User login
Best treatment approach for early stage follicular lymphoma is unclear
Randomized trials are needed to determine the optimal treatment approach for early stage follicular lymphoma (FL), according to researchers.
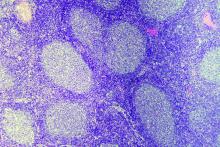
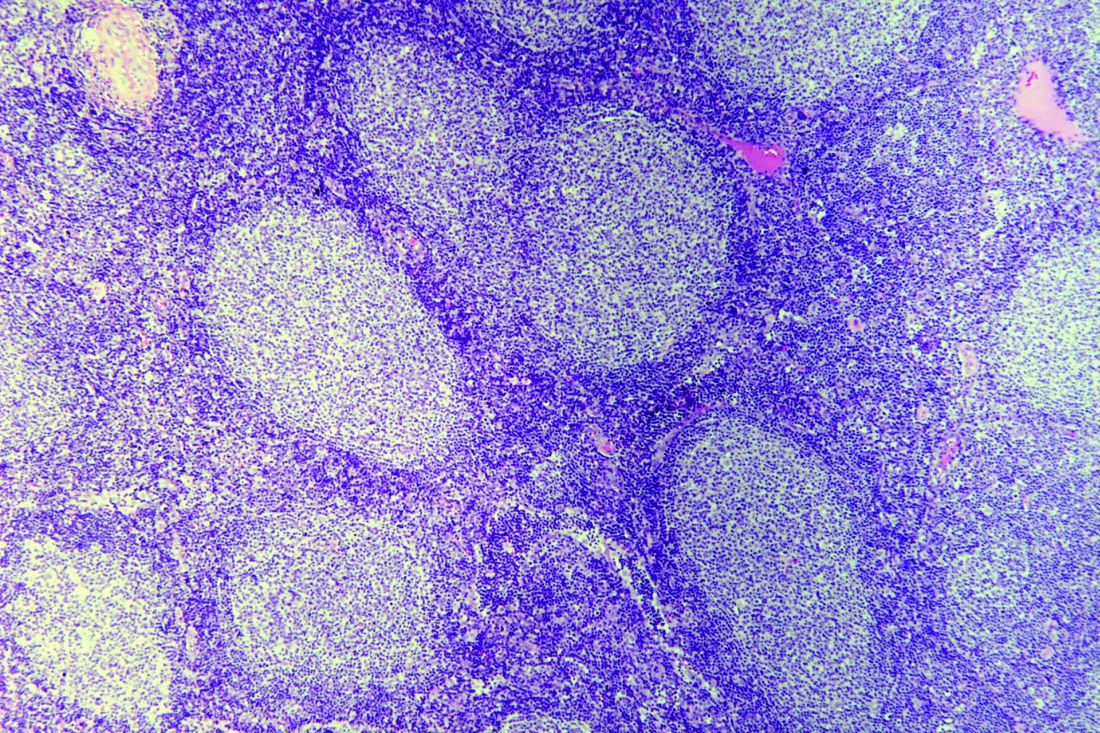
A retrospective study showed similar outcomes among patients who received radiotherapy, immunochemotherapy, combined modality treatment (CMT), and watchful waiting (WW).
There were some differences in progression-free survival (PFS) according to treatment approach. However, there were no significant differences in overall survival (OS) between any of the active treatments or between patients who received active treatment and those managed with WW.
Joshua W. D. Tobin, MD, of Princess Alexandra Hospital in Brisbane, Queensland, Australia, and colleagues conducted this research and reported the results in Blood Advances.
The researchers analyzed 365 patients with newly diagnosed, stage I/II FL. The patients had a median age of 63 years and more than half were men. They were diagnosed between 2005 and 2017, and the median follow-up was 45 months.
Most patients (n = 280) received active treatment, but 85 were managed with WW. The WW patients were older and had more extranodal involvement.
Types of active treatment included radiotherapy alone (n = 171), immunochemotherapy alone (n = 63), and CMT (n = 46). Compared with the other groups, patients who received radiotherapy alone had less bulk, fewer nodal sites, and fewer B symptoms, and were more likely to have stage I disease. Patients who received CMT had fewer B symptoms and lower FLIPI scores compared with patients who received immunochemotherapy.
The immunochemotherapy regimens used were largely rituximab based. In all, 106 patients received rituximab (alone or in combination) for induction, and 49 received maintenance rituximab (37 in the immunochemotherapy group and 12 in the CMT group).
Results
Response rates were similar among the active treatment groups. The overall response rate was 95% in the radiotherapy group, 96% in the immunochemotherapy group, and 95% in the CMT group (P = .87).
There was a significant difference in PFS between the radiotherapy, immunochemotherapy, and CMT groups (P = .023), but there was no difference in OS between these groups (P = .38).
There was no significant difference in PFS between the immunochemotherapy and CMT groups (hazard ratio [HR], 1.78; P = .24), so the researchers combined these groups into a single group called “systemic therapy.” The patients treated with systemic therapy had PFS (HR, 1.32; P = .96) and OS (HR, 0.46; P = .21) similar to that of patients treated with radiotherapy alone.
Maintenance rituximab was associated with prolonged PFS among patients treated with systemic therapy (HR, 0.24; P = .017). However, there was no significant difference in OS between patients who received maintenance and those who did not (HR, 0.89; P = .90).
Relapse was less common among patients who received maintenance, and there were no cases of transformation in that group. Relapse occurred in 24.6% of the radiotherapy group, 18.3% of the systemic therapy group, and 4.1% of the group that received systemic therapy plus maintenance (P = .006). Transformation was less likely in the systemic therapy group (1.8%) than in the radiotherapy (6.4%) and WW (9.4%) groups (HR, 0.20; P = .034).
Overall, the active treatment group had better PFS than the WW group (HR, 0.52; P = .002), but there was no significant difference in OS between the groups (HR, 0.94; P = .90).
“Based on our comparable OS between WW and actively treated patients, WW could be considered as an initial management strategy in early stage FL,” Dr. Tobin and colleagues wrote. “However, long-term follow-up is required to determine if a survival benefit exists favoring active treatment.”
The researchers reported relationships with many pharmaceutical companies.
SOURCE: Tobin JWD et al. Blood Adv. 2019 Oct 8;3(19):2804-11.
Randomized trials are needed to determine the optimal treatment approach for early stage follicular lymphoma (FL), according to researchers.
A retrospective study showed similar outcomes among patients who received radiotherapy, immunochemotherapy, combined modality treatment (CMT), and watchful waiting (WW).
There were some differences in progression-free survival (PFS) according to treatment approach. However, there were no significant differences in overall survival (OS) between any of the active treatments or between patients who received active treatment and those managed with WW.
Joshua W. D. Tobin, MD, of Princess Alexandra Hospital in Brisbane, Queensland, Australia, and colleagues conducted this research and reported the results in Blood Advances.
The researchers analyzed 365 patients with newly diagnosed, stage I/II FL. The patients had a median age of 63 years and more than half were men. They were diagnosed between 2005 and 2017, and the median follow-up was 45 months.
Most patients (n = 280) received active treatment, but 85 were managed with WW. The WW patients were older and had more extranodal involvement.
Types of active treatment included radiotherapy alone (n = 171), immunochemotherapy alone (n = 63), and CMT (n = 46). Compared with the other groups, patients who received radiotherapy alone had less bulk, fewer nodal sites, and fewer B symptoms, and were more likely to have stage I disease. Patients who received CMT had fewer B symptoms and lower FLIPI scores compared with patients who received immunochemotherapy.
The immunochemotherapy regimens used were largely rituximab based. In all, 106 patients received rituximab (alone or in combination) for induction, and 49 received maintenance rituximab (37 in the immunochemotherapy group and 12 in the CMT group).
Results
Response rates were similar among the active treatment groups. The overall response rate was 95% in the radiotherapy group, 96% in the immunochemotherapy group, and 95% in the CMT group (P = .87).
There was a significant difference in PFS between the radiotherapy, immunochemotherapy, and CMT groups (P = .023), but there was no difference in OS between these groups (P = .38).
There was no significant difference in PFS between the immunochemotherapy and CMT groups (hazard ratio [HR], 1.78; P = .24), so the researchers combined these groups into a single group called “systemic therapy.” The patients treated with systemic therapy had PFS (HR, 1.32; P = .96) and OS (HR, 0.46; P = .21) similar to that of patients treated with radiotherapy alone.
Maintenance rituximab was associated with prolonged PFS among patients treated with systemic therapy (HR, 0.24; P = .017). However, there was no significant difference in OS between patients who received maintenance and those who did not (HR, 0.89; P = .90).
Relapse was less common among patients who received maintenance, and there were no cases of transformation in that group. Relapse occurred in 24.6% of the radiotherapy group, 18.3% of the systemic therapy group, and 4.1% of the group that received systemic therapy plus maintenance (P = .006). Transformation was less likely in the systemic therapy group (1.8%) than in the radiotherapy (6.4%) and WW (9.4%) groups (HR, 0.20; P = .034).
Overall, the active treatment group had better PFS than the WW group (HR, 0.52; P = .002), but there was no significant difference in OS between the groups (HR, 0.94; P = .90).
“Based on our comparable OS between WW and actively treated patients, WW could be considered as an initial management strategy in early stage FL,” Dr. Tobin and colleagues wrote. “However, long-term follow-up is required to determine if a survival benefit exists favoring active treatment.”
The researchers reported relationships with many pharmaceutical companies.
SOURCE: Tobin JWD et al. Blood Adv. 2019 Oct 8;3(19):2804-11.
Randomized trials are needed to determine the optimal treatment approach for early stage follicular lymphoma (FL), according to researchers.
A retrospective study showed similar outcomes among patients who received radiotherapy, immunochemotherapy, combined modality treatment (CMT), and watchful waiting (WW).
There were some differences in progression-free survival (PFS) according to treatment approach. However, there were no significant differences in overall survival (OS) between any of the active treatments or between patients who received active treatment and those managed with WW.
Joshua W. D. Tobin, MD, of Princess Alexandra Hospital in Brisbane, Queensland, Australia, and colleagues conducted this research and reported the results in Blood Advances.
The researchers analyzed 365 patients with newly diagnosed, stage I/II FL. The patients had a median age of 63 years and more than half were men. They were diagnosed between 2005 and 2017, and the median follow-up was 45 months.
Most patients (n = 280) received active treatment, but 85 were managed with WW. The WW patients were older and had more extranodal involvement.
Types of active treatment included radiotherapy alone (n = 171), immunochemotherapy alone (n = 63), and CMT (n = 46). Compared with the other groups, patients who received radiotherapy alone had less bulk, fewer nodal sites, and fewer B symptoms, and were more likely to have stage I disease. Patients who received CMT had fewer B symptoms and lower FLIPI scores compared with patients who received immunochemotherapy.
The immunochemotherapy regimens used were largely rituximab based. In all, 106 patients received rituximab (alone or in combination) for induction, and 49 received maintenance rituximab (37 in the immunochemotherapy group and 12 in the CMT group).
Results
Response rates were similar among the active treatment groups. The overall response rate was 95% in the radiotherapy group, 96% in the immunochemotherapy group, and 95% in the CMT group (P = .87).
There was a significant difference in PFS between the radiotherapy, immunochemotherapy, and CMT groups (P = .023), but there was no difference in OS between these groups (P = .38).
There was no significant difference in PFS between the immunochemotherapy and CMT groups (hazard ratio [HR], 1.78; P = .24), so the researchers combined these groups into a single group called “systemic therapy.” The patients treated with systemic therapy had PFS (HR, 1.32; P = .96) and OS (HR, 0.46; P = .21) similar to that of patients treated with radiotherapy alone.
Maintenance rituximab was associated with prolonged PFS among patients treated with systemic therapy (HR, 0.24; P = .017). However, there was no significant difference in OS between patients who received maintenance and those who did not (HR, 0.89; P = .90).
Relapse was less common among patients who received maintenance, and there were no cases of transformation in that group. Relapse occurred in 24.6% of the radiotherapy group, 18.3% of the systemic therapy group, and 4.1% of the group that received systemic therapy plus maintenance (P = .006). Transformation was less likely in the systemic therapy group (1.8%) than in the radiotherapy (6.4%) and WW (9.4%) groups (HR, 0.20; P = .034).
Overall, the active treatment group had better PFS than the WW group (HR, 0.52; P = .002), but there was no significant difference in OS between the groups (HR, 0.94; P = .90).
“Based on our comparable OS between WW and actively treated patients, WW could be considered as an initial management strategy in early stage FL,” Dr. Tobin and colleagues wrote. “However, long-term follow-up is required to determine if a survival benefit exists favoring active treatment.”
The researchers reported relationships with many pharmaceutical companies.
SOURCE: Tobin JWD et al. Blood Adv. 2019 Oct 8;3(19):2804-11.
FROM BLOOD ADVANCES
Follow-up shows favorable results with acalabrutinib in MCL
Acalabrutinib monotherapy can produce durable responses in relapsed/refractory mantle cell lymphoma (MCL), according to updated results from a phase 2 trial.
The drug produced an overall response rate (ORR) of 81%, and the median duration of response was 26 months.
These are the highest such figures reported “among all approved single-agent therapies for the treatment of relapsed/refractory MCL,” Michael Wang, MD, of the MD Anderson Cancer Center at the University of Texas in Houston and colleagues wrote in a letter in Leukemia.
