User login
Sustained Benefits of CGRP Antibodies in Migraine and Medication Overuse Headache
Key clinical point: Prophylactic migraine therapy with calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) antibodies showed sustained benefits in patients with migraine and medication overuse headache (MOH) or medication overuse (MO) for up to a year.
Major findings: All patients, including those with episodic migraine (EM) with MO, EM without MO, chronic migraine (CM) with MOH, or CM without MOH, had significant reductions in monthly headache days, monthly migraine days, and acute medication days at the last observation timepoint within the first year of CGRP therapy from baseline (all P < .0001). Relapse rates were lower (15.4%) in patients with CM with MOH after successful initiation of CGRP treatment.
Study details: This retrospective real-world analysis included 112 patients with EM (35 with MO and 77 without MO) and 179 patients with CM (109 with MOH and 70 without MOH).
Disclosures: This study was funded by Projekt DEAL. Some authors declared receiving travel fees, honoraria, or scientific support from or serving as consultants or advisors for various sources.
Source: Scheffler A, Basten J, Menzel L, et al. Persistent effectiveness of CGRP antibody therapy in migraine and comorbid medication overuse or medication overuse headache - a retrospective real-world analysis. J Headache Pain. 2024;25:109 (Jul 4). Doi: 10.1186/s10194-024-01813-3 Source
Key clinical point: Prophylactic migraine therapy with calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) antibodies showed sustained benefits in patients with migraine and medication overuse headache (MOH) or medication overuse (MO) for up to a year.
Major findings: All patients, including those with episodic migraine (EM) with MO, EM without MO, chronic migraine (CM) with MOH, or CM without MOH, had significant reductions in monthly headache days, monthly migraine days, and acute medication days at the last observation timepoint within the first year of CGRP therapy from baseline (all P < .0001). Relapse rates were lower (15.4%) in patients with CM with MOH after successful initiation of CGRP treatment.
Study details: This retrospective real-world analysis included 112 patients with EM (35 with MO and 77 without MO) and 179 patients with CM (109 with MOH and 70 without MOH).
Disclosures: This study was funded by Projekt DEAL. Some authors declared receiving travel fees, honoraria, or scientific support from or serving as consultants or advisors for various sources.
Source: Scheffler A, Basten J, Menzel L, et al. Persistent effectiveness of CGRP antibody therapy in migraine and comorbid medication overuse or medication overuse headache - a retrospective real-world analysis. J Headache Pain. 2024;25:109 (Jul 4). Doi: 10.1186/s10194-024-01813-3 Source
Key clinical point: Prophylactic migraine therapy with calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) antibodies showed sustained benefits in patients with migraine and medication overuse headache (MOH) or medication overuse (MO) for up to a year.
Major findings: All patients, including those with episodic migraine (EM) with MO, EM without MO, chronic migraine (CM) with MOH, or CM without MOH, had significant reductions in monthly headache days, monthly migraine days, and acute medication days at the last observation timepoint within the first year of CGRP therapy from baseline (all P < .0001). Relapse rates were lower (15.4%) in patients with CM with MOH after successful initiation of CGRP treatment.
Study details: This retrospective real-world analysis included 112 patients with EM (35 with MO and 77 without MO) and 179 patients with CM (109 with MOH and 70 without MOH).
Disclosures: This study was funded by Projekt DEAL. Some authors declared receiving travel fees, honoraria, or scientific support from or serving as consultants or advisors for various sources.
Source: Scheffler A, Basten J, Menzel L, et al. Persistent effectiveness of CGRP antibody therapy in migraine and comorbid medication overuse or medication overuse headache - a retrospective real-world analysis. J Headache Pain. 2024;25:109 (Jul 4). Doi: 10.1186/s10194-024-01813-3 Source
Neck Pain With Headache During Migraine Tied to Poor Migraine Health
Key clinical point: Patients with migraine who experienced neck pain with headache (NPWH) had a higher prevalence of disability, depression, anxiety, and allodynia, as well as a lower quality of life, greater work productivity losses, and poorer acute treatment optimization than those without NPWH.
Major findings: Patients with vs without NPWH showed a higher prevalence of moderate to severe disability (47.7% vs 28.9%), depression (40.2% vs 28.2%), anxiety (41.2% vs 29.2%), allodynia (54.0% vs 36.6%), and poor acute treatment optimization (61.1% vs 53.3%; P < .001 for all). They also had lower quality of life scores (60.0 vs 68.6) and higher work productivity loss scores (50.0 vs 30.0; P < .001 for both).
Study details: This analysis of the Chronic Migraine Epidemiology and Outcomes – International study included 14, 492 patients with migraine, of whom 9896 (68.3%) had NPWH.
Disclosures: This study was funded by Allergan (now AbbVie). One author declared being an employee or a stockholder of AbbVie. Several authors declared having ties with various sources, including AbbVie.
Source: Matharu M, Katsarava Z, Buse DC, et al. Characterizing neck pain during headache among people with migraine: Multicountry results from the Chronic Migraine Epidemiology and Outcomes – International (CaMEO-I) cross-sectional study. Headache. 2024;64:750-763 (Jun 22). Doi: 10.1111/head.14753 Source
Key clinical point: Patients with migraine who experienced neck pain with headache (NPWH) had a higher prevalence of disability, depression, anxiety, and allodynia, as well as a lower quality of life, greater work productivity losses, and poorer acute treatment optimization than those without NPWH.
Major findings: Patients with vs without NPWH showed a higher prevalence of moderate to severe disability (47.7% vs 28.9%), depression (40.2% vs 28.2%), anxiety (41.2% vs 29.2%), allodynia (54.0% vs 36.6%), and poor acute treatment optimization (61.1% vs 53.3%; P < .001 for all). They also had lower quality of life scores (60.0 vs 68.6) and higher work productivity loss scores (50.0 vs 30.0; P < .001 for both).
Study details: This analysis of the Chronic Migraine Epidemiology and Outcomes – International study included 14, 492 patients with migraine, of whom 9896 (68.3%) had NPWH.
Disclosures: This study was funded by Allergan (now AbbVie). One author declared being an employee or a stockholder of AbbVie. Several authors declared having ties with various sources, including AbbVie.
Source: Matharu M, Katsarava Z, Buse DC, et al. Characterizing neck pain during headache among people with migraine: Multicountry results from the Chronic Migraine Epidemiology and Outcomes – International (CaMEO-I) cross-sectional study. Headache. 2024;64:750-763 (Jun 22). Doi: 10.1111/head.14753 Source
Key clinical point: Patients with migraine who experienced neck pain with headache (NPWH) had a higher prevalence of disability, depression, anxiety, and allodynia, as well as a lower quality of life, greater work productivity losses, and poorer acute treatment optimization than those without NPWH.
Major findings: Patients with vs without NPWH showed a higher prevalence of moderate to severe disability (47.7% vs 28.9%), depression (40.2% vs 28.2%), anxiety (41.2% vs 29.2%), allodynia (54.0% vs 36.6%), and poor acute treatment optimization (61.1% vs 53.3%; P < .001 for all). They also had lower quality of life scores (60.0 vs 68.6) and higher work productivity loss scores (50.0 vs 30.0; P < .001 for both).
Study details: This analysis of the Chronic Migraine Epidemiology and Outcomes – International study included 14, 492 patients with migraine, of whom 9896 (68.3%) had NPWH.
Disclosures: This study was funded by Allergan (now AbbVie). One author declared being an employee or a stockholder of AbbVie. Several authors declared having ties with various sources, including AbbVie.
Source: Matharu M, Katsarava Z, Buse DC, et al. Characterizing neck pain during headache among people with migraine: Multicountry results from the Chronic Migraine Epidemiology and Outcomes – International (CaMEO-I) cross-sectional study. Headache. 2024;64:750-763 (Jun 22). Doi: 10.1111/head.14753 Source
Does Migraine Influence Serum Alpha-CGRP Levels in Patients With IBD?
Key clinical point: Patients with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) and chronic migraine (CM) had higher serum levels of alpha-calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) than patients with only IBD.
Major findings: The alpha-CGRP levels were significantly higher in patients with IBD (56.9 vs 37.2 pg/mL; P = .003) or CM (53.0 vs 37.2 pg/mL; P = .019) than healthy control participants without a history of IBD and CM. The levels of this peptide in the serum were further increased in patients with IBD and concomitant migraine compared with those with only IBD (70.9 vs 53.7 pg/mL; P = .046).
Study details: This cross-sectional study compared the serum CGRP levels in 96 patients with IBD, 50 patients with CM, and 50 healthy control participants without a history of IBD and CM.
Disclosures: This study was funded by Instituto de Salud Carlos III, Spain. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Source: Pascual-Mato M, Gárate G, González-Quintanilla V, et al. Differences in circulating alpha-calcitonin gene-related peptide levels in inflammatory bowel disease and its relation to migraine comorbidity: A cross-sectional study. Headache. 2024;64:849-858 (Jun 24). Doi: 10.1111/head.14768 Source
Key clinical point: Patients with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) and chronic migraine (CM) had higher serum levels of alpha-calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) than patients with only IBD.
Major findings: The alpha-CGRP levels were significantly higher in patients with IBD (56.9 vs 37.2 pg/mL; P = .003) or CM (53.0 vs 37.2 pg/mL; P = .019) than healthy control participants without a history of IBD and CM. The levels of this peptide in the serum were further increased in patients with IBD and concomitant migraine compared with those with only IBD (70.9 vs 53.7 pg/mL; P = .046).
Study details: This cross-sectional study compared the serum CGRP levels in 96 patients with IBD, 50 patients with CM, and 50 healthy control participants without a history of IBD and CM.
Disclosures: This study was funded by Instituto de Salud Carlos III, Spain. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Source: Pascual-Mato M, Gárate G, González-Quintanilla V, et al. Differences in circulating alpha-calcitonin gene-related peptide levels in inflammatory bowel disease and its relation to migraine comorbidity: A cross-sectional study. Headache. 2024;64:849-858 (Jun 24). Doi: 10.1111/head.14768 Source
Key clinical point: Patients with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) and chronic migraine (CM) had higher serum levels of alpha-calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) than patients with only IBD.
