User login
Self-directed digital exercise plan improves knee OA
Adults with knee osteoarthritis (OA) who participated in a self-directed, web-based exercise program with automated text-message reminders and encouragement for 6 months showed significant improvement in overall knee pain and physical function, compared with patients who received web-based OA information alone, in a randomized trial of 180 individuals.
The results support a role for web-based exercise intervention to improve knee OA patients’ access to recommended exercises and to assist clinicians in managing patients on a population level, according to the first author of the study, Rachel Kate Nelligan, of the University of Melbourne, and colleagues. Their report is in JAMA Internal Medicine.
“Our free-to-access, unsupervised program could serve as an entry-level intervention, with participants who do not experience clinical benefits progressing to subsequent steps for more intensive, personalized management,” they said. “Such an approach has the potential to better distribute limited health care resources and reduce demand for contact with health professionals, thus improving access for those requiring it.”
Only two other randomized, clinical trials have evaluated web-based interventions for OA without contact from health professionals, according to the authors. While one of those did not find any differences in outcomes at 4 months when comparing a self-directed progressive lower-limb strength, flexibility, and walking program to being on a wait list, a separate trial evaluating a 9-module physical activity program in adults with knee and/or hip OA vs. a wait-list control group found evidence for efficacy for physical function at 3 months, but not quality of life or function in sport and recreation.
For the current study, researchers recruited 206 adults in Australia with clinically diagnosed knee OA via online advertisements and a volunteer database. Participants were aged 45 years or older, and reported activity-related knee pain and morning knee stiffness lasting at least 30 minutes; knee pain on most days for at least 3 months; and average knee pain severity of 4 or higher on an 11-point numeric rating scale in the previous week. In addition, participants were required to own a cell phone with text messaging, have Internet access, and be able to complete assessments.
Patients randomized to the intervention of the My Knee Exercise website received web-based information about OA and the value of exercise, with a 24-week self-directed program of strengthening exercises plus automated text messages to motivate behavior changes and encourage adherence to the exercise program. Controls received access to web-based information about OA and the value of exercise, but without the prescribed exercises or texts. Patients in the intervention group received an average of 60 text messages during the study period, and the average reply rate was 73%.
The primary study outcomes were changes in overall knee pain based on a numeric 0-10 rating scale and changes in physical function based on the Western Ontario and McMaster Universities Osteoarthritis Index 0-68 scale. A total of 180 participants completed both primary outcome measures at 24 weeks. The average age of the participants was 60 years, and 61% were women.
After 24 weeks, the intervention group averaged significantly greater improvement of 1.6 units for overall knee pain (P < .001) and 5.2 units for physical function (P = .002), compared with controls.
In addition, the proportion of patients who exceeded the minimal clinically important difference in pain improvement of at least 1.8 units was significantly higher in the intervention group, compared with controls (72.1% vs. 42.0%; P < .001). Similarly, more intervention-group patients achieved the minimal clinically important difference in WOMAC physical function of improvement of at least 6 units (68.0% vs. 40.8%; P < .001).
Secondary outcomes included additional measures of knee pain, knee function for sport and recreation, quality of life, physical activity, self-efficacy, overall improvement, and treatment satisfaction. Between-group differences favored the intervention on most measures, including Knee Injury and Osteoarthritis Outcome Score subscales for pain, sports/recreation, and quality of life; health-related quality of life; Arthritis Self-Efficacy Scale (ASES) pain subscale, individual change since baseline, and overall patient satisfaction. “Changes in PASE [Physical Activity Scale for the Elderly], ASES function, and SEE [Self Efficacy Exercise] were similar in both groups,” the researchers said.
No serious adverse events were reported by any study participants. Eight patients in the intervention group reported knee pain during the study, compared with one of the controls, and use of pain medications was similar between the groups, except that more control participants used massage, heat or cold, and topical anti-inflammatories.
The results suggest that a majority of participants in the intervention group improved pain and function without the need for in-person contact with a health professional, the researchers noted. However, more intensive management may be needed to support the 30% who did not benefit from the unsupervised approach, they said.
The study findings were limited by several factors, including the potential bias of a volunteer study population, possible lack of generalizability to individuals with lower levels of education or self-efficacy, and lack of direct comparison between web-based intervention and clinician-delivered intervention, the researchers noted.
The study was funded by the National Health and Medical Research Council, whose fellowships supported two of the authors. Lead author Ms. Nelligan disclosed a PhD scholarship from the Australian Government Research Training Program and personal fees from the University of Melbourne unrelated to the current study.
Adults with knee osteoarthritis (OA) who participated in a self-directed, web-based exercise program with automated text-message reminders and encouragement for 6 months showed significant improvement in overall knee pain and physical function, compared with patients who received web-based OA information alone, in a randomized trial of 180 individuals.
The results support a role for web-based exercise intervention to improve knee OA patients’ access to recommended exercises and to assist clinicians in managing patients on a population level, according to the first author of the study, Rachel Kate Nelligan, of the University of Melbourne, and colleagues. Their report is in JAMA Internal Medicine.
“Our free-to-access, unsupervised program could serve as an entry-level intervention, with participants who do not experience clinical benefits progressing to subsequent steps for more intensive, personalized management,” they said. “Such an approach has the potential to better distribute limited health care resources and reduce demand for contact with health professionals, thus improving access for those requiring it.”
Only two other randomized, clinical trials have evaluated web-based interventions for OA without contact from health professionals, according to the authors. While one of those did not find any differences in outcomes at 4 months when comparing a self-directed progressive lower-limb strength, flexibility, and walking program to being on a wait list, a separate trial evaluating a 9-module physical activity program in adults with knee and/or hip OA vs. a wait-list control group found evidence for efficacy for physical function at 3 months, but not quality of life or function in sport and recreation.
For the current study, researchers recruited 206 adults in Australia with clinically diagnosed knee OA via online advertisements and a volunteer database. Participants were aged 45 years or older, and reported activity-related knee pain and morning knee stiffness lasting at least 30 minutes; knee pain on most days for at least 3 months; and average knee pain severity of 4 or higher on an 11-point numeric rating scale in the previous week. In addition, participants were required to own a cell phone with text messaging, have Internet access, and be able to complete assessments.
Patients randomized to the intervention of the My Knee Exercise website received web-based information about OA and the value of exercise, with a 24-week self-directed program of strengthening exercises plus automated text messages to motivate behavior changes and encourage adherence to the exercise program. Controls received access to web-based information about OA and the value of exercise, but without the prescribed exercises or texts. Patients in the intervention group received an average of 60 text messages during the study period, and the average reply rate was 73%.
The primary study outcomes were changes in overall knee pain based on a numeric 0-10 rating scale and changes in physical function based on the Western Ontario and McMaster Universities Osteoarthritis Index 0-68 scale. A total of 180 participants completed both primary outcome measures at 24 weeks. The average age of the participants was 60 years, and 61% were women.
After 24 weeks, the intervention group averaged significantly greater improvement of 1.6 units for overall knee pain (P < .001) and 5.2 units for physical function (P = .002), compared with controls.
In addition, the proportion of patients who exceeded the minimal clinically important difference in pain improvement of at least 1.8 units was significantly higher in the intervention group, compared with controls (72.1% vs. 42.0%; P < .001). Similarly, more intervention-group patients achieved the minimal clinically important difference in WOMAC physical function of improvement of at least 6 units (68.0% vs. 40.8%; P < .001).
Secondary outcomes included additional measures of knee pain, knee function for sport and recreation, quality of life, physical activity, self-efficacy, overall improvement, and treatment satisfaction. Between-group differences favored the intervention on most measures, including Knee Injury and Osteoarthritis Outcome Score subscales for pain, sports/recreation, and quality of life; health-related quality of life; Arthritis Self-Efficacy Scale (ASES) pain subscale, individual change since baseline, and overall patient satisfaction. “Changes in PASE [Physical Activity Scale for the Elderly], ASES function, and SEE [Self Efficacy Exercise] were similar in both groups,” the researchers said.
No serious adverse events were reported by any study participants. Eight patients in the intervention group reported knee pain during the study, compared with one of the controls, and use of pain medications was similar between the groups, except that more control participants used massage, heat or cold, and topical anti-inflammatories.
The results suggest that a majority of participants in the intervention group improved pain and function without the need for in-person contact with a health professional, the researchers noted. However, more intensive management may be needed to support the 30% who did not benefit from the unsupervised approach, they said.
The study findings were limited by several factors, including the potential bias of a volunteer study population, possible lack of generalizability to individuals with lower levels of education or self-efficacy, and lack of direct comparison between web-based intervention and clinician-delivered intervention, the researchers noted.
The study was funded by the National Health and Medical Research Council, whose fellowships supported two of the authors. Lead author Ms. Nelligan disclosed a PhD scholarship from the Australian Government Research Training Program and personal fees from the University of Melbourne unrelated to the current study.
Adults with knee osteoarthritis (OA) who participated in a self-directed, web-based exercise program with automated text-message reminders and encouragement for 6 months showed significant improvement in overall knee pain and physical function, compared with patients who received web-based OA information alone, in a randomized trial of 180 individuals.
The results support a role for web-based exercise intervention to improve knee OA patients’ access to recommended exercises and to assist clinicians in managing patients on a population level, according to the first author of the study, Rachel Kate Nelligan, of the University of Melbourne, and colleagues. Their report is in JAMA Internal Medicine.
“Our free-to-access, unsupervised program could serve as an entry-level intervention, with participants who do not experience clinical benefits progressing to subsequent steps for more intensive, personalized management,” they said. “Such an approach has the potential to better distribute limited health care resources and reduce demand for contact with health professionals, thus improving access for those requiring it.”
Only two other randomized, clinical trials have evaluated web-based interventions for OA without contact from health professionals, according to the authors. While one of those did not find any differences in outcomes at 4 months when comparing a self-directed progressive lower-limb strength, flexibility, and walking program to being on a wait list, a separate trial evaluating a 9-module physical activity program in adults with knee and/or hip OA vs. a wait-list control group found evidence for efficacy for physical function at 3 months, but not quality of life or function in sport and recreation.
For the current study, researchers recruited 206 adults in Australia with clinically diagnosed knee OA via online advertisements and a volunteer database. Participants were aged 45 years or older, and reported activity-related knee pain and morning knee stiffness lasting at least 30 minutes; knee pain on most days for at least 3 months; and average knee pain severity of 4 or higher on an 11-point numeric rating scale in the previous week. In addition, participants were required to own a cell phone with text messaging, have Internet access, and be able to complete assessments.
Patients randomized to the intervention of the My Knee Exercise website received web-based information about OA and the value of exercise, with a 24-week self-directed program of strengthening exercises plus automated text messages to motivate behavior changes and encourage adherence to the exercise program. Controls received access to web-based information about OA and the value of exercise, but without the prescribed exercises or texts. Patients in the intervention group received an average of 60 text messages during the study period, and the average reply rate was 73%.
The primary study outcomes were changes in overall knee pain based on a numeric 0-10 rating scale and changes in physical function based on the Western Ontario and McMaster Universities Osteoarthritis Index 0-68 scale. A total of 180 participants completed both primary outcome measures at 24 weeks. The average age of the participants was 60 years, and 61% were women.
After 24 weeks, the intervention group averaged significantly greater improvement of 1.6 units for overall knee pain (P < .001) and 5.2 units for physical function (P = .002), compared with controls.
In addition, the proportion of patients who exceeded the minimal clinically important difference in pain improvement of at least 1.8 units was significantly higher in the intervention group, compared with controls (72.1% vs. 42.0%; P < .001). Similarly, more intervention-group patients achieved the minimal clinically important difference in WOMAC physical function of improvement of at least 6 units (68.0% vs. 40.8%; P < .001).
Secondary outcomes included additional measures of knee pain, knee function for sport and recreation, quality of life, physical activity, self-efficacy, overall improvement, and treatment satisfaction. Between-group differences favored the intervention on most measures, including Knee Injury and Osteoarthritis Outcome Score subscales for pain, sports/recreation, and quality of life; health-related quality of life; Arthritis Self-Efficacy Scale (ASES) pain subscale, individual change since baseline, and overall patient satisfaction. “Changes in PASE [Physical Activity Scale for the Elderly], ASES function, and SEE [Self Efficacy Exercise] were similar in both groups,” the researchers said.
No serious adverse events were reported by any study participants. Eight patients in the intervention group reported knee pain during the study, compared with one of the controls, and use of pain medications was similar between the groups, except that more control participants used massage, heat or cold, and topical anti-inflammatories.
The results suggest that a majority of participants in the intervention group improved pain and function without the need for in-person contact with a health professional, the researchers noted. However, more intensive management may be needed to support the 30% who did not benefit from the unsupervised approach, they said.
The study findings were limited by several factors, including the potential bias of a volunteer study population, possible lack of generalizability to individuals with lower levels of education or self-efficacy, and lack of direct comparison between web-based intervention and clinician-delivered intervention, the researchers noted.
The study was funded by the National Health and Medical Research Council, whose fellowships supported two of the authors. Lead author Ms. Nelligan disclosed a PhD scholarship from the Australian Government Research Training Program and personal fees from the University of Melbourne unrelated to the current study.
