User login
Analysis of Nail Excision Practice Patterns in the Medicare Provider Utilization and Payment Database 2012-2017
To the Editor:
Partial or total nail plate excisions commonly are used for the treatment of onychocryptosis and nail spicules. Procedures involving the nail unit require advanced technical skills to achieve optimal functional and aesthetic outcomes, avoid complications, and minimize health care costs. Data on the frequency of nail plate excisions performed by dermatologists and their relative frequency compared to other medical providers are limited. The objective of our study was to analyze trends in nail excision practice patterns among medical providers in the United States.
A retrospective analysis on nail excisions using the Current Procedural Terminology (CPT) code 11750 (excision of nail and nail matrix, partial or complete [eg, ingrown or deformed nail] for permanent removal), which is distinct from code 11755 (biopsy of nail unit [eg, plate, bed, matrix, hyponychium, proximal and lateral nail folds][separate procedure]), was performed using data from the Medicare Provider Utilization and Payment Database 2012-2017.1,2 This file also is used by Peck et al3 in an article submitted to the Journal of the American Podiatric Medical Association and currently under consideration for publication. Procedures were recorded by year and provider type—dermatologist, podiatrist, physician assistant (PA)/nurse practitioner (NP), nondermatologist physician—and subcategorized by provider specialty (Table). Practice locations subcategorized by provider type were mapped using Tableau Software (Salesforce)(Figure). Descriptive statistics including number of providers, mean and median excisions per provider, and minimum/maximum nail excisions were calculated (Table). Practice types of PAs/NPs and specialization of nondermatologist physicians were determined using provider name, identification number, and practice address. This study did not require institutional review board review, as only publicly available data were utilized in our analysis.
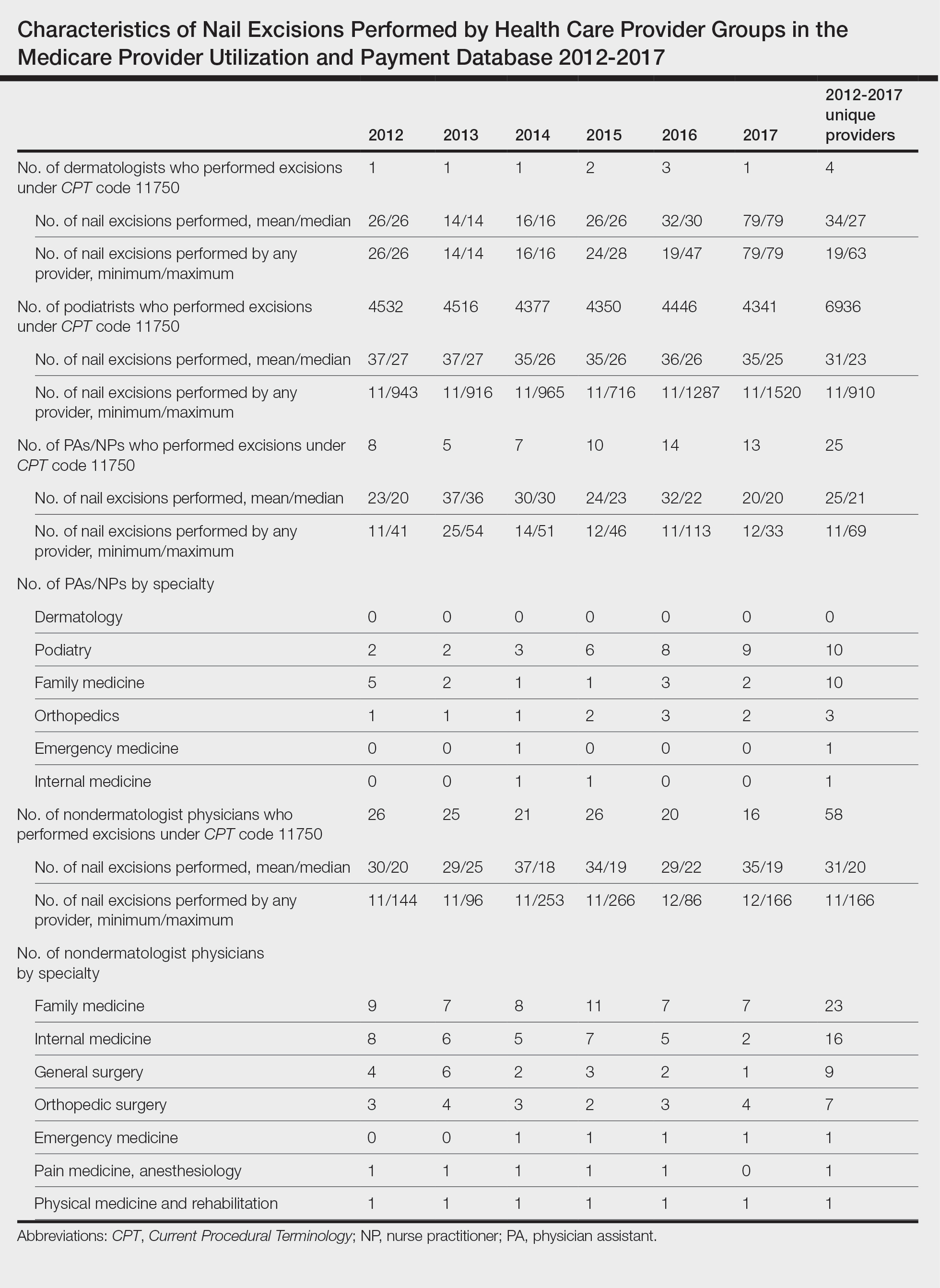
A total of 6936 podiatrists, 58 nondermatologist physicians, 25 PAs/NPs, and 4 dermatologists performed 10 or more nail excisions annually under CPT code 11750 from January 2012 to December 2017 with annual means of 31, 31, 25, and 34, respectively (Table). No PAs/NPs included in the dataset worked in dermatology practices during the study period. Physician assistants and NPs most often practiced in podiatry and family medicine (FM) settings (both 40% [10/25]). Nondermatologist physicians most often specialized in FM (40% [23/58])(Table). The greatest number of providers practiced in 3 of the 4 most-populous states: California, Texas, and Florida; the fewest number practiced in 3 of the 10 least-populous states: Alaska, Hawaii, and Vermont. Vermont, Wyoming, and North Dakota—3 of the 5 least-populous states—had the fewest practitioners among the contiguous United States (Figure).
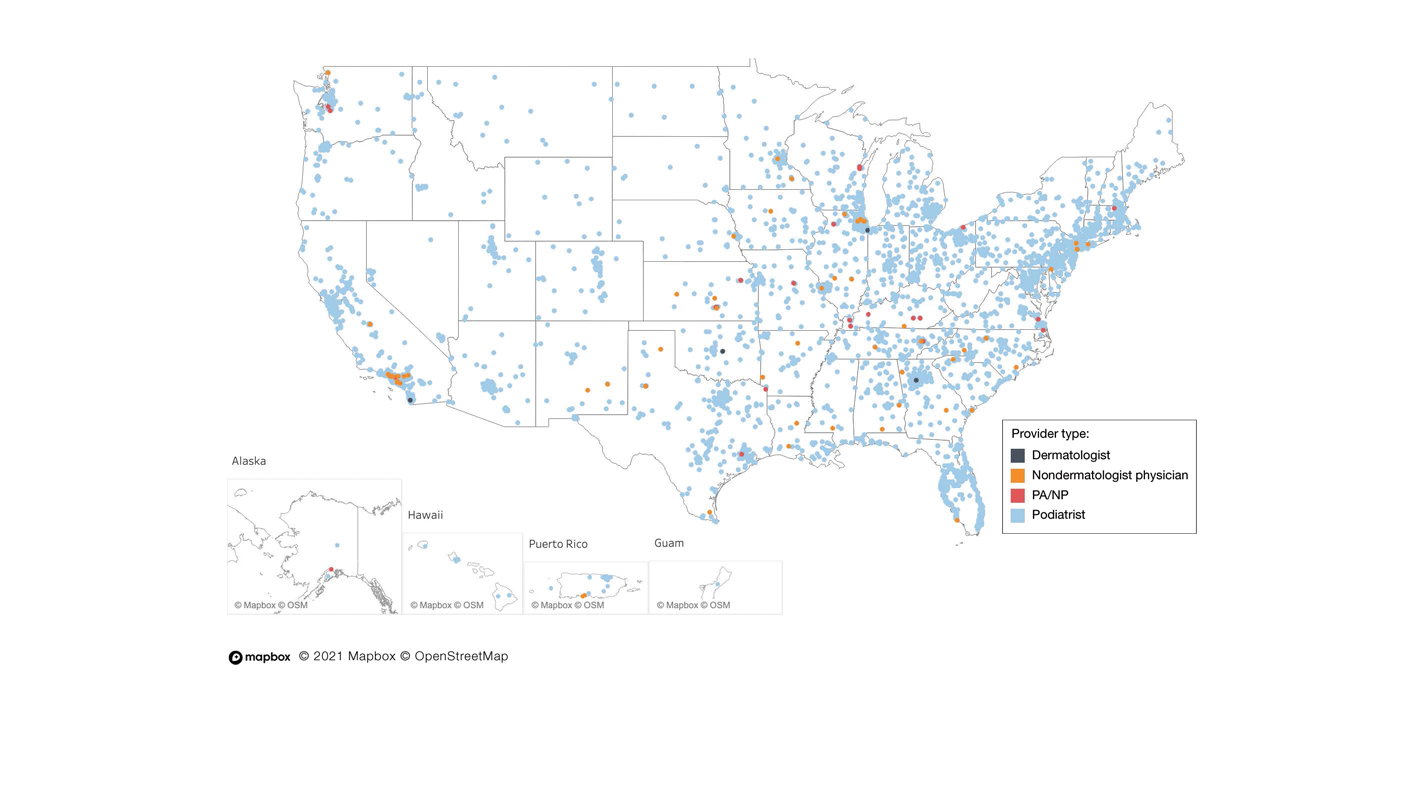
Our study showed that from January 2012 to December 2017, fewer dermatologists performed nail excisions than any other provider type (0.06%, 4 dermatologists of 7023 total providers), and dermatologists performed 1734-fold fewer nail excisions than podiatrists (99%, 6936 podiatrists of 7023 total providers). Only dermatologists practicing in California, Georgia, Indiana, and Oklahoma performed nail excisions. Conversely, podiatrists were more geographically distributed across the United States and other territories, with representation in all 50 states as well as the District of Columbia, Puerto Rico, and Guam.
