User login
Cutis is a peer-reviewed clinical journal for the dermatologist, allergist, and general practitioner published monthly since 1965. Concise clinical articles present the practical side of dermatology, helping physicians to improve patient care. Cutis is referenced in Index Medicus/MEDLINE and is written and edited by industry leaders.
ass lick
assault rifle
balls
ballsac
black jack
bleach
Boko Haram
bondage
causas
cheap
child abuse
cocaine
compulsive behaviors
cost of miracles
cunt
Daech
display network stats
drug paraphernalia
explosion
fart
fda and death
fda AND warn
fda AND warning
fda AND warns
feom
fuck
gambling
gfc
gun
human trafficking
humira AND expensive
illegal
ISIL
ISIS
Islamic caliphate
Islamic state
madvocate
masturbation
mixed martial arts
MMA
molestation
national rifle association
NRA
nsfw
nuccitelli
pedophile
pedophilia
poker
porn
porn
pornography
psychedelic drug
recreational drug
sex slave rings
shit
slot machine
snort
substance abuse
terrorism
terrorist
texarkana
Texas hold 'em
UFC
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden')]
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden active')
A peer-reviewed, indexed journal for dermatologists with original research, image quizzes, cases and reviews, and columns.
Eruptive Annular Papules on the Trunk of an Organ Transplant Recipient
The Diagnosis: Epidermodysplasia Verruciformis
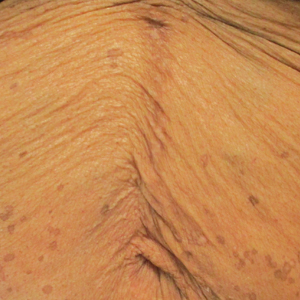
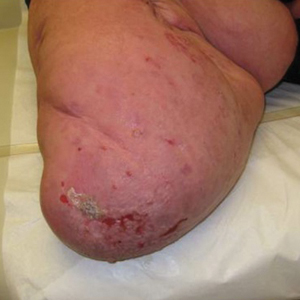
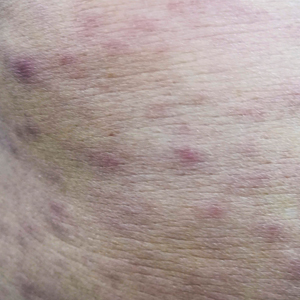
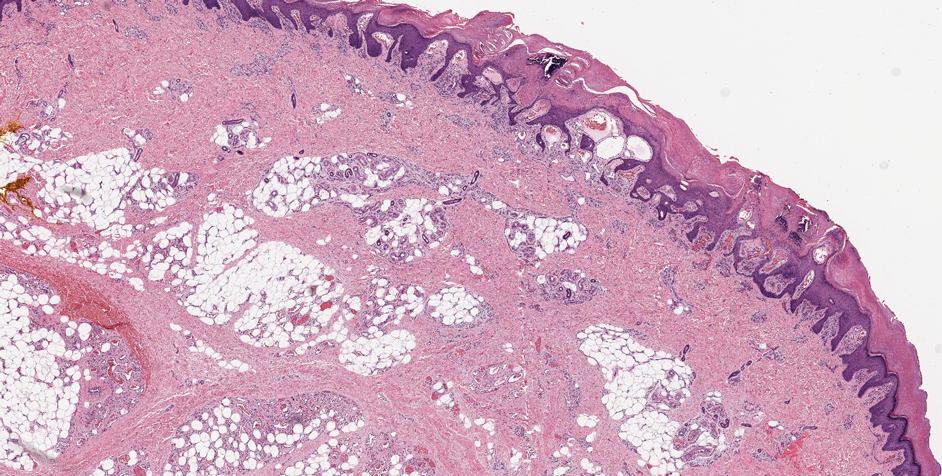
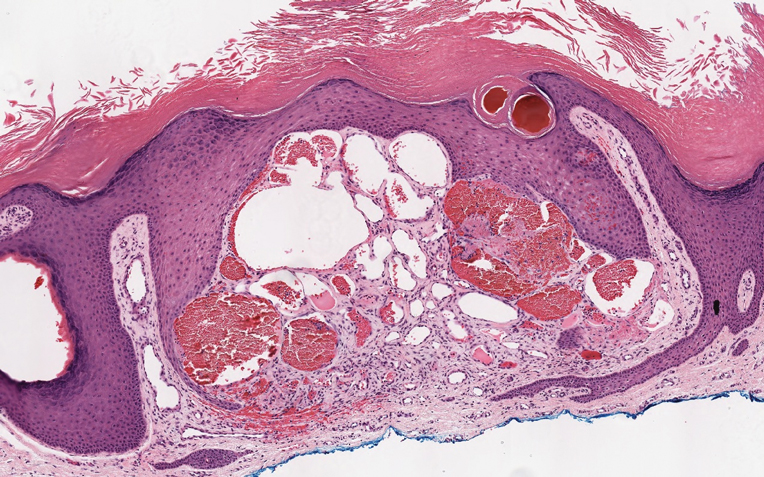
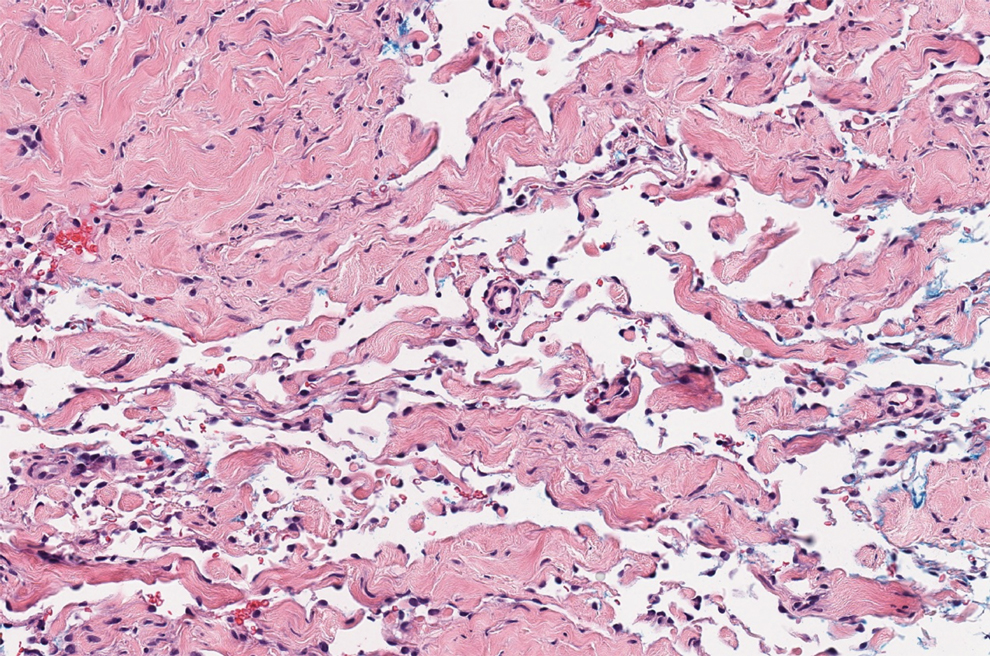
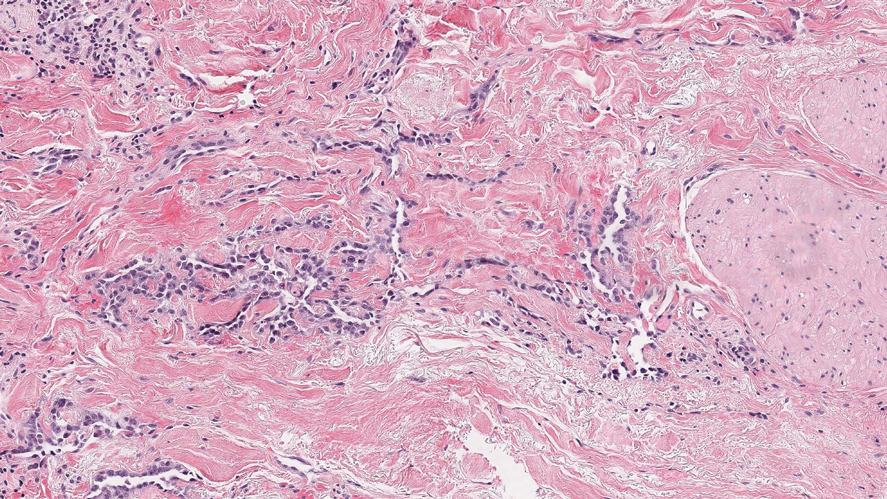
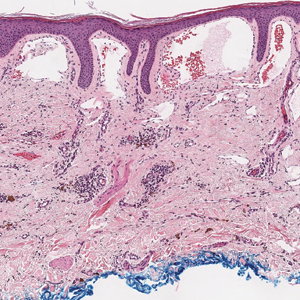
Histopathologic examination of our patient's biopsy specimen revealed mild acanthosis with prominent hypergranulosis and enlarged keratinocytes with blue-gray cytoplasm (Figure). A diagnosis of acquired epidermodysplasia verruciformis (EV) was rendered. The patient was treated with photodynamic therapy utilizing 5-aminolevulinic acid.
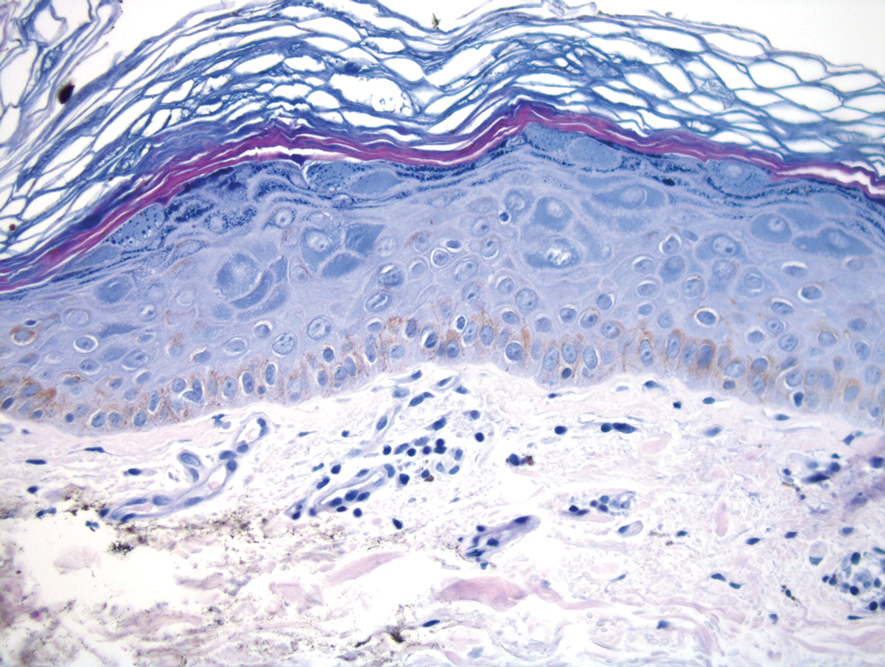
Epidermodysplasia verruciformis is characterized by susceptibility to human papillomavirus (HPV) infections via a defect in cellular immunity. Epidermodysplasia verruciformis was first described as an autosomal-recessive genodermatosis, but it can be acquired in immunosuppressed states with an atypical clinical appearance.1 There are few case reports in skin of color. Acquired EV appears in patients with acquired immunodeficiencies that are susceptible to EV-causing HPVs via a similar mechanism found in inherited EV.2 The most common HPV serotypes involved in EV are HPV-5 and HPV-8. The duration of immunosuppression has been found to be positively correlated with the risk for EV development, with the majority of patients developing lesions after 5 years of immunosuppression.3 There is an approximately 60% risk of malignant transformation of EV lesions into nonmelanoma skin cancer.2 This risk is believed to be lower in patients with darker skin.4
Preventative measures including sun protection and annual surveillance are crucial in EV patients given the high rate of malignant transformation in sun-exposed lesions.5 Treatment options for EV are anecdotal and have variable results, ranging from topicals including 5-fluorouracil and imiquimod to systemic medications including acitretin and interferon.3 Photodynamic therapy can be used for extensive EV. Surgical modalities and other destructive methods also have been tried.6
Epidermodysplasia verruciformis often can be confused with similar dermatoses. Porokeratosis appears as annular pink papules with waferlike peripheral scales. Tinea versicolor is a dermatophyte infection caused by Malassezia furfur and presents as multiple dyspigmented, finely scaling, thin papules and plaques. Subacute cutaneous lupus erythematosus presents as pink, scaly, annular or psoriasiform papules and plaques most commonly on the trunk. Discoid lupus erythematosus presents as pink, hypopigmented or depigmented, atrophic plaques with a peripheral rim of erythema that indicates activity. Secondary syphilis, commonly denoted as the "great mimicker," presents as psoriasiform papules and plaques among other variable morphologies.
- Sa NB, Guerini MB, Barbato MT, et al. Epidermodysplasia verruciformis: clinical presentation with varied forms of lesions. An Bras Dermatol. 2011;86(4 suppl 1):S57-S60.
- Rogers HD, Macgregor JL, Nord KM, et al. Acquired epidermodysplasia verruciformis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2009;60:315-320.
- Henley JK, Hossler EW. Acquired epidermodysplasia verruciformis occurring in a renal transplant recipient. Cutis. 2017;99:E9-E12.
- Jacyk WK, De Villiers EM. Epidermodysplasia verruciformis in Africans. Int J Dermatol. 1993;32:806-810.
- Fox SH, Elston DM. Epidermodysplasia verruciformis and the risk for malignancy. Cutis. 2016;98:E10-E12.
- Shruti S, Siraj F, Singh A, et al. Epidermodysplasia verruciformis: three case reports and a brief review. Acta Dermatovenerol Alp Pannonica Adriat. 2017;26:59-61.
The Diagnosis: Epidermodysplasia Verruciformis
Histopathologic examination of our patient's biopsy specimen revealed mild acanthosis with prominent hypergranulosis and enlarged keratinocytes with blue-gray cytoplasm (Figure). A diagnosis of acquired epidermodysplasia verruciformis (EV) was rendered. The patient was treated with photodynamic therapy utilizing 5-aminolevulinic acid.

Epidermodysplasia verruciformis is characterized by susceptibility to human papillomavirus (HPV) infections via a defect in cellular immunity. Epidermodysplasia verruciformis was first described as an autosomal-recessive genodermatosis, but it can be acquired in immunosuppressed states with an atypical clinical appearance.1 There are few case reports in skin of color. Acquired EV appears in patients with acquired immunodeficiencies that are susceptible to EV-causing HPVs via a similar mechanism found in inherited EV.2 The most common HPV serotypes involved in EV are HPV-5 and HPV-8. The duration of immunosuppression has been found to be positively correlated with the risk for EV development, with the majority of patients developing lesions after 5 years of immunosuppression.3 There is an approximately 60% risk of malignant transformation of EV lesions into nonmelanoma skin cancer.2 This risk is believed to be lower in patients with darker skin.4
Preventative measures including sun protection and annual surveillance are crucial in EV patients given the high rate of malignant transformation in sun-exposed lesions.5 Treatment options for EV are anecdotal and have variable results, ranging from topicals including 5-fluorouracil and imiquimod to systemic medications including acitretin and interferon.3 Photodynamic therapy can be used for extensive EV. Surgical modalities and other destructive methods also have been tried.6
Epidermodysplasia verruciformis often can be confused with similar dermatoses. Porokeratosis appears as annular pink papules with waferlike peripheral scales. Tinea versicolor is a dermatophyte infection caused by Malassezia furfur and presents as multiple dyspigmented, finely scaling, thin papules and plaques. Subacute cutaneous lupus erythematosus presents as pink, scaly, annular or psoriasiform papules and plaques most commonly on the trunk. Discoid lupus erythematosus presents as pink, hypopigmented or depigmented, atrophic plaques with a peripheral rim of erythema that indicates activity. Secondary syphilis, commonly denoted as the "great mimicker," presents as psoriasiform papules and plaques among other variable morphologies.
The Diagnosis: Epidermodysplasia Verruciformis
Histopathologic examination of our patient's biopsy specimen revealed mild acanthosis with prominent hypergranulosis and enlarged keratinocytes with blue-gray cytoplasm (Figure). A diagnosis of acquired epidermodysplasia verruciformis (EV) was rendered. The patient was treated with photodynamic therapy utilizing 5-aminolevulinic acid.

Epidermodysplasia verruciformis is characterized by susceptibility to human papillomavirus (HPV) infections via a defect in cellular immunity. Epidermodysplasia verruciformis was first described as an autosomal-recessive genodermatosis, but it can be acquired in immunosuppressed states with an atypical clinical appearance.1 There are few case reports in skin of color. Acquired EV appears in patients with acquired immunodeficiencies that are susceptible to EV-causing HPVs via a similar mechanism found in inherited EV.2 The most common HPV serotypes involved in EV are HPV-5 and HPV-8. The duration of immunosuppression has been found to be positively correlated with the risk for EV development, with the majority of patients developing lesions after 5 years of immunosuppression.3 There is an approximately 60% risk of malignant transformation of EV lesions into nonmelanoma skin cancer.2 This risk is believed to be lower in patients with darker skin.4
Preventative measures including sun protection and annual surveillance are crucial in EV patients given the high rate of malignant transformation in sun-exposed lesions.5 Treatment options for EV are anecdotal and have variable results, ranging from topicals including 5-fluorouracil and imiquimod to systemic medications including acitretin and interferon.3 Photodynamic therapy can be used for extensive EV. Surgical modalities and other destructive methods also have been tried.6
Epidermodysplasia verruciformis often can be confused with similar dermatoses. Porokeratosis appears as annular pink papules with waferlike peripheral scales. Tinea versicolor is a dermatophyte infection caused by Malassezia furfur and presents as multiple dyspigmented, finely scaling, thin papules and plaques. Subacute cutaneous lupus erythematosus presents as pink, scaly, annular or psoriasiform papules and plaques most commonly on the trunk. Discoid lupus erythematosus presents as pink, hypopigmented or depigmented, atrophic plaques with a peripheral rim of erythema that indicates activity. Secondary syphilis, commonly denoted as the "great mimicker," presents as psoriasiform papules and plaques among other variable morphologies.
- Sa NB, Guerini MB, Barbato MT, et al. Epidermodysplasia verruciformis: clinical presentation with varied forms of lesions. An Bras Dermatol. 2011;86(4 suppl 1):S57-S60.
- Rogers HD, Macgregor JL, Nord KM, et al. Acquired epidermodysplasia verruciformis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2009;60:315-320.
- Henley JK, Hossler EW. Acquired epidermodysplasia verruciformis occurring in a renal transplant recipient. Cutis. 2017;99:E9-E12.
- Jacyk WK, De Villiers EM. Epidermodysplasia verruciformis in Africans. Int J Dermatol. 1993;32:806-810.
- Fox SH, Elston DM. Epidermodysplasia verruciformis and the risk for malignancy. Cutis. 2016;98:E10-E12.
- Shruti S, Siraj F, Singh A, et al. Epidermodysplasia verruciformis: three case reports and a brief review. Acta Dermatovenerol Alp Pannonica Adriat. 2017;26:59-61.
- Sa NB, Guerini MB, Barbato MT, et al. Epidermodysplasia verruciformis: clinical presentation with varied forms of lesions. An Bras Dermatol. 2011;86(4 suppl 1):S57-S60.
- Rogers HD, Macgregor JL, Nord KM, et al. Acquired epidermodysplasia verruciformis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2009;60:315-320.
- Henley JK, Hossler EW. Acquired epidermodysplasia verruciformis occurring in a renal transplant recipient. Cutis. 2017;99:E9-E12.
- Jacyk WK, De Villiers EM. Epidermodysplasia verruciformis in Africans. Int J Dermatol. 1993;32:806-810.
- Fox SH, Elston DM. Epidermodysplasia verruciformis and the risk for malignancy. Cutis. 2016;98:E10-E12.
- Shruti S, Siraj F, Singh A, et al. Epidermodysplasia verruciformis: three case reports and a brief review. Acta Dermatovenerol Alp Pannonica Adriat. 2017;26:59-61.
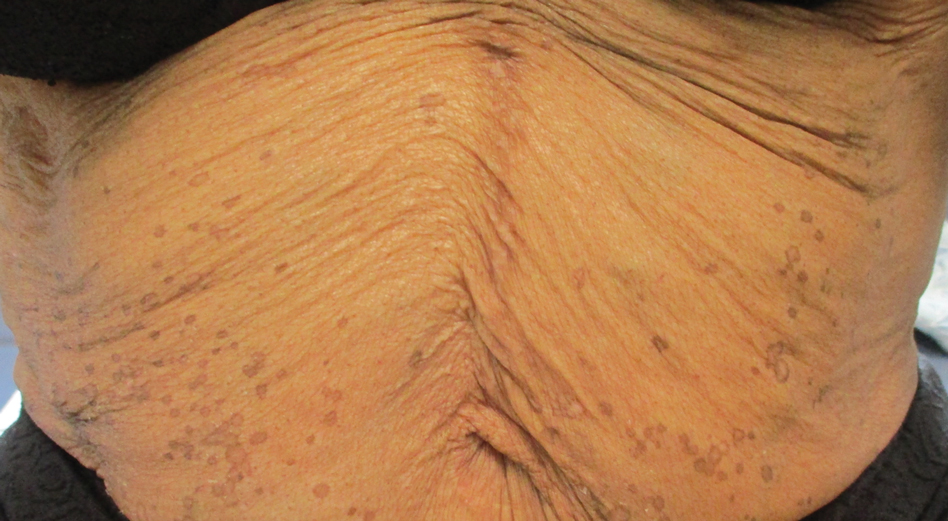
A 50-year-old Black woman with systemic lupus erythematosus and a renal transplant 15 years prior due to lupus nephritis presented with a nonpruritic rash on the abdomen of 1 year’s duration. Her immunosuppressive regimen consisted of tacrolimus, azathioprine, and prednisone. Physical examination revealed numerous monomorphic, annular, hyperpigmented, and thin papules with central clearing present on the abdomen extending to the flanks and groin. The patient denied any family history of similar lesions. A 4-mm punch biopsy of an abdominal lesion was performed.
Vibrio vulnificus: Review of Mild to Life-threatening Skin Infections
Vibrio vulnificus is a member of the Vibrio genus. Most Vibrio species are nonpathogenic in humans; however, V vulnificus is one of the pathogenic strains.1 In Latin, the term vulnificus means “wounding,” and V vulnificus can cause life-threatening infections in patients. The mortality rate of V vulnificus infections is approximately 33% in the United States.2Vibrio vulnificus is a gram-negative bacterium that was first isolated by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention in 1964 and was given its current name in 1979.3-6 It has been found in numerous organisms, including oysters, crabs, clams, shrimp, mussels, mullets, and sea bass.4 The vast majority of infections in the United States are due to oyster exposure and consumption.2,7Vibrio vulnificus is responsible for more than 95% of seafood-related deaths in the United States and has the highest mortality rate of all food-borne illness in the United States.2,5 It also has the highest per-case economic impact of all food-related diseases in the United States.1
What distinguishes a pathogenic vs nonpathogenic Vibrio isolate remains unknown; Vibrio species rapidly undergo horizontal gene transfer, making DNA isolation difficult.1 Some characteristics of V vulnificus that may confer virulence are the capsular polysaccharide, lipopolysaccharide, binding proteins, and tissue-degrading enzymes.1,5 First, encapsulated strains are more virulent and invasive than unencapsulated strains.1 The mucopolysaccharide capsule protects the bacterium from the immune system, allowing it to evade immune surveillance, cause more severe infection, and invade into the subcutaneous tissue.3,5 Second, production of sialic acid–like molecules alter the lipopolysaccharide, allowing for motility and biofilm formation.1 This allows the bacterium to survive in marine waters and within the bloodstream, the latter leading to sepsis in humans. Third, production of N-acetylglucosamine–binding protein A allows for adhesion to chitin. Shellfish consume chitin, and chitin accumulates in shellfish. N-acetylglucosamine–binding protein A also binds mucin; this may be how V vulnificus binds to mucin in the gastrointestinal tract in humans, causing gastroenteritis.1 Binding to the human mucosae also may allow the bacteria to gain access to the blood supply, leading to septicemia.4 Finally, tissue-degrading enzymes such as proteases are responsible for necrotizing wound infections associated with V vulnificus, as the enzymes allow for invasion into the skin and subcutaneous tissues. Proteases also increase vascular permeability and lead to edema.3 Hence, these virulence factors may provide V vulnificus the pathogenicity to cause infection in humans.
Three biotypes of V vulnificus have been discovered. Biotype 1 is the most common and is found worldwide in brackish water.8 It can cause the entire spectrum of illnesses, and it has a case fatality rate of 50% in humans. Biotype 1 is presumably responsible for all infections in the United States. Biotype 2 is found in the Far East and Western Europe; it inhabits a unique niche—saltwater used for eel farming. It typically causes infection in eels, but rarely it can cause wound infections in humans. Biotype 3 is found in freshwater fish farming in Israel, and it is a hybrid of biotypes 1 and 2.It can cause severe soft tissue infections in humans, sometimes requiring amputation.8
Epidemiology
Vibrio vulnificus is a motile, gram-negative, halophilic, aquatic bacterium.1,4,5,8,9 It is part of the normal estuarine microbiome and typically is found in warm coastal waters.1,5,10 The ideal conditions for growth and survival of V vulnificus are water temperatures at 18 °C (64.4 °F) and water salinities between 15 to 25 parts per thousand.2,8,9 These conditions are found in tropical and subtropical regions.2Vibrio vulnificus is found all over the world, including Denmark, Italy, Japan, Australia, Brazil, and the United States,2 where most infections come from oyster exposure and consumption in the Gulf of Mexico.2,8,11 The incidence of infection in the United States is highest between April and October.8,11
Some populations are at a higher risk of infection. Risk factors include male sex, liver cirrhosis, hemochromatosis, end-stage renal disease, immunosuppression, and diabetes mellitus.1,8,11 Healthy patients with no risk factors account for less than 5% of US V vulnificus infections.8
Male Predilection
Men are 6 times more likely to be affected by V vulnificus than women.Some hypotheses for this discrepancy are that estrogen is protective againstV vulnificus and that women may be less likely to engage in risky water activities and seafood handling.5 Additionally, older males (aged >60 years) are most often affected,1,8 likely due to the association between increasing age with number of comorbidities, such as diabetes mellitus, heart disease, and chronic disease.8
Iron Levels
Iron appears to play an important role in V vulnificus infection. Iron is essential for bacterial growth, and the ability to obtain iron from a host increases the organism’s pathogenicity.3Vibrio vulnificus rapidly grows when transferrin saturation exceeds 70%.8 Additionally, iron overload decreases the inoculum needed to cause sepsis in animal studies, which could play a role in human pathogenesis.4 Iron levels are elevated in patients with hemochromatosis due to increased iron absorption, cirrhosis and chronic liver disease due to impaired iron metabolism, and end-stage renal disease, especially in patients receiving parenteral iron.8
Immunosuppression
Patients who are immunocompromised and those with chronic liver disease are at an increased risk of infection because of neutrophils having decreased phagocytic activity.4
Diabetes Mellitus
Patients with diabetes mellitus may have peripheral neuropathy and may be unaware of pre-existing wounds that serve as entry points for V vulnificus.12
Etiology
Vibrio vulnificus infects humans via seafood consumption and handling as well as exposure to contaminated water.2,5 With respect to seafood consumption, raw shellfish are the primary type of seafood that harbor high levels of V vulnificus.5 Oysters are the most common etiology, but consumption of crabs, clams, and shrimp also can lead to infection.5,7Vibrio vulnificus contamination does not change the appearance, taste, or odor of shellfish, making it hard to detect.8 An inoculate of 1 million bacteria typically is necessary for infection after consumption.5 Contaminated seawater is another primary cause of V vulnificus infection. When open wounds are exposed to seawater harboring the bacteria, wound infections can arise.7 Infections can be acquired when swimming, fishing, or participating in water sports. Wound infections also occur while handling contaminated seafood, such as oyster shucking.5 There is a short incubation period for V vulnificus infections; the onset of symptoms and clinical outcome typically occur within 24 hours.5
Clinical Presentation
Vibrio vulnificus infections can have numerous clinical presentations, including gastroenteritis, wound infections, necrotizing fasciitis, and sepsis.1,8 There also is a spectrum of clinical outcomes; for instance, gastroenteritis typically is self-limited, whereas necrotizing fasciitis or sepsis can be fatal.2
Gastroenteritis
Vibrio vulnificus gastroenteritis is due to ingestion of contaminated shellfish.2,9 Symptoms typically are mild to moderate and include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, fever, chills, abdominal pain, and cramping.2,4,8 Cases likely are underreported in the United States because gastroenteritis is self-limited, and many patients do not seek treatment.2,11
Wound Infections
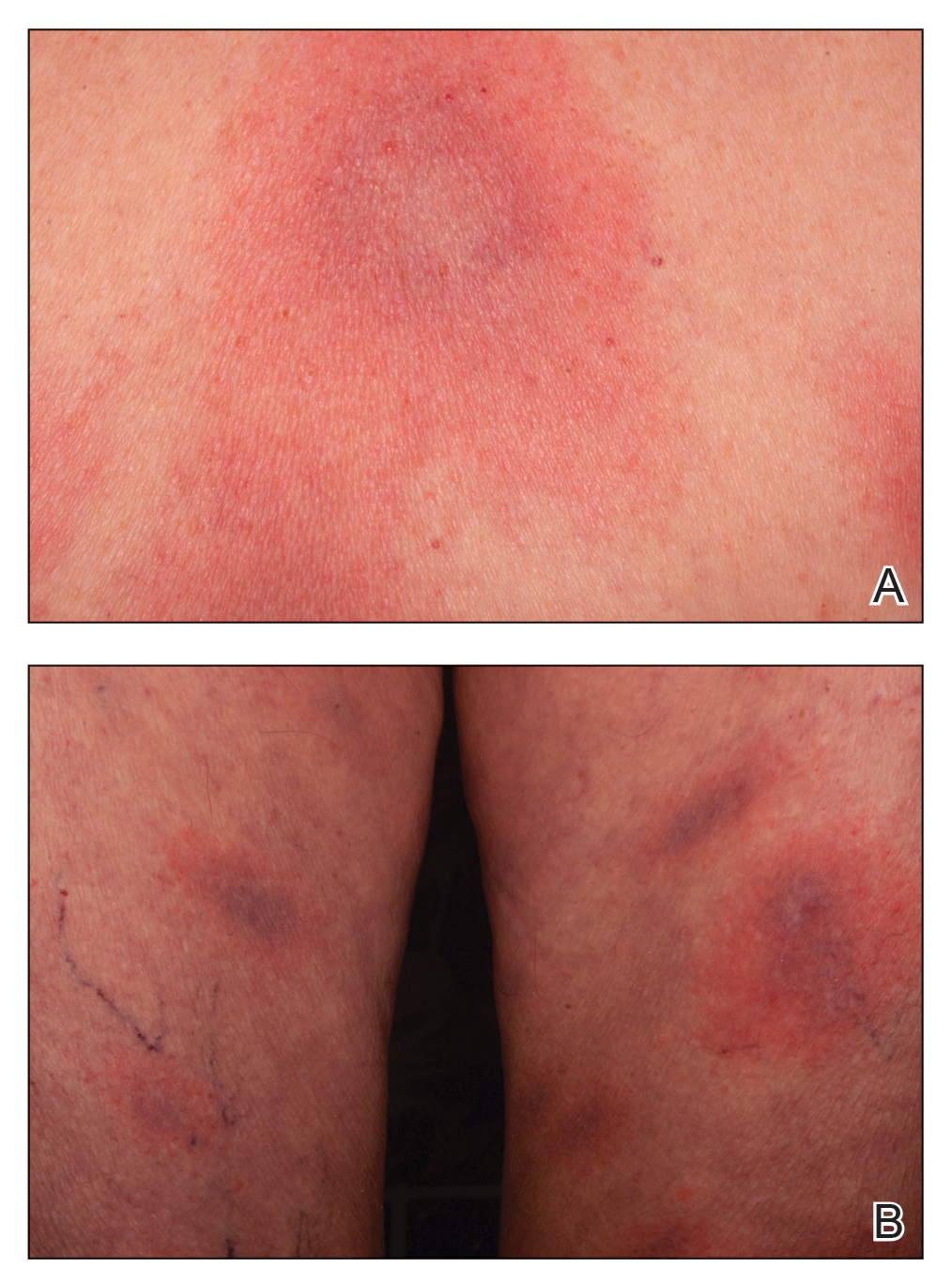
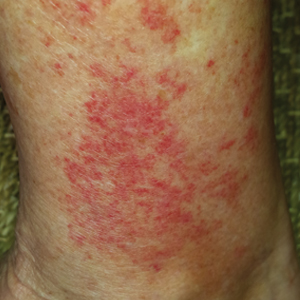
Wound infections with V vulnificus have a cutaneous port of entry. Exposure to contaminated seawater or seafood can inoculate an open wound, leading to infection.7,8 Wound infections usually stem from 1 of 2 routes: (1) a pre-existing open wound gets infected while the patient is swimming in contaminated water, or (2) a traumatic injury occurs while the patient is handling contaminated shellfish, knives, or fishhooks. Many shellfish, such as oysters, have sharp points on their shells that can lacerate the skin.8 A wound on the hand can be contaminated by V vulnificus while handling contaminated seafood (eg, oyster shucking).13 Minor abrasions should not be dismissed; in fact, a small puncture or skin break often acts as the port of entry.9,11 Wound infections tend to arise within 7 days of exposure, though they can manifest up to 12 days after exposure.8 Wound infections can present as cellulitis, bullae, or ecchymoses.7 Lesions are exquisitely tender, and the skin is erythematous with marked surrounding soft tissue edema.3,4,8 Cellulitis typically arises first, with hemorrhagic bullae rapidly following.14 Lesions are limited to the affected extremity or area of inoculation.8 Systemic symptoms are rare, but fever and chills may accompany the infection.8,14 Unfortunately, lesions can become necrotic and progress rapidly to necrotizing fasciitis if left untreated.4,7,11 In these cases, secondary sepsis can occur.8
Necrotizing Fasciitis
Wound infections caused by V vulnificus can progress to necrotizing skin and soft tissue infections, such as necrotizing fasciitis and gangrene.5 Necrotizing fasciitis accounts for approximately one-third of V vulnificus infections.9 It usually stems from an open wound that is inoculated by contact with contaminated seafood or seawater.2,9 The wound infection begins as cellulitis with extreme tenderness, erythematous skin, and marked soft tissue edema, then rapidly progresses, becoming necrotic. These necrotic lesions present as black and purple eschars as the skin, blood supply, and subcutaneous tissues are infiltrated by the bacteria and destroyed. Lesions may have blistering or exudation. Many patients have accompanying systemic symptoms, including fever, chills, abdominal pain, diarrhea, hypotension, and sepsis.11,14 However, some patients may not present with systemic symptoms, so it is important to maintain a high index of suspicion even in the absence of these symptoms. The infection typically is limited to the affected extremity; necrotizing infections can lead to amputation and even death, depending on the extent of destruction and spread of the bacteria.11,13 The infection may spread beyond the inoculated extremity if the bacteria gains access to the bloodstream.8,9 In these cases, fulminant purpura or secondary septicemia can occur.8,15 Fatalityrates in the United States for necrotizing V vulnificus infections approach 30%.2 Necrotizing fasciitis accounts for approximately 8% of deaths associated with the pathogen in the United States.9
Interestingly, one reported case of necrotizing fasciitis associated with V vulnificus infection was triggered by acupuncture.16 The patient worked in a fish hatchery, where he was exposed to V vulnificus, and subsequent acupuncture led to the inoculation of bacteria into his bloodstream. This case raises the important point that we typically sequence the pathogenesis of V vulnificus infection as a patient having an open wound that is subsequently exposed to contaminated water; however, it also can follow the reverse sequence. Thus, proper cleansing of the skin after swimming in brackish water or handling shellfish is important to prevent V vulnificus infection.16 Additionally, dermatologists should be sure to cleanse patients’ skin thoroughly before performing procedures that could cause breaks in the skin.
