User login
Addition of atezolizumab to carboplatin+paclitaxel improves pCR in stage II-III TNBC
Key clinical point: Addition of atezolizumab to carboplatin+paclitaxel in the neoadjuvant setting improved the pathological complete response (pCR) rate in patients with stage II-III triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC).
Major finding: After a median follow-up of 6.6 months, a significantly higher proportion of patients achieved pCR in the atezolizumab+chemotherapy vs chemotherapy-only group (55.6% vs 18.8%; P = .018). However, the increase in the percentage of tumor infiltrating lymphocytes was nominal and not significantly different between both groups (P = .36). Grade ≥3 treatment-related adverse events were reported by 62.5% vs 57.8% of patients in the only chemotherapy vs atezolizumab+chemotherapy group, respectively.
Study details: Findings are from the phase 2 NCI-10013 study including 67 patients with previously untreated stage II and III TNBC who were randomly assigned to receive neoadjuvant carboplatin+paclitaxel with or without atezolizumab.
Disclosures: This study was supported by the US National Cancer Institute Cancer Therapy Evaluation Program. Some authors declared receiving research grants or having other financial or non-financial ties with several sources.
Source: Ademuyiwa FO et al. A randomized phase 2 study of neoadjuvant carboplatin and paclitaxel with or without atezolizumab in triple negative breast cancer (TNBC) - NCI 10013. NPJ Breast Cancer. 2022;8(1):134 (Dec 30). Doi: 10.1038/s41523-022-00500-3
Key clinical point: Addition of atezolizumab to carboplatin+paclitaxel in the neoadjuvant setting improved the pathological complete response (pCR) rate in patients with stage II-III triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC).
Major finding: After a median follow-up of 6.6 months, a significantly higher proportion of patients achieved pCR in the atezolizumab+chemotherapy vs chemotherapy-only group (55.6% vs 18.8%; P = .018). However, the increase in the percentage of tumor infiltrating lymphocytes was nominal and not significantly different between both groups (P = .36). Grade ≥3 treatment-related adverse events were reported by 62.5% vs 57.8% of patients in the only chemotherapy vs atezolizumab+chemotherapy group, respectively.
Study details: Findings are from the phase 2 NCI-10013 study including 67 patients with previously untreated stage II and III TNBC who were randomly assigned to receive neoadjuvant carboplatin+paclitaxel with or without atezolizumab.
Disclosures: This study was supported by the US National Cancer Institute Cancer Therapy Evaluation Program. Some authors declared receiving research grants or having other financial or non-financial ties with several sources.
Source: Ademuyiwa FO et al. A randomized phase 2 study of neoadjuvant carboplatin and paclitaxel with or without atezolizumab in triple negative breast cancer (TNBC) - NCI 10013. NPJ Breast Cancer. 2022;8(1):134 (Dec 30). Doi: 10.1038/s41523-022-00500-3
Key clinical point: Addition of atezolizumab to carboplatin+paclitaxel in the neoadjuvant setting improved the pathological complete response (pCR) rate in patients with stage II-III triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC).
Major finding: After a median follow-up of 6.6 months, a significantly higher proportion of patients achieved pCR in the atezolizumab+chemotherapy vs chemotherapy-only group (55.6% vs 18.8%; P = .018). However, the increase in the percentage of tumor infiltrating lymphocytes was nominal and not significantly different between both groups (P = .36). Grade ≥3 treatment-related adverse events were reported by 62.5% vs 57.8% of patients in the only chemotherapy vs atezolizumab+chemotherapy group, respectively.
Study details: Findings are from the phase 2 NCI-10013 study including 67 patients with previously untreated stage II and III TNBC who were randomly assigned to receive neoadjuvant carboplatin+paclitaxel with or without atezolizumab.
Disclosures: This study was supported by the US National Cancer Institute Cancer Therapy Evaluation Program. Some authors declared receiving research grants or having other financial or non-financial ties with several sources.
Source: Ademuyiwa FO et al. A randomized phase 2 study of neoadjuvant carboplatin and paclitaxel with or without atezolizumab in triple negative breast cancer (TNBC) - NCI 10013. NPJ Breast Cancer. 2022;8(1):134 (Dec 30). Doi: 10.1038/s41523-022-00500-3
ER/PgR+ BC: Adjuvant exemestane+ovarian suppression reduces recurrence risk
Key clinical point: Exemestane plus ovarian function suppression (OFS) led to a greater reduction in recurrence risk than tamoxifen+OFS in premenopausal women with estrogen or progesterone receptor-positive (ER/PgR+) early breast cancer (BC).
Major finding: There was a significant improvement in 12-year disease-free survival (hazard ratio [HR] 0.79; P < .001) and distant recurrence-free interval (HR 0.83; P = .03) with exemestane+OFS vs tamoxifen+OFS, with overall survival outcomes (90.1% vs 89.1%) being excellent in both treatment arms.
Study details: Findings are from a combined analysis of the SOFT and TEXT trials including 4690 premenopausal women with ER/PgR+ early BC who were randomly assigned to receive OFS plus exemestane or tamoxifen.
Disclosures: The SOFT and TEXT are supported by ETOP IBCSG (European Thoracic Oncology Platform, International Breast Cancer Study Group) Partners Foundation, Switzerland. The authors declared serving as consultants or advisors or receiving honoraria, research funding, or travel and accommodation expenses from several sources.
Source: Pagani O, Walley BA, et al for the SOFT and TEXT Investigators and the International Breast Cancer Study Group (a division of ETOP IBCSG Partners Foundation). Adjuvant exemestane with ovarian suppression in premenopausal breast cancer: Long-term follow-up of the combined TEXT and SOFT trials. J Clin Oncol. 2022 (Dec 15). Doi: 10.1200/JCO.22.01064
Key clinical point: Exemestane plus ovarian function suppression (OFS) led to a greater reduction in recurrence risk than tamoxifen+OFS in premenopausal women with estrogen or progesterone receptor-positive (ER/PgR+) early breast cancer (BC).
Major finding: There was a significant improvement in 12-year disease-free survival (hazard ratio [HR] 0.79; P < .001) and distant recurrence-free interval (HR 0.83; P = .03) with exemestane+OFS vs tamoxifen+OFS, with overall survival outcomes (90.1% vs 89.1%) being excellent in both treatment arms.
