User login
Veterans’ Well-Being Tools Aim to Improve Quality of Life
Could assessing the well-being of older patients create better treatment plans?
Researchers with the US Department of Veterans Affairs posit that doing so just might improve patient quality of life.
In an article in Medical Care, Dawne Vogt, PhD, and her colleagues described two surveys of well-being developed for use in clinical settings.
“Well-Being Signs” (WBS), a 1-minute screening, asks patients about how satisfied they are with the most important parts of their daily life, which could include time with family. It also asks how regularly involved they are in the activities and their level of functioning.
“Well-Being Brief” (WBB) is self-administered and asks more in-depth questions about finances, health, social relationships, and vocation. Clinicians can use the tool to make referrals to appropriate services like counseling or resources like senior centers.
“They’re not things that we’ve historically paid a lot of attention to, at least in the healthcare setting,” said Vogt, a research psychologist in the Women’s Health Sciences Division of the VA Boston Healthcare System in Massachusetts. “A growing body of research shows that they have really big implications for health.”
The two approaches stem from an increased awareness of the relationship between social determinants of health and outcomes. Both screenings can be implemented more effectively in a clinical setting than other measures because of their brevity and ease of use, she said.
Vogt shared that anecdotally, she finds patients are pleasantly surprised by the questionnaires “because they’re being seen in a way that they don’t always feel like they’re seen.”
Vogt said that the two well-being measurements are more nuanced than standard screenings for depression.
“A measure of depression tells you something much more narrow than a measure of well-being tells you,” she said, adding that identifying problem areas early can help prevent developing mental health disorders. For example, Vogt said that veterans with higher well-being are less likely to develop posttraumatic stress disorder when exposed to trauma.
The WBS has been validated, while the WBB questionnaire awaits final testing.
James Michail, MD, a family and geriatric physician with Providence Health & Services in Los Angeles, California, said he views the well-being screeners as launching points into discussing whether a treatment is enhancing or inhibiting a patient’s life.
“We have screenings for everything else but not for wellness, and the goal of care isn’t necessarily always treatment,” Michail said. “It’s taking the whole person into consideration. There’s a person behind the disease.”
Kendra Segura, MD, an obstetrician-gynecologist in Los Angeles, said she is open to using a well-being screener. Usually, building repertoire with a patient takes time, and sometimes only then can it allow for a more candid assessment of well-being.
“Over the course of several visits, that is when patients open up,” she said. “It’s when that starts to happen where they start to tell you about their well-being. It’s not an easy thing to establish.”
The authors of the article reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Could assessing the well-being of older patients create better treatment plans?
Researchers with the US Department of Veterans Affairs posit that doing so just might improve patient quality of life.
In an article in Medical Care, Dawne Vogt, PhD, and her colleagues described two surveys of well-being developed for use in clinical settings.
“Well-Being Signs” (WBS), a 1-minute screening, asks patients about how satisfied they are with the most important parts of their daily life, which could include time with family. It also asks how regularly involved they are in the activities and their level of functioning.
“Well-Being Brief” (WBB) is self-administered and asks more in-depth questions about finances, health, social relationships, and vocation. Clinicians can use the tool to make referrals to appropriate services like counseling or resources like senior centers.
“They’re not things that we’ve historically paid a lot of attention to, at least in the healthcare setting,” said Vogt, a research psychologist in the Women’s Health Sciences Division of the VA Boston Healthcare System in Massachusetts. “A growing body of research shows that they have really big implications for health.”
The two approaches stem from an increased awareness of the relationship between social determinants of health and outcomes. Both screenings can be implemented more effectively in a clinical setting than other measures because of their brevity and ease of use, she said.
Vogt shared that anecdotally, she finds patients are pleasantly surprised by the questionnaires “because they’re being seen in a way that they don’t always feel like they’re seen.”
Vogt said that the two well-being measurements are more nuanced than standard screenings for depression.
“A measure of depression tells you something much more narrow than a measure of well-being tells you,” she said, adding that identifying problem areas early can help prevent developing mental health disorders. For example, Vogt said that veterans with higher well-being are less likely to develop posttraumatic stress disorder when exposed to trauma.
The WBS has been validated, while the WBB questionnaire awaits final testing.
James Michail, MD, a family and geriatric physician with Providence Health & Services in Los Angeles, California, said he views the well-being screeners as launching points into discussing whether a treatment is enhancing or inhibiting a patient’s life.
“We have screenings for everything else but not for wellness, and the goal of care isn’t necessarily always treatment,” Michail said. “It’s taking the whole person into consideration. There’s a person behind the disease.”
Kendra Segura, MD, an obstetrician-gynecologist in Los Angeles, said she is open to using a well-being screener. Usually, building repertoire with a patient takes time, and sometimes only then can it allow for a more candid assessment of well-being.
“Over the course of several visits, that is when patients open up,” she said. “It’s when that starts to happen where they start to tell you about their well-being. It’s not an easy thing to establish.”
The authors of the article reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Could assessing the well-being of older patients create better treatment plans?
Researchers with the US Department of Veterans Affairs posit that doing so just might improve patient quality of life.
In an article in Medical Care, Dawne Vogt, PhD, and her colleagues described two surveys of well-being developed for use in clinical settings.
“Well-Being Signs” (WBS), a 1-minute screening, asks patients about how satisfied they are with the most important parts of their daily life, which could include time with family. It also asks how regularly involved they are in the activities and their level of functioning.
“Well-Being Brief” (WBB) is self-administered and asks more in-depth questions about finances, health, social relationships, and vocation. Clinicians can use the tool to make referrals to appropriate services like counseling or resources like senior centers.
“They’re not things that we’ve historically paid a lot of attention to, at least in the healthcare setting,” said Vogt, a research psychologist in the Women’s Health Sciences Division of the VA Boston Healthcare System in Massachusetts. “A growing body of research shows that they have really big implications for health.”
The two approaches stem from an increased awareness of the relationship between social determinants of health and outcomes. Both screenings can be implemented more effectively in a clinical setting than other measures because of their brevity and ease of use, she said.
Vogt shared that anecdotally, she finds patients are pleasantly surprised by the questionnaires “because they’re being seen in a way that they don’t always feel like they’re seen.”
Vogt said that the two well-being measurements are more nuanced than standard screenings for depression.
“A measure of depression tells you something much more narrow than a measure of well-being tells you,” she said, adding that identifying problem areas early can help prevent developing mental health disorders. For example, Vogt said that veterans with higher well-being are less likely to develop posttraumatic stress disorder when exposed to trauma.
The WBS has been validated, while the WBB questionnaire awaits final testing.
James Michail, MD, a family and geriatric physician with Providence Health & Services in Los Angeles, California, said he views the well-being screeners as launching points into discussing whether a treatment is enhancing or inhibiting a patient’s life.
“We have screenings for everything else but not for wellness, and the goal of care isn’t necessarily always treatment,” Michail said. “It’s taking the whole person into consideration. There’s a person behind the disease.”
Kendra Segura, MD, an obstetrician-gynecologist in Los Angeles, said she is open to using a well-being screener. Usually, building repertoire with a patient takes time, and sometimes only then can it allow for a more candid assessment of well-being.
“Over the course of several visits, that is when patients open up,” she said. “It’s when that starts to happen where they start to tell you about their well-being. It’s not an easy thing to establish.”
The authors of the article reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM MEDICAL CARE
Higher Dose of Naloxone Has No Impact on Overdose Survival; Increases Withdrawal Symptoms
TOPLINE:
A new report from the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) showed that administering an 8 mg dose of intranasal naloxone does not increase the odds of surviving an opioid overdose; a higher dose than the usual 4 mg may result in a greater risk for onset of opioid withdrawal symptoms.
METHODOLOGY:
- The Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report from the CDC presents data from a New York State Department of Health initiative.
- New York State Police troops administered either 8-mg or 4-mg doses of intranasal naloxone in response to suspected opiate overdose cases between March 2022 and August 2023.
- People who had died before the administration of the naloxone were excluded from the study.
- A total of 354 people were included in the study, 101 of whom received an 8-mg dose, while the others received the usual 4-mg dosage.
- Police officers documented the behavior and symptoms of people after receiving each dose, which could have included vomiting, disorientation, refusal to be transported to an emergency department, lethargy, and anger or combativeness.
TAKEAWAY:
- Survival rates were nearly identical regardless of intranasal naloxone dosage: 99% of people who received 8 mg compared with 99.2% of those who received 4 mg of the drug.
- Opioid withdrawal signs, including vomiting, were more prevalent among 8 mg naloxone recipients (37.6%) than among 4 mg recipients (19.4%) (risk ratio [RR], 2.51; P < .001).
- Police officers documented that people who received 8 mg were more frequently displayed anger or combativeness after revival than those who received the lower dose (RR, 1.42; P = .37).
IN PRACTICE:
The study “suggests that there are no benefits to law enforcement administration of higher-dose naloxone ... even in light of the increased prevalence of synthetic opioids, including fentanyl, in the drug supply.”
SOURCE:
Emily R. Payne, MSPH, of the New York State Department of Health, was the lead author of the study published in the Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report on February 8, 2024.
LIMITATIONS:
The sample size of people receiving 8-mg doses was not equal to that of those receiving the usual dosage. Medical professionals did not report on the symptoms and behavior of people after receiving naloxone, law enforcement workers did, and may not have accurately captured what was occurring. In addition, researchers lacked complete data on the substances people used before an overdose, and the results may only be generalizable to New York State.
DISCLOSURES:
Study author Sharon Stancliff reported institutional support from the New York State Stewardship Funding Harm Reduction. No other potential conflicts of interest were disclosed.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
A new report from the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) showed that administering an 8 mg dose of intranasal naloxone does not increase the odds of surviving an opioid overdose; a higher dose than the usual 4 mg may result in a greater risk for onset of opioid withdrawal symptoms.
METHODOLOGY:
- The Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report from the CDC presents data from a New York State Department of Health initiative.
- New York State Police troops administered either 8-mg or 4-mg doses of intranasal naloxone in response to suspected opiate overdose cases between March 2022 and August 2023.
- People who had died before the administration of the naloxone were excluded from the study.
- A total of 354 people were included in the study, 101 of whom received an 8-mg dose, while the others received the usual 4-mg dosage.
- Police officers documented the behavior and symptoms of people after receiving each dose, which could have included vomiting, disorientation, refusal to be transported to an emergency department, lethargy, and anger or combativeness.
TAKEAWAY:
- Survival rates were nearly identical regardless of intranasal naloxone dosage: 99% of people who received 8 mg compared with 99.2% of those who received 4 mg of the drug.
- Opioid withdrawal signs, including vomiting, were more prevalent among 8 mg naloxone recipients (37.6%) than among 4 mg recipients (19.4%) (risk ratio [RR], 2.51; P < .001).
- Police officers documented that people who received 8 mg were more frequently displayed anger or combativeness after revival than those who received the lower dose (RR, 1.42; P = .37).
IN PRACTICE:
The study “suggests that there are no benefits to law enforcement administration of higher-dose naloxone ... even in light of the increased prevalence of synthetic opioids, including fentanyl, in the drug supply.”
SOURCE:
Emily R. Payne, MSPH, of the New York State Department of Health, was the lead author of the study published in the Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report on February 8, 2024.
LIMITATIONS:
The sample size of people receiving 8-mg doses was not equal to that of those receiving the usual dosage. Medical professionals did not report on the symptoms and behavior of people after receiving naloxone, law enforcement workers did, and may not have accurately captured what was occurring. In addition, researchers lacked complete data on the substances people used before an overdose, and the results may only be generalizable to New York State.
DISCLOSURES:
Study author Sharon Stancliff reported institutional support from the New York State Stewardship Funding Harm Reduction. No other potential conflicts of interest were disclosed.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
A new report from the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) showed that administering an 8 mg dose of intranasal naloxone does not increase the odds of surviving an opioid overdose; a higher dose than the usual 4 mg may result in a greater risk for onset of opioid withdrawal symptoms.
METHODOLOGY:
- The Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report from the CDC presents data from a New York State Department of Health initiative.
- New York State Police troops administered either 8-mg or 4-mg doses of intranasal naloxone in response to suspected opiate overdose cases between March 2022 and August 2023.
- People who had died before the administration of the naloxone were excluded from the study.