Major findings: The alpha-CGRP levels were significantly higher in patients with IBD (56.9 vs 37.2 pg/mL; P = .003) or CM (53.0 vs 37.2 pg/mL; P = .019) than healthy control participants without a history of IBD and CM. The levels of this peptide in the serum were further increased in patients with IBD and concomitant migraine compared with those with only IBD (70.9 vs 53.7 pg/mL; P = .046).
Study details: This cross-sectional study compared the serum CGRP levels in 96 patients with IBD, 50 patients with CM, and 50 healthy control participants without a history of IBD and CM.
Disclosures: This study was funded by Instituto de Salud Carlos III, Spain. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Source: Pascual-Mato M, Gárate G, González-Quintanilla V, et al. Differences in circulating alpha-calcitonin gene-related peptide levels in inflammatory bowel disease and its relation to migraine comorbidity: A cross-sectional study. Headache. 2024;64:849-858 (Jun 24). Doi: 10.1111/head.14768 Source
Long-term Eptinezumab Benefits Patients With Chronic Migraine and Medication-Overuse Headache
Key clinical point: Long-term eptinezumab treatment showed benefits in patients with chronic migraine (CM) who had concomitant medication-overuse headache (MOH).
Major findings: After eptinezumab treatment, the average number of headache days per 3 months reduced from 15.8 days (mean 47.5 headache days/month) at baseline to 3.8 days (mean 11.3 headache days/month) at 104 weeks, along with reductions observed in the Migraine Disability Assessment (mean change −51.9 points) and 6-item Headache Impact Test (mean change −9.7 points) scores. More than half (57.1%) the patients showed an improvement in their patient-identified most bothersome symptom at as early as 4 weeks.
Study details: This post hoc analysis of the PREVAIL study included 49 patients with CM and concomitant MOH.
Disclosures: This publication was supported by H. Lundbeck A/S, Copenhagen, Denmark. Two authors declared being employees of H. Lundbeck A/S. The other authors declared having ties with various sources, including H. Lundbeck A/S.
Source: Blumenfeld A, Kudrow D, McAllister P, et al. Long-term effectiveness of eptinezumab in the treatment of patients with chronic migraine and medication-overuse headache. Headache. 2024;64:738-749 (Jun 24). Doi: 10.1111/head.14767 Source
Key clinical point: Long-term eptinezumab treatment showed benefits in patients with chronic migraine (CM) who had concomitant medication-overuse headache (MOH).
Major findings: After eptinezumab treatment, the average number of headache days per 3 months reduced from 15.8 days (mean 47.5 headache days/month) at baseline to 3.8 days (mean 11.3 headache days/month) at 104 weeks, along with reductions observed in the Migraine Disability Assessment (mean change −51.9 points) and 6-item Headache Impact Test (mean change −9.7 points) scores. More than half (57.1%) the patients showed an improvement in their patient-identified most bothersome symptom at as early as 4 weeks.
Study details: This post hoc analysis of the PREVAIL study included 49 patients with CM and concomitant MOH.
Disclosures: This publication was supported by H. Lundbeck A/S, Copenhagen, Denmark. Two authors declared being employees of H. Lundbeck A/S. The other authors declared having ties with various sources, including H. Lundbeck A/S.
Source: Blumenfeld A, Kudrow D, McAllister P, et al. Long-term effectiveness of eptinezumab in the treatment of patients with chronic migraine and medication-overuse headache. Headache. 2024;64:738-749 (Jun 24). Doi: 10.1111/head.14767 Source
Key clinical point: Long-term eptinezumab treatment showed benefits in patients with chronic migraine (CM) who had concomitant medication-overuse headache (MOH).
Major findings: After eptinezumab treatment, the average number of headache days per 3 months reduced from 15.8 days (mean 47.5 headache days/month) at baseline to 3.8 days (mean 11.3 headache days/month) at 104 weeks, along with reductions observed in the Migraine Disability Assessment (mean change −51.9 points) and 6-item Headache Impact Test (mean change −9.7 points) scores. More than half (57.1%) the patients showed an improvement in their patient-identified most bothersome symptom at as early as 4 weeks.
Study details: This post hoc analysis of the PREVAIL study included 49 patients with CM and concomitant MOH.
Disclosures: This publication was supported by H. Lundbeck A/S, Copenhagen, Denmark. Two authors declared being employees of H. Lundbeck A/S. The other authors declared having ties with various sources, including H. Lundbeck A/S.
Source: Blumenfeld A, Kudrow D, McAllister P, et al. Long-term effectiveness of eptinezumab in the treatment of patients with chronic migraine and medication-overuse headache. Headache. 2024;64:738-749 (Jun 24). Doi: 10.1111/head.14767 Source
Patients with CGRP-Induced Migraine Attacks Can Benefit With Erenumab
Key clinical point: Calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP)–induced migraine attacks did not affect therapeutic response to erenumab in patients with migraine.
Major finding: Overall, a similar proportion of patients who experienced vs did not experience CGRP-induced migraine attacks had a ≥50% reduction in monthly migraine days during weeks 13-24 following erenumab treatment (61% vs 52%; odds ratio [OR] 1.42; P = .498). No significant differences were seen between the two patient groups that achieved a ≥50% reduction in monthly migraine or headache days of moderate to severe intensity (OR 1.25; P = .625).
Study details: This interim analysis of the REFORM study included 124 patients with migraine who received CGRP infusion on a single experimental day and subsequently a 24-week treatment with erenumab.
Disclosures: This study was funded by Novartis Pharma and the Lundbeck Foundation. Two authors declared being employees of or holding shares in Novartis Pharma AG. Several authors declared receiving personal fees from various sources, including Novartis, outside of the submitted work. One author is an associate editor for Cephalalgia.
Source: Al-Khazali HM, Ashina H, Christensen RH, et al. Hypersensitivity to CGRP as a predictive biomarker of migraine prevention with erenumab. Cephalalgia. 2024;44(6):3331024241258734 (Jun 11). Doi: 10.1177/03331024241258734 Source
Key clinical point: Calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP)–induced migraine attacks did not affect therapeutic response to erenumab in patients with migraine.
Major finding: Overall, a similar proportion of patients who experienced vs did not experience CGRP-induced migraine attacks had a ≥50% reduction in monthly migraine days during weeks 13-24 following erenumab treatment (61% vs 52%; odds ratio [OR] 1.42; P = .498). No significant differences were seen between the two patient groups that achieved a ≥50% reduction in monthly migraine or headache days of moderate to severe intensity (OR 1.25; P = .625).
Study details: This interim analysis of the REFORM study included 124 patients with migraine who received CGRP infusion on a single experimental day and subsequently a 24-week treatment with erenumab.
Disclosures: This study was funded by Novartis Pharma and the Lundbeck Foundation. Two authors declared being employees of or holding shares in Novartis Pharma AG. Several authors declared receiving personal fees from various sources, including Novartis, outside of the submitted work. One author is an associate editor for Cephalalgia.
Source: Al-Khazali HM, Ashina H, Christensen RH, et al. Hypersensitivity to CGRP as a predictive biomarker of migraine prevention with erenumab. Cephalalgia. 2024;44(6):3331024241258734 (Jun 11). Doi: 10.1177/03331024241258734 Source
Key clinical point: Calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP)–induced migraine attacks did not affect therapeutic response to erenumab in patients with migraine.
Major finding: Overall, a similar proportion of patients who experienced vs did not experience CGRP-induced migraine attacks had a ≥50% reduction in monthly migraine days during weeks 13-24 following erenumab treatment (61% vs 52%; odds ratio [OR] 1.42; P = .498). No significant differences were seen between the two patient groups that achieved a ≥50% reduction in monthly migraine or headache days of moderate to severe intensity (OR 1.25; P = .625).
Study details: This interim analysis of the REFORM study included 124 patients with migraine who received CGRP infusion on a single experimental day and subsequently a 24-week treatment with erenumab.
Disclosures: This study was funded by Novartis Pharma and the Lundbeck Foundation. Two authors declared being employees of or holding shares in Novartis Pharma AG. Several authors declared receiving personal fees from various sources, including Novartis, outside of the submitted work. One author is an associate editor for Cephalalgia.
Source: Al-Khazali HM, Ashina H, Christensen RH, et al. Hypersensitivity to CGRP as a predictive biomarker of migraine prevention with erenumab. Cephalalgia. 2024;44(6):3331024241258734 (Jun 11). Doi: 10.1177/03331024241258734 Source
Erenumab Treatment Interruption May Worsen Episodic or Chronic Migraine Symptoms
Key clinical point: In patients with episodic migraine (EM) or chronic migraine (CM), erenumab treatment interruption was associated with increased monthly migraine days (MMD) and worsening of migraine disability; these effects ameliorated on treatment restart.
Major finding: After erenumab treatment interruption for 3 months, the number of monthly migraine days (MMD) increased from 6.1 to 10.9 days for patients with EM and from 11.4 to 16.8 days for patients with CM; the modified Migraine Disability Assessment scores (mMIDAS) also worsened during this period. Both MMD and mMIDAS scores improved upon restarting treatment.
Study details: This interim analysis of the 24-month, multicentric, non-interventional observational study included 172 patients with CM or EM who received erenumab and underwent treatment interruptions on average 11.2 months after initiation, with interruptions lasting for a mean duration of 4 months.
Disclosures: This study was funded by Novartis Pharma Schweiz AG. Four authors declared being full-time employees of Novartis Pharma Schweiz AG, and others declared having ties with various sources, including Novartis.
Source: Gantenbein AR, Bonvin C, Kamm CP, et al. Implications of therapy interruption on monthly migraine days and modified migraine disability assessment in patients treated with erenumab for chronic and episodic migraine: SQUARE study interim results. J Neurol. 2024 (Jun 13). Doi: 10.1007/s00415-024-12470-6 Source
Key clinical point: In patients with episodic migraine (EM) or chronic migraine (CM), erenumab treatment interruption was associated with increased monthly migraine days (MMD) and worsening of migraine disability; these effects ameliorated on treatment restart.