Study details: Findings are from a combined analysis of the SOFT and TEXT trials including 4690 premenopausal women with ER/PgR+ early BC who were randomly assigned to receive OFS plus exemestane or tamoxifen.
Disclosures: The SOFT and TEXT are supported by ETOP IBCSG (European Thoracic Oncology Platform, International Breast Cancer Study Group) Partners Foundation, Switzerland. The authors declared serving as consultants or advisors or receiving honoraria, research funding, or travel and accommodation expenses from several sources.
Source: Pagani O, Walley BA, et al for the SOFT and TEXT Investigators and the International Breast Cancer Study Group (a division of ETOP IBCSG Partners Foundation). Adjuvant exemestane with ovarian suppression in premenopausal breast cancer: Long-term follow-up of the combined TEXT and SOFT trials. J Clin Oncol. 2022 (Dec 15). Doi: 10.1200/JCO.22.01064
Key clinical point: Exemestane plus ovarian function suppression (OFS) led to a greater reduction in recurrence risk than tamoxifen+OFS in premenopausal women with estrogen or progesterone receptor-positive (ER/PgR+) early breast cancer (BC).
Major finding: There was a significant improvement in 12-year disease-free survival (hazard ratio [HR] 0.79; P < .001) and distant recurrence-free interval (HR 0.83; P = .03) with exemestane+OFS vs tamoxifen+OFS, with overall survival outcomes (90.1% vs 89.1%) being excellent in both treatment arms.
Study details: Findings are from a combined analysis of the SOFT and TEXT trials including 4690 premenopausal women with ER/PgR+ early BC who were randomly assigned to receive OFS plus exemestane or tamoxifen.
Disclosures: The SOFT and TEXT are supported by ETOP IBCSG (European Thoracic Oncology Platform, International Breast Cancer Study Group) Partners Foundation, Switzerland. The authors declared serving as consultants or advisors or receiving honoraria, research funding, or travel and accommodation expenses from several sources.
Source: Pagani O, Walley BA, et al for the SOFT and TEXT Investigators and the International Breast Cancer Study Group (a division of ETOP IBCSG Partners Foundation). Adjuvant exemestane with ovarian suppression in premenopausal breast cancer: Long-term follow-up of the combined TEXT and SOFT trials. J Clin Oncol. 2022 (Dec 15). Doi: 10.1200/JCO.22.01064
Adding veliparib to cisplatin improves PFS in BRCA-like metastatic TNBC
Key clinical point: In patients with germline BRCA1/2-wildtype metastatic triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) with a BRCA-like phenotype, cisplatin plus veliparib significantly improved progression-free survival (PFS) without causing any unprecedented adverse events.
Major finding: PFS was significantly improved with cisplatin+veliparib vs cisplatin+placebo (hazard ratio 0.57; log-rank P = .01) in patients with BRCA-like TNBC, but not in germline BRCA1/2-mutated (P = .54) and non-BRCA-like (P = .57) groups. No new toxicity signals were observed.
Study details: Findings are from the phase 2 S1416 study including 320 patients with metastatic TNBC (n = 305) or estrogen receptor (ER)-positive/progesterone receptor (PR)-positive/both ER and PR positive, human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-negative BC (n = 15) who were randomly assigned to receive cisplatin with either veliparib or placebo.
Disclosures: This study was funded by the US National Cancer Institute and other sources. Some authors declared receiving grants, payments, or honoraria from; serving on advisory boards for; or having other financial or non-financial ties with several sources.
Source: Rodler E et al. Cisplatin with veliparib or placebo in metastatic triple-negative breast cancer and BRCA mutation-associated breast cancer (S1416): A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2023 (Jan 6). Doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(22)00739-2
Key clinical point: In patients with germline BRCA1/2-wildtype metastatic triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) with a BRCA-like phenotype, cisplatin plus veliparib significantly improved progression-free survival (PFS) without causing any unprecedented adverse events.
Major finding: PFS was significantly improved with cisplatin+veliparib vs cisplatin+placebo (hazard ratio 0.57; log-rank P = .01) in patients with BRCA-like TNBC, but not in germline BRCA1/2-mutated (P = .54) and non-BRCA-like (P = .57) groups. No new toxicity signals were observed.
Study details: Findings are from the phase 2 S1416 study including 320 patients with metastatic TNBC (n = 305) or estrogen receptor (ER)-positive/progesterone receptor (PR)-positive/both ER and PR positive, human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-negative BC (n = 15) who were randomly assigned to receive cisplatin with either veliparib or placebo.
Disclosures: This study was funded by the US National Cancer Institute and other sources. Some authors declared receiving grants, payments, or honoraria from; serving on advisory boards for; or having other financial or non-financial ties with several sources.
Source: Rodler E et al. Cisplatin with veliparib or placebo in metastatic triple-negative breast cancer and BRCA mutation-associated breast cancer (S1416): A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2023 (Jan 6). Doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(22)00739-2
Key clinical point: In patients with germline BRCA1/2-wildtype metastatic triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) with a BRCA-like phenotype, cisplatin plus veliparib significantly improved progression-free survival (PFS) without causing any unprecedented adverse events.
Major finding: PFS was significantly improved with cisplatin+veliparib vs cisplatin+placebo (hazard ratio 0.57; log-rank P = .01) in patients with BRCA-like TNBC, but not in germline BRCA1/2-mutated (P = .54) and non-BRCA-like (P = .57) groups. No new toxicity signals were observed.
Study details: Findings are from the phase 2 S1416 study including 320 patients with metastatic TNBC (n = 305) or estrogen receptor (ER)-positive/progesterone receptor (PR)-positive/both ER and PR positive, human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-negative BC (n = 15) who were randomly assigned to receive cisplatin with either veliparib or placebo.
Disclosures: This study was funded by the US National Cancer Institute and other sources. Some authors declared receiving grants, payments, or honoraria from; serving on advisory boards for; or having other financial or non-financial ties with several sources.