FROM JAMA INTERNAL MEDICINE
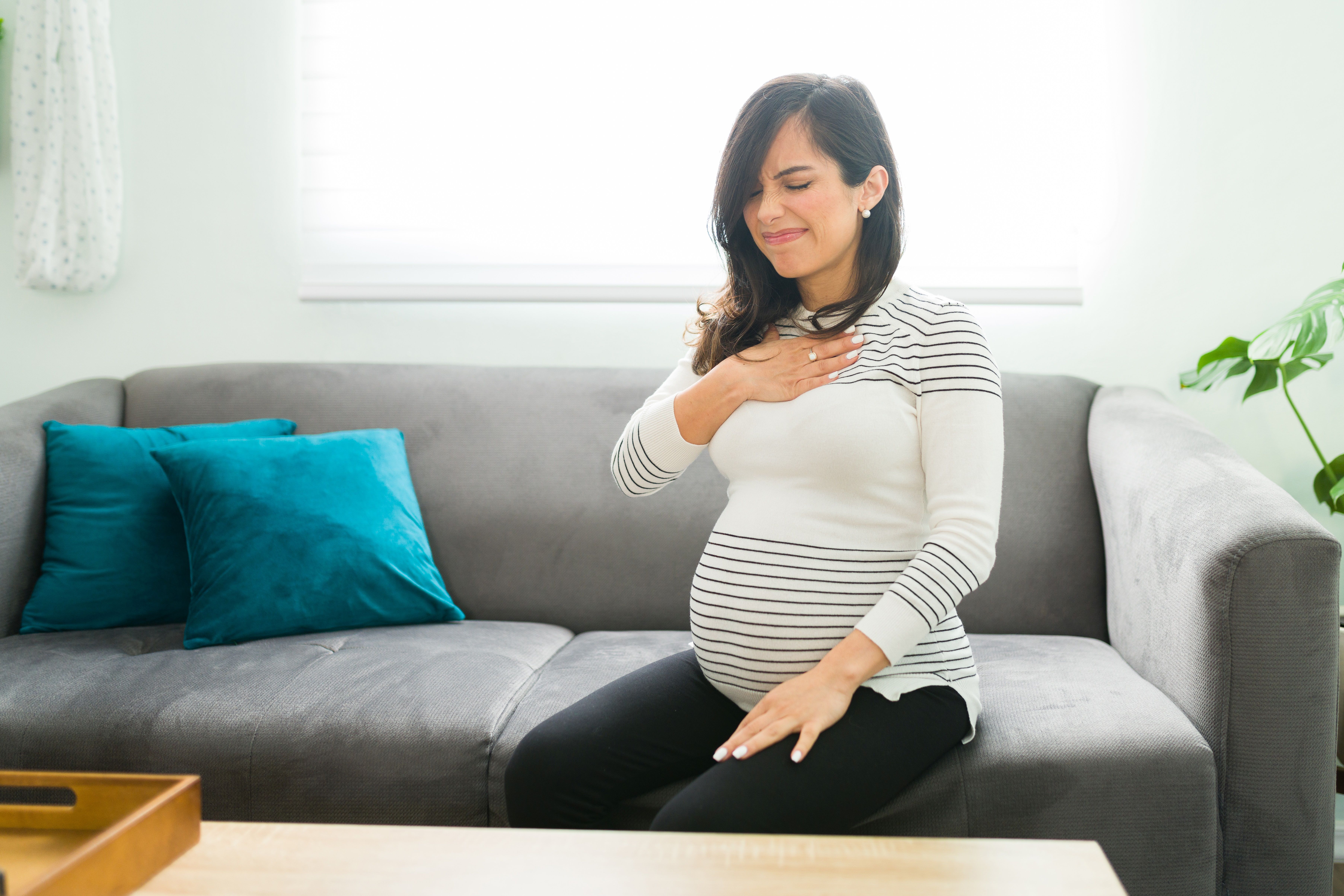
Bedtime soon after meals raises reflux risk in pregnancy
A shorter period between eating and going to sleep increased the risk of GERD during pregnancy by approximately 12%, according to data from 400 women.
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) is a common condition in pregnancy because of changes in gastrointestinal motility caused by hormonal changes, and a short meal-to-bed time (MTBT) also has been associated with increased GERD symptoms, but data on the impact of MTBT on GERD in pregnant women in particular are lacking, wrote Duc T. Quach, MD, of the University of Medicine and Pharmacy in Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam, and colleagues.
In a cross-sectional study published in the Journal of Clinical Gastroenterology, the researchers identified 400 pregnant women aged 18 years and older in various stages of pregnancy who were seen at a single hospital in Vietnam. A short MTBT was defined as going to bed 2 hours or less after eating. Primary outcomes were GERD, defined as troublesome heartburn and/or regurgitation at least once a week, and reflux-related insomnia, defined as trouble initiating or maintaining nighttime sleep. Participants also reported the number of days of troublesome reflux symptoms and frequency of reflux-related insomnia over the last 7 days.
A total of 154 participants had a diagnosis of GERD, for an overall prevalence of 38.5%, similar to that seen in GERD studies of GERD and pregnancy, the researchers noted, and of those with GERD, 20 participants (13.0%) reported reflux-related insomnia.
The overall prevalence of heartburn, regurgitation, nausea with or without vomiting, and epigastric pain were 11.8%, 35.8%, 30.0%, and 5.5%, respectively. A total of 139 women reported reflux symptoms on at least 2 of the past 7 days, and 40 women reported both daytime and nighttime reflux symptoms.
Short meal-to-bed time shows strongest association
A short MTBT was the strongest predictor of GERD in multivariate analysis (odds ratio, 12.73; 95% confidence interval, 2.92-55.45; P = .001); previous history of reflux symptoms (OR, 9.05; 95% CI, 5.29-15.50; P < 001) and being in the third trimester versus first or second of pregnancy (OR, 1.66, 95% CI, 1.03-2.69; P = .039) also remained significant predictors in a multivariate analysis. In addition, nighttime short MTBT (but not daytime short MTBT) was the strongest risk factor for reflux-related insomnia (OR, 4.60), although alcohol consumption and a history of reflux-related symptoms also remained significant in multivariate analysis.
“Interestingly, the number of days during which reflux symptoms were experienced during the last 7 days sequentially increased across subgroups of participants with no short MTBT, either daytime or nighttime short MTBT, and with both daytime and nighttime MTBT,” the researchers wrote. At 4-7 days, none of the patients with no short MTBT reported reflux symptoms, compared with 7.5% of those with either daytime or nighttime MTBT and 20.9% of those with both daytime and nighttime MTBT.
The study findings were limited by several factors, including the inability to accurately record participants’ diets and the potential for overestimating the odds ratio of risk factors in patients with reflux-related insomnia because of the small numbers. However, the results support findings from previous studies and suggest that dietary modifications could provide a nonpharmacological treatment target for managing GERD in pregnant women, they concluded.
Behavioral intervention may benefit pregnant women
The study is important because heartburn and regurgitation are common challenges during pregnancy, Ziad F. Gellad, MD, of Duke University, Durham, N.C., said in an interview. “Understanding risk factors for these conditions can be helpful in designing behavioral and pharmaceutical therapeutic interventions.”
The link between short MTBT and increased risk for GERD is well-known, said Dr. Gellad. “Lengthening the time to laying supine after a meal is a common recommendation given to patients with GERD and is included in published GERD guidelines.” Although pregnant woman may have been excluded from trials on which the guidelines and recommendations are based, “it is reasonable to expect that findings would translate to this population that is generally higher risk for reflux,” he noted.
Dr. Gellad was interested to see the dose response between MTBT and reflux, with those patients having both daytime and nighttime short MTBT experiencing reflux more often than those with short MTBT in only one of those time periods (4-7 days vs. 1-3 days).
The key message for clinicians is that, for all individuals, pregnant or not, “avoiding late night meals and short meal-to-bed time is an appropriate behavioral intervention to recommend for patients with troublesome heartburn or regurgitation,” Dr. Gellad emphasized. However, more research is needed in some areas, “implementation studies would be helpful to understand how best to educate patients on behavioral modifications known to decrease reflux symptoms.”
The study received no outside funding. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose. Dr. Gellad had no relevant financial disclosures, but serves as a member of the GI & Hepatology News board of editors.
A shorter period between eating and going to sleep increased the risk of GERD during pregnancy by approximately 12%, according to data from 400 women.
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) is a common condition in pregnancy because of changes in gastrointestinal motility caused by hormonal changes, and a short meal-to-bed time (MTBT) also has been associated with increased GERD symptoms, but data on the impact of MTBT on GERD in pregnant women in particular are lacking, wrote Duc T. Quach, MD, of the University of Medicine and Pharmacy in Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam, and colleagues.
In a cross-sectional study published in the Journal of Clinical Gastroenterology, the researchers identified 400 pregnant women aged 18 years and older in various stages of pregnancy who were seen at a single hospital in Vietnam. A short MTBT was defined as going to bed 2 hours or less after eating. Primary outcomes were GERD, defined as troublesome heartburn and/or regurgitation at least once a week, and reflux-related insomnia, defined as trouble initiating or maintaining nighttime sleep. Participants also reported the number of days of troublesome reflux symptoms and frequency of reflux-related insomnia over the last 7 days.
A total of 154 participants had a diagnosis of GERD, for an overall prevalence of 38.5%, similar to that seen in GERD studies of GERD and pregnancy, the researchers noted, and of those with GERD, 20 participants (13.0%) reported reflux-related insomnia.
The overall prevalence of heartburn, regurgitation, nausea with or without vomiting, and epigastric pain were 11.8%, 35.8%, 30.0%, and 5.5%, respectively. A total of 139 women reported reflux symptoms on at least 2 of the past 7 days, and 40 women reported both daytime and nighttime reflux symptoms.
Short meal-to-bed time shows strongest association
A short MTBT was the strongest predictor of GERD in multivariate analysis (odds ratio, 12.73; 95% confidence interval, 2.92-55.45; P = .001); previous history of reflux symptoms (OR, 9.05; 95% CI, 5.29-15.50; P < 001) and being in the third trimester versus first or second of pregnancy (OR, 1.66, 95% CI, 1.03-2.69; P = .039) also remained significant predictors in a multivariate analysis. In addition, nighttime short MTBT (but not daytime short MTBT) was the strongest risk factor for reflux-related insomnia (OR, 4.60), although alcohol consumption and a history of reflux-related symptoms also remained significant in multivariate analysis.
“Interestingly, the number of days during which reflux symptoms were experienced during the last 7 days sequentially increased across subgroups of participants with no short MTBT, either daytime or nighttime short MTBT, and with both daytime and nighttime MTBT,” the researchers wrote. At 4-7 days, none of the patients with no short MTBT reported reflux symptoms, compared with 7.5% of those with either daytime or nighttime MTBT and 20.9% of those with both daytime and nighttime MTBT.
The study findings were limited by several factors, including the inability to accurately record participants’ diets and the potential for overestimating the odds ratio of risk factors in patients with reflux-related insomnia because of the small numbers. However, the results support findings from previous studies and suggest that dietary modifications could provide a nonpharmacological treatment target for managing GERD in pregnant women, they concluded.
Behavioral intervention may benefit pregnant women
The study is important because heartburn and regurgitation are common challenges during pregnancy, Ziad F. Gellad, MD, of Duke University, Durham, N.C., said in an interview. “Understanding risk factors for these conditions can be helpful in designing behavioral and pharmaceutical therapeutic interventions.”
The link between short MTBT and increased risk for GERD is well-known, said Dr. Gellad. “Lengthening the time to laying supine after a meal is a common recommendation given to patients with GERD and is included in published GERD guidelines.” Although pregnant woman may have been excluded from trials on which the guidelines and recommendations are based, “it is reasonable to expect that findings would translate to this population that is generally higher risk for reflux,” he noted.
Dr. Gellad was interested to see the dose response between MTBT and reflux, with those patients having both daytime and nighttime short MTBT experiencing reflux more often than those with short MTBT in only one of those time periods (4-7 days vs. 1-3 days).
The key message for clinicians is that, for all individuals, pregnant or not, “avoiding late night meals and short meal-to-bed time is an appropriate behavioral intervention to recommend for patients with troublesome heartburn or regurgitation,” Dr. Gellad emphasized. However, more research is needed in some areas, “implementation studies would be helpful to understand how best to educate patients on behavioral modifications known to decrease reflux symptoms.”
The study received no outside funding. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose. Dr. Gellad had no relevant financial disclosures, but serves as a member of the GI & Hepatology News board of editors.
A shorter period between eating and going to sleep increased the risk of GERD during pregnancy by approximately 12%, according to data from 400 women.
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) is a common condition in pregnancy because of changes in gastrointestinal motility caused by hormonal changes, and a short meal-to-bed time (MTBT) also has been associated with increased GERD symptoms, but data on the impact of MTBT on GERD in pregnant women in particular are lacking, wrote Duc T. Quach, MD, of the University of Medicine and Pharmacy in Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam, and colleagues.
In a cross-sectional study published in the Journal of Clinical Gastroenterology, the researchers identified 400 pregnant women aged 18 years and older in various stages of pregnancy who were seen at a single hospital in Vietnam. A short MTBT was defined as going to bed 2 hours or less after eating. Primary outcomes were GERD, defined as troublesome heartburn and/or regurgitation at least once a week, and reflux-related insomnia, defined as trouble initiating or maintaining nighttime sleep. Participants also reported the number of days of troublesome reflux symptoms and frequency of reflux-related insomnia over the last 7 days.
A total of 154 participants had a diagnosis of GERD, for an overall prevalence of 38.5%, similar to that seen in GERD studies of GERD and pregnancy, the researchers noted, and of those with GERD, 20 participants (13.0%) reported reflux-related insomnia.
The overall prevalence of heartburn, regurgitation, nausea with or without vomiting, and epigastric pain were 11.8%, 35.8%, 30.0%, and 5.5%, respectively. A total of 139 women reported reflux symptoms on at least 2 of the past 7 days, and 40 women reported both daytime and nighttime reflux symptoms.
Short meal-to-bed time shows strongest association
A short MTBT was the strongest predictor of GERD in multivariate analysis (odds ratio, 12.73; 95% confidence interval, 2.92-55.45; P = .001); previous history of reflux symptoms (OR, 9.05; 95% CI, 5.29-15.50; P < 001) and being in the third trimester versus first or second of pregnancy (OR, 1.66, 95% CI, 1.03-2.69; P = .039) also remained significant predictors in a multivariate analysis. In addition, nighttime short MTBT (but not daytime short MTBT) was the strongest risk factor for reflux-related insomnia (OR, 4.60), although alcohol consumption and a history of reflux-related symptoms also remained significant in multivariate analysis.
“Interestingly, the number of days during which reflux symptoms were experienced during the last 7 days sequentially increased across subgroups of participants with no short MTBT, either daytime or nighttime short MTBT, and with both daytime and nighttime MTBT,” the researchers wrote. At 4-7 days, none of the patients with no short MTBT reported reflux symptoms, compared with 7.5% of those with either daytime or nighttime MTBT and 20.9% of those with both daytime and nighttime MTBT.
The study findings were limited by several factors, including the inability to accurately record participants’ diets and the potential for overestimating the odds ratio of risk factors in patients with reflux-related insomnia because of the small numbers. However, the results support findings from previous studies and suggest that dietary modifications could provide a nonpharmacological treatment target for managing GERD in pregnant women, they concluded.