- A total of 354 people were included in the study, 101 of whom received an 8-mg dose, while the others received the usual 4-mg dosage.
- Police officers documented the behavior and symptoms of people after receiving each dose, which could have included vomiting, disorientation, refusal to be transported to an emergency department, lethargy, and anger or combativeness.
TAKEAWAY:
- Survival rates were nearly identical regardless of intranasal naloxone dosage: 99% of people who received 8 mg compared with 99.2% of those who received 4 mg of the drug.
- Opioid withdrawal signs, including vomiting, were more prevalent among 8 mg naloxone recipients (37.6%) than among 4 mg recipients (19.4%) (risk ratio [RR], 2.51; P < .001).
- Police officers documented that people who received 8 mg were more frequently displayed anger or combativeness after revival than those who received the lower dose (RR, 1.42; P = .37).
IN PRACTICE:
The study “suggests that there are no benefits to law enforcement administration of higher-dose naloxone ... even in light of the increased prevalence of synthetic opioids, including fentanyl, in the drug supply.”
SOURCE:
Emily R. Payne, MSPH, of the New York State Department of Health, was the lead author of the study published in the Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report on February 8, 2024.
LIMITATIONS:
The sample size of people receiving 8-mg doses was not equal to that of those receiving the usual dosage. Medical professionals did not report on the symptoms and behavior of people after receiving naloxone, law enforcement workers did, and may not have accurately captured what was occurring. In addition, researchers lacked complete data on the substances people used before an overdose, and the results may only be generalizable to New York State.
DISCLOSURES:
Study author Sharon Stancliff reported institutional support from the New York State Stewardship Funding Harm Reduction. No other potential conflicts of interest were disclosed.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Growing ‘tranq’ threat poses challenges for PCPs
The widening threat of the animal tranquilizer xylazine, otherwise known as tranq, which has been found in illegally manufactured fentanyl, necessitates wider testing, a better understanding of its effects, and more research on treatment options, according to a narrative review published in the Annals of Internal Medicine.
“A lot of doctors and providers are asking about this drug,” said Joseph D’Orazio, MD, an addiction medicine specialist and medical toxicologist at Cooper University Healthcare, Camden, N.J., who led the review.
Xylazine is believed to prolong or intensify the effects of opioids, making it a popular additive to illegally produced opioids, particularly fentanyl, according to the Drug Enforcement Administration. Users end up in a zombie-like state with slowed breathing, and they sometimes develop skin ulcers. Because xylazine is not an opioid, common antidotes such as naloxone are ineffective. The White House has called the fentanyl-xylazine combo an “emerging threat.”
“Xylazine is making the deadliest drug threat our country has ever faced, fentanyl, even deadlier,” said DEA administrator Anne Milgram, in a statement on the agency’s website. “DEA has seized xylazine and fentanyl mixtures in 48 of 50 States. The DEA Laboratory System is reporting that in 2022 approximately 23% of fentanyl powder and 7% of fentanyl pills seized by the DEA contained xylazine.”
Dr. D’Orazio paired clinical experience with available research to provide guidance on the care of patients exposed to xylazine.
He and his team issued a call for more research on the drug’s effects, including more details on dependency and withdrawal.
Testing a patient who may have been exposed to xylazine requires forensic lab capabilities, which makes testing complicated and costly. The review found no evidence of the origin of the drug or why it causes open sores.
The review calls for more education of providers, including primary care physicians, on the treatment and care of patients who have used xylazine and fentanyl. The authors also call for expanding standard urine analysis to test for xylazine and for intensifying surveillance of the drug supply and distribution of xylazine test strips.
The authors of an editorial that accompanied the journal article urged the health care community to get ahead of xylazine before the crisis worsens.
“Not testing for xylazine in current unaffected areas and populations may lead to delays in responding if and when the drug becomes prevalent in the drug supply,” the authors wrote.
Xylazine was detected in 90% of street opioid samples tested in Philadelphia in 2021, and a toxic surveillance study of drug paraphernalia in Maryland found xylazine in 80% of samples tested between 2021 and 2022.
Dr. D’Orazio stressed that although Narcan is ineffective in treating xylazine, because the sedative is almost always mixed with fentanyl or another opiate, the opioid antagonist should still be used in emergencies.
Angelique Campen, MD, an emergency medicine physician at Providence St. Joseph Medical Center, Burbank, Calif., said she has seen an increase in patients entering the emergency department under the influence of what seems like fentanyl or heroin, but standard treatments such as Narcan have a limited effect. These patients remain in a prolonged period of sedation.
Recently, she admitted to her hospital’s intensive care unit a patient suspected of a xylazine overdose who was not responding to treatment.
Dr. Campen said that patients are screened for fentanyl, but because no test is available for xylazine, she presumed xylazine was causing the complication.
“It makes perfect medical sense to me that that’s what was going on,” Dr. Campen, who has worked at St. Joseph’s for 25 years, said. “I’m hoping with physicians being more aware of it that we can have that part of our regular urine drug screen.”
Dr. Campen also said she hopes an antidote is soon developed.
“If we can just keep delivering that message, hopefully, [to] more and more people, it will get through to them,” she said. “Every time you’re taking this, even though you may have taken it a week before and been fine, you never know: The next dose you take may be the lethal dose.”
A review author reports being awarded $1,000 to cover travel cost for Best Overall Abstract at the American Society of Addiction Medicine 2023 Annual Meeting. Another author reports receiving payments for training conducted as part of a NJDMAHS training grant to educate on substance use disorders. Dr. D’Orazio reports a $500 honorarium for a one-time lecture on xylazine at Yale; and a $500 honorarium for speaking one to three times per year on various topics regarding opioid use disorder at the Health Federation of Philadelphia. No other disclosures were reported.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The widening threat of the animal tranquilizer xylazine, otherwise known as tranq, which has been found in illegally manufactured fentanyl, necessitates wider testing, a better understanding of its effects, and more research on treatment options, according to a narrative review published in the Annals of Internal Medicine.
“A lot of doctors and providers are asking about this drug,” said Joseph D’Orazio, MD, an addiction medicine specialist and medical toxicologist at Cooper University Healthcare, Camden, N.J., who led the review.
Xylazine is believed to prolong or intensify the effects of opioids, making it a popular additive to illegally produced opioids, particularly fentanyl, according to the Drug Enforcement Administration. Users end up in a zombie-like state with slowed breathing, and they sometimes develop skin ulcers. Because xylazine is not an opioid, common antidotes such as naloxone are ineffective. The White House has called the fentanyl-xylazine combo an “emerging threat.”
“Xylazine is making the deadliest drug threat our country has ever faced, fentanyl, even deadlier,” said DEA administrator Anne Milgram, in a statement on the agency’s website. “DEA has seized xylazine and fentanyl mixtures in 48 of 50 States. The DEA Laboratory System is reporting that in 2022 approximately 23% of fentanyl powder and 7% of fentanyl pills seized by the DEA contained xylazine.”
Dr. D’Orazio paired clinical experience with available research to provide guidance on the care of patients exposed to xylazine.
He and his team issued a call for more research on the drug’s effects, including more details on dependency and withdrawal.
Testing a patient who may have been exposed to xylazine requires forensic lab capabilities, which makes testing complicated and costly. The review found no evidence of the origin of the drug or why it causes open sores.
The review calls for more education of providers, including primary care physicians, on the treatment and care of patients who have used xylazine and fentanyl. The authors also call for expanding standard urine analysis to test for xylazine and for intensifying surveillance of the drug supply and distribution of xylazine test strips.
The authors of an editorial that accompanied the journal article urged the health care community to get ahead of xylazine before the crisis worsens.
“Not testing for xylazine in current unaffected areas and populations may lead to delays in responding if and when the drug becomes prevalent in the drug supply,” the authors wrote.
Xylazine was detected in 90% of street opioid samples tested in Philadelphia in 2021, and a toxic surveillance study of drug paraphernalia in Maryland found xylazine in 80% of samples tested between 2021 and 2022.
Dr. D’Orazio stressed that although Narcan is ineffective in treating xylazine, because the sedative is almost always mixed with fentanyl or another opiate, the opioid antagonist should still be used in emergencies.
Angelique Campen, MD, an emergency medicine physician at Providence St. Joseph Medical Center, Burbank, Calif., said she has seen an increase in patients entering the emergency department under the influence of what seems like fentanyl or heroin, but standard treatments such as Narcan have a limited effect. These patients remain in a prolonged period of sedation.
Recently, she admitted to her hospital’s intensive care unit a patient suspected of a xylazine overdose who was not responding to treatment.
Dr. Campen said that patients are screened for fentanyl, but because no test is available for xylazine, she presumed xylazine was causing the complication.
“It makes perfect medical sense to me that that’s what was going on,” Dr. Campen, who has worked at St. Joseph’s for 25 years, said. “I’m hoping with physicians being more aware of it that we can have that part of our regular urine drug screen.”
Dr. Campen also said she hopes an antidote is soon developed.
“If we can just keep delivering that message, hopefully, [to] more and more people, it will get through to them,” she said. “Every time you’re taking this, even though you may have taken it a week before and been fine, you never know: The next dose you take may be the lethal dose.”
A review author reports being awarded $1,000 to cover travel cost for Best Overall Abstract at the American Society of Addiction Medicine 2023 Annual Meeting. Another author reports receiving payments for training conducted as part of a NJDMAHS training grant to educate on substance use disorders. Dr. D’Orazio reports a $500 honorarium for a one-time lecture on xylazine at Yale; and a $500 honorarium for speaking one to three times per year on various topics regarding opioid use disorder at the Health Federation of Philadelphia. No other disclosures were reported.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The widening threat of the animal tranquilizer xylazine, otherwise known as tranq, which has been found in illegally manufactured fentanyl, necessitates wider testing, a better understanding of its effects, and more research on treatment options, according to a narrative review published in the Annals of Internal Medicine.
“A lot of doctors and providers are asking about this drug,” said Joseph D’Orazio, MD, an addiction medicine specialist and medical toxicologist at Cooper University Healthcare, Camden, N.J., who led the review.
Xylazine is believed to prolong or intensify the effects of opioids, making it a popular additive to illegally produced opioids, particularly fentanyl, according to the Drug Enforcement Administration. Users end up in a zombie-like state with slowed breathing, and they sometimes develop skin ulcers. Because xylazine is not an opioid, common antidotes such as naloxone are ineffective. The White House has called the fentanyl-xylazine combo an “emerging threat.”
“Xylazine is making the deadliest drug threat our country has ever faced, fentanyl, even deadlier,” said DEA administrator Anne Milgram, in a statement on the agency’s website. “DEA has seized xylazine and fentanyl mixtures in 48 of 50 States. The DEA Laboratory System is reporting that in 2022 approximately 23% of fentanyl powder and 7% of fentanyl pills seized by the DEA contained xylazine.”
Dr. D’Orazio paired clinical experience with available research to provide guidance on the care of patients exposed to xylazine.
He and his team issued a call for more research on the drug’s effects, including more details on dependency and withdrawal.
Testing a patient who may have been exposed to xylazine requires forensic lab capabilities, which makes testing complicated and costly. The review found no evidence of the origin of the drug or why it causes open sores.
The review calls for more education of providers, including primary care physicians, on the treatment and care of patients who have used xylazine and fentanyl. The authors also call for expanding standard urine analysis to test for xylazine and for intensifying surveillance of the drug supply and distribution of xylazine test strips.
The authors of an editorial that accompanied the journal article urged the health care community to get ahead of xylazine before the crisis worsens.
“Not testing for xylazine in current unaffected areas and populations may lead to delays in responding if and when the drug becomes prevalent in the drug supply,” the authors wrote.
Xylazine was detected in 90% of street opioid samples tested in Philadelphia in 2021, and a toxic surveillance study of drug paraphernalia in Maryland found xylazine in 80% of samples tested between 2021 and 2022.
Dr. D’Orazio stressed that although Narcan is ineffective in treating xylazine, because the sedative is almost always mixed with fentanyl or another opiate, the opioid antagonist should still be used in emergencies.
Angelique Campen, MD, an emergency medicine physician at Providence St. Joseph Medical Center, Burbank, Calif., said she has seen an increase in patients entering the emergency department under the influence of what seems like fentanyl or heroin, but standard treatments such as Narcan have a limited effect. These patients remain in a prolonged period of sedation.