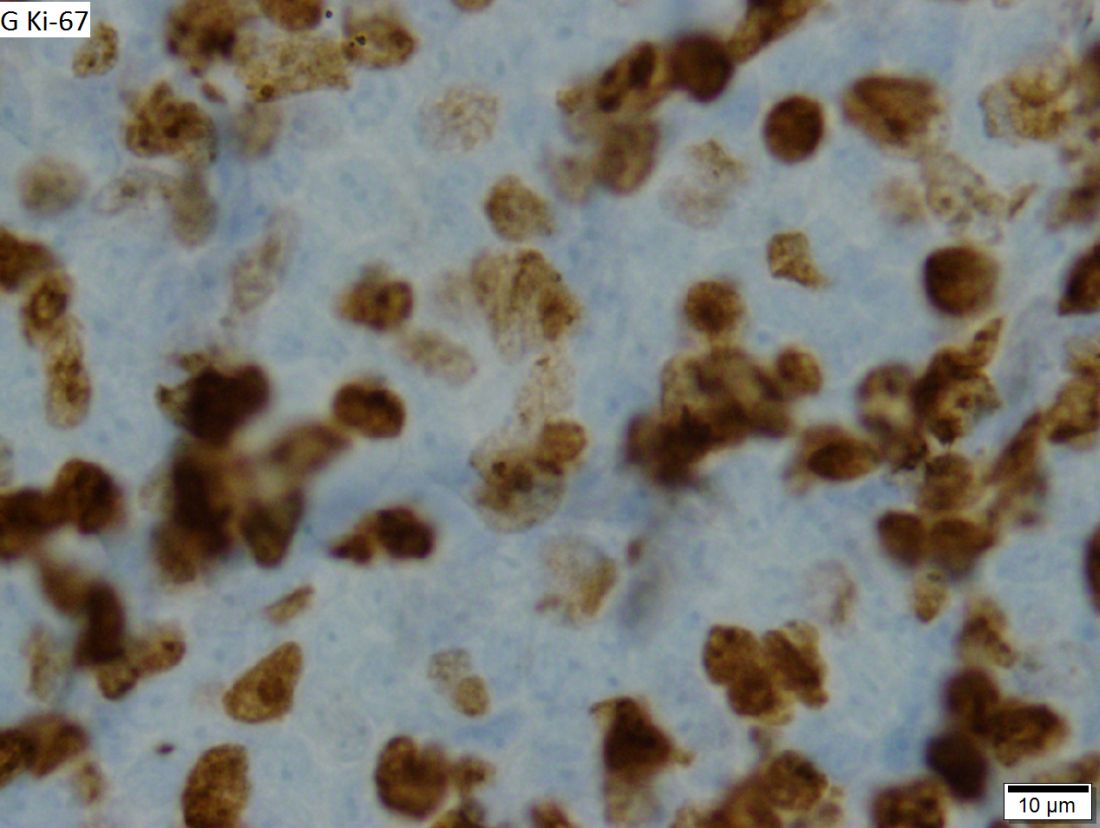
Dr. Wang and colleagues reported updated results in 124 patients treated on the ACE-LY-004 trial. At baseline, the patients had a median age of 68 years (range, 42-90 years), and 80% were men. Three-quarters of patients had stage IV disease, 72% had extranodal disease, 21% had blastoid/pleomorphic MCL, and 26% had a Ki-67 proliferation index of 50% or greater.
At a median follow-up of 26 months, 40% (n = 49) of patients were still on acalabrutinib, and 61% (n = 76) were still in follow-up for survival. Six patients went on to allogeneic transplant at a median of 19 days after stopping acalabrutinib.
The ORR was 81% (100/124), and the complete response (CR) rate was 43% (n = 53). Four patients who initially had a partial response converted to a CR with longer follow-up. The estimated 24-month duration of response was 52.4%.
“ORR was consistent across patients with refractory disease and those with blastoid/pleomorphic MCL, despite those patients having a higher mean Ki-67 index [of 50% or greater], suggesting that some patients with poorer prognosis may also benefit from acalabrutinib,” Dr. Wang and colleagues wrote.
There were 29 patients evaluable for minimal residual disease (MRD) assessment. Seven patients (24%) had MRD-negative disease in the peripheral blood after they achieved a CR. An additional patient with a CR became MRD negative when a second blood sample was taken about 6 months after the first.
“Despite limited samples, these results demonstrate that continued use of acalabrutinib can lead to undetectable MRD in patients with CR,” Dr. Wang and his colleagues wrote. “Since most patients with MRD data are still on treatment (27/29), relationships between MRD negativity and durability of response cannot be made at this time.”
The median progression-free survival was 20 months, and the median overall survival was not reached. The estimated 24-month progression-free survival rate was 49.0%, and the estimated 24-month overall survival rate was 72.4%. Patients with low/intermediate Mantle Cell Lymphoma International Prognostic Index scores, classical MCL, and a Ki-67 index less than 50% had a longer duration of response and survival.
The adverse event profile was “largely consistent with earlier reporting,” Dr. Wang and colleagues wrote. The most frequent adverse events were headache (38%), diarrhea (36%), fatigue (28%), cough (22%), and myalgia (21%). The most common grade 3/4 adverse events were anemia (10%), neutropenia (10%), and pneumonia (6%).
Ten patients developed second primary cancers. There were no new atrial fibrillation events and no new hypertension events. The frequency of infections decreased over time, as did the number of bleeding events. However, two of three major hemorrhage events occurred after the previous report was published.
There were 43 deaths (35%), 29 of them because of disease progression. Six patients died of adverse events, two died of unknown causes, and two died of secondary acute myeloid leukemia. Other causes of death included multiorgan failure, intestinal obstruction, lung cancer, and graft-versus-host disease.
This study was sponsored by Acerta Pharma, a member of the AstraZeneca Group. The researchers reported relationships with AstraZeneca/Acerta Pharma and many other companies.
SOURCE: Wang M et al. Leukemia. 2019 Sep 26. doi: 10.1038/s41375-019-0575-9.
Acalabrutinib monotherapy can produce durable responses in relapsed/refractory mantle cell lymphoma (MCL), according to updated results from a phase 2 trial.
The drug produced an overall response rate (ORR) of 81%, and the median duration of response was 26 months.
These are the highest such figures reported “among all approved single-agent therapies for the treatment of relapsed/refractory MCL,” Michael Wang, MD, of the MD Anderson Cancer Center at the University of Texas in Houston and colleagues wrote in a letter in Leukemia.
Dr. Wang and colleagues reported updated results in 124 patients treated on the ACE-LY-004 trial. At baseline, the patients had a median age of 68 years (range, 42-90 years), and 80% were men. Three-quarters of patients had stage IV disease, 72% had extranodal disease, 21% had blastoid/pleomorphic MCL, and 26% had a Ki-67 proliferation index of 50% or greater.
At a median follow-up of 26 months, 40% (n = 49) of patients were still on acalabrutinib, and 61% (n = 76) were still in follow-up for survival. Six patients went on to allogeneic transplant at a median of 19 days after stopping acalabrutinib.
The ORR was 81% (100/124), and the complete response (CR) rate was 43% (n = 53). Four patients who initially had a partial response converted to a CR with longer follow-up. The estimated 24-month duration of response was 52.4%.
“ORR was consistent across patients with refractory disease and those with blastoid/pleomorphic MCL, despite those patients having a higher mean Ki-67 index [of 50% or greater], suggesting that some patients with poorer prognosis may also benefit from acalabrutinib,” Dr. Wang and colleagues wrote.
There were 29 patients evaluable for minimal residual disease (MRD) assessment. Seven patients (24%) had MRD-negative disease in the peripheral blood after they achieved a CR. An additional patient with a CR became MRD negative when a second blood sample was taken about 6 months after the first.
“Despite limited samples, these results demonstrate that continued use of acalabrutinib can lead to undetectable MRD in patients with CR,” Dr. Wang and his colleagues wrote. “Since most patients with MRD data are still on treatment (27/29), relationships between MRD negativity and durability of response cannot be made at this time.”
The median progression-free survival was 20 months, and the median overall survival was not reached. The estimated 24-month progression-free survival rate was 49.0%, and the estimated 24-month overall survival rate was 72.4%. Patients with low/intermediate Mantle Cell Lymphoma International Prognostic Index scores, classical MCL, and a Ki-67 index less than 50% had a longer duration of response and survival.
The adverse event profile was “largely consistent with earlier reporting,” Dr. Wang and colleagues wrote. The most frequent adverse events were headache (38%), diarrhea (36%), fatigue (28%), cough (22%), and myalgia (21%). The most common grade 3/4 adverse events were anemia (10%), neutropenia (10%), and pneumonia (6%).
Ten patients developed second primary cancers. There were no new atrial fibrillation events and no new hypertension events. The frequency of infections decreased over time, as did the number of bleeding events. However, two of three major hemorrhage events occurred after the previous report was published.
There were 43 deaths (35%), 29 of them because of disease progression. Six patients died of adverse events, two died of unknown causes, and two died of secondary acute myeloid leukemia. Other causes of death included multiorgan failure, intestinal obstruction, lung cancer, and graft-versus-host disease.
This study was sponsored by Acerta Pharma, a member of the AstraZeneca Group. The researchers reported relationships with AstraZeneca/Acerta Pharma and many other companies.
SOURCE: Wang M et al. Leukemia. 2019 Sep 26. doi: 10.1038/s41375-019-0575-9.
Acalabrutinib monotherapy can produce durable responses in relapsed/refractory mantle cell lymphoma (MCL), according to updated results from a phase 2 trial.
The drug produced an overall response rate (ORR) of 81%, and the median duration of response was 26 months.
These are the highest such figures reported “among all approved single-agent therapies for the treatment of relapsed/refractory MCL,” Michael Wang, MD, of the MD Anderson Cancer Center at the University of Texas in Houston and colleagues wrote in a letter in Leukemia.
Dr. Wang and colleagues reported updated results in 124 patients treated on the ACE-LY-004 trial. At baseline, the patients had a median age of 68 years (range, 42-90 years), and 80% were men. Three-quarters of patients had stage IV disease, 72% had extranodal disease, 21% had blastoid/pleomorphic MCL, and 26% had a Ki-67 proliferation index of 50% or greater.
At a median follow-up of 26 months, 40% (n = 49) of patients were still on acalabrutinib, and 61% (n = 76) were still in follow-up for survival. Six patients went on to allogeneic transplant at a median of 19 days after stopping acalabrutinib.
The ORR was 81% (100/124), and the complete response (CR) rate was 43% (n = 53). Four patients who initially had a partial response converted to a CR with longer follow-up. The estimated 24-month duration of response was 52.4%.
“ORR was consistent across patients with refractory disease and those with blastoid/pleomorphic MCL, despite those patients having a higher mean Ki-67 index [of 50% or greater], suggesting that some patients with poorer prognosis may also benefit from acalabrutinib,” Dr. Wang and colleagues wrote.
There were 29 patients evaluable for minimal residual disease (MRD) assessment. Seven patients (24%) had MRD-negative disease in the peripheral blood after they achieved a CR. An additional patient with a CR became MRD negative when a second blood sample was taken about 6 months after the first.
“Despite limited samples, these results demonstrate that continued use of acalabrutinib can lead to undetectable MRD in patients with CR,” Dr. Wang and his colleagues wrote. “Since most patients with MRD data are still on treatment (27/29), relationships between MRD negativity and durability of response cannot be made at this time.”
The median progression-free survival was 20 months, and the median overall survival was not reached. The estimated 24-month progression-free survival rate was 49.0%, and the estimated 24-month overall survival rate was 72.4%. Patients with low/intermediate Mantle Cell Lymphoma International Prognostic Index scores, classical MCL, and a Ki-67 index less than 50% had a longer duration of response and survival.
The adverse event profile was “largely consistent with earlier reporting,” Dr. Wang and colleagues wrote. The most frequent adverse events were headache (38%), diarrhea (36%), fatigue (28%), cough (22%), and myalgia (21%). The most common grade 3/4 adverse events were anemia (10%), neutropenia (10%), and pneumonia (6%).
Ten patients developed second primary cancers. There were no new atrial fibrillation events and no new hypertension events. The frequency of infections decreased over time, as did the number of bleeding events. However, two of three major hemorrhage events occurred after the previous report was published.
There were 43 deaths (35%), 29 of them because of disease progression. Six patients died of adverse events, two died of unknown causes, and two died of secondary acute myeloid leukemia. Other causes of death included multiorgan failure, intestinal obstruction, lung cancer, and graft-versus-host disease.
This study was sponsored by Acerta Pharma, a member of the AstraZeneca Group. The researchers reported relationships with AstraZeneca/Acerta Pharma and many other companies.
SOURCE: Wang M et al. Leukemia. 2019 Sep 26. doi: 10.1038/s41375-019-0575-9.
FROM LEUKEMIA
Targeted agents vs. chemoimmunotherapy as first-line treatment of CLL
SAN FRANCISCO – Should targeted agents replace chemoimmunotherapy (CIT) as first-line treatment for chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL)? A recent debate suggests there’s no consensus.
William G. Wierda, MD, PhD, of The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center in Houston, and Jennifer R. Brown, MD, PhD, of Dana-Farber Cancer Institute in Boston, debated the topic at the National Comprehensive Cancer Network Hematologic Malignancies Annual Congress.
Dr. Wierda argued that CLL patients should receive a BTK inhibitor or BCL2 inhibitor, with or without obinutuzumab, as first-line therapy because these targeted agents have been shown to provide better progression-free survival (PFS) than CIT, and the targeted therapies may prolong overall survival (OS) as well.
Dr. Brown countered that targeted agents don’t improve PFS for all CLL patients, improved PFS doesn’t always translate to improved OS, and targeted agents cost more than CIT.
No role for CIT as first-line treatment
“We have two approaches right now, with nonchemoimmunotherapy-based treatment,” Dr. Wierda said. “One approach, with small-molecule inhibitors, is to have a sustained and durable period of disease control, particularly with BTK inhibitors. The other strategy that has emerged is deep remissions with fixed-duration treatment with BCL2 small-molecule inhibitor-based therapy, which, I would argue, is better than being exposed to genotoxic chemoimmunotherapy.”
Dr. Wierda went on to explain that the BTK inhibitor ibrutinib has been shown to improve PFS, compared with CIT, in phase 3 trials.