Major finding: After erenumab treatment interruption for 3 months, the number of monthly migraine days (MMD) increased from 6.1 to 10.9 days for patients with EM and from 11.4 to 16.8 days for patients with CM; the modified Migraine Disability Assessment scores (mMIDAS) also worsened during this period. Both MMD and mMIDAS scores improved upon restarting treatment.
Study details: This interim analysis of the 24-month, multicentric, non-interventional observational study included 172 patients with CM or EM who received erenumab and underwent treatment interruptions on average 11.2 months after initiation, with interruptions lasting for a mean duration of 4 months.
Disclosures: This study was funded by Novartis Pharma Schweiz AG. Four authors declared being full-time employees of Novartis Pharma Schweiz AG, and others declared having ties with various sources, including Novartis.
Source: Gantenbein AR, Bonvin C, Kamm CP, et al. Implications of therapy interruption on monthly migraine days and modified migraine disability assessment in patients treated with erenumab for chronic and episodic migraine: SQUARE study interim results. J Neurol. 2024 (Jun 13). Doi: 10.1007/s00415-024-12470-6 Source
Key clinical point: In patients with episodic migraine (EM) or chronic migraine (CM), erenumab treatment interruption was associated with increased monthly migraine days (MMD) and worsening of migraine disability; these effects ameliorated on treatment restart.
Major finding: After erenumab treatment interruption for 3 months, the number of monthly migraine days (MMD) increased from 6.1 to 10.9 days for patients with EM and from 11.4 to 16.8 days for patients with CM; the modified Migraine Disability Assessment scores (mMIDAS) also worsened during this period. Both MMD and mMIDAS scores improved upon restarting treatment.
Study details: This interim analysis of the 24-month, multicentric, non-interventional observational study included 172 patients with CM or EM who received erenumab and underwent treatment interruptions on average 11.2 months after initiation, with interruptions lasting for a mean duration of 4 months.
Disclosures: This study was funded by Novartis Pharma Schweiz AG. Four authors declared being full-time employees of Novartis Pharma Schweiz AG, and others declared having ties with various sources, including Novartis.
Source: Gantenbein AR, Bonvin C, Kamm CP, et al. Implications of therapy interruption on monthly migraine days and modified migraine disability assessment in patients treated with erenumab for chronic and episodic migraine: SQUARE study interim results. J Neurol. 2024 (Jun 13). Doi: 10.1007/s00415-024-12470-6 Source
Patients With Migraine Have Higher Risk for Retinal Vascular Occlusion
Key clinical point: Patients with migraine, migraine with aura (MA), or migraine without aura (MO) faced a significantly higher risk for retinal vascular occlusion.
Major findings: Compared with control individuals without migraine, those with migraine (adjusted hazard ratio [aHR] 1.69; 95% CI 1.57-1.83), MA (aHR 1.77; 95% CI 1.58-1.98), or MO (aHR 1.92; 95% CI 1.64-2.25; P < .001 for all) had a significantly higher risk for retinal vascular occlusion. The risk was, however, reduced in the migraine population that received nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (aHR 0.19; 95% CI 0.16-0.22), propranolol (aHR 0.73; 95% CI 0.62-0.86), or flunarizine (aHR 0.84; 95% CI 0.76-0.93; P < .001 for all).
Study details: This population-based retrospective cohort study included 628,760 patients with migraine and 628,760 control individuals without migraine.
Disclosures: This study was supported in part by the Taiwan Ministry of Health and Welfare Clinical Trial Center, China Medical University Hospital, and National Science and Technology Council. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Source: Ho K-Y, Lin C-D, Hsu T-J, et al. Increased risks of retinal vascular occlusion in patients with migraine and the protective effects of migraine treatment: A population-based retrospective cohort study. Sci Rep. 2024;14:15429 (Jul 4). Doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-66363-9 Source
Key clinical point: Patients with migraine, migraine with aura (MA), or migraine without aura (MO) faced a significantly higher risk for retinal vascular occlusion.
Major findings: Compared with control individuals without migraine, those with migraine (adjusted hazard ratio [aHR] 1.69; 95% CI 1.57-1.83), MA (aHR 1.77; 95% CI 1.58-1.98), or MO (aHR 1.92; 95% CI 1.64-2.25; P < .001 for all) had a significantly higher risk for retinal vascular occlusion. The risk was, however, reduced in the migraine population that received nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (aHR 0.19; 95% CI 0.16-0.22), propranolol (aHR 0.73; 95% CI 0.62-0.86), or flunarizine (aHR 0.84; 95% CI 0.76-0.93; P < .001 for all).
Study details: This population-based retrospective cohort study included 628,760 patients with migraine and 628,760 control individuals without migraine.
Disclosures: This study was supported in part by the Taiwan Ministry of Health and Welfare Clinical Trial Center, China Medical University Hospital, and National Science and Technology Council. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Source: Ho K-Y, Lin C-D, Hsu T-J, et al. Increased risks of retinal vascular occlusion in patients with migraine and the protective effects of migraine treatment: A population-based retrospective cohort study. Sci Rep. 2024;14:15429 (Jul 4). Doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-66363-9 Source
Key clinical point: Patients with migraine, migraine with aura (MA), or migraine without aura (MO) faced a significantly higher risk for retinal vascular occlusion.
Major findings: Compared with control individuals without migraine, those with migraine (adjusted hazard ratio [aHR] 1.69; 95% CI 1.57-1.83), MA (aHR 1.77; 95% CI 1.58-1.98), or MO (aHR 1.92; 95% CI 1.64-2.25; P < .001 for all) had a significantly higher risk for retinal vascular occlusion. The risk was, however, reduced in the migraine population that received nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (aHR 0.19; 95% CI 0.16-0.22), propranolol (aHR 0.73; 95% CI 0.62-0.86), or flunarizine (aHR 0.84; 95% CI 0.76-0.93; P < .001 for all).
Study details: This population-based retrospective cohort study included 628,760 patients with migraine and 628,760 control individuals without migraine.
Disclosures: This study was supported in part by the Taiwan Ministry of Health and Welfare Clinical Trial Center, China Medical University Hospital, and National Science and Technology Council. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Source: Ho K-Y, Lin C-D, Hsu T-J, et al. Increased risks of retinal vascular occlusion in patients with migraine and the protective effects of migraine treatment: A population-based retrospective cohort study. Sci Rep. 2024;14:15429 (Jul 4). Doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-66363-9 Source
Atogepant Effective in Chronic Migraine, Irrespective of Acute Medication Overuse
Key clinical point: Atogepant was effective in reducing monthly migraine days (MMD), monthly headache days (MHD), and acute medication use days in patients with chronic migraine (CM), irrespective of acute medication overuse.
Major findings: Patients with acute medication overuse receiving 30 mg or 60 mg atogepant vs placebo had a significantly greater reduction in MMD (least squares mean difference [LSMD] −2.7 and −1.9, respectively), MHD (LSMD −2.8 and −2.1, respectively), and monthly acute medication use days (LSMD −2.8 and −2.6, respectively). Similar reductions were observed in patients without acute medication overuse.
Study details: This subgroup analysis of the PROGRESS trial included 755 patients with CM with or without acute medication overuse who were randomly assigned to receive atogepant (30 mg or 60 mg) or placebo.
Disclosures: This study was funded by AbbVie. Six authors declared being employees or stockholders of AbbVie. Several authors declared having ties with various sources, including AbbVie.
Source: Goadsby PJ, Friedman DI, Holle-Lee D, et al. Efficacy of atogepant in chronic migraine with and without acute medication overuse in the randomized, double-blind, phase 3 PROGRESS trial. Neurology. 2024;103(2):e209584 (July 23). Doi: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000209584 Source
Key clinical point: Atogepant was effective in reducing monthly migraine days (MMD), monthly headache days (MHD), and acute medication use days in patients with chronic migraine (CM), irrespective of acute medication overuse.
Major findings: Patients with acute medication overuse receiving 30 mg or 60 mg atogepant vs placebo had a significantly greater reduction in MMD (least squares mean difference [LSMD] −2.7 and −1.9, respectively), MHD (LSMD −2.8 and −2.1, respectively), and monthly acute medication use days (LSMD −2.8 and −2.6, respectively). Similar reductions were observed in patients without acute medication overuse.
Study details: This subgroup analysis of the PROGRESS trial included 755 patients with CM with or without acute medication overuse who were randomly assigned to receive atogepant (30 mg or 60 mg) or placebo.
Disclosures: This study was funded by AbbVie. Six authors declared being employees or stockholders of AbbVie. Several authors declared having ties with various sources, including AbbVie.
Source: Goadsby PJ, Friedman DI, Holle-Lee D, et al. Efficacy of atogepant in chronic migraine with and without acute medication overuse in the randomized, double-blind, phase 3 PROGRESS trial. Neurology. 2024;103(2):e209584 (July 23). Doi: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000209584 Source
Key clinical point: Atogepant was effective in reducing monthly migraine days (MMD), monthly headache days (MHD), and acute medication use days in patients with chronic migraine (CM), irrespective of acute medication overuse.
Major findings: Patients with acute medication overuse receiving 30 mg or 60 mg atogepant vs placebo had a significantly greater reduction in MMD (least squares mean difference [LSMD] −2.7 and −1.9, respectively), MHD (LSMD −2.8 and −2.1, respectively), and monthly acute medication use days (LSMD −2.8 and −2.6, respectively). Similar reductions were observed in patients without acute medication overuse.
Study details: This subgroup analysis of the PROGRESS trial included 755 patients with CM with or without acute medication overuse who were randomly assigned to receive atogepant (30 mg or 60 mg) or placebo.
Disclosures: This study was funded by AbbVie. Six authors declared being employees or stockholders of AbbVie. Several authors declared having ties with various sources, including AbbVie.