Reasons for these large discrepancies in practice between dermatologists and other providers likely are multifactorial, encompassing a lack of emphasis on nail procedures in dermatology training, patient perception of the scope of dermatologic practice, and nail excision reimbursement patterns. Most dermatologists likely lack experience in performing nail procedures. The Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education requirements mandate that dermatology residents observe or perform 3 nail procedures over 3 years of residency, including 1 that may be performed on a human cadaver.4 In contrast, podiatry trainees must gain competency in toenail avulsion (both partial and complete), participate in anesthesia workshops, and become proficient in administering lower extremity blocks by the end of their training.5 Therefore, incorporating aspects of podiatric surgical training into dermatology residency requirements may increase the competency and comfort of dermatologists in performing nail excisions and practicing as nail experts as attending physicians.
It is likely that US patients do not perceive dermatologists as nail specialists and instead primarily consult podiatrists or FM and/or internal medicine physicians for treatment; for example, nail disease was one of the least common reasons for consulting a dermatologist (5%) in a German nationwide survey-based study (N=1015).6 Therefore, increased efforts are needed to educate the general public about the expertise of dermatologists in the diagnosis and management of nail conditions.
Reimbursement also may be a barrier to dermatologists performing nail procedures as part of their scope of practice; for example, in a retrospective study of nail biopsies using the Medicare Provider Utilization and Payment Database, there was no statistically significant difference in reimbursements for nail biopsies vs skin biopsies from 2012 to 2017 (P=0.69).7 Similar to nail biopsies, nail excisions typically are much more time consuming and technically demanding than skin biopsies, which may discourage dermatologists from routinely performing nail excision procedures.
Our study is subject to a number of limitations. The data reflected only US-based practice patterns and may not be applicable to nail procedures globally. There also is the potential for miscoding of procedures in the Medicare database. The data included only Part B Medicare fee-for-service and excludes non-Medicare insured, uninsured, and self-pay patients, as well as aggregated records from 10 or fewer Medicare beneficiaries.
Dermatologists rarely perform nail excisions and perform fewer nail excisions than any other provider type in the United States. There currently is an unmet need for comprehensive nail surgery education in US-based dermatology residency programs. We hope that our study fosters interdisciplinary collegiality and training between podiatrists and dermatologists and promotes expanded access to care across the United States to serve patients with nail disorders.
- Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services. Medicare Fee-For-Service Provider Utilization & Payment Data Physician and Other Supplier Public Use File: A Methodological Overview . Updated September 22, 2020. Accessed January 5, 2024. https://www.cms.gov/research-statistics-data-and-systems/statistics-trends-and-reports/medicare-provider-charge-data/downloads/medicare-physician-and-other-supplier-puf-methodology.pdf
- Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services. Billing and Coding: Surgical Treatment of Nails. Updated November 9, 2023. Accessed January 8, 2024. https://www.cms.gov/medicare-coverage-database/view/article.aspx?articleID=52998#:~:text=The%20description%20of%20CPT%20codes,date%20of%20service%20(DOS).
- Peck GM, Vlahovic TC, Hill R, et al. Senior podiatrists in solo practice are high performers of nail excisions. JAPMA. In press.
- Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education. Case log minimums. review committee for dermatology. Published May 2019. Accessed January 5, 2024. https://www.acgme.org/Portals/0/PFAssets/ProgramResources/CaseLogMinimums.pdf?ver=2018-04-03-102751-650
- Council on Podiatric Medical Education. Standards and Requirements for Approval of Podiatric Medicine and Surgery Residencies. Published July 2023. Accessed January 17, 2024. https://www.cpme.org/files/320%20Council%20Approved%20October%202022%20-%20April%202023%20edits.pdf
- Augustin M, Eissing L, Elsner P, et al. Perception and image of dermatology in the German general population 2002-2014. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2017;31:2124-2130.
- Wang Y, Lipner SR. Retrospective analysis of nail biopsies performed using the Medicare provider utilization and payment database 2012 to 2017. Dermatol Ther. 2021;34:E14928.
To the Editor:
Partial or total nail plate excisions commonly are used for the treatment of onychocryptosis and nail spicules. Procedures involving the nail unit require advanced technical skills to achieve optimal functional and aesthetic outcomes, avoid complications, and minimize health care costs. Data on the frequency of nail plate excisions performed by dermatologists and their relative frequency compared to other medical providers are limited. The objective of our study was to analyze trends in nail excision practice patterns among medical providers in the United States.
A retrospective analysis on nail excisions using the Current Procedural Terminology (CPT) code 11750 (excision of nail and nail matrix, partial or complete [eg, ingrown or deformed nail] for permanent removal), which is distinct from code 11755 (biopsy of nail unit [eg, plate, bed, matrix, hyponychium, proximal and lateral nail folds][separate procedure]), was performed using data from the Medicare Provider Utilization and Payment Database 2012-2017.1,2 This file also is used by Peck et al3 in an article submitted to the Journal of the American Podiatric Medical Association and currently under consideration for publication. Procedures were recorded by year and provider type—dermatologist, podiatrist, physician assistant (PA)/nurse practitioner (NP), nondermatologist physician—and subcategorized by provider specialty (Table). Practice locations subcategorized by provider type were mapped using Tableau Software (Salesforce)(Figure). Descriptive statistics including number of providers, mean and median excisions per provider, and minimum/maximum nail excisions were calculated (Table). Practice types of PAs/NPs and specialization of nondermatologist physicians were determined using provider name, identification number, and practice address. This study did not require institutional review board review, as only publicly available data were utilized in our analysis.

A total of 6936 podiatrists, 58 nondermatologist physicians, 25 PAs/NPs, and 4 dermatologists performed 10 or more nail excisions annually under CPT code 11750 from January 2012 to December 2017 with annual means of 31, 31, 25, and 34, respectively (Table). No PAs/NPs included in the dataset worked in dermatology practices during the study period. Physician assistants and NPs most often practiced in podiatry and family medicine (FM) settings (both 40% [10/25]). Nondermatologist physicians most often specialized in FM (40% [23/58])(Table). The greatest number of providers practiced in 3 of the 4 most-populous states: California, Texas, and Florida; the fewest number practiced in 3 of the 10 least-populous states: Alaska, Hawaii, and Vermont. Vermont, Wyoming, and North Dakota—3 of the 5 least-populous states—had the fewest practitioners among the contiguous United States (Figure).

Our study showed that from January 2012 to December 2017, fewer dermatologists performed nail excisions than any other provider type (0.06%, 4 dermatologists of 7023 total providers), and dermatologists performed 1734-fold fewer nail excisions than podiatrists (99%, 6936 podiatrists of 7023 total providers). Only dermatologists practicing in California, Georgia, Indiana, and Oklahoma performed nail excisions. Conversely, podiatrists were more geographically distributed across the United States and other territories, with representation in all 50 states as well as the District of Columbia, Puerto Rico, and Guam.
Reasons for these large discrepancies in practice between dermatologists and other providers likely are multifactorial, encompassing a lack of emphasis on nail procedures in dermatology training, patient perception of the scope of dermatologic practice, and nail excision reimbursement patterns. Most dermatologists likely lack experience in performing nail procedures. The Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education requirements mandate that dermatology residents observe or perform 3 nail procedures over 3 years of residency, including 1 that may be performed on a human cadaver.4 In contrast, podiatry trainees must gain competency in toenail avulsion (both partial and complete), participate in anesthesia workshops, and become proficient in administering lower extremity blocks by the end of their training.5 Therefore, incorporating aspects of podiatric surgical training into dermatology residency requirements may increase the competency and comfort of dermatologists in performing nail excisions and practicing as nail experts as attending physicians.
It is likely that US patients do not perceive dermatologists as nail specialists and instead primarily consult podiatrists or FM and/or internal medicine physicians for treatment; for example, nail disease was one of the least common reasons for consulting a dermatologist (5%) in a German nationwide survey-based study (N=1015).6 Therefore, increased efforts are needed to educate the general public about the expertise of dermatologists in the diagnosis and management of nail conditions.
Reimbursement also may be a barrier to dermatologists performing nail procedures as part of their scope of practice; for example, in a retrospective study of nail biopsies using the Medicare Provider Utilization and Payment Database, there was no statistically significant difference in reimbursements for nail biopsies vs skin biopsies from 2012 to 2017 (P=0.69).7 Similar to nail biopsies, nail excisions typically are much more time consuming and technically demanding than skin biopsies, which may discourage dermatologists from routinely performing nail excision procedures.
Our study is subject to a number of limitations. The data reflected only US-based practice patterns and may not be applicable to nail procedures globally. There also is the potential for miscoding of procedures in the Medicare database. The data included only Part B Medicare fee-for-service and excludes non-Medicare insured, uninsured, and self-pay patients, as well as aggregated records from 10 or fewer Medicare beneficiaries.
Dermatologists rarely perform nail excisions and perform fewer nail excisions than any other provider type in the United States. There currently is an unmet need for comprehensive nail surgery education in US-based dermatology residency programs. We hope that our study fosters interdisciplinary collegiality and training between podiatrists and dermatologists and promotes expanded access to care across the United States to serve patients with nail disorders.