Behavioral intervention may benefit pregnant women
The study is important because heartburn and regurgitation are common challenges during pregnancy, Ziad F. Gellad, MD, of Duke University, Durham, N.C., said in an interview. “Understanding risk factors for these conditions can be helpful in designing behavioral and pharmaceutical therapeutic interventions.”
The link between short MTBT and increased risk for GERD is well-known, said Dr. Gellad. “Lengthening the time to laying supine after a meal is a common recommendation given to patients with GERD and is included in published GERD guidelines.” Although pregnant woman may have been excluded from trials on which the guidelines and recommendations are based, “it is reasonable to expect that findings would translate to this population that is generally higher risk for reflux,” he noted.
Dr. Gellad was interested to see the dose response between MTBT and reflux, with those patients having both daytime and nighttime short MTBT experiencing reflux more often than those with short MTBT in only one of those time periods (4-7 days vs. 1-3 days).
The key message for clinicians is that, for all individuals, pregnant or not, “avoiding late night meals and short meal-to-bed time is an appropriate behavioral intervention to recommend for patients with troublesome heartburn or regurgitation,” Dr. Gellad emphasized. However, more research is needed in some areas, “implementation studies would be helpful to understand how best to educate patients on behavioral modifications known to decrease reflux symptoms.”
The study received no outside funding. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose. Dr. Gellad had no relevant financial disclosures, but serves as a member of the GI & Hepatology News board of editors.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY
COVID-19 leaves thousands of U.S. children without a parent
Approximately 40,000 children in the United States have lost a parent to COVID-19, based on data from a combination of death counts and simulation models.
The scale of mortality from COVID-19 among adults in the United States merits efforts to monitor how many children have lost a parent as a result of the pandemic, wrote Rachel Kidman, PhD, of Stony Brook (N.Y.) University and colleagues.
In a study published in JAMA Pediatrics, the researchers used kinship networks of White and Black individuals in the United States to estimate parental bereavement. They combined deaths from COVID-19 as of February 2021 and combined them with excess deaths, and estimated future bereavement based on a herd immunity scenario.
Overall, the model suggested that each death from COVID-19 results in potential parental bereavement for 0.78 children aged 0-17 years, representing an increase of 17.5%-20.2% in parental bereavement. The model indicated that, as of February 2021, 37,337 children aged 0-17 years had lost a parent to COVID-19, including 11,366 children age 0-9 years and 31,661 children and teens aged 10-17 years. A total of 20,600 of these children were non-Hispanic White and 7,600 were Black. Black children accounted for 20% of the bereaved children, although they account for approximately 14% of children aged 0-17 years in the United States, the researchers noted.
Including the excess death estimate, which refers to the difference between observed and expected deaths for the remainder of the pandemic, raised the total bereaved children to 43,000. A future mortality scenario using a total of 1,500,000 deaths from COVID-19 based on a natural herd immunity strategy increased the total estimate of bereaved children to 116,922.
The study findings were limited by several factors including the lack of data on nonparental primary caregivers, and the use of demographic models rather than survey or administrative data, the researchers noted.
However, the huge number of children who have experienced the death of a parent because of COVID-19 emphasizes the need for reforms to address health, educational, and economic impacts of this mass bereavement on children and teens, they said.
“Parentally bereaved children will also need targeted support to help with grief, particularly during this period of heightened social isolation,” they emphasized.
Establishment of a national child bereavement cohort could identify children early in the bereavement process to help ensure that they are connected to local supportive care and monitored for health and behavior problems, the researchers said. In addition, such a cohort could be used as a basis for a longitudinal study of the impact of mass parental bereavement during a unique period of social isolation and economic uncertainty, they concluded.
Study spotlights gaps in mental health care
The study is an important reminder of how COVID-19 has disrupted children’s lives, said Herschel Lessin, MD, of Children’s Medical Group in Poughkeepsie, N.Y., in an interview. Losing a parent because of COVID-19 is one more tragedy on the list of social and emotional disasters the pandemic has wrought on children, he said.
“There has to be some sort of national response to help children through all of this, not just one item at a time,” Dr. Lessin said. However, the management of children’s mental health in the United States has been subpar for decades, he noted, with few clinicians trained to specialize in treating behavioral and mental health issues in children. Consequently, more general pediatricians will continue to be faced with the mental health issues of bereaved children who desperately need support, he said.
Money remains a key barrier, as it keeps qualified clinicians from entering the field of pediatric mental and behavioral health, and even where there are mental health providers, most do not take insurance and have long waiting lists, Dr. Lessin noted.
General pediatricians were seeing more patients with ADHD, anxiety, and depression before the advent of COVID-19, though most are not trained in managing these conditions, said Dr. Lessin. “Approximately 25%-30% of my visits now are mental health related, and the pandemic will make it geometrically worse,” he said.
The current study, with its dramatic estimates of the number of children who have lost a parent because of COVID-19, may bring attention to the fact that more training and money are needed to support mental health programs for children, he said.
Lead author Dr. Kidman had no financial conflicts to disclose. The study was supported by grants to corresponding author Ashton M. Verdery, PhD, from the National Institute on Aging and the Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development. Dr. Lessin had no financial conflicts but serves on the Pediatric News editorial advisory board.
SOURCE: Kidman R et al. JAMA Pediatr. .
Approximately 40,000 children in the United States have lost a parent to COVID-19, based on data from a combination of death counts and simulation models.
The scale of mortality from COVID-19 among adults in the United States merits efforts to monitor how many children have lost a parent as a result of the pandemic, wrote Rachel Kidman, PhD, of Stony Brook (N.Y.) University and colleagues.
In a study published in JAMA Pediatrics, the researchers used kinship networks of White and Black individuals in the United States to estimate parental bereavement. They combined deaths from COVID-19 as of February 2021 and combined them with excess deaths, and estimated future bereavement based on a herd immunity scenario.
Overall, the model suggested that each death from COVID-19 results in potential parental bereavement for 0.78 children aged 0-17 years, representing an increase of 17.5%-20.2% in parental bereavement. The model indicated that, as of February 2021, 37,337 children aged 0-17 years had lost a parent to COVID-19, including 11,366 children age 0-9 years and 31,661 children and teens aged 10-17 years. A total of 20,600 of these children were non-Hispanic White and 7,600 were Black. Black children accounted for 20% of the bereaved children, although they account for approximately 14% of children aged 0-17 years in the United States, the researchers noted.
Including the excess death estimate, which refers to the difference between observed and expected deaths for the remainder of the pandemic, raised the total bereaved children to 43,000. A future mortality scenario using a total of 1,500,000 deaths from COVID-19 based on a natural herd immunity strategy increased the total estimate of bereaved children to 116,922.
The study findings were limited by several factors including the lack of data on nonparental primary caregivers, and the use of demographic models rather than survey or administrative data, the researchers noted.
However, the huge number of children who have experienced the death of a parent because of COVID-19 emphasizes the need for reforms to address health, educational, and economic impacts of this mass bereavement on children and teens, they said.
“Parentally bereaved children will also need targeted support to help with grief, particularly during this period of heightened social isolation,” they emphasized.
Establishment of a national child bereavement cohort could identify children early in the bereavement process to help ensure that they are connected to local supportive care and monitored for health and behavior problems, the researchers said. In addition, such a cohort could be used as a basis for a longitudinal study of the impact of mass parental bereavement during a unique period of social isolation and economic uncertainty, they concluded.
Study spotlights gaps in mental health care
The study is an important reminder of how COVID-19 has disrupted children’s lives, said Herschel Lessin, MD, of Children’s Medical Group in Poughkeepsie, N.Y., in an interview. Losing a parent because of COVID-19 is one more tragedy on the list of social and emotional disasters the pandemic has wrought on children, he said.
“There has to be some sort of national response to help children through all of this, not just one item at a time,” Dr. Lessin said. However, the management of children’s mental health in the United States has been subpar for decades, he noted, with few clinicians trained to specialize in treating behavioral and mental health issues in children. Consequently, more general pediatricians will continue to be faced with the mental health issues of bereaved children who desperately need support, he said.
Money remains a key barrier, as it keeps qualified clinicians from entering the field of pediatric mental and behavioral health, and even where there are mental health providers, most do not take insurance and have long waiting lists, Dr. Lessin noted.
General pediatricians were seeing more patients with ADHD, anxiety, and depression before the advent of COVID-19, though most are not trained in managing these conditions, said Dr. Lessin. “Approximately 25%-30% of my visits now are mental health related, and the pandemic will make it geometrically worse,” he said.
The current study, with its dramatic estimates of the number of children who have lost a parent because of COVID-19, may bring attention to the fact that more training and money are needed to support mental health programs for children, he said.
Lead author Dr. Kidman had no financial conflicts to disclose. The study was supported by grants to corresponding author Ashton M. Verdery, PhD, from the National Institute on Aging and the Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development. Dr. Lessin had no financial conflicts but serves on the Pediatric News editorial advisory board.
SOURCE: Kidman R et al. JAMA Pediatr. .
Approximately 40,000 children in the United States have lost a parent to COVID-19, based on data from a combination of death counts and simulation models.
The scale of mortality from COVID-19 among adults in the United States merits efforts to monitor how many children have lost a parent as a result of the pandemic, wrote Rachel Kidman, PhD, of Stony Brook (N.Y.) University and colleagues.
In a study published in JAMA Pediatrics, the researchers used kinship networks of White and Black individuals in the United States to estimate parental bereavement. They combined deaths from COVID-19 as of February 2021 and combined them with excess deaths, and estimated future bereavement based on a herd immunity scenario.
Overall, the model suggested that each death from COVID-19 results in potential parental bereavement for 0.78 children aged 0-17 years, representing an increase of 17.5%-20.2% in parental bereavement. The model indicated that, as of February 2021, 37,337 children aged 0-17 years had lost a parent to COVID-19, including 11,366 children age 0-9 years and 31,661 children and teens aged 10-17 years. A total of 20,600 of these children were non-Hispanic White and 7,600 were Black. Black children accounted for 20% of the bereaved children, although they account for approximately 14% of children aged 0-17 years in the United States, the researchers noted.
Including the excess death estimate, which refers to the difference between observed and expected deaths for the remainder of the pandemic, raised the total bereaved children to 43,000. A future mortality scenario using a total of 1,500,000 deaths from COVID-19 based on a natural herd immunity strategy increased the total estimate of bereaved children to 116,922.
The study findings were limited by several factors including the lack of data on nonparental primary caregivers, and the use of demographic models rather than survey or administrative data, the researchers noted.
However, the huge number of children who have experienced the death of a parent because of COVID-19 emphasizes the need for reforms to address health, educational, and economic impacts of this mass bereavement on children and teens, they said.
“Parentally bereaved children will also need targeted support to help with grief, particularly during this period of heightened social isolation,” they emphasized.
Establishment of a national child bereavement cohort could identify children early in the bereavement process to help ensure that they are connected to local supportive care and monitored for health and behavior problems, the researchers said. In addition, such a cohort could be used as a basis for a longitudinal study of the impact of mass parental bereavement during a unique period of social isolation and economic uncertainty, they concluded.
Study spotlights gaps in mental health care
The study is an important reminder of how COVID-19 has disrupted children’s lives, said Herschel Lessin, MD, of Children’s Medical Group in Poughkeepsie, N.Y., in an interview. Losing a parent because of COVID-19 is one more tragedy on the list of social and emotional disasters the pandemic has wrought on children, he said.
“There has to be some sort of national response to help children through all of this, not just one item at a time,” Dr. Lessin said. However, the management of children’s mental health in the United States has been subpar for decades, he noted, with few clinicians trained to specialize in treating behavioral and mental health issues in children. Consequently, more general pediatricians will continue to be faced with the mental health issues of bereaved children who desperately need support, he said.
Money remains a key barrier, as it keeps qualified clinicians from entering the field of pediatric mental and behavioral health, and even where there are mental health providers, most do not take insurance and have long waiting lists, Dr. Lessin noted.
General pediatricians were seeing more patients with ADHD, anxiety, and depression before the advent of COVID-19, though most are not trained in managing these conditions, said Dr. Lessin. “Approximately 25%-30% of my visits now are mental health related, and the pandemic will make it geometrically worse,” he said.
The current study, with its dramatic estimates of the number of children who have lost a parent because of COVID-19, may bring attention to the fact that more training and money are needed to support mental health programs for children, he said.
Lead author Dr. Kidman had no financial conflicts to disclose. The study was supported by grants to corresponding author Ashton M. Verdery, PhD, from the National Institute on Aging and the Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development. Dr. Lessin had no financial conflicts but serves on the Pediatric News editorial advisory board.
SOURCE: Kidman R et al. JAMA Pediatr. .
FROM JAMA PEDIATRICS
Clinically important deterioration predicts poor future outcomes in COPD
Patients with COPD may benefit from stepped-up treatment of short-term disease progression with triple therapy to stave off longer-term exacerbations and all-cause mortality.
, a study based on data from more than 10,000 patients has shown.
For this study, clinically important deterioration (CID) as a measure of COPD is defined as a combination of change in lung function and/or health status, or a first acute moderate to severe COPD exacerbation, wrote MeiLan K. Han, MD, of the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, and colleagues.
The study was published in ERJ Open Research The investigators analyzed data from the IMPACT trial, a phase III, double-blind, multicenter, 52-week study of symptomatic COPD patients aged 40 years and older.
In the intent-to-treat population, patients with symptomatic COPD and at least one moderate or severe exacerbation in the past year were randomized to a once-daily dose of fluticasone furoate/umeclidinium/vilanterol (FF/UMEC/VI) 100/62.5/25 mcg (4,151 patients); FF/VI 100/25 mcg (4,134 patients); or UMEC/VI 62.5/25 mcg using a single dry-power inhaler (2,070 patients).
The researchers explored both the prognostic value of a CID event on future clinical outcomes and the impact of single-inhaler triple versus dual therapy on reducing CID risk. CID was defined as any of the following: moderate/severe exacerbation; deterioration in lung function (defined as a decrease of 100 mL or more from baseline in trough forced expiratory volume per second); or deterioration in health status based on increases of 4.0 units or more on the St George’s Respiratory Questionnaire (SGRQ) total score or 2.0 units or more on the COPD Assessment Test (CAT) score.
Overall, patients with a CID by 28 weeks had significantly increased exacerbation rates after week 28, as well as smaller improvements in lung function and health status at week 52 (P < .001 for all). In addition, CID patients had an increased risk of all-cause mortality after 28 weeks, compared with patients without CID. However, FF/UMEC/VI significantly reduced CID risk, compared with dual therapies, the researchers noted.
