User login
Fillers, Hyaluronidase Relieve Orofacial Changes in Patients with Scleroderma
CARLSBAD, CALIFORNIA — In 2003, researchers asked 303 patients with systemic sclerosis (scleroderma) what bothered them most about their disease from an aesthetic standpoint: Orofacial features, such as thin lips and mouth furrows, or non-facial features, such as fingertip ulceration and waxy changes to the skin.
Respondents expressed significant concern about specific orofacial features, including thin lips (73%), mouth furrows (80%), loss of facial lines (68%), and a smaller, tighter mouth (77%).
“Patients with systemic sclerosis may have loss of vermilion lip, microstomia, and perioral rhytids,” Kathleen Cook Suozzi, MD, who directs the Aesthetic Dermatology Program at Yale University School of Medicine, New Haven, Connecticut, said at the Controversies and Conversations in Laser and Cosmetic Surgery annual symposium. “How can we address these changes for our patients?”
Recent research has shown that hyaluronidase injections can help improve orofacial changes commonly experienced by patients with scleroderma. In 2019, researchers in Alabama reported the case of a 53-year-old woman treated with hyaluronidase for scleroderma-induced microstomia. After four visits over 7 months and a total hyaluronidase dose of 470 IU, the patient reported an improved Mouth Handicap in Systemic Sclerosis (MHISS) score (38 of 48); subjective improvement of symptoms, including greater ease in eating and undergoing dental treatment; and improved mouth closure.
In 2023, researchers published a cohort study of four women between the ages of 43 and 61 with autoimmune sclerosing conditions that resulted in oral microstomia. Following hyaluronidase injections, all improved in mouth opening capacity and MHISS, with change stabilizing between three and five treatments. More recently, in a study pending publication in JAAD Case Reports, Dr. Suozzi and colleagues retrospectively evaluated 12 women with scleroderma who received between 150 and 300 units of hyaluronic acid (HA) filler for microstomia between 2020 and 2023. Of the 12 women, 58% had diffuse disease, and 42% had limited disease. Overall, oral aperture width increased by 0.65 cm (P = .0027) and oral aperture height increased by 0.88 cm (P < .0001). “In general, patients needed three to four treatments to reach peak effect, and then they reached a plateau,” Dr. Suozzi said. “It wasn’t that the treatment wasn’t working anymore, but it was because their oral aperture had gotten to a size of around 5 cm, which is clinically normal. Interestingly, we found that if the patient’s disease flared and their microstomia started to return, when you rechallenged them, they continued to respond. So, patients can continue to use this treatment over time.”
In a separate case series of seven patients, Dr. Suozzi and colleagues prospectively evaluated the effect of HA soft tissue filler with Restylane Silk for lip augmentation. Study participants experienced statistically significant increases in the difference between pre- and postinjection fullness in both upper and lower lips. Also, the mean posttreatment score fell between “much improved” (2) and “improved” (3) on both the Investigator Global Aesthetic Improvement Scale and the Subject Global Aesthetic Improvement Scale.
Dr. Suozzi recommends using nerve blocks for injecting HA filler or hyaluronidase in patients with scleroderma and minimizing the injection points. “Initially, we were using 30% lidocaine preparations around the mouth for an hour before the procedure, and patients were still having pain, so now we use nerve blocks,” she said. “For hyaluronidase, we do perform a test dose of 75-100 units, usually in the commissure. It’s amazing how well it works; people will usually come back after their test dose and have improvements in their measurements. This is a really easy treatment to perform, and I think it can be done in the office of a general dermatologist. There is concern about cross-reactivity with bee venom, so you want to ask patients about that.”
Dr. Suozzi reported having no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
CARLSBAD, CALIFORNIA — In 2003, researchers asked 303 patients with systemic sclerosis (scleroderma) what bothered them most about their disease from an aesthetic standpoint: Orofacial features, such as thin lips and mouth furrows, or non-facial features, such as fingertip ulceration and waxy changes to the skin.
Respondents expressed significant concern about specific orofacial features, including thin lips (73%), mouth furrows (80%), loss of facial lines (68%), and a smaller, tighter mouth (77%).
“Patients with systemic sclerosis may have loss of vermilion lip, microstomia, and perioral rhytids,” Kathleen Cook Suozzi, MD, who directs the Aesthetic Dermatology Program at Yale University School of Medicine, New Haven, Connecticut, said at the Controversies and Conversations in Laser and Cosmetic Surgery annual symposium. “How can we address these changes for our patients?”
Recent research has shown that hyaluronidase injections can help improve orofacial changes commonly experienced by patients with scleroderma. In 2019, researchers in Alabama reported the case of a 53-year-old woman treated with hyaluronidase for scleroderma-induced microstomia. After four visits over 7 months and a total hyaluronidase dose of 470 IU, the patient reported an improved Mouth Handicap in Systemic Sclerosis (MHISS) score (38 of 48); subjective improvement of symptoms, including greater ease in eating and undergoing dental treatment; and improved mouth closure.
In 2023, researchers published a cohort study of four women between the ages of 43 and 61 with autoimmune sclerosing conditions that resulted in oral microstomia. Following hyaluronidase injections, all improved in mouth opening capacity and MHISS, with change stabilizing between three and five treatments. More recently, in a study pending publication in JAAD Case Reports, Dr. Suozzi and colleagues retrospectively evaluated 12 women with scleroderma who received between 150 and 300 units of hyaluronic acid (HA) filler for microstomia between 2020 and 2023. Of the 12 women, 58% had diffuse disease, and 42% had limited disease. Overall, oral aperture width increased by 0.65 cm (P = .0027) and oral aperture height increased by 0.88 cm (P < .0001). “In general, patients needed three to four treatments to reach peak effect, and then they reached a plateau,” Dr. Suozzi said. “It wasn’t that the treatment wasn’t working anymore, but it was because their oral aperture had gotten to a size of around 5 cm, which is clinically normal. Interestingly, we found that if the patient’s disease flared and their microstomia started to return, when you rechallenged them, they continued to respond. So, patients can continue to use this treatment over time.”
In a separate case series of seven patients, Dr. Suozzi and colleagues prospectively evaluated the effect of HA soft tissue filler with Restylane Silk for lip augmentation. Study participants experienced statistically significant increases in the difference between pre- and postinjection fullness in both upper and lower lips. Also, the mean posttreatment score fell between “much improved” (2) and “improved” (3) on both the Investigator Global Aesthetic Improvement Scale and the Subject Global Aesthetic Improvement Scale.
Dr. Suozzi recommends using nerve blocks for injecting HA filler or hyaluronidase in patients with scleroderma and minimizing the injection points. “Initially, we were using 30% lidocaine preparations around the mouth for an hour before the procedure, and patients were still having pain, so now we use nerve blocks,” she said. “For hyaluronidase, we do perform a test dose of 75-100 units, usually in the commissure. It’s amazing how well it works; people will usually come back after their test dose and have improvements in their measurements. This is a really easy treatment to perform, and I think it can be done in the office of a general dermatologist. There is concern about cross-reactivity with bee venom, so you want to ask patients about that.”
Dr. Suozzi reported having no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
CARLSBAD, CALIFORNIA — In 2003, researchers asked 303 patients with systemic sclerosis (scleroderma) what bothered them most about their disease from an aesthetic standpoint: Orofacial features, such as thin lips and mouth furrows, or non-facial features, such as fingertip ulceration and waxy changes to the skin.
Respondents expressed significant concern about specific orofacial features, including thin lips (73%), mouth furrows (80%), loss of facial lines (68%), and a smaller, tighter mouth (77%).
“Patients with systemic sclerosis may have loss of vermilion lip, microstomia, and perioral rhytids,” Kathleen Cook Suozzi, MD, who directs the Aesthetic Dermatology Program at Yale University School of Medicine, New Haven, Connecticut, said at the Controversies and Conversations in Laser and Cosmetic Surgery annual symposium. “How can we address these changes for our patients?”
Recent research has shown that hyaluronidase injections can help improve orofacial changes commonly experienced by patients with scleroderma. In 2019, researchers in Alabama reported the case of a 53-year-old woman treated with hyaluronidase for scleroderma-induced microstomia. After four visits over 7 months and a total hyaluronidase dose of 470 IU, the patient reported an improved Mouth Handicap in Systemic Sclerosis (MHISS) score (38 of 48); subjective improvement of symptoms, including greater ease in eating and undergoing dental treatment; and improved mouth closure.
In 2023, researchers published a cohort study of four women between the ages of 43 and 61 with autoimmune sclerosing conditions that resulted in oral microstomia. Following hyaluronidase injections, all improved in mouth opening capacity and MHISS, with change stabilizing between three and five treatments. More recently, in a study pending publication in JAAD Case Reports, Dr. Suozzi and colleagues retrospectively evaluated 12 women with scleroderma who received between 150 and 300 units of hyaluronic acid (HA) filler for microstomia between 2020 and 2023. Of the 12 women, 58% had diffuse disease, and 42% had limited disease. Overall, oral aperture width increased by 0.65 cm (P = .0027) and oral aperture height increased by 0.88 cm (P < .0001). “In general, patients needed three to four treatments to reach peak effect, and then they reached a plateau,” Dr. Suozzi said. “It wasn’t that the treatment wasn’t working anymore, but it was because their oral aperture had gotten to a size of around 5 cm, which is clinically normal. Interestingly, we found that if the patient’s disease flared and their microstomia started to return, when you rechallenged them, they continued to respond. So, patients can continue to use this treatment over time.”
In a separate case series of seven patients, Dr. Suozzi and colleagues prospectively evaluated the effect of HA soft tissue filler with Restylane Silk for lip augmentation. Study participants experienced statistically significant increases in the difference between pre- and postinjection fullness in both upper and lower lips. Also, the mean posttreatment score fell between “much improved” (2) and “improved” (3) on both the Investigator Global Aesthetic Improvement Scale and the Subject Global Aesthetic Improvement Scale.
Dr. Suozzi recommends using nerve blocks for injecting HA filler or hyaluronidase in patients with scleroderma and minimizing the injection points. “Initially, we were using 30% lidocaine preparations around the mouth for an hour before the procedure, and patients were still having pain, so now we use nerve blocks,” she said. “For hyaluronidase, we do perform a test dose of 75-100 units, usually in the commissure. It’s amazing how well it works; people will usually come back after their test dose and have improvements in their measurements. This is a really easy treatment to perform, and I think it can be done in the office of a general dermatologist. There is concern about cross-reactivity with bee venom, so you want to ask patients about that.”
Dr. Suozzi reported having no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
When Does Different Types of Organ Damage From Lupus Occur? Long-Term Study Sheds Light
TOPLINE:
The first year after the diagnosis of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is crucial, with the highest percentage of patients experiencing organ damage. Cardiovascular issues are the second most prevalent after musculoskeletal damage in both early and later stages of SLE.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers assessed organ damage persisting at least 6 months over different stages of lupus in 4219 patients with SLE (mean age, 35.9 years; 89.6% women) from the Spanish Society of Rheumatology Lupus Registry.
- Damage was assessed using the Systemic Lupus International Collaborating Clinics/American College of Rheumatology Damage Index (SDI).
- Longitudinal analysis was conducted globally and by each SDI domain on 1274 patients with recorded damage event dates.
- Follow-up data were available out to 10 years in 1113 patients and to 20 years in 601.
TAKEAWAY:
- New damage was recorded in 20% of the patients with SLE within the first year after diagnosis, with the annual percentage of patients with new damage decreasing to 5% after the first 5 years of follow-up.
- In the first year, musculoskeletal damage was reported by the highest proportion of patients (21%), followed by cardiovascular damage inclusive of cerebrovascular accidents and claudication for 6 months (19%).
- The cardiovascular system remained the second most affected system even during the later stages of the diseases at years 10 and 20 of follow-up (20%-25%).
- Apart from musculoskeletal and cardiovascular damage, patients with lupus also showed renal and ocular damage in the early and later stages of the disease, respectively.
IN PRACTICE:
“Our study highlights the importance of cardiovascular damage and the need for its prevention during the earliest stages of the disease,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Irene Altabás-González, MD, PhD, Rheumatology Department, Vigo University Hospital Group, Vigo, Spain. It was published online in Lupus Science & Medicine.
LIMITATIONS:
The retrospective collection of data in the study may have led to missing items; for example, the dates of damage events for the whole cohort were not available.
DISCLOSURES:
The registry was supported by the Spanish Society of Rheumatology. No specific funding was received for the study. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
The first year after the diagnosis of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is crucial, with the highest percentage of patients experiencing organ damage. Cardiovascular issues are the second most prevalent after musculoskeletal damage in both early and later stages of SLE.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers assessed organ damage persisting at least 6 months over different stages of lupus in 4219 patients with SLE (mean age, 35.9 years; 89.6% women) from the Spanish Society of Rheumatology Lupus Registry.
- Damage was assessed using the Systemic Lupus International Collaborating Clinics/American College of Rheumatology Damage Index (SDI).
- Longitudinal analysis was conducted globally and by each SDI domain on 1274 patients with recorded damage event dates.
- Follow-up data were available out to 10 years in 1113 patients and to 20 years in 601.
TAKEAWAY:
- New damage was recorded in 20% of the patients with SLE within the first year after diagnosis, with the annual percentage of patients with new damage decreasing to 5% after the first 5 years of follow-up.
- In the first year, musculoskeletal damage was reported by the highest proportion of patients (21%), followed by cardiovascular damage inclusive of cerebrovascular accidents and claudication for 6 months (19%).
- The cardiovascular system remained the second most affected system even during the later stages of the diseases at years 10 and 20 of follow-up (20%-25%).
- Apart from musculoskeletal and cardiovascular damage, patients with lupus also showed renal and ocular damage in the early and later stages of the disease, respectively.
IN PRACTICE:
“Our study highlights the importance of cardiovascular damage and the need for its prevention during the earliest stages of the disease,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Irene Altabás-González, MD, PhD, Rheumatology Department, Vigo University Hospital Group, Vigo, Spain. It was published online in Lupus Science & Medicine.
LIMITATIONS:
The retrospective collection of data in the study may have led to missing items; for example, the dates of damage events for the whole cohort were not available.
DISCLOSURES:
The registry was supported by the Spanish Society of Rheumatology. No specific funding was received for the study. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
The first year after the diagnosis of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is crucial, with the highest percentage of patients experiencing organ damage. Cardiovascular issues are the second most prevalent after musculoskeletal damage in both early and later stages of SLE.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers assessed organ damage persisting at least 6 months over different stages of lupus in 4219 patients with SLE (mean age, 35.9 years; 89.6% women) from the Spanish Society of Rheumatology Lupus Registry.
- Damage was assessed using the Systemic Lupus International Collaborating Clinics/American College of Rheumatology Damage Index (SDI).
- Longitudinal analysis was conducted globally and by each SDI domain on 1274 patients with recorded damage event dates.
- Follow-up data were available out to 10 years in 1113 patients and to 20 years in 601.
TAKEAWAY:
- New damage was recorded in 20% of the patients with SLE within the first year after diagnosis, with the annual percentage of patients with new damage decreasing to 5% after the first 5 years of follow-up.
- In the first year, musculoskeletal damage was reported by the highest proportion of patients (21%), followed by cardiovascular damage inclusive of cerebrovascular accidents and claudication for 6 months (19%).
- The cardiovascular system remained the second most affected system even during the later stages of the diseases at years 10 and 20 of follow-up (20%-25%).
- Apart from musculoskeletal and cardiovascular damage, patients with lupus also showed renal and ocular damage in the early and later stages of the disease, respectively.
IN PRACTICE:
“Our study highlights the importance of cardiovascular damage and the need for its prevention during the earliest stages of the disease,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Irene Altabás-González, MD, PhD, Rheumatology Department, Vigo University Hospital Group, Vigo, Spain. It was published online in Lupus Science & Medicine.
LIMITATIONS:
The retrospective collection of data in the study may have led to missing items; for example, the dates of damage events for the whole cohort were not available.
DISCLOSURES:
The registry was supported by the Spanish Society of Rheumatology. No specific funding was received for the study. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Saxophone Penis: A Forgotten Manifestation of Hidradenitis Suppurativa
To the Editor:
Hidradenitis suppurativa (HS) is a multifactorial chronic inflammatory skin disease affecting 1% to 4% of Europeans. It is characterized by recurrent inflamed nodules, abscesses, and sinus tracts in intertriginous regions.1 The genital area is affected in 11% of cases2 and usually is connected to severe forms of HS in both men and women.3 The prevalence of HS-associated genital lymphedema remains unknown.
Saxophone penis is a specific penile malformation characterized by a saxophone shape due to inflammation of the major penile lymphatic vessels that cause fibrosis of the surrounding connective tissue. Poor blood flow further causes contracture and distortion of the penile axis.4 Saxophone penis also has been associated with primary lymphedema, lymphogranuloma venereum, filariasis,5 and administration of paraffin injections.6 We describe 3 men with HS who presented with saxophone penis.
A 33-year-old man with Hurley stage III HS presented with a medical history of groin lesions and progressive penoscrotal edema of 13 years’ duration. He had a body mass index (BMI) of 37, no family history of HS or comorbidities, and a 15-year history of smoking 20 cigarettes per day. After repeated surgical drainage of the HS lesions as well as antibiotic treatment with clindamycin 600 mg/d and rifampicin 600 mg/d, the patient was kept on a maintenance therapy with adalimumab 40 mg/wk. Due to lack of response, treatment was discontinued at week 16. Clindamycin and rifampicin 300 mg were immediately reintroduced with no benefit on the genital lesions. The patient underwent genital reconstruction, including penile degloving, scrotoplasty, infrapubic fat pad removal, and perineoplasty (Figure 1). The patient currently is not undergoing any therapies.
A 55-year-old man presented with Hurley stage II HS of 33 years’ duration. He had a BMI of 52; a history of hypertension, hyperuricemia, severe hip and knee osteoarthritis, and orchiopexy in childhood; a smoking history of 40 cigarettes per day; and an alcohol consumption history of 200 mL per day since 18 years of age. He had radical excision of axillary lesions 8 years prior. One year later, he was treated with concomitant clindamycin and rifampicin 300 mg twice daily for 3 months with no desirable effects. Adalimumab 40 mg/wk was initiated. After 12 weeks of treatment, he experienced 80% improvement in all areas except the genital region. He continued adalimumab for 3 years with good clinical response in all HS-affected sites except the genital region.
A 66-year-old man presented with Hurley stage III HS of 37 years’ duration. He had a smoking history of 10 cigarettes per day for 30 years, a BMI of 24.6, and a medical history of long-standing hypertension and hypothyroidism. A 3-month course of clindamycin and rifampicin 600 mg/d was ineffective; adalimumab 40 mg/wk was initiated. All affected areas improved, except for the saxophone penis. He continues his fifth year of therapy with adalimumab (Figure 2).
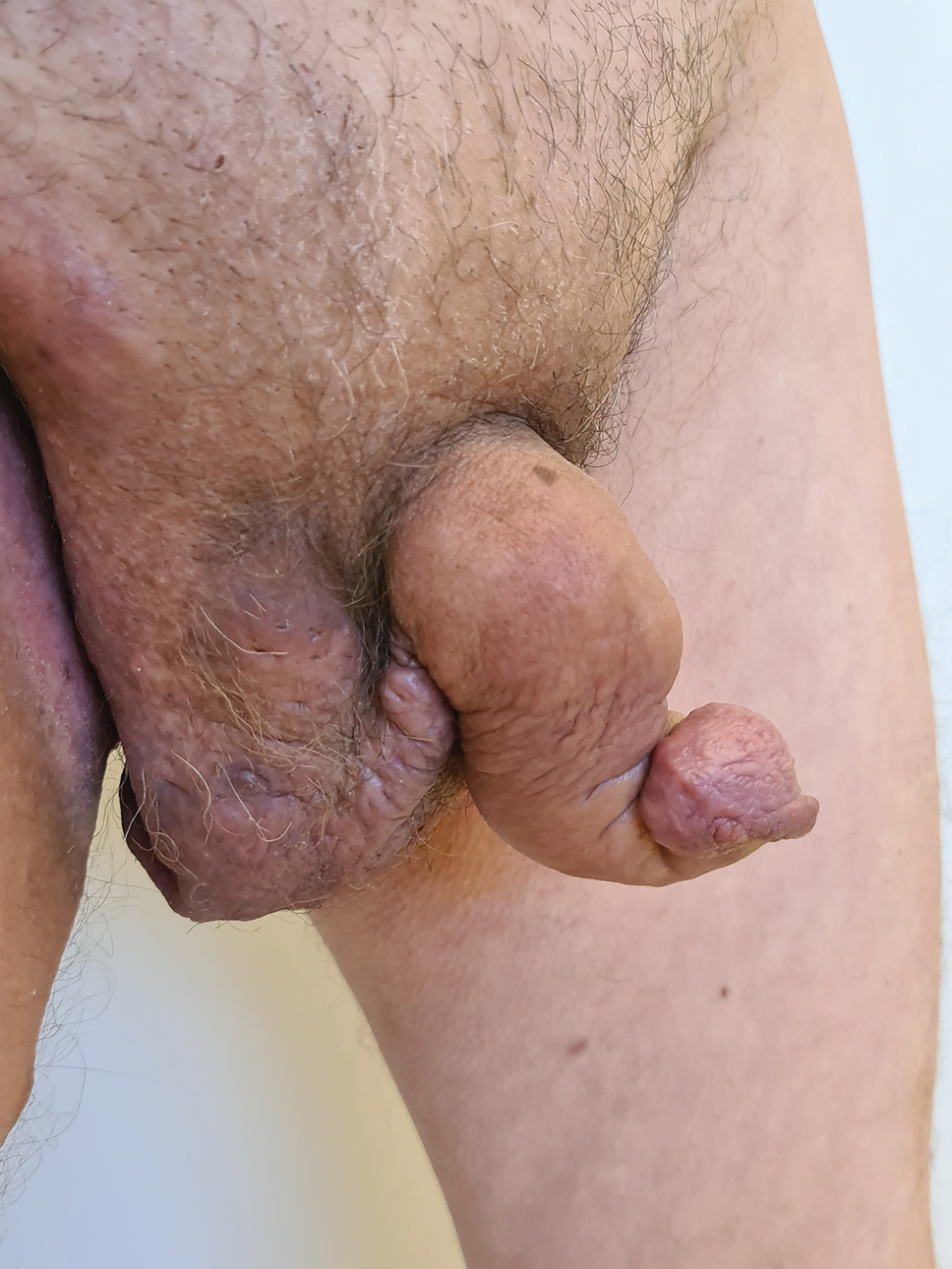

Hidradenitis suppurativa is associated with chronic pain, purulent malodor, and scarring with structural deformity. Repetitive inflammation causes fibrosis, scar formation, and soft-tissue destruction of lymphatic vessels, leading to lymphedema; primary lymphedema of the genitals in men has been reported to result in a saxophone penis.4
The only approved biologic treatments for moderate to severe HS are the tumor necrosis factor α inhibitor adalimumab and anti-IL-17 secukinumab.1 All 3 of our patients with HS were treated with adalimumab with reasonable success; however, the penile condition remained refractory, which we speculate may be due to adalimumab’s ability to control only active inflammatory lesions but not scars or fibrotic tissue.7 Higher adalimumab dosages were unlikely to be beneficial for their penile condition; some improvements have been reported following fluoroquinolone therapy. To our knowledge, there is no effective medical treatment for saxophone penis. However, surgery showed good results in one of our patients. Among our 3 adalimumab-treated patients, only 1 patient had corrective surgery that resulted in improvement in the penile deformity, further confirming adalimumab’s limited role in genital lymphedema.7 Extensive resection of the lymphedematous tissue, scrotoplasty, and Charles procedure are treatment options.8
Genital lymphedema has been associated with lymphangiectasia, lymphangioma circumscriptum, infections, and neoplasms such as lymphangiosarcoma and squamous cell carcinoma.9 Our patients reported discomfort, hygiene issues, and swelling. One patient reported micturition, and 2 patients reported sexual dysfunction.
