (PFM) tends to occur as a solitary lesion in younger female patients in contrast to the multiple lesions that typically appear in older male patients with FMF. Histologically, PFM usually manifests as large, cystic, mucin-filled spaces and polyclonal perivascular and periadnexal lymphocytic infiltrate without notable cellular atypia or epidermotropism (Figure 3). Because follicular mucinosis is a common feature of FMF, its distinction from PFM can be challenging and often is aided by the absence of cellular atypia and relatively mild lymphocytic infiltrate in the latter.7
Cutaneous lupus erythematosus with its characteristic folliculocentric lymphocytic infiltration and associated dermal mucin also qualifies as a potential differential possibility for FMF; however, the perivascular and periadnexal pattern of lymphocytic infiltration as well as the localization of mucin to the reticular dermal interstitium8,9 are key histopathologic distinctions (Figure 4). Furthermore, although the histologic presentation of lupus erythematosus can be variable, it also classically shows interface dermatitis, basement membrane thickening, and follicular plugging.
Pityrosporum folliculitis is the most common cause of fungal folliculitis and is caused by the Malassezia species. On histology, there typically is an unremarkable epithelium with plugged follicles and suppurative folliculitis. Serial sections of the biopsy specimen often are required to identify dilated, follicle-containing, budding yeast cells (Figure 5). Organisms are located predominantly within the infundibulum and orifice of follicular lumen, are positive for periodic acid-Schiff, and are diastase resistant.10
- Willemze R, Jaffe ES, Burg G, et al. WHO-EORTC classification for cutaneous lymphomas. Blood. 2005;105:3768-3785.
- van Doorn R, Scheffer E, Willemze R. Follicular mycosis fungoides, a distinct disease entity with or without associated follicular mucinosis. a clinicopathologic and follow-up study of 51 patients. Arch Dermatol. 2002;138:191-198.
- DeBloom J 2nd, Severson J, Gaspari A, et al. Follicular mycosis fungoides: a case report and review of the literature. J Cutan Pathol. 2001;28:318-324.
- Flaig MJ, Cerroni L, Schuhmann K, et al. Follicular mycosis fungoides: a histopathologic analysis of nine cases. J Cutan Pathol. 2001;28:525-530.
- Fujiyama T, Tokura Y. Clinical and histopathological differential diagnosis of eosinophilic pustular folliculitis. J Dermatol. 2013;40:419-423.
- Lee JY, Tsai YM, Sheu HM. Ofuji's disease with follicular mucinosis and its differential diagnosis from alopecia mucinosa. J Cutan Pathol. 2003;30:307-313.
- Rongioletti F, De Lucchi S, Meyes D, et al. Follicular mucinosis: a clinicopathologic, histochemical, immunohistochemical and molecular study comparing the primary benign form and the mycosis fungoides-associated follicular mucinosis. J Cutan Pathol. 2010;37:15-19.
- Vincent JG, Chan MP. Specificity of dermal mucin in the diagnosis of lupus erythematosus: comparison with other dermatitides and normal skin. J Cutan Pathol. 2015;42:722-729.
- Yell JA, Mbuagbaw J, Burge SM. Cutaneous manifestations of systemic lupus erythematosus. Br J Dermatol. 1996;135:355-362.
- Durdu M, Ilkit M. First step in the differential diagnosis of folliculitis: cytology. Crit Rev Microbiol. 2013;39:9-25.
Folliculotropic Mycosis Fungoides
Folliculotropic mycosis fungoides (FMF) is a variant of mycosis fungoides (MF) that occurs mostly in adults with a male predilection. The disease clinically favors the head and neck. Patients commonly present with pruritic papules that often are grouped, alopecia, and frequent secondary bacterial infections. Less commonly patients present with acneiform lesions and mucinorrhea. Patients often experience more pruritus in FMF than in classic MF, which can provide a good means of assessing disease activity. Disease-specific 5-year survival is approximately 70% to 80%, which is worse than classic plaque-stage MF and similar to tumor-stage MF.1
Treatment of FMF differs from classic MF in that the lesions are less responsive to skin-targeted therapies due to the perifollicular nature of dermal infiltrates. Superficial skin lesions can be treated with psoralen plus UVA (PUVA) therapy. Other options include PUVA in combination with interferon alfa or retinoids and local radiotherapy for solitary thick tumors; however, in patients who have more infiltrative skin lesions or had PUVA therapy that failed, total skin electron beam therapy may be required.2
On histologic examination, there typically is perivascular and periadnexal localization of dermal infiltrates with varied involvement of the follicular epithelium and damage to hair follicles by atypical small, medium, and large hyperchromatic lymphocytes with cerebriform nuclei. Mucinous degeneration of the follicular epithelium can be seen, as highlighted on Alcian blue staining, and a mixed infiltrate of eosinophils and plasma cells often is present (quiz image and Figure 1). Frequent sparing of the epidermis is noteworthy.2-4 In most cases, the neoplastic T lymphocytes are characterized by a CD3+CD4+CD8-immunophenotype as is seen in classic MF. Sometimes an admixture of CD30+ blast cells is seen.1

Histologic differential considerations for FMF include eosinophilic pustular folliculitis (EPF), primary follicular mucinosis, lupus erythematosus, and pityrosporum folliculitis.
Eosinophilic pustular folliculitis has several clinical subtypes, such as classic Ofuji disease and immunosuppression-associated EPF secondary to human immunodeficiency virus. Histologically, EPF is characterized by spongiosis of the hair follicle epithelium with exocytosis of a mixed infiltrate of lymphocytes and eosinophils extending from the sebaceous gland and its duct to the infundibulum with formation of hallmark eosinophilic pustules (Figure 2). Infiltration of neutrophils in inflamed lesions generally is seen. Eosinophilic pustular folliculitis is an important differential for FMF, as follicular mucinosis has been observed in lesions of EPF.5 Both EPF and FMF can exhibit eosinophils and lymphocytes in the upper dermis, spongiosis of the hair follicle epithelium, and mucinous degeneration of follicles,6 though lymphocytic atypia and relatively fewer eosinophils are suggestive of the latter.

Primary follicular mucinosis (PFM) tends to occur as a solitary lesion in younger female patients in contrast to the multiple lesions that typically appear in older male patients with FMF. Histologically, PFM usually manifests as large, cystic, mucin-filled spaces and polyclonal perivascular and periadnexal lymphocytic infiltrate without notable cellular atypia or epidermotropism (Figure 3). Because follicular mucinosis is a common feature of FMF, its distinction from PFM can be challenging and often is aided by the absence of cellular atypia and relatively mild lymphocytic infiltrate in the latter.7

Cutaneous lupus erythematosus with its characteristic folliculocentric lymphocytic infiltration and associated dermal mucin also qualifies as a potential differential possibility for FMF; however, the perivascular and periadnexal pattern of lymphocytic infiltration as well as the localization of mucin to the reticular dermal interstitium8,9 are key histopathologic distinctions (Figure 4). Furthermore, although the histologic presentation of lupus erythematosus can be variable, it also classically shows interface dermatitis, basement membrane thickening, and follicular plugging.

Pityrosporum folliculitis is the most common cause of fungal folliculitis and is caused by the Malassezia species. On histology, there typically is an unremarkable epithelium with plugged follicles and suppurative folliculitis. Serial sections of the biopsy specimen often are required to identify dilated, follicle-containing, budding yeast cells (Figure 5). Organisms are located predominantly within the infundibulum and orifice of follicular lumen, are positive for periodic acid-Schiff, and are diastase resistant.10

Folliculotropic Mycosis Fungoides
Folliculotropic mycosis fungoides (FMF) is a variant of mycosis fungoides (MF) that occurs mostly in adults with a male predilection. The disease clinically favors the head and neck. Patients commonly present with pruritic papules that often are grouped, alopecia, and frequent secondary bacterial infections. Less commonly patients present with acneiform lesions and mucinorrhea. Patients often experience more pruritus in FMF than in classic MF, which can provide a good means of assessing disease activity. Disease-specific 5-year survival is approximately 70% to 80%, which is worse than classic plaque-stage MF and similar to tumor-stage MF.1
Treatment of FMF differs from classic MF in that the lesions are less responsive to skin-targeted therapies due to the perifollicular nature of dermal infiltrates. Superficial skin lesions can be treated with psoralen plus UVA (PUVA) therapy. Other options include PUVA in combination with interferon alfa or retinoids and local radiotherapy for solitary thick tumors; however, in patients who have more infiltrative skin lesions or had PUVA therapy that failed, total skin electron beam therapy may be required.2
On histologic examination, there typically is perivascular and periadnexal localization of dermal infiltrates with varied involvement of the follicular epithelium and damage to hair follicles by atypical small, medium, and large hyperchromatic lymphocytes with cerebriform nuclei. Mucinous degeneration of the follicular epithelium can be seen, as highlighted on Alcian blue staining, and a mixed infiltrate of eosinophils and plasma cells often is present (quiz image and Figure 1). Frequent sparing of the epidermis is noteworthy.2-4 In most cases, the neoplastic T lymphocytes are characterized by a CD3+CD4+CD8-immunophenotype as is seen in classic MF. Sometimes an admixture of CD30+ blast cells is seen.1

Histologic differential considerations for FMF include eosinophilic pustular folliculitis (EPF), primary follicular mucinosis, lupus erythematosus, and pityrosporum folliculitis.
Eosinophilic pustular folliculitis has several clinical subtypes, such as classic Ofuji disease and immunosuppression-associated EPF secondary to human immunodeficiency virus. Histologically, EPF is characterized by spongiosis of the hair follicle epithelium with exocytosis of a mixed infiltrate of lymphocytes and eosinophils extending from the sebaceous gland and its duct to the infundibulum with formation of hallmark eosinophilic pustules (Figure 2). Infiltration of neutrophils in inflamed lesions generally is seen. Eosinophilic pustular folliculitis is an important differential for FMF, as follicular mucinosis has been observed in lesions of EPF.5 Both EPF and FMF can exhibit eosinophils and lymphocytes in the upper dermis, spongiosis of the hair follicle epithelium, and mucinous degeneration of follicles,6 though lymphocytic atypia and relatively fewer eosinophils are suggestive of the latter.

Primary follicular mucinosis (PFM) tends to occur as a solitary lesion in younger female patients in contrast to the multiple lesions that typically appear in older male patients with FMF. Histologically, PFM usually manifests as large, cystic, mucin-filled spaces and polyclonal perivascular and periadnexal lymphocytic infiltrate without notable cellular atypia or epidermotropism (Figure 3). Because follicular mucinosis is a common feature of FMF, its distinction from PFM can be challenging and often is aided by the absence of cellular atypia and relatively mild lymphocytic infiltrate in the latter.7

Cutaneous lupus erythematosus with its characteristic folliculocentric lymphocytic infiltration and associated dermal mucin also qualifies as a potential differential possibility for FMF; however, the perivascular and periadnexal pattern of lymphocytic infiltration as well as the localization of mucin to the reticular dermal interstitium8,9 are key histopathologic distinctions (Figure 4). Furthermore, although the histologic presentation of lupus erythematosus can be variable, it also classically shows interface dermatitis, basement membrane thickening, and follicular plugging.

Pityrosporum folliculitis is the most common cause of fungal folliculitis and is caused by the Malassezia species. On histology, there typically is an unremarkable epithelium with plugged follicles and suppurative folliculitis. Serial sections of the biopsy specimen often are required to identify dilated, follicle-containing, budding yeast cells (Figure 5). Organisms are located predominantly within the infundibulum and orifice of follicular lumen, are positive for periodic acid-Schiff, and are diastase resistant.10

- Willemze R, Jaffe ES, Burg G, et al. WHO-EORTC classification for cutaneous lymphomas. Blood. 2005;105:3768-3785.
- van Doorn R, Scheffer E, Willemze R. Follicular mycosis fungoides, a distinct disease entity with or without associated follicular mucinosis. a clinicopathologic and follow-up study of 51 patients. Arch Dermatol. 2002;138:191-198.
- DeBloom J 2nd, Severson J, Gaspari A, et al. Follicular mycosis fungoides: a case report and review of the literature. J Cutan Pathol. 2001;28:318-324.
- Flaig MJ, Cerroni L, Schuhmann K, et al. Follicular mycosis fungoides: a histopathologic analysis of nine cases. J Cutan Pathol. 2001;28:525-530.
- Fujiyama T, Tokura Y. Clinical and histopathological differential diagnosis of eosinophilic pustular folliculitis. J Dermatol. 2013;40:419-423.
- Lee JY, Tsai YM, Sheu HM. Ofuji's disease with follicular mucinosis and its differential diagnosis from alopecia mucinosa. J Cutan Pathol. 2003;30:307-313.
- Rongioletti F, De Lucchi S, Meyes D, et al. Follicular mucinosis: a clinicopathologic, histochemical, immunohistochemical and molecular study comparing the primary benign form and the mycosis fungoides-associated follicular mucinosis. J Cutan Pathol. 2010;37:15-19.
- Vincent JG, Chan MP. Specificity of dermal mucin in the diagnosis of lupus erythematosus: comparison with other dermatitides and normal skin. J Cutan Pathol. 2015;42:722-729.
- Yell JA, Mbuagbaw J, Burge SM. Cutaneous manifestations of systemic lupus erythematosus. Br J Dermatol. 1996;135:355-362.
- Durdu M, Ilkit M. First step in the differential diagnosis of folliculitis: cytology. Crit Rev Microbiol. 2013;39:9-25.
- Willemze R, Jaffe ES, Burg G, et al. WHO-EORTC classification for cutaneous lymphomas. Blood. 2005;105:3768-3785.
- van Doorn R, Scheffer E, Willemze R. Follicular mycosis fungoides, a distinct disease entity with or without associated follicular mucinosis. a clinicopathologic and follow-up study of 51 patients. Arch Dermatol. 2002;138:191-198.
- DeBloom J 2nd, Severson J, Gaspari A, et al. Follicular mycosis fungoides: a case report and review of the literature. J Cutan Pathol. 2001;28:318-324.
- Flaig MJ, Cerroni L, Schuhmann K, et al. Follicular mycosis fungoides: a histopathologic analysis of nine cases. J Cutan Pathol. 2001;28:525-530.
- Fujiyama T, Tokura Y. Clinical and histopathological differential diagnosis of eosinophilic pustular folliculitis. J Dermatol. 2013;40:419-423.
- Lee JY, Tsai YM, Sheu HM. Ofuji's disease with follicular mucinosis and its differential diagnosis from alopecia mucinosa. J Cutan Pathol. 2003;30:307-313.
- Rongioletti F, De Lucchi S, Meyes D, et al. Follicular mucinosis: a clinicopathologic, histochemical, immunohistochemical and molecular study comparing the primary benign form and the mycosis fungoides-associated follicular mucinosis. J Cutan Pathol. 2010;37:15-19.
- Vincent JG, Chan MP. Specificity of dermal mucin in the diagnosis of lupus erythematosus: comparison with other dermatitides and normal skin. J Cutan Pathol. 2015;42:722-729.
- Yell JA, Mbuagbaw J, Burge SM. Cutaneous manifestations of systemic lupus erythematosus. Br J Dermatol. 1996;135:355-362.
- Durdu M, Ilkit M. First step in the differential diagnosis of folliculitis: cytology. Crit Rev Microbiol. 2013;39:9-25.
A 60-year-old man presented with a 3-month history of itchy bumps on the scalp and arms. He also noticed some patches of hair loss in these areas. He had no history of other skin conditions and was otherwise healthy with no other medical comorbidities.
Rapidly Growing Scalp Nodule
Cutaneous Metastasis of Pulmonary Adenocarcinoma
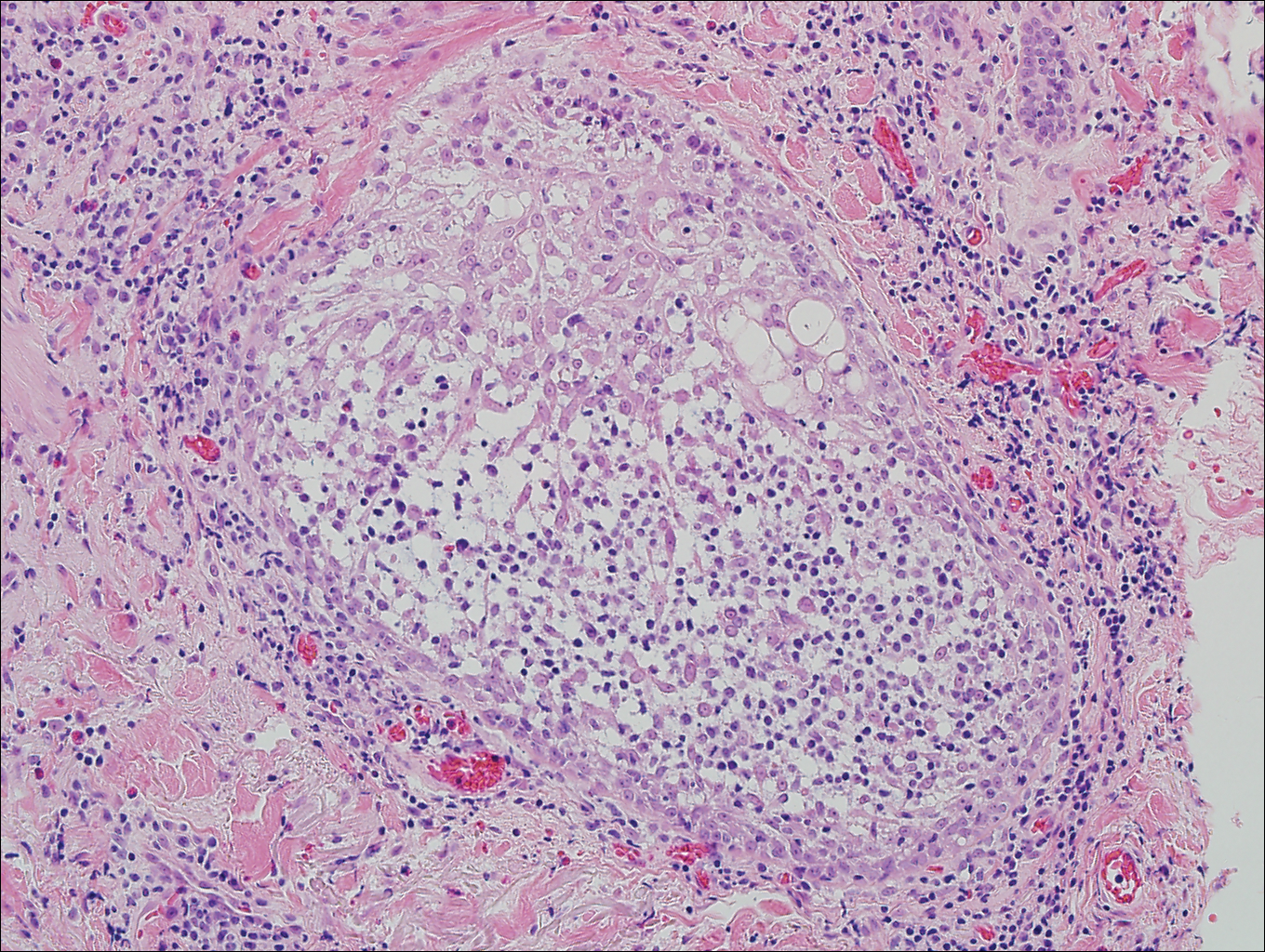
Cutaneous metastasis of pulmonary adenocarcinoma (CMPA) is a rare phenomenon with an overall survival rate of less than 5 months.1,2 Often, CMPA can be the heralding feature of an aggressive systemic malignancy in 2.8% to 22% of reported cases.2-4 Clinically, CMPAs often present as fixed, violaceous, ulcerated nodules on the chest wall, scalp, or site of a prior procedure.3,5,6 Other clinical presentations have been described including zosteriform and inflammatory carcinomalike CMPA and CMPA on the tip of the nose.7 Histologically, CMPA presents as a subdermal collection of atypical glands arranged as clustered aggregates of infiltrative glands penetrating the dermal stroma (quiz image). The atypical glands have large oval nuclei with high nuclear to cytoplasm ratios with scant pale cytoplasm.
Cutaneous metastasis of pulmonary adenocarcinoma is difficult to distinguish from other metastatic or primary glandular malignancies based on histology alone. Immunohistochemical analysis can aid in the diagnosis of the primary tumor. Pulmonary adenocarcinomas are positive for cytokeratin (CK) 7 and thyroid transcription factor 1 (TTF-1), and they are negative for CK5/6 and CK20.7 The differential diagnosis for CMPA includes other internal malignancies such as invasive ductal adenocarcinoma of the breast and gastrointestinal adenocarcinomas (eg, gastric or colorectal carcinoma [CRC]). Additionally, endometriosis and primary sebaceous carcinomas can mimic cutaneous metastatic adenocarcinomas.
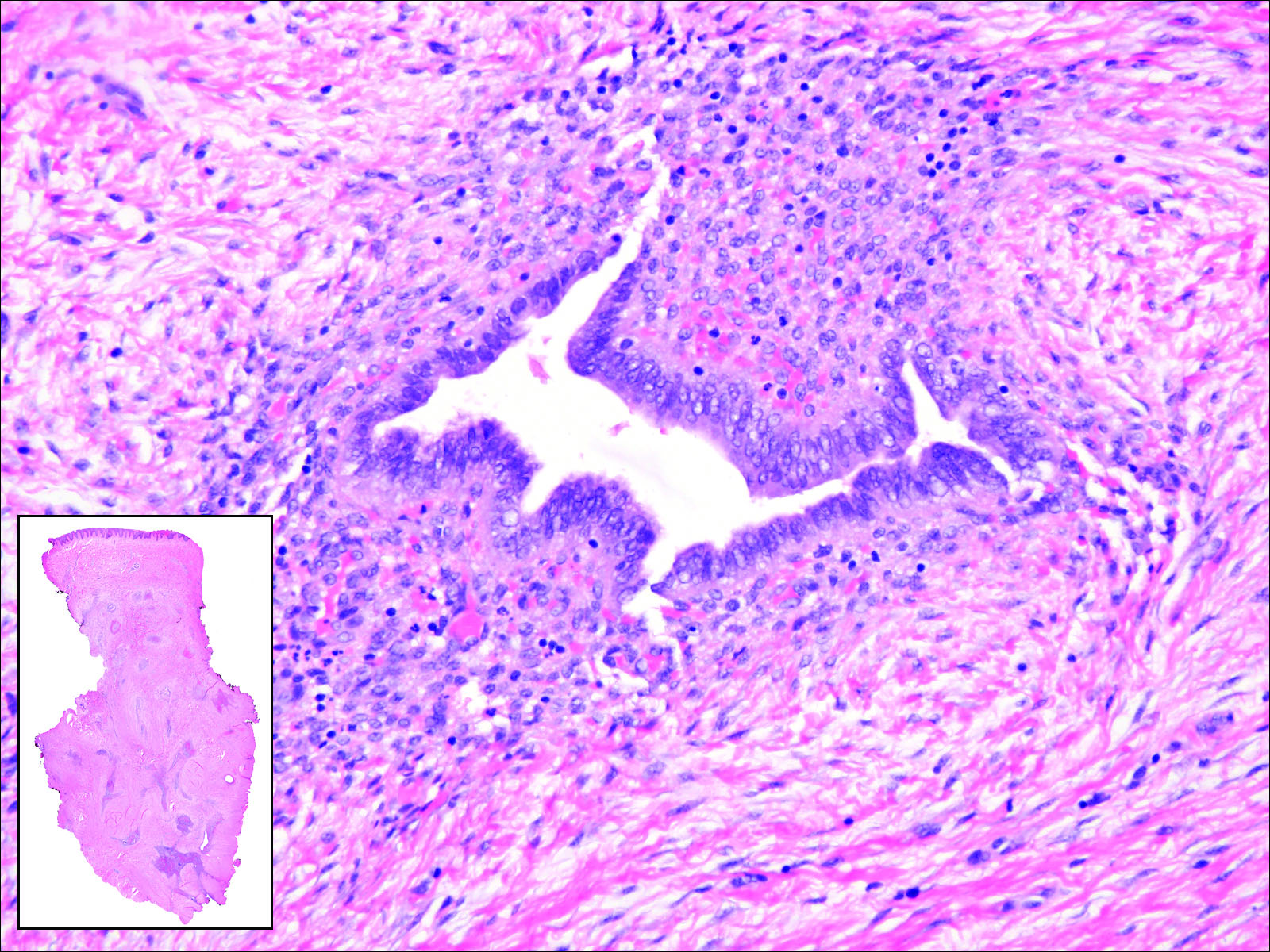
Endometriosis can mimic adenocarcinoma, especially when presenting as a subdermal nodule. However, the scattered dermal glands are cytologically banal and are surrounded by uterine-type stroma and extravasated hemorrhage, a classic presentation of endometriosis (Figure 1).
Invasive ductal carcinoma of the breast is one of the most common cutaneous metastases of internal malignancy.3 Clinically, these lesions present on the chest wall or abdomen as flesh-colored nodules. Histopathology generally reveals either tubular or single tumor cells infiltrating the dermis with surrounding desmoplastic fibrosis (Figure 2). Immunohistochemistry typically is positive for CK7, estrogen receptor, and mammaglobin, and negative for CK20, CK5/6, and TTF-1.