Source: Goadsby PJ, Friedman DI, Holle-Lee D, et al. Efficacy of atogepant in chronic migraine with and without acute medication overuse in the randomized, double-blind, phase 3 PROGRESS trial. Neurology. 2024;103(2):e209584 (July 23). Doi: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000209584 Source
Cyclosporine for Recalcitrant Bullous Pemphigoid Induced by Nivolumab Therapy for Malignant Melanoma
To the Editor:
Immune checkpoint inhibitors have revolutionized the treatment of advanced-stage melanoma, with remarkably improved progression-free survival.1 Anti–programmed death receptor 1 (anti–PD-1) therapies, such as nivolumab and pembrolizumab, are a class of checkpoint inhibitors that have been approved by the US Food and Drug Administration for unresectable metastatic melanoma. Anti–PD-1 agents block the interaction of programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1) found on tumor cells with the PD-1 receptor on T cells, facilitating a positive immune response.2
Although these therapies have demonstrated notable antitumor efficacy, they also give rise to numerous immune-related adverse events (irAEs). As many as 70% of patients treated with PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors experience some type of organ system irAE, of which 30% to 40% are cutaneous.3-6 Dermatologic adverse events are the most common irAEs, specifically spongiotic dermatitis, lichenoid dermatitis, pruritus, and vitiligo.7 Bullous pemphigoid (BP), an autoimmune bullous skin disorder caused by autoantibodies to basement membrane zone antigens, is a rare but potentially serious cutaneous irAE.8 Systemic corticosteroids commonly are used to treat immune checkpoint inhibitor–induced BP; other options include tetracyclines for maintenance therapy and rituximab for corticosteroid-refractory BP associated with anti-PD-1.9 We present a case of recalcitrant BP secondary to nivolumab therapy in a patient with metastatic melanoma who had near-complete resolution of BP following 2 months of cyclosporine.
A 41-year-old man presented with a generalized papular skin eruption of 1 month’s duration. He had a history of stage IIIC malignant melanoma of the lower right leg with positive sentinel lymph node biopsy. The largest lymph node deposit was 0.03 mm without extracapsular extension. Whole-body positron emission tomography–computed tomography showed no evidence of distant disease. The patient was treated with wide local excision with clear surgical margins plus 12 cycles of nivolumab, which was discontinued due to colitis. Four months after the final cycle of nivolumab, the patient developed widespread erythematous papules with hemorrhagic yellow crusting and no mucosal involvement. He was referred to dermatology by his primary oncologist for further evaluation.
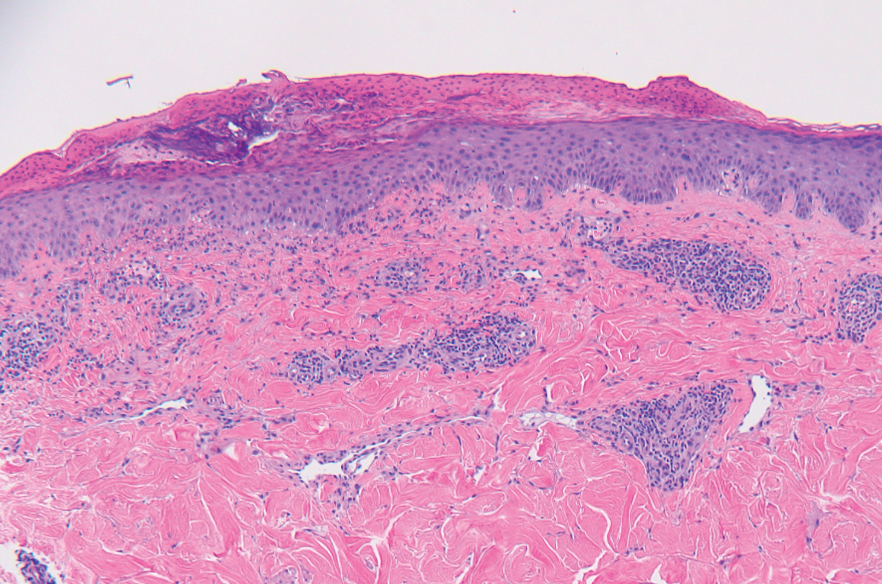
A punch biopsy from the abdomen showed parakeratosis with leukocytoclasis and a superficial dermal infiltrate of neutrophils and eosinophils (Figure 1). Direct immunofluorescence revealed linear basement membrane deposits of IgG and C3, consistent with subepidermal blistering disease. Indirect immunofluorescence demonstrated trace IgG and IgG4 antibodies localized to the epidermal roof of salt-split skin and was negative for IgA antibodies. An enzyme-linked immunoassay was positive for BP antigen 2 (BP180) antibodies (98.4 U/mL [positive, ≥9 U/mL]) and negative for BP antigen 1 (BP230) antibodies (4.3 U/mL [positive, ≥9 U/mL]). Overall, these findings were consistent with a diagnosis of BP.
The patient was treated with prednisone 60 mg daily with initial response; however, there was disease recurrence with tapering. Doxycycline 100 mg twice daily and nicotinamide 500 mg twice daily were added as steroid-sparing agents, as prednisone was discontinued due to mood changes. Three months after the prednisone taper, the patient continued to develop new blisters. He completed treatment with doxycycline and nicotinamide. Rituximab 375 mg weekly was then initiated for 4 weeks.
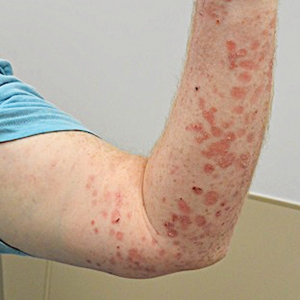
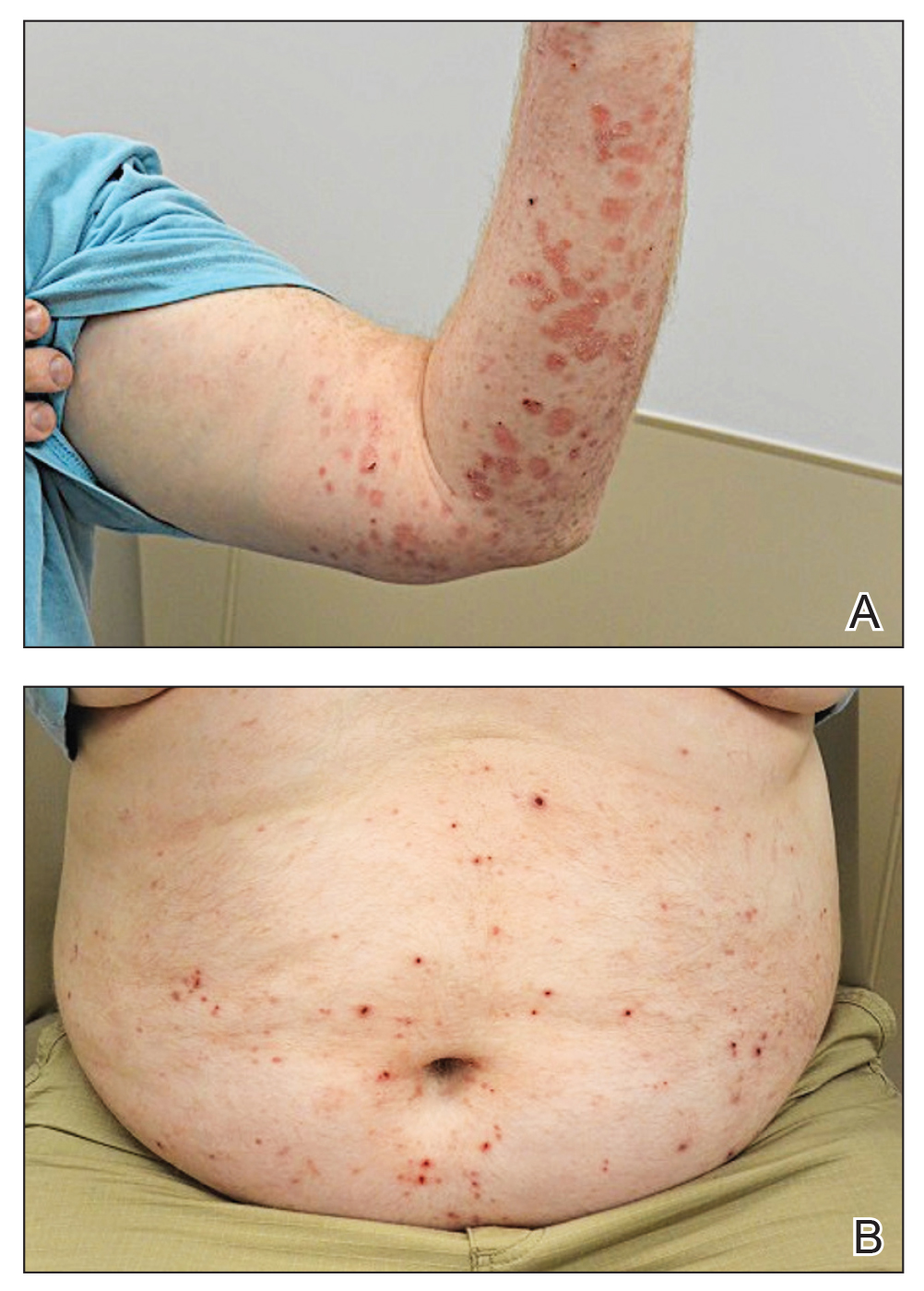
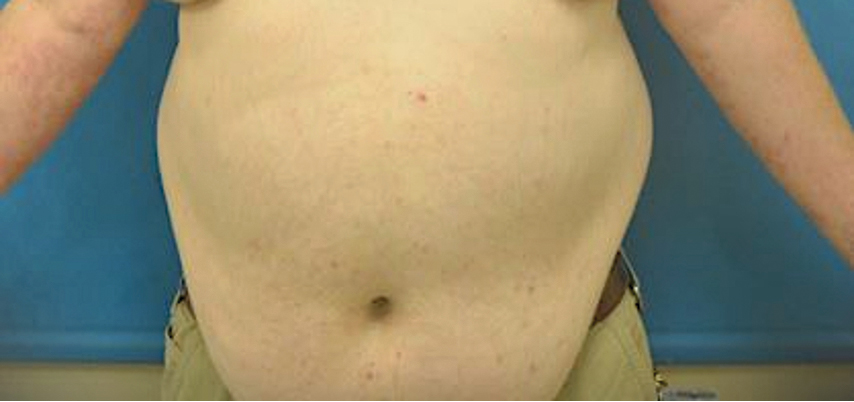
At 2-week follow-up after completing the rituximab course, the patient reported worsening symptoms and presented with new bullae on the abdomen and upper extremities (Figure 2). Because of the recent history of mood changes while taking prednisone, a trial of cyclosporine 100 mg twice daily (1.37 mg/kg/d) was initiated, with notable improvement within 2 weeks of treatment. After 2 months of cyclosporine, approximately 90% of the rash had resolved with a few tense bullae remaining on the left frontal scalp but no new flares (Figure 3). One month after treatment ended, the patient remained clear of lesions without relapse.