Septicemia
Primary septicemia is the most common presentation of V vulnificus infection.2,8 Septicemia accounts for approximately 58% of V vulnificus infections in the United States.9 Infection typically occurs after ingestion of contaminated oysters, with subsequent absorption into the bloodstream through the ileum or cecum.2,8,9 Patients with chronic liver disease are 80 times more likely to develop primary sepsis than healthy individuals.8 Patients typically present with sudden-onset fever and chills, vomiting, diarrhea, and pain in the abdomen and/or extremities within hours to days of ingestion.4,8,9 The median time from ingestion to symptom onset is 18 hours.4,16 However, symptoms can be delayed up to 14 days.2 Progression is rapid; secondary lesions such as bullae, ecchymoses, cellulitis, purpura, macular or maculopapular eruptions, pustules, vasculitis, urticaria, and erythema multiforme–like lesions appear on the extremities within 24 hours of symptom onset. 2,3,4,8,17 Hemorrhagic bullae are the most common cutaneous manifestation of sepsis.4 Lesions are extremely tender to palpation.3 Cutaneous lesions can progress to necrotic ulcers, necrotizing fasciitis, gangrene, necrotizing vasculitis, or myonecrosis.4,8 Evidence of petechiae may indicate progression to disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC). Elevated D-dimer and fibrin split products also may indicate DIC, and elevated creatine kinase may signify rhabdomyolysis.3 Unfortunately, septicemia has the worst outcomes of all V vulnificus presentations, with morality rates greater than 50% in the United States.1,2,4Vibrio vulnificus septicemia has a similar case-fatality rate to pathogens such as anthrax, Ebola virus disease, and the bubonic plague.5 Septicemia accounts for approximately 80% of the deaths associated with V vulnificus in the United States.8,9
Septicemia due to V vulnificus progresses to septic shock in two-thirds of cases.8 Septic shock presents with hypotension, mental status changes, and thrombocytopenia.2,8,17 Patients can become tachycardic, tachypneic, and hypoxic. Intubation may be required for resuscitation. In cases of septic shock secondary to V vulnificus infection, mortality rates reach 92%.3 Hypotension with a systolic blood pressure less than 90 mm Hg is a poor prognostic factor; patients presenting with hypotension secondary to V vulnificus infection have a fatality rate approaching 75% within 12 hours.2
Atypical Presentations
Rare atypical presentations of V vulnificus infection that have been reported in the literature include meningitis, corneal ulcers, epiglottitis, tonsillitis, spontaneous bacterial peritonitis, pneumonia, endometritis, septic arthritis, osteomyelitis, rhabdomyolysis endophthalmitis, and keratitis.2,4,6,13,18,19
Diagnosis
When diagnosing V vulnificus, providers need to obtain a thorough patient history, including any history of consumption or handling of raw seafood and recent water activities. Providers practicing in tropical climates or in warm summer months should keep V vulnificus in mind, as it is the ideal climate for the pathogen.9 Vital signs can range from unremarkable to fever, hypotension, tachycardia, and/or hypoxia. Skin examination may show exquisitely tender, erythematous skin with marked soft tissue edema, hemorrhagic bullae, ecchymoses, and/or necrosis. As physical examination findings can be nonspecific, wound cultures, blood cultures, and skin biopsies should be taken.
A wound culture and blood culture should be taken immediately if V vulnificus is suspected.8,11 A wound culture using discharge or fluid from necrotic or bullous lesions should be analyzed via gram stain.8,9 Gram stains of V vulnificus show short, slim, curved gram-negative rods under light microscopy.9,20 Special stains also can be done on cultures; V vulnificus is an oxidase-positive, lactose-positive, lysine-positive, salicin-positive, and arginine-negative organism. This knowledge can help differentiate V vulnificus from other gram-negative rods.13 Blood cultures will be positive in approximately 97% of patients with primary septicemia and 30% of patients with septicemia secondary to V vulnificus wound infections.3,9
Histologically, perilesional skin biopsies show epidermal necrosis with dermal and subcutaneous inflammation.12,17 There typically is an inflammatory infiltrate with neutrophilic abscesses and extensive tissue destruction in the subcutaneous tissue extending into the deep dermis.12,17 The superficial dermis is edematous but can lack the inflammatory infiltrate found in the subcutaneous tissue.17 Subepidermal bullae can form with numerous organisms within the fluid of the bullae. There also may be evidence of leukocytoclastic vasculitis with accompanying vessel wall necrosis. Fibrin clot formation and extravasated red blood cells may be visualized with few inflammatory cells but numerous organisms around the involved vessels.17
Management
Early diagnosis and treatment are vital.5,17 Cultures should be taken before aggressive treatment is started.3 Treatment is multifaceted; it requires antibiotics and wound care, except in cases of self-limited gastroenteritis.2,11 Aggressive debridement, fasciotomy, amputation, and supportive measures also may be necessary depending on the patient’s presentation.2,3,8,9 Establishing 2 peripheral intravenous lines is important in case rapid resuscitation becomes necessary.
Antibiotics
Primary cellulitis wound infections should be treated with doxycycline or a quinolone. If untreated, the wound can rapidly progress to necrotizing fasciitis.11 For necrotizing fasciitis and septicemia, broader-spectrum antibiotics are needed. For adults, ceftazidime plus doxycycline is the mainstay of antibiotic treatment for V vulnificus.2,9,11 For children, trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole plus an aminoglycoside is preferred (Table).2,11
Antibiotic treatment has become more difficult as resistance arises. Antibiotic resistance likely is due to extensive antibiotic use in health care along with the agriculture and aquaculture industries using prophylactic and therapeutic antibiotics that wash into or are directly added to marine waters, where V vulnificus resides. Thus, antibiotic treatment should be tailored to the resistance profile of V vulnificus in various regions; for example, ceftazidime has an intermediate resistance profile in the United States, so cefotaxime and ceftriaxone may be better options.2
Wound Care
Wound infections must be extensively irrigated.9,21 For mild wound infections, proper wound care and oral antibiotics are appropriate (Table).21 Mild wounds should be irrigated thoroughly and followed by wound coverage to prevent progression, secondary infection, and necrosis. The dressing of choice will depend on the presenting lesion and provider preference; nonadherent, occlusive, or wet-to-dry dressings often are the best choices.22 Nonadherent dressings, such as petrolatum-covered gauze, do not pull off the newly formed epithelium when removed, making them beneficial to the skin’s healing process. Another option is occlusive dressings, which maintain a moist environment to hasten healing. They also enhance the autodigestion of necrotic tissue, which can be beneficial for necrotizing V vulnificus infections. Wet-to-dry dressings also may be used; these typically are comprised of gauze soaked with water, an astringent, and an antimicrobial or antiseptic solution. These dressings help to treat acute inflammation and also remove any exudate from the wound.22
Soft tissue and necrotizing infections require debridement.2,8 Early debridement decreases mortality rates.2,8,9 Necrotizing fasciitis often requires serial debridement to clear all the dead tissue and reduce the bacterial burden.8,9 Debridement prevents contiguous spread and metastatic seeding of the bacteria; it is important to prevent spread to the blood vessels, as vasculitis can necrose vessels, preventing antibiotics from reaching the dead tissue.17 Providers also should monitor for compartment syndrome, which should be treated with fasciotomy to decrease mortality.9,23 Many physicians leave V vulnificus–infected wounds open in order to heal by secondary intention.9 Hyperbaric oxygen therapy may be helpful as an adjunct to aggressive antimicrobial treatment for wound healing.8
Supportive Measures
Supportive care for dehydration, sepsis, DIC, and septic shock may be necessary, depending on the patient’s course. Treatment for severe V vulnificus infection includes intravenous fluids, crystalloids, oxygen, and/or intubation. Furthermore, if DIC develops, fresh frozen plasma, cryoprecipitate, a packed red blood cell transfusion, and/or anticoagulation may be required for resuscitation.3
Timing
Time to treatment and fatality rate are directly proportional in V vulnificus infection; the greater the delay in treatment, the higher the fatality rate.2 A 24-hour delay in antibiotic treatment is associated with a 33% case-fatality rate, and a 72-hour delay is associated with a 100% case-fatality rate.9 Even with early, appropriate treatment, mortality rates remain high.4
Prevention
Prevention of V vulnificus infections is an important consideration, especially for patients with chronic liver disease, immunosuppression, and hemochromatosis. Public education about the risks of eating raw shellfish is important.4 Oysters need to be treated properly to prevent growth and survival of V vulnificus.2 The most reliable method for destroying the bacteria is cooking shellfish.8,13 Only 15% of high-risk patients in the United States are aware of the risks associated with raw oyster consumption.3 High-risk patients should avoid eating raw oysters and shellfish and should cook seafood thoroughly before consumption.2,8 They also should wear protective clothing (ie, gloves) and eye protection when handling seafood and protective footwear (ie, wading shoes) while in seawater.2,8,13 It also is important to avoid contact with brackish water if one has any open wounds and to cleanse properly after exposure to brackish water or shellfish.2,8,16 Because severe V vulnificus infections can lead to death, prevention should be strongly encouraged by providers.2
Conclusion
Vibrio vulnificus infection typically occurs due to consumption of contaminated seafood or exposure to contaminated seawater. It most frequently affects older male patients with chronic liver disease, immunosuppression, hemochromatosis, or diabetes mellitus. Vibrio vulnificus can cause a vast spectrum of diseases, including gastroenteritis, wound infections, necrotizing fasciitis, and sepsis. Septicemia is the most common presentation of V vulnificus infection and accounts for the most fatalities from the bacteria. Septicemia often presents with fever, chills, vomiting, diarrhea, and hemorrhagic bullae. Vibrio vulnificus also commonly causes necrotizing fasciitis, which initially presents as cellulitis and rapidly progresses to hemorrhagic bullae or necrosis with accompanying systemic symptoms. Prompt diagnosis and treatment are vital to prevent mortality.
Interestingly, regions impacted by V vulnificus are expanding because of global warming.5,7Vibrio vulnificus thrives in warm waters, and increasing water temperatures are enhancing V vulnificus growth and survival.1,9 As global warming continues, the incidence of V vulnificus infections may rise. In fact, the number of infections increased by 78% between 1996 and 2006 in the United States.5 This rise likely was due to a combination of factors, including an aging population with more comorbidities, improvements in diagnosis, and climate change. Thus, as the number of V vulnificus infections rises, so too must providers’ suspicion for the pathogen.
- Phillips KE, Satchell KJF. Vibrio vulnificus: from oyster colonist to human pathogen [published online January 5, 2017]. PLOS Pathog. doi:10.1371/journal.ppat.1006053
- Heng SP, Letchumanan V, Deng CY, et al. Vibrio vulnificus: an environmental and clinical burden. Front Microbiol. 2017;8:997.
- Kumamoto KS, Vukich DJ. Clinical infections of Vibrio vulnificus: a case report and review of the literature. J Emerg Med. 1998;16:61-66.
- Borenstein M, Kerdel F. Infections with Vibrio vulnificus. Dermatol Clin. 2003;21:245-248.
- Baker-Austin C, Oliver JD. Vibrio vulnificus: new insights into a deadly opportunistic pathogen. Environ Microbiol. 2018;20:423-430.
- Kim SJ, Kim BC, Kim DC, et al. A fatal case of Vibrio vulnificus meningoencephalitis. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2003;9:568-571.
- Jones MK, Oliver JD. Vibrio vulnificus: disease and pathogenesis. Infect Immun. 2009;77:1723-1733.
- Horseman MA, Surani S. A comprehensive review of Vibrio vulnificus infection: an important cause of severe sepsis and skin and soft-tissue infection. Int J Infect Dis. 2011;15:E157-E166.
- Diaz JH. Skin and soft tissue infections following marine injuries and exposures in travelers. J Travel Med. 2014;21:207-213.
- Kikawa K, Yamasaki K, Sukiura T, et al. A successfully treated case of Vibrio vulnificus septicemia with shock. Jpn J Med. 1990;29:313-319.
- Perkins AP, Trimmier M. Recreational waterborne illnesses: recognition, treatment, and prevention. Am Fam Physician. 2017;95:554-560.
- Patel VJ, Gardner E, Burton CS. Vibrio vulnificus septicemia and leg ulcer. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2002;46(5 suppl):S144-S145.
- Ulusarac O, Carter E. Varied clinical presentations of Vibrio vulnificus infections: a report of four unusual cases and review of the literature. South Med J. 2004;97:613-618.
- Bross MH, Soch K, Morales R, et al. Vibrio vulnificus infection: diagnosis and treatment. Am Fam Physician. 2007;76:539-544.
- Hori M, Nakayama A, Kitagawa D, et al. A case of Vibrio vulnificus infection complicated with fulminant purpura: gene and biotype analysis of the pathogen [published online May 19, 2017]. JMM Case Rep. doi:10.1099/jmmcr.0.005096
- Kotton Y, Soboh S, Bisharat N. Vibrio vulnificus necrotizing fasciitis associated with acupuncture. Infect Dis Rep. 2015;7:5901.
- Hoffman TJ, Nelson B, Darouiche R, et al. Vibrio vulnificus septicemia. Arch Intern Med. 1988;148:1825-1827.
- Alsaad AA, Sotello D, Kruse BT, et al. Vibrio vulnificus tonsillitis after swimming in the Gulf of Mexico [published online June 28, 2017]. BMJ Case Rep. doi:10.1136/bcr-2017-221161
- Tison DL, Kelly MT. Vibrio vulnificus endometritis. J Clin Microbiol. 1984;20:185-186.
- Beatty NL, Marquez J, Mohajer MA. Skin manifestations of primary Vibrio vulnificus septicemia. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2017;97:1-2.
- Foote A, Henderson R, Lindberg A, et al. The Australian mid-west coastal marine wound infections study. Aust Fam Physician. 2017;46:923-927.
- Marks JG Jr, Miller JJ. Lookingbill and Marks’ Principles of Dermatology. 6th ed. Elsevier; 2019.
- Kim CS, Bae EH, Ma SK, et al. Severe septicemia, necrotizing fasciitis, and peritonitis due to Vibrio vulnificus in a patient undergoing continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis: a case report. BMC Infect Dis. 2015;15:422.
Vibrio vulnificus is a member of the Vibrio genus. Most Vibrio species are nonpathogenic in humans; however, V vulnificus is one of the pathogenic strains.1 In Latin, the term vulnificus means “wounding,” and V vulnificus can cause life-threatening infections in patients. The mortality rate of V vulnificus infections is approximately 33% in the United States.2Vibrio vulnificus is a gram-negative bacterium that was first isolated by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention in 1964 and was given its current name in 1979.3-6 It has been found in numerous organisms, including oysters, crabs, clams, shrimp, mussels, mullets, and sea bass.4 The vast majority of infections in the United States are due to oyster exposure and consumption.2,7Vibrio vulnificus is responsible for more than 95% of seafood-related deaths in the United States and has the highest mortality rate of all food-borne illness in the United States.2,5 It also has the highest per-case economic impact of all food-related diseases in the United States.1
What distinguishes a pathogenic vs nonpathogenic Vibrio isolate remains unknown; Vibrio species rapidly undergo horizontal gene transfer, making DNA isolation difficult.1 Some characteristics of V vulnificus that may confer virulence are the capsular polysaccharide, lipopolysaccharide, binding proteins, and tissue-degrading enzymes.1,5 First, encapsulated strains are more virulent and invasive than unencapsulated strains.1 The mucopolysaccharide capsule protects the bacterium from the immune system, allowing it to evade immune surveillance, cause more severe infection, and invade into the subcutaneous tissue.3,5 Second, production of sialic acid–like molecules alter the lipopolysaccharide, allowing for motility and biofilm formation.1 This allows the bacterium to survive in marine waters and within the bloodstream, the latter leading to sepsis in humans. Third, production of N-acetylglucosamine–binding protein A allows for adhesion to chitin. Shellfish consume chitin, and chitin accumulates in shellfish. N-acetylglucosamine–binding protein A also binds mucin; this may be how V vulnificus binds to mucin in the gastrointestinal tract in humans, causing gastroenteritis.1 Binding to the human mucosae also may allow the bacteria to gain access to the blood supply, leading to septicemia.4 Finally, tissue-degrading enzymes such as proteases are responsible for necrotizing wound infections associated with V vulnificus, as the enzymes allow for invasion into the skin and subcutaneous tissues. Proteases also increase vascular permeability and lead to edema.3 Hence, these virulence factors may provide V vulnificus the pathogenicity to cause infection in humans.
Three biotypes of V vulnificus have been discovered. Biotype 1 is the most common and is found worldwide in brackish water.8 It can cause the entire spectrum of illnesses, and it has a case fatality rate of 50% in humans. Biotype 1 is presumably responsible for all infections in the United States. Biotype 2 is found in the Far East and Western Europe; it inhabits a unique niche—saltwater used for eel farming. It typically causes infection in eels, but rarely it can cause wound infections in humans. Biotype 3 is found in freshwater fish farming in Israel, and it is a hybrid of biotypes 1 and 2.It can cause severe soft tissue infections in humans, sometimes requiring amputation.8
Epidemiology
Vibrio vulnificus is a motile, gram-negative, halophilic, aquatic bacterium.1,4,5,8,9 It is part of the normal estuarine microbiome and typically is found in warm coastal waters.1,5,10 The ideal conditions for growth and survival of V vulnificus are water temperatures at 18 °C (64.4 °F) and water salinities between 15 to 25 parts per thousand.2,8,9 These conditions are found in tropical and subtropical regions.2Vibrio vulnificus is found all over the world, including Denmark, Italy, Japan, Australia, Brazil, and the United States,2 where most infections come from oyster exposure and consumption in the Gulf of Mexico.2,8,11 The incidence of infection in the United States is highest between April and October.8,11
Some populations are at a higher risk of infection. Risk factors include male sex, liver cirrhosis, hemochromatosis, end-stage renal disease, immunosuppression, and diabetes mellitus.1,8,11 Healthy patients with no risk factors account for less than 5% of US V vulnificus infections.8
Male Predilection
Men are 6 times more likely to be affected by V vulnificus than women.Some hypotheses for this discrepancy are that estrogen is protective againstV vulnificus and that women may be less likely to engage in risky water activities and seafood handling.5 Additionally, older males (aged >60 years) are most often affected,1,8 likely due to the association between increasing age with number of comorbidities, such as diabetes mellitus, heart disease, and chronic disease.8
Iron Levels
Iron appears to play an important role in V vulnificus infection. Iron is essential for bacterial growth, and the ability to obtain iron from a host increases the organism’s pathogenicity.3Vibrio vulnificus rapidly grows when transferrin saturation exceeds 70%.8 Additionally, iron overload decreases the inoculum needed to cause sepsis in animal studies, which could play a role in human pathogenesis.4 Iron levels are elevated in patients with hemochromatosis due to increased iron absorption, cirrhosis and chronic liver disease due to impaired iron metabolism, and end-stage renal disease, especially in patients receiving parenteral iron.8
Immunosuppression
Patients who are immunocompromised and those with chronic liver disease are at an increased risk of infection because of neutrophils having decreased phagocytic activity.4
Diabetes Mellitus
Patients with diabetes mellitus may have peripheral neuropathy and may be unaware of pre-existing wounds that serve as entry points for V vulnificus.12
Etiology
Vibrio vulnificus infects humans via seafood consumption and handling as well as exposure to contaminated water.2,5 With respect to seafood consumption, raw shellfish are the primary type of seafood that harbor high levels of V vulnificus.5 Oysters are the most common etiology, but consumption of crabs, clams, and shrimp also can lead to infection.5,7Vibrio vulnificus contamination does not change the appearance, taste, or odor of shellfish, making it hard to detect.8 An inoculate of 1 million bacteria typically is necessary for infection after consumption.5 Contaminated seawater is another primary cause of V vulnificus infection. When open wounds are exposed to seawater harboring the bacteria, wound infections can arise.7 Infections can be acquired when swimming, fishing, or participating in water sports. Wound infections also occur while handling contaminated seafood, such as oyster shucking.5 There is a short incubation period for V vulnificus infections; the onset of symptoms and clinical outcome typically occur within 24 hours.5
Clinical Presentation
Vibrio vulnificus infections can have numerous clinical presentations, including gastroenteritis, wound infections, necrotizing fasciitis, and sepsis.1,8 There also is a spectrum of clinical outcomes; for instance, gastroenteritis typically is self-limited, whereas necrotizing fasciitis or sepsis can be fatal.2
Gastroenteritis
Vibrio vulnificus gastroenteritis is due to ingestion of contaminated shellfish.2,9 Symptoms typically are mild to moderate and include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, fever, chills, abdominal pain, and cramping.2,4,8 Cases likely are underreported in the United States because gastroenteritis is self-limited, and many patients do not seek treatment.2,11
Wound Infections
Wound infections with V vulnificus have a cutaneous port of entry. Exposure to contaminated seawater or seafood can inoculate an open wound, leading to infection.7,8 Wound infections usually stem from 1 of 2 routes: (1) a pre-existing open wound gets infected while the patient is swimming in contaminated water, or (2) a traumatic injury occurs while the patient is handling contaminated shellfish, knives, or fishhooks. Many shellfish, such as oysters, have sharp points on their shells that can lacerate the skin.8 A wound on the hand can be contaminated by V vulnificus while handling contaminated seafood (eg, oyster shucking).13 Minor abrasions should not be dismissed; in fact, a small puncture or skin break often acts as the port of entry.9,11 Wound infections tend to arise within 7 days of exposure, though they can manifest up to 12 days after exposure.8 Wound infections can present as cellulitis, bullae, or ecchymoses.7 Lesions are exquisitely tender, and the skin is erythematous with marked surrounding soft tissue edema.3,4,8 Cellulitis typically arises first, with hemorrhagic bullae rapidly following.14 Lesions are limited to the affected extremity or area of inoculation.8 Systemic symptoms are rare, but fever and chills may accompany the infection.8,14 Unfortunately, lesions can become necrotic and progress rapidly to necrotizing fasciitis if left untreated.4,7,11 In these cases, secondary sepsis can occur.8
Necrotizing Fasciitis
Wound infections caused by V vulnificus can progress to necrotizing skin and soft tissue infections, such as necrotizing fasciitis and gangrene.5 Necrotizing fasciitis accounts for approximately one-third of V vulnificus infections.9 It usually stems from an open wound that is inoculated by contact with contaminated seafood or seawater.2,9 The wound infection begins as cellulitis with extreme tenderness, erythematous skin, and marked soft tissue edema, then rapidly progresses, becoming necrotic. These necrotic lesions present as black and purple eschars as the skin, blood supply, and subcutaneous tissues are infiltrated by the bacteria and destroyed. Lesions may have blistering or exudation. Many patients have accompanying systemic symptoms, including fever, chills, abdominal pain, diarrhea, hypotension, and sepsis.11,14 However, some patients may not present with systemic symptoms, so it is important to maintain a high index of suspicion even in the absence of these symptoms. The infection typically is limited to the affected extremity; necrotizing infections can lead to amputation and even death, depending on the extent of destruction and spread of the bacteria.11,13 The infection may spread beyond the inoculated extremity if the bacteria gains access to the bloodstream.8,9 In these cases, fulminant purpura or secondary septicemia can occur.8,15 Fatalityrates in the United States for necrotizing V vulnificus infections approach 30%.2 Necrotizing fasciitis accounts for approximately 8% of deaths associated with the pathogen in the United States.9
Interestingly, one reported case of necrotizing fasciitis associated with V vulnificus infection was triggered by acupuncture.16 The patient worked in a fish hatchery, where he was exposed to V vulnificus, and subsequent acupuncture led to the inoculation of bacteria into his bloodstream. This case raises the important point that we typically sequence the pathogenesis of V vulnificus infection as a patient having an open wound that is subsequently exposed to contaminated water; however, it also can follow the reverse sequence. Thus, proper cleansing of the skin after swimming in brackish water or handling shellfish is important to prevent V vulnificus infection.16 Additionally, dermatologists should be sure to cleanse patients’ skin thoroughly before performing procedures that could cause breaks in the skin.
Septicemia
Primary septicemia is the most common presentation of V vulnificus infection.2,8 Septicemia accounts for approximately 58% of V vulnificus infections in the United States.9 Infection typically occurs after ingestion of contaminated oysters, with subsequent absorption into the bloodstream through the ileum or cecum.2,8,9 Patients with chronic liver disease are 80 times more likely to develop primary sepsis than healthy individuals.8 Patients typically present with sudden-onset fever and chills, vomiting, diarrhea, and pain in the abdomen and/or extremities within hours to days of ingestion.4,8,9 The median time from ingestion to symptom onset is 18 hours.4,16 However, symptoms can be delayed up to 14 days.2 Progression is rapid; secondary lesions such as bullae, ecchymoses, cellulitis, purpura, macular or maculopapular eruptions, pustules, vasculitis, urticaria, and erythema multiforme–like lesions appear on the extremities within 24 hours of symptom onset. 2,3,4,8,17 Hemorrhagic bullae are the most common cutaneous manifestation of sepsis.4 Lesions are extremely tender to palpation.3 Cutaneous lesions can progress to necrotic ulcers, necrotizing fasciitis, gangrene, necrotizing vasculitis, or myonecrosis.4,8 Evidence of petechiae may indicate progression to disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC). Elevated D-dimer and fibrin split products also may indicate DIC, and elevated creatine kinase may signify rhabdomyolysis.3 Unfortunately, septicemia has the worst outcomes of all V vulnificus presentations, with morality rates greater than 50% in the United States.1,2,4Vibrio vulnificus septicemia has a similar case-fatality rate to pathogens such as anthrax, Ebola virus disease, and the bubonic plague.5 Septicemia accounts for approximately 80% of the deaths associated with V vulnificus in the United States.8,9
Septicemia due to V vulnificus progresses to septic shock in two-thirds of cases.8 Septic shock presents with hypotension, mental status changes, and thrombocytopenia.2,8,17 Patients can become tachycardic, tachypneic, and hypoxic. Intubation may be required for resuscitation. In cases of septic shock secondary to V vulnificus infection, mortality rates reach 92%.3 Hypotension with a systolic blood pressure less than 90 mm Hg is a poor prognostic factor; patients presenting with hypotension secondary to V vulnificus infection have a fatality rate approaching 75% within 12 hours.2
Atypical Presentations
Rare atypical presentations of V vulnificus infection that have been reported in the literature include meningitis, corneal ulcers, epiglottitis, tonsillitis, spontaneous bacterial peritonitis, pneumonia, endometritis, septic arthritis, osteomyelitis, rhabdomyolysis endophthalmitis, and keratitis.2,4,6,13,18,19
Diagnosis
When diagnosing V vulnificus, providers need to obtain a thorough patient history, including any history of consumption or handling of raw seafood and recent water activities. Providers practicing in tropical climates or in warm summer months should keep V vulnificus in mind, as it is the ideal climate for the pathogen.9 Vital signs can range from unremarkable to fever, hypotension, tachycardia, and/or hypoxia. Skin examination may show exquisitely tender, erythematous skin with marked soft tissue edema, hemorrhagic bullae, ecchymoses, and/or necrosis. As physical examination findings can be nonspecific, wound cultures, blood cultures, and skin biopsies should be taken.