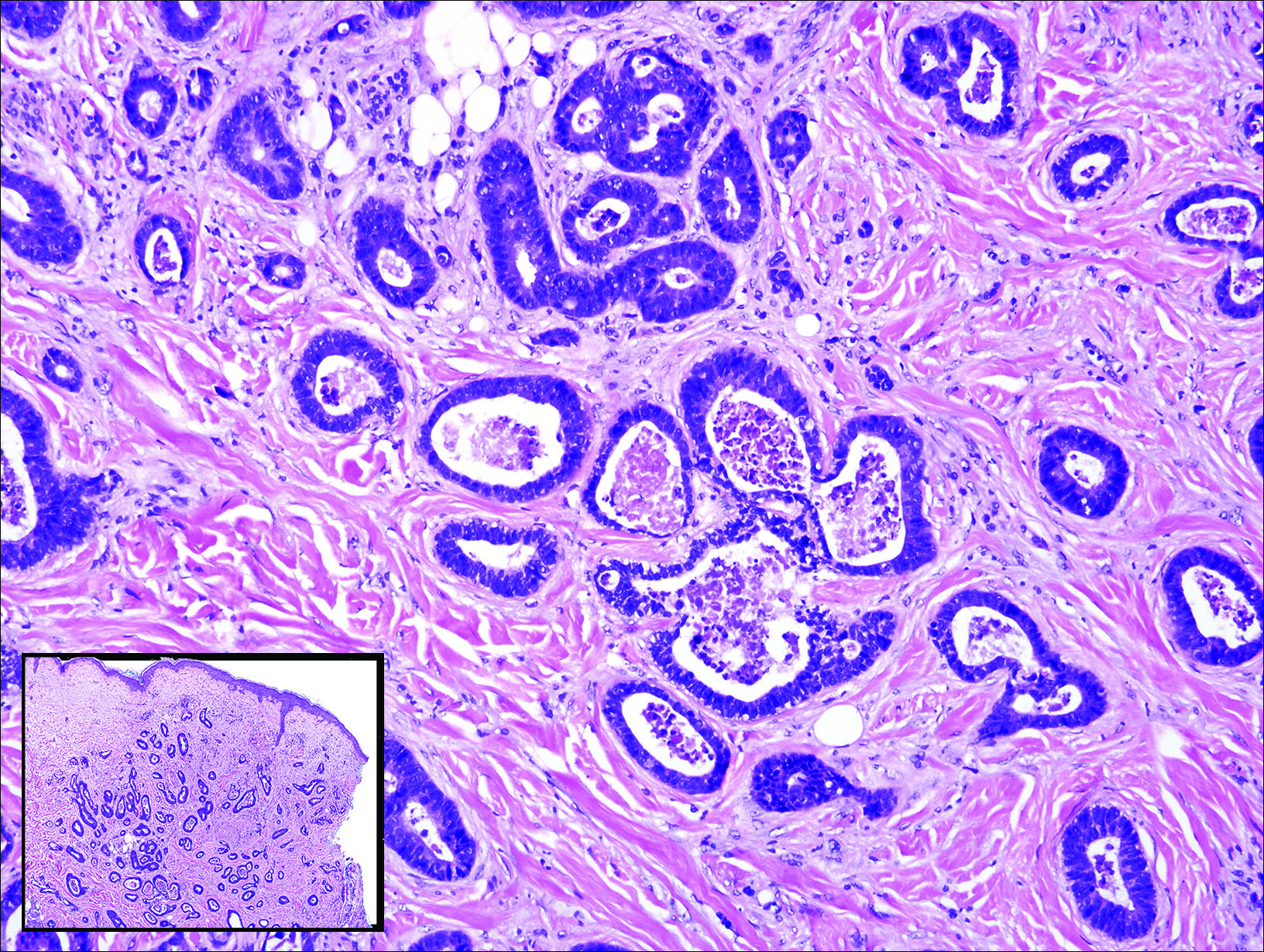
Gastrointestinal adenocarcinomas encompass a variety of primary sites that can metastasize to the skin including CRC. Clinically, cutaneous metastases of CRC present as multiple nodules on the trunk, abdomen, or umbilicus (also known as Sister Mary Joseph nodule).7,8 Distinguishing CRC as the primary site of origin can be difficult; however, there are subtle differences depending on the histologic subtype. In well-differentiated CRCs, well-defined atypical glands are haphazardly arranged within the dermis (Figure 3), while poorly differentiated lesions can present as single cells or with a signet ring-like morphology (Figure 4). For perianal lesions, extramammary Paget disease should be considered when biopsies show large, amphophilic, intraepithelial cells. These lesions often present with mucin and CK20 expression and are frequently associated with colorectal malignancies.9 Another characteristic feature of CRC is central necrosis with karyorrhectic debris, known as dirty necrosis. Immunohistochemical analysis typically shows expression of caudal type homeobox 2 and CK20 with infrequent expression of CK7 and no expression of TTF-1; however, additional clinical history (eg, history of colorectal adenocarcinoma, positive fecal occult blood test) often is the best distinguishing feature.
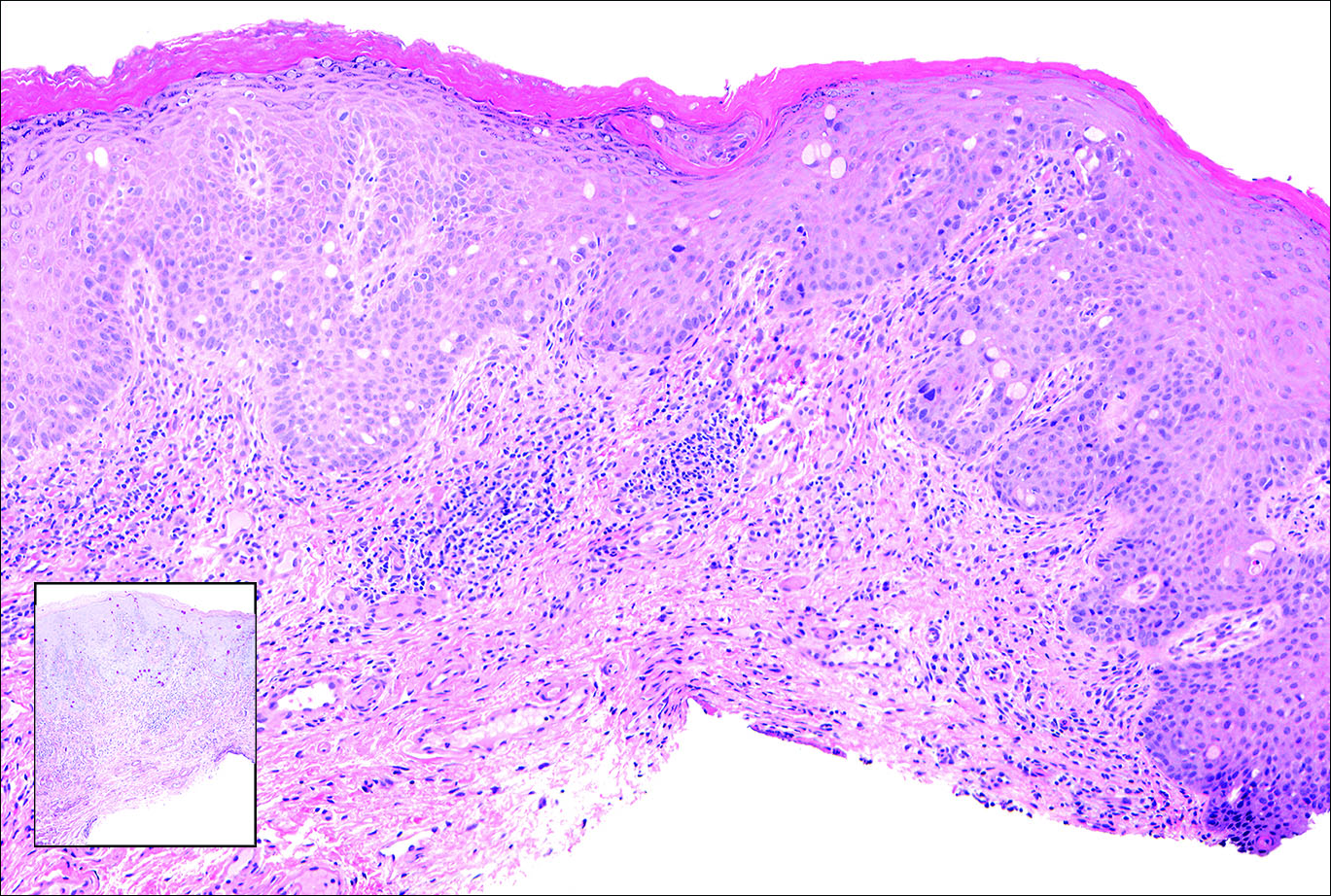
Primary sebaceous carcinoma also can mimic metastatic adenocarcinoma within the skin and is histologically similar to metastatic adenocarcinomas. The most distinguishing feature is sebaceous differentiation characterized by sebocytes, which have a vacuolated cytoplasm giving the nucleus a scalloped appearance, frequently with adjacent ductlike structures (Figure 5). Epidermotropism sometimes is present in sebaceous carcinomas but cannot be relied on as a distinguishing feature. Immunohistochemical analysis also is a helpful tool; these tumors typically are positive for p63 and podoplanin, distinguishing them from negative-staining metastatic adenocarcinomas.10,11
- Terashima T, Kanazawa M. Lung cancer with skin metastasis. Chest. 1994;106:1448-1450.
- Song Z, Lin B, Shao L, et al. Cutaneous metastasis as a initial presentation in advanced non-small cell lung cancer and its poor survival prognosis. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2012;138:1613-1617.
- Lookingbill DP, Spangler N, Helm KF. Cutaneous metastases in patients with metastatic carcinoma: a retrospective study of 4020 patients. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1993;29(2, pt 1):228-236.
- Saeed S, Keehn CA, Morgan MB. Cutaneous metastasis: a clinical, pathological, and immunohistochemical appraisal. J Cutan Pathol. 2004;31:419-430.
- Chang SE, Choi JC, Moon KC. A papillary carcinoma: cutaneous metastases from lung cancer. J Dermatol. 2001;28:110-111.
- Snow S, Madjar D, Reizner G, et al. Renal cell carcinoma metastatic to the scalp: case report and review of the literature. Dermatol Surg. 2001;27:192-194.
- Alcaraz I, Cerroni L, Rutten A, et al. Cutaneous metastases from internal malignancies: a clinicopathologic and immunohistochemical review. Am J Dermatopathol. 2012;34:347-393.
- Schwartz IS. Sister (Mary?) Joseph's nodule. N Engl J Med. 1987;316:1348-1349.
- Goldblum J, Hart W. Perianal Paget's disease: a histologic and immunohistochemical study of 11 cases with and without associated rectal adenocarcinoma. Am J Surg Pathol. 1998;22:170-179.
- Ivan D, Nash J, Preito V, et al. Use of p63 expression in distinguishing primary and metastatic cutaneous adnexal neoplasms from metastatic adenocarcinoma to skin. J Cutan Pathol. 2006;34:474-480.
- Liang H, Wu H, Giorgadze T, et al. Podoplanin is a highly sensitive and specific marker to distinguish primary skin adnexal carcinomas from adenocarcinomas metastatic to skin. Am J Surg Pathol. 2007;31:304-310.
Cutaneous Metastasis of Pulmonary Adenocarcinoma
Cutaneous metastasis of pulmonary adenocarcinoma (CMPA) is a rare phenomenon with an overall survival rate of less than 5 months.1,2 Often, CMPA can be the heralding feature of an aggressive systemic malignancy in 2.8% to 22% of reported cases.2-4 Clinically, CMPAs often present as fixed, violaceous, ulcerated nodules on the chest wall, scalp, or site of a prior procedure.3,5,6 Other clinical presentations have been described including zosteriform and inflammatory carcinomalike CMPA and CMPA on the tip of the nose.7 Histologically, CMPA presents as a subdermal collection of atypical glands arranged as clustered aggregates of infiltrative glands penetrating the dermal stroma (quiz image). The atypical glands have large oval nuclei with high nuclear to cytoplasm ratios with scant pale cytoplasm.
Cutaneous metastasis of pulmonary adenocarcinoma is difficult to distinguish from other metastatic or primary glandular malignancies based on histology alone. Immunohistochemical analysis can aid in the diagnosis of the primary tumor. Pulmonary adenocarcinomas are positive for cytokeratin (CK) 7 and thyroid transcription factor 1 (TTF-1), and they are negative for CK5/6 and CK20.7 The differential diagnosis for CMPA includes other internal malignancies such as invasive ductal adenocarcinoma of the breast and gastrointestinal adenocarcinomas (eg, gastric or colorectal carcinoma [CRC]). Additionally, endometriosis and primary sebaceous carcinomas can mimic cutaneous metastatic adenocarcinomas.
Endometriosis can mimic adenocarcinoma, especially when presenting as a subdermal nodule. However, the scattered dermal glands are cytologically banal and are surrounded by uterine-type stroma and extravasated hemorrhage, a classic presentation of endometriosis (Figure 1).

Invasive ductal carcinoma of the breast is one of the most common cutaneous metastases of internal malignancy.3 Clinically, these lesions present on the chest wall or abdomen as flesh-colored nodules. Histopathology generally reveals either tubular or single tumor cells infiltrating the dermis with surrounding desmoplastic fibrosis (Figure 2). Immunohistochemistry typically is positive for CK7, estrogen receptor, and mammaglobin, and negative for CK20, CK5/6, and TTF-1.

Gastrointestinal adenocarcinomas encompass a variety of primary sites that can metastasize to the skin including CRC. Clinically, cutaneous metastases of CRC present as multiple nodules on the trunk, abdomen, or umbilicus (also known as Sister Mary Joseph nodule).7,8 Distinguishing CRC as the primary site of origin can be difficult; however, there are subtle differences depending on the histologic subtype. In well-differentiated CRCs, well-defined atypical glands are haphazardly arranged within the dermis (Figure 3), while poorly differentiated lesions can present as single cells or with a signet ring-like morphology (Figure 4). For perianal lesions, extramammary Paget disease should be considered when biopsies show large, amphophilic, intraepithelial cells. These lesions often present with mucin and CK20 expression and are frequently associated with colorectal malignancies.9 Another characteristic feature of CRC is central necrosis with karyorrhectic debris, known as dirty necrosis. Immunohistochemical analysis typically shows expression of caudal type homeobox 2 and CK20 with infrequent expression of CK7 and no expression of TTF-1; however, additional clinical history (eg, history of colorectal adenocarcinoma, positive fecal occult blood test) often is the best distinguishing feature.


Primary sebaceous carcinoma also can mimic metastatic adenocarcinoma within the skin and is histologically similar to metastatic adenocarcinomas. The most distinguishing feature is sebaceous differentiation characterized by sebocytes, which have a vacuolated cytoplasm giving the nucleus a scalloped appearance, frequently with adjacent ductlike structures (Figure 5). Epidermotropism sometimes is present in sebaceous carcinomas but cannot be relied on as a distinguishing feature. Immunohistochemical analysis also is a helpful tool; these tumors typically are positive for p63 and podoplanin, distinguishing them from negative-staining metastatic adenocarcinomas.10,11

Cutaneous Metastasis of Pulmonary Adenocarcinoma
Cutaneous metastasis of pulmonary adenocarcinoma (CMPA) is a rare phenomenon with an overall survival rate of less than 5 months.1,2 Often, CMPA can be the heralding feature of an aggressive systemic malignancy in 2.8% to 22% of reported cases.2-4 Clinically, CMPAs often present as fixed, violaceous, ulcerated nodules on the chest wall, scalp, or site of a prior procedure.3,5,6 Other clinical presentations have been described including zosteriform and inflammatory carcinomalike CMPA and CMPA on the tip of the nose.7 Histologically, CMPA presents as a subdermal collection of atypical glands arranged as clustered aggregates of infiltrative glands penetrating the dermal stroma (quiz image). The atypical glands have large oval nuclei with high nuclear to cytoplasm ratios with scant pale cytoplasm.
Cutaneous metastasis of pulmonary adenocarcinoma is difficult to distinguish from other metastatic or primary glandular malignancies based on histology alone. Immunohistochemical analysis can aid in the diagnosis of the primary tumor. Pulmonary adenocarcinomas are positive for cytokeratin (CK) 7 and thyroid transcription factor 1 (TTF-1), and they are negative for CK5/6 and CK20.7 The differential diagnosis for CMPA includes other internal malignancies such as invasive ductal adenocarcinoma of the breast and gastrointestinal adenocarcinomas (eg, gastric or colorectal carcinoma [CRC]). Additionally, endometriosis and primary sebaceous carcinomas can mimic cutaneous metastatic adenocarcinomas.
Endometriosis can mimic adenocarcinoma, especially when presenting as a subdermal nodule. However, the scattered dermal glands are cytologically banal and are surrounded by uterine-type stroma and extravasated hemorrhage, a classic presentation of endometriosis (Figure 1).

Invasive ductal carcinoma of the breast is one of the most common cutaneous metastases of internal malignancy.3 Clinically, these lesions present on the chest wall or abdomen as flesh-colored nodules. Histopathology generally reveals either tubular or single tumor cells infiltrating the dermis with surrounding desmoplastic fibrosis (Figure 2). Immunohistochemistry typically is positive for CK7, estrogen receptor, and mammaglobin, and negative for CK20, CK5/6, and TTF-1.

Gastrointestinal adenocarcinomas encompass a variety of primary sites that can metastasize to the skin including CRC. Clinically, cutaneous metastases of CRC present as multiple nodules on the trunk, abdomen, or umbilicus (also known as Sister Mary Joseph nodule).7,8 Distinguishing CRC as the primary site of origin can be difficult; however, there are subtle differences depending on the histologic subtype. In well-differentiated CRCs, well-defined atypical glands are haphazardly arranged within the dermis (Figure 3), while poorly differentiated lesions can present as single cells or with a signet ring-like morphology (Figure 4). For perianal lesions, extramammary Paget disease should be considered when biopsies show large, amphophilic, intraepithelial cells. These lesions often present with mucin and CK20 expression and are frequently associated with colorectal malignancies.9 Another characteristic feature of CRC is central necrosis with karyorrhectic debris, known as dirty necrosis. Immunohistochemical analysis typically shows expression of caudal type homeobox 2 and CK20 with infrequent expression of CK7 and no expression of TTF-1; however, additional clinical history (eg, history of colorectal adenocarcinoma, positive fecal occult blood test) often is the best distinguishing feature.


