User login
COVID-19 death rate was twice as high in cancer patients in NYC study
COVID-19 patients with cancer had double the fatality rate of COVID-19 patients without cancer treated in an urban New York hospital system, according to data from a retrospective study.
with COVID-19 treated during the same time period in the same hospital system.
Vikas Mehta, MD, of Montefiore Medical Center, New York, and colleagues reported these results in Cancer Discovery.
“As New York has emerged as the current epicenter of the pandemic, we sought to investigate the risk posed by COVID-19 to our cancer population,” the authors wrote.
They identified 218 cancer patients treated for COVID-19 in the Montefiore Health System between March 18 and April 8, 2020. Three-quarters of patients had solid tumors, and 25% had hematologic malignancies. Most patients were adults (98.6%), their median age was 69 years (range, 10-92 years), and 58% were men.
In all, 28% of the cancer patients (61/218) died from COVID-19, including 25% (41/164) of those with solid tumors and 37% (20/54) of those with hematologic malignancies.
Deaths by cancer type
Among the 164 patients with solid tumors, case fatality rates were as follows:
- Pancreatic – 67% (2/3)
- Lung – 55% (6/11)
- Colorectal – 38% (8/21)
- Upper gastrointestinal – 38% (3/8)
- Gynecologic – 38% (5/13)
- Skin – 33% (1/3)
- Hepatobiliary – 29% (2/7)
- Bone/soft tissue – 20% (1/5)
- Genitourinary – 15% (7/46)
- Breast – 14% (4/28)
- Neurologic – 13% (1/8)
- Head and neck – 13% (1/8).
None of the three patients with neuroendocrine tumors died.
Among the 54 patients with hematologic malignancies, case fatality rates were as follows:
- Chronic myeloid leukemia – 100% (1/1)
- Hodgkin lymphoma – 60% (3/5)
- Myelodysplastic syndromes – 60% (3/5)
- Multiple myeloma – 38% (5/13)
- Non-Hodgkin lymphoma – 33% (5/15)
- Chronic lymphocytic leukemia – 33% (1/3)
- Myeloproliferative neoplasms – 29% (2/7).
None of the four patients with acute lymphoblastic leukemia died, and there was one patient with acute myeloid leukemia who did not die.
Factors associated with increased mortality
The researchers compared the 218 cancer patients with COVID-19 with 1,090 age- and sex-matched noncancer patients with COVID-19 treated in the Montefiore Health System between March 18 and April 8, 2020.
Case fatality rates in cancer patients with COVID-19 were significantly increased in all age groups, but older age was associated with higher mortality.
“We observed case fatality rates were elevated in all age cohorts in cancer patients and achieved statistical significance in the age groups 45-64 and in patients older than 75 years of age,” the authors reported.
Other factors significantly associated with higher mortality in a multivariable analysis included the presence of multiple comorbidities; the need for ICU support; and increased levels of d-dimer, lactate, and lactate dehydrogenase.
Additional factors, such as socioeconomic and health disparities, may also be significant predictors of mortality, according to the authors. They noted that this cohort largely consisted of patients from a socioeconomically underprivileged community where mortality because of COVID-19 is reportedly higher.
Proactive strategies moving forward
“We have been addressing the significant burden of the COVID-19 pandemic on our vulnerable cancer patients through a variety of ways,” said study author Balazs Halmos, MD, of Montefiore Medical Center.
The center set up a separate infusion unit exclusively for COVID-positive patients and established separate inpatient areas. Dr. Halmos and colleagues are also providing telemedicine, virtual supportive care services, telephonic counseling, and bilingual peer-support programs.
“Many questions remain as we continue to establish new practices for our cancer patients,” Dr. Halmos said. “We will find answers to these questions as we continue to focus on adaptation and not acceptance in response to the COVID crisis. Our patients deserve nothing less.”
The Albert Einstein Cancer Center supported this study. The authors reported having no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Mehta V et al. Cancer Discov. 2020 May 1. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-20-0516.
COVID-19 patients with cancer had double the fatality rate of COVID-19 patients without cancer treated in an urban New York hospital system, according to data from a retrospective study.
with COVID-19 treated during the same time period in the same hospital system.
Vikas Mehta, MD, of Montefiore Medical Center, New York, and colleagues reported these results in Cancer Discovery.
“As New York has emerged as the current epicenter of the pandemic, we sought to investigate the risk posed by COVID-19 to our cancer population,” the authors wrote.
They identified 218 cancer patients treated for COVID-19 in the Montefiore Health System between March 18 and April 8, 2020. Three-quarters of patients had solid tumors, and 25% had hematologic malignancies. Most patients were adults (98.6%), their median age was 69 years (range, 10-92 years), and 58% were men.
In all, 28% of the cancer patients (61/218) died from COVID-19, including 25% (41/164) of those with solid tumors and 37% (20/54) of those with hematologic malignancies.
Deaths by cancer type
Among the 164 patients with solid tumors, case fatality rates were as follows:
- Pancreatic – 67% (2/3)
- Lung – 55% (6/11)
- Colorectal – 38% (8/21)
- Upper gastrointestinal – 38% (3/8)
- Gynecologic – 38% (5/13)
- Skin – 33% (1/3)
- Hepatobiliary – 29% (2/7)
- Bone/soft tissue – 20% (1/5)
- Genitourinary – 15% (7/46)
- Breast – 14% (4/28)
- Neurologic – 13% (1/8)
- Head and neck – 13% (1/8).
None of the three patients with neuroendocrine tumors died.
Among the 54 patients with hematologic malignancies, case fatality rates were as follows:
- Chronic myeloid leukemia – 100% (1/1)
- Hodgkin lymphoma – 60% (3/5)
- Myelodysplastic syndromes – 60% (3/5)
- Multiple myeloma – 38% (5/13)
- Non-Hodgkin lymphoma – 33% (5/15)
- Chronic lymphocytic leukemia – 33% (1/3)
- Myeloproliferative neoplasms – 29% (2/7).
None of the four patients with acute lymphoblastic leukemia died, and there was one patient with acute myeloid leukemia who did not die.
Factors associated with increased mortality
The researchers compared the 218 cancer patients with COVID-19 with 1,090 age- and sex-matched noncancer patients with COVID-19 treated in the Montefiore Health System between March 18 and April 8, 2020.
Case fatality rates in cancer patients with COVID-19 were significantly increased in all age groups, but older age was associated with higher mortality.
“We observed case fatality rates were elevated in all age cohorts in cancer patients and achieved statistical significance in the age groups 45-64 and in patients older than 75 years of age,” the authors reported.
Other factors significantly associated with higher mortality in a multivariable analysis included the presence of multiple comorbidities; the need for ICU support; and increased levels of d-dimer, lactate, and lactate dehydrogenase.
Additional factors, such as socioeconomic and health disparities, may also be significant predictors of mortality, according to the authors. They noted that this cohort largely consisted of patients from a socioeconomically underprivileged community where mortality because of COVID-19 is reportedly higher.
Proactive strategies moving forward
“We have been addressing the significant burden of the COVID-19 pandemic on our vulnerable cancer patients through a variety of ways,” said study author Balazs Halmos, MD, of Montefiore Medical Center.
The center set up a separate infusion unit exclusively for COVID-positive patients and established separate inpatient areas. Dr. Halmos and colleagues are also providing telemedicine, virtual supportive care services, telephonic counseling, and bilingual peer-support programs.
“Many questions remain as we continue to establish new practices for our cancer patients,” Dr. Halmos said. “We will find answers to these questions as we continue to focus on adaptation and not acceptance in response to the COVID crisis. Our patients deserve nothing less.”
The Albert Einstein Cancer Center supported this study. The authors reported having no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Mehta V et al. Cancer Discov. 2020 May 1. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-20-0516.
COVID-19 patients with cancer had double the fatality rate of COVID-19 patients without cancer treated in an urban New York hospital system, according to data from a retrospective study.
with COVID-19 treated during the same time period in the same hospital system.
Vikas Mehta, MD, of Montefiore Medical Center, New York, and colleagues reported these results in Cancer Discovery.
“As New York has emerged as the current epicenter of the pandemic, we sought to investigate the risk posed by COVID-19 to our cancer population,” the authors wrote.
They identified 218 cancer patients treated for COVID-19 in the Montefiore Health System between March 18 and April 8, 2020. Three-quarters of patients had solid tumors, and 25% had hematologic malignancies. Most patients were adults (98.6%), their median age was 69 years (range, 10-92 years), and 58% were men.
In all, 28% of the cancer patients (61/218) died from COVID-19, including 25% (41/164) of those with solid tumors and 37% (20/54) of those with hematologic malignancies.
Deaths by cancer type
Among the 164 patients with solid tumors, case fatality rates were as follows:
- Pancreatic – 67% (2/3)
- Lung – 55% (6/11)
- Colorectal – 38% (8/21)
- Upper gastrointestinal – 38% (3/8)
- Gynecologic – 38% (5/13)
- Skin – 33% (1/3)
- Hepatobiliary – 29% (2/7)
- Bone/soft tissue – 20% (1/5)
- Genitourinary – 15% (7/46)
- Breast – 14% (4/28)
- Neurologic – 13% (1/8)
- Head and neck – 13% (1/8).
None of the three patients with neuroendocrine tumors died.
Among the 54 patients with hematologic malignancies, case fatality rates were as follows:
- Chronic myeloid leukemia – 100% (1/1)
- Hodgkin lymphoma – 60% (3/5)
- Myelodysplastic syndromes – 60% (3/5)
- Multiple myeloma – 38% (5/13)
- Non-Hodgkin lymphoma – 33% (5/15)
- Chronic lymphocytic leukemia – 33% (1/3)
- Myeloproliferative neoplasms – 29% (2/7).
None of the four patients with acute lymphoblastic leukemia died, and there was one patient with acute myeloid leukemia who did not die.
Factors associated with increased mortality
The researchers compared the 218 cancer patients with COVID-19 with 1,090 age- and sex-matched noncancer patients with COVID-19 treated in the Montefiore Health System between March 18 and April 8, 2020.
Case fatality rates in cancer patients with COVID-19 were significantly increased in all age groups, but older age was associated with higher mortality.
“We observed case fatality rates were elevated in all age cohorts in cancer patients and achieved statistical significance in the age groups 45-64 and in patients older than 75 years of age,” the authors reported.
Other factors significantly associated with higher mortality in a multivariable analysis included the presence of multiple comorbidities; the need for ICU support; and increased levels of d-dimer, lactate, and lactate dehydrogenase.
Additional factors, such as socioeconomic and health disparities, may also be significant predictors of mortality, according to the authors. They noted that this cohort largely consisted of patients from a socioeconomically underprivileged community where mortality because of COVID-19 is reportedly higher.
Proactive strategies moving forward
“We have been addressing the significant burden of the COVID-19 pandemic on our vulnerable cancer patients through a variety of ways,” said study author Balazs Halmos, MD, of Montefiore Medical Center.
The center set up a separate infusion unit exclusively for COVID-positive patients and established separate inpatient areas. Dr. Halmos and colleagues are also providing telemedicine, virtual supportive care services, telephonic counseling, and bilingual peer-support programs.
“Many questions remain as we continue to establish new practices for our cancer patients,” Dr. Halmos said. “We will find answers to these questions as we continue to focus on adaptation and not acceptance in response to the COVID crisis. Our patients deserve nothing less.”
The Albert Einstein Cancer Center supported this study. The authors reported having no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Mehta V et al. Cancer Discov. 2020 May 1. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-20-0516.
FROM CANCER DISCOVERY
Three months of COVID-19 may mean 80,000 missed cancer diagnoses
, according to a report by the IQVIA Institute for Human Data Science looking at trends in the United States.
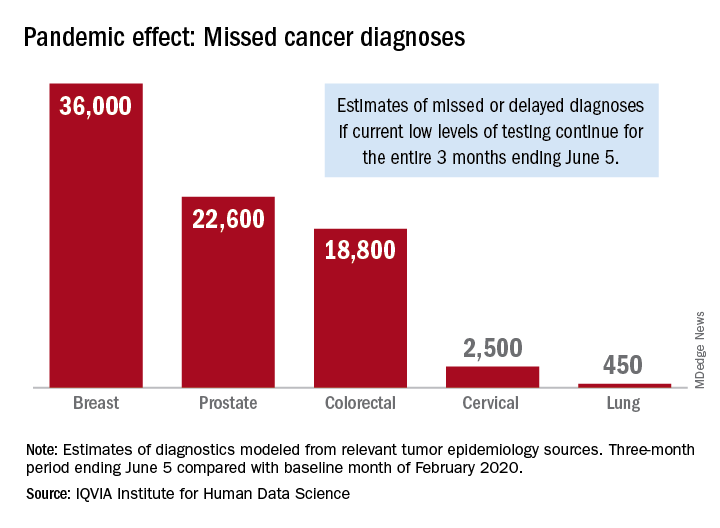
Screening and monitoring tests for breast, prostate, colorectal, cervical, and lung cancer were down 39%-90% in early April, compared with the baseline month of February, according to report authors Murray Aitken and Michael Kleinrock, both of IQVIA.
These findings are based on data from IQVIA’s medical claims database, which includes more than 205 million patients, over 1.7 billion claims, and 3 billion service records obtained annually.
The data suggest that, at current positivity rates, there could be 36,000 missed or delayed diagnoses of breast cancer during the 3-month period from early March through early June. Estimates for missed diagnoses of the four other cancers analyzed include 450 for lung cancer, 2,500 for cervical cancer, 18,800 for colorectal cancer, and 22,600 for prostate cancer.
The authors project a total of 22 million canceled or delayed tests for the five cancers over the 3-month period ending June 5, based on a comparison of claims data for early April with the February baseline. Catching up on this backlog will be problematic, according to the authors.
“Current excess health care capacity ... would require providers to shift priorities to make time and space in schedules and facilities as well as the cooperation of patients to return to health care providers,” the authors wrote. “Both of these could be further disrupted by economic factors or reintroduction of social distancing in a reemergence of the outbreak.”
The report was produced by the IQVIA Institute for Human Data Science without industry or government funding.
SOURCE: Murray A and Kleinrock M. Shifts in healthcare demand, delivery and care during the COVID-19 era. IQVIA Institute for Human Data Science. April 2020.
, according to a report by the IQVIA Institute for Human Data Science looking at trends in the United States.

Screening and monitoring tests for breast, prostate, colorectal, cervical, and lung cancer were down 39%-90% in early April, compared with the baseline month of February, according to report authors Murray Aitken and Michael Kleinrock, both of IQVIA.
These findings are based on data from IQVIA’s medical claims database, which includes more than 205 million patients, over 1.7 billion claims, and 3 billion service records obtained annually.
The data suggest that, at current positivity rates, there could be 36,000 missed or delayed diagnoses of breast cancer during the 3-month period from early March through early June. Estimates for missed diagnoses of the four other cancers analyzed include 450 for lung cancer, 2,500 for cervical cancer, 18,800 for colorectal cancer, and 22,600 for prostate cancer.
The authors project a total of 22 million canceled or delayed tests for the five cancers over the 3-month period ending June 5, based on a comparison of claims data for early April with the February baseline. Catching up on this backlog will be problematic, according to the authors.
“Current excess health care capacity ... would require providers to shift priorities to make time and space in schedules and facilities as well as the cooperation of patients to return to health care providers,” the authors wrote. “Both of these could be further disrupted by economic factors or reintroduction of social distancing in a reemergence of the outbreak.”
The report was produced by the IQVIA Institute for Human Data Science without industry or government funding.
SOURCE: Murray A and Kleinrock M. Shifts in healthcare demand, delivery and care during the COVID-19 era. IQVIA Institute for Human Data Science. April 2020.
, according to a report by the IQVIA Institute for Human Data Science looking at trends in the United States.