Based on the CID SGRQ definition, patients with CID had a 75% increase in moderate to severe exacerbations by week 28 and a 96% in severe exacerbations over weeks 29-52. The increases were similar using the CID CAT definition (72% and 91%, respectively).
Patients with CID also showed significantly reduced improvements in both lung function and health status after 1 year, and a significantly increased risk of all-cause mortality compared to patients without CID.
In comparing triple vs. double therapies, FF/UMEC/VI patients showed significant reductions in CID risk by 52 weeks, compared with patients treated with FF/VI and UMEC/VI. This difference was true across all subgroups, except for the subgroup of patients who were on long-acting beta2-agonist (LABA) and long-acting muscarinic antagonist (LAMA) therapy prior to screening, the researchers said.
In addition, “treatment effect was greater at higher blood eosinophil counts for FF/UMEC/VI versus UMEC/VI,” the researchers noted.
The study findings were limited by several factors including the lack of CID as a primary endpoint, the relatively short 5-month follow-up period, and the use of a symptomatic patient population with an established risk of exacerbation, which could limit generalizability, the researchers noted. However, the findings support the value of preventing short-term CID and adding inhaled corticosteroids (ICS) or bronchodilation for patients in this study population, they said.
Data may help drive tailored treatments
“This study is a post hoc analysis of data from the IMPACT trial, an RCT examining triple therapy vs ICS/LABA vs LABA/LAMA,” Dr. Han, lead and corresponding author, said in an interview. “In this particular paper, we conducted a treatment independent analysis examining individuals who experienced clinically important deteriorations at week 28 and then compared outcomes at week 52 based on CID status at week 28. Patients with a CID by week 28 had significantly increased exacerbation rates after week 28, smaller improvements in lung function and health status at week 52, and increased risk of all-cause mortality after week 28 versus patients who were CID free,” she emphasized. “We also saw that FF/UMEC/VI significantly reduced CID risk versus dual therapies.” These data suggest that shorter-term changes are associated with longer term outcomes, and provide important information both for the purposes of clinical trials design as well as patient clinical assessments, she added.
Dr. Han said she was not surprised by the findings. “I think these results are consistent with prior analyses but suggest that short-term outcomes relate to longer-term ones,” she said. However, she stressed the need for individualized treatment.
“While there are relationships between symptoms, lung function, and exacerbations as demonstrated by these analyses, in any individual patient sometimes these three disease axes do not perfectly align,” she explained. Dr. Han’s main message for clinicians in practice is that optimization of triple therapy in patients with severe disease and high risk for exacerbations was associated not only with short-term improvements in symptoms and lung function, but also with longer-term reductions in exacerbations and mortality.
As for additional research, prospective studies using CID as a primary or secondary outcome would help validate the composite outcome in this study, as regulatory agencies have been slow to adopt composite outcomes, Dr. Han said.
Dr. Han disclosed relationships with GlaxoSmithKline, which funded the study, as well as AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Novartis, Sunovion, Mylan, Merck, and Verona.
Patients with COPD may benefit from stepped-up treatment of short-term disease progression with triple therapy to stave off longer-term exacerbations and all-cause mortality.
, a study based on data from more than 10,000 patients has shown.
For this study, clinically important deterioration (CID) as a measure of COPD is defined as a combination of change in lung function and/or health status, or a first acute moderate to severe COPD exacerbation, wrote MeiLan K. Han, MD, of the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, and colleagues.
The study was published in ERJ Open Research The investigators analyzed data from the IMPACT trial, a phase III, double-blind, multicenter, 52-week study of symptomatic COPD patients aged 40 years and older.
In the intent-to-treat population, patients with symptomatic COPD and at least one moderate or severe exacerbation in the past year were randomized to a once-daily dose of fluticasone furoate/umeclidinium/vilanterol (FF/UMEC/VI) 100/62.5/25 mcg (4,151 patients); FF/VI 100/25 mcg (4,134 patients); or UMEC/VI 62.5/25 mcg using a single dry-power inhaler (2,070 patients).
The researchers explored both the prognostic value of a CID event on future clinical outcomes and the impact of single-inhaler triple versus dual therapy on reducing CID risk. CID was defined as any of the following: moderate/severe exacerbation; deterioration in lung function (defined as a decrease of 100 mL or more from baseline in trough forced expiratory volume per second); or deterioration in health status based on increases of 4.0 units or more on the St George’s Respiratory Questionnaire (SGRQ) total score or 2.0 units or more on the COPD Assessment Test (CAT) score.
Overall, patients with a CID by 28 weeks had significantly increased exacerbation rates after week 28, as well as smaller improvements in lung function and health status at week 52 (P < .001 for all). In addition, CID patients had an increased risk of all-cause mortality after 28 weeks, compared with patients without CID. However, FF/UMEC/VI significantly reduced CID risk, compared with dual therapies, the researchers noted.
Based on the CID SGRQ definition, patients with CID had a 75% increase in moderate to severe exacerbations by week 28 and a 96% in severe exacerbations over weeks 29-52. The increases were similar using the CID CAT definition (72% and 91%, respectively).
Patients with CID also showed significantly reduced improvements in both lung function and health status after 1 year, and a significantly increased risk of all-cause mortality compared to patients without CID.
In comparing triple vs. double therapies, FF/UMEC/VI patients showed significant reductions in CID risk by 52 weeks, compared with patients treated with FF/VI and UMEC/VI. This difference was true across all subgroups, except for the subgroup of patients who were on long-acting beta2-agonist (LABA) and long-acting muscarinic antagonist (LAMA) therapy prior to screening, the researchers said.
In addition, “treatment effect was greater at higher blood eosinophil counts for FF/UMEC/VI versus UMEC/VI,” the researchers noted.
The study findings were limited by several factors including the lack of CID as a primary endpoint, the relatively short 5-month follow-up period, and the use of a symptomatic patient population with an established risk of exacerbation, which could limit generalizability, the researchers noted. However, the findings support the value of preventing short-term CID and adding inhaled corticosteroids (ICS) or bronchodilation for patients in this study population, they said.
Data may help drive tailored treatments
“This study is a post hoc analysis of data from the IMPACT trial, an RCT examining triple therapy vs ICS/LABA vs LABA/LAMA,” Dr. Han, lead and corresponding author, said in an interview. “In this particular paper, we conducted a treatment independent analysis examining individuals who experienced clinically important deteriorations at week 28 and then compared outcomes at week 52 based on CID status at week 28. Patients with a CID by week 28 had significantly increased exacerbation rates after week 28, smaller improvements in lung function and health status at week 52, and increased risk of all-cause mortality after week 28 versus patients who were CID free,” she emphasized. “We also saw that FF/UMEC/VI significantly reduced CID risk versus dual therapies.” These data suggest that shorter-term changes are associated with longer term outcomes, and provide important information both for the purposes of clinical trials design as well as patient clinical assessments, she added.
Dr. Han said she was not surprised by the findings. “I think these results are consistent with prior analyses but suggest that short-term outcomes relate to longer-term ones,” she said. However, she stressed the need for individualized treatment.
“While there are relationships between symptoms, lung function, and exacerbations as demonstrated by these analyses, in any individual patient sometimes these three disease axes do not perfectly align,” she explained. Dr. Han’s main message for clinicians in practice is that optimization of triple therapy in patients with severe disease and high risk for exacerbations was associated not only with short-term improvements in symptoms and lung function, but also with longer-term reductions in exacerbations and mortality.
As for additional research, prospective studies using CID as a primary or secondary outcome would help validate the composite outcome in this study, as regulatory agencies have been slow to adopt composite outcomes, Dr. Han said.
Dr. Han disclosed relationships with GlaxoSmithKline, which funded the study, as well as AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Novartis, Sunovion, Mylan, Merck, and Verona.
Patients with COPD may benefit from stepped-up treatment of short-term disease progression with triple therapy to stave off longer-term exacerbations and all-cause mortality.
, a study based on data from more than 10,000 patients has shown.
For this study, clinically important deterioration (CID) as a measure of COPD is defined as a combination of change in lung function and/or health status, or a first acute moderate to severe COPD exacerbation, wrote MeiLan K. Han, MD, of the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, and colleagues.
The study was published in ERJ Open Research The investigators analyzed data from the IMPACT trial, a phase III, double-blind, multicenter, 52-week study of symptomatic COPD patients aged 40 years and older.
In the intent-to-treat population, patients with symptomatic COPD and at least one moderate or severe exacerbation in the past year were randomized to a once-daily dose of fluticasone furoate/umeclidinium/vilanterol (FF/UMEC/VI) 100/62.5/25 mcg (4,151 patients); FF/VI 100/25 mcg (4,134 patients); or UMEC/VI 62.5/25 mcg using a single dry-power inhaler (2,070 patients).
The researchers explored both the prognostic value of a CID event on future clinical outcomes and the impact of single-inhaler triple versus dual therapy on reducing CID risk. CID was defined as any of the following: moderate/severe exacerbation; deterioration in lung function (defined as a decrease of 100 mL or more from baseline in trough forced expiratory volume per second); or deterioration in health status based on increases of 4.0 units or more on the St George’s Respiratory Questionnaire (SGRQ) total score or 2.0 units or more on the COPD Assessment Test (CAT) score.
Overall, patients with a CID by 28 weeks had significantly increased exacerbation rates after week 28, as well as smaller improvements in lung function and health status at week 52 (P < .001 for all). In addition, CID patients had an increased risk of all-cause mortality after 28 weeks, compared with patients without CID. However, FF/UMEC/VI significantly reduced CID risk, compared with dual therapies, the researchers noted.
Based on the CID SGRQ definition, patients with CID had a 75% increase in moderate to severe exacerbations by week 28 and a 96% in severe exacerbations over weeks 29-52. The increases were similar using the CID CAT definition (72% and 91%, respectively).
Patients with CID also showed significantly reduced improvements in both lung function and health status after 1 year, and a significantly increased risk of all-cause mortality compared to patients without CID.
In comparing triple vs. double therapies, FF/UMEC/VI patients showed significant reductions in CID risk by 52 weeks, compared with patients treated with FF/VI and UMEC/VI. This difference was true across all subgroups, except for the subgroup of patients who were on long-acting beta2-agonist (LABA) and long-acting muscarinic antagonist (LAMA) therapy prior to screening, the researchers said.
In addition, “treatment effect was greater at higher blood eosinophil counts for FF/UMEC/VI versus UMEC/VI,” the researchers noted.
The study findings were limited by several factors including the lack of CID as a primary endpoint, the relatively short 5-month follow-up period, and the use of a symptomatic patient population with an established risk of exacerbation, which could limit generalizability, the researchers noted. However, the findings support the value of preventing short-term CID and adding inhaled corticosteroids (ICS) or bronchodilation for patients in this study population, they said.
Data may help drive tailored treatments
“This study is a post hoc analysis of data from the IMPACT trial, an RCT examining triple therapy vs ICS/LABA vs LABA/LAMA,” Dr. Han, lead and corresponding author, said in an interview. “In this particular paper, we conducted a treatment independent analysis examining individuals who experienced clinically important deteriorations at week 28 and then compared outcomes at week 52 based on CID status at week 28. Patients with a CID by week 28 had significantly increased exacerbation rates after week 28, smaller improvements in lung function and health status at week 52, and increased risk of all-cause mortality after week 28 versus patients who were CID free,” she emphasized. “We also saw that FF/UMEC/VI significantly reduced CID risk versus dual therapies.” These data suggest that shorter-term changes are associated with longer term outcomes, and provide important information both for the purposes of clinical trials design as well as patient clinical assessments, she added.
Dr. Han said she was not surprised by the findings. “I think these results are consistent with prior analyses but suggest that short-term outcomes relate to longer-term ones,” she said. However, she stressed the need for individualized treatment.
“While there are relationships between symptoms, lung function, and exacerbations as demonstrated by these analyses, in any individual patient sometimes these three disease axes do not perfectly align,” she explained. Dr. Han’s main message for clinicians in practice is that optimization of triple therapy in patients with severe disease and high risk for exacerbations was associated not only with short-term improvements in symptoms and lung function, but also with longer-term reductions in exacerbations and mortality.
As for additional research, prospective studies using CID as a primary or secondary outcome would help validate the composite outcome in this study, as regulatory agencies have been slow to adopt composite outcomes, Dr. Han said.
Dr. Han disclosed relationships with GlaxoSmithKline, which funded the study, as well as AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Novartis, Sunovion, Mylan, Merck, and Verona.
FROM ERJ OPEN RESEARCH
Ob.Gyn. giant Dr. Charles Hammond dies
Ob.Gyn. News acknowledges the passing of Charles B. Hammond, MD, a longtime editorial board member, who died on Feb. 1, 2021.
Dr. Hammond served on the Ob.Gyn. News Advisory Board for 33 years. His service as a board member was one of many leadership roles to which he dedicated his time and expertise. Dr. Hammond served as president of the American College of Obstetrics & Gynecology (ACOG) from 2002 to 2003, and received a Lifetime Achievement Award from ACOG in 2015. He also served as president of the American Society of Reproductive Medicine, president of the American Gynecological and Obstetrical Society, and president of the North Carolina Obstetrical and Gynecological Society.
Dr. Hammond was honored by Duke University, Durham, N.C., as E.C. Hamblen Professor Emeritus in 2010, after more than 40 years in academia. He held the title of Edwin Crowell Hamblen Distinguished Professor of Reproductive Biology and Family Planning and Chair of the Department of Obstetrics & Gynecology from 1980 to 2002. During this time, he distinguished himself for his work in pioneering treatments for gestational trophoblastic disease. As an extension of this research, he was a founder of the Southeast Regional Trophoblastic Disease Center. In addition, Dr. Hammond was often consulted for his expertise on issues related to menopause and hormone replacement therapy.
Dr. Hammond began his medical career at Duke University after graduating from The Citadel with a bachelor of science degree in 1958. After earning his medical degree in 1961, he remained at Duke as a resident in obstetrics and gynecology, followed by completion of a fellowship in reproductive endocrinology in 1964. From 1964 to 1966, he served at the National Institutes of Health as a fellow in the National Cancer Institute and the Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development.
A few years later, in 1969, Dr. Hammond launched his long and distinguished academic career with an assistant professor position in the department of obstetrics & gynecology at Duke.