Saxophone penis remains a disabling sequela of HS. Early diagnosis and treatment of HS may help prevent development of this condition.
- Lee EY, Alhusayen R, Lansang P, et al. What is hidradenitis suppurativa? Can Fam Physician. 2017;63:114-120.
- Fertitta L, Hotz C, Wolkenstein P, et al. Efficacy and satisfaction of surgical treatment for hidradenitis suppurativa. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2020;34:839-845.
- Micieli R, Alavi A. Lymphedema in patients with hidradenitis suppurativa: a systematic review of published literature. Int J Dermatol. 2018;57:1471-1480.
- Maatouk I, Moutran R. Saxophone penis. JAMA Dermatol. 2013;149:802.
- Koley S, Mandal RK. Saxophone penis after unilateral inguinal bubo of lymphogranuloma venereum. Indian J Sex Transm Dis AIDS. 2013;34:149-151.
- D’Antuono A, Lambertini M, Gaspari V, et al. Visual dermatology: self-induced chronic saxophone penis due to paraffin injections. J Cutan Med Surg. 2019;23:330.
- Musumeci ML, Scilletta A, Sorci F, et al. Genital lymphedema associated with hidradenitis suppurativa unresponsive to adalimumab treatment. JAAD Case Rep. 2019;5:326-328.
- Jain V, Singh S, Garge S, et al. Saxophone penis due to primary lymphoedema. J Indian Assoc Pediatr Surg. 2009;14:230-231.
- Moosbrugger EA, Mutasim DF. Hidradenitis suppurativa complicated by severe lymphedema and lymphangiectasias. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2011;64:1223-1224.
To the Editor:
Hidradenitis suppurativa (HS) is a multifactorial chronic inflammatory skin disease affecting 1% to 4% of Europeans. It is characterized by recurrent inflamed nodules, abscesses, and sinus tracts in intertriginous regions.1 The genital area is affected in 11% of cases2 and usually is connected to severe forms of HS in both men and women.3 The prevalence of HS-associated genital lymphedema remains unknown.
Saxophone penis is a specific penile malformation characterized by a saxophone shape due to inflammation of the major penile lymphatic vessels that cause fibrosis of the surrounding connective tissue. Poor blood flow further causes contracture and distortion of the penile axis.4 Saxophone penis also has been associated with primary lymphedema, lymphogranuloma venereum, filariasis,5 and administration of paraffin injections.6 We describe 3 men with HS who presented with saxophone penis.
A 33-year-old man with Hurley stage III HS presented with a medical history of groin lesions and progressive penoscrotal edema of 13 years’ duration. He had a body mass index (BMI) of 37, no family history of HS or comorbidities, and a 15-year history of smoking 20 cigarettes per day. After repeated surgical drainage of the HS lesions as well as antibiotic treatment with clindamycin 600 mg/d and rifampicin 600 mg/d, the patient was kept on a maintenance therapy with adalimumab 40 mg/wk. Due to lack of response, treatment was discontinued at week 16. Clindamycin and rifampicin 300 mg were immediately reintroduced with no benefit on the genital lesions. The patient underwent genital reconstruction, including penile degloving, scrotoplasty, infrapubic fat pad removal, and perineoplasty (Figure 1). The patient currently is not undergoing any therapies.
A 55-year-old man presented with Hurley stage II HS of 33 years’ duration. He had a BMI of 52; a history of hypertension, hyperuricemia, severe hip and knee osteoarthritis, and orchiopexy in childhood; a smoking history of 40 cigarettes per day; and an alcohol consumption history of 200 mL per day since 18 years of age. He had radical excision of axillary lesions 8 years prior. One year later, he was treated with concomitant clindamycin and rifampicin 300 mg twice daily for 3 months with no desirable effects. Adalimumab 40 mg/wk was initiated. After 12 weeks of treatment, he experienced 80% improvement in all areas except the genital region. He continued adalimumab for 3 years with good clinical response in all HS-affected sites except the genital region.
A 66-year-old man presented with Hurley stage III HS of 37 years’ duration. He had a smoking history of 10 cigarettes per day for 30 years, a BMI of 24.6, and a medical history of long-standing hypertension and hypothyroidism. A 3-month course of clindamycin and rifampicin 600 mg/d was ineffective; adalimumab 40 mg/wk was initiated. All affected areas improved, except for the saxophone penis. He continues his fifth year of therapy with adalimumab (Figure 2).

Hidradenitis suppurativa is associated with chronic pain, purulent malodor, and scarring with structural deformity. Repetitive inflammation causes fibrosis, scar formation, and soft-tissue destruction of lymphatic vessels, leading to lymphedema; primary lymphedema of the genitals in men has been reported to result in a saxophone penis.4
The only approved biologic treatments for moderate to severe HS are the tumor necrosis factor α inhibitor adalimumab and anti-IL-17 secukinumab.1 All 3 of our patients with HS were treated with adalimumab with reasonable success; however, the penile condition remained refractory, which we speculate may be due to adalimumab’s ability to control only active inflammatory lesions but not scars or fibrotic tissue.7 Higher adalimumab dosages were unlikely to be beneficial for their penile condition; some improvements have been reported following fluoroquinolone therapy. To our knowledge, there is no effective medical treatment for saxophone penis. However, surgery showed good results in one of our patients. Among our 3 adalimumab-treated patients, only 1 patient had corrective surgery that resulted in improvement in the penile deformity, further confirming adalimumab’s limited role in genital lymphedema.7 Extensive resection of the lymphedematous tissue, scrotoplasty, and Charles procedure are treatment options.8
Genital lymphedema has been associated with lymphangiectasia, lymphangioma circumscriptum, infections, and neoplasms such as lymphangiosarcoma and squamous cell carcinoma.9 Our patients reported discomfort, hygiene issues, and swelling. One patient reported micturition, and 2 patients reported sexual dysfunction.
Saxophone penis remains a disabling sequela of HS. Early diagnosis and treatment of HS may help prevent development of this condition.
To the Editor:
Hidradenitis suppurativa (HS) is a multifactorial chronic inflammatory skin disease affecting 1% to 4% of Europeans. It is characterized by recurrent inflamed nodules, abscesses, and sinus tracts in intertriginous regions.1 The genital area is affected in 11% of cases2 and usually is connected to severe forms of HS in both men and women.3 The prevalence of HS-associated genital lymphedema remains unknown.
Saxophone penis is a specific penile malformation characterized by a saxophone shape due to inflammation of the major penile lymphatic vessels that cause fibrosis of the surrounding connective tissue. Poor blood flow further causes contracture and distortion of the penile axis.4 Saxophone penis also has been associated with primary lymphedema, lymphogranuloma venereum, filariasis,5 and administration of paraffin injections.6 We describe 3 men with HS who presented with saxophone penis.
A 33-year-old man with Hurley stage III HS presented with a medical history of groin lesions and progressive penoscrotal edema of 13 years’ duration. He had a body mass index (BMI) of 37, no family history of HS or comorbidities, and a 15-year history of smoking 20 cigarettes per day. After repeated surgical drainage of the HS lesions as well as antibiotic treatment with clindamycin 600 mg/d and rifampicin 600 mg/d, the patient was kept on a maintenance therapy with adalimumab 40 mg/wk. Due to lack of response, treatment was discontinued at week 16. Clindamycin and rifampicin 300 mg were immediately reintroduced with no benefit on the genital lesions. The patient underwent genital reconstruction, including penile degloving, scrotoplasty, infrapubic fat pad removal, and perineoplasty (Figure 1). The patient currently is not undergoing any therapies.
A 55-year-old man presented with Hurley stage II HS of 33 years’ duration. He had a BMI of 52; a history of hypertension, hyperuricemia, severe hip and knee osteoarthritis, and orchiopexy in childhood; a smoking history of 40 cigarettes per day; and an alcohol consumption history of 200 mL per day since 18 years of age. He had radical excision of axillary lesions 8 years prior. One year later, he was treated with concomitant clindamycin and rifampicin 300 mg twice daily for 3 months with no desirable effects. Adalimumab 40 mg/wk was initiated. After 12 weeks of treatment, he experienced 80% improvement in all areas except the genital region. He continued adalimumab for 3 years with good clinical response in all HS-affected sites except the genital region.
A 66-year-old man presented with Hurley stage III HS of 37 years’ duration. He had a smoking history of 10 cigarettes per day for 30 years, a BMI of 24.6, and a medical history of long-standing hypertension and hypothyroidism. A 3-month course of clindamycin and rifampicin 600 mg/d was ineffective; adalimumab 40 mg/wk was initiated. All affected areas improved, except for the saxophone penis. He continues his fifth year of therapy with adalimumab (Figure 2).

Hidradenitis suppurativa is associated with chronic pain, purulent malodor, and scarring with structural deformity. Repetitive inflammation causes fibrosis, scar formation, and soft-tissue destruction of lymphatic vessels, leading to lymphedema; primary lymphedema of the genitals in men has been reported to result in a saxophone penis.4
The only approved biologic treatments for moderate to severe HS are the tumor necrosis factor α inhibitor adalimumab and anti-IL-17 secukinumab.1 All 3 of our patients with HS were treated with adalimumab with reasonable success; however, the penile condition remained refractory, which we speculate may be due to adalimumab’s ability to control only active inflammatory lesions but not scars or fibrotic tissue.7 Higher adalimumab dosages were unlikely to be beneficial for their penile condition; some improvements have been reported following fluoroquinolone therapy. To our knowledge, there is no effective medical treatment for saxophone penis. However, surgery showed good results in one of our patients. Among our 3 adalimumab-treated patients, only 1 patient had corrective surgery that resulted in improvement in the penile deformity, further confirming adalimumab’s limited role in genital lymphedema.7 Extensive resection of the lymphedematous tissue, scrotoplasty, and Charles procedure are treatment options.8
Genital lymphedema has been associated with lymphangiectasia, lymphangioma circumscriptum, infections, and neoplasms such as lymphangiosarcoma and squamous cell carcinoma.9 Our patients reported discomfort, hygiene issues, and swelling. One patient reported micturition, and 2 patients reported sexual dysfunction.
Saxophone penis remains a disabling sequela of HS. Early diagnosis and treatment of HS may help prevent development of this condition.
- Lee EY, Alhusayen R, Lansang P, et al. What is hidradenitis suppurativa? Can Fam Physician. 2017;63:114-120.
- Fertitta L, Hotz C, Wolkenstein P, et al. Efficacy and satisfaction of surgical treatment for hidradenitis suppurativa. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2020;34:839-845.
- Micieli R, Alavi A. Lymphedema in patients with hidradenitis suppurativa: a systematic review of published literature. Int J Dermatol. 2018;57:1471-1480.
- Maatouk I, Moutran R. Saxophone penis. JAMA Dermatol. 2013;149:802.
- Koley S, Mandal RK. Saxophone penis after unilateral inguinal bubo of lymphogranuloma venereum. Indian J Sex Transm Dis AIDS. 2013;34:149-151.
- D’Antuono A, Lambertini M, Gaspari V, et al. Visual dermatology: self-induced chronic saxophone penis due to paraffin injections. J Cutan Med Surg. 2019;23:330.
- Musumeci ML, Scilletta A, Sorci F, et al. Genital lymphedema associated with hidradenitis suppurativa unresponsive to adalimumab treatment. JAAD Case Rep. 2019;5:326-328.
- Jain V, Singh S, Garge S, et al. Saxophone penis due to primary lymphoedema. J Indian Assoc Pediatr Surg. 2009;14:230-231.
- Moosbrugger EA, Mutasim DF. Hidradenitis suppurativa complicated by severe lymphedema and lymphangiectasias. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2011;64:1223-1224.
- Lee EY, Alhusayen R, Lansang P, et al. What is hidradenitis suppurativa? Can Fam Physician. 2017;63:114-120.
- Fertitta L, Hotz C, Wolkenstein P, et al. Efficacy and satisfaction of surgical treatment for hidradenitis suppurativa. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2020;34:839-845.
- Micieli R, Alavi A. Lymphedema in patients with hidradenitis suppurativa: a systematic review of published literature. Int J Dermatol. 2018;57:1471-1480.
- Maatouk I, Moutran R. Saxophone penis. JAMA Dermatol. 2013;149:802.
- Koley S, Mandal RK. Saxophone penis after unilateral inguinal bubo of lymphogranuloma venereum. Indian J Sex Transm Dis AIDS. 2013;34:149-151.
- D’Antuono A, Lambertini M, Gaspari V, et al. Visual dermatology: self-induced chronic saxophone penis due to paraffin injections. J Cutan Med Surg. 2019;23:330.
- Musumeci ML, Scilletta A, Sorci F, et al. Genital lymphedema associated with hidradenitis suppurativa unresponsive to adalimumab treatment. JAAD Case Rep. 2019;5:326-328.
- Jain V, Singh S, Garge S, et al. Saxophone penis due to primary lymphoedema. J Indian Assoc Pediatr Surg. 2009;14:230-231.
- Moosbrugger EA, Mutasim DF. Hidradenitis suppurativa complicated by severe lymphedema and lymphangiectasias. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2011;64:1223-1224.
Practice Points
- Hidradenitis suppurativa (HS) is a multifactorial chronic inflammatory skin disease.
- Saxophone penis is a specific penile malformation characterized by a saxophone shape due to inflammation.
- Repetitive inflammation within the context of HS may cause structural deformity of the penis, resulting in a saxophone penis.
- Early diagnosis and treatment of HS may help prevent development of this condition.
Future of Lupus Treatments Looks Brighter With Multiple Promising Therapeutic Approaches
VIENNA — It may have been a while since there have been any major breakthroughs in the treatment of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), but there are high hopes that this is a situation that may be about to change, experts agreed at the annual European Congress of Rheumatology.
“It’s an incredibly vivid area of development,” Laurent Arnaud, MD, PhD, professor of rheumatology at the University of Strasbourg in Strasbourg, France, said during one of the first sessions of the meeting. He reported that there were at least 17 phase 2 and 14 phase 3 trials that were expected to start within the next few years, all with investigational agents that target different immune cells or pathways that have been implicated in the pathogenesis of SLE.
In a systematic review published last year, Dr. Arnaud and coauthors found that there were 92 investigational biologic or novel targeted agents in various phases of clinical testing. This included B-cell–targeting agents such as ianalumab, plasma cell-targeting agents such as daratumumab, and drugs with novel mechanisms of action such as KPG-818, which targets the CRL4-Cereblon (CRBN) E3 ubiquitin ligase complex. Phase 2 data on all three of these investigational agents were presented during various sessions at EULAR 2024, all with positive results, suggesting that their further development in SLE is worth pursuing.
There are of course “many more candidates in the pipeline,” Dr. Arnaud said. “I’m very happy that I think we are going to see great days for lupus right in front of our eyes.”
Targeting B Cells
Drugs that target B cells have been at the forefront of lupus treatment for several years, as David Isenberg, MD, professor of rheumatology at University College London, pointed out during an interview for EULAR TV.
“It’s clearly important to target the cells which are likely to be causing the problem in lupus, and in the main, that tends to be B cells,” he said.
Dr. Isenberg, who is renowned for his work with the B-cell–targeting agent rituximab, added: “But we know that obviously T cells integrate with B cells, so anything which interrupts the link between the T cell and the B cell is likely to be important.”
Chimeric Antigen Receptor (CAR) T-Cell Therapy ‘Revolution’
One new way of targeting B cells is with CAR T-cell therapy, which David D’Cruz , MD, PhD, a consultant rheumatologist for Guy’s and St. Thomas’ Hospital NHS Foundation Trust in London, picked as one of the “most striking” topics highlighted at EULAR 2024.
This is “truly personalized medicine,” Dr. D’Cruz said. This is an autologous therapy because a patient’s T cells are removed by leukapheresis, transfected with a CAR T vector directed against a component of the B cell, and then returned to them.
“I do feel that we’re on the cusp of a major revolution,” Dr. D’Cruz told this news organization. Not only in lupus but also in other rheumatic conditions that have proved really difficult to treat, such as systemic sclerosis and myositis, he said.
“Basically, it’s a very powerful B-cell–depleting tool, but it’s much more profound B-cell–depleting tool than, for example, rituximab or belimumab,” explained Dr. D’Cruz. “What you’re doing is reprogramming T cells to attack the B cells.”
Although rituximab and belimumab clear all the B cells in the circulation, there are still some cells left behind in the bone marrow, “and it’s very difficult to get rid of those,” Dr. D’Cruz said. “What CAR T-cell therapy appears to do is wipe out all the CD19-positive B cells everywhere, in the blood and the tissue. So you get a really profound B-cell depletion.”
Eric Morand, MBBS, PhD, head of rheumatology at Monash Health in Melbourne, Australia, told this news organization that there was obviously “a lot of buzz” about CAR T-cell therapy.
“We’re waiting to see if the exciting data from Erlangen can be reproduced in other centers with other CAR T products to show that it is a universal effect. We haven’t seen that yet, but I think we will by next year.”
Cost and expertise are two major considerations and potential limiting factors, however, as Dr. D’Cruz and Dr. Isenberg both pointed out in separate interviews with this news organization.
Dr. D’Cruz said: “It’s very expensive, it takes a while, and it doesn’t always work is what I’m hearing. It’s usually successful, but again, a little bit depends on the technique and the people doing the process.”
Dr. Isenberg said: “CAR T-cell therapy is, I think, very exciting because it does look to be quite promising. But as it costs 350,000 euros per patient, I don’t think that it is going to be widely adopted.”
Even if it could be afforded by certain centers in the West, he added, this just would not be feasible in poorer nations. “So, we’ve got to find other effective, cheaper ways to go,” Dr. Isenberg said.
“I think there are some very interesting ideas with monoclonal antibodies which target at least two different targets — one on the B cell, one on the T cell — and that could well be the way to take this forward,” he suggested.
Ianalumab ‘Double Blocking’ B Cells
Another way could be to develop more potent B-cell–depleting drugs, as Nancy Agmon-Levin , MD, head of the Clinical Immunology, Angioedema and Allergy Unit, Lupus and Autoimmune Diseases Clinic, at Sheba Medical Center, Tel Aviv University in Tel Aviv, Israel, reported during one of the clinical abstract sessions at EULAR 2024.
Dr. Agmon-Levin presented data on 67 individuals with SLE who had participated in a multicenter phase 2 study of ianalumab, a fully human immunoglobulin (Ig) G1 monoclonal antibody that results in a “double blocking of the B-cell lineage.”
Ianalumab targets the B-cell–activating factor receptor (BAFFR), but what makes it distinct from other BAFF-targeting drugs is that it has had a fructose molecule removed from its Fc portion, which renders it more likely to trigger antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity.
“This is a B-cell depletion therapy,” Agmon-Levin said, but it also blocks BAFFR-mediated survival of B cells, so the subsequent recuperation process of BAFFR-expressing B cells is affected, leading to continued B-cell depletion.
The phase 2 study she presented consisted of an initial 28-week, double-blind period, during which time participants had been randomly allocated to receive either subcutaneous injections of ianalumab 300 mg or a matching placebo every 4 weeks. This was followed by a 24-week, open-label period where all participants were treated with ianalumab, and then an off-treatment, minimal follow-up period that lasted up to 68 weeks, with continued data collection for safety.
The primary outcome measure was a composite of meeting criteria for the SLE Responder Index 4 and a sustained reduction in corticosteroid use at 28 weeks. This was achieved in 15 of the 34 (44.1%) people treated with ianalumab vs only 3 (9.1%) of the 33 people who had been given a placebo.
Dr. Agmon-Levin reported that the effect on this outcome was sustained to the end of the open-label period, at 1 year, in 15 (45.5%) of 33 participants who had continued treatment with ianalumab and achieved in 13 (40.6%) of 32 participants who had switched from placebo to ianalumab treatment.
Moreover, longer durations of treatment were associated with a host of improved outcomes, Dr. Agmon-Levin said: “Treatment was improved along the 52 weeks, and we can see from the LLDAS [Lupus Low Disease Activity State], DORIS [Definition Of Remission In SLE], and SRI-6 and -8 that as you continue the therapy, you improve the outcomes.”
The potential benefits of ianalumab in the treatment of SLE and lupus nephritis will now be further examined in the phase 3 SIRIUS-SLE1 , SIRIUS-SLE2, and SIRIUS-LN trials, which are estimated to provide initial results in 2027 and complete in early 2029 or 2030.
Targeting Plasma Cells With Daratumumab
Another drug showing signs that it might be useful as a treatment for SLE is daratumumab, as Tobias Alexander, MD, of Charité — Universitätsmedizin Berlin, reported during one of the late-breaking abstract sessions at EULAR 2024.
“Daratumumab is a human, first-in-class anti-CD38 antibody that efficiently depletes plasma cells,” Dr. Alexander said. CD38 is both a receptor and an enzyme, and while it is found on the surface of most immune cells, it’s particularly expressed by plasma cells, he added.
Daratumumab is not a total newcomer, however, as it’s already approved for the treatment of multiple myeloma under the trade name Darzalex. The rationale for using it in SLE comes from two case reports, Dr. Alexander explained. The first, published in 2020 in The New England Journal of Medicine, involved two patients with severe and life-threatening lupus who were given off-label treatment for a period of 4 weeks and experienced good clinical and serologic responses. The second, published last year in Nature Medicine, involved six patients with refractory lupus nephritis, five of whom had a clinical response at 6 months.
“On this background, we conducted an investigator-initiated trial, which was an open-label, single-center, proof-of-concept study,” Dr. Alexander said. A total of 10 female patients whose ages ranged from 24 to 43 years were included in the phase 2 trial that was dubbed DARALUP. For inclusion, all had to have a Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Disease Activity Index 2000 (SLEDAI-2K) of four or more for clinical manifestations, have been treated with at least two prior disease-modifying drugs to no avail, and be anti–double-stranded DNA (anti-dsDNA) antibody positive. Dr. Alexander reported that the median baseline SLEDAI-2K score was 12 and ranged from 8 to 20, with the number of prior therapies ranging from two to nine.
Daratumumab was given at a dose of 1800 mg via subcutaneous injection every week for 8 weeks. This is the same dose that is used to treat multiple myeloma, Dr. Alexander explained, although the dosing is not stopped. The reason for stopping after 8 weeks in the current trial was to be able to see what happened once the treatment was stopped. The follow-up was for 36 weeks.
Dr. Alexander reported that there was a “very dramatic and significant” effect on the primary endpoint of a reduction in anti-dsDNA antibody levels, decreasing from a median of 166.3 U/mL at baseline to 61.1 U/mL at week 12 (P = .002). Alongside, there was a reduction in the SLEDAI-2K score from 12 to 4 within 12 weeks, which was sustained at the 36-week follow-up assessment. Improvements in skin, joint, kidney, and level of proteinuria were also seen.