Primary sebaceous carcinoma also can mimic metastatic adenocarcinoma within the skin and is histologically similar to metastatic adenocarcinomas. The most distinguishing feature is sebaceous differentiation characterized by sebocytes, which have a vacuolated cytoplasm giving the nucleus a scalloped appearance, frequently with adjacent ductlike structures (Figure 5). Epidermotropism sometimes is present in sebaceous carcinomas but cannot be relied on as a distinguishing feature. Immunohistochemical analysis also is a helpful tool; these tumors typically are positive for p63 and podoplanin, distinguishing them from negative-staining metastatic adenocarcinomas.10,11

- Terashima T, Kanazawa M. Lung cancer with skin metastasis. Chest. 1994;106:1448-1450.
- Song Z, Lin B, Shao L, et al. Cutaneous metastasis as a initial presentation in advanced non-small cell lung cancer and its poor survival prognosis. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2012;138:1613-1617.
- Lookingbill DP, Spangler N, Helm KF. Cutaneous metastases in patients with metastatic carcinoma: a retrospective study of 4020 patients. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1993;29(2, pt 1):228-236.
- Saeed S, Keehn CA, Morgan MB. Cutaneous metastasis: a clinical, pathological, and immunohistochemical appraisal. J Cutan Pathol. 2004;31:419-430.
- Chang SE, Choi JC, Moon KC. A papillary carcinoma: cutaneous metastases from lung cancer. J Dermatol. 2001;28:110-111.
- Snow S, Madjar D, Reizner G, et al. Renal cell carcinoma metastatic to the scalp: case report and review of the literature. Dermatol Surg. 2001;27:192-194.
- Alcaraz I, Cerroni L, Rutten A, et al. Cutaneous metastases from internal malignancies: a clinicopathologic and immunohistochemical review. Am J Dermatopathol. 2012;34:347-393.
- Schwartz IS. Sister (Mary?) Joseph's nodule. N Engl J Med. 1987;316:1348-1349.
- Goldblum J, Hart W. Perianal Paget's disease: a histologic and immunohistochemical study of 11 cases with and without associated rectal adenocarcinoma. Am J Surg Pathol. 1998;22:170-179.
- Ivan D, Nash J, Preito V, et al. Use of p63 expression in distinguishing primary and metastatic cutaneous adnexal neoplasms from metastatic adenocarcinoma to skin. J Cutan Pathol. 2006;34:474-480.
- Liang H, Wu H, Giorgadze T, et al. Podoplanin is a highly sensitive and specific marker to distinguish primary skin adnexal carcinomas from adenocarcinomas metastatic to skin. Am J Surg Pathol. 2007;31:304-310.
- Terashima T, Kanazawa M. Lung cancer with skin metastasis. Chest. 1994;106:1448-1450.
- Song Z, Lin B, Shao L, et al. Cutaneous metastasis as a initial presentation in advanced non-small cell lung cancer and its poor survival prognosis. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2012;138:1613-1617.
- Lookingbill DP, Spangler N, Helm KF. Cutaneous metastases in patients with metastatic carcinoma: a retrospective study of 4020 patients. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1993;29(2, pt 1):228-236.
- Saeed S, Keehn CA, Morgan MB. Cutaneous metastasis: a clinical, pathological, and immunohistochemical appraisal. J Cutan Pathol. 2004;31:419-430.
- Chang SE, Choi JC, Moon KC. A papillary carcinoma: cutaneous metastases from lung cancer. J Dermatol. 2001;28:110-111.
- Snow S, Madjar D, Reizner G, et al. Renal cell carcinoma metastatic to the scalp: case report and review of the literature. Dermatol Surg. 2001;27:192-194.
- Alcaraz I, Cerroni L, Rutten A, et al. Cutaneous metastases from internal malignancies: a clinicopathologic and immunohistochemical review. Am J Dermatopathol. 2012;34:347-393.
- Schwartz IS. Sister (Mary?) Joseph's nodule. N Engl J Med. 1987;316:1348-1349.
- Goldblum J, Hart W. Perianal Paget's disease: a histologic and immunohistochemical study of 11 cases with and without associated rectal adenocarcinoma. Am J Surg Pathol. 1998;22:170-179.
- Ivan D, Nash J, Preito V, et al. Use of p63 expression in distinguishing primary and metastatic cutaneous adnexal neoplasms from metastatic adenocarcinoma to skin. J Cutan Pathol. 2006;34:474-480.
- Liang H, Wu H, Giorgadze T, et al. Podoplanin is a highly sensitive and specific marker to distinguish primary skin adnexal carcinomas from adenocarcinomas metastatic to skin. Am J Surg Pathol. 2007;31:304-310.
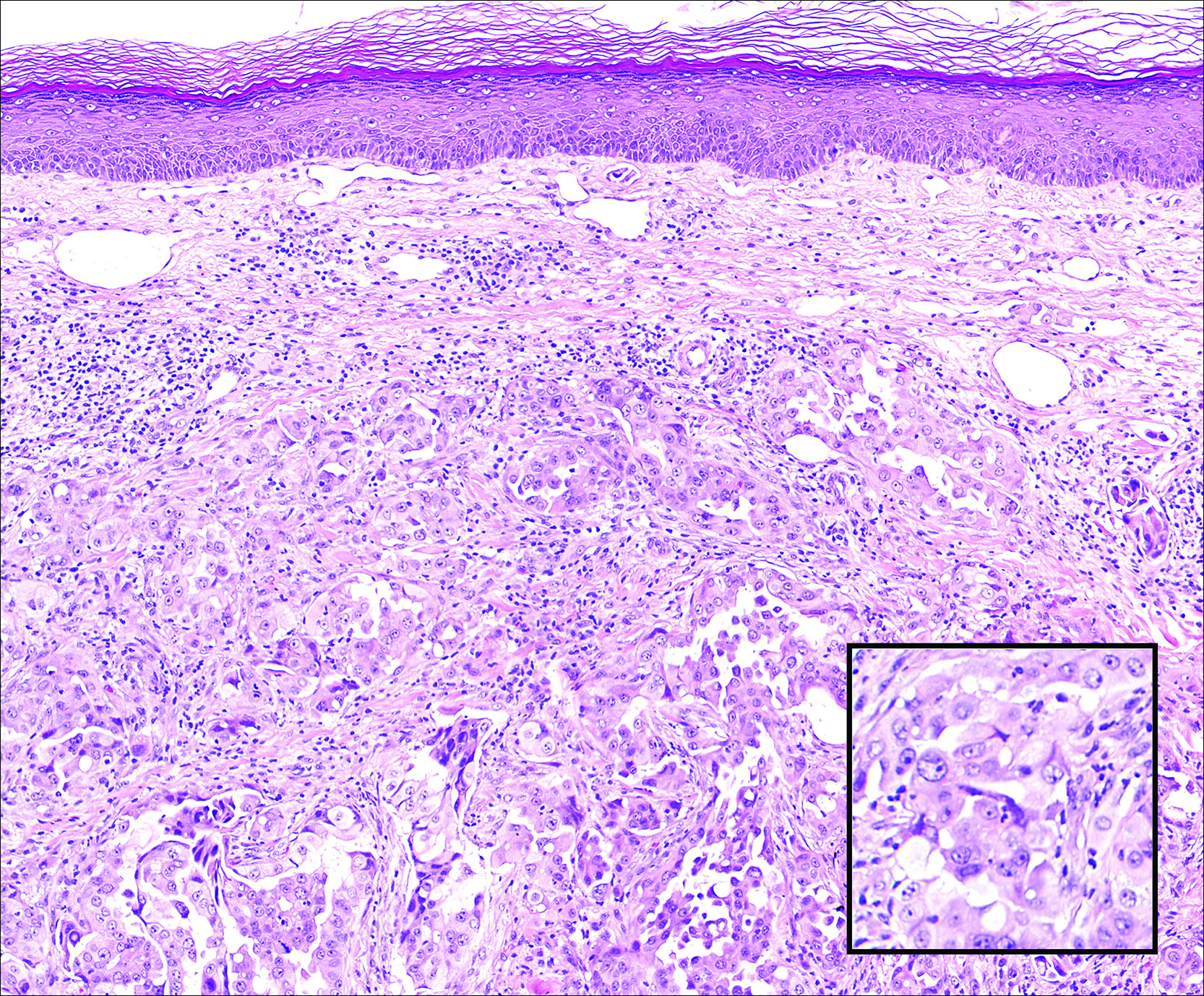
A 67-year-old woman with no history of malignancy presented with a scalp nodule. The photomicrograph showed atypical glands forming a subepidermal nodule with pleomorphic cells characterized by scant eosinophilic cytoplasm and large prominent nucleoli. Immunohistochemical analysis revealed diffuse thyroid transcription factor 1 and cytokeratin 7 positivity.
Circumscribed Nodule in a Renal Transplant Patient
The Diagnosis: Subcutaneous Phaeohyphomycosis
Subcutaneous phaeohyphomycosis (SP), also called mycotic cyst, is characterized by a painless, nodular lesion that develops in response to traumatic implantation of dematiaceous, pigment-forming fungi.1 Similar to other fungal infections, SP can arise opportunistically in immunocompromised patients.2,3 More than 60 genera (and more than 100 species) are known etiologic agents of phaeohyphomycosis; the 2 main causes of infection are Bipolaris spicifera and Exophiala jeanselmei.4,5 Given this variety, phaeohyphomycosis can present superficially as black piedra or tinea nigra, cutaneously as scytalidiosis, subcutaneously as SP, or disseminated as sinusitis or systemic phaeohyphomycosis.
Coined in 1974 by Ajello et al,6 the term phaeohyphomycosis translates to “condition of dark hyphal fungus,” a term used to designate mycoses caused by fungi with melanized hyphae. Histologically, SP demonstrates a circumscribed chronic cyst or abscess with a dense fibrous wall (quiz image A). At high power, the wall is composed of chronic granulomatous inflammation with foamy macrophages, and the cystic cavity contains necrotic debris admixed with neutrophils. Pigmented filamentous hyphae and yeastlike entities can be seen in the cyst wall, in multinucleated giant cells, in the necrotic debris, or directly attached to the implanted foreign material (quiz image B).7 The first-line treatment of SP is wide local excision and oral itraconazole. It often requires adjustments to dosage or change to antifungal due to recurrence and etiologic variation.8 Furthermore, if SP is not definitively treated, immunocompromised patients are at an increased risk for developing potentially fatal systemic phaeohyphomycosis.3
Chromoblastomycosis (CBM), also caused by dematiaceous fungi, is characterized by an initially indolent clinical presentation. Typically found on the legs and lower thighs of agricultural workers, the lesion begins as a slow-growing, nodular papule with subsequent transformation into an edematous verrucous plaque with peripheral erythema.9 Lesions can be annular with central clearing, and lymphedema with elephantiasis may be present.10 Histologically, CBM shows pseudoepitheliomatous hyperplasia and intraepidermal pustules as the host rids the infection via transepithelial elimination. Dematiaceous fungi often are seen in the dermis, either freestanding or attached to foreign plant material. Medlar bodies, also called copper penny spores or sclerotic bodies, are the most defining histologic finding and are characterized by groups of brown, thick-walled cells found in giant cells or neutrophil abscesses (Figure 1). Hyphae are not typically found in this type of infection.11

Granulomatous foreign body reactions occur in response to the inoculation of nonhuman material and are characterized by dermal or subcutaneous nodules. Tissue macrophages phagocytize material not removed shortly after implantation, which initiates an inflammatory response that attempts to isolate the material from the uninvolved surrounding tissue. Vegetative foreign bodies will cause the most severe inflammatory reactions.12 Histologically, foreign body granulomas are noncaseating with epithelioid histiocytes surrounding a central foreign body (Figure 2). Occasionally, foreign bodies may be difficult to detect; some are birefringent to polarized light.13 Additionally, inoculation injuries can predispose patients to SP, CBM, and other fungal infections.

Tattoos are characterized by exogenous pigment deposition into the dermis.14 Histologically, tattoos display exogenous pigment deposited throughout the reticular dermis, attached to collagen bundles, within macrophages, or adjacent to adnexal structures (eg, pilosebaceous units or eccrine glands). Although all tattoo pigments can cause adverse reactions, hypersensitivity reactions occur most commonly in response to red pigment, resulting in discrete areas of spongiosis and granulomatous or lichenoid inflammation. Occasionally, hypersensitivity reactions can induce necrobiotic granulomatous reactions characterized by collagen alteration surrounded by palisaded histiocytes and lymphocytes (Figure 3).15,16 There also may be focally dense areas of superficial and deep perivascular lymphohistiocytic infiltrate. Clinical context is important, as brown tattoo pigment (Figure 3) can be easily confused with the pigmented hyphae of phaeohyphomycosis, melanin, or hemosiderin.
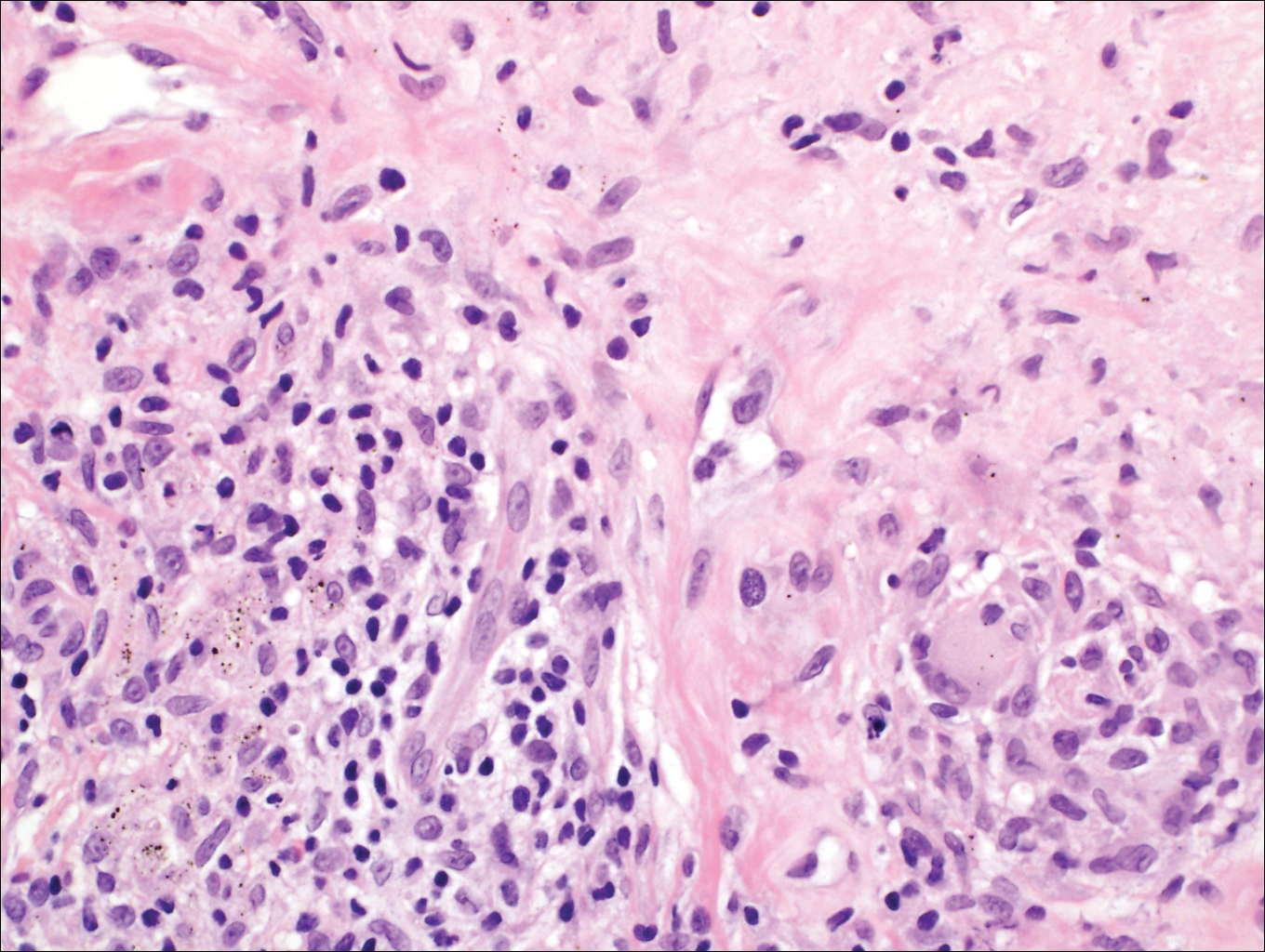
Subcutaneous hyalohyphomycosis is a nondemat-iaceous (nonpigmented) infection that is caused by hyaline septate hyphal cells.17 Hyalohyphomycosis skin lesions can present as painful erythematous nodules that evolve into excoriated pustules.18 Hyalohyphomycosis most often arises in immunocompromised patients. Causative organisms are ubiquitous soil saprophytes and plant pathogens, most often Aspergillus and Fusarium species, with a predilection for affecting severely immunocompromised hosts, particularly children.19 These species tend to be vasculotropic, which can result in tissue necrosis and systemic dissemination. Histologically, fungi are dispersed within tissue. They have a bright, bubbly, mildly basophilic cytoplasm and are nonpigmented, branching, and septate (Figure 4).11

- Isa-Isa R, García C, Isa M, et al. Subcutaneous phaeohyphomycosis (mycotic cyst). Clin Dermatol. 2012;30:425-431.
- Rubin RH. Infectious disease complications of renal transplantation. Kidney Int. 1993;44:221-236.
- Ogawa MM, Galante NZ, Godoy P, et al. Treatment of subcutaneous phaeohyphomycosis and prospective follow-up of 17 kidney transplant recipients. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2009;61:977-985.
- Matsumoto T, Ajello L, Matsuda T, et al. Developments in hyalohyphomycosis and phaeohyphomycosis. J Med Vet Mycol. 1994;32(suppl 1):329-349.
- Rinaldi MG. Phaeohyphomycosis. Dermatol Clin. 1996;14:147-153.
- Ajello L, Georg LK, Steigbigel RT, et al. A case of phaeohyphomycosis caused by a new species of Phialophora. Mycologia. 1974;66:490-498.
- Patterson J. Weedon’s Skin Pathology. 4th ed. London, England: Churchill Livingstone Elsevier; 2014.
- Patel U, Chu J, Patel R, et al. Subcutaneous dematiaceous fungal infection. Dermatol Online J. 2011;17:19.
- Bonifaz A, Carrasco-Gerard E, Saúl A. Chromoblastomycosis: clinical and mycologic experience of 51 cases. Mycoses. 2001;44:1-7.
- Ameen M. Chromoblastomycosis: clinical presentation and management. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2009;34:849-854.
- Elston D, Ferringer T, Peckham S, et al, eds. Dermatopathology. 2nd ed. St. Louis, MO: Elsevier Saunders; 2014.
- Lammers RL. Soft tissue foreign bodies. In: Tintinalli J, Stapczynski S, Ma O, et al, eds. Tintinalli’s Emergency Medicine: A Comprehensive Study Guide. 7th ed. New York, NY: McGraw Hill Professional; 2011.
- Murphy GF, Saavedra AP, Mihm MC. Nodular/interstitial dermatitis. In: Murphy GF, Saavedra AP, Mihm MC, eds. Atlas of Nontumor Pathology: Inflammatory Disorders of the Skin. Vol 10. Washington, DC: American Registry of Pathology; 2012:337-395.
- Laumann A. Body art. In: Goldsmith L, Katz S, Gilchrest B, et al, eds. Fitzpatrick’s Dermatology in General Medicine. 8th ed. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill; 2012. http://access medicine.mhmedical.com.proxy.lib.uiowa.edu/content.aspx?bookid=392&Sectionid=41138811. Accessed July 17,2016.
- Wood A, Hamilton SA, Wallace WA, et al. Necrobiotic granulomatous tattoo reaction: report of an unusual case showing features of both necrobiosis lipoidica and granuloma annulare patterns. Am J Dermatopathol. 2014;36:e152-e155.
- Mortimer N, Chave T, Johnston G. Red tattoo reactions. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2003;28:508-510.
- Ajello L. Hyalohyphomycosis and phaeohyphomycosis: two global disease entities of public health importance. Eur J Epidemiol. 1986;2:243-251.
- Safdar A. Progressive cutaneous hyalohyphomycosis due to Paecilomyces lilacinus: rapid response to treatment with caspofungin and itraconazole. Clin Infect Dis. 2002;34:1415-1417.
- Marcoux D, Jafarian F, Joncas V, et al. Deep cutaneous fungal infections in immunocompromised children. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2009;61:857-864.
The Diagnosis: Subcutaneous Phaeohyphomycosis
Subcutaneous phaeohyphomycosis (SP), also called mycotic cyst, is characterized by a painless, nodular lesion that develops in response to traumatic implantation of dematiaceous, pigment-forming fungi.1 Similar to other fungal infections, SP can arise opportunistically in immunocompromised patients.2,3 More than 60 genera (and more than 100 species) are known etiologic agents of phaeohyphomycosis; the 2 main causes of infection are Bipolaris spicifera and Exophiala jeanselmei.4,5 Given this variety, phaeohyphomycosis can present superficially as black piedra or tinea nigra, cutaneously as scytalidiosis, subcutaneously as SP, or disseminated as sinusitis or systemic phaeohyphomycosis.
Coined in 1974 by Ajello et al,6 the term phaeohyphomycosis translates to “condition of dark hyphal fungus,” a term used to designate mycoses caused by fungi with melanized hyphae. Histologically, SP demonstrates a circumscribed chronic cyst or abscess with a dense fibrous wall (quiz image A). At high power, the wall is composed of chronic granulomatous inflammation with foamy macrophages, and the cystic cavity contains necrotic debris admixed with neutrophils. Pigmented filamentous hyphae and yeastlike entities can be seen in the cyst wall, in multinucleated giant cells, in the necrotic debris, or directly attached to the implanted foreign material (quiz image B).7 The first-line treatment of SP is wide local excision and oral itraconazole. It often requires adjustments to dosage or change to antifungal due to recurrence and etiologic variation.8 Furthermore, if SP is not definitively treated, immunocompromised patients are at an increased risk for developing potentially fatal systemic phaeohyphomycosis.3
Chromoblastomycosis (CBM), also caused by dematiaceous fungi, is characterized by an initially indolent clinical presentation. Typically found on the legs and lower thighs of agricultural workers, the lesion begins as a slow-growing, nodular papule with subsequent transformation into an edematous verrucous plaque with peripheral erythema.9 Lesions can be annular with central clearing, and lymphedema with elephantiasis may be present.10 Histologically, CBM shows pseudoepitheliomatous hyperplasia and intraepidermal pustules as the host rids the infection via transepithelial elimination. Dematiaceous fungi often are seen in the dermis, either freestanding or attached to foreign plant material. Medlar bodies, also called copper penny spores or sclerotic bodies, are the most defining histologic finding and are characterized by groups of brown, thick-walled cells found in giant cells or neutrophil abscesses (Figure 1). Hyphae are not typically found in this type of infection.11

Granulomatous foreign body reactions occur in response to the inoculation of nonhuman material and are characterized by dermal or subcutaneous nodules. Tissue macrophages phagocytize material not removed shortly after implantation, which initiates an inflammatory response that attempts to isolate the material from the uninvolved surrounding tissue. Vegetative foreign bodies will cause the most severe inflammatory reactions.12 Histologically, foreign body granulomas are noncaseating with epithelioid histiocytes surrounding a central foreign body (Figure 2). Occasionally, foreign bodies may be difficult to detect; some are birefringent to polarized light.13 Additionally, inoculation injuries can predispose patients to SP, CBM, and other fungal infections.

Tattoos are characterized by exogenous pigment deposition into the dermis.14 Histologically, tattoos display exogenous pigment deposited throughout the reticular dermis, attached to collagen bundles, within macrophages, or adjacent to adnexal structures (eg, pilosebaceous units or eccrine glands). Although all tattoo pigments can cause adverse reactions, hypersensitivity reactions occur most commonly in response to red pigment, resulting in discrete areas of spongiosis and granulomatous or lichenoid inflammation. Occasionally, hypersensitivity reactions can induce necrobiotic granulomatous reactions characterized by collagen alteration surrounded by palisaded histiocytes and lymphocytes (Figure 3).15,16 There also may be focally dense areas of superficial and deep perivascular lymphohistiocytic infiltrate. Clinical context is important, as brown tattoo pigment (Figure 3) can be easily confused with the pigmented hyphae of phaeohyphomycosis, melanin, or hemosiderin.

Subcutaneous hyalohyphomycosis is a nondemat-iaceous (nonpigmented) infection that is caused by hyaline septate hyphal cells.17 Hyalohyphomycosis skin lesions can present as painful erythematous nodules that evolve into excoriated pustules.18 Hyalohyphomycosis most often arises in immunocompromised patients. Causative organisms are ubiquitous soil saprophytes and plant pathogens, most often Aspergillus and Fusarium species, with a predilection for affecting severely immunocompromised hosts, particularly children.19 These species tend to be vasculotropic, which can result in tissue necrosis and systemic dissemination. Histologically, fungi are dispersed within tissue. They have a bright, bubbly, mildly basophilic cytoplasm and are nonpigmented, branching, and septate (Figure 4).11

The Diagnosis: Subcutaneous Phaeohyphomycosis
Subcutaneous phaeohyphomycosis (SP), also called mycotic cyst, is characterized by a painless, nodular lesion that develops in response to traumatic implantation of dematiaceous, pigment-forming fungi.1 Similar to other fungal infections, SP can arise opportunistically in immunocompromised patients.2,3 More than 60 genera (and more than 100 species) are known etiologic agents of phaeohyphomycosis; the 2 main causes of infection are Bipolaris spicifera and Exophiala jeanselmei.4,5 Given this variety, phaeohyphomycosis can present superficially as black piedra or tinea nigra, cutaneously as scytalidiosis, subcutaneously as SP, or disseminated as sinusitis or systemic phaeohyphomycosis.
Coined in 1974 by Ajello et al,6 the term phaeohyphomycosis translates to “condition of dark hyphal fungus,” a term used to designate mycoses caused by fungi with melanized hyphae. Histologically, SP demonstrates a circumscribed chronic cyst or abscess with a dense fibrous wall (quiz image A). At high power, the wall is composed of chronic granulomatous inflammation with foamy macrophages, and the cystic cavity contains necrotic debris admixed with neutrophils. Pigmented filamentous hyphae and yeastlike entities can be seen in the cyst wall, in multinucleated giant cells, in the necrotic debris, or directly attached to the implanted foreign material (quiz image B).7 The first-line treatment of SP is wide local excision and oral itraconazole. It often requires adjustments to dosage or change to antifungal due to recurrence and etiologic variation.8 Furthermore, if SP is not definitively treated, immunocompromised patients are at an increased risk for developing potentially fatal systemic phaeohyphomycosis.3
Chromoblastomycosis (CBM), also caused by dematiaceous fungi, is characterized by an initially indolent clinical presentation. Typically found on the legs and lower thighs of agricultural workers, the lesion begins as a slow-growing, nodular papule with subsequent transformation into an edematous verrucous plaque with peripheral erythema.9 Lesions can be annular with central clearing, and lymphedema with elephantiasis may be present.10 Histologically, CBM shows pseudoepitheliomatous hyperplasia and intraepidermal pustules as the host rids the infection via transepithelial elimination. Dematiaceous fungi often are seen in the dermis, either freestanding or attached to foreign plant material. Medlar bodies, also called copper penny spores or sclerotic bodies, are the most defining histologic finding and are characterized by groups of brown, thick-walled cells found in giant cells or neutrophil abscesses (Figure 1). Hyphae are not typically found in this type of infection.11

Granulomatous foreign body reactions occur in response to the inoculation of nonhuman material and are characterized by dermal or subcutaneous nodules. Tissue macrophages phagocytize material not removed shortly after implantation, which initiates an inflammatory response that attempts to isolate the material from the uninvolved surrounding tissue. Vegetative foreign bodies will cause the most severe inflammatory reactions.12 Histologically, foreign body granulomas are noncaseating with epithelioid histiocytes surrounding a central foreign body (Figure 2). Occasionally, foreign bodies may be difficult to detect; some are birefringent to polarized light.13 Additionally, inoculation injuries can predispose patients to SP, CBM, and other fungal infections.