To the Editor:
Partial or total nail plate excisions commonly are used for the treatment of onychocryptosis and nail spicules. Procedures involving the nail unit require advanced technical skills to achieve optimal functional and aesthetic outcomes, avoid complications, and minimize health care costs. Data on the frequency of nail plate excisions performed by dermatologists and their relative frequency compared to other medical providers are limited. The objective of our study was to analyze trends in nail excision practice patterns among medical providers in the United States.
A retrospective analysis on nail excisions using the Current Procedural Terminology (CPT) code 11750 (excision of nail and nail matrix, partial or complete [eg, ingrown or deformed nail] for permanent removal), which is distinct from code 11755 (biopsy of nail unit [eg, plate, bed, matrix, hyponychium, proximal and lateral nail folds][separate procedure]), was performed using data from the Medicare Provider Utilization and Payment Database 2012-2017.1,2 This file also is used by Peck et al3 in an article submitted to the Journal of the American Podiatric Medical Association and currently under consideration for publication. Procedures were recorded by year and provider type—dermatologist, podiatrist, physician assistant (PA)/nurse practitioner (NP), nondermatologist physician—and subcategorized by provider specialty (Table). Practice locations subcategorized by provider type were mapped using Tableau Software (Salesforce)(Figure). Descriptive statistics including number of providers, mean and median excisions per provider, and minimum/maximum nail excisions were calculated (Table). Practice types of PAs/NPs and specialization of nondermatologist physicians were determined using provider name, identification number, and practice address. This study did not require institutional review board review, as only publicly available data were utilized in our analysis.

A total of 6936 podiatrists, 58 nondermatologist physicians, 25 PAs/NPs, and 4 dermatologists performed 10 or more nail excisions annually under CPT code 11750 from January 2012 to December 2017 with annual means of 31, 31, 25, and 34, respectively (Table). No PAs/NPs included in the dataset worked in dermatology practices during the study period. Physician assistants and NPs most often practiced in podiatry and family medicine (FM) settings (both 40% [10/25]). Nondermatologist physicians most often specialized in FM (40% [23/58])(Table). The greatest number of providers practiced in 3 of the 4 most-populous states: California, Texas, and Florida; the fewest number practiced in 3 of the 10 least-populous states: Alaska, Hawaii, and Vermont. Vermont, Wyoming, and North Dakota—3 of the 5 least-populous states—had the fewest practitioners among the contiguous United States (Figure).

Our study showed that from January 2012 to December 2017, fewer dermatologists performed nail excisions than any other provider type (0.06%, 4 dermatologists of 7023 total providers), and dermatologists performed 1734-fold fewer nail excisions than podiatrists (99%, 6936 podiatrists of 7023 total providers). Only dermatologists practicing in California, Georgia, Indiana, and Oklahoma performed nail excisions. Conversely, podiatrists were more geographically distributed across the United States and other territories, with representation in all 50 states as well as the District of Columbia, Puerto Rico, and Guam.
Reasons for these large discrepancies in practice between dermatologists and other providers likely are multifactorial, encompassing a lack of emphasis on nail procedures in dermatology training, patient perception of the scope of dermatologic practice, and nail excision reimbursement patterns. Most dermatologists likely lack experience in performing nail procedures. The Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education requirements mandate that dermatology residents observe or perform 3 nail procedures over 3 years of residency, including 1 that may be performed on a human cadaver.4 In contrast, podiatry trainees must gain competency in toenail avulsion (both partial and complete), participate in anesthesia workshops, and become proficient in administering lower extremity blocks by the end of their training.5 Therefore, incorporating aspects of podiatric surgical training into dermatology residency requirements may increase the competency and comfort of dermatologists in performing nail excisions and practicing as nail experts as attending physicians.
It is likely that US patients do not perceive dermatologists as nail specialists and instead primarily consult podiatrists or FM and/or internal medicine physicians for treatment; for example, nail disease was one of the least common reasons for consulting a dermatologist (5%) in a German nationwide survey-based study (N=1015).6 Therefore, increased efforts are needed to educate the general public about the expertise of dermatologists in the diagnosis and management of nail conditions.
Reimbursement also may be a barrier to dermatologists performing nail procedures as part of their scope of practice; for example, in a retrospective study of nail biopsies using the Medicare Provider Utilization and Payment Database, there was no statistically significant difference in reimbursements for nail biopsies vs skin biopsies from 2012 to 2017 (P=0.69).7 Similar to nail biopsies, nail excisions typically are much more time consuming and technically demanding than skin biopsies, which may discourage dermatologists from routinely performing nail excision procedures.
Our study is subject to a number of limitations. The data reflected only US-based practice patterns and may not be applicable to nail procedures globally. There also is the potential for miscoding of procedures in the Medicare database. The data included only Part B Medicare fee-for-service and excludes non-Medicare insured, uninsured, and self-pay patients, as well as aggregated records from 10 or fewer Medicare beneficiaries.
Dermatologists rarely perform nail excisions and perform fewer nail excisions than any other provider type in the United States. There currently is an unmet need for comprehensive nail surgery education in US-based dermatology residency programs. We hope that our study fosters interdisciplinary collegiality and training between podiatrists and dermatologists and promotes expanded access to care across the United States to serve patients with nail disorders.
- Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services. Medicare Fee-For-Service Provider Utilization & Payment Data Physician and Other Supplier Public Use File: A Methodological Overview . Updated September 22, 2020. Accessed January 5, 2024. https://www.cms.gov/research-statistics-data-and-systems/statistics-trends-and-reports/medicare-provider-charge-data/downloads/medicare-physician-and-other-supplier-puf-methodology.pdf
- Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services. Billing and Coding: Surgical Treatment of Nails. Updated November 9, 2023. Accessed January 8, 2024. https://www.cms.gov/medicare-coverage-database/view/article.aspx?articleID=52998#:~:text=The%20description%20of%20CPT%20codes,date%20of%20service%20(DOS).
- Peck GM, Vlahovic TC, Hill R, et al. Senior podiatrists in solo practice are high performers of nail excisions. JAPMA. In press.
- Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education. Case log minimums. review committee for dermatology. Published May 2019. Accessed January 5, 2024. https://www.acgme.org/Portals/0/PFAssets/ProgramResources/CaseLogMinimums.pdf?ver=2018-04-03-102751-650
- Council on Podiatric Medical Education. Standards and Requirements for Approval of Podiatric Medicine and Surgery Residencies. Published July 2023. Accessed January 17, 2024. https://www.cpme.org/files/320%20Council%20Approved%20October%202022%20-%20April%202023%20edits.pdf
- Augustin M, Eissing L, Elsner P, et al. Perception and image of dermatology in the German general population 2002-2014. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2017;31:2124-2130.
- Wang Y, Lipner SR. Retrospective analysis of nail biopsies performed using the Medicare provider utilization and payment database 2012 to 2017. Dermatol Ther. 2021;34:E14928.
- Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services. Medicare Fee-For-Service Provider Utilization & Payment Data Physician and Other Supplier Public Use File: A Methodological Overview . Updated September 22, 2020. Accessed January 5, 2024. https://www.cms.gov/research-statistics-data-and-systems/statistics-trends-and-reports/medicare-provider-charge-data/downloads/medicare-physician-and-other-supplier-puf-methodology.pdf
- Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services. Billing and Coding: Surgical Treatment of Nails. Updated November 9, 2023. Accessed January 8, 2024. https://www.cms.gov/medicare-coverage-database/view/article.aspx?articleID=52998#:~:text=The%20description%20of%20CPT%20codes,date%20of%20service%20(DOS).
- Peck GM, Vlahovic TC, Hill R, et al. Senior podiatrists in solo practice are high performers of nail excisions. JAPMA. In press.
- Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education. Case log minimums. review committee for dermatology. Published May 2019. Accessed January 5, 2024. https://www.acgme.org/Portals/0/PFAssets/ProgramResources/CaseLogMinimums.pdf?ver=2018-04-03-102751-650
- Council on Podiatric Medical Education. Standards and Requirements for Approval of Podiatric Medicine and Surgery Residencies. Published July 2023. Accessed January 17, 2024. https://www.cpme.org/files/320%20Council%20Approved%20October%202022%20-%20April%202023%20edits.pdf
- Augustin M, Eissing L, Elsner P, et al. Perception and image of dermatology in the German general population 2002-2014. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2017;31:2124-2130.
- Wang Y, Lipner SR. Retrospective analysis of nail biopsies performed using the Medicare provider utilization and payment database 2012 to 2017. Dermatol Ther. 2021;34:E14928.
Practice Points
- Dermatologists are considered nail experts but perform nail excisions less frequently than their podiatric counterparts and physicians in other specialties.
- Aspects of podiatric surgical training should be incorporated into dermatology residency to increase competency and comfort of dermatologists in nail excision procedures.
- Dermatologists may not be perceived as nail experts by the public, indicating a need for increased community education on the role of dermatologists in treating nail disease.