Although all patients experienced adverse events, none were serious. Infections and infestations (mostly nasopharyngitis, COVID-19, and gastroenteritis) were the most common, experienced by 80% of the participants; 70% had injection site reactions or fatigue, 60% had gastrointestinal symptoms, 50% had a fall of IgG < 5 g/L, 40% had headache, and 20% had back pain.
“This is a positive trial. I think we could demonstrate that [daratumumab] produced very strong, rapid, and durable clinical improvements,” Dr. Alexander said. “We think that targeting CD38 is relevant; plasma cells had been depleted based on the reduction of anti-dsDNA antibodies,” he added.
From the audience, however, Peter Nash, MBBS, of Griffith University in Brisbane, Australia, questioned whether the results could be attributed to “a steroid effect” because patients had been treated with oral dexamethasone throughout the study.
Dr. Alexander noted that steroid use had been part of the treatment schedule but acknowledged it was a possible confounder.
“I think we can be confident that [daratumumab] had a major effect on plasma cells decreasing…because we see that also the vaccine titers decreased,” Dr. Alexander said. “Time will tell, but even more important is the durability of the responses over time, which you don’t achieve under steroids.”
KPG-818’s Novel Mechanism of Action
Elsewhere at EULAR 2024, positive results of another phase 2 study involving a drug with an entirely different mechanism of action, KPG-818, were reported in a poster presentation. KPG-818 modulates CRBN, which results in the degradation of two transcription factors (Aiolos and Ikaros) that are involved in the development, maturation, and proliferation of innate and adaptive immune cells and have been linked to genetic risk in SLE, according to the poster’s authors. It is currently in development for the treatment of SLE, Behçet disease, inflammatory bowel disease, multiple myeloma, and non-Hodgkin lymphoma.
Yao Wang, MD, chief medical officer of KPG-818’s developer Kangpu Biopharmaceuticals, Hefei, China, and associates found that oral doses of 0.15 or 0.6 mg KPG-818 were “generally well-tolerated” and produced immunomodulatory changes that could be beneficial in people with SLE over a 12-week treatment period.
“Only two new agents have been approved for the treatment of SLE in the past five decades in USA and Europe,” Dr. Wang and team wrote, which highlights “a significant unmet need for more effective and safe treatment options.”
They believe that KPG-818 might well fit the bill based on the results of their study, in which 35 of 37 recruited patients completed the treatment. Compared with placebo, they observed reduced numbers of total B cells, Aiolos+ T and B cells, and increased Treg cells.
SLEDAI-2K and Cutaneous Lupus Erythematosus Disease Area and Severity Index activity scores in the 0.15-mg group were improved relative to baseline and placebo.
“The proof-of-concept findings suggest a favorable benefit/risk ratio in SLE for KPG-818,” Dr. Wang and coauthors said, supporting its further development in SLE.
Need for Treatments
Dr. Isenberg told this news organization that both daratumumab and KPG-818 would be welcome additions as treatment options if further trials proved their worth.
“The great frustration about lupus is that, compared to patients with rheumatoid arthritis, the choice has been so limited,” Dr. Isenberg said. Aside from rituximab (Rituxan) and belimumab (Benlysta), which are used with certain restrictions, there are no other biologic targeted treatments available in the United Kingdom. Anifrolumab (Saphnelo) has a license in the United States and some European countries but is not yet available for him to use in his practice.
Daratumumab and KPG-818 are “different types of molecules, and if they work that will be great. It would be nice to have the choice,” Dr. Isenberg said. “Whether they will be as effective as I think rituximab is, I don’t know, but these are some very encouraging results.”
Of course, these are all phase 2 trials, and the “big problem” is that such positive results do not always translate when it comes to phase 3, as Dr. D’Cruz told this news organization.
“Until a few years ago, there had been about 25 or 30 industry-led trails, and they’d all failed, except for belimumab and anifrolumab,” Dr. D’Cruz said. These drugs were found to work and be generally safe in phase 1 and 2 trials, but “when they come to phase 3, they all seem to fail, and we don’t know why.”
These are large global studies, D’Cruz added, observing that problems with patient selection, steroid use, and choice of outcome measures were possible factors for why the EXPLORER and LUNAR studies had shown no benefit for rituximab despite the drug being widely used to treat SLE.
Dr. Isenberg, who has coauthored an article on the topic of why drugs seem to fail at the final hurdle, noted: “I think it has a lot to do with the nature of the disease. It’s a complicated disease.” From having “savvy physicians doing the trials for you” to the placebo response, there are “a whole bunch or reasons why these things haven’t worked in lupus.”
Dr. Morand commented: “We’ve got many programs in phase 2 and 3, and because there’s so many, they’re all facing recruitment challenges, and as a consequence of so much activity, every program is going a little slower than hoped for.”
As for other drugs on the horizon, Dr. Morand noted: “We’re very optimistic about things like litifilimab and deucravacitinib; that’s two examples that are in phase 3. Earlier in the program of development, [there are] a huge range of targets being addressed. The future looks bright. But we might have to wait a while.”
Dr. Arnaud has consulted for AstraZeneca, AbbVie, Alpine Immune Sciences, Biogen, Bristol Myers Squibb, Boehringer Ingelheim, Chugai Pharmaceutical, GlaxoSmithKline, Grifols, Janssen, Kezar Life Sciences, LFB, Lilly, Medac, Merck, Novartis, Pfizer, Roche, and UCB. Dr. Isenberg has served as an adviser to Merck Serono, AstraZeneca, Eli Lilly, Servier, and ImmuPharma. Any honoraria received is passed on to a local arthritis charity connected to his hospital. Dr. D’Cruz has served as a consultant and advisory board member for GlaxoSmithKline and CSL Vifor. Dr. Morand has received research support, consultancy fees, or both from multiple pharmaceutical companies paid to his institution including AbbVie, Amgen, AstraZeneca, Biogen, Bristol Myers Squibb, Eli Lilly, EMD Serono, Dragonfly, Genentech, GlaxoSmithKline, Janssen, Novartis, RemeGen, Takeda, UCB, and Zenas. The ianalumab trial presented by Dr. Agmon-Levin was sponsored by Novartis Pharma; however, she reported having no conflicts of interest. The DARALUP study was an investigator-initiated trial supported by Janssen. Dr. Alexander has received consulting fees, study support, honoraria, and travel grants from various pharmaceutical companies including AbbVie, Amgen, AstraZeneca, Bayer, GlaxoSmithKline, Janssen, and Lilly. Dr. Nash has consulted for The Rheumatology Education Group Consultants. The KPG-818 study reported by Dr. Wang was sponsored by Kangpu Biopharmaceuticals.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
VIENNA — It may have been a while since there have been any major breakthroughs in the treatment of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), but there are high hopes that this is a situation that may be about to change, experts agreed at the annual European Congress of Rheumatology.
“It’s an incredibly vivid area of development,” Laurent Arnaud, MD, PhD, professor of rheumatology at the University of Strasbourg in Strasbourg, France, said during one of the first sessions of the meeting. He reported that there were at least 17 phase 2 and 14 phase 3 trials that were expected to start within the next few years, all with investigational agents that target different immune cells or pathways that have been implicated in the pathogenesis of SLE.
In a systematic review published last year, Dr. Arnaud and coauthors found that there were 92 investigational biologic or novel targeted agents in various phases of clinical testing. This included B-cell–targeting agents such as ianalumab, plasma cell-targeting agents such as daratumumab, and drugs with novel mechanisms of action such as KPG-818, which targets the CRL4-Cereblon (CRBN) E3 ubiquitin ligase complex. Phase 2 data on all three of these investigational agents were presented during various sessions at EULAR 2024, all with positive results, suggesting that their further development in SLE is worth pursuing.
There are of course “many more candidates in the pipeline,” Dr. Arnaud said. “I’m very happy that I think we are going to see great days for lupus right in front of our eyes.”
Targeting B Cells
Drugs that target B cells have been at the forefront of lupus treatment for several years, as David Isenberg, MD, professor of rheumatology at University College London, pointed out during an interview for EULAR TV.
“It’s clearly important to target the cells which are likely to be causing the problem in lupus, and in the main, that tends to be B cells,” he said.
Dr. Isenberg, who is renowned for his work with the B-cell–targeting agent rituximab, added: “But we know that obviously T cells integrate with B cells, so anything which interrupts the link between the T cell and the B cell is likely to be important.”
Chimeric Antigen Receptor (CAR) T-Cell Therapy ‘Revolution’
One new way of targeting B cells is with CAR T-cell therapy, which David D’Cruz , MD, PhD, a consultant rheumatologist for Guy’s and St. Thomas’ Hospital NHS Foundation Trust in London, picked as one of the “most striking” topics highlighted at EULAR 2024.
This is “truly personalized medicine,” Dr. D’Cruz said. This is an autologous therapy because a patient’s T cells are removed by leukapheresis, transfected with a CAR T vector directed against a component of the B cell, and then returned to them.
“I do feel that we’re on the cusp of a major revolution,” Dr. D’Cruz told this news organization. Not only in lupus but also in other rheumatic conditions that have proved really difficult to treat, such as systemic sclerosis and myositis, he said.
“Basically, it’s a very powerful B-cell–depleting tool, but it’s much more profound B-cell–depleting tool than, for example, rituximab or belimumab,” explained Dr. D’Cruz. “What you’re doing is reprogramming T cells to attack the B cells.”
Although rituximab and belimumab clear all the B cells in the circulation, there are still some cells left behind in the bone marrow, “and it’s very difficult to get rid of those,” Dr. D’Cruz said. “What CAR T-cell therapy appears to do is wipe out all the CD19-positive B cells everywhere, in the blood and the tissue. So you get a really profound B-cell depletion.”
Eric Morand, MBBS, PhD, head of rheumatology at Monash Health in Melbourne, Australia, told this news organization that there was obviously “a lot of buzz” about CAR T-cell therapy.
“We’re waiting to see if the exciting data from Erlangen can be reproduced in other centers with other CAR T products to show that it is a universal effect. We haven’t seen that yet, but I think we will by next year.”
Cost and expertise are two major considerations and potential limiting factors, however, as Dr. D’Cruz and Dr. Isenberg both pointed out in separate interviews with this news organization.
Dr. D’Cruz said: “It’s very expensive, it takes a while, and it doesn’t always work is what I’m hearing. It’s usually successful, but again, a little bit depends on the technique and the people doing the process.”
Dr. Isenberg said: “CAR T-cell therapy is, I think, very exciting because it does look to be quite promising. But as it costs 350,000 euros per patient, I don’t think that it is going to be widely adopted.”
Even if it could be afforded by certain centers in the West, he added, this just would not be feasible in poorer nations. “So, we’ve got to find other effective, cheaper ways to go,” Dr. Isenberg said.
“I think there are some very interesting ideas with monoclonal antibodies which target at least two different targets — one on the B cell, one on the T cell — and that could well be the way to take this forward,” he suggested.
Ianalumab ‘Double Blocking’ B Cells
Another way could be to develop more potent B-cell–depleting drugs, as Nancy Agmon-Levin , MD, head of the Clinical Immunology, Angioedema and Allergy Unit, Lupus and Autoimmune Diseases Clinic, at Sheba Medical Center, Tel Aviv University in Tel Aviv, Israel, reported during one of the clinical abstract sessions at EULAR 2024.
Dr. Agmon-Levin presented data on 67 individuals with SLE who had participated in a multicenter phase 2 study of ianalumab, a fully human immunoglobulin (Ig) G1 monoclonal antibody that results in a “double blocking of the B-cell lineage.”
Ianalumab targets the B-cell–activating factor receptor (BAFFR), but what makes it distinct from other BAFF-targeting drugs is that it has had a fructose molecule removed from its Fc portion, which renders it more likely to trigger antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity.
“This is a B-cell depletion therapy,” Agmon-Levin said, but it also blocks BAFFR-mediated survival of B cells, so the subsequent recuperation process of BAFFR-expressing B cells is affected, leading to continued B-cell depletion.
The phase 2 study she presented consisted of an initial 28-week, double-blind period, during which time participants had been randomly allocated to receive either subcutaneous injections of ianalumab 300 mg or a matching placebo every 4 weeks. This was followed by a 24-week, open-label period where all participants were treated with ianalumab, and then an off-treatment, minimal follow-up period that lasted up to 68 weeks, with continued data collection for safety.
The primary outcome measure was a composite of meeting criteria for the SLE Responder Index 4 and a sustained reduction in corticosteroid use at 28 weeks. This was achieved in 15 of the 34 (44.1%) people treated with ianalumab vs only 3 (9.1%) of the 33 people who had been given a placebo.
Dr. Agmon-Levin reported that the effect on this outcome was sustained to the end of the open-label period, at 1 year, in 15 (45.5%) of 33 participants who had continued treatment with ianalumab and achieved in 13 (40.6%) of 32 participants who had switched from placebo to ianalumab treatment.
Moreover, longer durations of treatment were associated with a host of improved outcomes, Dr. Agmon-Levin said: “Treatment was improved along the 52 weeks, and we can see from the LLDAS [Lupus Low Disease Activity State], DORIS [Definition Of Remission In SLE], and SRI-6 and -8 that as you continue the therapy, you improve the outcomes.”
The potential benefits of ianalumab in the treatment of SLE and lupus nephritis will now be further examined in the phase 3 SIRIUS-SLE1 , SIRIUS-SLE2, and SIRIUS-LN trials, which are estimated to provide initial results in 2027 and complete in early 2029 or 2030.
Targeting Plasma Cells With Daratumumab
Another drug showing signs that it might be useful as a treatment for SLE is daratumumab, as Tobias Alexander, MD, of Charité — Universitätsmedizin Berlin, reported during one of the late-breaking abstract sessions at EULAR 2024.
“Daratumumab is a human, first-in-class anti-CD38 antibody that efficiently depletes plasma cells,” Dr. Alexander said. CD38 is both a receptor and an enzyme, and while it is found on the surface of most immune cells, it’s particularly expressed by plasma cells, he added.
Daratumumab is not a total newcomer, however, as it’s already approved for the treatment of multiple myeloma under the trade name Darzalex. The rationale for using it in SLE comes from two case reports, Dr. Alexander explained. The first, published in 2020 in The New England Journal of Medicine, involved two patients with severe and life-threatening lupus who were given off-label treatment for a period of 4 weeks and experienced good clinical and serologic responses. The second, published last year in Nature Medicine, involved six patients with refractory lupus nephritis, five of whom had a clinical response at 6 months.
“On this background, we conducted an investigator-initiated trial, which was an open-label, single-center, proof-of-concept study,” Dr. Alexander said. A total of 10 female patients whose ages ranged from 24 to 43 years were included in the phase 2 trial that was dubbed DARALUP. For inclusion, all had to have a Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Disease Activity Index 2000 (SLEDAI-2K) of four or more for clinical manifestations, have been treated with at least two prior disease-modifying drugs to no avail, and be anti–double-stranded DNA (anti-dsDNA) antibody positive. Dr. Alexander reported that the median baseline SLEDAI-2K score was 12 and ranged from 8 to 20, with the number of prior therapies ranging from two to nine.
Daratumumab was given at a dose of 1800 mg via subcutaneous injection every week for 8 weeks. This is the same dose that is used to treat multiple myeloma, Dr. Alexander explained, although the dosing is not stopped. The reason for stopping after 8 weeks in the current trial was to be able to see what happened once the treatment was stopped. The follow-up was for 36 weeks.
Dr. Alexander reported that there was a “very dramatic and significant” effect on the primary endpoint of a reduction in anti-dsDNA antibody levels, decreasing from a median of 166.3 U/mL at baseline to 61.1 U/mL at week 12 (P = .002). Alongside, there was a reduction in the SLEDAI-2K score from 12 to 4 within 12 weeks, which was sustained at the 36-week follow-up assessment. Improvements in skin, joint, kidney, and level of proteinuria were also seen.
Although all patients experienced adverse events, none were serious. Infections and infestations (mostly nasopharyngitis, COVID-19, and gastroenteritis) were the most common, experienced by 80% of the participants; 70% had injection site reactions or fatigue, 60% had gastrointestinal symptoms, 50% had a fall of IgG < 5 g/L, 40% had headache, and 20% had back pain.
“This is a positive trial. I think we could demonstrate that [daratumumab] produced very strong, rapid, and durable clinical improvements,” Dr. Alexander said. “We think that targeting CD38 is relevant; plasma cells had been depleted based on the reduction of anti-dsDNA antibodies,” he added.
From the audience, however, Peter Nash, MBBS, of Griffith University in Brisbane, Australia, questioned whether the results could be attributed to “a steroid effect” because patients had been treated with oral dexamethasone throughout the study.
Dr. Alexander noted that steroid use had been part of the treatment schedule but acknowledged it was a possible confounder.
“I think we can be confident that [daratumumab] had a major effect on plasma cells decreasing…because we see that also the vaccine titers decreased,” Dr. Alexander said. “Time will tell, but even more important is the durability of the responses over time, which you don’t achieve under steroids.”
KPG-818’s Novel Mechanism of Action
Elsewhere at EULAR 2024, positive results of another phase 2 study involving a drug with an entirely different mechanism of action, KPG-818, were reported in a poster presentation. KPG-818 modulates CRBN, which results in the degradation of two transcription factors (Aiolos and Ikaros) that are involved in the development, maturation, and proliferation of innate and adaptive immune cells and have been linked to genetic risk in SLE, according to the poster’s authors. It is currently in development for the treatment of SLE, Behçet disease, inflammatory bowel disease, multiple myeloma, and non-Hodgkin lymphoma.
Yao Wang, MD, chief medical officer of KPG-818’s developer Kangpu Biopharmaceuticals, Hefei, China, and associates found that oral doses of 0.15 or 0.6 mg KPG-818 were “generally well-tolerated” and produced immunomodulatory changes that could be beneficial in people with SLE over a 12-week treatment period.
“Only two new agents have been approved for the treatment of SLE in the past five decades in USA and Europe,” Dr. Wang and team wrote, which highlights “a significant unmet need for more effective and safe treatment options.”
They believe that KPG-818 might well fit the bill based on the results of their study, in which 35 of 37 recruited patients completed the treatment. Compared with placebo, they observed reduced numbers of total B cells, Aiolos+ T and B cells, and increased Treg cells.
SLEDAI-2K and Cutaneous Lupus Erythematosus Disease Area and Severity Index activity scores in the 0.15-mg group were improved relative to baseline and placebo.
“The proof-of-concept findings suggest a favorable benefit/risk ratio in SLE for KPG-818,” Dr. Wang and coauthors said, supporting its further development in SLE.
Need for Treatments
Dr. Isenberg told this news organization that both daratumumab and KPG-818 would be welcome additions as treatment options if further trials proved their worth.
“The great frustration about lupus is that, compared to patients with rheumatoid arthritis, the choice has been so limited,” Dr. Isenberg said. Aside from rituximab (Rituxan) and belimumab (Benlysta), which are used with certain restrictions, there are no other biologic targeted treatments available in the United Kingdom. Anifrolumab (Saphnelo) has a license in the United States and some European countries but is not yet available for him to use in his practice.
Daratumumab and KPG-818 are “different types of molecules, and if they work that will be great. It would be nice to have the choice,” Dr. Isenberg said. “Whether they will be as effective as I think rituximab is, I don’t know, but these are some very encouraging results.”
Of course, these are all phase 2 trials, and the “big problem” is that such positive results do not always translate when it comes to phase 3, as Dr. D’Cruz told this news organization.
“Until a few years ago, there had been about 25 or 30 industry-led trails, and they’d all failed, except for belimumab and anifrolumab,” Dr. D’Cruz said. These drugs were found to work and be generally safe in phase 1 and 2 trials, but “when they come to phase 3, they all seem to fail, and we don’t know why.”
These are large global studies, D’Cruz added, observing that problems with patient selection, steroid use, and choice of outcome measures were possible factors for why the EXPLORER and LUNAR studies had shown no benefit for rituximab despite the drug being widely used to treat SLE.
Dr. Isenberg, who has coauthored an article on the topic of why drugs seem to fail at the final hurdle, noted: “I think it has a lot to do with the nature of the disease. It’s a complicated disease.” From having “savvy physicians doing the trials for you” to the placebo response, there are “a whole bunch or reasons why these things haven’t worked in lupus.”
Dr. Morand commented: “We’ve got many programs in phase 2 and 3, and because there’s so many, they’re all facing recruitment challenges, and as a consequence of so much activity, every program is going a little slower than hoped for.”
As for other drugs on the horizon, Dr. Morand noted: “We’re very optimistic about things like litifilimab and deucravacitinib; that’s two examples that are in phase 3. Earlier in the program of development, [there are] a huge range of targets being addressed. The future looks bright. But we might have to wait a while.”
Dr. Arnaud has consulted for AstraZeneca, AbbVie, Alpine Immune Sciences, Biogen, Bristol Myers Squibb, Boehringer Ingelheim, Chugai Pharmaceutical, GlaxoSmithKline, Grifols, Janssen, Kezar Life Sciences, LFB, Lilly, Medac, Merck, Novartis, Pfizer, Roche, and UCB. Dr. Isenberg has served as an adviser to Merck Serono, AstraZeneca, Eli Lilly, Servier, and ImmuPharma. Any honoraria received is passed on to a local arthritis charity connected to his hospital. Dr. D’Cruz has served as a consultant and advisory board member for GlaxoSmithKline and CSL Vifor. Dr. Morand has received research support, consultancy fees, or both from multiple pharmaceutical companies paid to his institution including AbbVie, Amgen, AstraZeneca, Biogen, Bristol Myers Squibb, Eli Lilly, EMD Serono, Dragonfly, Genentech, GlaxoSmithKline, Janssen, Novartis, RemeGen, Takeda, UCB, and Zenas. The ianalumab trial presented by Dr. Agmon-Levin was sponsored by Novartis Pharma; however, she reported having no conflicts of interest. The DARALUP study was an investigator-initiated trial supported by Janssen. Dr. Alexander has received consulting fees, study support, honoraria, and travel grants from various pharmaceutical companies including AbbVie, Amgen, AstraZeneca, Bayer, GlaxoSmithKline, Janssen, and Lilly. Dr. Nash has consulted for The Rheumatology Education Group Consultants. The KPG-818 study reported by Dr. Wang was sponsored by Kangpu Biopharmaceuticals.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
VIENNA — It may have been a while since there have been any major breakthroughs in the treatment of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), but there are high hopes that this is a situation that may be about to change, experts agreed at the annual European Congress of Rheumatology.
“It’s an incredibly vivid area of development,” Laurent Arnaud, MD, PhD, professor of rheumatology at the University of Strasbourg in Strasbourg, France, said during one of the first sessions of the meeting. He reported that there were at least 17 phase 2 and 14 phase 3 trials that were expected to start within the next few years, all with investigational agents that target different immune cells or pathways that have been implicated in the pathogenesis of SLE.
In a systematic review published last year, Dr. Arnaud and coauthors found that there were 92 investigational biologic or novel targeted agents in various phases of clinical testing. This included B-cell–targeting agents such as ianalumab, plasma cell-targeting agents such as daratumumab, and drugs with novel mechanisms of action such as KPG-818, which targets the CRL4-Cereblon (CRBN) E3 ubiquitin ligase complex. Phase 2 data on all three of these investigational agents were presented during various sessions at EULAR 2024, all with positive results, suggesting that their further development in SLE is worth pursuing.
There are of course “many more candidates in the pipeline,” Dr. Arnaud said. “I’m very happy that I think we are going to see great days for lupus right in front of our eyes.”