Recently, she admitted to her hospital’s intensive care unit a patient suspected of a xylazine overdose who was not responding to treatment.
Dr. Campen said that patients are screened for fentanyl, but because no test is available for xylazine, she presumed xylazine was causing the complication.
“It makes perfect medical sense to me that that’s what was going on,” Dr. Campen, who has worked at St. Joseph’s for 25 years, said. “I’m hoping with physicians being more aware of it that we can have that part of our regular urine drug screen.”
Dr. Campen also said she hopes an antidote is soon developed.
“If we can just keep delivering that message, hopefully, [to] more and more people, it will get through to them,” she said. “Every time you’re taking this, even though you may have taken it a week before and been fine, you never know: The next dose you take may be the lethal dose.”
A review author reports being awarded $1,000 to cover travel cost for Best Overall Abstract at the American Society of Addiction Medicine 2023 Annual Meeting. Another author reports receiving payments for training conducted as part of a NJDMAHS training grant to educate on substance use disorders. Dr. D’Orazio reports a $500 honorarium for a one-time lecture on xylazine at Yale; and a $500 honorarium for speaking one to three times per year on various topics regarding opioid use disorder at the Health Federation of Philadelphia. No other disclosures were reported.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Surge in pediatric ADHD med errors prompts call for prevention
according to results of a study published in the journal Pediatrics.
The dramatic jump is likely attributable to an increase in the prescribing of ADHD medications for children. According to the study authors, in 2019, nearly 10% of children in the United States had been diagnosed with ADHD, and some 3.3 million – or about 5% of all children in the country – had received a prescription for an ADHD medication.
“Because therapeutic errors are preventable, more attention should be given to patient and caregiver education and development of improved child-resistant medication dispensing and tracking systems,” the authors commented.
The investigators analyzed data from the National Poison Data System from 2000 through 2021 for therapeutic errors associated with ADHD medication among patients younger than 20 years.
“As medicine changes, it’s nice to look back at some of these things and see how some of these problems have changed,” said Natalie I. Rine, PharmD, a coauthor of the study and director of the Central Ohio Poison Center at Nationwide Children’s Hospital in Columbus.
The researchers identified 124,383 such errors reported to U.S. poison centers during the study period. The frequency increased by 299%.
Two-thirds (66.6%) of the exposures involved children aged 6-12 years, three-fourths (76.4%) were among males, and half (50.5%) involved amphetamines and related compounds. Most (79.7%) therapeutic errors were linked to exposure to a single substance. Nearly 83% of patients did not receive treatment at a health care facility; however, 2.3% were admitted to the hospital, and 4.2% had a “serious medical outcome,” the researchers found.
The most common scenarios were “inadvertently took or given medication twice” (53.9%), followed by “inadvertently took or given someone else’s medication” (13.4%) and “wrong medication taken or given” (12.9%), according to the researchers. Two percent involved mistakes by a pharmacist or nurse.
Easily preventable
Dr. Rine attributed the errors to simple mistakes and said they were likely the product of busy households and distracted caregivers. She added that the errors are easily avoided by storing the medication properly, keeping a sheet with the medication to document what was taken and when, and using a pillbox or one of many apps that can assist in documenting the dispensing of medications.
“I think the biggest thing is that a lot of these errors are preventable, more than anything else,” Dr. Rine said.
The increase in ADHD diagnoses among children and the subsequent prescribing of medications are reasons for the nearly 300% increase in poison control calls. A 2018 study showed that the estimated prevalence of ADHD diagnoses among U.S. children and adolescents increased from 6.1% in 1997-1998 to 10.2% in 2015-2016. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention states that 6 million children and adolescents aged 3-17 years have been diagnosed with ADHD, and 62% have received ADHD medication.
Colleen Kraft, MD, a pediatrician at Children’s Hospital Los Angeles, said she was not surprised by the reported increase in errors. In addition to the simple uptick in ADHD diagnoses and prescriptions in the past 2 decades, Dr. Kraft said the growing variety of ADHD medication is a cause for more errors.
“Because we have so many more different types of these medications, it’s easy to confuse them, and it’s easy to make an error when you give this to a child,” she said in an interview.
Dr. Kraft also hypothesized that because ADHD can have a genetic component, some parents with undiagnosed and untreated ADHD are responsible for their child’s medication, a scenario ripe for mistakes.
Potential dangers
Not all ADHD medicinal overdosing is created equal, Dr. Kraft pointed out. Doubling up on a stimulant such as methylphenidate (Ritalin) or the combination of amphetamine and dextroamphetamine (Adderall) may cause headaches, suppress appetite, and cause an upset stomach, although those symptoms usually clear up in a few hours.
However, she noted, the use of alpha-1 adrenergic blockers is more concerning. Also used to treat high blood pressure, medications such as guanfacine and clonidine cause sedation. A double dose can cause blood pressure to decrease to dangerous levels.
The study’s primary limitation was bias in self-reporting, which may have led to underreporting of incidences, according to the researchers. Not every case in which an error occurs that involves a child’s taking ADHD medication gets reported to poison control, because some will take a wait-and-see approach and may not call if their child is asymptomatic.
“Our data is only as good as what the callers report to us,” Dr. Rine said.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
according to results of a study published in the journal Pediatrics.
The dramatic jump is likely attributable to an increase in the prescribing of ADHD medications for children. According to the study authors, in 2019, nearly 10% of children in the United States had been diagnosed with ADHD, and some 3.3 million – or about 5% of all children in the country – had received a prescription for an ADHD medication.
“Because therapeutic errors are preventable, more attention should be given to patient and caregiver education and development of improved child-resistant medication dispensing and tracking systems,” the authors commented.
The investigators analyzed data from the National Poison Data System from 2000 through 2021 for therapeutic errors associated with ADHD medication among patients younger than 20 years.
“As medicine changes, it’s nice to look back at some of these things and see how some of these problems have changed,” said Natalie I. Rine, PharmD, a coauthor of the study and director of the Central Ohio Poison Center at Nationwide Children’s Hospital in Columbus.
The researchers identified 124,383 such errors reported to U.S. poison centers during the study period. The frequency increased by 299%.
Two-thirds (66.6%) of the exposures involved children aged 6-12 years, three-fourths (76.4%) were among males, and half (50.5%) involved amphetamines and related compounds. Most (79.7%) therapeutic errors were linked to exposure to a single substance. Nearly 83% of patients did not receive treatment at a health care facility; however, 2.3% were admitted to the hospital, and 4.2% had a “serious medical outcome,” the researchers found.
The most common scenarios were “inadvertently took or given medication twice” (53.9%), followed by “inadvertently took or given someone else’s medication” (13.4%) and “wrong medication taken or given” (12.9%), according to the researchers. Two percent involved mistakes by a pharmacist or nurse.
Easily preventable
Dr. Rine attributed the errors to simple mistakes and said they were likely the product of busy households and distracted caregivers. She added that the errors are easily avoided by storing the medication properly, keeping a sheet with the medication to document what was taken and when, and using a pillbox or one of many apps that can assist in documenting the dispensing of medications.
“I think the biggest thing is that a lot of these errors are preventable, more than anything else,” Dr. Rine said.
The increase in ADHD diagnoses among children and the subsequent prescribing of medications are reasons for the nearly 300% increase in poison control calls. A 2018 study showed that the estimated prevalence of ADHD diagnoses among U.S. children and adolescents increased from 6.1% in 1997-1998 to 10.2% in 2015-2016. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention states that 6 million children and adolescents aged 3-17 years have been diagnosed with ADHD, and 62% have received ADHD medication.
Colleen Kraft, MD, a pediatrician at Children’s Hospital Los Angeles, said she was not surprised by the reported increase in errors. In addition to the simple uptick in ADHD diagnoses and prescriptions in the past 2 decades, Dr. Kraft said the growing variety of ADHD medication is a cause for more errors.
“Because we have so many more different types of these medications, it’s easy to confuse them, and it’s easy to make an error when you give this to a child,” she said in an interview.
Dr. Kraft also hypothesized that because ADHD can have a genetic component, some parents with undiagnosed and untreated ADHD are responsible for their child’s medication, a scenario ripe for mistakes.
Potential dangers
Not all ADHD medicinal overdosing is created equal, Dr. Kraft pointed out. Doubling up on a stimulant such as methylphenidate (Ritalin) or the combination of amphetamine and dextroamphetamine (Adderall) may cause headaches, suppress appetite, and cause an upset stomach, although those symptoms usually clear up in a few hours.
However, she noted, the use of alpha-1 adrenergic blockers is more concerning. Also used to treat high blood pressure, medications such as guanfacine and clonidine cause sedation. A double dose can cause blood pressure to decrease to dangerous levels.
The study’s primary limitation was bias in self-reporting, which may have led to underreporting of incidences, according to the researchers. Not every case in which an error occurs that involves a child’s taking ADHD medication gets reported to poison control, because some will take a wait-and-see approach and may not call if their child is asymptomatic.
“Our data is only as good as what the callers report to us,” Dr. Rine said.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
according to results of a study published in the journal Pediatrics.
The dramatic jump is likely attributable to an increase in the prescribing of ADHD medications for children. According to the study authors, in 2019, nearly 10% of children in the United States had been diagnosed with ADHD, and some 3.3 million – or about 5% of all children in the country – had received a prescription for an ADHD medication.
“Because therapeutic errors are preventable, more attention should be given to patient and caregiver education and development of improved child-resistant medication dispensing and tracking systems,” the authors commented.
The investigators analyzed data from the National Poison Data System from 2000 through 2021 for therapeutic errors associated with ADHD medication among patients younger than 20 years.
“As medicine changes, it’s nice to look back at some of these things and see how some of these problems have changed,” said Natalie I. Rine, PharmD, a coauthor of the study and director of the Central Ohio Poison Center at Nationwide Children’s Hospital in Columbus.
The researchers identified 124,383 such errors reported to U.S. poison centers during the study period. The frequency increased by 299%.
Two-thirds (66.6%) of the exposures involved children aged 6-12 years, three-fourths (76.4%) were among males, and half (50.5%) involved amphetamines and related compounds. Most (79.7%) therapeutic errors were linked to exposure to a single substance. Nearly 83% of patients did not receive treatment at a health care facility; however, 2.3% were admitted to the hospital, and 4.2% had a “serious medical outcome,” the researchers found.
The most common scenarios were “inadvertently took or given medication twice” (53.9%), followed by “inadvertently took or given someone else’s medication” (13.4%) and “wrong medication taken or given” (12.9%), according to the researchers. Two percent involved mistakes by a pharmacist or nurse.
Easily preventable
Dr. Rine attributed the errors to simple mistakes and said they were likely the product of busy households and distracted caregivers. She added that the errors are easily avoided by storing the medication properly, keeping a sheet with the medication to document what was taken and when, and using a pillbox or one of many apps that can assist in documenting the dispensing of medications.
“I think the biggest thing is that a lot of these errors are preventable, more than anything else,” Dr. Rine said.
The increase in ADHD diagnoses among children and the subsequent prescribing of medications are reasons for the nearly 300% increase in poison control calls. A 2018 study showed that the estimated prevalence of ADHD diagnoses among U.S. children and adolescents increased from 6.1% in 1997-1998 to 10.2% in 2015-2016. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention states that 6 million children and adolescents aged 3-17 years have been diagnosed with ADHD, and 62% have received ADHD medication.
Colleen Kraft, MD, a pediatrician at Children’s Hospital Los Angeles, said she was not surprised by the reported increase in errors. In addition to the simple uptick in ADHD diagnoses and prescriptions in the past 2 decades, Dr. Kraft said the growing variety of ADHD medication is a cause for more errors.
“Because we have so many more different types of these medications, it’s easy to confuse them, and it’s easy to make an error when you give this to a child,” she said in an interview.
Dr. Kraft also hypothesized that because ADHD can have a genetic component, some parents with undiagnosed and untreated ADHD are responsible for their child’s medication, a scenario ripe for mistakes.
Potential dangers
Not all ADHD medicinal overdosing is created equal, Dr. Kraft pointed out. Doubling up on a stimulant such as methylphenidate (Ritalin) or the combination of amphetamine and dextroamphetamine (Adderall) may cause headaches, suppress appetite, and cause an upset stomach, although those symptoms usually clear up in a few hours.
