User login
Genomic sequencing sheds light on development of pediatric cancer
Genome sequencing technologies are providing a valuable new window into the development and progression of pediatric cancers, according to the authors of a review.
In contrast to adult cancers, which are frequently driven by oncogenic mutations, many pediatric cancers have a low burden of somatic mutations, wrote E. Alejandro Sweet-Cordero, MD, from the University of California, San Francisco, and Jaclyn A. Biegel, MD, from the University of Southern California in Science. Instead, large-scale sequencing studies have found that childhood cancers have a much higher likelihood of being caused by germline mutations in genes that predispose development of cancer.
“Particularly surprising was the observation that even high-risk, highly aggressive cancers in many cases had no identifiable driver gene or pathway,” the authors wrote.
Some pediatric cancers do have identified driver genes, but even these are often different to those seen in adult cancers. The authors gave the example of one study of 1,699 patients and six types of cancer: This study identified 142 likely oncogenes, but only 45% of these matched those seen in the adult cancers.
Many pediatric cancers also have unique genetic features, such as the age-dependent gene fusion events, in which two genes join to form an oncogenic hybrid, and focal areas of gene deletion, which are often seen in pediatric acute myeloid leukemia but less so in adult forms of this cancer.
“In some instances, the fusion events involve genes that are known to be cancer drivers; this raises the intriguing possibility that some pediatric cancers are driven by ‘private’ oncogenic fusions,” the authors wrote, pointing out that this has daunting implications for the development of precision medicine. However they also noted that the presence of common gene fusion events could hold significance for choice of therapies; for example, central nervous system gliomas with the common BRAF V600E mutation may respond to specific BRAF inhibitors.
The authors drew particular attention to the role that genomic analysis could play in studying cancer during treatment and relapse, but they said few studies have explored this in pediatric patients.
“Such studies are critical given what we have learned from adult cancers, which show a capacity to evolve rapidly and acquire new driver mutations,” they wrote. One study found that only one-third of tumors with a potentially targetable genetic mutation had retained that target when analyzed at a later time.
On the issue of targeted therapy, the authors noted that no prospective study has yet looked at the use of sequencing approaches to define new therapies for pediatric cancer. However, they did refer to the Pediatric MATCH clinical trial, which is currently evaluating targeted therapies for relapsed solid tumors in children.
They also identified a need for research on predictors of treatment response in pediatric cancer.
“As the genetic variants that are associated with drug response are, by nature and design, variants present in the normal population, they are typically not included in DNA sequencing panels and are filtered out in WES [whole-exome sequencing] or WGS [whole-genome sequencing] bioinformatics pipelines,” they wrote.
They addressed the question of when to do germline testing in pediatric cancer, saying that, for most pediatric cancer patients, germline testing was indicated by the presence of a pathogenic genetic alternative affecting a gene known to be associated with a predisposition for germline cancer.
The authors suggested that data sharing was important to advancing genomic analysis in pediatric cancers because most of the studies so far had been relatively small. However, they highlighted emerging resources for large-scale analysis of pediatric cancer data, such as public portals for investigating discovery genomic data sets and data repositories of clinical-grade sequencing data.
The review was funded by the National Cancer Institute. No conflicts of interest were declared.
SOURCE: Sweet-Cordero A et al. Science 2019;363:1170-5.
Genome sequencing technologies are providing a valuable new window into the development and progression of pediatric cancers, according to the authors of a review.
In contrast to adult cancers, which are frequently driven by oncogenic mutations, many pediatric cancers have a low burden of somatic mutations, wrote E. Alejandro Sweet-Cordero, MD, from the University of California, San Francisco, and Jaclyn A. Biegel, MD, from the University of Southern California in Science. Instead, large-scale sequencing studies have found that childhood cancers have a much higher likelihood of being caused by germline mutations in genes that predispose development of cancer.
“Particularly surprising was the observation that even high-risk, highly aggressive cancers in many cases had no identifiable driver gene or pathway,” the authors wrote.
Some pediatric cancers do have identified driver genes, but even these are often different to those seen in adult cancers. The authors gave the example of one study of 1,699 patients and six types of cancer: This study identified 142 likely oncogenes, but only 45% of these matched those seen in the adult cancers.
Many pediatric cancers also have unique genetic features, such as the age-dependent gene fusion events, in which two genes join to form an oncogenic hybrid, and focal areas of gene deletion, which are often seen in pediatric acute myeloid leukemia but less so in adult forms of this cancer.
“In some instances, the fusion events involve genes that are known to be cancer drivers; this raises the intriguing possibility that some pediatric cancers are driven by ‘private’ oncogenic fusions,” the authors wrote, pointing out that this has daunting implications for the development of precision medicine. However they also noted that the presence of common gene fusion events could hold significance for choice of therapies; for example, central nervous system gliomas with the common BRAF V600E mutation may respond to specific BRAF inhibitors.
The authors drew particular attention to the role that genomic analysis could play in studying cancer during treatment and relapse, but they said few studies have explored this in pediatric patients.
“Such studies are critical given what we have learned from adult cancers, which show a capacity to evolve rapidly and acquire new driver mutations,” they wrote. One study found that only one-third of tumors with a potentially targetable genetic mutation had retained that target when analyzed at a later time.
On the issue of targeted therapy, the authors noted that no prospective study has yet looked at the use of sequencing approaches to define new therapies for pediatric cancer. However, they did refer to the Pediatric MATCH clinical trial, which is currently evaluating targeted therapies for relapsed solid tumors in children.
They also identified a need for research on predictors of treatment response in pediatric cancer.
“As the genetic variants that are associated with drug response are, by nature and design, variants present in the normal population, they are typically not included in DNA sequencing panels and are filtered out in WES [whole-exome sequencing] or WGS [whole-genome sequencing] bioinformatics pipelines,” they wrote.
They addressed the question of when to do germline testing in pediatric cancer, saying that, for most pediatric cancer patients, germline testing was indicated by the presence of a pathogenic genetic alternative affecting a gene known to be associated with a predisposition for germline cancer.
The authors suggested that data sharing was important to advancing genomic analysis in pediatric cancers because most of the studies so far had been relatively small. However, they highlighted emerging resources for large-scale analysis of pediatric cancer data, such as public portals for investigating discovery genomic data sets and data repositories of clinical-grade sequencing data.
The review was funded by the National Cancer Institute. No conflicts of interest were declared.
SOURCE: Sweet-Cordero A et al. Science 2019;363:1170-5.
Genome sequencing technologies are providing a valuable new window into the development and progression of pediatric cancers, according to the authors of a review.
In contrast to adult cancers, which are frequently driven by oncogenic mutations, many pediatric cancers have a low burden of somatic mutations, wrote E. Alejandro Sweet-Cordero, MD, from the University of California, San Francisco, and Jaclyn A. Biegel, MD, from the University of Southern California in Science. Instead, large-scale sequencing studies have found that childhood cancers have a much higher likelihood of being caused by germline mutations in genes that predispose development of cancer.
“Particularly surprising was the observation that even high-risk, highly aggressive cancers in many cases had no identifiable driver gene or pathway,” the authors wrote.
Some pediatric cancers do have identified driver genes, but even these are often different to those seen in adult cancers. The authors gave the example of one study of 1,699 patients and six types of cancer: This study identified 142 likely oncogenes, but only 45% of these matched those seen in the adult cancers.
Many pediatric cancers also have unique genetic features, such as the age-dependent gene fusion events, in which two genes join to form an oncogenic hybrid, and focal areas of gene deletion, which are often seen in pediatric acute myeloid leukemia but less so in adult forms of this cancer.
“In some instances, the fusion events involve genes that are known to be cancer drivers; this raises the intriguing possibility that some pediatric cancers are driven by ‘private’ oncogenic fusions,” the authors wrote, pointing out that this has daunting implications for the development of precision medicine. However they also noted that the presence of common gene fusion events could hold significance for choice of therapies; for example, central nervous system gliomas with the common BRAF V600E mutation may respond to specific BRAF inhibitors.
The authors drew particular attention to the role that genomic analysis could play in studying cancer during treatment and relapse, but they said few studies have explored this in pediatric patients.
“Such studies are critical given what we have learned from adult cancers, which show a capacity to evolve rapidly and acquire new driver mutations,” they wrote. One study found that only one-third of tumors with a potentially targetable genetic mutation had retained that target when analyzed at a later time.
On the issue of targeted therapy, the authors noted that no prospective study has yet looked at the use of sequencing approaches to define new therapies for pediatric cancer. However, they did refer to the Pediatric MATCH clinical trial, which is currently evaluating targeted therapies for relapsed solid tumors in children.
They also identified a need for research on predictors of treatment response in pediatric cancer.
“As the genetic variants that are associated with drug response are, by nature and design, variants present in the normal population, they are typically not included in DNA sequencing panels and are filtered out in WES [whole-exome sequencing] or WGS [whole-genome sequencing] bioinformatics pipelines,” they wrote.
They addressed the question of when to do germline testing in pediatric cancer, saying that, for most pediatric cancer patients, germline testing was indicated by the presence of a pathogenic genetic alternative affecting a gene known to be associated with a predisposition for germline cancer.
The authors suggested that data sharing was important to advancing genomic analysis in pediatric cancers because most of the studies so far had been relatively small. However, they highlighted emerging resources for large-scale analysis of pediatric cancer data, such as public portals for investigating discovery genomic data sets and data repositories of clinical-grade sequencing data.
The review was funded by the National Cancer Institute. No conflicts of interest were declared.
SOURCE: Sweet-Cordero A et al. Science 2019;363:1170-5.
FROM SCIENCE
Key clinical point: Genome sequencing is providing valuable information on pediatric cancer development and progression.
Major finding: Many pediatric cancers have very different oncogenic drivers to adult cancers.
Study details: Review.
Disclosures: The review was funded by the National Cancer Institute. No conflicts of interest were declared.
Source: Sweet-Cordero EA et al. Science. 2019;363:1170-5.
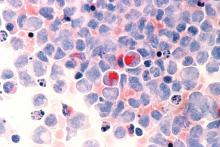
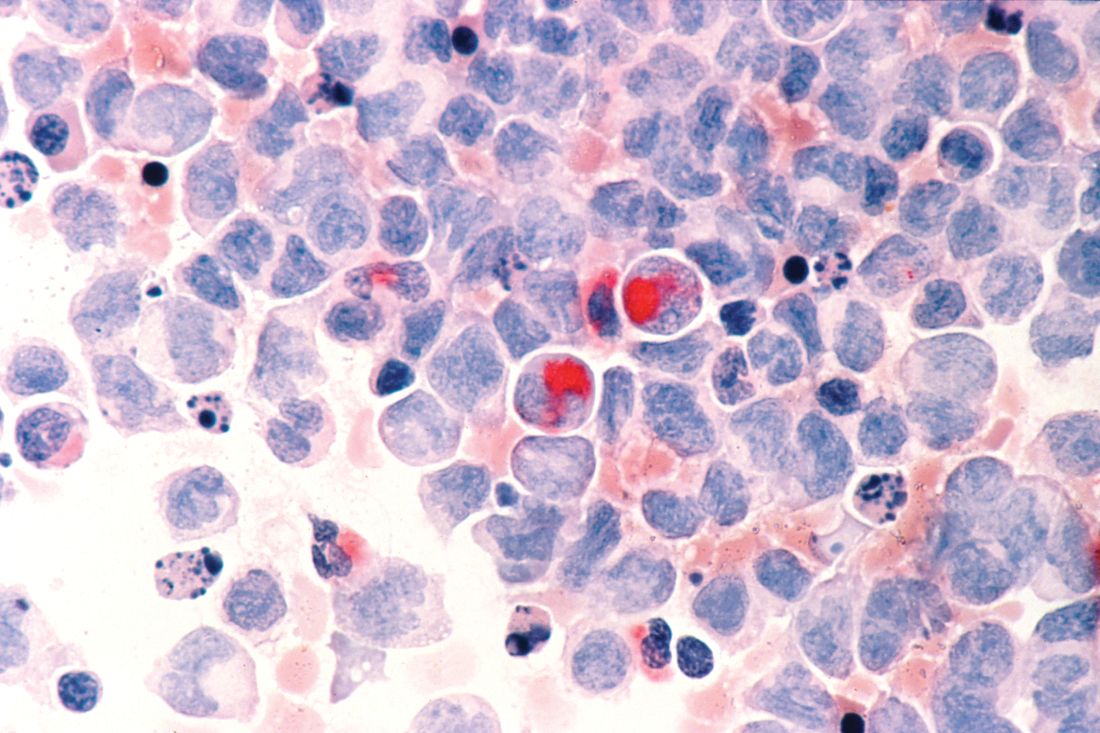
Secondary AML in first remission predicts outcomes
HOUSTON – Secondary acute myeloid leukemia (sAML) predicts outcomes after stem cell transplantation in first complete remission, whereas factors such as age, cytogenetics, and performance status are more relevant predictors of outcomes in patients with de novo AML, according to a large, registry-based analysis.
Of 11,439 patients with de novo AML and 1,325 with sAML identified in the registry, 7,691 and 909, respectively, underwent a stem cell transplant (SCT) in first complete remission (CR1), Bipin Savani, MD, said at the Transplantation & Cellular Therapies Meetings.
The 3-year cumulative incidence of relapse (CIR) and nonrelapse mortality (NRM) rates in those who underwent SCT in CR1 were higher in the sAML versus de novo AML groups (35% vs. 28.5% for CIR and 23.4% vs. 16.4% for NRM, respectively), said Dr. Savani, professor of medicine, director of the Long-Term Transplant Clinic, and medical director of the Stem Cell Transplant Processing Laboratory at Vanderbilt University Medical Center & Veterans Affairs Medical Center, Nashville, Tenn.
