User login
First CAR T-cell therapy approved in Canada
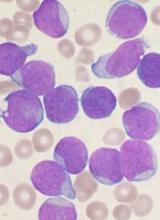
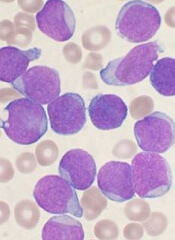
Health Canada has authorized use of tisagenlecleucel (Kymriah™), making it the first chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy to receive regulatory approval in Canada.
Tisagenlecleucel (formerly CTL019) is approved to treat patients ages 3 to 25 with B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) who have relapsed after allogeneic stem cell transplant (SCT) or are otherwise ineligible for SCT, have experienced second or later relapse, or have refractory disease.
Tisagenlecleucel is also approved in Canada to treat adults who have received two or more lines of systemic therapy and have relapsed or refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) not otherwise specified, high grade B-cell lymphoma, or DLBCL arising from follicular lymphoma.
Novartis, the company marketing tisagenlecleucel, said it is working with qualified treatment centers in Canada to prepare for the delivery of tisagenlecleucel. Certification and training are underway at these centers, and Novartis is enhancing manufacturing capacity to meet patient needs.
Tisagenlecleucel has been studied in a pair of phase 2 trials—ELIANA and JULIET.
JULIET trial
JULIET enrolled 165 adults with relapsed/refractory DLBCL, and 111 of them received a single infusion of tisagenlecleucel. Ninety-two percent of patients received bridging therapy, and 93% received lymphodepleting chemotherapy prior to tisagenlecleucel.
The overall response rate was 52%, and the complete response (CR) rate was 40%. The median duration of response was not reached with a median follow-up of 13.9 months. At last follow-up, none of the responders had gone on to SCT.
The 12-month overall survival (OS) rate was 49%, and the median OS was 11.7 months. The median OS was not reached for patients in CR.
Within 8 weeks of tisagenlecleucel infusion, 22% of patients had developed grade 3/4 cytokine release syndrome (CRS). Other adverse events (AEs) of interest included grade 3/4 neurologic events (12%), grade 3/4 cytopenias lasting more than 28 days (32%), grade 3/4 infections (20%), and grade 3/4 febrile neutropenia (15%).
These results were presented at the 23rd Annual Congress of the European Hematology Association in June (abstract S799).
ELIANA trial
ELIANA included 75 children and young adults with relapsed/refractory ALL. The patients’ median age was 11 (range, 3 to 23).
All patients received a single infusion of tisagenlecleucel, and 72 received lymphodepleting chemotherapy.
The median duration of follow-up was 13.1 months. The study’s primary endpoint was overall remission rate, which was defined as the rate of a best overall response of either CR or CR with incomplete hematologic recovery (CRi) within 3 months.
The overall remission rate was 81% (61/75), with 60% of patients (n=45) achieving a CR and 21% (n=16) achieving a CRi. All patients whose best response was CR/CRi were negative for minimal residual disease. The median duration of response was not met.
Eight patients proceeded to SCT while in remission. At last follow-up, four were still in remission, and four had unknown disease status.
At 6 months, the event-free survival rate was 73%, and the OS rate was 90%. At 12 months, the rates were 50% and 76%, respectively.
Ninety-five percent of patients had AEs thought to be related to tisagenlecleucel. The incidence of treatment-related grade 3/4 AEs was 73%.
AEs of special interest included CRS (77%), neurologic events (40%), infections (43%), febrile neutropenia (35%), cytopenias not resolved by day 28 (37%), and tumor lysis syndrome (4%).
These results were published in The New England Journal of Medicine in February.
Health Canada has authorized use of tisagenlecleucel (Kymriah™), making it the first chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy to receive regulatory approval in Canada.
Tisagenlecleucel (formerly CTL019) is approved to treat patients ages 3 to 25 with B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) who have relapsed after allogeneic stem cell transplant (SCT) or are otherwise ineligible for SCT, have experienced second or later relapse, or have refractory disease.
Tisagenlecleucel is also approved in Canada to treat adults who have received two or more lines of systemic therapy and have relapsed or refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) not otherwise specified, high grade B-cell lymphoma, or DLBCL arising from follicular lymphoma.
Novartis, the company marketing tisagenlecleucel, said it is working with qualified treatment centers in Canada to prepare for the delivery of tisagenlecleucel. Certification and training are underway at these centers, and Novartis is enhancing manufacturing capacity to meet patient needs.
Tisagenlecleucel has been studied in a pair of phase 2 trials—ELIANA and JULIET.
JULIET trial
JULIET enrolled 165 adults with relapsed/refractory DLBCL, and 111 of them received a single infusion of tisagenlecleucel. Ninety-two percent of patients received bridging therapy, and 93% received lymphodepleting chemotherapy prior to tisagenlecleucel.
The overall response rate was 52%, and the complete response (CR) rate was 40%. The median duration of response was not reached with a median follow-up of 13.9 months. At last follow-up, none of the responders had gone on to SCT.
The 12-month overall survival (OS) rate was 49%, and the median OS was 11.7 months. The median OS was not reached for patients in CR.
Within 8 weeks of tisagenlecleucel infusion, 22% of patients had developed grade 3/4 cytokine release syndrome (CRS). Other adverse events (AEs) of interest included grade 3/4 neurologic events (12%), grade 3/4 cytopenias lasting more than 28 days (32%), grade 3/4 infections (20%), and grade 3/4 febrile neutropenia (15%).
These results were presented at the 23rd Annual Congress of the European Hematology Association in June (abstract S799).
ELIANA trial
ELIANA included 75 children and young adults with relapsed/refractory ALL. The patients’ median age was 11 (range, 3 to 23).
All patients received a single infusion of tisagenlecleucel, and 72 received lymphodepleting chemotherapy.
The median duration of follow-up was 13.1 months. The study’s primary endpoint was overall remission rate, which was defined as the rate of a best overall response of either CR or CR with incomplete hematologic recovery (CRi) within 3 months.
The overall remission rate was 81% (61/75), with 60% of patients (n=45) achieving a CR and 21% (n=16) achieving a CRi. All patients whose best response was CR/CRi were negative for minimal residual disease. The median duration of response was not met.
Eight patients proceeded to SCT while in remission. At last follow-up, four were still in remission, and four had unknown disease status.
At 6 months, the event-free survival rate was 73%, and the OS rate was 90%. At 12 months, the rates were 50% and 76%, respectively.
Ninety-five percent of patients had AEs thought to be related to tisagenlecleucel. The incidence of treatment-related grade 3/4 AEs was 73%.
AEs of special interest included CRS (77%), neurologic events (40%), infections (43%), febrile neutropenia (35%), cytopenias not resolved by day 28 (37%), and tumor lysis syndrome (4%).
These results were published in The New England Journal of Medicine in February.
Health Canada has authorized use of tisagenlecleucel (Kymriah™), making it the first chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy to receive regulatory approval in Canada.
Tisagenlecleucel (formerly CTL019) is approved to treat patients ages 3 to 25 with B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) who have relapsed after allogeneic stem cell transplant (SCT) or are otherwise ineligible for SCT, have experienced second or later relapse, or have refractory disease.
Tisagenlecleucel is also approved in Canada to treat adults who have received two or more lines of systemic therapy and have relapsed or refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) not otherwise specified, high grade B-cell lymphoma, or DLBCL arising from follicular lymphoma.
Novartis, the company marketing tisagenlecleucel, said it is working with qualified treatment centers in Canada to prepare for the delivery of tisagenlecleucel. Certification and training are underway at these centers, and Novartis is enhancing manufacturing capacity to meet patient needs.
Tisagenlecleucel has been studied in a pair of phase 2 trials—ELIANA and JULIET.
JULIET trial
JULIET enrolled 165 adults with relapsed/refractory DLBCL, and 111 of them received a single infusion of tisagenlecleucel. Ninety-two percent of patients received bridging therapy, and 93% received lymphodepleting chemotherapy prior to tisagenlecleucel.
The overall response rate was 52%, and the complete response (CR) rate was 40%. The median duration of response was not reached with a median follow-up of 13.9 months. At last follow-up, none of the responders had gone on to SCT.
The 12-month overall survival (OS) rate was 49%, and the median OS was 11.7 months. The median OS was not reached for patients in CR.
Within 8 weeks of tisagenlecleucel infusion, 22% of patients had developed grade 3/4 cytokine release syndrome (CRS). Other adverse events (AEs) of interest included grade 3/4 neurologic events (12%), grade 3/4 cytopenias lasting more than 28 days (32%), grade 3/4 infections (20%), and grade 3/4 febrile neutropenia (15%).
These results were presented at the 23rd Annual Congress of the European Hematology Association in June (abstract S799).
ELIANA trial
ELIANA included 75 children and young adults with relapsed/refractory ALL. The patients’ median age was 11 (range, 3 to 23).
All patients received a single infusion of tisagenlecleucel, and 72 received lymphodepleting chemotherapy.
The median duration of follow-up was 13.1 months. The study’s primary endpoint was overall remission rate, which was defined as the rate of a best overall response of either CR or CR with incomplete hematologic recovery (CRi) within 3 months.
The overall remission rate was 81% (61/75), with 60% of patients (n=45) achieving a CR and 21% (n=16) achieving a CRi. All patients whose best response was CR/CRi were negative for minimal residual disease. The median duration of response was not met.
Eight patients proceeded to SCT while in remission. At last follow-up, four were still in remission, and four had unknown disease status.
At 6 months, the event-free survival rate was 73%, and the OS rate was 90%. At 12 months, the rates were 50% and 76%, respectively.
Ninety-five percent of patients had AEs thought to be related to tisagenlecleucel. The incidence of treatment-related grade 3/4 AEs was 73%.
AEs of special interest included CRS (77%), neurologic events (40%), infections (43%), febrile neutropenia (35%), cytopenias not resolved by day 28 (37%), and tumor lysis syndrome (4%).
These results were published in The New England Journal of Medicine in February.
Regimens produce similar results in FL
Rituximab plus lenalidomide had efficacy similar to that of rituximab plus chemotherapy in the treatment of follicular lymphoma (FL) in a phase 3 trial.
Patients with previously untreated FL had similar complete response (CR) rates and progression-free survival (PFS) rates whether they received rituximab-based chemotherapy or rituximab plus lenalidomide.
These results were published in The New England Journal of Medicine.
The trial, RELEVANCE, included 1,030 patients with previously untreated FL. They were randomized to receive rituximab plus chemotherapy (n=517) or rituximab plus lenalidomide (n=513) for 18 cycles.
Patients in the chemotherapy arm received one of three regimens—R-CHOP (rituximab, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone), rituximab and bendamustine, or R-CVP (rituximab, cyclophosphamide, vincristine, and prednisone).