In the iLLUMINATE trial, researchers compared ibrutinib plus obinutuzumab to chlorambucil plus obinutuzumab as first-line treatment in CLL. At a median follow-up of 31.3 months, the median PFS was not reached in the ibrutinib arm and was 19 months in the chlorambucil arm (P less than .0001; Lancet Oncol. 2019 Jan;20[1]:43-56).
In the A041202 study, researchers compared ibrutinib alone (Ib) or in combination with rituximab (Ib-R) to bendamustine plus rituximab (BR) in untreated, older patients with CLL. The 2-year PFS estimates were 74% in the BR arm, 87% in the Ib arm, and 88% in the Ib-R arm (P less than .001 for BR vs. Ib or Ib-R; N Engl J Med. 2018; 379:2517-28).
In the E1912 trial, researchers compared Ib-R to fludarabine, cyclophosphamide, and rituximab (FCR) in younger, untreated CLL patients. The 3-year PFS was 89.4% with Ib-R and 72.9% with FCR (P less than .001; N Engl J Med. 2019 Aug 1;381:432-43).
Dr. Wierda noted that the E1912 trial also showed superior OS with Ib-R. The 3-year OS rate was 98.8% with Ib-R and 91.5% with FCR (P less than .001). However, there was no significant difference in OS between the treatment arms in the A041202 trial or the iLLUMINATE trial.
“But I would argue that is, in part, because of short follow-up,” Dr. Wierda said. “The trials were all designed to look at progression-free survival, not overall survival. With longer follow-up, we may see differences in overall survival emerging.”
Dr. Wierda went on to say that fixed‐duration treatment with the BCL2 inhibitor venetoclax can improve PFS over CIT.
In the phase 3 CLL14 trial, researchers compared fixed-duration treatment with venetoclax plus obinutuzumab to chlorambucil plus obinutuzumab in previously untreated CLL patients with comorbidities. The estimated PFS at 2 years was 88.2% in the venetoclax group and 64.1% in the chlorambucil group (P less than .001; N Engl J Med. 2019; 380:2225-36).
“[There was] no difference in overall survival,” Dr. Wierda noted. “But, again, I would argue ... that follow-up is relatively limited. We may ultimately see a difference in overall survival.”
Based on these findings, Dr. Wierda made the following treatment recommendations:
- Any CLL patient with del(17p) or TP53 mutation, and older, unfit patients with unmutated IGHV should receive a BTK inhibitor, with or without obinutuzumab.
- All young, fit patients, and older, unfit patients with mutated IGHV should receive a BCL2 inhibitor plus obinutuzumab.
Dr. Wierda also noted that ibrutinib and venetoclax in combination have shown early promise for patients with previously untreated CLL (N Engl J Med. 2019; 380:2095-2103).
CIT still has a role as first-line treatment
Dr. Brown suggested that a PFS benefit may not be enough to recommend targeted agents over CIT. For one thing, the PFS benefit doesn’t apply to all patients, as the IGHV-mutated subgroup does equally well with CIT and targeted agents.
In the IGHV-mutated group from the E1912 trial, the 3-year PFS was 88% for patients who received Ib-R and those who received FCR (N Engl J Med. 2019 Aug 1;381:432-43). In the A041202 study, the 2-year PFS among IGHV-mutated patients was 87% in the BR arm, 86% in the Ib arm, and 88% in the Ib-R arm (N Engl J Med. 2018; 379:2517-28).
In the CLL14 trial, PFS rates were similar among IGHV-mutated patients who received chlorambucil plus obinutuzumab and IGHV-mutated or unmutated patients who received venetoclax and obinutuzumab (N Engl J Med. 2019; 380:2225-36).
Dr. Brown also noted that the overall improvement in PFS observed with ibrutinib and venetoclax doesn’t always translate to improved OS.
In the A041202 study, there was no significant difference in OS between the Ib, Ib-R, and BR arms (N Engl J Med. 2018; 379:2517-28). There was no significant difference in OS between the ibrutinib and chlorambucil arms in the iLLUMINATE trial (Lancet Oncol. 2019 Jan;20[1]:43-56). And there was no significant difference in OS between the venetoclax and chlorambucil arms in the CLL14 trial (N Engl J Med. 2019; 380:2225-36).
However, in the RESONATE-2 trial, ibrutinib provided an OS benefit over chlorambucil. The 2-year OS was 95% and 84%, respectively (P = .0145; Haematologica. Sept 2018;103:1502-10). Dr. Brown said the OS advantage in this study was due to the “very poor comparator of chlorambucil and very limited crossover.”
As Dr. Wierda mentioned, the OS rate was higher with Ib-R than with FCR in the E1912 trial. The 3-year OS rate was 98.8% and 91.5%, respectively (P less than .001; N Engl J Med. 2019 Aug 1;381:432-43). Dr. Brown noted, however, that there were few deaths in this study, and many of them “were not clearly related to the disease or its treatment.”
Dr. Brown also pointed out that FCR has been shown to have curative potential in IGHV-mutated CLL in both the FCR300 trial (Blood. 2016 127:303-9) and the CLL8 trial (Blood. 2016 127:208-15).
Another factor to consider is the greater cost of targeted agents. One analysis suggested the per-patient lifetime cost of CLL treatment in the United States will increase from $147,000 to $604,000 as targeted therapies overtake CIT as first-line treatment (J Clin Oncol. 2017 Jan 10;35[2]:166-174).
“Given all of the above, chemoimmunotherapy is going to remain part of the treatment repertoire for CLL,” Dr. Brown said. “It’s our only known potential cure for the fit, mutated patients ... and can also result in prolonged treatment-free intervals for patients who are older. As we manage CLL as a chronic disease over a lifetime, we need to continue to have this in our armamentarium.”
Specifically, Dr. Brown said CIT is appropriate for patients who don’t have del(17p) or mutated TP53. FCR should be given to young, fit patients with IGHV-mutated CLL, and FCR or BR should be given to older patients and young, fit patients with IGHV-unmutated CLL.
Dr. Brown and Dr. Wierda reported financial ties to multiple pharmaceutical companies, including makers of CLL treatments.
SAN FRANCISCO – Should targeted agents replace chemoimmunotherapy (CIT) as first-line treatment for chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL)? A recent debate suggests there’s no consensus.
William G. Wierda, MD, PhD, of The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center in Houston, and Jennifer R. Brown, MD, PhD, of Dana-Farber Cancer Institute in Boston, debated the topic at the National Comprehensive Cancer Network Hematologic Malignancies Annual Congress.
Dr. Wierda argued that CLL patients should receive a BTK inhibitor or BCL2 inhibitor, with or without obinutuzumab, as first-line therapy because these targeted agents have been shown to provide better progression-free survival (PFS) than CIT, and the targeted therapies may prolong overall survival (OS) as well.
Dr. Brown countered that targeted agents don’t improve PFS for all CLL patients, improved PFS doesn’t always translate to improved OS, and targeted agents cost more than CIT.
No role for CIT as first-line treatment
“We have two approaches right now, with nonchemoimmunotherapy-based treatment,” Dr. Wierda said. “One approach, with small-molecule inhibitors, is to have a sustained and durable period of disease control, particularly with BTK inhibitors. The other strategy that has emerged is deep remissions with fixed-duration treatment with BCL2 small-molecule inhibitor-based therapy, which, I would argue, is better than being exposed to genotoxic chemoimmunotherapy.”
Dr. Wierda went on to explain that the BTK inhibitor ibrutinib has been shown to improve PFS, compared with CIT, in phase 3 trials.
In the iLLUMINATE trial, researchers compared ibrutinib plus obinutuzumab to chlorambucil plus obinutuzumab as first-line treatment in CLL. At a median follow-up of 31.3 months, the median PFS was not reached in the ibrutinib arm and was 19 months in the chlorambucil arm (P less than .0001; Lancet Oncol. 2019 Jan;20[1]:43-56).
In the A041202 study, researchers compared ibrutinib alone (Ib) or in combination with rituximab (Ib-R) to bendamustine plus rituximab (BR) in untreated, older patients with CLL. The 2-year PFS estimates were 74% in the BR arm, 87% in the Ib arm, and 88% in the Ib-R arm (P less than .001 for BR vs. Ib or Ib-R; N Engl J Med. 2018; 379:2517-28).
In the E1912 trial, researchers compared Ib-R to fludarabine, cyclophosphamide, and rituximab (FCR) in younger, untreated CLL patients. The 3-year PFS was 89.4% with Ib-R and 72.9% with FCR (P less than .001; N Engl J Med. 2019 Aug 1;381:432-43).
Dr. Wierda noted that the E1912 trial also showed superior OS with Ib-R. The 3-year OS rate was 98.8% with Ib-R and 91.5% with FCR (P less than .001). However, there was no significant difference in OS between the treatment arms in the A041202 trial or the iLLUMINATE trial.
“But I would argue that is, in part, because of short follow-up,” Dr. Wierda said. “The trials were all designed to look at progression-free survival, not overall survival. With longer follow-up, we may see differences in overall survival emerging.”
Dr. Wierda went on to say that fixed‐duration treatment with the BCL2 inhibitor venetoclax can improve PFS over CIT.
In the phase 3 CLL14 trial, researchers compared fixed-duration treatment with venetoclax plus obinutuzumab to chlorambucil plus obinutuzumab in previously untreated CLL patients with comorbidities. The estimated PFS at 2 years was 88.2% in the venetoclax group and 64.1% in the chlorambucil group (P less than .001; N Engl J Med. 2019; 380:2225-36).
“[There was] no difference in overall survival,” Dr. Wierda noted. “But, again, I would argue ... that follow-up is relatively limited. We may ultimately see a difference in overall survival.”
Based on these findings, Dr. Wierda made the following treatment recommendations:
- Any CLL patient with del(17p) or TP53 mutation, and older, unfit patients with unmutated IGHV should receive a BTK inhibitor, with or without obinutuzumab.
- All young, fit patients, and older, unfit patients with mutated IGHV should receive a BCL2 inhibitor plus obinutuzumab.
Dr. Wierda also noted that ibrutinib and venetoclax in combination have shown early promise for patients with previously untreated CLL (N Engl J Med. 2019; 380:2095-2103).
CIT still has a role as first-line treatment
Dr. Brown suggested that a PFS benefit may not be enough to recommend targeted agents over CIT. For one thing, the PFS benefit doesn’t apply to all patients, as the IGHV-mutated subgroup does equally well with CIT and targeted agents.
In the IGHV-mutated group from the E1912 trial, the 3-year PFS was 88% for patients who received Ib-R and those who received FCR (N Engl J Med. 2019 Aug 1;381:432-43). In the A041202 study, the 2-year PFS among IGHV-mutated patients was 87% in the BR arm, 86% in the Ib arm, and 88% in the Ib-R arm (N Engl J Med. 2018; 379:2517-28).
In the CLL14 trial, PFS rates were similar among IGHV-mutated patients who received chlorambucil plus obinutuzumab and IGHV-mutated or unmutated patients who received venetoclax and obinutuzumab (N Engl J Med. 2019; 380:2225-36).
Dr. Brown also noted that the overall improvement in PFS observed with ibrutinib and venetoclax doesn’t always translate to improved OS.
In the A041202 study, there was no significant difference in OS between the Ib, Ib-R, and BR arms (N Engl J Med. 2018; 379:2517-28). There was no significant difference in OS between the ibrutinib and chlorambucil arms in the iLLUMINATE trial (Lancet Oncol. 2019 Jan;20[1]:43-56). And there was no significant difference in OS between the venetoclax and chlorambucil arms in the CLL14 trial (N Engl J Med. 2019; 380:2225-36).
However, in the RESONATE-2 trial, ibrutinib provided an OS benefit over chlorambucil. The 2-year OS was 95% and 84%, respectively (P = .0145; Haematologica. Sept 2018;103:1502-10). Dr. Brown said the OS advantage in this study was due to the “very poor comparator of chlorambucil and very limited crossover.”
As Dr. Wierda mentioned, the OS rate was higher with Ib-R than with FCR in the E1912 trial. The 3-year OS rate was 98.8% and 91.5%, respectively (P less than .001; N Engl J Med. 2019 Aug 1;381:432-43). Dr. Brown noted, however, that there were few deaths in this study, and many of them “were not clearly related to the disease or its treatment.”
Dr. Brown also pointed out that FCR has been shown to have curative potential in IGHV-mutated CLL in both the FCR300 trial (Blood. 2016 127:303-9) and the CLL8 trial (Blood. 2016 127:208-15).
Another factor to consider is the greater cost of targeted agents. One analysis suggested the per-patient lifetime cost of CLL treatment in the United States will increase from $147,000 to $604,000 as targeted therapies overtake CIT as first-line treatment (J Clin Oncol. 2017 Jan 10;35[2]:166-174).
“Given all of the above, chemoimmunotherapy is going to remain part of the treatment repertoire for CLL,” Dr. Brown said. “It’s our only known potential cure for the fit, mutated patients ... and can also result in prolonged treatment-free intervals for patients who are older. As we manage CLL as a chronic disease over a lifetime, we need to continue to have this in our armamentarium.”
Specifically, Dr. Brown said CIT is appropriate for patients who don’t have del(17p) or mutated TP53. FCR should be given to young, fit patients with IGHV-mutated CLL, and FCR or BR should be given to older patients and young, fit patients with IGHV-unmutated CLL.
Dr. Brown and Dr. Wierda reported financial ties to multiple pharmaceutical companies, including makers of CLL treatments.
SAN FRANCISCO – Should targeted agents replace chemoimmunotherapy (CIT) as first-line treatment for chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL)? A recent debate suggests there’s no consensus.
William G. Wierda, MD, PhD, of The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center in Houston, and Jennifer R. Brown, MD, PhD, of Dana-Farber Cancer Institute in Boston, debated the topic at the National Comprehensive Cancer Network Hematologic Malignancies Annual Congress.