Programmed death receptor 1 inhibitors have shown dramatic efficacy for a growing number of solid and hematologic malignancies, especially malignant melanoma. However, their use is accompanied by nonspecific activation of the immune system, resulting in a variety of adverse events, many manifesting on the skin. Several cases of BP in patients treated with PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors have been reported.9 Cutaneous irAEs usually manifest within 3 weeks of initiation of PD-1 inhibitor therapy; however, the onset of BP typically occurs later at approximately 21 weeks.4,9 Our patient developed cutaneous manifestations 4 months after cessation of nivolumab.
Bullous pemphigoid classically manifests with pruritus and tense bullae. Notably, our patient’s clinical presentation included a widespread eruption of papules without bullae, which was similar to a review by Tsiogka et al,9 which reported that one-third of patients first present with a nonspecific cutaneous eruption. Bullous pemphigoid induced by anti–PD-1 may manifest differently than traditional BP, illuminating the importance of a thorough diagnostic workup.
Although the pathogenesis of immune checkpoint inhibitor–induced BP has not been fully elucidated, it is hypothesized to be caused by increased T cell cytotoxic activity leading to tumor lysis and release of numerous autoantigens. These autoantigens cause priming of abnormal T cells that can lead to further tissue damage in peripheral tissue and to generation of aberrant B cells and subsequent autoantibodies such as BP180 in germinal centers.4,10,11
Cyclosporine is a calcineurin inhibitor that reduces synthesis of IL-2, resulting in reduced cell activation.12 Therefore, cyclosporine may alleviate BP in patients who are being treated, or were previously treated, with an immune checkpoint inhibitor by suppressing T cell–mediated immune reaction and may be a rapid alternative for patients who cannot tolerate systemic steroids.
Treatment options for mild to moderate cases of BP include topical corticosteroids and antihistamines, while severe cases may require high-dose systemic corticosteroids. In recalcitrant cases, rituximab infusion with or without intravenous immunoglobulin often is utilized.8,13 The use of cyclosporine for various bullous disorders, including pemphigus vulgaris and epidermolysis bullosa acquisita, has been described.14 In recent years there has been a shift away from the use of cyclosporine for these conditions following the introduction of rituximab, a monoclonal antibody directed against the CD20 antigen on B lymphocytes. We utilized cyclosporine in our patient after he experienced worsening symptoms 1 month after completing treatment with rituximab.
Improvement from rituximab therapy may be delayed because it can take months to deplete CD20+ B lymphocytes from circulation, which may necessitate additional immunosuppressants or re-treatment with rituximab.15,16 In these instances, cyclosporine may be beneficial as a low-cost alternative in patients who are unable to tolerate systemic steroids, with a relatively good safety profile. The dosage of cyclosporine prescribed to the patient was chosen based on Joint American Academy of Dermatology–National Psoriasis Foundation management guidelines for psoriasis with systemic nonbiologic therapies, which recommends an initial dosage of 1 to 3 mg/kg/d in 2 divided doses.17
As immunotherapy for treating various cancers gains popularity, the frequency of dermatologic irAEs will increase. Therefore, dermatologists must be aware of the array of cutaneous manifestations, such as BP, and potential treatment options. When first-line and second-line therapies are contraindicated or do not provide notable improvement, cyclosporine may be an effective alternative for immune checkpoint inhibitor–induced BP.
- Larkin J, Chiarion-Sileni V, Gonzalez R, et al. Combined nivolumab and ipilimumab or monotherapy in untreated melanoma. N Engl J Med. 2015;373:23-34. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1504030
- Alsaab HO, Sau S, Alzhrani R, et al. PD-1 and PD-L1 checkpoint signaling inhibition for cancer immunotherapy: mechanism, combinations, and clinical outcome. Front Pharmacol. 2017;8:561. doi:10.3389/fphar.2017.00561
- Puzanov I, Diab A, Abdallah K, et al; . Managing toxicities associated with immune checkpoint inhibitors: consensus recommendations from the Society for Immunotherapy of Cancer (SITC) Toxicity Management Working Group. J Immunother Cancer. 2017;5:95. doi:10.1186/s40425-017-0300-z
- Geisler AN, Phillips GS, Barrios DM, et al. Immune checkpoint inhibitor-related dermatologic adverse events. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;83:1255-1268. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2020.03.132
- Villadolid J, Amin A. Immune checkpoint inhibitors in clinical practice: update on management of immune-related toxicities. Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2015;4:560-575. doi:10.3978/j.issn.2218-6751.2015.06.06
- Kumar V, Chaudhary N, Garg M, et al. Current diagnosis and management of immune related adverse events (irAEs) induced by immune checkpoint inhibitor therapy. Front Pharmacol. 2017;8:49. doi:10.3389/fphar.2017.00049
- Belum VR, Benhuri B, Postow MA, et al. Characterisation and management of dermatologic adverse events to agents targeting the PD-1 receptor. Eur J Cancer. 2016;60:12-25. doi:10.1016/j.ejca.2016.02.010
- Schauer F, Rafei-Shamsabadi D, Mai S, et al. Hemidesmosomal reactivity and treatment recommendations in immune checkpoint inhibitor-induced bullous pemphigoid—a retrospective, monocentric study. Front Immunol. 2022;13:953546. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2022.953546
- Tsiogka A, Bauer JW, Patsatsi A. Bullous pemphigoid associated with anti-programmed cell death protein 1 and anti-programmed cell death ligand 1 therapy: a review of the literature. Acta Derm Venereol. 2021;101:adv00377. doi:10.2340/00015555-3740
- Lopez AT, Khanna T, Antonov N, et al. A review of bullous pemphigoid associated with PD-1 and PD-L1 inhibitors. Int J Dermatol. 2018;57:664-669. doi:10.1111/ijd.13984
- Yang H, Yao Z, Zhou X, et al. Immune-related adverse events of checkpoint inhibitors: insights into immunological dysregulation. Clin Immunol. 2020;213:108377. doi:10.1016/j.clim.2020.108377
- Russell G, Graveley R, Seid J, et al. Mechanisms of action of cyclosporine and effects on connective tissues. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 1992;21(6 suppl 3):16-22. doi:10.1016/0049-0172(92)90009-3
- Ahmed AR, Shetty S, Kaveri S, et al. Treatment of recalcitrant bullous pemphigoid (BP) with a novel protocol: a retrospective study with a 6-year follow-up. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2016;74:700-708.e3. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2015.11.030
- Amor KT, Ryan C, Menter A. The use of cyclosporine in dermatology: part I. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2010;63:925-946. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2010.02.063
- Schmidt E, Hunzelmann N, Zillikens D, et al. Rituximab in refractory autoimmune bullous diseases. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2006;31:503-508. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2230.2006.02151.x
- Kasperkiewicz M, Shimanovich I, Ludwig RJ, et al. Rituximab for treatment-refractory pemphigus and pemphigoid: a case series of 17 patients. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2011;65:552-558.
- Menter A, Gelfand JM, Connor C, et al. Joint American Academy of Dermatology–National Psoriasis Foundation guidelines of care for the management of psoriasis with systemic nonbiologic therapies. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;82:1445-1486. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2020.02.044
To the Editor:
Immune checkpoint inhibitors have revolutionized the treatment of advanced-stage melanoma, with remarkably improved progression-free survival.1 Anti–programmed death receptor 1 (anti–PD-1) therapies, such as nivolumab and pembrolizumab, are a class of checkpoint inhibitors that have been approved by the US Food and Drug Administration for unresectable metastatic melanoma. Anti–PD-1 agents block the interaction of programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1) found on tumor cells with the PD-1 receptor on T cells, facilitating a positive immune response.2
Although these therapies have demonstrated notable antitumor efficacy, they also give rise to numerous immune-related adverse events (irAEs). As many as 70% of patients treated with PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors experience some type of organ system irAE, of which 30% to 40% are cutaneous.3-6 Dermatologic adverse events are the most common irAEs, specifically spongiotic dermatitis, lichenoid dermatitis, pruritus, and vitiligo.7 Bullous pemphigoid (BP), an autoimmune bullous skin disorder caused by autoantibodies to basement membrane zone antigens, is a rare but potentially serious cutaneous irAE.8 Systemic corticosteroids commonly are used to treat immune checkpoint inhibitor–induced BP; other options include tetracyclines for maintenance therapy and rituximab for corticosteroid-refractory BP associated with anti-PD-1.9 We present a case of recalcitrant BP secondary to nivolumab therapy in a patient with metastatic melanoma who had near-complete resolution of BP following 2 months of cyclosporine.
A 41-year-old man presented with a generalized papular skin eruption of 1 month’s duration. He had a history of stage IIIC malignant melanoma of the lower right leg with positive sentinel lymph node biopsy. The largest lymph node deposit was 0.03 mm without extracapsular extension. Whole-body positron emission tomography–computed tomography showed no evidence of distant disease. The patient was treated with wide local excision with clear surgical margins plus 12 cycles of nivolumab, which was discontinued due to colitis. Four months after the final cycle of nivolumab, the patient developed widespread erythematous papules with hemorrhagic yellow crusting and no mucosal involvement. He was referred to dermatology by his primary oncologist for further evaluation.
A punch biopsy from the abdomen showed parakeratosis with leukocytoclasis and a superficial dermal infiltrate of neutrophils and eosinophils (Figure 1). Direct immunofluorescence revealed linear basement membrane deposits of IgG and C3, consistent with subepidermal blistering disease. Indirect immunofluorescence demonstrated trace IgG and IgG4 antibodies localized to the epidermal roof of salt-split skin and was negative for IgA antibodies. An enzyme-linked immunoassay was positive for BP antigen 2 (BP180) antibodies (98.4 U/mL [positive, ≥9 U/mL]) and negative for BP antigen 1 (BP230) antibodies (4.3 U/mL [positive, ≥9 U/mL]). Overall, these findings were consistent with a diagnosis of BP.