Tattoos are characterized by exogenous pigment deposition into the dermis.14 Histologically, tattoos display exogenous pigment deposited throughout the reticular dermis, attached to collagen bundles, within macrophages, or adjacent to adnexal structures (eg, pilosebaceous units or eccrine glands). Although all tattoo pigments can cause adverse reactions, hypersensitivity reactions occur most commonly in response to red pigment, resulting in discrete areas of spongiosis and granulomatous or lichenoid inflammation. Occasionally, hypersensitivity reactions can induce necrobiotic granulomatous reactions characterized by collagen alteration surrounded by palisaded histiocytes and lymphocytes (Figure 3).15,16 There also may be focally dense areas of superficial and deep perivascular lymphohistiocytic infiltrate. Clinical context is important, as brown tattoo pigment (Figure 3) can be easily confused with the pigmented hyphae of phaeohyphomycosis, melanin, or hemosiderin.

Subcutaneous hyalohyphomycosis is a nondemat-iaceous (nonpigmented) infection that is caused by hyaline septate hyphal cells.17 Hyalohyphomycosis skin lesions can present as painful erythematous nodules that evolve into excoriated pustules.18 Hyalohyphomycosis most often arises in immunocompromised patients. Causative organisms are ubiquitous soil saprophytes and plant pathogens, most often Aspergillus and Fusarium species, with a predilection for affecting severely immunocompromised hosts, particularly children.19 These species tend to be vasculotropic, which can result in tissue necrosis and systemic dissemination. Histologically, fungi are dispersed within tissue. They have a bright, bubbly, mildly basophilic cytoplasm and are nonpigmented, branching, and septate (Figure 4).11

- Isa-Isa R, García C, Isa M, et al. Subcutaneous phaeohyphomycosis (mycotic cyst). Clin Dermatol. 2012;30:425-431.
- Rubin RH. Infectious disease complications of renal transplantation. Kidney Int. 1993;44:221-236.
- Ogawa MM, Galante NZ, Godoy P, et al. Treatment of subcutaneous phaeohyphomycosis and prospective follow-up of 17 kidney transplant recipients. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2009;61:977-985.
- Matsumoto T, Ajello L, Matsuda T, et al. Developments in hyalohyphomycosis and phaeohyphomycosis. J Med Vet Mycol. 1994;32(suppl 1):329-349.
- Rinaldi MG. Phaeohyphomycosis. Dermatol Clin. 1996;14:147-153.
- Ajello L, Georg LK, Steigbigel RT, et al. A case of phaeohyphomycosis caused by a new species of Phialophora. Mycologia. 1974;66:490-498.
- Patterson J. Weedon’s Skin Pathology. 4th ed. London, England: Churchill Livingstone Elsevier; 2014.
- Patel U, Chu J, Patel R, et al. Subcutaneous dematiaceous fungal infection. Dermatol Online J. 2011;17:19.
- Bonifaz A, Carrasco-Gerard E, Saúl A. Chromoblastomycosis: clinical and mycologic experience of 51 cases. Mycoses. 2001;44:1-7.
- Ameen M. Chromoblastomycosis: clinical presentation and management. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2009;34:849-854.
- Elston D, Ferringer T, Peckham S, et al, eds. Dermatopathology. 2nd ed. St. Louis, MO: Elsevier Saunders; 2014.
- Lammers RL. Soft tissue foreign bodies. In: Tintinalli J, Stapczynski S, Ma O, et al, eds. Tintinalli’s Emergency Medicine: A Comprehensive Study Guide. 7th ed. New York, NY: McGraw Hill Professional; 2011.
- Murphy GF, Saavedra AP, Mihm MC. Nodular/interstitial dermatitis. In: Murphy GF, Saavedra AP, Mihm MC, eds. Atlas of Nontumor Pathology: Inflammatory Disorders of the Skin. Vol 10. Washington, DC: American Registry of Pathology; 2012:337-395.
- Laumann A. Body art. In: Goldsmith L, Katz S, Gilchrest B, et al, eds. Fitzpatrick’s Dermatology in General Medicine. 8th ed. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill; 2012. http://access medicine.mhmedical.com.proxy.lib.uiowa.edu/content.aspx?bookid=392&Sectionid=41138811. Accessed July 17,2016.
- Wood A, Hamilton SA, Wallace WA, et al. Necrobiotic granulomatous tattoo reaction: report of an unusual case showing features of both necrobiosis lipoidica and granuloma annulare patterns. Am J Dermatopathol. 2014;36:e152-e155.
- Mortimer N, Chave T, Johnston G. Red tattoo reactions. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2003;28:508-510.
- Ajello L. Hyalohyphomycosis and phaeohyphomycosis: two global disease entities of public health importance. Eur J Epidemiol. 1986;2:243-251.
- Safdar A. Progressive cutaneous hyalohyphomycosis due to Paecilomyces lilacinus: rapid response to treatment with caspofungin and itraconazole. Clin Infect Dis. 2002;34:1415-1417.
- Marcoux D, Jafarian F, Joncas V, et al. Deep cutaneous fungal infections in immunocompromised children. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2009;61:857-864.
- Isa-Isa R, García C, Isa M, et al. Subcutaneous phaeohyphomycosis (mycotic cyst). Clin Dermatol. 2012;30:425-431.
- Rubin RH. Infectious disease complications of renal transplantation. Kidney Int. 1993;44:221-236.
- Ogawa MM, Galante NZ, Godoy P, et al. Treatment of subcutaneous phaeohyphomycosis and prospective follow-up of 17 kidney transplant recipients. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2009;61:977-985.
- Matsumoto T, Ajello L, Matsuda T, et al. Developments in hyalohyphomycosis and phaeohyphomycosis. J Med Vet Mycol. 1994;32(suppl 1):329-349.
- Rinaldi MG. Phaeohyphomycosis. Dermatol Clin. 1996;14:147-153.
- Ajello L, Georg LK, Steigbigel RT, et al. A case of phaeohyphomycosis caused by a new species of Phialophora. Mycologia. 1974;66:490-498.
- Patterson J. Weedon’s Skin Pathology. 4th ed. London, England: Churchill Livingstone Elsevier; 2014.
- Patel U, Chu J, Patel R, et al. Subcutaneous dematiaceous fungal infection. Dermatol Online J. 2011;17:19.
- Bonifaz A, Carrasco-Gerard E, Saúl A. Chromoblastomycosis: clinical and mycologic experience of 51 cases. Mycoses. 2001;44:1-7.
- Ameen M. Chromoblastomycosis: clinical presentation and management. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2009;34:849-854.
- Elston D, Ferringer T, Peckham S, et al, eds. Dermatopathology. 2nd ed. St. Louis, MO: Elsevier Saunders; 2014.
- Lammers RL. Soft tissue foreign bodies. In: Tintinalli J, Stapczynski S, Ma O, et al, eds. Tintinalli’s Emergency Medicine: A Comprehensive Study Guide. 7th ed. New York, NY: McGraw Hill Professional; 2011.
- Murphy GF, Saavedra AP, Mihm MC. Nodular/interstitial dermatitis. In: Murphy GF, Saavedra AP, Mihm MC, eds. Atlas of Nontumor Pathology: Inflammatory Disorders of the Skin. Vol 10. Washington, DC: American Registry of Pathology; 2012:337-395.
- Laumann A. Body art. In: Goldsmith L, Katz S, Gilchrest B, et al, eds. Fitzpatrick’s Dermatology in General Medicine. 8th ed. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill; 2012. http://access medicine.mhmedical.com.proxy.lib.uiowa.edu/content.aspx?bookid=392&Sectionid=41138811. Accessed July 17,2016.
- Wood A, Hamilton SA, Wallace WA, et al. Necrobiotic granulomatous tattoo reaction: report of an unusual case showing features of both necrobiosis lipoidica and granuloma annulare patterns. Am J Dermatopathol. 2014;36:e152-e155.
- Mortimer N, Chave T, Johnston G. Red tattoo reactions. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2003;28:508-510.
- Ajello L. Hyalohyphomycosis and phaeohyphomycosis: two global disease entities of public health importance. Eur J Epidemiol. 1986;2:243-251.
- Safdar A. Progressive cutaneous hyalohyphomycosis due to Paecilomyces lilacinus: rapid response to treatment with caspofungin and itraconazole. Clin Infect Dis. 2002;34:1415-1417.
- Marcoux D, Jafarian F, Joncas V, et al. Deep cutaneous fungal infections in immunocompromised children. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2009;61:857-864.
A 63-year-old man on immunosuppressive therapy following renal transplantation 5 years prior presented with a nontender circumscribed nodule above the left knee of 6 months’ duration. The patient denied any trauma or injury to the site.
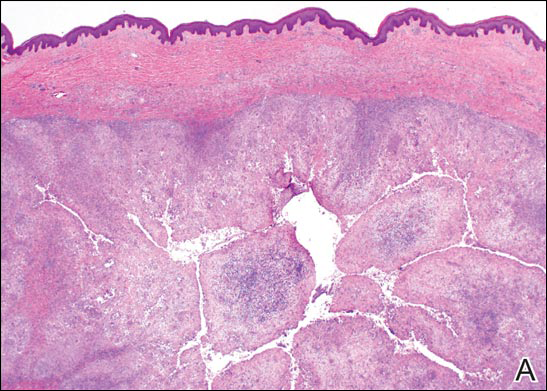
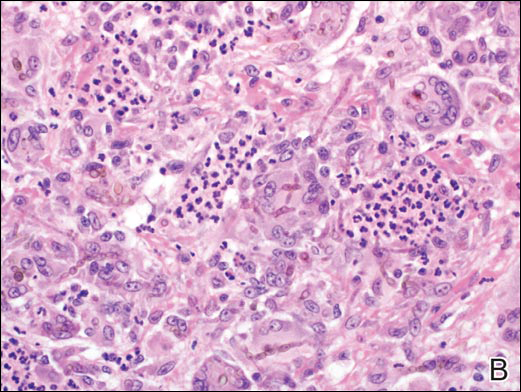
Erythema and Induration on the Right Ear and Maxilla
Lepromatous Leprosy
Lepromatous leprosy (LL) is a chronic, cutaneous, granulomatous infection caused by Mycobacterium leprae or the newly discovered Mycobacterium lepromatosis, both acid-fast, intracellular, bacillus bacterium.1 Although decreasing in prevalence due to effective treatment with antimicrobials, LL continues to be endemic in warm tropical or subtropical areas in Southeast Asia, sub-Saharan Africa, the Indian subcontinent, and South America.1 The mode of transmission of infection is not well established.
The cutaneous manifestation of leprosy was previously classified based on the cell-mediated immune response of the patient, as described by Ridley and Jopling,2 ranging from tuberculoid leprosy (TT) to LL. In this spectrum of leprosy are the borderline lesions including borderline tuberculoid, borderline, and borderline lepromatous.2,3 Although this classification is popular, in 2012 the World Health Organization implemented a new 2-category classification system to standardize treatment regimens: paucibacillary (2–5 lesions or 1 nerve involvement) and multibacillary (>5 lesions or multiple nerve involvement).4
In LL, a cell-mediated immune response is not mounted against the infection in the patient. Clinically, the disease can manifest as macular and nodular erythematous cutaneous lesions with poorly defined borders that are preferentially located on the face, earlobes, and nasal mucosa. Chronic infections are associated with sensory loss. Histologically, the dermis is densely infiltrated by foamy macrophages (Virchow cells or lepra cells), which do not form granulomas (quiz image A). The infiltrate may have varying accompanying lymphocytes and plasma cells, which can extend deep into the subcutaneous adipose tissue. Between the dermal infiltrate and epidermis is an uninvolved band of superficial dermis called the Grenz zone. The epidermis is flattened and atrophic. Nerves often are surrounded by macrophages with degrees of hyalinization but rarely are swollen. On acid-fast staining (Wade-Fite or Ziehl-Neelsen), numerous acid-fast bacilli are present within dermal cells in densely packed, intracellular collections called globi (quiz image B).2,3,5
In TT, the robust immune response causes epithelioid granuloma formation, similar to cutaneous sarcoidosis, and few, if any, organisms can be found on special stains. The remaining borderline lesions have varying numbers of bacilli and varying amounts of granuloma formation.3,6,7 Many cases of TT resolve without specific treatment. For most leprous diseases, the World Health Organization currently recommends a regimen of dapsone, rifampin, and clofazimine combination treatments for 6 to 12 months depending on the type of leprosy.8
Cutaneous leishmaniasis should be included in the differential diagnosis for patients from LL endemic areas. Early lesions can have a histiocytic infiltration with associated mixed inflammation and prominent epidermal hyperplasia. These early lesions usually have parasitic organisms located within the periphery of the cytoplasm of macrophages (“marquee sign”) to help differentiate it from leprous diseases (Figure 1).9
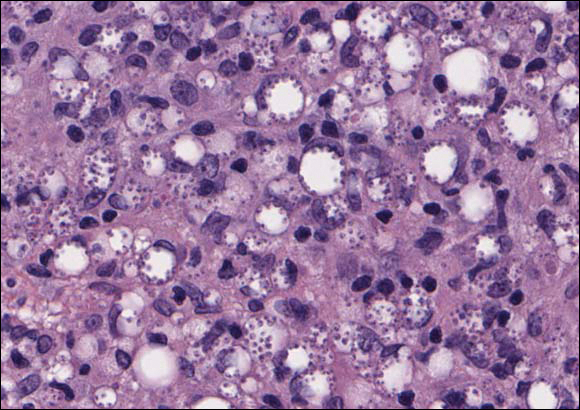
In nonendemic areas, leprous diseases often are mistaken for sarcoidosis, xanthomas, granular cell tumors, paraffinomas, or other histiocytic-rich lesions.10 Cutaneous sarcoidosis may be difficult to distinguish from TT, as both have noncaseating granulomas (Figure 2). Rare acid-fast bacilli may aid in the diagnosis, and sarcoid granulomas are not typically associated with cutaneous nerve involvement. New diagnostic tools such as polymerase chain reaction or genome sequencing can pick up rare organisms.
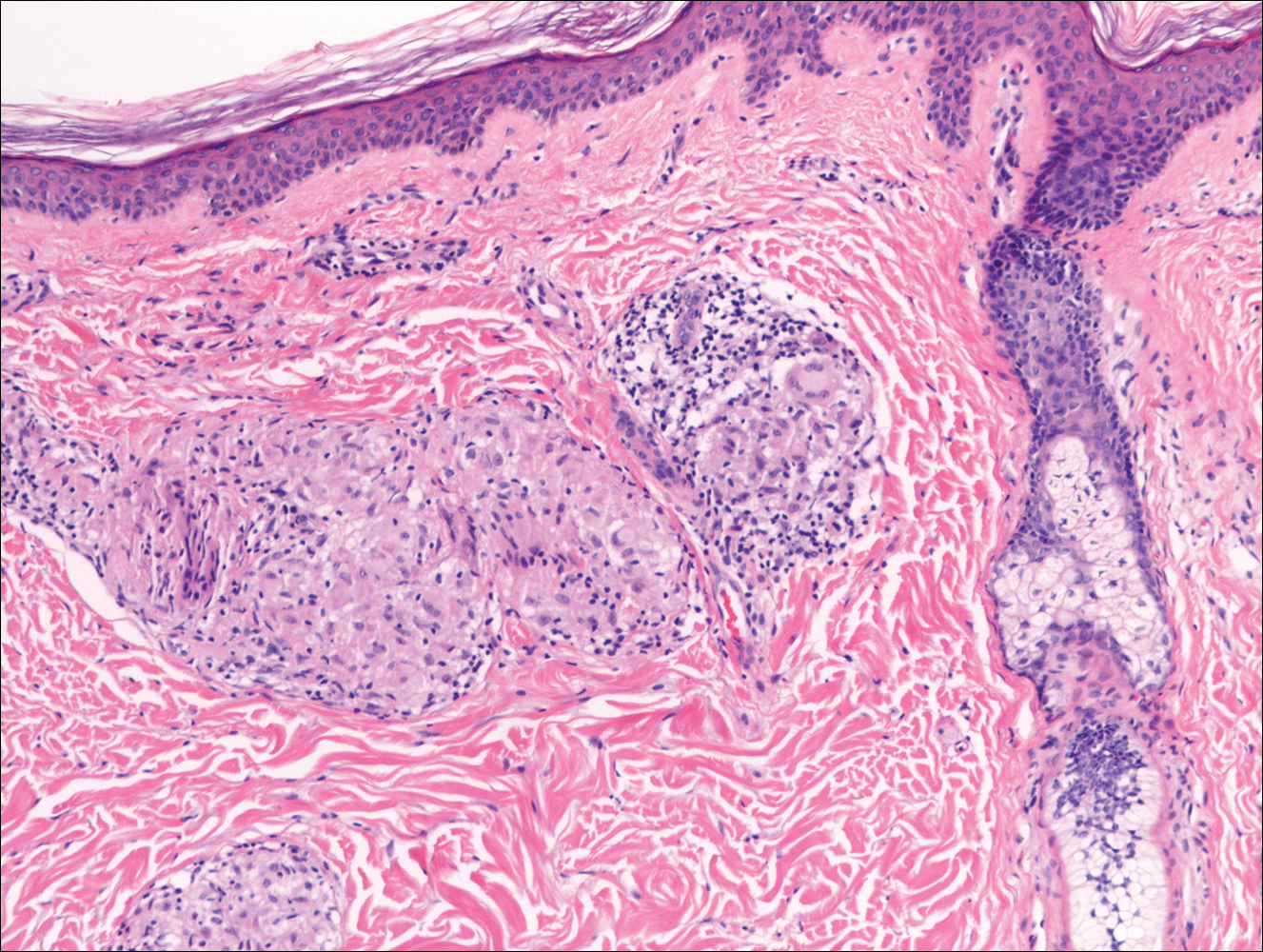
Xanthogranuolomas and xanthomas may histologically resemble LL with a dense dermal infiltrate of foamy histiocytes. No organisms are found in the infiltrate. Histologically, xanthogranulomas (juvenile or adult) will be a mixed infiltrate with foamy histiocytes; giant cell formation, especially Touton giant cells; lymphocytes; and granulocytes (Figure 3). Touton giant cells have a wreathlike formation of nuclei and an outer vacuolated cytoplasm. Xanthomas have sheets of large histiocytes with a foamy, lipid-filled interior and mild lymphocytic infiltrate (Figure 4).
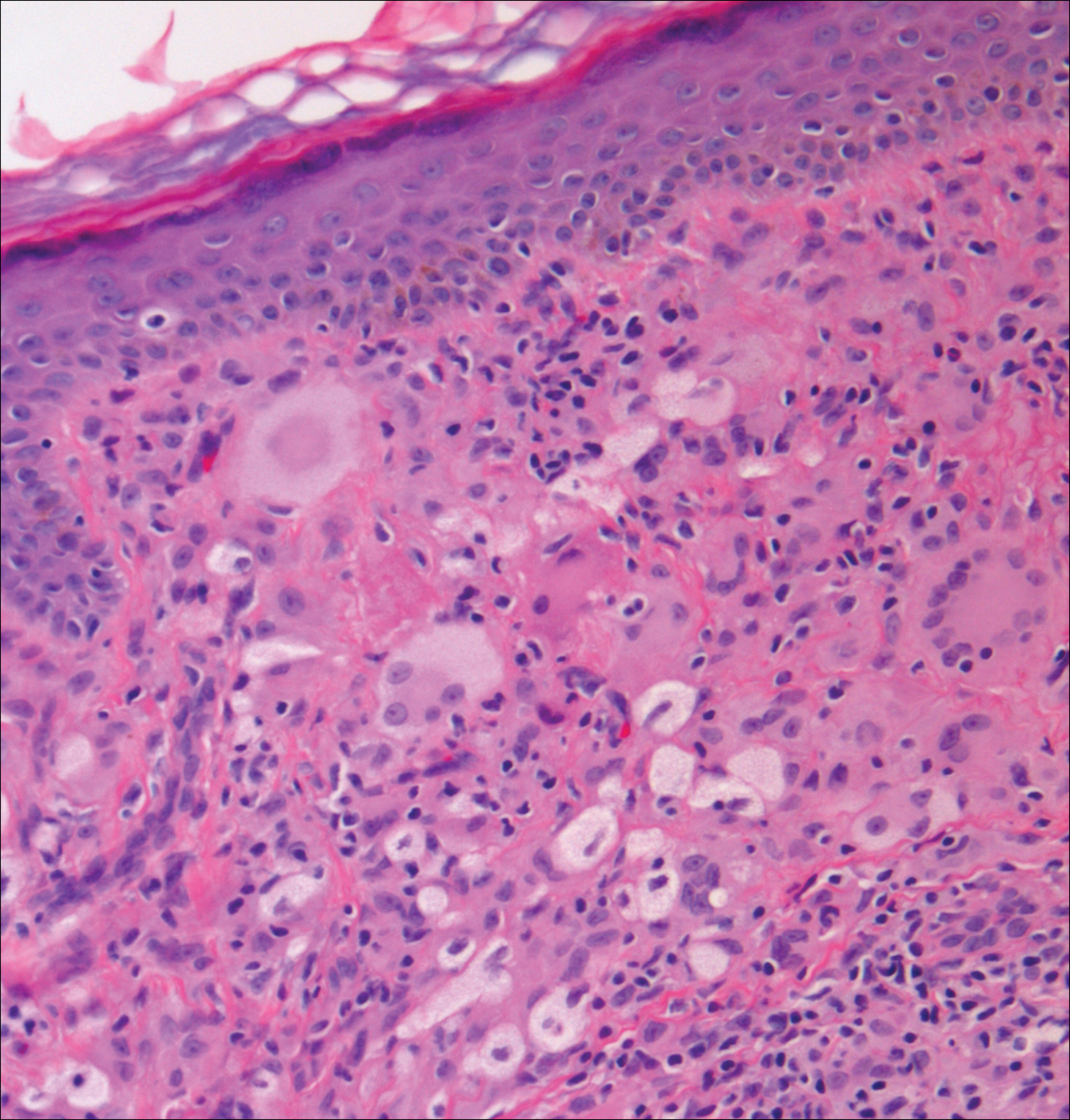
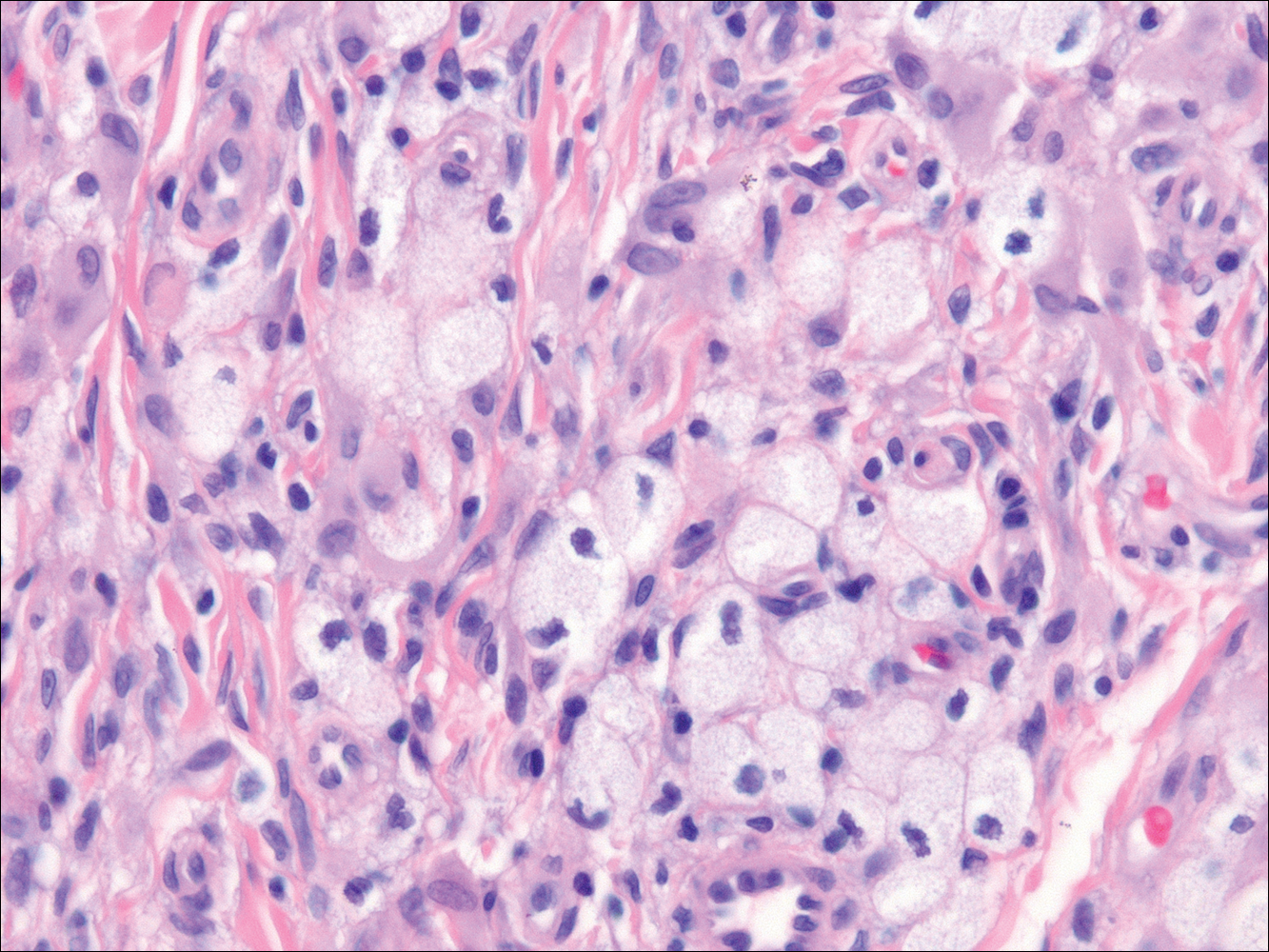
- Han XY, Seo YH, Sizer KC, et al. A new Mycobacterium species causing diffuse lepromatous leprosy. Am J Clin Pathol. 2008;130:856-864.
- Ridley DS, Jopling WH. Classification of leprosy according to immunity. a five-group system. Int J Lepr Other Mycobact Dis. 1966;34:255-273.
- Ridley DS. Histological classification and the immunological spectrum of leprosy. Bull World Health Organ. 1974;51:451-465.
- World Health Organization. WHO Expert Committee on Leprosy. World Health Organ Tech Rep Ser. 2012;968:1-61.
- Massone C, Belachew WA, Schettini A. Histopathology of the lepromatous skin biopsy. Clin Dermatol. 2015;33:38-45.
- Britton WJ, Lockwood DN. Leprosy. Lancet. 2004;363:1209-1219.
- Crowson AN, Magro C, Mihm M Jr. Treponemal diseases. In: Elder DE, Elenitsas R, Johnson Jr BL, et al. Lever’s Histopathology of the Skin. 10th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2009:540-579.
- Dacso MM, Jacobson RR, Scollard DM, et al. Evaluation of multi-drug therapy for leprosy in the United States using daily rifampin. South Med J. 2011;104:689-694.
- Handler MZ, Patel PA, Kapila R, et al. Cutaneous and mucocutaneous leishmaniasis: differential diagnosis, diagnosis, histopathology, and management. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2015;73:911-926.
- Massone C, Nunzi E, Cerroni L. Histopathologic diagnosis of leprosy in a nonendemic area. Am J Dermatopathol. 2010;32:417-419.
Lepromatous Leprosy
Lepromatous leprosy (LL) is a chronic, cutaneous, granulomatous infection caused by Mycobacterium leprae or the newly discovered Mycobacterium lepromatosis, both acid-fast, intracellular, bacillus bacterium.1 Although decreasing in prevalence due to effective treatment with antimicrobials, LL continues to be endemic in warm tropical or subtropical areas in Southeast Asia, sub-Saharan Africa, the Indian subcontinent, and South America.1 The mode of transmission of infection is not well established.
The cutaneous manifestation of leprosy was previously classified based on the cell-mediated immune response of the patient, as described by Ridley and Jopling,2 ranging from tuberculoid leprosy (TT) to LL. In this spectrum of leprosy are the borderline lesions including borderline tuberculoid, borderline, and borderline lepromatous.2,3 Although this classification is popular, in 2012 the World Health Organization implemented a new 2-category classification system to standardize treatment regimens: paucibacillary (2–5 lesions or 1 nerve involvement) and multibacillary (>5 lesions or multiple nerve involvement).4
In LL, a cell-mediated immune response is not mounted against the infection in the patient. Clinically, the disease can manifest as macular and nodular erythematous cutaneous lesions with poorly defined borders that are preferentially located on the face, earlobes, and nasal mucosa. Chronic infections are associated with sensory loss. Histologically, the dermis is densely infiltrated by foamy macrophages (Virchow cells or lepra cells), which do not form granulomas (quiz image A). The infiltrate may have varying accompanying lymphocytes and plasma cells, which can extend deep into the subcutaneous adipose tissue. Between the dermal infiltrate and epidermis is an uninvolved band of superficial dermis called the Grenz zone. The epidermis is flattened and atrophic. Nerves often are surrounded by macrophages with degrees of hyalinization but rarely are swollen. On acid-fast staining (Wade-Fite or Ziehl-Neelsen), numerous acid-fast bacilli are present within dermal cells in densely packed, intracellular collections called globi (quiz image B).2,3,5
In TT, the robust immune response causes epithelioid granuloma formation, similar to cutaneous sarcoidosis, and few, if any, organisms can be found on special stains. The remaining borderline lesions have varying numbers of bacilli and varying amounts of granuloma formation.3,6,7 Many cases of TT resolve without specific treatment. For most leprous diseases, the World Health Organization currently recommends a regimen of dapsone, rifampin, and clofazimine combination treatments for 6 to 12 months depending on the type of leprosy.8
Cutaneous leishmaniasis should be included in the differential diagnosis for patients from LL endemic areas. Early lesions can have a histiocytic infiltration with associated mixed inflammation and prominent epidermal hyperplasia. These early lesions usually have parasitic organisms located within the periphery of the cytoplasm of macrophages (“marquee sign”) to help differentiate it from leprous diseases (Figure 1).9