Patients in both treatment arms went on to receive rituximab maintenance every 8 weeks for 12 cycles. The total duration of treatment was 120 weeks. The median age of the combined groups was 59 years.
The coprimary endpoints were CR (confirmed or unconfirmed) and PFS. After a median follow-up of 37.9 months, the rates of coprimary endpoints were similar between the treatment arms.
CR was observed in 48% of the rituximab-lenalidomide arm and 53% of the rituximab-chemotherapy arm (P=0.13).
The interim 3-year PFS rate was 77% in the rituximab-lenalidomide arm and 78% in the rituximab-chemotherapy arm. The hazard ratio for progression or death from any cause was 1.10 (P=0.48).
The efficacy of rituximab plus chemotherapy was greater in low-risk patients (based on Follicular Lymphoma International Prognostic Index scores) and in patients whose disease was Ann Arbor stage I or II, whereas the efficacy of rituximab-lenalidomide was independent of prognostic factors.
Safety was the biggest area of difference, with some adverse events (AEs) being more common in one arm than the other.
AEs that were more common with rituximab-lenalidomide include cutaneous reactions (43% vs 24%), diarrhea (37% vs 19%), rash (29% vs 8%), abdominal pain (15% vs 9%), peripheral edema (14% vs 9%), muscle spasms (13% vs 4%), myalgia (14% vs 6%), and tumor flare reaction (6% vs <1%).
AEs that were more common with rituximab-chemotherapy were anemia (89% vs 66%), fatigue (29% vs 23%), nausea (42% vs 20%), vomiting (19% vs 7%), febrile neutropenia (7% vs 2%), leukopenia (10% vs 4%), and peripheral neuropathy (16% vs 7%).
Grade 3/4 cutaneous reactions were more common with rituximab-lenalidomide (7% vs 1%), and grade 3/4 neutropenia was more common with rituximab-chemotherapy (50% vs 32%).
The RELEVANCE trial was sponsored by Celgene and the Lymphoma Academic Research Organisation. The study authors reported various disclosures, including financial ties to Celgene.
Rituximab plus lenalidomide had efficacy similar to that of rituximab plus chemotherapy in the treatment of follicular lymphoma (FL) in a phase 3 trial.
Patients with previously untreated FL had similar complete response (CR) rates and progression-free survival (PFS) rates whether they received rituximab-based chemotherapy or rituximab plus lenalidomide.
These results were published in The New England Journal of Medicine.
The trial, RELEVANCE, included 1,030 patients with previously untreated FL. They were randomized to receive rituximab plus chemotherapy (n=517) or rituximab plus lenalidomide (n=513) for 18 cycles.
Patients in the chemotherapy arm received one of three regimens—R-CHOP (rituximab, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone), rituximab and bendamustine, or R-CVP (rituximab, cyclophosphamide, vincristine, and prednisone).
Patients in both treatment arms went on to receive rituximab maintenance every 8 weeks for 12 cycles. The total duration of treatment was 120 weeks. The median age of the combined groups was 59 years.
The coprimary endpoints were CR (confirmed or unconfirmed) and PFS. After a median follow-up of 37.9 months, the rates of coprimary endpoints were similar between the treatment arms.
CR was observed in 48% of the rituximab-lenalidomide arm and 53% of the rituximab-chemotherapy arm (P=0.13).
The interim 3-year PFS rate was 77% in the rituximab-lenalidomide arm and 78% in the rituximab-chemotherapy arm. The hazard ratio for progression or death from any cause was 1.10 (P=0.48).
The efficacy of rituximab plus chemotherapy was greater in low-risk patients (based on Follicular Lymphoma International Prognostic Index scores) and in patients whose disease was Ann Arbor stage I or II, whereas the efficacy of rituximab-lenalidomide was independent of prognostic factors.
Safety was the biggest area of difference, with some adverse events (AEs) being more common in one arm than the other.
AEs that were more common with rituximab-lenalidomide include cutaneous reactions (43% vs 24%), diarrhea (37% vs 19%), rash (29% vs 8%), abdominal pain (15% vs 9%), peripheral edema (14% vs 9%), muscle spasms (13% vs 4%), myalgia (14% vs 6%), and tumor flare reaction (6% vs <1%).
AEs that were more common with rituximab-chemotherapy were anemia (89% vs 66%), fatigue (29% vs 23%), nausea (42% vs 20%), vomiting (19% vs 7%), febrile neutropenia (7% vs 2%), leukopenia (10% vs 4%), and peripheral neuropathy (16% vs 7%).
Grade 3/4 cutaneous reactions were more common with rituximab-lenalidomide (7% vs 1%), and grade 3/4 neutropenia was more common with rituximab-chemotherapy (50% vs 32%).
The RELEVANCE trial was sponsored by Celgene and the Lymphoma Academic Research Organisation. The study authors reported various disclosures, including financial ties to Celgene.
Rituximab plus lenalidomide had efficacy similar to that of rituximab plus chemotherapy in the treatment of follicular lymphoma (FL) in a phase 3 trial.
Patients with previously untreated FL had similar complete response (CR) rates and progression-free survival (PFS) rates whether they received rituximab-based chemotherapy or rituximab plus lenalidomide.
These results were published in The New England Journal of Medicine.
The trial, RELEVANCE, included 1,030 patients with previously untreated FL. They were randomized to receive rituximab plus chemotherapy (n=517) or rituximab plus lenalidomide (n=513) for 18 cycles.
Patients in the chemotherapy arm received one of three regimens—R-CHOP (rituximab, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone), rituximab and bendamustine, or R-CVP (rituximab, cyclophosphamide, vincristine, and prednisone).
Patients in both treatment arms went on to receive rituximab maintenance every 8 weeks for 12 cycles. The total duration of treatment was 120 weeks. The median age of the combined groups was 59 years.
The coprimary endpoints were CR (confirmed or unconfirmed) and PFS. After a median follow-up of 37.9 months, the rates of coprimary endpoints were similar between the treatment arms.
CR was observed in 48% of the rituximab-lenalidomide arm and 53% of the rituximab-chemotherapy arm (P=0.13).
The interim 3-year PFS rate was 77% in the rituximab-lenalidomide arm and 78% in the rituximab-chemotherapy arm. The hazard ratio for progression or death from any cause was 1.10 (P=0.48).
The efficacy of rituximab plus chemotherapy was greater in low-risk patients (based on Follicular Lymphoma International Prognostic Index scores) and in patients whose disease was Ann Arbor stage I or II, whereas the efficacy of rituximab-lenalidomide was independent of prognostic factors.
Safety was the biggest area of difference, with some adverse events (AEs) being more common in one arm than the other.
AEs that were more common with rituximab-lenalidomide include cutaneous reactions (43% vs 24%), diarrhea (37% vs 19%), rash (29% vs 8%), abdominal pain (15% vs 9%), peripheral edema (14% vs 9%), muscle spasms (13% vs 4%), myalgia (14% vs 6%), and tumor flare reaction (6% vs <1%).
AEs that were more common with rituximab-chemotherapy were anemia (89% vs 66%), fatigue (29% vs 23%), nausea (42% vs 20%), vomiting (19% vs 7%), febrile neutropenia (7% vs 2%), leukopenia (10% vs 4%), and peripheral neuropathy (16% vs 7%).
Grade 3/4 cutaneous reactions were more common with rituximab-lenalidomide (7% vs 1%), and grade 3/4 neutropenia was more common with rituximab-chemotherapy (50% vs 32%).
The RELEVANCE trial was sponsored by Celgene and the Lymphoma Academic Research Organisation. The study authors reported various disclosures, including financial ties to Celgene.
Ibrutinib maintains efficacy over time
Extended follow-up of the RESONATE-2 trial showed that first-line ibrutinib sustained efficacy in elderly patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL).
Patients who received ibrutinib had a long-term progression-free survival benefit over those who received chlorambucil.
The depth of response to ibrutinib improved over time, which meant there was a substantial increase in the proportion of patients achieving complete response.
Additionally, rates of some serious adverse events associated with ibrutinib decreased over time.
Paul M. Barr, MD, of the University of Rochester in New York, and his colleagues reported these findings in Haematologica.
Previously reported results of the RESONATE-2 trial, which showed an 84% reduction in the risk of death for ibrutinib versus chlorambucil, led to the approval of ibrutinib for first-line CLL treatment, the authors said.
The study included 269 patients with untreated CLL or small lymphocytic lymphoma who had active disease and were at least 65 years of age. They were randomized to receive ibrutinib (n=136) or chlorambucil (n=133).
At a median follow-up of 29 months, 79% (107/136) of patients remained on ibrutinib.
There was an 88% reduction in the risk of progression or death for patients randomized to ibrutinib (P<0.0001).
The rate of complete response improved over time in ibrutinib-treated patients, from 7% at 12 months to 15% at 24 months and 18% at 36 months (maximum follow-up).
The overall response rate (ORR) with ibrutinib was 92%, with comparable findings in high-risk subgroups. The ORR was 100% in patients with del(11q) and 95% in those with unmutated IGHV.
Lymphadenopathy improved in most ibrutinib-treated patients, with complete resolution in 42%, compared to 7% of patients who received chlorambucil.
Splenomegaly improved by at least 50% in 95% of ibrutinib-treated patients and 52% in chlorambucil recipients, with complete resolution in 56% and 22%, respectively.
Adverse events of grade 3 or greater were generally seen more often in the first year of ibrutinib therapy and decreased over time.
The rate of grade 3 or higher neutropenia decreased from 8.1% in the first 12 months of treatment to 0% in the third year. The rate of grade 3 or higher anemia decreased from 5.9% to 1%. And the rate of grade 3 or higher thrombocytopenia decreased from 2.2% to 0%.
The rate of atrial fibrillation increased from 6% in the primary analysis to 10% in extended follow-up. However, investigators said ibrutinib dose reductions and discontinuations because of this adverse event were uncommon and less frequent with extended treatment.
“Atrial fibrillation therefore appears manageable and does not frequently necessitate ibrutinib discontinuation,” they concluded.
This study was supported by Pharmacyclics, an AbbVie company, and by grants from the National Institutes of Health and the MD Anderson Moon Shot Program in CLL. Pharmacyclics designed the study and performed analysis of the data. Several study authors reported funding from various companies, including Pharmacyclics.
Extended follow-up of the RESONATE-2 trial showed that first-line ibrutinib sustained efficacy in elderly patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL).
Patients who received ibrutinib had a long-term progression-free survival benefit over those who received chlorambucil.
The depth of response to ibrutinib improved over time, which meant there was a substantial increase in the proportion of patients achieving complete response.
Additionally, rates of some serious adverse events associated with ibrutinib decreased over time.
Paul M. Barr, MD, of the University of Rochester in New York, and his colleagues reported these findings in Haematologica.