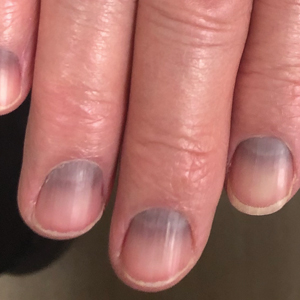
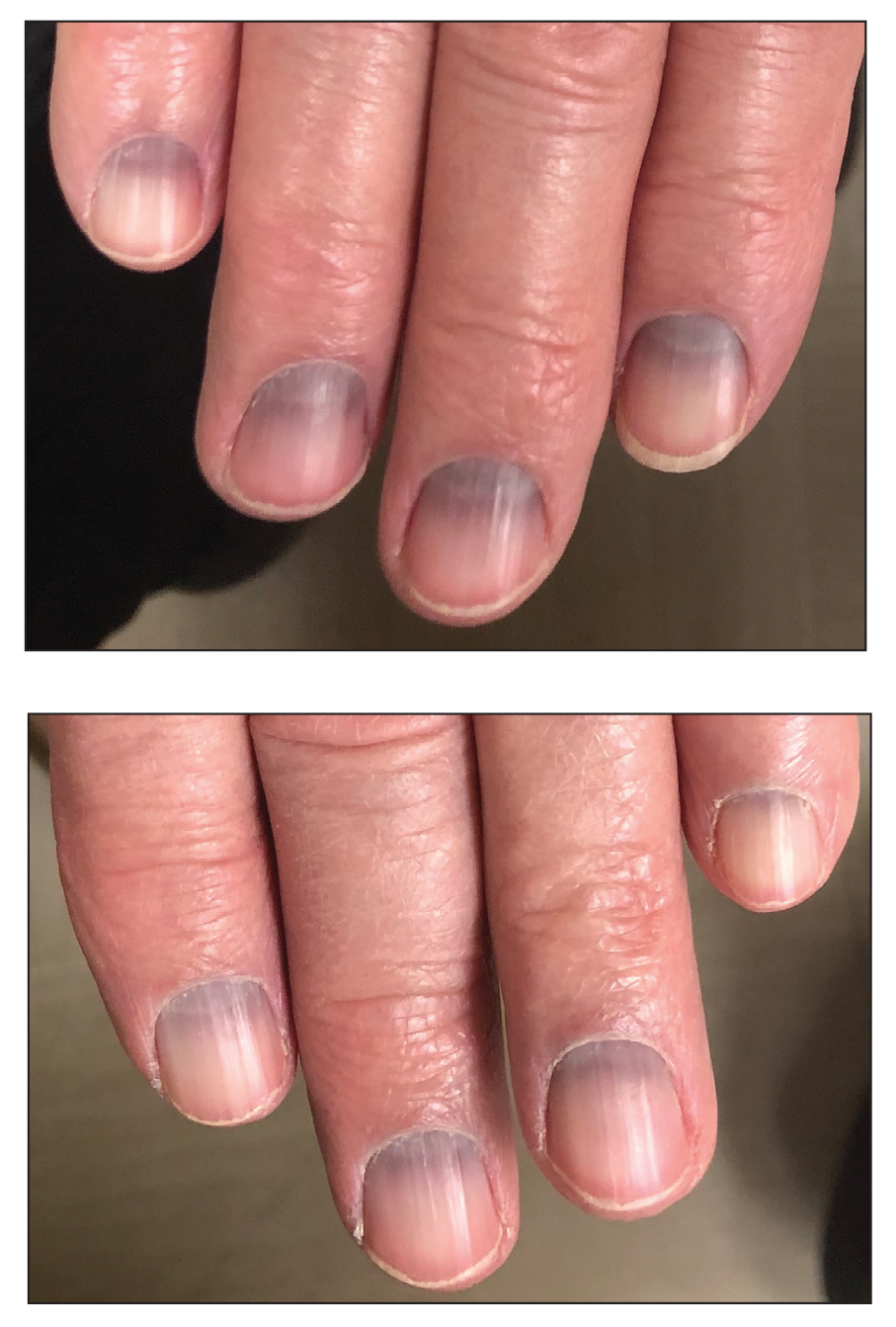
Blue to Slate Gray Discoloration of the Proximal Fingernails
The Diagnosis: Argyria-Induced Azure Lunulae
Argyria is an acquired condition resulting from excessive exogenous exposure to silver with subsequent gastrointestinal absorption and pigmentary tissue deposition. Upon further questioning, our patient disclosed a lifetime history of colloidal silver use, both as a topical antiseptic agent and intraorally for aphthous ulcers. Silver has a predilection for granular deposition in stromal tissues and basement membranes with sparing of the epidermis, manifesting as progressive, permanent, blue to slate gray discoloration of sunexposed skin, mucous membranes, and nail beds.1 The patient was advised to discontinue use of colloidal silver to avoid development of further pigmentary changes. The appearance of his nails remained unchanged in the months following initial presentation, as expected, since argyria pigmentation is not anticipated to reverse upon colloidal silver cessation.
Nail involvement may be an early presentation of generalized argyria or may be found in isolation, as seen in our patient. Early recognition and patient education are essential to minimize cumulative silver deposition. Although dyspigmentation may impact psychosocial well-being secondary to aesthetic concerns, there is limited research supporting adverse systemic effects of argyria confined to the nail beds. Similarly, the majority of generalized cases are not associated with systemic complications; however, potential toxicities, as described in isolated case reports without conclusive causal relationships, include nyctalopia, renal or hepatic toxicity, pulmonary fibrosis, and neuropsychiatric events.1-6 Successful treatment of cutaneous argyria has been reported with the 1064-nm Q-switched Nd:YAG laser; however, there have been no reported treatments for nail bed involvement.7 Due to the absence of systemic symptoms, additional mucocutaneous dyspigmentation, or cosmetic concerns regarding nail bed lunulae discoloration in our patient, no further intervention was pursued, except for continued colloidal silver cessation.
The differential diagnosis of blue-gray nail bed dyspigmentation is broad and includes cyanosis secondary to cardiopulmonary disease, drug-induced dyspigmentation, Wilson disease, argyria, chrysiasis, hereditary acrolabial telangiectasia, and pseudomonal infection or chloronychia.1,8,9 Etiologic insight may be provided from a thorough review of prescription and over-the-counter medications as well as careful attention to the distribution of dyspigmentation. Medications commonly associated with bluish nail bed dyspigmentation include antimalarials, amiodarone, minocycline, clofazimine, chlorpromazine/phenothiazines, and various chemotherapeutic drugs; our patient was not taking any of these.1,9
Cyanotic nail bed dyspigmentation secondary to cardiopulmonary disease likely manifests with more diffuse nail bed dyspigmentation and is not confined solely to the lunulae. Only drug-induced dyspigmentation, classically due to phenolphthalein-containing laxatives; Wilson disease; and argyria have a tendency to spare the distal nail bed, which is a presentation termed azure lunulae.8 The toenails typically are spared in argyria, while toenail involvement is variable in Wilson disease, and additional systemic symptoms—including hepatic, ophthalmologic, and neuropsychiatric—as well as potential family history would be expected.8 Phenolphthalein is no longer available in over-the-counter laxatives, as it was formally banned by the US Food and Drug Administration in 1999 due to concerns of carcinogenicity.10
Hereditary acrolabial telangiectasia is a familial condition with autosomal-dominant inheritance that can manifest similarly to argyria with blue-gray discoloration of the proximal nail bed; however, this condition also would demonstrate involvement of the vermilion border and nipple areolae, often with associated telangiectasia and migraine headaches.11
Chloronychia (also known as green nail syndrome) is an infection of the nail bed with Pseudomonas aeruginosa that more commonly presents with greenblack discoloration with variable involvement of the fingernails and toenails. Chloronychia, often with associated onycholysis, typically is found in individuals with repeated exposure to water, soaps, and detergents.12 Our patient’s long-standing and unwavering nail bed appearance, involvement of all fingernail lunulae, lack of additional symptoms, and disclosed use of over-the-counter colloidal silver supported a clinical diagnosis of argyriainduced azure lunulae.
Argyria-induced azure lunulae secondary to colloidal silver exposure is an uncommon yet clinically significant cause of nail bed dyspigmentation. Prompt identification and cessation of the offending agent can prevent progression of mucocutaneous dyspigmentation and avoid potential long-term sequelae from systemic deposition.
- Mota L, Dinis-Oliveira RJ. Clinical and forensic aspects of the different subtypes of argyria. J Clin Med. 2021;10:2086. doi:10.3390/ jcm10102086
- Osin´ska J, Poborc-Godlewska J, Kiec´-Swierczyn´ska M, et al. 6 cases of argyria among workers engaged in silverplating radio subunits. Med Pr. 1982;33:361-364.
- Mayr M, Kim MJ, Wanner D, et al. Argyria and decreased kidney function: are silver compounds toxic to the kidney? Am J Kidney Dis. 2009;53:890-894. doi:10.1053/j.ajkd.2008.08.028
- Trop M, Novak M, Rodl S, et al. Silver-coated dressing acticoat caused raised liver enzymes and argyria-like symptoms in burn patient. J Trauma. 2006;60:648-652. doi:10.1097/01.ta.0000208126 .22089.b6
- Mirsattari SM, Hammond RR, Sharpe MD, et al. Myoclonic status epilepticus following repeated oral ingestion of colloidal silver. Neurology. 2004;62:1408-1410. doi:10.1212/01.wnl.0000120671.73335.ec
- Barrie HJ, Harding HE. Argyro-siderosis of the lungs in silver finishers. Br J Ind Med. 1947;4:225-229. doi:10.1136/oem.4.4.225
- Griffith RD, Simmons BJ, Bray FN, et al. 1064 nm Q-switched Nd:YAG laser for the treatment of argyria: a systematic review. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2015;29:2100-2103. doi:10.111 1/jdv.13117
- Rubin AI, Jellinek NJ, Daniel CR III, et al, eds. Scher and Daniel’s Nails: Diagnosis, Surgery, Therapy. 4th ed. Springer; 2018.
- Slater K, Sommariva E, Kartono F. A case study of argyria of the nails secondary to colloidal silver ingestion [published online October 28, 2022]. Cureus. 2022;14:E30818. doi:10.7759/cureus.30818
- Hubbard WK. Laxative drug products for over-the-counter human use. Fed Register. 1999;64:4535-4540. Accessed January 5, 2024. https://www.govinfo.gov/content/pkg/FR-1999-01-29/html/99-1938.htm
- Millns JL, Dicken CH. Hereditary acrolabial telangiectasia. a report of familial blue lips, nails, and nipples. Arch Dermatol. 1979;115:474-478. doi:10.1001/archderm.115.4.474
- Chiriac A, Brzezinski P, Foia L, et al. Chloronychia: green nail syndrome caused by Pseudomonas aeruginosa in elderly persons [published online January 14, 2015]. Clin Interv Aging. 2015;10:265-267. doi:10.2147/CIA.S75525
The Diagnosis: Argyria-Induced Azure Lunulae
Argyria is an acquired condition resulting from excessive exogenous exposure to silver with subsequent gastrointestinal absorption and pigmentary tissue deposition. Upon further questioning, our patient disclosed a lifetime history of colloidal silver use, both as a topical antiseptic agent and intraorally for aphthous ulcers. Silver has a predilection for granular deposition in stromal tissues and basement membranes with sparing of the epidermis, manifesting as progressive, permanent, blue to slate gray discoloration of sunexposed skin, mucous membranes, and nail beds.1 The patient was advised to discontinue use of colloidal silver to avoid development of further pigmentary changes. The appearance of his nails remained unchanged in the months following initial presentation, as expected, since argyria pigmentation is not anticipated to reverse upon colloidal silver cessation.