Dr. Hammond’s many honors include a National Association for Women’s Health Lifetime Achievement Award and membership in the Institute of Medicine, now the National Academy of Medicine. He also was named a fellow of the Royal College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists, and an honorary member of the Canadian Society of Obstetrics and Gynecology. Dr. Hammond will be remembered not only as a physician, researcher, educator, and mentor, but also an advocate for women’s health.
Ob.Gyn. News acknowledges the passing of Charles B. Hammond, MD, a longtime editorial board member, who died on Feb. 1, 2021.
Dr. Hammond served on the Ob.Gyn. News Advisory Board for 33 years. His service as a board member was one of many leadership roles to which he dedicated his time and expertise. Dr. Hammond served as president of the American College of Obstetrics & Gynecology (ACOG) from 2002 to 2003, and received a Lifetime Achievement Award from ACOG in 2015. He also served as president of the American Society of Reproductive Medicine, president of the American Gynecological and Obstetrical Society, and president of the North Carolina Obstetrical and Gynecological Society.
Dr. Hammond was honored by Duke University, Durham, N.C., as E.C. Hamblen Professor Emeritus in 2010, after more than 40 years in academia. He held the title of Edwin Crowell Hamblen Distinguished Professor of Reproductive Biology and Family Planning and Chair of the Department of Obstetrics & Gynecology from 1980 to 2002. During this time, he distinguished himself for his work in pioneering treatments for gestational trophoblastic disease. As an extension of this research, he was a founder of the Southeast Regional Trophoblastic Disease Center. In addition, Dr. Hammond was often consulted for his expertise on issues related to menopause and hormone replacement therapy.
Dr. Hammond began his medical career at Duke University after graduating from The Citadel with a bachelor of science degree in 1958. After earning his medical degree in 1961, he remained at Duke as a resident in obstetrics and gynecology, followed by completion of a fellowship in reproductive endocrinology in 1964. From 1964 to 1966, he served at the National Institutes of Health as a fellow in the National Cancer Institute and the Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development.
A few years later, in 1969, Dr. Hammond launched his long and distinguished academic career with an assistant professor position in the department of obstetrics & gynecology at Duke.
Dr. Hammond’s many honors include a National Association for Women’s Health Lifetime Achievement Award and membership in the Institute of Medicine, now the National Academy of Medicine. He also was named a fellow of the Royal College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists, and an honorary member of the Canadian Society of Obstetrics and Gynecology. Dr. Hammond will be remembered not only as a physician, researcher, educator, and mentor, but also an advocate for women’s health.
Ob.Gyn. News acknowledges the passing of Charles B. Hammond, MD, a longtime editorial board member, who died on Feb. 1, 2021.
Dr. Hammond served on the Ob.Gyn. News Advisory Board for 33 years. His service as a board member was one of many leadership roles to which he dedicated his time and expertise. Dr. Hammond served as president of the American College of Obstetrics & Gynecology (ACOG) from 2002 to 2003, and received a Lifetime Achievement Award from ACOG in 2015. He also served as president of the American Society of Reproductive Medicine, president of the American Gynecological and Obstetrical Society, and president of the North Carolina Obstetrical and Gynecological Society.
Dr. Hammond was honored by Duke University, Durham, N.C., as E.C. Hamblen Professor Emeritus in 2010, after more than 40 years in academia. He held the title of Edwin Crowell Hamblen Distinguished Professor of Reproductive Biology and Family Planning and Chair of the Department of Obstetrics & Gynecology from 1980 to 2002. During this time, he distinguished himself for his work in pioneering treatments for gestational trophoblastic disease. As an extension of this research, he was a founder of the Southeast Regional Trophoblastic Disease Center. In addition, Dr. Hammond was often consulted for his expertise on issues related to menopause and hormone replacement therapy.
Dr. Hammond began his medical career at Duke University after graduating from The Citadel with a bachelor of science degree in 1958. After earning his medical degree in 1961, he remained at Duke as a resident in obstetrics and gynecology, followed by completion of a fellowship in reproductive endocrinology in 1964. From 1964 to 1966, he served at the National Institutes of Health as a fellow in the National Cancer Institute and the Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development.
A few years later, in 1969, Dr. Hammond launched his long and distinguished academic career with an assistant professor position in the department of obstetrics & gynecology at Duke.
Dr. Hammond’s many honors include a National Association for Women’s Health Lifetime Achievement Award and membership in the Institute of Medicine, now the National Academy of Medicine. He also was named a fellow of the Royal College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists, and an honorary member of the Canadian Society of Obstetrics and Gynecology. Dr. Hammond will be remembered not only as a physician, researcher, educator, and mentor, but also an advocate for women’s health.
Nonfatal opioid overdose rises in teen girls
More adolescent girls than boys experienced nonfatal opioid overdose and reported baseline levels of anxiety, depression, and self-harm, according to data from a retrospective cohort study of more than 20,000 youth in the United States.
Previous studies have identified sex-based differences in opioid overdose such as a higher prevalence of co-occurring psychiatric disorders in women compared with men, wrote Sarah M. Bagley, MD, of Boston University, and colleagues. “However, few studies have examined whether such sex-based differences in opioid overdose risk extend to the population of adolescents and young adults,” they said.
In a retrospective cohort study published in JAMA Network Open, the researchers identified 20,312 commercially insured youth aged 11-24 years who experienced a nonfatal opioid overdose between Jan. 1, 2006, and Dec. 31, 2017, and reviewed data using the IBM MarketScan Commercial Database. The average age of the study population was 20 years and approximately 42% were female.
Females aged 11-16 years had a significantly higher incidence of nonfatal opioid overdose (60%) compared with males, but this trend reversed at age 17 years, after which the incidence of nonfatal opioid overdose became significantly higher in males. “Our finding that females younger than 17 years had a higher incidence of NFOD is consistent with epidemiologic data that have indicated changes in alcohol and drug prevalence among female youths,” the researchers wrote.
Overall, 57.8% of the cohort had mood and anxiety disorders, 12.8% had trauma- or stress-related disorders, and 11.7% had attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder.
When analyzed by sex, females had a significantly higher prevalence than that of males of mood or anxiety disorders (65.5% vs. 51.9%) trauma or stress-related disorders (16.4% vs. 10.1%) and attempts at suicide or self-harm (14.6% vs. 9.9%). Males had significantly higher prevalence than that of females of opioid use disorder (44.7% vs. 29.2%), cannabis use disorder (18.3% vs. 11.3%), and alcohol use disorder (20.3% vs. 14.4%).
“Although in our study, female youths had a lower prevalence of all substance use disorders, including OUD [opioid use disorder], and a higher prevalence of mood and trauma-associated disorders, both male and female youths had a higher prevalence of psychiatric illness and substance use disorder than youths in the general population,” the researchers noted.
The study findings were limited by several factors including the inclusion only of youth with commercial insurance, with no uninsured or publicly insured youth, and only those youth who sought health care after a nonfatal opioid overdose, the researchers noted. The prevalence of substance use and mental health disorders may be over- or underdiagnosed, and race was not included as a variable because of unreliable data, they added. The database also did not allow for gender identity beyond sex as listed by the insurance carrier, they said.
However, the results indicate significant differences in the incidence of nonfatal opioid overdose and accompanying mental health and substance use disorders based on age and sex, they said.
“These differences may have important implications for developing effective interventions to prevent first-time NFOD and to engage youths in care after an NFOD,” they concluded.
The study was supported by grants to several researchers from the National Institute on Drug Abuse, National Institutes of Health, and the Charles A. King Trust. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose.
More adolescent girls than boys experienced nonfatal opioid overdose and reported baseline levels of anxiety, depression, and self-harm, according to data from a retrospective cohort study of more than 20,000 youth in the United States.
Previous studies have identified sex-based differences in opioid overdose such as a higher prevalence of co-occurring psychiatric disorders in women compared with men, wrote Sarah M. Bagley, MD, of Boston University, and colleagues. “However, few studies have examined whether such sex-based differences in opioid overdose risk extend to the population of adolescents and young adults,” they said.
In a retrospective cohort study published in JAMA Network Open, the researchers identified 20,312 commercially insured youth aged 11-24 years who experienced a nonfatal opioid overdose between Jan. 1, 2006, and Dec. 31, 2017, and reviewed data using the IBM MarketScan Commercial Database. The average age of the study population was 20 years and approximately 42% were female.
Females aged 11-16 years had a significantly higher incidence of nonfatal opioid overdose (60%) compared with males, but this trend reversed at age 17 years, after which the incidence of nonfatal opioid overdose became significantly higher in males. “Our finding that females younger than 17 years had a higher incidence of NFOD is consistent with epidemiologic data that have indicated changes in alcohol and drug prevalence among female youths,” the researchers wrote.
Overall, 57.8% of the cohort had mood and anxiety disorders, 12.8% had trauma- or stress-related disorders, and 11.7% had attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder.
When analyzed by sex, females had a significantly higher prevalence than that of males of mood or anxiety disorders (65.5% vs. 51.9%) trauma or stress-related disorders (16.4% vs. 10.1%) and attempts at suicide or self-harm (14.6% vs. 9.9%). Males had significantly higher prevalence than that of females of opioid use disorder (44.7% vs. 29.2%), cannabis use disorder (18.3% vs. 11.3%), and alcohol use disorder (20.3% vs. 14.4%).
“Although in our study, female youths had a lower prevalence of all substance use disorders, including OUD [opioid use disorder], and a higher prevalence of mood and trauma-associated disorders, both male and female youths had a higher prevalence of psychiatric illness and substance use disorder than youths in the general population,” the researchers noted.
The study findings were limited by several factors including the inclusion only of youth with commercial insurance, with no uninsured or publicly insured youth, and only those youth who sought health care after a nonfatal opioid overdose, the researchers noted. The prevalence of substance use and mental health disorders may be over- or underdiagnosed, and race was not included as a variable because of unreliable data, they added. The database also did not allow for gender identity beyond sex as listed by the insurance carrier, they said.
However, the results indicate significant differences in the incidence of nonfatal opioid overdose and accompanying mental health and substance use disorders based on age and sex, they said.
“These differences may have important implications for developing effective interventions to prevent first-time NFOD and to engage youths in care after an NFOD,” they concluded.
The study was supported by grants to several researchers from the National Institute on Drug Abuse, National Institutes of Health, and the Charles A. King Trust. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose.
More adolescent girls than boys experienced nonfatal opioid overdose and reported baseline levels of anxiety, depression, and self-harm, according to data from a retrospective cohort study of more than 20,000 youth in the United States.
Previous studies have identified sex-based differences in opioid overdose such as a higher prevalence of co-occurring psychiatric disorders in women compared with men, wrote Sarah M. Bagley, MD, of Boston University, and colleagues. “However, few studies have examined whether such sex-based differences in opioid overdose risk extend to the population of adolescents and young adults,” they said.
In a retrospective cohort study published in JAMA Network Open, the researchers identified 20,312 commercially insured youth aged 11-24 years who experienced a nonfatal opioid overdose between Jan. 1, 2006, and Dec. 31, 2017, and reviewed data using the IBM MarketScan Commercial Database. The average age of the study population was 20 years and approximately 42% were female.
Females aged 11-16 years had a significantly higher incidence of nonfatal opioid overdose (60%) compared with males, but this trend reversed at age 17 years, after which the incidence of nonfatal opioid overdose became significantly higher in males. “Our finding that females younger than 17 years had a higher incidence of NFOD is consistent with epidemiologic data that have indicated changes in alcohol and drug prevalence among female youths,” the researchers wrote.
Overall, 57.8% of the cohort had mood and anxiety disorders, 12.8% had trauma- or stress-related disorders, and 11.7% had attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder.
When analyzed by sex, females had a significantly higher prevalence than that of males of mood or anxiety disorders (65.5% vs. 51.9%) trauma or stress-related disorders (16.4% vs. 10.1%) and attempts at suicide or self-harm (14.6% vs. 9.9%). Males had significantly higher prevalence than that of females of opioid use disorder (44.7% vs. 29.2%), cannabis use disorder (18.3% vs. 11.3%), and alcohol use disorder (20.3% vs. 14.4%).
“Although in our study, female youths had a lower prevalence of all substance use disorders, including OUD [opioid use disorder], and a higher prevalence of mood and trauma-associated disorders, both male and female youths had a higher prevalence of psychiatric illness and substance use disorder than youths in the general population,” the researchers noted.
The study findings were limited by several factors including the inclusion only of youth with commercial insurance, with no uninsured or publicly insured youth, and only those youth who sought health care after a nonfatal opioid overdose, the researchers noted. The prevalence of substance use and mental health disorders may be over- or underdiagnosed, and race was not included as a variable because of unreliable data, they added. The database also did not allow for gender identity beyond sex as listed by the insurance carrier, they said.
However, the results indicate significant differences in the incidence of nonfatal opioid overdose and accompanying mental health and substance use disorders based on age and sex, they said.
“These differences may have important implications for developing effective interventions to prevent first-time NFOD and to engage youths in care after an NFOD,” they concluded.
The study was supported by grants to several researchers from the National Institute on Drug Abuse, National Institutes of Health, and the Charles A. King Trust. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose.
FROM JAMA NETWORK OPEN
Contact dermatitis content varies among social media sites
on YouTube, Facebook, Instagram, Google, Twitter, and Reddit.
Data on social media use suggest that approximately 65% of U.S. adults regularly use social media, and 40% of individuals use it in making medical decisions, Morgan Nguyen, a medical student at Northwestern University, Chicago, said at the annual meeting of the American Contact Dermatitis Society, held virtually this year.
“Dermatologists’ awareness of social media discussions can further their understanding of where patients go for information and what they might encounter,” she said. In particular, “contact dermatitis practitioners can tailor their counseling by knowing what their patients are seeing online.”
To characterize the social media landscape for content related to allergic contact dermatitis (ACD), Ms. Nguyen and colleagues assessed metrics on content and authorship on six different platforms.
For YouTube, the authors reviewed 15 videos related to ACD with views ranging from 24,262 to 232,300. Of these videos, two were produced as medical education, four were produced by patients, and nine were produced by physicians. The content of many videos was poor quality, with an average QUEST score of 7.4/28 overall and 8.7 for physician videos. Video quality was not associated with increased views. Video titles included “What to do if you have a rash on your face,” and “Contact dermatitis on lips!”