The 3-year overall survival (OS), leukemia-free survival (LFS), and graft-versus-host disease/relapse-free survival (GRFS) were significantly lower in the sAML group versus the de novo AML group (46.7% vs. 60.8% for OS; 41.6% vs. 55.1% for LFS; and 28.4% vs. 28.6% for GRFS).
Multivariate analysis controlling for risk factors and stratified by disease stage at SCT showed that sAML in CR1 was significantly associated with higher NRM (hazard ratio, 1.32) and CIR (HR, 1.28), and with lower LFS (HR, 1.30), OS (HR, 1.32) and GRFS (HR, 1.20).
Other significant predictors of OS in the model were age, cytogenetics, patient/donor sex combination, Karnofsky performance status (KPS), and donor, he said at the meeting held by the American Society for Blood and Marrow Transplantation and the Center for International Blood and Marrow Transplant Research. At its meeting, the American Society for Blood and Marrow Transplantation announced a new name for the society: American Society for Transplantation and Cellular Therapy (ASTCT).
In the patients who underwent SCT for primary refractory AML (607 with de novo AML and 199 with sAML) or relapsed AML (1,009 with de novo AML and 124 with sAML), the outcomes were generally inferior to those seen with SCT in CR1. However, sAML in those patients did not predict outcomes, Dr. Savani said, noting that outcome in those cases were predicted by age, cytogenetics, and KPS.
In an analysis of 877 pairs matched for age, disease stage at SCT, KPS, conditioning, in vivo/ex vivo T-cell depletion, donor, donor/recipient sex and cytomegalovirus-status combination, cytogenetics, and graft source, the finding that sAML was associated with significantly higher NRM, and lower LFS, OS, and GRFS overall was confirmed.
However, stratification by stage at the time of SCT again showed that the differences between groups were only seen among those transplanted in CR1, and not in those with advanced disease at the time of transplant.
Patients included in the study were adults aged 18 years and older who underwent SCT for de novo or sAML from a matched related, unrelated, or T-cell replete haploidentical donor between 2000 and 2016.
The findings confirm the general belief that the prognosis in AML secondary to another hematologic neoplasia or malignant disease is poorer than that for de novo AML, and clarify the role of this difference for SCT, Dr. Savani said.
“These data may help to improve risk stratification and prognostic estimates after allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation for acute myeloid leukemia,” he concluded.
Dr. Savani reported having no financial disclosures.
SOURCE: Savani B et al. TCT 2019, Abstract 12.
HOUSTON – Secondary acute myeloid leukemia (sAML) predicts outcomes after stem cell transplantation in first complete remission, whereas factors such as age, cytogenetics, and performance status are more relevant predictors of outcomes in patients with de novo AML, according to a large, registry-based analysis.
Of 11,439 patients with de novo AML and 1,325 with sAML identified in the registry, 7,691 and 909, respectively, underwent a stem cell transplant (SCT) in first complete remission (CR1), Bipin Savani, MD, said at the Transplantation & Cellular Therapies Meetings.
The 3-year cumulative incidence of relapse (CIR) and nonrelapse mortality (NRM) rates in those who underwent SCT in CR1 were higher in the sAML versus de novo AML groups (35% vs. 28.5% for CIR and 23.4% vs. 16.4% for NRM, respectively), said Dr. Savani, professor of medicine, director of the Long-Term Transplant Clinic, and medical director of the Stem Cell Transplant Processing Laboratory at Vanderbilt University Medical Center & Veterans Affairs Medical Center, Nashville, Tenn.
The 3-year overall survival (OS), leukemia-free survival (LFS), and graft-versus-host disease/relapse-free survival (GRFS) were significantly lower in the sAML group versus the de novo AML group (46.7% vs. 60.8% for OS; 41.6% vs. 55.1% for LFS; and 28.4% vs. 28.6% for GRFS).
Multivariate analysis controlling for risk factors and stratified by disease stage at SCT showed that sAML in CR1 was significantly associated with higher NRM (hazard ratio, 1.32) and CIR (HR, 1.28), and with lower LFS (HR, 1.30), OS (HR, 1.32) and GRFS (HR, 1.20).
Other significant predictors of OS in the model were age, cytogenetics, patient/donor sex combination, Karnofsky performance status (KPS), and donor, he said at the meeting held by the American Society for Blood and Marrow Transplantation and the Center for International Blood and Marrow Transplant Research. At its meeting, the American Society for Blood and Marrow Transplantation announced a new name for the society: American Society for Transplantation and Cellular Therapy (ASTCT).
In the patients who underwent SCT for primary refractory AML (607 with de novo AML and 199 with sAML) or relapsed AML (1,009 with de novo AML and 124 with sAML), the outcomes were generally inferior to those seen with SCT in CR1. However, sAML in those patients did not predict outcomes, Dr. Savani said, noting that outcome in those cases were predicted by age, cytogenetics, and KPS.
In an analysis of 877 pairs matched for age, disease stage at SCT, KPS, conditioning, in vivo/ex vivo T-cell depletion, donor, donor/recipient sex and cytomegalovirus-status combination, cytogenetics, and graft source, the finding that sAML was associated with significantly higher NRM, and lower LFS, OS, and GRFS overall was confirmed.
However, stratification by stage at the time of SCT again showed that the differences between groups were only seen among those transplanted in CR1, and not in those with advanced disease at the time of transplant.
Patients included in the study were adults aged 18 years and older who underwent SCT for de novo or sAML from a matched related, unrelated, or T-cell replete haploidentical donor between 2000 and 2016.
The findings confirm the general belief that the prognosis in AML secondary to another hematologic neoplasia or malignant disease is poorer than that for de novo AML, and clarify the role of this difference for SCT, Dr. Savani said.
“These data may help to improve risk stratification and prognostic estimates after allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation for acute myeloid leukemia,” he concluded.
Dr. Savani reported having no financial disclosures.
SOURCE: Savani B et al. TCT 2019, Abstract 12.
HOUSTON – Secondary acute myeloid leukemia (sAML) predicts outcomes after stem cell transplantation in first complete remission, whereas factors such as age, cytogenetics, and performance status are more relevant predictors of outcomes in patients with de novo AML, according to a large, registry-based analysis.
Of 11,439 patients with de novo AML and 1,325 with sAML identified in the registry, 7,691 and 909, respectively, underwent a stem cell transplant (SCT) in first complete remission (CR1), Bipin Savani, MD, said at the Transplantation & Cellular Therapies Meetings.
The 3-year cumulative incidence of relapse (CIR) and nonrelapse mortality (NRM) rates in those who underwent SCT in CR1 were higher in the sAML versus de novo AML groups (35% vs. 28.5% for CIR and 23.4% vs. 16.4% for NRM, respectively), said Dr. Savani, professor of medicine, director of the Long-Term Transplant Clinic, and medical director of the Stem Cell Transplant Processing Laboratory at Vanderbilt University Medical Center & Veterans Affairs Medical Center, Nashville, Tenn.
The 3-year overall survival (OS), leukemia-free survival (LFS), and graft-versus-host disease/relapse-free survival (GRFS) were significantly lower in the sAML group versus the de novo AML group (46.7% vs. 60.8% for OS; 41.6% vs. 55.1% for LFS; and 28.4% vs. 28.6% for GRFS).
Multivariate analysis controlling for risk factors and stratified by disease stage at SCT showed that sAML in CR1 was significantly associated with higher NRM (hazard ratio, 1.32) and CIR (HR, 1.28), and with lower LFS (HR, 1.30), OS (HR, 1.32) and GRFS (HR, 1.20).
Other significant predictors of OS in the model were age, cytogenetics, patient/donor sex combination, Karnofsky performance status (KPS), and donor, he said at the meeting held by the American Society for Blood and Marrow Transplantation and the Center for International Blood and Marrow Transplant Research. At its meeting, the American Society for Blood and Marrow Transplantation announced a new name for the society: American Society for Transplantation and Cellular Therapy (ASTCT).
In the patients who underwent SCT for primary refractory AML (607 with de novo AML and 199 with sAML) or relapsed AML (1,009 with de novo AML and 124 with sAML), the outcomes were generally inferior to those seen with SCT in CR1. However, sAML in those patients did not predict outcomes, Dr. Savani said, noting that outcome in those cases were predicted by age, cytogenetics, and KPS.
In an analysis of 877 pairs matched for age, disease stage at SCT, KPS, conditioning, in vivo/ex vivo T-cell depletion, donor, donor/recipient sex and cytomegalovirus-status combination, cytogenetics, and graft source, the finding that sAML was associated with significantly higher NRM, and lower LFS, OS, and GRFS overall was confirmed.
However, stratification by stage at the time of SCT again showed that the differences between groups were only seen among those transplanted in CR1, and not in those with advanced disease at the time of transplant.
Patients included in the study were adults aged 18 years and older who underwent SCT for de novo or sAML from a matched related, unrelated, or T-cell replete haploidentical donor between 2000 and 2016.
The findings confirm the general belief that the prognosis in AML secondary to another hematologic neoplasia or malignant disease is poorer than that for de novo AML, and clarify the role of this difference for SCT, Dr. Savani said.
“These data may help to improve risk stratification and prognostic estimates after allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation for acute myeloid leukemia,” he concluded.
Dr. Savani reported having no financial disclosures.
SOURCE: Savani B et al. TCT 2019, Abstract 12.
REPORTING FROM TCT 2019
Anti-CD45 conditioning looks safe, feasible in relapsed AML
HOUSTON – A novel anti-CD45 targeted conditioning regimen is feasible for use in older patients with relapsed or refractory acute myeloid leukemia undergoing transplant, according to preliminary results of a randomized, phase 3 trial.
Treatment with iodine-131 apamistamab (Iomab-B) has thus far has resulted in successful engraftment for all patients who have received it and gone on to transplant, despite active disease and high bone marrow blast burden prior to transplantation, according to Sergio A. Giralt, MD, of Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, New York.
There has been no nonrelapse mortality related to the novel regimen in the ongoing trial, which compares Iomab-B as targeted conditioning prior to allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplant (HCT) with standard of care regimens, Dr. Giralt said in an update on the trial, known as SIERRA.
SIERRA is the only ongoing, randomized, phase 3 clinical trial to offer a transplant option in patients aged 55 years or older with active relapsed or refractory acute myeloid leukemia (AML), Dr. Giralt said at the Transplantation & Cellular Therapy Meetings.
“This is an underserved population in which traditional transplant techniques have very poor results, and there are limited options for patients with active disease,” Dr. Giralt said. “Of note, many transplant centers today do not consider these patients eligible for transplant.”
A total of 150 patients are to be enrolled in SIERRA and randomized either to investigator’s choice of salvage induction chemotherapy including approved targeted agents or to the experimental arm, which consists of an individualized dose of Iomab-B 12 days prior to HCT with fludarabine and total body irradiation as transplant conditioning.
Dr. Giralt presented an update on the first 38 patients in SIERRA, representing 25% of the total enrollment target.
Of 18 patients randomized to Iomab-B and transplanted, the median number of days to absolute neutrophil count engraftment was 13, Dr. Giralt said.
In the control arm, 15 of 19 (79%) failed to achieve complete remission, and of those 10 crossed over to receive Iomab-B and transplant. Days to engraftment, full donor chimerism, and dose delivered to the bone marrow were all similar in the crossover group, compared with those initially randomized to the novel therapy.
Nonhematologic grade 3 or 4 toxicities were similar between the Iomab-B arm and the conventional care arm, and included febrile neutropenia, stomatitis, and other side effects typical for these patients.
There were no grade 3 or 4 Iomab-B infusion-related reactions, and four mild cases of chronic graft-versus-host disease occurred in Iomab-B treated patients.
Nonrelapse mortality was “extremely low” with no cases in the 100 days post transplant in those initially randomized to Iomab-B, and only one case in a crossover patient, Dr. Giralt said.
“These results are encouraging, and can broaden transplant eligibility and improve outcomes,” he added.
The meeting is held by the American Society for Blood and Marrow Transplantation and the Center for International Blood and Marrow Transplant Research. At its meeting, the American Society for Blood and Marrow Transplantation announced a new name for the society: American Society for Transplantation and Cellular Therapy (ASTCT).
The SIERRA study is supported by Actinium Pharmaceuticals. Dr. Giralt reported disclosures related to Actinium and several other companies.
SOURCE: Giralt SA et al. TCT 2019, Abstract LBA3.
HOUSTON – A novel anti-CD45 targeted conditioning regimen is feasible for use in older patients with relapsed or refractory acute myeloid leukemia undergoing transplant, according to preliminary results of a randomized, phase 3 trial.
Treatment with iodine-131 apamistamab (Iomab-B) has thus far has resulted in successful engraftment for all patients who have received it and gone on to transplant, despite active disease and high bone marrow blast burden prior to transplantation, according to Sergio A. Giralt, MD, of Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, New York.
There has been no nonrelapse mortality related to the novel regimen in the ongoing trial, which compares Iomab-B as targeted conditioning prior to allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplant (HCT) with standard of care regimens, Dr. Giralt said in an update on the trial, known as SIERRA.
SIERRA is the only ongoing, randomized, phase 3 clinical trial to offer a transplant option in patients aged 55 years or older with active relapsed or refractory acute myeloid leukemia (AML), Dr. Giralt said at the Transplantation & Cellular Therapy Meetings.
