User login
New data further define role of PD-L1 status, immunotherapy in metastatic breast cancer
BARCELONA – Programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1) status in patients with advanced triple negative or HER2-positive breast cancer appears to identify distinct disease entities with varying likelihood of benefit from immune checkpoint inhibition, according to Giampaolo Bianchini, MD.
This observation, which contrasts with findings in other solid tumors and expands the road map to improved outcomes with immunotherapy for metastatic breast cancer, is based in part on new findings presented at the European Society for Medical Oncology Congress.
Among additional lessons from those findings: PD-L1 assays are not easily interchangeable, and studies with a “one size fits all” approach should be avoided, Dr. Bianchini, head of the Breast Cancer Group – Medical Oncology and clinical translational and immunotherapy research at Ospedale San Raffaele, Milan, said at the congress.
IMPassion130 and PD-L1 assays
In the phase 3 IMpassion130 trial assessing nanoparticle, albumin-bound (nab)-paclitaxel chemotherapy + either the anti-PD-L1 monoclonal antibody atezolizumab or placebo for the first-line treatment of metastatic triple-negative breast cancer (mTNBC), investigators used, and validated, the VENTANA PD-L1 SP142 assay to evaluate PD-L1 expression in immune cells (IC). PD-L1 positivity was defined using a 1% cutoff, meaning that PD-L1-stained IC encompassed at least 1% of the tumor area.
The trial demonstrated significantly improved progression-free survival (PFS) in the atezolizumab arm, both in the intention-to-treat (ITT) analysis (7.2 vs. 5.5 months in the placebo arm; hazard ratio, 0.80), and the PD-L1-positive subgroup (7.5 vs. 5.0 months; HR, 0.62), and the results were published in November 2018 (N Engl J Med. 2018; 379:2108-21).
“IMpassion130 is the first phase 3 trial demonstrating clinical benefit of cancer immunotherapy in patients with PD-L1-positive, metastatic triple-negative breast cancer,” Hope S. Rugo, MD, said at the congress. “The combination of atezolizumab and nab-paclitaxel is now approved in the United States and Europe for this indication.”
In addition, the SP142 antibody (which binds to PD-L1), at the 1% cutoff, predicted PFS and overall survival (OS) with atezolizumab + nab-paclitaxel, compared with nab-paclitaxel + placebo; the absolute improvement in OS in the PD-L1-positive population was 7 months (HR, 0.71), whereas no impact was seen in PFS or OS in patients who were PD-L1-negative using the SP142 assay, said Dr. Rugo, professor of hematology/oncology, and director of breast oncology and clinical trials education at the University of California, San Francisco.
Based on the IMPassion130 findings, the Food and Drug Administration approved the SP142 assay, using the 1% cutoff, as a “companion diagnostic device for selecting TNBC patients for atezolizumab.”
However, questions remain about how to best identify patients who could benefit from the atezolizumab + nab-paclitaxel combination, Dr. Rugo said.
Therefore, she and her colleagues performed a retrospective post hoc subgroup analysis of data from the trial to assess the performance and analytical concordance of the SP142 assay and two other commonly used PD-L1 immunohistochemistry (IHC) assays: the VENTANA SP263 IHC assay typically used as a companion diagnostic with durvalumab, and the Dako PD-L1 IHC 22C3 assay typically used with pembrolizumab.
In addition, the investigators assessed PD-L1 prevalence and clinical activity.
“We also included an evaluation of important factors related to PD-L1 testing and ... relationship to clinical outcome,” Dr. Rugo said.
In 614 biomarker-evaluable patients, representing 68% of the IMPassion130 ITT population, PD-L1-positive prevalence was 46% with the SP142 assay, 75% with the SP263 assay (also based on a 1% IC cutoff), and 81% with the 22C3 assay (with positivity defined as a combined positive score [CPS] of 1 or more based on an algorithm including both tumor and IC counts).
“Almost all SP142-positive cases are captured by either 22C3 or SP263. However, about a third of patients’ tumors were positive for PD-L1 using only one of the other two assays,” she noted, explaining that “this leads to suboptimal analytical concordance.”
The overall percentage agreement between SP142 and the other assays was only 64%-68%, she said.
Positive percentage agreement rates of 98% for both SP263 and 22C3 suggest that the patients identified as PD-L1 positive using the SP142 assay are captured by the other two assays. However, negative percentage agreement rates were less than 45%.
The HRs for PFS were 0.60 in SP142-positive patients, 0.64 in SP263-positive patients, and 0.68 in 22C3-positive patients, and the HRs for OS were 0.74, 0.75, and 0.78, respectively.
Subgroup analyses indicated that PFS and OS benefit with atezolizumab + nab-paclitaxel vs. nab-paclitaxel alone was greater in double-positive patients (those with SP142 positivity and either SP263 or 22C3 positivity) than in patients who were SP263-positive/SP142-negative or 22C3-positive/SP142-negative.