Targeting B Cells
Drugs that target B cells have been at the forefront of lupus treatment for several years, as David Isenberg, MD, professor of rheumatology at University College London, pointed out during an interview for EULAR TV.
“It’s clearly important to target the cells which are likely to be causing the problem in lupus, and in the main, that tends to be B cells,” he said.
Dr. Isenberg, who is renowned for his work with the B-cell–targeting agent rituximab, added: “But we know that obviously T cells integrate with B cells, so anything which interrupts the link between the T cell and the B cell is likely to be important.”
Chimeric Antigen Receptor (CAR) T-Cell Therapy ‘Revolution’
One new way of targeting B cells is with CAR T-cell therapy, which David D’Cruz , MD, PhD, a consultant rheumatologist for Guy’s and St. Thomas’ Hospital NHS Foundation Trust in London, picked as one of the “most striking” topics highlighted at EULAR 2024.
This is “truly personalized medicine,” Dr. D’Cruz said. This is an autologous therapy because a patient’s T cells are removed by leukapheresis, transfected with a CAR T vector directed against a component of the B cell, and then returned to them.
“I do feel that we’re on the cusp of a major revolution,” Dr. D’Cruz told this news organization. Not only in lupus but also in other rheumatic conditions that have proved really difficult to treat, such as systemic sclerosis and myositis, he said.
“Basically, it’s a very powerful B-cell–depleting tool, but it’s much more profound B-cell–depleting tool than, for example, rituximab or belimumab,” explained Dr. D’Cruz. “What you’re doing is reprogramming T cells to attack the B cells.”
Although rituximab and belimumab clear all the B cells in the circulation, there are still some cells left behind in the bone marrow, “and it’s very difficult to get rid of those,” Dr. D’Cruz said. “What CAR T-cell therapy appears to do is wipe out all the CD19-positive B cells everywhere, in the blood and the tissue. So you get a really profound B-cell depletion.”
Eric Morand, MBBS, PhD, head of rheumatology at Monash Health in Melbourne, Australia, told this news organization that there was obviously “a lot of buzz” about CAR T-cell therapy.
“We’re waiting to see if the exciting data from Erlangen can be reproduced in other centers with other CAR T products to show that it is a universal effect. We haven’t seen that yet, but I think we will by next year.”
Cost and expertise are two major considerations and potential limiting factors, however, as Dr. D’Cruz and Dr. Isenberg both pointed out in separate interviews with this news organization.
Dr. D’Cruz said: “It’s very expensive, it takes a while, and it doesn’t always work is what I’m hearing. It’s usually successful, but again, a little bit depends on the technique and the people doing the process.”
Dr. Isenberg said: “CAR T-cell therapy is, I think, very exciting because it does look to be quite promising. But as it costs 350,000 euros per patient, I don’t think that it is going to be widely adopted.”
Even if it could be afforded by certain centers in the West, he added, this just would not be feasible in poorer nations. “So, we’ve got to find other effective, cheaper ways to go,” Dr. Isenberg said.
“I think there are some very interesting ideas with monoclonal antibodies which target at least two different targets — one on the B cell, one on the T cell — and that could well be the way to take this forward,” he suggested.
Ianalumab ‘Double Blocking’ B Cells
Another way could be to develop more potent B-cell–depleting drugs, as Nancy Agmon-Levin , MD, head of the Clinical Immunology, Angioedema and Allergy Unit, Lupus and Autoimmune Diseases Clinic, at Sheba Medical Center, Tel Aviv University in Tel Aviv, Israel, reported during one of the clinical abstract sessions at EULAR 2024.
Dr. Agmon-Levin presented data on 67 individuals with SLE who had participated in a multicenter phase 2 study of ianalumab, a fully human immunoglobulin (Ig) G1 monoclonal antibody that results in a “double blocking of the B-cell lineage.”
Ianalumab targets the B-cell–activating factor receptor (BAFFR), but what makes it distinct from other BAFF-targeting drugs is that it has had a fructose molecule removed from its Fc portion, which renders it more likely to trigger antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity.
“This is a B-cell depletion therapy,” Agmon-Levin said, but it also blocks BAFFR-mediated survival of B cells, so the subsequent recuperation process of BAFFR-expressing B cells is affected, leading to continued B-cell depletion.
The phase 2 study she presented consisted of an initial 28-week, double-blind period, during which time participants had been randomly allocated to receive either subcutaneous injections of ianalumab 300 mg or a matching placebo every 4 weeks. This was followed by a 24-week, open-label period where all participants were treated with ianalumab, and then an off-treatment, minimal follow-up period that lasted up to 68 weeks, with continued data collection for safety.
The primary outcome measure was a composite of meeting criteria for the SLE Responder Index 4 and a sustained reduction in corticosteroid use at 28 weeks. This was achieved in 15 of the 34 (44.1%) people treated with ianalumab vs only 3 (9.1%) of the 33 people who had been given a placebo.
Dr. Agmon-Levin reported that the effect on this outcome was sustained to the end of the open-label period, at 1 year, in 15 (45.5%) of 33 participants who had continued treatment with ianalumab and achieved in 13 (40.6%) of 32 participants who had switched from placebo to ianalumab treatment.
Moreover, longer durations of treatment were associated with a host of improved outcomes, Dr. Agmon-Levin said: “Treatment was improved along the 52 weeks, and we can see from the LLDAS [Lupus Low Disease Activity State], DORIS [Definition Of Remission In SLE], and SRI-6 and -8 that as you continue the therapy, you improve the outcomes.”
The potential benefits of ianalumab in the treatment of SLE and lupus nephritis will now be further examined in the phase 3 SIRIUS-SLE1 , SIRIUS-SLE2, and SIRIUS-LN trials, which are estimated to provide initial results in 2027 and complete in early 2029 or 2030.
Targeting Plasma Cells With Daratumumab
Another drug showing signs that it might be useful as a treatment for SLE is daratumumab, as Tobias Alexander, MD, of Charité — Universitätsmedizin Berlin, reported during one of the late-breaking abstract sessions at EULAR 2024.
“Daratumumab is a human, first-in-class anti-CD38 antibody that efficiently depletes plasma cells,” Dr. Alexander said. CD38 is both a receptor and an enzyme, and while it is found on the surface of most immune cells, it’s particularly expressed by plasma cells, he added.
Daratumumab is not a total newcomer, however, as it’s already approved for the treatment of multiple myeloma under the trade name Darzalex. The rationale for using it in SLE comes from two case reports, Dr. Alexander explained. The first, published in 2020 in The New England Journal of Medicine, involved two patients with severe and life-threatening lupus who were given off-label treatment for a period of 4 weeks and experienced good clinical and serologic responses. The second, published last year in Nature Medicine, involved six patients with refractory lupus nephritis, five of whom had a clinical response at 6 months.
“On this background, we conducted an investigator-initiated trial, which was an open-label, single-center, proof-of-concept study,” Dr. Alexander said. A total of 10 female patients whose ages ranged from 24 to 43 years were included in the phase 2 trial that was dubbed DARALUP. For inclusion, all had to have a Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Disease Activity Index 2000 (SLEDAI-2K) of four or more for clinical manifestations, have been treated with at least two prior disease-modifying drugs to no avail, and be anti–double-stranded DNA (anti-dsDNA) antibody positive. Dr. Alexander reported that the median baseline SLEDAI-2K score was 12 and ranged from 8 to 20, with the number of prior therapies ranging from two to nine.
Daratumumab was given at a dose of 1800 mg via subcutaneous injection every week for 8 weeks. This is the same dose that is used to treat multiple myeloma, Dr. Alexander explained, although the dosing is not stopped. The reason for stopping after 8 weeks in the current trial was to be able to see what happened once the treatment was stopped. The follow-up was for 36 weeks.
Dr. Alexander reported that there was a “very dramatic and significant” effect on the primary endpoint of a reduction in anti-dsDNA antibody levels, decreasing from a median of 166.3 U/mL at baseline to 61.1 U/mL at week 12 (P = .002). Alongside, there was a reduction in the SLEDAI-2K score from 12 to 4 within 12 weeks, which was sustained at the 36-week follow-up assessment. Improvements in skin, joint, kidney, and level of proteinuria were also seen.
Although all patients experienced adverse events, none were serious. Infections and infestations (mostly nasopharyngitis, COVID-19, and gastroenteritis) were the most common, experienced by 80% of the participants; 70% had injection site reactions or fatigue, 60% had gastrointestinal symptoms, 50% had a fall of IgG < 5 g/L, 40% had headache, and 20% had back pain.
“This is a positive trial. I think we could demonstrate that [daratumumab] produced very strong, rapid, and durable clinical improvements,” Dr. Alexander said. “We think that targeting CD38 is relevant; plasma cells had been depleted based on the reduction of anti-dsDNA antibodies,” he added.
From the audience, however, Peter Nash, MBBS, of Griffith University in Brisbane, Australia, questioned whether the results could be attributed to “a steroid effect” because patients had been treated with oral dexamethasone throughout the study.
Dr. Alexander noted that steroid use had been part of the treatment schedule but acknowledged it was a possible confounder.
“I think we can be confident that [daratumumab] had a major effect on plasma cells decreasing…because we see that also the vaccine titers decreased,” Dr. Alexander said. “Time will tell, but even more important is the durability of the responses over time, which you don’t achieve under steroids.”
KPG-818’s Novel Mechanism of Action
Elsewhere at EULAR 2024, positive results of another phase 2 study involving a drug with an entirely different mechanism of action, KPG-818, were reported in a poster presentation. KPG-818 modulates CRBN, which results in the degradation of two transcription factors (Aiolos and Ikaros) that are involved in the development, maturation, and proliferation of innate and adaptive immune cells and have been linked to genetic risk in SLE, according to the poster’s authors. It is currently in development for the treatment of SLE, Behçet disease, inflammatory bowel disease, multiple myeloma, and non-Hodgkin lymphoma.
Yao Wang, MD, chief medical officer of KPG-818’s developer Kangpu Biopharmaceuticals, Hefei, China, and associates found that oral doses of 0.15 or 0.6 mg KPG-818 were “generally well-tolerated” and produced immunomodulatory changes that could be beneficial in people with SLE over a 12-week treatment period.
“Only two new agents have been approved for the treatment of SLE in the past five decades in USA and Europe,” Dr. Wang and team wrote, which highlights “a significant unmet need for more effective and safe treatment options.”
They believe that KPG-818 might well fit the bill based on the results of their study, in which 35 of 37 recruited patients completed the treatment. Compared with placebo, they observed reduced numbers of total B cells, Aiolos+ T and B cells, and increased Treg cells.
SLEDAI-2K and Cutaneous Lupus Erythematosus Disease Area and Severity Index activity scores in the 0.15-mg group were improved relative to baseline and placebo.
“The proof-of-concept findings suggest a favorable benefit/risk ratio in SLE for KPG-818,” Dr. Wang and coauthors said, supporting its further development in SLE.
Need for Treatments
Dr. Isenberg told this news organization that both daratumumab and KPG-818 would be welcome additions as treatment options if further trials proved their worth.
“The great frustration about lupus is that, compared to patients with rheumatoid arthritis, the choice has been so limited,” Dr. Isenberg said. Aside from rituximab (Rituxan) and belimumab (Benlysta), which are used with certain restrictions, there are no other biologic targeted treatments available in the United Kingdom. Anifrolumab (Saphnelo) has a license in the United States and some European countries but is not yet available for him to use in his practice.
Daratumumab and KPG-818 are “different types of molecules, and if they work that will be great. It would be nice to have the choice,” Dr. Isenberg said. “Whether they will be as effective as I think rituximab is, I don’t know, but these are some very encouraging results.”
Of course, these are all phase 2 trials, and the “big problem” is that such positive results do not always translate when it comes to phase 3, as Dr. D’Cruz told this news organization.
“Until a few years ago, there had been about 25 or 30 industry-led trails, and they’d all failed, except for belimumab and anifrolumab,” Dr. D’Cruz said. These drugs were found to work and be generally safe in phase 1 and 2 trials, but “when they come to phase 3, they all seem to fail, and we don’t know why.”
These are large global studies, D’Cruz added, observing that problems with patient selection, steroid use, and choice of outcome measures were possible factors for why the EXPLORER and LUNAR studies had shown no benefit for rituximab despite the drug being widely used to treat SLE.
Dr. Isenberg, who has coauthored an article on the topic of why drugs seem to fail at the final hurdle, noted: “I think it has a lot to do with the nature of the disease. It’s a complicated disease.” From having “savvy physicians doing the trials for you” to the placebo response, there are “a whole bunch or reasons why these things haven’t worked in lupus.”
Dr. Morand commented: “We’ve got many programs in phase 2 and 3, and because there’s so many, they’re all facing recruitment challenges, and as a consequence of so much activity, every program is going a little slower than hoped for.”
As for other drugs on the horizon, Dr. Morand noted: “We’re very optimistic about things like litifilimab and deucravacitinib; that’s two examples that are in phase 3. Earlier in the program of development, [there are] a huge range of targets being addressed. The future looks bright. But we might have to wait a while.”
Dr. Arnaud has consulted for AstraZeneca, AbbVie, Alpine Immune Sciences, Biogen, Bristol Myers Squibb, Boehringer Ingelheim, Chugai Pharmaceutical, GlaxoSmithKline, Grifols, Janssen, Kezar Life Sciences, LFB, Lilly, Medac, Merck, Novartis, Pfizer, Roche, and UCB. Dr. Isenberg has served as an adviser to Merck Serono, AstraZeneca, Eli Lilly, Servier, and ImmuPharma. Any honoraria received is passed on to a local arthritis charity connected to his hospital. Dr. D’Cruz has served as a consultant and advisory board member for GlaxoSmithKline and CSL Vifor. Dr. Morand has received research support, consultancy fees, or both from multiple pharmaceutical companies paid to his institution including AbbVie, Amgen, AstraZeneca, Biogen, Bristol Myers Squibb, Eli Lilly, EMD Serono, Dragonfly, Genentech, GlaxoSmithKline, Janssen, Novartis, RemeGen, Takeda, UCB, and Zenas. The ianalumab trial presented by Dr. Agmon-Levin was sponsored by Novartis Pharma; however, she reported having no conflicts of interest. The DARALUP study was an investigator-initiated trial supported by Janssen. Dr. Alexander has received consulting fees, study support, honoraria, and travel grants from various pharmaceutical companies including AbbVie, Amgen, AstraZeneca, Bayer, GlaxoSmithKline, Janssen, and Lilly. Dr. Nash has consulted for The Rheumatology Education Group Consultants. The KPG-818 study reported by Dr. Wang was sponsored by Kangpu Biopharmaceuticals.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM EULAR 2024
Advantages of a Pediatric Rheumatology/Dermatology Clinic Evaluated
results from a retrospective cohort study showed.
“This finding highlights the complexity of patients referred to this clinic,” the study’s first author, Jessica Crockett, a fourth-year medical student at UCSF, told this news organization following the annual meeting of the Society for Pediatric Dermatology, where the study was presented during a poster session. “Integrated care models such as rheumatology/dermatology clinics (RDCs) have been shown to facilitate complete clinical evaluations, establish new or revised diagnoses, and streamline care for adult patients with complex autoimmune skin diseases. However, few pediatric RDCs exist nationwide, and data therefore is quite limited.”
To advance the understanding of pediatric RDC practice patterns, the influence of the care model on patient care, and professional development for trainees and clinicians, Ms. Crockett collaborated with senior author Kelly Cordoro, MD, professor of dermatology and pediatrics at UCSF, and colleagues to evaluate a cohort of 71 patients who received care at the UCSF pediatric RDC. The clinic, which was launched in 2017, includes two dermatologists, two rheumatologists, trainees, a social worker, and a nurse. Team members participate in a preclinic conference to review patient data and images, discuss relevant literature, and develop an approach to each patient.
In a separate part of the study, the researchers distributed a survey to 17 pediatric dermatologists who participate in unique RDCs in North America. Respondents were asked to describe the variability of clinical operations, participants, administrative/clinical support, and educational value for participating physicians and trainees.
Of the 71 patients cared for at the UCSF pediatric RDC, 69% were female, 44% were White, 51% were aged 13-21 years, 42% were aged 3-12 years, and 7% were aged 0-11 years at their first clinic visit. The top four primary RDC diagnoses were linear morphea (33%), lupus (23%), psoriasis (13%), and juvenile dermatomyositis (10%).
Nearly one in four patients (17, or 24%) presented to the RDC without a confirmed diagnosis. A diagnosis was established at the first RDC visit for 7 of these 17 patients (41%). Among 54 patients who presented with an established diagnosis, the first RDC visit confirmed the diagnosis for 52 (96%) and revised it for 2 (4%). “Initial pediatric RDC evaluation significantly influenced patient care by confirming or revising preexisting diagnoses, rendering new diagnoses, and streamlining additional laboratory and imaging recommendations,” the researchers wrote in their poster.
The evaluation also resulted in modified disease management in the form of systemic medication changes or dosage adjustments as well as the initiation of novel therapies. For example, systemic medication changes were made during the first RDC visit in 34 of the 46 patients (74%) who were on systemic medication at presentation.
“Seeing complex patients together in real time allows specialists and other team members (social work, nursing, PT/OT, for example) to share ideas, communicate clearly to families, and efficiently develop recommendations,” Ms. Crockett said of the UCSF pediatric RDC. “Exposure to other specialists while caring for patients enhances medical knowledge, communication skills, and professional competency of faculty and trainees alike.”
In the survey portion of the study, each of the 17 dermatologists reported that the pediatric RDC is valuable for patient care, and 88% believed the RDC was a valuable use of their time. However, only 59% of respondents reported having administrative support, and only 29% had a dedicated clinic coordinator or navigator.
“We were surprised to find that only a quarter of pediatric RDCs incorporate an educational conference,” Dr. Cordoro told this news organization. “We have found that assembling the care team prior to seeing patients to review clinical data, discuss relevant literature, and define the clinical questions for each patient is an integral part of the clinical operation. The trainees are involved in these conference presentations, and it really enhances their understanding of the complex diagnoses we manage in this clinic and the issues faced by affected children and families. The preclinical conference increases efficiency, positively influences patient care, and supports professional development for all participants.”
The study was indirectly supported by a fellowship grant awarded to Ms. Crockett from the Pediatric Dermatology Research Alliance. The researchers reported having no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
results from a retrospective cohort study showed.
“This finding highlights the complexity of patients referred to this clinic,” the study’s first author, Jessica Crockett, a fourth-year medical student at UCSF, told this news organization following the annual meeting of the Society for Pediatric Dermatology, where the study was presented during a poster session. “Integrated care models such as rheumatology/dermatology clinics (RDCs) have been shown to facilitate complete clinical evaluations, establish new or revised diagnoses, and streamline care for adult patients with complex autoimmune skin diseases. However, few pediatric RDCs exist nationwide, and data therefore is quite limited.”
To advance the understanding of pediatric RDC practice patterns, the influence of the care model on patient care, and professional development for trainees and clinicians, Ms. Crockett collaborated with senior author Kelly Cordoro, MD, professor of dermatology and pediatrics at UCSF, and colleagues to evaluate a cohort of 71 patients who received care at the UCSF pediatric RDC. The clinic, which was launched in 2017, includes two dermatologists, two rheumatologists, trainees, a social worker, and a nurse. Team members participate in a preclinic conference to review patient data and images, discuss relevant literature, and develop an approach to each patient.
In a separate part of the study, the researchers distributed a survey to 17 pediatric dermatologists who participate in unique RDCs in North America. Respondents were asked to describe the variability of clinical operations, participants, administrative/clinical support, and educational value for participating physicians and trainees.
Of the 71 patients cared for at the UCSF pediatric RDC, 69% were female, 44% were White, 51% were aged 13-21 years, 42% were aged 3-12 years, and 7% were aged 0-11 years at their first clinic visit. The top four primary RDC diagnoses were linear morphea (33%), lupus (23%), psoriasis (13%), and juvenile dermatomyositis (10%).
Nearly one in four patients (17, or 24%) presented to the RDC without a confirmed diagnosis. A diagnosis was established at the first RDC visit for 7 of these 17 patients (41%). Among 54 patients who presented with an established diagnosis, the first RDC visit confirmed the diagnosis for 52 (96%) and revised it for 2 (4%). “Initial pediatric RDC evaluation significantly influenced patient care by confirming or revising preexisting diagnoses, rendering new diagnoses, and streamlining additional laboratory and imaging recommendations,” the researchers wrote in their poster.
The evaluation also resulted in modified disease management in the form of systemic medication changes or dosage adjustments as well as the initiation of novel therapies. For example, systemic medication changes were made during the first RDC visit in 34 of the 46 patients (74%) who were on systemic medication at presentation.
“Seeing complex patients together in real time allows specialists and other team members (social work, nursing, PT/OT, for example) to share ideas, communicate clearly to families, and efficiently develop recommendations,” Ms. Crockett said of the UCSF pediatric RDC. “Exposure to other specialists while caring for patients enhances medical knowledge, communication skills, and professional competency of faculty and trainees alike.”
In the survey portion of the study, each of the 17 dermatologists reported that the pediatric RDC is valuable for patient care, and 88% believed the RDC was a valuable use of their time. However, only 59% of respondents reported having administrative support, and only 29% had a dedicated clinic coordinator or navigator.
“We were surprised to find that only a quarter of pediatric RDCs incorporate an educational conference,” Dr. Cordoro told this news organization. “We have found that assembling the care team prior to seeing patients to review clinical data, discuss relevant literature, and define the clinical questions for each patient is an integral part of the clinical operation. The trainees are involved in these conference presentations, and it really enhances their understanding of the complex diagnoses we manage in this clinic and the issues faced by affected children and families. The preclinical conference increases efficiency, positively influences patient care, and supports professional development for all participants.”
The study was indirectly supported by a fellowship grant awarded to Ms. Crockett from the Pediatric Dermatology Research Alliance. The researchers reported having no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
results from a retrospective cohort study showed.
“This finding highlights the complexity of patients referred to this clinic,” the study’s first author, Jessica Crockett, a fourth-year medical student at UCSF, told this news organization following the annual meeting of the Society for Pediatric Dermatology, where the study was presented during a poster session. “Integrated care models such as rheumatology/dermatology clinics (RDCs) have been shown to facilitate complete clinical evaluations, establish new or revised diagnoses, and streamline care for adult patients with complex autoimmune skin diseases. However, few pediatric RDCs exist nationwide, and data therefore is quite limited.”
To advance the understanding of pediatric RDC practice patterns, the influence of the care model on patient care, and professional development for trainees and clinicians, Ms. Crockett collaborated with senior author Kelly Cordoro, MD, professor of dermatology and pediatrics at UCSF, and colleagues to evaluate a cohort of 71 patients who received care at the UCSF pediatric RDC. The clinic, which was launched in 2017, includes two dermatologists, two rheumatologists, trainees, a social worker, and a nurse. Team members participate in a preclinic conference to review patient data and images, discuss relevant literature, and develop an approach to each patient.
In a separate part of the study, the researchers distributed a survey to 17 pediatric dermatologists who participate in unique RDCs in North America. Respondents were asked to describe the variability of clinical operations, participants, administrative/clinical support, and educational value for participating physicians and trainees.
Of the 71 patients cared for at the UCSF pediatric RDC, 69% were female, 44% were White, 51% were aged 13-21 years, 42% were aged 3-12 years, and 7% were aged 0-11 years at their first clinic visit. The top four primary RDC diagnoses were linear morphea (33%), lupus (23%), psoriasis (13%), and juvenile dermatomyositis (10%).