The patient was treated with prednisone 60 mg daily with initial response; however, there was disease recurrence with tapering. Doxycycline 100 mg twice daily and nicotinamide 500 mg twice daily were added as steroid-sparing agents, as prednisone was discontinued due to mood changes. Three months after the prednisone taper, the patient continued to develop new blisters. He completed treatment with doxycycline and nicotinamide. Rituximab 375 mg weekly was then initiated for 4 weeks.
At 2-week follow-up after completing the rituximab course, the patient reported worsening symptoms and presented with new bullae on the abdomen and upper extremities (Figure 2). Because of the recent history of mood changes while taking prednisone, a trial of cyclosporine 100 mg twice daily (1.37 mg/kg/d) was initiated, with notable improvement within 2 weeks of treatment. After 2 months of cyclosporine, approximately 90% of the rash had resolved with a few tense bullae remaining on the left frontal scalp but no new flares (Figure 3). One month after treatment ended, the patient remained clear of lesions without relapse.
Programmed death receptor 1 inhibitors have shown dramatic efficacy for a growing number of solid and hematologic malignancies, especially malignant melanoma. However, their use is accompanied by nonspecific activation of the immune system, resulting in a variety of adverse events, many manifesting on the skin. Several cases of BP in patients treated with PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors have been reported.9 Cutaneous irAEs usually manifest within 3 weeks of initiation of PD-1 inhibitor therapy; however, the onset of BP typically occurs later at approximately 21 weeks.4,9 Our patient developed cutaneous manifestations 4 months after cessation of nivolumab.



Bullous pemphigoid classically manifests with pruritus and tense bullae. Notably, our patient’s clinical presentation included a widespread eruption of papules without bullae, which was similar to a review by Tsiogka et al,9 which reported that one-third of patients first present with a nonspecific cutaneous eruption. Bullous pemphigoid induced by anti–PD-1 may manifest differently than traditional BP, illuminating the importance of a thorough diagnostic workup.
Although the pathogenesis of immune checkpoint inhibitor–induced BP has not been fully elucidated, it is hypothesized to be caused by increased T cell cytotoxic activity leading to tumor lysis and release of numerous autoantigens. These autoantigens cause priming of abnormal T cells that can lead to further tissue damage in peripheral tissue and to generation of aberrant B cells and subsequent autoantibodies such as BP180 in germinal centers.4,10,11
Cyclosporine is a calcineurin inhibitor that reduces synthesis of IL-2, resulting in reduced cell activation.12 Therefore, cyclosporine may alleviate BP in patients who are being treated, or were previously treated, with an immune checkpoint inhibitor by suppressing T cell–mediated immune reaction and may be a rapid alternative for patients who cannot tolerate systemic steroids.
Treatment options for mild to moderate cases of BP include topical corticosteroids and antihistamines, while severe cases may require high-dose systemic corticosteroids. In recalcitrant cases, rituximab infusion with or without intravenous immunoglobulin often is utilized.8,13 The use of cyclosporine for various bullous disorders, including pemphigus vulgaris and epidermolysis bullosa acquisita, has been described.14 In recent years there has been a shift away from the use of cyclosporine for these conditions following the introduction of rituximab, a monoclonal antibody directed against the CD20 antigen on B lymphocytes. We utilized cyclosporine in our patient after he experienced worsening symptoms 1 month after completing treatment with rituximab.
Improvement from rituximab therapy may be delayed because it can take months to deplete CD20+ B lymphocytes from circulation, which may necessitate additional immunosuppressants or re-treatment with rituximab.15,16 In these instances, cyclosporine may be beneficial as a low-cost alternative in patients who are unable to tolerate systemic steroids, with a relatively good safety profile. The dosage of cyclosporine prescribed to the patient was chosen based on Joint American Academy of Dermatology–National Psoriasis Foundation management guidelines for psoriasis with systemic nonbiologic therapies, which recommends an initial dosage of 1 to 3 mg/kg/d in 2 divided doses.17
As immunotherapy for treating various cancers gains popularity, the frequency of dermatologic irAEs will increase. Therefore, dermatologists must be aware of the array of cutaneous manifestations, such as BP, and potential treatment options. When first-line and second-line therapies are contraindicated or do not provide notable improvement, cyclosporine may be an effective alternative for immune checkpoint inhibitor–induced BP.
To the Editor:
Immune checkpoint inhibitors have revolutionized the treatment of advanced-stage melanoma, with remarkably improved progression-free survival.1 Anti–programmed death receptor 1 (anti–PD-1) therapies, such as nivolumab and pembrolizumab, are a class of checkpoint inhibitors that have been approved by the US Food and Drug Administration for unresectable metastatic melanoma. Anti–PD-1 agents block the interaction of programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1) found on tumor cells with the PD-1 receptor on T cells, facilitating a positive immune response.2
Although these therapies have demonstrated notable antitumor efficacy, they also give rise to numerous immune-related adverse events (irAEs). As many as 70% of patients treated with PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors experience some type of organ system irAE, of which 30% to 40% are cutaneous.3-6 Dermatologic adverse events are the most common irAEs, specifically spongiotic dermatitis, lichenoid dermatitis, pruritus, and vitiligo.7 Bullous pemphigoid (BP), an autoimmune bullous skin disorder caused by autoantibodies to basement membrane zone antigens, is a rare but potentially serious cutaneous irAE.8 Systemic corticosteroids commonly are used to treat immune checkpoint inhibitor–induced BP; other options include tetracyclines for maintenance therapy and rituximab for corticosteroid-refractory BP associated with anti-PD-1.9 We present a case of recalcitrant BP secondary to nivolumab therapy in a patient with metastatic melanoma who had near-complete resolution of BP following 2 months of cyclosporine.
A 41-year-old man presented with a generalized papular skin eruption of 1 month’s duration. He had a history of stage IIIC malignant melanoma of the lower right leg with positive sentinel lymph node biopsy. The largest lymph node deposit was 0.03 mm without extracapsular extension. Whole-body positron emission tomography–computed tomography showed no evidence of distant disease. The patient was treated with wide local excision with clear surgical margins plus 12 cycles of nivolumab, which was discontinued due to colitis. Four months after the final cycle of nivolumab, the patient developed widespread erythematous papules with hemorrhagic yellow crusting and no mucosal involvement. He was referred to dermatology by his primary oncologist for further evaluation.
A punch biopsy from the abdomen showed parakeratosis with leukocytoclasis and a superficial dermal infiltrate of neutrophils and eosinophils (Figure 1). Direct immunofluorescence revealed linear basement membrane deposits of IgG and C3, consistent with subepidermal blistering disease. Indirect immunofluorescence demonstrated trace IgG and IgG4 antibodies localized to the epidermal roof of salt-split skin and was negative for IgA antibodies. An enzyme-linked immunoassay was positive for BP antigen 2 (BP180) antibodies (98.4 U/mL [positive, ≥9 U/mL]) and negative for BP antigen 1 (BP230) antibodies (4.3 U/mL [positive, ≥9 U/mL]). Overall, these findings were consistent with a diagnosis of BP.
The patient was treated with prednisone 60 mg daily with initial response; however, there was disease recurrence with tapering. Doxycycline 100 mg twice daily and nicotinamide 500 mg twice daily were added as steroid-sparing agents, as prednisone was discontinued due to mood changes. Three months after the prednisone taper, the patient continued to develop new blisters. He completed treatment with doxycycline and nicotinamide. Rituximab 375 mg weekly was then initiated for 4 weeks.
At 2-week follow-up after completing the rituximab course, the patient reported worsening symptoms and presented with new bullae on the abdomen and upper extremities (Figure 2). Because of the recent history of mood changes while taking prednisone, a trial of cyclosporine 100 mg twice daily (1.37 mg/kg/d) was initiated, with notable improvement within 2 weeks of treatment. After 2 months of cyclosporine, approximately 90% of the rash had resolved with a few tense bullae remaining on the left frontal scalp but no new flares (Figure 3). One month after treatment ended, the patient remained clear of lesions without relapse.
Programmed death receptor 1 inhibitors have shown dramatic efficacy for a growing number of solid and hematologic malignancies, especially malignant melanoma. However, their use is accompanied by nonspecific activation of the immune system, resulting in a variety of adverse events, many manifesting on the skin. Several cases of BP in patients treated with PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors have been reported.9 Cutaneous irAEs usually manifest within 3 weeks of initiation of PD-1 inhibitor therapy; however, the onset of BP typically occurs later at approximately 21 weeks.4,9 Our patient developed cutaneous manifestations 4 months after cessation of nivolumab.



Bullous pemphigoid classically manifests with pruritus and tense bullae. Notably, our patient’s clinical presentation included a widespread eruption of papules without bullae, which was similar to a review by Tsiogka et al,9 which reported that one-third of patients first present with a nonspecific cutaneous eruption. Bullous pemphigoid induced by anti–PD-1 may manifest differently than traditional BP, illuminating the importance of a thorough diagnostic workup.
Although the pathogenesis of immune checkpoint inhibitor–induced BP has not been fully elucidated, it is hypothesized to be caused by increased T cell cytotoxic activity leading to tumor lysis and release of numerous autoantigens. These autoantigens cause priming of abnormal T cells that can lead to further tissue damage in peripheral tissue and to generation of aberrant B cells and subsequent autoantibodies such as BP180 in germinal centers.4,10,11
Cyclosporine is a calcineurin inhibitor that reduces synthesis of IL-2, resulting in reduced cell activation.12 Therefore, cyclosporine may alleviate BP in patients who are being treated, or were previously treated, with an immune checkpoint inhibitor by suppressing T cell–mediated immune reaction and may be a rapid alternative for patients who cannot tolerate systemic steroids.
Treatment options for mild to moderate cases of BP include topical corticosteroids and antihistamines, while severe cases may require high-dose systemic corticosteroids. In recalcitrant cases, rituximab infusion with or without intravenous immunoglobulin often is utilized.8,13 The use of cyclosporine for various bullous disorders, including pemphigus vulgaris and epidermolysis bullosa acquisita, has been described.14 In recent years there has been a shift away from the use of cyclosporine for these conditions following the introduction of rituximab, a monoclonal antibody directed against the CD20 antigen on B lymphocytes. We utilized cyclosporine in our patient after he experienced worsening symptoms 1 month after completing treatment with rituximab.