Dr. Rugo and her colleagues also found that the benefits with atezolizumab + nab-paclitaxel in PD-L1-positive patients were apparent regardless of the source of tissue for testing (breast or distant metastases).
They concluded that the findings of the assays are not equivalent; 22C3 and SP263 identified more patients as PD-L1 positive, and SP142-positivity was encompassed in positive tests for both.
“The clinical benefit in the 22C3-positive and the SP263-positive subgroups appear to be driven by the SP142-positive subgroup, and [SP142] identifies patients with the longest median progression-free and overall survival from the addition of atezolizumab to nab-paclitaxel,” she said “The SP142 assay with an IC cutoff of 1% or greater is the approved diagnostic test used to identify patients with metastatic triple-negative breast cancer who are most likely to benefit from the addition of the checkpoint inhibitor atezolizumab to nab-paclitaxel.”
As for whether the SP142 should be the assay of choice in other settings in which it hasn’t been validated, Dr. Rugo said it is advisable to use the assay that has been validated in a positive trial.
“That’s what we would generally do ... however, recognizing that some countries are not using SP142, and some sites may not have access, certainly you encompass that population in the patients whose tumors are positive by both other assays,” she said. “The risk is that you might overtreat, and the cost of treatment is greater.”
Excess toxicity is also a concern in that situation, she said, adding that “hopefully in the future we’ll be able to figure out ways to have even more patients benefit from the addition of immunotherapy so that won’t be an issue.”
“What this data shows is that you can feel secure that you are encompassing the patient population identified by the parent trial to benefit from the addition of atezolizumab by using either of the other two assays; you’re only missing 1% – so that’s very reasonable,” she said. “The risk is that you’re overtreating; it’s quite likely that there’s a population there that isn’t benefiting as much, but that’s a balance.”
The findings from IMPassion130 with regard to OS in the unselected population that included PD-L1-negative patients (18.7 vs. 21.0 months with vs. without atezolizumab; HR, 0.86) underscore the fact that “one size does not fit all” when it comes to immunotherapy benefit, Dr. Bianchini said.
This is further demonstrated by the post hoc analysis comparing IHC assays, he said, explaining that 63% of IMPassion130 patients who were considered PD-L1-negative based on the SP142 “actually scored as PD-L1-positive by the other tests.
“So the very clinically important question is if there is any evidence from the data that [the PD-L1-negative group] benefits in a significant way from the addition of atezolizumab,” he said. “I don’t see evidence for a clinical benefit, I see evidence to look for new biomarkers to identify a potential population who will benefit.”
The “absence of evidence is not evidence of absence,” he stressed, noting that it may be possible – with the right biomarkers – to identify PD-L1-negative patients who would benefit.
What the findings do show, however, is support for the FDA decision to approve the SP142 assay with an IC cutoff of 1% as a companion diagnostic tool, and that PD-L1 is ideally assessed using samples from both the primary and metastatic site, as the IMPassion130 data “do not inform whether PD-L1 assessment in primary and metastatic sites is equally informative,” he said.
In addition, Dr. Bianchini said the findings suggest that more information is needed about using different cutoffs for SP263 and 22C3, and he cautioned against “directly translating these finding to other disease settings or immune combinations.
“Defining new biomarkers to identify who within the PD-L1-negative group might benefit from this combination remains an unmet need,” he said. “For sure, I don’t see a space for the other tests to define this population,” he added.
KEYNOTE-119, KATE2, and future directions
Both the randomized, open-label, phase 3 KEYNOTE-119 study of the checkpoint inhibitor pembrolizumab vs. single-agent chemotherapy for mTNBC, and the phase 2 KATE2 trial of the antibody-drug conjugate trastuzumab emtansine (T-DM1) + either atezolizumab or placebo in previously treated HER2-positive breast cancer patients, failed to meet their respective primary study endpoints.
But the news isn’t all bad, Dr. Bianchini said.
For example, in KEYNOTE-119, second- or third-line pembrolizumab monotherapy did not significantly improve OS vs. chemotherapy for mTNBC, but the pembrolizumab treatment effect increased as PD-L1 enrichment increased, he explained.
Pembrolizumab showed promising antitumor activity and manageable safety in mTNBC in prior trials, and was therefore further assessed in the KEYNOTE-119 study of 601 patients with centrally confirmed TNBC, 1-2 prior systemic treatments for mTNBC, progression on the latest therapy, and a prior anthracycline or taxane, Javier Cortés, MD, PhD, of Instituto Oncológico, Madrid, reported at the congress.
Pembrolizumab was given at a dose of 200 mg every 3 weeks, and chemotherapy was physician’s choice of capecitabine, eribulin, gemcitabine, or vinorelbine.