Nearly one in four patients (17, or 24%) presented to the RDC without a confirmed diagnosis. A diagnosis was established at the first RDC visit for 7 of these 17 patients (41%). Among 54 patients who presented with an established diagnosis, the first RDC visit confirmed the diagnosis for 52 (96%) and revised it for 2 (4%). “Initial pediatric RDC evaluation significantly influenced patient care by confirming or revising preexisting diagnoses, rendering new diagnoses, and streamlining additional laboratory and imaging recommendations,” the researchers wrote in their poster.
The evaluation also resulted in modified disease management in the form of systemic medication changes or dosage adjustments as well as the initiation of novel therapies. For example, systemic medication changes were made during the first RDC visit in 34 of the 46 patients (74%) who were on systemic medication at presentation.
“Seeing complex patients together in real time allows specialists and other team members (social work, nursing, PT/OT, for example) to share ideas, communicate clearly to families, and efficiently develop recommendations,” Ms. Crockett said of the UCSF pediatric RDC. “Exposure to other specialists while caring for patients enhances medical knowledge, communication skills, and professional competency of faculty and trainees alike.”
In the survey portion of the study, each of the 17 dermatologists reported that the pediatric RDC is valuable for patient care, and 88% believed the RDC was a valuable use of their time. However, only 59% of respondents reported having administrative support, and only 29% had a dedicated clinic coordinator or navigator.
“We were surprised to find that only a quarter of pediatric RDCs incorporate an educational conference,” Dr. Cordoro told this news organization. “We have found that assembling the care team prior to seeing patients to review clinical data, discuss relevant literature, and define the clinical questions for each patient is an integral part of the clinical operation. The trainees are involved in these conference presentations, and it really enhances their understanding of the complex diagnoses we manage in this clinic and the issues faced by affected children and families. The preclinical conference increases efficiency, positively influences patient care, and supports professional development for all participants.”
The study was indirectly supported by a fellowship grant awarded to Ms. Crockett from the Pediatric Dermatology Research Alliance. The researchers reported having no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM SPD 2024
Steroids’ 75th Anniversary: Clinicians Strive to Use Less
Now, 75 years after the first presentations were made on the “sensational” effects of cortisone in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis (RA), glucocorticoids (GCs) are still highly relevant and widely used in the management of RA and other immune-mediated inflammatory diseases.
“It makes me smile because this is such an old drug, and we need it still so much. It still hasn’t been replaced,” Josef S. Smolen, MD, observed at annual European Congress of Rheumatology.
At low doses, GCs are highly effective as anti-inflammatory and anti-destructive agents in RA and many other diseases, said Dr. Smolen, a rheumatologist and immunologist and professor emeritus at the Medical University of Vienna, Austria.
But even after all this time, the mechanisms that lead to efficacy vs toxicity have yet to be clarified. “Such separation may provide further insights into future treatment options,” said Dr. Smolen.
His comments, made during a special session on the 75th anniversary of GCs at EULAR 2024, underscore the endless saga to manage GCs while finding better alternatives. Opinions differ on what the research says on toxicity and dosage and whether a long-term, low-dose option is viable. Alternative therapies are being studied, but those endeavors are still in the early stages of development.
While GCs are still used chronically in many patients, clinicians should always attempt to discontinue them whenever possible, Frank Buttgereit, MD, professor of rheumatology and deputy head of the Department of Rheumatology and Clinical Immunology at Charité – Universitätsmedizin Berlin, Germany, told attendees at the congress. Up to 60% of patients in registries use GCs, and many patients with early or established RA enter randomized controlled trials on GCs as maintenance therapy.
The ubiquity of GC usage stems in part from overprescribing by non-rheumatologist physicians who might not have access to or aren’t aware of newer biologics or disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs). “We see a lot of patients on long-term glucocorticoids, chronic use for years and years, decades of glucocorticoids,” said Giovanni Adami, MD, PhD, a rheumatologist at the University of Verona, Italy, who has coauthored several studies on the use of GCs.
Societies Agree: Discontinue as Fast as Possible
GCs have been associated with a long list of adverse events, most notably Cushing syndrome, hypertension, cardiovascular disease, osteoporosis, myopathy, peptic ulcer, adrenal insufficiency (AI), infections, mood disorders, ophthalmologic disorders such as cataracts, skin disorders, menstrual septic necrosis, and pancreatitis.
Dose matters, Dr. Smolen said, citing studies that found that cumulative GC doses of 1000 or 1100 mg increase risks. One study by German researchers found that doses above 10 mg/d significantly raised the hazard ratio for death.
Because high disease activity is also associated with an equally high mortality risk, “we have to balance this out: Active disease vs glucocorticoid use, especially in countries that have less access to modern therapies than we have in the more affluent Western regions,” Dr. Smolen said.
Rheumatology societies generally agree that clinicians should try to minimize GC use or eventually discontinue the therapy.
The American College of Rheumatology recommends not using GCs as part of the first-line treatment of RA. “And if you want to use [them], you should do that for less than 3 months, taper and discontinue as fast as possible, and use the lowest dose possible,” Dr. Adami said.
EULAR’s recommendation is more nuanced in that it allows for a lower dose but gives physicians more choice in how they want to handle GCs, Dr. Adami said. The task force added that all patients should try to taper down or discontinue as fast as possible, he said.
For GCs in the management of systemic lupus erythematosus, a EULAR task force recommended that the type and severity of organ involvement should determine dose, with a long-term goal of maintaining the dose < 5 mg/d or possibly withdrawing it.
EULAR also recommends GC bridging when initiating or changing conventional synthetic (cs) DMARDs. This effectively dismisses the use of GCs when using biologic DMARDs or targeted synthetic DMARDs. As a bridging therapy, EULAR recommends either a single parenteral dose of GC or a predefined tapering or discontinuation scheme within 3 months, when starting an oral GC.
Low-Dose Approach Gains Ground
While saying he’d be the first physician to eliminate GCs whenever possible, Dr. Buttgereit made the case before the EULAR Congress that GCs in low doses could still play a role in treatment.
Many physicians believe that very low doses between 2 and 4 mg/d are a realistic therapy option for RA, he said, adding that a mean daily usage < 5 mg could be used over a longer period with relatively low risk.
Several studies he coauthored tested the 5-mg approach. The GLORIA trial compared 5 mg/d prednisolone and placebo in 451 patients aged 65 years and older with active RA over the course of 2 years. The researchers found that patients on prednisolone had a mean Disease Activity Score in 28 joints (DAS28) that was 0.37 points lower and mean joint damage score that was 1.7 points lower than those of patients on placebo, suggesting that the GC had long-term benefits in these patients with RA.
The tradeoff was a 24% increase in the risk of having at least one adverse event of special interest, but most of these events were non-severe infections, Dr. Buttgereit said.
Another study, the SEMIRA trial, assigned 128 patients to a continued regimen of prednisone 5 mg/d for 24 weeks. Another group of 131 patients received a tapered-prednisone regimen. All patients received tocilizumab 162 mg with or without csDMARDs, maintained at stable doses.
Patients in the first cohort achieved superior disease activity control than those in the tapered regimen group. “The side effects showed that in the tapering prednisone group, there were more treatment-emergent adverse effects in this double-blind trial as compared to the continued prednisone group,” Dr. Buttgereit said.
One limitation of the SEMIRA trial was that it studied the effect of tocilizumab as a GC-sparing agent, and it didn’t consider using a tumor necrosis factor or Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitor, which might have a more potent effect on pain and GC dose reduction, Dr. Adami said. “Why do we need to use glucocorticoids if we know they might be detrimental, if we know there might be some other option in our armamentarium?”
Other studies have shown that low-dose GC protocols can be used with standard treatment, according to Sebastian E. Sattui, MD, assistant professor of medicine and director of the Vasculitis Center at the University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine.
“Examples of this are the LoVAS and PEXIVAS studies for antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody-associated [ANCA] vasculitis. This has been highlighted in existing treatment recommendations for ANCA vasculitis and systemic lupus erythematosus nephritis,” Dr. Sattui said.
Two-year results from LoVAS showed noninferiority in remission induction rates and rates of relapse and significantly less frequent serious adverse events between a reduced-dose GC regimen at 0.5 mg/kg/d and conventional high-dose GC regimen at 1 mg/kg/d plus rituximab for ANCA vasculitis.
PEXIVAS demonstrated the noninferiority of a reduced-dose regimen of GCs vs a standard-dose regimen with respect to death or end-stage kidney disease in patients with severe disease involvement.
Debating the Toxicity Threshold
Are low GC dosages significantly associated with adverse events like mortality, cardiovascular, or diabetes risk? It depends on who you ask.
Much of the toxicity data on GCs come from inadequately powered or controlled studies and often refer to doses that currently are considered too high, Dr. Buttgereit said. His presentation highlighted a study from Hong Kong, a time-varying analysis of GC dose and incident risk for major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE) in more than 12,000 patients with RA. Researchers found that GC regimens ≥ 5 mg/d significantly increased the risk for MACE. Comparatively, doses below this threshold did not confer excessive risk, he said.
Low-dose GCs are lesser toxic than high-dose GCs, noted Joan Merrill, MD, a professor with the Arthritis and Clinical Immunology Research Program at The University of Oklahoma Health Sciences Center, Oklahoma City. “There may be less weight gain, less chance of acne, and less risk for all the slower, more organ-threatening side effects.”
Dr. Merrill, who cares for patients with lupus, said physicians can keep lupus in check for years, using constant, low-dose GCs. “The one thing we know is that steroids work.” But over many years, damage may still occur, she cautioned.
But even a low dose could present health problems to patients. The GLORIA trial of patients with RA, which showed promising results on disease control with 5 mg/d, found an association between GCs and increased risk for infection and osteoporosis. There was a higher overall risk for adverse events related to skin, infections, and bone mineral density changes. Bone mineral density loss and fractures were more common in the GC group, Adami noted.
Surprisingly, some of the trial’s authors said patients could handle such adverse events. But what is your threshold of “acceptable?” Dr. Adami asked.
Other studies have found associations between low-dose GC regimens and adverse events. Researchers of a 2023 study reported bone mineral density loss in patients with inflammatory rheumatic musculoskeletal diseases on a 2.5-mg/d regimen. Another decade-long analysis of Medicare and Optum data found a link between serious infection and low-dose GCs in patients receiving stable DMARD therapy. Investigators reported risk even at daily doses of ≤ 5 mg.
Dr. Adami acknowledged that these studies may have “confounding by indication,” a channeling bias in which people with severe RA are more likely to be treated with GCs. For this reason, it’s a challenge to disentangle the independent role of GCs from the disease activity itself, he said.
The big question is: Why don’t these observational studies show an increased risk for adverse events with biologic drugs that are given to more severe patients? “That confirms the hypothesis that confounding by indication for GCs is minimal, and most of the risk is driven by GCs,” he said.
Tapering Options Across Diseases
Rheumatologists in the field continue to navigate GC-tapering options and treatment combinations that reduce the cumulative use of GCs over time, finding their own solutions based on the conditions they treat.
In his EULAR presentation, Dr. Buttgereit suggested that current therapeutic approaches for RA may be too narrow when they don’t consider the possibility of including very low doses of GCs.
For RA, “why shouldn’t we not do a combination of something like methotrexate plus a JAK inhibitor or a biological,” plus a very low dose of GCs < 5 mg/d, he asked.
However, Dr. Adami said he generally avoids GCs if RA disease activity is not severe (based on DAS28) and if the patient has a visual analog scale pain score < 7. “Nonetheless, even in patients with more severe disease, I would avoid GCs for more than 3 months. Usually, 1 month of steroids, tapered rapidly and discontinued.”
All patients should receive an appropriate treat-to-target strategy with csDMARDs and biologics if needed, he added.
A patient coming to clinic with difficult-to-treat RA who chronically uses GCs deserves special attention. The priority is bone protection with an anti-osteoporosis medication. “I found that JAK inhibitors, in some cases, help with the discontinuation of steroids, especially in those with residual pain. Therefore, I would think of switching medication,” Dr. Adami said.
For polymyalgia rheumatica, most clinicians will likely try to taper GCs around 52 weeks, similar to ACR/EULAR guidelines, according to Robert F. Spiera, MD, director of the Scleroderma and Vasculitis Program at Hospital for Special Surgery, New York City.
“I usually challenge patients with a more rapid taper, hoping to get them off GCs in 6 or even 4 months in some patients, recognizing that many will flare, and we will have to bump up their GC dose,” Dr. Spiera said.
For patients with lupus, GCs remain the most effective treatment, Dr. Merrill said. “The toxicities are unacceptable for long-term use. So we try to get in fast when we need them and get out as soon as possible after that, tapering down as fast as the patient can tolerate it.”
Unfortunately, that’s not always as fast as the clinician or patient hopes for, she said.
“New treatments are being developed that may help us avoid the constant use of steroids. However, it would be wonderful to see how these new safer types of steroids work in lupus,” she said.
Minimizing GCs is an important goal that should be considered and aimed for in every single patient, Dr. Sattui said. “Risk of GC toxicity should be considered in all patients, assessing [them] for cardiometabolic comorbidities, bone metabolic diseases, risk of infection, among many others.” Sticking to one specific GC-tapering protocol might not be achievable for every patient, however, based on disease characteristics, response, and other factors, he added.
Monitoring for GC toxicity is important and should occur during and after every single clinical visit, he emphasized. Patient education is critical. “Different tools have been developed and employed in clinical trials, both patient- and physician-facing instruments. Implementation to clinical practice of some of these should be the next step in order to achieve a more systematic approach.”
What to Consider for AI Symptoms
Clinicians also need to address AI in patients who are coming off GCs, Dr. Sattui said. He advised that symptoms suggestive of AI, including malaise, fatigue, nausea, and muscle and/or joint pain, should guide testing.
Even in the absence of symptoms, clinicians should consider assessing patients who have been on high doses for prolonged periods or obese or older adults who might be at a high risk for AI. “Signs to consider include weight loss, hypotension, or orthostatism,” he said.
Differentiating between AI symptoms and symptoms from the underlying disease can be a challenge. This requires a physical exam and workup, including morning serum cortisol. Collaboration with endocrinology colleagues and other treating providers is important, as well as patient education of symptoms and monitoring for possible adjustments in treating AI and other acute diseases, he said.
Dr. Smolen received research grants from AbbVie, AstraZeneca, Galapagos, and Eli Lilly. Dr. Adami received speaker fees and/or was a consultant for Galapagos, Theramex, Amgen, Eli Lilly, UCB, Fresenius Kabi, Bristol Myers Squibb, Abiogen, and Pfizer. Dr. Buttgereit’s disclosures included AbbVie, AstraZeneca, Grünenthal, Horizon Therapeutics, Mundipharma, Pfizer, and Roche. Dr. Merrill had no relevant disclosures. Dr. Spiera has been a consultant for Roche-Genentech, GlaxoSmithKline, Sanofi, ChemoCentryx, Novartis, Galderma, Cytori, AstraZeneca, Amgen, and AbbVie and received research grant support from GlaxoSmithKline, Roche-Genentech, AstraZeneca, Bristol Myers Squibb, Kadmon, Boehringer Ingelheim, Cytori, ChemoCentryx, Corbus, Novartis, Amgen, and AbbVie. Dr. Sattui reported receiving research support from AstraZeneca and GlaxoSmithKline (clinical trials), receiving consulting fees from Sanofi (funds toward research support), serving on advisory boards for Sanofi and Amgen (funds toward research support), and receiving speaker fees from Fresenius Kabi (funds toward research support).
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Now, 75 years after the first presentations were made on the “sensational” effects of cortisone in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis (RA), glucocorticoids (GCs) are still highly relevant and widely used in the management of RA and other immune-mediated inflammatory diseases.
“It makes me smile because this is such an old drug, and we need it still so much. It still hasn’t been replaced,” Josef S. Smolen, MD, observed at annual European Congress of Rheumatology.
At low doses, GCs are highly effective as anti-inflammatory and anti-destructive agents in RA and many other diseases, said Dr. Smolen, a rheumatologist and immunologist and professor emeritus at the Medical University of Vienna, Austria.
But even after all this time, the mechanisms that lead to efficacy vs toxicity have yet to be clarified. “Such separation may provide further insights into future treatment options,” said Dr. Smolen.
His comments, made during a special session on the 75th anniversary of GCs at EULAR 2024, underscore the endless saga to manage GCs while finding better alternatives. Opinions differ on what the research says on toxicity and dosage and whether a long-term, low-dose option is viable. Alternative therapies are being studied, but those endeavors are still in the early stages of development.
While GCs are still used chronically in many patients, clinicians should always attempt to discontinue them whenever possible, Frank Buttgereit, MD, professor of rheumatology and deputy head of the Department of Rheumatology and Clinical Immunology at Charité – Universitätsmedizin Berlin, Germany, told attendees at the congress. Up to 60% of patients in registries use GCs, and many patients with early or established RA enter randomized controlled trials on GCs as maintenance therapy.
The ubiquity of GC usage stems in part from overprescribing by non-rheumatologist physicians who might not have access to or aren’t aware of newer biologics or disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs). “We see a lot of patients on long-term glucocorticoids, chronic use for years and years, decades of glucocorticoids,” said Giovanni Adami, MD, PhD, a rheumatologist at the University of Verona, Italy, who has coauthored several studies on the use of GCs.
Societies Agree: Discontinue as Fast as Possible
GCs have been associated with a long list of adverse events, most notably Cushing syndrome, hypertension, cardiovascular disease, osteoporosis, myopathy, peptic ulcer, adrenal insufficiency (AI), infections, mood disorders, ophthalmologic disorders such as cataracts, skin disorders, menstrual septic necrosis, and pancreatitis.
Dose matters, Dr. Smolen said, citing studies that found that cumulative GC doses of 1000 or 1100 mg increase risks. One study by German researchers found that doses above 10 mg/d significantly raised the hazard ratio for death.
Because high disease activity is also associated with an equally high mortality risk, “we have to balance this out: Active disease vs glucocorticoid use, especially in countries that have less access to modern therapies than we have in the more affluent Western regions,” Dr. Smolen said.
Rheumatology societies generally agree that clinicians should try to minimize GC use or eventually discontinue the therapy.
The American College of Rheumatology recommends not using GCs as part of the first-line treatment of RA. “And if you want to use [them], you should do that for less than 3 months, taper and discontinue as fast as possible, and use the lowest dose possible,” Dr. Adami said.
EULAR’s recommendation is more nuanced in that it allows for a lower dose but gives physicians more choice in how they want to handle GCs, Dr. Adami said. The task force added that all patients should try to taper down or discontinue as fast as possible, he said.
For GCs in the management of systemic lupus erythematosus, a EULAR task force recommended that the type and severity of organ involvement should determine dose, with a long-term goal of maintaining the dose < 5 mg/d or possibly withdrawing it.
EULAR also recommends GC bridging when initiating or changing conventional synthetic (cs) DMARDs. This effectively dismisses the use of GCs when using biologic DMARDs or targeted synthetic DMARDs. As a bridging therapy, EULAR recommends either a single parenteral dose of GC or a predefined tapering or discontinuation scheme within 3 months, when starting an oral GC.
Low-Dose Approach Gains Ground
While saying he’d be the first physician to eliminate GCs whenever possible, Dr. Buttgereit made the case before the EULAR Congress that GCs in low doses could still play a role in treatment.
Many physicians believe that very low doses between 2 and 4 mg/d are a realistic therapy option for RA, he said, adding that a mean daily usage < 5 mg could be used over a longer period with relatively low risk.
Several studies he coauthored tested the 5-mg approach. The GLORIA trial compared 5 mg/d prednisolone and placebo in 451 patients aged 65 years and older with active RA over the course of 2 years. The researchers found that patients on prednisolone had a mean Disease Activity Score in 28 joints (DAS28) that was 0.37 points lower and mean joint damage score that was 1.7 points lower than those of patients on placebo, suggesting that the GC had long-term benefits in these patients with RA.
The tradeoff was a 24% increase in the risk of having at least one adverse event of special interest, but most of these events were non-severe infections, Dr. Buttgereit said.
Another study, the SEMIRA trial, assigned 128 patients to a continued regimen of prednisone 5 mg/d for 24 weeks. Another group of 131 patients received a tapered-prednisone regimen. All patients received tocilizumab 162 mg with or without csDMARDs, maintained at stable doses.
Patients in the first cohort achieved superior disease activity control than those in the tapered regimen group. “The side effects showed that in the tapering prednisone group, there were more treatment-emergent adverse effects in this double-blind trial as compared to the continued prednisone group,” Dr. Buttgereit said.
One limitation of the SEMIRA trial was that it studied the effect of tocilizumab as a GC-sparing agent, and it didn’t consider using a tumor necrosis factor or Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitor, which might have a more potent effect on pain and GC dose reduction, Dr. Adami said. “Why do we need to use glucocorticoids if we know they might be detrimental, if we know there might be some other option in our armamentarium?”
Other studies have shown that low-dose GC protocols can be used with standard treatment, according to Sebastian E. Sattui, MD, assistant professor of medicine and director of the Vasculitis Center at the University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine.
“Examples of this are the LoVAS and PEXIVAS studies for antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody-associated [ANCA] vasculitis. This has been highlighted in existing treatment recommendations for ANCA vasculitis and systemic lupus erythematosus nephritis,” Dr. Sattui said.
Two-year results from LoVAS showed noninferiority in remission induction rates and rates of relapse and significantly less frequent serious adverse events between a reduced-dose GC regimen at 0.5 mg/kg/d and conventional high-dose GC regimen at 1 mg/kg/d plus rituximab for ANCA vasculitis.
PEXIVAS demonstrated the noninferiority of a reduced-dose regimen of GCs vs a standard-dose regimen with respect to death or end-stage kidney disease in patients with severe disease involvement.
Debating the Toxicity Threshold
Are low GC dosages significantly associated with adverse events like mortality, cardiovascular, or diabetes risk? It depends on who you ask.
Much of the toxicity data on GCs come from inadequately powered or controlled studies and often refer to doses that currently are considered too high, Dr. Buttgereit said. His presentation highlighted a study from Hong Kong, a time-varying analysis of GC dose and incident risk for major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE) in more than 12,000 patients with RA. Researchers found that GC regimens ≥ 5 mg/d significantly increased the risk for MACE. Comparatively, doses below this threshold did not confer excessive risk, he said.
Low-dose GCs are lesser toxic than high-dose GCs, noted Joan Merrill, MD, a professor with the Arthritis and Clinical Immunology Research Program at The University of Oklahoma Health Sciences Center, Oklahoma City. “There may be less weight gain, less chance of acne, and less risk for all the slower, more organ-threatening side effects.”
Dr. Merrill, who cares for patients with lupus, said physicians can keep lupus in check for years, using constant, low-dose GCs. “The one thing we know is that steroids work.” But over many years, damage may still occur, she cautioned.
But even a low dose could present health problems to patients. The GLORIA trial of patients with RA, which showed promising results on disease control with 5 mg/d, found an association between GCs and increased risk for infection and osteoporosis. There was a higher overall risk for adverse events related to skin, infections, and bone mineral density changes. Bone mineral density loss and fractures were more common in the GC group, Adami noted.
Surprisingly, some of the trial’s authors said patients could handle such adverse events. But what is your threshold of “acceptable?” Dr. Adami asked.