“This is an underserved population in which traditional transplant techniques have very poor results, and there are limited options for patients with active disease,” Dr. Giralt said. “Of note, many transplant centers today do not consider these patients eligible for transplant.”
A total of 150 patients are to be enrolled in SIERRA and randomized either to investigator’s choice of salvage induction chemotherapy including approved targeted agents or to the experimental arm, which consists of an individualized dose of Iomab-B 12 days prior to HCT with fludarabine and total body irradiation as transplant conditioning.
Dr. Giralt presented an update on the first 38 patients in SIERRA, representing 25% of the total enrollment target.
Of 18 patients randomized to Iomab-B and transplanted, the median number of days to absolute neutrophil count engraftment was 13, Dr. Giralt said.
In the control arm, 15 of 19 (79%) failed to achieve complete remission, and of those 10 crossed over to receive Iomab-B and transplant. Days to engraftment, full donor chimerism, and dose delivered to the bone marrow were all similar in the crossover group, compared with those initially randomized to the novel therapy.
Nonhematologic grade 3 or 4 toxicities were similar between the Iomab-B arm and the conventional care arm, and included febrile neutropenia, stomatitis, and other side effects typical for these patients.
There were no grade 3 or 4 Iomab-B infusion-related reactions, and four mild cases of chronic graft-versus-host disease occurred in Iomab-B treated patients.
Nonrelapse mortality was “extremely low” with no cases in the 100 days post transplant in those initially randomized to Iomab-B, and only one case in a crossover patient, Dr. Giralt said.
“These results are encouraging, and can broaden transplant eligibility and improve outcomes,” he added.
The meeting is held by the American Society for Blood and Marrow Transplantation and the Center for International Blood and Marrow Transplant Research. At its meeting, the American Society for Blood and Marrow Transplantation announced a new name for the society: American Society for Transplantation and Cellular Therapy (ASTCT).
The SIERRA study is supported by Actinium Pharmaceuticals. Dr. Giralt reported disclosures related to Actinium and several other companies.
SOURCE: Giralt SA et al. TCT 2019, Abstract LBA3.
HOUSTON – A novel anti-CD45 targeted conditioning regimen is feasible for use in older patients with relapsed or refractory acute myeloid leukemia undergoing transplant, according to preliminary results of a randomized, phase 3 trial.
Treatment with iodine-131 apamistamab (Iomab-B) has thus far has resulted in successful engraftment for all patients who have received it and gone on to transplant, despite active disease and high bone marrow blast burden prior to transplantation, according to Sergio A. Giralt, MD, of Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, New York.
There has been no nonrelapse mortality related to the novel regimen in the ongoing trial, which compares Iomab-B as targeted conditioning prior to allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplant (HCT) with standard of care regimens, Dr. Giralt said in an update on the trial, known as SIERRA.
SIERRA is the only ongoing, randomized, phase 3 clinical trial to offer a transplant option in patients aged 55 years or older with active relapsed or refractory acute myeloid leukemia (AML), Dr. Giralt said at the Transplantation & Cellular Therapy Meetings.
“This is an underserved population in which traditional transplant techniques have very poor results, and there are limited options for patients with active disease,” Dr. Giralt said. “Of note, many transplant centers today do not consider these patients eligible for transplant.”
A total of 150 patients are to be enrolled in SIERRA and randomized either to investigator’s choice of salvage induction chemotherapy including approved targeted agents or to the experimental arm, which consists of an individualized dose of Iomab-B 12 days prior to HCT with fludarabine and total body irradiation as transplant conditioning.
Dr. Giralt presented an update on the first 38 patients in SIERRA, representing 25% of the total enrollment target.
Of 18 patients randomized to Iomab-B and transplanted, the median number of days to absolute neutrophil count engraftment was 13, Dr. Giralt said.
In the control arm, 15 of 19 (79%) failed to achieve complete remission, and of those 10 crossed over to receive Iomab-B and transplant. Days to engraftment, full donor chimerism, and dose delivered to the bone marrow were all similar in the crossover group, compared with those initially randomized to the novel therapy.
Nonhematologic grade 3 or 4 toxicities were similar between the Iomab-B arm and the conventional care arm, and included febrile neutropenia, stomatitis, and other side effects typical for these patients.
There were no grade 3 or 4 Iomab-B infusion-related reactions, and four mild cases of chronic graft-versus-host disease occurred in Iomab-B treated patients.
Nonrelapse mortality was “extremely low” with no cases in the 100 days post transplant in those initially randomized to Iomab-B, and only one case in a crossover patient, Dr. Giralt said.
“These results are encouraging, and can broaden transplant eligibility and improve outcomes,” he added.
The meeting is held by the American Society for Blood and Marrow Transplantation and the Center for International Blood and Marrow Transplant Research. At its meeting, the American Society for Blood and Marrow Transplantation announced a new name for the society: American Society for Transplantation and Cellular Therapy (ASTCT).
The SIERRA study is supported by Actinium Pharmaceuticals. Dr. Giralt reported disclosures related to Actinium and several other companies.
SOURCE: Giralt SA et al. TCT 2019, Abstract LBA3.
REPORTING FROM TCT 2019
HDACi, HMA combo improves survival for older AML patients
For patients older than 65 years with newly diagnosed acute myeloid leukemia (AML) who were ineligible for standard induction therapy, adding the investigational pan-histone deacetylase (pan-HDAC) inhibitor pracinostat to azacitidine resulted in better complete remission and overall survival rates than azacitidine alone, results of a multicenter phase 2 trial showed.
Among 50 patients treated with the combination, 26 (52%) achieved the primary endpoint of either a complete remission (CR), CR with incomplete recovery of blood counts (CRi), or morphologic leukemia-free state (MLFS).
The median overall survival (OS) was 19.1 months, which compares favorably with historical data on similar patients treated with single-agent azacitidine, reported Guillermo Garcia-Manero, MD, from the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center in Houston and his colleagues.
“[T]his study shows that pracinostat in combination with azacitidine has the potential to be a safe and effective regimen in the frontline treatment of older patients with AML unfit for [induction chemotherapy],” they wrote in Blood Advances.
Pracinostat is an oral pan-HDAC inhibitor that has been shown to have modest activity against AML as a single agent, but synergistic activity when combined with hypomethylating agent azacitidine, a standard of care for older patients with AML in the trial.
The investigators enrolled 50 patients with a median age of 75 years (range, 66-84 years). The cohort included 33 patients with de novo AML, 12 with AML secondary to myelodysplasia syndrome or myleoproliferative neoplasia, and five with therapy-related AML.
The patients were treated with pracinostat 60 mg daily for 3 days each week for 3 consecutive weeks in addition to azacitidine 75 mg/m2 daily for 7 days in a 28-day cycle.
As noted, 26 patients reached the clinical endpoint, including 21 with a CR, 2 with a CRi, and 3 with MLFS. Additionally, two patients had a partial response (PR) and four had a PR with incomplete recovery of blood counts.
The median OS was 19.1 months, and the median progression-free survival (PFS) was 12.6 months. The 1-year OS rate was 62%. The 60-day mortality rate was 10%.
The authors noted that the survival data were superior to those seen in the phase 3 AZA-AML-001 study, which compared azacitidine therapy with conventional regimens in patients older than 65 years with newly diagnosed AML who were not eligible for stem cell transplants. In that trial, median OS was 10.4 months, the CR rate was 19.5% (vs. 49% in the present study), the 1-year OS rate was 46.5%, and the 60-day mortality rate was 16.2%.
They acknowledged, however, that the validity of the comparison is limited by their study’s small sample size, potential differences between the study populations, and lack of a control group in the present study. The investigators also found that clearance rates of baseline somatic mutations correlated with response to treatment.
Grade 3 or greater treatment-emergent adverse events occurred in 43 of the 50 patients, including infections, thrombocytopenias, and febrile neutropenias.
“On the basis of these encouraging results, a phase 3, multicenter, double-blind, randomized study of pracinostat vs. placebo with azacitidine (NCT03151408) is currently ongoing to confirm superiority of the combination in this difficult-to-treat AML population,” the investigators wrote.
The study was supported by research funding from MEI Pharma, which helped develop pracinostat. Dr. Garcia-Manero reported having no disclosures. Multiple coauthors reported financial relationships with MEI and others. One coauthor is an MEI employee.
SOURCE: Garcia-Manero G et al. Blood Adv. 2019 Feb 26;3(4):508-18.
For patients older than 65 years with newly diagnosed acute myeloid leukemia (AML) who were ineligible for standard induction therapy, adding the investigational pan-histone deacetylase (pan-HDAC) inhibitor pracinostat to azacitidine resulted in better complete remission and overall survival rates than azacitidine alone, results of a multicenter phase 2 trial showed.
Among 50 patients treated with the combination, 26 (52%) achieved the primary endpoint of either a complete remission (CR), CR with incomplete recovery of blood counts (CRi), or morphologic leukemia-free state (MLFS).
The median overall survival (OS) was 19.1 months, which compares favorably with historical data on similar patients treated with single-agent azacitidine, reported Guillermo Garcia-Manero, MD, from the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center in Houston and his colleagues.
“[T]his study shows that pracinostat in combination with azacitidine has the potential to be a safe and effective regimen in the frontline treatment of older patients with AML unfit for [induction chemotherapy],” they wrote in Blood Advances.
Pracinostat is an oral pan-HDAC inhibitor that has been shown to have modest activity against AML as a single agent, but synergistic activity when combined with hypomethylating agent azacitidine, a standard of care for older patients with AML in the trial.
The investigators enrolled 50 patients with a median age of 75 years (range, 66-84 years). The cohort included 33 patients with de novo AML, 12 with AML secondary to myelodysplasia syndrome or myleoproliferative neoplasia, and five with therapy-related AML.
The patients were treated with pracinostat 60 mg daily for 3 days each week for 3 consecutive weeks in addition to azacitidine 75 mg/m2 daily for 7 days in a 28-day cycle.
As noted, 26 patients reached the clinical endpoint, including 21 with a CR, 2 with a CRi, and 3 with MLFS. Additionally, two patients had a partial response (PR) and four had a PR with incomplete recovery of blood counts.
The median OS was 19.1 months, and the median progression-free survival (PFS) was 12.6 months. The 1-year OS rate was 62%. The 60-day mortality rate was 10%.
The authors noted that the survival data were superior to those seen in the phase 3 AZA-AML-001 study, which compared azacitidine therapy with conventional regimens in patients older than 65 years with newly diagnosed AML who were not eligible for stem cell transplants. In that trial, median OS was 10.4 months, the CR rate was 19.5% (vs. 49% in the present study), the 1-year OS rate was 46.5%, and the 60-day mortality rate was 16.2%.
They acknowledged, however, that the validity of the comparison is limited by their study’s small sample size, potential differences between the study populations, and lack of a control group in the present study. The investigators also found that clearance rates of baseline somatic mutations correlated with response to treatment.
Grade 3 or greater treatment-emergent adverse events occurred in 43 of the 50 patients, including infections, thrombocytopenias, and febrile neutropenias.
“On the basis of these encouraging results, a phase 3, multicenter, double-blind, randomized study of pracinostat vs. placebo with azacitidine (NCT03151408) is currently ongoing to confirm superiority of the combination in this difficult-to-treat AML population,” the investigators wrote.
The study was supported by research funding from MEI Pharma, which helped develop pracinostat. Dr. Garcia-Manero reported having no disclosures. Multiple coauthors reported financial relationships with MEI and others. One coauthor is an MEI employee.
SOURCE: Garcia-Manero G et al. Blood Adv. 2019 Feb 26;3(4):508-18.
For patients older than 65 years with newly diagnosed acute myeloid leukemia (AML) who were ineligible for standard induction therapy, adding the investigational pan-histone deacetylase (pan-HDAC) inhibitor pracinostat to azacitidine resulted in better complete remission and overall survival rates than azacitidine alone, results of a multicenter phase 2 trial showed.
Among 50 patients treated with the combination, 26 (52%) achieved the primary endpoint of either a complete remission (CR), CR with incomplete recovery of blood counts (CRi), or morphologic leukemia-free state (MLFS).
The median overall survival (OS) was 19.1 months, which compares favorably with historical data on similar patients treated with single-agent azacitidine, reported Guillermo Garcia-Manero, MD, from the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center in Houston and his colleagues.
“[T]his study shows that pracinostat in combination with azacitidine has the potential to be a safe and effective regimen in the frontline treatment of older patients with AML unfit for [induction chemotherapy],” they wrote in Blood Advances.
Pracinostat is an oral pan-HDAC inhibitor that has been shown to have modest activity against AML as a single agent, but synergistic activity when combined with hypomethylating agent azacitidine, a standard of care for older patients with AML in the trial.
The investigators enrolled 50 patients with a median age of 75 years (range, 66-84 years). The cohort included 33 patients with de novo AML, 12 with AML secondary to myelodysplasia syndrome or myleoproliferative neoplasia, and five with therapy-related AML.
The patients were treated with pracinostat 60 mg daily for 3 days each week for 3 consecutive weeks in addition to azacitidine 75 mg/m2 daily for 7 days in a 28-day cycle.
As noted, 26 patients reached the clinical endpoint, including 21 with a CR, 2 with a CRi, and 3 with MLFS. Additionally, two patients had a partial response (PR) and four had a PR with incomplete recovery of blood counts.
The median OS was 19.1 months, and the median progression-free survival (PFS) was 12.6 months. The 1-year OS rate was 62%. The 60-day mortality rate was 10%.