Source: Rodler E et al. Cisplatin with veliparib or placebo in metastatic triple-negative breast cancer and BRCA mutation-associated breast cancer (S1416): A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2023 (Jan 6). Doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(22)00739-2
Contralateral BC risk elevated in women with germline pathogenic variants
Key clinical point: Women with invasive breast cancer (BC) who have germline pathogenic variants (PV) in BRCA1, BRCA2, CHEK2, or PALB2 have 2-3 times higher risk for contralateral BC than those without these PVs.
Major finding: The overall risk for contralateral BC was significantly elevated in all women with germline PV in BRCA1 (hazard ratio [HR] 2.7; P < .001), BRCA2 (HR 3.0; P < .001), and CHEK2 (HR 1.9; P = .03), and in the subset of women with estrogen receptor-negative BC and germline PV in PALB2 (HR 2.9; P = .006).
Study details: Findings are from an analysis of the CARRIERS study including 15,104 women with invasive BC who underwent ipsilateral surgery.
Disclosures: This study was supported by US National Institutes of Health grants and other sources. The authors declared serving as consultants or advisors and on speakers’ bureaus; receiving research funding, travel, accommodation expenses, or honoraria; and having other ties with several sources.
Source: Yadav S, Boddicker NJ, et al. Contralateral breast cancer risk among carriers of germline pathogenic variants in ATM, BRCA1, BRCA2, CHEK2, and PALB2. J Clin Oncol. 2023 (Jan 9). Doi: 10.1200/JCO.22.01239
Key clinical point: Women with invasive breast cancer (BC) who have germline pathogenic variants (PV) in BRCA1, BRCA2, CHEK2, or PALB2 have 2-3 times higher risk for contralateral BC than those without these PVs.
Major finding: The overall risk for contralateral BC was significantly elevated in all women with germline PV in BRCA1 (hazard ratio [HR] 2.7; P < .001), BRCA2 (HR 3.0; P < .001), and CHEK2 (HR 1.9; P = .03), and in the subset of women with estrogen receptor-negative BC and germline PV in PALB2 (HR 2.9; P = .006).
Study details: Findings are from an analysis of the CARRIERS study including 15,104 women with invasive BC who underwent ipsilateral surgery.
Disclosures: This study was supported by US National Institutes of Health grants and other sources. The authors declared serving as consultants or advisors and on speakers’ bureaus; receiving research funding, travel, accommodation expenses, or honoraria; and having other ties with several sources.
Source: Yadav S, Boddicker NJ, et al. Contralateral breast cancer risk among carriers of germline pathogenic variants in ATM, BRCA1, BRCA2, CHEK2, and PALB2. J Clin Oncol. 2023 (Jan 9). Doi: 10.1200/JCO.22.01239
Key clinical point: Women with invasive breast cancer (BC) who have germline pathogenic variants (PV) in BRCA1, BRCA2, CHEK2, or PALB2 have 2-3 times higher risk for contralateral BC than those without these PVs.
Major finding: The overall risk for contralateral BC was significantly elevated in all women with germline PV in BRCA1 (hazard ratio [HR] 2.7; P < .001), BRCA2 (HR 3.0; P < .001), and CHEK2 (HR 1.9; P = .03), and in the subset of women with estrogen receptor-negative BC and germline PV in PALB2 (HR 2.9; P = .006).
Study details: Findings are from an analysis of the CARRIERS study including 15,104 women with invasive BC who underwent ipsilateral surgery.
Disclosures: This study was supported by US National Institutes of Health grants and other sources. The authors declared serving as consultants or advisors and on speakers’ bureaus; receiving research funding, travel, accommodation expenses, or honoraria; and having other ties with several sources.
Source: Yadav S, Boddicker NJ, et al. Contralateral breast cancer risk among carriers of germline pathogenic variants in ATM, BRCA1, BRCA2, CHEK2, and PALB2. J Clin Oncol. 2023 (Jan 9). Doi: 10.1200/JCO.22.01239
More type 2 diabetes deaths from cancer than heart disease
Cancer appears to have overtaken cardiovascular disease (CVD) as a leading cause of death in adults with type 2 diabetes, a 20-year population study in England suggests.
The researchers found that, from 1998 to 2018, in more than 130,000 adults aged 35 and older with type 2 diabetes, all-cause mortality declined for all ages, but cancer mortality increased for those aged 75 and older; people with type 2 diabetes who were smokers had higher and steadily increasing cancer mortality rates; and people with type 2 diabetes had more than twice the rate of colorectal, pancreatic, liver, and endometrial cancer mortality than age- and sex-matched individuals in the general population.
The findings suggest that “cancer prevention strategies therefore deserve at least a similar level of attention as cardiovascular disease prevention, particularly in older people and for some cancers such as liver, colorectal, and pancreatic cancer,” the researchers wrote.
Tailored cancer prevention and early-detection strategies are needed to address persistent inequalities in the older population, the most deprived, and smokers, they added.
Breast cancer rates in younger women with type 2 diabetes rising
According to the researchers, “early cancer detection through changes to existing screening [programs], or more in-depth investigations for suspected/nonspecific symptoms, may reduce the number of avoidable cancer deaths in people with type 2 diabetes.”
Moreover, breast cancer rates in younger women with type 2 diabetes are rising by 4.1% per year, they wrote, which suggests such women are high risk and should be screened at a younger age, but screening age would need to be determined in cost-effectiveness analyses.
The study by Suping Ling, PhD, and colleagues was published online in Diabetologia.
Results challenge belief that preventing CVD is priority in type 2 diabetes
“The prevention of cardiovascular disease has been, and is still considered, a priority in people with diabetes,” the researchers wrote.
“Our results challenge this view by showing that cancer may have overtaken cardiovascular disease as a leading cause of death in people with type 2 diabetes.”
“The proportion of cancer deaths out of all-cause deaths remains high (> 30%) in young ages, and it was steadily increasing in older ages,” Dr. Ling, from the department of noncommunicable disease epidemiology, London School of Hygiene & Tropical Medicine, said in a comment.
“Combined with previous studies reporting decreasing CVD mortality rates,” she said, “we concluded that cancer might have overtaken CVD as the leading cause of death in people with type 2 diabetes.”
Many evidence-based cancer-prevention strategies related to lifestyle (such as being physically active, being a healthy weight, eating a better diet, stopping smoking, as summarized by the World Cancer Research Fund), are helpful for preventing both cancer and CVD, Ling observed.