Screening and monitoring tests for breast, prostate, colorectal, cervical, and lung cancer were down 39%-90% in early April, compared with the baseline month of February, according to report authors Murray Aitken and Michael Kleinrock, both of IQVIA.
These findings are based on data from IQVIA’s medical claims database, which includes more than 205 million patients, over 1.7 billion claims, and 3 billion service records obtained annually.
The data suggest that, at current positivity rates, there could be 36,000 missed or delayed diagnoses of breast cancer during the 3-month period from early March through early June. Estimates for missed diagnoses of the four other cancers analyzed include 450 for lung cancer, 2,500 for cervical cancer, 18,800 for colorectal cancer, and 22,600 for prostate cancer.
The authors project a total of 22 million canceled or delayed tests for the five cancers over the 3-month period ending June 5, based on a comparison of claims data for early April with the February baseline. Catching up on this backlog will be problematic, according to the authors.
“Current excess health care capacity ... would require providers to shift priorities to make time and space in schedules and facilities as well as the cooperation of patients to return to health care providers,” the authors wrote. “Both of these could be further disrupted by economic factors or reintroduction of social distancing in a reemergence of the outbreak.”
The report was produced by the IQVIA Institute for Human Data Science without industry or government funding.
SOURCE: Murray A and Kleinrock M. Shifts in healthcare demand, delivery and care during the COVID-19 era. IQVIA Institute for Human Data Science. April 2020.
Cancer screening, monitoring down during pandemic
according to a report by the IQVIA Institute for Human Data Science.
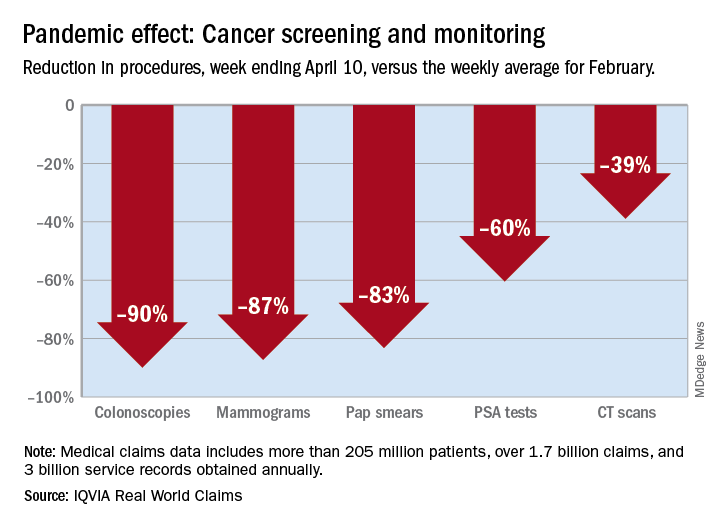
There were 90% fewer colonoscopies ordered during the week ending April 10, compared with the weekly average for Feb. 1-28, based on claims data analyzed by IQVIA.
IQVIA’s medical claims database includes more than 205 million patients, over 1.7 billion claims, and 3 billion service records obtained annually.
The data also showed an 87% reduction in mammograms and an 83% reduction in Pap smears during the week ending April 10. Prostate-specific antigen tests for prostate cancer decreased by 60%, and CT scans for lung cancer decreased by 39%.
The smaller decrease in CT scans for lung cancer “may reflect the generally more serious nature of those tumors or be due to concerns about ruling out COVID-related issues in some patients,” according to report authors Murray Aitken and Michael Kleinrock, both of IQVIA.
The report also showed that overall patient interactions with oncologists were down by 20% through April 3, based on medical and pharmacy claims processed since February, but there was variation by tumor type.
The authors noted “little or no disruption” in oncologist visits in March for patients with aggressive tumors or those diagnosed at advanced stages, compared with February. However, for patients with skin cancer or prostate cancer, visit rates were down by 20%-50% in March.
“This may reflect that oncologists who are providing care across multiple tumor types are prioritizing their time and efforts to those patients with more advanced or aggressive tumors,” the authors wrote.
This report was produced by the IQVIA Institute for Human Data Science without industry or government funding.
SOURCE: Murray A and Kleinrock M. Shifts in healthcare demand, delivery and care during the COVID-19 era. IQVIA Institute for Human Data Science. April 2020.
according to a report by the IQVIA Institute for Human Data Science.

There were 90% fewer colonoscopies ordered during the week ending April 10, compared with the weekly average for Feb. 1-28, based on claims data analyzed by IQVIA.
IQVIA’s medical claims database includes more than 205 million patients, over 1.7 billion claims, and 3 billion service records obtained annually.
The data also showed an 87% reduction in mammograms and an 83% reduction in Pap smears during the week ending April 10. Prostate-specific antigen tests for prostate cancer decreased by 60%, and CT scans for lung cancer decreased by 39%.
The smaller decrease in CT scans for lung cancer “may reflect the generally more serious nature of those tumors or be due to concerns about ruling out COVID-related issues in some patients,” according to report authors Murray Aitken and Michael Kleinrock, both of IQVIA.
The report also showed that overall patient interactions with oncologists were down by 20% through April 3, based on medical and pharmacy claims processed since February, but there was variation by tumor type.
The authors noted “little or no disruption” in oncologist visits in March for patients with aggressive tumors or those diagnosed at advanced stages, compared with February. However, for patients with skin cancer or prostate cancer, visit rates were down by 20%-50% in March.
“This may reflect that oncologists who are providing care across multiple tumor types are prioritizing their time and efforts to those patients with more advanced or aggressive tumors,” the authors wrote.
This report was produced by the IQVIA Institute for Human Data Science without industry or government funding.
SOURCE: Murray A and Kleinrock M. Shifts in healthcare demand, delivery and care during the COVID-19 era. IQVIA Institute for Human Data Science. April 2020.
according to a report by the IQVIA Institute for Human Data Science.

There were 90% fewer colonoscopies ordered during the week ending April 10, compared with the weekly average for Feb. 1-28, based on claims data analyzed by IQVIA.
IQVIA’s medical claims database includes more than 205 million patients, over 1.7 billion claims, and 3 billion service records obtained annually.
The data also showed an 87% reduction in mammograms and an 83% reduction in Pap smears during the week ending April 10. Prostate-specific antigen tests for prostate cancer decreased by 60%, and CT scans for lung cancer decreased by 39%.
The smaller decrease in CT scans for lung cancer “may reflect the generally more serious nature of those tumors or be due to concerns about ruling out COVID-related issues in some patients,” according to report authors Murray Aitken and Michael Kleinrock, both of IQVIA.
The report also showed that overall patient interactions with oncologists were down by 20% through April 3, based on medical and pharmacy claims processed since February, but there was variation by tumor type.
The authors noted “little or no disruption” in oncologist visits in March for patients with aggressive tumors or those diagnosed at advanced stages, compared with February. However, for patients with skin cancer or prostate cancer, visit rates were down by 20%-50% in March.
“This may reflect that oncologists who are providing care across multiple tumor types are prioritizing their time and efforts to those patients with more advanced or aggressive tumors,” the authors wrote.
This report was produced by the IQVIA Institute for Human Data Science without industry or government funding.
SOURCE: Murray A and Kleinrock M. Shifts in healthcare demand, delivery and care during the COVID-19 era. IQVIA Institute for Human Data Science. April 2020.
Adding a blood test to standard screening may improve early cancer detection
A minimally invasive multicancer blood test used with standard-of-care screening is safe, effective, and feasible for use in routine clinical care, according to interim findings from a large, prospective study.
The DETECT-A blood test, an early version of the CancerSEEK test currently in development, effectively guided patient management in real time, in some cases leading to diagnosis of early cancer and potentially curative surgery in asymptomatic women with no history of cancer.
Nickolas Papadopoulos, PhD, of Johns Hopkins Medicine in Baltimore, reported these findings at the AACR virtual meeting I. The findings were simultaneously published in Science.
The study enrolled 10,006 women, aged 65-75 years, with no prior cancer diagnosis. After exclusion and loss to follow-up, 9,911 women remained.
There were 26 patients who had cancer detected by the DETECT-A blood test, 15 of whom underwent follow-up PET-CT imaging and 9 of whom underwent surgical excision. An additional 24 cancers were detected by standard screening, and 46 were detected by other means.
The positive predictive value of the blood test was 19%. When the blood test was combined with imaging, the positive predictive value was 41%.
Improving upon standard screening
“Standard-of-care screening [was used] for three different organs: breast, lung, and colon. It was more sensitive for breast cancer,” Dr. Papadopoulos noted. “Blood testing, though, identified cancer in 10 different organs.”
In fact, the DETECT-A blood test detected 14 of 45 cancers in 7 organs for which no standard screening test is available.
In addition, 12 cancers in 3 organs (breast, lung, and colon) were first detected by DETECT-A rather than by standard screening. This increased the sensitivity of cancer detection from 47% with standard screening alone to 71% with standard screening plus blood testing.
“More important, 65% [of the cancers detected by blood test] were localized or regional, which have higher chance of successful treatment with intent to cure,” Dr. Papadopoulos said.
DETECT-A covers regions of 16 commonly mutated genes and 9 proteins known to be associated with cancer. In this study, 57% of cancers were detected by mutations.
Safety and additional screening
DETECT-A also proved safe, “without incurring a large number of futile invasive follow-up tests,” Dr. Papadopoulos said.
In fact, only 1% of patients without cancer underwent PET-CT imaging, and only 0.22% underwent a “futile” invasive follow-up procedure.
Three surgeries occurred in patients who were counted as false-positives, but the surgeries were determined to be indicated, Dr. Papadopoulos said. He explained that one was for large colonic polyps with high-grade dysplasia that could not be removed endoscopically, one was for an in situ carcinoma of the appendix, and one was for a 10-cm ovarian lesion that was found to be a mucinous cystadenoma.
The investigators also analyzed whether the availability of a “liquid biopsy” test like DETECT-A would inadvertently reduce patients’ use of standard screening and found that it did not. Mammography screening habits after receiving the baseline DETECT-A blood test did not differ significantly from those prior to study enrollment.
These findings are important because early detection is a key factor in reducing cancer-specific morbidity and mortality, and although minimally invasive screening tests, including liquid biopsies like DETECT-A, hold great promise, prospective clinical studies of these new methods are needed to ensure that the anticipated benefits outweigh the potential risks, Dr. Papadopoulos explained.
“The problem is that most cancers are detected at advanced stages when they are difficult to treat,” he said. “The earlier cancer is detected, the greater the chance of successful treatment.”
Unanswered questions and future studies
This study demonstrates that it is feasible for a minimally invasive blood test to safely detect multiple cancer types in patients without a history of cancer and to enable treatment with curative intent, at least in a subset of individuals, Dr. Papadopoulos said. He added that the findings also inform the design of future randomized trials “to establish clinical utility, cost-effectiveness, and benefit-to-risk ratio of future tests.”
Further studies will also be required to determine the clinical validity and utility of the strategy of using liquid biopsy as a complement to standard-of-care screening, Dr. Papadopoulos said.
Invited discussant David G. Huntsman, MD, of the University of British Columbia in Vancouver, applauded the investigators, saying this study serves to “move the field forward.” However, it still isn’t clear how sensitivity and negative predictive value will be determined and what the optimal testing schedule is.
“This is a prospective study that will provide the data on how this assay will be used [and] whether it should be used going forward,” Dr. Huntsman said, noting that the “much bigger and more important question” is whether it improves survival.
Cost-effectiveness will also be critical, he said.
This research was supported by The Marcus Foundation, Lustgarten Foundation for Pancreatic Cancer Research, The Virginia and D.K. Ludwig Fund for Cancer Research, The Sol Goldman Center for Pancreatic Cancer Research, Susan Wojcicki and Dennis Troper, the Rolfe Foundation, The Conrad R. Hilton Foundation, The John Templeton Foundation, Burroughs Wellcome Career Award For Medical Scientists, and grants/contracts from the National Institutes of Health.
Dr. Papadopoulos disclosed relationships with Thrive Earlier Detection Inc., PGDx Inc., NeoPhore, Cage Pharma, and other companies. Dr. Huntsman is a founder, shareholder, and chief medical officer for Contextual Genomics.
SOURCE: Papadopoulos N et al. AACR 2020, Abstract CT022; Lennon AM et al. Science. 2020 Apr 28. pii: eabb9601. doi: 10.1126/science.abb9601.
A minimally invasive multicancer blood test used with standard-of-care screening is safe, effective, and feasible for use in routine clinical care, according to interim findings from a large, prospective study.
The DETECT-A blood test, an early version of the CancerSEEK test currently in development, effectively guided patient management in real time, in some cases leading to diagnosis of early cancer and potentially curative surgery in asymptomatic women with no history of cancer.
Nickolas Papadopoulos, PhD, of Johns Hopkins Medicine in Baltimore, reported these findings at the AACR virtual meeting I. The findings were simultaneously published in Science.
The study enrolled 10,006 women, aged 65-75 years, with no prior cancer diagnosis. After exclusion and loss to follow-up, 9,911 women remained.
There were 26 patients who had cancer detected by the DETECT-A blood test, 15 of whom underwent follow-up PET-CT imaging and 9 of whom underwent surgical excision. An additional 24 cancers were detected by standard screening, and 46 were detected by other means.
The positive predictive value of the blood test was 19%. When the blood test was combined with imaging, the positive predictive value was 41%.
Improving upon standard screening
“Standard-of-care screening [was used] for three different organs: breast, lung, and colon. It was more sensitive for breast cancer,” Dr. Papadopoulos noted. “Blood testing, though, identified cancer in 10 different organs.”
In fact, the DETECT-A blood test detected 14 of 45 cancers in 7 organs for which no standard screening test is available.
In addition, 12 cancers in 3 organs (breast, lung, and colon) were first detected by DETECT-A rather than by standard screening. This increased the sensitivity of cancer detection from 47% with standard screening alone to 71% with standard screening plus blood testing.
“More important, 65% [of the cancers detected by blood test] were localized or regional, which have higher chance of successful treatment with intent to cure,” Dr. Papadopoulos said.
DETECT-A covers regions of 16 commonly mutated genes and 9 proteins known to be associated with cancer. In this study, 57% of cancers were detected by mutations.
Safety and additional screening
DETECT-A also proved safe, “without incurring a large number of futile invasive follow-up tests,” Dr. Papadopoulos said.
In fact, only 1% of patients without cancer underwent PET-CT imaging, and only 0.22% underwent a “futile” invasive follow-up procedure.
Three surgeries occurred in patients who were counted as false-positives, but the surgeries were determined to be indicated, Dr. Papadopoulos said. He explained that one was for large colonic polyps with high-grade dysplasia that could not be removed endoscopically, one was for an in situ carcinoma of the appendix, and one was for a 10-cm ovarian lesion that was found to be a mucinous cystadenoma.
The investigators also analyzed whether the availability of a “liquid biopsy” test like DETECT-A would inadvertently reduce patients’ use of standard screening and found that it did not. Mammography screening habits after receiving the baseline DETECT-A blood test did not differ significantly from those prior to study enrollment.
These findings are important because early detection is a key factor in reducing cancer-specific morbidity and mortality, and although minimally invasive screening tests, including liquid biopsies like DETECT-A, hold great promise, prospective clinical studies of these new methods are needed to ensure that the anticipated benefits outweigh the potential risks, Dr. Papadopoulos explained.
“The problem is that most cancers are detected at advanced stages when they are difficult to treat,” he said. “The earlier cancer is detected, the greater the chance of successful treatment.”
Unanswered questions and future studies
This study demonstrates that it is feasible for a minimally invasive blood test to safely detect multiple cancer types in patients without a history of cancer and to enable treatment with curative intent, at least in a subset of individuals, Dr. Papadopoulos said. He added that the findings also inform the design of future randomized trials “to establish clinical utility, cost-effectiveness, and benefit-to-risk ratio of future tests.”