The authors noted that the survival data were superior to those seen in the phase 3 AZA-AML-001 study, which compared azacitidine therapy with conventional regimens in patients older than 65 years with newly diagnosed AML who were not eligible for stem cell transplants. In that trial, median OS was 10.4 months, the CR rate was 19.5% (vs. 49% in the present study), the 1-year OS rate was 46.5%, and the 60-day mortality rate was 16.2%.
They acknowledged, however, that the validity of the comparison is limited by their study’s small sample size, potential differences between the study populations, and lack of a control group in the present study. The investigators also found that clearance rates of baseline somatic mutations correlated with response to treatment.
Grade 3 or greater treatment-emergent adverse events occurred in 43 of the 50 patients, including infections, thrombocytopenias, and febrile neutropenias.
“On the basis of these encouraging results, a phase 3, multicenter, double-blind, randomized study of pracinostat vs. placebo with azacitidine (NCT03151408) is currently ongoing to confirm superiority of the combination in this difficult-to-treat AML population,” the investigators wrote.
The study was supported by research funding from MEI Pharma, which helped develop pracinostat. Dr. Garcia-Manero reported having no disclosures. Multiple coauthors reported financial relationships with MEI and others. One coauthor is an MEI employee.
SOURCE: Garcia-Manero G et al. Blood Adv. 2019 Feb 26;3(4):508-18.
FROM BLOOD ADVANCES
Guadecitabine may be option for certain MDS/AML patients
New research suggests guadecitabine may be an option for select patients with myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS) or acute myeloid leukemia (AML) who have failed treatment with azacitidine.
In a phase 2 trial, eight of 56 patients with high-risk MDS or low-blast-count AML responded to guadecitabine after azacitidine failure. Patients were significantly more likely to respond if they had few or no somatic mutations.
Marie Sébert, MD, of Hôpital Saint Louis in Paris and her colleagues conducted this trial and reported the results in Haematologica.
The trial (NCT02197676) included 56 patients with the following disease types:
- Refractory anemia with excess blasts (RAEB) type 2 (n = 31; 55%).
- RAEB type 1 (n = 11; 20%).
- Low-blast-count AML (n = 11; 20%).
- Refractory cytopenias with multilineage dysplasia (RCMD; n = 2; 4%).
- Chronic myelomonocytic leukemia (n = 1; 2%).
The patients had a median age of 75 years (range, 70-79) at baseline, and 37 (66%) were men. Thirty-four patients (61%) had very-high-risk disease according to the revised International Prognostic Scoring System. Forty-nine patients (87.5%) had at least one somatic mutation. The most commonly mutated genes were ASXL1, RUNX1, TP53, U2AF1, and DNMT3A.
Most patients (n = 41, 73%) had relapsed after azacitidine, and 15 (27%) had primary resistance to the drug. Patients had received a median of 13 azacitidine cycles (range, 6-23).
The patients received guadecitabine subcutaneously at 60 mg/m2 on days 1-5 of a 28-day cycle. They were treated until progression, death, unacceptable toxicity, or no response after six to nine cycles. Patients received a median of three cycles (range, 0-27). One patient died of infection before receiving guadecitabine, but the remaining 55 patients received at least one cycle of treatment. Eighteen patients had a dose reduction.
Eight patients (14.3%) responded to guadecitabine. Two patients achieved a complete response (CR) – one who had RAEB-2 and one with AML. Two patients with RAEB-1 had marrow CRs. Two patients – one with RAEB-2 and one with AML – had marrow CRs with hematologic improvement. A patient with RCMD had hematologic improvement, and a patient with RAEB-2 had a partial response.
The researchers said mutation frequency was the only significant predictor of response. The response rate was significantly higher in patients who did not have somatic mutations (P = .036). The median number of mutations was one (range, zero to three) in responders and two (range, zero to six) in nonresponders (P = .035). None of the patients with TP53 mutations achieved a response.
The median duration of response was 11.5 months. The median overall survival was 17.9 months in responders and 7.1 months in the overall population.
In a multivariate analysis, the following factors were significantly associated with longer survival:
- Having low- to high-risk (vs. very-high-risk) disease (P = .03).
- Having experienced primary (vs. secondary) azacitidine failure (P = .01).
- Having a high rate of demethylation in blood during the first treatment cycle (P = .03).
There were 99 serious adverse events (AEs) reported in 44 patients. Most AEs were hematologic events, and the most common of these was myelosuppression (n = 88; 88%). The most common grade 3/4 nonhematologic AE was pulmonary toxicity (n = 7; 12.5%). Thirteen patients were hospitalized for febrile neutropenia for a median of 14 days.
The researchers said patients reported less pain and fewer secondary lesions with guadecitabine than they had with azacitidine.
This trial was sponsored by Groupe Francophone des Myelodysplasies in collaboration with Astex Pharmaceuticals. The researchers reported having no competing interests.
SOURCE: Sébert M et al. Haematologica. 2019 Feb 7. doi: 0.3324/haematol.2018.207118.
New research suggests guadecitabine may be an option for select patients with myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS) or acute myeloid leukemia (AML) who have failed treatment with azacitidine.
In a phase 2 trial, eight of 56 patients with high-risk MDS or low-blast-count AML responded to guadecitabine after azacitidine failure. Patients were significantly more likely to respond if they had few or no somatic mutations.
Marie Sébert, MD, of Hôpital Saint Louis in Paris and her colleagues conducted this trial and reported the results in Haematologica.
The trial (NCT02197676) included 56 patients with the following disease types:
- Refractory anemia with excess blasts (RAEB) type 2 (n = 31; 55%).
- RAEB type 1 (n = 11; 20%).
- Low-blast-count AML (n = 11; 20%).
- Refractory cytopenias with multilineage dysplasia (RCMD; n = 2; 4%).
- Chronic myelomonocytic leukemia (n = 1; 2%).
The patients had a median age of 75 years (range, 70-79) at baseline, and 37 (66%) were men. Thirty-four patients (61%) had very-high-risk disease according to the revised International Prognostic Scoring System. Forty-nine patients (87.5%) had at least one somatic mutation. The most commonly mutated genes were ASXL1, RUNX1, TP53, U2AF1, and DNMT3A.
Most patients (n = 41, 73%) had relapsed after azacitidine, and 15 (27%) had primary resistance to the drug. Patients had received a median of 13 azacitidine cycles (range, 6-23).
The patients received guadecitabine subcutaneously at 60 mg/m2 on days 1-5 of a 28-day cycle. They were treated until progression, death, unacceptable toxicity, or no response after six to nine cycles. Patients received a median of three cycles (range, 0-27). One patient died of infection before receiving guadecitabine, but the remaining 55 patients received at least one cycle of treatment. Eighteen patients had a dose reduction.
Eight patients (14.3%) responded to guadecitabine. Two patients achieved a complete response (CR) – one who had RAEB-2 and one with AML. Two patients with RAEB-1 had marrow CRs. Two patients – one with RAEB-2 and one with AML – had marrow CRs with hematologic improvement. A patient with RCMD had hematologic improvement, and a patient with RAEB-2 had a partial response.
The researchers said mutation frequency was the only significant predictor of response. The response rate was significantly higher in patients who did not have somatic mutations (P = .036). The median number of mutations was one (range, zero to three) in responders and two (range, zero to six) in nonresponders (P = .035). None of the patients with TP53 mutations achieved a response.
The median duration of response was 11.5 months. The median overall survival was 17.9 months in responders and 7.1 months in the overall population.
In a multivariate analysis, the following factors were significantly associated with longer survival:
- Having low- to high-risk (vs. very-high-risk) disease (P = .03).
- Having experienced primary (vs. secondary) azacitidine failure (P = .01).
- Having a high rate of demethylation in blood during the first treatment cycle (P = .03).
There were 99 serious adverse events (AEs) reported in 44 patients. Most AEs were hematologic events, and the most common of these was myelosuppression (n = 88; 88%). The most common grade 3/4 nonhematologic AE was pulmonary toxicity (n = 7; 12.5%). Thirteen patients were hospitalized for febrile neutropenia for a median of 14 days.
The researchers said patients reported less pain and fewer secondary lesions with guadecitabine than they had with azacitidine.
This trial was sponsored by Groupe Francophone des Myelodysplasies in collaboration with Astex Pharmaceuticals. The researchers reported having no competing interests.
SOURCE: Sébert M et al. Haematologica. 2019 Feb 7. doi: 0.3324/haematol.2018.207118.
New research suggests guadecitabine may be an option for select patients with myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS) or acute myeloid leukemia (AML) who have failed treatment with azacitidine.
In a phase 2 trial, eight of 56 patients with high-risk MDS or low-blast-count AML responded to guadecitabine after azacitidine failure. Patients were significantly more likely to respond if they had few or no somatic mutations.
Marie Sébert, MD, of Hôpital Saint Louis in Paris and her colleagues conducted this trial and reported the results in Haematologica.
The trial (NCT02197676) included 56 patients with the following disease types:
- Refractory anemia with excess blasts (RAEB) type 2 (n = 31; 55%).
- RAEB type 1 (n = 11; 20%).
- Low-blast-count AML (n = 11; 20%).
- Refractory cytopenias with multilineage dysplasia (RCMD; n = 2; 4%).
- Chronic myelomonocytic leukemia (n = 1; 2%).
The patients had a median age of 75 years (range, 70-79) at baseline, and 37 (66%) were men. Thirty-four patients (61%) had very-high-risk disease according to the revised International Prognostic Scoring System. Forty-nine patients (87.5%) had at least one somatic mutation. The most commonly mutated genes were ASXL1, RUNX1, TP53, U2AF1, and DNMT3A.
Most patients (n = 41, 73%) had relapsed after azacitidine, and 15 (27%) had primary resistance to the drug. Patients had received a median of 13 azacitidine cycles (range, 6-23).
The patients received guadecitabine subcutaneously at 60 mg/m2 on days 1-5 of a 28-day cycle. They were treated until progression, death, unacceptable toxicity, or no response after six to nine cycles. Patients received a median of three cycles (range, 0-27). One patient died of infection before receiving guadecitabine, but the remaining 55 patients received at least one cycle of treatment. Eighteen patients had a dose reduction.
Eight patients (14.3%) responded to guadecitabine. Two patients achieved a complete response (CR) – one who had RAEB-2 and one with AML. Two patients with RAEB-1 had marrow CRs. Two patients – one with RAEB-2 and one with AML – had marrow CRs with hematologic improvement. A patient with RCMD had hematologic improvement, and a patient with RAEB-2 had a partial response.
The researchers said mutation frequency was the only significant predictor of response. The response rate was significantly higher in patients who did not have somatic mutations (P = .036). The median number of mutations was one (range, zero to three) in responders and two (range, zero to six) in nonresponders (P = .035). None of the patients with TP53 mutations achieved a response.
The median duration of response was 11.5 months. The median overall survival was 17.9 months in responders and 7.1 months in the overall population.
In a multivariate analysis, the following factors were significantly associated with longer survival:
- Having low- to high-risk (vs. very-high-risk) disease (P = .03).
- Having experienced primary (vs. secondary) azacitidine failure (P = .01).
- Having a high rate of demethylation in blood during the first treatment cycle (P = .03).
There were 99 serious adverse events (AEs) reported in 44 patients. Most AEs were hematologic events, and the most common of these was myelosuppression (n = 88; 88%). The most common grade 3/4 nonhematologic AE was pulmonary toxicity (n = 7; 12.5%). Thirteen patients were hospitalized for febrile neutropenia for a median of 14 days.
The researchers said patients reported less pain and fewer secondary lesions with guadecitabine than they had with azacitidine.
This trial was sponsored by Groupe Francophone des Myelodysplasies in collaboration with Astex Pharmaceuticals. The researchers reported having no competing interests.
SOURCE: Sébert M et al. Haematologica. 2019 Feb 7. doi: 0.3324/haematol.2018.207118.
REPORTING FROM HAEMATOLOGICA
Midostaurin maintenance may reduce relapse risk in FLT3-ITD+ AML
HOUSTON – Midostaurin maintenance therapy along with standard-of-care treatment after allogeneic stem cell transplant (alloSCT) in patients with acute myeloid leukemia (AML) appears to reduce the risk of relapse, according to findings from the randomized, phase 2 RADIUS trial.
Notably, the effect of midostaurin in this open-label, exploratory trial was most pronounced in patients with high levels of phosphorylated FLT3 (pFLT3) inhibition as assessed by plasma inhibitor activity assay, Richard T. Maziarz, MD, reported at the Transplantation & Cellular Therapy Meetings.
“The median [pFLT3 reduction] was less than 70% ... those patients who had the deepest level inhibition maintained the highest likelihood of staying free of disease,” Dr. Maziarz, a professor of medicine at Oregon Health & Science University, Portland, said at the meeting held by the American Society for Blood and Marrow Transplantation and the Center for International Blood and Marrow Transplant Research. At its meeting, the American Society for Blood and Marrow Transplantation announced a new name for the society: American Society for Transplantation and Cellular Therapy (ASTCT).
Midostaurin is a multitargeted tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI) that was shown in the pivotal RATIFY trial to significantly improve event-free and overall survival versus placebo when interspersed with induction and consolidation chemotherapy and also when used for maintenance in adults with newly diagnosed FLT3-mutated AML, Dr. Maziarz explained. He noted that patients in the RATIFY study who underwent alloSCT did not receive midostaurin maintenance (N Engl J Med. 2017; 377:454-64).
Although alloSCT provides the greatest likelihood of sustained remission in AML, relapse rates remain high at 30%-59%, he said, adding that, “in the setting of transplantation, FLT3 expression, or FLT3-ITD [internal tandem duplication] ... is a poor risk feature.”