Overall, Instagram was more popular than Twitter, particularly among patients. The investigators searched using the hashtags #ContactDermatitis, #AllergicContactDermatitis, and #ContactDerm and reviewed the 100 most recent posts for authorship. The most recent 100 posts occurred over 16 days; physicians, patients, and companies each contributed approximately one-third of the content, but patient content was more focused on symptoms, treatment progress, and advice.
For Instagram, the hashtag search phrase made a notable difference in authorship, Ms. Nguyen said. Physicians were disproportionately more likely to use #AllergicContactDermatitis (43%) compared with patients (22%).
On Twitter, the most recent 100 posts were spread over 152 days, and professional organizations and companies generated approximately two-thirds of the posts. The #ContactDermatitis hashtag was the most common, and accounted for 94% of tweets.
Although patient support groups specific to ACD exist on Facebook, the researchers found none on Reddit. These two venues are designed for creating online communities, rather than simply providing information, and the researchers searched for support groups related to contact dermatitis. One of the main differences between the two is that Facebook allows for the creation of private groups, while Reddit is an open forum.
The largest contact dermatitis Facebook group, the “Eczema, Contact Dermatitis and Patch Testing Alliance,” had 4,665 members at the time of the study, and most groups were private. Although no support groups existed on Reddit, titles of Reddit forums discussing ACD included allergies, askdoctors, fragrance, haircarescience, legaladvice, skincareaddicts, beauty, dermatologyquestions, medical_advice, skincare_addiction, tretinoin, and vulvodynia.
For Google, the researchers used terms similar to “contact dermatitis” as generated by the Google Keyword Planner tool, and used Google Adwords data to estimate monthly searches. The top estimated term was “contact dermatitis,” with 8,322 searches, followed by “contact dermatitis pictures,” with 1,666 searches, and “contact dermatitis treatment” with 595 searches. By contrast, “allergic dermatitis” had an estimated 346 monthly searches, and “allergic contact dermatitis” had 194.
Overall, approximately 9,000 searches each month involve “contact dermatitis,” “allergic contact dermatitis,” or “allergic dermatitis,” said Ms. Nguyen. However, these estimated searches seemed comparatively low, given the high burden of ACD, she said. Although ACD ranks eighth among skin diseases based on health care costs, psoriasis (fourteenth based on health care costs) shows an estimated monthly Google search volume of 600,462, she pointed out.
The study findings were limited by several factors including the potential impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on social media use, and by the lack of specificity associated with the search term “contact dermatitis,” which is not unique to ACD, Ms. Nguyen said.
Although more research on quality assessment is needed, the results suggest that social media is a popular venue for ACD patients to seek and share information, Ms. Nguyen emphasized. There is an opportunity for patch testing physicians to create and disperse educational content for patients using these sites, she concluded.
Study highlights education opportunities
“Due to the pandemic, patients have been increasingly interacting with online resources in lieu of coming to a physician’s office,” corresponding author Walter J. Liszewski, MD, of the department of dermatology, Northwestern University, Chicago, said in an interview. “As social media is increasingly used by patients and physicians, it is important to get a sense of its footprint,” he said.
He and Ms. Nguyen were surprised by several of their findings: First, searches for ACD on Google were not particularly common given its relatively high prevalence and economic cost to society. In addition, they found that physicians often used different language than that of patients to describe ACD on Twitter and Instagram. They were also surprised at how often ACD appeared in Reddit posts, which they noted highlights that ACD impacts multiple sections of society.
The greatest challenge in studying social media and medicine is the quality of material available, Dr. Liszewski and Ms. Nguyen observed, emphasizing that while there are numerous videos on ACD on YouTube, the quality is highly variable, and there is a need for more patient-centered, educational materials. However, the results of their study highlight the opportunity for physicians and industry to create medically-accurate educational materials, they added.
Ms. Nguyen and Dr. Liszewski had no financial conflicts to disclose.
on YouTube, Facebook, Instagram, Google, Twitter, and Reddit.
Data on social media use suggest that approximately 65% of U.S. adults regularly use social media, and 40% of individuals use it in making medical decisions, Morgan Nguyen, a medical student at Northwestern University, Chicago, said at the annual meeting of the American Contact Dermatitis Society, held virtually this year.
“Dermatologists’ awareness of social media discussions can further their understanding of where patients go for information and what they might encounter,” she said. In particular, “contact dermatitis practitioners can tailor their counseling by knowing what their patients are seeing online.”
To characterize the social media landscape for content related to allergic contact dermatitis (ACD), Ms. Nguyen and colleagues assessed metrics on content and authorship on six different platforms.
For YouTube, the authors reviewed 15 videos related to ACD with views ranging from 24,262 to 232,300. Of these videos, two were produced as medical education, four were produced by patients, and nine were produced by physicians. The content of many videos was poor quality, with an average QUEST score of 7.4/28 overall and 8.7 for physician videos. Video quality was not associated with increased views. Video titles included “What to do if you have a rash on your face,” and “Contact dermatitis on lips!”
Overall, Instagram was more popular than Twitter, particularly among patients. The investigators searched using the hashtags #ContactDermatitis, #AllergicContactDermatitis, and #ContactDerm and reviewed the 100 most recent posts for authorship. The most recent 100 posts occurred over 16 days; physicians, patients, and companies each contributed approximately one-third of the content, but patient content was more focused on symptoms, treatment progress, and advice.
For Instagram, the hashtag search phrase made a notable difference in authorship, Ms. Nguyen said. Physicians were disproportionately more likely to use #AllergicContactDermatitis (43%) compared with patients (22%).
On Twitter, the most recent 100 posts were spread over 152 days, and professional organizations and companies generated approximately two-thirds of the posts. The #ContactDermatitis hashtag was the most common, and accounted for 94% of tweets.
Although patient support groups specific to ACD exist on Facebook, the researchers found none on Reddit. These two venues are designed for creating online communities, rather than simply providing information, and the researchers searched for support groups related to contact dermatitis. One of the main differences between the two is that Facebook allows for the creation of private groups, while Reddit is an open forum.
The largest contact dermatitis Facebook group, the “Eczema, Contact Dermatitis and Patch Testing Alliance,” had 4,665 members at the time of the study, and most groups were private. Although no support groups existed on Reddit, titles of Reddit forums discussing ACD included allergies, askdoctors, fragrance, haircarescience, legaladvice, skincareaddicts, beauty, dermatologyquestions, medical_advice, skincare_addiction, tretinoin, and vulvodynia.
For Google, the researchers used terms similar to “contact dermatitis” as generated by the Google Keyword Planner tool, and used Google Adwords data to estimate monthly searches. The top estimated term was “contact dermatitis,” with 8,322 searches, followed by “contact dermatitis pictures,” with 1,666 searches, and “contact dermatitis treatment” with 595 searches. By contrast, “allergic dermatitis” had an estimated 346 monthly searches, and “allergic contact dermatitis” had 194.
Overall, approximately 9,000 searches each month involve “contact dermatitis,” “allergic contact dermatitis,” or “allergic dermatitis,” said Ms. Nguyen. However, these estimated searches seemed comparatively low, given the high burden of ACD, she said. Although ACD ranks eighth among skin diseases based on health care costs, psoriasis (fourteenth based on health care costs) shows an estimated monthly Google search volume of 600,462, she pointed out.
The study findings were limited by several factors including the potential impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on social media use, and by the lack of specificity associated with the search term “contact dermatitis,” which is not unique to ACD, Ms. Nguyen said.
Although more research on quality assessment is needed, the results suggest that social media is a popular venue for ACD patients to seek and share information, Ms. Nguyen emphasized. There is an opportunity for patch testing physicians to create and disperse educational content for patients using these sites, she concluded.
Study highlights education opportunities
“Due to the pandemic, patients have been increasingly interacting with online resources in lieu of coming to a physician’s office,” corresponding author Walter J. Liszewski, MD, of the department of dermatology, Northwestern University, Chicago, said in an interview. “As social media is increasingly used by patients and physicians, it is important to get a sense of its footprint,” he said.
He and Ms. Nguyen were surprised by several of their findings: First, searches for ACD on Google were not particularly common given its relatively high prevalence and economic cost to society. In addition, they found that physicians often used different language than that of patients to describe ACD on Twitter and Instagram. They were also surprised at how often ACD appeared in Reddit posts, which they noted highlights that ACD impacts multiple sections of society.
The greatest challenge in studying social media and medicine is the quality of material available, Dr. Liszewski and Ms. Nguyen observed, emphasizing that while there are numerous videos on ACD on YouTube, the quality is highly variable, and there is a need for more patient-centered, educational materials. However, the results of their study highlight the opportunity for physicians and industry to create medically-accurate educational materials, they added.
Ms. Nguyen and Dr. Liszewski had no financial conflicts to disclose.
on YouTube, Facebook, Instagram, Google, Twitter, and Reddit.
Data on social media use suggest that approximately 65% of U.S. adults regularly use social media, and 40% of individuals use it in making medical decisions, Morgan Nguyen, a medical student at Northwestern University, Chicago, said at the annual meeting of the American Contact Dermatitis Society, held virtually this year.
“Dermatologists’ awareness of social media discussions can further their understanding of where patients go for information and what they might encounter,” she said. In particular, “contact dermatitis practitioners can tailor their counseling by knowing what their patients are seeing online.”
To characterize the social media landscape for content related to allergic contact dermatitis (ACD), Ms. Nguyen and colleagues assessed metrics on content and authorship on six different platforms.
For YouTube, the authors reviewed 15 videos related to ACD with views ranging from 24,262 to 232,300. Of these videos, two were produced as medical education, four were produced by patients, and nine were produced by physicians. The content of many videos was poor quality, with an average QUEST score of 7.4/28 overall and 8.7 for physician videos. Video quality was not associated with increased views. Video titles included “What to do if you have a rash on your face,” and “Contact dermatitis on lips!”
Overall, Instagram was more popular than Twitter, particularly among patients. The investigators searched using the hashtags #ContactDermatitis, #AllergicContactDermatitis, and #ContactDerm and reviewed the 100 most recent posts for authorship. The most recent 100 posts occurred over 16 days; physicians, patients, and companies each contributed approximately one-third of the content, but patient content was more focused on symptoms, treatment progress, and advice.
For Instagram, the hashtag search phrase made a notable difference in authorship, Ms. Nguyen said. Physicians were disproportionately more likely to use #AllergicContactDermatitis (43%) compared with patients (22%).
On Twitter, the most recent 100 posts were spread over 152 days, and professional organizations and companies generated approximately two-thirds of the posts. The #ContactDermatitis hashtag was the most common, and accounted for 94% of tweets.
Although patient support groups specific to ACD exist on Facebook, the researchers found none on Reddit. These two venues are designed for creating online communities, rather than simply providing information, and the researchers searched for support groups related to contact dermatitis. One of the main differences between the two is that Facebook allows for the creation of private groups, while Reddit is an open forum.
The largest contact dermatitis Facebook group, the “Eczema, Contact Dermatitis and Patch Testing Alliance,” had 4,665 members at the time of the study, and most groups were private. Although no support groups existed on Reddit, titles of Reddit forums discussing ACD included allergies, askdoctors, fragrance, haircarescience, legaladvice, skincareaddicts, beauty, dermatologyquestions, medical_advice, skincare_addiction, tretinoin, and vulvodynia.
For Google, the researchers used terms similar to “contact dermatitis” as generated by the Google Keyword Planner tool, and used Google Adwords data to estimate monthly searches. The top estimated term was “contact dermatitis,” with 8,322 searches, followed by “contact dermatitis pictures,” with 1,666 searches, and “contact dermatitis treatment” with 595 searches. By contrast, “allergic dermatitis” had an estimated 346 monthly searches, and “allergic contact dermatitis” had 194.
Overall, approximately 9,000 searches each month involve “contact dermatitis,” “allergic contact dermatitis,” or “allergic dermatitis,” said Ms. Nguyen. However, these estimated searches seemed comparatively low, given the high burden of ACD, she said. Although ACD ranks eighth among skin diseases based on health care costs, psoriasis (fourteenth based on health care costs) shows an estimated monthly Google search volume of 600,462, she pointed out.
The study findings were limited by several factors including the potential impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on social media use, and by the lack of specificity associated with the search term “contact dermatitis,” which is not unique to ACD, Ms. Nguyen said.
Although more research on quality assessment is needed, the results suggest that social media is a popular venue for ACD patients to seek and share information, Ms. Nguyen emphasized. There is an opportunity for patch testing physicians to create and disperse educational content for patients using these sites, she concluded.
Study highlights education opportunities
“Due to the pandemic, patients have been increasingly interacting with online resources in lieu of coming to a physician’s office,” corresponding author Walter J. Liszewski, MD, of the department of dermatology, Northwestern University, Chicago, said in an interview. “As social media is increasingly used by patients and physicians, it is important to get a sense of its footprint,” he said.
He and Ms. Nguyen were surprised by several of their findings: First, searches for ACD on Google were not particularly common given its relatively high prevalence and economic cost to society. In addition, they found that physicians often used different language than that of patients to describe ACD on Twitter and Instagram. They were also surprised at how often ACD appeared in Reddit posts, which they noted highlights that ACD impacts multiple sections of society.
The greatest challenge in studying social media and medicine is the quality of material available, Dr. Liszewski and Ms. Nguyen observed, emphasizing that while there are numerous videos on ACD on YouTube, the quality is highly variable, and there is a need for more patient-centered, educational materials. However, the results of their study highlight the opportunity for physicians and industry to create medically-accurate educational materials, they added.
Ms. Nguyen and Dr. Liszewski had no financial conflicts to disclose.
FROM ACDS 2021
Check all components in cases of suspected shoe allergy
according to a retrospective study of more than 30,000 patients.
Contact allergy to shoes remains a common but difficult problem for many reasons, including the limited information from shoe manufacturers, differences in shoe manufacturing processes, and changes in shoe trends, said Raina Bembry, MD, a dermatitis research fellow at Duke University, Durham, N.C., in a presentation at the annual meeting of the American Contact Dermatitis Society.
The North American Contact Dermatitis Group (NACDG) published data on shoe allergens from 2001-2004 in a 2007 review. To update this information to reflect changes in shoe manufacturing and trends, she and her coinvestigators characterized demographics, clinical characteristics, patch test results, and occupational data for NACDG patients with shoe contact allergy. They identified 33,661 patients who were patch tested with the standard series with or without a supplemental allergen between 2005 and 2018; over half were over aged 40.