Further studies will also be required to determine the clinical validity and utility of the strategy of using liquid biopsy as a complement to standard-of-care screening, Dr. Papadopoulos said.
Invited discussant David G. Huntsman, MD, of the University of British Columbia in Vancouver, applauded the investigators, saying this study serves to “move the field forward.” However, it still isn’t clear how sensitivity and negative predictive value will be determined and what the optimal testing schedule is.
“This is a prospective study that will provide the data on how this assay will be used [and] whether it should be used going forward,” Dr. Huntsman said, noting that the “much bigger and more important question” is whether it improves survival.
Cost-effectiveness will also be critical, he said.
This research was supported by The Marcus Foundation, Lustgarten Foundation for Pancreatic Cancer Research, The Virginia and D.K. Ludwig Fund for Cancer Research, The Sol Goldman Center for Pancreatic Cancer Research, Susan Wojcicki and Dennis Troper, the Rolfe Foundation, The Conrad R. Hilton Foundation, The John Templeton Foundation, Burroughs Wellcome Career Award For Medical Scientists, and grants/contracts from the National Institutes of Health.
Dr. Papadopoulos disclosed relationships with Thrive Earlier Detection Inc., PGDx Inc., NeoPhore, Cage Pharma, and other companies. Dr. Huntsman is a founder, shareholder, and chief medical officer for Contextual Genomics.
SOURCE: Papadopoulos N et al. AACR 2020, Abstract CT022; Lennon AM et al. Science. 2020 Apr 28. pii: eabb9601. doi: 10.1126/science.abb9601.
A minimally invasive multicancer blood test used with standard-of-care screening is safe, effective, and feasible for use in routine clinical care, according to interim findings from a large, prospective study.
The DETECT-A blood test, an early version of the CancerSEEK test currently in development, effectively guided patient management in real time, in some cases leading to diagnosis of early cancer and potentially curative surgery in asymptomatic women with no history of cancer.
Nickolas Papadopoulos, PhD, of Johns Hopkins Medicine in Baltimore, reported these findings at the AACR virtual meeting I. The findings were simultaneously published in Science.
The study enrolled 10,006 women, aged 65-75 years, with no prior cancer diagnosis. After exclusion and loss to follow-up, 9,911 women remained.
There were 26 patients who had cancer detected by the DETECT-A blood test, 15 of whom underwent follow-up PET-CT imaging and 9 of whom underwent surgical excision. An additional 24 cancers were detected by standard screening, and 46 were detected by other means.
The positive predictive value of the blood test was 19%. When the blood test was combined with imaging, the positive predictive value was 41%.
Improving upon standard screening
“Standard-of-care screening [was used] for three different organs: breast, lung, and colon. It was more sensitive for breast cancer,” Dr. Papadopoulos noted. “Blood testing, though, identified cancer in 10 different organs.”
In fact, the DETECT-A blood test detected 14 of 45 cancers in 7 organs for which no standard screening test is available.
In addition, 12 cancers in 3 organs (breast, lung, and colon) were first detected by DETECT-A rather than by standard screening. This increased the sensitivity of cancer detection from 47% with standard screening alone to 71% with standard screening plus blood testing.
“More important, 65% [of the cancers detected by blood test] were localized or regional, which have higher chance of successful treatment with intent to cure,” Dr. Papadopoulos said.
DETECT-A covers regions of 16 commonly mutated genes and 9 proteins known to be associated with cancer. In this study, 57% of cancers were detected by mutations.
Safety and additional screening
DETECT-A also proved safe, “without incurring a large number of futile invasive follow-up tests,” Dr. Papadopoulos said.
In fact, only 1% of patients without cancer underwent PET-CT imaging, and only 0.22% underwent a “futile” invasive follow-up procedure.
Three surgeries occurred in patients who were counted as false-positives, but the surgeries were determined to be indicated, Dr. Papadopoulos said. He explained that one was for large colonic polyps with high-grade dysplasia that could not be removed endoscopically, one was for an in situ carcinoma of the appendix, and one was for a 10-cm ovarian lesion that was found to be a mucinous cystadenoma.
The investigators also analyzed whether the availability of a “liquid biopsy” test like DETECT-A would inadvertently reduce patients’ use of standard screening and found that it did not. Mammography screening habits after receiving the baseline DETECT-A blood test did not differ significantly from those prior to study enrollment.
These findings are important because early detection is a key factor in reducing cancer-specific morbidity and mortality, and although minimally invasive screening tests, including liquid biopsies like DETECT-A, hold great promise, prospective clinical studies of these new methods are needed to ensure that the anticipated benefits outweigh the potential risks, Dr. Papadopoulos explained.
“The problem is that most cancers are detected at advanced stages when they are difficult to treat,” he said. “The earlier cancer is detected, the greater the chance of successful treatment.”
Unanswered questions and future studies
This study demonstrates that it is feasible for a minimally invasive blood test to safely detect multiple cancer types in patients without a history of cancer and to enable treatment with curative intent, at least in a subset of individuals, Dr. Papadopoulos said. He added that the findings also inform the design of future randomized trials “to establish clinical utility, cost-effectiveness, and benefit-to-risk ratio of future tests.”
Further studies will also be required to determine the clinical validity and utility of the strategy of using liquid biopsy as a complement to standard-of-care screening, Dr. Papadopoulos said.
Invited discussant David G. Huntsman, MD, of the University of British Columbia in Vancouver, applauded the investigators, saying this study serves to “move the field forward.” However, it still isn’t clear how sensitivity and negative predictive value will be determined and what the optimal testing schedule is.
“This is a prospective study that will provide the data on how this assay will be used [and] whether it should be used going forward,” Dr. Huntsman said, noting that the “much bigger and more important question” is whether it improves survival.
Cost-effectiveness will also be critical, he said.
This research was supported by The Marcus Foundation, Lustgarten Foundation for Pancreatic Cancer Research, The Virginia and D.K. Ludwig Fund for Cancer Research, The Sol Goldman Center for Pancreatic Cancer Research, Susan Wojcicki and Dennis Troper, the Rolfe Foundation, The Conrad R. Hilton Foundation, The John Templeton Foundation, Burroughs Wellcome Career Award For Medical Scientists, and grants/contracts from the National Institutes of Health.
Dr. Papadopoulos disclosed relationships with Thrive Earlier Detection Inc., PGDx Inc., NeoPhore, Cage Pharma, and other companies. Dr. Huntsman is a founder, shareholder, and chief medical officer for Contextual Genomics.
SOURCE: Papadopoulos N et al. AACR 2020, Abstract CT022; Lennon AM et al. Science. 2020 Apr 28. pii: eabb9601. doi: 10.1126/science.abb9601.
FROM AACR 2020
Novel immune activator boosts immunotherapy benefit in TNBC
Triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) is a particularly aggressive form of this disease, with a poor prognosis, so there is great interest in any new treatment approach. Immunotherapy has raised hopes in TNBC, but more recently, studies have produced conflicting results.
New results show that adding a novel immune activator, Imprime PGG (Biothera), to immunotherapy with pembrolizumab (Keytruda, Merck) appears to improve the clinical benefit. The overall survival seen with the combination was twice that seen in a separate trial with pembrolizumab alone.
The new results were presented during the American Association for Cancer Research (AACR) virtual annual meeting I.
They come from the IMPRIME 1 trial, conducted in 44 women with metastatic TNBC who had anti-glucan antibodies.
“These were patients who had had prior chemotherapy and had extensive disease, including the majority with visceral disease and even liver metastasis,” said investigator Steven O’Day, MD, from the John Wayne Cancer Institute in Santa Monica, California.
All patients were treated with the combination. “We see encouraging clinical benefit evidence across all of our clinical measurements: response, durable response, and median and overall survival compared to historical single-agent [anti] PD-1 in a similar metastatic triple-negative breast cancer population,” he said.
At a median follow-up of 22.5 months, median overall survival with the combination among the 44 patients treated was 16.4 months.
In contrast, in the Keynote-086 trial of pembrolizumab monotherapy in patients with TNBC, median overall survival was 9 months, O’Day said.
He emphasized, however, that the IMPRIME 1 trial was not designed or powered to directly compare the combination therapy with pembrolizumab monotherapy.
Clinical benefit with the combination was particularly pronounced for patients who were so-called TNBC “converters” — that is, they originally had estrogen receptor (ER)-positive tumors that had progressed on endocrine therapy and, prior to starting treatment with Imprime PGG and pembrolizumab, they had biopsy results confirming TNBC, O’Day said.
The overall response rate (ORR) for all 44 patients included in the efficacy analysis was 15.9%. But among the 12 patients whose disease converted from ER-positive to TNBC after endocrine therapy, six had a response, for an ORR of 50% and a median overall survival of 17.1 months.
“It is not clear whether hormone resistance may have led to the increased responses versus secondary triple-negative status, but it is of great interest to us,” O’Day said.
Why This Special Benefit?
Invited discussant Ben Ho Park, MD, PhD, from Vanderbilt University Medical Center in Nashville, Tennessee, commented that the finding of special benefit among TNBC converters raises the question of biomarkers to determine which patients might most benefit from the combination.
“We already know that anti-beta-glucan antibodies were required to be actually eligible for this study, but is it that, in combination with immune activation, or prior ER-positive disease?” he said. “What about the role of PD-L1 staining? Can we actually combine all this data to come up with some sort of predictive score for whether or not a patient is more or less likely to respond, and more or less likely to have toxicities?”
Yeast-Derived Compound
Imprime PGG is a novel beta-glucan isolated from the cell walls of saccharomyces yeast that binds to endogenous anti-beta-glucan antibodies to form an immune complex.
The immune complex, which is the active drug, binds to a receptor known as dectin-1 to activate innate immunity and reprogram the immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment, enhance antigen presentation, and trigger T-cell activation to improve the efficacy of immune checkpoint inhibitor therapy, O’Day explained.
The complex has been administered to date to approximately 600 healthy volunteers and patients. In these studies, it was administered intravenously at doses of 2 mg/kg to 6 mg/kg weekly as monotherapy or in combination with anti-angiogenic antibodies or tumor-targeting antibodies, with or without chemotherapy.
Studies in volunteers showed that the complex activated innate immunity. Patients have tolerated it well, with no significant safety signals in either monotherapy or combination, with grade 1 or 2 infusion-related reactions being the most common adverse events to date, O’Day reported.
Study Details
Imprime 1 was a single-arm phase 2 trial enrolling 44 women with TNBC who had received at least one prior line of treatment, but not with an immune checkpoint inhibitor. They were all required to have anti-beta-glucan antibody levels of at least 20 mcg/mL.
All patients received the combination, which comprised Imprime PGG 4 mg/kg weekly plus pembrolizumab 200 mg IV every 3 weeks.
Twenty one patients were under age 50 years, and 23 were 50 years old and older. Seventeen patients were premenopausal, and 27 were postmenopausal. In all, 15 patients had more than three prior lines of therapy for metastatic disease, 30 had visceral disease, and 12 had liver metastases; only four had metastases confined to lymph nodes.
As noted above, median overall survival for all patients was 16.4 months. The ORR was 15.9%, and the disease control rate (a combination of complete and partial responses plus stable disease) was 25%. The median progression-free survival was 2.7 months (vs 2 months in Keynote-086).
In all, 39 of the 44 patients had treatment-related adverse events, with the most common being nausea, back pain, chills, fatigue, diarrhea, arthralgia, and headache. Four patients had grade 3 or 4 events, which included an infusion-related reaction, hyperglycemia, pericarditis, and pancreatitis.
Infusion-related reactions were seen in 27 patients, but only one of these reactions was grade 3 or 4.
The most common immune-mediated events were grade 1 or 2 thyroid dysfunction, which is commonly seen with PD-1 inhibitors, and there were single low-grade events of pancreatitis, pneumonitis, and pericarditis “most likely related to PD-1 inhibitor therapy,” O’Day said.
Translational data showed that innate and adaptive immunity in peripheral blood correlates with clinical benefit, with longer overall survival among patients with either monocyte activation (P = .0045) or T-cell activation (P = .012) compared with patients without activation of those components.
Taken together, the findings suggest that larger controlled studies of the combination are warranted, O’Day said.
The study was sponsored by Biothera and Merck. O’Day disclosed advisory board activities and research funding from both companies and others, and consulting for Biothera. Park disclosed royalties and consulting activities from several companies, not including the Imprime 1 sponsors.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) is a particularly aggressive form of this disease, with a poor prognosis, so there is great interest in any new treatment approach. Immunotherapy has raised hopes in TNBC, but more recently, studies have produced conflicting results.
New results show that adding a novel immune activator, Imprime PGG (Biothera), to immunotherapy with pembrolizumab (Keytruda, Merck) appears to improve the clinical benefit. The overall survival seen with the combination was twice that seen in a separate trial with pembrolizumab alone.
The new results were presented during the American Association for Cancer Research (AACR) virtual annual meeting I.
They come from the IMPRIME 1 trial, conducted in 44 women with metastatic TNBC who had anti-glucan antibodies.
“These were patients who had had prior chemotherapy and had extensive disease, including the majority with visceral disease and even liver metastasis,” said investigator Steven O’Day, MD, from the John Wayne Cancer Institute in Santa Monica, California.
All patients were treated with the combination. “We see encouraging clinical benefit evidence across all of our clinical measurements: response, durable response, and median and overall survival compared to historical single-agent [anti] PD-1 in a similar metastatic triple-negative breast cancer population,” he said.
At a median follow-up of 22.5 months, median overall survival with the combination among the 44 patients treated was 16.4 months.
In contrast, in the Keynote-086 trial of pembrolizumab monotherapy in patients with TNBC, median overall survival was 9 months, O’Day said.
He emphasized, however, that the IMPRIME 1 trial was not designed or powered to directly compare the combination therapy with pembrolizumab monotherapy.
Clinical benefit with the combination was particularly pronounced for patients who were so-called TNBC “converters” — that is, they originally had estrogen receptor (ER)-positive tumors that had progressed on endocrine therapy and, prior to starting treatment with Imprime PGG and pembrolizumab, they had biopsy results confirming TNBC, O’Day said.
The overall response rate (ORR) for all 44 patients included in the efficacy analysis was 15.9%. But among the 12 patients whose disease converted from ER-positive to TNBC after endocrine therapy, six had a response, for an ORR of 50% and a median overall survival of 17.1 months.
“It is not clear whether hormone resistance may have led to the increased responses versus secondary triple-negative status, but it is of great interest to us,” O’Day said.
Why This Special Benefit?
Invited discussant Ben Ho Park, MD, PhD, from Vanderbilt University Medical Center in Nashville, Tennessee, commented that the finding of special benefit among TNBC converters raises the question of biomarkers to determine which patients might most benefit from the combination.
“We already know that anti-beta-glucan antibodies were required to be actually eligible for this study, but is it that, in combination with immune activation, or prior ER-positive disease?” he said. “What about the role of PD-L1 staining? Can we actually combine all this data to come up with some sort of predictive score for whether or not a patient is more or less likely to respond, and more or less likely to have toxicities?”
Yeast-Derived Compound
Imprime PGG is a novel beta-glucan isolated from the cell walls of saccharomyces yeast that binds to endogenous anti-beta-glucan antibodies to form an immune complex.
The immune complex, which is the active drug, binds to a receptor known as dectin-1 to activate innate immunity and reprogram the immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment, enhance antigen presentation, and trigger T-cell activation to improve the efficacy of immune checkpoint inhibitor therapy, O’Day explained.
The complex has been administered to date to approximately 600 healthy volunteers and patients. In these studies, it was administered intravenously at doses of 2 mg/kg to 6 mg/kg weekly as monotherapy or in combination with anti-angiogenic antibodies or tumor-targeting antibodies, with or without chemotherapy.