Studies are increasingly suggesting that posttransplant maintenance therapy may improve this outcome. For example, the small, randomized, phase 2 SORMAIN study presented at the 2018 annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology showed a signal for benefit with posttransplant maintenance with the TKI sorafenib. Data regarding midostaurin in this setting are limited, Dr. Maziarz noted.
The RADIUS trial was a small study designed to look for a similar signal with midostaurin and thus was not adequately powered to detect a statistical difference between the arms, he explained.
RADIUS included 60 AML patients aged 18-70 years who underwent myeloablative alloSCT and were in their first complete remission. The primary endpoint was relapse-free survival (RFS) at 18 months after transplant. Results were presented at ASH 2018.
RFS was 89% in 16 of 30 patients who were randomized to receive 50 mg of midostaurin twice daily along with standard-of-care (SOC) treatment and completed 12 4-week cycles. This compared with an RFS rate of 76% in 14 of 30 patients who received SOC only and completed 12 cycles (hazard ratio, 0.46).
The predicted relative reduction in the risk of relapse with the addition of midostaurin was 54%, and at 24 months, both RFS and overall survival were 85% in the midostaurin group and 76% in the SOC-only group, Dr. Maziarz reported.
The median duration of exposure to midostaurin was 10.5 months and the median dose intensity was 93 mg/day, indicating that full-dose therapy was achievable in most patients who stayed on the study.
Treatment was generally well tolerated; there was a comparable number of early discontinuations in the midostaurin and SOC-only arms. The discontinuations were caused mainly by adverse events (typically gastrointestinal toxicities) in the midostaurin arm and by consent withdrawal in the SOC-only arm, he said, adding that there were no significant differences between the groups with respect to serious adverse events or acute or chronic graft-versus-host disease.
Following the presentation of the primary RADIUS results at ASH 2018, an exploratory analysis was conducted to assess midostaurin’s inhibitory effects on FLT3 in plasma.
FLT3 plasma inhibitor activity, assessed by coculturing plasma samples taken on the first day of the treatment cycles with the FLT3-positive AML to look for a reduction in pFLT3, was evaluable in 28 patients in each arm.
“What we see is when you start there are high levels of FLT3, but the pFLT3 drops significantly with exposure to the plasma,” he said, noting that the effect was most prominent during the first two cycles of therapy.
The patients with the highest levels of inhibition had the greatest likelihood of RFS, whereas RFS in those with suboptimal pFLT3 inhibition was similar to that seen in the SOC-only arm, Dr. Maziarz said. Two patients in the midostaurin group who relapsed did so after 12 months – when midostaurin had been discontinued, he noted.
“Our conclusion is that maintenance midostaurin may contribute to a reduction in relapse risk at 18 months post transplant ... and can be safely administered in the posttransplant setting,” Dr. Maziarz said. “pFLT3 inhibition to less than 70% of baseline, at least in this study, was associated with improved relapse-free survival and overall survival, and it was achieved in more than 50% of patients on the midostaurin.”
It is likely that a more definitive answer will be provided by the Blood and Marrow Transplant Clinical Trials Network Protocol 1506, a large, multinational, placebo-controlled trial now recruiting to look at this question of whether maintenance therapy in the posttransplant setting will improve outcomes.
However, it is important to note that no patient in the RADIUS trial received pretransplant midostaurin, as RADIUS was conducted at the same time as the RATIFY trial.
“Patients today who will go to transplant with FLT3-ITD, the vast majority will have been treated during induction ... and we may have a totally different biology going forward,” he said.
Dr. Maziarz reported financial relationships with Incyte, Novartis, Celgene/Juno, Kite/Gilead, Juno Therapeutics, Kite Therapeutics, and Athersys.
HOUSTON – Midostaurin maintenance therapy along with standard-of-care treatment after allogeneic stem cell transplant (alloSCT) in patients with acute myeloid leukemia (AML) appears to reduce the risk of relapse, according to findings from the randomized, phase 2 RADIUS trial.
Notably, the effect of midostaurin in this open-label, exploratory trial was most pronounced in patients with high levels of phosphorylated FLT3 (pFLT3) inhibition as assessed by plasma inhibitor activity assay, Richard T. Maziarz, MD, reported at the Transplantation & Cellular Therapy Meetings.
“The median [pFLT3 reduction] was less than 70% ... those patients who had the deepest level inhibition maintained the highest likelihood of staying free of disease,” Dr. Maziarz, a professor of medicine at Oregon Health & Science University, Portland, said at the meeting held by the American Society for Blood and Marrow Transplantation and the Center for International Blood and Marrow Transplant Research. At its meeting, the American Society for Blood and Marrow Transplantation announced a new name for the society: American Society for Transplantation and Cellular Therapy (ASTCT).
Midostaurin is a multitargeted tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI) that was shown in the pivotal RATIFY trial to significantly improve event-free and overall survival versus placebo when interspersed with induction and consolidation chemotherapy and also when used for maintenance in adults with newly diagnosed FLT3-mutated AML, Dr. Maziarz explained. He noted that patients in the RATIFY study who underwent alloSCT did not receive midostaurin maintenance (N Engl J Med. 2017; 377:454-64).
Although alloSCT provides the greatest likelihood of sustained remission in AML, relapse rates remain high at 30%-59%, he said, adding that, “in the setting of transplantation, FLT3 expression, or FLT3-ITD [internal tandem duplication] ... is a poor risk feature.”
Studies are increasingly suggesting that posttransplant maintenance therapy may improve this outcome. For example, the small, randomized, phase 2 SORMAIN study presented at the 2018 annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology showed a signal for benefit with posttransplant maintenance with the TKI sorafenib. Data regarding midostaurin in this setting are limited, Dr. Maziarz noted.
The RADIUS trial was a small study designed to look for a similar signal with midostaurin and thus was not adequately powered to detect a statistical difference between the arms, he explained.
RADIUS included 60 AML patients aged 18-70 years who underwent myeloablative alloSCT and were in their first complete remission. The primary endpoint was relapse-free survival (RFS) at 18 months after transplant. Results were presented at ASH 2018.
RFS was 89% in 16 of 30 patients who were randomized to receive 50 mg of midostaurin twice daily along with standard-of-care (SOC) treatment and completed 12 4-week cycles. This compared with an RFS rate of 76% in 14 of 30 patients who received SOC only and completed 12 cycles (hazard ratio, 0.46).
The predicted relative reduction in the risk of relapse with the addition of midostaurin was 54%, and at 24 months, both RFS and overall survival were 85% in the midostaurin group and 76% in the SOC-only group, Dr. Maziarz reported.
The median duration of exposure to midostaurin was 10.5 months and the median dose intensity was 93 mg/day, indicating that full-dose therapy was achievable in most patients who stayed on the study.
Treatment was generally well tolerated; there was a comparable number of early discontinuations in the midostaurin and SOC-only arms. The discontinuations were caused mainly by adverse events (typically gastrointestinal toxicities) in the midostaurin arm and by consent withdrawal in the SOC-only arm, he said, adding that there were no significant differences between the groups with respect to serious adverse events or acute or chronic graft-versus-host disease.
Following the presentation of the primary RADIUS results at ASH 2018, an exploratory analysis was conducted to assess midostaurin’s inhibitory effects on FLT3 in plasma.
FLT3 plasma inhibitor activity, assessed by coculturing plasma samples taken on the first day of the treatment cycles with the FLT3-positive AML to look for a reduction in pFLT3, was evaluable in 28 patients in each arm.
“What we see is when you start there are high levels of FLT3, but the pFLT3 drops significantly with exposure to the plasma,” he said, noting that the effect was most prominent during the first two cycles of therapy.
The patients with the highest levels of inhibition had the greatest likelihood of RFS, whereas RFS in those with suboptimal pFLT3 inhibition was similar to that seen in the SOC-only arm, Dr. Maziarz said. Two patients in the midostaurin group who relapsed did so after 12 months – when midostaurin had been discontinued, he noted.
“Our conclusion is that maintenance midostaurin may contribute to a reduction in relapse risk at 18 months post transplant ... and can be safely administered in the posttransplant setting,” Dr. Maziarz said. “pFLT3 inhibition to less than 70% of baseline, at least in this study, was associated with improved relapse-free survival and overall survival, and it was achieved in more than 50% of patients on the midostaurin.”
It is likely that a more definitive answer will be provided by the Blood and Marrow Transplant Clinical Trials Network Protocol 1506, a large, multinational, placebo-controlled trial now recruiting to look at this question of whether maintenance therapy in the posttransplant setting will improve outcomes.
However, it is important to note that no patient in the RADIUS trial received pretransplant midostaurin, as RADIUS was conducted at the same time as the RATIFY trial.
“Patients today who will go to transplant with FLT3-ITD, the vast majority will have been treated during induction ... and we may have a totally different biology going forward,” he said.
Dr. Maziarz reported financial relationships with Incyte, Novartis, Celgene/Juno, Kite/Gilead, Juno Therapeutics, Kite Therapeutics, and Athersys.
HOUSTON – Midostaurin maintenance therapy along with standard-of-care treatment after allogeneic stem cell transplant (alloSCT) in patients with acute myeloid leukemia (AML) appears to reduce the risk of relapse, according to findings from the randomized, phase 2 RADIUS trial.
Notably, the effect of midostaurin in this open-label, exploratory trial was most pronounced in patients with high levels of phosphorylated FLT3 (pFLT3) inhibition as assessed by plasma inhibitor activity assay, Richard T. Maziarz, MD, reported at the Transplantation & Cellular Therapy Meetings.
“The median [pFLT3 reduction] was less than 70% ... those patients who had the deepest level inhibition maintained the highest likelihood of staying free of disease,” Dr. Maziarz, a professor of medicine at Oregon Health & Science University, Portland, said at the meeting held by the American Society for Blood and Marrow Transplantation and the Center for International Blood and Marrow Transplant Research. At its meeting, the American Society for Blood and Marrow Transplantation announced a new name for the society: American Society for Transplantation and Cellular Therapy (ASTCT).
Midostaurin is a multitargeted tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI) that was shown in the pivotal RATIFY trial to significantly improve event-free and overall survival versus placebo when interspersed with induction and consolidation chemotherapy and also when used for maintenance in adults with newly diagnosed FLT3-mutated AML, Dr. Maziarz explained. He noted that patients in the RATIFY study who underwent alloSCT did not receive midostaurin maintenance (N Engl J Med. 2017; 377:454-64).
Although alloSCT provides the greatest likelihood of sustained remission in AML, relapse rates remain high at 30%-59%, he said, adding that, “in the setting of transplantation, FLT3 expression, or FLT3-ITD [internal tandem duplication] ... is a poor risk feature.”
Studies are increasingly suggesting that posttransplant maintenance therapy may improve this outcome. For example, the small, randomized, phase 2 SORMAIN study presented at the 2018 annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology showed a signal for benefit with posttransplant maintenance with the TKI sorafenib. Data regarding midostaurin in this setting are limited, Dr. Maziarz noted.
The RADIUS trial was a small study designed to look for a similar signal with midostaurin and thus was not adequately powered to detect a statistical difference between the arms, he explained.
RADIUS included 60 AML patients aged 18-70 years who underwent myeloablative alloSCT and were in their first complete remission. The primary endpoint was relapse-free survival (RFS) at 18 months after transplant. Results were presented at ASH 2018.
RFS was 89% in 16 of 30 patients who were randomized to receive 50 mg of midostaurin twice daily along with standard-of-care (SOC) treatment and completed 12 4-week cycles. This compared with an RFS rate of 76% in 14 of 30 patients who received SOC only and completed 12 cycles (hazard ratio, 0.46).
The predicted relative reduction in the risk of relapse with the addition of midostaurin was 54%, and at 24 months, both RFS and overall survival were 85% in the midostaurin group and 76% in the SOC-only group, Dr. Maziarz reported.
The median duration of exposure to midostaurin was 10.5 months and the median dose intensity was 93 mg/day, indicating that full-dose therapy was achievable in most patients who stayed on the study.
Treatment was generally well tolerated; there was a comparable number of early discontinuations in the midostaurin and SOC-only arms. The discontinuations were caused mainly by adverse events (typically gastrointestinal toxicities) in the midostaurin arm and by consent withdrawal in the SOC-only arm, he said, adding that there were no significant differences between the groups with respect to serious adverse events or acute or chronic graft-versus-host disease.
Following the presentation of the primary RADIUS results at ASH 2018, an exploratory analysis was conducted to assess midostaurin’s inhibitory effects on FLT3 in plasma.
FLT3 plasma inhibitor activity, assessed by coculturing plasma samples taken on the first day of the treatment cycles with the FLT3-positive AML to look for a reduction in pFLT3, was evaluable in 28 patients in each arm.
“What we see is when you start there are high levels of FLT3, but the pFLT3 drops significantly with exposure to the plasma,” he said, noting that the effect was most prominent during the first two cycles of therapy.
The patients with the highest levels of inhibition had the greatest likelihood of RFS, whereas RFS in those with suboptimal pFLT3 inhibition was similar to that seen in the SOC-only arm, Dr. Maziarz said. Two patients in the midostaurin group who relapsed did so after 12 months – when midostaurin had been discontinued, he noted.
“Our conclusion is that maintenance midostaurin may contribute to a reduction in relapse risk at 18 months post transplant ... and can be safely administered in the posttransplant setting,” Dr. Maziarz said. “pFLT3 inhibition to less than 70% of baseline, at least in this study, was associated with improved relapse-free survival and overall survival, and it was achieved in more than 50% of patients on the midostaurin.”