At a median follow-up of 9.9 months in the pembrolizumab group and 10.9 months in the chemotherapy group, OS did not differ significantly between the groups; this was true overall, in patients with a CPS of 10 or greater, and in those with a CPS of 1 or greater.
In all-comers, the HR for OS was 0.97, compared with 0.78 in patients with CPS of 10 or greater, and 0.86 in those with CPS of 1 or greater, Dr. Cortés said.
“One of the most interesting exploratory analyses was OS in those patients with CPS of 20 or higher,” he said, noting that median OS in that group was 14.9 vs.12.5 months with pembrolizumab vs. with chemotherapy (HR, 0.58).
Pembrolizumab did not improve overall PFS, but again, the rates improved with higher CPS. Duration of response, however, was longer with pembrolizumab vs. chemotherapy (12.2 vs. 8.3 months overall; 12.2 vs. 6.5 months for CPS of 1 or greater; and not reached vs. 7.1 months for CPS of 10 or greater).
Grade 3-5 AEs occurred in 35% vs. 49% of patients in the pembrolizumab vs. chemotherapy groups, with nine deaths occurring in each, Dr. Cortés said, adding that treatment-related AEs occurred in 14% (with one death) and 36% (with two deaths), respectively, and grade 3-4 immune-mediated AEs and infusion reactions occurred in 3.2% vs. 1.0% (no deaths), respectively.
In the double-blind, signal-seeking KATE2 trial, as reported in 2018 at the San Antonio Breast Cancer Symposium, no overall PFS improvement was seen with atezolizumab + T-DM1 (median of 8.2 vs. 6.8 months; HR, 0.82; 12-month PFS 38% vs. 34%), but again, a possible benefit was seen in PD-L1-positive patients (8.5 vs. 4.1 months; HR, 0.60).
KATE2 included 202 patients with advanced HER2-positive breast cancer that progressed after treatment with T-DM1 and a taxane. They were randomized 2:1 to receive intravenous T-DM1 at a dose of 3.6 mg/kg plus atezolizumab (1,200 mg) or placebo every 3 weeks until loss of clinical benefit or intolerable toxicity.
The “overall survival and final safety results” show that at a median follow-up of 19.0 months in the atezolizumab arm and 18.2 months in the placebo arm, with 52 OS events reported, median OS was not reached in either arm and 1-year survival was similar in the two groups (89.1% and 89.0%), Leisha A. Emens, MD, PhD, professor of medicine in hematology/oncology and co-leader of the Hillman Cancer Immunology and Immunotherapy Program at Hillman Cancer Center, University of Pittsburgh Medical Center (UPMC) reported at the congress.
The 1-year OS rate in the PD-L1-positive subgroup, however, was numerically higher with vs. without atezolizumab (94.2% vs. 87.9%), said Dr. Emens, director of translational immunotherapy for the Women’s Cancer Research Center at UPMC.
Of note, all additional biomarkers of T-cell activation and quantity analyzed, including PD-L1 gene expression, CD8 gene expression, T effector signature gene expression, and stromal tumor infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs), were enriched in the PD-L1-positive subgroup vs. the PD-L1-negative patients.
Further, OS rates in other immune biomarker subgroups (those with PD-L1 RNA expression, CD8 RNA expression, and T effector signature at or below vs. above the median, and those with TILs less than 5% vs. 5% or greater) were consistent with those in the PD-L1 IC-positive subgroup, and the biggest difference between the atezolizumab and placebo arms related to stromal TILs, she said.
The safety profile in this final analysis was consistent with the known safety profile of each drug, she added, noting that grade 3 or greater AEs occurred in 52.6% vs. 44.8% of patients in the atezolizumab vs. placebo arms, and serious AEs – primarily pyrexia – occurred in 36.1% vs 20.9%, respectively.
The rate of grade 5 AEs was similar in the groups.
T-DM1 is indicated for the treatment of HER2-positive metastatic breast cancer previously treated with trastuzumab and a taxane, either separately or in combination, Dr. Emens said.
“In addition to its cytotoxic activity, T-DM1 may potentiate tumor immunity,” she explained, adding that KATE2 was designed to assess whether combining T-DM1 with atezolizumab, an anti-PD-L1 antibody that restores anti-tumor immunity, would result in greater clinical activity than either drug alone.
Although the number of OS events was small, the data suggest an OS benefit with the addition of atezolizumab to T-DM1, specifically in the PD-L1 IC-positive patients, but follow-up was short and the study lacked statistical power, therefore additional study of HER2-targeted agents with atezolizumab in previously treated HER2-positive, PD-L1 IC-positive advanced breast cancer is warranted, Dr. Emens concluded.