Studies in volunteers showed that the complex activated innate immunity. Patients have tolerated it well, with no significant safety signals in either monotherapy or combination, with grade 1 or 2 infusion-related reactions being the most common adverse events to date, O’Day reported.
Study Details
Imprime 1 was a single-arm phase 2 trial enrolling 44 women with TNBC who had received at least one prior line of treatment, but not with an immune checkpoint inhibitor. They were all required to have anti-beta-glucan antibody levels of at least 20 mcg/mL.
All patients received the combination, which comprised Imprime PGG 4 mg/kg weekly plus pembrolizumab 200 mg IV every 3 weeks.
Twenty one patients were under age 50 years, and 23 were 50 years old and older. Seventeen patients were premenopausal, and 27 were postmenopausal. In all, 15 patients had more than three prior lines of therapy for metastatic disease, 30 had visceral disease, and 12 had liver metastases; only four had metastases confined to lymph nodes.
As noted above, median overall survival for all patients was 16.4 months. The ORR was 15.9%, and the disease control rate (a combination of complete and partial responses plus stable disease) was 25%. The median progression-free survival was 2.7 months (vs 2 months in Keynote-086).
In all, 39 of the 44 patients had treatment-related adverse events, with the most common being nausea, back pain, chills, fatigue, diarrhea, arthralgia, and headache. Four patients had grade 3 or 4 events, which included an infusion-related reaction, hyperglycemia, pericarditis, and pancreatitis.
Infusion-related reactions were seen in 27 patients, but only one of these reactions was grade 3 or 4.
The most common immune-mediated events were grade 1 or 2 thyroid dysfunction, which is commonly seen with PD-1 inhibitors, and there were single low-grade events of pancreatitis, pneumonitis, and pericarditis “most likely related to PD-1 inhibitor therapy,” O’Day said.
Translational data showed that innate and adaptive immunity in peripheral blood correlates with clinical benefit, with longer overall survival among patients with either monocyte activation (P = .0045) or T-cell activation (P = .012) compared with patients without activation of those components.
Taken together, the findings suggest that larger controlled studies of the combination are warranted, O’Day said.
The study was sponsored by Biothera and Merck. O’Day disclosed advisory board activities and research funding from both companies and others, and consulting for Biothera. Park disclosed royalties and consulting activities from several companies, not including the Imprime 1 sponsors.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) is a particularly aggressive form of this disease, with a poor prognosis, so there is great interest in any new treatment approach. Immunotherapy has raised hopes in TNBC, but more recently, studies have produced conflicting results.
New results show that adding a novel immune activator, Imprime PGG (Biothera), to immunotherapy with pembrolizumab (Keytruda, Merck) appears to improve the clinical benefit. The overall survival seen with the combination was twice that seen in a separate trial with pembrolizumab alone.
The new results were presented during the American Association for Cancer Research (AACR) virtual annual meeting I.
They come from the IMPRIME 1 trial, conducted in 44 women with metastatic TNBC who had anti-glucan antibodies.
“These were patients who had had prior chemotherapy and had extensive disease, including the majority with visceral disease and even liver metastasis,” said investigator Steven O’Day, MD, from the John Wayne Cancer Institute in Santa Monica, California.
All patients were treated with the combination. “We see encouraging clinical benefit evidence across all of our clinical measurements: response, durable response, and median and overall survival compared to historical single-agent [anti] PD-1 in a similar metastatic triple-negative breast cancer population,” he said.
At a median follow-up of 22.5 months, median overall survival with the combination among the 44 patients treated was 16.4 months.
In contrast, in the Keynote-086 trial of pembrolizumab monotherapy in patients with TNBC, median overall survival was 9 months, O’Day said.
He emphasized, however, that the IMPRIME 1 trial was not designed or powered to directly compare the combination therapy with pembrolizumab monotherapy.
Clinical benefit with the combination was particularly pronounced for patients who were so-called TNBC “converters” — that is, they originally had estrogen receptor (ER)-positive tumors that had progressed on endocrine therapy and, prior to starting treatment with Imprime PGG and pembrolizumab, they had biopsy results confirming TNBC, O’Day said.
The overall response rate (ORR) for all 44 patients included in the efficacy analysis was 15.9%. But among the 12 patients whose disease converted from ER-positive to TNBC after endocrine therapy, six had a response, for an ORR of 50% and a median overall survival of 17.1 months.
“It is not clear whether hormone resistance may have led to the increased responses versus secondary triple-negative status, but it is of great interest to us,” O’Day said.
Why This Special Benefit?
Invited discussant Ben Ho Park, MD, PhD, from Vanderbilt University Medical Center in Nashville, Tennessee, commented that the finding of special benefit among TNBC converters raises the question of biomarkers to determine which patients might most benefit from the combination.
“We already know that anti-beta-glucan antibodies were required to be actually eligible for this study, but is it that, in combination with immune activation, or prior ER-positive disease?” he said. “What about the role of PD-L1 staining? Can we actually combine all this data to come up with some sort of predictive score for whether or not a patient is more or less likely to respond, and more or less likely to have toxicities?”
Yeast-Derived Compound
Imprime PGG is a novel beta-glucan isolated from the cell walls of saccharomyces yeast that binds to endogenous anti-beta-glucan antibodies to form an immune complex.
The immune complex, which is the active drug, binds to a receptor known as dectin-1 to activate innate immunity and reprogram the immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment, enhance antigen presentation, and trigger T-cell activation to improve the efficacy of immune checkpoint inhibitor therapy, O’Day explained.
The complex has been administered to date to approximately 600 healthy volunteers and patients. In these studies, it was administered intravenously at doses of 2 mg/kg to 6 mg/kg weekly as monotherapy or in combination with anti-angiogenic antibodies or tumor-targeting antibodies, with or without chemotherapy.
Studies in volunteers showed that the complex activated innate immunity. Patients have tolerated it well, with no significant safety signals in either monotherapy or combination, with grade 1 or 2 infusion-related reactions being the most common adverse events to date, O’Day reported.
Study Details
Imprime 1 was a single-arm phase 2 trial enrolling 44 women with TNBC who had received at least one prior line of treatment, but not with an immune checkpoint inhibitor. They were all required to have anti-beta-glucan antibody levels of at least 20 mcg/mL.
All patients received the combination, which comprised Imprime PGG 4 mg/kg weekly plus pembrolizumab 200 mg IV every 3 weeks.
Twenty one patients were under age 50 years, and 23 were 50 years old and older. Seventeen patients were premenopausal, and 27 were postmenopausal. In all, 15 patients had more than three prior lines of therapy for metastatic disease, 30 had visceral disease, and 12 had liver metastases; only four had metastases confined to lymph nodes.
As noted above, median overall survival for all patients was 16.4 months. The ORR was 15.9%, and the disease control rate (a combination of complete and partial responses plus stable disease) was 25%. The median progression-free survival was 2.7 months (vs 2 months in Keynote-086).
In all, 39 of the 44 patients had treatment-related adverse events, with the most common being nausea, back pain, chills, fatigue, diarrhea, arthralgia, and headache. Four patients had grade 3 or 4 events, which included an infusion-related reaction, hyperglycemia, pericarditis, and pancreatitis.
Infusion-related reactions were seen in 27 patients, but only one of these reactions was grade 3 or 4.
The most common immune-mediated events were grade 1 or 2 thyroid dysfunction, which is commonly seen with PD-1 inhibitors, and there were single low-grade events of pancreatitis, pneumonitis, and pericarditis “most likely related to PD-1 inhibitor therapy,” O’Day said.
Translational data showed that innate and adaptive immunity in peripheral blood correlates with clinical benefit, with longer overall survival among patients with either monocyte activation (P = .0045) or T-cell activation (P = .012) compared with patients without activation of those components.
Taken together, the findings suggest that larger controlled studies of the combination are warranted, O’Day said.
The study was sponsored by Biothera and Merck. O’Day disclosed advisory board activities and research funding from both companies and others, and consulting for Biothera. Park disclosed royalties and consulting activities from several companies, not including the Imprime 1 sponsors.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM AACR 20
Excess cancer deaths predicted as care is disrupted by COVID-19
The majority of patients who have cancer or are suspected of having cancer are not accessing healthcare services in the United Kingdom or the United States because of the COVID-19 pandemic, the first report of its kind estimates.
As a result, there will be an excess of deaths among patients who have cancer and multiple comorbidities in both countries during the current coronavirus emergency, the report warns.
The authors calculate that there will be 6,270 excess deaths among cancer patients 1 year from now in England and 33,890 excess deaths among cancer patients in the United States. (In the United States, the estimated excess number of deaths applies only to patients older than 40 years, they note.)
“The recorded underlying cause of these excess deaths may be cancer, COVID-19, or comorbidity (such as myocardial infarction),” Alvina Lai, PhD, University College London, United Kingdom, and colleagues observe.
“Our data have highlighted how cancer patients with multimorbidity are a particularly at-risk group during the current pandemic,” they emphasize.
The study was published on ResearchGate as a preprint and has not undergone peer review.
Commenting on the study on the UK Science Media Center, several experts emphasized the lack of peer review, noting that interpretation of these data needs to be further refined on the basis of that input. One expert suggested that there are “substantial uncertainties that this paper does not adequately communicate.” But others argued that this topic was important enough to warrant early release of the data.
Chris Bunce, PhD, University of Birmingham, United Kingdom, said this study represents “a highly valuable contribution.”
“It is universally accepted that early diagnosis and treatment and adherence to treatment regimens saves lives,” he pointed out.
“Therefore, these COVID-19-related impacts will cost lives,” Bunce said.
“And if this information is to influence cancer care and guide policy during the COVID-19 crisis, then it is important that the findings are disseminated and discussed immediately, warranting their release ahead of peer view,” he added.
In a Medscape UK commentary, oncologist Karol Sikora, MD, PhD, argues that “restarting cancer services can’t come soon enough.”
“Resonably Argued Numerical Estimate”
“It’s well known that there have been considerable changes in the provision of health care for many conditions, including cancers, as a result of all the measures to deal with the COVID-19 crisis,” said Kevin McConway, PhD, professor emeritus of applied statistics, the Open University, Milton Keynes, United Kingdom.
“It seems inevitable that there will be increased deaths in cancer patients if they are infected with the virus or because of changes in the health services available to them, and quite possibly also from socio-economic effects of the responses to the crisis,” he continued.
“This study is the first that I have seen that produces a reasonably argued numerical estimate of the number of excess deaths of people with cancer arising from these factors in the UK and the USA,” he added.
Declines in Urgent Referrals and Chemo Attendance
For the study, the team used DATA-CAN, the UK National Health Data Research Hub for Cancer, to assess weekly returns for urgent cancer referrals for early diagnosis and also chemotherapy attendances for hospitals in Leeds, London, and Northern Ireland going back to 2018.
The data revealed that there have been major declines in chemotherapy attendances. There has been, on average, a 60% decrease from prepandemic levels in eight hospitals in the three regions that were assessed.
Urgent cancer referrals have dropped by an average of 76% compared to prepandemic levels in the three regions.
On the conservative assumption that the COVID-19 pandemic will only affect patients with newly diagnosed cancer (incident cases), the researchers estimate that the proportion of the population affected by the emergency (PAE) is 40% and that the relative impact of the emergency (RIE) is 1.5.
PAE is a summary measure of exposure to the adverse health consequences of the emergency; RIE is a summary measure of the combined impact on mortality of infection, health service change, physical distancing, and economic downturn, the authors explain.
Comorbidities Common
“Comorbidities were common in people with cancer,” the study authors note. For example, more than one quarter of the study population had at least one comorbidity; more than 14% had two.
For incident cancers, the number of excess deaths steadily increased in conjunction with an increase in the number of comorbidities, such that more than 80% of deaths occurred in patients with one or more comorbidities.
“When considering both prevalent and incident cancers together with a COVID-19 PAE of 40%, we estimated 17,991 excess deaths at a RIE of 1.5; 78.1% of these deaths occur in patients with ≥1 comorbidities,” the authors report.
“The excess risk of death in people living with cancer during the COVID-19 emergency may be due not only to COVID-19 infection, but also to the unintended health consequences of changes in health service provision, the physical or psychological effects of social distancing, and economic upheaval,” they state.
“This is the first study demonstrating profound recent changes in cancer care delivery in multiple centers,” the authors observe.
Lai has disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Several coauthors have various relationships with industry, as listed in their article. The commentators have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The majority of patients who have cancer or are suspected of having cancer are not accessing healthcare services in the United Kingdom or the United States because of the COVID-19 pandemic, the first report of its kind estimates.
As a result, there will be an excess of deaths among patients who have cancer and multiple comorbidities in both countries during the current coronavirus emergency, the report warns.
The authors calculate that there will be 6,270 excess deaths among cancer patients 1 year from now in England and 33,890 excess deaths among cancer patients in the United States. (In the United States, the estimated excess number of deaths applies only to patients older than 40 years, they note.)
“The recorded underlying cause of these excess deaths may be cancer, COVID-19, or comorbidity (such as myocardial infarction),” Alvina Lai, PhD, University College London, United Kingdom, and colleagues observe.
“Our data have highlighted how cancer patients with multimorbidity are a particularly at-risk group during the current pandemic,” they emphasize.
The study was published on ResearchGate as a preprint and has not undergone peer review.
Commenting on the study on the UK Science Media Center, several experts emphasized the lack of peer review, noting that interpretation of these data needs to be further refined on the basis of that input. One expert suggested that there are “substantial uncertainties that this paper does not adequately communicate.” But others argued that this topic was important enough to warrant early release of the data.
Chris Bunce, PhD, University of Birmingham, United Kingdom, said this study represents “a highly valuable contribution.”
“It is universally accepted that early diagnosis and treatment and adherence to treatment regimens saves lives,” he pointed out.
“Therefore, these COVID-19-related impacts will cost lives,” Bunce said.
“And if this information is to influence cancer care and guide policy during the COVID-19 crisis, then it is important that the findings are disseminated and discussed immediately, warranting their release ahead of peer view,” he added.
In a Medscape UK commentary, oncologist Karol Sikora, MD, PhD, argues that “restarting cancer services can’t come soon enough.”
“Resonably Argued Numerical Estimate”
“It’s well known that there have been considerable changes in the provision of health care for many conditions, including cancers, as a result of all the measures to deal with the COVID-19 crisis,” said Kevin McConway, PhD, professor emeritus of applied statistics, the Open University, Milton Keynes, United Kingdom.
“It seems inevitable that there will be increased deaths in cancer patients if they are infected with the virus or because of changes in the health services available to them, and quite possibly also from socio-economic effects of the responses to the crisis,” he continued.
“This study is the first that I have seen that produces a reasonably argued numerical estimate of the number of excess deaths of people with cancer arising from these factors in the UK and the USA,” he added.
Declines in Urgent Referrals and Chemo Attendance
For the study, the team used DATA-CAN, the UK National Health Data Research Hub for Cancer, to assess weekly returns for urgent cancer referrals for early diagnosis and also chemotherapy attendances for hospitals in Leeds, London, and Northern Ireland going back to 2018.
The data revealed that there have been major declines in chemotherapy attendances. There has been, on average, a 60% decrease from prepandemic levels in eight hospitals in the three regions that were assessed.
Urgent cancer referrals have dropped by an average of 76% compared to prepandemic levels in the three regions.
On the conservative assumption that the COVID-19 pandemic will only affect patients with newly diagnosed cancer (incident cases), the researchers estimate that the proportion of the population affected by the emergency (PAE) is 40% and that the relative impact of the emergency (RIE) is 1.5.
PAE is a summary measure of exposure to the adverse health consequences of the emergency; RIE is a summary measure of the combined impact on mortality of infection, health service change, physical distancing, and economic downturn, the authors explain.