Previously reported results of the RESONATE-2 trial, which showed an 84% reduction in the risk of death for ibrutinib versus chlorambucil, led to the approval of ibrutinib for first-line CLL treatment, the authors said.
The study included 269 patients with untreated CLL or small lymphocytic lymphoma who had active disease and were at least 65 years of age. They were randomized to receive ibrutinib (n=136) or chlorambucil (n=133).
At a median follow-up of 29 months, 79% (107/136) of patients remained on ibrutinib.
There was an 88% reduction in the risk of progression or death for patients randomized to ibrutinib (P<0.0001).
The rate of complete response improved over time in ibrutinib-treated patients, from 7% at 12 months to 15% at 24 months and 18% at 36 months (maximum follow-up).
The overall response rate (ORR) with ibrutinib was 92%, with comparable findings in high-risk subgroups. The ORR was 100% in patients with del(11q) and 95% in those with unmutated IGHV.
Lymphadenopathy improved in most ibrutinib-treated patients, with complete resolution in 42%, compared to 7% of patients who received chlorambucil.
Splenomegaly improved by at least 50% in 95% of ibrutinib-treated patients and 52% in chlorambucil recipients, with complete resolution in 56% and 22%, respectively.
Adverse events of grade 3 or greater were generally seen more often in the first year of ibrutinib therapy and decreased over time.
The rate of grade 3 or higher neutropenia decreased from 8.1% in the first 12 months of treatment to 0% in the third year. The rate of grade 3 or higher anemia decreased from 5.9% to 1%. And the rate of grade 3 or higher thrombocytopenia decreased from 2.2% to 0%.
The rate of atrial fibrillation increased from 6% in the primary analysis to 10% in extended follow-up. However, investigators said ibrutinib dose reductions and discontinuations because of this adverse event were uncommon and less frequent with extended treatment.
“Atrial fibrillation therefore appears manageable and does not frequently necessitate ibrutinib discontinuation,” they concluded.
This study was supported by Pharmacyclics, an AbbVie company, and by grants from the National Institutes of Health and the MD Anderson Moon Shot Program in CLL. Pharmacyclics designed the study and performed analysis of the data. Several study authors reported funding from various companies, including Pharmacyclics.
Extended follow-up of the RESONATE-2 trial showed that first-line ibrutinib sustained efficacy in elderly patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL).
Patients who received ibrutinib had a long-term progression-free survival benefit over those who received chlorambucil.
The depth of response to ibrutinib improved over time, which meant there was a substantial increase in the proportion of patients achieving complete response.
Additionally, rates of some serious adverse events associated with ibrutinib decreased over time.
Paul M. Barr, MD, of the University of Rochester in New York, and his colleagues reported these findings in Haematologica.
Previously reported results of the RESONATE-2 trial, which showed an 84% reduction in the risk of death for ibrutinib versus chlorambucil, led to the approval of ibrutinib for first-line CLL treatment, the authors said.
The study included 269 patients with untreated CLL or small lymphocytic lymphoma who had active disease and were at least 65 years of age. They were randomized to receive ibrutinib (n=136) or chlorambucil (n=133).
At a median follow-up of 29 months, 79% (107/136) of patients remained on ibrutinib.
There was an 88% reduction in the risk of progression or death for patients randomized to ibrutinib (P<0.0001).
The rate of complete response improved over time in ibrutinib-treated patients, from 7% at 12 months to 15% at 24 months and 18% at 36 months (maximum follow-up).
The overall response rate (ORR) with ibrutinib was 92%, with comparable findings in high-risk subgroups. The ORR was 100% in patients with del(11q) and 95% in those with unmutated IGHV.
Lymphadenopathy improved in most ibrutinib-treated patients, with complete resolution in 42%, compared to 7% of patients who received chlorambucil.
Splenomegaly improved by at least 50% in 95% of ibrutinib-treated patients and 52% in chlorambucil recipients, with complete resolution in 56% and 22%, respectively.
Adverse events of grade 3 or greater were generally seen more often in the first year of ibrutinib therapy and decreased over time.
The rate of grade 3 or higher neutropenia decreased from 8.1% in the first 12 months of treatment to 0% in the third year. The rate of grade 3 or higher anemia decreased from 5.9% to 1%. And the rate of grade 3 or higher thrombocytopenia decreased from 2.2% to 0%.
The rate of atrial fibrillation increased from 6% in the primary analysis to 10% in extended follow-up. However, investigators said ibrutinib dose reductions and discontinuations because of this adverse event were uncommon and less frequent with extended treatment.
“Atrial fibrillation therefore appears manageable and does not frequently necessitate ibrutinib discontinuation,” they concluded.
This study was supported by Pharmacyclics, an AbbVie company, and by grants from the National Institutes of Health and the MD Anderson Moon Shot Program in CLL. Pharmacyclics designed the study and performed analysis of the data. Several study authors reported funding from various companies, including Pharmacyclics.
RESONATE-2 update: First-line ibrutinib has sustained efficacy in older CLL patients
In older patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL), first-line treatment with ibrutinib resulted in a long-term progression-free survival benefit versus chemotherapy, according to extended follow-up results of a phase 3 trial.
The quality of response to ibrutinib continued to improve over time in the study, including a substantial increase in the proportion of patients achieving complete response, the updated results of the RESONATE-2 trial show.
Rates of serious adverse events decreased over time in the study, while common reasons for initiating treatment, such as marrow failure and disease symptoms, all improved to a greater extent than with chlorambucil, reported Paul M. Barr, MD, of the University of Rochester (N.Y.) and colleagues.
“These data support the use of ibrutinib in the first-line treatment of CLL as a chemotherapy-free option that can be taken continuously, achieving long-term disease control for the majority of patients, including those with high-risk features,” Dr. Barr and coauthors said in the journal Haematologica.
Previously reported primary results of the RESONATE-2 trial, which showed an 84% reduction in risk of death for ibrutinib versus chlorambucil with a median follow-up of 18 months, led to the approval of ibrutinib for first-line CLL treatment, the authors said.
The study included 269 patients with untreated CLL or small lymphocytic lymphoma who had active disease and were at least 65 years of age. They were randomized 1:1 to ibrutinib or chlorambucil.
Out of 136 ibrutinib-treated patients, 107 (79%) remained on therapy at this extended analysis, which had a median follow-up of 29 months.
The extended analysis also showed an 88% reduction in risk of progression or death for those patients randomized to ibrutinib (P less than .0001), with significant improvements in subgroups evaluated, which include groups typically considered high risk, according to Dr. Barr and colleagues.
The rate of complete response improved over time in ibrutinib-treated patients, from 7% at 12 months, to 15% at 24 months, and to 18% with a maximum of 36 months’ follow-up, they said.
The overall response rate for ibrutinib was 92% in this extended analysis, with comparable findings in high-risk subgroups, including those with del(11q) at 100% and unmutated IGHV at 95%, according to the report.
Lymphadenopathy improved in most ibrutinib-treated patients, with complete resolution in 42% versus 7% with chlorambucil. Splenomegaly improved by at least 50% in 95% of ibrutinib-treated patients versus 52% for chlorambucil, with complete resolution in 56% of ibrutinib-treated patients and 22% of chlorambucil-treated patients.
Adverse events of grade 3 or greater were generally seen more often in the first year of ibrutinib therapy and decreased over time. Rates of grade 3 or greater neutropenia, anemia, and thrombocytopenia were 8.1%, 5.9%, and 2.2%, respectively, in the first 12 months of treatment; those decreased to 0%, 1%, and 0% in the third year.
The rate of atrial fibrillation increased from 6% in the primary analysis to 10% in extended follow-up; however, investigators said ibrutinib dose reductions and discontinuations because of this adverse effect were uncommon and less frequent with extended treatment.
“Atrial fibrillation therefore appears manageable and does not frequently necessitate ibrutinib discontinuation,” they concluded.
The study was supported by Pharmacyclics, an AbbVie company, and by grants from the National Institutes of Health and the MD Anderson Moon Shot Program in CLL. Pharmacyclics designed the study and performed analysis of the data. Several study authors reported funding from various companies, including Pharmacyclics.
SOURCE: Barr PM, et al. Haematologica. 2018;103(9):1502-10.
In older patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL), first-line treatment with ibrutinib resulted in a long-term progression-free survival benefit versus chemotherapy, according to extended follow-up results of a phase 3 trial.
The quality of response to ibrutinib continued to improve over time in the study, including a substantial increase in the proportion of patients achieving complete response, the updated results of the RESONATE-2 trial show.
Rates of serious adverse events decreased over time in the study, while common reasons for initiating treatment, such as marrow failure and disease symptoms, all improved to a greater extent than with chlorambucil, reported Paul M. Barr, MD, of the University of Rochester (N.Y.) and colleagues.
“These data support the use of ibrutinib in the first-line treatment of CLL as a chemotherapy-free option that can be taken continuously, achieving long-term disease control for the majority of patients, including those with high-risk features,” Dr. Barr and coauthors said in the journal Haematologica.
Previously reported primary results of the RESONATE-2 trial, which showed an 84% reduction in risk of death for ibrutinib versus chlorambucil with a median follow-up of 18 months, led to the approval of ibrutinib for first-line CLL treatment, the authors said.
The study included 269 patients with untreated CLL or small lymphocytic lymphoma who had active disease and were at least 65 years of age. They were randomized 1:1 to ibrutinib or chlorambucil.
Out of 136 ibrutinib-treated patients, 107 (79%) remained on therapy at this extended analysis, which had a median follow-up of 29 months.
The extended analysis also showed an 88% reduction in risk of progression or death for those patients randomized to ibrutinib (P less than .0001), with significant improvements in subgroups evaluated, which include groups typically considered high risk, according to Dr. Barr and colleagues.
The rate of complete response improved over time in ibrutinib-treated patients, from 7% at 12 months, to 15% at 24 months, and to 18% with a maximum of 36 months’ follow-up, they said.
The overall response rate for ibrutinib was 92% in this extended analysis, with comparable findings in high-risk subgroups, including those with del(11q) at 100% and unmutated IGHV at 95%, according to the report.
Lymphadenopathy improved in most ibrutinib-treated patients, with complete resolution in 42% versus 7% with chlorambucil. Splenomegaly improved by at least 50% in 95% of ibrutinib-treated patients versus 52% for chlorambucil, with complete resolution in 56% of ibrutinib-treated patients and 22% of chlorambucil-treated patients.
Adverse events of grade 3 or greater were generally seen more often in the first year of ibrutinib therapy and decreased over time. Rates of grade 3 or greater neutropenia, anemia, and thrombocytopenia were 8.1%, 5.9%, and 2.2%, respectively, in the first 12 months of treatment; those decreased to 0%, 1%, and 0% in the third year.