However, in the medical community, many additional efforts were made for monitoring, early detection, and innovating medications for CVD, she noted. “Therefore, we would like to propose a similar level of attention and effort for cancer in people with type 2 diabetes.”
Deaths from cancer vs. all causes in patients with diabetes
The researchers identified 137,804 patients aged 35 and older who were newly diagnosed with type 2 diabetes from 1998 to 2018 in general practices in the UK that were part of the Clinical Practice Research Datalink.
Patients were a median age of 64 years and 45% were women. Most (83%) were White, followed by South Asian (3.5%), Black (2.0%), and other (3%); 8.4% had missing information for race. Patients had a median body mass index (BMI) of 30.6 kg/m2.
Researchers divided patients into socioeconomic quintiles of most to least deprived based on income, employment, education, and other factors. During a median follow-up of 8.4 years, there were 39,212 deaths (28.5%).
Cancer mortality in subgroups of patients with type 2 diabetes
Researchers analyzed annual deaths from cancer and from all causes over 20 years in subgroups of patients with type 2 diabetes.
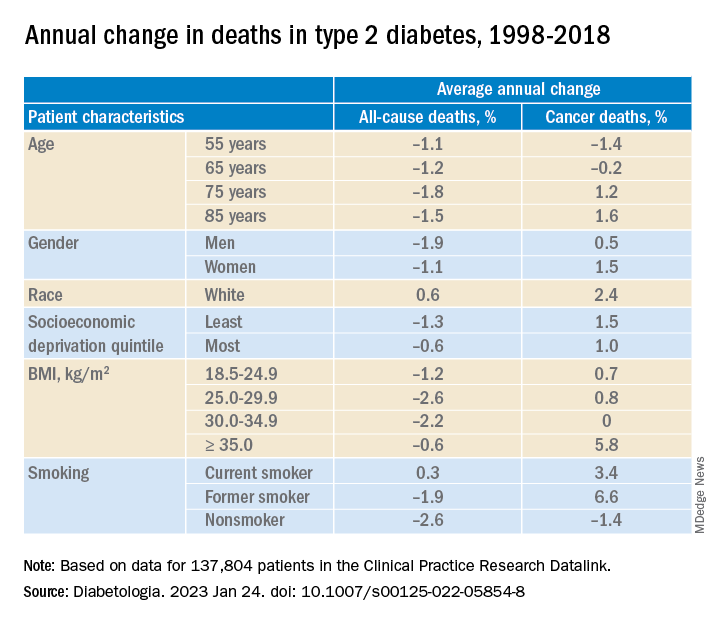
In adults with type 2 diabetes, the average percentage change in cancer mortality per year, from 1998 to 2018 decreased in people aged 55 and 65 (–1.4% and –0.2%, respectively), but increased in people aged 75 and 85 (1.2% and 1.6%, respectively); increased more in women than in men (1.5% vs 1.0%), although women had lower cancer mortality than men; and increased more in the least deprived (wealthiest) individuals than in the most deprived (1.5% vs 1.0%). Cancer mortality rates were consistently higher in the most deprived individuals, Dr. Ling noted.
Cancer mortality also increased more in people with class III obesity (BMI ≥ 35) versus normal weight (5.8% vs 0.7%) and versus other weights. In addition, there was an upward trend in cancer mortality in people who were White or former/current smokers.
Deaths from specific cancers in diabetes vs. general population
Next, researchers determined cancer mortality ratios – the cancer mortality of the patients with diabetes divided by the cancer mortality of the general population.
They determined this for all cancers, the four most common cancers in the United Kingdom (lung, colorectal, breast, and prostate), and cancers caused by type 2 diabetes (pancreatic, liver, gallbladder, and endometrial cancer), standardized by sex and age.
Mortality from all cancer was 18% higher in patients with type 2 diabetes, compared with the general population.
Overall, mortality from colorectal cancer, pancreatic cancer, and liver cancer was 2.4 times, 2.12 times, and 2.13 times higher, respectively, in patients with type 2 diabetes than in the general population.
Mortality from breast cancer was 9% higher and mortality from endometrial cancer was 2.08 times higher in women with type 2 diabetes than in women in the general population.
There was a constant upward trend for mortality rates for pancreatic, liver, and lung cancer at all ages, colorectal cancer at most ages, breast cancer at younger ages, and prostate and endometrial cancer at older ages.
The study was funded by Hope Against Cancer. Dr. Ling reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Cancer appears to have overtaken cardiovascular disease (CVD) as a leading cause of death in adults with type 2 diabetes, a 20-year population study in England suggests.
The researchers found that, from 1998 to 2018, in more than 130,000 adults aged 35 and older with type 2 diabetes, all-cause mortality declined for all ages, but cancer mortality increased for those aged 75 and older; people with type 2 diabetes who were smokers had higher and steadily increasing cancer mortality rates; and people with type 2 diabetes had more than twice the rate of colorectal, pancreatic, liver, and endometrial cancer mortality than age- and sex-matched individuals in the general population.
The findings suggest that “cancer prevention strategies therefore deserve at least a similar level of attention as cardiovascular disease prevention, particularly in older people and for some cancers such as liver, colorectal, and pancreatic cancer,” the researchers wrote.
Tailored cancer prevention and early-detection strategies are needed to address persistent inequalities in the older population, the most deprived, and smokers, they added.
Breast cancer rates in younger women with type 2 diabetes rising
According to the researchers, “early cancer detection through changes to existing screening [programs], or more in-depth investigations for suspected/nonspecific symptoms, may reduce the number of avoidable cancer deaths in people with type 2 diabetes.”
Moreover, breast cancer rates in younger women with type 2 diabetes are rising by 4.1% per year, they wrote, which suggests such women are high risk and should be screened at a younger age, but screening age would need to be determined in cost-effectiveness analyses.
The study by Suping Ling, PhD, and colleagues was published online in Diabetologia.
Results challenge belief that preventing CVD is priority in type 2 diabetes
“The prevention of cardiovascular disease has been, and is still considered, a priority in people with diabetes,” the researchers wrote.
“Our results challenge this view by showing that cancer may have overtaken cardiovascular disease as a leading cause of death in people with type 2 diabetes.”