Improvement from rituximab therapy may be delayed because it can take months to deplete CD20+ B lymphocytes from circulation, which may necessitate additional immunosuppressants or re-treatment with rituximab.15,16 In these instances, cyclosporine may be beneficial as a low-cost alternative in patients who are unable to tolerate systemic steroids, with a relatively good safety profile. The dosage of cyclosporine prescribed to the patient was chosen based on Joint American Academy of Dermatology–National Psoriasis Foundation management guidelines for psoriasis with systemic nonbiologic therapies, which recommends an initial dosage of 1 to 3 mg/kg/d in 2 divided doses.17
As immunotherapy for treating various cancers gains popularity, the frequency of dermatologic irAEs will increase. Therefore, dermatologists must be aware of the array of cutaneous manifestations, such as BP, and potential treatment options. When first-line and second-line therapies are contraindicated or do not provide notable improvement, cyclosporine may be an effective alternative for immune checkpoint inhibitor–induced BP.
- Larkin J, Chiarion-Sileni V, Gonzalez R, et al. Combined nivolumab and ipilimumab or monotherapy in untreated melanoma. N Engl J Med. 2015;373:23-34. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1504030
- Alsaab HO, Sau S, Alzhrani R, et al. PD-1 and PD-L1 checkpoint signaling inhibition for cancer immunotherapy: mechanism, combinations, and clinical outcome. Front Pharmacol. 2017;8:561. doi:10.3389/fphar.2017.00561
- Puzanov I, Diab A, Abdallah K, et al; . Managing toxicities associated with immune checkpoint inhibitors: consensus recommendations from the Society for Immunotherapy of Cancer (SITC) Toxicity Management Working Group. J Immunother Cancer. 2017;5:95. doi:10.1186/s40425-017-0300-z
- Geisler AN, Phillips GS, Barrios DM, et al. Immune checkpoint inhibitor-related dermatologic adverse events. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;83:1255-1268. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2020.03.132
- Villadolid J, Amin A. Immune checkpoint inhibitors in clinical practice: update on management of immune-related toxicities. Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2015;4:560-575. doi:10.3978/j.issn.2218-6751.2015.06.06
- Kumar V, Chaudhary N, Garg M, et al. Current diagnosis and management of immune related adverse events (irAEs) induced by immune checkpoint inhibitor therapy. Front Pharmacol. 2017;8:49. doi:10.3389/fphar.2017.00049
- Belum VR, Benhuri B, Postow MA, et al. Characterisation and management of dermatologic adverse events to agents targeting the PD-1 receptor. Eur J Cancer. 2016;60:12-25. doi:10.1016/j.ejca.2016.02.010
- Schauer F, Rafei-Shamsabadi D, Mai S, et al. Hemidesmosomal reactivity and treatment recommendations in immune checkpoint inhibitor-induced bullous pemphigoid—a retrospective, monocentric study. Front Immunol. 2022;13:953546. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2022.953546
- Tsiogka A, Bauer JW, Patsatsi A. Bullous pemphigoid associated with anti-programmed cell death protein 1 and anti-programmed cell death ligand 1 therapy: a review of the literature. Acta Derm Venereol. 2021;101:adv00377. doi:10.2340/00015555-3740
- Lopez AT, Khanna T, Antonov N, et al. A review of bullous pemphigoid associated with PD-1 and PD-L1 inhibitors. Int J Dermatol. 2018;57:664-669. doi:10.1111/ijd.13984
- Yang H, Yao Z, Zhou X, et al. Immune-related adverse events of checkpoint inhibitors: insights into immunological dysregulation. Clin Immunol. 2020;213:108377. doi:10.1016/j.clim.2020.108377
- Russell G, Graveley R, Seid J, et al. Mechanisms of action of cyclosporine and effects on connective tissues. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 1992;21(6 suppl 3):16-22. doi:10.1016/0049-0172(92)90009-3
- Ahmed AR, Shetty S, Kaveri S, et al. Treatment of recalcitrant bullous pemphigoid (BP) with a novel protocol: a retrospective study with a 6-year follow-up. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2016;74:700-708.e3. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2015.11.030
- Amor KT, Ryan C, Menter A. The use of cyclosporine in dermatology: part I. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2010;63:925-946. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2010.02.063
- Schmidt E, Hunzelmann N, Zillikens D, et al. Rituximab in refractory autoimmune bullous diseases. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2006;31:503-508. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2230.2006.02151.x
- Kasperkiewicz M, Shimanovich I, Ludwig RJ, et al. Rituximab for treatment-refractory pemphigus and pemphigoid: a case series of 17 patients. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2011;65:552-558.
- Menter A, Gelfand JM, Connor C, et al. Joint American Academy of Dermatology–National Psoriasis Foundation guidelines of care for the management of psoriasis with systemic nonbiologic therapies. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;82:1445-1486. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2020.02.044
- Larkin J, Chiarion-Sileni V, Gonzalez R, et al. Combined nivolumab and ipilimumab or monotherapy in untreated melanoma. N Engl J Med. 2015;373:23-34. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1504030
- Alsaab HO, Sau S, Alzhrani R, et al. PD-1 and PD-L1 checkpoint signaling inhibition for cancer immunotherapy: mechanism, combinations, and clinical outcome. Front Pharmacol. 2017;8:561. doi:10.3389/fphar.2017.00561
- Puzanov I, Diab A, Abdallah K, et al; . Managing toxicities associated with immune checkpoint inhibitors: consensus recommendations from the Society for Immunotherapy of Cancer (SITC) Toxicity Management Working Group. J Immunother Cancer. 2017;5:95. doi:10.1186/s40425-017-0300-z
- Geisler AN, Phillips GS, Barrios DM, et al. Immune checkpoint inhibitor-related dermatologic adverse events. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;83:1255-1268. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2020.03.132
- Villadolid J, Amin A. Immune checkpoint inhibitors in clinical practice: update on management of immune-related toxicities. Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2015;4:560-575. doi:10.3978/j.issn.2218-6751.2015.06.06
- Kumar V, Chaudhary N, Garg M, et al. Current diagnosis and management of immune related adverse events (irAEs) induced by immune checkpoint inhibitor therapy. Front Pharmacol. 2017;8:49. doi:10.3389/fphar.2017.00049
- Belum VR, Benhuri B, Postow MA, et al. Characterisation and management of dermatologic adverse events to agents targeting the PD-1 receptor. Eur J Cancer. 2016;60:12-25. doi:10.1016/j.ejca.2016.02.010
- Schauer F, Rafei-Shamsabadi D, Mai S, et al. Hemidesmosomal reactivity and treatment recommendations in immune checkpoint inhibitor-induced bullous pemphigoid—a retrospective, monocentric study. Front Immunol. 2022;13:953546. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2022.953546
- Tsiogka A, Bauer JW, Patsatsi A. Bullous pemphigoid associated with anti-programmed cell death protein 1 and anti-programmed cell death ligand 1 therapy: a review of the literature. Acta Derm Venereol. 2021;101:adv00377. doi:10.2340/00015555-3740
- Lopez AT, Khanna T, Antonov N, et al. A review of bullous pemphigoid associated with PD-1 and PD-L1 inhibitors. Int J Dermatol. 2018;57:664-669. doi:10.1111/ijd.13984
- Yang H, Yao Z, Zhou X, et al. Immune-related adverse events of checkpoint inhibitors: insights into immunological dysregulation. Clin Immunol. 2020;213:108377. doi:10.1016/j.clim.2020.108377
- Russell G, Graveley R, Seid J, et al. Mechanisms of action of cyclosporine and effects on connective tissues. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 1992;21(6 suppl 3):16-22. doi:10.1016/0049-0172(92)90009-3
- Ahmed AR, Shetty S, Kaveri S, et al. Treatment of recalcitrant bullous pemphigoid (BP) with a novel protocol: a retrospective study with a 6-year follow-up. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2016;74:700-708.e3. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2015.11.030
- Amor KT, Ryan C, Menter A. The use of cyclosporine in dermatology: part I. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2010;63:925-946. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2010.02.063
- Schmidt E, Hunzelmann N, Zillikens D, et al. Rituximab in refractory autoimmune bullous diseases. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2006;31:503-508. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2230.2006.02151.x
- Kasperkiewicz M, Shimanovich I, Ludwig RJ, et al. Rituximab for treatment-refractory pemphigus and pemphigoid: a case series of 17 patients. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2011;65:552-558.
- Menter A, Gelfand JM, Connor C, et al. Joint American Academy of Dermatology–National Psoriasis Foundation guidelines of care for the management of psoriasis with systemic nonbiologic therapies. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;82:1445-1486. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2020.02.044
Practice Points
- Bullous pemphigoid is a rare dermatologic immune-related adverse event that can occur secondary to anti–programmed death receptor 1 therapy.
- For cases of immune checkpoint inhibitor–induced bullous pemphigoid that are recalcitrant to corticosteroids and rituximab, cyclosporine might be an effective alternative.
Circulating Tumor DNA Hints at BC Recurrence Risk
CHICAGO — Circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA) can predict relapse risk in some cases of early, high-risk breast cancer, but it’s too soon to use it to guide adjuvant therapy decisions, according to a study presented at the American Society of Clinical Oncology annual meeting.
Detectable ctDNA is “highly prognostic of worse outcomes, particularly in patients who [remain] persistently positive,” but the correlation isn’t perfect, said lead investigator Sherene Loi, MMBS, PhD, a breast cancer specialist at the Peter MacCallum Cancer Centre in Melbourne, Australia.
Although less likely, relapses also occurred in the study among women without ctDNA elevation. Conversely, there were women with elevated ctDNA who did not relapse, she said. The study was a subanalysis of the monarchE trial of adjuvant abemaciclib, a CDK 4/6 inhibitor.