Other studies have found associations between low-dose GC regimens and adverse events. Researchers of a 2023 study reported bone mineral density loss in patients with inflammatory rheumatic musculoskeletal diseases on a 2.5-mg/d regimen. Another decade-long analysis of Medicare and Optum data found a link between serious infection and low-dose GCs in patients receiving stable DMARD therapy. Investigators reported risk even at daily doses of ≤ 5 mg.
Dr. Adami acknowledged that these studies may have “confounding by indication,” a channeling bias in which people with severe RA are more likely to be treated with GCs. For this reason, it’s a challenge to disentangle the independent role of GCs from the disease activity itself, he said.
The big question is: Why don’t these observational studies show an increased risk for adverse events with biologic drugs that are given to more severe patients? “That confirms the hypothesis that confounding by indication for GCs is minimal, and most of the risk is driven by GCs,” he said.
Tapering Options Across Diseases
Rheumatologists in the field continue to navigate GC-tapering options and treatment combinations that reduce the cumulative use of GCs over time, finding their own solutions based on the conditions they treat.
In his EULAR presentation, Dr. Buttgereit suggested that current therapeutic approaches for RA may be too narrow when they don’t consider the possibility of including very low doses of GCs.
For RA, “why shouldn’t we not do a combination of something like methotrexate plus a JAK inhibitor or a biological,” plus a very low dose of GCs < 5 mg/d, he asked.
However, Dr. Adami said he generally avoids GCs if RA disease activity is not severe (based on DAS28) and if the patient has a visual analog scale pain score < 7. “Nonetheless, even in patients with more severe disease, I would avoid GCs for more than 3 months. Usually, 1 month of steroids, tapered rapidly and discontinued.”
All patients should receive an appropriate treat-to-target strategy with csDMARDs and biologics if needed, he added.
A patient coming to clinic with difficult-to-treat RA who chronically uses GCs deserves special attention. The priority is bone protection with an anti-osteoporosis medication. “I found that JAK inhibitors, in some cases, help with the discontinuation of steroids, especially in those with residual pain. Therefore, I would think of switching medication,” Dr. Adami said.
For polymyalgia rheumatica, most clinicians will likely try to taper GCs around 52 weeks, similar to ACR/EULAR guidelines, according to Robert F. Spiera, MD, director of the Scleroderma and Vasculitis Program at Hospital for Special Surgery, New York City.
“I usually challenge patients with a more rapid taper, hoping to get them off GCs in 6 or even 4 months in some patients, recognizing that many will flare, and we will have to bump up their GC dose,” Dr. Spiera said.
For patients with lupus, GCs remain the most effective treatment, Dr. Merrill said. “The toxicities are unacceptable for long-term use. So we try to get in fast when we need them and get out as soon as possible after that, tapering down as fast as the patient can tolerate it.”
Unfortunately, that’s not always as fast as the clinician or patient hopes for, she said.
“New treatments are being developed that may help us avoid the constant use of steroids. However, it would be wonderful to see how these new safer types of steroids work in lupus,” she said.
Minimizing GCs is an important goal that should be considered and aimed for in every single patient, Dr. Sattui said. “Risk of GC toxicity should be considered in all patients, assessing [them] for cardiometabolic comorbidities, bone metabolic diseases, risk of infection, among many others.” Sticking to one specific GC-tapering protocol might not be achievable for every patient, however, based on disease characteristics, response, and other factors, he added.
Monitoring for GC toxicity is important and should occur during and after every single clinical visit, he emphasized. Patient education is critical. “Different tools have been developed and employed in clinical trials, both patient- and physician-facing instruments. Implementation to clinical practice of some of these should be the next step in order to achieve a more systematic approach.”
What to Consider for AI Symptoms
Clinicians also need to address AI in patients who are coming off GCs, Dr. Sattui said. He advised that symptoms suggestive of AI, including malaise, fatigue, nausea, and muscle and/or joint pain, should guide testing.
Even in the absence of symptoms, clinicians should consider assessing patients who have been on high doses for prolonged periods or obese or older adults who might be at a high risk for AI. “Signs to consider include weight loss, hypotension, or orthostatism,” he said.
Differentiating between AI symptoms and symptoms from the underlying disease can be a challenge. This requires a physical exam and workup, including morning serum cortisol. Collaboration with endocrinology colleagues and other treating providers is important, as well as patient education of symptoms and monitoring for possible adjustments in treating AI and other acute diseases, he said.
Dr. Smolen received research grants from AbbVie, AstraZeneca, Galapagos, and Eli Lilly. Dr. Adami received speaker fees and/or was a consultant for Galapagos, Theramex, Amgen, Eli Lilly, UCB, Fresenius Kabi, Bristol Myers Squibb, Abiogen, and Pfizer. Dr. Buttgereit’s disclosures included AbbVie, AstraZeneca, Grünenthal, Horizon Therapeutics, Mundipharma, Pfizer, and Roche. Dr. Merrill had no relevant disclosures. Dr. Spiera has been a consultant for Roche-Genentech, GlaxoSmithKline, Sanofi, ChemoCentryx, Novartis, Galderma, Cytori, AstraZeneca, Amgen, and AbbVie and received research grant support from GlaxoSmithKline, Roche-Genentech, AstraZeneca, Bristol Myers Squibb, Kadmon, Boehringer Ingelheim, Cytori, ChemoCentryx, Corbus, Novartis, Amgen, and AbbVie. Dr. Sattui reported receiving research support from AstraZeneca and GlaxoSmithKline (clinical trials), receiving consulting fees from Sanofi (funds toward research support), serving on advisory boards for Sanofi and Amgen (funds toward research support), and receiving speaker fees from Fresenius Kabi (funds toward research support).
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Now, 75 years after the first presentations were made on the “sensational” effects of cortisone in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis (RA), glucocorticoids (GCs) are still highly relevant and widely used in the management of RA and other immune-mediated inflammatory diseases.
“It makes me smile because this is such an old drug, and we need it still so much. It still hasn’t been replaced,” Josef S. Smolen, MD, observed at annual European Congress of Rheumatology.
At low doses, GCs are highly effective as anti-inflammatory and anti-destructive agents in RA and many other diseases, said Dr. Smolen, a rheumatologist and immunologist and professor emeritus at the Medical University of Vienna, Austria.
But even after all this time, the mechanisms that lead to efficacy vs toxicity have yet to be clarified. “Such separation may provide further insights into future treatment options,” said Dr. Smolen.
His comments, made during a special session on the 75th anniversary of GCs at EULAR 2024, underscore the endless saga to manage GCs while finding better alternatives. Opinions differ on what the research says on toxicity and dosage and whether a long-term, low-dose option is viable. Alternative therapies are being studied, but those endeavors are still in the early stages of development.
While GCs are still used chronically in many patients, clinicians should always attempt to discontinue them whenever possible, Frank Buttgereit, MD, professor of rheumatology and deputy head of the Department of Rheumatology and Clinical Immunology at Charité – Universitätsmedizin Berlin, Germany, told attendees at the congress. Up to 60% of patients in registries use GCs, and many patients with early or established RA enter randomized controlled trials on GCs as maintenance therapy.
The ubiquity of GC usage stems in part from overprescribing by non-rheumatologist physicians who might not have access to or aren’t aware of newer biologics or disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs). “We see a lot of patients on long-term glucocorticoids, chronic use for years and years, decades of glucocorticoids,” said Giovanni Adami, MD, PhD, a rheumatologist at the University of Verona, Italy, who has coauthored several studies on the use of GCs.
Societies Agree: Discontinue as Fast as Possible
GCs have been associated with a long list of adverse events, most notably Cushing syndrome, hypertension, cardiovascular disease, osteoporosis, myopathy, peptic ulcer, adrenal insufficiency (AI), infections, mood disorders, ophthalmologic disorders such as cataracts, skin disorders, menstrual septic necrosis, and pancreatitis.
Dose matters, Dr. Smolen said, citing studies that found that cumulative GC doses of 1000 or 1100 mg increase risks. One study by German researchers found that doses above 10 mg/d significantly raised the hazard ratio for death.
Because high disease activity is also associated with an equally high mortality risk, “we have to balance this out: Active disease vs glucocorticoid use, especially in countries that have less access to modern therapies than we have in the more affluent Western regions,” Dr. Smolen said.
Rheumatology societies generally agree that clinicians should try to minimize GC use or eventually discontinue the therapy.
The American College of Rheumatology recommends not using GCs as part of the first-line treatment of RA. “And if you want to use [them], you should do that for less than 3 months, taper and discontinue as fast as possible, and use the lowest dose possible,” Dr. Adami said.
EULAR’s recommendation is more nuanced in that it allows for a lower dose but gives physicians more choice in how they want to handle GCs, Dr. Adami said. The task force added that all patients should try to taper down or discontinue as fast as possible, he said.
For GCs in the management of systemic lupus erythematosus, a EULAR task force recommended that the type and severity of organ involvement should determine dose, with a long-term goal of maintaining the dose < 5 mg/d or possibly withdrawing it.
EULAR also recommends GC bridging when initiating or changing conventional synthetic (cs) DMARDs. This effectively dismisses the use of GCs when using biologic DMARDs or targeted synthetic DMARDs. As a bridging therapy, EULAR recommends either a single parenteral dose of GC or a predefined tapering or discontinuation scheme within 3 months, when starting an oral GC.
Low-Dose Approach Gains Ground
While saying he’d be the first physician to eliminate GCs whenever possible, Dr. Buttgereit made the case before the EULAR Congress that GCs in low doses could still play a role in treatment.
Many physicians believe that very low doses between 2 and 4 mg/d are a realistic therapy option for RA, he said, adding that a mean daily usage < 5 mg could be used over a longer period with relatively low risk.
Several studies he coauthored tested the 5-mg approach. The GLORIA trial compared 5 mg/d prednisolone and placebo in 451 patients aged 65 years and older with active RA over the course of 2 years. The researchers found that patients on prednisolone had a mean Disease Activity Score in 28 joints (DAS28) that was 0.37 points lower and mean joint damage score that was 1.7 points lower than those of patients on placebo, suggesting that the GC had long-term benefits in these patients with RA.
The tradeoff was a 24% increase in the risk of having at least one adverse event of special interest, but most of these events were non-severe infections, Dr. Buttgereit said.
Another study, the SEMIRA trial, assigned 128 patients to a continued regimen of prednisone 5 mg/d for 24 weeks. Another group of 131 patients received a tapered-prednisone regimen. All patients received tocilizumab 162 mg with or without csDMARDs, maintained at stable doses.
Patients in the first cohort achieved superior disease activity control than those in the tapered regimen group. “The side effects showed that in the tapering prednisone group, there were more treatment-emergent adverse effects in this double-blind trial as compared to the continued prednisone group,” Dr. Buttgereit said.
One limitation of the SEMIRA trial was that it studied the effect of tocilizumab as a GC-sparing agent, and it didn’t consider using a tumor necrosis factor or Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitor, which might have a more potent effect on pain and GC dose reduction, Dr. Adami said. “Why do we need to use glucocorticoids if we know they might be detrimental, if we know there might be some other option in our armamentarium?”
Other studies have shown that low-dose GC protocols can be used with standard treatment, according to Sebastian E. Sattui, MD, assistant professor of medicine and director of the Vasculitis Center at the University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine.
“Examples of this are the LoVAS and PEXIVAS studies for antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody-associated [ANCA] vasculitis. This has been highlighted in existing treatment recommendations for ANCA vasculitis and systemic lupus erythematosus nephritis,” Dr. Sattui said.
Two-year results from LoVAS showed noninferiority in remission induction rates and rates of relapse and significantly less frequent serious adverse events between a reduced-dose GC regimen at 0.5 mg/kg/d and conventional high-dose GC regimen at 1 mg/kg/d plus rituximab for ANCA vasculitis.
PEXIVAS demonstrated the noninferiority of a reduced-dose regimen of GCs vs a standard-dose regimen with respect to death or end-stage kidney disease in patients with severe disease involvement.
Debating the Toxicity Threshold
Are low GC dosages significantly associated with adverse events like mortality, cardiovascular, or diabetes risk? It depends on who you ask.
Much of the toxicity data on GCs come from inadequately powered or controlled studies and often refer to doses that currently are considered too high, Dr. Buttgereit said. His presentation highlighted a study from Hong Kong, a time-varying analysis of GC dose and incident risk for major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE) in more than 12,000 patients with RA. Researchers found that GC regimens ≥ 5 mg/d significantly increased the risk for MACE. Comparatively, doses below this threshold did not confer excessive risk, he said.
Low-dose GCs are lesser toxic than high-dose GCs, noted Joan Merrill, MD, a professor with the Arthritis and Clinical Immunology Research Program at The University of Oklahoma Health Sciences Center, Oklahoma City. “There may be less weight gain, less chance of acne, and less risk for all the slower, more organ-threatening side effects.”
Dr. Merrill, who cares for patients with lupus, said physicians can keep lupus in check for years, using constant, low-dose GCs. “The one thing we know is that steroids work.” But over many years, damage may still occur, she cautioned.
But even a low dose could present health problems to patients. The GLORIA trial of patients with RA, which showed promising results on disease control with 5 mg/d, found an association between GCs and increased risk for infection and osteoporosis. There was a higher overall risk for adverse events related to skin, infections, and bone mineral density changes. Bone mineral density loss and fractures were more common in the GC group, Adami noted.
Surprisingly, some of the trial’s authors said patients could handle such adverse events. But what is your threshold of “acceptable?” Dr. Adami asked.
Other studies have found associations between low-dose GC regimens and adverse events. Researchers of a 2023 study reported bone mineral density loss in patients with inflammatory rheumatic musculoskeletal diseases on a 2.5-mg/d regimen. Another decade-long analysis of Medicare and Optum data found a link between serious infection and low-dose GCs in patients receiving stable DMARD therapy. Investigators reported risk even at daily doses of ≤ 5 mg.
Dr. Adami acknowledged that these studies may have “confounding by indication,” a channeling bias in which people with severe RA are more likely to be treated with GCs. For this reason, it’s a challenge to disentangle the independent role of GCs from the disease activity itself, he said.
The big question is: Why don’t these observational studies show an increased risk for adverse events with biologic drugs that are given to more severe patients? “That confirms the hypothesis that confounding by indication for GCs is minimal, and most of the risk is driven by GCs,” he said.
Tapering Options Across Diseases
Rheumatologists in the field continue to navigate GC-tapering options and treatment combinations that reduce the cumulative use of GCs over time, finding their own solutions based on the conditions they treat.
In his EULAR presentation, Dr. Buttgereit suggested that current therapeutic approaches for RA may be too narrow when they don’t consider the possibility of including very low doses of GCs.
For RA, “why shouldn’t we not do a combination of something like methotrexate plus a JAK inhibitor or a biological,” plus a very low dose of GCs < 5 mg/d, he asked.
However, Dr. Adami said he generally avoids GCs if RA disease activity is not severe (based on DAS28) and if the patient has a visual analog scale pain score < 7. “Nonetheless, even in patients with more severe disease, I would avoid GCs for more than 3 months. Usually, 1 month of steroids, tapered rapidly and discontinued.”
All patients should receive an appropriate treat-to-target strategy with csDMARDs and biologics if needed, he added.
A patient coming to clinic with difficult-to-treat RA who chronically uses GCs deserves special attention. The priority is bone protection with an anti-osteoporosis medication. “I found that JAK inhibitors, in some cases, help with the discontinuation of steroids, especially in those with residual pain. Therefore, I would think of switching medication,” Dr. Adami said.
For polymyalgia rheumatica, most clinicians will likely try to taper GCs around 52 weeks, similar to ACR/EULAR guidelines, according to Robert F. Spiera, MD, director of the Scleroderma and Vasculitis Program at Hospital for Special Surgery, New York City.
“I usually challenge patients with a more rapid taper, hoping to get them off GCs in 6 or even 4 months in some patients, recognizing that many will flare, and we will have to bump up their GC dose,” Dr. Spiera said.
For patients with lupus, GCs remain the most effective treatment, Dr. Merrill said. “The toxicities are unacceptable for long-term use. So we try to get in fast when we need them and get out as soon as possible after that, tapering down as fast as the patient can tolerate it.”
Unfortunately, that’s not always as fast as the clinician or patient hopes for, she said.
“New treatments are being developed that may help us avoid the constant use of steroids. However, it would be wonderful to see how these new safer types of steroids work in lupus,” she said.
Minimizing GCs is an important goal that should be considered and aimed for in every single patient, Dr. Sattui said. “Risk of GC toxicity should be considered in all patients, assessing [them] for cardiometabolic comorbidities, bone metabolic diseases, risk of infection, among many others.” Sticking to one specific GC-tapering protocol might not be achievable for every patient, however, based on disease characteristics, response, and other factors, he added.
Monitoring for GC toxicity is important and should occur during and after every single clinical visit, he emphasized. Patient education is critical. “Different tools have been developed and employed in clinical trials, both patient- and physician-facing instruments. Implementation to clinical practice of some of these should be the next step in order to achieve a more systematic approach.”
What to Consider for AI Symptoms
Clinicians also need to address AI in patients who are coming off GCs, Dr. Sattui said. He advised that symptoms suggestive of AI, including malaise, fatigue, nausea, and muscle and/or joint pain, should guide testing.
Even in the absence of symptoms, clinicians should consider assessing patients who have been on high doses for prolonged periods or obese or older adults who might be at a high risk for AI. “Signs to consider include weight loss, hypotension, or orthostatism,” he said.
Differentiating between AI symptoms and symptoms from the underlying disease can be a challenge. This requires a physical exam and workup, including morning serum cortisol. Collaboration with endocrinology colleagues and other treating providers is important, as well as patient education of symptoms and monitoring for possible adjustments in treating AI and other acute diseases, he said.
Dr. Smolen received research grants from AbbVie, AstraZeneca, Galapagos, and Eli Lilly. Dr. Adami received speaker fees and/or was a consultant for Galapagos, Theramex, Amgen, Eli Lilly, UCB, Fresenius Kabi, Bristol Myers Squibb, Abiogen, and Pfizer. Dr. Buttgereit’s disclosures included AbbVie, AstraZeneca, Grünenthal, Horizon Therapeutics, Mundipharma, Pfizer, and Roche. Dr. Merrill had no relevant disclosures. Dr. Spiera has been a consultant for Roche-Genentech, GlaxoSmithKline, Sanofi, ChemoCentryx, Novartis, Galderma, Cytori, AstraZeneca, Amgen, and AbbVie and received research grant support from GlaxoSmithKline, Roche-Genentech, AstraZeneca, Bristol Myers Squibb, Kadmon, Boehringer Ingelheim, Cytori, ChemoCentryx, Corbus, Novartis, Amgen, and AbbVie. Dr. Sattui reported receiving research support from AstraZeneca and GlaxoSmithKline (clinical trials), receiving consulting fees from Sanofi (funds toward research support), serving on advisory boards for Sanofi and Amgen (funds toward research support), and receiving speaker fees from Fresenius Kabi (funds toward research support).
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM EULAR 2024
Infection Co-occurring With Lupus Raises Flare Risk
TOPLINE:
Intercurrent infections are associated with an increased risk for systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) flares within 3 months, with major infections associated with a 7.4 times higher risk for major flares.
METHODOLOGY:
- The researchers prospectively examined the association between intercurrent infections and subsequent SLE flares in 203 patients (median age, 40 years; 91% women) with SLE from the Amsterdam SLE cohort study.
- SLE flares were defined as an increase in disease activity combined with an intensification of immunosuppressive therapy. They were categorized into minor and major flares according to the severity and required treatment.
- Major infections were defined as those requiring hospital admission or intravenous antibiotic therapy, while minor infections did not require hospital admission.
- The risk interval for the occurrence of a disease flare was defined as 3 months from the index date of an infection.
- Patients were followed for a median duration of 6 years.
TAKEAWAY:
- The incidence of major and minor infections was 5.3 (95% CI, 4.1-6.9) and 63.9 per 100 patient-years (95% CI, 59.3-69.0), respectively.
- Intercurrent infections were associated with a 1.9 times higher risk for SLE flares within 3 months (95% CI, 1.3-2.9).
- Intercurrent infections were significantly associated with minor SLE flares (hazard ratio, 1.9; 95% CI, 1.2-3.0) but not with major flares.
- Major infections were linked to a 7.4 times higher risk for major SLE flares within 3 months (95% CI, 2.2-24.6).
IN PRACTICE:
“This finding stresses the importance of awareness and strict monitoring of disease activity in patients with SLE suffering a major infection and prompt adequate treatment in case of the development of a disease flare,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Fatma el Hadiyen, Amsterdam Rheumatology and Immunology Center, Amsterdam University Medical Center in the Netherlands. It was published online on July 1, 2024, in Lupus Science & Medicine.
LIMITATIONS:
The reliance on patient recall for minor infections may have introduced recall bias. The small number of patients with identified causative organisms limited the generalizability of the findings. The Bootsma criteria were used for defining SLE flares, which may not align with more recent international standards.
DISCLOSURES:
No specific funding source was reported. One author reported receiving personal fees from various pharmaceutical companies outside the submitted work.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Intercurrent infections are associated with an increased risk for systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) flares within 3 months, with major infections associated with a 7.4 times higher risk for major flares.
METHODOLOGY:
- The researchers prospectively examined the association between intercurrent infections and subsequent SLE flares in 203 patients (median age, 40 years; 91% women) with SLE from the Amsterdam SLE cohort study.
- SLE flares were defined as an increase in disease activity combined with an intensification of immunosuppressive therapy. They were categorized into minor and major flares according to the severity and required treatment.
- Major infections were defined as those requiring hospital admission or intravenous antibiotic therapy, while minor infections did not require hospital admission.
- The risk interval for the occurrence of a disease flare was defined as 3 months from the index date of an infection.
- Patients were followed for a median duration of 6 years.
TAKEAWAY:
- The incidence of major and minor infections was 5.3 (95% CI, 4.1-6.9) and 63.9 per 100 patient-years (95% CI, 59.3-69.0), respectively.
- Intercurrent infections were associated with a 1.9 times higher risk for SLE flares within 3 months (95% CI, 1.3-2.9).
- Intercurrent infections were significantly associated with minor SLE flares (hazard ratio, 1.9; 95% CI, 1.2-3.0) but not with major flares.
- Major infections were linked to a 7.4 times higher risk for major SLE flares within 3 months (95% CI, 2.2-24.6).
IN PRACTICE:
“This finding stresses the importance of awareness and strict monitoring of disease activity in patients with SLE suffering a major infection and prompt adequate treatment in case of the development of a disease flare,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Fatma el Hadiyen, Amsterdam Rheumatology and Immunology Center, Amsterdam University Medical Center in the Netherlands. It was published online on July 1, 2024, in Lupus Science & Medicine.
LIMITATIONS:
The reliance on patient recall for minor infections may have introduced recall bias. The small number of patients with identified causative organisms limited the generalizability of the findings. The Bootsma criteria were used for defining SLE flares, which may not align with more recent international standards.
DISCLOSURES:
No specific funding source was reported. One author reported receiving personal fees from various pharmaceutical companies outside the submitted work.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Intercurrent infections are associated with an increased risk for systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) flares within 3 months, with major infections associated with a 7.4 times higher risk for major flares.
METHODOLOGY:
- The researchers prospectively examined the association between intercurrent infections and subsequent SLE flares in 203 patients (median age, 40 years; 91% women) with SLE from the Amsterdam SLE cohort study.