“The proportion of cancer deaths out of all-cause deaths remains high (> 30%) in young ages, and it was steadily increasing in older ages,” Dr. Ling, from the department of noncommunicable disease epidemiology, London School of Hygiene & Tropical Medicine, said in a comment.
“Combined with previous studies reporting decreasing CVD mortality rates,” she said, “we concluded that cancer might have overtaken CVD as the leading cause of death in people with type 2 diabetes.”
Many evidence-based cancer-prevention strategies related to lifestyle (such as being physically active, being a healthy weight, eating a better diet, stopping smoking, as summarized by the World Cancer Research Fund), are helpful for preventing both cancer and CVD, Ling observed.
However, in the medical community, many additional efforts were made for monitoring, early detection, and innovating medications for CVD, she noted. “Therefore, we would like to propose a similar level of attention and effort for cancer in people with type 2 diabetes.”
Deaths from cancer vs. all causes in patients with diabetes
The researchers identified 137,804 patients aged 35 and older who were newly diagnosed with type 2 diabetes from 1998 to 2018 in general practices in the UK that were part of the Clinical Practice Research Datalink.
Patients were a median age of 64 years and 45% were women. Most (83%) were White, followed by South Asian (3.5%), Black (2.0%), and other (3%); 8.4% had missing information for race. Patients had a median body mass index (BMI) of 30.6 kg/m2.
Researchers divided patients into socioeconomic quintiles of most to least deprived based on income, employment, education, and other factors. During a median follow-up of 8.4 years, there were 39,212 deaths (28.5%).
Cancer mortality in subgroups of patients with type 2 diabetes
Researchers analyzed annual deaths from cancer and from all causes over 20 years in subgroups of patients with type 2 diabetes.

In adults with type 2 diabetes, the average percentage change in cancer mortality per year, from 1998 to 2018 decreased in people aged 55 and 65 (–1.4% and –0.2%, respectively), but increased in people aged 75 and 85 (1.2% and 1.6%, respectively); increased more in women than in men (1.5% vs 1.0%), although women had lower cancer mortality than men; and increased more in the least deprived (wealthiest) individuals than in the most deprived (1.5% vs 1.0%). Cancer mortality rates were consistently higher in the most deprived individuals, Dr. Ling noted.
Cancer mortality also increased more in people with class III obesity (BMI ≥ 35) versus normal weight (5.8% vs 0.7%) and versus other weights. In addition, there was an upward trend in cancer mortality in people who were White or former/current smokers.
Deaths from specific cancers in diabetes vs. general population
Next, researchers determined cancer mortality ratios – the cancer mortality of the patients with diabetes divided by the cancer mortality of the general population.
They determined this for all cancers, the four most common cancers in the United Kingdom (lung, colorectal, breast, and prostate), and cancers caused by type 2 diabetes (pancreatic, liver, gallbladder, and endometrial cancer), standardized by sex and age.
Mortality from all cancer was 18% higher in patients with type 2 diabetes, compared with the general population.
Overall, mortality from colorectal cancer, pancreatic cancer, and liver cancer was 2.4 times, 2.12 times, and 2.13 times higher, respectively, in patients with type 2 diabetes than in the general population.
Mortality from breast cancer was 9% higher and mortality from endometrial cancer was 2.08 times higher in women with type 2 diabetes than in women in the general population.
There was a constant upward trend for mortality rates for pancreatic, liver, and lung cancer at all ages, colorectal cancer at most ages, breast cancer at younger ages, and prostate and endometrial cancer at older ages.
The study was funded by Hope Against Cancer. Dr. Ling reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Cancer appears to have overtaken cardiovascular disease (CVD) as a leading cause of death in adults with type 2 diabetes, a 20-year population study in England suggests.
The researchers found that, from 1998 to 2018, in more than 130,000 adults aged 35 and older with type 2 diabetes, all-cause mortality declined for all ages, but cancer mortality increased for those aged 75 and older; people with type 2 diabetes who were smokers had higher and steadily increasing cancer mortality rates; and people with type 2 diabetes had more than twice the rate of colorectal, pancreatic, liver, and endometrial cancer mortality than age- and sex-matched individuals in the general population.
The findings suggest that “cancer prevention strategies therefore deserve at least a similar level of attention as cardiovascular disease prevention, particularly in older people and for some cancers such as liver, colorectal, and pancreatic cancer,” the researchers wrote.
Tailored cancer prevention and early-detection strategies are needed to address persistent inequalities in the older population, the most deprived, and smokers, they added.
Breast cancer rates in younger women with type 2 diabetes rising
According to the researchers, “early cancer detection through changes to existing screening [programs], or more in-depth investigations for suspected/nonspecific symptoms, may reduce the number of avoidable cancer deaths in people with type 2 diabetes.”
Moreover, breast cancer rates in younger women with type 2 diabetes are rising by 4.1% per year, they wrote, which suggests such women are high risk and should be screened at a younger age, but screening age would need to be determined in cost-effectiveness analyses.
The study by Suping Ling, PhD, and colleagues was published online in Diabetologia.
Results challenge belief that preventing CVD is priority in type 2 diabetes
“The prevention of cardiovascular disease has been, and is still considered, a priority in people with diabetes,” the researchers wrote.
“Our results challenge this view by showing that cancer may have overtaken cardiovascular disease as a leading cause of death in people with type 2 diabetes.”
“The proportion of cancer deaths out of all-cause deaths remains high (> 30%) in young ages, and it was steadily increasing in older ages,” Dr. Ling, from the department of noncommunicable disease epidemiology, London School of Hygiene & Tropical Medicine, said in a comment.
“Combined with previous studies reporting decreasing CVD mortality rates,” she said, “we concluded that cancer might have overtaken CVD as the leading cause of death in people with type 2 diabetes.”
Many evidence-based cancer-prevention strategies related to lifestyle (such as being physically active, being a healthy weight, eating a better diet, stopping smoking, as summarized by the World Cancer Research Fund), are helpful for preventing both cancer and CVD, Ling observed.
However, in the medical community, many additional efforts were made for monitoring, early detection, and innovating medications for CVD, she noted. “Therefore, we would like to propose a similar level of attention and effort for cancer in people with type 2 diabetes.”