Comorbidities Common
“Comorbidities were common in people with cancer,” the study authors note. For example, more than one quarter of the study population had at least one comorbidity; more than 14% had two.
For incident cancers, the number of excess deaths steadily increased in conjunction with an increase in the number of comorbidities, such that more than 80% of deaths occurred in patients with one or more comorbidities.
“When considering both prevalent and incident cancers together with a COVID-19 PAE of 40%, we estimated 17,991 excess deaths at a RIE of 1.5; 78.1% of these deaths occur in patients with ≥1 comorbidities,” the authors report.
“The excess risk of death in people living with cancer during the COVID-19 emergency may be due not only to COVID-19 infection, but also to the unintended health consequences of changes in health service provision, the physical or psychological effects of social distancing, and economic upheaval,” they state.
“This is the first study demonstrating profound recent changes in cancer care delivery in multiple centers,” the authors observe.
Lai has disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Several coauthors have various relationships with industry, as listed in their article. The commentators have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The majority of patients who have cancer or are suspected of having cancer are not accessing healthcare services in the United Kingdom or the United States because of the COVID-19 pandemic, the first report of its kind estimates.
As a result, there will be an excess of deaths among patients who have cancer and multiple comorbidities in both countries during the current coronavirus emergency, the report warns.
The authors calculate that there will be 6,270 excess deaths among cancer patients 1 year from now in England and 33,890 excess deaths among cancer patients in the United States. (In the United States, the estimated excess number of deaths applies only to patients older than 40 years, they note.)
“The recorded underlying cause of these excess deaths may be cancer, COVID-19, or comorbidity (such as myocardial infarction),” Alvina Lai, PhD, University College London, United Kingdom, and colleagues observe.
“Our data have highlighted how cancer patients with multimorbidity are a particularly at-risk group during the current pandemic,” they emphasize.
The study was published on ResearchGate as a preprint and has not undergone peer review.
Commenting on the study on the UK Science Media Center, several experts emphasized the lack of peer review, noting that interpretation of these data needs to be further refined on the basis of that input. One expert suggested that there are “substantial uncertainties that this paper does not adequately communicate.” But others argued that this topic was important enough to warrant early release of the data.
Chris Bunce, PhD, University of Birmingham, United Kingdom, said this study represents “a highly valuable contribution.”
“It is universally accepted that early diagnosis and treatment and adherence to treatment regimens saves lives,” he pointed out.
“Therefore, these COVID-19-related impacts will cost lives,” Bunce said.
“And if this information is to influence cancer care and guide policy during the COVID-19 crisis, then it is important that the findings are disseminated and discussed immediately, warranting their release ahead of peer view,” he added.
In a Medscape UK commentary, oncologist Karol Sikora, MD, PhD, argues that “restarting cancer services can’t come soon enough.”
“Resonably Argued Numerical Estimate”
“It’s well known that there have been considerable changes in the provision of health care for many conditions, including cancers, as a result of all the measures to deal with the COVID-19 crisis,” said Kevin McConway, PhD, professor emeritus of applied statistics, the Open University, Milton Keynes, United Kingdom.
“It seems inevitable that there will be increased deaths in cancer patients if they are infected with the virus or because of changes in the health services available to them, and quite possibly also from socio-economic effects of the responses to the crisis,” he continued.
“This study is the first that I have seen that produces a reasonably argued numerical estimate of the number of excess deaths of people with cancer arising from these factors in the UK and the USA,” he added.
Declines in Urgent Referrals and Chemo Attendance
For the study, the team used DATA-CAN, the UK National Health Data Research Hub for Cancer, to assess weekly returns for urgent cancer referrals for early diagnosis and also chemotherapy attendances for hospitals in Leeds, London, and Northern Ireland going back to 2018.
The data revealed that there have been major declines in chemotherapy attendances. There has been, on average, a 60% decrease from prepandemic levels in eight hospitals in the three regions that were assessed.
Urgent cancer referrals have dropped by an average of 76% compared to prepandemic levels in the three regions.
On the conservative assumption that the COVID-19 pandemic will only affect patients with newly diagnosed cancer (incident cases), the researchers estimate that the proportion of the population affected by the emergency (PAE) is 40% and that the relative impact of the emergency (RIE) is 1.5.
PAE is a summary measure of exposure to the adverse health consequences of the emergency; RIE is a summary measure of the combined impact on mortality of infection, health service change, physical distancing, and economic downturn, the authors explain.
Comorbidities Common
“Comorbidities were common in people with cancer,” the study authors note. For example, more than one quarter of the study population had at least one comorbidity; more than 14% had two.
For incident cancers, the number of excess deaths steadily increased in conjunction with an increase in the number of comorbidities, such that more than 80% of deaths occurred in patients with one or more comorbidities.
“When considering both prevalent and incident cancers together with a COVID-19 PAE of 40%, we estimated 17,991 excess deaths at a RIE of 1.5; 78.1% of these deaths occur in patients with ≥1 comorbidities,” the authors report.
“The excess risk of death in people living with cancer during the COVID-19 emergency may be due not only to COVID-19 infection, but also to the unintended health consequences of changes in health service provision, the physical or psychological effects of social distancing, and economic upheaval,” they state.
“This is the first study demonstrating profound recent changes in cancer care delivery in multiple centers,” the authors observe.
Lai has disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Several coauthors have various relationships with industry, as listed in their article. The commentators have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Antitumor treatment may increase risk of severe events in COVID-19 patients
Cancer patients who received antitumor treatment within 14 days of COVID-19 diagnosis had an increased risk of severe events, according to data from three hospitals in Wuhan.
Patients with patchy consolidation at hospital admission also had an increased risk of severe events, defined as ICU admission, mechanical ventilation, or death.
However, these findings are limited by the small number of patients studied and the retrospective nature of the analysis, according to researchers.
Li Zhang, MD, PhD, of Tongji Hospital in Wuhan, China, presented this research at the AACR virtual meeting I. Some of the data were previously published in Annals of Oncology.
The researchers studied 28 patients with cancer among 1,276 patients with COVID-19 treated at three hospitals in Wuhan. The most common cancer types were lung (n = 7), esophageal (n = 4), and breast (n = 3). Patients had other gastrointestinal, gynecologic, genitourinary, and head and neck cancers as well.
The patients’ median age was 65 years (range, 56-70 years), 60.9% were men, 35.7% had stage IV cancer, and 28.6% had hospital-acquired COVID-19. Antitumor treatments included chemotherapy (n = 22), surgery (n = 21), radiotherapy (n = 21), targeted therapy (n = 5), and immune checkpoint inhibitors (n = 2).
COVID-19 treatment
Most patients (n = 22) received oxygen as their only respiratory intervention, although 10 received mechanical ventilation.
For systemic therapy, patients received antibiotic treatment (n = 23), corticosteroids (n = 15), intravenous immunoglobulin (n = 10), and tocilizumab (n = 1).
Antiviral treatments included umifenovir (n = 14), lopinavir/ritonavir (n = 10), ganciclovir (n = 9), ribavirin (n = 1), or a combination of antiviral drugs (n = 9).
“No cancer patients were enrolled in clinical trials, so no one received hydroxychloroquine or remdesivir,” Dr. Zhang noted.
Outcomes
In all, 15 patients (53.6%) had severe events. The median time from COVID-19 diagnosis to severe events was 7 days (range, 5-15 days).
A total of eight patients (28.6%) died – three with lung cancer, two with prostate cancer, one with liver cancer, one with rectal cancer, and one with testicular cancer.
Causes of death were acute respiratory distress syndrome (n = 5), septic shock (n = 1), suspected pulmonary embolism (n = 1), and acute myocardial infarction (n = 1).
By April 4, 14 patients had been discharged from the hospital, and 6 were still hospitalized. The median duration of hospitalization was 18.4 days for discharged patients and 29.4 days for patients still in hospital.
Follow-up CT scans showed improvement in 13 patients, no changes in 5 patients, and deterioration in 6 patients.
Factors associated with severe events
In a multivariable analysis, receiving antitumor treatment within 14 days of COVID-19 diagnosis was associated with severe events (hazard ratio, 4.079; P = .037).
However, only seven patients received antitumor treatments within 14 days of COVID-19 diagnosis – three chemotherapy, two targeted therapy, one radiotherapy, and one immune checkpoint inhibitor. Five of these seven patients had severe events.
Another factor associated with severe events in multivariable analysis was patchy consolidation on CT scan at admission (HR, 5.438; P = .01). Age and gender were not significantly associated with severe events.
Immune checkpoint inhibitors
Dr. Zhang and colleagues also analyzed a second group of cancer patients and their family members to determine if patients on immune checkpoint inhibitors have an increased risk of COVID-19.
This group included 124 cancer patients treated with immune checkpoint inhibitors for at least 2 months. The patients had a median age of 59 years (range, 54-65 years), and 61.8% were men. Most patients (95.2%) had stage IV cancer, and the most common cancers were lung (54.0%), esophageal (18.6%), and head and neck (10.7%).
In this group, only one cancer patient developed COVID-19 (via nosocomial infection). In another case, a patient’s spouse developed COVID-19, but the patient did not.
Dr. Zhang said this “limited information did not suggest cancer patients treated with immune checkpoint inhibitors were more vulnerable to COVID infection.”
Dr. Zhang and colleagues reported no conflicts of interest. This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China and Huazhong University of Science and Technology COVID-19 Rapid Response Call China.
SOURCE: Zhang L et al. Ann Oncol. 2020 Mar 26. doi: 10.1016/j.annonc.2020.03.296.
Cancer patients who received antitumor treatment within 14 days of COVID-19 diagnosis had an increased risk of severe events, according to data from three hospitals in Wuhan.
Patients with patchy consolidation at hospital admission also had an increased risk of severe events, defined as ICU admission, mechanical ventilation, or death.
However, these findings are limited by the small number of patients studied and the retrospective nature of the analysis, according to researchers.
Li Zhang, MD, PhD, of Tongji Hospital in Wuhan, China, presented this research at the AACR virtual meeting I. Some of the data were previously published in Annals of Oncology.
The researchers studied 28 patients with cancer among 1,276 patients with COVID-19 treated at three hospitals in Wuhan. The most common cancer types were lung (n = 7), esophageal (n = 4), and breast (n = 3). Patients had other gastrointestinal, gynecologic, genitourinary, and head and neck cancers as well.
The patients’ median age was 65 years (range, 56-70 years), 60.9% were men, 35.7% had stage IV cancer, and 28.6% had hospital-acquired COVID-19. Antitumor treatments included chemotherapy (n = 22), surgery (n = 21), radiotherapy (n = 21), targeted therapy (n = 5), and immune checkpoint inhibitors (n = 2).
COVID-19 treatment
Most patients (n = 22) received oxygen as their only respiratory intervention, although 10 received mechanical ventilation.
For systemic therapy, patients received antibiotic treatment (n = 23), corticosteroids (n = 15), intravenous immunoglobulin (n = 10), and tocilizumab (n = 1).
Antiviral treatments included umifenovir (n = 14), lopinavir/ritonavir (n = 10), ganciclovir (n = 9), ribavirin (n = 1), or a combination of antiviral drugs (n = 9).
“No cancer patients were enrolled in clinical trials, so no one received hydroxychloroquine or remdesivir,” Dr. Zhang noted.
Outcomes
In all, 15 patients (53.6%) had severe events. The median time from COVID-19 diagnosis to severe events was 7 days (range, 5-15 days).
A total of eight patients (28.6%) died – three with lung cancer, two with prostate cancer, one with liver cancer, one with rectal cancer, and one with testicular cancer.
Causes of death were acute respiratory distress syndrome (n = 5), septic shock (n = 1), suspected pulmonary embolism (n = 1), and acute myocardial infarction (n = 1).
By April 4, 14 patients had been discharged from the hospital, and 6 were still hospitalized. The median duration of hospitalization was 18.4 days for discharged patients and 29.4 days for patients still in hospital.
Follow-up CT scans showed improvement in 13 patients, no changes in 5 patients, and deterioration in 6 patients.
Factors associated with severe events
In a multivariable analysis, receiving antitumor treatment within 14 days of COVID-19 diagnosis was associated with severe events (hazard ratio, 4.079; P = .037).
However, only seven patients received antitumor treatments within 14 days of COVID-19 diagnosis – three chemotherapy, two targeted therapy, one radiotherapy, and one immune checkpoint inhibitor. Five of these seven patients had severe events.
Another factor associated with severe events in multivariable analysis was patchy consolidation on CT scan at admission (HR, 5.438; P = .01). Age and gender were not significantly associated with severe events.
Immune checkpoint inhibitors
Dr. Zhang and colleagues also analyzed a second group of cancer patients and their family members to determine if patients on immune checkpoint inhibitors have an increased risk of COVID-19.
This group included 124 cancer patients treated with immune checkpoint inhibitors for at least 2 months. The patients had a median age of 59 years (range, 54-65 years), and 61.8% were men. Most patients (95.2%) had stage IV cancer, and the most common cancers were lung (54.0%), esophageal (18.6%), and head and neck (10.7%).
In this group, only one cancer patient developed COVID-19 (via nosocomial infection). In another case, a patient’s spouse developed COVID-19, but the patient did not.
Dr. Zhang said this “limited information did not suggest cancer patients treated with immune checkpoint inhibitors were more vulnerable to COVID infection.”
Dr. Zhang and colleagues reported no conflicts of interest. This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China and Huazhong University of Science and Technology COVID-19 Rapid Response Call China.
SOURCE: Zhang L et al. Ann Oncol. 2020 Mar 26. doi: 10.1016/j.annonc.2020.03.296.
Cancer patients who received antitumor treatment within 14 days of COVID-19 diagnosis had an increased risk of severe events, according to data from three hospitals in Wuhan.
Patients with patchy consolidation at hospital admission also had an increased risk of severe events, defined as ICU admission, mechanical ventilation, or death.
However, these findings are limited by the small number of patients studied and the retrospective nature of the analysis, according to researchers.
Li Zhang, MD, PhD, of Tongji Hospital in Wuhan, China, presented this research at the AACR virtual meeting I. Some of the data were previously published in Annals of Oncology.
The researchers studied 28 patients with cancer among 1,276 patients with COVID-19 treated at three hospitals in Wuhan. The most common cancer types were lung (n = 7), esophageal (n = 4), and breast (n = 3). Patients had other gastrointestinal, gynecologic, genitourinary, and head and neck cancers as well.
The patients’ median age was 65 years (range, 56-70 years), 60.9% were men, 35.7% had stage IV cancer, and 28.6% had hospital-acquired COVID-19. Antitumor treatments included chemotherapy (n = 22), surgery (n = 21), radiotherapy (n = 21), targeted therapy (n = 5), and immune checkpoint inhibitors (n = 2).
COVID-19 treatment
Most patients (n = 22) received oxygen as their only respiratory intervention, although 10 received mechanical ventilation.
For systemic therapy, patients received antibiotic treatment (n = 23), corticosteroids (n = 15), intravenous immunoglobulin (n = 10), and tocilizumab (n = 1).
Antiviral treatments included umifenovir (n = 14), lopinavir/ritonavir (n = 10), ganciclovir (n = 9), ribavirin (n = 1), or a combination of antiviral drugs (n = 9).
“No cancer patients were enrolled in clinical trials, so no one received hydroxychloroquine or remdesivir,” Dr. Zhang noted.
Outcomes
In all, 15 patients (53.6%) had severe events. The median time from COVID-19 diagnosis to severe events was 7 days (range, 5-15 days).
A total of eight patients (28.6%) died – three with lung cancer, two with prostate cancer, one with liver cancer, one with rectal cancer, and one with testicular cancer.
Causes of death were acute respiratory distress syndrome (n = 5), septic shock (n = 1), suspected pulmonary embolism (n = 1), and acute myocardial infarction (n = 1).