A wound culture and blood culture should be taken immediately if V vulnificus is suspected.8,11 A wound culture using discharge or fluid from necrotic or bullous lesions should be analyzed via gram stain.8,9 Gram stains of V vulnificus show short, slim, curved gram-negative rods under light microscopy.9,20 Special stains also can be done on cultures; V vulnificus is an oxidase-positive, lactose-positive, lysine-positive, salicin-positive, and arginine-negative organism. This knowledge can help differentiate V vulnificus from other gram-negative rods.13 Blood cultures will be positive in approximately 97% of patients with primary septicemia and 30% of patients with septicemia secondary to V vulnificus wound infections.3,9
Histologically, perilesional skin biopsies show epidermal necrosis with dermal and subcutaneous inflammation.12,17 There typically is an inflammatory infiltrate with neutrophilic abscesses and extensive tissue destruction in the subcutaneous tissue extending into the deep dermis.12,17 The superficial dermis is edematous but can lack the inflammatory infiltrate found in the subcutaneous tissue.17 Subepidermal bullae can form with numerous organisms within the fluid of the bullae. There also may be evidence of leukocytoclastic vasculitis with accompanying vessel wall necrosis. Fibrin clot formation and extravasated red blood cells may be visualized with few inflammatory cells but numerous organisms around the involved vessels.17
Management
Early diagnosis and treatment are vital.5,17 Cultures should be taken before aggressive treatment is started.3 Treatment is multifaceted; it requires antibiotics and wound care, except in cases of self-limited gastroenteritis.2,11 Aggressive debridement, fasciotomy, amputation, and supportive measures also may be necessary depending on the patient’s presentation.2,3,8,9 Establishing 2 peripheral intravenous lines is important in case rapid resuscitation becomes necessary.
Antibiotics
Primary cellulitis wound infections should be treated with doxycycline or a quinolone. If untreated, the wound can rapidly progress to necrotizing fasciitis.11 For necrotizing fasciitis and septicemia, broader-spectrum antibiotics are needed. For adults, ceftazidime plus doxycycline is the mainstay of antibiotic treatment for V vulnificus.2,9,11 For children, trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole plus an aminoglycoside is preferred (Table).2,11
Antibiotic treatment has become more difficult as resistance arises. Antibiotic resistance likely is due to extensive antibiotic use in health care along with the agriculture and aquaculture industries using prophylactic and therapeutic antibiotics that wash into or are directly added to marine waters, where V vulnificus resides. Thus, antibiotic treatment should be tailored to the resistance profile of V vulnificus in various regions; for example, ceftazidime has an intermediate resistance profile in the United States, so cefotaxime and ceftriaxone may be better options.2
Wound Care
Wound infections must be extensively irrigated.9,21 For mild wound infections, proper wound care and oral antibiotics are appropriate (Table).21 Mild wounds should be irrigated thoroughly and followed by wound coverage to prevent progression, secondary infection, and necrosis. The dressing of choice will depend on the presenting lesion and provider preference; nonadherent, occlusive, or wet-to-dry dressings often are the best choices.22 Nonadherent dressings, such as petrolatum-covered gauze, do not pull off the newly formed epithelium when removed, making them beneficial to the skin’s healing process. Another option is occlusive dressings, which maintain a moist environment to hasten healing. They also enhance the autodigestion of necrotic tissue, which can be beneficial for necrotizing V vulnificus infections. Wet-to-dry dressings also may be used; these typically are comprised of gauze soaked with water, an astringent, and an antimicrobial or antiseptic solution. These dressings help to treat acute inflammation and also remove any exudate from the wound.22
Soft tissue and necrotizing infections require debridement.2,8 Early debridement decreases mortality rates.2,8,9 Necrotizing fasciitis often requires serial debridement to clear all the dead tissue and reduce the bacterial burden.8,9 Debridement prevents contiguous spread and metastatic seeding of the bacteria; it is important to prevent spread to the blood vessels, as vasculitis can necrose vessels, preventing antibiotics from reaching the dead tissue.17 Providers also should monitor for compartment syndrome, which should be treated with fasciotomy to decrease mortality.9,23 Many physicians leave V vulnificus–infected wounds open in order to heal by secondary intention.9 Hyperbaric oxygen therapy may be helpful as an adjunct to aggressive antimicrobial treatment for wound healing.8
Supportive Measures
Supportive care for dehydration, sepsis, DIC, and septic shock may be necessary, depending on the patient’s course. Treatment for severe V vulnificus infection includes intravenous fluids, crystalloids, oxygen, and/or intubation. Furthermore, if DIC develops, fresh frozen plasma, cryoprecipitate, a packed red blood cell transfusion, and/or anticoagulation may be required for resuscitation.3
Timing
Time to treatment and fatality rate are directly proportional in V vulnificus infection; the greater the delay in treatment, the higher the fatality rate.2 A 24-hour delay in antibiotic treatment is associated with a 33% case-fatality rate, and a 72-hour delay is associated with a 100% case-fatality rate.9 Even with early, appropriate treatment, mortality rates remain high.4
Prevention
Prevention of V vulnificus infections is an important consideration, especially for patients with chronic liver disease, immunosuppression, and hemochromatosis. Public education about the risks of eating raw shellfish is important.4 Oysters need to be treated properly to prevent growth and survival of V vulnificus.2 The most reliable method for destroying the bacteria is cooking shellfish.8,13 Only 15% of high-risk patients in the United States are aware of the risks associated with raw oyster consumption.3 High-risk patients should avoid eating raw oysters and shellfish and should cook seafood thoroughly before consumption.2,8 They also should wear protective clothing (ie, gloves) and eye protection when handling seafood and protective footwear (ie, wading shoes) while in seawater.2,8,13 It also is important to avoid contact with brackish water if one has any open wounds and to cleanse properly after exposure to brackish water or shellfish.2,8,16 Because severe V vulnificus infections can lead to death, prevention should be strongly encouraged by providers.2
Conclusion
Vibrio vulnificus infection typically occurs due to consumption of contaminated seafood or exposure to contaminated seawater. It most frequently affects older male patients with chronic liver disease, immunosuppression, hemochromatosis, or diabetes mellitus. Vibrio vulnificus can cause a vast spectrum of diseases, including gastroenteritis, wound infections, necrotizing fasciitis, and sepsis. Septicemia is the most common presentation of V vulnificus infection and accounts for the most fatalities from the bacteria. Septicemia often presents with fever, chills, vomiting, diarrhea, and hemorrhagic bullae. Vibrio vulnificus also commonly causes necrotizing fasciitis, which initially presents as cellulitis and rapidly progresses to hemorrhagic bullae or necrosis with accompanying systemic symptoms. Prompt diagnosis and treatment are vital to prevent mortality.
Interestingly, regions impacted by V vulnificus are expanding because of global warming.5,7Vibrio vulnificus thrives in warm waters, and increasing water temperatures are enhancing V vulnificus growth and survival.1,9 As global warming continues, the incidence of V vulnificus infections may rise. In fact, the number of infections increased by 78% between 1996 and 2006 in the United States.5 This rise likely was due to a combination of factors, including an aging population with more comorbidities, improvements in diagnosis, and climate change. Thus, as the number of V vulnificus infections rises, so too must providers’ suspicion for the pathogen.
Vibrio vulnificus is a member of the Vibrio genus. Most Vibrio species are nonpathogenic in humans; however, V vulnificus is one of the pathogenic strains.1 In Latin, the term vulnificus means “wounding,” and V vulnificus can cause life-threatening infections in patients. The mortality rate of V vulnificus infections is approximately 33% in the United States.2Vibrio vulnificus is a gram-negative bacterium that was first isolated by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention in 1964 and was given its current name in 1979.3-6 It has been found in numerous organisms, including oysters, crabs, clams, shrimp, mussels, mullets, and sea bass.4 The vast majority of infections in the United States are due to oyster exposure and consumption.2,7Vibrio vulnificus is responsible for more than 95% of seafood-related deaths in the United States and has the highest mortality rate of all food-borne illness in the United States.2,5 It also has the highest per-case economic impact of all food-related diseases in the United States.1
What distinguishes a pathogenic vs nonpathogenic Vibrio isolate remains unknown; Vibrio species rapidly undergo horizontal gene transfer, making DNA isolation difficult.1 Some characteristics of V vulnificus that may confer virulence are the capsular polysaccharide, lipopolysaccharide, binding proteins, and tissue-degrading enzymes.1,5 First, encapsulated strains are more virulent and invasive than unencapsulated strains.1 The mucopolysaccharide capsule protects the bacterium from the immune system, allowing it to evade immune surveillance, cause more severe infection, and invade into the subcutaneous tissue.3,5 Second, production of sialic acid–like molecules alter the lipopolysaccharide, allowing for motility and biofilm formation.1 This allows the bacterium to survive in marine waters and within the bloodstream, the latter leading to sepsis in humans. Third, production of N-acetylglucosamine–binding protein A allows for adhesion to chitin. Shellfish consume chitin, and chitin accumulates in shellfish. N-acetylglucosamine–binding protein A also binds mucin; this may be how V vulnificus binds to mucin in the gastrointestinal tract in humans, causing gastroenteritis.1 Binding to the human mucosae also may allow the bacteria to gain access to the blood supply, leading to septicemia.4 Finally, tissue-degrading enzymes such as proteases are responsible for necrotizing wound infections associated with V vulnificus, as the enzymes allow for invasion into the skin and subcutaneous tissues. Proteases also increase vascular permeability and lead to edema.3 Hence, these virulence factors may provide V vulnificus the pathogenicity to cause infection in humans.
Three biotypes of V vulnificus have been discovered. Biotype 1 is the most common and is found worldwide in brackish water.8 It can cause the entire spectrum of illnesses, and it has a case fatality rate of 50% in humans. Biotype 1 is presumably responsible for all infections in the United States. Biotype 2 is found in the Far East and Western Europe; it inhabits a unique niche—saltwater used for eel farming. It typically causes infection in eels, but rarely it can cause wound infections in humans. Biotype 3 is found in freshwater fish farming in Israel, and it is a hybrid of biotypes 1 and 2.It can cause severe soft tissue infections in humans, sometimes requiring amputation.8
Epidemiology
Vibrio vulnificus is a motile, gram-negative, halophilic, aquatic bacterium.1,4,5,8,9 It is part of the normal estuarine microbiome and typically is found in warm coastal waters.1,5,10 The ideal conditions for growth and survival of V vulnificus are water temperatures at 18 °C (64.4 °F) and water salinities between 15 to 25 parts per thousand.2,8,9 These conditions are found in tropical and subtropical regions.2Vibrio vulnificus is found all over the world, including Denmark, Italy, Japan, Australia, Brazil, and the United States,2 where most infections come from oyster exposure and consumption in the Gulf of Mexico.2,8,11 The incidence of infection in the United States is highest between April and October.8,11
Some populations are at a higher risk of infection. Risk factors include male sex, liver cirrhosis, hemochromatosis, end-stage renal disease, immunosuppression, and diabetes mellitus.1,8,11 Healthy patients with no risk factors account for less than 5% of US V vulnificus infections.8
Male Predilection
Men are 6 times more likely to be affected by V vulnificus than women.Some hypotheses for this discrepancy are that estrogen is protective againstV vulnificus and that women may be less likely to engage in risky water activities and seafood handling.5 Additionally, older males (aged >60 years) are most often affected,1,8 likely due to the association between increasing age with number of comorbidities, such as diabetes mellitus, heart disease, and chronic disease.8
Iron Levels
Iron appears to play an important role in V vulnificus infection. Iron is essential for bacterial growth, and the ability to obtain iron from a host increases the organism’s pathogenicity.3Vibrio vulnificus rapidly grows when transferrin saturation exceeds 70%.8 Additionally, iron overload decreases the inoculum needed to cause sepsis in animal studies, which could play a role in human pathogenesis.4 Iron levels are elevated in patients with hemochromatosis due to increased iron absorption, cirrhosis and chronic liver disease due to impaired iron metabolism, and end-stage renal disease, especially in patients receiving parenteral iron.8
Immunosuppression
Patients who are immunocompromised and those with chronic liver disease are at an increased risk of infection because of neutrophils having decreased phagocytic activity.4
Diabetes Mellitus
Patients with diabetes mellitus may have peripheral neuropathy and may be unaware of pre-existing wounds that serve as entry points for V vulnificus.12
Etiology
Vibrio vulnificus infects humans via seafood consumption and handling as well as exposure to contaminated water.2,5 With respect to seafood consumption, raw shellfish are the primary type of seafood that harbor high levels of V vulnificus.5 Oysters are the most common etiology, but consumption of crabs, clams, and shrimp also can lead to infection.5,7Vibrio vulnificus contamination does not change the appearance, taste, or odor of shellfish, making it hard to detect.8 An inoculate of 1 million bacteria typically is necessary for infection after consumption.5 Contaminated seawater is another primary cause of V vulnificus infection. When open wounds are exposed to seawater harboring the bacteria, wound infections can arise.7 Infections can be acquired when swimming, fishing, or participating in water sports. Wound infections also occur while handling contaminated seafood, such as oyster shucking.5 There is a short incubation period for V vulnificus infections; the onset of symptoms and clinical outcome typically occur within 24 hours.5
Clinical Presentation
Vibrio vulnificus infections can have numerous clinical presentations, including gastroenteritis, wound infections, necrotizing fasciitis, and sepsis.1,8 There also is a spectrum of clinical outcomes; for instance, gastroenteritis typically is self-limited, whereas necrotizing fasciitis or sepsis can be fatal.2
Gastroenteritis
Vibrio vulnificus gastroenteritis is due to ingestion of contaminated shellfish.2,9 Symptoms typically are mild to moderate and include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, fever, chills, abdominal pain, and cramping.2,4,8 Cases likely are underreported in the United States because gastroenteritis is self-limited, and many patients do not seek treatment.2,11
Wound Infections
Wound infections with V vulnificus have a cutaneous port of entry. Exposure to contaminated seawater or seafood can inoculate an open wound, leading to infection.7,8 Wound infections usually stem from 1 of 2 routes: (1) a pre-existing open wound gets infected while the patient is swimming in contaminated water, or (2) a traumatic injury occurs while the patient is handling contaminated shellfish, knives, or fishhooks. Many shellfish, such as oysters, have sharp points on their shells that can lacerate the skin.8 A wound on the hand can be contaminated by V vulnificus while handling contaminated seafood (eg, oyster shucking).13 Minor abrasions should not be dismissed; in fact, a small puncture or skin break often acts as the port of entry.9,11 Wound infections tend to arise within 7 days of exposure, though they can manifest up to 12 days after exposure.8 Wound infections can present as cellulitis, bullae, or ecchymoses.7 Lesions are exquisitely tender, and the skin is erythematous with marked surrounding soft tissue edema.3,4,8 Cellulitis typically arises first, with hemorrhagic bullae rapidly following.14 Lesions are limited to the affected extremity or area of inoculation.8 Systemic symptoms are rare, but fever and chills may accompany the infection.8,14 Unfortunately, lesions can become necrotic and progress rapidly to necrotizing fasciitis if left untreated.4,7,11 In these cases, secondary sepsis can occur.8
Necrotizing Fasciitis
Wound infections caused by V vulnificus can progress to necrotizing skin and soft tissue infections, such as necrotizing fasciitis and gangrene.5 Necrotizing fasciitis accounts for approximately one-third of V vulnificus infections.9 It usually stems from an open wound that is inoculated by contact with contaminated seafood or seawater.2,9 The wound infection begins as cellulitis with extreme tenderness, erythematous skin, and marked soft tissue edema, then rapidly progresses, becoming necrotic. These necrotic lesions present as black and purple eschars as the skin, blood supply, and subcutaneous tissues are infiltrated by the bacteria and destroyed. Lesions may have blistering or exudation. Many patients have accompanying systemic symptoms, including fever, chills, abdominal pain, diarrhea, hypotension, and sepsis.11,14 However, some patients may not present with systemic symptoms, so it is important to maintain a high index of suspicion even in the absence of these symptoms. The infection typically is limited to the affected extremity; necrotizing infections can lead to amputation and even death, depending on the extent of destruction and spread of the bacteria.11,13 The infection may spread beyond the inoculated extremity if the bacteria gains access to the bloodstream.8,9 In these cases, fulminant purpura or secondary septicemia can occur.8,15 Fatalityrates in the United States for necrotizing V vulnificus infections approach 30%.2 Necrotizing fasciitis accounts for approximately 8% of deaths associated with the pathogen in the United States.9
Interestingly, one reported case of necrotizing fasciitis associated with V vulnificus infection was triggered by acupuncture.16 The patient worked in a fish hatchery, where he was exposed to V vulnificus, and subsequent acupuncture led to the inoculation of bacteria into his bloodstream. This case raises the important point that we typically sequence the pathogenesis of V vulnificus infection as a patient having an open wound that is subsequently exposed to contaminated water; however, it also can follow the reverse sequence. Thus, proper cleansing of the skin after swimming in brackish water or handling shellfish is important to prevent V vulnificus infection.16 Additionally, dermatologists should be sure to cleanse patients’ skin thoroughly before performing procedures that could cause breaks in the skin.
Septicemia
Primary septicemia is the most common presentation of V vulnificus infection.2,8 Septicemia accounts for approximately 58% of V vulnificus infections in the United States.9 Infection typically occurs after ingestion of contaminated oysters, with subsequent absorption into the bloodstream through the ileum or cecum.2,8,9 Patients with chronic liver disease are 80 times more likely to develop primary sepsis than healthy individuals.8 Patients typically present with sudden-onset fever and chills, vomiting, diarrhea, and pain in the abdomen and/or extremities within hours to days of ingestion.4,8,9 The median time from ingestion to symptom onset is 18 hours.4,16 However, symptoms can be delayed up to 14 days.2 Progression is rapid; secondary lesions such as bullae, ecchymoses, cellulitis, purpura, macular or maculopapular eruptions, pustules, vasculitis, urticaria, and erythema multiforme–like lesions appear on the extremities within 24 hours of symptom onset. 2,3,4,8,17 Hemorrhagic bullae are the most common cutaneous manifestation of sepsis.4 Lesions are extremely tender to palpation.3 Cutaneous lesions can progress to necrotic ulcers, necrotizing fasciitis, gangrene, necrotizing vasculitis, or myonecrosis.4,8 Evidence of petechiae may indicate progression to disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC). Elevated D-dimer and fibrin split products also may indicate DIC, and elevated creatine kinase may signify rhabdomyolysis.3 Unfortunately, septicemia has the worst outcomes of all V vulnificus presentations, with morality rates greater than 50% in the United States.1,2,4Vibrio vulnificus septicemia has a similar case-fatality rate to pathogens such as anthrax, Ebola virus disease, and the bubonic plague.5 Septicemia accounts for approximately 80% of the deaths associated with V vulnificus in the United States.8,9
Septicemia due to V vulnificus progresses to septic shock in two-thirds of cases.8 Septic shock presents with hypotension, mental status changes, and thrombocytopenia.2,8,17 Patients can become tachycardic, tachypneic, and hypoxic. Intubation may be required for resuscitation. In cases of septic shock secondary to V vulnificus infection, mortality rates reach 92%.3 Hypotension with a systolic blood pressure less than 90 mm Hg is a poor prognostic factor; patients presenting with hypotension secondary to V vulnificus infection have a fatality rate approaching 75% within 12 hours.2
Atypical Presentations
Rare atypical presentations of V vulnificus infection that have been reported in the literature include meningitis, corneal ulcers, epiglottitis, tonsillitis, spontaneous bacterial peritonitis, pneumonia, endometritis, septic arthritis, osteomyelitis, rhabdomyolysis endophthalmitis, and keratitis.2,4,6,13,18,19
Diagnosis
When diagnosing V vulnificus, providers need to obtain a thorough patient history, including any history of consumption or handling of raw seafood and recent water activities. Providers practicing in tropical climates or in warm summer months should keep V vulnificus in mind, as it is the ideal climate for the pathogen.9 Vital signs can range from unremarkable to fever, hypotension, tachycardia, and/or hypoxia. Skin examination may show exquisitely tender, erythematous skin with marked soft tissue edema, hemorrhagic bullae, ecchymoses, and/or necrosis. As physical examination findings can be nonspecific, wound cultures, blood cultures, and skin biopsies should be taken.
A wound culture and blood culture should be taken immediately if V vulnificus is suspected.8,11 A wound culture using discharge or fluid from necrotic or bullous lesions should be analyzed via gram stain.8,9 Gram stains of V vulnificus show short, slim, curved gram-negative rods under light microscopy.9,20 Special stains also can be done on cultures; V vulnificus is an oxidase-positive, lactose-positive, lysine-positive, salicin-positive, and arginine-negative organism. This knowledge can help differentiate V vulnificus from other gram-negative rods.13 Blood cultures will be positive in approximately 97% of patients with primary septicemia and 30% of patients with septicemia secondary to V vulnificus wound infections.3,9
Histologically, perilesional skin biopsies show epidermal necrosis with dermal and subcutaneous inflammation.12,17 There typically is an inflammatory infiltrate with neutrophilic abscesses and extensive tissue destruction in the subcutaneous tissue extending into the deep dermis.12,17 The superficial dermis is edematous but can lack the inflammatory infiltrate found in the subcutaneous tissue.17 Subepidermal bullae can form with numerous organisms within the fluid of the bullae. There also may be evidence of leukocytoclastic vasculitis with accompanying vessel wall necrosis. Fibrin clot formation and extravasated red blood cells may be visualized with few inflammatory cells but numerous organisms around the involved vessels.17
Management
Early diagnosis and treatment are vital.5,17 Cultures should be taken before aggressive treatment is started.3 Treatment is multifaceted; it requires antibiotics and wound care, except in cases of self-limited gastroenteritis.2,11 Aggressive debridement, fasciotomy, amputation, and supportive measures also may be necessary depending on the patient’s presentation.2,3,8,9 Establishing 2 peripheral intravenous lines is important in case rapid resuscitation becomes necessary.
Antibiotics
Primary cellulitis wound infections should be treated with doxycycline or a quinolone. If untreated, the wound can rapidly progress to necrotizing fasciitis.11 For necrotizing fasciitis and septicemia, broader-spectrum antibiotics are needed. For adults, ceftazidime plus doxycycline is the mainstay of antibiotic treatment for V vulnificus.2,9,11 For children, trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole plus an aminoglycoside is preferred (Table).2,11
Antibiotic treatment has become more difficult as resistance arises. Antibiotic resistance likely is due to extensive antibiotic use in health care along with the agriculture and aquaculture industries using prophylactic and therapeutic antibiotics that wash into or are directly added to marine waters, where V vulnificus resides. Thus, antibiotic treatment should be tailored to the resistance profile of V vulnificus in various regions; for example, ceftazidime has an intermediate resistance profile in the United States, so cefotaxime and ceftriaxone may be better options.2
Wound Care
Wound infections must be extensively irrigated.9,21 For mild wound infections, proper wound care and oral antibiotics are appropriate (Table).21 Mild wounds should be irrigated thoroughly and followed by wound coverage to prevent progression, secondary infection, and necrosis. The dressing of choice will depend on the presenting lesion and provider preference; nonadherent, occlusive, or wet-to-dry dressings often are the best choices.22 Nonadherent dressings, such as petrolatum-covered gauze, do not pull off the newly formed epithelium when removed, making them beneficial to the skin’s healing process. Another option is occlusive dressings, which maintain a moist environment to hasten healing. They also enhance the autodigestion of necrotic tissue, which can be beneficial for necrotizing V vulnificus infections. Wet-to-dry dressings also may be used; these typically are comprised of gauze soaked with water, an astringent, and an antimicrobial or antiseptic solution. These dressings help to treat acute inflammation and also remove any exudate from the wound.22
Soft tissue and necrotizing infections require debridement.2,8 Early debridement decreases mortality rates.2,8,9 Necrotizing fasciitis often requires serial debridement to clear all the dead tissue and reduce the bacterial burden.8,9 Debridement prevents contiguous spread and metastatic seeding of the bacteria; it is important to prevent spread to the blood vessels, as vasculitis can necrose vessels, preventing antibiotics from reaching the dead tissue.17 Providers also should monitor for compartment syndrome, which should be treated with fasciotomy to decrease mortality.9,23 Many physicians leave V vulnificus–infected wounds open in order to heal by secondary intention.9 Hyperbaric oxygen therapy may be helpful as an adjunct to aggressive antimicrobial treatment for wound healing.8
Supportive Measures
Supportive care for dehydration, sepsis, DIC, and septic shock may be necessary, depending on the patient’s course. Treatment for severe V vulnificus infection includes intravenous fluids, crystalloids, oxygen, and/or intubation. Furthermore, if DIC develops, fresh frozen plasma, cryoprecipitate, a packed red blood cell transfusion, and/or anticoagulation may be required for resuscitation.3
Timing
Time to treatment and fatality rate are directly proportional in V vulnificus infection; the greater the delay in treatment, the higher the fatality rate.2 A 24-hour delay in antibiotic treatment is associated with a 33% case-fatality rate, and a 72-hour delay is associated with a 100% case-fatality rate.9 Even with early, appropriate treatment, mortality rates remain high.4
Prevention
Prevention of V vulnificus infections is an important consideration, especially for patients with chronic liver disease, immunosuppression, and hemochromatosis. Public education about the risks of eating raw shellfish is important.4 Oysters need to be treated properly to prevent growth and survival of V vulnificus.2 The most reliable method for destroying the bacteria is cooking shellfish.8,13 Only 15% of high-risk patients in the United States are aware of the risks associated with raw oyster consumption.3 High-risk patients should avoid eating raw oysters and shellfish and should cook seafood thoroughly before consumption.2,8 They also should wear protective clothing (ie, gloves) and eye protection when handling seafood and protective footwear (ie, wading shoes) while in seawater.2,8,13 It also is important to avoid contact with brackish water if one has any open wounds and to cleanse properly after exposure to brackish water or shellfish.2,8,16 Because severe V vulnificus infections can lead to death, prevention should be strongly encouraged by providers.2
Conclusion
Vibrio vulnificus infection typically occurs due to consumption of contaminated seafood or exposure to contaminated seawater. It most frequently affects older male patients with chronic liver disease, immunosuppression, hemochromatosis, or diabetes mellitus. Vibrio vulnificus can cause a vast spectrum of diseases, including gastroenteritis, wound infections, necrotizing fasciitis, and sepsis. Septicemia is the most common presentation of V vulnificus infection and accounts for the most fatalities from the bacteria. Septicemia often presents with fever, chills, vomiting, diarrhea, and hemorrhagic bullae. Vibrio vulnificus also commonly causes necrotizing fasciitis, which initially presents as cellulitis and rapidly progresses to hemorrhagic bullae or necrosis with accompanying systemic symptoms. Prompt diagnosis and treatment are vital to prevent mortality.
Interestingly, regions impacted by V vulnificus are expanding because of global warming.5,7Vibrio vulnificus thrives in warm waters, and increasing water temperatures are enhancing V vulnificus growth and survival.1,9 As global warming continues, the incidence of V vulnificus infections may rise. In fact, the number of infections increased by 78% between 1996 and 2006 in the United States.5 This rise likely was due to a combination of factors, including an aging population with more comorbidities, improvements in diagnosis, and climate change. Thus, as the number of V vulnificus infections rises, so too must providers’ suspicion for the pathogen.
- Phillips KE, Satchell KJF. Vibrio vulnificus: from oyster colonist to human pathogen [published online January 5, 2017]. PLOS Pathog. doi:10.1371/journal.ppat.1006053
- Heng SP, Letchumanan V, Deng CY, et al. Vibrio vulnificus: an environmental and clinical burden. Front Microbiol. 2017;8:997.
- Kumamoto KS, Vukich DJ. Clinical infections of Vibrio vulnificus: a case report and review of the literature. J Emerg Med. 1998;16:61-66.
- Borenstein M, Kerdel F. Infections with Vibrio vulnificus. Dermatol Clin. 2003;21:245-248.
- Baker-Austin C, Oliver JD. Vibrio vulnificus: new insights into a deadly opportunistic pathogen. Environ Microbiol. 2018;20:423-430.
- Kim SJ, Kim BC, Kim DC, et al. A fatal case of Vibrio vulnificus meningoencephalitis. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2003;9:568-571.
- Jones MK, Oliver JD. Vibrio vulnificus: disease and pathogenesis. Infect Immun. 2009;77:1723-1733.
- Horseman MA, Surani S. A comprehensive review of Vibrio vulnificus infection: an important cause of severe sepsis and skin and soft-tissue infection. Int J Infect Dis. 2011;15:E157-E166.
- Diaz JH. Skin and soft tissue infections following marine injuries and exposures in travelers. J Travel Med. 2014;21:207-213.
- Kikawa K, Yamasaki K, Sukiura T, et al. A successfully treated case of Vibrio vulnificus septicemia with shock. Jpn J Med. 1990;29:313-319.
- Perkins AP, Trimmier M. Recreational waterborne illnesses: recognition, treatment, and prevention. Am Fam Physician. 2017;95:554-560.
- Patel VJ, Gardner E, Burton CS. Vibrio vulnificus septicemia and leg ulcer. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2002;46(5 suppl):S144-S145.
- Ulusarac O, Carter E. Varied clinical presentations of Vibrio vulnificus infections: a report of four unusual cases and review of the literature. South Med J. 2004;97:613-618.
- Bross MH, Soch K, Morales R, et al. Vibrio vulnificus infection: diagnosis and treatment. Am Fam Physician. 2007;76:539-544.
- Hori M, Nakayama A, Kitagawa D, et al. A case of Vibrio vulnificus infection complicated with fulminant purpura: gene and biotype analysis of the pathogen [published online May 19, 2017]. JMM Case Rep. doi:10.1099/jmmcr.0.005096
- Kotton Y, Soboh S, Bisharat N. Vibrio vulnificus necrotizing fasciitis associated with acupuncture. Infect Dis Rep. 2015;7:5901.
- Hoffman TJ, Nelson B, Darouiche R, et al. Vibrio vulnificus septicemia. Arch Intern Med. 1988;148:1825-1827.
- Alsaad AA, Sotello D, Kruse BT, et al. Vibrio vulnificus tonsillitis after swimming in the Gulf of Mexico [published online June 28, 2017]. BMJ Case Rep. doi:10.1136/bcr-2017-221161
- Tison DL, Kelly MT. Vibrio vulnificus endometritis. J Clin Microbiol. 1984;20:185-186.
- Beatty NL, Marquez J, Mohajer MA. Skin manifestations of primary Vibrio vulnificus septicemia. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2017;97:1-2.
- Foote A, Henderson R, Lindberg A, et al. The Australian mid-west coastal marine wound infections study. Aust Fam Physician. 2017;46:923-927.
- Marks JG Jr, Miller JJ. Lookingbill and Marks’ Principles of Dermatology. 6th ed. Elsevier; 2019.
- Kim CS, Bae EH, Ma SK, et al. Severe septicemia, necrotizing fasciitis, and peritonitis due to Vibrio vulnificus in a patient undergoing continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis: a case report. BMC Infect Dis. 2015;15:422.
- Phillips KE, Satchell KJF. Vibrio vulnificus: from oyster colonist to human pathogen [published online January 5, 2017]. PLOS Pathog. doi:10.1371/journal.ppat.1006053
- Heng SP, Letchumanan V, Deng CY, et al. Vibrio vulnificus: an environmental and clinical burden. Front Microbiol. 2017;8:997.
- Kumamoto KS, Vukich DJ. Clinical infections of Vibrio vulnificus: a case report and review of the literature. J Emerg Med. 1998;16:61-66.
- Borenstein M, Kerdel F. Infections with Vibrio vulnificus. Dermatol Clin. 2003;21:245-248.
- Baker-Austin C, Oliver JD. Vibrio vulnificus: new insights into a deadly opportunistic pathogen. Environ Microbiol. 2018;20:423-430.
- Kim SJ, Kim BC, Kim DC, et al. A fatal case of Vibrio vulnificus meningoencephalitis. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2003;9:568-571.
- Jones MK, Oliver JD. Vibrio vulnificus: disease and pathogenesis. Infect Immun. 2009;77:1723-1733.
- Horseman MA, Surani S. A comprehensive review of Vibrio vulnificus infection: an important cause of severe sepsis and skin and soft-tissue infection. Int J Infect Dis. 2011;15:E157-E166.
- Diaz JH. Skin and soft tissue infections following marine injuries and exposures in travelers. J Travel Med. 2014;21:207-213.
- Kikawa K, Yamasaki K, Sukiura T, et al. A successfully treated case of Vibrio vulnificus septicemia with shock. Jpn J Med. 1990;29:313-319.