Dr. Wierda argued that CLL patients should receive a BTK inhibitor or BCL2 inhibitor, with or without obinutuzumab, as first-line therapy because these targeted agents have been shown to provide better progression-free survival (PFS) than CIT, and the targeted therapies may prolong overall survival (OS) as well.
Dr. Brown countered that targeted agents don’t improve PFS for all CLL patients, improved PFS doesn’t always translate to improved OS, and targeted agents cost more than CIT.
No role for CIT as first-line treatment
“We have two approaches right now, with nonchemoimmunotherapy-based treatment,” Dr. Wierda said. “One approach, with small-molecule inhibitors, is to have a sustained and durable period of disease control, particularly with BTK inhibitors. The other strategy that has emerged is deep remissions with fixed-duration treatment with BCL2 small-molecule inhibitor-based therapy, which, I would argue, is better than being exposed to genotoxic chemoimmunotherapy.”
Dr. Wierda went on to explain that the BTK inhibitor ibrutinib has been shown to improve PFS, compared with CIT, in phase 3 trials.
In the iLLUMINATE trial, researchers compared ibrutinib plus obinutuzumab to chlorambucil plus obinutuzumab as first-line treatment in CLL. At a median follow-up of 31.3 months, the median PFS was not reached in the ibrutinib arm and was 19 months in the chlorambucil arm (P less than .0001; Lancet Oncol. 2019 Jan;20[1]:43-56).
In the A041202 study, researchers compared ibrutinib alone (Ib) or in combination with rituximab (Ib-R) to bendamustine plus rituximab (BR) in untreated, older patients with CLL. The 2-year PFS estimates were 74% in the BR arm, 87% in the Ib arm, and 88% in the Ib-R arm (P less than .001 for BR vs. Ib or Ib-R; N Engl J Med. 2018; 379:2517-28).
In the E1912 trial, researchers compared Ib-R to fludarabine, cyclophosphamide, and rituximab (FCR) in younger, untreated CLL patients. The 3-year PFS was 89.4% with Ib-R and 72.9% with FCR (P less than .001; N Engl J Med. 2019 Aug 1;381:432-43).
Dr. Wierda noted that the E1912 trial also showed superior OS with Ib-R. The 3-year OS rate was 98.8% with Ib-R and 91.5% with FCR (P less than .001). However, there was no significant difference in OS between the treatment arms in the A041202 trial or the iLLUMINATE trial.
“But I would argue that is, in part, because of short follow-up,” Dr. Wierda said. “The trials were all designed to look at progression-free survival, not overall survival. With longer follow-up, we may see differences in overall survival emerging.”
Dr. Wierda went on to say that fixed‐duration treatment with the BCL2 inhibitor venetoclax can improve PFS over CIT.
In the phase 3 CLL14 trial, researchers compared fixed-duration treatment with venetoclax plus obinutuzumab to chlorambucil plus obinutuzumab in previously untreated CLL patients with comorbidities. The estimated PFS at 2 years was 88.2% in the venetoclax group and 64.1% in the chlorambucil group (P less than .001; N Engl J Med. 2019; 380:2225-36).
“[There was] no difference in overall survival,” Dr. Wierda noted. “But, again, I would argue ... that follow-up is relatively limited. We may ultimately see a difference in overall survival.”
Based on these findings, Dr. Wierda made the following treatment recommendations:
- Any CLL patient with del(17p) or TP53 mutation, and older, unfit patients with unmutated IGHV should receive a BTK inhibitor, with or without obinutuzumab.
- All young, fit patients, and older, unfit patients with mutated IGHV should receive a BCL2 inhibitor plus obinutuzumab.
Dr. Wierda also noted that ibrutinib and venetoclax in combination have shown early promise for patients with previously untreated CLL (N Engl J Med. 2019; 380:2095-2103).
CIT still has a role as first-line treatment
Dr. Brown suggested that a PFS benefit may not be enough to recommend targeted agents over CIT. For one thing, the PFS benefit doesn’t apply to all patients, as the IGHV-mutated subgroup does equally well with CIT and targeted agents.
In the IGHV-mutated group from the E1912 trial, the 3-year PFS was 88% for patients who received Ib-R and those who received FCR (N Engl J Med. 2019 Aug 1;381:432-43). In the A041202 study, the 2-year PFS among IGHV-mutated patients was 87% in the BR arm, 86% in the Ib arm, and 88% in the Ib-R arm (N Engl J Med. 2018; 379:2517-28).
In the CLL14 trial, PFS rates were similar among IGHV-mutated patients who received chlorambucil plus obinutuzumab and IGHV-mutated or unmutated patients who received venetoclax and obinutuzumab (N Engl J Med. 2019; 380:2225-36).
Dr. Brown also noted that the overall improvement in PFS observed with ibrutinib and venetoclax doesn’t always translate to improved OS.
In the A041202 study, there was no significant difference in OS between the Ib, Ib-R, and BR arms (N Engl J Med. 2018; 379:2517-28). There was no significant difference in OS between the ibrutinib and chlorambucil arms in the iLLUMINATE trial (Lancet Oncol. 2019 Jan;20[1]:43-56). And there was no significant difference in OS between the venetoclax and chlorambucil arms in the CLL14 trial (N Engl J Med. 2019; 380:2225-36).
However, in the RESONATE-2 trial, ibrutinib provided an OS benefit over chlorambucil. The 2-year OS was 95% and 84%, respectively (P = .0145; Haematologica. Sept 2018;103:1502-10). Dr. Brown said the OS advantage in this study was due to the “very poor comparator of chlorambucil and very limited crossover.”
As Dr. Wierda mentioned, the OS rate was higher with Ib-R than with FCR in the E1912 trial. The 3-year OS rate was 98.8% and 91.5%, respectively (P less than .001; N Engl J Med. 2019 Aug 1;381:432-43). Dr. Brown noted, however, that there were few deaths in this study, and many of them “were not clearly related to the disease or its treatment.”
Dr. Brown also pointed out that FCR has been shown to have curative potential in IGHV-mutated CLL in both the FCR300 trial (Blood. 2016 127:303-9) and the CLL8 trial (Blood. 2016 127:208-15).
Another factor to consider is the greater cost of targeted agents. One analysis suggested the per-patient lifetime cost of CLL treatment in the United States will increase from $147,000 to $604,000 as targeted therapies overtake CIT as first-line treatment (J Clin Oncol. 2017 Jan 10;35[2]:166-174).
“Given all of the above, chemoimmunotherapy is going to remain part of the treatment repertoire for CLL,” Dr. Brown said. “It’s our only known potential cure for the fit, mutated patients ... and can also result in prolonged treatment-free intervals for patients who are older. As we manage CLL as a chronic disease over a lifetime, we need to continue to have this in our armamentarium.”
Specifically, Dr. Brown said CIT is appropriate for patients who don’t have del(17p) or mutated TP53. FCR should be given to young, fit patients with IGHV-mutated CLL, and FCR or BR should be given to older patients and young, fit patients with IGHV-unmutated CLL.
Dr. Brown and Dr. Wierda reported financial ties to multiple pharmaceutical companies, including makers of CLL treatments.
REPORTING FROM NCCN HEMATOLOGIC MALIGNANCIES
Decoding biosimilar approvals
SAN FRANCISCO – Several factors must be considered when extrapolating biosimilar results, according to a speaker at the National Comprehensive Cancer Network Hematologic Malignancies Annual Congress.
In this context, “extrapolation” means expanding the use of an approved biosimilar from one indication to another, based on efficacy and safety data from the first indication, Andrew D. Zelenetz, MD, PhD, of Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, New York, explained at the meeting.
To determine if extrapolation is appropriate, regulatory agencies consider the biosimilar’s mechanism of action in each indication; pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics, and immunogenicity in the different patient populations; differences in expected toxicities for each condition and population; and any other factor that may affect safety or efficacy.
To illustrate the process, Dr. Zelenetz explained how results with a rituximab biosimilar in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) cannot be extrapolated to B‐cell non‐Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL), but results with that same biosimilar in follicular lymphoma can be extrapolated to other types of B-cell NHL.
The biosimilar is rituximab-abbs (CT‐P10, Truxima). In a phase 1 trial of patients with RA, rituximab-abbs demonstrated biosimilarity to the reference product (Ann Rheum Dis. 2017;76[3]:566‐70).
The RA results cannot be extrapolated to B-cell NHL for a few reasons, according to Dr. Zelenetz. He noted that rituximab’s mechanism of action is antibody-dependent cell‐mediated cytotoxicity in both RA and NHL. However, the target in RA is the normal B cell, and the target in NHL is the malignant B cell.
In addition, the pharmacokinetics of rituximab are “drastically different” in RA and NHL, Dr. Zelenetz said. Differences in pharmacokinetics support different dosing approaches in the two diseases.
Another big difference is immunogenicity. Anti‐CD20 antibodies develop in 15%-17% of RA patients, Dr. Zelenetz said, but the risk of antibody development is less than 1% in lymphoma.
Though extrapolation from RA to B‐cell NHL was not possible, it was possible to extrapolate results with rituximab-abbs in follicular lymphoma to other B-cell NHLs.
The study used was a phase 3 trial comparing rituximab-abbs to rituximab – both in combination with cyclophosphamide, vincristine, and prednisone – in patients with newly diagnosed, advanced stage follicular lymphoma.
This study showed no difference in pharmacokinetics or pharmacodynamics between rituximab-abbs and rituximab. The two agents also had comparable safety profiles and produced similar response rates (Lancet Haematol. 2017 Jul 13;4:e362‐73).
Rituximab‐abbs was approved in the United States based on these data, and results from this trial were extrapolated to other types of B-cell NHL. The results were extrapolated because the mechanism of action, pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics, and immunogenicity of rituximab are the same across B-cell NHLs, Dr. Zelenetz noted.
“Extrapolation is a critical part of biosimilarity development,” he said. “As long as scientific justification for extrapolation exists, I believe that extrapolation makes good sense.”
Dr. Zelenetz reported relationships with AbbVie, Adaptive Biotechnologies, Amgen, AstraZeneca, BeiGene, Celgene, Genentech, Gilead Sciences, Janssen, MEI Pharma, MorphoSys AG, Novartis, Pharmacyclics, and Roche.
SAN FRANCISCO – Several factors must be considered when extrapolating biosimilar results, according to a speaker at the National Comprehensive Cancer Network Hematologic Malignancies Annual Congress.
In this context, “extrapolation” means expanding the use of an approved biosimilar from one indication to another, based on efficacy and safety data from the first indication, Andrew D. Zelenetz, MD, PhD, of Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, New York, explained at the meeting.
To determine if extrapolation is appropriate, regulatory agencies consider the biosimilar’s mechanism of action in each indication; pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics, and immunogenicity in the different patient populations; differences in expected toxicities for each condition and population; and any other factor that may affect safety or efficacy.
To illustrate the process, Dr. Zelenetz explained how results with a rituximab biosimilar in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) cannot be extrapolated to B‐cell non‐Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL), but results with that same biosimilar in follicular lymphoma can be extrapolated to other types of B-cell NHL.
The biosimilar is rituximab-abbs (CT‐P10, Truxima). In a phase 1 trial of patients with RA, rituximab-abbs demonstrated biosimilarity to the reference product (Ann Rheum Dis. 2017;76[3]:566‐70).
The RA results cannot be extrapolated to B-cell NHL for a few reasons, according to Dr. Zelenetz. He noted that rituximab’s mechanism of action is antibody-dependent cell‐mediated cytotoxicity in both RA and NHL. However, the target in RA is the normal B cell, and the target in NHL is the malignant B cell.
In addition, the pharmacokinetics of rituximab are “drastically different” in RA and NHL, Dr. Zelenetz said. Differences in pharmacokinetics support different dosing approaches in the two diseases.
Another big difference is immunogenicity. Anti‐CD20 antibodies develop in 15%-17% of RA patients, Dr. Zelenetz said, but the risk of antibody development is less than 1% in lymphoma.
Though extrapolation from RA to B‐cell NHL was not possible, it was possible to extrapolate results with rituximab-abbs in follicular lymphoma to other B-cell NHLs.
The study used was a phase 3 trial comparing rituximab-abbs to rituximab – both in combination with cyclophosphamide, vincristine, and prednisone – in patients with newly diagnosed, advanced stage follicular lymphoma.
This study showed no difference in pharmacokinetics or pharmacodynamics between rituximab-abbs and rituximab. The two agents also had comparable safety profiles and produced similar response rates (Lancet Haematol. 2017 Jul 13;4:e362‐73).
Rituximab‐abbs was approved in the United States based on these data, and results from this trial were extrapolated to other types of B-cell NHL. The results were extrapolated because the mechanism of action, pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics, and immunogenicity of rituximab are the same across B-cell NHLs, Dr. Zelenetz noted.
“Extrapolation is a critical part of biosimilarity development,” he said. “As long as scientific justification for extrapolation exists, I believe that extrapolation makes good sense.”
Dr. Zelenetz reported relationships with AbbVie, Adaptive Biotechnologies, Amgen, AstraZeneca, BeiGene, Celgene, Genentech, Gilead Sciences, Janssen, MEI Pharma, MorphoSys AG, Novartis, Pharmacyclics, and Roche.
SAN FRANCISCO – Several factors must be considered when extrapolating biosimilar results, according to a speaker at the National Comprehensive Cancer Network Hematologic Malignancies Annual Congress.
In this context, “extrapolation” means expanding the use of an approved biosimilar from one indication to another, based on efficacy and safety data from the first indication, Andrew D. Zelenetz, MD, PhD, of Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, New York, explained at the meeting.
To determine if extrapolation is appropriate, regulatory agencies consider the biosimilar’s mechanism of action in each indication; pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics, and immunogenicity in the different patient populations; differences in expected toxicities for each condition and population; and any other factor that may affect safety or efficacy.