Deaths from cancer vs. all causes in patients with diabetes
The researchers identified 137,804 patients aged 35 and older who were newly diagnosed with type 2 diabetes from 1998 to 2018 in general practices in the UK that were part of the Clinical Practice Research Datalink.
Patients were a median age of 64 years and 45% were women. Most (83%) were White, followed by South Asian (3.5%), Black (2.0%), and other (3%); 8.4% had missing information for race. Patients had a median body mass index (BMI) of 30.6 kg/m2.
Researchers divided patients into socioeconomic quintiles of most to least deprived based on income, employment, education, and other factors. During a median follow-up of 8.4 years, there were 39,212 deaths (28.5%).
Cancer mortality in subgroups of patients with type 2 diabetes
Researchers analyzed annual deaths from cancer and from all causes over 20 years in subgroups of patients with type 2 diabetes.

In adults with type 2 diabetes, the average percentage change in cancer mortality per year, from 1998 to 2018 decreased in people aged 55 and 65 (–1.4% and –0.2%, respectively), but increased in people aged 75 and 85 (1.2% and 1.6%, respectively); increased more in women than in men (1.5% vs 1.0%), although women had lower cancer mortality than men; and increased more in the least deprived (wealthiest) individuals than in the most deprived (1.5% vs 1.0%). Cancer mortality rates were consistently higher in the most deprived individuals, Dr. Ling noted.
Cancer mortality also increased more in people with class III obesity (BMI ≥ 35) versus normal weight (5.8% vs 0.7%) and versus other weights. In addition, there was an upward trend in cancer mortality in people who were White or former/current smokers.
Deaths from specific cancers in diabetes vs. general population
Next, researchers determined cancer mortality ratios – the cancer mortality of the patients with diabetes divided by the cancer mortality of the general population.
They determined this for all cancers, the four most common cancers in the United Kingdom (lung, colorectal, breast, and prostate), and cancers caused by type 2 diabetes (pancreatic, liver, gallbladder, and endometrial cancer), standardized by sex and age.
Mortality from all cancer was 18% higher in patients with type 2 diabetes, compared with the general population.
Overall, mortality from colorectal cancer, pancreatic cancer, and liver cancer was 2.4 times, 2.12 times, and 2.13 times higher, respectively, in patients with type 2 diabetes than in the general population.
Mortality from breast cancer was 9% higher and mortality from endometrial cancer was 2.08 times higher in women with type 2 diabetes than in women in the general population.
There was a constant upward trend for mortality rates for pancreatic, liver, and lung cancer at all ages, colorectal cancer at most ages, breast cancer at younger ages, and prostate and endometrial cancer at older ages.
The study was funded by Hope Against Cancer. Dr. Ling reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM DIABETOLOGIA
BC with metabolic abnormalities: No benefit of adding metformin to neoadjuvant chemotherapy
Key clinical point: Addition of metformin to the neoadjuvant docetaxel, epirubicin, and cyclophosphamide (TEC) regimen did not improve disease outcomes in patients with breast cancer (BC) and metabolic abnormalities.
Major finding: The total pathological complete response was achieved by a similar proportion of patients receiving TEC vs TEC+metformin (12.5% vs 14.6%; P = .777). Neutropenia and leucopenia, the most common grade ≥3 adverse events, were reported by 42.5% and 55.0% of patients in the TEC arm and 22.9% and 45.8% of patients in the TEC+metformin arm, respectively.
Study details: Findings are from the phase 2 NeoMET study including 92 patients with stage IIB/III BC and ≥1 metabolic syndrome component who were randomly assigned to receive six cycles of TEC or TEC+metformin.
Disclosures: This study was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China and other sources. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Source: Huang J, Tong Y et al. Neoadjuvant docetaxel, epirubicin, and cyclophosphamide with or without metformin in breast cancer patients with metabolic abnormality: Results from the randomized phase II NeoMET trial. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2022 (Dec 16). Doi: 10.1007/s10549-022-06821-y
Key clinical point: Addition of metformin to the neoadjuvant docetaxel, epirubicin, and cyclophosphamide (TEC) regimen did not improve disease outcomes in patients with breast cancer (BC) and metabolic abnormalities.
Major finding: The total pathological complete response was achieved by a similar proportion of patients receiving TEC vs TEC+metformin (12.5% vs 14.6%; P = .777). Neutropenia and leucopenia, the most common grade ≥3 adverse events, were reported by 42.5% and 55.0% of patients in the TEC arm and 22.9% and 45.8% of patients in the TEC+metformin arm, respectively.
Study details: Findings are from the phase 2 NeoMET study including 92 patients with stage IIB/III BC and ≥1 metabolic syndrome component who were randomly assigned to receive six cycles of TEC or TEC+metformin.
Disclosures: This study was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China and other sources. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Source: Huang J, Tong Y et al. Neoadjuvant docetaxel, epirubicin, and cyclophosphamide with or without metformin in breast cancer patients with metabolic abnormality: Results from the randomized phase II NeoMET trial. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2022 (Dec 16). Doi: 10.1007/s10549-022-06821-y
Key clinical point: Addition of metformin to the neoadjuvant docetaxel, epirubicin, and cyclophosphamide (TEC) regimen did not improve disease outcomes in patients with breast cancer (BC) and metabolic abnormalities.
Major finding: The total pathological complete response was achieved by a similar proportion of patients receiving TEC vs TEC+metformin (12.5% vs 14.6%; P = .777). Neutropenia and leucopenia, the most common grade ≥3 adverse events, were reported by 42.5% and 55.0% of patients in the TEC arm and 22.9% and 45.8% of patients in the TEC+metformin arm, respectively.
Study details: Findings are from the phase 2 NeoMET study including 92 patients with stage IIB/III BC and ≥1 metabolic syndrome component who were randomly assigned to receive six cycles of TEC or TEC+metformin.
Disclosures: This study was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China and other sources. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Source: Huang J, Tong Y et al. Neoadjuvant docetaxel, epirubicin, and cyclophosphamide with or without metformin in breast cancer patients with metabolic abnormality: Results from the randomized phase II NeoMET trial. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2022 (Dec 16). Doi: 10.1007/s10549-022-06821-y
Microcalcifications and high breast density increase risk for breast cancer
Key clinical point: Microcalcifications and breast density, as assessed by the Breast Imaging Reporting and Data System 4th edition (BI-RADS) were associated with a significantly increased risk for breast cancer (BC).