- Perkins AP, Trimmier M. Recreational waterborne illnesses: recognition, treatment, and prevention. Am Fam Physician. 2017;95:554-560.
- Patel VJ, Gardner E, Burton CS. Vibrio vulnificus septicemia and leg ulcer. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2002;46(5 suppl):S144-S145.
- Ulusarac O, Carter E. Varied clinical presentations of Vibrio vulnificus infections: a report of four unusual cases and review of the literature. South Med J. 2004;97:613-618.
- Bross MH, Soch K, Morales R, et al. Vibrio vulnificus infection: diagnosis and treatment. Am Fam Physician. 2007;76:539-544.
- Hori M, Nakayama A, Kitagawa D, et al. A case of Vibrio vulnificus infection complicated with fulminant purpura: gene and biotype analysis of the pathogen [published online May 19, 2017]. JMM Case Rep. doi:10.1099/jmmcr.0.005096
- Kotton Y, Soboh S, Bisharat N. Vibrio vulnificus necrotizing fasciitis associated with acupuncture. Infect Dis Rep. 2015;7:5901.
- Hoffman TJ, Nelson B, Darouiche R, et al. Vibrio vulnificus septicemia. Arch Intern Med. 1988;148:1825-1827.
- Alsaad AA, Sotello D, Kruse BT, et al. Vibrio vulnificus tonsillitis after swimming in the Gulf of Mexico [published online June 28, 2017]. BMJ Case Rep. doi:10.1136/bcr-2017-221161
- Tison DL, Kelly MT. Vibrio vulnificus endometritis. J Clin Microbiol. 1984;20:185-186.
- Beatty NL, Marquez J, Mohajer MA. Skin manifestations of primary Vibrio vulnificus septicemia. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2017;97:1-2.
- Foote A, Henderson R, Lindberg A, et al. The Australian mid-west coastal marine wound infections study. Aust Fam Physician. 2017;46:923-927.
- Marks JG Jr, Miller JJ. Lookingbill and Marks’ Principles of Dermatology. 6th ed. Elsevier; 2019.
- Kim CS, Bae EH, Ma SK, et al. Severe septicemia, necrotizing fasciitis, and peritonitis due to Vibrio vulnificus in a patient undergoing continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis: a case report. BMC Infect Dis. 2015;15:422.
Practice Points
- Vibrio vulnificus infection should be high on the differential for patients who present with chronic liver disease and immunosuppression; a history of raw seafood consumption or exposure to brackish water; and bullae, cellulitis, necrotic lesions, or sepsis.
- Time to treatment is directly proportional to mortality rates in V vulnificus infections, and prompt treatment with antibiotics, wound care, debridement, and supportive measures is necessary to decrease mortality rates.
- The incidence of V vulnificus infection is rising in the United States, likely due to a combination of factors, including an aging population with multiple comorbidities, improvements in diagnosis, and climate change.
Improving Dermatologic Care for South Asian Patients: Understanding Religious and Cultural Practices
Traditional garments are particularly important in both Sikhism and Islam. Sikhs began wearing symbolic garments in the 16th century as markers of their identity during periods of religious persecution. Today, many Sikhs continue to maintain this tradition of wearing the Five Ks—kesh (uncut hair, often tied in a turban), kanga (wooden hair comb), kirpan (symbolic dagger), kachha (cotton underwear), and kara (steel bracelet).2 Similarly, Islamic traditions also provide guidance for clothing. Many Muslim women wear the hijab (headscarf), a garment that originated as protective headgear for nomadic desert cultures and has come to symbolize modest dress. Traditionally, the hijab is worn in the presence of all men who are not immediate relatives, although patients may make exceptions for medical care. Some Muslim men also may cover their heads with a skullcap and/or maintain long beards (occasionally dyed with henna pigment) as a way of keeping continuity with the tradition of the Prophet Muhammad and his companions.3
Certain styles of headwear can cause high tension on hair follicles and have been associated with traction alopecia.4 Persistent use of the same turban, hijab, or comb also may lead to seborrheic dermatitis or fungal scalp infections. Dermatologists should advise patients about these potential challenges and suggest modifications in accordance with the patient’s religious beliefs; for example, providers can suggest removing headwear at night, using prophylactic antifungal shampoos, and/or tying the hair in a ponytail or loosening the headgear to reduce traction.
Although Hinduism does not have a unifying garment or hair tradition in the vein of Sikhism or Islam, all 3 religions share a strong emphasis on bodily modesty, which may affect dermatologic examinations. Patients from all 3 religions may seek to expose as little skin as possible during a physical examination, and many patients may be uncomfortable with a physician of the opposite gender. Dermatologists may find the following practices to be helpful5:
• Talk through each aspect of the skin examination while it is being performed and expose the least amount of skin necessary during the process
• Offer the patient a chaperone or a same-gender provider, if possible
• Empower patients to assist in adjusting garments themselves to help the physician visualize all parts of the skin
Some Sikhs also may have specific concerns regarding cutting their hair. One aspect of kesh is that every hair is sacred, and thus, many Sikhs refrain from removing hair on any part of the body. As such, providers should carefully obtain the patient’s informed consent before performing any procedure or physical examination maneuvers (eg, hair pull test) that may result in loss of hair.2
Physicians of all disciplines can help address these challenges through increased outreach and cultural awareness; for example, dermatologists can create skin care pamphlets translated into various South Asian languages and distribute them at houses of worship or other community centers. This may help patients identify their skin needs and seek appropriate care. The onus must be on physicians to make these patients feel comfortable seeking care by creating nonjudgmental, culturally knowledgeable clinical environments. When asking about social history, the physician might consider asking an open-ended question such as, “What role does religion/spirituality play in your life?” They can then proceed to ask specific questions about practices that might affect the patient’s care.5
Given the current coronavirus disease 2019 pandemic, South Asian patients may be even further discouraged from seeking dermatologic care. By understanding religious traditions and taking steps to address biases, dermatologists can help mitigate health care disparities and provide culturally competent care to South Asian patients.
- Nadimpalli SB, Cleland CM, Hutchinson MK, et al. The association between discrimination and the health of Sikh Asian Indians. Health Psychol. 2016;35:351-355.
- The five Ks. BBC website. Updated September 29, 2009. Accessed February 4, 2021. https://www.bbc.co.uk/religion/religions/sikhism/customs/fiveks.shtml
- Islam. BBC website. Accessed February 2, 2021. https://www.bbc.co.uk/religion/religions/islam/
- James J, Saladi RN, Fox JL. Traction alopecia in Sikh male patients. J Am Board Fam Med. 2007;20:497-498.
- Hussain A. Recommendations for culturally competent dermatology care of Muslim patients. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2017;77:388-389.
Traditional garments are particularly important in both Sikhism and Islam. Sikhs began wearing symbolic garments in the 16th century as markers of their identity during periods of religious persecution. Today, many Sikhs continue to maintain this tradition of wearing the Five Ks—kesh (uncut hair, often tied in a turban), kanga (wooden hair comb), kirpan (symbolic dagger), kachha (cotton underwear), and kara (steel bracelet).2 Similarly, Islamic traditions also provide guidance for clothing. Many Muslim women wear the hijab (headscarf), a garment that originated as protective headgear for nomadic desert cultures and has come to symbolize modest dress. Traditionally, the hijab is worn in the presence of all men who are not immediate relatives, although patients may make exceptions for medical care. Some Muslim men also may cover their heads with a skullcap and/or maintain long beards (occasionally dyed with henna pigment) as a way of keeping continuity with the tradition of the Prophet Muhammad and his companions.3
Certain styles of headwear can cause high tension on hair follicles and have been associated with traction alopecia.4 Persistent use of the same turban, hijab, or comb also may lead to seborrheic dermatitis or fungal scalp infections. Dermatologists should advise patients about these potential challenges and suggest modifications in accordance with the patient’s religious beliefs; for example, providers can suggest removing headwear at night, using prophylactic antifungal shampoos, and/or tying the hair in a ponytail or loosening the headgear to reduce traction.
Although Hinduism does not have a unifying garment or hair tradition in the vein of Sikhism or Islam, all 3 religions share a strong emphasis on bodily modesty, which may affect dermatologic examinations. Patients from all 3 religions may seek to expose as little skin as possible during a physical examination, and many patients may be uncomfortable with a physician of the opposite gender. Dermatologists may find the following practices to be helpful5:
• Talk through each aspect of the skin examination while it is being performed and expose the least amount of skin necessary during the process
• Offer the patient a chaperone or a same-gender provider, if possible
• Empower patients to assist in adjusting garments themselves to help the physician visualize all parts of the skin
Some Sikhs also may have specific concerns regarding cutting their hair. One aspect of kesh is that every hair is sacred, and thus, many Sikhs refrain from removing hair on any part of the body. As such, providers should carefully obtain the patient’s informed consent before performing any procedure or physical examination maneuvers (eg, hair pull test) that may result in loss of hair.2
Physicians of all disciplines can help address these challenges through increased outreach and cultural awareness; for example, dermatologists can create skin care pamphlets translated into various South Asian languages and distribute them at houses of worship or other community centers. This may help patients identify their skin needs and seek appropriate care. The onus must be on physicians to make these patients feel comfortable seeking care by creating nonjudgmental, culturally knowledgeable clinical environments. When asking about social history, the physician might consider asking an open-ended question such as, “What role does religion/spirituality play in your life?” They can then proceed to ask specific questions about practices that might affect the patient’s care.5
Given the current coronavirus disease 2019 pandemic, South Asian patients may be even further discouraged from seeking dermatologic care. By understanding religious traditions and taking steps to address biases, dermatologists can help mitigate health care disparities and provide culturally competent care to South Asian patients.
Traditional garments are particularly important in both Sikhism and Islam. Sikhs began wearing symbolic garments in the 16th century as markers of their identity during periods of religious persecution. Today, many Sikhs continue to maintain this tradition of wearing the Five Ks—kesh (uncut hair, often tied in a turban), kanga (wooden hair comb), kirpan (symbolic dagger), kachha (cotton underwear), and kara (steel bracelet).2 Similarly, Islamic traditions also provide guidance for clothing. Many Muslim women wear the hijab (headscarf), a garment that originated as protective headgear for nomadic desert cultures and has come to symbolize modest dress. Traditionally, the hijab is worn in the presence of all men who are not immediate relatives, although patients may make exceptions for medical care. Some Muslim men also may cover their heads with a skullcap and/or maintain long beards (occasionally dyed with henna pigment) as a way of keeping continuity with the tradition of the Prophet Muhammad and his companions.3
Certain styles of headwear can cause high tension on hair follicles and have been associated with traction alopecia.4 Persistent use of the same turban, hijab, or comb also may lead to seborrheic dermatitis or fungal scalp infections. Dermatologists should advise patients about these potential challenges and suggest modifications in accordance with the patient’s religious beliefs; for example, providers can suggest removing headwear at night, using prophylactic antifungal shampoos, and/or tying the hair in a ponytail or loosening the headgear to reduce traction.
Although Hinduism does not have a unifying garment or hair tradition in the vein of Sikhism or Islam, all 3 religions share a strong emphasis on bodily modesty, which may affect dermatologic examinations. Patients from all 3 religions may seek to expose as little skin as possible during a physical examination, and many patients may be uncomfortable with a physician of the opposite gender. Dermatologists may find the following practices to be helpful5:
• Talk through each aspect of the skin examination while it is being performed and expose the least amount of skin necessary during the process
• Offer the patient a chaperone or a same-gender provider, if possible
• Empower patients to assist in adjusting garments themselves to help the physician visualize all parts of the skin
Some Sikhs also may have specific concerns regarding cutting their hair. One aspect of kesh is that every hair is sacred, and thus, many Sikhs refrain from removing hair on any part of the body. As such, providers should carefully obtain the patient’s informed consent before performing any procedure or physical examination maneuvers (eg, hair pull test) that may result in loss of hair.2
Physicians of all disciplines can help address these challenges through increased outreach and cultural awareness; for example, dermatologists can create skin care pamphlets translated into various South Asian languages and distribute them at houses of worship or other community centers. This may help patients identify their skin needs and seek appropriate care. The onus must be on physicians to make these patients feel comfortable seeking care by creating nonjudgmental, culturally knowledgeable clinical environments. When asking about social history, the physician might consider asking an open-ended question such as, “What role does religion/spirituality play in your life?” They can then proceed to ask specific questions about practices that might affect the patient’s care.5
Given the current coronavirus disease 2019 pandemic, South Asian patients may be even further discouraged from seeking dermatologic care. By understanding religious traditions and taking steps to address biases, dermatologists can help mitigate health care disparities and provide culturally competent care to South Asian patients.
- Nadimpalli SB, Cleland CM, Hutchinson MK, et al. The association between discrimination and the health of Sikh Asian Indians. Health Psychol. 2016;35:351-355.
- The five Ks. BBC website. Updated September 29, 2009. Accessed February 4, 2021. https://www.bbc.co.uk/religion/religions/sikhism/customs/fiveks.shtml
- Islam. BBC website. Accessed February 2, 2021. https://www.bbc.co.uk/religion/religions/islam/
- James J, Saladi RN, Fox JL. Traction alopecia in Sikh male patients. J Am Board Fam Med. 2007;20:497-498.
- Hussain A. Recommendations for culturally competent dermatology care of Muslim patients. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2017;77:388-389.
- Nadimpalli SB, Cleland CM, Hutchinson MK, et al. The association between discrimination and the health of Sikh Asian Indians. Health Psychol. 2016;35:351-355.
- The five Ks. BBC website. Updated September 29, 2009. Accessed February 4, 2021. https://www.bbc.co.uk/religion/religions/sikhism/customs/fiveks.shtml
- Islam. BBC website. Accessed February 2, 2021. https://www.bbc.co.uk/religion/religions/islam/
- James J, Saladi RN, Fox JL. Traction alopecia in Sikh male patients. J Am Board Fam Med. 2007;20:497-498.
- Hussain A. Recommendations for culturally competent dermatology care of Muslim patients. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2017;77:388-389.
Practice Points
- Providers should familiarize themselves with traditional garments of Sikhism and Islam, including head coverings and other symbolic items.
- Inform patients about health-conscious methods of wearing traditional headwear, such as removing certain headwear at night and tying hair in methods to avoid causing traction alopecia.
- Talk through each aspect of the skin examination while it is being performed and expose the least amount of skin necessary during the process. Offer the patient a chaperone or a same-gender provider, if possible.
- Empower patients to assist in adjusting garments themselves to help the physician visualize all parts of the skin.
Multifocal Annular Pink Plaques With a Central Violaceous Hue
The Diagnosis: Disseminated Erythema Chronicum Migrans
Empiric treatment with doxycycline 100 mg twice daily for 14 days was initiated for suspected early disseminated Lyme disease manifesting as disseminated multifocal erythema chronicum migrans (Figure). Lyme screening immunoassay and confirmatory IgM Western blot testing subsequently were found to be positive. The clinical history of recent travel to an endemic area and tick bite combined with the recent onset of multifocal erythema migrans lesions, systemic symptoms, elevated erythrocyte sedimentation rate, and positive Lyme serology supported the diagnosis of Lyme disease.
The appropriate clinical context and cutaneous morphology are key when considering the differential diagnosis for multifocal annular lesions. Several entities comprised the differential diagnosis considered in our patient. Sweet syndrome is a neutrophilic dermatosis that can present with fever and varying painful cutaneous lesions. It often is associated with certain medications, underlying illnesses, and infections.1 Our patient’s lesions were not painful, and she had no notable medical history, recent infections, or new medication use, making Sweet syndrome unlikely. A fixed drug eruption was low on the differential, as the patient denied starting any new medications within the 3 months prior to presentation. Erythema multiforme is an acute-onset immunemediated condition of the skin and mucous membranes that typically affects young adults and often is associated with infection (eg, herpes simplex virus, Mycoplasma pneumoniae) or medication use. Cutaneous lesions typically are self-limited, less than 3 cm targets with 3 concentric distinct color zones, often with central bullae or erosions. Although erythema multiforme was higher on the differential, it was less likely, as the patient lacked mucosal lesions and did not have symptoms of underlying herpetic or mycoplasma infection, and the clinical picture was more consistent with Lyme disease. Lastly, the failure for individual skin lesions to resolve within
24 hours excluded the diagnosis of urticaria.
Lyme disease is a tick-borne illness caused by 3 species of the Borrelia spirochete: Borrelia burgdorferi, Borrelia afzelii, and Borrelia garinii.2 In the United States, the disease predominantly is caused by B burgdorferi that is endemic in the upper Midwest and Northeast regions.3 There are 3 stages of Lyme disease: early localized, early disseminated, and late disseminated disease. Early localized disease typically presents with a characteristic single erythema migrans (EM) lesion 3 to 30 days following a bite by the tick Ixodes scapularis.2 The EM lesion gradually can enlarge over a period of several days, reaching up to 12 inches in diameter.2 Early disseminated disease can occur weeks to months following a tick bite and may present with systemic symptoms, multiple widespread
EM lesions, neurologic features such as meningitis or facial nerve palsy, and/or cardiac manifestations such as atrioventricular block or myocarditis. Late disseminated disease can present with chronic arthritis or encephalopathy after months to years if the disease is left untreated.4
Early localized Lyme disease can be diagnosed clinically if the characteristic EM lesion is present in a patient who visited an endemic area. Laboratory testing and Lyme serology are neither required nor recommended in these cases, as the lesion often appears before adequate time has lapsed to develop an adaptive immune response to the organism.5 In contrast, Lyme serology should be ordered in any patient who meets all of the following criteria: (1) patient lives in or has recently traveled to an area endemic for Lyme disease, (2) presence of a risk factor for tick exposure, and (3) symptoms consistent with early disseminated or late Lyme disease. Patients with signs of early or late disseminated disease typically are seropositive, as IgM antibodies can be detected within 2 weeks of onset of the EM lesion and IgG antibodies within 2 to 6 weeks.6 The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommends a 2-tiered approach when testing for Lyme disease.7 A screening test with high sensitivity such as an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay or an immunofluorescence assay initially should be performed.7 If results of the screening test are equivocal or positive, secondary confirmatory testing should be performed via IgM, with or without IgG Western immunoblot assay.7 Biopsy with histologic evaluation can reveal nonspecific findings of vascular endothelial injury and increased mucin deposition. Patients with suspected Lyme disease should immediately be started on empiric treatment with doxycycline 100 mg twice daily for a minimum of 10 days (14–28 days if there is concern for dissemination) to prevent post-Lyme sequelae.5 Our patient’s cutaneous lesions responded to oral doxycycline.
- Sweet’s syndrome. Mayo Clinic. Accessed January 8, 2021. https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/sweets-syndrome /symptoms-causes/syc-20351117
- Steere AC. Lyme disease. N Engl J Med. 2001;345:115-125.
- Lyme disease maps: most recent year. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Updated November 22, 2019. Accessed January 8, 2021. https://www.cdc.gov/lyme/datasurveillance /maps-recent.html.
- Steere AC, Sikand VK. The present manifestations of Lyme disease and the outcomes of treatment. N Engl J Med. 2003;348:2472-2474.
- Sanchez E, Vannier E, Wormser GP, et al. Diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of Lyme disease, human granulocytic anaplasmosis, and babesiosis: a review. JAMA. 2016;315:1767-1777.
- Shapiro ED. Borrelia burgdorferi (Lyme disease). Pediatr Rev. 2014; 35:500-509.
- Mead P, Petersen J, Hinckley A. Updated CDC recommendation for serologic diagnosis of Lyme disease. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2019;68:703
The Diagnosis: Disseminated Erythema Chronicum Migrans
Empiric treatment with doxycycline 100 mg twice daily for 14 days was initiated for suspected early disseminated Lyme disease manifesting as disseminated multifocal erythema chronicum migrans (Figure). Lyme screening immunoassay and confirmatory IgM Western blot testing subsequently were found to be positive. The clinical history of recent travel to an endemic area and tick bite combined with the recent onset of multifocal erythema migrans lesions, systemic symptoms, elevated erythrocyte sedimentation rate, and positive Lyme serology supported the diagnosis of Lyme disease.
The appropriate clinical context and cutaneous morphology are key when considering the differential diagnosis for multifocal annular lesions. Several entities comprised the differential diagnosis considered in our patient. Sweet syndrome is a neutrophilic dermatosis that can present with fever and varying painful cutaneous lesions. It often is associated with certain medications, underlying illnesses, and infections.1 Our patient’s lesions were not painful, and she had no notable medical history, recent infections, or new medication use, making Sweet syndrome unlikely. A fixed drug eruption was low on the differential, as the patient denied starting any new medications within the 3 months prior to presentation. Erythema multiforme is an acute-onset immunemediated condition of the skin and mucous membranes that typically affects young adults and often is associated with infection (eg, herpes simplex virus, Mycoplasma pneumoniae) or medication use. Cutaneous lesions typically are self-limited, less than 3 cm targets with 3 concentric distinct color zones, often with central bullae or erosions. Although erythema multiforme was higher on the differential, it was less likely, as the patient lacked mucosal lesions and did not have symptoms of underlying herpetic or mycoplasma infection, and the clinical picture was more consistent with Lyme disease. Lastly, the failure for individual skin lesions to resolve within
24 hours excluded the diagnosis of urticaria.
Lyme disease is a tick-borne illness caused by 3 species of the Borrelia spirochete: Borrelia burgdorferi, Borrelia afzelii, and Borrelia garinii.2 In the United States, the disease predominantly is caused by B burgdorferi that is endemic in the upper Midwest and Northeast regions.3 There are 3 stages of Lyme disease: early localized, early disseminated, and late disseminated disease. Early localized disease typically presents with a characteristic single erythema migrans (EM) lesion 3 to 30 days following a bite by the tick Ixodes scapularis.2 The EM lesion gradually can enlarge over a period of several days, reaching up to 12 inches in diameter.2 Early disseminated disease can occur weeks to months following a tick bite and may present with systemic symptoms, multiple widespread
EM lesions, neurologic features such as meningitis or facial nerve palsy, and/or cardiac manifestations such as atrioventricular block or myocarditis. Late disseminated disease can present with chronic arthritis or encephalopathy after months to years if the disease is left untreated.4
Early localized Lyme disease can be diagnosed clinically if the characteristic EM lesion is present in a patient who visited an endemic area. Laboratory testing and Lyme serology are neither required nor recommended in these cases, as the lesion often appears before adequate time has lapsed to develop an adaptive immune response to the organism.5 In contrast, Lyme serology should be ordered in any patient who meets all of the following criteria: (1) patient lives in or has recently traveled to an area endemic for Lyme disease, (2) presence of a risk factor for tick exposure, and (3) symptoms consistent with early disseminated or late Lyme disease. Patients with signs of early or late disseminated disease typically are seropositive, as IgM antibodies can be detected within 2 weeks of onset of the EM lesion and IgG antibodies within 2 to 6 weeks.6 The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommends a 2-tiered approach when testing for Lyme disease.7 A screening test with high sensitivity such as an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay or an immunofluorescence assay initially should be performed.7 If results of the screening test are equivocal or positive, secondary confirmatory testing should be performed via IgM, with or without IgG Western immunoblot assay.7 Biopsy with histologic evaluation can reveal nonspecific findings of vascular endothelial injury and increased mucin deposition. Patients with suspected Lyme disease should immediately be started on empiric treatment with doxycycline 100 mg twice daily for a minimum of 10 days (14–28 days if there is concern for dissemination) to prevent post-Lyme sequelae.5 Our patient’s cutaneous lesions responded to oral doxycycline.
The Diagnosis: Disseminated Erythema Chronicum Migrans
Empiric treatment with doxycycline 100 mg twice daily for 14 days was initiated for suspected early disseminated Lyme disease manifesting as disseminated multifocal erythema chronicum migrans (Figure). Lyme screening immunoassay and confirmatory IgM Western blot testing subsequently were found to be positive. The clinical history of recent travel to an endemic area and tick bite combined with the recent onset of multifocal erythema migrans lesions, systemic symptoms, elevated erythrocyte sedimentation rate, and positive Lyme serology supported the diagnosis of Lyme disease.
The appropriate clinical context and cutaneous morphology are key when considering the differential diagnosis for multifocal annular lesions. Several entities comprised the differential diagnosis considered in our patient. Sweet syndrome is a neutrophilic dermatosis that can present with fever and varying painful cutaneous lesions. It often is associated with certain medications, underlying illnesses, and infections.1 Our patient’s lesions were not painful, and she had no notable medical history, recent infections, or new medication use, making Sweet syndrome unlikely. A fixed drug eruption was low on the differential, as the patient denied starting any new medications within the 3 months prior to presentation. Erythema multiforme is an acute-onset immunemediated condition of the skin and mucous membranes that typically affects young adults and often is associated with infection (eg, herpes simplex virus, Mycoplasma pneumoniae) or medication use. Cutaneous lesions typically are self-limited, less than 3 cm targets with 3 concentric distinct color zones, often with central bullae or erosions. Although erythema multiforme was higher on the differential, it was less likely, as the patient lacked mucosal lesions and did not have symptoms of underlying herpetic or mycoplasma infection, and the clinical picture was more consistent with Lyme disease. Lastly, the failure for individual skin lesions to resolve within
24 hours excluded the diagnosis of urticaria.
Lyme disease is a tick-borne illness caused by 3 species of the Borrelia spirochete: Borrelia burgdorferi, Borrelia afzelii, and Borrelia garinii.2 In the United States, the disease predominantly is caused by B burgdorferi that is endemic in the upper Midwest and Northeast regions.3 There are 3 stages of Lyme disease: early localized, early disseminated, and late disseminated disease. Early localized disease typically presents with a characteristic single erythema migrans (EM) lesion 3 to 30 days following a bite by the tick Ixodes scapularis.2 The EM lesion gradually can enlarge over a period of several days, reaching up to 12 inches in diameter.2 Early disseminated disease can occur weeks to months following a tick bite and may present with systemic symptoms, multiple widespread
EM lesions, neurologic features such as meningitis or facial nerve palsy, and/or cardiac manifestations such as atrioventricular block or myocarditis. Late disseminated disease can present with chronic arthritis or encephalopathy after months to years if the disease is left untreated.4
Early localized Lyme disease can be diagnosed clinically if the characteristic EM lesion is present in a patient who visited an endemic area. Laboratory testing and Lyme serology are neither required nor recommended in these cases, as the lesion often appears before adequate time has lapsed to develop an adaptive immune response to the organism.5 In contrast, Lyme serology should be ordered in any patient who meets all of the following criteria: (1) patient lives in or has recently traveled to an area endemic for Lyme disease, (2) presence of a risk factor for tick exposure, and (3) symptoms consistent with early disseminated or late Lyme disease. Patients with signs of early or late disseminated disease typically are seropositive, as IgM antibodies can be detected within 2 weeks of onset of the EM lesion and IgG antibodies within 2 to 6 weeks.6 The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommends a 2-tiered approach when testing for Lyme disease.7 A screening test with high sensitivity such as an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay or an immunofluorescence assay initially should be performed.7 If results of the screening test are equivocal or positive, secondary confirmatory testing should be performed via IgM, with or without IgG Western immunoblot assay.7 Biopsy with histologic evaluation can reveal nonspecific findings of vascular endothelial injury and increased mucin deposition. Patients with suspected Lyme disease should immediately be started on empiric treatment with doxycycline 100 mg twice daily for a minimum of 10 days (14–28 days if there is concern for dissemination) to prevent post-Lyme sequelae.5 Our patient’s cutaneous lesions responded to oral doxycycline.
- Sweet’s syndrome. Mayo Clinic. Accessed January 8, 2021. https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/sweets-syndrome /symptoms-causes/syc-20351117
- Steere AC. Lyme disease. N Engl J Med. 2001;345:115-125.
- Lyme disease maps: most recent year. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Updated November 22, 2019. Accessed January 8, 2021. https://www.cdc.gov/lyme/datasurveillance /maps-recent.html.
- Steere AC, Sikand VK. The present manifestations of Lyme disease and the outcomes of treatment. N Engl J Med. 2003;348:2472-2474.
- Sanchez E, Vannier E, Wormser GP, et al. Diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of Lyme disease, human granulocytic anaplasmosis, and babesiosis: a review. JAMA. 2016;315:1767-1777.
- Shapiro ED. Borrelia burgdorferi (Lyme disease). Pediatr Rev. 2014; 35:500-509.
- Mead P, Petersen J, Hinckley A. Updated CDC recommendation for serologic diagnosis of Lyme disease. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2019;68:703
- Sweet’s syndrome. Mayo Clinic. Accessed January 8, 2021. https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/sweets-syndrome /symptoms-causes/syc-20351117
- Steere AC. Lyme disease. N Engl J Med. 2001;345:115-125.
- Lyme disease maps: most recent year. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Updated November 22, 2019. Accessed January 8, 2021. https://www.cdc.gov/lyme/datasurveillance /maps-recent.html.
- Steere AC, Sikand VK. The present manifestations of Lyme disease and the outcomes of treatment. N Engl J Med. 2003;348:2472-2474.
- Sanchez E, Vannier E, Wormser GP, et al. Diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of Lyme disease, human granulocytic anaplasmosis, and babesiosis: a review. JAMA. 2016;315:1767-1777.
- Shapiro ED. Borrelia burgdorferi (Lyme disease). Pediatr Rev. 2014; 35:500-509.
- Mead P, Petersen J, Hinckley A. Updated CDC recommendation for serologic diagnosis of Lyme disease. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2019;68:703
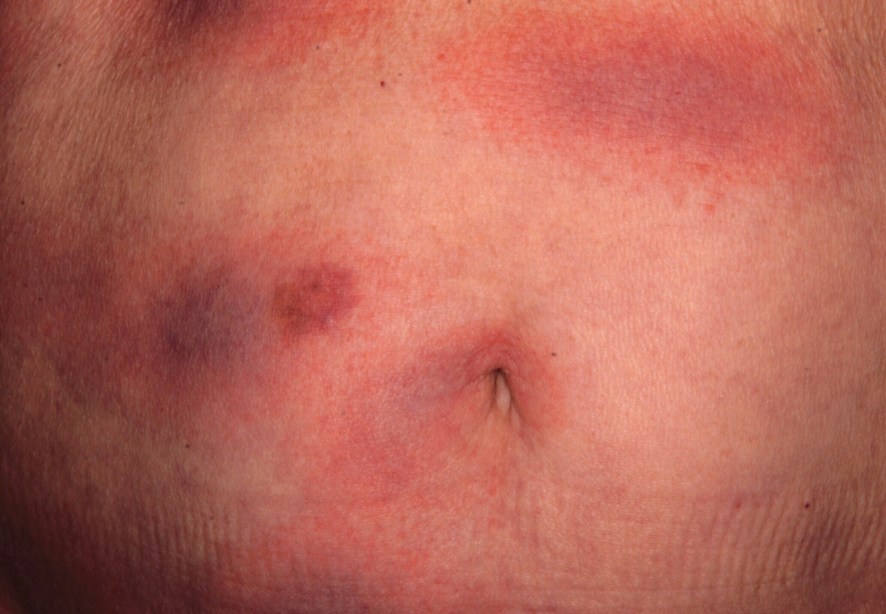
An otherwise healthy 78-year-old woman presented with a diffuse, mildly itchy rash of 5 days’ duration with associated fatigue, chills, decreased appetite, and nausea. She reported waking up with her arms “feeling like they weigh a ton.” She denied any pain, bleeding, or oozing and was unsure if new spots were continuing to develop. The patient reported having allergies to numerous medications but denied any new medications or recent illnesses. She had recently spent time on a farm in Minnesota, and upon further questioning she recalled a tick bite 2 months prior to presentation. She stated that she removed the nonengorged tick and that it could not have been attached for more than 24 hours. Her medical and family history were unremarkable. Physical examination showed multiple annular pink plaques with a central violaceous hue in a generalized distribution involving the face, trunk, arms, and legs with mild erythema of the palms. The plantar surfaces were clear, and there was no evidence of lymphadenopathy. The remainder of the physical examination and review of systems was negative. Laboratory screening was notable for an elevated erythrocyte sedimentation rate and C-reactive protein level with negative antinuclear antibodies.