In nonendemic areas, leprous diseases often are mistaken for sarcoidosis, xanthomas, granular cell tumors, paraffinomas, or other histiocytic-rich lesions.10 Cutaneous sarcoidosis may be difficult to distinguish from TT, as both have noncaseating granulomas (Figure 2). Rare acid-fast bacilli may aid in the diagnosis, and sarcoid granulomas are not typically associated with cutaneous nerve involvement. New diagnostic tools such as polymerase chain reaction or genome sequencing can pick up rare organisms.

Xanthogranuolomas and xanthomas may histologically resemble LL with a dense dermal infiltrate of foamy histiocytes. No organisms are found in the infiltrate. Histologically, xanthogranulomas (juvenile or adult) will be a mixed infiltrate with foamy histiocytes; giant cell formation, especially Touton giant cells; lymphocytes; and granulocytes (Figure 3). Touton giant cells have a wreathlike formation of nuclei and an outer vacuolated cytoplasm. Xanthomas have sheets of large histiocytes with a foamy, lipid-filled interior and mild lymphocytic infiltrate (Figure 4).


Lepromatous Leprosy
Lepromatous leprosy (LL) is a chronic, cutaneous, granulomatous infection caused by Mycobacterium leprae or the newly discovered Mycobacterium lepromatosis, both acid-fast, intracellular, bacillus bacterium.1 Although decreasing in prevalence due to effective treatment with antimicrobials, LL continues to be endemic in warm tropical or subtropical areas in Southeast Asia, sub-Saharan Africa, the Indian subcontinent, and South America.1 The mode of transmission of infection is not well established.
The cutaneous manifestation of leprosy was previously classified based on the cell-mediated immune response of the patient, as described by Ridley and Jopling,2 ranging from tuberculoid leprosy (TT) to LL. In this spectrum of leprosy are the borderline lesions including borderline tuberculoid, borderline, and borderline lepromatous.2,3 Although this classification is popular, in 2012 the World Health Organization implemented a new 2-category classification system to standardize treatment regimens: paucibacillary (2–5 lesions or 1 nerve involvement) and multibacillary (>5 lesions or multiple nerve involvement).4
In LL, a cell-mediated immune response is not mounted against the infection in the patient. Clinically, the disease can manifest as macular and nodular erythematous cutaneous lesions with poorly defined borders that are preferentially located on the face, earlobes, and nasal mucosa. Chronic infections are associated with sensory loss. Histologically, the dermis is densely infiltrated by foamy macrophages (Virchow cells or lepra cells), which do not form granulomas (quiz image A). The infiltrate may have varying accompanying lymphocytes and plasma cells, which can extend deep into the subcutaneous adipose tissue. Between the dermal infiltrate and epidermis is an uninvolved band of superficial dermis called the Grenz zone. The epidermis is flattened and atrophic. Nerves often are surrounded by macrophages with degrees of hyalinization but rarely are swollen. On acid-fast staining (Wade-Fite or Ziehl-Neelsen), numerous acid-fast bacilli are present within dermal cells in densely packed, intracellular collections called globi (quiz image B).2,3,5
In TT, the robust immune response causes epithelioid granuloma formation, similar to cutaneous sarcoidosis, and few, if any, organisms can be found on special stains. The remaining borderline lesions have varying numbers of bacilli and varying amounts of granuloma formation.3,6,7 Many cases of TT resolve without specific treatment. For most leprous diseases, the World Health Organization currently recommends a regimen of dapsone, rifampin, and clofazimine combination treatments for 6 to 12 months depending on the type of leprosy.8
Cutaneous leishmaniasis should be included in the differential diagnosis for patients from LL endemic areas. Early lesions can have a histiocytic infiltration with associated mixed inflammation and prominent epidermal hyperplasia. These early lesions usually have parasitic organisms located within the periphery of the cytoplasm of macrophages (“marquee sign”) to help differentiate it from leprous diseases (Figure 1).9

In nonendemic areas, leprous diseases often are mistaken for sarcoidosis, xanthomas, granular cell tumors, paraffinomas, or other histiocytic-rich lesions.10 Cutaneous sarcoidosis may be difficult to distinguish from TT, as both have noncaseating granulomas (Figure 2). Rare acid-fast bacilli may aid in the diagnosis, and sarcoid granulomas are not typically associated with cutaneous nerve involvement. New diagnostic tools such as polymerase chain reaction or genome sequencing can pick up rare organisms.

Xanthogranuolomas and xanthomas may histologically resemble LL with a dense dermal infiltrate of foamy histiocytes. No organisms are found in the infiltrate. Histologically, xanthogranulomas (juvenile or adult) will be a mixed infiltrate with foamy histiocytes; giant cell formation, especially Touton giant cells; lymphocytes; and granulocytes (Figure 3). Touton giant cells have a wreathlike formation of nuclei and an outer vacuolated cytoplasm. Xanthomas have sheets of large histiocytes with a foamy, lipid-filled interior and mild lymphocytic infiltrate (Figure 4).


- Han XY, Seo YH, Sizer KC, et al. A new Mycobacterium species causing diffuse lepromatous leprosy. Am J Clin Pathol. 2008;130:856-864.
- Ridley DS, Jopling WH. Classification of leprosy according to immunity. a five-group system. Int J Lepr Other Mycobact Dis. 1966;34:255-273.
- Ridley DS. Histological classification and the immunological spectrum of leprosy. Bull World Health Organ. 1974;51:451-465.
- World Health Organization. WHO Expert Committee on Leprosy. World Health Organ Tech Rep Ser. 2012;968:1-61.
- Massone C, Belachew WA, Schettini A. Histopathology of the lepromatous skin biopsy. Clin Dermatol. 2015;33:38-45.
- Britton WJ, Lockwood DN. Leprosy. Lancet. 2004;363:1209-1219.
- Crowson AN, Magro C, Mihm M Jr. Treponemal diseases. In: Elder DE, Elenitsas R, Johnson Jr BL, et al. Lever’s Histopathology of the Skin. 10th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2009:540-579.
- Dacso MM, Jacobson RR, Scollard DM, et al. Evaluation of multi-drug therapy for leprosy in the United States using daily rifampin. South Med J. 2011;104:689-694.
- Handler MZ, Patel PA, Kapila R, et al. Cutaneous and mucocutaneous leishmaniasis: differential diagnosis, diagnosis, histopathology, and management. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2015;73:911-926.
- Massone C, Nunzi E, Cerroni L. Histopathologic diagnosis of leprosy in a nonendemic area. Am J Dermatopathol. 2010;32:417-419.
- Han XY, Seo YH, Sizer KC, et al. A new Mycobacterium species causing diffuse lepromatous leprosy. Am J Clin Pathol. 2008;130:856-864.
- Ridley DS, Jopling WH. Classification of leprosy according to immunity. a five-group system. Int J Lepr Other Mycobact Dis. 1966;34:255-273.
- Ridley DS. Histological classification and the immunological spectrum of leprosy. Bull World Health Organ. 1974;51:451-465.
- World Health Organization. WHO Expert Committee on Leprosy. World Health Organ Tech Rep Ser. 2012;968:1-61.
- Massone C, Belachew WA, Schettini A. Histopathology of the lepromatous skin biopsy. Clin Dermatol. 2015;33:38-45.
- Britton WJ, Lockwood DN. Leprosy. Lancet. 2004;363:1209-1219.
- Crowson AN, Magro C, Mihm M Jr. Treponemal diseases. In: Elder DE, Elenitsas R, Johnson Jr BL, et al. Lever’s Histopathology of the Skin. 10th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2009:540-579.
- Dacso MM, Jacobson RR, Scollard DM, et al. Evaluation of multi-drug therapy for leprosy in the United States using daily rifampin. South Med J. 2011;104:689-694.
- Handler MZ, Patel PA, Kapila R, et al. Cutaneous and mucocutaneous leishmaniasis: differential diagnosis, diagnosis, histopathology, and management. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2015;73:911-926.
- Massone C, Nunzi E, Cerroni L. Histopathologic diagnosis of leprosy in a nonendemic area. Am J Dermatopathol. 2010;32:417-419.
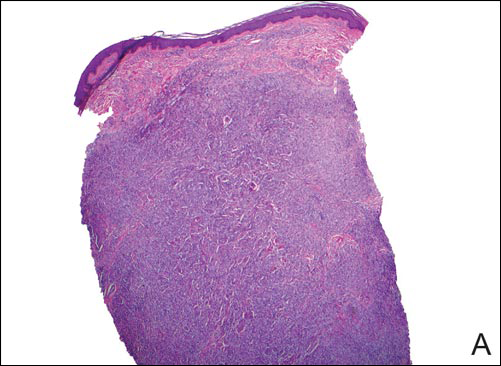
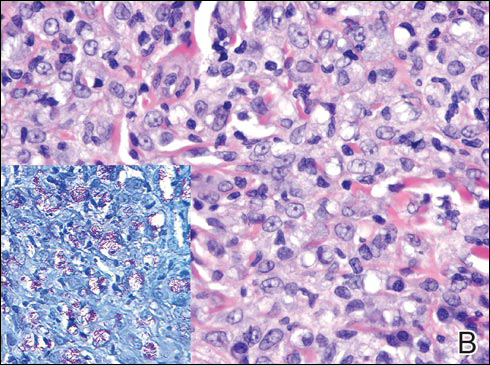
A 43-year-old man from Ghana presented with erythema and induration on the skin of the right maxillary region and right ear of several weeks’ duration.
The best diagnosis is:
a. cutaneous leishmaniasis
b. lepromatous leprosy
c. sarcoidosis
d. xanthogranuloma
e. xanthoma
Growing Papule on the Right Shoulder of an Elderly Man
Granular Cell Basal Cell Carcinoma
Basal cell carcinoma (BCC) is the most common human epithelial malignancy. There are several histologic variants, the rarest being granular cell BCC (GBCC).1 Granular cell BCC is reported most commonly in men with a mean age of 63 years. Sixty-four percent of cases develop on the face, with the remainder arising on the chest or trunk. Granular cell BCC has distinct histologic features but has no specific epidemiologic or clinical features that differentiate it from more common forms of BCC. Treatment of GBCC is identical to BCC and demonstrates similar outcomes. The presence of granular cells can make GBCC difficult to differentiate from other benign and malignant lesions that display similar granular histologic changes.1,2 Rarely, tumors that are histologically similar to human GBCC have been reported in animals.1
Histologically, GBCC commonly demonstrates the architecture of a nodular BCC or may extend from an existing nodular BCC (quiz images A and B). Granular cell BCC is comprised of large islands of basaloid cells extending from the epidermis with rare mitotic activity. Certain variants showing no epidermal attachments have been described,1,3 as in the current case. Classically, BCC and GBCC both demonstrate a peripheral palisade of blue basal cells; however, GBCC may lack this palisading feature in some cases. Therefore, GBCC may be comprised of granular cells only, which may be more easily confused with other tumors with granular cell differentiation. Even when GBCC retains the traditional peripheral palisade of blue basal cells, the central cells are filled with eosinophilic granules.1,2
Electron microscopy of GBCC usually reveals bundles of cytoplasmic tonofilaments and desmosomes in both granular cells and the peripherally palisaded cells. Electron microscopy imaging also demonstrates 0.1- to 0.5-µm membrane-bound lysosomelike structures. In certain reports, these structures show focal positivity for lysozymes.1,2 The etiology of the granules is unclear; however, they are thought to represent degenerative changes related to metabolic alteration and accumulation of lysosomelike structures. These lysosomelike structures have been highlighted with CD68 staining, which was negative in our case.1,2 The lesional cells in GBCC stain positively for cytokeratins, p63, and Ber-EP4, and negatively for S-100 protein, epithelial membrane antigen, and carcinoembryonic antigen. The granules in GBCC generally are positive on periodic acid–Schiff staining.1-4
The histologic differential diagnosis for GBCC includes granular cell tumor as well as other tumors that can present with granular cell changes such as ameloblastoma, leiomyoma, leiomyosarcoma, angiosarcoma, malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumor, and granular cell trichoblastoma. Granular cell ameloblastomas have histologic features and staining patterns that are identical to GBCC; however, ameloblastomas are distinguished by their location within the oral cavity. Granular cell tumors and malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumors stain positive for S-100 protein, and angiosarcomas stain positive for D2-40 and CD31. Leiomyomas and leiomyosarcomas can be differentiated by staining with smooth muscle actin or desmin.1 Granular cell trichoblastomas can be differentiated by the follicular stem cell marker protein PHLDA1 positivity.5
Desmoplastic trichilemmoma is difficult to distinguish from BCC. These tumors are comprised of superficial lobules of basaloid cells with a perilobular hyaline mantel surrounding a central desmoplastic stroma (Figure 1). The basaloid cells in desmoplastic trichoepithelioma demonstrate clear cell change; however, granular features are not seen. The cells within the desmoplastic areas are arranged haphazardly in cords and nests and can mimic an invasive carcinoma; however, nuclear atypia and mitotic activity generally are absent in desmoplastic trichilemmoma.6
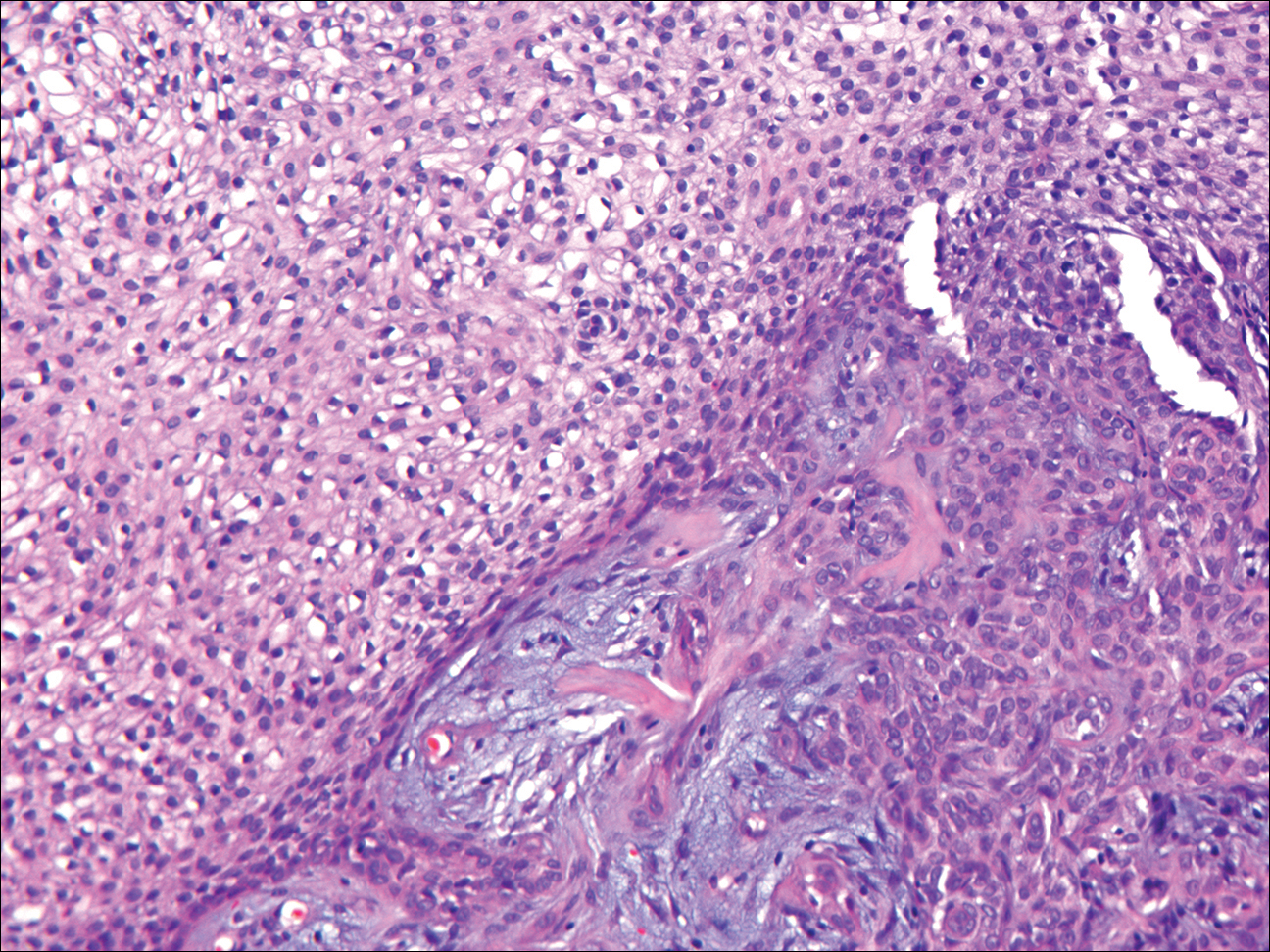
Granular cell tumors generally are poorly circumscribed dermal nodules comprised of large polygonal cells with an eosinophilic granular cytoplasm (Figure 2). The nuclei are generally small and round, and cytological atypia, necrosis, and mitotic activity are uncommon. The cells are positive for S-100 protein and neuron-specific enolase but negative for CD68. The granules are positive for periodic acid–Schiff stain and are diastase resistant. Rarely, these tumors can be malignant.7