Eventually, “we would like to use” ctDNA to guide adjuvant treatment decisions, but the research isn’t there yet, Dr. Loi said. It’s possible, for instance, that persistently detectable ctDNA indicates early treatment failure and the need for treatment intensification. Future research should tackle the issue.
Study discussant Francois-Clement Bidard, MD, PhD, a breast cancer specialist at Institut Curie, Paris, agreed that ctDNA isn’t ready for primetime in adjuvant early, high-risk breast cancer.
“There is no clinical evidence to suggest that there is clinical utility in this setting. There are several trials that are ongoing,” he said, but for now “you shouldn’t,” for example, “use ctDNA to de-escalate adjuvant CDK4/6 [inhibitors]. It could be in the future that we could have data on this, but at the moment, [the] clear clinical message [is] no way.”
At 5-year follow-up, the monarchE trial found a 7.6% invasive disease-free survival (IDFS) improvement when abemaciclib was added to the first 2 years of endocrine therapy in women with HR+, HER2-, node positive, high-risk early breast cancer. The combination is now a standard adjuvant option for the disease.
The ctDNA study focused on a subset of 910 subjects with adequate ctDNA testing to run the analysis. The study population was also selected to be enriched for overall IDFS events (27% versus 18% across the trial’s 5,637 subjects). An IDFS event was defined as a local, regional, contralateral or distant invasive recurrence; a new primary tumor; or death from any cause.
Testing was performed using the Signatera ctDNA assay. Baseline samples were taken after completion of adjuvant chemotherapy, then again at 3, 6, or 24 months.
Overall, ctDNA detection was infrequent. Just 8% of patients were positive at baseline and 17% were positive at any point during the trial. Even so, ctDNA detection at any point was adversely prognostic.
Patients who were ctDNA positive at baseline were more likely to experience an IDFS event, compared with those who were ctDNA negative at baseline (80% at 4 years follow-up versus 23%).
Similarly, those who remained positive or became positive during testing were more likely to experience an IDFS event compared with those who became negative or remained negative throughout testing.
For instance, all 34 patients who were positive at baseline and remained positive had an IDFS event by year 4, versus just 40% who started positive but then cleared their ctDNA.
Among women who were negative at baseline and remained negative, 13% had an IDFS event versus 89% who started negative but then turned positive. Subjects who turned positive also had the shortest time to an IDFS event, a median of 7 months.
Among women who recurred, those who were ctDNA negative tended to have local, regional, or contralateral recurrences, while ctDNA positive patients tended to have distant recurrences.
The finding “really highlights that ctDNA antedates the metastatic clinical relapse. What the ctDNA is telling you is that the metastatic process has been completed, and metastases are about to grow,” Dr. Bidard said.
The work was funded by Eli Lilly, maker of abemaciclib, with collaboration from Natera, maker of the Signatera assay. Dr. Loi is an adviser and researcher for Lilly, among other industry ties. Dr. Bidard is a speaker and consultant for Lilly, among other ties.
CHICAGO — Circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA) can predict relapse risk in some cases of early, high-risk breast cancer, but it’s too soon to use it to guide adjuvant therapy decisions, according to a study presented at the American Society of Clinical Oncology annual meeting.
Detectable ctDNA is “highly prognostic of worse outcomes, particularly in patients who [remain] persistently positive,” but the correlation isn’t perfect, said lead investigator Sherene Loi, MMBS, PhD, a breast cancer specialist at the Peter MacCallum Cancer Centre in Melbourne, Australia.
Although less likely, relapses also occurred in the study among women without ctDNA elevation. Conversely, there were women with elevated ctDNA who did not relapse, she said. The study was a subanalysis of the monarchE trial of adjuvant abemaciclib, a CDK 4/6 inhibitor.
Eventually, “we would like to use” ctDNA to guide adjuvant treatment decisions, but the research isn’t there yet, Dr. Loi said. It’s possible, for instance, that persistently detectable ctDNA indicates early treatment failure and the need for treatment intensification. Future research should tackle the issue.
Study discussant Francois-Clement Bidard, MD, PhD, a breast cancer specialist at Institut Curie, Paris, agreed that ctDNA isn’t ready for primetime in adjuvant early, high-risk breast cancer.
“There is no clinical evidence to suggest that there is clinical utility in this setting. There are several trials that are ongoing,” he said, but for now “you shouldn’t,” for example, “use ctDNA to de-escalate adjuvant CDK4/6 [inhibitors]. It could be in the future that we could have data on this, but at the moment, [the] clear clinical message [is] no way.”
At 5-year follow-up, the monarchE trial found a 7.6% invasive disease-free survival (IDFS) improvement when abemaciclib was added to the first 2 years of endocrine therapy in women with HR+, HER2-, node positive, high-risk early breast cancer. The combination is now a standard adjuvant option for the disease.
The ctDNA study focused on a subset of 910 subjects with adequate ctDNA testing to run the analysis. The study population was also selected to be enriched for overall IDFS events (27% versus 18% across the trial’s 5,637 subjects). An IDFS event was defined as a local, regional, contralateral or distant invasive recurrence; a new primary tumor; or death from any cause.
Testing was performed using the Signatera ctDNA assay. Baseline samples were taken after completion of adjuvant chemotherapy, then again at 3, 6, or 24 months.
Overall, ctDNA detection was infrequent. Just 8% of patients were positive at baseline and 17% were positive at any point during the trial. Even so, ctDNA detection at any point was adversely prognostic.
Patients who were ctDNA positive at baseline were more likely to experience an IDFS event, compared with those who were ctDNA negative at baseline (80% at 4 years follow-up versus 23%).
Similarly, those who remained positive or became positive during testing were more likely to experience an IDFS event compared with those who became negative or remained negative throughout testing.
For instance, all 34 patients who were positive at baseline and remained positive had an IDFS event by year 4, versus just 40% who started positive but then cleared their ctDNA.
Among women who were negative at baseline and remained negative, 13% had an IDFS event versus 89% who started negative but then turned positive. Subjects who turned positive also had the shortest time to an IDFS event, a median of 7 months.
Among women who recurred, those who were ctDNA negative tended to have local, regional, or contralateral recurrences, while ctDNA positive patients tended to have distant recurrences.
The finding “really highlights that ctDNA antedates the metastatic clinical relapse. What the ctDNA is telling you is that the metastatic process has been completed, and metastases are about to grow,” Dr. Bidard said.
The work was funded by Eli Lilly, maker of abemaciclib, with collaboration from Natera, maker of the Signatera assay. Dr. Loi is an adviser and researcher for Lilly, among other industry ties. Dr. Bidard is a speaker and consultant for Lilly, among other ties.
CHICAGO — Circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA) can predict relapse risk in some cases of early, high-risk breast cancer, but it’s too soon to use it to guide adjuvant therapy decisions, according to a study presented at the American Society of Clinical Oncology annual meeting.
Detectable ctDNA is “highly prognostic of worse outcomes, particularly in patients who [remain] persistently positive,” but the correlation isn’t perfect, said lead investigator Sherene Loi, MMBS, PhD, a breast cancer specialist at the Peter MacCallum Cancer Centre in Melbourne, Australia.
Although less likely, relapses also occurred in the study among women without ctDNA elevation. Conversely, there were women with elevated ctDNA who did not relapse, she said. The study was a subanalysis of the monarchE trial of adjuvant abemaciclib, a CDK 4/6 inhibitor.
Eventually, “we would like to use” ctDNA to guide adjuvant treatment decisions, but the research isn’t there yet, Dr. Loi said. It’s possible, for instance, that persistently detectable ctDNA indicates early treatment failure and the need for treatment intensification. Future research should tackle the issue.
Study discussant Francois-Clement Bidard, MD, PhD, a breast cancer specialist at Institut Curie, Paris, agreed that ctDNA isn’t ready for primetime in adjuvant early, high-risk breast cancer.
“There is no clinical evidence to suggest that there is clinical utility in this setting. There are several trials that are ongoing,” he said, but for now “you shouldn’t,” for example, “use ctDNA to de-escalate adjuvant CDK4/6 [inhibitors]. It could be in the future that we could have data on this, but at the moment, [the] clear clinical message [is] no way.”
At 5-year follow-up, the monarchE trial found a 7.6% invasive disease-free survival (IDFS) improvement when abemaciclib was added to the first 2 years of endocrine therapy in women with HR+, HER2-, node positive, high-risk early breast cancer. The combination is now a standard adjuvant option for the disease.
The ctDNA study focused on a subset of 910 subjects with adequate ctDNA testing to run the analysis. The study population was also selected to be enriched for overall IDFS events (27% versus 18% across the trial’s 5,637 subjects). An IDFS event was defined as a local, regional, contralateral or distant invasive recurrence; a new primary tumor; or death from any cause.
Testing was performed using the Signatera ctDNA assay. Baseline samples were taken after completion of adjuvant chemotherapy, then again at 3, 6, or 24 months.
Overall, ctDNA detection was infrequent. Just 8% of patients were positive at baseline and 17% were positive at any point during the trial. Even so, ctDNA detection at any point was adversely prognostic.
Patients who were ctDNA positive at baseline were more likely to experience an IDFS event, compared with those who were ctDNA negative at baseline (80% at 4 years follow-up versus 23%).
Similarly, those who remained positive or became positive during testing were more likely to experience an IDFS event compared with those who became negative or remained negative throughout testing.
For instance, all 34 patients who were positive at baseline and remained positive had an IDFS event by year 4, versus just 40% who started positive but then cleared their ctDNA.
Among women who were negative at baseline and remained negative, 13% had an IDFS event versus 89% who started negative but then turned positive. Subjects who turned positive also had the shortest time to an IDFS event, a median of 7 months.
Among women who recurred, those who were ctDNA negative tended to have local, regional, or contralateral recurrences, while ctDNA positive patients tended to have distant recurrences.
The finding “really highlights that ctDNA antedates the metastatic clinical relapse. What the ctDNA is telling you is that the metastatic process has been completed, and metastases are about to grow,” Dr. Bidard said.
The work was funded by Eli Lilly, maker of abemaciclib, with collaboration from Natera, maker of the Signatera assay. Dr. Loi is an adviser and researcher for Lilly, among other industry ties. Dr. Bidard is a speaker and consultant for Lilly, among other ties.
FROM ASCO 2024