To illustrate the process, Dr. Zelenetz explained how results with a rituximab biosimilar in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) cannot be extrapolated to B‐cell non‐Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL), but results with that same biosimilar in follicular lymphoma can be extrapolated to other types of B-cell NHL.
The biosimilar is rituximab-abbs (CT‐P10, Truxima). In a phase 1 trial of patients with RA, rituximab-abbs demonstrated biosimilarity to the reference product (Ann Rheum Dis. 2017;76[3]:566‐70).
The RA results cannot be extrapolated to B-cell NHL for a few reasons, according to Dr. Zelenetz. He noted that rituximab’s mechanism of action is antibody-dependent cell‐mediated cytotoxicity in both RA and NHL. However, the target in RA is the normal B cell, and the target in NHL is the malignant B cell.
In addition, the pharmacokinetics of rituximab are “drastically different” in RA and NHL, Dr. Zelenetz said. Differences in pharmacokinetics support different dosing approaches in the two diseases.
Another big difference is immunogenicity. Anti‐CD20 antibodies develop in 15%-17% of RA patients, Dr. Zelenetz said, but the risk of antibody development is less than 1% in lymphoma.
Though extrapolation from RA to B‐cell NHL was not possible, it was possible to extrapolate results with rituximab-abbs in follicular lymphoma to other B-cell NHLs.
The study used was a phase 3 trial comparing rituximab-abbs to rituximab – both in combination with cyclophosphamide, vincristine, and prednisone – in patients with newly diagnosed, advanced stage follicular lymphoma.
This study showed no difference in pharmacokinetics or pharmacodynamics between rituximab-abbs and rituximab. The two agents also had comparable safety profiles and produced similar response rates (Lancet Haematol. 2017 Jul 13;4:e362‐73).
Rituximab‐abbs was approved in the United States based on these data, and results from this trial were extrapolated to other types of B-cell NHL. The results were extrapolated because the mechanism of action, pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics, and immunogenicity of rituximab are the same across B-cell NHLs, Dr. Zelenetz noted.
“Extrapolation is a critical part of biosimilarity development,” he said. “As long as scientific justification for extrapolation exists, I believe that extrapolation makes good sense.”
Dr. Zelenetz reported relationships with AbbVie, Adaptive Biotechnologies, Amgen, AstraZeneca, BeiGene, Celgene, Genentech, Gilead Sciences, Janssen, MEI Pharma, MorphoSys AG, Novartis, Pharmacyclics, and Roche.
REPORTING FROM NCCN HEMATOLOGIC MALIGNANCIES
German CLLM1 study: 4-year data raise concerns about lenalidomide maintenance
EDINBURGH – Lenalidomide maintenance therapy after chemoimmunotherapy in high-risk chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) improved progression- and event-free survival, but not overall survival, and was associated with three unexpected cases of B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (B-ALL), according to 4-year follow-up in the German, phase 3 CLLM1 study.
Given these findings, and in particular the B-ALL cases, lenalidomide cannot be generally recommended as maintenance therapy in high-risk CLL, Moritz Fürstenau, MD, of the University of Cologne, reported in a poster at the International Workshop on Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia.
At a median follow-up of 47.6 months, median progression-free survival (PFS) by investigator assessment was 54.7 months in 60 patients randomized to receive lenalidomide maintenance therapy, compared with 23.2 months for 29 who received placebo (hazard ratio, 0.22), and median event-free survival (EFS) was 46.2 months vs. 14.6 months in the groups, respectively (hazard ratio, 0.24), Dr. Fürstenau said during an oral poster presentation at the conference.
“So ... after 4 years of observation, we still see improvement in PFS, EFS, and time to next treatment,” he said, also noting that minimal residual disease (MRD) negativity was achieved by eight patients in the lenalidomide group, and in none of the patients in the placebo group.
However, overall survival was 79% and 87% in the lenalidomide and placebo groups, respectively (HR, 1.53). In total, 12 patients died, including 9 in the lenalidomide group from fatal infections, concomitant disease, CLL progression, or unknown causes. Three patients in the placebo group died from CLL progression or fatal infection.
In the lenalidomide group, hematological and solid tumor second primary malignancies were reported in three and four patients, respectively (5% and 7%), compared with zero and two patients, respectively (0% and 7%), in the placebo group.
The CLLM1 study of the German CLL Study Group evaluated maintenance with lenalidomide vs. placebo in patients with high risk of progression after first-line chemoimmunotherapy. Previously reported results also favored lenalidomide maintenance for PFS, but not OS, Dr. Fürstenau said, adding that the study was unblinded at a median follow-up of 17.9 months, and in November 2017 treatment was stopped when two cases of B-ALL were observed. A third case was reported in 2018.
The current analysis includes data available through December 2018, and the findings warrant further investigation to analyze the unexpectedly high incidence of B-ALL, he said.
The CLLM1 study was funded by Celgene.
sworcester@mdedge.com
EDINBURGH – Lenalidomide maintenance therapy after chemoimmunotherapy in high-risk chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) improved progression- and event-free survival, but not overall survival, and was associated with three unexpected cases of B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (B-ALL), according to 4-year follow-up in the German, phase 3 CLLM1 study.
Given these findings, and in particular the B-ALL cases, lenalidomide cannot be generally recommended as maintenance therapy in high-risk CLL, Moritz Fürstenau, MD, of the University of Cologne, reported in a poster at the International Workshop on Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia.
At a median follow-up of 47.6 months, median progression-free survival (PFS) by investigator assessment was 54.7 months in 60 patients randomized to receive lenalidomide maintenance therapy, compared with 23.2 months for 29 who received placebo (hazard ratio, 0.22), and median event-free survival (EFS) was 46.2 months vs. 14.6 months in the groups, respectively (hazard ratio, 0.24), Dr. Fürstenau said during an oral poster presentation at the conference.
“So ... after 4 years of observation, we still see improvement in PFS, EFS, and time to next treatment,” he said, also noting that minimal residual disease (MRD) negativity was achieved by eight patients in the lenalidomide group, and in none of the patients in the placebo group.
However, overall survival was 79% and 87% in the lenalidomide and placebo groups, respectively (HR, 1.53). In total, 12 patients died, including 9 in the lenalidomide group from fatal infections, concomitant disease, CLL progression, or unknown causes. Three patients in the placebo group died from CLL progression or fatal infection.
In the lenalidomide group, hematological and solid tumor second primary malignancies were reported in three and four patients, respectively (5% and 7%), compared with zero and two patients, respectively (0% and 7%), in the placebo group.
The CLLM1 study of the German CLL Study Group evaluated maintenance with lenalidomide vs. placebo in patients with high risk of progression after first-line chemoimmunotherapy. Previously reported results also favored lenalidomide maintenance for PFS, but not OS, Dr. Fürstenau said, adding that the study was unblinded at a median follow-up of 17.9 months, and in November 2017 treatment was stopped when two cases of B-ALL were observed. A third case was reported in 2018.
The current analysis includes data available through December 2018, and the findings warrant further investigation to analyze the unexpectedly high incidence of B-ALL, he said.
The CLLM1 study was funded by Celgene.
sworcester@mdedge.com
EDINBURGH – Lenalidomide maintenance therapy after chemoimmunotherapy in high-risk chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) improved progression- and event-free survival, but not overall survival, and was associated with three unexpected cases of B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (B-ALL), according to 4-year follow-up in the German, phase 3 CLLM1 study.
Given these findings, and in particular the B-ALL cases, lenalidomide cannot be generally recommended as maintenance therapy in high-risk CLL, Moritz Fürstenau, MD, of the University of Cologne, reported in a poster at the International Workshop on Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia.
At a median follow-up of 47.6 months, median progression-free survival (PFS) by investigator assessment was 54.7 months in 60 patients randomized to receive lenalidomide maintenance therapy, compared with 23.2 months for 29 who received placebo (hazard ratio, 0.22), and median event-free survival (EFS) was 46.2 months vs. 14.6 months in the groups, respectively (hazard ratio, 0.24), Dr. Fürstenau said during an oral poster presentation at the conference.
“So ... after 4 years of observation, we still see improvement in PFS, EFS, and time to next treatment,” he said, also noting that minimal residual disease (MRD) negativity was achieved by eight patients in the lenalidomide group, and in none of the patients in the placebo group.
However, overall survival was 79% and 87% in the lenalidomide and placebo groups, respectively (HR, 1.53). In total, 12 patients died, including 9 in the lenalidomide group from fatal infections, concomitant disease, CLL progression, or unknown causes. Three patients in the placebo group died from CLL progression or fatal infection.
In the lenalidomide group, hematological and solid tumor second primary malignancies were reported in three and four patients, respectively (5% and 7%), compared with zero and two patients, respectively (0% and 7%), in the placebo group.
The CLLM1 study of the German CLL Study Group evaluated maintenance with lenalidomide vs. placebo in patients with high risk of progression after first-line chemoimmunotherapy. Previously reported results also favored lenalidomide maintenance for PFS, but not OS, Dr. Fürstenau said, adding that the study was unblinded at a median follow-up of 17.9 months, and in November 2017 treatment was stopped when two cases of B-ALL were observed. A third case was reported in 2018.
The current analysis includes data available through December 2018, and the findings warrant further investigation to analyze the unexpectedly high incidence of B-ALL, he said.
The CLLM1 study was funded by Celgene.
sworcester@mdedge.com
REPORTING FROM iwCLL 2019
ICLL-07 trial: MRD-driven strategy yields prolonged survival
EDINBURGH – Treatment induction with obinutuzumab and ibrutinib followed by a minimal residual disease (MRD)–driven treatment strategy in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) yields a high long-term complete response rate and prolonged progression-free and overall survival, according to findings from the phase 2 ICLL-07 trial.
The intent-to-treat (ITT) complete response rate at 16 months in 135 patients who were treated with this strategy was 62%, Anne-Sophie Michallet, MD, reported at the International Workshop on Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia.
Patients in the multicenter, open-label trial conducted by the French Innovative Leukemia Organization (FILO) were previously untreated, medically fit patients with CLL and no 17p deletion. They were enrolled between November 2015 and May 2017 to receive eight 1,000 mg IV doses of obinutuzumab over six 4-week cycles along with oral Bruton’s tyrosine kinase (BTK) inhibitor ibrutinib at a dose of 420 mg daily for 9 months.
Ten patients (7.7%) achieved complete response with bone marrow MRD less than 0.01% (undetectable) at 9 months and, by study protocol, continued on only the ibrutinib for 6 additional months. The remaining 120 evaluable patients received four 4-week cycles of fludarabine/cyclophosphamide along with the obinutuzumab and ibrutinib for 6 additional months, explained Dr. Michallet of Centre Léon Bérard, Lyon, France.
The ITT rate at 16 months – the primary endpoint of the study – was achieved with no more than four cycles of fludarabine/cyclophosphamide and obinutuzumab, and exceeded the primary objective of demonstrating a 30% or higher rate of complete response with bone marrow MRD less than 0.01% at the month 16 ITT analysis, she said.
“The ... strategy yielded an overall response rate of 100%, a complete response rate, according to iwCLL [criteria], of 73%, a bone marrow MRD–undetectable rate of 79% [in the ITT population],” she said, adding that the primary objective was achieved with a complete response with a peripheral blood and bone marrow MRD–undetectable rate of 62%.
Response assessments at months 9 and 16 involved whole-body computed tomography scans with tumor measurements and bone marrow trephine biopsy for patients in clinical complete response. MRD testing was performed by eight-color flow cytometry in both peripheral blood and bone marrow.
After month 16, response was clinically assessed every 3 months, and peripheral blood MRD was assessed every 6 months until month 40.
“With a median follow-up of 26.3 months, the 2-year progression-free survival and overall survival were, respectively, 97% and 97.5%,” Dr. Michallet said, noting that the longitudinal follow-up of peripheral blood MRD in the entire cohort showed durability of a deep response. The rate of peripheral blood MRD less than 0.01% at 22 months was 77% in the 10 patients who received only ibrutinib after the 9-month assessment, and 93% in those who received fludarabine/cyclophosphamide after the 9-month assessment.
In patients with immunoglobulin heavy gene variable (IGHV) mutations, the rate of peripheral blood MRD less than 0.01% at month 22 was 96%, and in those without IGHV mutations, the rate was 77%, she noted.
The findings demonstrate that the approach has merit in medically fit, treatment-naive patients with CLL and no 17p deletion, she said, explaining that the fixed-duration, MRD-driven strategy used in this study was developed to “avoid or at least reduce chemotherapy exposure” in the first-line treatment of such patients.
Indeed, the approach was associated with “a high [complete response] rate, a high level of undetectable bone marrow MRD, an acceptable safety profile, and a sustained MRD negativity rate at 12 months after the end of the treatment,” she said.
“This highly effective strategy combining a BTK inhibitor and abbreviated immunochemotherapy deserves further investigation with randomized trials,” she concluded.
ICLL-07 FILO was funded by Roche and Janssen. Dr. Michallet reported having no disclosures.
EDINBURGH – Treatment induction with obinutuzumab and ibrutinib followed by a minimal residual disease (MRD)–driven treatment strategy in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) yields a high long-term complete response rate and prolonged progression-free and overall survival, according to findings from the phase 2 ICLL-07 trial.
The intent-to-treat (ITT) complete response rate at 16 months in 135 patients who were treated with this strategy was 62%, Anne-Sophie Michallet, MD, reported at the International Workshop on Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia.
Patients in the multicenter, open-label trial conducted by the French Innovative Leukemia Organization (FILO) were previously untreated, medically fit patients with CLL and no 17p deletion. They were enrolled between November 2015 and May 2017 to receive eight 1,000 mg IV doses of obinutuzumab over six 4-week cycles along with oral Bruton’s tyrosine kinase (BTK) inhibitor ibrutinib at a dose of 420 mg daily for 9 months.