Exercise-Induced Vasculitis in a Patient With Negative Ultrasound Venous Reflux Study: A Mimic of Stasis Dermatitis
To the Editor:
The transient and generic appearance of exercise-induced vasculitis (EIV) makes it a commonly misdiagnosed condition. The lesion often is only encountered through photographs brought by the patient or by taking a thorough history. The lack of findings on clinical inspection and the generic appearance of EIV may lead to misdiagnosis as stasis dermatitis due to its presentation as erythematous lesions on the medial lower legs.
A 68-year-old woman with no notable medical history was referred to our clinic for suspected stasis dermatitis. At presentation, no lesions were identified on the legs, but she brought photographs of an erythematous urticarial eruption on the medial lower legs, extending from just above the sock line to the mid-calves (Figure). The eruptions had occurred over the last 16 years, typically presenting suddenly after playing tennis or an extended period of walking and spontaneously resolving in 4 days. The lesions were painless, restricted to the calves, and were not pruritic, though the initial presentation 16 years prior included pruritic pigmented patches on the anterior thighs. Because the condition spontaneously improved within days, no treatment was attempted. An ultrasound venous reflux study ruled out venous reflux and stasis dermatitis.
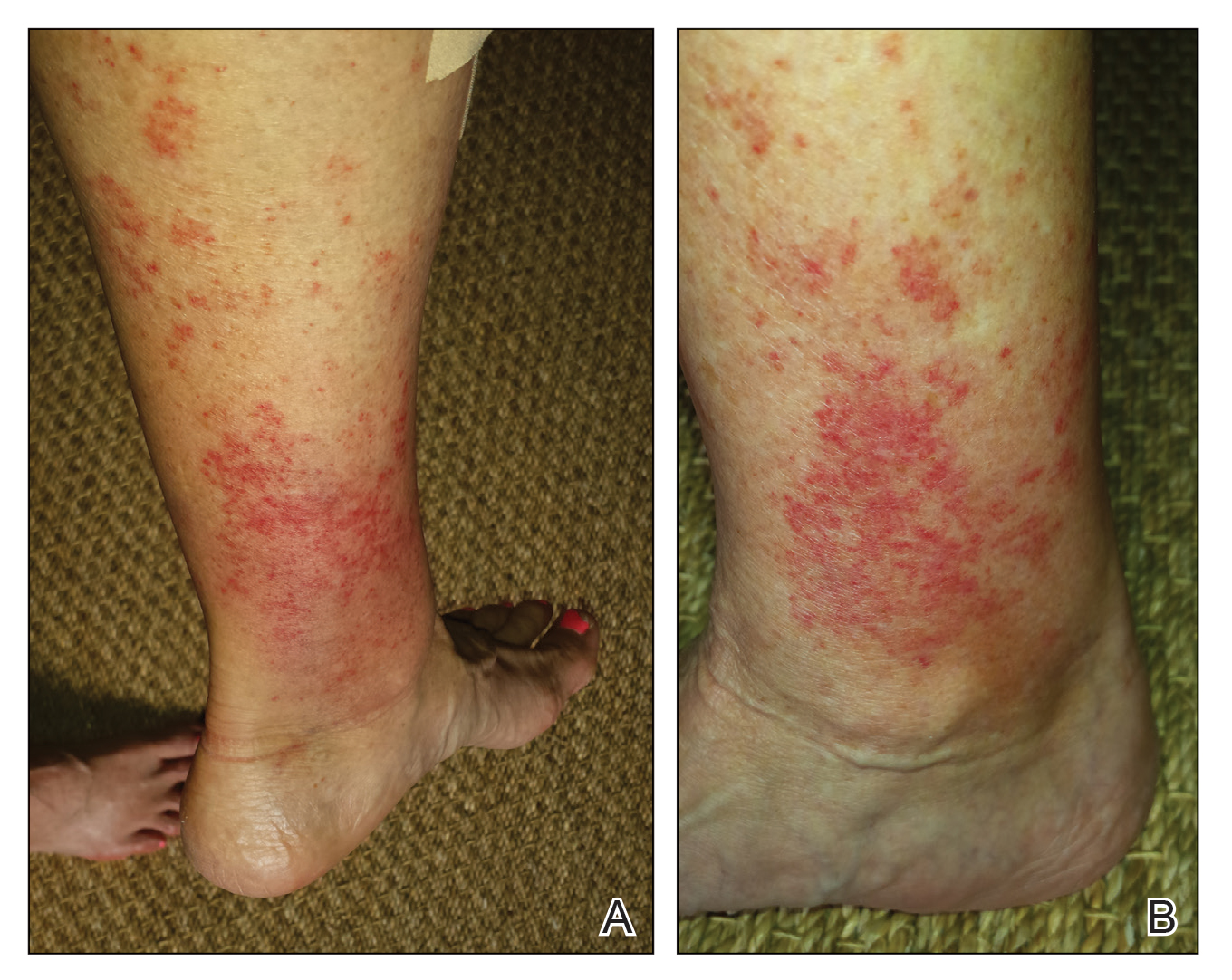
Our patient stated that her 64-year-old sister had reported the same presentation over the last 8 years. Her physical activity was limited strictly to walking, and the lesions occurred after walking for many hours during the day in the heat, involving the medial aspects of the lower legs extending from the ankles to the full length of the calves. Her eruption was warm but was not painful or pruritic. It resolved spontaneously after 5 days with no therapy.
Our patient was advised to wear compression stockings as a preventative measure, but she did not adhere to these recommendations, stating it was impractical to wear compression garments while playing tennis.
Exercise-induced vasculitis most commonly is seen in the medial aspects of the lower extremities as an erythematous urticarial eruption or pigmented purpuric plaque rapidly occurring after a period of exercise.1,2 Lesions often are symmetric and can be pruritic and painful with a lack of systemic symptoms.3 These generic clinical manifestations may lead to a misdiagnosis of stasis dermatitis. One case report included initial treatment of presumptive cellulitis.4 Important clinical findings include a sparing of skin compressed by tight clothing such as socks, a lack of systemic symptoms, rapid appearance after exercise, and spontaneous resolution within a few days. No correlation with chronic venous disease has been demonstrated, as EIV can occur in patients with or without chronic venous insufficiency.5 Duplex ultrasound evaluation showed no venous reflux in our patient.
The pathophysiology of EIV remains unknown, but the concept of exercise-altered microcirculation has been proposed. Heat generated from exercise is normally dissipated by thermoregulatory mechanisms such as cutaneous vasodilation and sweat.1,6 When exercise is extended, done concomitantly in the heat, or performed in legs with preexisting edema or substantial adipose tissue that limit heat attenuation, the thermoregulatory capacity is overloaded and heat-induced muscle fiber breakdown occurs.1,7 Atrophy impairs the skeletal muscle’s ability to pump the increased venous return demanded by exercise to the heart, leading to backflow of venous return and eventual venous stasis.1 Reduction of venous return together with cutaneous vasodilation is thought to induce erythrocyte extravasation.
Histologic examination demonstrates features of leukocytoclastic vasculitis with perivascular lymphocytic and neutrophilic infiltrates.2 Erythrocyte extravasation, IgM deposits, and identification of C3 also have been reported.8,9 The spontaneous resolution of EIV has led to treatment efforts being focused on preventative measures. Several cases have reported some degree of success in preventing EIV with compression therapy, venoactive drugs, systemic steroids, and application of topical steroids before exercise.3
The clinical morphology and lower leg location of EIV leads to a common misdiagnosis of stasis dermatitis. Clinical history of a transient nature is the mainstay in the diagnosis of EIV, and ultrasound venous reflux study may be required in some cases. Preventative measures are superior to treatment and mainly include compression therapy.
- Ramelet AA. Exercise-induced vasculitis. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2006;20:423-427.
- Kelly RI, Opie J, Nixon R. Golfer’s vasculitis. Australas J Dermatol. 2005;46:11-14.
- Ramelet AA. Exercise-induced purpura. Dermatology. 2004;208:293-296.
- Cushman D, Rydberg L. A general rehabilitation inpatient with exercise-induced vasculitis. PM R. 2013;5:900-902.
- Veraart JC, Prins M, Hulsmans RF, et al. Influence of endurance exercise on the venous refilling time of the leg. Phlebology. 1994;23:120-123.
- Noakes T. Fluid replacement during marathon running. Clin J Sport Med. 2003;13:309-318.
- Armstrong RB. Muscle damage and endurance events. Sports Med. 1986;3:370-381.
- Prins M, Veraart JC, Vermeulen AH, et al. Leucocytoclastic vasculitis induced by prolonged exercise. Br J Dermatol. 1996;134:915-918.
- Sagdeo A, Gormley RH, Wanat KA, et al. Purpuric eruption on the feet of a healthy young woman. “flip-flop vasculitis” (exercise-induced vasculitis). JAMA Dermatol. 2013;149:751-756.
To the Editor:
The transient and generic appearance of exercise-induced vasculitis (EIV) makes it a commonly misdiagnosed condition. The lesion often is only encountered through photographs brought by the patient or by taking a thorough history. The lack of findings on clinical inspection and the generic appearance of EIV may lead to misdiagnosis as stasis dermatitis due to its presentation as erythematous lesions on the medial lower legs.
A 68-year-old woman with no notable medical history was referred to our clinic for suspected stasis dermatitis. At presentation, no lesions were identified on the legs, but she brought photographs of an erythematous urticarial eruption on the medial lower legs, extending from just above the sock line to the mid-calves (Figure). The eruptions had occurred over the last 16 years, typically presenting suddenly after playing tennis or an extended period of walking and spontaneously resolving in 4 days. The lesions were painless, restricted to the calves, and were not pruritic, though the initial presentation 16 years prior included pruritic pigmented patches on the anterior thighs. Because the condition spontaneously improved within days, no treatment was attempted. An ultrasound venous reflux study ruled out venous reflux and stasis dermatitis.

Our patient stated that her 64-year-old sister had reported the same presentation over the last 8 years. Her physical activity was limited strictly to walking, and the lesions occurred after walking for many hours during the day in the heat, involving the medial aspects of the lower legs extending from the ankles to the full length of the calves. Her eruption was warm but was not painful or pruritic. It resolved spontaneously after 5 days with no therapy.
Our patient was advised to wear compression stockings as a preventative measure, but she did not adhere to these recommendations, stating it was impractical to wear compression garments while playing tennis.
Exercise-induced vasculitis most commonly is seen in the medial aspects of the lower extremities as an erythematous urticarial eruption or pigmented purpuric plaque rapidly occurring after a period of exercise.1,2 Lesions often are symmetric and can be pruritic and painful with a lack of systemic symptoms.3 These generic clinical manifestations may lead to a misdiagnosis of stasis dermatitis. One case report included initial treatment of presumptive cellulitis.4 Important clinical findings include a sparing of skin compressed by tight clothing such as socks, a lack of systemic symptoms, rapid appearance after exercise, and spontaneous resolution within a few days. No correlation with chronic venous disease has been demonstrated, as EIV can occur in patients with or without chronic venous insufficiency.5 Duplex ultrasound evaluation showed no venous reflux in our patient.
The pathophysiology of EIV remains unknown, but the concept of exercise-altered microcirculation has been proposed. Heat generated from exercise is normally dissipated by thermoregulatory mechanisms such as cutaneous vasodilation and sweat.1,6 When exercise is extended, done concomitantly in the heat, or performed in legs with preexisting edema or substantial adipose tissue that limit heat attenuation, the thermoregulatory capacity is overloaded and heat-induced muscle fiber breakdown occurs.1,7 Atrophy impairs the skeletal muscle’s ability to pump the increased venous return demanded by exercise to the heart, leading to backflow of venous return and eventual venous stasis.1 Reduction of venous return together with cutaneous vasodilation is thought to induce erythrocyte extravasation.
Histologic examination demonstrates features of leukocytoclastic vasculitis with perivascular lymphocytic and neutrophilic infiltrates.2 Erythrocyte extravasation, IgM deposits, and identification of C3 also have been reported.8,9 The spontaneous resolution of EIV has led to treatment efforts being focused on preventative measures. Several cases have reported some degree of success in preventing EIV with compression therapy, venoactive drugs, systemic steroids, and application of topical steroids before exercise.3
The clinical morphology and lower leg location of EIV leads to a common misdiagnosis of stasis dermatitis. Clinical history of a transient nature is the mainstay in the diagnosis of EIV, and ultrasound venous reflux study may be required in some cases. Preventative measures are superior to treatment and mainly include compression therapy.
To the Editor:
The transient and generic appearance of exercise-induced vasculitis (EIV) makes it a commonly misdiagnosed condition. The lesion often is only encountered through photographs brought by the patient or by taking a thorough history. The lack of findings on clinical inspection and the generic appearance of EIV may lead to misdiagnosis as stasis dermatitis due to its presentation as erythematous lesions on the medial lower legs.
A 68-year-old woman with no notable medical history was referred to our clinic for suspected stasis dermatitis. At presentation, no lesions were identified on the legs, but she brought photographs of an erythematous urticarial eruption on the medial lower legs, extending from just above the sock line to the mid-calves (Figure). The eruptions had occurred over the last 16 years, typically presenting suddenly after playing tennis or an extended period of walking and spontaneously resolving in 4 days. The lesions were painless, restricted to the calves, and were not pruritic, though the initial presentation 16 years prior included pruritic pigmented patches on the anterior thighs. Because the condition spontaneously improved within days, no treatment was attempted. An ultrasound venous reflux study ruled out venous reflux and stasis dermatitis.

Our patient stated that her 64-year-old sister had reported the same presentation over the last 8 years. Her physical activity was limited strictly to walking, and the lesions occurred after walking for many hours during the day in the heat, involving the medial aspects of the lower legs extending from the ankles to the full length of the calves. Her eruption was warm but was not painful or pruritic. It resolved spontaneously after 5 days with no therapy.
Our patient was advised to wear compression stockings as a preventative measure, but she did not adhere to these recommendations, stating it was impractical to wear compression garments while playing tennis.
Exercise-induced vasculitis most commonly is seen in the medial aspects of the lower extremities as an erythematous urticarial eruption or pigmented purpuric plaque rapidly occurring after a period of exercise.1,2 Lesions often are symmetric and can be pruritic and painful with a lack of systemic symptoms.3 These generic clinical manifestations may lead to a misdiagnosis of stasis dermatitis. One case report included initial treatment of presumptive cellulitis.4 Important clinical findings include a sparing of skin compressed by tight clothing such as socks, a lack of systemic symptoms, rapid appearance after exercise, and spontaneous resolution within a few days. No correlation with chronic venous disease has been demonstrated, as EIV can occur in patients with or without chronic venous insufficiency.5 Duplex ultrasound evaluation showed no venous reflux in our patient.
The pathophysiology of EIV remains unknown, but the concept of exercise-altered microcirculation has been proposed. Heat generated from exercise is normally dissipated by thermoregulatory mechanisms such as cutaneous vasodilation and sweat.1,6 When exercise is extended, done concomitantly in the heat, or performed in legs with preexisting edema or substantial adipose tissue that limit heat attenuation, the thermoregulatory capacity is overloaded and heat-induced muscle fiber breakdown occurs.1,7 Atrophy impairs the skeletal muscle’s ability to pump the increased venous return demanded by exercise to the heart, leading to backflow of venous return and eventual venous stasis.1 Reduction of venous return together with cutaneous vasodilation is thought to induce erythrocyte extravasation.
Histologic examination demonstrates features of leukocytoclastic vasculitis with perivascular lymphocytic and neutrophilic infiltrates.2 Erythrocyte extravasation, IgM deposits, and identification of C3 also have been reported.8,9 The spontaneous resolution of EIV has led to treatment efforts being focused on preventative measures. Several cases have reported some degree of success in preventing EIV with compression therapy, venoactive drugs, systemic steroids, and application of topical steroids before exercise.3
The clinical morphology and lower leg location of EIV leads to a common misdiagnosis of stasis dermatitis. Clinical history of a transient nature is the mainstay in the diagnosis of EIV, and ultrasound venous reflux study may be required in some cases. Preventative measures are superior to treatment and mainly include compression therapy.
- Ramelet AA. Exercise-induced vasculitis. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2006;20:423-427.
- Kelly RI, Opie J, Nixon R. Golfer’s vasculitis. Australas J Dermatol. 2005;46:11-14.
- Ramelet AA. Exercise-induced purpura. Dermatology. 2004;208:293-296.
- Cushman D, Rydberg L. A general rehabilitation inpatient with exercise-induced vasculitis. PM R. 2013;5:900-902.
- Veraart JC, Prins M, Hulsmans RF, et al. Influence of endurance exercise on the venous refilling time of the leg. Phlebology. 1994;23:120-123.
- Noakes T. Fluid replacement during marathon running. Clin J Sport Med. 2003;13:309-318.
- Armstrong RB. Muscle damage and endurance events. Sports Med. 1986;3:370-381.
- Prins M, Veraart JC, Vermeulen AH, et al. Leucocytoclastic vasculitis induced by prolonged exercise. Br J Dermatol. 1996;134:915-918.
- Sagdeo A, Gormley RH, Wanat KA, et al. Purpuric eruption on the feet of a healthy young woman. “flip-flop vasculitis” (exercise-induced vasculitis). JAMA Dermatol. 2013;149:751-756.
- Ramelet AA. Exercise-induced vasculitis. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2006;20:423-427.
- Kelly RI, Opie J, Nixon R. Golfer’s vasculitis. Australas J Dermatol. 2005;46:11-14.
- Ramelet AA. Exercise-induced purpura. Dermatology. 2004;208:293-296.
- Cushman D, Rydberg L. A general rehabilitation inpatient with exercise-induced vasculitis. PM R. 2013;5:900-902.
- Veraart JC, Prins M, Hulsmans RF, et al. Influence of endurance exercise on the venous refilling time of the leg. Phlebology. 1994;23:120-123.
- Noakes T. Fluid replacement during marathon running. Clin J Sport Med. 2003;13:309-318.
- Armstrong RB. Muscle damage and endurance events. Sports Med. 1986;3:370-381.
- Prins M, Veraart JC, Vermeulen AH, et al. Leucocytoclastic vasculitis induced by prolonged exercise. Br J Dermatol. 1996;134:915-918.
- Sagdeo A, Gormley RH, Wanat KA, et al. Purpuric eruption on the feet of a healthy young woman. “flip-flop vasculitis” (exercise-induced vasculitis). JAMA Dermatol. 2013;149:751-756.
Practice Points
- Clinical history of a transient nature is the mainstay in the diagnosis of exercise-induced vasculitis.
- Exercise-induced vasculitis largely is documented in photographs or by history and may be misdiagnosed as stasis dermatitis due to its clinical morphology and lower leg location.
- Dermatologists should be aware of this disorder and consider performing further workup to rule out stasis dermatitis and diagnose this mimic.
- Preventative measures are superior to treatment and mainly include compression therapy.
Unilateral Nail Clubbing in a Hemiparetic Patient
To the Editor:
Few cases of unilateral nail changes affecting only the hemiplegic side after a stroke have been reported. We present a case of acquired unilateral nail clubbing and longitudinal melanonychia in a hemiparetic patient.
A 79-year-old Black man with a history of smoking and stroke presented with concerns of discoloration of the fingernails. His medical history was notable for congestive heart failure; hypertension; diabetes mellitus; hypercholesterolemia; and stroke 11 years prior, which resulted in right-sided hemiparesis. Physical examination revealed longitudinal, even hyperpigmentation of several fingernails on the hands, in addition to whitening of the nail beds, sparing the tips (Terry nails). Clubbing was noted only on the fingernails of the right hand; the fingernails of the left hand exhibited normal curvature (Figure). Pulse oximetry was conducted and demonstrated the following readings: unaffected left index finger, 98%; unaffected left middle finger, 100%; affected right index finger, 95%; and affected right middle finger, 97%. The patient was diagnosed with benign longitudinal melanonychia secondary to ethnic variation, Terry nails without underlying anemia or hypoalbuminemic state, and unilateral right-sided clubbing of the fingernails in the setting of right-sided hemiparesis.
Prior reports have documented the occurrence of nail pathologies after stroke and affecting hemiplegic limbs. Unilateral digital nail clubbing following a stroke was first reported in 19751; 2 reports concluded clubbing developed in all digits affected by the stroke, and the severity of clubbing was associated with the duration of the stroke.1,2 One study noted longitudinal reddish striation, Neapolitan nails, and unilateral clubbing more commonly in hemiplegic patients.3 Longitudinal reddish striation was the most frequent condition observed in this population, always affecting the entire thumbnail of the hemiplegic limb.3 A similar report observed clubbing only on the fingernails of the hemiplegic side.4
Digital clubbing describes an exaggerated nail curvature and bulbous overgrowth of the fingertips due to an expansion of connective tissue between the nail plate and the nail bed.3,5 Clubbed fingers are found in various chronic conditions affecting the heart, lungs, and liver. Although the pathogenesis of clubbing remains unknown, many hypothesize that it is a state of proliferation in response to digital hypoxia.5 Fittingly, our patient exhibited a relative hypoperfusion of the clubbed fingers in comparison to the unaffected side.
This case provides additional support for the phenomenon of unilateral nail changes limited to hemiplegic or hemiparetic limbs. The unique presentation of longitudinal melanonychia, clubbing, and a lowered pulse oximetry reading only affecting the hemiparetic side demonstrates the possible connection between hypoxia and nail clubbing in this patient population.
- Denham M, Hodkinson H, Wright B. Unilateral clubbing in hemiplegia. Gerontology Clin (Basel). 1975;17:7-12.
- Alveraz A, McNair D, Wildman J, et al. Unilateral clubbing of the fingernails in patients with hemiplegia. Gerontology Clin (Basel). 1975;17:1-6.
- Siragusa M, Schepis C, Cosentino F, et al. Nail pathology in patients with hemiplegia. Br J Dermatol. 2001;144:557-560.
- Gül Ü, Çakmak S, Özel S, et al. Skin disorders in patients with hemiplegia and paraplegia. J Rehabil Med. 2009;41:681-683.
- Sarkar M, Mahesh D, Madabhavi I. Digital clubbing. Lung India. 2012;29:354-362.
To the Editor:
Few cases of unilateral nail changes affecting only the hemiplegic side after a stroke have been reported. We present a case of acquired unilateral nail clubbing and longitudinal melanonychia in a hemiparetic patient.
A 79-year-old Black man with a history of smoking and stroke presented with concerns of discoloration of the fingernails. His medical history was notable for congestive heart failure; hypertension; diabetes mellitus; hypercholesterolemia; and stroke 11 years prior, which resulted in right-sided hemiparesis. Physical examination revealed longitudinal, even hyperpigmentation of several fingernails on the hands, in addition to whitening of the nail beds, sparing the tips (Terry nails). Clubbing was noted only on the fingernails of the right hand; the fingernails of the left hand exhibited normal curvature (Figure). Pulse oximetry was conducted and demonstrated the following readings: unaffected left index finger, 98%; unaffected left middle finger, 100%; affected right index finger, 95%; and affected right middle finger, 97%. The patient was diagnosed with benign longitudinal melanonychia secondary to ethnic variation, Terry nails without underlying anemia or hypoalbuminemic state, and unilateral right-sided clubbing of the fingernails in the setting of right-sided hemiparesis.

Prior reports have documented the occurrence of nail pathologies after stroke and affecting hemiplegic limbs. Unilateral digital nail clubbing following a stroke was first reported in 19751; 2 reports concluded clubbing developed in all digits affected by the stroke, and the severity of clubbing was associated with the duration of the stroke.1,2 One study noted longitudinal reddish striation, Neapolitan nails, and unilateral clubbing more commonly in hemiplegic patients.3 Longitudinal reddish striation was the most frequent condition observed in this population, always affecting the entire thumbnail of the hemiplegic limb.3 A similar report observed clubbing only on the fingernails of the hemiplegic side.4
Digital clubbing describes an exaggerated nail curvature and bulbous overgrowth of the fingertips due to an expansion of connective tissue between the nail plate and the nail bed.3,5 Clubbed fingers are found in various chronic conditions affecting the heart, lungs, and liver. Although the pathogenesis of clubbing remains unknown, many hypothesize that it is a state of proliferation in response to digital hypoxia.5 Fittingly, our patient exhibited a relative hypoperfusion of the clubbed fingers in comparison to the unaffected side.
This case provides additional support for the phenomenon of unilateral nail changes limited to hemiplegic or hemiparetic limbs. The unique presentation of longitudinal melanonychia, clubbing, and a lowered pulse oximetry reading only affecting the hemiparetic side demonstrates the possible connection between hypoxia and nail clubbing in this patient population.
To the Editor:
Few cases of unilateral nail changes affecting only the hemiplegic side after a stroke have been reported. We present a case of acquired unilateral nail clubbing and longitudinal melanonychia in a hemiparetic patient.
A 79-year-old Black man with a history of smoking and stroke presented with concerns of discoloration of the fingernails. His medical history was notable for congestive heart failure; hypertension; diabetes mellitus; hypercholesterolemia; and stroke 11 years prior, which resulted in right-sided hemiparesis. Physical examination revealed longitudinal, even hyperpigmentation of several fingernails on the hands, in addition to whitening of the nail beds, sparing the tips (Terry nails). Clubbing was noted only on the fingernails of the right hand; the fingernails of the left hand exhibited normal curvature (Figure). Pulse oximetry was conducted and demonstrated the following readings: unaffected left index finger, 98%; unaffected left middle finger, 100%; affected right index finger, 95%; and affected right middle finger, 97%. The patient was diagnosed with benign longitudinal melanonychia secondary to ethnic variation, Terry nails without underlying anemia or hypoalbuminemic state, and unilateral right-sided clubbing of the fingernails in the setting of right-sided hemiparesis.

Prior reports have documented the occurrence of nail pathologies after stroke and affecting hemiplegic limbs. Unilateral digital nail clubbing following a stroke was first reported in 19751; 2 reports concluded clubbing developed in all digits affected by the stroke, and the severity of clubbing was associated with the duration of the stroke.1,2 One study noted longitudinal reddish striation, Neapolitan nails, and unilateral clubbing more commonly in hemiplegic patients.3 Longitudinal reddish striation was the most frequent condition observed in this population, always affecting the entire thumbnail of the hemiplegic limb.3 A similar report observed clubbing only on the fingernails of the hemiplegic side.4
Digital clubbing describes an exaggerated nail curvature and bulbous overgrowth of the fingertips due to an expansion of connective tissue between the nail plate and the nail bed.3,5 Clubbed fingers are found in various chronic conditions affecting the heart, lungs, and liver. Although the pathogenesis of clubbing remains unknown, many hypothesize that it is a state of proliferation in response to digital hypoxia.5 Fittingly, our patient exhibited a relative hypoperfusion of the clubbed fingers in comparison to the unaffected side.
This case provides additional support for the phenomenon of unilateral nail changes limited to hemiplegic or hemiparetic limbs. The unique presentation of longitudinal melanonychia, clubbing, and a lowered pulse oximetry reading only affecting the hemiparetic side demonstrates the possible connection between hypoxia and nail clubbing in this patient population.
- Denham M, Hodkinson H, Wright B. Unilateral clubbing in hemiplegia. Gerontology Clin (Basel). 1975;17:7-12.
- Alveraz A, McNair D, Wildman J, et al. Unilateral clubbing of the fingernails in patients with hemiplegia. Gerontology Clin (Basel). 1975;17:1-6.
- Siragusa M, Schepis C, Cosentino F, et al. Nail pathology in patients with hemiplegia. Br J Dermatol. 2001;144:557-560.
- Gül Ü, Çakmak S, Özel S, et al. Skin disorders in patients with hemiplegia and paraplegia. J Rehabil Med. 2009;41:681-683.
- Sarkar M, Mahesh D, Madabhavi I. Digital clubbing. Lung India. 2012;29:354-362.
- Denham M, Hodkinson H, Wright B. Unilateral clubbing in hemiplegia. Gerontology Clin (Basel). 1975;17:7-12.
- Alveraz A, McNair D, Wildman J, et al. Unilateral clubbing of the fingernails in patients with hemiplegia. Gerontology Clin (Basel). 1975;17:1-6.
- Siragusa M, Schepis C, Cosentino F, et al. Nail pathology in patients with hemiplegia. Br J Dermatol. 2001;144:557-560.
- Gül Ü, Çakmak S, Özel S, et al. Skin disorders in patients with hemiplegia and paraplegia. J Rehabil Med. 2009;41:681-683.
- Sarkar M, Mahesh D, Madabhavi I. Digital clubbing. Lung India. 2012;29:354-362.
Practice Points
- Unilateral nail changes can be limited to hemiplegic or hemiparetic limbs.
- Lowered pulse oximetry reading only affecting the hemiparetic side demonstrates the possible connection between hypoxia and nail clubbing in this patient population.
Stump Pemphigoid Demonstrating Circulating Anti–BP180 and BP230 Antibodies
To the Editor:
Bullous pemphigoid (BP) is a rare complication of lower limb amputation. Termed stump pemphigoid, it previously was described as a late complication arising on the stumps of leg amputees and tends to remain localized. We describe a case of stump pemphigoid presenting with an urticarial prodromal phase without generalized progression, confirmed by serum assay for circulating anti–basement membrane antibodies.
A 62-year-old man with a history of a right above-knee amputation initially presented with erythema as well as coalescing erosions and ulcers with fluid-filled vesicles and bullae on the amputation stump (Figure 1). The amputation was performed 15 years prior after a motorcycle accident. A skin biopsy of a vesicle on the amputation stump revealed subepidermal and focal intraepidermal clefting with hemorrhage and rare inflammatory cells composed of neutrophils and eosinophils (Figure 2). A tissue direct immunofluorescence test demonstrated linear C3 and IgG deposition along the dermoepidermal junction. Serum enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) demonstrated an anti-BP180 IgG of 50.90 U/mL and anti-BP230 IgG of 129.40 U/mL (reference range, <9.00 U/mL [for both]).
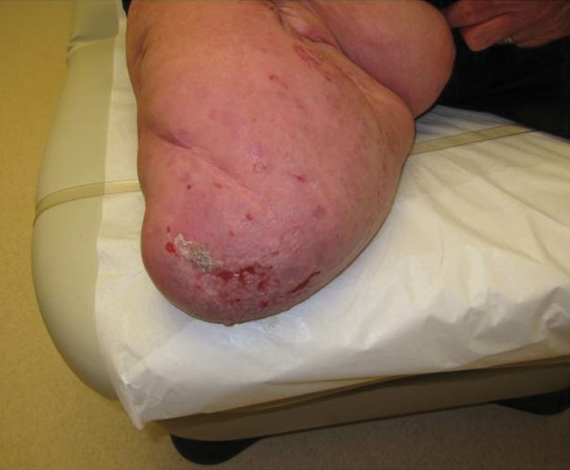
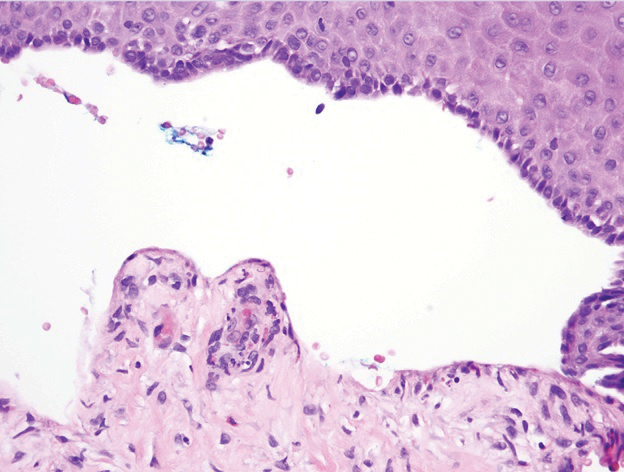
Topical clobetasol led to only modest improvement of blistering on the stump. Minor frictional trauma related to his leg prosthesis continued to trigger new vesicles and bullae on the stump. Oral prednisone 0.5 mg/kg daily was administered and tapered slowly over the course of 6 months. He also received oral niacinamide and doxycycline. He was completely clear after 3 weeks of initiating treatment and remained clear while prednisone was slowly tapered. One month after stopping prednisone he had recurrence of blisters on the stump only after he resumed wearing his prosthesis. Mycophenolate mofetil was started at a dosage of 1 g twice daily while he refrained from wearing the prosthesis. After 3 months he was able to wear the prosthesis without developing blisters. Two years after the initial presentation, repeat serum ELISA demonstrated normalization of the anti-BP180 IgG and anti-BP230 IgG titers. Thirty months after the initial presentation, mycophenolate mofetil was tapered and discontinued. The patient remained blisterfree and continued to wear his leg prosthesis without further blistering.