Major finding: Microcalcification appeared to be a significant risk factor for BC irrespective of breast density (adjusted hazard ratio [aHR] 3.09; 95% CI 2.83-3.36). Both microcalcification and high breast density (BI-RADS density classification 4) were associated with a 6.65-fold (95% CI 5.59-7.72) higher risk for BC, with the risk being the highest in postmenopausal women with microcalcifications and high breast density (aHR 7.26; 95% CI 5.01-10.53).
Study details: Findings are from a retrospective cohort study including 3,910,815 women who underwent breast cancer screening, of which 58,315 women were diagnosed with BC during a median follow-up of 10.8 years.
Disclosures: This study was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea and other sources. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Source: Kim S et al. Microcalcifications, mammographic breast density, and risk of breast cancer: A cohort study. Breast Cancer Res. 2022;24:96 (Dec 21). Doi: 10.1186/s13058-022-01594-0
Key clinical point: Microcalcifications and breast density, as assessed by the Breast Imaging Reporting and Data System 4th edition (BI-RADS) were associated with a significantly increased risk for breast cancer (BC).
Major finding: Microcalcification appeared to be a significant risk factor for BC irrespective of breast density (adjusted hazard ratio [aHR] 3.09; 95% CI 2.83-3.36). Both microcalcification and high breast density (BI-RADS density classification 4) were associated with a 6.65-fold (95% CI 5.59-7.72) higher risk for BC, with the risk being the highest in postmenopausal women with microcalcifications and high breast density (aHR 7.26; 95% CI 5.01-10.53).
Study details: Findings are from a retrospective cohort study including 3,910,815 women who underwent breast cancer screening, of which 58,315 women were diagnosed with BC during a median follow-up of 10.8 years.
Disclosures: This study was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea and other sources. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Source: Kim S et al. Microcalcifications, mammographic breast density, and risk of breast cancer: A cohort study. Breast Cancer Res. 2022;24:96 (Dec 21). Doi: 10.1186/s13058-022-01594-0
Key clinical point: Microcalcifications and breast density, as assessed by the Breast Imaging Reporting and Data System 4th edition (BI-RADS) were associated with a significantly increased risk for breast cancer (BC).
Major finding: Microcalcification appeared to be a significant risk factor for BC irrespective of breast density (adjusted hazard ratio [aHR] 3.09; 95% CI 2.83-3.36). Both microcalcification and high breast density (BI-RADS density classification 4) were associated with a 6.65-fold (95% CI 5.59-7.72) higher risk for BC, with the risk being the highest in postmenopausal women with microcalcifications and high breast density (aHR 7.26; 95% CI 5.01-10.53).
Study details: Findings are from a retrospective cohort study including 3,910,815 women who underwent breast cancer screening, of which 58,315 women were diagnosed with BC during a median follow-up of 10.8 years.
Disclosures: This study was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea and other sources. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Source: Kim S et al. Microcalcifications, mammographic breast density, and risk of breast cancer: A cohort study. Breast Cancer Res. 2022;24:96 (Dec 21). Doi: 10.1186/s13058-022-01594-0
Breast cancer: Nipple-sparing mastectomy after neoadjuvant chemotherapy is oncologically safe
Key clinical point: Nipple-sparing mastectomy (NSM), even when performed after neoadjuvant chemotherapy (NACT), resulted in a very low rate of locoregional recurrence and therefore was considered oncologically safe in women with breast cancer (BC).
Major finding: Cumulative incidences of local (P = .570), regional (P = .150), and systemic (P = .87) relapses were similar between patients who received vs did not receive NACT, with no cases of locoregional relapses being reported by the 30.3% of patients who had achieved pathological complete response in the NACT group. The rate of all complications was also similar with vs without NACT.
Study details: Findings are from a retrospective study including 112 cases of NSM after NACT in 111 women and 321 cases of primary NSM in 306 women.
Disclosures: This study was supported by Fondazione Prometeus, ONLUS, Italy. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Source: Meli EZ et al. Nipple-sparing mastectomy after neoadjuvant chemotherapy: Definitive results with a long-term follow-up evaluation. Ann Surg Oncol. 2023 (Jan 4). Doi: 10.1245/s10434-022-13035-5
Key clinical point: Nipple-sparing mastectomy (NSM), even when performed after neoadjuvant chemotherapy (NACT), resulted in a very low rate of locoregional recurrence and therefore was considered oncologically safe in women with breast cancer (BC).
Major finding: Cumulative incidences of local (P = .570), regional (P = .150), and systemic (P = .87) relapses were similar between patients who received vs did not receive NACT, with no cases of locoregional relapses being reported by the 30.3% of patients who had achieved pathological complete response in the NACT group. The rate of all complications was also similar with vs without NACT.
Study details: Findings are from a retrospective study including 112 cases of NSM after NACT in 111 women and 321 cases of primary NSM in 306 women.
Disclosures: This study was supported by Fondazione Prometeus, ONLUS, Italy. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Source: Meli EZ et al. Nipple-sparing mastectomy after neoadjuvant chemotherapy: Definitive results with a long-term follow-up evaluation. Ann Surg Oncol. 2023 (Jan 4). Doi: 10.1245/s10434-022-13035-5
Key clinical point: Nipple-sparing mastectomy (NSM), even when performed after neoadjuvant chemotherapy (NACT), resulted in a very low rate of locoregional recurrence and therefore was considered oncologically safe in women with breast cancer (BC).
Major finding: Cumulative incidences of local (P = .570), regional (P = .150), and systemic (P = .87) relapses were similar between patients who received vs did not receive NACT, with no cases of locoregional relapses being reported by the 30.3% of patients who had achieved pathological complete response in the NACT group. The rate of all complications was also similar with vs without NACT.
Study details: Findings are from a retrospective study including 112 cases of NSM after NACT in 111 women and 321 cases of primary NSM in 306 women.