Ten patients (7.7%) achieved complete response with bone marrow MRD less than 0.01% (undetectable) at 9 months and, by study protocol, continued on only the ibrutinib for 6 additional months. The remaining 120 evaluable patients received four 4-week cycles of fludarabine/cyclophosphamide along with the obinutuzumab and ibrutinib for 6 additional months, explained Dr. Michallet of Centre Léon Bérard, Lyon, France.
The ITT rate at 16 months – the primary endpoint of the study – was achieved with no more than four cycles of fludarabine/cyclophosphamide and obinutuzumab, and exceeded the primary objective of demonstrating a 30% or higher rate of complete response with bone marrow MRD less than 0.01% at the month 16 ITT analysis, she said.
“The ... strategy yielded an overall response rate of 100%, a complete response rate, according to iwCLL [criteria], of 73%, a bone marrow MRD–undetectable rate of 79% [in the ITT population],” she said, adding that the primary objective was achieved with a complete response with a peripheral blood and bone marrow MRD–undetectable rate of 62%.
Response assessments at months 9 and 16 involved whole-body computed tomography scans with tumor measurements and bone marrow trephine biopsy for patients in clinical complete response. MRD testing was performed by eight-color flow cytometry in both peripheral blood and bone marrow.
After month 16, response was clinically assessed every 3 months, and peripheral blood MRD was assessed every 6 months until month 40.
“With a median follow-up of 26.3 months, the 2-year progression-free survival and overall survival were, respectively, 97% and 97.5%,” Dr. Michallet said, noting that the longitudinal follow-up of peripheral blood MRD in the entire cohort showed durability of a deep response. The rate of peripheral blood MRD less than 0.01% at 22 months was 77% in the 10 patients who received only ibrutinib after the 9-month assessment, and 93% in those who received fludarabine/cyclophosphamide after the 9-month assessment.
In patients with immunoglobulin heavy gene variable (IGHV) mutations, the rate of peripheral blood MRD less than 0.01% at month 22 was 96%, and in those without IGHV mutations, the rate was 77%, she noted.
The findings demonstrate that the approach has merit in medically fit, treatment-naive patients with CLL and no 17p deletion, she said, explaining that the fixed-duration, MRD-driven strategy used in this study was developed to “avoid or at least reduce chemotherapy exposure” in the first-line treatment of such patients.
Indeed, the approach was associated with “a high [complete response] rate, a high level of undetectable bone marrow MRD, an acceptable safety profile, and a sustained MRD negativity rate at 12 months after the end of the treatment,” she said.
“This highly effective strategy combining a BTK inhibitor and abbreviated immunochemotherapy deserves further investigation with randomized trials,” she concluded.
ICLL-07 FILO was funded by Roche and Janssen. Dr. Michallet reported having no disclosures.
EDINBURGH – Treatment induction with obinutuzumab and ibrutinib followed by a minimal residual disease (MRD)–driven treatment strategy in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) yields a high long-term complete response rate and prolonged progression-free and overall survival, according to findings from the phase 2 ICLL-07 trial.
The intent-to-treat (ITT) complete response rate at 16 months in 135 patients who were treated with this strategy was 62%, Anne-Sophie Michallet, MD, reported at the International Workshop on Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia.
Patients in the multicenter, open-label trial conducted by the French Innovative Leukemia Organization (FILO) were previously untreated, medically fit patients with CLL and no 17p deletion. They were enrolled between November 2015 and May 2017 to receive eight 1,000 mg IV doses of obinutuzumab over six 4-week cycles along with oral Bruton’s tyrosine kinase (BTK) inhibitor ibrutinib at a dose of 420 mg daily for 9 months.
Ten patients (7.7%) achieved complete response with bone marrow MRD less than 0.01% (undetectable) at 9 months and, by study protocol, continued on only the ibrutinib for 6 additional months. The remaining 120 evaluable patients received four 4-week cycles of fludarabine/cyclophosphamide along with the obinutuzumab and ibrutinib for 6 additional months, explained Dr. Michallet of Centre Léon Bérard, Lyon, France.
The ITT rate at 16 months – the primary endpoint of the study – was achieved with no more than four cycles of fludarabine/cyclophosphamide and obinutuzumab, and exceeded the primary objective of demonstrating a 30% or higher rate of complete response with bone marrow MRD less than 0.01% at the month 16 ITT analysis, she said.
“The ... strategy yielded an overall response rate of 100%, a complete response rate, according to iwCLL [criteria], of 73%, a bone marrow MRD–undetectable rate of 79% [in the ITT population],” she said, adding that the primary objective was achieved with a complete response with a peripheral blood and bone marrow MRD–undetectable rate of 62%.
Response assessments at months 9 and 16 involved whole-body computed tomography scans with tumor measurements and bone marrow trephine biopsy for patients in clinical complete response. MRD testing was performed by eight-color flow cytometry in both peripheral blood and bone marrow.
After month 16, response was clinically assessed every 3 months, and peripheral blood MRD was assessed every 6 months until month 40.
“With a median follow-up of 26.3 months, the 2-year progression-free survival and overall survival were, respectively, 97% and 97.5%,” Dr. Michallet said, noting that the longitudinal follow-up of peripheral blood MRD in the entire cohort showed durability of a deep response. The rate of peripheral blood MRD less than 0.01% at 22 months was 77% in the 10 patients who received only ibrutinib after the 9-month assessment, and 93% in those who received fludarabine/cyclophosphamide after the 9-month assessment.
In patients with immunoglobulin heavy gene variable (IGHV) mutations, the rate of peripheral blood MRD less than 0.01% at month 22 was 96%, and in those without IGHV mutations, the rate was 77%, she noted.
The findings demonstrate that the approach has merit in medically fit, treatment-naive patients with CLL and no 17p deletion, she said, explaining that the fixed-duration, MRD-driven strategy used in this study was developed to “avoid or at least reduce chemotherapy exposure” in the first-line treatment of such patients.
Indeed, the approach was associated with “a high [complete response] rate, a high level of undetectable bone marrow MRD, an acceptable safety profile, and a sustained MRD negativity rate at 12 months after the end of the treatment,” she said.
“This highly effective strategy combining a BTK inhibitor and abbreviated immunochemotherapy deserves further investigation with randomized trials,” she concluded.
ICLL-07 FILO was funded by Roche and Janssen. Dr. Michallet reported having no disclosures.
REPORTING FROM iwCLL 2019
GALACTIC CLL trial: Obinutuzumab consolidation helps eradicate MRD
EDINBURGH – Consolidation therapy with obinutuzumab after chemoimmunotherapy for B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia (B-CLL) was highly effective for eradicating minimal residual disease (MRD) within 6 months following randomization in the seamless phase 2/3 GALACTIC trial.
Of 14 patients who were MRD positive after chemoimmunotherapy and randomized to consolidation with the type II monoclonal antibody targeting the CD20 antigen, 10 achieved MRD negativity in the bone marrow by 6 months, and 13 achieved MRD negativity in the peripheral blood by 6 months, Talha Munir, MD, reported at the International Workshop on Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia.
“And that translated into [progression-free survival] improvement in the consolidation arm,” said Dr. Munir of St. James’s University, Leeds, England.
The median progression-free survival in that arm was not reached, whereas progression-free survival in 15 MRD-positive patients randomized to the nonconsolidation arm was 16.6 months, he said.
Further, no difference was seen in median progression-free survival, overall survival, or MRD duration between the consolidation arm and 19 patients who were not randomized because of MRD negativity after chemoimmunotherapy, he noted.
Achieving MRD negativity in CLL confers a survival advantage, and obinutuzumab has shown greater efficacy with respect to MRD in CLL when compared with previous anti-CD20 antibodies, and it is less immune suppressive than the anti-CD52 antibody alemtuzumab, he explained.
The GALACTIC trial was designed to assess the safety and efficacy of obinutuzumab consolidation for eradicating MRD and whether its effects would prolong progression-free survival in patients with B-CLL who recently responded to chemoimmunotherapy. Those achieving complete response or partial response at 3-24 months after chemoimmunotherapy, and who remained MRD-positive, were eligible for randomization.
The planned sample size was 188 patients, but the trial was closed early in February 2017 because of poor recruitment; a total of 48 patients were enrolled, including the 19 nonrandomized, MRD-negative patients.
Patients randomized to consolidation received 1,000 mg of obinutuzumab weekly for the first four doses, and then every other week for four additional doses.
Obinutuzumab was well tolerated with minimal infusion-related reactions and toxicity, Dr. Munir said.
Despite the low recruitment, both the phase 2 and 3 endpoints were assessed as positive, because the consolidation strategy was so efficacious, Dr. Munir noted, concluding that the findings provide further evidence of the value of MRD negativity for improving outcomes in CLL.
The GALACTIC trial was developed by the GALACTIC Trial Management Group with the support of the UKCLL/NCRI CLL Clinical Trials Subgroup. The trial is funded by Cancer Research UK and Roche and sponsored by the University of Leeds. Dr. Munir reported having no disclosures.
sworcester@mdedge.com
EDINBURGH – Consolidation therapy with obinutuzumab after chemoimmunotherapy for B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia (B-CLL) was highly effective for eradicating minimal residual disease (MRD) within 6 months following randomization in the seamless phase 2/3 GALACTIC trial.
Of 14 patients who were MRD positive after chemoimmunotherapy and randomized to consolidation with the type II monoclonal antibody targeting the CD20 antigen, 10 achieved MRD negativity in the bone marrow by 6 months, and 13 achieved MRD negativity in the peripheral blood by 6 months, Talha Munir, MD, reported at the International Workshop on Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia.
“And that translated into [progression-free survival] improvement in the consolidation arm,” said Dr. Munir of St. James’s University, Leeds, England.
The median progression-free survival in that arm was not reached, whereas progression-free survival in 15 MRD-positive patients randomized to the nonconsolidation arm was 16.6 months, he said.
Further, no difference was seen in median progression-free survival, overall survival, or MRD duration between the consolidation arm and 19 patients who were not randomized because of MRD negativity after chemoimmunotherapy, he noted.
Achieving MRD negativity in CLL confers a survival advantage, and obinutuzumab has shown greater efficacy with respect to MRD in CLL when compared with previous anti-CD20 antibodies, and it is less immune suppressive than the anti-CD52 antibody alemtuzumab, he explained.
The GALACTIC trial was designed to assess the safety and efficacy of obinutuzumab consolidation for eradicating MRD and whether its effects would prolong progression-free survival in patients with B-CLL who recently responded to chemoimmunotherapy. Those achieving complete response or partial response at 3-24 months after chemoimmunotherapy, and who remained MRD-positive, were eligible for randomization.
The planned sample size was 188 patients, but the trial was closed early in February 2017 because of poor recruitment; a total of 48 patients were enrolled, including the 19 nonrandomized, MRD-negative patients.
Patients randomized to consolidation received 1,000 mg of obinutuzumab weekly for the first four doses, and then every other week for four additional doses.
Obinutuzumab was well tolerated with minimal infusion-related reactions and toxicity, Dr. Munir said.
Despite the low recruitment, both the phase 2 and 3 endpoints were assessed as positive, because the consolidation strategy was so efficacious, Dr. Munir noted, concluding that the findings provide further evidence of the value of MRD negativity for improving outcomes in CLL.
The GALACTIC trial was developed by the GALACTIC Trial Management Group with the support of the UKCLL/NCRI CLL Clinical Trials Subgroup. The trial is funded by Cancer Research UK and Roche and sponsored by the University of Leeds. Dr. Munir reported having no disclosures.
sworcester@mdedge.com
EDINBURGH – Consolidation therapy with obinutuzumab after chemoimmunotherapy for B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia (B-CLL) was highly effective for eradicating minimal residual disease (MRD) within 6 months following randomization in the seamless phase 2/3 GALACTIC trial.
Of 14 patients who were MRD positive after chemoimmunotherapy and randomized to consolidation with the type II monoclonal antibody targeting the CD20 antigen, 10 achieved MRD negativity in the bone marrow by 6 months, and 13 achieved MRD negativity in the peripheral blood by 6 months, Talha Munir, MD, reported at the International Workshop on Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia.
“And that translated into [progression-free survival] improvement in the consolidation arm,” said Dr. Munir of St. James’s University, Leeds, England.
The median progression-free survival in that arm was not reached, whereas progression-free survival in 15 MRD-positive patients randomized to the nonconsolidation arm was 16.6 months, he said.
Further, no difference was seen in median progression-free survival, overall survival, or MRD duration between the consolidation arm and 19 patients who were not randomized because of MRD negativity after chemoimmunotherapy, he noted.
Achieving MRD negativity in CLL confers a survival advantage, and obinutuzumab has shown greater efficacy with respect to MRD in CLL when compared with previous anti-CD20 antibodies, and it is less immune suppressive than the anti-CD52 antibody alemtuzumab, he explained.
The GALACTIC trial was designed to assess the safety and efficacy of obinutuzumab consolidation for eradicating MRD and whether its effects would prolong progression-free survival in patients with B-CLL who recently responded to chemoimmunotherapy. Those achieving complete response or partial response at 3-24 months after chemoimmunotherapy, and who remained MRD-positive, were eligible for randomization.
The planned sample size was 188 patients, but the trial was closed early in February 2017 because of poor recruitment; a total of 48 patients were enrolled, including the 19 nonrandomized, MRD-negative patients.
Patients randomized to consolidation received 1,000 mg of obinutuzumab weekly for the first four doses, and then every other week for four additional doses.
Obinutuzumab was well tolerated with minimal infusion-related reactions and toxicity, Dr. Munir said.
Despite the low recruitment, both the phase 2 and 3 endpoints were assessed as positive, because the consolidation strategy was so efficacious, Dr. Munir noted, concluding that the findings provide further evidence of the value of MRD negativity for improving outcomes in CLL.