Nail involvement may be an early presentation of generalized argyria or may be found in isolation, as seen in our patient. Early recognition and patient education are essential to minimize cumulative silver deposition. Although dyspigmentation may impact psychosocial well-being secondary to aesthetic concerns, there is limited research supporting adverse systemic effects of argyria confined to the nail beds. Similarly, the majority of generalized cases are not associated with systemic complications; however, potential toxicities, as described in isolated case reports without conclusive causal relationships, include nyctalopia, renal or hepatic toxicity, pulmonary fibrosis, and neuropsychiatric events.1-6 Successful treatment of cutaneous argyria has been reported with the 1064-nm Q-switched Nd:YAG laser; however, there have been no reported treatments for nail bed involvement.7 Due to the absence of systemic symptoms, additional mucocutaneous dyspigmentation, or cosmetic concerns regarding nail bed lunulae discoloration in our patient, no further intervention was pursued, except for continued colloidal silver cessation.
The differential diagnosis of blue-gray nail bed dyspigmentation is broad and includes cyanosis secondary to cardiopulmonary disease, drug-induced dyspigmentation, Wilson disease, argyria, chrysiasis, hereditary acrolabial telangiectasia, and pseudomonal infection or chloronychia.1,8,9 Etiologic insight may be provided from a thorough review of prescription and over-the-counter medications as well as careful attention to the distribution of dyspigmentation. Medications commonly associated with bluish nail bed dyspigmentation include antimalarials, amiodarone, minocycline, clofazimine, chlorpromazine/phenothiazines, and various chemotherapeutic drugs; our patient was not taking any of these.1,9
Cyanotic nail bed dyspigmentation secondary to cardiopulmonary disease likely manifests with more diffuse nail bed dyspigmentation and is not confined solely to the lunulae. Only drug-induced dyspigmentation, classically due to phenolphthalein-containing laxatives; Wilson disease; and argyria have a tendency to spare the distal nail bed, which is a presentation termed azure lunulae.8 The toenails typically are spared in argyria, while toenail involvement is variable in Wilson disease, and additional systemic symptoms—including hepatic, ophthalmologic, and neuropsychiatric—as well as potential family history would be expected.8 Phenolphthalein is no longer available in over-the-counter laxatives, as it was formally banned by the US Food and Drug Administration in 1999 due to concerns of carcinogenicity.10
Hereditary acrolabial telangiectasia is a familial condition with autosomal-dominant inheritance that can manifest similarly to argyria with blue-gray discoloration of the proximal nail bed; however, this condition also would demonstrate involvement of the vermilion border and nipple areolae, often with associated telangiectasia and migraine headaches.11
Chloronychia (also known as green nail syndrome) is an infection of the nail bed with Pseudomonas aeruginosa that more commonly presents with greenblack discoloration with variable involvement of the fingernails and toenails. Chloronychia, often with associated onycholysis, typically is found in individuals with repeated exposure to water, soaps, and detergents.12 Our patient’s long-standing and unwavering nail bed appearance, involvement of all fingernail lunulae, lack of additional symptoms, and disclosed use of over-the-counter colloidal silver supported a clinical diagnosis of argyriainduced azure lunulae.
Argyria-induced azure lunulae secondary to colloidal silver exposure is an uncommon yet clinically significant cause of nail bed dyspigmentation. Prompt identification and cessation of the offending agent can prevent progression of mucocutaneous dyspigmentation and avoid potential long-term sequelae from systemic deposition.
The Diagnosis: Argyria-Induced Azure Lunulae
Argyria is an acquired condition resulting from excessive exogenous exposure to silver with subsequent gastrointestinal absorption and pigmentary tissue deposition. Upon further questioning, our patient disclosed a lifetime history of colloidal silver use, both as a topical antiseptic agent and intraorally for aphthous ulcers. Silver has a predilection for granular deposition in stromal tissues and basement membranes with sparing of the epidermis, manifesting as progressive, permanent, blue to slate gray discoloration of sunexposed skin, mucous membranes, and nail beds.1 The patient was advised to discontinue use of colloidal silver to avoid development of further pigmentary changes. The appearance of his nails remained unchanged in the months following initial presentation, as expected, since argyria pigmentation is not anticipated to reverse upon colloidal silver cessation.
Nail involvement may be an early presentation of generalized argyria or may be found in isolation, as seen in our patient. Early recognition and patient education are essential to minimize cumulative silver deposition. Although dyspigmentation may impact psychosocial well-being secondary to aesthetic concerns, there is limited research supporting adverse systemic effects of argyria confined to the nail beds. Similarly, the majority of generalized cases are not associated with systemic complications; however, potential toxicities, as described in isolated case reports without conclusive causal relationships, include nyctalopia, renal or hepatic toxicity, pulmonary fibrosis, and neuropsychiatric events.1-6 Successful treatment of cutaneous argyria has been reported with the 1064-nm Q-switched Nd:YAG laser; however, there have been no reported treatments for nail bed involvement.7 Due to the absence of systemic symptoms, additional mucocutaneous dyspigmentation, or cosmetic concerns regarding nail bed lunulae discoloration in our patient, no further intervention was pursued, except for continued colloidal silver cessation.
The differential diagnosis of blue-gray nail bed dyspigmentation is broad and includes cyanosis secondary to cardiopulmonary disease, drug-induced dyspigmentation, Wilson disease, argyria, chrysiasis, hereditary acrolabial telangiectasia, and pseudomonal infection or chloronychia.1,8,9 Etiologic insight may be provided from a thorough review of prescription and over-the-counter medications as well as careful attention to the distribution of dyspigmentation. Medications commonly associated with bluish nail bed dyspigmentation include antimalarials, amiodarone, minocycline, clofazimine, chlorpromazine/phenothiazines, and various chemotherapeutic drugs; our patient was not taking any of these.1,9
Cyanotic nail bed dyspigmentation secondary to cardiopulmonary disease likely manifests with more diffuse nail bed dyspigmentation and is not confined solely to the lunulae. Only drug-induced dyspigmentation, classically due to phenolphthalein-containing laxatives; Wilson disease; and argyria have a tendency to spare the distal nail bed, which is a presentation termed azure lunulae.8 The toenails typically are spared in argyria, while toenail involvement is variable in Wilson disease, and additional systemic symptoms—including hepatic, ophthalmologic, and neuropsychiatric—as well as potential family history would be expected.8 Phenolphthalein is no longer available in over-the-counter laxatives, as it was formally banned by the US Food and Drug Administration in 1999 due to concerns of carcinogenicity.10
Hereditary acrolabial telangiectasia is a familial condition with autosomal-dominant inheritance that can manifest similarly to argyria with blue-gray discoloration of the proximal nail bed; however, this condition also would demonstrate involvement of the vermilion border and nipple areolae, often with associated telangiectasia and migraine headaches.11
Chloronychia (also known as green nail syndrome) is an infection of the nail bed with Pseudomonas aeruginosa that more commonly presents with greenblack discoloration with variable involvement of the fingernails and toenails. Chloronychia, often with associated onycholysis, typically is found in individuals with repeated exposure to water, soaps, and detergents.12 Our patient’s long-standing and unwavering nail bed appearance, involvement of all fingernail lunulae, lack of additional symptoms, and disclosed use of over-the-counter colloidal silver supported a clinical diagnosis of argyriainduced azure lunulae.
Argyria-induced azure lunulae secondary to colloidal silver exposure is an uncommon yet clinically significant cause of nail bed dyspigmentation. Prompt identification and cessation of the offending agent can prevent progression of mucocutaneous dyspigmentation and avoid potential long-term sequelae from systemic deposition.
- Mota L, Dinis-Oliveira RJ. Clinical and forensic aspects of the different subtypes of argyria. J Clin Med. 2021;10:2086. doi:10.3390/ jcm10102086
- Osin´ska J, Poborc-Godlewska J, Kiec´-Swierczyn´ska M, et al. 6 cases of argyria among workers engaged in silverplating radio subunits. Med Pr. 1982;33:361-364.
- Mayr M, Kim MJ, Wanner D, et al. Argyria and decreased kidney function: are silver compounds toxic to the kidney? Am J Kidney Dis. 2009;53:890-894. doi:10.1053/j.ajkd.2008.08.028
- Trop M, Novak M, Rodl S, et al. Silver-coated dressing acticoat caused raised liver enzymes and argyria-like symptoms in burn patient. J Trauma. 2006;60:648-652. doi:10.1097/01.ta.0000208126 .22089.b6
- Mirsattari SM, Hammond RR, Sharpe MD, et al. Myoclonic status epilepticus following repeated oral ingestion of colloidal silver. Neurology. 2004;62:1408-1410. doi:10.1212/01.wnl.0000120671.73335.ec
- Barrie HJ, Harding HE. Argyro-siderosis of the lungs in silver finishers. Br J Ind Med. 1947;4:225-229. doi:10.1136/oem.4.4.225
- Griffith RD, Simmons BJ, Bray FN, et al. 1064 nm Q-switched Nd:YAG laser for the treatment of argyria: a systematic review. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2015;29:2100-2103. doi:10.111 1/jdv.13117
- Rubin AI, Jellinek NJ, Daniel CR III, et al, eds. Scher and Daniel’s Nails: Diagnosis, Surgery, Therapy. 4th ed. Springer; 2018.