By April 4, 14 patients had been discharged from the hospital, and 6 were still hospitalized. The median duration of hospitalization was 18.4 days for discharged patients and 29.4 days for patients still in hospital.
Follow-up CT scans showed improvement in 13 patients, no changes in 5 patients, and deterioration in 6 patients.
Factors associated with severe events
In a multivariable analysis, receiving antitumor treatment within 14 days of COVID-19 diagnosis was associated with severe events (hazard ratio, 4.079; P = .037).
However, only seven patients received antitumor treatments within 14 days of COVID-19 diagnosis – three chemotherapy, two targeted therapy, one radiotherapy, and one immune checkpoint inhibitor. Five of these seven patients had severe events.
Another factor associated with severe events in multivariable analysis was patchy consolidation on CT scan at admission (HR, 5.438; P = .01). Age and gender were not significantly associated with severe events.
Immune checkpoint inhibitors
Dr. Zhang and colleagues also analyzed a second group of cancer patients and their family members to determine if patients on immune checkpoint inhibitors have an increased risk of COVID-19.
This group included 124 cancer patients treated with immune checkpoint inhibitors for at least 2 months. The patients had a median age of 59 years (range, 54-65 years), and 61.8% were men. Most patients (95.2%) had stage IV cancer, and the most common cancers were lung (54.0%), esophageal (18.6%), and head and neck (10.7%).
In this group, only one cancer patient developed COVID-19 (via nosocomial infection). In another case, a patient’s spouse developed COVID-19, but the patient did not.
Dr. Zhang said this “limited information did not suggest cancer patients treated with immune checkpoint inhibitors were more vulnerable to COVID infection.”
Dr. Zhang and colleagues reported no conflicts of interest. This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China and Huazhong University of Science and Technology COVID-19 Rapid Response Call China.
SOURCE: Zhang L et al. Ann Oncol. 2020 Mar 26. doi: 10.1016/j.annonc.2020.03.296.
FROM AACR 2020
EMBRACA shows no overall survival benefit with talazoparib
Talazoparib did not confer an overall survival benefit over chemotherapy in patients with germline BRCA1/2-mutated HER2-negative advanced breast cancer, according to a final analysis of the phase 3 EMBRACA trial.
The progression-free survival benefit previously seen with talazoparib did not translate to an overall survival benefit. However, patient-reported quality of life continued to favor talazoparib in the final analysis, Jennifer K. Litton, MD, of the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center in Houston, reported at the AACR virtual meeting I.
The EMBRACA trial enrolled adults with HER2-negative locally advanced or metastatic breast cancer and a deleterious or suspected deleterious germline BRCA mutation. They were randomized to talazoparib at 1 mg daily (n = 287) or to physician’s choice of single-agent chemotherapy (n = 144).
In the primary analysis, talazoparib was associated with significantly improved progression-free survival. The median progression-free survival was 8.6 months in the talazoparib arm and 5.6 months in the chemotherapy arm (hazard ratio, 0.54).
“At the time of the primary analysis, the overall survival data were immature, and the hazard ratio for the interim overall survival was 0.761, which was not statistically significant,” Dr. Litton said.
However, patient-reported outcomes favored talazoparib in the primary analysis, with patients in that arm showing “significant overall improvements with a significant delay in time to clinically meaningful deterioration in multiple cancer-related and breast cancer–specific symptoms, functions, quality of life, and global health,” Dr. Litton said.
Final overall survival
At the final analysis, the median follow-up was 44.9 months for the talazoparib arm and 36.8 months for the chemotherapy arm.
The median overall survival was 19.3 months in the talazoparib arm and 19.5 months in the chemotherapy arm (HR, 0.848; P = .17)
The results were “generally consistent” across patient subgroups,” Dr. Litton said, adding that “the effect of treatment with talazoparib was also similar irrespective of BRCA status, as well as triple-negative or hormone-receptor-positive subtypes.”
Of note, most patients received poststudy therapies. These included PARP inhibitors in 4.5% of patients in the talazoparib arm and 32.6% of patients in the chemotherapy arm, and platinum drugs in 46.3% and 41.7%, respectively.
Patients who received chemotherapy on study but did not receive a subsequent PARP inhibitor or platinum therapy had both shorter total treatment duration and shorter overall survival, compared with patients who did receive subsequent treatment.
In the talazoparib arm, outcomes were similar whether or not patients received a subsequent PARP inhibitor or platinum therapy.
“Interpretation of the overall survival results may have been confounded by subsequent treatment, so two sensitivity analyses accounting for subsequent PARP inhibition or platinum therapy were carried out,” Dr. Litton said.
She noted that adjustment for poststudy treatment lowered the hazard ratio, but there was still no significant difference between the talazoparib and chemotherapy arms. These results suggest “the primary overall survival analysis underestimated the treatment benefit of talazoparib,” Dr. Litton said. She also noted that a longer platinum-free interval prior to study entry was generally associated with a longer duration of survival, particularly in the talazoparib arm.
Quality of life and safety
Patient-reported outcomes continued to favor talazoparib with extended follow-up and were consistent with the initial analysis, Dr. Litton noted.
The updated analysis revealed “a significant improvement in estimated overall change from baseline in the global health quality of life scores for those patients receiving talazoparib, while a significant deterioration was observed in patients receiving chemotherapy,” she said.
The estimated overall change in score was a 2.1-point increase in the talazoparib arm and a 5.7-point decrease in the chemotherapy arm (P = .001). The median time to clinically meaningful deterioration in global health quality of life scores was 26.3 months in the talazoparib arm and 6.7 months in the chemotherapy arm (HR, 0.385).
At the final analysis, the overall safety profile was consistent with that reported previously. Talazoparib was generally well tolerated, and no new safety signals were identified.
Grade 3/4 serious adverse events occurred in 28.3% of patients in the talazoparib arm and 27% of those in the chemotherapy arm. Adverse events led to treatment discontinuation in 7.7% and 9.5% of patients, respectively.
Most grade 3/4 adverse events were hematologic, and most were successfully managed by supportive care, including transfusions and dose modifications, Dr. Litton said.
She noted that one patient in the chemotherapy arm assigned to receive capecitabine had been diagnosed with acute myeloid leukemia at the time of the first analysis. “And now we report an additional case of [acute myeloid leukemia] in a patient who was randomized to the talazoparib arm,” Dr. Litton said.
Jury’s still out
Based on existing data, including from EMBRACA, the jury is still out on whether PARP inhibition is associated with an overall survival benefit in this setting, said invited discussant Susan Domcheck, MD, of the University of Pennsylvania in Philadelphia.
She suggested that could change with ongoing efforts to identify biomarkers for treatment response and new approaches to treatment, such as earlier lines of therapy and combinations.
“At this time, germline BRCA 1 and 2 pathogenic variants are the best predictor of PARP inhibitor sensitivity in breast cancer,” Dr. Domcheck said. “Not all the tumors are sensitive, but this is true of [estrogen receptor–positive] breast cancer and hormonal therapy, and HER2-positive breast cancer as well.”
Studies investigating approaches to improve survival are “incredibly important, because the progression-free survival is not as long as we would like it to be and there’s not an overwhelming overall survival benefit, for sure,” she said.
The EMBRACA trial was funded by Medivation (Pfizer). Dr. Litton and colleagues disclosed numerous relationships with pharmaceutical companies and other organizations. Dr. Domcheck disclosed relationships with AstraZeneca, Clovis, and Bristol Myers Squibb.
SOURCE: Litton J et al., AACR 20, Abstract CT071.
Talazoparib did not confer an overall survival benefit over chemotherapy in patients with germline BRCA1/2-mutated HER2-negative advanced breast cancer, according to a final analysis of the phase 3 EMBRACA trial.
The progression-free survival benefit previously seen with talazoparib did not translate to an overall survival benefit. However, patient-reported quality of life continued to favor talazoparib in the final analysis, Jennifer K. Litton, MD, of the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center in Houston, reported at the AACR virtual meeting I.
The EMBRACA trial enrolled adults with HER2-negative locally advanced or metastatic breast cancer and a deleterious or suspected deleterious germline BRCA mutation. They were randomized to talazoparib at 1 mg daily (n = 287) or to physician’s choice of single-agent chemotherapy (n = 144).
In the primary analysis, talazoparib was associated with significantly improved progression-free survival. The median progression-free survival was 8.6 months in the talazoparib arm and 5.6 months in the chemotherapy arm (hazard ratio, 0.54).
“At the time of the primary analysis, the overall survival data were immature, and the hazard ratio for the interim overall survival was 0.761, which was not statistically significant,” Dr. Litton said.
However, patient-reported outcomes favored talazoparib in the primary analysis, with patients in that arm showing “significant overall improvements with a significant delay in time to clinically meaningful deterioration in multiple cancer-related and breast cancer–specific symptoms, functions, quality of life, and global health,” Dr. Litton said.
Final overall survival
At the final analysis, the median follow-up was 44.9 months for the talazoparib arm and 36.8 months for the chemotherapy arm.
The median overall survival was 19.3 months in the talazoparib arm and 19.5 months in the chemotherapy arm (HR, 0.848; P = .17)
The results were “generally consistent” across patient subgroups,” Dr. Litton said, adding that “the effect of treatment with talazoparib was also similar irrespective of BRCA status, as well as triple-negative or hormone-receptor-positive subtypes.”
Of note, most patients received poststudy therapies. These included PARP inhibitors in 4.5% of patients in the talazoparib arm and 32.6% of patients in the chemotherapy arm, and platinum drugs in 46.3% and 41.7%, respectively.
Patients who received chemotherapy on study but did not receive a subsequent PARP inhibitor or platinum therapy had both shorter total treatment duration and shorter overall survival, compared with patients who did receive subsequent treatment.
In the talazoparib arm, outcomes were similar whether or not patients received a subsequent PARP inhibitor or platinum therapy.
“Interpretation of the overall survival results may have been confounded by subsequent treatment, so two sensitivity analyses accounting for subsequent PARP inhibition or platinum therapy were carried out,” Dr. Litton said.
She noted that adjustment for poststudy treatment lowered the hazard ratio, but there was still no significant difference between the talazoparib and chemotherapy arms. These results suggest “the primary overall survival analysis underestimated the treatment benefit of talazoparib,” Dr. Litton said. She also noted that a longer platinum-free interval prior to study entry was generally associated with a longer duration of survival, particularly in the talazoparib arm.
Quality of life and safety
Patient-reported outcomes continued to favor talazoparib with extended follow-up and were consistent with the initial analysis, Dr. Litton noted.
The updated analysis revealed “a significant improvement in estimated overall change from baseline in the global health quality of life scores for those patients receiving talazoparib, while a significant deterioration was observed in patients receiving chemotherapy,” she said.
The estimated overall change in score was a 2.1-point increase in the talazoparib arm and a 5.7-point decrease in the chemotherapy arm (P = .001). The median time to clinically meaningful deterioration in global health quality of life scores was 26.3 months in the talazoparib arm and 6.7 months in the chemotherapy arm (HR, 0.385).
At the final analysis, the overall safety profile was consistent with that reported previously. Talazoparib was generally well tolerated, and no new safety signals were identified.
Grade 3/4 serious adverse events occurred in 28.3% of patients in the talazoparib arm and 27% of those in the chemotherapy arm. Adverse events led to treatment discontinuation in 7.7% and 9.5% of patients, respectively.
Most grade 3/4 adverse events were hematologic, and most were successfully managed by supportive care, including transfusions and dose modifications, Dr. Litton said.
She noted that one patient in the chemotherapy arm assigned to receive capecitabine had been diagnosed with acute myeloid leukemia at the time of the first analysis. “And now we report an additional case of [acute myeloid leukemia] in a patient who was randomized to the talazoparib arm,” Dr. Litton said.
Jury’s still out
Based on existing data, including from EMBRACA, the jury is still out on whether PARP inhibition is associated with an overall survival benefit in this setting, said invited discussant Susan Domcheck, MD, of the University of Pennsylvania in Philadelphia.
She suggested that could change with ongoing efforts to identify biomarkers for treatment response and new approaches to treatment, such as earlier lines of therapy and combinations.
“At this time, germline BRCA 1 and 2 pathogenic variants are the best predictor of PARP inhibitor sensitivity in breast cancer,” Dr. Domcheck said. “Not all the tumors are sensitive, but this is true of [estrogen receptor–positive] breast cancer and hormonal therapy, and HER2-positive breast cancer as well.”
Studies investigating approaches to improve survival are “incredibly important, because the progression-free survival is not as long as we would like it to be and there’s not an overwhelming overall survival benefit, for sure,” she said.
The EMBRACA trial was funded by Medivation (Pfizer). Dr. Litton and colleagues disclosed numerous relationships with pharmaceutical companies and other organizations. Dr. Domcheck disclosed relationships with AstraZeneca, Clovis, and Bristol Myers Squibb.
SOURCE: Litton J et al., AACR 20, Abstract CT071.
Talazoparib did not confer an overall survival benefit over chemotherapy in patients with germline BRCA1/2-mutated HER2-negative advanced breast cancer, according to a final analysis of the phase 3 EMBRACA trial.
The progression-free survival benefit previously seen with talazoparib did not translate to an overall survival benefit. However, patient-reported quality of life continued to favor talazoparib in the final analysis, Jennifer K. Litton, MD, of the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center in Houston, reported at the AACR virtual meeting I.
The EMBRACA trial enrolled adults with HER2-negative locally advanced or metastatic breast cancer and a deleterious or suspected deleterious germline BRCA mutation. They were randomized to talazoparib at 1 mg daily (n = 287) or to physician’s choice of single-agent chemotherapy (n = 144).
In the primary analysis, talazoparib was associated with significantly improved progression-free survival. The median progression-free survival was 8.6 months in the talazoparib arm and 5.6 months in the chemotherapy arm (hazard ratio, 0.54).
“At the time of the primary analysis, the overall survival data were immature, and the hazard ratio for the interim overall survival was 0.761, which was not statistically significant,” Dr. Litton said.
However, patient-reported outcomes favored talazoparib in the primary analysis, with patients in that arm showing “significant overall improvements with a significant delay in time to clinically meaningful deterioration in multiple cancer-related and breast cancer–specific symptoms, functions, quality of life, and global health,” Dr. Litton said.
Final overall survival
At the final analysis, the median follow-up was 44.9 months for the talazoparib arm and 36.8 months for the chemotherapy arm.
The median overall survival was 19.3 months in the talazoparib arm and 19.5 months in the chemotherapy arm (HR, 0.848; P = .17)
The results were “generally consistent” across patient subgroups,” Dr. Litton said, adding that “the effect of treatment with talazoparib was also similar irrespective of BRCA status, as well as triple-negative or hormone-receptor-positive subtypes.”
Of note, most patients received poststudy therapies. These included PARP inhibitors in 4.5% of patients in the talazoparib arm and 32.6% of patients in the chemotherapy arm, and platinum drugs in 46.3% and 41.7%, respectively.
Patients who received chemotherapy on study but did not receive a subsequent PARP inhibitor or platinum therapy had both shorter total treatment duration and shorter overall survival, compared with patients who did receive subsequent treatment.
In the talazoparib arm, outcomes were similar whether or not patients received a subsequent PARP inhibitor or platinum therapy.
“Interpretation of the overall survival results may have been confounded by subsequent treatment, so two sensitivity analyses accounting for subsequent PARP inhibition or platinum therapy were carried out,” Dr. Litton said.
She noted that adjustment for poststudy treatment lowered the hazard ratio, but there was still no significant difference between the talazoparib and chemotherapy arms. These results suggest “the primary overall survival analysis underestimated the treatment benefit of talazoparib,” Dr. Litton said. She also noted that a longer platinum-free interval prior to study entry was generally associated with a longer duration of survival, particularly in the talazoparib arm.
Quality of life and safety
Patient-reported outcomes continued to favor talazoparib with extended follow-up and were consistent with the initial analysis, Dr. Litton noted.