The GALACTIC trial was developed by the GALACTIC Trial Management Group with the support of the UKCLL/NCRI CLL Clinical Trials Subgroup. The trial is funded by Cancer Research UK and Roche and sponsored by the University of Leeds. Dr. Munir reported having no disclosures.
sworcester@mdedge.com
REPORTING FROM iwCLL 2019
ASCT may cure follicular lymphoma for some rituximab-naive patients
Prompt autologous stem cell transplantation (ASCT) is often curative in rituximab-naive patients with follicular lymphoma who have experienced early failure of first-line therapy and achieved a response to second-line therapy, suggest results from a registry-based study conducted by GELTAMO (the Spanish Lymphoma and Bone Marrow Transplant Group).
“Overall, our results suggest that, whereas some patients might benefit from more aggressive therapies, such as allogenic stem cell transplantations, or novel drugs, such as immunomodulatory agents, monoclonal antibodies, phosphoinositide 3-kinase inhibitors, or even the application of bispecific T-cell engagers and chimeric antigen receptor T cells, there are a considerable number of patients in this high-risk [early therapy failure] subgroup that can be cured with ASCT, even in the absence of rituximab,” Ana Jiménez-Ubieto, MD, PhD, of the Hospital Universitario, 12 de Octubre, Madrid, Spain, and colleagues wrote.
The results are more favorable when ASCT is performed in patients experiencing early therapy failure, with less than 1 year from first relapse after primary treatment to ASCT.
“Early ASCT could be a hopeful option in patients with difficult access to rituximab,” the researchers wrote in Hematology/Oncology and Stem Cell Therapy.
Patients with follicular lymphoma who experience relapse or progression during or soon after first-line therapy have poor overall survival, and there is no standard therapy for this population, according to the researchers. Previous research has shown that ASCT prolongs survival in those who have received rituximab before transplantation, but benefit in the absence of this agent is unknown.
Dr. Jiménez-Ubieto and colleagues conducted a multicenter registry-based retrospective cohort study of 134 patients with nontransformed follicular lymphoma who underwent ASCT during 1989-2007 while in second complete or partial response to rescue chemotherapy and had not received rituximab.
Overall, 65% of the patients had experienced early therapy failure (relapse or progression within 2 years of starting first-line chemotherapy). Within this group, 78% underwent ASCT within 1 year, and 67% underwent ASCT while in second complete response. Median posttransplantation follow-up for the entire study cohort was 13.4 years.
Study results showed that patients who had experienced early therapy failure versus who had not had poorer 5-year progression-free survival (43% vs. 57%; P = .048) but similar 5-year overall survival (69% vs. 77%; P = .4). However, those patients with early therapy failure who underwent ASCT within 1 year had a statistically indistinguishable 5-year progression-free survival relative to counterparts without early therapy failure (48% vs. 66%; P = .44).
Additionally, the 48% progression-free survival seen in this subset was almost identical to the 49% seen in a historical cohort of patients with early therapy failure who similarly underwent ASCT within 1 year of first relapse but received rituximab before transplantation (Hematol Oncol. 2018;36[5]:765-72). This suggests “that the possible synergistic effect of rituximab plus ASCT is not as relevant if ASCT is offered soon in the course of the disease,” the researchers wrote.
Patients who had experienced early therapy failure achieved better overall survival if they underwent ASCT while in second complete response, as opposed to second partial response. Notably, 56% of those who underwent ASCT while in second complete response were alive at 13.7 years of follow-up and remained so long term.
The study was funded by the Foundation Research Institute at the Hospital Universitario 12 de Octubre. The researchers reported having no relevant conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Jiménez-Ubieto A et al. Hematol Oncol Stem Cell Ther. 2019 Jul 9. doi: 10.1016/j.hemonc.2019.06.001.
Prompt autologous stem cell transplantation (ASCT) is often curative in rituximab-naive patients with follicular lymphoma who have experienced early failure of first-line therapy and achieved a response to second-line therapy, suggest results from a registry-based study conducted by GELTAMO (the Spanish Lymphoma and Bone Marrow Transplant Group).
“Overall, our results suggest that, whereas some patients might benefit from more aggressive therapies, such as allogenic stem cell transplantations, or novel drugs, such as immunomodulatory agents, monoclonal antibodies, phosphoinositide 3-kinase inhibitors, or even the application of bispecific T-cell engagers and chimeric antigen receptor T cells, there are a considerable number of patients in this high-risk [early therapy failure] subgroup that can be cured with ASCT, even in the absence of rituximab,” Ana Jiménez-Ubieto, MD, PhD, of the Hospital Universitario, 12 de Octubre, Madrid, Spain, and colleagues wrote.
The results are more favorable when ASCT is performed in patients experiencing early therapy failure, with less than 1 year from first relapse after primary treatment to ASCT.
“Early ASCT could be a hopeful option in patients with difficult access to rituximab,” the researchers wrote in Hematology/Oncology and Stem Cell Therapy.
Patients with follicular lymphoma who experience relapse or progression during or soon after first-line therapy have poor overall survival, and there is no standard therapy for this population, according to the researchers. Previous research has shown that ASCT prolongs survival in those who have received rituximab before transplantation, but benefit in the absence of this agent is unknown.
Dr. Jiménez-Ubieto and colleagues conducted a multicenter registry-based retrospective cohort study of 134 patients with nontransformed follicular lymphoma who underwent ASCT during 1989-2007 while in second complete or partial response to rescue chemotherapy and had not received rituximab.
Overall, 65% of the patients had experienced early therapy failure (relapse or progression within 2 years of starting first-line chemotherapy). Within this group, 78% underwent ASCT within 1 year, and 67% underwent ASCT while in second complete response. Median posttransplantation follow-up for the entire study cohort was 13.4 years.
Study results showed that patients who had experienced early therapy failure versus who had not had poorer 5-year progression-free survival (43% vs. 57%; P = .048) but similar 5-year overall survival (69% vs. 77%; P = .4). However, those patients with early therapy failure who underwent ASCT within 1 year had a statistically indistinguishable 5-year progression-free survival relative to counterparts without early therapy failure (48% vs. 66%; P = .44).
Additionally, the 48% progression-free survival seen in this subset was almost identical to the 49% seen in a historical cohort of patients with early therapy failure who similarly underwent ASCT within 1 year of first relapse but received rituximab before transplantation (Hematol Oncol. 2018;36[5]:765-72). This suggests “that the possible synergistic effect of rituximab plus ASCT is not as relevant if ASCT is offered soon in the course of the disease,” the researchers wrote.
Patients who had experienced early therapy failure achieved better overall survival if they underwent ASCT while in second complete response, as opposed to second partial response. Notably, 56% of those who underwent ASCT while in second complete response were alive at 13.7 years of follow-up and remained so long term.
The study was funded by the Foundation Research Institute at the Hospital Universitario 12 de Octubre. The researchers reported having no relevant conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Jiménez-Ubieto A et al. Hematol Oncol Stem Cell Ther. 2019 Jul 9. doi: 10.1016/j.hemonc.2019.06.001.
Prompt autologous stem cell transplantation (ASCT) is often curative in rituximab-naive patients with follicular lymphoma who have experienced early failure of first-line therapy and achieved a response to second-line therapy, suggest results from a registry-based study conducted by GELTAMO (the Spanish Lymphoma and Bone Marrow Transplant Group).
“Overall, our results suggest that, whereas some patients might benefit from more aggressive therapies, such as allogenic stem cell transplantations, or novel drugs, such as immunomodulatory agents, monoclonal antibodies, phosphoinositide 3-kinase inhibitors, or even the application of bispecific T-cell engagers and chimeric antigen receptor T cells, there are a considerable number of patients in this high-risk [early therapy failure] subgroup that can be cured with ASCT, even in the absence of rituximab,” Ana Jiménez-Ubieto, MD, PhD, of the Hospital Universitario, 12 de Octubre, Madrid, Spain, and colleagues wrote.
The results are more favorable when ASCT is performed in patients experiencing early therapy failure, with less than 1 year from first relapse after primary treatment to ASCT.
“Early ASCT could be a hopeful option in patients with difficult access to rituximab,” the researchers wrote in Hematology/Oncology and Stem Cell Therapy.
Patients with follicular lymphoma who experience relapse or progression during or soon after first-line therapy have poor overall survival, and there is no standard therapy for this population, according to the researchers. Previous research has shown that ASCT prolongs survival in those who have received rituximab before transplantation, but benefit in the absence of this agent is unknown.
Dr. Jiménez-Ubieto and colleagues conducted a multicenter registry-based retrospective cohort study of 134 patients with nontransformed follicular lymphoma who underwent ASCT during 1989-2007 while in second complete or partial response to rescue chemotherapy and had not received rituximab.
Overall, 65% of the patients had experienced early therapy failure (relapse or progression within 2 years of starting first-line chemotherapy). Within this group, 78% underwent ASCT within 1 year, and 67% underwent ASCT while in second complete response. Median posttransplantation follow-up for the entire study cohort was 13.4 years.
Study results showed that patients who had experienced early therapy failure versus who had not had poorer 5-year progression-free survival (43% vs. 57%; P = .048) but similar 5-year overall survival (69% vs. 77%; P = .4). However, those patients with early therapy failure who underwent ASCT within 1 year had a statistically indistinguishable 5-year progression-free survival relative to counterparts without early therapy failure (48% vs. 66%; P = .44).
Additionally, the 48% progression-free survival seen in this subset was almost identical to the 49% seen in a historical cohort of patients with early therapy failure who similarly underwent ASCT within 1 year of first relapse but received rituximab before transplantation (Hematol Oncol. 2018;36[5]:765-72). This suggests “that the possible synergistic effect of rituximab plus ASCT is not as relevant if ASCT is offered soon in the course of the disease,” the researchers wrote.
Patients who had experienced early therapy failure achieved better overall survival if they underwent ASCT while in second complete response, as opposed to second partial response. Notably, 56% of those who underwent ASCT while in second complete response were alive at 13.7 years of follow-up and remained so long term.
The study was funded by the Foundation Research Institute at the Hospital Universitario 12 de Octubre. The researchers reported having no relevant conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Jiménez-Ubieto A et al. Hematol Oncol Stem Cell Ther. 2019 Jul 9. doi: 10.1016/j.hemonc.2019.06.001.
FROM HEMATOLOGY/ONCOLOGY AND STEM CELL THERAPY
CAR T-cell therapy found safe, effective for HIV-associated lymphoma
HIV positivity does not preclude chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy for patients with aggressive lymphoma, a report of two cases suggests. Both of the HIV-positive patients, one of whom had long-term psychiatric comorbidity, achieved durable remission on axicabtagene ciloleucel (Yescarta) without undue toxicity.
“To our knowledge, these are the first reported cases of CAR T-cell therapy administered to HIV-infected patients with lymphoma,” Jeremy S. Abramson, MD, of Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston and his colleagues wrote in Cancer. “Patients with HIV and AIDS, as well as those with preexisting mental illness, should not be considered disqualified from CAR T-cell therapy and deserve ongoing studies to optimize efficacy and safety in this population.”
The Food and Drug Administration has approved two CAR T-cell products that target the B-cell antigen CD19 for the treatment of refractory lymphoma. But their efficacy and safety in HIV-positive patients are unknown because this group has been excluded from pivotal clinical trials.
Dr. Abramson and coauthors detail the two cases of successful anti-CD19 CAR T-cell therapy with axicabtagene ciloleucel in patients with HIV-associated, refractory, high-grade B-cell lymphoma.
The first patient was an HIV-positive man with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) of germinal center B-cell subtype who was intermittently adherent to antiretroviral therapy. His comorbidities included posttraumatic stress disorder and schizoaffective disorder.
Previous treatments for DLBCL included dose-adjusted etoposide, prednisone, vincristine, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, and rituximab (EPOCH-R), and rituximab, ifosfamide, carboplatin, and etoposide (RICE). A recurrence precluded high-dose chemotherapy with autologous stem cell support.
With close multidisciplinary management, including psychiatric consultation, the patient became a candidate for CAR T-cell therapy and received axicabtagene ciloleucel. He experienced grade 2 cytokine release syndrome and grade 3 neurologic toxicity, both of which resolved with treatment. Imaging showed complete remission at approximately 3 months that was sustained at 1 year. Additionally, he had an undetectable HIV viral load and was psychiatrically stable.
The second patient was a man with AIDS-associated, non–germinal center B-cell, Epstein-Barr virus–positive DLBCL who was adherent to antiretroviral therapy. His lymphoma had recurred rapidly after initially responding to dose-adjusted EPOCH-R and then was refractory to combination rituximab and lenalidomide. He previously had hepatitis B virus, cytomegalovirus, and Mycobacterium avium complex infections.
Because of prolonged cytopenias and infectious complications after the previous lymphoma treatments, the patient was considered a poor candidate for high-dose chemotherapy. He underwent CAR T-cell therapy with axicabtagene ciloleucel and had a complete remission on day 28. Additionally, his HIV infection remained well controlled.
“Although much remains to be learned regarding CAR T-cell therapy in patients with refractory hematologic malignancies, with or without HIV infection, the cases presented herein demonstrate that patients with chemotherapy-refractory, high-grade B-cell lymphoma can successfully undergo autologous CAR T-cell manufacturing, and subsequently can safely tolerate CAR T-cell therapy and achieve a durable complete remission,” the researchers wrote. “These cases have further demonstrated the proactive, multidisciplinary care required to navigate a patient with high-risk lymphoma through CAR T-cell therapy with attention to significant medical and psychiatric comorbidities.”
Dr. Abramson reported that he has acted as a paid member of the scientific advisory board and as a paid consultant for Kite Pharma, which markets Yescarta, and several other companies.
SOURCE: Abramson JS et al. Cancer. 2019 Sep 10. doi: 10.1002/cncr.32411.
HIV positivity does not preclude chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy for patients with aggressive lymphoma, a report of two cases suggests. Both of the HIV-positive patients, one of whom had long-term psychiatric comorbidity, achieved durable remission on axicabtagene ciloleucel (Yescarta) without undue toxicity.