The rate of atrial fibrillation increased from 6% in the primary analysis to 10% in extended follow-up; however, investigators said ibrutinib dose reductions and discontinuations because of this adverse effect were uncommon and less frequent with extended treatment.
“Atrial fibrillation therefore appears manageable and does not frequently necessitate ibrutinib discontinuation,” they concluded.
The study was supported by Pharmacyclics, an AbbVie company, and by grants from the National Institutes of Health and the MD Anderson Moon Shot Program in CLL. Pharmacyclics designed the study and performed analysis of the data. Several study authors reported funding from various companies, including Pharmacyclics.
SOURCE: Barr PM, et al. Haematologica. 2018;103(9):1502-10.
In older patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL), first-line treatment with ibrutinib resulted in a long-term progression-free survival benefit versus chemotherapy, according to extended follow-up results of a phase 3 trial.
The quality of response to ibrutinib continued to improve over time in the study, including a substantial increase in the proportion of patients achieving complete response, the updated results of the RESONATE-2 trial show.
Rates of serious adverse events decreased over time in the study, while common reasons for initiating treatment, such as marrow failure and disease symptoms, all improved to a greater extent than with chlorambucil, reported Paul M. Barr, MD, of the University of Rochester (N.Y.) and colleagues.
“These data support the use of ibrutinib in the first-line treatment of CLL as a chemotherapy-free option that can be taken continuously, achieving long-term disease control for the majority of patients, including those with high-risk features,” Dr. Barr and coauthors said in the journal Haematologica.
Previously reported primary results of the RESONATE-2 trial, which showed an 84% reduction in risk of death for ibrutinib versus chlorambucil with a median follow-up of 18 months, led to the approval of ibrutinib for first-line CLL treatment, the authors said.
The study included 269 patients with untreated CLL or small lymphocytic lymphoma who had active disease and were at least 65 years of age. They were randomized 1:1 to ibrutinib or chlorambucil.
Out of 136 ibrutinib-treated patients, 107 (79%) remained on therapy at this extended analysis, which had a median follow-up of 29 months.
The extended analysis also showed an 88% reduction in risk of progression or death for those patients randomized to ibrutinib (P less than .0001), with significant improvements in subgroups evaluated, which include groups typically considered high risk, according to Dr. Barr and colleagues.
The rate of complete response improved over time in ibrutinib-treated patients, from 7% at 12 months, to 15% at 24 months, and to 18% with a maximum of 36 months’ follow-up, they said.
The overall response rate for ibrutinib was 92% in this extended analysis, with comparable findings in high-risk subgroups, including those with del(11q) at 100% and unmutated IGHV at 95%, according to the report.
Lymphadenopathy improved in most ibrutinib-treated patients, with complete resolution in 42% versus 7% with chlorambucil. Splenomegaly improved by at least 50% in 95% of ibrutinib-treated patients versus 52% for chlorambucil, with complete resolution in 56% of ibrutinib-treated patients and 22% of chlorambucil-treated patients.
Adverse events of grade 3 or greater were generally seen more often in the first year of ibrutinib therapy and decreased over time. Rates of grade 3 or greater neutropenia, anemia, and thrombocytopenia were 8.1%, 5.9%, and 2.2%, respectively, in the first 12 months of treatment; those decreased to 0%, 1%, and 0% in the third year.
The rate of atrial fibrillation increased from 6% in the primary analysis to 10% in extended follow-up; however, investigators said ibrutinib dose reductions and discontinuations because of this adverse effect were uncommon and less frequent with extended treatment.
“Atrial fibrillation therefore appears manageable and does not frequently necessitate ibrutinib discontinuation,” they concluded.
The study was supported by Pharmacyclics, an AbbVie company, and by grants from the National Institutes of Health and the MD Anderson Moon Shot Program in CLL. Pharmacyclics designed the study and performed analysis of the data. Several study authors reported funding from various companies, including Pharmacyclics.
SOURCE: Barr PM, et al. Haematologica. 2018;103(9):1502-10.
FROM HAEMATOLOGICA
Key clinical point:
Major finding: There was an 88% reduction in risk of progression-free survival events for those patients randomized to ibrutinib (P less than .0001).
Study details: Extended phase 3 results from the RESONATE-2 trial, including 269 older patients with untreated CLL or small lymphocytic lymphoma.
Disclosures: This study was supported by Pharmacyclics, an AbbVie company, and by grants from the National Institutes of Health and the MD Anderson Moon Shot Program in CLL. Pharmacyclics designed the study and performed analysis of the data.
Source: Barr PM et al. Haematologica. 2018;103(9):1502-10.
Rituximab/lenalidomide similar to rituximab/chemotherapy for follicular lymphoma
Rituximab plus lenalidomide had efficacy similar to that of rituximab plus chemotherapy in treatment of follicular lymphoma, according to results from a phase 3 trial.
RELEVANCE (NCT01476787) was a multicenter, international, randomized, open-label trial designed to determine the superiority of rituximab/lenalidomide over rituximab/chemotherapy.
This trial randomized 1,030 patients with previously untreated follicular lymphoma to receive either rituximab plus lenalidomide (n = 513) or rituximab plus chemotherapy (n = 517) for 18 cycles; both groups then went on to receive rituximab maintenance therapy for 12 cycles. The total duration of treatment was 120 weeks. The median age of the combined groups was 59 years. The study was published in the New England Journal of Medicine.
One of the coprimary endpoints was complete response (confirmed or unconfirmed) by the end of the treatment period; the other was progression-free survival, which was planned to be assessed through three analyses, including two interim analyses, the first of which was reported in this study.
After a median follow-up of 37.9 months, the rates of coprimary endpoints were similar between the two groups. Complete response (confirmed or unconfirmed) was seen in 48% of the rituximab/lenalidomide group (95% confidence interval [CI], 44-53) and in 53% of the rituximab/chemotherapy group (95% CI, 49-57; P = .13). The hazard ratio for progression or death from any cause was 1.10 (95% CI, 0.85-1.43; P = .48).
In the subgroup analyses, the efficacy of rituximab plus chemotherapy was greater in low-risk patients (based on Follicular Lymphoma International Prognostic Index scores) and in patients whose follicular lymphoma was Ann Arbor stage I or II, whereas efficacy of rituximab/lenalidomide was independent of prognostic factors.
Safety was the biggest area of difference, with some events being more common in one group than in the other. For example, cutaneous reactions, diarrhea, rash, and myalgia were more common with rituximab/lenalidomide treatment, whereas anemia, fatigue, nausea, and febrile neutropenia were more common with rituximab/chemotherapy treatment. Among grade 3 or 4 events, cutaneous reactions were more common with rituximab/lenalidomide, and grade 3 or 4 neutropenia was more common with rituximab/chemotherapy.
“Overall, both treatment groups showed good outcomes, and a median has not yet been reached for either progression-free survival or overall survival,” the study authors wrote.
The RELEVANCE trial was sponsored by Celgene and the Lymphoma Academic Research Organisation. The study authors reported various disclosures, including financial ties to Celgene.
SOURCE: Morschhauser F et al. N Engl J Med. 2018;379:934-47.
Rituximab plus lenalidomide had efficacy similar to that of rituximab plus chemotherapy in treatment of follicular lymphoma, according to results from a phase 3 trial.
RELEVANCE (NCT01476787) was a multicenter, international, randomized, open-label trial designed to determine the superiority of rituximab/lenalidomide over rituximab/chemotherapy.
This trial randomized 1,030 patients with previously untreated follicular lymphoma to receive either rituximab plus lenalidomide (n = 513) or rituximab plus chemotherapy (n = 517) for 18 cycles; both groups then went on to receive rituximab maintenance therapy for 12 cycles. The total duration of treatment was 120 weeks. The median age of the combined groups was 59 years. The study was published in the New England Journal of Medicine.
One of the coprimary endpoints was complete response (confirmed or unconfirmed) by the end of the treatment period; the other was progression-free survival, which was planned to be assessed through three analyses, including two interim analyses, the first of which was reported in this study.
After a median follow-up of 37.9 months, the rates of coprimary endpoints were similar between the two groups. Complete response (confirmed or unconfirmed) was seen in 48% of the rituximab/lenalidomide group (95% confidence interval [CI], 44-53) and in 53% of the rituximab/chemotherapy group (95% CI, 49-57; P = .13). The hazard ratio for progression or death from any cause was 1.10 (95% CI, 0.85-1.43; P = .48).
In the subgroup analyses, the efficacy of rituximab plus chemotherapy was greater in low-risk patients (based on Follicular Lymphoma International Prognostic Index scores) and in patients whose follicular lymphoma was Ann Arbor stage I or II, whereas efficacy of rituximab/lenalidomide was independent of prognostic factors.
Safety was the biggest area of difference, with some events being more common in one group than in the other. For example, cutaneous reactions, diarrhea, rash, and myalgia were more common with rituximab/lenalidomide treatment, whereas anemia, fatigue, nausea, and febrile neutropenia were more common with rituximab/chemotherapy treatment. Among grade 3 or 4 events, cutaneous reactions were more common with rituximab/lenalidomide, and grade 3 or 4 neutropenia was more common with rituximab/chemotherapy.
“Overall, both treatment groups showed good outcomes, and a median has not yet been reached for either progression-free survival or overall survival,” the study authors wrote.
The RELEVANCE trial was sponsored by Celgene and the Lymphoma Academic Research Organisation. The study authors reported various disclosures, including financial ties to Celgene.
SOURCE: Morschhauser F et al. N Engl J Med. 2018;379:934-47.
Rituximab plus lenalidomide had efficacy similar to that of rituximab plus chemotherapy in treatment of follicular lymphoma, according to results from a phase 3 trial.
RELEVANCE (NCT01476787) was a multicenter, international, randomized, open-label trial designed to determine the superiority of rituximab/lenalidomide over rituximab/chemotherapy.
This trial randomized 1,030 patients with previously untreated follicular lymphoma to receive either rituximab plus lenalidomide (n = 513) or rituximab plus chemotherapy (n = 517) for 18 cycles; both groups then went on to receive rituximab maintenance therapy for 12 cycles. The total duration of treatment was 120 weeks. The median age of the combined groups was 59 years. The study was published in the New England Journal of Medicine.
One of the coprimary endpoints was complete response (confirmed or unconfirmed) by the end of the treatment period; the other was progression-free survival, which was planned to be assessed through three analyses, including two interim analyses, the first of which was reported in this study.
After a median follow-up of 37.9 months, the rates of coprimary endpoints were similar between the two groups. Complete response (confirmed or unconfirmed) was seen in 48% of the rituximab/lenalidomide group (95% confidence interval [CI], 44-53) and in 53% of the rituximab/chemotherapy group (95% CI, 49-57; P = .13). The hazard ratio for progression or death from any cause was 1.10 (95% CI, 0.85-1.43; P = .48).