Indeed, the finding of improved OS in the PD-L1-positive subgroups of both KEYNOTE-119 and KATE2, is of interest, Dr. Bianchini said.
Both trials failed to meet their primary endpoints, but a closer look into KEYNOTE-119 shows that PD-L1 as a continuous biomarker (using CPS, 22C3) was associated with a “continuous and strong trend” toward improved ORR with the addition of pembrolizumab.
The ORR was 9.6% vs. 10.6% in unselected patients, compared with 26.3% vs. 11.5% in those with CPS of 20 or greater.
“And when you look at duration of response, you see an increase not just in the number ... but the quality of the response,” he said, noting that for PFS, as well, a trend toward superiority is seen “that is consistent with all the other endpoints.”
“So overall, the application of incrementally restrictive cut-off of CPS lends weight to the exploratory analysis showing better survival from pembrolizumab in tumors with CPS more than 20,” Dr. Bianchini said, noting that the “real question,” however, is whether the finding “is worth clinical implementation.
“We know a lot about the primary tumor and immune infiltration. We’ve learned ... that if you wait and look ahead at immune infiltration in the advanced stage, you find that the tumor becomes smart,” he said, explaining that tumor/immune co-evolution leads to increased immuno-editing and immune subversion and it becomes “much harder to just hit the tumor with PD-L1, because this is not the only mechanism of immune escape.”
A review of several studies shows that in similar populations defined by biomarkers, response rates in patients treated with checkpoint inhibitors decrease in the second- and third-line setting vs. the first-line setting, he said.
For example, pembrolizumab response rates in the first-line and second-line or greater setting in cohort B of the KEYNOTE-086 study were 21.4% and 5.7%, respectively, compared with 12.3% in the second- to third-line setting in KEYNOTE-119, he said.
Another consideration is whether monotherapy or combination therapy is preferable, and the data suggest that regardless of how PD-L1-positivity is defined (by CPS cutoff of 1 vs. 20, for example), most patients treated with monotherapy progress within the first 3 months, he said.
“I don’t see that this is a safe approach for the majority of these patients. So without better biomarkers, combinations should always be preferred, at least to avoid early progression,” Dr. Bianchini said, adding that the open question, then, is: “If we set the new standard in the first-line as the combination of nab-paclitaxel and atezolizumab for PD-L1-positive patients defined by the VENTANA [SP142 assay], should we continue with immune checkpoint [inhibition] using different combinations?”
“Of course, at the time the trial was designed, the results of IMpassion were not available, but it’s very important, because [the findings] add to the evidence that immunotherapy is extremely relevant for some patients,” he said.
KATE2 further demonstrated the importance of PD-L1 status, he said, adding that due to its limitations, including small sample size and short follow-up, longer follow-up is needed to better evaluate duration of response and PFS.
“Despite the trial limitations, the qualitative effect seen in all clinical endpoints – overall response rate, progression-free survival, overall survival – in PD-L1-positive tumors defined by SP142 ... provided strong and robust signals supporting the investigation of immune checkpoint inhibitors in HER-positive breast cancer,” he said, noting that “many trials are ongoing in the early setting and the advanced setting.”
In addition to the lessons of these trials with respect to the interchangeability of PD-L1 IHC assays and the value of PD-L1 assessment for identifying the likelihood of benefit from immune checkpoint inhibitors, the findings highlight the possibility that PD-L1-negative tumors require different immunotherapy approaches or alternative therapeutic strategies, and underscore that the benefit of immunotherapy in PD-L1-positive patients is still restricted to a minority.
“So new studies and approaches with immuno-oncology are needed, and we need more effective biomarkers, because we need to have precision oncology applied – we need to go in that direction,” he concluded.
Dr. Bianchini reported consultancy/honorarium and or advisory board activity associated with Roche, MSD, AstraZeneca, Pfizer, Chugai, EISAI, Lilly, Novartis, Amgen, Sanofi, Neopharm, and Genomic Health. The IMPassion30 trial was funded by F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd.; Dr. Rugo reported research grants, other funding, and or travel/accommodation/expenses from Pfizer, Novartis, Eli Lilly, Merck, OBI, EISAI, Plexxikon, Genentech/Roche, MacroGenics, PUMA, Mylan, Immunomedics, Daiichi Sankyo, and Celltrion. KEYNOTE-119 was funded by Merck Sharp & Dohme Corp.; Dr. Cortés and Dr. Emens reported numerous funding relationships but none with F. Hoffman-La Roche. KATE2 was funded by F. Hoffmann-La Roche.
Sources: IMPassion130; ESMO Abstract LBA20; KEYNOTE-119: ESMO Abstract LBA21; KATE2: ESMO Abstract 305O.
BARCELONA – Programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1) status in patients with advanced triple negative or HER2-positive breast cancer appears to identify distinct disease entities with varying likelihood of benefit from immune checkpoint inhibition, according to Giampaolo Bianchini, MD.