However, she noted, the use of alpha-1 adrenergic blockers is more concerning. Also used to treat high blood pressure, medications such as guanfacine and clonidine cause sedation. A double dose can cause blood pressure to decrease to dangerous levels.
The study’s primary limitation was bias in self-reporting, which may have led to underreporting of incidences, according to the researchers. Not every case in which an error occurs that involves a child’s taking ADHD medication gets reported to poison control, because some will take a wait-and-see approach and may not call if their child is asymptomatic.
“Our data is only as good as what the callers report to us,” Dr. Rine said.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM PEDIATRICS
Gender-affirming surgeries nearly tripled between 2016 and 2019: Study
a new study published in JAMA Network Open found.
Breast and chest surgeries were the most common procedures performed, and the number of surgical procedures carried out increased with age. The researchers said that, in addition to legal shifts, the established safety of the surgeries and resulting increase in quality of life may also help explain the increase.
“The point of this is to raise awareness and to really document the patterns of care in the United States,” said Jason Wright, MD, an associate professor at Columbia University, New York. “We hope that people understand that these procedures are being performed more commonly and they’re out there.”
A study published in 2022 in JAMA Pediatrics found that the number of chest reconstruction surgeries among U.S. adolescents rose fourfold between 2016 and 2019.
The new study included data from 2016 to 2020 in the Nationwide Ambulatory Surgery Sample and the National Inpatient Sample. More than 48,000 patients with diagnosis codes for gender identity disorder, transsexualism, or a personal history of sex reassignment were identified. Age ranges were grouped as 12-18 (7.7%), 19-30 (52.3%), and 31-40 (21.8%).
The number of gender-affirming procedures rose from 4,552 in 2016 to a peak of 13,011 in 2019. (A slight decline to 12,818 procedures in 2020 was attributed to the COVID-19 pandemic.) The surgeries were grouped into three categories: breast and chest procedures, which occurred in 56.6% of patients; genital reconstructive surgeries (35.1%), and other facial cosmetic procedures (13.9%).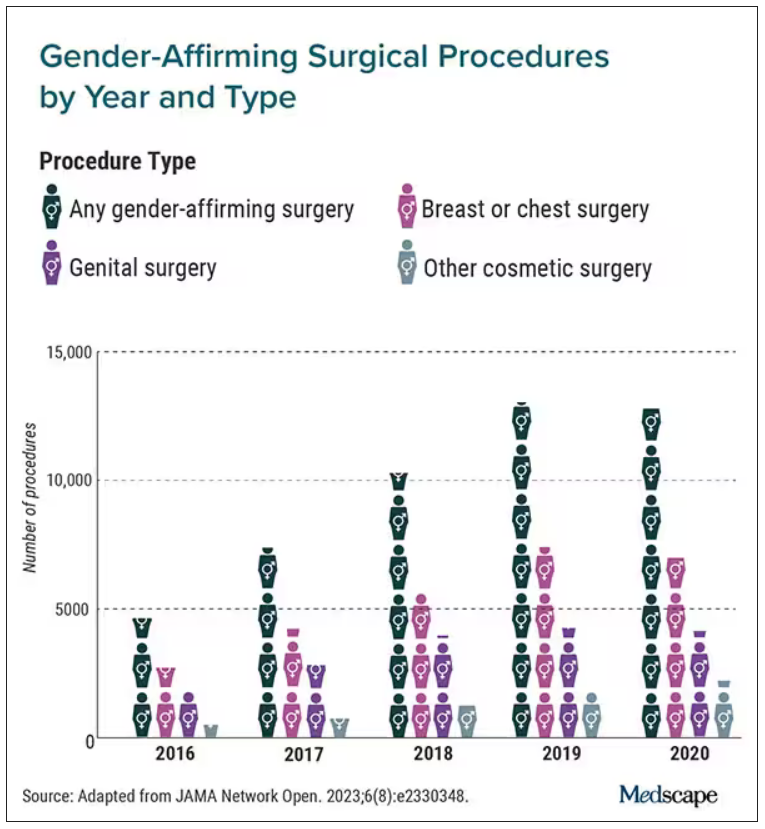
“We really wanted to try to make this as representative as we could,” Dr. Wright said. “I think this is really the best estimates that are available to date.”
Chest and breast procedures made up a higher percentage of surgeries in younger patients, while genital surgical procedures made up a higher percentage in older patients. For example, patients aged 19-30 made up 59.1% of breast or chest surgeries and 44.2% of genital surgeries. However, those aged 31-40 accounted for 26.2% of genital surgeries and 18.1% of breast or chest surgeries. For ages 41-50, the spread was more than double, accounting for 12.8% of genital surgeries and only 6.1% of breast or chest surgeries, according to the researchers.
Undocumented uptick
In addition to more inclusive health insurance, Dr. Wright said the increase in these procedures can also be attributed to studies showing their safety and the long-term association with high patient satisfaction.
Kevin Wang, MD, medical director of Providence–Swedish Health Services’ LGBTQIA+ program in Seattle, agreed that changes in health insurance coverage for gender-affirming surgery likely account in part for their increase. But he added that more clinicians are performing these procedures.
He said gender-affirming surgeries improve quality of life for the people who undergo them. The American Academy of Pediatrics has said it would be conducting a thorough review of the effects of transgender care on youth. A 2018 policy statement from the group said transgender youth should “have access to comprehensive, gender-affirming, and developmentally appropriate health care that is provided in a safe and inclusive clinical space.”
Dr. Wright cited several limitations to his group’s study that may result in the undercapture of transgender individuals and gender-affirming surgery; in particular, while the study captured inpatient and ambulatory surgical procedures in large, nationwide datasets, a small number of the procedures could have been performed in other settings.
Guiding a patient through gender-affirming care and surgical procedures can be an arduous process, including understanding their goals, using hormone therapy, and making referrals to specialists. Dr. Wang said he works to maximize his patients’ physical, mental, and emotional health, and helps them understand the risks.
He cited the double standard of a cisgender woman wanting breast augmentation without justification, but someone who identifies as transgender has many more boxes to check – for example, seeing a behavior health specialist to demonstrate they understand the risks and securing a letter of support from their primary care physician to undergo a similar procedure.
“It’s just interesting how the transgender community has to jump through so many more barriers and hoops for affirming, lifesaving procedures where you have other people who are doing it for aesthetic purposes and do not require any type of authorization,” Dr. Wang said.
Dr. Wright said he hopes the findings call attention to the need for more professionals working in the gender-affirming care field.
“I think for the medical community, it’s important to raise the idea that these procedures are becoming more common,” Dr. Wright said. “We are going to need specialists who have expertise in transgender care and surgeons who have the ability to perform these operations. Hopefully, this sheds light on the resources that are going to be required to care for these patients going forward.”
Dr. Wright reported receiving grants from Merck and personal fees from UpToDate outside the submitted work. No other disclosures were reported.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
a new study published in JAMA Network Open found.
Breast and chest surgeries were the most common procedures performed, and the number of surgical procedures carried out increased with age. The researchers said that, in addition to legal shifts, the established safety of the surgeries and resulting increase in quality of life may also help explain the increase.
“The point of this is to raise awareness and to really document the patterns of care in the United States,” said Jason Wright, MD, an associate professor at Columbia University, New York. “We hope that people understand that these procedures are being performed more commonly and they’re out there.”
A study published in 2022 in JAMA Pediatrics found that the number of chest reconstruction surgeries among U.S. adolescents rose fourfold between 2016 and 2019.
The new study included data from 2016 to 2020 in the Nationwide Ambulatory Surgery Sample and the National Inpatient Sample. More than 48,000 patients with diagnosis codes for gender identity disorder, transsexualism, or a personal history of sex reassignment were identified. Age ranges were grouped as 12-18 (7.7%), 19-30 (52.3%), and 31-40 (21.8%).
The number of gender-affirming procedures rose from 4,552 in 2016 to a peak of 13,011 in 2019. (A slight decline to 12,818 procedures in 2020 was attributed to the COVID-19 pandemic.) The surgeries were grouped into three categories: breast and chest procedures, which occurred in 56.6% of patients; genital reconstructive surgeries (35.1%), and other facial cosmetic procedures (13.9%).
“We really wanted to try to make this as representative as we could,” Dr. Wright said. “I think this is really the best estimates that are available to date.”
Chest and breast procedures made up a higher percentage of surgeries in younger patients, while genital surgical procedures made up a higher percentage in older patients. For example, patients aged 19-30 made up 59.1% of breast or chest surgeries and 44.2% of genital surgeries. However, those aged 31-40 accounted for 26.2% of genital surgeries and 18.1% of breast or chest surgeries. For ages 41-50, the spread was more than double, accounting for 12.8% of genital surgeries and only 6.1% of breast or chest surgeries, according to the researchers.
Undocumented uptick
In addition to more inclusive health insurance, Dr. Wright said the increase in these procedures can also be attributed to studies showing their safety and the long-term association with high patient satisfaction.
Kevin Wang, MD, medical director of Providence–Swedish Health Services’ LGBTQIA+ program in Seattle, agreed that changes in health insurance coverage for gender-affirming surgery likely account in part for their increase. But he added that more clinicians are performing these procedures.
He said gender-affirming surgeries improve quality of life for the people who undergo them. The American Academy of Pediatrics has said it would be conducting a thorough review of the effects of transgender care on youth. A 2018 policy statement from the group said transgender youth should “have access to comprehensive, gender-affirming, and developmentally appropriate health care that is provided in a safe and inclusive clinical space.”
Dr. Wright cited several limitations to his group’s study that may result in the undercapture of transgender individuals and gender-affirming surgery; in particular, while the study captured inpatient and ambulatory surgical procedures in large, nationwide datasets, a small number of the procedures could have been performed in other settings.
Guiding a patient through gender-affirming care and surgical procedures can be an arduous process, including understanding their goals, using hormone therapy, and making referrals to specialists. Dr. Wang said he works to maximize his patients’ physical, mental, and emotional health, and helps them understand the risks.
He cited the double standard of a cisgender woman wanting breast augmentation without justification, but someone who identifies as transgender has many more boxes to check – for example, seeing a behavior health specialist to demonstrate they understand the risks and securing a letter of support from their primary care physician to undergo a similar procedure.
“It’s just interesting how the transgender community has to jump through so many more barriers and hoops for affirming, lifesaving procedures where you have other people who are doing it for aesthetic purposes and do not require any type of authorization,” Dr. Wang said.
Dr. Wright said he hopes the findings call attention to the need for more professionals working in the gender-affirming care field.
“I think for the medical community, it’s important to raise the idea that these procedures are becoming more common,” Dr. Wright said. “We are going to need specialists who have expertise in transgender care and surgeons who have the ability to perform these operations. Hopefully, this sheds light on the resources that are going to be required to care for these patients going forward.”
Dr. Wright reported receiving grants from Merck and personal fees from UpToDate outside the submitted work. No other disclosures were reported.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
a new study published in JAMA Network Open found.
Breast and chest surgeries were the most common procedures performed, and the number of surgical procedures carried out increased with age. The researchers said that, in addition to legal shifts, the established safety of the surgeries and resulting increase in quality of life may also help explain the increase.
“The point of this is to raise awareness and to really document the patterns of care in the United States,” said Jason Wright, MD, an associate professor at Columbia University, New York. “We hope that people understand that these procedures are being performed more commonly and they’re out there.”
A study published in 2022 in JAMA Pediatrics found that the number of chest reconstruction surgeries among U.S. adolescents rose fourfold between 2016 and 2019.
The new study included data from 2016 to 2020 in the Nationwide Ambulatory Surgery Sample and the National Inpatient Sample. More than 48,000 patients with diagnosis codes for gender identity disorder, transsexualism, or a personal history of sex reassignment were identified. Age ranges were grouped as 12-18 (7.7%), 19-30 (52.3%), and 31-40 (21.8%).
The number of gender-affirming procedures rose from 4,552 in 2016 to a peak of 13,011 in 2019. (A slight decline to 12,818 procedures in 2020 was attributed to the COVID-19 pandemic.) The surgeries were grouped into three categories: breast and chest procedures, which occurred in 56.6% of patients; genital reconstructive surgeries (35.1%), and other facial cosmetic procedures (13.9%).