It is likely that a more definitive answer will be provided by the Blood and Marrow Transplant Clinical Trials Network Protocol 1506, a large, multinational, placebo-controlled trial now recruiting to look at this question of whether maintenance therapy in the posttransplant setting will improve outcomes.
However, it is important to note that no patient in the RADIUS trial received pretransplant midostaurin, as RADIUS was conducted at the same time as the RATIFY trial.
“Patients today who will go to transplant with FLT3-ITD, the vast majority will have been treated during induction ... and we may have a totally different biology going forward,” he said.
Dr. Maziarz reported financial relationships with Incyte, Novartis, Celgene/Juno, Kite/Gilead, Juno Therapeutics, Kite Therapeutics, and Athersys.
REPORTING FROM TCT 2019
Treosulfan may become standard in allo-HCT for AML/MDS
HOUSTON – A treosulfan-based conditioning regimen could become standard prior to allogeneic transplant in elderly or comorbid patients with acute myeloid leukemia or myelodysplastic syndromes, according to the lead investigator in a phase 3 trial.
The treosulfan/fludarabine myeloablative conditioning regimen had noninferior event-free survival, compared with a reduced-intensity busulfan-based regimen in the large, randomized trial that included elderly patients and those with multiple comorbidities, said researcher Dietrich Wilhelm Beelen, MD, PhD.
The experimental regimen was superior to busulfan in overall survival, nonrelapse mortality, and complete donor chimerism in the trial, added Dr. Beelen, who is with the department of bone marrow transplantation at the West German Cancer Center, University Hospital of Essen, Germany.
“The study results point to a potential benefit of the treosulfan/fludarabine regimen, while the early safety profile, engraftment kinetics, acute or chronic graft-versus-host-disease (GvHD), and the relapse risk of both regimens appear comparable,” Dr. Beelen said at the Transplantation & Cellular Therapy Meetings.
Allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation (HCT) is challenging in elderly and comorbid patients, who have an increased risk of nonrelapse mortality with standard myeloablative regimens, according to Dr. Beelen, who presented results on behalf of investigators from the international MC-FludT.14/L Study Group.
Their phase 3 randomized trial included patients who were 50-70 years of age, or who had a Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation Comorbidity Index of 2 or greater. The final analysis included 551 patients (352 with AML and 199 with MDS).
The primary endpoint of the study was event-free survival at 2 years. That endpoint comprised relapse/progression of disease, graft failure, or death.
Patient enrollment was terminated early the MC-FludT.14/L study following an interim analysis that investigators said “clearly demonstrated” the noninferiority of the treosulfan/fludarabine regimen versus the reduced intensity busulfan/fludarabine regimen.
In the final analysis, event-free survival at 2 years was about 14.5 percentage points higher in the treosulfan group, at 65.7% versus 51.2% (P = .0000001), Dr. Beelen reported at the meeting.
A number of other secondary endpoints also favored treosulfan/fludarabine over busulfan, including overall survival (P = .0037), nonrelapse mortality (P = .0343), and survival free of chronic GvHD or relapse (P = .0030).
These results help establish the new treosulfan/fludarabine regimen as a “relatively well-tolerable and effective preparative regimen” in elderly or comorbid AML/MDS patients, Dr. Beelen said.
However, treosulfan has not been authorized for use in allogeneic HCT conditioning regimens, and so should be considered experimental in this setting, he said at the meeting held by the American Society for Blood and Marrow Transplantation and the Center for International Blood and Marrow Transplant Research. At its meeting, the American Society for Blood and Marrow Transplantation announced a new name for the society: American Society for Transplantation and Cellular Therapy (ASTCT).
Dr. Beelen reported honoraria, travel support, and trial documentation support provided by medac GmbH, which sponsored the trial.
SOURCE: Beelen DW et al. TCT 2019, Abstract 4.
HOUSTON – A treosulfan-based conditioning regimen could become standard prior to allogeneic transplant in elderly or comorbid patients with acute myeloid leukemia or myelodysplastic syndromes, according to the lead investigator in a phase 3 trial.
The treosulfan/fludarabine myeloablative conditioning regimen had noninferior event-free survival, compared with a reduced-intensity busulfan-based regimen in the large, randomized trial that included elderly patients and those with multiple comorbidities, said researcher Dietrich Wilhelm Beelen, MD, PhD.
The experimental regimen was superior to busulfan in overall survival, nonrelapse mortality, and complete donor chimerism in the trial, added Dr. Beelen, who is with the department of bone marrow transplantation at the West German Cancer Center, University Hospital of Essen, Germany.
“The study results point to a potential benefit of the treosulfan/fludarabine regimen, while the early safety profile, engraftment kinetics, acute or chronic graft-versus-host-disease (GvHD), and the relapse risk of both regimens appear comparable,” Dr. Beelen said at the Transplantation & Cellular Therapy Meetings.
Allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation (HCT) is challenging in elderly and comorbid patients, who have an increased risk of nonrelapse mortality with standard myeloablative regimens, according to Dr. Beelen, who presented results on behalf of investigators from the international MC-FludT.14/L Study Group.
Their phase 3 randomized trial included patients who were 50-70 years of age, or who had a Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation Comorbidity Index of 2 or greater. The final analysis included 551 patients (352 with AML and 199 with MDS).
The primary endpoint of the study was event-free survival at 2 years. That endpoint comprised relapse/progression of disease, graft failure, or death.
Patient enrollment was terminated early the MC-FludT.14/L study following an interim analysis that investigators said “clearly demonstrated” the noninferiority of the treosulfan/fludarabine regimen versus the reduced intensity busulfan/fludarabine regimen.
In the final analysis, event-free survival at 2 years was about 14.5 percentage points higher in the treosulfan group, at 65.7% versus 51.2% (P = .0000001), Dr. Beelen reported at the meeting.
A number of other secondary endpoints also favored treosulfan/fludarabine over busulfan, including overall survival (P = .0037), nonrelapse mortality (P = .0343), and survival free of chronic GvHD or relapse (P = .0030).
These results help establish the new treosulfan/fludarabine regimen as a “relatively well-tolerable and effective preparative regimen” in elderly or comorbid AML/MDS patients, Dr. Beelen said.
However, treosulfan has not been authorized for use in allogeneic HCT conditioning regimens, and so should be considered experimental in this setting, he said at the meeting held by the American Society for Blood and Marrow Transplantation and the Center for International Blood and Marrow Transplant Research. At its meeting, the American Society for Blood and Marrow Transplantation announced a new name for the society: American Society for Transplantation and Cellular Therapy (ASTCT).
Dr. Beelen reported honoraria, travel support, and trial documentation support provided by medac GmbH, which sponsored the trial.
SOURCE: Beelen DW et al. TCT 2019, Abstract 4.
HOUSTON – A treosulfan-based conditioning regimen could become standard prior to allogeneic transplant in elderly or comorbid patients with acute myeloid leukemia or myelodysplastic syndromes, according to the lead investigator in a phase 3 trial.
The treosulfan/fludarabine myeloablative conditioning regimen had noninferior event-free survival, compared with a reduced-intensity busulfan-based regimen in the large, randomized trial that included elderly patients and those with multiple comorbidities, said researcher Dietrich Wilhelm Beelen, MD, PhD.
The experimental regimen was superior to busulfan in overall survival, nonrelapse mortality, and complete donor chimerism in the trial, added Dr. Beelen, who is with the department of bone marrow transplantation at the West German Cancer Center, University Hospital of Essen, Germany.
“The study results point to a potential benefit of the treosulfan/fludarabine regimen, while the early safety profile, engraftment kinetics, acute or chronic graft-versus-host-disease (GvHD), and the relapse risk of both regimens appear comparable,” Dr. Beelen said at the Transplantation & Cellular Therapy Meetings.
Allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation (HCT) is challenging in elderly and comorbid patients, who have an increased risk of nonrelapse mortality with standard myeloablative regimens, according to Dr. Beelen, who presented results on behalf of investigators from the international MC-FludT.14/L Study Group.
Their phase 3 randomized trial included patients who were 50-70 years of age, or who had a Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation Comorbidity Index of 2 or greater. The final analysis included 551 patients (352 with AML and 199 with MDS).
The primary endpoint of the study was event-free survival at 2 years. That endpoint comprised relapse/progression of disease, graft failure, or death.
Patient enrollment was terminated early the MC-FludT.14/L study following an interim analysis that investigators said “clearly demonstrated” the noninferiority of the treosulfan/fludarabine regimen versus the reduced intensity busulfan/fludarabine regimen.
In the final analysis, event-free survival at 2 years was about 14.5 percentage points higher in the treosulfan group, at 65.7% versus 51.2% (P = .0000001), Dr. Beelen reported at the meeting.
A number of other secondary endpoints also favored treosulfan/fludarabine over busulfan, including overall survival (P = .0037), nonrelapse mortality (P = .0343), and survival free of chronic GvHD or relapse (P = .0030).
These results help establish the new treosulfan/fludarabine regimen as a “relatively well-tolerable and effective preparative regimen” in elderly or comorbid AML/MDS patients, Dr. Beelen said.
However, treosulfan has not been authorized for use in allogeneic HCT conditioning regimens, and so should be considered experimental in this setting, he said at the meeting held by the American Society for Blood and Marrow Transplantation and the Center for International Blood and Marrow Transplant Research. At its meeting, the American Society for Blood and Marrow Transplantation announced a new name for the society: American Society for Transplantation and Cellular Therapy (ASTCT).
Dr. Beelen reported honoraria, travel support, and trial documentation support provided by medac GmbH, which sponsored the trial.
SOURCE: Beelen DW et al. TCT 2019, Abstract 4.
REPORTING FROM TCT 2019
Eltrombopag ‘cannot be recommended’ during AML induction
The thrombopoietic agent eltrombopag (Promacta) did more harm than good when given to adults with acute myeloid leukemia (AML) during standard induction chemotherapy, results of a randomized phase 2 trial show.
Patients who were randomly assigned to receive standard induction chemotherapy with daunorubicin and cytarabine plus eltrombopag had a higher incidence of serious adverse events and death from hemorrhage within 30 days of the last eltrombopag dose, compared with patients who received chemotherapy and placebo, reported Noelle Frey, MD, from the University of Pennsylvania in Philadelphia, and colleagues.
“Overall survival was also numerically longer in the placebo group, compared with the eltrombopag group. It remains unclear why there were more deaths, particularly due to hemorrhage within 30 days after the last dose of treatment, in the eltrombopag group,” they wrote in the Lancet Haematology.
The investigators had expected better results, based on eltrombopag’s demonstrated efficacy against thrombocytopenia (a common feature of AML, exacerbated by chemotherapy), and because of evidence suggesting that the thrombopoietin-receptor agonist might also have antileukemic properties.
They set out to test the safety, tolerability, and efficacy of eltrombopag added to standard induction therapy in patients with treatment-naive AML of any subtype except M3 (acute promyelocytic leukemia) or M7 (acute megakaryocytic leukemia).
Patients received chemotherapy with daunorubicin in a bolus intravenous infusion at a dose of 90 mg/m2 on days 1-3 for patients 18-60 years of age, or 60 mg/m2 for patients older than 60 years, plus cytarabine continuous intravenous infusion at a dose of 100 mg/m2 on days 1-7. The 148 patients were randomized in groups of 74 each to receive either eltrombopag 200 mg (100 mg for patients of east Asian heritage) or placebo, once daily.
Eltrombopag was continued until platelet counts were 200 × 109/L or higher, remission, or 42 days after the start of induction chemotherapy.
Grade 3 or 4 adverse events occurring in 10% or more of patients – a primary endpoint – were febrile neutropenia, which occurred in 42% of patients receiving eltrombopag, compared with 39% receiving placebo, decreased white blood cell count in 11% vs. 7%, and hypophosphatemia in 4% and 13%, respectively,
Serious adverse events occurred in 34% of patients on eltrombopag, compared with 20% on placebo. Similarly, 53% of patients receiving eltrombopag died, compared with 41% of patients receiving the placebo.
Most of the deaths were attributable to AML, including 19 patients (26%) on eltrombopag and 10 (14%) on placebo. Eleven patients on eltrombopag and four on placebo died within 30 days of the last dose of study treatment.
Hemorrhage accounted for the deaths of five patients on eltrombopag and three on placebo, and sepsis accounted for the deaths of five and six patients, respectively.
Both the incidence of thromboembolic events and mean change in left ventricular ejection fraction were similar between the groups.
Median overall survival was 15.4 months in the eltrombopag group vs. 25.7 months in the placebo group, although this difference was not statistically significant, likely because of the sample size.
The investigators were at a loss to explain why the eltrombopag-treated patients had numerically worse outcomes.
“In the present study, eltrombopag did not improve the time to platelet recovery or the incidences of grade 3-4 thrombocytopenia, neutropenia, or anemia, compared with placebo. Furthermore, the study did not reveal any differences in investigator-assessed response to treatment. These findings were unexpected given outcomes from previous studies of eltrombopag monotherapy in patients with myelodysplastic syndromes or acute myeloid leukemia,” they wrote.
Although the reasons behind the findings are unclear, “the data from this trial do not support a favorable benefit-risk profile for eltrombopag in combination with induction chemotherapy in patients with acute myeloid leukemia,” the investigators wrote.
The study was funded by Novartis. Dr. Frey reported nonfinancial support from Novartis during the conduct of the study and consultancy fees from Novartis outside of the submitted work. Multiple coauthors reported similar relationships with Novartis and/or other companies.
SOURCE: Frey N et al. Lancet Haematol. 2019 Jan 28. doi: 10.1016/S2352-3026(18)30231-X.