This observation, which contrasts with findings in other solid tumors and expands the road map to improved outcomes with immunotherapy for metastatic breast cancer, is based in part on new findings presented at the European Society for Medical Oncology Congress.
Among additional lessons from those findings: PD-L1 assays are not easily interchangeable, and studies with a “one size fits all” approach should be avoided, Dr. Bianchini, head of the Breast Cancer Group – Medical Oncology and clinical translational and immunotherapy research at Ospedale San Raffaele, Milan, said at the congress.
IMPassion130 and PD-L1 assays
In the phase 3 IMpassion130 trial assessing nanoparticle, albumin-bound (nab)-paclitaxel chemotherapy + either the anti-PD-L1 monoclonal antibody atezolizumab or placebo for the first-line treatment of metastatic triple-negative breast cancer (mTNBC), investigators used, and validated, the VENTANA PD-L1 SP142 assay to evaluate PD-L1 expression in immune cells (IC). PD-L1 positivity was defined using a 1% cutoff, meaning that PD-L1-stained IC encompassed at least 1% of the tumor area.
The trial demonstrated significantly improved progression-free survival (PFS) in the atezolizumab arm, both in the intention-to-treat (ITT) analysis (7.2 vs. 5.5 months in the placebo arm; hazard ratio, 0.80), and the PD-L1-positive subgroup (7.5 vs. 5.0 months; HR, 0.62), and the results were published in November 2018 (N Engl J Med. 2018; 379:2108-21).
“IMpassion130 is the first phase 3 trial demonstrating clinical benefit of cancer immunotherapy in patients with PD-L1-positive, metastatic triple-negative breast cancer,” Hope S. Rugo, MD, said at the congress. “The combination of atezolizumab and nab-paclitaxel is now approved in the United States and Europe for this indication.”
In addition, the SP142 antibody (which binds to PD-L1), at the 1% cutoff, predicted PFS and overall survival (OS) with atezolizumab + nab-paclitaxel, compared with nab-paclitaxel + placebo; the absolute improvement in OS in the PD-L1-positive population was 7 months (HR, 0.71), whereas no impact was seen in PFS or OS in patients who were PD-L1-negative using the SP142 assay, said Dr. Rugo, professor of hematology/oncology, and director of breast oncology and clinical trials education at the University of California, San Francisco.
Based on the IMPassion130 findings, the Food and Drug Administration approved the SP142 assay, using the 1% cutoff, as a “companion diagnostic device for selecting TNBC patients for atezolizumab.”
However, questions remain about how to best identify patients who could benefit from the atezolizumab + nab-paclitaxel combination, Dr. Rugo said.
Therefore, she and her colleagues performed a retrospective post hoc subgroup analysis of data from the trial to assess the performance and analytical concordance of the SP142 assay and two other commonly used PD-L1 immunohistochemistry (IHC) assays: the VENTANA SP263 IHC assay typically used as a companion diagnostic with durvalumab, and the Dako PD-L1 IHC 22C3 assay typically used with pembrolizumab.
In addition, the investigators assessed PD-L1 prevalence and clinical activity.
“We also included an evaluation of important factors related to PD-L1 testing and ... relationship to clinical outcome,” Dr. Rugo said.
In 614 biomarker-evaluable patients, representing 68% of the IMPassion130 ITT population, PD-L1-positive prevalence was 46% with the SP142 assay, 75% with the SP263 assay (also based on a 1% IC cutoff), and 81% with the 22C3 assay (with positivity defined as a combined positive score [CPS] of 1 or more based on an algorithm including both tumor and IC counts).
“Almost all SP142-positive cases are captured by either 22C3 or SP263. However, about a third of patients’ tumors were positive for PD-L1 using only one of the other two assays,” she noted, explaining that “this leads to suboptimal analytical concordance.”
The overall percentage agreement between SP142 and the other assays was only 64%-68%, she said.
Positive percentage agreement rates of 98% for both SP263 and 22C3 suggest that the patients identified as PD-L1 positive using the SP142 assay are captured by the other two assays. However, negative percentage agreement rates were less than 45%.
The HRs for PFS were 0.60 in SP142-positive patients, 0.64 in SP263-positive patients, and 0.68 in 22C3-positive patients, and the HRs for OS were 0.74, 0.75, and 0.78, respectively.
Subgroup analyses indicated that PFS and OS benefit with atezolizumab + nab-paclitaxel vs. nab-paclitaxel alone was greater in double-positive patients (those with SP142 positivity and either SP263 or 22C3 positivity) than in patients who were SP263-positive/SP142-negative or 22C3-positive/SP142-negative.