“We really wanted to try to make this as representative as we could,” Dr. Wright said. “I think this is really the best estimates that are available to date.”
Chest and breast procedures made up a higher percentage of surgeries in younger patients, while genital surgical procedures made up a higher percentage in older patients. For example, patients aged 19-30 made up 59.1% of breast or chest surgeries and 44.2% of genital surgeries. However, those aged 31-40 accounted for 26.2% of genital surgeries and 18.1% of breast or chest surgeries. For ages 41-50, the spread was more than double, accounting for 12.8% of genital surgeries and only 6.1% of breast or chest surgeries, according to the researchers.
Undocumented uptick
In addition to more inclusive health insurance, Dr. Wright said the increase in these procedures can also be attributed to studies showing their safety and the long-term association with high patient satisfaction.
Kevin Wang, MD, medical director of Providence–Swedish Health Services’ LGBTQIA+ program in Seattle, agreed that changes in health insurance coverage for gender-affirming surgery likely account in part for their increase. But he added that more clinicians are performing these procedures.
He said gender-affirming surgeries improve quality of life for the people who undergo them. The American Academy of Pediatrics has said it would be conducting a thorough review of the effects of transgender care on youth. A 2018 policy statement from the group said transgender youth should “have access to comprehensive, gender-affirming, and developmentally appropriate health care that is provided in a safe and inclusive clinical space.”
Dr. Wright cited several limitations to his group’s study that may result in the undercapture of transgender individuals and gender-affirming surgery; in particular, while the study captured inpatient and ambulatory surgical procedures in large, nationwide datasets, a small number of the procedures could have been performed in other settings.
Guiding a patient through gender-affirming care and surgical procedures can be an arduous process, including understanding their goals, using hormone therapy, and making referrals to specialists. Dr. Wang said he works to maximize his patients’ physical, mental, and emotional health, and helps them understand the risks.
He cited the double standard of a cisgender woman wanting breast augmentation without justification, but someone who identifies as transgender has many more boxes to check – for example, seeing a behavior health specialist to demonstrate they understand the risks and securing a letter of support from their primary care physician to undergo a similar procedure.
“It’s just interesting how the transgender community has to jump through so many more barriers and hoops for affirming, lifesaving procedures where you have other people who are doing it for aesthetic purposes and do not require any type of authorization,” Dr. Wang said.
Dr. Wright said he hopes the findings call attention to the need for more professionals working in the gender-affirming care field.
“I think for the medical community, it’s important to raise the idea that these procedures are becoming more common,” Dr. Wright said. “We are going to need specialists who have expertise in transgender care and surgeons who have the ability to perform these operations. Hopefully, this sheds light on the resources that are going to be required to care for these patients going forward.”
Dr. Wright reported receiving grants from Merck and personal fees from UpToDate outside the submitted work. No other disclosures were reported.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM JAMA NETWORK OPEN
Continuous glucose monitors for pregnant patients?
Patients with pregestational diabetes may benefit from use of a continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion pump paired with a continuous glucose monitor. Use of the tools has been associated with a reduction in maternal and neonatal morbidity, a recent study found.
“We were seeing an unacceptable burden of both maternal and fetal disease in our diabetic population,” said Neil Hamill, MD, a maternal-fetal medicine specialist at Methodist Women’s Hospital, Omaha, Neb., and an author of the study. “We thought the success with this technology in the nonpregnant population would and should translate into the pregnant population.”
Dr. Hamill and his colleagues analyzed data from 55 pregnant patients who received care at the Women’s Hospital Perinatal Center at the Nebraska Methodist Health System between October 2019 and October 2022. Everyone in the cohort had pregestational diabetes and required insulin prior to week 20 of pregnancy. They used CGMs for more than 2 weeks. The study set blood glucose levels of less than 140 mg/dL as a healthy benchmark.
Participants who had severe preeclampsia, who had delivered preterm, who had delivered a neonate with respiratory distress syndrome, and/or who had given birth to a larger-than-expected infant spent less time in the safe zone – having a blood glucose level below 140 mg/dL – than women who did not have those risk factors.
“When blood sugar control is better, maternal and fetal outcomes are improved,” Dr. Hamill said.
Neetu Sodhi, MD, an ob.gyn. at Providence Cedars-Sinai Tarzana Medical Center, Los Angeles, expressed optimism that use of blood glucose monitors and insulin pumps can improve outcomes for pregnant patients with pregestational diabetes.
“This is just another case for why it’s so important for patients to have access to these types of devices that really, really improve their outcomes and their health, and now it’s proven in the case of pregnancy outcomes too – or at least suggested strongly with this data,” Dr. Sodhi said.
Mark Ebell, MD, a professor of epidemiology at the University of Georgia, Athens, was more skeptical, pointing out that study participants might have used other methods in addition to the technology to lower their blood sugar levels.
The findings suggest that insulin pumps are more manageable than multiple, daily self-injections. About 1 in 9 women have diabetes in the United States, and 35% of people newly diagnosed with the condition are women of reproductive age.
Dr. Hamill said that in future research, use of a stricter criterion for baseline blood sugar levels (< 140 mg/dL) would be helpful, as would exploring how much time patients need to spend below that level for optimal outcomes.
“Those questions are really absent in the literature,” Dr. Hamill said. “Most of our obstetrical literature is comparing treatment types. All those things are secondary. It’s the blood sugar that confers the risk, and if we get the blood sugar better, risk is reduced.”
Dr. Hamill added that the benefits of these technologies for patients with gestational diabetes are unclear in consideration of the limited duration of the disease and the time required to implant or install a monitor and pump, as well as associated risks and the cost of the devices.
Dr. Sodhi said clinicians who see patients during family planning visits should review morbidities and medical problems related to diabetes.
“I think this is a study that’s maybe too early,” Dr. Sodhi said. “They did ‘guesstimates’ on what target blood glucose ranges to be looking at, but I think over time, we might, with more studies like this, be building a case to try to put these types of monitors in for patients who are young for the purpose of optimizing pregnancy outcomes.”
The authors have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Patients with pregestational diabetes may benefit from use of a continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion pump paired with a continuous glucose monitor. Use of the tools has been associated with a reduction in maternal and neonatal morbidity, a recent study found.
“We were seeing an unacceptable burden of both maternal and fetal disease in our diabetic population,” said Neil Hamill, MD, a maternal-fetal medicine specialist at Methodist Women’s Hospital, Omaha, Neb., and an author of the study. “We thought the success with this technology in the nonpregnant population would and should translate into the pregnant population.”
Dr. Hamill and his colleagues analyzed data from 55 pregnant patients who received care at the Women’s Hospital Perinatal Center at the Nebraska Methodist Health System between October 2019 and October 2022. Everyone in the cohort had pregestational diabetes and required insulin prior to week 20 of pregnancy. They used CGMs for more than 2 weeks. The study set blood glucose levels of less than 140 mg/dL as a healthy benchmark.
Participants who had severe preeclampsia, who had delivered preterm, who had delivered a neonate with respiratory distress syndrome, and/or who had given birth to a larger-than-expected infant spent less time in the safe zone – having a blood glucose level below 140 mg/dL – than women who did not have those risk factors.
“When blood sugar control is better, maternal and fetal outcomes are improved,” Dr. Hamill said.
Neetu Sodhi, MD, an ob.gyn. at Providence Cedars-Sinai Tarzana Medical Center, Los Angeles, expressed optimism that use of blood glucose monitors and insulin pumps can improve outcomes for pregnant patients with pregestational diabetes.
“This is just another case for why it’s so important for patients to have access to these types of devices that really, really improve their outcomes and their health, and now it’s proven in the case of pregnancy outcomes too – or at least suggested strongly with this data,” Dr. Sodhi said.
Mark Ebell, MD, a professor of epidemiology at the University of Georgia, Athens, was more skeptical, pointing out that study participants might have used other methods in addition to the technology to lower their blood sugar levels.
The findings suggest that insulin pumps are more manageable than multiple, daily self-injections. About 1 in 9 women have diabetes in the United States, and 35% of people newly diagnosed with the condition are women of reproductive age.
Dr. Hamill said that in future research, use of a stricter criterion for baseline blood sugar levels (< 140 mg/dL) would be helpful, as would exploring how much time patients need to spend below that level for optimal outcomes.
“Those questions are really absent in the literature,” Dr. Hamill said. “Most of our obstetrical literature is comparing treatment types. All those things are secondary. It’s the blood sugar that confers the risk, and if we get the blood sugar better, risk is reduced.”
Dr. Hamill added that the benefits of these technologies for patients with gestational diabetes are unclear in consideration of the limited duration of the disease and the time required to implant or install a monitor and pump, as well as associated risks and the cost of the devices.
Dr. Sodhi said clinicians who see patients during family planning visits should review morbidities and medical problems related to diabetes.
“I think this is a study that’s maybe too early,” Dr. Sodhi said. “They did ‘guesstimates’ on what target blood glucose ranges to be looking at, but I think over time, we might, with more studies like this, be building a case to try to put these types of monitors in for patients who are young for the purpose of optimizing pregnancy outcomes.”
The authors have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Patients with pregestational diabetes may benefit from use of a continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion pump paired with a continuous glucose monitor. Use of the tools has been associated with a reduction in maternal and neonatal morbidity, a recent study found.
“We were seeing an unacceptable burden of both maternal and fetal disease in our diabetic population,” said Neil Hamill, MD, a maternal-fetal medicine specialist at Methodist Women’s Hospital, Omaha, Neb., and an author of the study. “We thought the success with this technology in the nonpregnant population would and should translate into the pregnant population.”
Dr. Hamill and his colleagues analyzed data from 55 pregnant patients who received care at the Women’s Hospital Perinatal Center at the Nebraska Methodist Health System between October 2019 and October 2022. Everyone in the cohort had pregestational diabetes and required insulin prior to week 20 of pregnancy. They used CGMs for more than 2 weeks. The study set blood glucose levels of less than 140 mg/dL as a healthy benchmark.
Participants who had severe preeclampsia, who had delivered preterm, who had delivered a neonate with respiratory distress syndrome, and/or who had given birth to a larger-than-expected infant spent less time in the safe zone – having a blood glucose level below 140 mg/dL – than women who did not have those risk factors.
“When blood sugar control is better, maternal and fetal outcomes are improved,” Dr. Hamill said.
Neetu Sodhi, MD, an ob.gyn. at Providence Cedars-Sinai Tarzana Medical Center, Los Angeles, expressed optimism that use of blood glucose monitors and insulin pumps can improve outcomes for pregnant patients with pregestational diabetes.
“This is just another case for why it’s so important for patients to have access to these types of devices that really, really improve their outcomes and their health, and now it’s proven in the case of pregnancy outcomes too – or at least suggested strongly with this data,” Dr. Sodhi said.
Mark Ebell, MD, a professor of epidemiology at the University of Georgia, Athens, was more skeptical, pointing out that study participants might have used other methods in addition to the technology to lower their blood sugar levels.
The findings suggest that insulin pumps are more manageable than multiple, daily self-injections. About 1 in 9 women have diabetes in the United States, and 35% of people newly diagnosed with the condition are women of reproductive age.
Dr. Hamill said that in future research, use of a stricter criterion for baseline blood sugar levels (< 140 mg/dL) would be helpful, as would exploring how much time patients need to spend below that level for optimal outcomes.
“Those questions are really absent in the literature,” Dr. Hamill said. “Most of our obstetrical literature is comparing treatment types. All those things are secondary. It’s the blood sugar that confers the risk, and if we get the blood sugar better, risk is reduced.”
Dr. Hamill added that the benefits of these technologies for patients with gestational diabetes are unclear in consideration of the limited duration of the disease and the time required to implant or install a monitor and pump, as well as associated risks and the cost of the devices.
Dr. Sodhi said clinicians who see patients during family planning visits should review morbidities and medical problems related to diabetes.
“I think this is a study that’s maybe too early,” Dr. Sodhi said. “They did ‘guesstimates’ on what target blood glucose ranges to be looking at, but I think over time, we might, with more studies like this, be building a case to try to put these types of monitors in for patients who are young for the purpose of optimizing pregnancy outcomes.”