Sebaceous adenoma is a well-circumscribed tumor comprised of lobules of characteristic mature sebocytes with bubbly or multivacuolated cytoplasm and crenated nuclei (Figure 3). There is an expansion and increased prominence of the peripherally located basaloid cells; however, in contrast to sebaceous epithelioma, less than 50% of the tumor usually is comprised of these basaloid cells.8
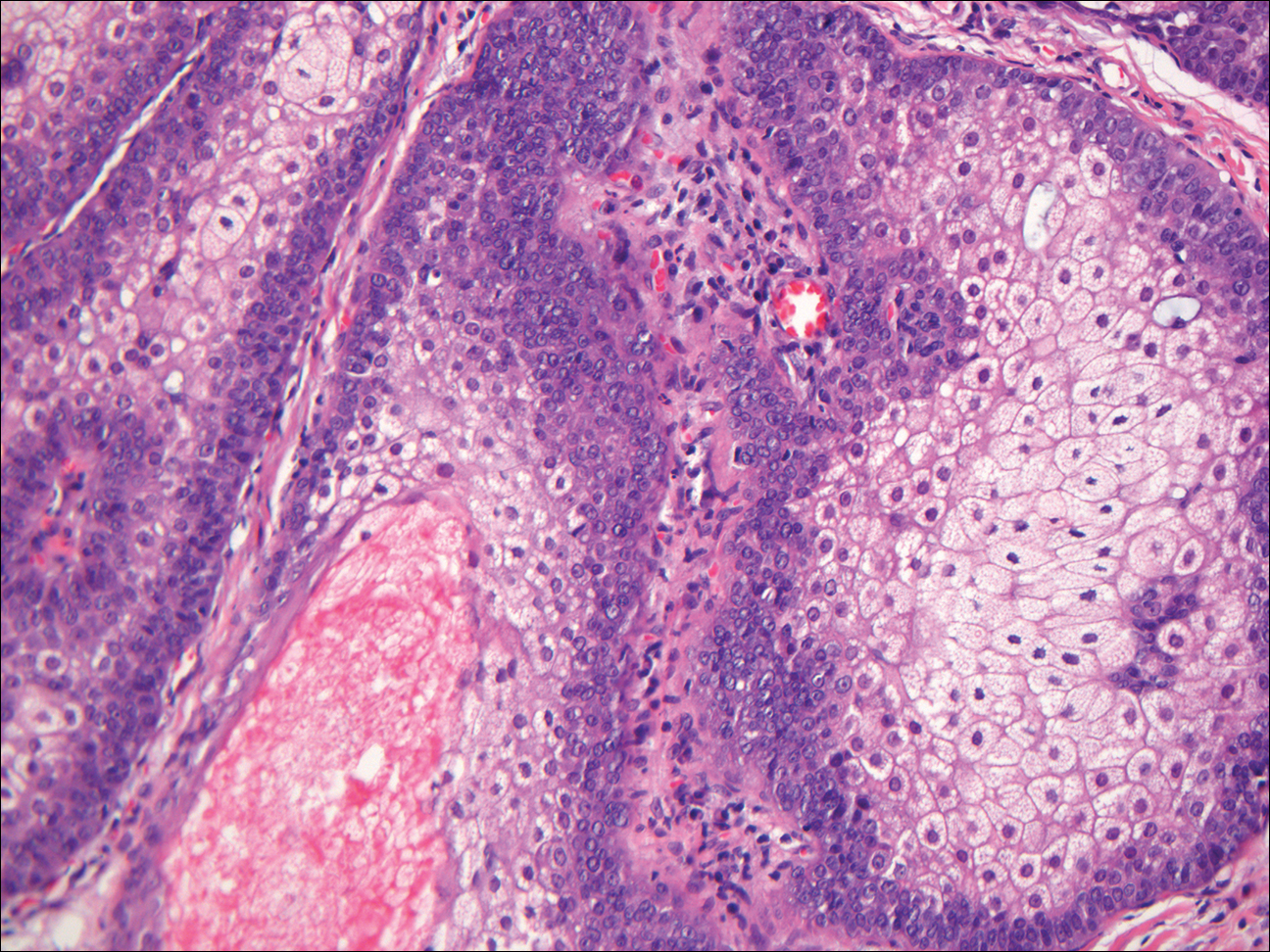
Xanthogranuloma demonstrates a dense collection of histiocytes in the dermis, commonly with Touton giant cell formation (Figure 4). The cells often have a foamy cytoplasm and cytoplasmic vacuoles are observed. The histiocytes are positive for factor XIIIa and CD68, and generally negative for S-100 protein and CD1a, which allows for differentiation from Langerhans cells.9
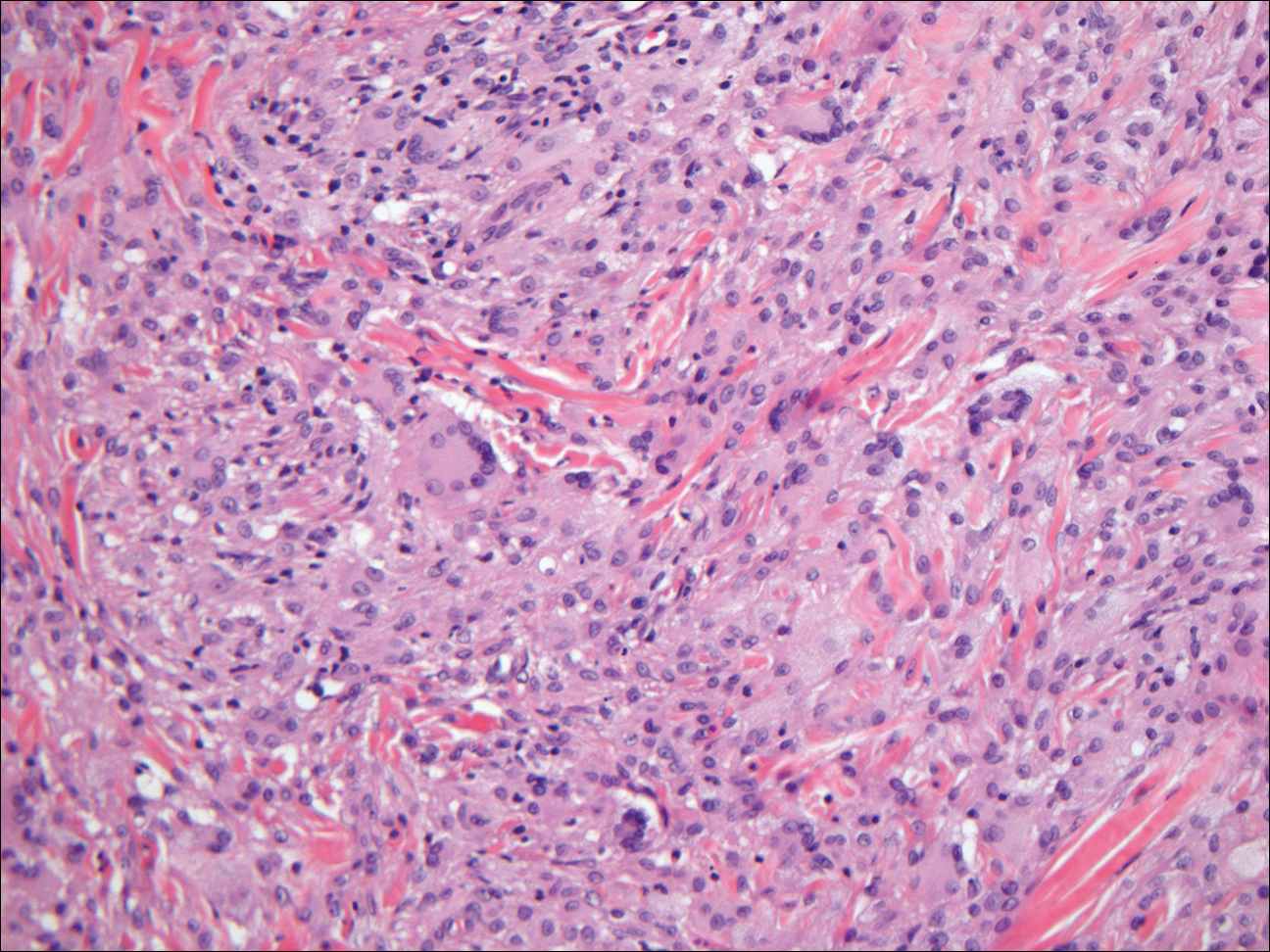
- Kanitakis J, Chouvet B. Granular-cell basal cell carcinoma of the skin. Eur J Dermatol. 2005;15:301-303.
- Dundr P, Stork J, Povysil C, et al. Granular cell basal cell carcinoma. Australas J Dermatol. 2004;45:70-72.
- Hayden AA, Shamma HN. Ber-EP4 and MNF-116 in a previously undescribed morphologic pattern of granular basal cell carcinoma. Am J Dermatopathol. 2001;23:530-532.
- Ansai S, Takayama R, Kimura T, et al. Ber-EP4 is a useful marker for follicular germinative cell differentiation of cutaneous epithelial neoplasms. J Dermatol. 2012;39:688-692.
- Battistella M, Peltre B, Cribier B. PHLDA1, a follicular stem cell marker, differentiates clear-cell/granular-cell trichoblastoma and clear-cell/granular cell basal cell carcinoma: a case-control study, with first description of granular-cell trichoblastoma. Am J Dermatopathol. 2014;36:643-650.
- Tellechea O, Reis JP, Baptista AP. Desmoplastic trichilemmoma. Am J Dermatopathol. 1992;14:107-114.
- Battistella M, Cribier B, Feugeas JP, et al. Vascular invasion and other invasive features in granular cell tumours of the skin: a multicentre study of 119 cases. J Clin Pathol. 2014;67:19-25.
- Shalin SC, Lyle S, Calonje E, et al. Sebaceous neoplasia and the Muir-Torre syndrome: important connections with clinical implications. Histopathology. 2010;56:133-147.
- Janssen D, Harms D. Juvenile xanthogranuloma in childhood and adolescence: a clinicopathologic study of 129 patients from the kiel pediatric tumor registry. Am J Surg Pathol. 2005;29:21-28.
Granular Cell Basal Cell Carcinoma
Basal cell carcinoma (BCC) is the most common human epithelial malignancy. There are several histologic variants, the rarest being granular cell BCC (GBCC).1 Granular cell BCC is reported most commonly in men with a mean age of 63 years. Sixty-four percent of cases develop on the face, with the remainder arising on the chest or trunk. Granular cell BCC has distinct histologic features but has no specific epidemiologic or clinical features that differentiate it from more common forms of BCC. Treatment of GBCC is identical to BCC and demonstrates similar outcomes. The presence of granular cells can make GBCC difficult to differentiate from other benign and malignant lesions that display similar granular histologic changes.1,2 Rarely, tumors that are histologically similar to human GBCC have been reported in animals.1
Histologically, GBCC commonly demonstrates the architecture of a nodular BCC or may extend from an existing nodular BCC (quiz images A and B). Granular cell BCC is comprised of large islands of basaloid cells extending from the epidermis with rare mitotic activity. Certain variants showing no epidermal attachments have been described,1,3 as in the current case. Classically, BCC and GBCC both demonstrate a peripheral palisade of blue basal cells; however, GBCC may lack this palisading feature in some cases. Therefore, GBCC may be comprised of granular cells only, which may be more easily confused with other tumors with granular cell differentiation. Even when GBCC retains the traditional peripheral palisade of blue basal cells, the central cells are filled with eosinophilic granules.1,2
Electron microscopy of GBCC usually reveals bundles of cytoplasmic tonofilaments and desmosomes in both granular cells and the peripherally palisaded cells. Electron microscopy imaging also demonstrates 0.1- to 0.5-µm membrane-bound lysosomelike structures. In certain reports, these structures show focal positivity for lysozymes.1,2 The etiology of the granules is unclear; however, they are thought to represent degenerative changes related to metabolic alteration and accumulation of lysosomelike structures. These lysosomelike structures have been highlighted with CD68 staining, which was negative in our case.1,2 The lesional cells in GBCC stain positively for cytokeratins, p63, and Ber-EP4, and negatively for S-100 protein, epithelial membrane antigen, and carcinoembryonic antigen. The granules in GBCC generally are positive on periodic acid–Schiff staining.1-4
The histologic differential diagnosis for GBCC includes granular cell tumor as well as other tumors that can present with granular cell changes such as ameloblastoma, leiomyoma, leiomyosarcoma, angiosarcoma, malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumor, and granular cell trichoblastoma. Granular cell ameloblastomas have histologic features and staining patterns that are identical to GBCC; however, ameloblastomas are distinguished by their location within the oral cavity. Granular cell tumors and malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumors stain positive for S-100 protein, and angiosarcomas stain positive for D2-40 and CD31. Leiomyomas and leiomyosarcomas can be differentiated by staining with smooth muscle actin or desmin.1 Granular cell trichoblastomas can be differentiated by the follicular stem cell marker protein PHLDA1 positivity.5
Desmoplastic trichilemmoma is difficult to distinguish from BCC. These tumors are comprised of superficial lobules of basaloid cells with a perilobular hyaline mantel surrounding a central desmoplastic stroma (Figure 1). The basaloid cells in desmoplastic trichoepithelioma demonstrate clear cell change; however, granular features are not seen. The cells within the desmoplastic areas are arranged haphazardly in cords and nests and can mimic an invasive carcinoma; however, nuclear atypia and mitotic activity generally are absent in desmoplastic trichilemmoma.6

Granular cell tumors generally are poorly circumscribed dermal nodules comprised of large polygonal cells with an eosinophilic granular cytoplasm (Figure 2). The nuclei are generally small and round, and cytological atypia, necrosis, and mitotic activity are uncommon. The cells are positive for S-100 protein and neuron-specific enolase but negative for CD68. The granules are positive for periodic acid–Schiff stain and are diastase resistant. Rarely, these tumors can be malignant.7

Sebaceous adenoma is a well-circumscribed tumor comprised of lobules of characteristic mature sebocytes with bubbly or multivacuolated cytoplasm and crenated nuclei (Figure 3). There is an expansion and increased prominence of the peripherally located basaloid cells; however, in contrast to sebaceous epithelioma, less than 50% of the tumor usually is comprised of these basaloid cells.8

Xanthogranuloma demonstrates a dense collection of histiocytes in the dermis, commonly with Touton giant cell formation (Figure 4). The cells often have a foamy cytoplasm and cytoplasmic vacuoles are observed. The histiocytes are positive for factor XIIIa and CD68, and generally negative for S-100 protein and CD1a, which allows for differentiation from Langerhans cells.9

Granular Cell Basal Cell Carcinoma
Basal cell carcinoma (BCC) is the most common human epithelial malignancy. There are several histologic variants, the rarest being granular cell BCC (GBCC).1 Granular cell BCC is reported most commonly in men with a mean age of 63 years. Sixty-four percent of cases develop on the face, with the remainder arising on the chest or trunk. Granular cell BCC has distinct histologic features but has no specific epidemiologic or clinical features that differentiate it from more common forms of BCC. Treatment of GBCC is identical to BCC and demonstrates similar outcomes. The presence of granular cells can make GBCC difficult to differentiate from other benign and malignant lesions that display similar granular histologic changes.1,2 Rarely, tumors that are histologically similar to human GBCC have been reported in animals.1
Histologically, GBCC commonly demonstrates the architecture of a nodular BCC or may extend from an existing nodular BCC (quiz images A and B). Granular cell BCC is comprised of large islands of basaloid cells extending from the epidermis with rare mitotic activity. Certain variants showing no epidermal attachments have been described,1,3 as in the current case. Classically, BCC and GBCC both demonstrate a peripheral palisade of blue basal cells; however, GBCC may lack this palisading feature in some cases. Therefore, GBCC may be comprised of granular cells only, which may be more easily confused with other tumors with granular cell differentiation. Even when GBCC retains the traditional peripheral palisade of blue basal cells, the central cells are filled with eosinophilic granules.1,2
Electron microscopy of GBCC usually reveals bundles of cytoplasmic tonofilaments and desmosomes in both granular cells and the peripherally palisaded cells. Electron microscopy imaging also demonstrates 0.1- to 0.5-µm membrane-bound lysosomelike structures. In certain reports, these structures show focal positivity for lysozymes.1,2 The etiology of the granules is unclear; however, they are thought to represent degenerative changes related to metabolic alteration and accumulation of lysosomelike structures. These lysosomelike structures have been highlighted with CD68 staining, which was negative in our case.1,2 The lesional cells in GBCC stain positively for cytokeratins, p63, and Ber-EP4, and negatively for S-100 protein, epithelial membrane antigen, and carcinoembryonic antigen. The granules in GBCC generally are positive on periodic acid–Schiff staining.1-4
The histologic differential diagnosis for GBCC includes granular cell tumor as well as other tumors that can present with granular cell changes such as ameloblastoma, leiomyoma, leiomyosarcoma, angiosarcoma, malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumor, and granular cell trichoblastoma. Granular cell ameloblastomas have histologic features and staining patterns that are identical to GBCC; however, ameloblastomas are distinguished by their location within the oral cavity. Granular cell tumors and malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumors stain positive for S-100 protein, and angiosarcomas stain positive for D2-40 and CD31. Leiomyomas and leiomyosarcomas can be differentiated by staining with smooth muscle actin or desmin.1 Granular cell trichoblastomas can be differentiated by the follicular stem cell marker protein PHLDA1 positivity.5
Desmoplastic trichilemmoma is difficult to distinguish from BCC. These tumors are comprised of superficial lobules of basaloid cells with a perilobular hyaline mantel surrounding a central desmoplastic stroma (Figure 1). The basaloid cells in desmoplastic trichoepithelioma demonstrate clear cell change; however, granular features are not seen. The cells within the desmoplastic areas are arranged haphazardly in cords and nests and can mimic an invasive carcinoma; however, nuclear atypia and mitotic activity generally are absent in desmoplastic trichilemmoma.6

Granular cell tumors generally are poorly circumscribed dermal nodules comprised of large polygonal cells with an eosinophilic granular cytoplasm (Figure 2). The nuclei are generally small and round, and cytological atypia, necrosis, and mitotic activity are uncommon. The cells are positive for S-100 protein and neuron-specific enolase but negative for CD68. The granules are positive for periodic acid–Schiff stain and are diastase resistant. Rarely, these tumors can be malignant.7

Sebaceous adenoma is a well-circumscribed tumor comprised of lobules of characteristic mature sebocytes with bubbly or multivacuolated cytoplasm and crenated nuclei (Figure 3). There is an expansion and increased prominence of the peripherally located basaloid cells; however, in contrast to sebaceous epithelioma, less than 50% of the tumor usually is comprised of these basaloid cells.8

Xanthogranuloma demonstrates a dense collection of histiocytes in the dermis, commonly with Touton giant cell formation (Figure 4). The cells often have a foamy cytoplasm and cytoplasmic vacuoles are observed. The histiocytes are positive for factor XIIIa and CD68, and generally negative for S-100 protein and CD1a, which allows for differentiation from Langerhans cells.9

- Kanitakis J, Chouvet B. Granular-cell basal cell carcinoma of the skin. Eur J Dermatol. 2005;15:301-303.
- Dundr P, Stork J, Povysil C, et al. Granular cell basal cell carcinoma. Australas J Dermatol. 2004;45:70-72.
- Hayden AA, Shamma HN. Ber-EP4 and MNF-116 in a previously undescribed morphologic pattern of granular basal cell carcinoma. Am J Dermatopathol. 2001;23:530-532.
- Ansai S, Takayama R, Kimura T, et al. Ber-EP4 is a useful marker for follicular germinative cell differentiation of cutaneous epithelial neoplasms. J Dermatol. 2012;39:688-692.
- Battistella M, Peltre B, Cribier B. PHLDA1, a follicular stem cell marker, differentiates clear-cell/granular-cell trichoblastoma and clear-cell/granular cell basal cell carcinoma: a case-control study, with first description of granular-cell trichoblastoma. Am J Dermatopathol. 2014;36:643-650.
- Tellechea O, Reis JP, Baptista AP. Desmoplastic trichilemmoma. Am J Dermatopathol. 1992;14:107-114.
- Battistella M, Cribier B, Feugeas JP, et al. Vascular invasion and other invasive features in granular cell tumours of the skin: a multicentre study of 119 cases. J Clin Pathol. 2014;67:19-25.
- Shalin SC, Lyle S, Calonje E, et al. Sebaceous neoplasia and the Muir-Torre syndrome: important connections with clinical implications. Histopathology. 2010;56:133-147.
- Janssen D, Harms D. Juvenile xanthogranuloma in childhood and adolescence: a clinicopathologic study of 129 patients from the kiel pediatric tumor registry. Am J Surg Pathol. 2005;29:21-28.
- Kanitakis J, Chouvet B. Granular-cell basal cell carcinoma of the skin. Eur J Dermatol. 2005;15:301-303.
- Dundr P, Stork J, Povysil C, et al. Granular cell basal cell carcinoma. Australas J Dermatol. 2004;45:70-72.
- Hayden AA, Shamma HN. Ber-EP4 and MNF-116 in a previously undescribed morphologic pattern of granular basal cell carcinoma. Am J Dermatopathol. 2001;23:530-532.
- Ansai S, Takayama R, Kimura T, et al. Ber-EP4 is a useful marker for follicular germinative cell differentiation of cutaneous epithelial neoplasms. J Dermatol. 2012;39:688-692.
- Battistella M, Peltre B, Cribier B. PHLDA1, a follicular stem cell marker, differentiates clear-cell/granular-cell trichoblastoma and clear-cell/granular cell basal cell carcinoma: a case-control study, with first description of granular-cell trichoblastoma. Am J Dermatopathol. 2014;36:643-650.
- Tellechea O, Reis JP, Baptista AP. Desmoplastic trichilemmoma. Am J Dermatopathol. 1992;14:107-114.
- Battistella M, Cribier B, Feugeas JP, et al. Vascular invasion and other invasive features in granular cell tumours of the skin: a multicentre study of 119 cases. J Clin Pathol. 2014;67:19-25.
- Shalin SC, Lyle S, Calonje E, et al. Sebaceous neoplasia and the Muir-Torre syndrome: important connections with clinical implications. Histopathology. 2010;56:133-147.
- Janssen D, Harms D. Juvenile xanthogranuloma in childhood and adolescence: a clinicopathologic study of 129 patients from the kiel pediatric tumor registry. Am J Surg Pathol. 2005;29:21-28.