In the subgroup analyses, the efficacy of rituximab plus chemotherapy was greater in low-risk patients (based on Follicular Lymphoma International Prognostic Index scores) and in patients whose follicular lymphoma was Ann Arbor stage I or II, whereas efficacy of rituximab/lenalidomide was independent of prognostic factors.
Safety was the biggest area of difference, with some events being more common in one group than in the other. For example, cutaneous reactions, diarrhea, rash, and myalgia were more common with rituximab/lenalidomide treatment, whereas anemia, fatigue, nausea, and febrile neutropenia were more common with rituximab/chemotherapy treatment. Among grade 3 or 4 events, cutaneous reactions were more common with rituximab/lenalidomide, and grade 3 or 4 neutropenia was more common with rituximab/chemotherapy.
“Overall, both treatment groups showed good outcomes, and a median has not yet been reached for either progression-free survival or overall survival,” the study authors wrote.
The RELEVANCE trial was sponsored by Celgene and the Lymphoma Academic Research Organisation. The study authors reported various disclosures, including financial ties to Celgene.
SOURCE: Morschhauser F et al. N Engl J Med. 2018;379:934-47.
FROM THE NEW ENGLAND JOURNAL OF MEDICINE
Key clinical point:
Major finding: Complete responses were seen in 48% of rituximab/lenalidomide patients versus 53% in the rituximab/chemotherapy patients (P = .13).
Study details: A phase 3 superiority trial of 1,030 patients with previously untreated follicular lymphoma.
Disclosures: Celgene and the Lymphoma Academic Research Organization funded the study. The authors reported various disclosures, including financial ties to Celgene.
Source: Morschhauser F et al. N Engl J Med. 2018;379:934-47.
Escalating methotrexate may improve survival in T-cell ALL
An escalating methotrexate strategy provided superior survival outcomes compared with high-dose methotrexate in a chemotherapy regimen for children and young adults with T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (T-ALL), results of a large, randomized trial show.
There were also fewer relapses reported for escalating versus high-dose methotrexate in the study, which evaluated the effects of these two intensification strategies in patients receiving an augmented Berlin-Frankfurt-Muenster (ABFM) chemotherapy regimen.
These findings come from a report in the Journal of Clinical Oncology on the Children’s Oncology Group (COG) AALL0434 trial, which to the knowledge of the investigators is the largest T-ALL study ever conducted.
The improved survival outcomes in AALL0434 are the “opposite effect” of what was observed in a parallel trial, AALL0232, showing that high-dose methotrexate was superior to the escalating strategy in B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (B-ALL), the authors reported.
The parallel trial design was in fact used because of the known differences between T-ALL and B-ALL in sensitivity to methotrexate and pegaspargase, according to investigator Stuart S. Winter, MD, of Children’s Minnesota Cancer and Blood Disorders Program, Minneapolis, and his coauthors.
“Although treatment intensification has improved survival for children with ALL, the best timing and sequence of key therapeutic interventions, such as asparaginase and methotrexate, which seem to be particularly important for T-ALL, remain unclear,” Dr. Winter and his colleagues said.
In the AALL0434 study, a total of 1,031 T-ALL patients between 1 and 31 years of age without CNS3 disease or testicular leukemia were randomized to postinduction therapy that included either the so-called Capizzi-style escalating intravenous methotrexate or high-dose methotrexate.
The escalating intravenous regimen was superior to high-dose methotrexate, according to investigators. Respectively, the 5-year rate of disease-free survival was 91.5% versus 85.3% (P = .005) and the 5-year rate of overall survival was 93.7% versus 89.4% (P = .036).
Relapses were observed in 32 patients receiving the escalating regimen, versus 59 for patients receiving high-dose methotrexate.
By contrast, the parallel AALL0232 study of B-ALL patients showed that high-dose methotrexate had superior 5-year event-free survival and overall survival, leading Dr. Winter and his colleagues to speculate on how the findings could be reconciled.
Neither trial was a strict comparison of two different methotrexate schedules, due to differences in doses of pegaspargase, 6-MP, and vincristine between arms, as well as differences in the timing of cranial radiation therapy.
Of note, patients randomized to escalated methotrexate had two additional doses of pegaspargase. As a result, enhanced asparagine depletion in that arm may have also prevented relapse events, the investigators said.
Differences in adherence could also have played a role, as the cost and time burden of the escalated approach are “substantially less” than the high-dose approach, they added.
The AALL0434 trial also included a second randomization to an addition of five, 6-day cycles of nelarabine versus no nelarabine. Results of that randomization, reported earlier this year, showed that nelarabine improved disease-free survival, including a 91% 4-year disease-free survival rate for patients receiving both nelarabine and escalating-dose methotrexate.
The study was supported by grants from the National Institutes of Health and by St. Baldrick’s Foundation. Dr. Winter reported relationships with Amgen and Jazz Pharmaceuticals. Study coauthors reported relationships with Novo Nordisk, Tandem, Pfizer, Novartis, and TypeZero Technologies, among others.
SOURCE: Winter SS et al. J Clin Oncol. 2018 Aug 23: doi: 10.1200/JCO.2018.77.7250.
An escalating methotrexate strategy provided superior survival outcomes compared with high-dose methotrexate in a chemotherapy regimen for children and young adults with T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (T-ALL), results of a large, randomized trial show.
There were also fewer relapses reported for escalating versus high-dose methotrexate in the study, which evaluated the effects of these two intensification strategies in patients receiving an augmented Berlin-Frankfurt-Muenster (ABFM) chemotherapy regimen.
These findings come from a report in the Journal of Clinical Oncology on the Children’s Oncology Group (COG) AALL0434 trial, which to the knowledge of the investigators is the largest T-ALL study ever conducted.
The improved survival outcomes in AALL0434 are the “opposite effect” of what was observed in a parallel trial, AALL0232, showing that high-dose methotrexate was superior to the escalating strategy in B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (B-ALL), the authors reported.
The parallel trial design was in fact used because of the known differences between T-ALL and B-ALL in sensitivity to methotrexate and pegaspargase, according to investigator Stuart S. Winter, MD, of Children’s Minnesota Cancer and Blood Disorders Program, Minneapolis, and his coauthors.
“Although treatment intensification has improved survival for children with ALL, the best timing and sequence of key therapeutic interventions, such as asparaginase and methotrexate, which seem to be particularly important for T-ALL, remain unclear,” Dr. Winter and his colleagues said.
In the AALL0434 study, a total of 1,031 T-ALL patients between 1 and 31 years of age without CNS3 disease or testicular leukemia were randomized to postinduction therapy that included either the so-called Capizzi-style escalating intravenous methotrexate or high-dose methotrexate.
The escalating intravenous regimen was superior to high-dose methotrexate, according to investigators. Respectively, the 5-year rate of disease-free survival was 91.5% versus 85.3% (P = .005) and the 5-year rate of overall survival was 93.7% versus 89.4% (P = .036).
Relapses were observed in 32 patients receiving the escalating regimen, versus 59 for patients receiving high-dose methotrexate.
By contrast, the parallel AALL0232 study of B-ALL patients showed that high-dose methotrexate had superior 5-year event-free survival and overall survival, leading Dr. Winter and his colleagues to speculate on how the findings could be reconciled.
Neither trial was a strict comparison of two different methotrexate schedules, due to differences in doses of pegaspargase, 6-MP, and vincristine between arms, as well as differences in the timing of cranial radiation therapy.
Of note, patients randomized to escalated methotrexate had two additional doses of pegaspargase. As a result, enhanced asparagine depletion in that arm may have also prevented relapse events, the investigators said.
Differences in adherence could also have played a role, as the cost and time burden of the escalated approach are “substantially less” than the high-dose approach, they added.
The AALL0434 trial also included a second randomization to an addition of five, 6-day cycles of nelarabine versus no nelarabine. Results of that randomization, reported earlier this year, showed that nelarabine improved disease-free survival, including a 91% 4-year disease-free survival rate for patients receiving both nelarabine and escalating-dose methotrexate.
The study was supported by grants from the National Institutes of Health and by St. Baldrick’s Foundation. Dr. Winter reported relationships with Amgen and Jazz Pharmaceuticals. Study coauthors reported relationships with Novo Nordisk, Tandem, Pfizer, Novartis, and TypeZero Technologies, among others.
SOURCE: Winter SS et al. J Clin Oncol. 2018 Aug 23: doi: 10.1200/JCO.2018.77.7250.
An escalating methotrexate strategy provided superior survival outcomes compared with high-dose methotrexate in a chemotherapy regimen for children and young adults with T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (T-ALL), results of a large, randomized trial show.
There were also fewer relapses reported for escalating versus high-dose methotrexate in the study, which evaluated the effects of these two intensification strategies in patients receiving an augmented Berlin-Frankfurt-Muenster (ABFM) chemotherapy regimen.
These findings come from a report in the Journal of Clinical Oncology on the Children’s Oncology Group (COG) AALL0434 trial, which to the knowledge of the investigators is the largest T-ALL study ever conducted.
The improved survival outcomes in AALL0434 are the “opposite effect” of what was observed in a parallel trial, AALL0232, showing that high-dose methotrexate was superior to the escalating strategy in B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (B-ALL), the authors reported.
The parallel trial design was in fact used because of the known differences between T-ALL and B-ALL in sensitivity to methotrexate and pegaspargase, according to investigator Stuart S. Winter, MD, of Children’s Minnesota Cancer and Blood Disorders Program, Minneapolis, and his coauthors.
“Although treatment intensification has improved survival for children with ALL, the best timing and sequence of key therapeutic interventions, such as asparaginase and methotrexate, which seem to be particularly important for T-ALL, remain unclear,” Dr. Winter and his colleagues said.
In the AALL0434 study, a total of 1,031 T-ALL patients between 1 and 31 years of age without CNS3 disease or testicular leukemia were randomized to postinduction therapy that included either the so-called Capizzi-style escalating intravenous methotrexate or high-dose methotrexate.
The escalating intravenous regimen was superior to high-dose methotrexate, according to investigators. Respectively, the 5-year rate of disease-free survival was 91.5% versus 85.3% (P = .005) and the 5-year rate of overall survival was 93.7% versus 89.4% (P = .036).
Relapses were observed in 32 patients receiving the escalating regimen, versus 59 for patients receiving high-dose methotrexate.
By contrast, the parallel AALL0232 study of B-ALL patients showed that high-dose methotrexate had superior 5-year event-free survival and overall survival, leading Dr. Winter and his colleagues to speculate on how the findings could be reconciled.
Neither trial was a strict comparison of two different methotrexate schedules, due to differences in doses of pegaspargase, 6-MP, and vincristine between arms, as well as differences in the timing of cranial radiation therapy.