The primary focus was individuals with a confirmed shoe (defined as shoes, boots, sandals, or slippers) as the source of a screening allergen or supplemental allergen, a positive patch test, and the foot as one of three sites of involvement. A total of 352 individuals met these criteria and had a confirmed final diagnosis of allergic contact dermatitis, Dr. Bembry said. Compared with individuals who had positive patch tests without a confirmed diagnosis, those with confirmed allergic dermatitis were significantly more likely to be male (odds ratio, 3.36) and less likely to be over aged 40 years (OR, 0.49).
The most common NACDG screening allergen, potassium dichromate, was found in 29.8% of the study population, followed by p-tert-butylphenol formaldehyde resin in 20.1%, thiuram mix (13.3%), mixed dialkyl thioureas (12.6%) and carba mix (12%).
Notably, 29.8% of the patients showed positive patch test reactions to supplemental allergens, and 12.2% only reacted to supplemental allergens, Dr. Bembry said.
The results were limited by several factors, including referral selection bias, reliance on clinical judgment for patch test interpretations, and lack of data on the specifics of the supplemental allergens other than the source code, she said. In addition, the study does not identify nonshoe sources of foot contact allergy, and six screening allergens were not testing during this study period.
Overall, the findings were similar to those from previous studies in that patients affected with contact dermatitis from shoe allergens tended to be younger and male, with no occupational relevance to the reaction, said Dr. Bembry.
The finding that almost 20% of allergens were not found with the screening series emphasizes the value of testing not only relevant supplemental allergens, but also patient products and shoe components, she concluded.
Dr. Bembry had no financial conflicts to disclose. Coauthor Amber Atwater, MD, the immediate past president of the ACDS, and associate professor of dermatology at Duke University, disclosed receiving the Pfizer Independent Grant for Learning & Change and consulting for Henkel.
according to a retrospective study of more than 30,000 patients.
Contact allergy to shoes remains a common but difficult problem for many reasons, including the limited information from shoe manufacturers, differences in shoe manufacturing processes, and changes in shoe trends, said Raina Bembry, MD, a dermatitis research fellow at Duke University, Durham, N.C., in a presentation at the annual meeting of the American Contact Dermatitis Society.
The North American Contact Dermatitis Group (NACDG) published data on shoe allergens from 2001-2004 in a 2007 review. To update this information to reflect changes in shoe manufacturing and trends, she and her coinvestigators characterized demographics, clinical characteristics, patch test results, and occupational data for NACDG patients with shoe contact allergy. They identified 33,661 patients who were patch tested with the standard series with or without a supplemental allergen between 2005 and 2018; over half were over aged 40.
The primary focus was individuals with a confirmed shoe (defined as shoes, boots, sandals, or slippers) as the source of a screening allergen or supplemental allergen, a positive patch test, and the foot as one of three sites of involvement. A total of 352 individuals met these criteria and had a confirmed final diagnosis of allergic contact dermatitis, Dr. Bembry said. Compared with individuals who had positive patch tests without a confirmed diagnosis, those with confirmed allergic dermatitis were significantly more likely to be male (odds ratio, 3.36) and less likely to be over aged 40 years (OR, 0.49).
The most common NACDG screening allergen, potassium dichromate, was found in 29.8% of the study population, followed by p-tert-butylphenol formaldehyde resin in 20.1%, thiuram mix (13.3%), mixed dialkyl thioureas (12.6%) and carba mix (12%).
Notably, 29.8% of the patients showed positive patch test reactions to supplemental allergens, and 12.2% only reacted to supplemental allergens, Dr. Bembry said.
The results were limited by several factors, including referral selection bias, reliance on clinical judgment for patch test interpretations, and lack of data on the specifics of the supplemental allergens other than the source code, she said. In addition, the study does not identify nonshoe sources of foot contact allergy, and six screening allergens were not testing during this study period.
Overall, the findings were similar to those from previous studies in that patients affected with contact dermatitis from shoe allergens tended to be younger and male, with no occupational relevance to the reaction, said Dr. Bembry.
The finding that almost 20% of allergens were not found with the screening series emphasizes the value of testing not only relevant supplemental allergens, but also patient products and shoe components, she concluded.
Dr. Bembry had no financial conflicts to disclose. Coauthor Amber Atwater, MD, the immediate past president of the ACDS, and associate professor of dermatology at Duke University, disclosed receiving the Pfizer Independent Grant for Learning & Change and consulting for Henkel.
according to a retrospective study of more than 30,000 patients.
Contact allergy to shoes remains a common but difficult problem for many reasons, including the limited information from shoe manufacturers, differences in shoe manufacturing processes, and changes in shoe trends, said Raina Bembry, MD, a dermatitis research fellow at Duke University, Durham, N.C., in a presentation at the annual meeting of the American Contact Dermatitis Society.
The North American Contact Dermatitis Group (NACDG) published data on shoe allergens from 2001-2004 in a 2007 review. To update this information to reflect changes in shoe manufacturing and trends, she and her coinvestigators characterized demographics, clinical characteristics, patch test results, and occupational data for NACDG patients with shoe contact allergy. They identified 33,661 patients who were patch tested with the standard series with or without a supplemental allergen between 2005 and 2018; over half were over aged 40.
The primary focus was individuals with a confirmed shoe (defined as shoes, boots, sandals, or slippers) as the source of a screening allergen or supplemental allergen, a positive patch test, and the foot as one of three sites of involvement. A total of 352 individuals met these criteria and had a confirmed final diagnosis of allergic contact dermatitis, Dr. Bembry said. Compared with individuals who had positive patch tests without a confirmed diagnosis, those with confirmed allergic dermatitis were significantly more likely to be male (odds ratio, 3.36) and less likely to be over aged 40 years (OR, 0.49).
The most common NACDG screening allergen, potassium dichromate, was found in 29.8% of the study population, followed by p-tert-butylphenol formaldehyde resin in 20.1%, thiuram mix (13.3%), mixed dialkyl thioureas (12.6%) and carba mix (12%).
Notably, 29.8% of the patients showed positive patch test reactions to supplemental allergens, and 12.2% only reacted to supplemental allergens, Dr. Bembry said.
The results were limited by several factors, including referral selection bias, reliance on clinical judgment for patch test interpretations, and lack of data on the specifics of the supplemental allergens other than the source code, she said. In addition, the study does not identify nonshoe sources of foot contact allergy, and six screening allergens were not testing during this study period.
Overall, the findings were similar to those from previous studies in that patients affected with contact dermatitis from shoe allergens tended to be younger and male, with no occupational relevance to the reaction, said Dr. Bembry.
The finding that almost 20% of allergens were not found with the screening series emphasizes the value of testing not only relevant supplemental allergens, but also patient products and shoe components, she concluded.
Dr. Bembry had no financial conflicts to disclose. Coauthor Amber Atwater, MD, the immediate past president of the ACDS, and associate professor of dermatology at Duke University, disclosed receiving the Pfizer Independent Grant for Learning & Change and consulting for Henkel.
FROM ACDS 2021
Febuxostat, allopurinol real-world cardiovascular risk appears equal
Febuxostat (Uloric) was not associated with increased cardiovascular risk in patients with gout when compared to those who used allopurinol, in an analysis of new users of the drugs in Medicare fee-for-service claims data from the period of 2008-2016.
The findings, published March 25 in the Journal of the American Heart Association, update and echo the results from a similar previous study by the same Brigham and Women’s Hospital research group that covered 2008-2013 Medicare claims data. That original claims data study from 2018 sought to confirm the findings of the postmarketing surveillance CARES (Cardiovascular Safety of Febuxostat and Allopurinol in Patients With Gout and Cardiovascular Morbidities) trial that led to a boxed warning for increased risk of cardiovascular and all-cause mortality vs. allopurinol. The trial, however, did not show a higher rate of major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE) overall with febuxostat.
The recency of the new data with more febuxostat-exposed patients overall provides greater reassurance on the safety of the drug, corresponding author Seoyoung C. Kim, MD, of Brigham and Women’s Hospital and Harvard Medical School, Boston, said in an interview. “We also were able to get data on cause of death, which we did not have before when we conducted our first paper.”
Dr. Kim said she was not surprised by any of the findings, which were consistent with the results of her earlier work. “Our result on CV death also was consistent and reassuring,” she noted.
The newest Medicare claims study also corroborates results from FAST (Febuxostat Versus Allopurinol Streamlined Trial), a separate postmarketing surveillance study that was ordered by the European Medicines Agency after febuxostat’s approval in 2009. It showed that the two drugs were noninferior to each other for the risk of all-cause mortality or a composite cardiovascular outcome (hospitalization for nonfatal myocardial infarction, biomarker-positive acute coronary syndrome, nonfatal stroke, or cardiovascular death).
“While CARES showed higher CV death and all-cause death rates in febuxostat compared to allopurinol, FAST did not,” Dr. Kim noted. “Our study of more than 111,000 older gout patients treated with either febuxostat or allopurinol in real-world settings also did not find a difference in the risk of MACE, CV mortality, or all-cause mortality,” she added. “Taking these data all together, I think we can be more certain about the CV safety of febuxostat when its use is clinically indicated or needed,” she said.
Study details
Dr. Kim, first author Ajinkya Pawar, PhD, of Brigham and Women’s, and colleagues identified 467,461 people with gout aged 65 years and older who had been enrolled in Medicare for at least a year. They then used propensity-score matching to compare 27,881 first-time users of febuxostat with 83,643 first-time users of allopurinol on the primary outcome of the incidence of major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE), defined as the first occurrence of myocardial infarction, stroke, or cardiovascular mortality.
In the updated study, the mean follow‐up periods for febuxostat and allopurinol were 284 days and 339 days, respectively. Overall, febuxostat was noninferior to allopurinol with regard to MACE (hazard ratio, 0.99; 95% confidence interval, 0.93-1.05), and the results were consistent among patients with baseline CVD (HR, 0.94). In addition, rates of secondary outcomes of MI, stroke, and cardiovascular mortality were not significantly different between febuxostat and allopurinol patients, except for all-cause mortality (HR, 0.92; 95% CI, 0.87-0.98).
The study findings were limited mainly by the potential bias caused by nonadherence to medications, and potential for residual confounding and misclassification bias, the researchers noted.
However, the study was strengthened by its incident new-user design that allowed only patients with no use of either medication for a year before the first dispensing and its active comparator design, and the data are generalizable to the greater population of older gout patients, they said.
Consequently, the data from this large, real-world study support the safety of febuxostat with regard to cardiovascular risk in gout patients, including those with baseline cardiovascular disease, they concluded.
The study was supported by the division of pharmacoepidemiology and pharmacoeconomics at Brigham and Women’s Hospital. Dr. Kim disclosed research grants to Brigham and Women’s Hospital from Roche, Pfizer, AbbVie, and Bristol‐Myers Squibb for unrelated studies. Another author reported serving as the principal investigator with research grants from Vertex, Bayer, and Novartis to Brigham and Women’s Hospital for unrelated projects.
Febuxostat (Uloric) was not associated with increased cardiovascular risk in patients with gout when compared to those who used allopurinol, in an analysis of new users of the drugs in Medicare fee-for-service claims data from the period of 2008-2016.
The findings, published March 25 in the Journal of the American Heart Association, update and echo the results from a similar previous study by the same Brigham and Women’s Hospital research group that covered 2008-2013 Medicare claims data. That original claims data study from 2018 sought to confirm the findings of the postmarketing surveillance CARES (Cardiovascular Safety of Febuxostat and Allopurinol in Patients With Gout and Cardiovascular Morbidities) trial that led to a boxed warning for increased risk of cardiovascular and all-cause mortality vs. allopurinol. The trial, however, did not show a higher rate of major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE) overall with febuxostat.
The recency of the new data with more febuxostat-exposed patients overall provides greater reassurance on the safety of the drug, corresponding author Seoyoung C. Kim, MD, of Brigham and Women’s Hospital and Harvard Medical School, Boston, said in an interview. “We also were able to get data on cause of death, which we did not have before when we conducted our first paper.”
Dr. Kim said she was not surprised by any of the findings, which were consistent with the results of her earlier work. “Our result on CV death also was consistent and reassuring,” she noted.
The newest Medicare claims study also corroborates results from FAST (Febuxostat Versus Allopurinol Streamlined Trial), a separate postmarketing surveillance study that was ordered by the European Medicines Agency after febuxostat’s approval in 2009. It showed that the two drugs were noninferior to each other for the risk of all-cause mortality or a composite cardiovascular outcome (hospitalization for nonfatal myocardial infarction, biomarker-positive acute coronary syndrome, nonfatal stroke, or cardiovascular death).
“While CARES showed higher CV death and all-cause death rates in febuxostat compared to allopurinol, FAST did not,” Dr. Kim noted. “Our study of more than 111,000 older gout patients treated with either febuxostat or allopurinol in real-world settings also did not find a difference in the risk of MACE, CV mortality, or all-cause mortality,” she added. “Taking these data all together, I think we can be more certain about the CV safety of febuxostat when its use is clinically indicated or needed,” she said.
Study details
Dr. Kim, first author Ajinkya Pawar, PhD, of Brigham and Women’s, and colleagues identified 467,461 people with gout aged 65 years and older who had been enrolled in Medicare for at least a year. They then used propensity-score matching to compare 27,881 first-time users of febuxostat with 83,643 first-time users of allopurinol on the primary outcome of the incidence of major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE), defined as the first occurrence of myocardial infarction, stroke, or cardiovascular mortality.
In the updated study, the mean follow‐up periods for febuxostat and allopurinol were 284 days and 339 days, respectively. Overall, febuxostat was noninferior to allopurinol with regard to MACE (hazard ratio, 0.99; 95% confidence interval, 0.93-1.05), and the results were consistent among patients with baseline CVD (HR, 0.94). In addition, rates of secondary outcomes of MI, stroke, and cardiovascular mortality were not significantly different between febuxostat and allopurinol patients, except for all-cause mortality (HR, 0.92; 95% CI, 0.87-0.98).
The study findings were limited mainly by the potential bias caused by nonadherence to medications, and potential for residual confounding and misclassification bias, the researchers noted.
However, the study was strengthened by its incident new-user design that allowed only patients with no use of either medication for a year before the first dispensing and its active comparator design, and the data are generalizable to the greater population of older gout patients, they said.