The authors have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Partial immunization leaves children and communities at risk, study finds
TOPLINE
A new American Academy of Pediatrics study reveals that 17.2% of toddlers started but did not finish at least one recommended early childhood vaccine series.
METHODOLOGY
- Examined data collected in 2019 from the National Immunization Survey – Child.
- 16,365 children ages 19-35 months were included.
- Vaccines for diphtheria, tetanus, acellular pertussis, pneumococcal infections, Haemophilus influenzae type b, hepatitis B, polio, measles, mumps, rubella, and varicella were included.
TAKEAWAY
- 72.9% of toddlers completed the seven-vaccine series.
- 17.2% initiated but did not complete one or more of a multidose vaccine series.
- The strongest association with not completing the vaccine series was moving across state lines and not having insurance.
- Children with more siblings at home were less likely to complete a vaccine series.
IN PRACTICE
The study suggests that the “children experienced structural barriers to vaccination,” and the authors urge an “increased focus on strategies to encourage multidose series completion ... to optimize protection from preventable diseases and achieve vaccination coverage goals.”
SOURCE
The study was funded by the National Institutes of Health and published online July 25 in Pediatrics. Sarah Y. Michels, an epidemiology specialist from the University of Montana in Missoula, was the lead author.
LIMITATIONS
Though the researchers studied the risk factors for series noncompletion, they did not have information on the specific reasons why children were missing vaccine doses. Children whose parents chose to participate in the National Immunization Survey – Child may have had higher vaccination coverage than children whose parents declined participation.
DISCLOSURES
The authors have reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE
A new American Academy of Pediatrics study reveals that 17.2% of toddlers started but did not finish at least one recommended early childhood vaccine series.
METHODOLOGY
- Examined data collected in 2019 from the National Immunization Survey – Child.
- 16,365 children ages 19-35 months were included.
- Vaccines for diphtheria, tetanus, acellular pertussis, pneumococcal infections, Haemophilus influenzae type b, hepatitis B, polio, measles, mumps, rubella, and varicella were included.
TAKEAWAY
- 72.9% of toddlers completed the seven-vaccine series.
- 17.2% initiated but did not complete one or more of a multidose vaccine series.
- The strongest association with not completing the vaccine series was moving across state lines and not having insurance.
- Children with more siblings at home were less likely to complete a vaccine series.
IN PRACTICE
The study suggests that the “children experienced structural barriers to vaccination,” and the authors urge an “increased focus on strategies to encourage multidose series completion ... to optimize protection from preventable diseases and achieve vaccination coverage goals.”
SOURCE
The study was funded by the National Institutes of Health and published online July 25 in Pediatrics. Sarah Y. Michels, an epidemiology specialist from the University of Montana in Missoula, was the lead author.
LIMITATIONS
Though the researchers studied the risk factors for series noncompletion, they did not have information on the specific reasons why children were missing vaccine doses. Children whose parents chose to participate in the National Immunization Survey – Child may have had higher vaccination coverage than children whose parents declined participation.
DISCLOSURES
The authors have reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE
A new American Academy of Pediatrics study reveals that 17.2% of toddlers started but did not finish at least one recommended early childhood vaccine series.
METHODOLOGY
- Examined data collected in 2019 from the National Immunization Survey – Child.
- 16,365 children ages 19-35 months were included.
- Vaccines for diphtheria, tetanus, acellular pertussis, pneumococcal infections, Haemophilus influenzae type b, hepatitis B, polio, measles, mumps, rubella, and varicella were included.
TAKEAWAY
- 72.9% of toddlers completed the seven-vaccine series.
- 17.2% initiated but did not complete one or more of a multidose vaccine series.
- The strongest association with not completing the vaccine series was moving across state lines and not having insurance.
- Children with more siblings at home were less likely to complete a vaccine series.
IN PRACTICE
The study suggests that the “children experienced structural barriers to vaccination,” and the authors urge an “increased focus on strategies to encourage multidose series completion ... to optimize protection from preventable diseases and achieve vaccination coverage goals.”
SOURCE
The study was funded by the National Institutes of Health and published online July 25 in Pediatrics. Sarah Y. Michels, an epidemiology specialist from the University of Montana in Missoula, was the lead author.
LIMITATIONS
Though the researchers studied the risk factors for series noncompletion, they did not have information on the specific reasons why children were missing vaccine doses. Children whose parents chose to participate in the National Immunization Survey – Child may have had higher vaccination coverage than children whose parents declined participation.
DISCLOSURES
The authors have reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
USPSTF maintains ‘insufficient evidence’ for lipid disorder screenings in kids and teens
The group’s final recommendation and corresponding evidence report were published in the Journal of the American Medical Association, following a draft recommendation in January.
The organization reached a similar conclusion following its evaluation in 2016.
“There’s just not enough evidence to determine whether or not screening all children for high cholesterol improves their heart health into adulthood,” said Katrina Donahue, MD, MPH, a USPSTF member and a professor in the department of family medicine at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill. “We’re calling for additional research on the effectiveness of screening for and treatment of high cholesterol in children and adolescents to prevent heart attacks, strokes, and death in adulthood.”
The task force recommended other evidence-based strategies to promote heart health, such as screening for obesity and interventions to prevent tobacco use.
The recommendation was the result of a review of 43 studies from MEDLINE and the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials through May 16, 2022. No randomized controlled trial directly addressed the effectiveness or harms of lipid screening for children and adolescents. The task force continued to use article alerts and targeted journal searches through March 24, 2023.
Conditions such as familial hypercholesterolemia and multifactorial dyslipidemia can cause abnormally high lipid levels in children, potentially leading to premature cardiovascular events such as myocardial infarction, stroke, and death in adulthood. According to the USPSTF, the prevalence of FH in U.S. children and adolescents ranges from 0.2% to 0.4% (one in every 250-500 youth). Multifactorial dyslipidemia is more common – the prevalence in children and adolescents ranges from 7.1% to 9.4%.
In an editorial response to the task force’s statement, the authors, including Sarah D. de Ferranti, MD, department of pediatrics at Harvard Medical School, Boston, question the impact of not screening children to identify FH and other conditions and caution against the subsequent delay in treatment.
“Treating FH during childhood slows the progression of vascular finding in atherosclerosis,” the authors write.
They note that the recommendation “leaves a void for clinicians seeking to provide care for patients today” while additional research is conducted.
Sarah Nosal, MD, a member of the board of directors of the American Academy of Family Physicians, said that despite the lack of a recommendation, primary care clinicians can still encourage proper nutrition and physical activity for patients.
Dr. Nosal said that even without clear recommendations from the USPSTF, in the rare case of a patient with a family history of FH, she would order a lipid test and discuss treatment plans with the patient and family, if needed.
“We really don’t want to do tests that we don’t know what to do with the information,” she said.
One USPSTF member reported receiving grants from Healthwise, a nonprofit organization, outside the submitted work.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The group’s final recommendation and corresponding evidence report were published in the Journal of the American Medical Association, following a draft recommendation in January.
The organization reached a similar conclusion following its evaluation in 2016.
“There’s just not enough evidence to determine whether or not screening all children for high cholesterol improves their heart health into adulthood,” said Katrina Donahue, MD, MPH, a USPSTF member and a professor in the department of family medicine at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill. “We’re calling for additional research on the effectiveness of screening for and treatment of high cholesterol in children and adolescents to prevent heart attacks, strokes, and death in adulthood.”
The task force recommended other evidence-based strategies to promote heart health, such as screening for obesity and interventions to prevent tobacco use.
The recommendation was the result of a review of 43 studies from MEDLINE and the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials through May 16, 2022. No randomized controlled trial directly addressed the effectiveness or harms of lipid screening for children and adolescents. The task force continued to use article alerts and targeted journal searches through March 24, 2023.
Conditions such as familial hypercholesterolemia and multifactorial dyslipidemia can cause abnormally high lipid levels in children, potentially leading to premature cardiovascular events such as myocardial infarction, stroke, and death in adulthood. According to the USPSTF, the prevalence of FH in U.S. children and adolescents ranges from 0.2% to 0.4% (one in every 250-500 youth). Multifactorial dyslipidemia is more common – the prevalence in children and adolescents ranges from 7.1% to 9.4%.
In an editorial response to the task force’s statement, the authors, including Sarah D. de Ferranti, MD, department of pediatrics at Harvard Medical School, Boston, question the impact of not screening children to identify FH and other conditions and caution against the subsequent delay in treatment.
“Treating FH during childhood slows the progression of vascular finding in atherosclerosis,” the authors write.
They note that the recommendation “leaves a void for clinicians seeking to provide care for patients today” while additional research is conducted.
Sarah Nosal, MD, a member of the board of directors of the American Academy of Family Physicians, said that despite the lack of a recommendation, primary care clinicians can still encourage proper nutrition and physical activity for patients.
Dr. Nosal said that even without clear recommendations from the USPSTF, in the rare case of a patient with a family history of FH, she would order a lipid test and discuss treatment plans with the patient and family, if needed.
“We really don’t want to do tests that we don’t know what to do with the information,” she said.
One USPSTF member reported receiving grants from Healthwise, a nonprofit organization, outside the submitted work.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The group’s final recommendation and corresponding evidence report were published in the Journal of the American Medical Association, following a draft recommendation in January.
The organization reached a similar conclusion following its evaluation in 2016.
“There’s just not enough evidence to determine whether or not screening all children for high cholesterol improves their heart health into adulthood,” said Katrina Donahue, MD, MPH, a USPSTF member and a professor in the department of family medicine at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill. “We’re calling for additional research on the effectiveness of screening for and treatment of high cholesterol in children and adolescents to prevent heart attacks, strokes, and death in adulthood.”
The task force recommended other evidence-based strategies to promote heart health, such as screening for obesity and interventions to prevent tobacco use.
The recommendation was the result of a review of 43 studies from MEDLINE and the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials through May 16, 2022. No randomized controlled trial directly addressed the effectiveness or harms of lipid screening for children and adolescents. The task force continued to use article alerts and targeted journal searches through March 24, 2023.
Conditions such as familial hypercholesterolemia and multifactorial dyslipidemia can cause abnormally high lipid levels in children, potentially leading to premature cardiovascular events such as myocardial infarction, stroke, and death in adulthood. According to the USPSTF, the prevalence of FH in U.S. children and adolescents ranges from 0.2% to 0.4% (one in every 250-500 youth). Multifactorial dyslipidemia is more common – the prevalence in children and adolescents ranges from 7.1% to 9.4%.
In an editorial response to the task force’s statement, the authors, including Sarah D. de Ferranti, MD, department of pediatrics at Harvard Medical School, Boston, question the impact of not screening children to identify FH and other conditions and caution against the subsequent delay in treatment.
“Treating FH during childhood slows the progression of vascular finding in atherosclerosis,” the authors write.
They note that the recommendation “leaves a void for clinicians seeking to provide care for patients today” while additional research is conducted.
Sarah Nosal, MD, a member of the board of directors of the American Academy of Family Physicians, said that despite the lack of a recommendation, primary care clinicians can still encourage proper nutrition and physical activity for patients.
Dr. Nosal said that even without clear recommendations from the USPSTF, in the rare case of a patient with a family history of FH, she would order a lipid test and discuss treatment plans with the patient and family, if needed.
“We really don’t want to do tests that we don’t know what to do with the information,” she said.
One USPSTF member reported receiving grants from Healthwise, a nonprofit organization, outside the submitted work.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
All in stride: Few age limitations for joint replacement
Kathy Blackwell is not going to allow a couple of aching joints stop her from living her best life.
The 73-year-old resident of Simi Valley, Calif., a bedroom community about 30 miles northwest of downtown Los Angeles, organizes regular activities for her group of seniors. The 20- to 30-member-strong band of seasoned citizens, mostly women, keep active. Over the coming weeks, they plan to catch the Beach Boys at the historic Hollywood Bowl and take a cruise to Alaska.
The busy schedule is why Ms. Blackwell intends to delay her second hip replacement surgery, opting instead for a cortisone shot in hopes of easing the pain enough to enjoy the upcoming excursions.
Not that she is shy about joint replacement. If her orthopedic surgeon offered a frequent customer punch card like the ones you get at the local coffee shop, hers would be nearly full. Ms. Blackwell’s knees and a hip have been replaced, and her other hip will be, too, once her calendar clears up.