- Slater K, Sommariva E, Kartono F. A case study of argyria of the nails secondary to colloidal silver ingestion [published online October 28, 2022]. Cureus. 2022;14:E30818. doi:10.7759/cureus.30818
- Hubbard WK. Laxative drug products for over-the-counter human use. Fed Register. 1999;64:4535-4540. Accessed January 5, 2024. https://www.govinfo.gov/content/pkg/FR-1999-01-29/html/99-1938.htm
- Millns JL, Dicken CH. Hereditary acrolabial telangiectasia. a report of familial blue lips, nails, and nipples. Arch Dermatol. 1979;115:474-478. doi:10.1001/archderm.115.4.474
- Chiriac A, Brzezinski P, Foia L, et al. Chloronychia: green nail syndrome caused by Pseudomonas aeruginosa in elderly persons [published online January 14, 2015]. Clin Interv Aging. 2015;10:265-267. doi:10.2147/CIA.S75525
- Mota L, Dinis-Oliveira RJ. Clinical and forensic aspects of the different subtypes of argyria. J Clin Med. 2021;10:2086. doi:10.3390/ jcm10102086
- Osin´ska J, Poborc-Godlewska J, Kiec´-Swierczyn´ska M, et al. 6 cases of argyria among workers engaged in silverplating radio subunits. Med Pr. 1982;33:361-364.
- Mayr M, Kim MJ, Wanner D, et al. Argyria and decreased kidney function: are silver compounds toxic to the kidney? Am J Kidney Dis. 2009;53:890-894. doi:10.1053/j.ajkd.2008.08.028
- Trop M, Novak M, Rodl S, et al. Silver-coated dressing acticoat caused raised liver enzymes and argyria-like symptoms in burn patient. J Trauma. 2006;60:648-652. doi:10.1097/01.ta.0000208126 .22089.b6
- Mirsattari SM, Hammond RR, Sharpe MD, et al. Myoclonic status epilepticus following repeated oral ingestion of colloidal silver. Neurology. 2004;62:1408-1410. doi:10.1212/01.wnl.0000120671.73335.ec
- Barrie HJ, Harding HE. Argyro-siderosis of the lungs in silver finishers. Br J Ind Med. 1947;4:225-229. doi:10.1136/oem.4.4.225
- Griffith RD, Simmons BJ, Bray FN, et al. 1064 nm Q-switched Nd:YAG laser for the treatment of argyria: a systematic review. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2015;29:2100-2103. doi:10.111 1/jdv.13117
- Rubin AI, Jellinek NJ, Daniel CR III, et al, eds. Scher and Daniel’s Nails: Diagnosis, Surgery, Therapy. 4th ed. Springer; 2018.
- Slater K, Sommariva E, Kartono F. A case study of argyria of the nails secondary to colloidal silver ingestion [published online October 28, 2022]. Cureus. 2022;14:E30818. doi:10.7759/cureus.30818
- Hubbard WK. Laxative drug products for over-the-counter human use. Fed Register. 1999;64:4535-4540. Accessed January 5, 2024. https://www.govinfo.gov/content/pkg/FR-1999-01-29/html/99-1938.htm
- Millns JL, Dicken CH. Hereditary acrolabial telangiectasia. a report of familial blue lips, nails, and nipples. Arch Dermatol. 1979;115:474-478. doi:10.1001/archderm.115.4.474
- Chiriac A, Brzezinski P, Foia L, et al. Chloronychia: green nail syndrome caused by Pseudomonas aeruginosa in elderly persons [published online January 14, 2015]. Clin Interv Aging. 2015;10:265-267. doi:10.2147/CIA.S75525
An 88-year-old man presented with asymptomatic and unchanging discoloration of the proximal fingernails of both hands of 50 years’ duration. Physical examination revealed blue to slate gray, subungual pigmentary changes of the fingernails of both hands sparing the nail bed distal to the lunulae. There was no overlying plate dystrophy, toenail involvement, or additional mucocutaneous abnormalities. His medical history was notable for heart failure, obstructive sleep apnea, and type 2 diabetes mellitus. He had no history of hepatic, ophthalmologic, or neurologic dysfunction.
Vitamin D levels are lower in patients with eosinophilic esophagitis
Key clinical point: The serum levels of vitamin D are significantly lower in patients with newly diagnosed eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE) than in control individuals without EoE; however, vitamin D levels are not strongly linked with the clinical, endoscopic, or histologic features of EoE.
Major finding: Mean serum 25-hydroxy-vitamin D3 levels were lower by 10.8 ng/mL in patients with EoE vs control individuals (95% CI −19.0 to −2.51). However, these levels were neither associated with differences in clinical or endoscopic features of EoE nor did they significantly correlate with EoE Endoscopic Reference Scores and eosinophil counts (Pearson’s R −0.28, P = .08; and −0.01, P = .93, respectively).
Study details: This secondary analysis of a prospective cohort study used the data of adults who underwent endoscopy and biopsy for upper gastrointestinal symptoms, of whom 40 were diagnosed with EoE and 40 were control individuals without EoE.
Disclosures: This study was supported by the US National Institutes of Health. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Source: Cameron BA et al. Vitamin D levels as a potential modifier of eosinophilic esophagitis severity in adults. Dig Dis Sci. 2024 (Jan 6). doi: 10.1007/s10620-023-08264-x
Key clinical point: The serum levels of vitamin D are significantly lower in patients with newly diagnosed eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE) than in control individuals without EoE; however, vitamin D levels are not strongly linked with the clinical, endoscopic, or histologic features of EoE.
Major finding: Mean serum 25-hydroxy-vitamin D3 levels were lower by 10.8 ng/mL in patients with EoE vs control individuals (95% CI −19.0 to −2.51). However, these levels were neither associated with differences in clinical or endoscopic features of EoE nor did they significantly correlate with EoE Endoscopic Reference Scores and eosinophil counts (Pearson’s R −0.28, P = .08; and −0.01, P = .93, respectively).
Study details: This secondary analysis of a prospective cohort study used the data of adults who underwent endoscopy and biopsy for upper gastrointestinal symptoms, of whom 40 were diagnosed with EoE and 40 were control individuals without EoE.
Disclosures: This study was supported by the US National Institutes of Health. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Source: Cameron BA et al. Vitamin D levels as a potential modifier of eosinophilic esophagitis severity in adults. Dig Dis Sci. 2024 (Jan 6). doi: 10.1007/s10620-023-08264-x
Key clinical point: The serum levels of vitamin D are significantly lower in patients with newly diagnosed eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE) than in control individuals without EoE; however, vitamin D levels are not strongly linked with the clinical, endoscopic, or histologic features of EoE.
Major finding: Mean serum 25-hydroxy-vitamin D3 levels were lower by 10.8 ng/mL in patients with EoE vs control individuals (95% CI −19.0 to −2.51). However, these levels were neither associated with differences in clinical or endoscopic features of EoE nor did they significantly correlate with EoE Endoscopic Reference Scores and eosinophil counts (Pearson’s R −0.28, P = .08; and −0.01, P = .93, respectively).
Study details: This secondary analysis of a prospective cohort study used the data of adults who underwent endoscopy and biopsy for upper gastrointestinal symptoms, of whom 40 were diagnosed with EoE and 40 were control individuals without EoE.
Disclosures: This study was supported by the US National Institutes of Health. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Source: Cameron BA et al. Vitamin D levels as a potential modifier of eosinophilic esophagitis severity in adults. Dig Dis Sci. 2024 (Jan 6). doi: 10.1007/s10620-023-08264-x
Allergic phenotypes may predict low response to proton-pump inhibitors in eosinophilic esophagitis
Key clinical point: Patients with eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE) who test positive for food and environmental allergens may report a lower response to proton-pump inhibitor (PPI) treatment, a first-line treatment for EoE.
Major finding: Positive food allergen testing predicted lower odds of histologic response (adjusted odds ratio [aOR] 0.15; P = .0006) and symptom response (aOR 0.22; P = .03) to PPI therapy. Patients with a higher number of positive environmental allergens detected on skin-prick testing (≥10 vs <10) were less likely to respond to PPI (21.0% vs 53.9%; P = .03).
Study details: Findings are from a retrospective study including 61 adults with newly diagnosed EoE who underwent formal allergy testing for food and environmental allergens and received PPI therapy twice daily after EoE diagnosis.
Disclosures: The corresponding author WW Chan declared serving on the scientific advisory board for a several pharmaceutical companies.
Source: Muftah M et al. Allergic phenotype identified on allergen testing is associated with proton pump inhibitor nonresponse in eosinophilic esophagitis. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2024 (Jan 7). doi: 10.1111/jgh.16469
Key clinical point: Patients with eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE) who test positive for food and environmental allergens may report a lower response to proton-pump inhibitor (PPI) treatment, a first-line treatment for EoE.
Major finding: Positive food allergen testing predicted lower odds of histologic response (adjusted odds ratio [aOR] 0.15; P = .0006) and symptom response (aOR 0.22; P = .03) to PPI therapy. Patients with a higher number of positive environmental allergens detected on skin-prick testing (≥10 vs <10) were less likely to respond to PPI (21.0% vs 53.9%; P = .03).
Study details: Findings are from a retrospective study including 61 adults with newly diagnosed EoE who underwent formal allergy testing for food and environmental allergens and received PPI therapy twice daily after EoE diagnosis.
Disclosures: The corresponding author WW Chan declared serving on the scientific advisory board for a several pharmaceutical companies.
Source: Muftah M et al. Allergic phenotype identified on allergen testing is associated with proton pump inhibitor nonresponse in eosinophilic esophagitis. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2024 (Jan 7). doi: 10.1111/jgh.16469
Key clinical point: Patients with eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE) who test positive for food and environmental allergens may report a lower response to proton-pump inhibitor (PPI) treatment, a first-line treatment for EoE.
Major finding: Positive food allergen testing predicted lower odds of histologic response (adjusted odds ratio [aOR] 0.15; P = .0006) and symptom response (aOR 0.22; P = .03) to PPI therapy. Patients with a higher number of positive environmental allergens detected on skin-prick testing (≥10 vs <10) were less likely to respond to PPI (21.0% vs 53.9%; P = .03).