Consequently, the data from this large, real-world study support the safety of febuxostat with regard to cardiovascular risk in gout patients, including those with baseline cardiovascular disease, they concluded.
The study was supported by the division of pharmacoepidemiology and pharmacoeconomics at Brigham and Women’s Hospital. Dr. Kim disclosed research grants to Brigham and Women’s Hospital from Roche, Pfizer, AbbVie, and Bristol‐Myers Squibb for unrelated studies. Another author reported serving as the principal investigator with research grants from Vertex, Bayer, and Novartis to Brigham and Women’s Hospital for unrelated projects.
Febuxostat (Uloric) was not associated with increased cardiovascular risk in patients with gout when compared to those who used allopurinol, in an analysis of new users of the drugs in Medicare fee-for-service claims data from the period of 2008-2016.
The findings, published March 25 in the Journal of the American Heart Association, update and echo the results from a similar previous study by the same Brigham and Women’s Hospital research group that covered 2008-2013 Medicare claims data. That original claims data study from 2018 sought to confirm the findings of the postmarketing surveillance CARES (Cardiovascular Safety of Febuxostat and Allopurinol in Patients With Gout and Cardiovascular Morbidities) trial that led to a boxed warning for increased risk of cardiovascular and all-cause mortality vs. allopurinol. The trial, however, did not show a higher rate of major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE) overall with febuxostat.
The recency of the new data with more febuxostat-exposed patients overall provides greater reassurance on the safety of the drug, corresponding author Seoyoung C. Kim, MD, of Brigham and Women’s Hospital and Harvard Medical School, Boston, said in an interview. “We also were able to get data on cause of death, which we did not have before when we conducted our first paper.”
Dr. Kim said she was not surprised by any of the findings, which were consistent with the results of her earlier work. “Our result on CV death also was consistent and reassuring,” she noted.
The newest Medicare claims study also corroborates results from FAST (Febuxostat Versus Allopurinol Streamlined Trial), a separate postmarketing surveillance study that was ordered by the European Medicines Agency after febuxostat’s approval in 2009. It showed that the two drugs were noninferior to each other for the risk of all-cause mortality or a composite cardiovascular outcome (hospitalization for nonfatal myocardial infarction, biomarker-positive acute coronary syndrome, nonfatal stroke, or cardiovascular death).
“While CARES showed higher CV death and all-cause death rates in febuxostat compared to allopurinol, FAST did not,” Dr. Kim noted. “Our study of more than 111,000 older gout patients treated with either febuxostat or allopurinol in real-world settings also did not find a difference in the risk of MACE, CV mortality, or all-cause mortality,” she added. “Taking these data all together, I think we can be more certain about the CV safety of febuxostat when its use is clinically indicated or needed,” she said.
Study details
Dr. Kim, first author Ajinkya Pawar, PhD, of Brigham and Women’s, and colleagues identified 467,461 people with gout aged 65 years and older who had been enrolled in Medicare for at least a year. They then used propensity-score matching to compare 27,881 first-time users of febuxostat with 83,643 first-time users of allopurinol on the primary outcome of the incidence of major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE), defined as the first occurrence of myocardial infarction, stroke, or cardiovascular mortality.
In the updated study, the mean follow‐up periods for febuxostat and allopurinol were 284 days and 339 days, respectively. Overall, febuxostat was noninferior to allopurinol with regard to MACE (hazard ratio, 0.99; 95% confidence interval, 0.93-1.05), and the results were consistent among patients with baseline CVD (HR, 0.94). In addition, rates of secondary outcomes of MI, stroke, and cardiovascular mortality were not significantly different between febuxostat and allopurinol patients, except for all-cause mortality (HR, 0.92; 95% CI, 0.87-0.98).
The study findings were limited mainly by the potential bias caused by nonadherence to medications, and potential for residual confounding and misclassification bias, the researchers noted.
However, the study was strengthened by its incident new-user design that allowed only patients with no use of either medication for a year before the first dispensing and its active comparator design, and the data are generalizable to the greater population of older gout patients, they said.
Consequently, the data from this large, real-world study support the safety of febuxostat with regard to cardiovascular risk in gout patients, including those with baseline cardiovascular disease, they concluded.
The study was supported by the division of pharmacoepidemiology and pharmacoeconomics at Brigham and Women’s Hospital. Dr. Kim disclosed research grants to Brigham and Women’s Hospital from Roche, Pfizer, AbbVie, and Bristol‐Myers Squibb for unrelated studies. Another author reported serving as the principal investigator with research grants from Vertex, Bayer, and Novartis to Brigham and Women’s Hospital for unrelated projects.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF THE AMERICAN HEART ASSOCIATION
COVID-19 vaccination in RMD patients: Safety data “reassuring”
Two reports support the safety and immunogenicity of SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccines in patients with rheumatic and musculoskeletal diseases (RMDs) and represent the first available data on such patients.
In an observational cohort study published in Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, Caoilfhionn M. Connolly, MD, of Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, and colleagues reviewed data from 325 adults with RMDs who received the first dose of SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccine during the period of Dec. 17, 2020, to Feb. 11, 2021. Of these, 51% received the Pfizer/BioNTech vaccine and 49% received the Moderna vaccine.
The patients, who were invited to participate on social media, were aged 34-54 years, 96% were women, and 89% were White. Inflammatory arthritis was the most common RMD condition (38%), followed by systemic lupus erythematosus (28%) and overlap connective tissue disease (19%). The patients were using a range of immunomodulatory treatment regimens, including nonbiologic disease modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) in 44%, biologics in 19%, and combination therapy in 37%.
Overall, 89% of patients reported localized symptoms of pain, swelling, and erythema, and 69% reported systemic symptoms. Fatigue was the most common systemic symptom, and 7.4% reported severe fatigue.
None of the patients experienced allergic reactions requiring epinephrine, and 3% reported new infections that required treatment.
“These early, reassuring results may ameliorate concern among patients and provide guidance for rheumatology providers in critical discussions regarding vaccine hesitancy or refusal,” they concluded.
Antibody responses
In another study published in Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases by the same group of researchers, antibody responses against the receptor binding domain of the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein were seen in 74% of 123 adults with an RMD at 18-26 days after receiving a first dose of SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccine (52% Pfizer vaccine and 48% Moderna) between Jan. 8, 2021, and Feb. 12, 2021.
The most common diagnoses in these patients were inflammatory arthritis (28%), systemic lupus erythematosus (20%), and Sjögren’s syndrome (13%). A total of 28% of participants reported taking no immunomodulatory agents, 19% reported nonbiologic DMARDs, 14% reported biologic DMARDs, and 19% reported combination therapy.
Although no differences appeared based on disease groups or overall categories of immunomodulatory therapies, patients whose treatment included mycophenolate or rituximab were significantly less likely to develop antibody responses than were patients not taking these medications (P = .001 and P = .04, respectively). Although rituximab and methotrexate have been associated with reduced responses to vaccines such as the flu vaccine, methotrexate was not associated with reduced vaccine response in this study. A total of 94% of patients taking a tumor necrosis factor inhibitor had detectable antibodies.
The studies’ findings were limited by several factors including a lack of longer-term safety data; the small, nonrandomized sample of mainly white women; limited information on immunomodulatory drug dosage and timing; lack of serial antibody measurements; use of an enzyme immunoassay designed to detect antibody response after natural infection; and the inclusion of data only on the first dose of a two-dose vaccine series, the researchers noted. However, the data should provide additional reassurance to RMD patients and their health care teams about vaccination against COVID-19, they said.
Both studies were supported by the Ben-Dov family. In addition, the studies were supported by grants to various study authors from the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases, the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, the National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases, and the Transplantation and Immunology Research Network of the American Society of Transplantation. One author disclosed financial relationships with Sanofi, Novartis, CSL Behring, Jazz Pharmaceuticals, Veloxis, Mallinckrodt, and Thermo Fisher Scientific. The other researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose.
Two reports support the safety and immunogenicity of SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccines in patients with rheumatic and musculoskeletal diseases (RMDs) and represent the first available data on such patients.
In an observational cohort study published in Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, Caoilfhionn M. Connolly, MD, of Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, and colleagues reviewed data from 325 adults with RMDs who received the first dose of SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccine during the period of Dec. 17, 2020, to Feb. 11, 2021. Of these, 51% received the Pfizer/BioNTech vaccine and 49% received the Moderna vaccine.
The patients, who were invited to participate on social media, were aged 34-54 years, 96% were women, and 89% were White. Inflammatory arthritis was the most common RMD condition (38%), followed by systemic lupus erythematosus (28%) and overlap connective tissue disease (19%). The patients were using a range of immunomodulatory treatment regimens, including nonbiologic disease modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) in 44%, biologics in 19%, and combination therapy in 37%.
Overall, 89% of patients reported localized symptoms of pain, swelling, and erythema, and 69% reported systemic symptoms. Fatigue was the most common systemic symptom, and 7.4% reported severe fatigue.
None of the patients experienced allergic reactions requiring epinephrine, and 3% reported new infections that required treatment.
“These early, reassuring results may ameliorate concern among patients and provide guidance for rheumatology providers in critical discussions regarding vaccine hesitancy or refusal,” they concluded.
Antibody responses
In another study published in Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases by the same group of researchers, antibody responses against the receptor binding domain of the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein were seen in 74% of 123 adults with an RMD at 18-26 days after receiving a first dose of SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccine (52% Pfizer vaccine and 48% Moderna) between Jan. 8, 2021, and Feb. 12, 2021.
The most common diagnoses in these patients were inflammatory arthritis (28%), systemic lupus erythematosus (20%), and Sjögren’s syndrome (13%). A total of 28% of participants reported taking no immunomodulatory agents, 19% reported nonbiologic DMARDs, 14% reported biologic DMARDs, and 19% reported combination therapy.
Although no differences appeared based on disease groups or overall categories of immunomodulatory therapies, patients whose treatment included mycophenolate or rituximab were significantly less likely to develop antibody responses than were patients not taking these medications (P = .001 and P = .04, respectively). Although rituximab and methotrexate have been associated with reduced responses to vaccines such as the flu vaccine, methotrexate was not associated with reduced vaccine response in this study. A total of 94% of patients taking a tumor necrosis factor inhibitor had detectable antibodies.
The studies’ findings were limited by several factors including a lack of longer-term safety data; the small, nonrandomized sample of mainly white women; limited information on immunomodulatory drug dosage and timing; lack of serial antibody measurements; use of an enzyme immunoassay designed to detect antibody response after natural infection; and the inclusion of data only on the first dose of a two-dose vaccine series, the researchers noted. However, the data should provide additional reassurance to RMD patients and their health care teams about vaccination against COVID-19, they said.
Both studies were supported by the Ben-Dov family. In addition, the studies were supported by grants to various study authors from the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases, the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, the National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases, and the Transplantation and Immunology Research Network of the American Society of Transplantation. One author disclosed financial relationships with Sanofi, Novartis, CSL Behring, Jazz Pharmaceuticals, Veloxis, Mallinckrodt, and Thermo Fisher Scientific. The other researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose.
Two reports support the safety and immunogenicity of SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccines in patients with rheumatic and musculoskeletal diseases (RMDs) and represent the first available data on such patients.
In an observational cohort study published in Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, Caoilfhionn M. Connolly, MD, of Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, and colleagues reviewed data from 325 adults with RMDs who received the first dose of SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccine during the period of Dec. 17, 2020, to Feb. 11, 2021. Of these, 51% received the Pfizer/BioNTech vaccine and 49% received the Moderna vaccine.
The patients, who were invited to participate on social media, were aged 34-54 years, 96% were women, and 89% were White. Inflammatory arthritis was the most common RMD condition (38%), followed by systemic lupus erythematosus (28%) and overlap connective tissue disease (19%). The patients were using a range of immunomodulatory treatment regimens, including nonbiologic disease modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) in 44%, biologics in 19%, and combination therapy in 37%.
Overall, 89% of patients reported localized symptoms of pain, swelling, and erythema, and 69% reported systemic symptoms. Fatigue was the most common systemic symptom, and 7.4% reported severe fatigue.
None of the patients experienced allergic reactions requiring epinephrine, and 3% reported new infections that required treatment.
“These early, reassuring results may ameliorate concern among patients and provide guidance for rheumatology providers in critical discussions regarding vaccine hesitancy or refusal,” they concluded.
Antibody responses
In another study published in Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases by the same group of researchers, antibody responses against the receptor binding domain of the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein were seen in 74% of 123 adults with an RMD at 18-26 days after receiving a first dose of SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccine (52% Pfizer vaccine and 48% Moderna) between Jan. 8, 2021, and Feb. 12, 2021.
The most common diagnoses in these patients were inflammatory arthritis (28%), systemic lupus erythematosus (20%), and Sjögren’s syndrome (13%). A total of 28% of participants reported taking no immunomodulatory agents, 19% reported nonbiologic DMARDs, 14% reported biologic DMARDs, and 19% reported combination therapy.
Although no differences appeared based on disease groups or overall categories of immunomodulatory therapies, patients whose treatment included mycophenolate or rituximab were significantly less likely to develop antibody responses than were patients not taking these medications (P = .001 and P = .04, respectively). Although rituximab and methotrexate have been associated with reduced responses to vaccines such as the flu vaccine, methotrexate was not associated with reduced vaccine response in this study. A total of 94% of patients taking a tumor necrosis factor inhibitor had detectable antibodies.
The studies’ findings were limited by several factors including a lack of longer-term safety data; the small, nonrandomized sample of mainly white women; limited information on immunomodulatory drug dosage and timing; lack of serial antibody measurements; use of an enzyme immunoassay designed to detect antibody response after natural infection; and the inclusion of data only on the first dose of a two-dose vaccine series, the researchers noted. However, the data should provide additional reassurance to RMD patients and their health care teams about vaccination against COVID-19, they said.
Both studies were supported by the Ben-Dov family. In addition, the studies were supported by grants to various study authors from the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases, the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, the National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases, and the Transplantation and Immunology Research Network of the American Society of Transplantation. One author disclosed financial relationships with Sanofi, Novartis, CSL Behring, Jazz Pharmaceuticals, Veloxis, Mallinckrodt, and Thermo Fisher Scientific. The other researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose.
FROM ANNALS OF THE RHEUMATIC DISEASES