“To our knowledge, these are the first reported cases of CAR T-cell therapy administered to HIV-infected patients with lymphoma,” Jeremy S. Abramson, MD, of Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston and his colleagues wrote in Cancer. “Patients with HIV and AIDS, as well as those with preexisting mental illness, should not be considered disqualified from CAR T-cell therapy and deserve ongoing studies to optimize efficacy and safety in this population.”
The Food and Drug Administration has approved two CAR T-cell products that target the B-cell antigen CD19 for the treatment of refractory lymphoma. But their efficacy and safety in HIV-positive patients are unknown because this group has been excluded from pivotal clinical trials.
Dr. Abramson and coauthors detail the two cases of successful anti-CD19 CAR T-cell therapy with axicabtagene ciloleucel in patients with HIV-associated, refractory, high-grade B-cell lymphoma.
The first patient was an HIV-positive man with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) of germinal center B-cell subtype who was intermittently adherent to antiretroviral therapy. His comorbidities included posttraumatic stress disorder and schizoaffective disorder.
Previous treatments for DLBCL included dose-adjusted etoposide, prednisone, vincristine, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, and rituximab (EPOCH-R), and rituximab, ifosfamide, carboplatin, and etoposide (RICE). A recurrence precluded high-dose chemotherapy with autologous stem cell support.
With close multidisciplinary management, including psychiatric consultation, the patient became a candidate for CAR T-cell therapy and received axicabtagene ciloleucel. He experienced grade 2 cytokine release syndrome and grade 3 neurologic toxicity, both of which resolved with treatment. Imaging showed complete remission at approximately 3 months that was sustained at 1 year. Additionally, he had an undetectable HIV viral load and was psychiatrically stable.
The second patient was a man with AIDS-associated, non–germinal center B-cell, Epstein-Barr virus–positive DLBCL who was adherent to antiretroviral therapy. His lymphoma had recurred rapidly after initially responding to dose-adjusted EPOCH-R and then was refractory to combination rituximab and lenalidomide. He previously had hepatitis B virus, cytomegalovirus, and Mycobacterium avium complex infections.
Because of prolonged cytopenias and infectious complications after the previous lymphoma treatments, the patient was considered a poor candidate for high-dose chemotherapy. He underwent CAR T-cell therapy with axicabtagene ciloleucel and had a complete remission on day 28. Additionally, his HIV infection remained well controlled.
“Although much remains to be learned regarding CAR T-cell therapy in patients with refractory hematologic malignancies, with or without HIV infection, the cases presented herein demonstrate that patients with chemotherapy-refractory, high-grade B-cell lymphoma can successfully undergo autologous CAR T-cell manufacturing, and subsequently can safely tolerate CAR T-cell therapy and achieve a durable complete remission,” the researchers wrote. “These cases have further demonstrated the proactive, multidisciplinary care required to navigate a patient with high-risk lymphoma through CAR T-cell therapy with attention to significant medical and psychiatric comorbidities.”
Dr. Abramson reported that he has acted as a paid member of the scientific advisory board and as a paid consultant for Kite Pharma, which markets Yescarta, and several other companies.
SOURCE: Abramson JS et al. Cancer. 2019 Sep 10. doi: 10.1002/cncr.32411.
HIV positivity does not preclude chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy for patients with aggressive lymphoma, a report of two cases suggests. Both of the HIV-positive patients, one of whom had long-term psychiatric comorbidity, achieved durable remission on axicabtagene ciloleucel (Yescarta) without undue toxicity.
“To our knowledge, these are the first reported cases of CAR T-cell therapy administered to HIV-infected patients with lymphoma,” Jeremy S. Abramson, MD, of Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston and his colleagues wrote in Cancer. “Patients with HIV and AIDS, as well as those with preexisting mental illness, should not be considered disqualified from CAR T-cell therapy and deserve ongoing studies to optimize efficacy and safety in this population.”
The Food and Drug Administration has approved two CAR T-cell products that target the B-cell antigen CD19 for the treatment of refractory lymphoma. But their efficacy and safety in HIV-positive patients are unknown because this group has been excluded from pivotal clinical trials.
Dr. Abramson and coauthors detail the two cases of successful anti-CD19 CAR T-cell therapy with axicabtagene ciloleucel in patients with HIV-associated, refractory, high-grade B-cell lymphoma.
The first patient was an HIV-positive man with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) of germinal center B-cell subtype who was intermittently adherent to antiretroviral therapy. His comorbidities included posttraumatic stress disorder and schizoaffective disorder.
Previous treatments for DLBCL included dose-adjusted etoposide, prednisone, vincristine, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, and rituximab (EPOCH-R), and rituximab, ifosfamide, carboplatin, and etoposide (RICE). A recurrence precluded high-dose chemotherapy with autologous stem cell support.
With close multidisciplinary management, including psychiatric consultation, the patient became a candidate for CAR T-cell therapy and received axicabtagene ciloleucel. He experienced grade 2 cytokine release syndrome and grade 3 neurologic toxicity, both of which resolved with treatment. Imaging showed complete remission at approximately 3 months that was sustained at 1 year. Additionally, he had an undetectable HIV viral load and was psychiatrically stable.
The second patient was a man with AIDS-associated, non–germinal center B-cell, Epstein-Barr virus–positive DLBCL who was adherent to antiretroviral therapy. His lymphoma had recurred rapidly after initially responding to dose-adjusted EPOCH-R and then was refractory to combination rituximab and lenalidomide. He previously had hepatitis B virus, cytomegalovirus, and Mycobacterium avium complex infections.
Because of prolonged cytopenias and infectious complications after the previous lymphoma treatments, the patient was considered a poor candidate for high-dose chemotherapy. He underwent CAR T-cell therapy with axicabtagene ciloleucel and had a complete remission on day 28. Additionally, his HIV infection remained well controlled.
“Although much remains to be learned regarding CAR T-cell therapy in patients with refractory hematologic malignancies, with or without HIV infection, the cases presented herein demonstrate that patients with chemotherapy-refractory, high-grade B-cell lymphoma can successfully undergo autologous CAR T-cell manufacturing, and subsequently can safely tolerate CAR T-cell therapy and achieve a durable complete remission,” the researchers wrote. “These cases have further demonstrated the proactive, multidisciplinary care required to navigate a patient with high-risk lymphoma through CAR T-cell therapy with attention to significant medical and psychiatric comorbidities.”
Dr. Abramson reported that he has acted as a paid member of the scientific advisory board and as a paid consultant for Kite Pharma, which markets Yescarta, and several other companies.
SOURCE: Abramson JS et al. Cancer. 2019 Sep 10. doi: 10.1002/cncr.32411.
FROM CANCER
Staging PET/CT better defines extent of mantle cell lymphoma
Use of staging PET/CT better defines the extent of mantle cell lymphoma (MCL) in certain compartments, adding important information for treatment decisions, a cohort study suggests. However, patient selection and evaluation criteria are important for its utility.
“A correct and early identification of initial disease could be crucial because it could affect patient management and therapeutic choice,” Domenico Albano, MD, a nuclear medicine physician at the University of Brescia (Italy) and Spedali Civili Brescia, and colleagues wrote in Clinical Lymphoma, Myeloma, & Leukemia.
Using retrospective data from two centers and 122 patients with MCL, the investigators compared the utility of staging 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose (18F-FDG) PET/CT with that of other modalities used for detecting disease in specific compartments. They also assessed its impact on patient management.
The study results showed that, with the exception of a single patient having bone marrow involvement, all patients had positive PET/CT results, with detection of at least one hypermetabolic lesion.
For assessing nodal involvement, compared with CT alone, PET/CT detected additional lesions in 21% of patients. Splenic lesions were detected by PET/CT in 49% of patients and by CT alone in 47%.
For assessing bone marrow involvement, compared with bone marrow biopsy, PET/CT had a sensitivity of 52%, a specificity of 98%, a positive predictive value of 97%, a negative predictive value of 65%, and an overall accuracy of 74%.
For gastrointestinal involvement, compared with endoscopy, PET/CT had a sensitivity of 64% (78% after excluding diabetic patients taking metformin), a specificity of 91% (92%), a positive predictive value of 69% (72%), a negative predictive value of 90% (94%), and an overall accuracy of 85% (89%).
Ultimately, relative to CT alone, PET/CT altered stage and management in 19% of patients. Specifically, this imaging led to up-staging in 17% of patients, prompting clinicians to switch to more-aggressive chemotherapy, and down-staging in 2% of patients, prompting clinicians to skip unnecessary invasive therapies.
“We demonstrated that 18F-FDG pathologic uptake in MCL occurred in almost all patients, with excellent detection rate in nodal and splenic disease – indeed, better than CT,” the researchers wrote. “When we analyzed bone marrow and gastrointestinal involvement, the selection of patients excluding all conditions potentially affecting organ uptake and the use of specific criteria for the evaluation of these organs seemed to be crucial. Within these caveats, PET/CT showed good specificity for bone marrow and gastrointestinal evaluation.”
Study funding was not disclosed. Dr. Albano reported having no relevant conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Albano D et al. Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2019 Aug;19(8):e457-64.
Use of staging PET/CT better defines the extent of mantle cell lymphoma (MCL) in certain compartments, adding important information for treatment decisions, a cohort study suggests. However, patient selection and evaluation criteria are important for its utility.
“A correct and early identification of initial disease could be crucial because it could affect patient management and therapeutic choice,” Domenico Albano, MD, a nuclear medicine physician at the University of Brescia (Italy) and Spedali Civili Brescia, and colleagues wrote in Clinical Lymphoma, Myeloma, & Leukemia.
Using retrospective data from two centers and 122 patients with MCL, the investigators compared the utility of staging 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose (18F-FDG) PET/CT with that of other modalities used for detecting disease in specific compartments. They also assessed its impact on patient management.
The study results showed that, with the exception of a single patient having bone marrow involvement, all patients had positive PET/CT results, with detection of at least one hypermetabolic lesion.
For assessing nodal involvement, compared with CT alone, PET/CT detected additional lesions in 21% of patients. Splenic lesions were detected by PET/CT in 49% of patients and by CT alone in 47%.
For assessing bone marrow involvement, compared with bone marrow biopsy, PET/CT had a sensitivity of 52%, a specificity of 98%, a positive predictive value of 97%, a negative predictive value of 65%, and an overall accuracy of 74%.
For gastrointestinal involvement, compared with endoscopy, PET/CT had a sensitivity of 64% (78% after excluding diabetic patients taking metformin), a specificity of 91% (92%), a positive predictive value of 69% (72%), a negative predictive value of 90% (94%), and an overall accuracy of 85% (89%).
Ultimately, relative to CT alone, PET/CT altered stage and management in 19% of patients. Specifically, this imaging led to up-staging in 17% of patients, prompting clinicians to switch to more-aggressive chemotherapy, and down-staging in 2% of patients, prompting clinicians to skip unnecessary invasive therapies.
“We demonstrated that 18F-FDG pathologic uptake in MCL occurred in almost all patients, with excellent detection rate in nodal and splenic disease – indeed, better than CT,” the researchers wrote. “When we analyzed bone marrow and gastrointestinal involvement, the selection of patients excluding all conditions potentially affecting organ uptake and the use of specific criteria for the evaluation of these organs seemed to be crucial. Within these caveats, PET/CT showed good specificity for bone marrow and gastrointestinal evaluation.”
Study funding was not disclosed. Dr. Albano reported having no relevant conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Albano D et al. Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2019 Aug;19(8):e457-64.
Use of staging PET/CT better defines the extent of mantle cell lymphoma (MCL) in certain compartments, adding important information for treatment decisions, a cohort study suggests. However, patient selection and evaluation criteria are important for its utility.
“A correct and early identification of initial disease could be crucial because it could affect patient management and therapeutic choice,” Domenico Albano, MD, a nuclear medicine physician at the University of Brescia (Italy) and Spedali Civili Brescia, and colleagues wrote in Clinical Lymphoma, Myeloma, & Leukemia.
Using retrospective data from two centers and 122 patients with MCL, the investigators compared the utility of staging 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose (18F-FDG) PET/CT with that of other modalities used for detecting disease in specific compartments. They also assessed its impact on patient management.
The study results showed that, with the exception of a single patient having bone marrow involvement, all patients had positive PET/CT results, with detection of at least one hypermetabolic lesion.
For assessing nodal involvement, compared with CT alone, PET/CT detected additional lesions in 21% of patients. Splenic lesions were detected by PET/CT in 49% of patients and by CT alone in 47%.
For assessing bone marrow involvement, compared with bone marrow biopsy, PET/CT had a sensitivity of 52%, a specificity of 98%, a positive predictive value of 97%, a negative predictive value of 65%, and an overall accuracy of 74%.
For gastrointestinal involvement, compared with endoscopy, PET/CT had a sensitivity of 64% (78% after excluding diabetic patients taking metformin), a specificity of 91% (92%), a positive predictive value of 69% (72%), a negative predictive value of 90% (94%), and an overall accuracy of 85% (89%).
Ultimately, relative to CT alone, PET/CT altered stage and management in 19% of patients. Specifically, this imaging led to up-staging in 17% of patients, prompting clinicians to switch to more-aggressive chemotherapy, and down-staging in 2% of patients, prompting clinicians to skip unnecessary invasive therapies.
“We demonstrated that 18F-FDG pathologic uptake in MCL occurred in almost all patients, with excellent detection rate in nodal and splenic disease – indeed, better than CT,” the researchers wrote. “When we analyzed bone marrow and gastrointestinal involvement, the selection of patients excluding all conditions potentially affecting organ uptake and the use of specific criteria for the evaluation of these organs seemed to be crucial. Within these caveats, PET/CT showed good specificity for bone marrow and gastrointestinal evaluation.”
Study funding was not disclosed. Dr. Albano reported having no relevant conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Albano D et al. Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2019 Aug;19(8):e457-64.
FROM CLINICAL LYMPHOMA, MYELOMA, & LEUKEMIA