Of note, patients randomized to escalated methotrexate had two additional doses of pegaspargase. As a result, enhanced asparagine depletion in that arm may have also prevented relapse events, the investigators said.
Differences in adherence could also have played a role, as the cost and time burden of the escalated approach are “substantially less” than the high-dose approach, they added.
The AALL0434 trial also included a second randomization to an addition of five, 6-day cycles of nelarabine versus no nelarabine. Results of that randomization, reported earlier this year, showed that nelarabine improved disease-free survival, including a 91% 4-year disease-free survival rate for patients receiving both nelarabine and escalating-dose methotrexate.
The study was supported by grants from the National Institutes of Health and by St. Baldrick’s Foundation. Dr. Winter reported relationships with Amgen and Jazz Pharmaceuticals. Study coauthors reported relationships with Novo Nordisk, Tandem, Pfizer, Novartis, and TypeZero Technologies, among others.
SOURCE: Winter SS et al. J Clin Oncol. 2018 Aug 23: doi: 10.1200/JCO.2018.77.7250.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF CLINICAL ONCOLOGY
Key clinical point: An (T-ALL).
Major finding: The 5-year disease-free survival rate was 91.5% versus 85.3% (P = .005) and overall survival was 93.7% versus 89.4% (P = .036), respectively, for the escalating and high-dose approaches.
Study details: Results after methotrexate randomization in 1,031 T-ALL patients without CNS3 disease or testicular leukemia in the Children’s Oncology Group (COG) AALL0434 trial.
Disclosures: The study was supported by grants from the National Institutes of Health and by St. Baldrick’s Foundation. The authors reported disclosures related to Amgen, Jazz Pharmaceuticals, Novo Nordisk, Tandem, Pfizer, Novartis, and TypeZero Technologies, among others.
Source: Winter SS et al. J Clin Oncol. 2018 Aug 23. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2018.77.7250.
TYK2 inhibitors could treat ALCL, team says
Preclinical research indicates that TYK2 inhibitors could be effective in treating anaplastic large-cell lymphoma (ALCL).
Researchers found evidence to suggest that TYK2 “is highly expressed in all cases of human ALCL.”
The team also discovered that TYK2 inhibition induces apoptosis in ALCL cells, and it delays tumor onset and prolongs survival in a mouse model of ALCL.
Olaf Merkel, PhD, of the Medical University of Vienna in Austria, and his colleagues detailed these findings in Leukemia.
The researchers said their analyses suggest TYK2 is expressed in all types of ALCL, regardless of ALK status, and TYK2 mediates the same anti-apoptotic response across ALCLs.
“Therefore, we could consider TYK2 signaling as the Achilles’ heel of ALCL, as, in all patients we have analyzed, the tumor cells relied on this activity to support the essential survival signal,” Dr. Merkel said.
He and his colleagues found that disrupting TYK2—either via gene knockdown or with small-molecule TYK2 inhibitors—induced apoptosis in human ALCL cells in vitro.
In a mouse model of NPM-ALK-induced lymphoma, Tyk2 deletion slowed the rate of tumor growth and significantly prolonged survival. The median survival was 53.3 weeks in mice with Tyk2 deletion and 16.0 weeks in control mice (P<0.0001).
Additional experiments in human ALCL cell lines showed that “TYK2 is activated by autocrine production of IL-10 and IL-22 and by interaction with specific receptors expressed by the cells,” the researchers said.
They also found that “activated TYK2 leads to STAT1 and STAT3 phosphorylation, activated expression of MCL1, and aberrant ALCL cell survival.”
Taking these findings together, the researchers concluded that TYK2 inhibitors could be effective for treating ALCL.
“We are looking forward to TYK2 inhibitors becoming available . . . ,” said study author Lukas Kenner, MD, of the Medical University of Vienna.
“[I]n the more rare lymphomas, we urgently need better therapies.”
Preclinical research indicates that TYK2 inhibitors could be effective in treating anaplastic large-cell lymphoma (ALCL).
Researchers found evidence to suggest that TYK2 “is highly expressed in all cases of human ALCL.”
The team also discovered that TYK2 inhibition induces apoptosis in ALCL cells, and it delays tumor onset and prolongs survival in a mouse model of ALCL.
Olaf Merkel, PhD, of the Medical University of Vienna in Austria, and his colleagues detailed these findings in Leukemia.
The researchers said their analyses suggest TYK2 is expressed in all types of ALCL, regardless of ALK status, and TYK2 mediates the same anti-apoptotic response across ALCLs.
“Therefore, we could consider TYK2 signaling as the Achilles’ heel of ALCL, as, in all patients we have analyzed, the tumor cells relied on this activity to support the essential survival signal,” Dr. Merkel said.
He and his colleagues found that disrupting TYK2—either via gene knockdown or with small-molecule TYK2 inhibitors—induced apoptosis in human ALCL cells in vitro.
In a mouse model of NPM-ALK-induced lymphoma, Tyk2 deletion slowed the rate of tumor growth and significantly prolonged survival. The median survival was 53.3 weeks in mice with Tyk2 deletion and 16.0 weeks in control mice (P<0.0001).
Additional experiments in human ALCL cell lines showed that “TYK2 is activated by autocrine production of IL-10 and IL-22 and by interaction with specific receptors expressed by the cells,” the researchers said.
They also found that “activated TYK2 leads to STAT1 and STAT3 phosphorylation, activated expression of MCL1, and aberrant ALCL cell survival.”
Taking these findings together, the researchers concluded that TYK2 inhibitors could be effective for treating ALCL.
“We are looking forward to TYK2 inhibitors becoming available . . . ,” said study author Lukas Kenner, MD, of the Medical University of Vienna.
“[I]n the more rare lymphomas, we urgently need better therapies.”
Preclinical research indicates that TYK2 inhibitors could be effective in treating anaplastic large-cell lymphoma (ALCL).
Researchers found evidence to suggest that TYK2 “is highly expressed in all cases of human ALCL.”
The team also discovered that TYK2 inhibition induces apoptosis in ALCL cells, and it delays tumor onset and prolongs survival in a mouse model of ALCL.
Olaf Merkel, PhD, of the Medical University of Vienna in Austria, and his colleagues detailed these findings in Leukemia.
The researchers said their analyses suggest TYK2 is expressed in all types of ALCL, regardless of ALK status, and TYK2 mediates the same anti-apoptotic response across ALCLs.
“Therefore, we could consider TYK2 signaling as the Achilles’ heel of ALCL, as, in all patients we have analyzed, the tumor cells relied on this activity to support the essential survival signal,” Dr. Merkel said.
He and his colleagues found that disrupting TYK2—either via gene knockdown or with small-molecule TYK2 inhibitors—induced apoptosis in human ALCL cells in vitro.
In a mouse model of NPM-ALK-induced lymphoma, Tyk2 deletion slowed the rate of tumor growth and significantly prolonged survival. The median survival was 53.3 weeks in mice with Tyk2 deletion and 16.0 weeks in control mice (P<0.0001).
Additional experiments in human ALCL cell lines showed that “TYK2 is activated by autocrine production of IL-10 and IL-22 and by interaction with specific receptors expressed by the cells,” the researchers said.
They also found that “activated TYK2 leads to STAT1 and STAT3 phosphorylation, activated expression of MCL1, and aberrant ALCL cell survival.”
Taking these findings together, the researchers concluded that TYK2 inhibitors could be effective for treating ALCL.
“We are looking forward to TYK2 inhibitors becoming available . . . ,” said study author Lukas Kenner, MD, of the Medical University of Vienna.
“[I]n the more rare lymphomas, we urgently need better therapies.”
Daratumumab approved in Europe for new myeloma indication
The drug is now authorized for use in combination with bortezomib, melphalan, and prednisone (VMP) to treat adults with newly diagnosed multiple myeloma (MM) who are ineligible for autologous stem cell transplant, according to a press release published on the Genmab website.
Daratumumab was previously approved by the European Commission (EC) for use in combination with lenalidomide and dexamethasone or bortezomib and dexamethasone to treat adults with MM who have received at least one prior therapy.
In addition, daratumumab is approved by the EC as monotherapy for adults with relapsed and refractory MM whose prior therapy included a proteasome inhibitor and an immunomodulatory agent and who had disease progression on their last therapy.
The EC’s latest approval for daratumumab is based on results from the phase 3 ALCYONE trial. Results from this study were presented at the 2017 annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology and simultaneously published in the New England Journal of Medicine.
ALCYONE enrolled 706 patients with newly diagnosed MM who were not eligible for high-dose chemotherapy with autologous stem cell transplant. Patients were randomized to receive VMP or daratumumab plus VMP (D-VMP).
The overall response rates were 91% in the D-VMP arm and 74% in the VMP arm (P less than.0001), and rates of complete response were 43% and 24%, respectively. Rates of minimal residual disease negativity were 22% and 6%, respectively.
The median progression-free survival (PFS) was not reached in the D-VMP arm and was 18.1 months in the VMP arm. The 12-month PFS was 87% and 76%, respectively, and the 18-month PFS was 72% and 50%, respectively.
The most common treatment-emergent adverse events (in the D-VMP and VMP arms, respectively) were neutropenia (50% and 53%), thrombocytopenia (49% and 54%), anemia (28% and 38%), peripheral sensory neuropathy (28% and 34%), upper respiratory tract infection (26% and 14%), diarrhea (24% and 25%), pyrexia (23% and 21%), and nausea (21% and 22%).
Infusion-related reactions occurred in 28% of patients in the D-VMP arm and in none of those in the VMP arm.
The rate of grade 3/4 infections was higher in the D-VMP arm than the VMP arm – 23% and 15%, respectively. In both arms, most infections resolved.
The most common grade 3/4 treatment-emergent adverse events (in the D-VMP and VMP arms, respectively) were neutropenia (40% and 39%), thrombocytopenia (34% and 38%), and anemia (16% and 20%).
The rate of discontinuation caused by adverse events was 5% in the D-VMP arm and 9% in the VMP arm.
The drug is now authorized for use in combination with bortezomib, melphalan, and prednisone (VMP) to treat adults with newly diagnosed multiple myeloma (MM) who are ineligible for autologous stem cell transplant, according to a press release published on the Genmab website.
Daratumumab was previously approved by the European Commission (EC) for use in combination with lenalidomide and dexamethasone or bortezomib and dexamethasone to treat adults with MM who have received at least one prior therapy.
In addition, daratumumab is approved by the EC as monotherapy for adults with relapsed and refractory MM whose prior therapy included a proteasome inhibitor and an immunomodulatory agent and who had disease progression on their last therapy.
The EC’s latest approval for daratumumab is based on results from the phase 3 ALCYONE trial. Results from this study were presented at the 2017 annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology and simultaneously published in the New England Journal of Medicine.