Dr. Rugo and her colleagues also found that the benefits with atezolizumab + nab-paclitaxel in PD-L1-positive patients were apparent regardless of the source of tissue for testing (breast or distant metastases).
They concluded that the findings of the assays are not equivalent; 22C3 and SP263 identified more patients as PD-L1 positive, and SP142-positivity was encompassed in positive tests for both.
“The clinical benefit in the 22C3-positive and the SP263-positive subgroups appear to be driven by the SP142-positive subgroup, and [SP142] identifies patients with the longest median progression-free and overall survival from the addition of atezolizumab to nab-paclitaxel,” she said “The SP142 assay with an IC cutoff of 1% or greater is the approved diagnostic test used to identify patients with metastatic triple-negative breast cancer who are most likely to benefit from the addition of the checkpoint inhibitor atezolizumab to nab-paclitaxel.”
As for whether the SP142 should be the assay of choice in other settings in which it hasn’t been validated, Dr. Rugo said it is advisable to use the assay that has been validated in a positive trial.
“That’s what we would generally do ... however, recognizing that some countries are not using SP142, and some sites may not have access, certainly you encompass that population in the patients whose tumors are positive by both other assays,” she said. “The risk is that you might overtreat, and the cost of treatment is greater.”
Excess toxicity is also a concern in that situation, she said, adding that “hopefully in the future we’ll be able to figure out ways to have even more patients benefit from the addition of immunotherapy so that won’t be an issue.”
“What this data shows is that you can feel secure that you are encompassing the patient population identified by the parent trial to benefit from the addition of atezolizumab by using either of the other two assays; you’re only missing 1% – so that’s very reasonable,” she said. “The risk is that you’re overtreating; it’s quite likely that there’s a population there that isn’t benefiting as much, but that’s a balance.”
The findings from IMPassion130 with regard to OS in the unselected population that included PD-L1-negative patients (18.7 vs. 21.0 months with vs. without atezolizumab; HR, 0.86) underscore the fact that “one size does not fit all” when it comes to immunotherapy benefit, Dr. Bianchini said.
This is further demonstrated by the post hoc analysis comparing IHC assays, he said, explaining that 63% of IMPassion130 patients who were considered PD-L1-negative based on the SP142 “actually scored as PD-L1-positive by the other tests.
“So the very clinically important question is if there is any evidence from the data that [the PD-L1-negative group] benefits in a significant way from the addition of atezolizumab,” he said. “I don’t see evidence for a clinical benefit, I see evidence to look for new biomarkers to identify a potential population who will benefit.”
The “absence of evidence is not evidence of absence,” he stressed, noting that it may be possible – with the right biomarkers – to identify PD-L1-negative patients who would benefit.
What the findings do show, however, is support for the FDA decision to approve the SP142 assay with an IC cutoff of 1% as a companion diagnostic tool, and that PD-L1 is ideally assessed using samples from both the primary and metastatic site, as the IMPassion130 data “do not inform whether PD-L1 assessment in primary and metastatic sites is equally informative,” he said.
In addition, Dr. Bianchini said the findings suggest that more information is needed about using different cutoffs for SP263 and 22C3, and he cautioned against “directly translating these finding to other disease settings or immune combinations.
“Defining new biomarkers to identify who within the PD-L1-negative group might benefit from this combination remains an unmet need,” he said. “For sure, I don’t see a space for the other tests to define this population,” he added.
KEYNOTE-119, KATE2, and future directions
Both the randomized, open-label, phase 3 KEYNOTE-119 study of the checkpoint inhibitor pembrolizumab vs. single-agent chemotherapy for mTNBC, and the phase 2 KATE2 trial of the antibody-drug conjugate trastuzumab emtansine (T-DM1) + either atezolizumab or placebo in previously treated HER2-positive breast cancer patients, failed to meet their respective primary study endpoints.
But the news isn’t all bad, Dr. Bianchini said.
For example, in KEYNOTE-119, second- or third-line pembrolizumab monotherapy did not significantly improve OS vs. chemotherapy for mTNBC, but the pembrolizumab treatment effect increased as PD-L1 enrichment increased, he explained.
Pembrolizumab showed promising antitumor activity and manageable safety in mTNBC in prior trials, and was therefore further assessed in the KEYNOTE-119 study of 601 patients with centrally confirmed TNBC, 1-2 prior systemic treatments for mTNBC, progression on the latest therapy, and a prior anthracycline or taxane, Javier Cortés, MD, PhD, of Instituto Oncológico, Madrid, reported at the congress.
Pembrolizumab was given at a dose of 200 mg every 3 weeks, and chemotherapy was physician’s choice of capecitabine, eribulin, gemcitabine, or vinorelbine.
At a median follow-up of 9.9 months in the pembrolizumab group and 10.9 months in the chemotherapy group, OS did not differ significantly between the groups; this was true overall, in patients with a CPS of 10 or greater, and in those with a CPS of 1 or greater.