“If you go on enough with chronic pain where there’s no relief, you get cranky,” Ms. Blackwell said.
More than 1 million new knees, hips
Joint replacements are getting more common, with about 790,000 total knee replacements and more than 450,000 hip replacements performed annually in the United States, according to the American College of Rheumatology.
Experts agree age is not a factor when considering candidates for joint replacement. Rafael Sierra, MD, of the Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minn., said he’s done hip replacements on patients as young as 12 and as old as 102. Orthopedic surgeon John Wang, MD, of the Hospital for Special Surgery, New York, has performed a total knee arthroscopy on a patient in their mid-90s. At 73, Ms. Blackwell is on the older side of the average age of 66 for a hip replacement.
“A lot of research and studies have shown that no matter what the age ranges, people end up doing great,” Dr. Wang said.
More importantly than age, older patients should be prepared for postsurgery therapy and treatment. For younger patients, the biggest drawback is outliving the estimated 25-year life span of a joint replacement. Complications are rare and occur in about 2% of procedures. These include infection, dislocation of the joint, and blood clots; other health issues you also have are not a factor.
Considering Ms. Blackwell’s hard time with her first knee replacement, it’s no small wonder that she ever set foot in a surgeon’s office again.
After putting it off for 7 years, Ms. Blackwell finally agreed to her doctor’s advice to replace her left knee in 2017 to relieve what she described as a “grinding,” chronic, bone-on-bone pain.
“It got to the point where there were no alternatives,” she said.
But her first orthopedic surgeon did a “lousy job,” leaving her with a gaping, festering wound that resulted in sepsis and required wound vacuum therapy to close the lesion. She eventually found another surgeon who removed and cleaned up her artificial knee before replacing the prosthesis. Luckily, the sepsis didn’t spread, and eight surgeries later, she was in the clear.
Ms. Blackwell’s second knee replacement in 2018 was a textbook surgery, as was a hip replacement in late 2019 .
“Your whole attitude changes,” she said.
What generalists should know
Orthopedic surgeons recommend that primary care doctors ask two things when weighing joint replacements: Have they exhausted nonsurgical treatments, and is the pain intolerable? They also advise avoiding narcotics to treat the symptoms.
The top issue to consider for a primary care doctor when weighing whether their patient may be a candidate for joint replacement is if the pain and the imaging are bad enough to warrant surgery.
“You don’t want to do it too soon,” Dr. Sierra said.
Dr. Sierra likes to tell the story of the golfer whose knee stiffens after playing 18 holes. To those patients, he recommends dialing back the activity; in this case, using a cart or playing only nine holes.
Dr. Wang agrees, asking if the pain is “lifestyle altering” and if the patient was unresponsive to nonsurgical treatments such as over-the-counter medications, anti-inflammatory medication and shots, home exercises or physical therapy, wearing a brace or sleeve, or simply changing their activity.
And no addictive pain pills to treat arthritis that can lead to other serious issues.
“This is not going to heal itself,” Dr. Wang said. “It’s not going to improve on its own. So, we don’t want to throw narcotics at it just to cover it up.”
Karen Smith, MD, has been a family doctor in rural North Carolina for more than 30 years. When she sees patients complaining about their joints, she first looks at function and pain. From there, she explores why they’re having discomfort. For example, is the problem an ergonomic issue at work or the result of carrying a lot of body weight?
“We look at those areas to determine what can be modified,” she said. “All of that’s done even before we get to having the orthopedic involvement.”
Dr. Smith said she also considers things beyond basic medicine: What is the patient’s mental status and tolerance for pain? Do they have a support system at home for post-operative care? And can they afford to miss work?
“We look at all of those factors together because that is going to determine the outcome that we’re hoping to achieve,” Dr. Smith said.
Great expectations
A recent study shows that older patients respond better to knee replacements than younger patients, particularly with pain relief and quality of life. The reason for this is believed to boil down to expectations. Whereas a younger person may want to return to the racquetball court and perform like they used to, older patients may just wish to walk down the hall without discomfort.
“It’s possible that these under 55-age-old patients may just take a little longer to heal to be satisfied,” Dr. Wang said. “We really can’t speak to why this is happening, but it’s possible that the younger patients are more active, and they expect more out of their knee.”
Jeevan Sall, MD, is a primary care sports medicine doctor with Providence Mission Heritage Medical Group in Laguna Niguel, Calif. He first discusses conservative management for patients struggling with arthritis in their joints. These measures include rehabilitation exercises, braces, shoe inserts, medication, and weight loss efforts. If these steps don’t improve a patient’s pain or lifestyle, surgery is on the table. Managing expectations is a significant factor.
“Is the patient mentally ready for surgery?” Dr. Sall said. “This includes what they hope to achieve with surgery as well as the risk and benefits of the procedure.”
Ms. Blackwell’s hip and knee pain came simply from a life well lived, with no marathon running or life-changing accident to speak of. She worked as a housewife raising her two children and owned an elevator company with her late husband, Robert Blackwell.
Yes, the elevator construction business has jokes.
“We have our ups and downs,” Ms. Blackwell said.
And with her new joints, so does she.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Kathy Blackwell is not going to allow a couple of aching joints stop her from living her best life.
The 73-year-old resident of Simi Valley, Calif., a bedroom community about 30 miles northwest of downtown Los Angeles, organizes regular activities for her group of seniors. The 20- to 30-member-strong band of seasoned citizens, mostly women, keep active. Over the coming weeks, they plan to catch the Beach Boys at the historic Hollywood Bowl and take a cruise to Alaska.
The busy schedule is why Ms. Blackwell intends to delay her second hip replacement surgery, opting instead for a cortisone shot in hopes of easing the pain enough to enjoy the upcoming excursions.
Not that she is shy about joint replacement. If her orthopedic surgeon offered a frequent customer punch card like the ones you get at the local coffee shop, hers would be nearly full. Ms. Blackwell’s knees and a hip have been replaced, and her other hip will be, too, once her calendar clears up.
“If you go on enough with chronic pain where there’s no relief, you get cranky,” Ms. Blackwell said.
More than 1 million new knees, hips
Joint replacements are getting more common, with about 790,000 total knee replacements and more than 450,000 hip replacements performed annually in the United States, according to the American College of Rheumatology.
Experts agree age is not a factor when considering candidates for joint replacement. Rafael Sierra, MD, of the Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minn., said he’s done hip replacements on patients as young as 12 and as old as 102. Orthopedic surgeon John Wang, MD, of the Hospital for Special Surgery, New York, has performed a total knee arthroscopy on a patient in their mid-90s. At 73, Ms. Blackwell is on the older side of the average age of 66 for a hip replacement.
“A lot of research and studies have shown that no matter what the age ranges, people end up doing great,” Dr. Wang said.
More importantly than age, older patients should be prepared for postsurgery therapy and treatment. For younger patients, the biggest drawback is outliving the estimated 25-year life span of a joint replacement. Complications are rare and occur in about 2% of procedures. These include infection, dislocation of the joint, and blood clots; other health issues you also have are not a factor.
Considering Ms. Blackwell’s hard time with her first knee replacement, it’s no small wonder that she ever set foot in a surgeon’s office again.
After putting it off for 7 years, Ms. Blackwell finally agreed to her doctor’s advice to replace her left knee in 2017 to relieve what she described as a “grinding,” chronic, bone-on-bone pain.
“It got to the point where there were no alternatives,” she said.
But her first orthopedic surgeon did a “lousy job,” leaving her with a gaping, festering wound that resulted in sepsis and required wound vacuum therapy to close the lesion. She eventually found another surgeon who removed and cleaned up her artificial knee before replacing the prosthesis. Luckily, the sepsis didn’t spread, and eight surgeries later, she was in the clear.
Ms. Blackwell’s second knee replacement in 2018 was a textbook surgery, as was a hip replacement in late 2019 .
“Your whole attitude changes,” she said.
What generalists should know
Orthopedic surgeons recommend that primary care doctors ask two things when weighing joint replacements: Have they exhausted nonsurgical treatments, and is the pain intolerable? They also advise avoiding narcotics to treat the symptoms.
The top issue to consider for a primary care doctor when weighing whether their patient may be a candidate for joint replacement is if the pain and the imaging are bad enough to warrant surgery.
“You don’t want to do it too soon,” Dr. Sierra said.
Dr. Sierra likes to tell the story of the golfer whose knee stiffens after playing 18 holes. To those patients, he recommends dialing back the activity; in this case, using a cart or playing only nine holes.
Dr. Wang agrees, asking if the pain is “lifestyle altering” and if the patient was unresponsive to nonsurgical treatments such as over-the-counter medications, anti-inflammatory medication and shots, home exercises or physical therapy, wearing a brace or sleeve, or simply changing their activity.
And no addictive pain pills to treat arthritis that can lead to other serious issues.
“This is not going to heal itself,” Dr. Wang said. “It’s not going to improve on its own. So, we don’t want to throw narcotics at it just to cover it up.”
Karen Smith, MD, has been a family doctor in rural North Carolina for more than 30 years. When she sees patients complaining about their joints, she first looks at function and pain. From there, she explores why they’re having discomfort. For example, is the problem an ergonomic issue at work or the result of carrying a lot of body weight?
“We look at those areas to determine what can be modified,” she said. “All of that’s done even before we get to having the orthopedic involvement.”
Dr. Smith said she also considers things beyond basic medicine: What is the patient’s mental status and tolerance for pain? Do they have a support system at home for post-operative care? And can they afford to miss work?
“We look at all of those factors together because that is going to determine the outcome that we’re hoping to achieve,” Dr. Smith said.
Great expectations
A recent study shows that older patients respond better to knee replacements than younger patients, particularly with pain relief and quality of life. The reason for this is believed to boil down to expectations. Whereas a younger person may want to return to the racquetball court and perform like they used to, older patients may just wish to walk down the hall without discomfort.
“It’s possible that these under 55-age-old patients may just take a little longer to heal to be satisfied,” Dr. Wang said. “We really can’t speak to why this is happening, but it’s possible that the younger patients are more active, and they expect more out of their knee.”
Jeevan Sall, MD, is a primary care sports medicine doctor with Providence Mission Heritage Medical Group in Laguna Niguel, Calif. He first discusses conservative management for patients struggling with arthritis in their joints. These measures include rehabilitation exercises, braces, shoe inserts, medication, and weight loss efforts. If these steps don’t improve a patient’s pain or lifestyle, surgery is on the table. Managing expectations is a significant factor.
“Is the patient mentally ready for surgery?” Dr. Sall said. “This includes what they hope to achieve with surgery as well as the risk and benefits of the procedure.”
Ms. Blackwell’s hip and knee pain came simply from a life well lived, with no marathon running or life-changing accident to speak of. She worked as a housewife raising her two children and owned an elevator company with her late husband, Robert Blackwell.
Yes, the elevator construction business has jokes.
“We have our ups and downs,” Ms. Blackwell said.
And with her new joints, so does she.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Kathy Blackwell is not going to allow a couple of aching joints stop her from living her best life.
The 73-year-old resident of Simi Valley, Calif., a bedroom community about 30 miles northwest of downtown Los Angeles, organizes regular activities for her group of seniors. The 20- to 30-member-strong band of seasoned citizens, mostly women, keep active. Over the coming weeks, they plan to catch the Beach Boys at the historic Hollywood Bowl and take a cruise to Alaska.
The busy schedule is why Ms. Blackwell intends to delay her second hip replacement surgery, opting instead for a cortisone shot in hopes of easing the pain enough to enjoy the upcoming excursions.
Not that she is shy about joint replacement. If her orthopedic surgeon offered a frequent customer punch card like the ones you get at the local coffee shop, hers would be nearly full. Ms. Blackwell’s knees and a hip have been replaced, and her other hip will be, too, once her calendar clears up.
“If you go on enough with chronic pain where there’s no relief, you get cranky,” Ms. Blackwell said.
More than 1 million new knees, hips
Joint replacements are getting more common, with about 790,000 total knee replacements and more than 450,000 hip replacements performed annually in the United States, according to the American College of Rheumatology.