Amputees experience a high rate of skin complications on their stump,1 including friction blisters, shear injury, contact dermatitis, infections, and autoimmune blistering disorders (ie, BP, epidermolysis bullosa acquisita). The etiology of stump pemphigoid is not entirely understood but could be related to exposure of structural components of the hemidesmosome (eg, BP230, BP180), leading to autoantibody production as a consequence of either the underlying limb injury or from recurrent trauma related to limb prosthetics.2
Two previously reported cases of stump pemphigoid demonstrated a positive direct immunofluorescence antibody test.3,4 Another case demonstrated the presence of circulating IgG antibodies on indirect immunofluorescence to salt-split skin.5 We report a case of stump pemphigoid confirmed by presence of circulating anti–basement membrane antibodies on ELISA, supporting its use in the diagnostic workup and monitoring treatment response.
- Colgecen E, Korkmaz M, Ozyurt K, et al. A clinical evaluation of skin disorders of lower limb amputation sites. Int J Dermatol. 2016;55:468-472.
- Lo Schiavo A, Ruocco E, Brancaccio G, et al. Bullous pemphigoid: etiology, pathogenesis, and inducing factors: facts and controversies. Clin Dermatol. 2013;31:391-399.
- Reilly GD, Boulton AJ, Harrington CI. Stump pemphigoid: a new complication of the amputee. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed). 1983;287:875-876.
- de Jong MC, Kardaun SH, Tupker RA, et al. Immunomapping in localized bullous pemphigoid. Hautarzt. 1989;40:226-230.
- Brodell RT, Korman NJ. Stump pemphigoid. Cutis. 1996;57:245-246.
To the Editor:
Bullous pemphigoid (BP) is a rare complication of lower limb amputation. Termed stump pemphigoid, it previously was described as a late complication arising on the stumps of leg amputees and tends to remain localized. We describe a case of stump pemphigoid presenting with an urticarial prodromal phase without generalized progression, confirmed by serum assay for circulating anti–basement membrane antibodies.
A 62-year-old man with a history of a right above-knee amputation initially presented with erythema as well as coalescing erosions and ulcers with fluid-filled vesicles and bullae on the amputation stump (Figure 1). The amputation was performed 15 years prior after a motorcycle accident. A skin biopsy of a vesicle on the amputation stump revealed subepidermal and focal intraepidermal clefting with hemorrhage and rare inflammatory cells composed of neutrophils and eosinophils (Figure 2). A tissue direct immunofluorescence test demonstrated linear C3 and IgG deposition along the dermoepidermal junction. Serum enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) demonstrated an anti-BP180 IgG of 50.90 U/mL and anti-BP230 IgG of 129.40 U/mL (reference range, <9.00 U/mL [for both]).


Topical clobetasol led to only modest improvement of blistering on the stump. Minor frictional trauma related to his leg prosthesis continued to trigger new vesicles and bullae on the stump. Oral prednisone 0.5 mg/kg daily was administered and tapered slowly over the course of 6 months. He also received oral niacinamide and doxycycline. He was completely clear after 3 weeks of initiating treatment and remained clear while prednisone was slowly tapered. One month after stopping prednisone he had recurrence of blisters on the stump only after he resumed wearing his prosthesis. Mycophenolate mofetil was started at a dosage of 1 g twice daily while he refrained from wearing the prosthesis. After 3 months he was able to wear the prosthesis without developing blisters. Two years after the initial presentation, repeat serum ELISA demonstrated normalization of the anti-BP180 IgG and anti-BP230 IgG titers. Thirty months after the initial presentation, mycophenolate mofetil was tapered and discontinued. The patient remained blisterfree and continued to wear his leg prosthesis without further blistering.
Amputees experience a high rate of skin complications on their stump,1 including friction blisters, shear injury, contact dermatitis, infections, and autoimmune blistering disorders (ie, BP, epidermolysis bullosa acquisita). The etiology of stump pemphigoid is not entirely understood but could be related to exposure of structural components of the hemidesmosome (eg, BP230, BP180), leading to autoantibody production as a consequence of either the underlying limb injury or from recurrent trauma related to limb prosthetics.2
Two previously reported cases of stump pemphigoid demonstrated a positive direct immunofluorescence antibody test.3,4 Another case demonstrated the presence of circulating IgG antibodies on indirect immunofluorescence to salt-split skin.5 We report a case of stump pemphigoid confirmed by presence of circulating anti–basement membrane antibodies on ELISA, supporting its use in the diagnostic workup and monitoring treatment response.
To the Editor:
Bullous pemphigoid (BP) is a rare complication of lower limb amputation. Termed stump pemphigoid, it previously was described as a late complication arising on the stumps of leg amputees and tends to remain localized. We describe a case of stump pemphigoid presenting with an urticarial prodromal phase without generalized progression, confirmed by serum assay for circulating anti–basement membrane antibodies.
A 62-year-old man with a history of a right above-knee amputation initially presented with erythema as well as coalescing erosions and ulcers with fluid-filled vesicles and bullae on the amputation stump (Figure 1). The amputation was performed 15 years prior after a motorcycle accident. A skin biopsy of a vesicle on the amputation stump revealed subepidermal and focal intraepidermal clefting with hemorrhage and rare inflammatory cells composed of neutrophils and eosinophils (Figure 2). A tissue direct immunofluorescence test demonstrated linear C3 and IgG deposition along the dermoepidermal junction. Serum enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) demonstrated an anti-BP180 IgG of 50.90 U/mL and anti-BP230 IgG of 129.40 U/mL (reference range, <9.00 U/mL [for both]).


Topical clobetasol led to only modest improvement of blistering on the stump. Minor frictional trauma related to his leg prosthesis continued to trigger new vesicles and bullae on the stump. Oral prednisone 0.5 mg/kg daily was administered and tapered slowly over the course of 6 months. He also received oral niacinamide and doxycycline. He was completely clear after 3 weeks of initiating treatment and remained clear while prednisone was slowly tapered. One month after stopping prednisone he had recurrence of blisters on the stump only after he resumed wearing his prosthesis. Mycophenolate mofetil was started at a dosage of 1 g twice daily while he refrained from wearing the prosthesis. After 3 months he was able to wear the prosthesis without developing blisters. Two years after the initial presentation, repeat serum ELISA demonstrated normalization of the anti-BP180 IgG and anti-BP230 IgG titers. Thirty months after the initial presentation, mycophenolate mofetil was tapered and discontinued. The patient remained blisterfree and continued to wear his leg prosthesis without further blistering.
Amputees experience a high rate of skin complications on their stump,1 including friction blisters, shear injury, contact dermatitis, infections, and autoimmune blistering disorders (ie, BP, epidermolysis bullosa acquisita). The etiology of stump pemphigoid is not entirely understood but could be related to exposure of structural components of the hemidesmosome (eg, BP230, BP180), leading to autoantibody production as a consequence of either the underlying limb injury or from recurrent trauma related to limb prosthetics.2
Two previously reported cases of stump pemphigoid demonstrated a positive direct immunofluorescence antibody test.3,4 Another case demonstrated the presence of circulating IgG antibodies on indirect immunofluorescence to salt-split skin.5 We report a case of stump pemphigoid confirmed by presence of circulating anti–basement membrane antibodies on ELISA, supporting its use in the diagnostic workup and monitoring treatment response.
- Colgecen E, Korkmaz M, Ozyurt K, et al. A clinical evaluation of skin disorders of lower limb amputation sites. Int J Dermatol. 2016;55:468-472.
- Lo Schiavo A, Ruocco E, Brancaccio G, et al. Bullous pemphigoid: etiology, pathogenesis, and inducing factors: facts and controversies. Clin Dermatol. 2013;31:391-399.
- Reilly GD, Boulton AJ, Harrington CI. Stump pemphigoid: a new complication of the amputee. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed). 1983;287:875-876.
- de Jong MC, Kardaun SH, Tupker RA, et al. Immunomapping in localized bullous pemphigoid. Hautarzt. 1989;40:226-230.
- Brodell RT, Korman NJ. Stump pemphigoid. Cutis. 1996;57:245-246.
- Colgecen E, Korkmaz M, Ozyurt K, et al. A clinical evaluation of skin disorders of lower limb amputation sites. Int J Dermatol. 2016;55:468-472.
- Lo Schiavo A, Ruocco E, Brancaccio G, et al. Bullous pemphigoid: etiology, pathogenesis, and inducing factors: facts and controversies. Clin Dermatol. 2013;31:391-399.
- Reilly GD, Boulton AJ, Harrington CI. Stump pemphigoid: a new complication of the amputee. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed). 1983;287:875-876.
- de Jong MC, Kardaun SH, Tupker RA, et al. Immunomapping in localized bullous pemphigoid. Hautarzt. 1989;40:226-230.
- Brodell RT, Korman NJ. Stump pemphigoid. Cutis. 1996;57:245-246.
Practice Points
- Bullous pemphigoid (BP) can mimic friction blisters and should be considered in amputees who present with vesicles and bullae on their amputation stump.
- Circulating anti–basement membrane antibodies BP230 and BP180 IgG may aid in diagnosis when skin biopsy results are equivocal and also may be helpful in gauging treatment response.
Scrub Typhus in Chile
To the Editor:
Scrub typhus (ST) is an infection caused by Orientia tsutsugamushi (genus Rickettsia), which is transmitted by the larvae of trombiculid mites, commonly called chiggers. The disease mainly has been described in Asia in an area known as the Tsutsugamushi Triangle, delineated by Pakistan, eastern Russia, and northern Australia. Although this classic distribution remains, recent reports have documented 1 case in the Arabian Peninsula1 and more than 16 cases in southern Chile.2-4 The first case in Chile was published in 2011 from Chiloé Island.2 To date, no other cases have been reported in the Americas.1-6
We describe a new case of ST from Chiloé Island and compare it to the first case reported in Chile in 2011.2 Both patients showed the typical clinical manifestation, but because ST has become an increasingly suspected disease in southern regions of Chile, new cases are now easily diagnosed. This infection is diagnosed mainly by skin lesions; therefore, dermatologists should be aware of this diagnosis when presented with a febrile rash.
A 67-year-old man from the city of Punta Arenas presented to the emergency department with a dark necrotic lesion on the right foot of 1 week’s duration. The patient later developed a generalized pruritic rash and fever. He also reported muscle pain, headache, cough, night sweats, and odynophagia. He reported recent travel to a rural area in the northern part of Chiloé Island, where he came into contact with firewood and participated in outdoor activities. He had no other relevant medical history.
Physical examination revealed a temperature of 38 °C and a macular rash, with some papules distributed mainly on the face, trunk, and proximal extremities (Figure 1). He had a necrotic eschar on the dorsum of the right foot, with an erythematous halo (tache noire)(Figure 2).
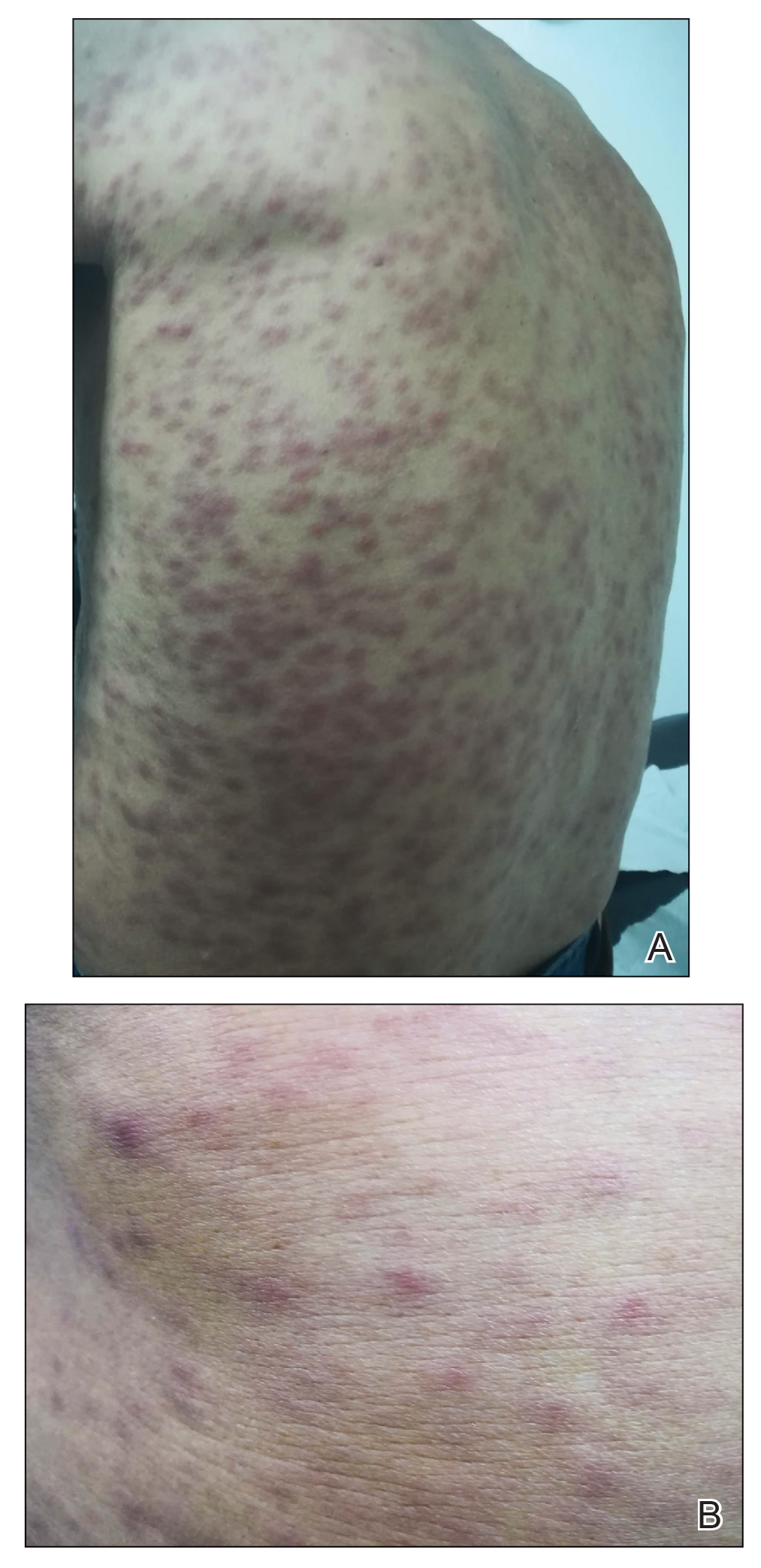
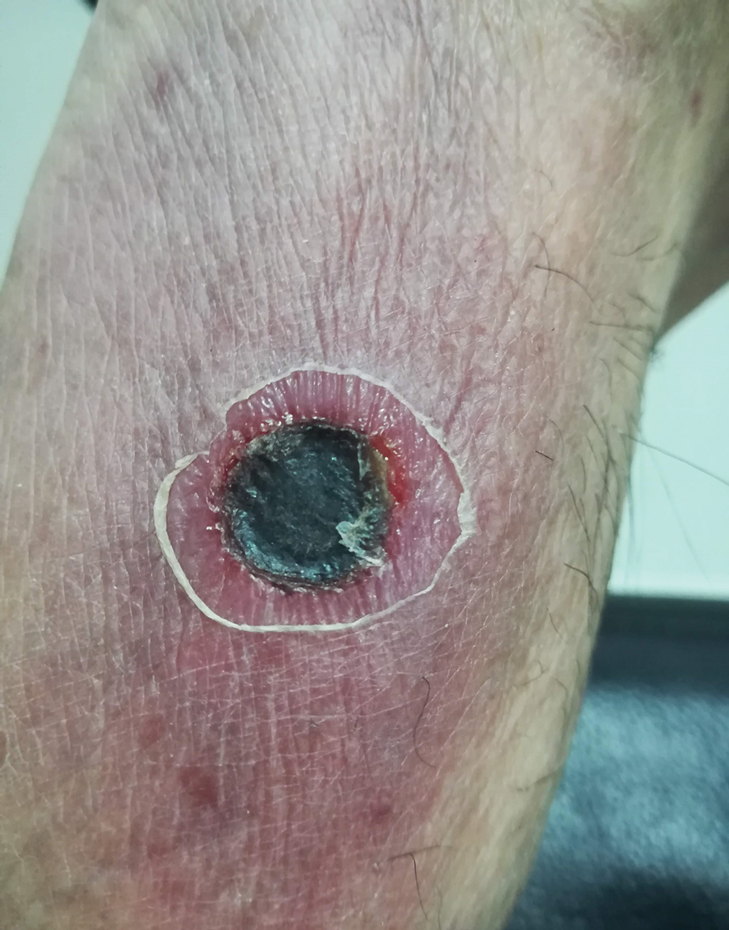
A complete blood cell count, urinalysis, and tests of hepatic and renal function were normal. C-reactive protein was elevated 18 times the normal value. Because of high awareness of ST in the region, eschar samples were taken and submitted for serologic testing and polymerase chain reaction (PCR) targeting the 16S rRNA Orientia gene. Empirical treatment with oral doxycycline 100 mg twice daily was started. Polymerase chain reaction analysis showed the presence of Orientia species, confirming the diagnosis of ST. The rash and eschar diminished considerably after 7 days of antibiotic treatment.
Scrub typhus is a high-impact disease in Asia, described mainly in an area known as the Tsutsugamushi Triangle. Recent reports show important epidemiologic changes in the distribution of the disease, with new published reports of cases outside this endemic area—1 in the Arabian peninsula1 and more than 16 in southern Chile.2-4
The disease begins with a painless, erythematous, and usually unnoticed papule at the site of the bite. After 48 to 72 hours, the papule changes to a necrotic form (tache noire), surrounded by a red halo that often is small, similar to a cigarette burn. This lesion is described in 20% to 90% of infected patients in different series.7 Two or 3 days later (1 to 3 weeks after exposure), high fever suddenly develops. Along with fever, a maculopapular rash distributed centrifugally develops, without compromise of the palms or soles. Patients frequently report headache and night sweating. Sometimes, ST is accompanied by muscle or joint pain, red eye, cough, and abdominal pain. Hearing loss and altered mental status less frequently have been reported.5,8
Common laboratory tests can be of use in diagnosis. An elevated C-reactive protein level and a slight to moderate increase in hepatic transaminases should be expected. Thrombocytopenia, leukopenia, and elevation of the lactate dehydrogenase level less frequently are present.5,9
Our case de1monstrated a typical presentation. The patient developed a febrile syndrome with a generalized rash and a tache noire–type eschar associated with muscle pain, headache, cough, night sweats, and odynophagia. Because of epidemiologic changes in the area, the familiar clinical findings, and laboratory confirmation, histologic studies were unnecessary. In cases in which the diagnosis is not evident, skin biopsy could be useful, as in the first case reported in Chile.2
In that first case, the patient initially was hospitalized because of a febrile syndrome; eventually, a necrotic eschar was noticed on his leg. He had been staying on Chiloé Island and reported being bitten by leeches on multiple occasions. Laboratory findings revealed only slightly raised levels of hepatic transaminases and alkaline phosphatase. After a more precise dermatologic evaluation, the eschar of a tache noire, combined with other clinical and laboratory findings, raised suspicion of ST. Because this entity had never been described in Chile, biopsy of the eschar was taken to consider other entities in the differential diagnosis. Biopsy showed necrotizing leukocytoclastic vasculitis in the dermis and subcutaneous tissue, perivascular inflammatory infiltrates comprising lymphocytes and macrophages, and rickettsial microorganisms inside endothelial cells under electron microscopic examination. The specimen was tested for the 16S ribosomal RNA Orientia gene; its presence confirmed the diagnosis.2
Classically, histology from the eschar shows signs of vasculitis and rickettsial microorganisms inside endothelial cells on electron microscopy.2,10 More recent publications describe important necrotic changes within keratinocytes as well as an inflammatory infiltrate comprising antigen-presenting cells, monocytes, macrophages, and dendritic cells. Using high-resolution thin sections with confocal laser scanning microscopy and staining of specific monoclonal antibodies against 56 kDa type-specific surface antigens, the bacteria were found inside antigen-presenting cells, many of them located perivascularly or passing through the endothelium.11
The causal agent in Asia is O tsutsugamushi, an obligate intracellular bacterium (genus Rickettsia). Orientia species are transmitted by larvae of trombiculid mites, commonly called chiggers. The reservoir is believed to be the same as with chiggers, in which some vertebrates become infected and trombiculid mites feed on them.12 Recent studies of Chilean cases have revealed the presence of a novel Orientia species, Candidatus Orientia chiloensis and its vector, trombiculid mites from the Herpetacarus species, Quadraseta species, and Paratrombicula species genera.13,14
A high seroprevalence of Orientia species in dogs was reported in the main cities of Chiloé Island. Rates were higher in rural settings and older dogs. Of 202 specimens, 21.3% were positive for IgG against Orientia species.15
In Chile, most cases of ST came from Chiloé Island; some reports of cases from continental Chilean regions have been published.6 Most cases have occurred in the context of activities that brought the patients in contact with plants and firewood in rural areas during the summer.3-6
The diagnosis of ST is eminently clinical, based on the triad of fever, macular or papular rash, and an inoculation necrotic eschar. The diagnosis is supported by epidemiologic facts and fast recovery after treatment is initiated.16 Although the diagnosis can be established based on a quick recovery in endemic countries, in areas such as Chile where incidence and distribution are not completely known, it is better to confirm the diagnosis with laboratory tests without delaying treatment. Several testing options exist, including serologic techniques (immunofluorescence or enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay), culture, and detection of the genetic material of Orientia species by PCR. Usually, IgM titers initially are negative, and IgG testing requires paired samples (acute and convalescent) to demonstrate seroconversion and therefore acute infection.17 Because culture requires a highly specialized laboratory, it is not frequently used. Polymerase chain reaction is recognized as the best confirmation method due to its high sensitivity and because it remains positive for a few days after treatment has been initiated. The specimen of choice is the eschar because of its high bacterial load. The base of the scar and the buffy coat are useful specimens when the eschar is unavailable.5,17-19
Due to potential complications of ST, empirical treatment with an antibiotic should be started based on clinical facts and never delayed because of diagnostic tests.18 Classically, ST is treated with a member of the tetracycline family, such as doxycycline, which provides a cure rate of 63% to 100% in ST.5
A 2017 systematic review of treatment options for this infection examined 11 studies from Southeast Asia, China, and South Korea (N=957).16 The review mainly compared doxycycline with azithromycin, chloramphenicol, and tetracycline. No significant difference in cure rate was noted in comparing doxycycline with any of the other 3 antibiotics; most of the studies examined were characterized by a moderate level of evidence. Regarding adverse effects, doxycycline showed a few more cases of gastrointestinal intolerance, and in 2 of 4 studies with chloramphenicol, patients presented with leukopenia.16 Several studies compared standard treatment (doxycycline) with rifampicin, telithromycin, erythromycin, and levofloxacin individually; similar cure rates were noted between doxycycline and each of those 4 agents.
Therapeutic failure in ST has been reported in several cases with the use of levofloxacin.20 Evidence for this novel antibiotic is still insufficient. Further studies are needed before rifampicin, telithromycin, erythromycin, or levofloxacin can be considered as options.Scrub typhus usually resolves within a few weeks. Left untreated, the disease can cause complications such as pneumonia, meningoencephalitis, renal failure, and even multiorgan failure and death. Without treatment, mortality is variable. A 2015 systematic review of mortality from untreated ST showed, on average, mortality of 6% (range, 0%–70%).21 When ST is treated, mortality falls to 0% to 30%.22 Cases reported in Chile have neither been lethal nor presented with severe complications.4,5
Scrub typhus is an infectious disease common in Asia, caused by O tsutsugamushi and transmitted by chiggers. It should be suspected when a febrile macular or papular rash and a tache noire appear. The diagnosis can be supported by laboratory findings, such as an elevated C-reactive protein level or a slight increase in the levels of hepatic transaminases, and response to treatment. The diagnosis is confirmed by serology or PCR of a specimen of the eschar. Empiric therapy with antibiotics is mandatory; doxycycline is the first option.
First described in Chile in 2011,2 ST was seen in a patient in whom disease was suspected because of clinical characteristics, laboratory and histologic findings, absence of prior reporting in South America, and confirmation with PCR targeting the 16S ribosomal RNA Orientia gene from specimens of the eschar. By 2020, 60 cases have been confirmed in Chile, not all of them published; there are no other reported cases in South America.
When comparing the first case in Chile2 with our case, we noted that both described classic clinical findings; however, the management approach and diagnostic challenges have evolved over time. Nowadays, ST is highly suspected, so it can be largely recognized and treated, which also provides better understanding of the nature of this disease in Chile. Because this infection is diagnosed mainly by characteristic cutaneous lesions, dermatologists should be aware of its epidemiology, clinical features, and transmission, and they should stay open to the possibility of this (until now) unusual diagnosis in South America.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the Chilean Rickettsia & Zoonosis Research Group (Thomas Weitzel, MD [Santiago, Chile]; Constanza Martínez-Valdebenito [Santiago, Chile]; and Gerardo Acosta-Jammet, DSc [Valdivia, Chile]), whose study in execution in the country allowed the detection of the case and confirmation by PCR. The authors also thank Juan Carlos Román, MD (Chiloé, Chile) who was part of the team that detected this case.
- Izzard L, Fuller A, Blacksell SD, et al. Isolation of a novel Orientia species (O. chuto sp. nov.) from a patient infected in Dubai. J Clin Microbiol. 2010;48:4404-4409.
- Balcells ME, Rabagliati R, García P, et al. Endemic scrub typhus-like illness, Chile. Emerg Infect Dis. 2011;17:1659-1663.
- Weitzel T, Dittrich S, López J, et al. Endemic scrub typhus in South America. N Engl J Med. 2016;375:954-961.
- Weitzel T, Acosta-Jamett G, Martínez-Valdebenito C, et al. Scrub typhus risk in travelers to southern Chile. Travel Med Infect Dis. 2019;29:78-79.
- Abarca K, Weitzel T, Martínez-Valdebenito C, et al. Scrub typhus, an emerging infectious disease in Chile. Rev Chilena Infectol. 2018;35:696-699.
- Weitzel T, Martínez-Valdebenito C, Acosta-Jamett G, et al. Scrub typhus in continental Chile, 2016-2018. Emerg Infect Dis. 2019;25:1214-1217.
- Guerrant RL, Walker DH, Weller PF, eds. Tropical Infectious Diseases: Principles, Pathogens and Practice. 3rd ed. Elsevier; 2011.
- Mahara F. Rickettsioses in Japan and the Far East. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2006;1078:60-73.
- Salje J. Orientia tsutsugamushi: a neglected but fascinating obligate intracellular bacterial pathogen. PLoS Pathog. 2017;13:e1006657.
- Lee JS, Park MY, Kim YJ, et al. Histopathological features in both the eschar and erythematous lesions of tsutsugamushi disease: identification of CD30+ cell infiltration in tsutsugamushi disease. Am J Dermatopathol. 2009;31:551-556.
- Paris DH, Phetsouvanh R, Tanganuchitcharnchai A, et al. Orientia tsutsugamushi in human scrub typhus eschars shows tropism for dendritic cells and monocytes rather than endothelium. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2012;6:E1466.
- Walker DH. Scrub typhus—scientific neglect, ever-widening impact. N Engl J Med. 2016;375:913-915.
- Acosta-Jamett G, Martínez-Valdebenito C, Beltrami E, et al. Identification of trombiculid mites (Acari: Trombiculidae) on rodents from Chiloé Island and molecular evidence of infection with Orientia species [published online January 23, 2020]. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. doi:10.1371/journal.pntd.0007619
- Martínez-Valdebenito C, Angulo J, et al. Molecular description of a novel Orientia species causing scrub typhus in Chile. Emerg Infect Dis. 2020;26:2148-2156.
- Weitzel T, Jiang J, Acosta-Jamett G, et al. Canine seroprevalence to Orientia species in southern Chile: a cross-sectional survey on the Chiloé Island. PLoS One. 2018;13:e0200362.
- Wee I, Lo A, Rodrigo C. Drug treatment of scrub typhus: a systematic review and meta-analysis of controlled clinical trials. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 2017;111:336-344.
- Koh GCKW, Maude RJ, Paris DH, et al. Diagnosis of scrub typhus. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2010;82:368-370.
- Weitzel T, Aylwin M, Martínez-Valdebenito C, et al. Imported scrub typhus: first case in South America and review of the literature. Trop Dis Travel Med Vaccines. 2018;4:10.
- Le Viet N, Laroche M, Thi Pham HL, et al. Use of eschar swabbing for the molecular diagnosis and genotyping of Orientia tsutsugamushi causing scrub typhus in Quang Nam province, Vietnam. 2017;11:e0005397.
- Jang HC, Choi SM, Jang MO, et al. Inappropriateness of quinolone in scrub typhus treatment due to gyrA mutation in Orientia tsutsugamushi Boryong strain. J Korean Med Sci. 2013;28:667-671.
- Taylor AJ, Paris DH, Newton PN. A systematic review of mortality from untreated scrub typhus (Orientia tsutsugamushi). PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2015;9:e0003971.
- Bonell A, Lubell Y, Newton PN, et al. Estimating the burden of scrub typhus: a systematic review. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2017;11:e0005838.
To the Editor:
Scrub typhus (ST) is an infection caused by Orientia tsutsugamushi (genus Rickettsia), which is transmitted by the larvae of trombiculid mites, commonly called chiggers. The disease mainly has been described in Asia in an area known as the Tsutsugamushi Triangle, delineated by Pakistan, eastern Russia, and northern Australia. Although this classic distribution remains, recent reports have documented 1 case in the Arabian Peninsula1 and more than 16 cases in southern Chile.2-4 The first case in Chile was published in 2011 from Chiloé Island.2 To date, no other cases have been reported in the Americas.1-6
We describe a new case of ST from Chiloé Island and compare it to the first case reported in Chile in 2011.2 Both patients showed the typical clinical manifestation, but because ST has become an increasingly suspected disease in southern regions of Chile, new cases are now easily diagnosed. This infection is diagnosed mainly by skin lesions; therefore, dermatologists should be aware of this diagnosis when presented with a febrile rash.
A 67-year-old man from the city of Punta Arenas presented to the emergency department with a dark necrotic lesion on the right foot of 1 week’s duration. The patient later developed a generalized pruritic rash and fever. He also reported muscle pain, headache, cough, night sweats, and odynophagia. He reported recent travel to a rural area in the northern part of Chiloé Island, where he came into contact with firewood and participated in outdoor activities. He had no other relevant medical history.
Physical examination revealed a temperature of 38 °C and a macular rash, with some papules distributed mainly on the face, trunk, and proximal extremities (Figure 1). He had a necrotic eschar on the dorsum of the right foot, with an erythematous halo (tache noire)(Figure 2).


A complete blood cell count, urinalysis, and tests of hepatic and renal function were normal. C-reactive protein was elevated 18 times the normal value. Because of high awareness of ST in the region, eschar samples were taken and submitted for serologic testing and polymerase chain reaction (PCR) targeting the 16S rRNA Orientia gene. Empirical treatment with oral doxycycline 100 mg twice daily was started. Polymerase chain reaction analysis showed the presence of Orientia species, confirming the diagnosis of ST. The rash and eschar diminished considerably after 7 days of antibiotic treatment.