The thrombopoietic agent eltrombopag (Promacta) did more harm than good when given to adults with acute myeloid leukemia (AML) during standard induction chemotherapy, results of a randomized phase 2 trial show.
Patients who were randomly assigned to receive standard induction chemotherapy with daunorubicin and cytarabine plus eltrombopag had a higher incidence of serious adverse events and death from hemorrhage within 30 days of the last eltrombopag dose, compared with patients who received chemotherapy and placebo, reported Noelle Frey, MD, from the University of Pennsylvania in Philadelphia, and colleagues.
“Overall survival was also numerically longer in the placebo group, compared with the eltrombopag group. It remains unclear why there were more deaths, particularly due to hemorrhage within 30 days after the last dose of treatment, in the eltrombopag group,” they wrote in the Lancet Haematology.
The investigators had expected better results, based on eltrombopag’s demonstrated efficacy against thrombocytopenia (a common feature of AML, exacerbated by chemotherapy), and because of evidence suggesting that the thrombopoietin-receptor agonist might also have antileukemic properties.
They set out to test the safety, tolerability, and efficacy of eltrombopag added to standard induction therapy in patients with treatment-naive AML of any subtype except M3 (acute promyelocytic leukemia) or M7 (acute megakaryocytic leukemia).
Patients received chemotherapy with daunorubicin in a bolus intravenous infusion at a dose of 90 mg/m2 on days 1-3 for patients 18-60 years of age, or 60 mg/m2 for patients older than 60 years, plus cytarabine continuous intravenous infusion at a dose of 100 mg/m2 on days 1-7. The 148 patients were randomized in groups of 74 each to receive either eltrombopag 200 mg (100 mg for patients of east Asian heritage) or placebo, once daily.
Eltrombopag was continued until platelet counts were 200 × 109/L or higher, remission, or 42 days after the start of induction chemotherapy.
Grade 3 or 4 adverse events occurring in 10% or more of patients – a primary endpoint – were febrile neutropenia, which occurred in 42% of patients receiving eltrombopag, compared with 39% receiving placebo, decreased white blood cell count in 11% vs. 7%, and hypophosphatemia in 4% and 13%, respectively,
Serious adverse events occurred in 34% of patients on eltrombopag, compared with 20% on placebo. Similarly, 53% of patients receiving eltrombopag died, compared with 41% of patients receiving the placebo.
Most of the deaths were attributable to AML, including 19 patients (26%) on eltrombopag and 10 (14%) on placebo. Eleven patients on eltrombopag and four on placebo died within 30 days of the last dose of study treatment.
Hemorrhage accounted for the deaths of five patients on eltrombopag and three on placebo, and sepsis accounted for the deaths of five and six patients, respectively.
Both the incidence of thromboembolic events and mean change in left ventricular ejection fraction were similar between the groups.
Median overall survival was 15.4 months in the eltrombopag group vs. 25.7 months in the placebo group, although this difference was not statistically significant, likely because of the sample size.
The investigators were at a loss to explain why the eltrombopag-treated patients had numerically worse outcomes.
“In the present study, eltrombopag did not improve the time to platelet recovery or the incidences of grade 3-4 thrombocytopenia, neutropenia, or anemia, compared with placebo. Furthermore, the study did not reveal any differences in investigator-assessed response to treatment. These findings were unexpected given outcomes from previous studies of eltrombopag monotherapy in patients with myelodysplastic syndromes or acute myeloid leukemia,” they wrote.
Although the reasons behind the findings are unclear, “the data from this trial do not support a favorable benefit-risk profile for eltrombopag in combination with induction chemotherapy in patients with acute myeloid leukemia,” the investigators wrote.
The study was funded by Novartis. Dr. Frey reported nonfinancial support from Novartis during the conduct of the study and consultancy fees from Novartis outside of the submitted work. Multiple coauthors reported similar relationships with Novartis and/or other companies.
SOURCE: Frey N et al. Lancet Haematol. 2019 Jan 28. doi: 10.1016/S2352-3026(18)30231-X.
The thrombopoietic agent eltrombopag (Promacta) did more harm than good when given to adults with acute myeloid leukemia (AML) during standard induction chemotherapy, results of a randomized phase 2 trial show.
Patients who were randomly assigned to receive standard induction chemotherapy with daunorubicin and cytarabine plus eltrombopag had a higher incidence of serious adverse events and death from hemorrhage within 30 days of the last eltrombopag dose, compared with patients who received chemotherapy and placebo, reported Noelle Frey, MD, from the University of Pennsylvania in Philadelphia, and colleagues.
“Overall survival was also numerically longer in the placebo group, compared with the eltrombopag group. It remains unclear why there were more deaths, particularly due to hemorrhage within 30 days after the last dose of treatment, in the eltrombopag group,” they wrote in the Lancet Haematology.
The investigators had expected better results, based on eltrombopag’s demonstrated efficacy against thrombocytopenia (a common feature of AML, exacerbated by chemotherapy), and because of evidence suggesting that the thrombopoietin-receptor agonist might also have antileukemic properties.
They set out to test the safety, tolerability, and efficacy of eltrombopag added to standard induction therapy in patients with treatment-naive AML of any subtype except M3 (acute promyelocytic leukemia) or M7 (acute megakaryocytic leukemia).
Patients received chemotherapy with daunorubicin in a bolus intravenous infusion at a dose of 90 mg/m2 on days 1-3 for patients 18-60 years of age, or 60 mg/m2 for patients older than 60 years, plus cytarabine continuous intravenous infusion at a dose of 100 mg/m2 on days 1-7. The 148 patients were randomized in groups of 74 each to receive either eltrombopag 200 mg (100 mg for patients of east Asian heritage) or placebo, once daily.
Eltrombopag was continued until platelet counts were 200 × 109/L or higher, remission, or 42 days after the start of induction chemotherapy.
Grade 3 or 4 adverse events occurring in 10% or more of patients – a primary endpoint – were febrile neutropenia, which occurred in 42% of patients receiving eltrombopag, compared with 39% receiving placebo, decreased white blood cell count in 11% vs. 7%, and hypophosphatemia in 4% and 13%, respectively,
Serious adverse events occurred in 34% of patients on eltrombopag, compared with 20% on placebo. Similarly, 53% of patients receiving eltrombopag died, compared with 41% of patients receiving the placebo.
Most of the deaths were attributable to AML, including 19 patients (26%) on eltrombopag and 10 (14%) on placebo. Eleven patients on eltrombopag and four on placebo died within 30 days of the last dose of study treatment.
Hemorrhage accounted for the deaths of five patients on eltrombopag and three on placebo, and sepsis accounted for the deaths of five and six patients, respectively.
Both the incidence of thromboembolic events and mean change in left ventricular ejection fraction were similar between the groups.
Median overall survival was 15.4 months in the eltrombopag group vs. 25.7 months in the placebo group, although this difference was not statistically significant, likely because of the sample size.
The investigators were at a loss to explain why the eltrombopag-treated patients had numerically worse outcomes.
“In the present study, eltrombopag did not improve the time to platelet recovery or the incidences of grade 3-4 thrombocytopenia, neutropenia, or anemia, compared with placebo. Furthermore, the study did not reveal any differences in investigator-assessed response to treatment. These findings were unexpected given outcomes from previous studies of eltrombopag monotherapy in patients with myelodysplastic syndromes or acute myeloid leukemia,” they wrote.
Although the reasons behind the findings are unclear, “the data from this trial do not support a favorable benefit-risk profile for eltrombopag in combination with induction chemotherapy in patients with acute myeloid leukemia,” the investigators wrote.
The study was funded by Novartis. Dr. Frey reported nonfinancial support from Novartis during the conduct of the study and consultancy fees from Novartis outside of the submitted work. Multiple coauthors reported similar relationships with Novartis and/or other companies.
SOURCE: Frey N et al. Lancet Haematol. 2019 Jan 28. doi: 10.1016/S2352-3026(18)30231-X.
FROM LANCET HAEMATOLOGY
Key clinical point:
Major finding: Overall survival was shorter for patients assigned to eltrombopag than placebo, at 15.4 months versus 25.7 months. The difference was not statistically significant.
Study details: Randomized phase 2 trial in 148 adults with treatment-naive acute myeloid leukemia.
Disclosures: The study was funded by Novartis. Dr. Frey reported nonfinancial support from Novartis during the conduct of the study and consultancy fees from Novartis outside of the submitted work. Multiple coauthors reported similar relationships with Novartis and other companies.
Source: Frey N et al. Lancet Haematol. 2019 Jan 28. doi: 10.1016/S2352-3026(18)30231-X.
AML, myeloma risk higher for breast cancer survivors
Breast cancer survivors should continue to be monitored for hematologic malignancies, especially acute myeloid leukemia (AML) and myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS), results of a population-based study from France suggest.
Among nearly 440,000 women with an incident breast cancer diagnosis, the incidence of AML was nearly three times higher and the incidence of MDS was five times higher than that of women in the general population. Women with breast cancer also were at higher risk for multiple myeloma (MM) and acute lymphoblastic leukemia/lymphocytic lymphoma (ALL/LL) compared with the background population, reported Marie Joelle Jabagi, PharmD, MPH, of the University of Paris Sud, France, and her colleagues.
“These findings serve to better inform practicing oncologists, and breast cancer survivors should be advised of the increased risk of developing certain hematologic malignant neoplasms after their first cancer diagnosis,” they wrote in JAMA Network Open.
Breast cancers are the malignant solid tumors most frequently associated with risk for myeloid neoplasms, but there is little information on the risk for secondary lymphoid malignancies among breast cancer patients, the investigators stated.
“In addition, real-life data on secondary hematologic malignant neoplasm incidence are scarce, especially in the recent period marked by major advances in breast cancer treatments,” they wrote.
To get better estimates of the incidence of myeloid and lymphoid neoplasms in this population, they conducted a retrospective review of information from the French National Health Data System on all French women from the ages of 20 to 85 years who had an incident breast cancer diagnosis from July 1, 2006, through Dec. 31, 2015.
In all, 439,704 women with a median age of 59 years were identified. They were followed until a diagnosis of a hematologic malignancy, death, or loss to follow-up, or until Dec. 31, 2016.
Data on the breast cancer patients were compared with those for all French women in the general population who were registered in the general national health insurance program from January 2007 through the end of 2016.
During a median follow-up of 5 years, there were 3,046 cases of hematologic neoplasms among the breast cancer patients, including 509 cases of AML, for a crude incidence rate (CIR) of 24.5 per 100,000 person-years (py); 832 cases of MDS for a CIR of 40.1/100,000 py; and 267 cases of myeloproliferative neoplasms (MPN), for a CIR of 12.8/100,000 py.
In addition, there were 420 cases of MM for a CIR of 20.3/100,000 py; 912 cases of Hodgkin or non-Hodgkin lymphoma (HL/NHL) for a CIR of 44.4/100,000 py, and 106 cases of ALL/LL for a CIR of 5.1/100,000 py.
Breast cancer survivors had significantly higher incidences, compared with the general population, of AML (standardized incidence ratio [SIR] 2.8, 95% confidence interval [CI], 2.5-3.2), MDS (SIR 5.0, CI, 4.4-5.7), MM (SIR 1.5, CI, 1.3-17), and ALL/LL (SIR 2.0, CI, 1.3-3.0). There was a trend toward significance for both MPN and HL/NHL, but the lower limit of the confidence intervals for these conditions either crossed or touched 1.
In a review of the literature, the authors found that “[s]everal studies linked AML and MDS to chemotherapeutic agents, radiation treatment, and supportive treatment with granulocyte colony-stimulating factor. These results are consistent with other available data showing a 2½-fold to 3½-fold increased risk of AML.”
They noted that their estimate of a five-fold increase in risk for MDS was higher than the 3.7-fold risk reported in a previous registry cohort analysis, suggesting that risk for MDS among breast cancer patients may be underestimated.
“The recent discovery of the gene signatures that guide treatment decisions in early-stage breast cancer might reduce the number of patients exposed to cytotoxic chemotherapy and its complications, including hematologic malignant neoplasm. Therefore, continuing to monitor hematologic malignant neoplasm trends is necessary, especially given that approaches to cancer treatment are rapidly evolving. Further research is also required to assess the modality of treatment for and the genetic predisposition to these secondary malignant neoplasms,” the authors concluded.
SOURCE: Jabagi MJ et al. JAMA Network Open. 2019 Jan 18. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2018.7147.
Breast cancer survivors should continue to be monitored for hematologic malignancies, especially acute myeloid leukemia (AML) and myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS), results of a population-based study from France suggest.
Among nearly 440,000 women with an incident breast cancer diagnosis, the incidence of AML was nearly three times higher and the incidence of MDS was five times higher than that of women in the general population. Women with breast cancer also were at higher risk for multiple myeloma (MM) and acute lymphoblastic leukemia/lymphocytic lymphoma (ALL/LL) compared with the background population, reported Marie Joelle Jabagi, PharmD, MPH, of the University of Paris Sud, France, and her colleagues.
“These findings serve to better inform practicing oncologists, and breast cancer survivors should be advised of the increased risk of developing certain hematologic malignant neoplasms after their first cancer diagnosis,” they wrote in JAMA Network Open.
Breast cancers are the malignant solid tumors most frequently associated with risk for myeloid neoplasms, but there is little information on the risk for secondary lymphoid malignancies among breast cancer patients, the investigators stated.
“In addition, real-life data on secondary hematologic malignant neoplasm incidence are scarce, especially in the recent period marked by major advances in breast cancer treatments,” they wrote.