Study details: Findings are from a retrospective study including 61 adults with newly diagnosed EoE who underwent formal allergy testing for food and environmental allergens and received PPI therapy twice daily after EoE diagnosis.
Disclosures: The corresponding author WW Chan declared serving on the scientific advisory board for a several pharmaceutical companies.
Source: Muftah M et al. Allergic phenotype identified on allergen testing is associated with proton pump inhibitor nonresponse in eosinophilic esophagitis. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2024 (Jan 7). doi: 10.1111/jgh.16469
Histological categories do not help in predicting treatment response in eosinophilic esophagitis
Key clinical point: Budesonide orodispersible tablet (BOT) induces clinicohistological remission irrespective of the distribution of esophageal eosinophilia. Histological categories are not predictors of treatment response in patients with eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE).
Major finding: Histological categories were not found to be significantly associated with treatment outcome (mid: adjusted odds ratio [aOR] 1.75; 95% CI 0.588-5.25; distal: aOR 1.42; 95% CI 0.535-3.60; diffuse: aOR 0.910; 95% CI 0.358-2.19).
Study details: This post hoc analysis of the phase 3 EOS-1 and EOS-2 trials included 263 patients with EoE having either proximal, mid, or distal esophagus predominant disease or diffuse disease who received a 6-week induction treatment with BOT.
Disclosures: This study was supported by the Swiss National Science Foundation and others. Some authors declared serving as consultants for or receiving speaker or consulting fees or travel grants from various sources.
Source: Godat A et al on behalf of the EoE eosinophil distribution research group. Eosinophil distribution in eosinophilic esophagitis and its impact on disease activity and response to treatment. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2023 (Dec 15). doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2023.12.003
Key clinical point: Budesonide orodispersible tablet (BOT) induces clinicohistological remission irrespective of the distribution of esophageal eosinophilia. Histological categories are not predictors of treatment response in patients with eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE).
Major finding: Histological categories were not found to be significantly associated with treatment outcome (mid: adjusted odds ratio [aOR] 1.75; 95% CI 0.588-5.25; distal: aOR 1.42; 95% CI 0.535-3.60; diffuse: aOR 0.910; 95% CI 0.358-2.19).
Study details: This post hoc analysis of the phase 3 EOS-1 and EOS-2 trials included 263 patients with EoE having either proximal, mid, or distal esophagus predominant disease or diffuse disease who received a 6-week induction treatment with BOT.
Disclosures: This study was supported by the Swiss National Science Foundation and others. Some authors declared serving as consultants for or receiving speaker or consulting fees or travel grants from various sources.
Source: Godat A et al on behalf of the EoE eosinophil distribution research group. Eosinophil distribution in eosinophilic esophagitis and its impact on disease activity and response to treatment. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2023 (Dec 15). doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2023.12.003
Key clinical point: Budesonide orodispersible tablet (BOT) induces clinicohistological remission irrespective of the distribution of esophageal eosinophilia. Histological categories are not predictors of treatment response in patients with eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE).
Major finding: Histological categories were not found to be significantly associated with treatment outcome (mid: adjusted odds ratio [aOR] 1.75; 95% CI 0.588-5.25; distal: aOR 1.42; 95% CI 0.535-3.60; diffuse: aOR 0.910; 95% CI 0.358-2.19).
Study details: This post hoc analysis of the phase 3 EOS-1 and EOS-2 trials included 263 patients with EoE having either proximal, mid, or distal esophagus predominant disease or diffuse disease who received a 6-week induction treatment with BOT.
Disclosures: This study was supported by the Swiss National Science Foundation and others. Some authors declared serving as consultants for or receiving speaker or consulting fees or travel grants from various sources.
Source: Godat A et al on behalf of the EoE eosinophil distribution research group. Eosinophil distribution in eosinophilic esophagitis and its impact on disease activity and response to treatment. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2023 (Dec 15). doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2023.12.003
Eosinophil-derived neurotoxin can help diagnose eosinophilic esophagitis in exclusive distal eosinophilia
Key clinical point: The levels of eosinophil-derived neurotoxin (EDN) may be used to track disease activity in patients with eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE) patients and may aid the diagnosis of EoE in patients with challenging conditions, such as distal eosinophilia.
Major finding: The average endoscopic reference score (EREFS; 3.4 vs 0.4; P < .001) and EDN concentrations (135.8 µg/mL vs 3.2 µg/mL; P < .001) were significantly higher in patients with active EoE vs control individuals. In patients with exclusive distant eosinophilia, positive (≥10 µg/mL) vs negative EDN concentrations correlated with significantly higher EREFS (3.33 vs 1.35, P < .001), which indicated a diagnosis of EoE.
Study details: Findings are from a retrospective study that included children and young adults who underwent routine endoscopy with biopsy and EDN esophageal epithelial brushings, of whom 140 had EoE and 91 were control individuals without EoE.
Disclosures: This study did not receive any external funding. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Source: Thomas J et al. Addressing diagnostic dilemmas in eosinophilic esophagitis using esophageal epithelial eosinophil-derived neurotoxin. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2023 (Dec 27). doi: 10.1002/jpn3.12054
Key clinical point: The levels of eosinophil-derived neurotoxin (EDN) may be used to track disease activity in patients with eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE) patients and may aid the diagnosis of EoE in patients with challenging conditions, such as distal eosinophilia.
Major finding: The average endoscopic reference score (EREFS; 3.4 vs 0.4; P < .001) and EDN concentrations (135.8 µg/mL vs 3.2 µg/mL; P < .001) were significantly higher in patients with active EoE vs control individuals. In patients with exclusive distant eosinophilia, positive (≥10 µg/mL) vs negative EDN concentrations correlated with significantly higher EREFS (3.33 vs 1.35, P < .001), which indicated a diagnosis of EoE.
Study details: Findings are from a retrospective study that included children and young adults who underwent routine endoscopy with biopsy and EDN esophageal epithelial brushings, of whom 140 had EoE and 91 were control individuals without EoE.
Disclosures: This study did not receive any external funding. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Source: Thomas J et al. Addressing diagnostic dilemmas in eosinophilic esophagitis using esophageal epithelial eosinophil-derived neurotoxin. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2023 (Dec 27). doi: 10.1002/jpn3.12054
Key clinical point: The levels of eosinophil-derived neurotoxin (EDN) may be used to track disease activity in patients with eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE) patients and may aid the diagnosis of EoE in patients with challenging conditions, such as distal eosinophilia.
Major finding: The average endoscopic reference score (EREFS; 3.4 vs 0.4; P < .001) and EDN concentrations (135.8 µg/mL vs 3.2 µg/mL; P < .001) were significantly higher in patients with active EoE vs control individuals. In patients with exclusive distant eosinophilia, positive (≥10 µg/mL) vs negative EDN concentrations correlated with significantly higher EREFS (3.33 vs 1.35, P < .001), which indicated a diagnosis of EoE.
Study details: Findings are from a retrospective study that included children and young adults who underwent routine endoscopy with biopsy and EDN esophageal epithelial brushings, of whom 140 had EoE and 91 were control individuals without EoE.
Disclosures: This study did not receive any external funding. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Source: Thomas J et al. Addressing diagnostic dilemmas in eosinophilic esophagitis using esophageal epithelial eosinophil-derived neurotoxin. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2023 (Dec 27). doi: 10.1002/jpn3.12054
Eosinophil levels may predict concomitant non-EoE diseases in patients with EoE
Key clinical point: Patients with eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE) may also present with non-EoE eosinophilic gastrointestinal diseases (EGID) with esophageal involvement (EI; EGID + EI) if they have high levels of peripheral blood eosinophils.
Major finding: Patients with EGID + EI vs EoE were more likely to have eczema (P = .003), food allergy (P < .001), abdominal pain (60.9% vs 45.0%; P = .002), and higher peripheral blood eosinophil levels (0.44 × 103/µL vs 0.38 × 103/µL; P = .027).
Study details: Findings are from an observational cohort study including 592 patients with isolated EoE and 190 patients with EGID + EI.
Disclosures: This study was supported by a grant from the US National Institutes of Health. ME Rothenberg and corresponding author T Shoda declared serving as a consultant or being inventors or co-inventors of patents.
Source: Sato H et al. Eosinophil involvement outside the esophagus in eosinophilic esophagitis. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2023 (Dec 14). doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2023.12.004
Key clinical point: Patients with eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE) may also present with non-EoE eosinophilic gastrointestinal diseases (EGID) with esophageal involvement (EI; EGID + EI) if they have high levels of peripheral blood eosinophils.
Major finding: Patients with EGID + EI vs EoE were more likely to have eczema (P = .003), food allergy (P < .001), abdominal pain (60.9% vs 45.0%; P = .002), and higher peripheral blood eosinophil levels (0.44 × 103/µL vs 0.38 × 103/µL; P = .027).
Study details: Findings are from an observational cohort study including 592 patients with isolated EoE and 190 patients with EGID + EI.
Disclosures: This study was supported by a grant from the US National Institutes of Health. ME Rothenberg and corresponding author T Shoda declared serving as a consultant or being inventors or co-inventors of patents.
Source: Sato H et al. Eosinophil involvement outside the esophagus in eosinophilic esophagitis. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2023 (Dec 14). doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2023.12.004
Key clinical point: Patients with eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE) may also present with non-EoE eosinophilic gastrointestinal diseases (EGID) with esophageal involvement (EI; EGID + EI) if they have high levels of peripheral blood eosinophils.
Major finding: Patients with EGID + EI vs EoE were more likely to have eczema (P = .003), food allergy (P < .001), abdominal pain (60.9% vs 45.0%; P = .002), and higher peripheral blood eosinophil levels (0.44 × 103/µL vs 0.38 × 103/µL; P = .027).
Study details: Findings are from an observational cohort study including 592 patients with isolated EoE and 190 patients with EGID + EI.