Scrub typhus is a high-impact disease in Asia, described mainly in an area known as the Tsutsugamushi Triangle. Recent reports show important epidemiologic changes in the distribution of the disease, with new published reports of cases outside this endemic area—1 in the Arabian peninsula1 and more than 16 in southern Chile.2-4
The disease begins with a painless, erythematous, and usually unnoticed papule at the site of the bite. After 48 to 72 hours, the papule changes to a necrotic form (tache noire), surrounded by a red halo that often is small, similar to a cigarette burn. This lesion is described in 20% to 90% of infected patients in different series.7 Two or 3 days later (1 to 3 weeks after exposure), high fever suddenly develops. Along with fever, a maculopapular rash distributed centrifugally develops, without compromise of the palms or soles. Patients frequently report headache and night sweating. Sometimes, ST is accompanied by muscle or joint pain, red eye, cough, and abdominal pain. Hearing loss and altered mental status less frequently have been reported.5,8
Common laboratory tests can be of use in diagnosis. An elevated C-reactive protein level and a slight to moderate increase in hepatic transaminases should be expected. Thrombocytopenia, leukopenia, and elevation of the lactate dehydrogenase level less frequently are present.5,9
Our case de1monstrated a typical presentation. The patient developed a febrile syndrome with a generalized rash and a tache noire–type eschar associated with muscle pain, headache, cough, night sweats, and odynophagia. Because of epidemiologic changes in the area, the familiar clinical findings, and laboratory confirmation, histologic studies were unnecessary. In cases in which the diagnosis is not evident, skin biopsy could be useful, as in the first case reported in Chile.2
In that first case, the patient initially was hospitalized because of a febrile syndrome; eventually, a necrotic eschar was noticed on his leg. He had been staying on Chiloé Island and reported being bitten by leeches on multiple occasions. Laboratory findings revealed only slightly raised levels of hepatic transaminases and alkaline phosphatase. After a more precise dermatologic evaluation, the eschar of a tache noire, combined with other clinical and laboratory findings, raised suspicion of ST. Because this entity had never been described in Chile, biopsy of the eschar was taken to consider other entities in the differential diagnosis. Biopsy showed necrotizing leukocytoclastic vasculitis in the dermis and subcutaneous tissue, perivascular inflammatory infiltrates comprising lymphocytes and macrophages, and rickettsial microorganisms inside endothelial cells under electron microscopic examination. The specimen was tested for the 16S ribosomal RNA Orientia gene; its presence confirmed the diagnosis.2
Classically, histology from the eschar shows signs of vasculitis and rickettsial microorganisms inside endothelial cells on electron microscopy.2,10 More recent publications describe important necrotic changes within keratinocytes as well as an inflammatory infiltrate comprising antigen-presenting cells, monocytes, macrophages, and dendritic cells. Using high-resolution thin sections with confocal laser scanning microscopy and staining of specific monoclonal antibodies against 56 kDa type-specific surface antigens, the bacteria were found inside antigen-presenting cells, many of them located perivascularly or passing through the endothelium.11
The causal agent in Asia is O tsutsugamushi, an obligate intracellular bacterium (genus Rickettsia). Orientia species are transmitted by larvae of trombiculid mites, commonly called chiggers. The reservoir is believed to be the same as with chiggers, in which some vertebrates become infected and trombiculid mites feed on them.12 Recent studies of Chilean cases have revealed the presence of a novel Orientia species, Candidatus Orientia chiloensis and its vector, trombiculid mites from the Herpetacarus species, Quadraseta species, and Paratrombicula species genera.13,14
A high seroprevalence of Orientia species in dogs was reported in the main cities of Chiloé Island. Rates were higher in rural settings and older dogs. Of 202 specimens, 21.3% were positive for IgG against Orientia species.15
In Chile, most cases of ST came from Chiloé Island; some reports of cases from continental Chilean regions have been published.6 Most cases have occurred in the context of activities that brought the patients in contact with plants and firewood in rural areas during the summer.3-6
The diagnosis of ST is eminently clinical, based on the triad of fever, macular or papular rash, and an inoculation necrotic eschar. The diagnosis is supported by epidemiologic facts and fast recovery after treatment is initiated.16 Although the diagnosis can be established based on a quick recovery in endemic countries, in areas such as Chile where incidence and distribution are not completely known, it is better to confirm the diagnosis with laboratory tests without delaying treatment. Several testing options exist, including serologic techniques (immunofluorescence or enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay), culture, and detection of the genetic material of Orientia species by PCR. Usually, IgM titers initially are negative, and IgG testing requires paired samples (acute and convalescent) to demonstrate seroconversion and therefore acute infection.17 Because culture requires a highly specialized laboratory, it is not frequently used. Polymerase chain reaction is recognized as the best confirmation method due to its high sensitivity and because it remains positive for a few days after treatment has been initiated. The specimen of choice is the eschar because of its high bacterial load. The base of the scar and the buffy coat are useful specimens when the eschar is unavailable.5,17-19
Due to potential complications of ST, empirical treatment with an antibiotic should be started based on clinical facts and never delayed because of diagnostic tests.18 Classically, ST is treated with a member of the tetracycline family, such as doxycycline, which provides a cure rate of 63% to 100% in ST.5
A 2017 systematic review of treatment options for this infection examined 11 studies from Southeast Asia, China, and South Korea (N=957).16 The review mainly compared doxycycline with azithromycin, chloramphenicol, and tetracycline. No significant difference in cure rate was noted in comparing doxycycline with any of the other 3 antibiotics; most of the studies examined were characterized by a moderate level of evidence. Regarding adverse effects, doxycycline showed a few more cases of gastrointestinal intolerance, and in 2 of 4 studies with chloramphenicol, patients presented with leukopenia.16 Several studies compared standard treatment (doxycycline) with rifampicin, telithromycin, erythromycin, and levofloxacin individually; similar cure rates were noted between doxycycline and each of those 4 agents.
Therapeutic failure in ST has been reported in several cases with the use of levofloxacin.20 Evidence for this novel antibiotic is still insufficient. Further studies are needed before rifampicin, telithromycin, erythromycin, or levofloxacin can be considered as options.Scrub typhus usually resolves within a few weeks. Left untreated, the disease can cause complications such as pneumonia, meningoencephalitis, renal failure, and even multiorgan failure and death. Without treatment, mortality is variable. A 2015 systematic review of mortality from untreated ST showed, on average, mortality of 6% (range, 0%–70%).21 When ST is treated, mortality falls to 0% to 30%.22 Cases reported in Chile have neither been lethal nor presented with severe complications.4,5
Scrub typhus is an infectious disease common in Asia, caused by O tsutsugamushi and transmitted by chiggers. It should be suspected when a febrile macular or papular rash and a tache noire appear. The diagnosis can be supported by laboratory findings, such as an elevated C-reactive protein level or a slight increase in the levels of hepatic transaminases, and response to treatment. The diagnosis is confirmed by serology or PCR of a specimen of the eschar. Empiric therapy with antibiotics is mandatory; doxycycline is the first option.
First described in Chile in 2011,2 ST was seen in a patient in whom disease was suspected because of clinical characteristics, laboratory and histologic findings, absence of prior reporting in South America, and confirmation with PCR targeting the 16S ribosomal RNA Orientia gene from specimens of the eschar. By 2020, 60 cases have been confirmed in Chile, not all of them published; there are no other reported cases in South America.
When comparing the first case in Chile2 with our case, we noted that both described classic clinical findings; however, the management approach and diagnostic challenges have evolved over time. Nowadays, ST is highly suspected, so it can be largely recognized and treated, which also provides better understanding of the nature of this disease in Chile. Because this infection is diagnosed mainly by characteristic cutaneous lesions, dermatologists should be aware of its epidemiology, clinical features, and transmission, and they should stay open to the possibility of this (until now) unusual diagnosis in South America.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the Chilean Rickettsia & Zoonosis Research Group (Thomas Weitzel, MD [Santiago, Chile]; Constanza Martínez-Valdebenito [Santiago, Chile]; and Gerardo Acosta-Jammet, DSc [Valdivia, Chile]), whose study in execution in the country allowed the detection of the case and confirmation by PCR. The authors also thank Juan Carlos Román, MD (Chiloé, Chile) who was part of the team that detected this case.
To the Editor:
Scrub typhus (ST) is an infection caused by Orientia tsutsugamushi (genus Rickettsia), which is transmitted by the larvae of trombiculid mites, commonly called chiggers. The disease mainly has been described in Asia in an area known as the Tsutsugamushi Triangle, delineated by Pakistan, eastern Russia, and northern Australia. Although this classic distribution remains, recent reports have documented 1 case in the Arabian Peninsula1 and more than 16 cases in southern Chile.2-4 The first case in Chile was published in 2011 from Chiloé Island.2 To date, no other cases have been reported in the Americas.1-6
We describe a new case of ST from Chiloé Island and compare it to the first case reported in Chile in 2011.2 Both patients showed the typical clinical manifestation, but because ST has become an increasingly suspected disease in southern regions of Chile, new cases are now easily diagnosed. This infection is diagnosed mainly by skin lesions; therefore, dermatologists should be aware of this diagnosis when presented with a febrile rash.
A 67-year-old man from the city of Punta Arenas presented to the emergency department with a dark necrotic lesion on the right foot of 1 week’s duration. The patient later developed a generalized pruritic rash and fever. He also reported muscle pain, headache, cough, night sweats, and odynophagia. He reported recent travel to a rural area in the northern part of Chiloé Island, where he came into contact with firewood and participated in outdoor activities. He had no other relevant medical history.
Physical examination revealed a temperature of 38 °C and a macular rash, with some papules distributed mainly on the face, trunk, and proximal extremities (Figure 1). He had a necrotic eschar on the dorsum of the right foot, with an erythematous halo (tache noire)(Figure 2).


A complete blood cell count, urinalysis, and tests of hepatic and renal function were normal. C-reactive protein was elevated 18 times the normal value. Because of high awareness of ST in the region, eschar samples were taken and submitted for serologic testing and polymerase chain reaction (PCR) targeting the 16S rRNA Orientia gene. Empirical treatment with oral doxycycline 100 mg twice daily was started. Polymerase chain reaction analysis showed the presence of Orientia species, confirming the diagnosis of ST. The rash and eschar diminished considerably after 7 days of antibiotic treatment.
Scrub typhus is a high-impact disease in Asia, described mainly in an area known as the Tsutsugamushi Triangle. Recent reports show important epidemiologic changes in the distribution of the disease, with new published reports of cases outside this endemic area—1 in the Arabian peninsula1 and more than 16 in southern Chile.2-4
The disease begins with a painless, erythematous, and usually unnoticed papule at the site of the bite. After 48 to 72 hours, the papule changes to a necrotic form (tache noire), surrounded by a red halo that often is small, similar to a cigarette burn. This lesion is described in 20% to 90% of infected patients in different series.7 Two or 3 days later (1 to 3 weeks after exposure), high fever suddenly develops. Along with fever, a maculopapular rash distributed centrifugally develops, without compromise of the palms or soles. Patients frequently report headache and night sweating. Sometimes, ST is accompanied by muscle or joint pain, red eye, cough, and abdominal pain. Hearing loss and altered mental status less frequently have been reported.5,8
Common laboratory tests can be of use in diagnosis. An elevated C-reactive protein level and a slight to moderate increase in hepatic transaminases should be expected. Thrombocytopenia, leukopenia, and elevation of the lactate dehydrogenase level less frequently are present.5,9
Our case de1monstrated a typical presentation. The patient developed a febrile syndrome with a generalized rash and a tache noire–type eschar associated with muscle pain, headache, cough, night sweats, and odynophagia. Because of epidemiologic changes in the area, the familiar clinical findings, and laboratory confirmation, histologic studies were unnecessary. In cases in which the diagnosis is not evident, skin biopsy could be useful, as in the first case reported in Chile.2
In that first case, the patient initially was hospitalized because of a febrile syndrome; eventually, a necrotic eschar was noticed on his leg. He had been staying on Chiloé Island and reported being bitten by leeches on multiple occasions. Laboratory findings revealed only slightly raised levels of hepatic transaminases and alkaline phosphatase. After a more precise dermatologic evaluation, the eschar of a tache noire, combined with other clinical and laboratory findings, raised suspicion of ST. Because this entity had never been described in Chile, biopsy of the eschar was taken to consider other entities in the differential diagnosis. Biopsy showed necrotizing leukocytoclastic vasculitis in the dermis and subcutaneous tissue, perivascular inflammatory infiltrates comprising lymphocytes and macrophages, and rickettsial microorganisms inside endothelial cells under electron microscopic examination. The specimen was tested for the 16S ribosomal RNA Orientia gene; its presence confirmed the diagnosis.2
Classically, histology from the eschar shows signs of vasculitis and rickettsial microorganisms inside endothelial cells on electron microscopy.2,10 More recent publications describe important necrotic changes within keratinocytes as well as an inflammatory infiltrate comprising antigen-presenting cells, monocytes, macrophages, and dendritic cells. Using high-resolution thin sections with confocal laser scanning microscopy and staining of specific monoclonal antibodies against 56 kDa type-specific surface antigens, the bacteria were found inside antigen-presenting cells, many of them located perivascularly or passing through the endothelium.11
The causal agent in Asia is O tsutsugamushi, an obligate intracellular bacterium (genus Rickettsia). Orientia species are transmitted by larvae of trombiculid mites, commonly called chiggers. The reservoir is believed to be the same as with chiggers, in which some vertebrates become infected and trombiculid mites feed on them.12 Recent studies of Chilean cases have revealed the presence of a novel Orientia species, Candidatus Orientia chiloensis and its vector, trombiculid mites from the Herpetacarus species, Quadraseta species, and Paratrombicula species genera.13,14
A high seroprevalence of Orientia species in dogs was reported in the main cities of Chiloé Island. Rates were higher in rural settings and older dogs. Of 202 specimens, 21.3% were positive for IgG against Orientia species.15
In Chile, most cases of ST came from Chiloé Island; some reports of cases from continental Chilean regions have been published.6 Most cases have occurred in the context of activities that brought the patients in contact with plants and firewood in rural areas during the summer.3-6
The diagnosis of ST is eminently clinical, based on the triad of fever, macular or papular rash, and an inoculation necrotic eschar. The diagnosis is supported by epidemiologic facts and fast recovery after treatment is initiated.16 Although the diagnosis can be established based on a quick recovery in endemic countries, in areas such as Chile where incidence and distribution are not completely known, it is better to confirm the diagnosis with laboratory tests without delaying treatment. Several testing options exist, including serologic techniques (immunofluorescence or enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay), culture, and detection of the genetic material of Orientia species by PCR. Usually, IgM titers initially are negative, and IgG testing requires paired samples (acute and convalescent) to demonstrate seroconversion and therefore acute infection.17 Because culture requires a highly specialized laboratory, it is not frequently used. Polymerase chain reaction is recognized as the best confirmation method due to its high sensitivity and because it remains positive for a few days after treatment has been initiated. The specimen of choice is the eschar because of its high bacterial load. The base of the scar and the buffy coat are useful specimens when the eschar is unavailable.5,17-19
Due to potential complications of ST, empirical treatment with an antibiotic should be started based on clinical facts and never delayed because of diagnostic tests.18 Classically, ST is treated with a member of the tetracycline family, such as doxycycline, which provides a cure rate of 63% to 100% in ST.5
A 2017 systematic review of treatment options for this infection examined 11 studies from Southeast Asia, China, and South Korea (N=957).16 The review mainly compared doxycycline with azithromycin, chloramphenicol, and tetracycline. No significant difference in cure rate was noted in comparing doxycycline with any of the other 3 antibiotics; most of the studies examined were characterized by a moderate level of evidence. Regarding adverse effects, doxycycline showed a few more cases of gastrointestinal intolerance, and in 2 of 4 studies with chloramphenicol, patients presented with leukopenia.16 Several studies compared standard treatment (doxycycline) with rifampicin, telithromycin, erythromycin, and levofloxacin individually; similar cure rates were noted between doxycycline and each of those 4 agents.
Therapeutic failure in ST has been reported in several cases with the use of levofloxacin.20 Evidence for this novel antibiotic is still insufficient. Further studies are needed before rifampicin, telithromycin, erythromycin, or levofloxacin can be considered as options.Scrub typhus usually resolves within a few weeks. Left untreated, the disease can cause complications such as pneumonia, meningoencephalitis, renal failure, and even multiorgan failure and death. Without treatment, mortality is variable. A 2015 systematic review of mortality from untreated ST showed, on average, mortality of 6% (range, 0%–70%).21 When ST is treated, mortality falls to 0% to 30%.22 Cases reported in Chile have neither been lethal nor presented with severe complications.4,5
Scrub typhus is an infectious disease common in Asia, caused by O tsutsugamushi and transmitted by chiggers. It should be suspected when a febrile macular or papular rash and a tache noire appear. The diagnosis can be supported by laboratory findings, such as an elevated C-reactive protein level or a slight increase in the levels of hepatic transaminases, and response to treatment. The diagnosis is confirmed by serology or PCR of a specimen of the eschar. Empiric therapy with antibiotics is mandatory; doxycycline is the first option.
First described in Chile in 2011,2 ST was seen in a patient in whom disease was suspected because of clinical characteristics, laboratory and histologic findings, absence of prior reporting in South America, and confirmation with PCR targeting the 16S ribosomal RNA Orientia gene from specimens of the eschar. By 2020, 60 cases have been confirmed in Chile, not all of them published; there are no other reported cases in South America.
When comparing the first case in Chile2 with our case, we noted that both described classic clinical findings; however, the management approach and diagnostic challenges have evolved over time. Nowadays, ST is highly suspected, so it can be largely recognized and treated, which also provides better understanding of the nature of this disease in Chile. Because this infection is diagnosed mainly by characteristic cutaneous lesions, dermatologists should be aware of its epidemiology, clinical features, and transmission, and they should stay open to the possibility of this (until now) unusual diagnosis in South America.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the Chilean Rickettsia & Zoonosis Research Group (Thomas Weitzel, MD [Santiago, Chile]; Constanza Martínez-Valdebenito [Santiago, Chile]; and Gerardo Acosta-Jammet, DSc [Valdivia, Chile]), whose study in execution in the country allowed the detection of the case and confirmation by PCR. The authors also thank Juan Carlos Román, MD (Chiloé, Chile) who was part of the team that detected this case.
- Izzard L, Fuller A, Blacksell SD, et al. Isolation of a novel Orientia species (O. chuto sp. nov.) from a patient infected in Dubai. J Clin Microbiol. 2010;48:4404-4409.
- Balcells ME, Rabagliati R, García P, et al. Endemic scrub typhus-like illness, Chile. Emerg Infect Dis. 2011;17:1659-1663.
- Weitzel T, Dittrich S, López J, et al. Endemic scrub typhus in South America. N Engl J Med. 2016;375:954-961.
- Weitzel T, Acosta-Jamett G, Martínez-Valdebenito C, et al. Scrub typhus risk in travelers to southern Chile. Travel Med Infect Dis. 2019;29:78-79.
- Abarca K, Weitzel T, Martínez-Valdebenito C, et al. Scrub typhus, an emerging infectious disease in Chile. Rev Chilena Infectol. 2018;35:696-699.
- Weitzel T, Martínez-Valdebenito C, Acosta-Jamett G, et al. Scrub typhus in continental Chile, 2016-2018. Emerg Infect Dis. 2019;25:1214-1217.
- Guerrant RL, Walker DH, Weller PF, eds. Tropical Infectious Diseases: Principles, Pathogens and Practice. 3rd ed. Elsevier; 2011.
- Mahara F. Rickettsioses in Japan and the Far East. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2006;1078:60-73.
- Salje J. Orientia tsutsugamushi: a neglected but fascinating obligate intracellular bacterial pathogen. PLoS Pathog. 2017;13:e1006657.
- Lee JS, Park MY, Kim YJ, et al. Histopathological features in both the eschar and erythematous lesions of tsutsugamushi disease: identification of CD30+ cell infiltration in tsutsugamushi disease. Am J Dermatopathol. 2009;31:551-556.
- Paris DH, Phetsouvanh R, Tanganuchitcharnchai A, et al. Orientia tsutsugamushi in human scrub typhus eschars shows tropism for dendritic cells and monocytes rather than endothelium. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2012;6:E1466.
- Walker DH. Scrub typhus—scientific neglect, ever-widening impact. N Engl J Med. 2016;375:913-915.
- Acosta-Jamett G, Martínez-Valdebenito C, Beltrami E, et al. Identification of trombiculid mites (Acari: Trombiculidae) on rodents from Chiloé Island and molecular evidence of infection with Orientia species [published online January 23, 2020]. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. doi:10.1371/journal.pntd.0007619
- Martínez-Valdebenito C, Angulo J, et al. Molecular description of a novel Orientia species causing scrub typhus in Chile. Emerg Infect Dis. 2020;26:2148-2156.
- Weitzel T, Jiang J, Acosta-Jamett G, et al. Canine seroprevalence to Orientia species in southern Chile: a cross-sectional survey on the Chiloé Island. PLoS One. 2018;13:e0200362.
- Wee I, Lo A, Rodrigo C. Drug treatment of scrub typhus: a systematic review and meta-analysis of controlled clinical trials. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 2017;111:336-344.
- Koh GCKW, Maude RJ, Paris DH, et al. Diagnosis of scrub typhus. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2010;82:368-370.
- Weitzel T, Aylwin M, Martínez-Valdebenito C, et al. Imported scrub typhus: first case in South America and review of the literature. Trop Dis Travel Med Vaccines. 2018;4:10.
- Le Viet N, Laroche M, Thi Pham HL, et al. Use of eschar swabbing for the molecular diagnosis and genotyping of Orientia tsutsugamushi causing scrub typhus in Quang Nam province, Vietnam. 2017;11:e0005397.
- Jang HC, Choi SM, Jang MO, et al. Inappropriateness of quinolone in scrub typhus treatment due to gyrA mutation in Orientia tsutsugamushi Boryong strain. J Korean Med Sci. 2013;28:667-671.
- Taylor AJ, Paris DH, Newton PN. A systematic review of mortality from untreated scrub typhus (Orientia tsutsugamushi). PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2015;9:e0003971.
- Bonell A, Lubell Y, Newton PN, et al. Estimating the burden of scrub typhus: a systematic review. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2017;11:e0005838.
- Izzard L, Fuller A, Blacksell SD, et al. Isolation of a novel Orientia species (O. chuto sp. nov.) from a patient infected in Dubai. J Clin Microbiol. 2010;48:4404-4409.
- Balcells ME, Rabagliati R, García P, et al. Endemic scrub typhus-like illness, Chile. Emerg Infect Dis. 2011;17:1659-1663.
- Weitzel T, Dittrich S, López J, et al. Endemic scrub typhus in South America. N Engl J Med. 2016;375:954-961.
- Weitzel T, Acosta-Jamett G, Martínez-Valdebenito C, et al. Scrub typhus risk in travelers to southern Chile. Travel Med Infect Dis. 2019;29:78-79.
- Abarca K, Weitzel T, Martínez-Valdebenito C, et al. Scrub typhus, an emerging infectious disease in Chile. Rev Chilena Infectol. 2018;35:696-699.
- Weitzel T, Martínez-Valdebenito C, Acosta-Jamett G, et al. Scrub typhus in continental Chile, 2016-2018. Emerg Infect Dis. 2019;25:1214-1217.
- Guerrant RL, Walker DH, Weller PF, eds. Tropical Infectious Diseases: Principles, Pathogens and Practice. 3rd ed. Elsevier; 2011.
- Mahara F. Rickettsioses in Japan and the Far East. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2006;1078:60-73.
- Salje J. Orientia tsutsugamushi: a neglected but fascinating obligate intracellular bacterial pathogen. PLoS Pathog. 2017;13:e1006657.
- Lee JS, Park MY, Kim YJ, et al. Histopathological features in both the eschar and erythematous lesions of tsutsugamushi disease: identification of CD30+ cell infiltration in tsutsugamushi disease. Am J Dermatopathol. 2009;31:551-556.
- Paris DH, Phetsouvanh R, Tanganuchitcharnchai A, et al. Orientia tsutsugamushi in human scrub typhus eschars shows tropism for dendritic cells and monocytes rather than endothelium. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2012;6:E1466.
- Walker DH. Scrub typhus—scientific neglect, ever-widening impact. N Engl J Med. 2016;375:913-915.
- Acosta-Jamett G, Martínez-Valdebenito C, Beltrami E, et al. Identification of trombiculid mites (Acari: Trombiculidae) on rodents from Chiloé Island and molecular evidence of infection with Orientia species [published online January 23, 2020]. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. doi:10.1371/journal.pntd.0007619
- Martínez-Valdebenito C, Angulo J, et al. Molecular description of a novel Orientia species causing scrub typhus in Chile. Emerg Infect Dis. 2020;26:2148-2156.
- Weitzel T, Jiang J, Acosta-Jamett G, et al. Canine seroprevalence to Orientia species in southern Chile: a cross-sectional survey on the Chiloé Island. PLoS One. 2018;13:e0200362.
- Wee I, Lo A, Rodrigo C. Drug treatment of scrub typhus: a systematic review and meta-analysis of controlled clinical trials. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 2017;111:336-344.
- Koh GCKW, Maude RJ, Paris DH, et al. Diagnosis of scrub typhus. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2010;82:368-370.
- Weitzel T, Aylwin M, Martínez-Valdebenito C, et al. Imported scrub typhus: first case in South America and review of the literature. Trop Dis Travel Med Vaccines. 2018;4:10.
- Le Viet N, Laroche M, Thi Pham HL, et al. Use of eschar swabbing for the molecular diagnosis and genotyping of Orientia tsutsugamushi causing scrub typhus in Quang Nam province, Vietnam. 2017;11:e0005397.
- Jang HC, Choi SM, Jang MO, et al. Inappropriateness of quinolone in scrub typhus treatment due to gyrA mutation in Orientia tsutsugamushi Boryong strain. J Korean Med Sci. 2013;28:667-671.
- Taylor AJ, Paris DH, Newton PN. A systematic review of mortality from untreated scrub typhus (Orientia tsutsugamushi). PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2015;9:e0003971.
- Bonell A, Lubell Y, Newton PN, et al. Estimating the burden of scrub typhus: a systematic review. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2017;11:e0005838.
Practice Points
- Scrub typhus is clinically suspected in patients who present with a febrile macular or papular rash and a characteristic necrotic eschar known as tache noire while residing in or traveling to rural areas.
- Scrub typhus can lead to serious complications. Due to its changing epidemiology, dermatologists outside the usual area of distribution should be aware in the event that new cases emerge.
Hidden Basal Cell Carcinoma in the Intergluteal Crease
Practice Gap
Basal cell carcinoma (BCC) is the most common cancer, and its incidence is on the rise.1 The risk of this skin cancer is increased when there is a history of squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) or BCC.2 Basal cell carcinoma often is found in sun-exposed areas, most commonly due to a history of intense sunburn.3 Other risk factors include male gender and increased age.4
Eighty percent to 85% of BCCs present on the head and neck5; however, BCC also can occur in unusual locations. When BCC presents in areas such as the perianal region, it is found to be larger than when found in more common areas,6 likely because neoplasms in this sensitive area often are overlooked. Literature on BCC of the intergluteal crease is limited.7 Being educated on the existence of BCC in this sensitive area can aid proper diagnosis.
The Technique and Case
An 83-year-old woman presented to the dermatology clinic for a suspicious lesion in the intergluteal crease that was tender to palpation with drainage. She first noticed this lesion and reported it to her primary care physician at a visit 6 months prior. The primary care physician did not pursue investigation of the lesion. One month later, the patient was seen by a gastroenterologist for the lesion and was referred to dermatology. The patient’s medical history included SCC and BCC on the face, both treated successfully with Mohs micrographic surgery.
Physical examination revealed a 2.6×1.1-cm, erythematous, nodular plaque in the coccygeal area of the intergluteal crease (Figure 1). A shave biopsy disclosed BCC, nodular type, ulcerated. Microscopically, there were nodular aggregates of basaloid cells with hyperchromatic nuclei and peripheral palisading, separated from mucinous stromal surroundings by artefactual clefts.
The initial differential diagnosis for this patient’s lesion included an ulcer or SCC. Basal cell carcinoma was not suspected due to the location and appearance of the lesion. The patient was successfully treated with Mohs micrographic surgery.
Practical Implications
Without thorough examination, this cancerous lesion would not have been seen (Figure 2). Therefore, it is important to practice thorough physical examination skills to avoid missing these cancers, particularly when examining a patient with a history of SCC or BCC. Furthermore, biopsy is recommended for suspicious lesions to rule out BCC.
Be careful not to get caught up in epidemiological or demographic considerations when making a diagnosis of this kind or when assessing the severity of a lesion. This patient, for instance, was female, which makes her less likely to present with BCC.8 Moreover, the cancer presented in a highly unlikely location for BCC, where there had not been significant sunburn.9 Patients and physicians should be educated about the incidence of BCC in unexpected areas; without a second and close look, this BCC could have been missed.
Final Thoughts
The literature continuously demonstrates the rarity of BCC in the intergluteal crease.10 However, when perianal BCC is properly identified and treated with local excision, prognosis is good.11 Basal cell carcinoma has been seen to arise in other sensitive locations; vulvar, nipple, and scrotal BCC neoplasms are among the uncommon locations where BCC has appeared.12 These areas are frequently—and easily—ignored. A total-body skin examination should be performed to ensure that these insidious-onset carcinomas are not overlooked to protect patients from the adverse consequences of untreated cancer.13
- Roewert-Huber J, Lange-Asschenfeldt B, Stockfleth E, et al. Epidemiology and aetiology of basal cell carcinoma. Br J Dermatol. 2007;157(suppl 2):47-51.
- Rogers HW, Weinstock MA, Feldman SR, et al. Incidence estimate of nonmelanoma skin cancer (keratinocyte carcinomas) in the US population, 2012. JAMA Dermatol. 2015;151:1081-1086.
- Zanetti R, Rosso S, Martinez C, et al. Comparison of risk patterns in carcinoma and melanoma of the skin in men: a multi-centre case–case–control study. Br J Cancer. 2006;94:743-751.
- Marzuka AG, Book SE. Basal cell carcinoma: pathogenesis, epidemiology, clinical features, diagnosis, histopathology, and management. Yale J Biol Med. 2015;88:167-179.
- Lorenzini M, Gatti S, Giannitrapani A. Giant basal cell carcinoma of the thoracic wall: a case report and review of the literature. Br J Plast Surg. 2005;58:1007-1010.
- Lee HS, Kim SK. Basal cell carcinoma presenting as a perianal ulcer and treated with radiotherapy. Ann Dermatol. 2015;27:212-214.
- Salih AM, Kakamad FH, Rauf GM. Basal cell carcinoma mimicking pilonidal sinus: a case report with literature review. Int J Surg Case Rep. 2016;28:121-123.
- Scrivener Y, Grosshans E, Cribier B. Variations of basal cell carcinomas according to gender, age, location and histopathological subtype. Br J Dermatol. 2002;147:41-47.
- Park J, Cho Y-S, Song K-H, et al. Basal cell carcinoma on the pubic area: report of a case and review of 19 Korean cases of BCC from non-sun-exposed areas. Ann Dermatol. 2011;23:405-408.
- Damin DC, Rosito MA, Gus P, et al. Perianal basal cell carcinoma. J Cutan Med Surg. 2002;6:26-28.
- Paterson CA, Young-Fadok TM, Dozois RR. Basal cell carcinoma of the perianal region: 20-year experience. Dis Colon Rectum. 1999;42:1200-1202.
- Mulvany NJ, Rayoo M, Allen DG. Basal cell carcinoma of the vulva: a case series. Pathology. 2012;44:528-533.
- Leonard D, Beddy D, Dozois EJ. Neoplasms of anal canal and perianal skin. Clin Colon Rectal Surg. 2011;24:54-63.