Disclosures: This study was supported by Fondazione Prometeus, ONLUS, Italy. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Source: Meli EZ et al. Nipple-sparing mastectomy after neoadjuvant chemotherapy: Definitive results with a long-term follow-up evaluation. Ann Surg Oncol. 2023 (Jan 4). Doi: 10.1245/s10434-022-13035-5
HER2+ metastatic BC: Meta-analysis demonstrates superior efficacy of pyrotinib over lapatinib
Key clinical point: Pyrotinib plus chemotherapy outperformed lapatinib plus chemotherapy in terms of improving survival outcomes in patients with human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-positive (HER2+) metastatic breast cancer (BC) but showed a worse toxicity profile.
Major finding: Progression-free survival was significantly improved with pyrotinib vs lapatinib in patients who had received prior trastuzumab therapy (hazard ratio [HR] 0.47; P < .001) and those with trastuzumab resistance (HR 0.52; P < .001). However, the incidence of grade ≥3 diarrhea was higher with pyrotinib vs lapatinib (risk ratio 2.68; P < .001).
Study details: Findings are from a meta-analysis of five studies including 843 patients with metastatic BC who received chemotherapy with pyrotinib (n = 392) or lapatinib (n = 451).
Disclosures: This study did not receive any funding. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Source: Yuan Y et al. Pyrotinib versus lapatinib therapy for HER2 positive metastatic breast cancer patients after first-line treatment failure: A meta-analysis and systematic review. PLoS One. 2023;18(1):e0279775 (Jan 5). Doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0279775
Key clinical point: Pyrotinib plus chemotherapy outperformed lapatinib plus chemotherapy in terms of improving survival outcomes in patients with human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-positive (HER2+) metastatic breast cancer (BC) but showed a worse toxicity profile.
Major finding: Progression-free survival was significantly improved with pyrotinib vs lapatinib in patients who had received prior trastuzumab therapy (hazard ratio [HR] 0.47; P < .001) and those with trastuzumab resistance (HR 0.52; P < .001). However, the incidence of grade ≥3 diarrhea was higher with pyrotinib vs lapatinib (risk ratio 2.68; P < .001).
Study details: Findings are from a meta-analysis of five studies including 843 patients with metastatic BC who received chemotherapy with pyrotinib (n = 392) or lapatinib (n = 451).
Disclosures: This study did not receive any funding. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Source: Yuan Y et al. Pyrotinib versus lapatinib therapy for HER2 positive metastatic breast cancer patients after first-line treatment failure: A meta-analysis and systematic review. PLoS One. 2023;18(1):e0279775 (Jan 5). Doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0279775
Key clinical point: Pyrotinib plus chemotherapy outperformed lapatinib plus chemotherapy in terms of improving survival outcomes in patients with human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-positive (HER2+) metastatic breast cancer (BC) but showed a worse toxicity profile.
Major finding: Progression-free survival was significantly improved with pyrotinib vs lapatinib in patients who had received prior trastuzumab therapy (hazard ratio [HR] 0.47; P < .001) and those with trastuzumab resistance (HR 0.52; P < .001). However, the incidence of grade ≥3 diarrhea was higher with pyrotinib vs lapatinib (risk ratio 2.68; P < .001).
Study details: Findings are from a meta-analysis of five studies including 843 patients with metastatic BC who received chemotherapy with pyrotinib (n = 392) or lapatinib (n = 451).
Disclosures: This study did not receive any funding. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Source: Yuan Y et al. Pyrotinib versus lapatinib therapy for HER2 positive metastatic breast cancer patients after first-line treatment failure: A meta-analysis and systematic review. PLoS One. 2023;18(1):e0279775 (Jan 5). Doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0279775
Improved survival with systemic treatment+local ablative therapy in oligometastatic BC
Key clinical point: Local ablative treatment (LAT) combined with systemic therapy demonstrated superior survival outcomes compared with systemic therapy alone and was well tolerated in patients with oligometastatic breast cancer (BC).
Major finding: LAT+systemic treatment vs only systemic treatment significantly improved progression-free survival (hazard ratio [HR] 0.35; P = .001) and overall survival (HR 0.13; P < .001). LAT was well tolerated, with only one case of grade 3 toxicity being reported.
Study details: Findings are from a retrospective single-center study including 102 patients with oligometastatic BC, of which 62 and 40 patients received systemic treatment and LAT+systemic treatment, respectively.
Disclosures: This study did not receive any funding. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Source: Glemarec G et al. Systemic treatment with or without ablative therapies in oligometastatic breast cancer: A single institution analysis of patient outcomes. Breast. 2022 (Dec 29). Doi: 10.1016/j.breast.2022.12.035
Key clinical point: Local ablative treatment (LAT) combined with systemic therapy demonstrated superior survival outcomes compared with systemic therapy alone and was well tolerated in patients with oligometastatic breast cancer (BC).
Major finding: LAT+systemic treatment vs only systemic treatment significantly improved progression-free survival (hazard ratio [HR] 0.35; P = .001) and overall survival (HR 0.13; P < .001). LAT was well tolerated, with only one case of grade 3 toxicity being reported.
Study details: Findings are from a retrospective single-center study including 102 patients with oligometastatic BC, of which 62 and 40 patients received systemic treatment and LAT+systemic treatment, respectively.
Disclosures: This study did not receive any funding. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Source: Glemarec G et al. Systemic treatment with or without ablative therapies in oligometastatic breast cancer: A single institution analysis of patient outcomes. Breast. 2022 (Dec 29). Doi: 10.1016/j.breast.2022.12.035
Key clinical point: Local ablative treatment (LAT) combined with systemic therapy demonstrated superior survival outcomes compared with systemic therapy alone and was well tolerated in patients with oligometastatic breast cancer (BC).
Major finding: LAT+systemic treatment vs only systemic treatment significantly improved progression-free survival (hazard ratio [HR] 0.35; P = .001) and overall survival (HR 0.13; P < .001). LAT was well tolerated, with only one case of grade 3 toxicity being reported.
Study details: Findings are from a retrospective single-center study including 102 patients with oligometastatic BC, of which 62 and 40 patients received systemic treatment and LAT+systemic treatment, respectively.
Disclosures: This study did not receive any funding. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Source: Glemarec G et al. Systemic treatment with or without ablative therapies in oligometastatic breast cancer: A single institution analysis of patient outcomes. Breast. 2022 (Dec 29). Doi: 10.1016/j.breast.2022.12.035