The updated analysis revealed “a significant improvement in estimated overall change from baseline in the global health quality of life scores for those patients receiving talazoparib, while a significant deterioration was observed in patients receiving chemotherapy,” she said.
The estimated overall change in score was a 2.1-point increase in the talazoparib arm and a 5.7-point decrease in the chemotherapy arm (P = .001). The median time to clinically meaningful deterioration in global health quality of life scores was 26.3 months in the talazoparib arm and 6.7 months in the chemotherapy arm (HR, 0.385).
At the final analysis, the overall safety profile was consistent with that reported previously. Talazoparib was generally well tolerated, and no new safety signals were identified.
Grade 3/4 serious adverse events occurred in 28.3% of patients in the talazoparib arm and 27% of those in the chemotherapy arm. Adverse events led to treatment discontinuation in 7.7% and 9.5% of patients, respectively.
Most grade 3/4 adverse events were hematologic, and most were successfully managed by supportive care, including transfusions and dose modifications, Dr. Litton said.
She noted that one patient in the chemotherapy arm assigned to receive capecitabine had been diagnosed with acute myeloid leukemia at the time of the first analysis. “And now we report an additional case of [acute myeloid leukemia] in a patient who was randomized to the talazoparib arm,” Dr. Litton said.
Jury’s still out
Based on existing data, including from EMBRACA, the jury is still out on whether PARP inhibition is associated with an overall survival benefit in this setting, said invited discussant Susan Domcheck, MD, of the University of Pennsylvania in Philadelphia.
She suggested that could change with ongoing efforts to identify biomarkers for treatment response and new approaches to treatment, such as earlier lines of therapy and combinations.
“At this time, germline BRCA 1 and 2 pathogenic variants are the best predictor of PARP inhibitor sensitivity in breast cancer,” Dr. Domcheck said. “Not all the tumors are sensitive, but this is true of [estrogen receptor–positive] breast cancer and hormonal therapy, and HER2-positive breast cancer as well.”
Studies investigating approaches to improve survival are “incredibly important, because the progression-free survival is not as long as we would like it to be and there’s not an overwhelming overall survival benefit, for sure,” she said.
The EMBRACA trial was funded by Medivation (Pfizer). Dr. Litton and colleagues disclosed numerous relationships with pharmaceutical companies and other organizations. Dr. Domcheck disclosed relationships with AstraZeneca, Clovis, and Bristol Myers Squibb.
SOURCE: Litton J et al., AACR 20, Abstract CT071.
FROM AACR 2020
Metastatic cancer linked to worse outcomes of COVID-19
Cancer type, stage, and recent treatment may affect outcomes of COVID-19 in cancer patients, according to a study of patients from China.
The data showed that patients with hematologic malignancies and those with metastatic cancers had higher risks of developing severe or critical COVID-19 symptoms, being admitted to the ICU, requiring ventilation, and dying.
On the other hand, patients with nonmetastatic cancer had outcomes comparable to those of noncancer patients with COVID-19.
Similarly, cancer patients who had recently undergone surgery or received immunotherapy were more likely to have poor outcomes, whereas cancer patients treated with radiotherapy had outcomes similar to those of noncancer COVID-19 patients.
Hongbing Cai, MD, of Zhongnan Hospital of Wuhan University in China, presented these results at the AACR virtual meeting I. The results also were published in Cancer Discovery.
Cancer vs. noncancer patients
The study included 105 cancer patients with COVID-19 who were treated from Jan. 1 to Feb. 24, 2020, at 14 hospitals in Wuhan, China. Patients had lung (20.95%), gastrointestinal (12.38%), breast (10.48%), and thyroid cancers (10.48%) as well as hematologic malignancies (8.57%). Dr. Cai and colleagues matched the COVID-19 cancer patients to 536 COVID-19 patients without cancer. Patients were matched by hospital, duration of hospitalization, and age.
“COVID-19 patients with cancer had higher risks of all severe outcomes,” Dr. Cai noted.
Compared with noncancer patients, the cancer patients had a higher risk of:
- Severe or critical COVID-19 symptoms – odds ratio, 2.79 (P < .01).
- Being admitted to the ICU – OR, 2.84 (P < .01).
- Requiring invasive mechanical ventilation – OR, 14 (P < .01).
- Death – OR, 2.34 (P = .03).
Cancer type and stage
Dr. Cai noted that outcomes were the worst among patients with hematologic malignancies and those with metastatic cancer (stage IV).
Compared with patients without cancer, those with hematologic malignancies had a higher risk of:
- Severe/critical symptoms – OR, 10.61 (P < .01).
- ICU admission – OR, 9.66 (P < .01).
- Invasive mechanical ventilation – OR, 38 (P < .01).
- Death – OR, 9.07 (P = .01).
Compared with patients without cancer, those with metastatic cancer had a higher risk of:
- Severe/critical symptoms – OR, 5.97 (P < .01).
- ICU admission – OR, 6.59 (P < 0.01).
- Invasive mechanical ventilation – OR, 55.42 (P < .01).
- Death – OR, 5.58 (P = .01).
On the other hand, outcomes in patients with nonmetastatic cancer were not significantly different from outcomes in patients without cancer (P > .05 for all outcomes).
Cancer treatment
The treatments cancer patients received within 40 days before the onset of COVID-19 symptoms were radiotherapy (12.26%), chemotherapy (14.15%), surgery (7.62%), targeted therapies (3.81%), and immunotherapy (5.71%).
Compared with patients without cancer, those who received immunotherapy had a higher risk of:
- Severe/critical symptoms – OR, 10.61 (P < .01).
- Death – OR, 9.07 (P = .04).
Patients who underwent surgery had a higher risk of:
- Severe/critical symptoms – OR, 8.84 (P < .01).
- ICU admission – OR, 7.24 (P = .02).
- Invasive mechanical ventilation – OR, 44.33 (P < .01).
Conversely, outcomes in cancer patients who received radiotherapy were not significantly different from outcomes in patients without cancer (P > .10 for all).
These results suggest that “postponing surgery should be considered in outbreak areas,” Dr. Cai said, adding that scheduled radiotherapy can go ahead but with “intensive protection and surveillance.”
Dr. Cai said it remains to be seen whether patients with early-stage cancer need to postpone their treatments during the COVID-19 pandemic or whether immunotherapy aggravates severe outcomes in cancer patients with COVID-19. For now, she said, cancer patients should have individualized treatment plans based on their tumor type and stage.
Dr. Cai disclosed no conflicts of interest. This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, the Singapore Ministry of Health’s National Medical Research Council, the National Institutes of Health/National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute, and the Xiu Research Fund.
SOURCE: Cai H. AACR 2020. Patients with cancer appear more vulnerable to SARS-COV-2: A multicenter study during the COVID-19 outbreak; Dai M et al. Cancer Discov. 2020 Apr 28. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-20-0422.
Cancer type, stage, and recent treatment may affect outcomes of COVID-19 in cancer patients, according to a study of patients from China.
The data showed that patients with hematologic malignancies and those with metastatic cancers had higher risks of developing severe or critical COVID-19 symptoms, being admitted to the ICU, requiring ventilation, and dying.
On the other hand, patients with nonmetastatic cancer had outcomes comparable to those of noncancer patients with COVID-19.
Similarly, cancer patients who had recently undergone surgery or received immunotherapy were more likely to have poor outcomes, whereas cancer patients treated with radiotherapy had outcomes similar to those of noncancer COVID-19 patients.
Hongbing Cai, MD, of Zhongnan Hospital of Wuhan University in China, presented these results at the AACR virtual meeting I. The results also were published in Cancer Discovery.
Cancer vs. noncancer patients
The study included 105 cancer patients with COVID-19 who were treated from Jan. 1 to Feb. 24, 2020, at 14 hospitals in Wuhan, China. Patients had lung (20.95%), gastrointestinal (12.38%), breast (10.48%), and thyroid cancers (10.48%) as well as hematologic malignancies (8.57%). Dr. Cai and colleagues matched the COVID-19 cancer patients to 536 COVID-19 patients without cancer. Patients were matched by hospital, duration of hospitalization, and age.
“COVID-19 patients with cancer had higher risks of all severe outcomes,” Dr. Cai noted.
Compared with noncancer patients, the cancer patients had a higher risk of:
- Severe or critical COVID-19 symptoms – odds ratio, 2.79 (P < .01).
- Being admitted to the ICU – OR, 2.84 (P < .01).
- Requiring invasive mechanical ventilation – OR, 14 (P < .01).
- Death – OR, 2.34 (P = .03).
Cancer type and stage
Dr. Cai noted that outcomes were the worst among patients with hematologic malignancies and those with metastatic cancer (stage IV).
Compared with patients without cancer, those with hematologic malignancies had a higher risk of:
- Severe/critical symptoms – OR, 10.61 (P < .01).
- ICU admission – OR, 9.66 (P < .01).
- Invasive mechanical ventilation – OR, 38 (P < .01).
- Death – OR, 9.07 (P = .01).
Compared with patients without cancer, those with metastatic cancer had a higher risk of:
- Severe/critical symptoms – OR, 5.97 (P < .01).
- ICU admission – OR, 6.59 (P < 0.01).
- Invasive mechanical ventilation – OR, 55.42 (P < .01).
- Death – OR, 5.58 (P = .01).
On the other hand, outcomes in patients with nonmetastatic cancer were not significantly different from outcomes in patients without cancer (P > .05 for all outcomes).
Cancer treatment
The treatments cancer patients received within 40 days before the onset of COVID-19 symptoms were radiotherapy (12.26%), chemotherapy (14.15%), surgery (7.62%), targeted therapies (3.81%), and immunotherapy (5.71%).
Compared with patients without cancer, those who received immunotherapy had a higher risk of:
- Severe/critical symptoms – OR, 10.61 (P < .01).
- Death – OR, 9.07 (P = .04).
Patients who underwent surgery had a higher risk of:
- Severe/critical symptoms – OR, 8.84 (P < .01).
- ICU admission – OR, 7.24 (P = .02).
- Invasive mechanical ventilation – OR, 44.33 (P < .01).
Conversely, outcomes in cancer patients who received radiotherapy were not significantly different from outcomes in patients without cancer (P > .10 for all).
These results suggest that “postponing surgery should be considered in outbreak areas,” Dr. Cai said, adding that scheduled radiotherapy can go ahead but with “intensive protection and surveillance.”
Dr. Cai said it remains to be seen whether patients with early-stage cancer need to postpone their treatments during the COVID-19 pandemic or whether immunotherapy aggravates severe outcomes in cancer patients with COVID-19. For now, she said, cancer patients should have individualized treatment plans based on their tumor type and stage.
Dr. Cai disclosed no conflicts of interest. This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, the Singapore Ministry of Health’s National Medical Research Council, the National Institutes of Health/National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute, and the Xiu Research Fund.
SOURCE: Cai H. AACR 2020. Patients with cancer appear more vulnerable to SARS-COV-2: A multicenter study during the COVID-19 outbreak; Dai M et al. Cancer Discov. 2020 Apr 28. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-20-0422.
Cancer type, stage, and recent treatment may affect outcomes of COVID-19 in cancer patients, according to a study of patients from China.
The data showed that patients with hematologic malignancies and those with metastatic cancers had higher risks of developing severe or critical COVID-19 symptoms, being admitted to the ICU, requiring ventilation, and dying.
On the other hand, patients with nonmetastatic cancer had outcomes comparable to those of noncancer patients with COVID-19.
Similarly, cancer patients who had recently undergone surgery or received immunotherapy were more likely to have poor outcomes, whereas cancer patients treated with radiotherapy had outcomes similar to those of noncancer COVID-19 patients.
Hongbing Cai, MD, of Zhongnan Hospital of Wuhan University in China, presented these results at the AACR virtual meeting I. The results also were published in Cancer Discovery.
Cancer vs. noncancer patients
The study included 105 cancer patients with COVID-19 who were treated from Jan. 1 to Feb. 24, 2020, at 14 hospitals in Wuhan, China. Patients had lung (20.95%), gastrointestinal (12.38%), breast (10.48%), and thyroid cancers (10.48%) as well as hematologic malignancies (8.57%). Dr. Cai and colleagues matched the COVID-19 cancer patients to 536 COVID-19 patients without cancer. Patients were matched by hospital, duration of hospitalization, and age.
“COVID-19 patients with cancer had higher risks of all severe outcomes,” Dr. Cai noted.
Compared with noncancer patients, the cancer patients had a higher risk of:
- Severe or critical COVID-19 symptoms – odds ratio, 2.79 (P < .01).
- Being admitted to the ICU – OR, 2.84 (P < .01).
- Requiring invasive mechanical ventilation – OR, 14 (P < .01).
- Death – OR, 2.34 (P = .03).
Cancer type and stage
Dr. Cai noted that outcomes were the worst among patients with hematologic malignancies and those with metastatic cancer (stage IV).
Compared with patients without cancer, those with hematologic malignancies had a higher risk of:
- Severe/critical symptoms – OR, 10.61 (P < .01).
- ICU admission – OR, 9.66 (P < .01).
- Invasive mechanical ventilation – OR, 38 (P < .01).
- Death – OR, 9.07 (P = .01).
Compared with patients without cancer, those with metastatic cancer had a higher risk of:
- Severe/critical symptoms – OR, 5.97 (P < .01).
- ICU admission – OR, 6.59 (P < 0.01).
- Invasive mechanical ventilation – OR, 55.42 (P < .01).
- Death – OR, 5.58 (P = .01).
On the other hand, outcomes in patients with nonmetastatic cancer were not significantly different from outcomes in patients without cancer (P > .05 for all outcomes).
Cancer treatment
The treatments cancer patients received within 40 days before the onset of COVID-19 symptoms were radiotherapy (12.26%), chemotherapy (14.15%), surgery (7.62%), targeted therapies (3.81%), and immunotherapy (5.71%).
Compared with patients without cancer, those who received immunotherapy had a higher risk of:
- Severe/critical symptoms – OR, 10.61 (P < .01).
- Death – OR, 9.07 (P = .04).
Patients who underwent surgery had a higher risk of:
- Severe/critical symptoms – OR, 8.84 (P < .01).
- ICU admission – OR, 7.24 (P = .02).
- Invasive mechanical ventilation – OR, 44.33 (P < .01).
Conversely, outcomes in cancer patients who received radiotherapy were not significantly different from outcomes in patients without cancer (P > .10 for all).
These results suggest that “postponing surgery should be considered in outbreak areas,” Dr. Cai said, adding that scheduled radiotherapy can go ahead but with “intensive protection and surveillance.”
Dr. Cai said it remains to be seen whether patients with early-stage cancer need to postpone their treatments during the COVID-19 pandemic or whether immunotherapy aggravates severe outcomes in cancer patients with COVID-19. For now, she said, cancer patients should have individualized treatment plans based on their tumor type and stage.
Dr. Cai disclosed no conflicts of interest. This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, the Singapore Ministry of Health’s National Medical Research Council, the National Institutes of Health/National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute, and the Xiu Research Fund.
SOURCE: Cai H. AACR 2020. Patients with cancer appear more vulnerable to SARS-COV-2: A multicenter study during the COVID-19 outbreak; Dai M et al. Cancer Discov. 2020 Apr 28. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-20-0422.
FROM AACR 2020
Novel combo boosts response in HER2-negative breast cancer
A novel combination has boosted responses in women with high-risk, HER2-negative breast cancer.
The new combo comprises the immune checkpoint inhibitor durvalumab (Imfinzi, AstraZeneca) and the poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) inhibitor olaparib (Lynparza, AstraZeneca).
When this combo was added to standard neoadjuvant chemotherapy, it yielded a significantly higher pathologic complete response (pCR) rate at the time of surgery than was seen with chemotherapy alone.