Disclosures: This study was supported by a grant from the US National Institutes of Health. ME Rothenberg and corresponding author T Shoda declared serving as a consultant or being inventors or co-inventors of patents.
Source: Sato H et al. Eosinophil involvement outside the esophagus in eosinophilic esophagitis. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2023 (Dec 14). doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2023.12.004
Real-world comparison of treatment pattern of CGRP antibodies in migraine
Key clinical point: Patients with migraine initiating calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) monoclonal antibody treatment with galcanezumab showed higher treatment persistence, lower treatment discontinuation, and similar adherence compared with those initiating fremanezumab or erenumab.
Major finding: Compared with fremanezumab, galcanezumab initiators showed higher rates of treatment persistence (P = .001) and lower treatment discontinuation (P = .005). Compared with erenumab, galcanezumab initiators had lower treatment discontinuation (P = .040). Patient adherence was similar among those who initiated galcanezumab vs fremanezumab or erenumab.
Study details: This retrospective real-world study included patients with migraine initiating galcanezumab treatment who were matched with those initiating fremanezumab (n = 2674) or erenumab (n = 3503) treatment using propensity score matching.
Disclosures: This study was funded by Eli Lilly and Company. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Source: Varnado OJ et al. Comparison of treatment patterns in patients with migraine initiating calcitonin gene-related peptide monoclonal antibodies: A Retrospective Real-World US Study. Patient Preference and Adherence. 2024;18:69-88 (Jan 9). doi: 10.2147/PPA.S437396
Key clinical point: Patients with migraine initiating calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) monoclonal antibody treatment with galcanezumab showed higher treatment persistence, lower treatment discontinuation, and similar adherence compared with those initiating fremanezumab or erenumab.
Major finding: Compared with fremanezumab, galcanezumab initiators showed higher rates of treatment persistence (P = .001) and lower treatment discontinuation (P = .005). Compared with erenumab, galcanezumab initiators had lower treatment discontinuation (P = .040). Patient adherence was similar among those who initiated galcanezumab vs fremanezumab or erenumab.
Study details: This retrospective real-world study included patients with migraine initiating galcanezumab treatment who were matched with those initiating fremanezumab (n = 2674) or erenumab (n = 3503) treatment using propensity score matching.
Disclosures: This study was funded by Eli Lilly and Company. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Source: Varnado OJ et al. Comparison of treatment patterns in patients with migraine initiating calcitonin gene-related peptide monoclonal antibodies: A Retrospective Real-World US Study. Patient Preference and Adherence. 2024;18:69-88 (Jan 9). doi: 10.2147/PPA.S437396
Key clinical point: Patients with migraine initiating calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) monoclonal antibody treatment with galcanezumab showed higher treatment persistence, lower treatment discontinuation, and similar adherence compared with those initiating fremanezumab or erenumab.
Major finding: Compared with fremanezumab, galcanezumab initiators showed higher rates of treatment persistence (P = .001) and lower treatment discontinuation (P = .005). Compared with erenumab, galcanezumab initiators had lower treatment discontinuation (P = .040). Patient adherence was similar among those who initiated galcanezumab vs fremanezumab or erenumab.
Study details: This retrospective real-world study included patients with migraine initiating galcanezumab treatment who were matched with those initiating fremanezumab (n = 2674) or erenumab (n = 3503) treatment using propensity score matching.
Disclosures: This study was funded by Eli Lilly and Company. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Source: Varnado OJ et al. Comparison of treatment patterns in patients with migraine initiating calcitonin gene-related peptide monoclonal antibodies: A Retrospective Real-World US Study. Patient Preference and Adherence. 2024;18:69-88 (Jan 9). doi: 10.2147/PPA.S437396
Higher delayed discounting rate among patients with episodic migraine without aura
Key clinical point: Patients with episodic migraine without aura (EMoA) presented a higher delayed discounting rate, which was positively associated with the migraine history.
Major finding: Patients with EMoA vs control individuals showed a significantly higher subjective discount rate (F = 4.74; P = .032), which was positively correlated with migraine history (r = 0.742; P < .001). The resting-state functional connectivity between the left ventral striatum and middle occipital gyrus was significantly associated with migraine history (r′ = 0.294; P = .036) and subjective discount rate (r′ = 0.380; P = .006).
Study details: This study included 51 patients with EMoA and 45 control individuals who underwent task-based and multi-model magnetic resonance imaging.
Disclosures: This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, Foundation for the Cultivation of Doctoral Research Talents, and the 2021 Youth Foundation Training Program of the First Affiliated Hospital of Anhui Medical University. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Source: Wang L et al. Patients with episodic migraine without aura have an increased rate of delayed discounting. Brain Behav. 2024;14(1):e3367 (Jan 2). doi: 10.1002/brb3.3367
Key clinical point: Patients with episodic migraine without aura (EMoA) presented a higher delayed discounting rate, which was positively associated with the migraine history.
Major finding: Patients with EMoA vs control individuals showed a significantly higher subjective discount rate (F = 4.74; P = .032), which was positively correlated with migraine history (r = 0.742; P < .001). The resting-state functional connectivity between the left ventral striatum and middle occipital gyrus was significantly associated with migraine history (r′ = 0.294; P = .036) and subjective discount rate (r′ = 0.380; P = .006).
Study details: This study included 51 patients with EMoA and 45 control individuals who underwent task-based and multi-model magnetic resonance imaging.
Disclosures: This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, Foundation for the Cultivation of Doctoral Research Talents, and the 2021 Youth Foundation Training Program of the First Affiliated Hospital of Anhui Medical University. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Source: Wang L et al. Patients with episodic migraine without aura have an increased rate of delayed discounting. Brain Behav. 2024;14(1):e3367 (Jan 2). doi: 10.1002/brb3.3367
Key clinical point: Patients with episodic migraine without aura (EMoA) presented a higher delayed discounting rate, which was positively associated with the migraine history.
Major finding: Patients with EMoA vs control individuals showed a significantly higher subjective discount rate (F = 4.74; P = .032), which was positively correlated with migraine history (r = 0.742; P < .001). The resting-state functional connectivity between the left ventral striatum and middle occipital gyrus was significantly associated with migraine history (r′ = 0.294; P = .036) and subjective discount rate (r′ = 0.380; P = .006).
Study details: This study included 51 patients with EMoA and 45 control individuals who underwent task-based and multi-model magnetic resonance imaging.
Disclosures: This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, Foundation for the Cultivation of Doctoral Research Talents, and the 2021 Youth Foundation Training Program of the First Affiliated Hospital of Anhui Medical University. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Source: Wang L et al. Patients with episodic migraine without aura have an increased rate of delayed discounting. Brain Behav. 2024;14(1):e3367 (Jan 2). doi: 10.1002/brb3.3367
Patients with migraine face an elevated risk for Parkinson's disease
Key clinical point: Patients with migraine have increased risk for incident Parkinson's disease (PD), with younger age and underlying dyslipidemia aggravating the risk for PD among women and men with migraine, respectively.
Major finding: The risk of incident PD was 1.35-fold (adjusted hazard ratio 1.35; 95% CI 1.29-1.41) higher in patients with vs without migraine, with the risk of PD being significantly higher among younger vs older women (age < 65 years vs ≥ 65 years; P = .038) and men with vs without dyslipidemia (P = .012).
Study details: This retrospective, nationwide, population-based cohort study included 214,193 individuals with migraine and 5,879,711 individuals without migraine, of whom 1973 (0.92%) and 30,664 (0.52%) individuals with and without migraine, respectively, were diagnosed with PD.
Disclosures: This research was supported by a grant from the National Research Foundation, Technology Development Program, and Technology Innovation Program. Korea. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Source: Ha WS et al. The association between migraine and Parkinson's disease: A nationwide cohort study. Epidemiol Health. 2023 (Dec 18). doi: 10.4178/epih.e2024010
Key clinical point: Patients with migraine have increased risk for incident Parkinson's disease (PD), with younger age and underlying dyslipidemia aggravating the risk for PD among women and men with migraine, respectively.
Major finding: The risk of incident PD was 1.35-fold (adjusted hazard ratio 1.35; 95% CI 1.29-1.41) higher in patients with vs without migraine, with the risk of PD being significantly higher among younger vs older women (age < 65 years vs ≥ 65 years; P = .038) and men with vs without dyslipidemia (P = .012).
Study details: This retrospective, nationwide, population-based cohort study included 214,193 individuals with migraine and 5,879,711 individuals without migraine, of whom 1973 (0.92%) and 30,664 (0.52%) individuals with and without migraine, respectively, were diagnosed with PD.
Disclosures: This research was supported by a grant from the National Research Foundation, Technology Development Program, and Technology Innovation Program. Korea. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Source: Ha WS et al. The association between migraine and Parkinson's disease: A nationwide cohort study. Epidemiol Health. 2023 (Dec 18). doi: 10.4178/epih.e2024010
Key clinical point: Patients with migraine have increased risk for incident Parkinson's disease (PD), with younger age and underlying dyslipidemia aggravating the risk for PD among women and men with migraine, respectively.
Major finding: The risk of incident PD was 1.35-fold (adjusted hazard ratio 1.35; 95% CI 1.29-1.41) higher in patients with vs without migraine, with the risk of PD being significantly higher among younger vs older women (age < 65 years vs ≥ 65 years; P = .038) and men with vs without dyslipidemia (P = .012).
Study details: This retrospective, nationwide, population-based cohort study included 214,193 individuals with migraine and 5,879,711 individuals without migraine, of whom 1973 (0.92%) and 30,664 (0.52%) individuals with and without migraine, respectively, were diagnosed with PD.
Disclosures: This research was supported by a grant from the National Research Foundation, Technology Development Program, and Technology Innovation Program. Korea. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Source: Ha WS et al. The association between migraine and Parkinson's disease: A nationwide cohort study. Epidemiol Health. 2023 (Dec 18). doi: 10.4178/epih.e2024010