- SLE flares were defined as an increase in disease activity combined with an intensification of immunosuppressive therapy. They were categorized into minor and major flares according to the severity and required treatment.
- Major infections were defined as those requiring hospital admission or intravenous antibiotic therapy, while minor infections did not require hospital admission.
- The risk interval for the occurrence of a disease flare was defined as 3 months from the index date of an infection.
- Patients were followed for a median duration of 6 years.
TAKEAWAY:
- The incidence of major and minor infections was 5.3 (95% CI, 4.1-6.9) and 63.9 per 100 patient-years (95% CI, 59.3-69.0), respectively.
- Intercurrent infections were associated with a 1.9 times higher risk for SLE flares within 3 months (95% CI, 1.3-2.9).
- Intercurrent infections were significantly associated with minor SLE flares (hazard ratio, 1.9; 95% CI, 1.2-3.0) but not with major flares.
- Major infections were linked to a 7.4 times higher risk for major SLE flares within 3 months (95% CI, 2.2-24.6).
IN PRACTICE:
“This finding stresses the importance of awareness and strict monitoring of disease activity in patients with SLE suffering a major infection and prompt adequate treatment in case of the development of a disease flare,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Fatma el Hadiyen, Amsterdam Rheumatology and Immunology Center, Amsterdam University Medical Center in the Netherlands. It was published online on July 1, 2024, in Lupus Science & Medicine.
LIMITATIONS:
The reliance on patient recall for minor infections may have introduced recall bias. The small number of patients with identified causative organisms limited the generalizability of the findings. The Bootsma criteria were used for defining SLE flares, which may not align with more recent international standards.
DISCLOSURES:
No specific funding source was reported. One author reported receiving personal fees from various pharmaceutical companies outside the submitted work.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Debate: Should Dermatologists or Rheumatologists Manage Musculoskeletal Symptoms in Patients With Psoriasis?
SEATTLE — That was the subject of a debate between a dermatologist and a rheumatologist at the annual meeting of the Group for Research and Assessment of Psoriasis and Psoriatic Arthritis.
Fabian Proft, MD, the rheumatologist, spoke first and emphasized the potential that MSK symptoms are a sign of psoriatic arthritis (PsA) and therefore should be managed by a rheumatologist.
“Obviously, the rheumatologist perspective [is that] I should be in the driver’s seat when taking care of patient with psoriasis and MSK symptoms, but I will still need to have a copilot there: [The dermatologist] will have a slot,” said Dr. Proft, who is a rheumatologist at Charité — Universitätsmedizin Berlin.
“It’s so important that we make the correct and early diagnosis of [psoriatic arthritis and psoriasis] symptoms,” said Dr. Proft. He specifically called out cases where patients have symptoms that are difficult to determine, whether the cause is inflammatory, and when experience with imaging can be a key factor in the diagnosis.
It’s important not to overdiagnose or overtreat patients, he said, providing an example of a patient with psoriasis who had been training for a marathon. The MRI image suggested that his Achilles tendonitis pain was related to his athletic training, not PsA-associated inflammation. “So I think this is very important that you have the knowledge to read MRIs, and especially also carefully assessing them so as not to overdiagnose patients,” said Dr. Proft.
Dermatologist Rebuttal
In her rebuttal, Laura Savage, MD, PhD, emphasized the need for more of a coequal partnership between the two specialties because of the ability of dermatologists to intervene early in the treatment and prevention of PsA.
“Traditionally, I agree rheumatologists would solely be responsible for the assessment and the management of psoriatic arthritis, but I think that paradigm has shifted in part due to the increased recognition of the need for earlier intervention to limit disease progression and to reduce or even prevent functional limitation,” said Dr. Savage, who is a consultant dermatologist at Leeds Teaching Hospitals NHS Trust and a senior lecturer at the University of Leeds, Leeds, England.
Ideally, molecular biomarkers would be available to predict the development of PsA, but there aren’t any. Still, “we have a huge biomarker in the form of the skin, and it’s recognized that the majority of patients who will develop psoriatic arthritis will have antecedent psoriasis in about 70% of cases,” Dr. Savage said. “There’s a typical time delay of around 7-12 years between the onset of the skin [disease] and the patients developing psoriatic arthritis, and so many of them are going to be into the care of other healthcare practitioners, and particularly the care of dermatologists.”
Dermatologists may also be able to play a role in the prevention of PsA, according to Dr. Savage. In one retrospective study, treatment of skin lesions with biologics was associated with a reduced frequency of progression to PsA (11.1% vs 16.4%) over 10 years (P = .0006). Studies with tumor necrosis factor inhibitors and other interventions have shown similar results.
Such findings have led to the treat intercept strategy, which targets patients with psoriasis who have risk factors for transition to PsA — such as nail pitting, gluteal cleft disease, scalp disease, type 2 diabetes, obesity, and a first-degree relative with PsA — as well as symptoms of prodromal PSA, such as arthralgia and fatigue.
“I think dermatologists are aware of the need to not leave our patients languishing on these therapies and actually escalating them onto effective treatments that may also be able to treat early psoriatic arthritis. We could be more mindful about our choice of treatments for these patients, going on to thinking about their increased risk of PSA and trying to intercept,” Dr. Savage said. “What we don’t want is our patients to be developing these musculoskeletal symptoms of pain and stiffness and functional limitation and disability. We want to be treating the patients with musculoskeletal symptoms of that earlier prodromal phase when they’re developing arthralgia and fatigue.”
She conceded that more complicated patients are good candidates for care by the rheumatologist. “You can do your fancy imaging, and we’ll leave that to you, and the difficult-to-treat patients to [the rheumatologist], but actually we need to just get on and treat them,” she said. “One could argue as well that as a dermatologist, I’m likely to broaden my horizons in terms of choice of therapy and treat all of the domains of the patient. So I would argue that actually it should be the dermatologist who is in that driving seat, particularly when it comes to the management of early psoriatic arthritis, and actually what we should be doing is driving our patients and steering them to earlier intervention and better control for all domains of disease.”
Collaborative Care
During the follow-up discussion, both Dr. Proft and Dr. Savage agreed that dermatologists and rheumatologists should be working together in managing patients. “What we need to do is steer our patients toward collaborative care with our rheumatologists by trying to minimize delays to treatment, by working together in parallel clinics, combined clinics, and on virtual [multidisciplinary teams],” said Dr. Savage.
Dr. Proft agreed. “We should join forces and make decisions together.”
Dr. Savage and Dr. Proft did not provide any financial disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
SEATTLE — That was the subject of a debate between a dermatologist and a rheumatologist at the annual meeting of the Group for Research and Assessment of Psoriasis and Psoriatic Arthritis.
Fabian Proft, MD, the rheumatologist, spoke first and emphasized the potential that MSK symptoms are a sign of psoriatic arthritis (PsA) and therefore should be managed by a rheumatologist.
“Obviously, the rheumatologist perspective [is that] I should be in the driver’s seat when taking care of patient with psoriasis and MSK symptoms, but I will still need to have a copilot there: [The dermatologist] will have a slot,” said Dr. Proft, who is a rheumatologist at Charité — Universitätsmedizin Berlin.
“It’s so important that we make the correct and early diagnosis of [psoriatic arthritis and psoriasis] symptoms,” said Dr. Proft. He specifically called out cases where patients have symptoms that are difficult to determine, whether the cause is inflammatory, and when experience with imaging can be a key factor in the diagnosis.
It’s important not to overdiagnose or overtreat patients, he said, providing an example of a patient with psoriasis who had been training for a marathon. The MRI image suggested that his Achilles tendonitis pain was related to his athletic training, not PsA-associated inflammation. “So I think this is very important that you have the knowledge to read MRIs, and especially also carefully assessing them so as not to overdiagnose patients,” said Dr. Proft.
Dermatologist Rebuttal
In her rebuttal, Laura Savage, MD, PhD, emphasized the need for more of a coequal partnership between the two specialties because of the ability of dermatologists to intervene early in the treatment and prevention of PsA.
“Traditionally, I agree rheumatologists would solely be responsible for the assessment and the management of psoriatic arthritis, but I think that paradigm has shifted in part due to the increased recognition of the need for earlier intervention to limit disease progression and to reduce or even prevent functional limitation,” said Dr. Savage, who is a consultant dermatologist at Leeds Teaching Hospitals NHS Trust and a senior lecturer at the University of Leeds, Leeds, England.
Ideally, molecular biomarkers would be available to predict the development of PsA, but there aren’t any. Still, “we have a huge biomarker in the form of the skin, and it’s recognized that the majority of patients who will develop psoriatic arthritis will have antecedent psoriasis in about 70% of cases,” Dr. Savage said. “There’s a typical time delay of around 7-12 years between the onset of the skin [disease] and the patients developing psoriatic arthritis, and so many of them are going to be into the care of other healthcare practitioners, and particularly the care of dermatologists.”
Dermatologists may also be able to play a role in the prevention of PsA, according to Dr. Savage. In one retrospective study, treatment of skin lesions with biologics was associated with a reduced frequency of progression to PsA (11.1% vs 16.4%) over 10 years (P = .0006). Studies with tumor necrosis factor inhibitors and other interventions have shown similar results.
Such findings have led to the treat intercept strategy, which targets patients with psoriasis who have risk factors for transition to PsA — such as nail pitting, gluteal cleft disease, scalp disease, type 2 diabetes, obesity, and a first-degree relative with PsA — as well as symptoms of prodromal PSA, such as arthralgia and fatigue.
“I think dermatologists are aware of the need to not leave our patients languishing on these therapies and actually escalating them onto effective treatments that may also be able to treat early psoriatic arthritis. We could be more mindful about our choice of treatments for these patients, going on to thinking about their increased risk of PSA and trying to intercept,” Dr. Savage said. “What we don’t want is our patients to be developing these musculoskeletal symptoms of pain and stiffness and functional limitation and disability. We want to be treating the patients with musculoskeletal symptoms of that earlier prodromal phase when they’re developing arthralgia and fatigue.”
She conceded that more complicated patients are good candidates for care by the rheumatologist. “You can do your fancy imaging, and we’ll leave that to you, and the difficult-to-treat patients to [the rheumatologist], but actually we need to just get on and treat them,” she said. “One could argue as well that as a dermatologist, I’m likely to broaden my horizons in terms of choice of therapy and treat all of the domains of the patient. So I would argue that actually it should be the dermatologist who is in that driving seat, particularly when it comes to the management of early psoriatic arthritis, and actually what we should be doing is driving our patients and steering them to earlier intervention and better control for all domains of disease.”
Collaborative Care
During the follow-up discussion, both Dr. Proft and Dr. Savage agreed that dermatologists and rheumatologists should be working together in managing patients. “What we need to do is steer our patients toward collaborative care with our rheumatologists by trying to minimize delays to treatment, by working together in parallel clinics, combined clinics, and on virtual [multidisciplinary teams],” said Dr. Savage.
Dr. Proft agreed. “We should join forces and make decisions together.”
Dr. Savage and Dr. Proft did not provide any financial disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
SEATTLE — That was the subject of a debate between a dermatologist and a rheumatologist at the annual meeting of the Group for Research and Assessment of Psoriasis and Psoriatic Arthritis.
Fabian Proft, MD, the rheumatologist, spoke first and emphasized the potential that MSK symptoms are a sign of psoriatic arthritis (PsA) and therefore should be managed by a rheumatologist.
“Obviously, the rheumatologist perspective [is that] I should be in the driver’s seat when taking care of patient with psoriasis and MSK symptoms, but I will still need to have a copilot there: [The dermatologist] will have a slot,” said Dr. Proft, who is a rheumatologist at Charité — Universitätsmedizin Berlin.
“It’s so important that we make the correct and early diagnosis of [psoriatic arthritis and psoriasis] symptoms,” said Dr. Proft. He specifically called out cases where patients have symptoms that are difficult to determine, whether the cause is inflammatory, and when experience with imaging can be a key factor in the diagnosis.
It’s important not to overdiagnose or overtreat patients, he said, providing an example of a patient with psoriasis who had been training for a marathon. The MRI image suggested that his Achilles tendonitis pain was related to his athletic training, not PsA-associated inflammation. “So I think this is very important that you have the knowledge to read MRIs, and especially also carefully assessing them so as not to overdiagnose patients,” said Dr. Proft.
Dermatologist Rebuttal
In her rebuttal, Laura Savage, MD, PhD, emphasized the need for more of a coequal partnership between the two specialties because of the ability of dermatologists to intervene early in the treatment and prevention of PsA.
“Traditionally, I agree rheumatologists would solely be responsible for the assessment and the management of psoriatic arthritis, but I think that paradigm has shifted in part due to the increased recognition of the need for earlier intervention to limit disease progression and to reduce or even prevent functional limitation,” said Dr. Savage, who is a consultant dermatologist at Leeds Teaching Hospitals NHS Trust and a senior lecturer at the University of Leeds, Leeds, England.
Ideally, molecular biomarkers would be available to predict the development of PsA, but there aren’t any. Still, “we have a huge biomarker in the form of the skin, and it’s recognized that the majority of patients who will develop psoriatic arthritis will have antecedent psoriasis in about 70% of cases,” Dr. Savage said. “There’s a typical time delay of around 7-12 years between the onset of the skin [disease] and the patients developing psoriatic arthritis, and so many of them are going to be into the care of other healthcare practitioners, and particularly the care of dermatologists.”
Dermatologists may also be able to play a role in the prevention of PsA, according to Dr. Savage. In one retrospective study, treatment of skin lesions with biologics was associated with a reduced frequency of progression to PsA (11.1% vs 16.4%) over 10 years (P = .0006). Studies with tumor necrosis factor inhibitors and other interventions have shown similar results.
Such findings have led to the treat intercept strategy, which targets patients with psoriasis who have risk factors for transition to PsA — such as nail pitting, gluteal cleft disease, scalp disease, type 2 diabetes, obesity, and a first-degree relative with PsA — as well as symptoms of prodromal PSA, such as arthralgia and fatigue.
“I think dermatologists are aware of the need to not leave our patients languishing on these therapies and actually escalating them onto effective treatments that may also be able to treat early psoriatic arthritis. We could be more mindful about our choice of treatments for these patients, going on to thinking about their increased risk of PSA and trying to intercept,” Dr. Savage said. “What we don’t want is our patients to be developing these musculoskeletal symptoms of pain and stiffness and functional limitation and disability. We want to be treating the patients with musculoskeletal symptoms of that earlier prodromal phase when they’re developing arthralgia and fatigue.”
She conceded that more complicated patients are good candidates for care by the rheumatologist. “You can do your fancy imaging, and we’ll leave that to you, and the difficult-to-treat patients to [the rheumatologist], but actually we need to just get on and treat them,” she said. “One could argue as well that as a dermatologist, I’m likely to broaden my horizons in terms of choice of therapy and treat all of the domains of the patient. So I would argue that actually it should be the dermatologist who is in that driving seat, particularly when it comes to the management of early psoriatic arthritis, and actually what we should be doing is driving our patients and steering them to earlier intervention and better control for all domains of disease.”
Collaborative Care
During the follow-up discussion, both Dr. Proft and Dr. Savage agreed that dermatologists and rheumatologists should be working together in managing patients. “What we need to do is steer our patients toward collaborative care with our rheumatologists by trying to minimize delays to treatment, by working together in parallel clinics, combined clinics, and on virtual [multidisciplinary teams],” said Dr. Savage.
Dr. Proft agreed. “We should join forces and make decisions together.”
Dr. Savage and Dr. Proft did not provide any financial disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM GRAPPA 2024
Women’s Risk for Lupus Rises With Greater Intake of Ultraprocessed Foods
TOPLINE:
A higher intake of ultraprocessed foods increases the risk for systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) by over 50% in women. The risk doubled in those with anti–double-stranded DNA antibodies.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers assessed 204,175 women from two Nurses’ Health Study cohorts from 1984 to 2016.
- Participants completed semiquantitative food frequency questionnaires every 4 years for the assessment of dietary intake.
- Incident SLE cases were self-reported and confirmed using medical records, with 212 cases identified.
TAKEAWAY:
- A higher cumulative average daily intake of ultraprocessed foods was associated with a 56% increased risk for SLE (95% confidence interval [CI], 1.04-2.32).
- The risk for anti–double-stranded DNA antibody-positive SLE was more than doubled (hazard ratio, 2.05; 95% CI, 1.15-3.65).
- Sugar or artificially sweetened beverages were associated with a 45% increased risk for SLE (95% CI, 1.01-2.09).
- No significant interactions with body mass index were observed in the association between ultraprocessed food intake and SLE.
IN PRACTICE:
This study is too preliminary to have practical application.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Sinara Rossato, PhD, Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health, Boston. It was published online in Arthritis Care & Research.
LIMITATIONS:
The study’s generalizability is limited due to the predominantly White female population of registered nurses. The relatively high baseline age of participants may not fully capture the peak incidence age range for SLE. The observational nature of the study cannot establish causality between ultraprocessed food intake and SLE risk.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was supported by the National Institutes of Health. The authors did not declare any competing interests.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
A higher intake of ultraprocessed foods increases the risk for systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) by over 50% in women. The risk doubled in those with anti–double-stranded DNA antibodies.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers assessed 204,175 women from two Nurses’ Health Study cohorts from 1984 to 2016.
- Participants completed semiquantitative food frequency questionnaires every 4 years for the assessment of dietary intake.
- Incident SLE cases were self-reported and confirmed using medical records, with 212 cases identified.
TAKEAWAY:
- A higher cumulative average daily intake of ultraprocessed foods was associated with a 56% increased risk for SLE (95% confidence interval [CI], 1.04-2.32).
- The risk for anti–double-stranded DNA antibody-positive SLE was more than doubled (hazard ratio, 2.05; 95% CI, 1.15-3.65).
- Sugar or artificially sweetened beverages were associated with a 45% increased risk for SLE (95% CI, 1.01-2.09).
- No significant interactions with body mass index were observed in the association between ultraprocessed food intake and SLE.
IN PRACTICE:
This study is too preliminary to have practical application.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Sinara Rossato, PhD, Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health, Boston. It was published online in Arthritis Care & Research.
LIMITATIONS:
The study’s generalizability is limited due to the predominantly White female population of registered nurses. The relatively high baseline age of participants may not fully capture the peak incidence age range for SLE. The observational nature of the study cannot establish causality between ultraprocessed food intake and SLE risk.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was supported by the National Institutes of Health. The authors did not declare any competing interests.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
A higher intake of ultraprocessed foods increases the risk for systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) by over 50% in women. The risk doubled in those with anti–double-stranded DNA antibodies.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers assessed 204,175 women from two Nurses’ Health Study cohorts from 1984 to 2016.
- Participants completed semiquantitative food frequency questionnaires every 4 years for the assessment of dietary intake.
- Incident SLE cases were self-reported and confirmed using medical records, with 212 cases identified.
TAKEAWAY:
- A higher cumulative average daily intake of ultraprocessed foods was associated with a 56% increased risk for SLE (95% confidence interval [CI], 1.04-2.32).
- The risk for anti–double-stranded DNA antibody-positive SLE was more than doubled (hazard ratio, 2.05; 95% CI, 1.15-3.65).
- Sugar or artificially sweetened beverages were associated with a 45% increased risk for SLE (95% CI, 1.01-2.09).
- No significant interactions with body mass index were observed in the association between ultraprocessed food intake and SLE.
IN PRACTICE:
This study is too preliminary to have practical application.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Sinara Rossato, PhD, Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health, Boston. It was published online in Arthritis Care & Research.
LIMITATIONS:
The study’s generalizability is limited due to the predominantly White female population of registered nurses. The relatively high baseline age of participants may not fully capture the peak incidence age range for SLE. The observational nature of the study cannot establish causality between ultraprocessed food intake and SLE risk.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was supported by the National Institutes of Health. The authors did not declare any competing interests.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
CAR T-Cell Treatment Data Expands in Refractory Rheumatic Diseases, Demonstrating Consistent Efficacy
VIENNA — From a dozen or so studies and sessions devoted to the role of chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T cells in rheumatic diseases at the annual European Congress of Rheumatology, the message was uniformly positive, supporting growing evidence that drugs in this class are heading toward a paradigm shift in refractory rheumatic diseases.
Of the reports, an update from a 15-patient case series with at least 1 year of follow-up provides “the first long-term evidence of safety and efficacy in multiple rheumatic diseases,” according to Georg Schett, MD, PhD, director of rheumatology and immunology, University of Erlangen-Nürnberg, Erlangen, Germany.
The report of high rates of activity and low relative risk of serious adverse events from the same series was published earlier this year in The New England Journal of Medicine when the median follow-up was 15 months. Almost all of the patients have now completed at least 1 year of follow-up and about a third have completed more than 2 years.
SLE Is Frequently Targeted in CAR T-Cell Studies
The three rheumatic diseases represented in this series of patients, all of whom had failed multiple previous immune suppressive treatments, were systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), idiopathic inflammatory myositis (IIM), and systemic sclerosis (SSc). After the autologous T cells were harvested, they were expanded and transfected with the CD19 CAR. The proprietary investigational product, called MB-CART19.1 (Miltenyi Biotec), was administered in a single dose of one million cells per kg bodyweight.
The response rates have been, and continue to be, impressive. For the eight patients with SLE, all achieved the definition of remission in SLE criteria after one dose of treatment. Complete resolution of all major symptom types was achieved after 6 months of follow-up. So far, no patient has relapsed.
For the three patients with IIM, all reached the American College of Rheumatology–EULAR criteria for a major response. All creatine kinase levels had normalized by 3 months. In this group, there was one relapse, which occurred after 18 months of follow-up.
All four patients with SSc achieved a major response on the European Scleroderma Trials and Research (EUSTAR) group activity index. The median reduction from baseline in the EUSTAR score was 4.2 points, and this has been maintained in follow-up to date.
Remissions Have Persisted Off All Therapies
These remissions were achieved and maintained after a single dose of CAR T-cell therapy despite discontinuation of all immunosuppressive therapies. With the exception of the single relapse, all remissions have persisted through follow-up to date.
These responses were achieved with manageable side effects, according to Dr. Schett. The most serious adverse event was a grade 4 neutropenia that developed 4 months after receiving CAR T cells. It resolved with granulocyte colony-stimulating factor treatment. Cytokine release syndrome (CRS) has occurred in 10 patients, but it was grade 1 in eight patients and grade 2 in the others. There has been no neurotoxicity.
Almost all patients have experienced an infection during follow-up, but there has been no discernible pattern in relationship to the timing or types of infections. The most common have involved the upper respiratory tract and have been of mild severity, with cases disseminated similarly over early vs late follow-up. There was one case of pneumonia involving antibiotic treatment and a hospital stay, but it resolved.
Dr. Schett acknowledged that safety is a bigger concern in autoimmune diseases, which are often serious but rarely fatal, than in the hematologic malignancies for which CAR T cells were initially tested, but the low rates of serious adverse events in his and other early studies have supported the premise that the risks are not the same.
Asked specifically if CAR T cells can be considered a game changer in autoimmune rheumatic diseases, Dr. Schett was cautious. One reason is the CAR T cells are a complex therapy relative to biologic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs. He thinks, therefore, that much more data are needed to confirm safety and efficacy. In addition, they are expensive, so it is not yet clear how they will be integrated with other options.
Yet, he thinks the evidence so far suggests a profound effect on the fundamental drivers of autoimmune disease. Their specific mechanism of benefit is still being evaluated, but he considers the clinical responses consistent with a “reset” hypothesis.