The superior pCR rate was seen across all HER2-negative breast cancer subtypes, including HER2-negative, estrogen receptor–positive tumors (Mammaprint high risk), and in women with triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC), reported lead investigator Lajos Pusztai, MD, DPhil, from Yale Cancer Center in New Haven, Connecticut.
“These results provide further evidence for the clinical value of immunotherapy in early-stage breast cancer and suggest new avenues for how to exploit these drugs in hormone receptor [HR]–positive breast cancers,” said Pusztai.
He presented the results at the American Association for Cancer Research (AACR) virtual annual meeting, which took place online, owing to the COVID-19 pandemic.
Toxicities, including financial
“The benefits from immunotherapy are clearly emerging in early and metastatic triple-negative breast cancer, likely with PD-L1 expression. However, there’s much more uncertainty in patients with hormone-sensitive tumors whether there is benefit and who will benefit from immunotherapy,” commented Pamela N. Munster, MD, from the University of California, San Francisco, who was the invited discussant.
“The signal of a better pCR rate among patients in the ultra-high Mammaprint group may allow selection of patients with HR-positive disease who may benefit from immunotherapeutic agents and/or PARP inhibitors,” she said.
Munster noted that the approximately 10% higher rate of immune-related adverse events of grade 3 or greater that was seen with the combination appears similar to that seen in other studies, but anemia and fatigue appeared to be less frequent with durvalumab/olaparaib and paclitaxel in comparison with paclitaxel alone.
“In the absence of a clear delineation of the contribution of olaparib, some weight should be given to the financial burden of adding both durvalumab and olaparib to a preoperative regimen,” she said.
The additional cost of durvalumab is approximately $34,000, and adding olaparib boosts that by about $22,000 more, Munster said.
Ongoing platform trial
The new results come from one arm of the ongoing Investigation of Serial Studies to Predict Your Therapeutic Response Through Imaging and Molecular Analysis 2 (I-SPY-2) trial. This is an ongoing platform trial that is exploring the use of new drugs in combination with a standard neoadjuvant therapy backbone for the treatment of high-risk cancers.
In this trial, women with stage II or III breast cancer with tumors 2.5 cm or larger are assessed for one of eight biomarker subtypes according to HER2 status, HR status, and genetic risk factors, as determined on the basis of a 70-gene assay. The patients within each biomarker subtype are randomly assigned to receive standard therapy either with or without an investigational agent.
For each subtrial, a primary endpoint is an improvement in pCR in comparison with the standard of care.
Changes in tumor volume on MRI are used to predict whether patients will achieve a pCR. Those who are considered to have a high Bayesian predictive probability of success are eligible for moving on to phase 3 trials.
The I-SPY-2 trial was described in detail by principal investigator Laura J. Esserman, MD, MBA, from the Helen Diller Comprehensive Cancer Center at the University of California, San Francisco, in a 2017 interview from the annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology.
As previously reported, the first drugs to “graduate” from the trial were the HER2/HER4 inhibitor neratinib (Nerlynx, Puma Biotechnology) and the investigational PARP inhibitor veliparib (AbbVie).
Study details
The I-SPY-2 results that Pusztai reported at the AACR meeting were based on an analysis of 73 HER2-negative patients, including 21 patients with TNBC and 52 with HR-positive tumors with Mammaprint high-risk features. These patients underwent treatment with durvalumab 1500 mg every 4 weeks for three cycles, olaparib 100 mg twice daily for weeks 1 through 11, and paclitaxel 80 mg/m2 weekly for 12 weeks, followed by AC chemotherapy (doxorubicin and cyclophosphamide) for four cycles.
The 299 patients in the control arm received paclitaxel and chemotherapy only.
In all three biomarker subsets studied, durvalumab and olaparib increased pCR rates compared with controls, as shown in the table.
The probability that the combination was superior to control in each subgroup approached 100%, Pusztai noted.
Adverse events with the combination were consistent with known side effects of the drugs, he commented. Immune-related grade 3 adverse events occurred in 19% of patients in the combination therapy arm, compared with 1.6% in the control arm.
Higher pCR rates were seen in the subset of immune-rich tumors among all cancer subtypes and in both study arms.
“Exploratory analysis suggests several potential predictive markers of durvalumab/olaparib benefit over chemotherapy alone,” Pusztai reported.
These markers included Mammaprint MP2 (ultra high) versus MP1 in HR+/HER2– tumors, and low CD3/CD8 gene signature ratio, high macrophage/Tc-class 2 gene signature ratio, and high proliferation signature, all of which were associated with higher pCR rates in the experimental arm among patients with TNBC.
The trial was supported by the William K. Bowes Jr Foundation, Foundation for the NIH, Give Breast Cancer the Boot, UCSF, the Biomarkers Consortium, IQVIA, the Breast Cancer Research Foundation, Safeway, California Breast Cancer Research Program, Breast Cancer Research–Atwater Trust, and Stand Up to Cancer. Pusztai has received honoraria and consulting fees from AstraZeneca and other companies. Munster has received research and travel support from and has served on the scientific advisory boards of AstraZeneca and other companies.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A novel combination has boosted responses in women with high-risk, HER2-negative breast cancer.
The new combo comprises the immune checkpoint inhibitor durvalumab (Imfinzi, AstraZeneca) and the poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) inhibitor olaparib (Lynparza, AstraZeneca).
When this combo was added to standard neoadjuvant chemotherapy, it yielded a significantly higher pathologic complete response (pCR) rate at the time of surgery than was seen with chemotherapy alone.
The superior pCR rate was seen across all HER2-negative breast cancer subtypes, including HER2-negative, estrogen receptor–positive tumors (Mammaprint high risk), and in women with triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC), reported lead investigator Lajos Pusztai, MD, DPhil, from Yale Cancer Center in New Haven, Connecticut.
“These results provide further evidence for the clinical value of immunotherapy in early-stage breast cancer and suggest new avenues for how to exploit these drugs in hormone receptor [HR]–positive breast cancers,” said Pusztai.
He presented the results at the American Association for Cancer Research (AACR) virtual annual meeting, which took place online, owing to the COVID-19 pandemic.
Toxicities, including financial
“The benefits from immunotherapy are clearly emerging in early and metastatic triple-negative breast cancer, likely with PD-L1 expression. However, there’s much more uncertainty in patients with hormone-sensitive tumors whether there is benefit and who will benefit from immunotherapy,” commented Pamela N. Munster, MD, from the University of California, San Francisco, who was the invited discussant.
“The signal of a better pCR rate among patients in the ultra-high Mammaprint group may allow selection of patients with HR-positive disease who may benefit from immunotherapeutic agents and/or PARP inhibitors,” she said.
Munster noted that the approximately 10% higher rate of immune-related adverse events of grade 3 or greater that was seen with the combination appears similar to that seen in other studies, but anemia and fatigue appeared to be less frequent with durvalumab/olaparaib and paclitaxel in comparison with paclitaxel alone.
“In the absence of a clear delineation of the contribution of olaparib, some weight should be given to the financial burden of adding both durvalumab and olaparib to a preoperative regimen,” she said.
The additional cost of durvalumab is approximately $34,000, and adding olaparib boosts that by about $22,000 more, Munster said.
Ongoing platform trial
The new results come from one arm of the ongoing Investigation of Serial Studies to Predict Your Therapeutic Response Through Imaging and Molecular Analysis 2 (I-SPY-2) trial. This is an ongoing platform trial that is exploring the use of new drugs in combination with a standard neoadjuvant therapy backbone for the treatment of high-risk cancers.
In this trial, women with stage II or III breast cancer with tumors 2.5 cm or larger are assessed for one of eight biomarker subtypes according to HER2 status, HR status, and genetic risk factors, as determined on the basis of a 70-gene assay. The patients within each biomarker subtype are randomly assigned to receive standard therapy either with or without an investigational agent.
For each subtrial, a primary endpoint is an improvement in pCR in comparison with the standard of care.
Changes in tumor volume on MRI are used to predict whether patients will achieve a pCR. Those who are considered to have a high Bayesian predictive probability of success are eligible for moving on to phase 3 trials.
The I-SPY-2 trial was described in detail by principal investigator Laura J. Esserman, MD, MBA, from the Helen Diller Comprehensive Cancer Center at the University of California, San Francisco, in a 2017 interview from the annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology.
As previously reported, the first drugs to “graduate” from the trial were the HER2/HER4 inhibitor neratinib (Nerlynx, Puma Biotechnology) and the investigational PARP inhibitor veliparib (AbbVie).
Study details
The I-SPY-2 results that Pusztai reported at the AACR meeting were based on an analysis of 73 HER2-negative patients, including 21 patients with TNBC and 52 with HR-positive tumors with Mammaprint high-risk features. These patients underwent treatment with durvalumab 1500 mg every 4 weeks for three cycles, olaparib 100 mg twice daily for weeks 1 through 11, and paclitaxel 80 mg/m2 weekly for 12 weeks, followed by AC chemotherapy (doxorubicin and cyclophosphamide) for four cycles.
The 299 patients in the control arm received paclitaxel and chemotherapy only.
In all three biomarker subsets studied, durvalumab and olaparib increased pCR rates compared with controls, as shown in the table.
The probability that the combination was superior to control in each subgroup approached 100%, Pusztai noted.
Adverse events with the combination were consistent with known side effects of the drugs, he commented. Immune-related grade 3 adverse events occurred in 19% of patients in the combination therapy arm, compared with 1.6% in the control arm.
Higher pCR rates were seen in the subset of immune-rich tumors among all cancer subtypes and in both study arms.
“Exploratory analysis suggests several potential predictive markers of durvalumab/olaparib benefit over chemotherapy alone,” Pusztai reported.
These markers included Mammaprint MP2 (ultra high) versus MP1 in HR+/HER2– tumors, and low CD3/CD8 gene signature ratio, high macrophage/Tc-class 2 gene signature ratio, and high proliferation signature, all of which were associated with higher pCR rates in the experimental arm among patients with TNBC.
The trial was supported by the William K. Bowes Jr Foundation, Foundation for the NIH, Give Breast Cancer the Boot, UCSF, the Biomarkers Consortium, IQVIA, the Breast Cancer Research Foundation, Safeway, California Breast Cancer Research Program, Breast Cancer Research–Atwater Trust, and Stand Up to Cancer. Pusztai has received honoraria and consulting fees from AstraZeneca and other companies. Munster has received research and travel support from and has served on the scientific advisory boards of AstraZeneca and other companies.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A novel combination has boosted responses in women with high-risk, HER2-negative breast cancer.
The new combo comprises the immune checkpoint inhibitor durvalumab (Imfinzi, AstraZeneca) and the poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) inhibitor olaparib (Lynparza, AstraZeneca).
When this combo was added to standard neoadjuvant chemotherapy, it yielded a significantly higher pathologic complete response (pCR) rate at the time of surgery than was seen with chemotherapy alone.
The superior pCR rate was seen across all HER2-negative breast cancer subtypes, including HER2-negative, estrogen receptor–positive tumors (Mammaprint high risk), and in women with triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC), reported lead investigator Lajos Pusztai, MD, DPhil, from Yale Cancer Center in New Haven, Connecticut.
“These results provide further evidence for the clinical value of immunotherapy in early-stage breast cancer and suggest new avenues for how to exploit these drugs in hormone receptor [HR]–positive breast cancers,” said Pusztai.
He presented the results at the American Association for Cancer Research (AACR) virtual annual meeting, which took place online, owing to the COVID-19 pandemic.
Toxicities, including financial
“The benefits from immunotherapy are clearly emerging in early and metastatic triple-negative breast cancer, likely with PD-L1 expression. However, there’s much more uncertainty in patients with hormone-sensitive tumors whether there is benefit and who will benefit from immunotherapy,” commented Pamela N. Munster, MD, from the University of California, San Francisco, who was the invited discussant.
“The signal of a better pCR rate among patients in the ultra-high Mammaprint group may allow selection of patients with HR-positive disease who may benefit from immunotherapeutic agents and/or PARP inhibitors,” she said.
Munster noted that the approximately 10% higher rate of immune-related adverse events of grade 3 or greater that was seen with the combination appears similar to that seen in other studies, but anemia and fatigue appeared to be less frequent with durvalumab/olaparaib and paclitaxel in comparison with paclitaxel alone.
“In the absence of a clear delineation of the contribution of olaparib, some weight should be given to the financial burden of adding both durvalumab and olaparib to a preoperative regimen,” she said.
The additional cost of durvalumab is approximately $34,000, and adding olaparib boosts that by about $22,000 more, Munster said.
Ongoing platform trial
The new results come from one arm of the ongoing Investigation of Serial Studies to Predict Your Therapeutic Response Through Imaging and Molecular Analysis 2 (I-SPY-2) trial. This is an ongoing platform trial that is exploring the use of new drugs in combination with a standard neoadjuvant therapy backbone for the treatment of high-risk cancers.
In this trial, women with stage II or III breast cancer with tumors 2.5 cm or larger are assessed for one of eight biomarker subtypes according to HER2 status, HR status, and genetic risk factors, as determined on the basis of a 70-gene assay. The patients within each biomarker subtype are randomly assigned to receive standard therapy either with or without an investigational agent.
For each subtrial, a primary endpoint is an improvement in pCR in comparison with the standard of care.
Changes in tumor volume on MRI are used to predict whether patients will achieve a pCR. Those who are considered to have a high Bayesian predictive probability of success are eligible for moving on to phase 3 trials.
The I-SPY-2 trial was described in detail by principal investigator Laura J. Esserman, MD, MBA, from the Helen Diller Comprehensive Cancer Center at the University of California, San Francisco, in a 2017 interview from the annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology.
As previously reported, the first drugs to “graduate” from the trial were the HER2/HER4 inhibitor neratinib (Nerlynx, Puma Biotechnology) and the investigational PARP inhibitor veliparib (AbbVie).
Study details
The I-SPY-2 results that Pusztai reported at the AACR meeting were based on an analysis of 73 HER2-negative patients, including 21 patients with TNBC and 52 with HR-positive tumors with Mammaprint high-risk features. These patients underwent treatment with durvalumab 1500 mg every 4 weeks for three cycles, olaparib 100 mg twice daily for weeks 1 through 11, and paclitaxel 80 mg/m2 weekly for 12 weeks, followed by AC chemotherapy (doxorubicin and cyclophosphamide) for four cycles.
The 299 patients in the control arm received paclitaxel and chemotherapy only.
In all three biomarker subsets studied, durvalumab and olaparib increased pCR rates compared with controls, as shown in the table.
The probability that the combination was superior to control in each subgroup approached 100%, Pusztai noted.
Adverse events with the combination were consistent with known side effects of the drugs, he commented. Immune-related grade 3 adverse events occurred in 19% of patients in the combination therapy arm, compared with 1.6% in the control arm.
Higher pCR rates were seen in the subset of immune-rich tumors among all cancer subtypes and in both study arms.
“Exploratory analysis suggests several potential predictive markers of durvalumab/olaparib benefit over chemotherapy alone,” Pusztai reported.
These markers included Mammaprint MP2 (ultra high) versus MP1 in HR+/HER2– tumors, and low CD3/CD8 gene signature ratio, high macrophage/Tc-class 2 gene signature ratio, and high proliferation signature, all of which were associated with higher pCR rates in the experimental arm among patients with TNBC.
The trial was supported by the William K. Bowes Jr Foundation, Foundation for the NIH, Give Breast Cancer the Boot, UCSF, the Biomarkers Consortium, IQVIA, the Breast Cancer Research Foundation, Safeway, California Breast Cancer Research Program, Breast Cancer Research–Atwater Trust, and Stand Up to Cancer. Pusztai has received honoraria and consulting fees from AstraZeneca and other companies. Munster has received research and travel support from and has served on the scientific advisory boards of AstraZeneca and other companies.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM AACR 2020