The best diagnosis is:
a. desmoplastic trichilemmoma
b. granular cell basal cell carcinoma
c. granular cell tumor
d. sebaceous adenoma
e. xanthogranuloma
Continue to the next page for the diagnosis >>
Benign Lesion on the Posterior Aspect of the Neck
Nuchal-Type Fibroma
Nuchal-type fibroma (NTF) is a rare benign proliferation of the dermis and subcutis associated with diabetes mellitus and Gardner syndrome.1,2 Forty-four percent of patients with NTF have diabetes mellitus.2 The posterior aspect of the neck is the most frequently affected site, but lesions also may present on the upper back, lumbosacral area, buttocks, and face. Physical examination generally reveals an indurated, asymptomatic, ill-defined, 3-cm or smaller nodule that is hard and white, unencapsulated, and poorly circumscribed.
Histopathologic examination of NTF typically reveals a nodular paucicellular proliferation of thick collagen bundles with inconspicuous fibroblasts, radiation of collagenous septa into the subcutaneous fat, and entrapment of mature adipose tissue and small nerves (quiz image A). Collagen bundles are thickened with entrapment of adipose tissue without increased cellularity (quiz image B). S-100 staining can show the entrapped nerves.
Similar to NTF, sclerotic fibroma is a firm dermal nodule with histologic examination usually demonstrating a paucicellular collagenous tumor. In sclerotic fibromas, the collagen pattern resembles Vincent van Gogh’s painting “The Starry Night” and may be a marker for Cowden disease (Figure 1).3 Solitary fibrous tumors are distinguished by more hypercellular areas, patternless pattern, and staghorn-shaped blood vessels (Figure 2).4 Spindle cell lipoma classically demonstrates a mixture of mature adipocytes and bland spindle cells in a mucinous or fibrous background with thick collagen bundles with no storiform pattern (Figure 3). Some variants of spindle cell lipoma have minimal or no fat.5 All of these conditions have positive immunohistochemical staining for CD34.
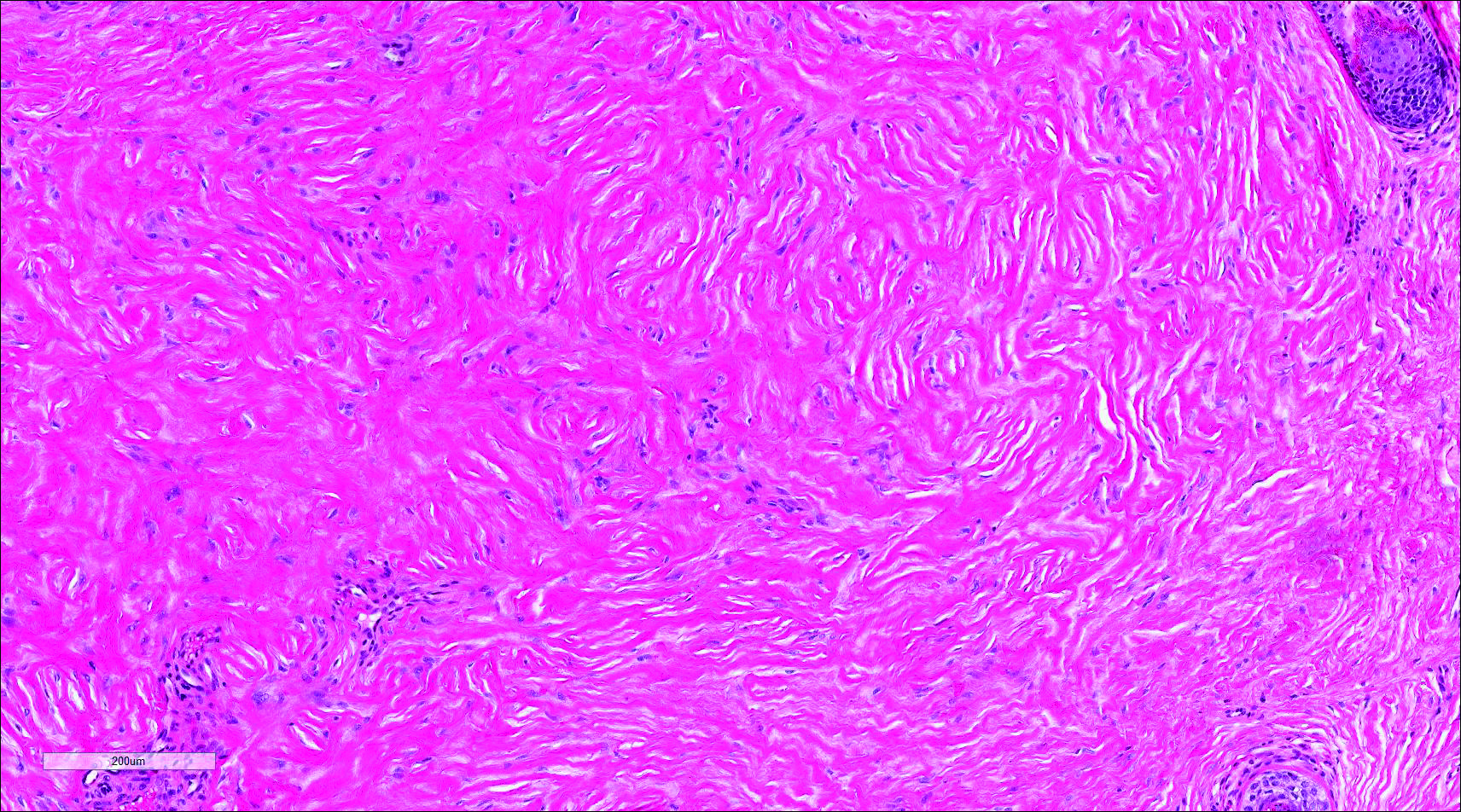
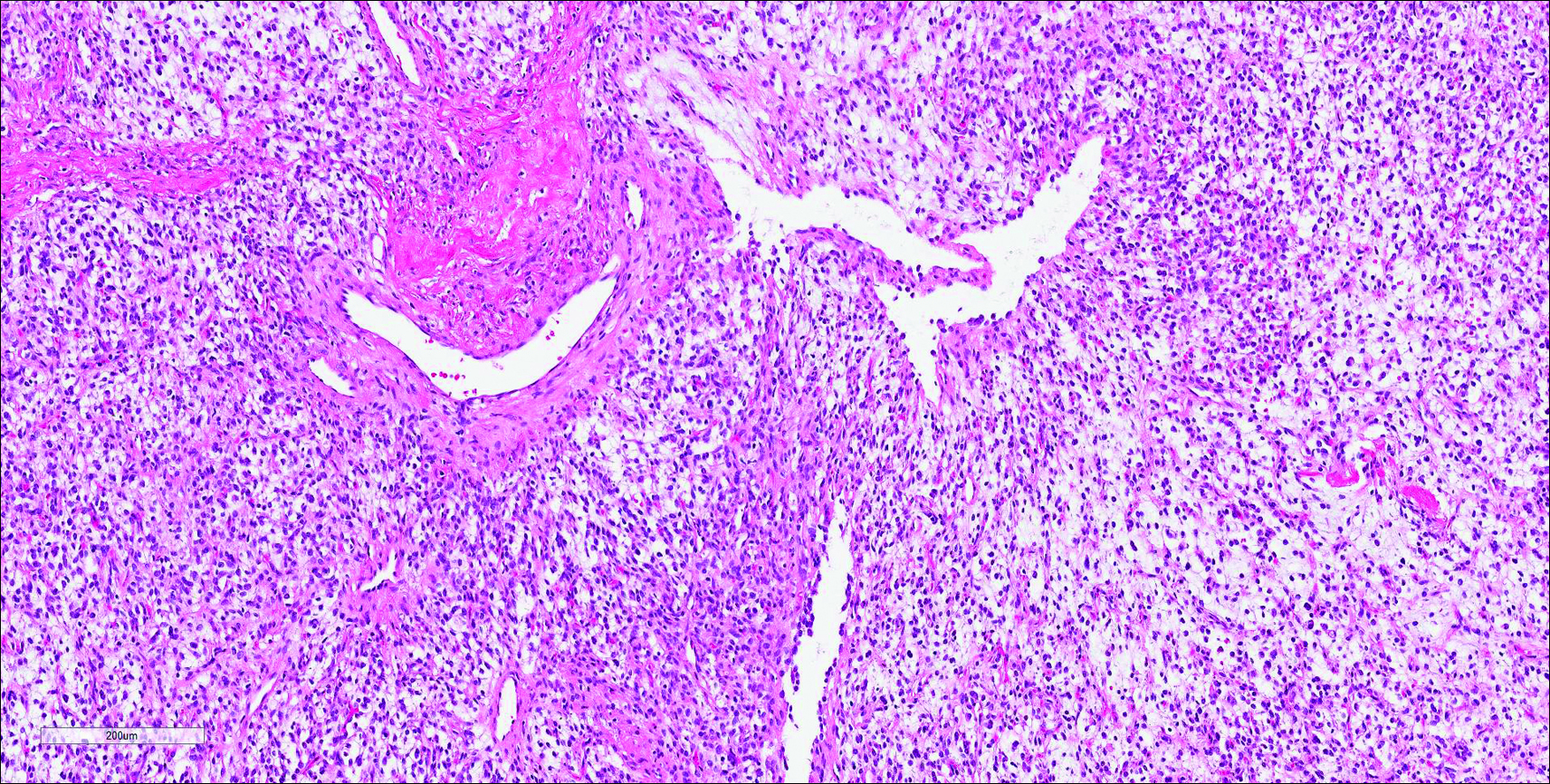
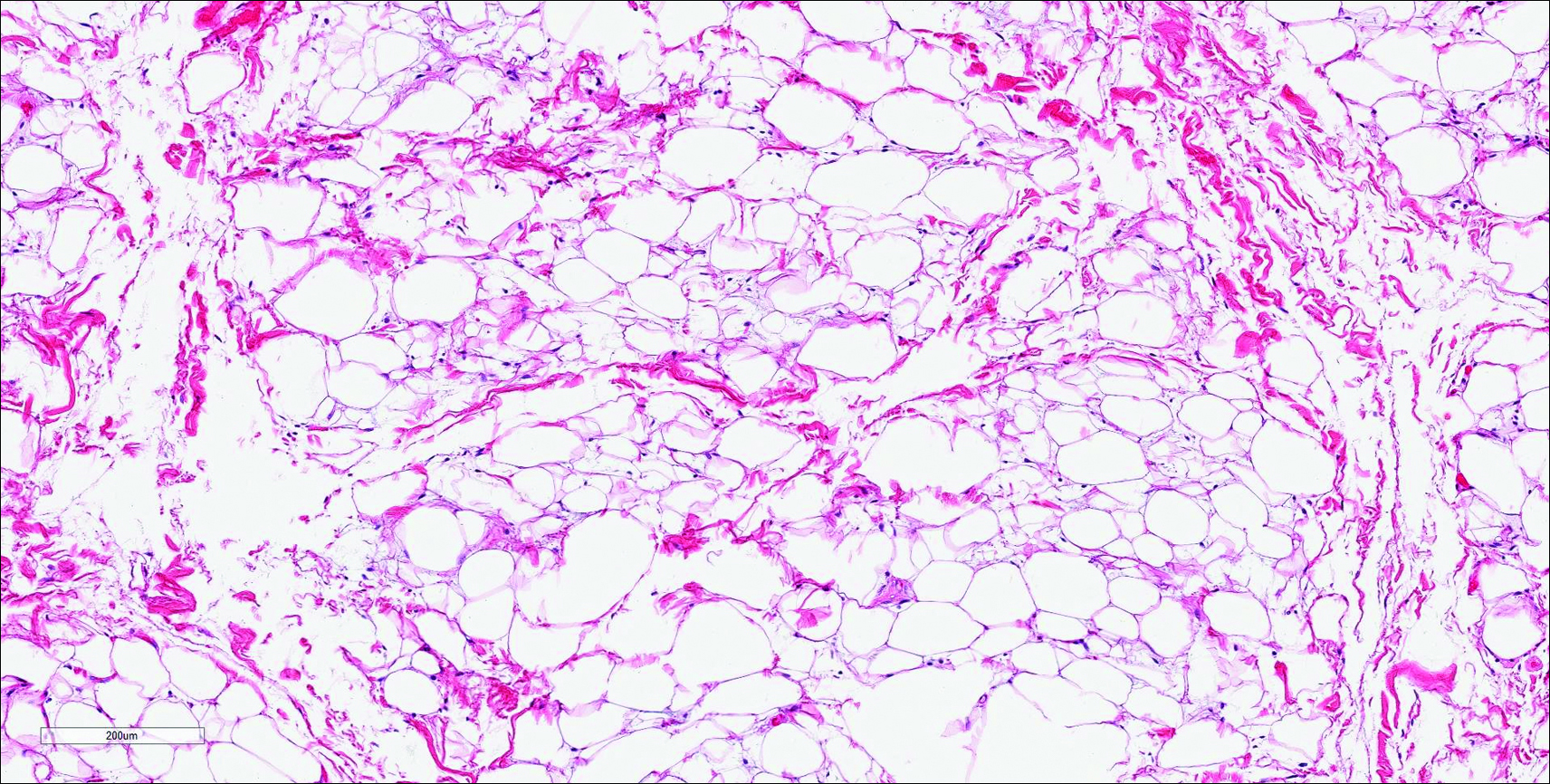
However, dermatofibroma is CD34‒. Dermatofibroma is characterized by an interstitial spindle cell proliferation with a loose storiform pattern, collagen trapping at the outer edges of the tumor, overlying platelike acanthosis, and sometimes follicular induction (Figure 4).

Nuchal-type fibroma also can resemble scleredema. Both lesions can show increased and thickened collagen bundles without notable fibroblast proliferation; the difference is the occurrence of mucin in scleredema. However, incases of late-stage scleredema, mucin is not always demonstrated. Therefore, one can conclude that histologically NTF is closely associated with late-stage scleredema.6
- Dawes LC, La Hei ER, Tobias V, et al. Nuchal fibroma should be recognized as a new extracolonic manifestation of Gardner-variant familial adenomatous polyposis. Aust N Z J Surg. 2000;70:824-826.
- Michal M, Fetsch JF, Hes O, et al. Nuchal-type fibroma: a clinicopathologic study of 52 cases. Cancer. 1999;85:156-163.
- Pernet C, Durand L, Bessis D, et al. Solitary sclerotic fibroma of the skin: a possible clue for Cowden syndrome. Eur J Dermatol. 2012;22:278-279.
- Omori Y, Saeki H, Ito K, et al. Solitary fibrous tumour of the scalp. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2014;39:539-541.
- Billings SD, Folpe AL. Diagnostically challenging spindle cell lipomas: a report of 34 “low-fat” and “fat-free” variants. Am J Dermatopathol. 2007;29:437-442.
- Banney LA, Weedon D, Muir JB. Nuchal fibroma associated with scleredema, diabetes mellitus and organic solvent exposure. Australas J Dermatol. 2000;41:39-41.
Nuchal-Type Fibroma
Nuchal-type fibroma (NTF) is a rare benign proliferation of the dermis and subcutis associated with diabetes mellitus and Gardner syndrome.1,2 Forty-four percent of patients with NTF have diabetes mellitus.2 The posterior aspect of the neck is the most frequently affected site, but lesions also may present on the upper back, lumbosacral area, buttocks, and face. Physical examination generally reveals an indurated, asymptomatic, ill-defined, 3-cm or smaller nodule that is hard and white, unencapsulated, and poorly circumscribed.
Histopathologic examination of NTF typically reveals a nodular paucicellular proliferation of thick collagen bundles with inconspicuous fibroblasts, radiation of collagenous septa into the subcutaneous fat, and entrapment of mature adipose tissue and small nerves (quiz image A). Collagen bundles are thickened with entrapment of adipose tissue without increased cellularity (quiz image B). S-100 staining can show the entrapped nerves.
Similar to NTF, sclerotic fibroma is a firm dermal nodule with histologic examination usually demonstrating a paucicellular collagenous tumor. In sclerotic fibromas, the collagen pattern resembles Vincent van Gogh’s painting “The Starry Night” and may be a marker for Cowden disease (Figure 1).3 Solitary fibrous tumors are distinguished by more hypercellular areas, patternless pattern, and staghorn-shaped blood vessels (Figure 2).4 Spindle cell lipoma classically demonstrates a mixture of mature adipocytes and bland spindle cells in a mucinous or fibrous background with thick collagen bundles with no storiform pattern (Figure 3). Some variants of spindle cell lipoma have minimal or no fat.5 All of these conditions have positive immunohistochemical staining for CD34.



However, dermatofibroma is CD34‒. Dermatofibroma is characterized by an interstitial spindle cell proliferation with a loose storiform pattern, collagen trapping at the outer edges of the tumor, overlying platelike acanthosis, and sometimes follicular induction (Figure 4).

Nuchal-type fibroma also can resemble scleredema. Both lesions can show increased and thickened collagen bundles without notable fibroblast proliferation; the difference is the occurrence of mucin in scleredema. However, incases of late-stage scleredema, mucin is not always demonstrated. Therefore, one can conclude that histologically NTF is closely associated with late-stage scleredema.6
Nuchal-Type Fibroma
Nuchal-type fibroma (NTF) is a rare benign proliferation of the dermis and subcutis associated with diabetes mellitus and Gardner syndrome.1,2 Forty-four percent of patients with NTF have diabetes mellitus.2 The posterior aspect of the neck is the most frequently affected site, but lesions also may present on the upper back, lumbosacral area, buttocks, and face. Physical examination generally reveals an indurated, asymptomatic, ill-defined, 3-cm or smaller nodule that is hard and white, unencapsulated, and poorly circumscribed.
Histopathologic examination of NTF typically reveals a nodular paucicellular proliferation of thick collagen bundles with inconspicuous fibroblasts, radiation of collagenous septa into the subcutaneous fat, and entrapment of mature adipose tissue and small nerves (quiz image A). Collagen bundles are thickened with entrapment of adipose tissue without increased cellularity (quiz image B). S-100 staining can show the entrapped nerves.
Similar to NTF, sclerotic fibroma is a firm dermal nodule with histologic examination usually demonstrating a paucicellular collagenous tumor. In sclerotic fibromas, the collagen pattern resembles Vincent van Gogh’s painting “The Starry Night” and may be a marker for Cowden disease (Figure 1).3 Solitary fibrous tumors are distinguished by more hypercellular areas, patternless pattern, and staghorn-shaped blood vessels (Figure 2).4 Spindle cell lipoma classically demonstrates a mixture of mature adipocytes and bland spindle cells in a mucinous or fibrous background with thick collagen bundles with no storiform pattern (Figure 3). Some variants of spindle cell lipoma have minimal or no fat.5 All of these conditions have positive immunohistochemical staining for CD34.



However, dermatofibroma is CD34‒. Dermatofibroma is characterized by an interstitial spindle cell proliferation with a loose storiform pattern, collagen trapping at the outer edges of the tumor, overlying platelike acanthosis, and sometimes follicular induction (Figure 4).