After a response, “we are seeing drug-free remissions in some patients as long as they have been followed,” Dr. Schett said. Based on the fact that disease control is being observed off all other therapies, “this only makes sense to me if there is some sort of immunologic reset.”
CAR T-Cell Studies in Autoimmune Diseases Are Proliferating
At last count, there were about 40 studies being performed with CAR T cells in various autoimmune diseases, most of which were rheumatologic disorders, according to Dr. Schett. He noted that funding is coming from multinational drug companies, small biotech startups, and investigator-initiated studies at academic centers.
At EULAR, beyond case studies and anecdotal reports, all of the clinical studies were still at the level of phase 1 or 1/2. Consistent with the data presented by Dr. Schett, the drugs have been nearly uniformly effective, with major responses persisting in patients off other therapies. Adverse events have been manageable.
Examples include a phase 1/2 multinational study with the investigational CAR T-cell therapy YTB323 (Novartis), which demonstrated acceptable safety and a strong signal of benefit in six patients with SLE. In this report, CRS was also common, but no case of CRS was more severe than grade 2. There was no neurotoxicity. Infections did occur but were of relatively mild grades and resolved with treatment.
For efficacy in the ongoing follow-up, SLE symptoms as measured with the SLE Disease Activity Index began to abate at about 14 days after the single-infusion treatment. Improvement on the Physician Global Assessment was also observed between 14 and 28 days. C3 and C4 complement levels started to rise at about 28 days. While the responses have correlated with the observed changes in biomarkers of immune function, they have endured through a median follow-up that now exceeds 6 months.
Complete B-Cell Depletion Is Followed by Full Recovery
“Pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic studies revealed peak expansion of CAR T cells approximately 13-21 days post infusion, which was accompanied by deep B-cell depletion followed by subsequent B-cell recovery,” reported Josefina Cortés-Hernández, MD, PhD, a senior lecturer at Vall d’Hebron Research Institute, Barcelona, Spain.
Dr. Schett had reported the same pattern of expansion followed by a rapid elimination of detectable CAR T cells despite the sustained clinical benefit.
Dr. Cortés-Hernández said that the signal of efficacy in the context of acceptable safety supports an expansion of clinical studies with this CAR T-cell product in SLE and perhaps other autoimmune disorders.
In another early-stage study, patients with SLE who had failed multiple prior lines of therapy have been enrolled in an ongoing study with a compound CAR (cCAR) T cell. This experimental proprietary product (iCAR Bio Therapeutics, Zhongshan, China) targets both the B-cell maturation antigen and CD19, according to Greg Deener, the chief executive officer of iCell Gene Therapeutics, New York City.
cCAR T-Cell Construct Targets Immune Reset
With this construct, the goal is to deplete long-lived plasma cells as well as B cells in order to achieve a more complete humoral reset. While preliminary data from the phase 1 trial were published earlier this year in Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, Mr. Deener focused his presentation at EULAR 2024 on 12 patients with SLE and lupus nephritis, a severe form of SLE that threatens glomerular structures and can lead to end-stage liver disease.
B cells in the peripheral blood could not be detected within 10 days of the cCAR infusion, and the immunoglobulins IgM and IgA were undetectable by day 42.
However, after B-cell recovery by day 150, “flow cytometry and B-cell receptor sequencing confirmed full humoral reset was achieved,” Mr. Deener said.
The remission has been durable in 11 of the 12 patients after a mean follow-up of 458 days, Mr. Deener reported. He noted that an improvement in renal function has been observed in the majority of patients.
Like others, he reported that treatment has been relatively well tolerated. In this series of patients, there have been no cases of CRS more severe than grade 1.
Overall, the cCAR data in lupus nephritis support the hypothesis that CAR T cells are reprogramming the immune system, according to Mr. Deener.
Combined with a reasonable safety profile, the consistency of benefit from CAR T cells in autoimmune rheumatic diseases is good news, but all of the investigators who spoke at EULAR agreed that there are still many unanswered questions. Not least, it is unclear whether patients can be effectively and safely retreated when and if relapses occur. Even though Dr. Schett did report a response with retreatment following a relapse, he said that there is no conclusion to draw from a single patient.
Yet, the high rates of remissions in patients with disease refractory to other therapeutic options is highly encouraging, particularly with the manageable side effects now reported by multiple investigators using different CAR T-cell products.
“Roughly 100 patients with rheumatic diseases have been treated with CAR T-cells, and we have not seen a high-grade CRS or neurotoxicity,” he said.
Long-term efficacy is less clear. With the first clinical studies in autoimmune diseases initiated in 2021, few patients have been followed for more than 2 years. Even with the high rates of response that will certainly fuel efforts to rapidly bring these treatments forward, long-term data are now the missing piece.
Other Case Series Presented at EULAR
Several other abstracts reported on patients with SSc who were treated with CD19-targeting CAR T cells:
Three patients for whom autologous hematopoietic stem cell transplantation was contraindicated or unsuccessful were successfully and safely treated.
Six patients with diffuse and progressive disease achieved stable disease activity without additional immunosuppression for up to 1 year after treatment.
Dr. Schett reported no potential conflicts of interest, and the study he presented was not funded by industry. Dr. Cortés-Hernández reported a financial relationship with Novartis, which funded the study of the CAR T-cell therapy YTB323, as well as with GlaxoSmithKline, which was not involved in the study she presented. Mr. Deener is an employee of iCell Gene Therapeutics, which provided funding for the trial he presented.
August 7, 2024 — Editor's note: This article was updated with additional disclosure information for Dr. Josefina Cortés-Hernández.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
VIENNA — From a dozen or so studies and sessions devoted to the role of chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T cells in rheumatic diseases at the annual European Congress of Rheumatology, the message was uniformly positive, supporting growing evidence that drugs in this class are heading toward a paradigm shift in refractory rheumatic diseases.
Of the reports, an update from a 15-patient case series with at least 1 year of follow-up provides “the first long-term evidence of safety and efficacy in multiple rheumatic diseases,” according to Georg Schett, MD, PhD, director of rheumatology and immunology, University of Erlangen-Nürnberg, Erlangen, Germany.
The report of high rates of activity and low relative risk of serious adverse events from the same series was published earlier this year in The New England Journal of Medicine when the median follow-up was 15 months. Almost all of the patients have now completed at least 1 year of follow-up and about a third have completed more than 2 years.
SLE Is Frequently Targeted in CAR T-Cell Studies
The three rheumatic diseases represented in this series of patients, all of whom had failed multiple previous immune suppressive treatments, were systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), idiopathic inflammatory myositis (IIM), and systemic sclerosis (SSc). After the autologous T cells were harvested, they were expanded and transfected with the CD19 CAR. The proprietary investigational product, called MB-CART19.1 (Miltenyi Biotec), was administered in a single dose of one million cells per kg bodyweight.
The response rates have been, and continue to be, impressive. For the eight patients with SLE, all achieved the definition of remission in SLE criteria after one dose of treatment. Complete resolution of all major symptom types was achieved after 6 months of follow-up. So far, no patient has relapsed.
For the three patients with IIM, all reached the American College of Rheumatology–EULAR criteria for a major response. All creatine kinase levels had normalized by 3 months. In this group, there was one relapse, which occurred after 18 months of follow-up.
All four patients with SSc achieved a major response on the European Scleroderma Trials and Research (EUSTAR) group activity index. The median reduction from baseline in the EUSTAR score was 4.2 points, and this has been maintained in follow-up to date.
Remissions Have Persisted Off All Therapies
These remissions were achieved and maintained after a single dose of CAR T-cell therapy despite discontinuation of all immunosuppressive therapies. With the exception of the single relapse, all remissions have persisted through follow-up to date.
These responses were achieved with manageable side effects, according to Dr. Schett. The most serious adverse event was a grade 4 neutropenia that developed 4 months after receiving CAR T cells. It resolved with granulocyte colony-stimulating factor treatment. Cytokine release syndrome (CRS) has occurred in 10 patients, but it was grade 1 in eight patients and grade 2 in the others. There has been no neurotoxicity.
Almost all patients have experienced an infection during follow-up, but there has been no discernible pattern in relationship to the timing or types of infections. The most common have involved the upper respiratory tract and have been of mild severity, with cases disseminated similarly over early vs late follow-up. There was one case of pneumonia involving antibiotic treatment and a hospital stay, but it resolved.
Dr. Schett acknowledged that safety is a bigger concern in autoimmune diseases, which are often serious but rarely fatal, than in the hematologic malignancies for which CAR T cells were initially tested, but the low rates of serious adverse events in his and other early studies have supported the premise that the risks are not the same.
Asked specifically if CAR T cells can be considered a game changer in autoimmune rheumatic diseases, Dr. Schett was cautious. One reason is the CAR T cells are a complex therapy relative to biologic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs. He thinks, therefore, that much more data are needed to confirm safety and efficacy. In addition, they are expensive, so it is not yet clear how they will be integrated with other options.
Yet, he thinks the evidence so far suggests a profound effect on the fundamental drivers of autoimmune disease. Their specific mechanism of benefit is still being evaluated, but he considers the clinical responses consistent with a “reset” hypothesis.
After a response, “we are seeing drug-free remissions in some patients as long as they have been followed,” Dr. Schett said. Based on the fact that disease control is being observed off all other therapies, “this only makes sense to me if there is some sort of immunologic reset.”
CAR T-Cell Studies in Autoimmune Diseases Are Proliferating
At last count, there were about 40 studies being performed with CAR T cells in various autoimmune diseases, most of which were rheumatologic disorders, according to Dr. Schett. He noted that funding is coming from multinational drug companies, small biotech startups, and investigator-initiated studies at academic centers.
At EULAR, beyond case studies and anecdotal reports, all of the clinical studies were still at the level of phase 1 or 1/2. Consistent with the data presented by Dr. Schett, the drugs have been nearly uniformly effective, with major responses persisting in patients off other therapies. Adverse events have been manageable.
Examples include a phase 1/2 multinational study with the investigational CAR T-cell therapy YTB323 (Novartis), which demonstrated acceptable safety and a strong signal of benefit in six patients with SLE. In this report, CRS was also common, but no case of CRS was more severe than grade 2. There was no neurotoxicity. Infections did occur but were of relatively mild grades and resolved with treatment.
For efficacy in the ongoing follow-up, SLE symptoms as measured with the SLE Disease Activity Index began to abate at about 14 days after the single-infusion treatment. Improvement on the Physician Global Assessment was also observed between 14 and 28 days. C3 and C4 complement levels started to rise at about 28 days. While the responses have correlated with the observed changes in biomarkers of immune function, they have endured through a median follow-up that now exceeds 6 months.
Complete B-Cell Depletion Is Followed by Full Recovery
“Pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic studies revealed peak expansion of CAR T cells approximately 13-21 days post infusion, which was accompanied by deep B-cell depletion followed by subsequent B-cell recovery,” reported Josefina Cortés-Hernández, MD, PhD, a senior lecturer at Vall d’Hebron Research Institute, Barcelona, Spain.
Dr. Schett had reported the same pattern of expansion followed by a rapid elimination of detectable CAR T cells despite the sustained clinical benefit.
Dr. Cortés-Hernández said that the signal of efficacy in the context of acceptable safety supports an expansion of clinical studies with this CAR T-cell product in SLE and perhaps other autoimmune disorders.
In another early-stage study, patients with SLE who had failed multiple prior lines of therapy have been enrolled in an ongoing study with a compound CAR (cCAR) T cell. This experimental proprietary product (iCAR Bio Therapeutics, Zhongshan, China) targets both the B-cell maturation antigen and CD19, according to Greg Deener, the chief executive officer of iCell Gene Therapeutics, New York City.
cCAR T-Cell Construct Targets Immune Reset
With this construct, the goal is to deplete long-lived plasma cells as well as B cells in order to achieve a more complete humoral reset. While preliminary data from the phase 1 trial were published earlier this year in Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, Mr. Deener focused his presentation at EULAR 2024 on 12 patients with SLE and lupus nephritis, a severe form of SLE that threatens glomerular structures and can lead to end-stage liver disease.
B cells in the peripheral blood could not be detected within 10 days of the cCAR infusion, and the immunoglobulins IgM and IgA were undetectable by day 42.
However, after B-cell recovery by day 150, “flow cytometry and B-cell receptor sequencing confirmed full humoral reset was achieved,” Mr. Deener said.
The remission has been durable in 11 of the 12 patients after a mean follow-up of 458 days, Mr. Deener reported. He noted that an improvement in renal function has been observed in the majority of patients.
Like others, he reported that treatment has been relatively well tolerated. In this series of patients, there have been no cases of CRS more severe than grade 1.
Overall, the cCAR data in lupus nephritis support the hypothesis that CAR T cells are reprogramming the immune system, according to Mr. Deener.
Combined with a reasonable safety profile, the consistency of benefit from CAR T cells in autoimmune rheumatic diseases is good news, but all of the investigators who spoke at EULAR agreed that there are still many unanswered questions. Not least, it is unclear whether patients can be effectively and safely retreated when and if relapses occur. Even though Dr. Schett did report a response with retreatment following a relapse, he said that there is no conclusion to draw from a single patient.
Yet, the high rates of remissions in patients with disease refractory to other therapeutic options is highly encouraging, particularly with the manageable side effects now reported by multiple investigators using different CAR T-cell products.
“Roughly 100 patients with rheumatic diseases have been treated with CAR T-cells, and we have not seen a high-grade CRS or neurotoxicity,” he said.
Long-term efficacy is less clear. With the first clinical studies in autoimmune diseases initiated in 2021, few patients have been followed for more than 2 years. Even with the high rates of response that will certainly fuel efforts to rapidly bring these treatments forward, long-term data are now the missing piece.
Other Case Series Presented at EULAR
Several other abstracts reported on patients with SSc who were treated with CD19-targeting CAR T cells:
Three patients for whom autologous hematopoietic stem cell transplantation was contraindicated or unsuccessful were successfully and safely treated.
Six patients with diffuse and progressive disease achieved stable disease activity without additional immunosuppression for up to 1 year after treatment.
Dr. Schett reported no potential conflicts of interest, and the study he presented was not funded by industry. Dr. Cortés-Hernández reported a financial relationship with Novartis, which funded the study of the CAR T-cell therapy YTB323, as well as with GlaxoSmithKline, which was not involved in the study she presented. Mr. Deener is an employee of iCell Gene Therapeutics, which provided funding for the trial he presented.
August 7, 2024 — Editor's note: This article was updated with additional disclosure information for Dr. Josefina Cortés-Hernández.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
VIENNA — From a dozen or so studies and sessions devoted to the role of chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T cells in rheumatic diseases at the annual European Congress of Rheumatology, the message was uniformly positive, supporting growing evidence that drugs in this class are heading toward a paradigm shift in refractory rheumatic diseases.
Of the reports, an update from a 15-patient case series with at least 1 year of follow-up provides “the first long-term evidence of safety and efficacy in multiple rheumatic diseases,” according to Georg Schett, MD, PhD, director of rheumatology and immunology, University of Erlangen-Nürnberg, Erlangen, Germany.
The report of high rates of activity and low relative risk of serious adverse events from the same series was published earlier this year in The New England Journal of Medicine when the median follow-up was 15 months. Almost all of the patients have now completed at least 1 year of follow-up and about a third have completed more than 2 years.
SLE Is Frequently Targeted in CAR T-Cell Studies
The three rheumatic diseases represented in this series of patients, all of whom had failed multiple previous immune suppressive treatments, were systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), idiopathic inflammatory myositis (IIM), and systemic sclerosis (SSc). After the autologous T cells were harvested, they were expanded and transfected with the CD19 CAR. The proprietary investigational product, called MB-CART19.1 (Miltenyi Biotec), was administered in a single dose of one million cells per kg bodyweight.
The response rates have been, and continue to be, impressive. For the eight patients with SLE, all achieved the definition of remission in SLE criteria after one dose of treatment. Complete resolution of all major symptom types was achieved after 6 months of follow-up. So far, no patient has relapsed.
For the three patients with IIM, all reached the American College of Rheumatology–EULAR criteria for a major response. All creatine kinase levels had normalized by 3 months. In this group, there was one relapse, which occurred after 18 months of follow-up.
All four patients with SSc achieved a major response on the European Scleroderma Trials and Research (EUSTAR) group activity index. The median reduction from baseline in the EUSTAR score was 4.2 points, and this has been maintained in follow-up to date.
Remissions Have Persisted Off All Therapies
These remissions were achieved and maintained after a single dose of CAR T-cell therapy despite discontinuation of all immunosuppressive therapies. With the exception of the single relapse, all remissions have persisted through follow-up to date.
These responses were achieved with manageable side effects, according to Dr. Schett. The most serious adverse event was a grade 4 neutropenia that developed 4 months after receiving CAR T cells. It resolved with granulocyte colony-stimulating factor treatment. Cytokine release syndrome (CRS) has occurred in 10 patients, but it was grade 1 in eight patients and grade 2 in the others. There has been no neurotoxicity.
Almost all patients have experienced an infection during follow-up, but there has been no discernible pattern in relationship to the timing or types of infections. The most common have involved the upper respiratory tract and have been of mild severity, with cases disseminated similarly over early vs late follow-up. There was one case of pneumonia involving antibiotic treatment and a hospital stay, but it resolved.
Dr. Schett acknowledged that safety is a bigger concern in autoimmune diseases, which are often serious but rarely fatal, than in the hematologic malignancies for which CAR T cells were initially tested, but the low rates of serious adverse events in his and other early studies have supported the premise that the risks are not the same.
Asked specifically if CAR T cells can be considered a game changer in autoimmune rheumatic diseases, Dr. Schett was cautious. One reason is the CAR T cells are a complex therapy relative to biologic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs. He thinks, therefore, that much more data are needed to confirm safety and efficacy. In addition, they are expensive, so it is not yet clear how they will be integrated with other options.
Yet, he thinks the evidence so far suggests a profound effect on the fundamental drivers of autoimmune disease. Their specific mechanism of benefit is still being evaluated, but he considers the clinical responses consistent with a “reset” hypothesis.
After a response, “we are seeing drug-free remissions in some patients as long as they have been followed,” Dr. Schett said. Based on the fact that disease control is being observed off all other therapies, “this only makes sense to me if there is some sort of immunologic reset.”
CAR T-Cell Studies in Autoimmune Diseases Are Proliferating
At last count, there were about 40 studies being performed with CAR T cells in various autoimmune diseases, most of which were rheumatologic disorders, according to Dr. Schett. He noted that funding is coming from multinational drug companies, small biotech startups, and investigator-initiated studies at academic centers.
At EULAR, beyond case studies and anecdotal reports, all of the clinical studies were still at the level of phase 1 or 1/2. Consistent with the data presented by Dr. Schett, the drugs have been nearly uniformly effective, with major responses persisting in patients off other therapies. Adverse events have been manageable.
Examples include a phase 1/2 multinational study with the investigational CAR T-cell therapy YTB323 (Novartis), which demonstrated acceptable safety and a strong signal of benefit in six patients with SLE. In this report, CRS was also common, but no case of CRS was more severe than grade 2. There was no neurotoxicity. Infections did occur but were of relatively mild grades and resolved with treatment.
For efficacy in the ongoing follow-up, SLE symptoms as measured with the SLE Disease Activity Index began to abate at about 14 days after the single-infusion treatment. Improvement on the Physician Global Assessment was also observed between 14 and 28 days. C3 and C4 complement levels started to rise at about 28 days. While the responses have correlated with the observed changes in biomarkers of immune function, they have endured through a median follow-up that now exceeds 6 months.
Complete B-Cell Depletion Is Followed by Full Recovery
“Pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic studies revealed peak expansion of CAR T cells approximately 13-21 days post infusion, which was accompanied by deep B-cell depletion followed by subsequent B-cell recovery,” reported Josefina Cortés-Hernández, MD, PhD, a senior lecturer at Vall d’Hebron Research Institute, Barcelona, Spain.
Dr. Schett had reported the same pattern of expansion followed by a rapid elimination of detectable CAR T cells despite the sustained clinical benefit.
Dr. Cortés-Hernández said that the signal of efficacy in the context of acceptable safety supports an expansion of clinical studies with this CAR T-cell product in SLE and perhaps other autoimmune disorders.
In another early-stage study, patients with SLE who had failed multiple prior lines of therapy have been enrolled in an ongoing study with a compound CAR (cCAR) T cell. This experimental proprietary product (iCAR Bio Therapeutics, Zhongshan, China) targets both the B-cell maturation antigen and CD19, according to Greg Deener, the chief executive officer of iCell Gene Therapeutics, New York City.
cCAR T-Cell Construct Targets Immune Reset
With this construct, the goal is to deplete long-lived plasma cells as well as B cells in order to achieve a more complete humoral reset. While preliminary data from the phase 1 trial were published earlier this year in Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, Mr. Deener focused his presentation at EULAR 2024 on 12 patients with SLE and lupus nephritis, a severe form of SLE that threatens glomerular structures and can lead to end-stage liver disease.
B cells in the peripheral blood could not be detected within 10 days of the cCAR infusion, and the immunoglobulins IgM and IgA were undetectable by day 42.
However, after B-cell recovery by day 150, “flow cytometry and B-cell receptor sequencing confirmed full humoral reset was achieved,” Mr. Deener said.
The remission has been durable in 11 of the 12 patients after a mean follow-up of 458 days, Mr. Deener reported. He noted that an improvement in renal function has been observed in the majority of patients.
Like others, he reported that treatment has been relatively well tolerated. In this series of patients, there have been no cases of CRS more severe than grade 1.
Overall, the cCAR data in lupus nephritis support the hypothesis that CAR T cells are reprogramming the immune system, according to Mr. Deener.
Combined with a reasonable safety profile, the consistency of benefit from CAR T cells in autoimmune rheumatic diseases is good news, but all of the investigators who spoke at EULAR agreed that there are still many unanswered questions. Not least, it is unclear whether patients can be effectively and safely retreated when and if relapses occur. Even though Dr. Schett did report a response with retreatment following a relapse, he said that there is no conclusion to draw from a single patient.
Yet, the high rates of remissions in patients with disease refractory to other therapeutic options is highly encouraging, particularly with the manageable side effects now reported by multiple investigators using different CAR T-cell products.
“Roughly 100 patients with rheumatic diseases have been treated with CAR T-cells, and we have not seen a high-grade CRS or neurotoxicity,” he said.
Long-term efficacy is less clear. With the first clinical studies in autoimmune diseases initiated in 2021, few patients have been followed for more than 2 years. Even with the high rates of response that will certainly fuel efforts to rapidly bring these treatments forward, long-term data are now the missing piece.
Other Case Series Presented at EULAR
Several other abstracts reported on patients with SSc who were treated with CD19-targeting CAR T cells:
Three patients for whom autologous hematopoietic stem cell transplantation was contraindicated or unsuccessful were successfully and safely treated.
Six patients with diffuse and progressive disease achieved stable disease activity without additional immunosuppression for up to 1 year after treatment.
Dr. Schett reported no potential conflicts of interest, and the study he presented was not funded by industry. Dr. Cortés-Hernández reported a financial relationship with Novartis, which funded the study of the CAR T-cell therapy YTB323, as well as with GlaxoSmithKline, which was not involved in the study she presented. Mr. Deener is an employee of iCell Gene Therapeutics, which provided funding for the trial he presented.
August 7, 2024 — Editor's note: This article was updated with additional disclosure information for Dr. Josefina Cortés-Hernández.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM EULAR 2024