In all-comers, the HR for OS was 0.97, compared with 0.78 in patients with CPS of 10 or greater, and 0.86 in those with CPS of 1 or greater, Dr. Cortés said.
“One of the most interesting exploratory analyses was OS in those patients with CPS of 20 or higher,” he said, noting that median OS in that group was 14.9 vs.12.5 months with pembrolizumab vs. with chemotherapy (HR, 0.58).
Pembrolizumab did not improve overall PFS, but again, the rates improved with higher CPS. Duration of response, however, was longer with pembrolizumab vs. chemotherapy (12.2 vs. 8.3 months overall; 12.2 vs. 6.5 months for CPS of 1 or greater; and not reached vs. 7.1 months for CPS of 10 or greater).
Grade 3-5 AEs occurred in 35% vs. 49% of patients in the pembrolizumab vs. chemotherapy groups, with nine deaths occurring in each, Dr. Cortés said, adding that treatment-related AEs occurred in 14% (with one death) and 36% (with two deaths), respectively, and grade 3-4 immune-mediated AEs and infusion reactions occurred in 3.2% vs. 1.0% (no deaths), respectively.
In the double-blind, signal-seeking KATE2 trial, as reported in 2018 at the San Antonio Breast Cancer Symposium, no overall PFS improvement was seen with atezolizumab + T-DM1 (median of 8.2 vs. 6.8 months; HR, 0.82; 12-month PFS 38% vs. 34%), but again, a possible benefit was seen in PD-L1-positive patients (8.5 vs. 4.1 months; HR, 0.60).
KATE2 included 202 patients with advanced HER2-positive breast cancer that progressed after treatment with T-DM1 and a taxane. They were randomized 2:1 to receive intravenous T-DM1 at a dose of 3.6 mg/kg plus atezolizumab (1,200 mg) or placebo every 3 weeks until loss of clinical benefit or intolerable toxicity.
The “overall survival and final safety results” show that at a median follow-up of 19.0 months in the atezolizumab arm and 18.2 months in the placebo arm, with 52 OS events reported, median OS was not reached in either arm and 1-year survival was similar in the two groups (89.1% and 89.0%), Leisha A. Emens, MD, PhD, professor of medicine in hematology/oncology and co-leader of the Hillman Cancer Immunology and Immunotherapy Program at Hillman Cancer Center, University of Pittsburgh Medical Center (UPMC) reported at the congress.
The 1-year OS rate in the PD-L1-positive subgroup, however, was numerically higher with vs. without atezolizumab (94.2% vs. 87.9%), said Dr. Emens, director of translational immunotherapy for the Women’s Cancer Research Center at UPMC.
Of note, all additional biomarkers of T-cell activation and quantity analyzed, including PD-L1 gene expression, CD8 gene expression, T effector signature gene expression, and stromal tumor infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs), were enriched in the PD-L1-positive subgroup vs. the PD-L1-negative patients.
Further, OS rates in other immune biomarker subgroups (those with PD-L1 RNA expression, CD8 RNA expression, and T effector signature at or below vs. above the median, and those with TILs less than 5% vs. 5% or greater) were consistent with those in the PD-L1 IC-positive subgroup, and the biggest difference between the atezolizumab and placebo arms related to stromal TILs, she said.
The safety profile in this final analysis was consistent with the known safety profile of each drug, she added, noting that grade 3 or greater AEs occurred in 52.6% vs. 44.8% of patients in the atezolizumab vs. placebo arms, and serious AEs – primarily pyrexia – occurred in 36.1% vs 20.9%, respectively.
The rate of grade 5 AEs was similar in the groups.
T-DM1 is indicated for the treatment of HER2-positive metastatic breast cancer previously treated with trastuzumab and a taxane, either separately or in combination, Dr. Emens said.
“In addition to its cytotoxic activity, T-DM1 may potentiate tumor immunity,” she explained, adding that KATE2 was designed to assess whether combining T-DM1 with atezolizumab, an anti-PD-L1 antibody that restores anti-tumor immunity, would result in greater clinical activity than either drug alone.
Although the number of OS events was small, the data suggest an OS benefit with the addition of atezolizumab to T-DM1, specifically in the PD-L1 IC-positive patients, but follow-up was short and the study lacked statistical power, therefore additional study of HER2-targeted agents with atezolizumab in previously treated HER2-positive, PD-L1 IC-positive advanced breast cancer is warranted, Dr. Emens concluded.
Indeed, the finding of improved OS in the PD-L1-positive subgroups of both KEYNOTE-119 and KATE2, is of interest, Dr. Bianchini said.
Both trials failed to meet their primary endpoints, but a closer look into KEYNOTE-119 shows that PD-L1 as a continuous biomarker (using CPS, 22C3) was associated with a “continuous and strong trend” toward improved ORR with the addition of pembrolizumab.