Nuchal-type fibroma also can resemble scleredema. Both lesions can show increased and thickened collagen bundles without notable fibroblast proliferation; the difference is the occurrence of mucin in scleredema. However, incases of late-stage scleredema, mucin is not always demonstrated. Therefore, one can conclude that histologically NTF is closely associated with late-stage scleredema.6
- Dawes LC, La Hei ER, Tobias V, et al. Nuchal fibroma should be recognized as a new extracolonic manifestation of Gardner-variant familial adenomatous polyposis. Aust N Z J Surg. 2000;70:824-826.
- Michal M, Fetsch JF, Hes O, et al. Nuchal-type fibroma: a clinicopathologic study of 52 cases. Cancer. 1999;85:156-163.
- Pernet C, Durand L, Bessis D, et al. Solitary sclerotic fibroma of the skin: a possible clue for Cowden syndrome. Eur J Dermatol. 2012;22:278-279.
- Omori Y, Saeki H, Ito K, et al. Solitary fibrous tumour of the scalp. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2014;39:539-541.
- Billings SD, Folpe AL. Diagnostically challenging spindle cell lipomas: a report of 34 “low-fat” and “fat-free” variants. Am J Dermatopathol. 2007;29:437-442.
- Banney LA, Weedon D, Muir JB. Nuchal fibroma associated with scleredema, diabetes mellitus and organic solvent exposure. Australas J Dermatol. 2000;41:39-41.
- Dawes LC, La Hei ER, Tobias V, et al. Nuchal fibroma should be recognized as a new extracolonic manifestation of Gardner-variant familial adenomatous polyposis. Aust N Z J Surg. 2000;70:824-826.
- Michal M, Fetsch JF, Hes O, et al. Nuchal-type fibroma: a clinicopathologic study of 52 cases. Cancer. 1999;85:156-163.
- Pernet C, Durand L, Bessis D, et al. Solitary sclerotic fibroma of the skin: a possible clue for Cowden syndrome. Eur J Dermatol. 2012;22:278-279.
- Omori Y, Saeki H, Ito K, et al. Solitary fibrous tumour of the scalp. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2014;39:539-541.
- Billings SD, Folpe AL. Diagnostically challenging spindle cell lipomas: a report of 34 “low-fat” and “fat-free” variants. Am J Dermatopathol. 2007;29:437-442.
- Banney LA, Weedon D, Muir JB. Nuchal fibroma associated with scleredema, diabetes mellitus and organic solvent exposure. Australas J Dermatol. 2000;41:39-41.
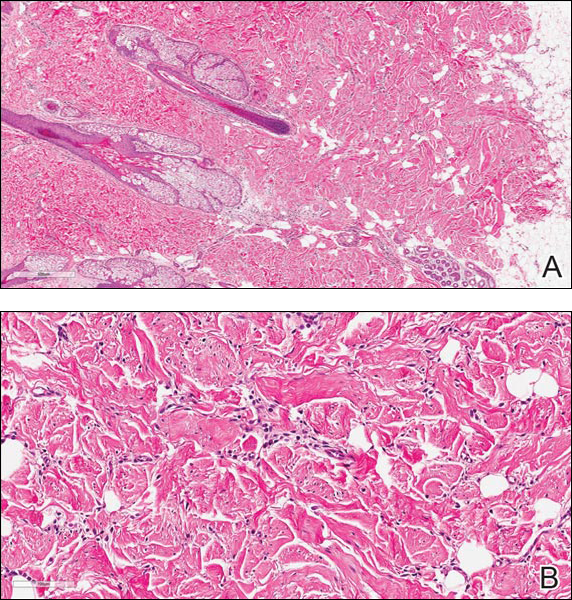
The best diagnosis is:
a. dermatofibroma
b. nuchal-type fibroma
c. sclerotic fibroma
d. solitary fibrous tumor
e. spindle cell lipoma
Continue to the next page for the diagnosis >>
Cyst on the Eyebrow
The best diagnosis is:
a. bronchogenic cyst
b. dermoid cyst
c. epidermal inclusion cyst
d. hidrocystoma
e. steatocystoma
|
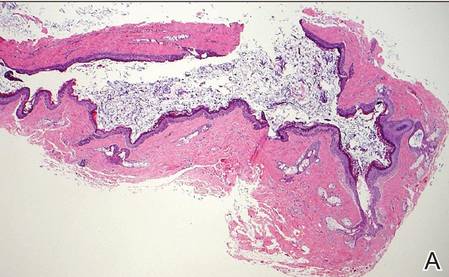 |
| H&E, original magnification ×40. |
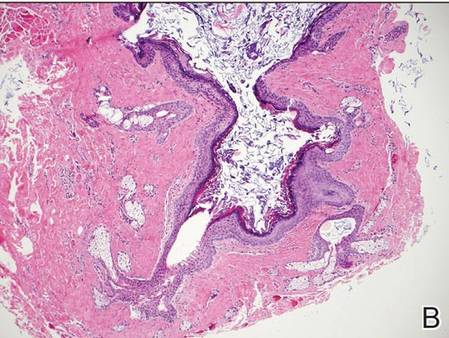 |
| H&E, original magnification ×100. |
Continue to the next page for the diagnosis >>
Dermoid Cyst
Dermoid cysts often present clinically as firm subcutaneous nodules on the head or neck in young children. They tend to arise along the lateral aspect of the eyebrow but also can occur on the nose, forehead, neck, chest, or scalp.1 Dermoid cysts are thought to arise from the sequestration of ectodermal tissues along the embryonic fusion planes during development.2 As such, they represent congenital defects and often are identified at birth; however, some are not noticed until much later when they enlarge or become inflamed or infected. Midline dermoid cysts may be associated with underlying dysraphism or intracranial extension.3,4 Thus, any midline lesion warrants evaluation that incorporates imaging with computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging.4,5 Histologically, dermoid cysts are lined by a keratinizing stratified squamous epithelium (quiz image A), but the lining may be brightly eosinophilic and wavy resembling shark teeth.1,3 The wall of a dermoid cyst commonly contains mature adnexal structures such as terminal hair follicles, sebaceous glands, apocrine glands, and/or eccrine glands (quiz image B).1 Smooth muscle also may be seen within the lining; however, bone and cartilage are not commonly reported in dermoid cysts.2 Lamellar keratin is typical of the cyst contents, and terminal hair shafts also are sometimes noted within the cystic space (quiz image B).1,2 Treatment options include excision at the time of diagnosis or close clinical monitoring with subsequent excision if the lesion grows or becomes symptomatic.4,5 Many practitioners opt to excise these cysts at diagnosis, as untreated lesions are at risk for infection and/or inflammation or may be cosmetically deforming.6,7 Surgical resection, including removal of the wall of the cyst, is curative and reoccurrence is rare.5
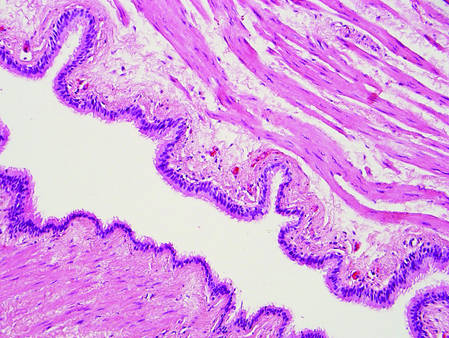 | |
Figure 1. Bronchogenic cyst demonstrating a ciliated pseudostratified epithelial lining encircled by smooth muscle (H&E, original magnification ×200). | |
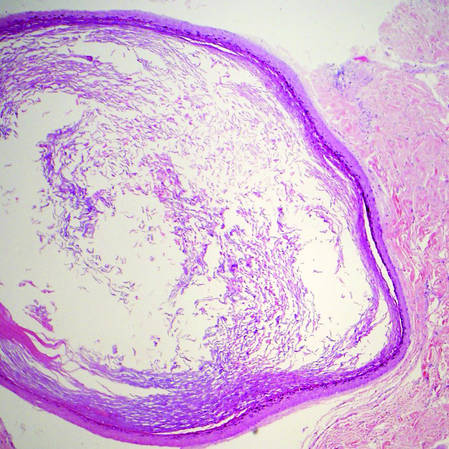 | |
| Figure 2. Epidermal inclusion cyst containing loose lamellar keratin and a lining that closely resembles the surface epidermis (H&E, original magnification ×40). |
|
Bronchogenic cysts demonstrate an epithelial lining that often is pseudostratified cuboidal or columnar as well as ciliated (Figure 1). Goblet cells are present in the lining in approximately 50% of cases. Smooth muscle may be seen circumferentially surrounding the cyst lining, and rare cases also contain cartilage.1 In contrast to dermoid cysts, other types of adnexal structures are not found within the lining. Bronchogenic cysts that arise in the skin are extremely rare.2 These cysts are thought to arise from respiratory epithelium that has been sequestered during embryologic formation of the tracheobronchial tree. They often are seen overlying the suprasternal notch and occasionally are found on the anterior aspect of the neck or chin. These cysts also are present at birth, similar to dermoid cysts.3
Epidermal inclusion cysts have a lining that histologically bears close resemblance to the surface epidermis. These cysts contain loose lamellar keratin, similar to a dermoid cyst. In contrast, the lining of an epidermal inclusion cyst will lack adnexal structures (Figure 2).1 Clinically, epidermal inclusion cysts often present as smooth, dome-shaped papules and nodules with a central punctum. They are classically found on the face, neck, and trunk. These cysts are thought to arise after a traumatic insult to the pilosebaceous unit.2
Hidrocystomas can be apocrine or eccrine.3 Eccrine hidrocystomas are unilocular cysts that are lined by 2 layers of flattened to cuboidal epithelial cells (Figure 3). The cysts are filled with clear fluid and often are found adjacent to normal eccrine glands.1 Apocrine hidrocystomas are unilocular or multilocular cysts that are lined by 1 to several layers of epithelial cells. The lining of an apocrine hidrocystoma will often exhibit luminal decapitation secretion.3 Apocrine and eccrine hidrocystomas are clinically identical and appear as blue translucent papules on the cheeks or eyelids of adults.1-3 They usually occur periorbitally but also can be seen on the trunk, popliteal fossa, external ears, or vulva. Eccrine hidrocystomas can wax and wane in accordance with the amount of sweat produced; thus, they often expand in size during the summer months.2
Steatocystomas, or simple sebaceous duct cysts, histologically demonstrate a characteristically wavy and eosinophilic cuticle resembling shark teeth (Figure 4) similar to the lining of the sebaceous duct where it enters the follicle.1 Sebaceous glands are an almost invariable feature, either present within the lining of the cyst (Figure 4) or in the adjacent tissue.2 In comparison, dermoid cysts may have a red wavy cuticle but also will usually have terminal hair follicles or eccrine or apocrine glands within the wall of the cyst. Steatocystomas typically are collapsed and empty or only contain sebaceous debris (Figure 4) rather than the lamellar keratin seen in dermoid and epidermoid inclusion cysts. Steatocystomas can occur as solitary (steatocystoma simplex) or multiple (steatocystoma multiplex) lesions.1,3 They are clinically comprised of small dome-shaped papules that often are translucent and yellow. These cysts are commonly found on the sternum of males and the axillae or groin of females.2
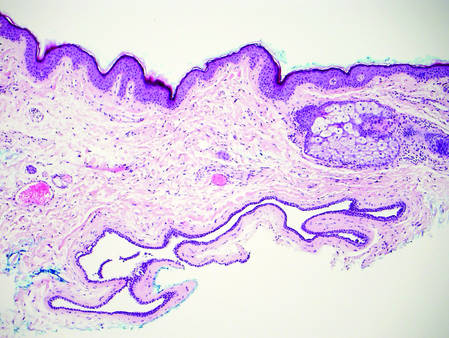 | 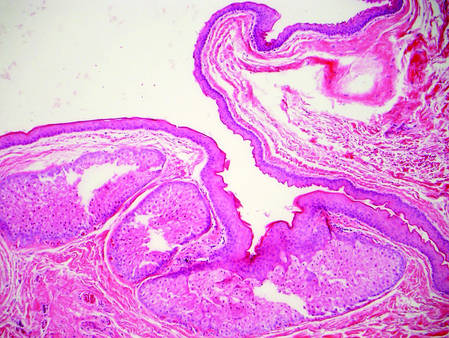 | |
Figure 3. Eccrine hidrocystoma with clear contents and lined by 2 layers of cuboidal epithelial cells (H&E, original magnification ×100). | Figure 4. Steatocystoma with a red wavy cuticle, sparse sebaceous contents, and sebaceous glands within the lining (H&E, original magnification ×100). |
|
1. Elston DM, Ferringer TC, Ko C, et al. Dermatopathology: Requisites in Dermatology. 2nd ed. Philadelphia, PA: Saunders Elsevier; 2014.
2. Calonje JE, Brenn T, Lazar AJ, et al. McKee’s Pathology of the Skin. 4th ed. St Louis, MO: Elsevier/Saunders; 2012.
3. Bolognia JL, Jorizzo JL, Shaffer JV. Dermatology. 3rd ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier/Saunders; 2012.
4. Orozco-Covarrubias L, Lara-Carpio R, Saez-De-Ocariz M, et al. Dermoid cysts: a report of 75 pediatric patients. Pediatr Dermatol. 2013;30:706-711.
5. Sorenson EP, Powel JE, Rozzelle CJ, et al. Scalp dermoids: a review of their anatomy, diagnosis, and treatment. Childs Nerv Syst. 2013;29:375-380.
6. Pryor SG, Lewis JE, Weaver AL, et al. Pediatric dermoid cysts of the head and neck. Otolarynol Head Neck Surg. 2005;132:938-942.
7. Abou-Rayyah Y, Rose GE, Konrad H, et al. Clinical, radiological and pathological examination of periocular dermoid cysts: evidence of inflammation from an early age. Eye (Lond). 2002;16:507-512.
The best diagnosis is:
a. bronchogenic cyst
b. dermoid cyst
c. epidermal inclusion cyst
d. hidrocystoma
e. steatocystoma
|
 |
| H&E, original magnification ×40. |
 |
| H&E, original magnification ×100. |
Continue to the next page for the diagnosis >>
Dermoid Cyst
Dermoid cysts often present clinically as firm subcutaneous nodules on the head or neck in young children. They tend to arise along the lateral aspect of the eyebrow but also can occur on the nose, forehead, neck, chest, or scalp.1 Dermoid cysts are thought to arise from the sequestration of ectodermal tissues along the embryonic fusion planes during development.2 As such, they represent congenital defects and often are identified at birth; however, some are not noticed until much later when they enlarge or become inflamed or infected. Midline dermoid cysts may be associated with underlying dysraphism or intracranial extension.3,4 Thus, any midline lesion warrants evaluation that incorporates imaging with computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging.4,5 Histologically, dermoid cysts are lined by a keratinizing stratified squamous epithelium (quiz image A), but the lining may be brightly eosinophilic and wavy resembling shark teeth.1,3 The wall of a dermoid cyst commonly contains mature adnexal structures such as terminal hair follicles, sebaceous glands, apocrine glands, and/or eccrine glands (quiz image B).1 Smooth muscle also may be seen within the lining; however, bone and cartilage are not commonly reported in dermoid cysts.2 Lamellar keratin is typical of the cyst contents, and terminal hair shafts also are sometimes noted within the cystic space (quiz image B).1,2 Treatment options include excision at the time of diagnosis or close clinical monitoring with subsequent excision if the lesion grows or becomes symptomatic.4,5 Many practitioners opt to excise these cysts at diagnosis, as untreated lesions are at risk for infection and/or inflammation or may be cosmetically deforming.6,7 Surgical resection, including removal of the wall of the cyst, is curative and reoccurrence is rare.5
 | |
Figure 1. Bronchogenic cyst demonstrating a ciliated pseudostratified epithelial lining encircled by smooth muscle (H&E, original magnification ×200). | |
 | |
| Figure 2. Epidermal inclusion cyst containing loose lamellar keratin and a lining that closely resembles the surface epidermis (H&E, original magnification ×40). |
|
Bronchogenic cysts demonstrate an epithelial lining that often is pseudostratified cuboidal or columnar as well as ciliated (Figure 1). Goblet cells are present in the lining in approximately 50% of cases. Smooth muscle may be seen circumferentially surrounding the cyst lining, and rare cases also contain cartilage.1 In contrast to dermoid cysts, other types of adnexal structures are not found within the lining. Bronchogenic cysts that arise in the skin are extremely rare.2 These cysts are thought to arise from respiratory epithelium that has been sequestered during embryologic formation of the tracheobronchial tree. They often are seen overlying the suprasternal notch and occasionally are found on the anterior aspect of the neck or chin. These cysts also are present at birth, similar to dermoid cysts.3
Epidermal inclusion cysts have a lining that histologically bears close resemblance to the surface epidermis. These cysts contain loose lamellar keratin, similar to a dermoid cyst. In contrast, the lining of an epidermal inclusion cyst will lack adnexal structures (Figure 2).1 Clinically, epidermal inclusion cysts often present as smooth, dome-shaped papules and nodules with a central punctum. They are classically found on the face, neck, and trunk. These cysts are thought to arise after a traumatic insult to the pilosebaceous unit.2
Hidrocystomas can be apocrine or eccrine.3 Eccrine hidrocystomas are unilocular cysts that are lined by 2 layers of flattened to cuboidal epithelial cells (Figure 3). The cysts are filled with clear fluid and often are found adjacent to normal eccrine glands.1 Apocrine hidrocystomas are unilocular or multilocular cysts that are lined by 1 to several layers of epithelial cells. The lining of an apocrine hidrocystoma will often exhibit luminal decapitation secretion.3 Apocrine and eccrine hidrocystomas are clinically identical and appear as blue translucent papules on the cheeks or eyelids of adults.1-3 They usually occur periorbitally but also can be seen on the trunk, popliteal fossa, external ears, or vulva. Eccrine hidrocystomas can wax and wane in accordance with the amount of sweat produced; thus, they often expand in size during the summer months.2
Steatocystomas, or simple sebaceous duct cysts, histologically demonstrate a characteristically wavy and eosinophilic cuticle resembling shark teeth (Figure 4) similar to the lining of the sebaceous duct where it enters the follicle.1 Sebaceous glands are an almost invariable feature, either present within the lining of the cyst (Figure 4) or in the adjacent tissue.2 In comparison, dermoid cysts may have a red wavy cuticle but also will usually have terminal hair follicles or eccrine or apocrine glands within the wall of the cyst. Steatocystomas typically are collapsed and empty or only contain sebaceous debris (Figure 4) rather than the lamellar keratin seen in dermoid and epidermoid inclusion cysts. Steatocystomas can occur as solitary (steatocystoma simplex) or multiple (steatocystoma multiplex) lesions.1,3 They are clinically comprised of small dome-shaped papules that often are translucent and yellow. These cysts are commonly found on the sternum of males and the axillae or groin of females.2
 |  | |
Figure 3. Eccrine hidrocystoma with clear contents and lined by 2 layers of cuboidal epithelial cells (H&E, original magnification ×100). | Figure 4. Steatocystoma with a red wavy cuticle, sparse sebaceous contents, and sebaceous glands within the lining (H&E, original magnification ×100). |
|
The best diagnosis is:
a. bronchogenic cyst
b. dermoid cyst
c. epidermal inclusion cyst
d. hidrocystoma
e. steatocystoma
|
 |
| H&E, original magnification ×40. |
 |
| H&E, original magnification ×100. |
Continue to the next page for the diagnosis >>
Dermoid Cyst
Dermoid cysts often present clinically as firm subcutaneous nodules on the head or neck in young children. They tend to arise along the lateral aspect of the eyebrow but also can occur on the nose, forehead, neck, chest, or scalp.1 Dermoid cysts are thought to arise from the sequestration of ectodermal tissues along the embryonic fusion planes during development.2 As such, they represent congenital defects and often are identified at birth; however, some are not noticed until much later when they enlarge or become inflamed or infected. Midline dermoid cysts may be associated with underlying dysraphism or intracranial extension.3,4 Thus, any midline lesion warrants evaluation that incorporates imaging with computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging.4,5 Histologically, dermoid cysts are lined by a keratinizing stratified squamous epithelium (quiz image A), but the lining may be brightly eosinophilic and wavy resembling shark teeth.1,3 The wall of a dermoid cyst commonly contains mature adnexal structures such as terminal hair follicles, sebaceous glands, apocrine glands, and/or eccrine glands (quiz image B).1 Smooth muscle also may be seen within the lining; however, bone and cartilage are not commonly reported in dermoid cysts.2 Lamellar keratin is typical of the cyst contents, and terminal hair shafts also are sometimes noted within the cystic space (quiz image B).1,2 Treatment options include excision at the time of diagnosis or close clinical monitoring with subsequent excision if the lesion grows or becomes symptomatic.4,5 Many practitioners opt to excise these cysts at diagnosis, as untreated lesions are at risk for infection and/or inflammation or may be cosmetically deforming.6,7 Surgical resection, including removal of the wall of the cyst, is curative and reoccurrence is rare.5
 | |
Figure 1. Bronchogenic cyst demonstrating a ciliated pseudostratified epithelial lining encircled by smooth muscle (H&E, original magnification ×200). | |
 | |
| Figure 2. Epidermal inclusion cyst containing loose lamellar keratin and a lining that closely resembles the surface epidermis (H&E, original magnification ×40). |
|
Bronchogenic cysts demonstrate an epithelial lining that often is pseudostratified cuboidal or columnar as well as ciliated (Figure 1). Goblet cells are present in the lining in approximately 50% of cases. Smooth muscle may be seen circumferentially surrounding the cyst lining, and rare cases also contain cartilage.1 In contrast to dermoid cysts, other types of adnexal structures are not found within the lining. Bronchogenic cysts that arise in the skin are extremely rare.2 These cysts are thought to arise from respiratory epithelium that has been sequestered during embryologic formation of the tracheobronchial tree. They often are seen overlying the suprasternal notch and occasionally are found on the anterior aspect of the neck or chin. These cysts also are present at birth, similar to dermoid cysts.3
Epidermal inclusion cysts have a lining that histologically bears close resemblance to the surface epidermis. These cysts contain loose lamellar keratin, similar to a dermoid cyst. In contrast, the lining of an epidermal inclusion cyst will lack adnexal structures (Figure 2).1 Clinically, epidermal inclusion cysts often present as smooth, dome-shaped papules and nodules with a central punctum. They are classically found on the face, neck, and trunk. These cysts are thought to arise after a traumatic insult to the pilosebaceous unit.2
Hidrocystomas can be apocrine or eccrine.3 Eccrine hidrocystomas are unilocular cysts that are lined by 2 layers of flattened to cuboidal epithelial cells (Figure 3). The cysts are filled with clear fluid and often are found adjacent to normal eccrine glands.1 Apocrine hidrocystomas are unilocular or multilocular cysts that are lined by 1 to several layers of epithelial cells. The lining of an apocrine hidrocystoma will often exhibit luminal decapitation secretion.3 Apocrine and eccrine hidrocystomas are clinically identical and appear as blue translucent papules on the cheeks or eyelids of adults.1-3 They usually occur periorbitally but also can be seen on the trunk, popliteal fossa, external ears, or vulva. Eccrine hidrocystomas can wax and wane in accordance with the amount of sweat produced; thus, they often expand in size during the summer months.2
Steatocystomas, or simple sebaceous duct cysts, histologically demonstrate a characteristically wavy and eosinophilic cuticle resembling shark teeth (Figure 4) similar to the lining of the sebaceous duct where it enters the follicle.1 Sebaceous glands are an almost invariable feature, either present within the lining of the cyst (Figure 4) or in the adjacent tissue.2 In comparison, dermoid cysts may have a red wavy cuticle but also will usually have terminal hair follicles or eccrine or apocrine glands within the wall of the cyst. Steatocystomas typically are collapsed and empty or only contain sebaceous debris (Figure 4) rather than the lamellar keratin seen in dermoid and epidermoid inclusion cysts. Steatocystomas can occur as solitary (steatocystoma simplex) or multiple (steatocystoma multiplex) lesions.1,3 They are clinically comprised of small dome-shaped papules that often are translucent and yellow. These cysts are commonly found on the sternum of males and the axillae or groin of females.2
 |  | |
Figure 3. Eccrine hidrocystoma with clear contents and lined by 2 layers of cuboidal epithelial cells (H&E, original magnification ×100). | Figure 4. Steatocystoma with a red wavy cuticle, sparse sebaceous contents, and sebaceous glands within the lining (H&E, original magnification ×100). |
|
1. Elston DM, Ferringer TC, Ko C, et al. Dermatopathology: Requisites in Dermatology. 2nd ed. Philadelphia, PA: Saunders Elsevier; 2014.
2. Calonje JE, Brenn T, Lazar AJ, et al. McKee’s Pathology of the Skin. 4th ed. St Louis, MO: Elsevier/Saunders; 2012.
3. Bolognia JL, Jorizzo JL, Shaffer JV. Dermatology. 3rd ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier/Saunders; 2012.
4. Orozco-Covarrubias L, Lara-Carpio R, Saez-De-Ocariz M, et al. Dermoid cysts: a report of 75 pediatric patients. Pediatr Dermatol. 2013;30:706-711.
5. Sorenson EP, Powel JE, Rozzelle CJ, et al. Scalp dermoids: a review of their anatomy, diagnosis, and treatment. Childs Nerv Syst. 2013;29:375-380.
6. Pryor SG, Lewis JE, Weaver AL, et al. Pediatric dermoid cysts of the head and neck. Otolarynol Head Neck Surg. 2005;132:938-942.
7. Abou-Rayyah Y, Rose GE, Konrad H, et al. Clinical, radiological and pathological examination of periocular dermoid cysts: evidence of inflammation from an early age. Eye (Lond). 2002;16:507-512.
1. Elston DM, Ferringer TC, Ko C, et al. Dermatopathology: Requisites in Dermatology. 2nd ed. Philadelphia, PA: Saunders Elsevier; 2014.
2. Calonje JE, Brenn T, Lazar AJ, et al. McKee’s Pathology of the Skin. 4th ed. St Louis, MO: Elsevier/Saunders; 2012.
3. Bolognia JL, Jorizzo JL, Shaffer JV. Dermatology. 3rd ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier/Saunders; 2012.
4. Orozco-Covarrubias L, Lara-Carpio R, Saez-De-Ocariz M, et al. Dermoid cysts: a report of 75 pediatric patients. Pediatr Dermatol. 2013;30:706-711.
5. Sorenson EP, Powel JE, Rozzelle CJ, et al. Scalp dermoids: a review of their anatomy, diagnosis, and treatment. Childs Nerv Syst. 2013;29:375-380.
6. Pryor SG, Lewis JE, Weaver AL, et al. Pediatric dermoid cysts of the head and neck. Otolarynol Head Neck Surg. 2005;132:938-942.
7. Abou-Rayyah Y, Rose GE, Konrad H, et al. Clinical, radiological and pathological examination of periocular dermoid cysts: evidence of inflammation from an early age. Eye (Lond). 2002;16:507-512.