Experts agree age is not a factor when considering candidates for joint replacement. Rafael Sierra, MD, of the Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minn., said he’s done hip replacements on patients as young as 12 and as old as 102. Orthopedic surgeon John Wang, MD, of the Hospital for Special Surgery, New York, has performed a total knee arthroscopy on a patient in their mid-90s. At 73, Ms. Blackwell is on the older side of the average age of 66 for a hip replacement.
“A lot of research and studies have shown that no matter what the age ranges, people end up doing great,” Dr. Wang said.
More importantly than age, older patients should be prepared for postsurgery therapy and treatment. For younger patients, the biggest drawback is outliving the estimated 25-year life span of a joint replacement. Complications are rare and occur in about 2% of procedures. These include infection, dislocation of the joint, and blood clots; other health issues you also have are not a factor.
Considering Ms. Blackwell’s hard time with her first knee replacement, it’s no small wonder that she ever set foot in a surgeon’s office again.
After putting it off for 7 years, Ms. Blackwell finally agreed to her doctor’s advice to replace her left knee in 2017 to relieve what she described as a “grinding,” chronic, bone-on-bone pain.
“It got to the point where there were no alternatives,” she said.
But her first orthopedic surgeon did a “lousy job,” leaving her with a gaping, festering wound that resulted in sepsis and required wound vacuum therapy to close the lesion. She eventually found another surgeon who removed and cleaned up her artificial knee before replacing the prosthesis. Luckily, the sepsis didn’t spread, and eight surgeries later, she was in the clear.
Ms. Blackwell’s second knee replacement in 2018 was a textbook surgery, as was a hip replacement in late 2019 .
“Your whole attitude changes,” she said.
What generalists should know
Orthopedic surgeons recommend that primary care doctors ask two things when weighing joint replacements: Have they exhausted nonsurgical treatments, and is the pain intolerable? They also advise avoiding narcotics to treat the symptoms.
The top issue to consider for a primary care doctor when weighing whether their patient may be a candidate for joint replacement is if the pain and the imaging are bad enough to warrant surgery.
“You don’t want to do it too soon,” Dr. Sierra said.
Dr. Sierra likes to tell the story of the golfer whose knee stiffens after playing 18 holes. To those patients, he recommends dialing back the activity; in this case, using a cart or playing only nine holes.
Dr. Wang agrees, asking if the pain is “lifestyle altering” and if the patient was unresponsive to nonsurgical treatments such as over-the-counter medications, anti-inflammatory medication and shots, home exercises or physical therapy, wearing a brace or sleeve, or simply changing their activity.
And no addictive pain pills to treat arthritis that can lead to other serious issues.
“This is not going to heal itself,” Dr. Wang said. “It’s not going to improve on its own. So, we don’t want to throw narcotics at it just to cover it up.”
Karen Smith, MD, has been a family doctor in rural North Carolina for more than 30 years. When she sees patients complaining about their joints, she first looks at function and pain. From there, she explores why they’re having discomfort. For example, is the problem an ergonomic issue at work or the result of carrying a lot of body weight?
“We look at those areas to determine what can be modified,” she said. “All of that’s done even before we get to having the orthopedic involvement.”
Dr. Smith said she also considers things beyond basic medicine: What is the patient’s mental status and tolerance for pain? Do they have a support system at home for post-operative care? And can they afford to miss work?
“We look at all of those factors together because that is going to determine the outcome that we’re hoping to achieve,” Dr. Smith said.
Great expectations
A recent study shows that older patients respond better to knee replacements than younger patients, particularly with pain relief and quality of life. The reason for this is believed to boil down to expectations. Whereas a younger person may want to return to the racquetball court and perform like they used to, older patients may just wish to walk down the hall without discomfort.
“It’s possible that these under 55-age-old patients may just take a little longer to heal to be satisfied,” Dr. Wang said. “We really can’t speak to why this is happening, but it’s possible that the younger patients are more active, and they expect more out of their knee.”
Jeevan Sall, MD, is a primary care sports medicine doctor with Providence Mission Heritage Medical Group in Laguna Niguel, Calif. He first discusses conservative management for patients struggling with arthritis in their joints. These measures include rehabilitation exercises, braces, shoe inserts, medication, and weight loss efforts. If these steps don’t improve a patient’s pain or lifestyle, surgery is on the table. Managing expectations is a significant factor.
“Is the patient mentally ready for surgery?” Dr. Sall said. “This includes what they hope to achieve with surgery as well as the risk and benefits of the procedure.”
Ms. Blackwell’s hip and knee pain came simply from a life well lived, with no marathon running or life-changing accident to speak of. She worked as a housewife raising her two children and owned an elevator company with her late husband, Robert Blackwell.
Yes, the elevator construction business has jokes.
“We have our ups and downs,” Ms. Blackwell said.
And with her new joints, so does she.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
CPAP not only solution for sleep apnea
Although continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) machines are the gold standard in the management of sleep apnea, several other treatments should be considered.
“Just because you have a hammer doesn’t mean everything is a nail,” Kimberly Hardin, MD, professor of clinical internal medicine at University of California, Davis, said at the annual meeting of the American College of Physicians.
“Sleep has been underestimated in the health arena for many, many years,” said Dr. Hardin, who likened sound sleep to the “sixth vital sign.” “We know that sleep plays an integral role in our health.”
Surgical options include nasal surgery and maxillomandibular advancement surgery, also known as double-jaw surgery. Such procedures should be considered only for patients who are unwilling or unable to use CPAP or other nonsurgical treatments.
Sleep apnea occurs in 4% of adult men and 2% of adult women aged 30-60. Most commonly, obstructive sleep apnea involves the cessation or significant decrease in airflow while sleeping. The Apnea Hypopnea Index (AHI) is the number of times a patient experiences apnea or hypopnea during one night divided by the hours of sleep. Normal sleep AHI is fewer than five events per hour on average; mild sleep apnea is five to 14 events; moderate, 15-29; and severe, at least 30 events.
To identify sleep apnea, physicians have several tools at their disposal, starting with preliminary questionnaires that query patients as to whether they are having trouble falling asleep, staying asleep, or are tired during the day. Additional assessment tools include sleep lab testing and at-home testing.
At-home testing has come to include more than the common devices that are worn around the chest and nose for a night.
“It’s not very fun looking,” Dr. Hardin said of the weighty, obtrusive monitoring devices. “So lots of folks have come up with some new ways of doing things.”
These new options incorporate headbands, wrist and finger devices, arterial tonometry, and sleep rings.
Studies show that U.S. adults do not get enough sleep, and poor-quality sleep is as inadequate as insufficient sleep. Barely a third of adults get the minimum 7 hours recommended by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Non-Hispanic Black adults are less likely to report sleeping 7-9 hours and are more likely to report sleeping 6 or fewer hours than are non-Hispanic White and Hispanic adults.
Dr. Hardin said doctors can advise patients to keep their bedrooms quiet, dark, and cool with no TVs or electronics, to maintain regular wake and sleep times, and to stop consuming caffeine late in the day.
Insufficient or poor sleep can have wide-ranging implications on medical conditions such as diabetes, heart disease, obesity, immunodeficiency, cognitive function, mental health, and, ultimately, mortality, according to Dr. Hardin.
“Some people say, ‘Oh, never mind, I can sleep when I’m dead,’ “ Dr. Hardin said. But such a mentality can have a bearing on life expectancy.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Although continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) machines are the gold standard in the management of sleep apnea, several other treatments should be considered.
“Just because you have a hammer doesn’t mean everything is a nail,” Kimberly Hardin, MD, professor of clinical internal medicine at University of California, Davis, said at the annual meeting of the American College of Physicians.
“Sleep has been underestimated in the health arena for many, many years,” said Dr. Hardin, who likened sound sleep to the “sixth vital sign.” “We know that sleep plays an integral role in our health.”
Surgical options include nasal surgery and maxillomandibular advancement surgery, also known as double-jaw surgery. Such procedures should be considered only for patients who are unwilling or unable to use CPAP or other nonsurgical treatments.
Sleep apnea occurs in 4% of adult men and 2% of adult women aged 30-60. Most commonly, obstructive sleep apnea involves the cessation or significant decrease in airflow while sleeping. The Apnea Hypopnea Index (AHI) is the number of times a patient experiences apnea or hypopnea during one night divided by the hours of sleep. Normal sleep AHI is fewer than five events per hour on average; mild sleep apnea is five to 14 events; moderate, 15-29; and severe, at least 30 events.
To identify sleep apnea, physicians have several tools at their disposal, starting with preliminary questionnaires that query patients as to whether they are having trouble falling asleep, staying asleep, or are tired during the day. Additional assessment tools include sleep lab testing and at-home testing.
At-home testing has come to include more than the common devices that are worn around the chest and nose for a night.
“It’s not very fun looking,” Dr. Hardin said of the weighty, obtrusive monitoring devices. “So lots of folks have come up with some new ways of doing things.”
These new options incorporate headbands, wrist and finger devices, arterial tonometry, and sleep rings.
Studies show that U.S. adults do not get enough sleep, and poor-quality sleep is as inadequate as insufficient sleep. Barely a third of adults get the minimum 7 hours recommended by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Non-Hispanic Black adults are less likely to report sleeping 7-9 hours and are more likely to report sleeping 6 or fewer hours than are non-Hispanic White and Hispanic adults.
Dr. Hardin said doctors can advise patients to keep their bedrooms quiet, dark, and cool with no TVs or electronics, to maintain regular wake and sleep times, and to stop consuming caffeine late in the day.
Insufficient or poor sleep can have wide-ranging implications on medical conditions such as diabetes, heart disease, obesity, immunodeficiency, cognitive function, mental health, and, ultimately, mortality, according to Dr. Hardin.
“Some people say, ‘Oh, never mind, I can sleep when I’m dead,’ “ Dr. Hardin said. But such a mentality can have a bearing on life expectancy.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Although continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) machines are the gold standard in the management of sleep apnea, several other treatments should be considered.
“Just because you have a hammer doesn’t mean everything is a nail,” Kimberly Hardin, MD, professor of clinical internal medicine at University of California, Davis, said at the annual meeting of the American College of Physicians.
“Sleep has been underestimated in the health arena for many, many years,” said Dr. Hardin, who likened sound sleep to the “sixth vital sign.” “We know that sleep plays an integral role in our health.”
Surgical options include nasal surgery and maxillomandibular advancement surgery, also known as double-jaw surgery. Such procedures should be considered only for patients who are unwilling or unable to use CPAP or other nonsurgical treatments.
Sleep apnea occurs in 4% of adult men and 2% of adult women aged 30-60. Most commonly, obstructive sleep apnea involves the cessation or significant decrease in airflow while sleeping. The Apnea Hypopnea Index (AHI) is the number of times a patient experiences apnea or hypopnea during one night divided by the hours of sleep. Normal sleep AHI is fewer than five events per hour on average; mild sleep apnea is five to 14 events; moderate, 15-29; and severe, at least 30 events.
To identify sleep apnea, physicians have several tools at their disposal, starting with preliminary questionnaires that query patients as to whether they are having trouble falling asleep, staying asleep, or are tired during the day. Additional assessment tools include sleep lab testing and at-home testing.
At-home testing has come to include more than the common devices that are worn around the chest and nose for a night.
“It’s not very fun looking,” Dr. Hardin said of the weighty, obtrusive monitoring devices. “So lots of folks have come up with some new ways of doing things.”
These new options incorporate headbands, wrist and finger devices, arterial tonometry, and sleep rings.
Studies show that U.S. adults do not get enough sleep, and poor-quality sleep is as inadequate as insufficient sleep. Barely a third of adults get the minimum 7 hours recommended by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Non-Hispanic Black adults are less likely to report sleeping 7-9 hours and are more likely to report sleeping 6 or fewer hours than are non-Hispanic White and Hispanic adults.
Dr. Hardin said doctors can advise patients to keep their bedrooms quiet, dark, and cool with no TVs or electronics, to maintain regular wake and sleep times, and to stop consuming caffeine late in the day.
Insufficient or poor sleep can have wide-ranging implications on medical conditions such as diabetes, heart disease, obesity, immunodeficiency, cognitive function, mental health, and, ultimately, mortality, according to Dr. Hardin.
“Some people say, ‘Oh, never mind, I can sleep when I’m dead,’ “ Dr. Hardin said. But such a mentality can have a bearing on life expectancy.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM INTERNAL MEDICINE 2023