ALCYONE enrolled 706 patients with newly diagnosed MM who were not eligible for high-dose chemotherapy with autologous stem cell transplant. Patients were randomized to receive VMP or daratumumab plus VMP (D-VMP).
The overall response rates were 91% in the D-VMP arm and 74% in the VMP arm (P less than.0001), and rates of complete response were 43% and 24%, respectively. Rates of minimal residual disease negativity were 22% and 6%, respectively.
The median progression-free survival (PFS) was not reached in the D-VMP arm and was 18.1 months in the VMP arm. The 12-month PFS was 87% and 76%, respectively, and the 18-month PFS was 72% and 50%, respectively.
The most common treatment-emergent adverse events (in the D-VMP and VMP arms, respectively) were neutropenia (50% and 53%), thrombocytopenia (49% and 54%), anemia (28% and 38%), peripheral sensory neuropathy (28% and 34%), upper respiratory tract infection (26% and 14%), diarrhea (24% and 25%), pyrexia (23% and 21%), and nausea (21% and 22%).
Infusion-related reactions occurred in 28% of patients in the D-VMP arm and in none of those in the VMP arm.
The rate of grade 3/4 infections was higher in the D-VMP arm than the VMP arm – 23% and 15%, respectively. In both arms, most infections resolved.
The most common grade 3/4 treatment-emergent adverse events (in the D-VMP and VMP arms, respectively) were neutropenia (40% and 39%), thrombocytopenia (34% and 38%), and anemia (16% and 20%).
The rate of discontinuation caused by adverse events was 5% in the D-VMP arm and 9% in the VMP arm.
The drug is now authorized for use in combination with bortezomib, melphalan, and prednisone (VMP) to treat adults with newly diagnosed multiple myeloma (MM) who are ineligible for autologous stem cell transplant, according to a press release published on the Genmab website.
Daratumumab was previously approved by the European Commission (EC) for use in combination with lenalidomide and dexamethasone or bortezomib and dexamethasone to treat adults with MM who have received at least one prior therapy.
In addition, daratumumab is approved by the EC as monotherapy for adults with relapsed and refractory MM whose prior therapy included a proteasome inhibitor and an immunomodulatory agent and who had disease progression on their last therapy.
The EC’s latest approval for daratumumab is based on results from the phase 3 ALCYONE trial. Results from this study were presented at the 2017 annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology and simultaneously published in the New England Journal of Medicine.
ALCYONE enrolled 706 patients with newly diagnosed MM who were not eligible for high-dose chemotherapy with autologous stem cell transplant. Patients were randomized to receive VMP or daratumumab plus VMP (D-VMP).
The overall response rates were 91% in the D-VMP arm and 74% in the VMP arm (P less than.0001), and rates of complete response were 43% and 24%, respectively. Rates of minimal residual disease negativity were 22% and 6%, respectively.
The median progression-free survival (PFS) was not reached in the D-VMP arm and was 18.1 months in the VMP arm. The 12-month PFS was 87% and 76%, respectively, and the 18-month PFS was 72% and 50%, respectively.
The most common treatment-emergent adverse events (in the D-VMP and VMP arms, respectively) were neutropenia (50% and 53%), thrombocytopenia (49% and 54%), anemia (28% and 38%), peripheral sensory neuropathy (28% and 34%), upper respiratory tract infection (26% and 14%), diarrhea (24% and 25%), pyrexia (23% and 21%), and nausea (21% and 22%).
Infusion-related reactions occurred in 28% of patients in the D-VMP arm and in none of those in the VMP arm.
The rate of grade 3/4 infections was higher in the D-VMP arm than the VMP arm – 23% and 15%, respectively. In both arms, most infections resolved.
The most common grade 3/4 treatment-emergent adverse events (in the D-VMP and VMP arms, respectively) were neutropenia (40% and 39%), thrombocytopenia (34% and 38%), and anemia (16% and 20%).
The rate of discontinuation caused by adverse events was 5% in the D-VMP arm and 9% in the VMP arm.
Adverse events outweigh promise of SGN-CD70A against NHL
An investigational antibody-drug conjugate labeled SGN-CD70A showed signs of efficacy against relapsed or refractory non-Hodgkin lymphomas in a phase 1 trial, but its future is clouded by a high incidence of treatment-associated thrombocytopenia, investigators reported.
Among 20 patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL), mantle cell lymphoma, and other histologies, SGN-CD70A was associated with one complete remission (CR) and three partial remissions (PR), two of which were ongoing at nearly 43 weeks of follow-up.
However, 15 of the 20 patients (75%) had treatment-related thrombocytopenias, and 13 of these adverse events (AEs) were grade 3 or greater in severity, reported Tycel Phillips, MD, of the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, and his colleagues.
Notwithstanding the antibody-drug conjugate’s apparent efficacy in this early trial, “the applicability of SGN-CD70A is limited by the frequency and severity of thrombocytopenia, despite the long-term of response with limited drug exposure. Given that we are currently unable to mitigate this AE, the rationale for further investigation of SGN-CD70A remains limited and is, therefore, not planned,” they wrote in the journal Investigational New Drugs.
SGN-CD70A consists of an antibody directed against the plasma membrane protein CD70, a protease-cleavable linker, and a DNA-crosslinking pyrrolobenzodiazepine dimer drug. Its mechanism of action is via double-strand DNA breaks in CD70-positive cells that eventually cause programmed cell death.
Dr. Phillips and his colleagues reported on the high-risk non-Hodgkin lymphoma cohort in the phase 1 trial. The cohort included nine patients with DLBCL, five with mantle cell lymphoma, two with transformed DLBCL, one with T- cell/histocyte–rich large B cell lymphoma, and three with unspecified NHL histologies.
The patients had undergone a median of 3.5 prior lines of systemic therapy, and all had relatively good performance status, with Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group scores of 0 or 1.
Patients were started on intravenous SGN-CD70A at a dose of 8 mcg/kg on day 1 of each 3-week cycle, with a planned dose escalation to 200 mcg/kg, The protocol was amended to dosing every 6 weeks, however, after the investigators observed prolonged thrombocytopenias in some patients. A total of 12 patients were treated every 3 weeks, and 8 were treated every 6 weeks.
The most common treatment-related AEs were thrombocytopenias, which occurred in three-quarters of all patients, and were largely grade 3 or greater in severity. Other treatment-related AEs of grade 3 or greater occurring in more than one patient include neutropenia in six patients; anemia in five patients; and congestive heart failure, Clostridium difficile infections, dyspnea, and decreased forced expiratory volume in two patients each.
Other common AEs were nausea and fatigue.
The investigators noted that the cause of the deep and durable thrombocytopenias could not be determined, despite assessment of known biomarkers for this complication.
The duration of the thrombocytopenia and the fact that some of the few responses that did occur were also durable after the end of treatment suggest that the dimer drug, the cytotoxic “payload” of the antibody-drug conjugate, was responsible for the effects they observed, the authors said.
The study was funded by Seattle Genetics. Dr. Phillips reported advisory board membership with the company, and four of the coauthors are employees of the company with equity interests.
SOURCE: Phillips T et al. Invest New Drugs. 2018 Aug 22. doi: 10.1007/s10637-018-0655-0.
An investigational antibody-drug conjugate labeled SGN-CD70A showed signs of efficacy against relapsed or refractory non-Hodgkin lymphomas in a phase 1 trial, but its future is clouded by a high incidence of treatment-associated thrombocytopenia, investigators reported.
Among 20 patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL), mantle cell lymphoma, and other histologies, SGN-CD70A was associated with one complete remission (CR) and three partial remissions (PR), two of which were ongoing at nearly 43 weeks of follow-up.
However, 15 of the 20 patients (75%) had treatment-related thrombocytopenias, and 13 of these adverse events (AEs) were grade 3 or greater in severity, reported Tycel Phillips, MD, of the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, and his colleagues.
Notwithstanding the antibody-drug conjugate’s apparent efficacy in this early trial, “the applicability of SGN-CD70A is limited by the frequency and severity of thrombocytopenia, despite the long-term of response with limited drug exposure. Given that we are currently unable to mitigate this AE, the rationale for further investigation of SGN-CD70A remains limited and is, therefore, not planned,” they wrote in the journal Investigational New Drugs.
SGN-CD70A consists of an antibody directed against the plasma membrane protein CD70, a protease-cleavable linker, and a DNA-crosslinking pyrrolobenzodiazepine dimer drug. Its mechanism of action is via double-strand DNA breaks in CD70-positive cells that eventually cause programmed cell death.
Dr. Phillips and his colleagues reported on the high-risk non-Hodgkin lymphoma cohort in the phase 1 trial. The cohort included nine patients with DLBCL, five with mantle cell lymphoma, two with transformed DLBCL, one with T- cell/histocyte–rich large B cell lymphoma, and three with unspecified NHL histologies.
The patients had undergone a median of 3.5 prior lines of systemic therapy, and all had relatively good performance status, with Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group scores of 0 or 1.
Patients were started on intravenous SGN-CD70A at a dose of 8 mcg/kg on day 1 of each 3-week cycle, with a planned dose escalation to 200 mcg/kg, The protocol was amended to dosing every 6 weeks, however, after the investigators observed prolonged thrombocytopenias in some patients. A total of 12 patients were treated every 3 weeks, and 8 were treated every 6 weeks.
The most common treatment-related AEs were thrombocytopenias, which occurred in three-quarters of all patients, and were largely grade 3 or greater in severity. Other treatment-related AEs of grade 3 or greater occurring in more than one patient include neutropenia in six patients; anemia in five patients; and congestive heart failure, Clostridium difficile infections, dyspnea, and decreased forced expiratory volume in two patients each.
Other common AEs were nausea and fatigue.
The investigators noted that the cause of the deep and durable thrombocytopenias could not be determined, despite assessment of known biomarkers for this complication.
The duration of the thrombocytopenia and the fact that some of the few responses that did occur were also durable after the end of treatment suggest that the dimer drug, the cytotoxic “payload” of the antibody-drug conjugate, was responsible for the effects they observed, the authors said.
The study was funded by Seattle Genetics. Dr. Phillips reported advisory board membership with the company, and four of the coauthors are employees of the company with equity interests.
SOURCE: Phillips T et al. Invest New Drugs. 2018 Aug 22. doi: 10.1007/s10637-018-0655-0.
An investigational antibody-drug conjugate labeled SGN-CD70A showed signs of efficacy against relapsed or refractory non-Hodgkin lymphomas in a phase 1 trial, but its future is clouded by a high incidence of treatment-associated thrombocytopenia, investigators reported.
Among 20 patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL), mantle cell lymphoma, and other histologies, SGN-CD70A was associated with one complete remission (CR) and three partial remissions (PR), two of which were ongoing at nearly 43 weeks of follow-up.