To get better estimates of the incidence of myeloid and lymphoid neoplasms in this population, they conducted a retrospective review of information from the French National Health Data System on all French women from the ages of 20 to 85 years who had an incident breast cancer diagnosis from July 1, 2006, through Dec. 31, 2015.
In all, 439,704 women with a median age of 59 years were identified. They were followed until a diagnosis of a hematologic malignancy, death, or loss to follow-up, or until Dec. 31, 2016.
Data on the breast cancer patients were compared with those for all French women in the general population who were registered in the general national health insurance program from January 2007 through the end of 2016.
During a median follow-up of 5 years, there were 3,046 cases of hematologic neoplasms among the breast cancer patients, including 509 cases of AML, for a crude incidence rate (CIR) of 24.5 per 100,000 person-years (py); 832 cases of MDS for a CIR of 40.1/100,000 py; and 267 cases of myeloproliferative neoplasms (MPN), for a CIR of 12.8/100,000 py.
In addition, there were 420 cases of MM for a CIR of 20.3/100,000 py; 912 cases of Hodgkin or non-Hodgkin lymphoma (HL/NHL) for a CIR of 44.4/100,000 py, and 106 cases of ALL/LL for a CIR of 5.1/100,000 py.
Breast cancer survivors had significantly higher incidences, compared with the general population, of AML (standardized incidence ratio [SIR] 2.8, 95% confidence interval [CI], 2.5-3.2), MDS (SIR 5.0, CI, 4.4-5.7), MM (SIR 1.5, CI, 1.3-17), and ALL/LL (SIR 2.0, CI, 1.3-3.0). There was a trend toward significance for both MPN and HL/NHL, but the lower limit of the confidence intervals for these conditions either crossed or touched 1.
In a review of the literature, the authors found that “[s]everal studies linked AML and MDS to chemotherapeutic agents, radiation treatment, and supportive treatment with granulocyte colony-stimulating factor. These results are consistent with other available data showing a 2½-fold to 3½-fold increased risk of AML.”
They noted that their estimate of a five-fold increase in risk for MDS was higher than the 3.7-fold risk reported in a previous registry cohort analysis, suggesting that risk for MDS among breast cancer patients may be underestimated.
“The recent discovery of the gene signatures that guide treatment decisions in early-stage breast cancer might reduce the number of patients exposed to cytotoxic chemotherapy and its complications, including hematologic malignant neoplasm. Therefore, continuing to monitor hematologic malignant neoplasm trends is necessary, especially given that approaches to cancer treatment are rapidly evolving. Further research is also required to assess the modality of treatment for and the genetic predisposition to these secondary malignant neoplasms,” the authors concluded.
SOURCE: Jabagi MJ et al. JAMA Network Open. 2019 Jan 18. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2018.7147.
Breast cancer survivors should continue to be monitored for hematologic malignancies, especially acute myeloid leukemia (AML) and myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS), results of a population-based study from France suggest.
Among nearly 440,000 women with an incident breast cancer diagnosis, the incidence of AML was nearly three times higher and the incidence of MDS was five times higher than that of women in the general population. Women with breast cancer also were at higher risk for multiple myeloma (MM) and acute lymphoblastic leukemia/lymphocytic lymphoma (ALL/LL) compared with the background population, reported Marie Joelle Jabagi, PharmD, MPH, of the University of Paris Sud, France, and her colleagues.
“These findings serve to better inform practicing oncologists, and breast cancer survivors should be advised of the increased risk of developing certain hematologic malignant neoplasms after their first cancer diagnosis,” they wrote in JAMA Network Open.
Breast cancers are the malignant solid tumors most frequently associated with risk for myeloid neoplasms, but there is little information on the risk for secondary lymphoid malignancies among breast cancer patients, the investigators stated.
“In addition, real-life data on secondary hematologic malignant neoplasm incidence are scarce, especially in the recent period marked by major advances in breast cancer treatments,” they wrote.
To get better estimates of the incidence of myeloid and lymphoid neoplasms in this population, they conducted a retrospective review of information from the French National Health Data System on all French women from the ages of 20 to 85 years who had an incident breast cancer diagnosis from July 1, 2006, through Dec. 31, 2015.
In all, 439,704 women with a median age of 59 years were identified. They were followed until a diagnosis of a hematologic malignancy, death, or loss to follow-up, or until Dec. 31, 2016.
Data on the breast cancer patients were compared with those for all French women in the general population who were registered in the general national health insurance program from January 2007 through the end of 2016.
During a median follow-up of 5 years, there were 3,046 cases of hematologic neoplasms among the breast cancer patients, including 509 cases of AML, for a crude incidence rate (CIR) of 24.5 per 100,000 person-years (py); 832 cases of MDS for a CIR of 40.1/100,000 py; and 267 cases of myeloproliferative neoplasms (MPN), for a CIR of 12.8/100,000 py.
In addition, there were 420 cases of MM for a CIR of 20.3/100,000 py; 912 cases of Hodgkin or non-Hodgkin lymphoma (HL/NHL) for a CIR of 44.4/100,000 py, and 106 cases of ALL/LL for a CIR of 5.1/100,000 py.
Breast cancer survivors had significantly higher incidences, compared with the general population, of AML (standardized incidence ratio [SIR] 2.8, 95% confidence interval [CI], 2.5-3.2), MDS (SIR 5.0, CI, 4.4-5.7), MM (SIR 1.5, CI, 1.3-17), and ALL/LL (SIR 2.0, CI, 1.3-3.0). There was a trend toward significance for both MPN and HL/NHL, but the lower limit of the confidence intervals for these conditions either crossed or touched 1.
In a review of the literature, the authors found that “[s]everal studies linked AML and MDS to chemotherapeutic agents, radiation treatment, and supportive treatment with granulocyte colony-stimulating factor. These results are consistent with other available data showing a 2½-fold to 3½-fold increased risk of AML.”
They noted that their estimate of a five-fold increase in risk for MDS was higher than the 3.7-fold risk reported in a previous registry cohort analysis, suggesting that risk for MDS among breast cancer patients may be underestimated.
“The recent discovery of the gene signatures that guide treatment decisions in early-stage breast cancer might reduce the number of patients exposed to cytotoxic chemotherapy and its complications, including hematologic malignant neoplasm. Therefore, continuing to monitor hematologic malignant neoplasm trends is necessary, especially given that approaches to cancer treatment are rapidly evolving. Further research is also required to assess the modality of treatment for and the genetic predisposition to these secondary malignant neoplasms,” the authors concluded.
SOURCE: Jabagi MJ et al. JAMA Network Open. 2019 Jan 18. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2018.7147.
FROM JAMA NETWORK OPEN
Key clinical point: Breast cancer survivors should be monitored for hematologic malignancies.
Major finding: The standardized incidence ratio for AML was 2.8 and the SIR for multiple myeloma was 5.0 among French breast cancer survivors compared with women in the general French population.
Study details: Retrospective analysis of data on 439,704 women aged 20-85 years with a breast cancer diagnosis.
Disclosures: The authors did not report a study funding source. Coauthor Anthony Goncalves, MD, reported nonfinancial support from Roche, Novartis, Pfizer, Celgene, MSD, Lilly, and Astra Zeneca outside of the submitted work. No other disclosures were reported.
Source: Jabagi MJ et al. JAMA Network Open. 2019 Jan 18. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2018.7147.
MD Anderson–led alliance seeks to advance leukemia drug development
The primarily for leukemia.
The collaboration, led by Hagop Kantarjian, MD, chair of leukemia at MD Anderson, will use Ascentage’s proprietary Protein-Protein Interaction drug discovery technology platform to develop the company’s apoptosis-targeted and tyrosine kinase inhibitor drug candidates.
The drug candidates will be studied as single-agent therapies and in combinations with other approved or investigational therapeutics. The candidates, chosen for their potential to treat acute myeloid leukemia (AML), chronic myeloid leukemia (CML), acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL), myeloproliferative neoplasms, and myelofibrosis, include:
- HQP1351, a third-generation BCR-ABL inhibitor that has been shown to be safe and “highly active” in treating patients with chronic- or accelerated-phase CML, with or without the T3151 mutation. Preliminary results of the phase 1 study were presented at the 2018 annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology (Abstract 791).
- APG-1252, a highly potent Bcl-2 family inhibitor, has high binding affinities to Bcl-2, Bcl-xL and Bcl-w. It has achieved tumor regression in small cell lung cancer, colon, breast, and ALL xenografts. A phase 1, dose-escalating study is currently being conducted (NCT03387332).
- APG-2575, a selective Bcl-2 inhibitor, is being studied in a phase 1, multicenter, single-agent trial in patients with B-cell hematologic malignancies, including multiple myeloma, chronic lymphocytic leukemia, lymphoplasmacytic lymphoma, non-Hodgkin lymphomas, and AML (NCT03537482).
- APG-1387, an inhibitor of apoptosis protein, is being studied in solid tumors and hematologic malignancies (NCT03386526). Investigators asserted that combining it with an anti–programmed death 1 antibody would be “a very attractive approach” for cancer therapy. In advanced solid tumors it has been well tolerated with manageable adverse events, according to a study presented at the 2018 annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology (Abstract 2593).
- APG-115 is an MDM2-p53 inhibitor that, when combined with radiotherapy, has been shown to enhance the antitumor effect in gastric adenocarcinoma, according to a paper published in the Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research.
“We will be investigating this pipeline of candidate therapies, and we are interested in the novel mechanism of their actions,” Dr. Kantarjian said in a statement.
The primarily for leukemia.
The collaboration, led by Hagop Kantarjian, MD, chair of leukemia at MD Anderson, will use Ascentage’s proprietary Protein-Protein Interaction drug discovery technology platform to develop the company’s apoptosis-targeted and tyrosine kinase inhibitor drug candidates.
The drug candidates will be studied as single-agent therapies and in combinations with other approved or investigational therapeutics. The candidates, chosen for their potential to treat acute myeloid leukemia (AML), chronic myeloid leukemia (CML), acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL), myeloproliferative neoplasms, and myelofibrosis, include:
- HQP1351, a third-generation BCR-ABL inhibitor that has been shown to be safe and “highly active” in treating patients with chronic- or accelerated-phase CML, with or without the T3151 mutation. Preliminary results of the phase 1 study were presented at the 2018 annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology (Abstract 791).
- APG-1252, a highly potent Bcl-2 family inhibitor, has high binding affinities to Bcl-2, Bcl-xL and Bcl-w. It has achieved tumor regression in small cell lung cancer, colon, breast, and ALL xenografts. A phase 1, dose-escalating study is currently being conducted (NCT03387332).
- APG-2575, a selective Bcl-2 inhibitor, is being studied in a phase 1, multicenter, single-agent trial in patients with B-cell hematologic malignancies, including multiple myeloma, chronic lymphocytic leukemia, lymphoplasmacytic lymphoma, non-Hodgkin lymphomas, and AML (NCT03537482).
- APG-1387, an inhibitor of apoptosis protein, is being studied in solid tumors and hematologic malignancies (NCT03386526). Investigators asserted that combining it with an anti–programmed death 1 antibody would be “a very attractive approach” for cancer therapy. In advanced solid tumors it has been well tolerated with manageable adverse events, according to a study presented at the 2018 annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology (Abstract 2593).
- APG-115 is an MDM2-p53 inhibitor that, when combined with radiotherapy, has been shown to enhance the antitumor effect in gastric adenocarcinoma, according to a paper published in the Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research.
“We will be investigating this pipeline of candidate therapies, and we are interested in the novel mechanism of their actions,” Dr. Kantarjian said in a statement.
The primarily for leukemia.
The collaboration, led by Hagop Kantarjian, MD, chair of leukemia at MD Anderson, will use Ascentage’s proprietary Protein-Protein Interaction drug discovery technology platform to develop the company’s apoptosis-targeted and tyrosine kinase inhibitor drug candidates.
The drug candidates will be studied as single-agent therapies and in combinations with other approved or investigational therapeutics. The candidates, chosen for their potential to treat acute myeloid leukemia (AML), chronic myeloid leukemia (CML), acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL), myeloproliferative neoplasms, and myelofibrosis, include:
- HQP1351, a third-generation BCR-ABL inhibitor that has been shown to be safe and “highly active” in treating patients with chronic- or accelerated-phase CML, with or without the T3151 mutation. Preliminary results of the phase 1 study were presented at the 2018 annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology (Abstract 791).
- APG-1252, a highly potent Bcl-2 family inhibitor, has high binding affinities to Bcl-2, Bcl-xL and Bcl-w. It has achieved tumor regression in small cell lung cancer, colon, breast, and ALL xenografts. A phase 1, dose-escalating study is currently being conducted (NCT03387332).
- APG-2575, a selective Bcl-2 inhibitor, is being studied in a phase 1, multicenter, single-agent trial in patients with B-cell hematologic malignancies, including multiple myeloma, chronic lymphocytic leukemia, lymphoplasmacytic lymphoma, non-Hodgkin lymphomas, and AML (NCT03537482).
- APG-1387, an inhibitor of apoptosis protein, is being studied in solid tumors and hematologic malignancies (NCT03386526). Investigators asserted that combining it with an anti–programmed death 1 antibody would be “a very attractive approach” for cancer therapy. In advanced solid tumors it has been well tolerated with manageable adverse events, according to a study presented at the 2018 annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology (Abstract 2593).
- APG-115 is an MDM2-p53 inhibitor that, when combined with radiotherapy, has been shown to enhance the antitumor effect in gastric adenocarcinoma, according to a paper published in the Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research.
“We will be investigating this pipeline of candidate therapies, and we are interested in the novel mechanism of their actions,” Dr. Kantarjian said in a statement.