Practice Gap
Basal cell carcinoma (BCC) is the most common cancer, and its incidence is on the rise.1 The risk of this skin cancer is increased when there is a history of squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) or BCC.2 Basal cell carcinoma often is found in sun-exposed areas, most commonly due to a history of intense sunburn.3 Other risk factors include male gender and increased age.4
Eighty percent to 85% of BCCs present on the head and neck5; however, BCC also can occur in unusual locations. When BCC presents in areas such as the perianal region, it is found to be larger than when found in more common areas,6 likely because neoplasms in this sensitive area often are overlooked. Literature on BCC of the intergluteal crease is limited.7 Being educated on the existence of BCC in this sensitive area can aid proper diagnosis.
The Technique and Case
An 83-year-old woman presented to the dermatology clinic for a suspicious lesion in the intergluteal crease that was tender to palpation with drainage. She first noticed this lesion and reported it to her primary care physician at a visit 6 months prior. The primary care physician did not pursue investigation of the lesion. One month later, the patient was seen by a gastroenterologist for the lesion and was referred to dermatology. The patient’s medical history included SCC and BCC on the face, both treated successfully with Mohs micrographic surgery.
Physical examination revealed a 2.6×1.1-cm, erythematous, nodular plaque in the coccygeal area of the intergluteal crease (Figure 1). A shave biopsy disclosed BCC, nodular type, ulcerated. Microscopically, there were nodular aggregates of basaloid cells with hyperchromatic nuclei and peripheral palisading, separated from mucinous stromal surroundings by artefactual clefts.
The initial differential diagnosis for this patient’s lesion included an ulcer or SCC. Basal cell carcinoma was not suspected due to the location and appearance of the lesion. The patient was successfully treated with Mohs micrographic surgery.
Practical Implications
Without thorough examination, this cancerous lesion would not have been seen (Figure 2). Therefore, it is important to practice thorough physical examination skills to avoid missing these cancers, particularly when examining a patient with a history of SCC or BCC. Furthermore, biopsy is recommended for suspicious lesions to rule out BCC.
Be careful not to get caught up in epidemiological or demographic considerations when making a diagnosis of this kind or when assessing the severity of a lesion. This patient, for instance, was female, which makes her less likely to present with BCC.8 Moreover, the cancer presented in a highly unlikely location for BCC, where there had not been significant sunburn.9 Patients and physicians should be educated about the incidence of BCC in unexpected areas; without a second and close look, this BCC could have been missed.
Final Thoughts
The literature continuously demonstrates the rarity of BCC in the intergluteal crease.10 However, when perianal BCC is properly identified and treated with local excision, prognosis is good.11 Basal cell carcinoma has been seen to arise in other sensitive locations; vulvar, nipple, and scrotal BCC neoplasms are among the uncommon locations where BCC has appeared.12 These areas are frequently—and easily—ignored. A total-body skin examination should be performed to ensure that these insidious-onset carcinomas are not overlooked to protect patients from the adverse consequences of untreated cancer.13
Practice Gap
Basal cell carcinoma (BCC) is the most common cancer, and its incidence is on the rise.1 The risk of this skin cancer is increased when there is a history of squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) or BCC.2 Basal cell carcinoma often is found in sun-exposed areas, most commonly due to a history of intense sunburn.3 Other risk factors include male gender and increased age.4
Eighty percent to 85% of BCCs present on the head and neck5; however, BCC also can occur in unusual locations. When BCC presents in areas such as the perianal region, it is found to be larger than when found in more common areas,6 likely because neoplasms in this sensitive area often are overlooked. Literature on BCC of the intergluteal crease is limited.7 Being educated on the existence of BCC in this sensitive area can aid proper diagnosis.
The Technique and Case
An 83-year-old woman presented to the dermatology clinic for a suspicious lesion in the intergluteal crease that was tender to palpation with drainage. She first noticed this lesion and reported it to her primary care physician at a visit 6 months prior. The primary care physician did not pursue investigation of the lesion. One month later, the patient was seen by a gastroenterologist for the lesion and was referred to dermatology. The patient’s medical history included SCC and BCC on the face, both treated successfully with Mohs micrographic surgery.
Physical examination revealed a 2.6×1.1-cm, erythematous, nodular plaque in the coccygeal area of the intergluteal crease (Figure 1). A shave biopsy disclosed BCC, nodular type, ulcerated. Microscopically, there were nodular aggregates of basaloid cells with hyperchromatic nuclei and peripheral palisading, separated from mucinous stromal surroundings by artefactual clefts.
The initial differential diagnosis for this patient’s lesion included an ulcer or SCC. Basal cell carcinoma was not suspected due to the location and appearance of the lesion. The patient was successfully treated with Mohs micrographic surgery.
Practical Implications
Without thorough examination, this cancerous lesion would not have been seen (Figure 2). Therefore, it is important to practice thorough physical examination skills to avoid missing these cancers, particularly when examining a patient with a history of SCC or BCC. Furthermore, biopsy is recommended for suspicious lesions to rule out BCC.
Be careful not to get caught up in epidemiological or demographic considerations when making a diagnosis of this kind or when assessing the severity of a lesion. This patient, for instance, was female, which makes her less likely to present with BCC.8 Moreover, the cancer presented in a highly unlikely location for BCC, where there had not been significant sunburn.9 Patients and physicians should be educated about the incidence of BCC in unexpected areas; without a second and close look, this BCC could have been missed.
Final Thoughts
The literature continuously demonstrates the rarity of BCC in the intergluteal crease.10 However, when perianal BCC is properly identified and treated with local excision, prognosis is good.11 Basal cell carcinoma has been seen to arise in other sensitive locations; vulvar, nipple, and scrotal BCC neoplasms are among the uncommon locations where BCC has appeared.12 These areas are frequently—and easily—ignored. A total-body skin examination should be performed to ensure that these insidious-onset carcinomas are not overlooked to protect patients from the adverse consequences of untreated cancer.13
- Roewert-Huber J, Lange-Asschenfeldt B, Stockfleth E, et al. Epidemiology and aetiology of basal cell carcinoma. Br J Dermatol. 2007;157(suppl 2):47-51.
- Rogers HW, Weinstock MA, Feldman SR, et al. Incidence estimate of nonmelanoma skin cancer (keratinocyte carcinomas) in the US population, 2012. JAMA Dermatol. 2015;151:1081-1086.
- Zanetti R, Rosso S, Martinez C, et al. Comparison of risk patterns in carcinoma and melanoma of the skin in men: a multi-centre case–case–control study. Br J Cancer. 2006;94:743-751.
- Marzuka AG, Book SE. Basal cell carcinoma: pathogenesis, epidemiology, clinical features, diagnosis, histopathology, and management. Yale J Biol Med. 2015;88:167-179.
- Lorenzini M, Gatti S, Giannitrapani A. Giant basal cell carcinoma of the thoracic wall: a case report and review of the literature. Br J Plast Surg. 2005;58:1007-1010.
- Lee HS, Kim SK. Basal cell carcinoma presenting as a perianal ulcer and treated with radiotherapy. Ann Dermatol. 2015;27:212-214.
- Salih AM, Kakamad FH, Rauf GM. Basal cell carcinoma mimicking pilonidal sinus: a case report with literature review. Int J Surg Case Rep. 2016;28:121-123.
- Scrivener Y, Grosshans E, Cribier B. Variations of basal cell carcinomas according to gender, age, location and histopathological subtype. Br J Dermatol. 2002;147:41-47.
- Park J, Cho Y-S, Song K-H, et al. Basal cell carcinoma on the pubic area: report of a case and review of 19 Korean cases of BCC from non-sun-exposed areas. Ann Dermatol. 2011;23:405-408.
- Damin DC, Rosito MA, Gus P, et al. Perianal basal cell carcinoma. J Cutan Med Surg. 2002;6:26-28.
- Paterson CA, Young-Fadok TM, Dozois RR. Basal cell carcinoma of the perianal region: 20-year experience. Dis Colon Rectum. 1999;42:1200-1202.
- Mulvany NJ, Rayoo M, Allen DG. Basal cell carcinoma of the vulva: a case series. Pathology. 2012;44:528-533.
- Leonard D, Beddy D, Dozois EJ. Neoplasms of anal canal and perianal skin. Clin Colon Rectal Surg. 2011;24:54-63.
- Roewert-Huber J, Lange-Asschenfeldt B, Stockfleth E, et al. Epidemiology and aetiology of basal cell carcinoma. Br J Dermatol. 2007;157(suppl 2):47-51.
- Rogers HW, Weinstock MA, Feldman SR, et al. Incidence estimate of nonmelanoma skin cancer (keratinocyte carcinomas) in the US population, 2012. JAMA Dermatol. 2015;151:1081-1086.
- Zanetti R, Rosso S, Martinez C, et al. Comparison of risk patterns in carcinoma and melanoma of the skin in men: a multi-centre case–case–control study. Br J Cancer. 2006;94:743-751.
- Marzuka AG, Book SE. Basal cell carcinoma: pathogenesis, epidemiology, clinical features, diagnosis, histopathology, and management. Yale J Biol Med. 2015;88:167-179.
- Lorenzini M, Gatti S, Giannitrapani A. Giant basal cell carcinoma of the thoracic wall: a case report and review of the literature. Br J Plast Surg. 2005;58:1007-1010.
- Lee HS, Kim SK. Basal cell carcinoma presenting as a perianal ulcer and treated with radiotherapy. Ann Dermatol. 2015;27:212-214.
- Salih AM, Kakamad FH, Rauf GM. Basal cell carcinoma mimicking pilonidal sinus: a case report with literature review. Int J Surg Case Rep. 2016;28:121-123.
- Scrivener Y, Grosshans E, Cribier B. Variations of basal cell carcinomas according to gender, age, location and histopathological subtype. Br J Dermatol. 2002;147:41-47.
- Park J, Cho Y-S, Song K-H, et al. Basal cell carcinoma on the pubic area: report of a case and review of 19 Korean cases of BCC from non-sun-exposed areas. Ann Dermatol. 2011;23:405-408.
- Damin DC, Rosito MA, Gus P, et al. Perianal basal cell carcinoma. J Cutan Med Surg. 2002;6:26-28.
- Paterson CA, Young-Fadok TM, Dozois RR. Basal cell carcinoma of the perianal region: 20-year experience. Dis Colon Rectum. 1999;42:1200-1202.
- Mulvany NJ, Rayoo M, Allen DG. Basal cell carcinoma of the vulva: a case series. Pathology. 2012;44:528-533.
- Leonard D, Beddy D, Dozois EJ. Neoplasms of anal canal and perianal skin. Clin Colon Rectal Surg. 2011;24:54-63.
Violaceous Papule With an Erythematous Rim
The Diagnosis: Targetoid Hemosiderotic Hemangioma
Targetoid hemosiderotic hemangioma (THH), also known as hobnail hemangioma, is a benign vascular tumor that usually occurs in young or middle-aged adults. It most commonly presents on the extremities or trunk as an isolated red-brown plaque or papule.1,2 Histologically, THH is characterized by superficial dilated ectatic vessels with underlying proliferating vascular channels lined by plump hobnail endothelial cells.1 Targetoid hemosiderotic hemangioma typically involves the dermis and spares the subcutis. The vascular channels may contain erythrocytes as well as pale eosinophilic lymph, as seen in our patient (quiz image). The deeper dermis contains vascular spaces that are more angulated and smaller and appear to be dissecting through the collagen bundles or collapsed.1,3 A variable amount of hemosiderin deposition and extravasated erythrocytes are seen.2,3 Histologic features evolve with the age of the lesion. Increasing amounts of hemosiderin deposition and erythrocyte extravasation may correspond histologically to the recent clinical color change reported by the patient.
Verrucous hemangioma is a rare congenital vascular abnormality that is characterized by dilated vessels in the papillary dermis along with acanthosis, hyperkeratosis, and irregular papillomatosis, as seen in angiokeratoma.4 However, the vascular proliferation composed of variably sized, thin-walled capillaries extends into the deep dermis as well as the subcutis (Figure 1). Verrucous hemangioma most commonly is reported on the legs and generally starts as a violaceous patch that progresses into a hyperkeratotic verrucous plaque or nodule.5,6
Angiokeratoma is characterized by superficial vascular ectasia of the papillary dermis in association with overlying acanthosis, hyperkeratosis, and rete elongation.7 The dilated vascular spaces appear encircled by the epidermis (Figure 2). Intravascular thrombosis can be seen within the ectatic vessels.7 In contrast to verrucous hemangioma, angiokeratoma is limited to the papillary dermis. Therefore, obtaining a biopsy of sufficient depth is necessary for differentiation.8 There are 5 clinical presentations of angiokeratoma: sporadic, angiokeratoma of Mibelli, angiokeratoma of Fordyce, angiokeratoma circumscriptum, and angiokeratoma corporis diffusum (Fabry disease). Angiokeratomas may present on the lower extremities, tongue, trunk, and scrotum as hyperkeratotic, dark red to purple or black papules.7
There are 3 clinical stages of Kaposi sarcoma: patch, plaque, and nodular stages. The patch stage is characterized histologically by vascular channels that dissect through the dermis and extend around native vessels (the promontory sign)(Figure 3).9,10 These features can show histologic overlap with THH. The plaque stage shows a more diffuse dermal vascular proliferation, increased cellularity of spindle cells, and possible extension into the subcutis.9,10 Focal plasma cells, hemosiderin, and extravasated red blood cells can be seen. The nodular stage is characterized by a proliferation of spindle cells with red blood cells squeezed between slitlike vascular spaces, hyaline globules, and scattered mitotic figures, but not atypical forms.10 In this stage, plasma cells and hemosiderin are more readily identifiable. A biopsy from the nodular stage is unlikely to enter the histologic differential diagnosis with THH. Clinically, there are 4 variants of Kaposi sarcoma: the classic or sporadic form, an endemic form, iatrogenic, and AIDS associated. Overall, it is more common in males and can occur at any age.10 Human herpesvirus 8 is seen in all forms, and infected cells can be highlighted by the immunohistochemical stain for latent nuclear antigen 1.9,10
Angiosarcoma is a malignant endothelial tumor of soft tissue, skin, bone, and visceral organs.11,12 Clinically, cutaneous angiosarcoma can present in a variety of ways, including single or multiple bluish red lesions that can ulcerate or bleed; violaceous nodules or plaques; and hematomalike lesions that can mimic epithelial neoplasms including squamous cell carcinoma, basal cell carcinoma, and malignant melanoma.11,13,14 The cutaneous lesions most commonly occur on sun-exposed skin, particularly on the face and scalp.12 Other clinical variants that are important to recognize are postradiation angiosarcoma, characterized by MYC gene amplification, and lymphedema-associated angiosarcoma (Stewart-Treves syndrome). Angiosarcoma can have a variety of morphologic features, ranging from well to poorly differentiated. Classically, angiosarcoma is characterized by infiltrating vascular spaces lined by atypical endothelial cells (Figure 4). Poorly differentiated angiosarcoma can demonstrate spindle, epithelioid, or polygonal cells with increased mitotic activity, pleomorphism, and irregular vascular spaces.11 Endothelial markers such as ERG (erythroblast transformation specific-related gene)(nuclear) and CD31 (membranous) can be used to aid in the diagnosis of a poorly differentiated lesion. Epithelioid angiosarcoma also occasionally stains with cytokeratins.13,14
- Joyce JC, Keith PJ, Szabo S, et al. Superficial hemosiderotic lymphovascular malformation (hobnail hemangioma): a report of six cases. Pediatr Dermatol. 2014;31:281-285.
- Sahin MT, Demir MA, Gunduz K, et al. Targetoid haemosiderotic haemangioma: dermoscopic monitoring of three cases and review of the literature. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2005;30:672-676.
- Kakizaki P, Valente NY, Paiva DL, et al. Targetoid hemosiderotic hemangioma--case report. An Bras Dermatol. 2014;89:956-959.
- Oppermann K, Boff AL, Bonamigo RR. Verrucous hemangioma and histopathological differential diagnosis with angiokeratoma circumscriptum neviforme. An Bras Dermatol. 2018;93:712-715.
- Boccara, O, Ariche-Maman, S, Hadj-Rabia, S, et al. Verrucous hemangioma (also known as verrucous venous malformation): a vascular anomaly frequently misdiagnosed as a lymphatic malformation. Pediatr Dermatol. 2018;35:E378-E381.
- Mestre T, Amaro C, Freitas I. Verrucous haemangioma: a diagnosis to consider [published online June 4, 2014]. BMJ Case Rep. doi:10.1136/bcr-2014-204612
- Ivy H, Julian CA. Angiokeratoma circumscriptum. StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing; 2019. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK549769/
- Shetty S, Geetha V, Rao R, et al. Verrucous hemangioma: importance of a deeper biopsy. Indian J Dermatopathol Diagn Dermatol. 2014;1:99-100.
- Bishop BN, Lynch DT. Cancer, Kaposi sarcoma. StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing; 2019. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK534839/
- Grayson W, Pantanowitz L. Histological variants of cutaneous Kaposi sarcoma. Diagn Pathol. 2008;3:31.
- Cao J, Wang J, He C, et al. Angiosarcoma: a review of diagnosis and current treatment. Am J Cancer Res. 2019;9:2303-2313.
- Papke DJ Jr, Hornick JL. What is new in endothelial neoplasia? Virchows Arch. 2020;476:17-28.
- Ambujam S, Audhya M, Reddy A, et al. Cutaneous angiosarcoma of the head, neck, and face of the elderly in type 5 skin. J Cutan Aesthet Surg. 2013;6:45-47.
- Shustef E, Kazlouskaya V, Prieto VG, et al. Cutaneous angiosarcoma: a current update. J Clin Pathol. 2017;70:917-925.
The Diagnosis: Targetoid Hemosiderotic Hemangioma
Targetoid hemosiderotic hemangioma (THH), also known as hobnail hemangioma, is a benign vascular tumor that usually occurs in young or middle-aged adults. It most commonly presents on the extremities or trunk as an isolated red-brown plaque or papule.1,2 Histologically, THH is characterized by superficial dilated ectatic vessels with underlying proliferating vascular channels lined by plump hobnail endothelial cells.1 Targetoid hemosiderotic hemangioma typically involves the dermis and spares the subcutis. The vascular channels may contain erythrocytes as well as pale eosinophilic lymph, as seen in our patient (quiz image). The deeper dermis contains vascular spaces that are more angulated and smaller and appear to be dissecting through the collagen bundles or collapsed.1,3 A variable amount of hemosiderin deposition and extravasated erythrocytes are seen.2,3 Histologic features evolve with the age of the lesion. Increasing amounts of hemosiderin deposition and erythrocyte extravasation may correspond histologically to the recent clinical color change reported by the patient.
Verrucous hemangioma is a rare congenital vascular abnormality that is characterized by dilated vessels in the papillary dermis along with acanthosis, hyperkeratosis, and irregular papillomatosis, as seen in angiokeratoma.4 However, the vascular proliferation composed of variably sized, thin-walled capillaries extends into the deep dermis as well as the subcutis (Figure 1). Verrucous hemangioma most commonly is reported on the legs and generally starts as a violaceous patch that progresses into a hyperkeratotic verrucous plaque or nodule.5,6
Angiokeratoma is characterized by superficial vascular ectasia of the papillary dermis in association with overlying acanthosis, hyperkeratosis, and rete elongation.7 The dilated vascular spaces appear encircled by the epidermis (Figure 2). Intravascular thrombosis can be seen within the ectatic vessels.7 In contrast to verrucous hemangioma, angiokeratoma is limited to the papillary dermis. Therefore, obtaining a biopsy of sufficient depth is necessary for differentiation.8 There are 5 clinical presentations of angiokeratoma: sporadic, angiokeratoma of Mibelli, angiokeratoma of Fordyce, angiokeratoma circumscriptum, and angiokeratoma corporis diffusum (Fabry disease). Angiokeratomas may present on the lower extremities, tongue, trunk, and scrotum as hyperkeratotic, dark red to purple or black papules.7
There are 3 clinical stages of Kaposi sarcoma: patch, plaque, and nodular stages. The patch stage is characterized histologically by vascular channels that dissect through the dermis and extend around native vessels (the promontory sign)(Figure 3).9,10 These features can show histologic overlap with THH. The plaque stage shows a more diffuse dermal vascular proliferation, increased cellularity of spindle cells, and possible extension into the subcutis.9,10 Focal plasma cells, hemosiderin, and extravasated red blood cells can be seen. The nodular stage is characterized by a proliferation of spindle cells with red blood cells squeezed between slitlike vascular spaces, hyaline globules, and scattered mitotic figures, but not atypical forms.10 In this stage, plasma cells and hemosiderin are more readily identifiable. A biopsy from the nodular stage is unlikely to enter the histologic differential diagnosis with THH. Clinically, there are 4 variants of Kaposi sarcoma: the classic or sporadic form, an endemic form, iatrogenic, and AIDS associated. Overall, it is more common in males and can occur at any age.10 Human herpesvirus 8 is seen in all forms, and infected cells can be highlighted by the immunohistochemical stain for latent nuclear antigen 1.9,10
Angiosarcoma is a malignant endothelial tumor of soft tissue, skin, bone, and visceral organs.11,12 Clinically, cutaneous angiosarcoma can present in a variety of ways, including single or multiple bluish red lesions that can ulcerate or bleed; violaceous nodules or plaques; and hematomalike lesions that can mimic epithelial neoplasms including squamous cell carcinoma, basal cell carcinoma, and malignant melanoma.11,13,14 The cutaneous lesions most commonly occur on sun-exposed skin, particularly on the face and scalp.12 Other clinical variants that are important to recognize are postradiation angiosarcoma, characterized by MYC gene amplification, and lymphedema-associated angiosarcoma (Stewart-Treves syndrome). Angiosarcoma can have a variety of morphologic features, ranging from well to poorly differentiated. Classically, angiosarcoma is characterized by infiltrating vascular spaces lined by atypical endothelial cells (Figure 4). Poorly differentiated angiosarcoma can demonstrate spindle, epithelioid, or polygonal cells with increased mitotic activity, pleomorphism, and irregular vascular spaces.11 Endothelial markers such as ERG (erythroblast transformation specific-related gene)(nuclear) and CD31 (membranous) can be used to aid in the diagnosis of a poorly differentiated lesion. Epithelioid angiosarcoma also occasionally stains with cytokeratins.13,14
The Diagnosis: Targetoid Hemosiderotic Hemangioma
Targetoid hemosiderotic hemangioma (THH), also known as hobnail hemangioma, is a benign vascular tumor that usually occurs in young or middle-aged adults. It most commonly presents on the extremities or trunk as an isolated red-brown plaque or papule.1,2 Histologically, THH is characterized by superficial dilated ectatic vessels with underlying proliferating vascular channels lined by plump hobnail endothelial cells.1 Targetoid hemosiderotic hemangioma typically involves the dermis and spares the subcutis. The vascular channels may contain erythrocytes as well as pale eosinophilic lymph, as seen in our patient (quiz image). The deeper dermis contains vascular spaces that are more angulated and smaller and appear to be dissecting through the collagen bundles or collapsed.1,3 A variable amount of hemosiderin deposition and extravasated erythrocytes are seen.2,3 Histologic features evolve with the age of the lesion. Increasing amounts of hemosiderin deposition and erythrocyte extravasation may correspond histologically to the recent clinical color change reported by the patient.
Verrucous hemangioma is a rare congenital vascular abnormality that is characterized by dilated vessels in the papillary dermis along with acanthosis, hyperkeratosis, and irregular papillomatosis, as seen in angiokeratoma.4 However, the vascular proliferation composed of variably sized, thin-walled capillaries extends into the deep dermis as well as the subcutis (Figure 1). Verrucous hemangioma most commonly is reported on the legs and generally starts as a violaceous patch that progresses into a hyperkeratotic verrucous plaque or nodule.5,6
Angiokeratoma is characterized by superficial vascular ectasia of the papillary dermis in association with overlying acanthosis, hyperkeratosis, and rete elongation.7 The dilated vascular spaces appear encircled by the epidermis (Figure 2). Intravascular thrombosis can be seen within the ectatic vessels.7 In contrast to verrucous hemangioma, angiokeratoma is limited to the papillary dermis. Therefore, obtaining a biopsy of sufficient depth is necessary for differentiation.8 There are 5 clinical presentations of angiokeratoma: sporadic, angiokeratoma of Mibelli, angiokeratoma of Fordyce, angiokeratoma circumscriptum, and angiokeratoma corporis diffusum (Fabry disease). Angiokeratomas may present on the lower extremities, tongue, trunk, and scrotum as hyperkeratotic, dark red to purple or black papules.7
There are 3 clinical stages of Kaposi sarcoma: patch, plaque, and nodular stages. The patch stage is characterized histologically by vascular channels that dissect through the dermis and extend around native vessels (the promontory sign)(Figure 3).9,10 These features can show histologic overlap with THH. The plaque stage shows a more diffuse dermal vascular proliferation, increased cellularity of spindle cells, and possible extension into the subcutis.9,10 Focal plasma cells, hemosiderin, and extravasated red blood cells can be seen. The nodular stage is characterized by a proliferation of spindle cells with red blood cells squeezed between slitlike vascular spaces, hyaline globules, and scattered mitotic figures, but not atypical forms.10 In this stage, plasma cells and hemosiderin are more readily identifiable. A biopsy from the nodular stage is unlikely to enter the histologic differential diagnosis with THH. Clinically, there are 4 variants of Kaposi sarcoma: the classic or sporadic form, an endemic form, iatrogenic, and AIDS associated. Overall, it is more common in males and can occur at any age.10 Human herpesvirus 8 is seen in all forms, and infected cells can be highlighted by the immunohistochemical stain for latent nuclear antigen 1.9,10
Angiosarcoma is a malignant endothelial tumor of soft tissue, skin, bone, and visceral organs.11,12 Clinically, cutaneous angiosarcoma can present in a variety of ways, including single or multiple bluish red lesions that can ulcerate or bleed; violaceous nodules or plaques; and hematomalike lesions that can mimic epithelial neoplasms including squamous cell carcinoma, basal cell carcinoma, and malignant melanoma.11,13,14 The cutaneous lesions most commonly occur on sun-exposed skin, particularly on the face and scalp.12 Other clinical variants that are important to recognize are postradiation angiosarcoma, characterized by MYC gene amplification, and lymphedema-associated angiosarcoma (Stewart-Treves syndrome). Angiosarcoma can have a variety of morphologic features, ranging from well to poorly differentiated. Classically, angiosarcoma is characterized by infiltrating vascular spaces lined by atypical endothelial cells (Figure 4). Poorly differentiated angiosarcoma can demonstrate spindle, epithelioid, or polygonal cells with increased mitotic activity, pleomorphism, and irregular vascular spaces.11 Endothelial markers such as ERG (erythroblast transformation specific-related gene)(nuclear) and CD31 (membranous) can be used to aid in the diagnosis of a poorly differentiated lesion. Epithelioid angiosarcoma also occasionally stains with cytokeratins.13,14
- Joyce JC, Keith PJ, Szabo S, et al. Superficial hemosiderotic lymphovascular malformation (hobnail hemangioma): a report of six cases. Pediatr Dermatol. 2014;31:281-285.
- Sahin MT, Demir MA, Gunduz K, et al. Targetoid haemosiderotic haemangioma: dermoscopic monitoring of three cases and review of the literature. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2005;30:672-676.
- Kakizaki P, Valente NY, Paiva DL, et al. Targetoid hemosiderotic hemangioma--case report. An Bras Dermatol. 2014;89:956-959.
- Oppermann K, Boff AL, Bonamigo RR. Verrucous hemangioma and histopathological differential diagnosis with angiokeratoma circumscriptum neviforme. An Bras Dermatol. 2018;93:712-715.
- Boccara, O, Ariche-Maman, S, Hadj-Rabia, S, et al. Verrucous hemangioma (also known as verrucous venous malformation): a vascular anomaly frequently misdiagnosed as a lymphatic malformation. Pediatr Dermatol. 2018;35:E378-E381.
- Mestre T, Amaro C, Freitas I. Verrucous haemangioma: a diagnosis to consider [published online June 4, 2014]. BMJ Case Rep. doi:10.1136/bcr-2014-204612
- Ivy H, Julian CA. Angiokeratoma circumscriptum. StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing; 2019. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK549769/
- Shetty S, Geetha V, Rao R, et al. Verrucous hemangioma: importance of a deeper biopsy. Indian J Dermatopathol Diagn Dermatol. 2014;1:99-100.
- Bishop BN, Lynch DT. Cancer, Kaposi sarcoma. StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing; 2019. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK534839/
- Grayson W, Pantanowitz L. Histological variants of cutaneous Kaposi sarcoma. Diagn Pathol. 2008;3:31.
- Cao J, Wang J, He C, et al. Angiosarcoma: a review of diagnosis and current treatment. Am J Cancer Res. 2019;9:2303-2313.
- Papke DJ Jr, Hornick JL. What is new in endothelial neoplasia? Virchows Arch. 2020;476:17-28.
- Ambujam S, Audhya M, Reddy A, et al. Cutaneous angiosarcoma of the head, neck, and face of the elderly in type 5 skin. J Cutan Aesthet Surg. 2013;6:45-47.
- Shustef E, Kazlouskaya V, Prieto VG, et al. Cutaneous angiosarcoma: a current update. J Clin Pathol. 2017;70:917-925.
- Joyce JC, Keith PJ, Szabo S, et al. Superficial hemosiderotic lymphovascular malformation (hobnail hemangioma): a report of six cases. Pediatr Dermatol. 2014;31:281-285.
- Sahin MT, Demir MA, Gunduz K, et al. Targetoid haemosiderotic haemangioma: dermoscopic monitoring of three cases and review of the literature. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2005;30:672-676.
- Kakizaki P, Valente NY, Paiva DL, et al. Targetoid hemosiderotic hemangioma--case report. An Bras Dermatol. 2014;89:956-959.
- Oppermann K, Boff AL, Bonamigo RR. Verrucous hemangioma and histopathological differential diagnosis with angiokeratoma circumscriptum neviforme. An Bras Dermatol. 2018;93:712-715.
- Boccara, O, Ariche-Maman, S, Hadj-Rabia, S, et al. Verrucous hemangioma (also known as verrucous venous malformation): a vascular anomaly frequently misdiagnosed as a lymphatic malformation. Pediatr Dermatol. 2018;35:E378-E381.
- Mestre T, Amaro C, Freitas I. Verrucous haemangioma: a diagnosis to consider [published online June 4, 2014]. BMJ Case Rep. doi:10.1136/bcr-2014-204612
- Ivy H, Julian CA. Angiokeratoma circumscriptum. StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing; 2019. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK549769/
- Shetty S, Geetha V, Rao R, et al. Verrucous hemangioma: importance of a deeper biopsy. Indian J Dermatopathol Diagn Dermatol. 2014;1:99-100.
- Bishop BN, Lynch DT. Cancer, Kaposi sarcoma. StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing; 2019. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK534839/
- Grayson W, Pantanowitz L. Histological variants of cutaneous Kaposi sarcoma. Diagn Pathol. 2008;3:31.
- Cao J, Wang J, He C, et al. Angiosarcoma: a review of diagnosis and current treatment. Am J Cancer Res. 2019;9:2303-2313.
- Papke DJ Jr, Hornick JL. What is new in endothelial neoplasia? Virchows Arch. 2020;476:17-28.
- Ambujam S, Audhya M, Reddy A, et al. Cutaneous angiosarcoma of the head, neck, and face of the elderly in type 5 skin. J Cutan Aesthet Surg. 2013;6:45-47.
- Shustef E, Kazlouskaya V, Prieto VG, et al. Cutaneous angiosarcoma: a current update. J Clin Pathol. 2017;70:917-925.
A 35-year-old man presented with a reddish brown papule on the left upper chest of 1 year’s duration that had changed color to reddish purple. Physical examination revealed a 6-mm violaceous papule with an erythematous rim.