However, 15 of the 20 patients (75%) had treatment-related thrombocytopenias, and 13 of these adverse events (AEs) were grade 3 or greater in severity, reported Tycel Phillips, MD, of the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, and his colleagues.
Notwithstanding the antibody-drug conjugate’s apparent efficacy in this early trial, “the applicability of SGN-CD70A is limited by the frequency and severity of thrombocytopenia, despite the long-term of response with limited drug exposure. Given that we are currently unable to mitigate this AE, the rationale for further investigation of SGN-CD70A remains limited and is, therefore, not planned,” they wrote in the journal Investigational New Drugs.
SGN-CD70A consists of an antibody directed against the plasma membrane protein CD70, a protease-cleavable linker, and a DNA-crosslinking pyrrolobenzodiazepine dimer drug. Its mechanism of action is via double-strand DNA breaks in CD70-positive cells that eventually cause programmed cell death.
Dr. Phillips and his colleagues reported on the high-risk non-Hodgkin lymphoma cohort in the phase 1 trial. The cohort included nine patients with DLBCL, five with mantle cell lymphoma, two with transformed DLBCL, one with T- cell/histocyte–rich large B cell lymphoma, and three with unspecified NHL histologies.
The patients had undergone a median of 3.5 prior lines of systemic therapy, and all had relatively good performance status, with Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group scores of 0 or 1.
Patients were started on intravenous SGN-CD70A at a dose of 8 mcg/kg on day 1 of each 3-week cycle, with a planned dose escalation to 200 mcg/kg, The protocol was amended to dosing every 6 weeks, however, after the investigators observed prolonged thrombocytopenias in some patients. A total of 12 patients were treated every 3 weeks, and 8 were treated every 6 weeks.
The most common treatment-related AEs were thrombocytopenias, which occurred in three-quarters of all patients, and were largely grade 3 or greater in severity. Other treatment-related AEs of grade 3 or greater occurring in more than one patient include neutropenia in six patients; anemia in five patients; and congestive heart failure, Clostridium difficile infections, dyspnea, and decreased forced expiratory volume in two patients each.
Other common AEs were nausea and fatigue.
The investigators noted that the cause of the deep and durable thrombocytopenias could not be determined, despite assessment of known biomarkers for this complication.
The duration of the thrombocytopenia and the fact that some of the few responses that did occur were also durable after the end of treatment suggest that the dimer drug, the cytotoxic “payload” of the antibody-drug conjugate, was responsible for the effects they observed, the authors said.
The study was funded by Seattle Genetics. Dr. Phillips reported advisory board membership with the company, and four of the coauthors are employees of the company with equity interests.
SOURCE: Phillips T et al. Invest New Drugs. 2018 Aug 22. doi: 10.1007/s10637-018-0655-0.
FROM INVESTIGATIONAL NEW DRUGS
Key clinical point: A high incidence of unexplained
Major finding: In total, 15 of 20 patients had treatment-related thrombocytopenias; 13 of these adverse events were grade 3 or greater in severity.
Study details: A 20-patient NHL cohort of a phase 1 dose-finding, pharmacologic, safety, and preliminary efficacy trial of the antibody-drug conjugate SGN-CD70A.
Disclosures: The study was funded by Seattle Genetics. Dr. Phillips reported advisory board membership with the company, and four of the coauthors are employees of the company with equity interests.
Source: Phillips T et al. Invest New Drugs. 2018 Aug 22. doi: 10.1007/s10637-018-0655-0.
Predicting early outcomes in DLBCL
Measurement of circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA) could be a new and useful tool for predicting survival outcomes and response to therapy in patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL), according to researchers.
Pretreatment ctDNA levels predicted 24-month event-free survival as well as overall survival in a prospective study.
Changes in ctDNA during treatment were prognostic for outcomes as early as 21 days into therapy.
Ash A. Alizadeh, MD, PhD, of Stanford University in California, and his colleagues reported these findings in the Journal of Clinical Oncology.
ctDNA was detected in 98% of the 217 patients evaluated, which demonstrated the “potentially universal applicability” of this approach, the researchers wrote.
In an evaluation of pretreatment ctDNA levels, the researchers found a 2.5 log haploid genome equivalents per milliliter threshold stratified patient outcomes. Event-free survival was significantly inferior at 24 months in patients with ctDNA above that threshold, with hazard ratios of 2.6 (P=0.007) for frontline treatment and 2.9 (P=0.01) for salvage therapy.
On-treatment ctDNA levels were favorably prognostic for outcomes in patients receiving frontline therapy.
An early molecular response (EMR), defined as a 2-log decrease in ctDNA levels after one cycle of treatment, was associated with a 24-month event-free survival of 83% versus 50% for no EMR (P=0.0015).
Major molecular response (MMR), defined as a 2.5-log drop in ctDNA after two cycles of treatment, was associated with a 24-month event-free survival of 82% versus 46% for no MMR in patients on frontline therapy (P<0.001).
In one cohort of patients receiving salvage therapy, EMR also predicted superior 24-month event-free survival.
The EMR measure was also favorably prognostic for overall survival in both the frontline and salvage settings.
The prognostic value of measuring ctDNA was independent of International Prognostic Index and interim PET/CT studies, results of multivariable analyses showed.
Patients had “excellent outcomes” if they had both molecular response and favorable interim PET results, according to researchers. Conversely, patients were at “extremely high risk” for treatment failure if they had no molecular response and a positive PET scan.
“The identification of patients at exceptionally high risk (i.e., interim PET/CT positive and not achieving EMR/MMR) could provide an opportunity for early intervention with alternative treatments, including autologous bone marrow transplantation or chimeric antigen receptor T cells,” the researchers wrote.
Patients in the study were all treated with combination immunochemotherapy according to local standards.
Dr. Alizadeh reported disclosures related to CiberMed, Forty Seven, Janssen Oncology, Celgene, Roche/Genentech, and Gilead, as well as patent filings on ctDNA detection assigned to Stanford University.
Measurement of circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA) could be a new and useful tool for predicting survival outcomes and response to therapy in patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL), according to researchers.
Pretreatment ctDNA levels predicted 24-month event-free survival as well as overall survival in a prospective study.
Changes in ctDNA during treatment were prognostic for outcomes as early as 21 days into therapy.
Ash A. Alizadeh, MD, PhD, of Stanford University in California, and his colleagues reported these findings in the Journal of Clinical Oncology.
ctDNA was detected in 98% of the 217 patients evaluated, which demonstrated the “potentially universal applicability” of this approach, the researchers wrote.
In an evaluation of pretreatment ctDNA levels, the researchers found a 2.5 log haploid genome equivalents per milliliter threshold stratified patient outcomes. Event-free survival was significantly inferior at 24 months in patients with ctDNA above that threshold, with hazard ratios of 2.6 (P=0.007) for frontline treatment and 2.9 (P=0.01) for salvage therapy.
On-treatment ctDNA levels were favorably prognostic for outcomes in patients receiving frontline therapy.
An early molecular response (EMR), defined as a 2-log decrease in ctDNA levels after one cycle of treatment, was associated with a 24-month event-free survival of 83% versus 50% for no EMR (P=0.0015).
Major molecular response (MMR), defined as a 2.5-log drop in ctDNA after two cycles of treatment, was associated with a 24-month event-free survival of 82% versus 46% for no MMR in patients on frontline therapy (P<0.001).
In one cohort of patients receiving salvage therapy, EMR also predicted superior 24-month event-free survival.
The EMR measure was also favorably prognostic for overall survival in both the frontline and salvage settings.
The prognostic value of measuring ctDNA was independent of International Prognostic Index and interim PET/CT studies, results of multivariable analyses showed.
Patients had “excellent outcomes” if they had both molecular response and favorable interim PET results, according to researchers. Conversely, patients were at “extremely high risk” for treatment failure if they had no molecular response and a positive PET scan.
“The identification of patients at exceptionally high risk (i.e., interim PET/CT positive and not achieving EMR/MMR) could provide an opportunity for early intervention with alternative treatments, including autologous bone marrow transplantation or chimeric antigen receptor T cells,” the researchers wrote.
Patients in the study were all treated with combination immunochemotherapy according to local standards.
Dr. Alizadeh reported disclosures related to CiberMed, Forty Seven, Janssen Oncology, Celgene, Roche/Genentech, and Gilead, as well as patent filings on ctDNA detection assigned to Stanford University.
Measurement of circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA) could be a new and useful tool for predicting survival outcomes and response to therapy in patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL), according to researchers.
Pretreatment ctDNA levels predicted 24-month event-free survival as well as overall survival in a prospective study.
Changes in ctDNA during treatment were prognostic for outcomes as early as 21 days into therapy.
Ash A. Alizadeh, MD, PhD, of Stanford University in California, and his colleagues reported these findings in the Journal of Clinical Oncology.
ctDNA was detected in 98% of the 217 patients evaluated, which demonstrated the “potentially universal applicability” of this approach, the researchers wrote.
In an evaluation of pretreatment ctDNA levels, the researchers found a 2.5 log haploid genome equivalents per milliliter threshold stratified patient outcomes. Event-free survival was significantly inferior at 24 months in patients with ctDNA above that threshold, with hazard ratios of 2.6 (P=0.007) for frontline treatment and 2.9 (P=0.01) for salvage therapy.
On-treatment ctDNA levels were favorably prognostic for outcomes in patients receiving frontline therapy.
An early molecular response (EMR), defined as a 2-log decrease in ctDNA levels after one cycle of treatment, was associated with a 24-month event-free survival of 83% versus 50% for no EMR (P=0.0015).
Major molecular response (MMR), defined as a 2.5-log drop in ctDNA after two cycles of treatment, was associated with a 24-month event-free survival of 82% versus 46% for no MMR in patients on frontline therapy (P<0.001).
In one cohort of patients receiving salvage therapy, EMR also predicted superior 24-month event-free survival.
The EMR measure was also favorably prognostic for overall survival in both the frontline and salvage settings.
The prognostic value of measuring ctDNA was independent of International Prognostic Index and interim PET/CT studies, results of multivariable analyses showed.
Patients had “excellent outcomes” if they had both molecular response and favorable interim PET results, according to researchers. Conversely, patients were at “extremely high risk” for treatment failure if they had no molecular response and a positive PET scan.
“The identification of patients at exceptionally high risk (i.e., interim PET/CT positive and not achieving EMR/MMR) could provide an opportunity for early intervention with alternative treatments, including autologous bone marrow transplantation or chimeric antigen receptor T cells,” the researchers wrote.
Patients in the study were all treated with combination immunochemotherapy according to local standards.
Dr. Alizadeh reported disclosures related to CiberMed, Forty Seven, Janssen Oncology, Celgene, Roche/Genentech, and Gilead, as well as patent filings on ctDNA detection assigned to Stanford University.