The ORR was 9.6% vs. 10.6% in unselected patients, compared with 26.3% vs. 11.5% in those with CPS of 20 or greater.
“And when you look at duration of response, you see an increase not just in the number ... but the quality of the response,” he said, noting that for PFS, as well, a trend toward superiority is seen “that is consistent with all the other endpoints.”
“So overall, the application of incrementally restrictive cut-off of CPS lends weight to the exploratory analysis showing better survival from pembrolizumab in tumors with CPS more than 20,” Dr. Bianchini said, noting that the “real question,” however, is whether the finding “is worth clinical implementation.
“We know a lot about the primary tumor and immune infiltration. We’ve learned ... that if you wait and look ahead at immune infiltration in the advanced stage, you find that the tumor becomes smart,” he said, explaining that tumor/immune co-evolution leads to increased immuno-editing and immune subversion and it becomes “much harder to just hit the tumor with PD-L1, because this is not the only mechanism of immune escape.”
A review of several studies shows that in similar populations defined by biomarkers, response rates in patients treated with checkpoint inhibitors decrease in the second- and third-line setting vs. the first-line setting, he said.
For example, pembrolizumab response rates in the first-line and second-line or greater setting in cohort B of the KEYNOTE-086 study were 21.4% and 5.7%, respectively, compared with 12.3% in the second- to third-line setting in KEYNOTE-119, he said.
Another consideration is whether monotherapy or combination therapy is preferable, and the data suggest that regardless of how PD-L1-positivity is defined (by CPS cutoff of 1 vs. 20, for example), most patients treated with monotherapy progress within the first 3 months, he said.
“I don’t see that this is a safe approach for the majority of these patients. So without better biomarkers, combinations should always be preferred, at least to avoid early progression,” Dr. Bianchini said, adding that the open question, then, is: “If we set the new standard in the first-line as the combination of nab-paclitaxel and atezolizumab for PD-L1-positive patients defined by the VENTANA [SP142 assay], should we continue with immune checkpoint [inhibition] using different combinations?”
“Of course, at the time the trial was designed, the results of IMpassion were not available, but it’s very important, because [the findings] add to the evidence that immunotherapy is extremely relevant for some patients,” he said.
KATE2 further demonstrated the importance of PD-L1 status, he said, adding that due to its limitations, including small sample size and short follow-up, longer follow-up is needed to better evaluate duration of response and PFS.
“Despite the trial limitations, the qualitative effect seen in all clinical endpoints – overall response rate, progression-free survival, overall survival – in PD-L1-positive tumors defined by SP142 ... provided strong and robust signals supporting the investigation of immune checkpoint inhibitors in HER-positive breast cancer,” he said, noting that “many trials are ongoing in the early setting and the advanced setting.”
In addition to the lessons of these trials with respect to the interchangeability of PD-L1 IHC assays and the value of PD-L1 assessment for identifying the likelihood of benefit from immune checkpoint inhibitors, the findings highlight the possibility that PD-L1-negative tumors require different immunotherapy approaches or alternative therapeutic strategies, and underscore that the benefit of immunotherapy in PD-L1-positive patients is still restricted to a minority.
“So new studies and approaches with immuno-oncology are needed, and we need more effective biomarkers, because we need to have precision oncology applied – we need to go in that direction,” he concluded.
Dr. Bianchini reported consultancy/honorarium and or advisory board activity associated with Roche, MSD, AstraZeneca, Pfizer, Chugai, EISAI, Lilly, Novartis, Amgen, Sanofi, Neopharm, and Genomic Health. The IMPassion30 trial was funded by F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd.; Dr. Rugo reported research grants, other funding, and or travel/accommodation/expenses from Pfizer, Novartis, Eli Lilly, Merck, OBI, EISAI, Plexxikon, Genentech/Roche, MacroGenics, PUMA, Mylan, Immunomedics, Daiichi Sankyo, and Celltrion. KEYNOTE-119 was funded by Merck Sharp & Dohme Corp.; Dr. Cortés and Dr. Emens reported numerous funding relationships but none with F. Hoffman-La Roche. KATE2 was funded by F. Hoffmann-La Roche.
Sources: IMPassion130; ESMO Abstract LBA20; KEYNOTE-119: ESMO Abstract LBA21; KATE2: ESMO Abstract 305O.
BARCELONA – Programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1) status in patients with advanced triple negative or HER2-positive breast cancer appears to identify distinct disease entities with varying likelihood of benefit from immune checkpoint inhibition, according to Giampaolo Bianchini, MD.
This observation, which contrasts with findings in other solid tumors and expands the road map to improved outcomes with immunotherapy for metastatic breast cancer, is based in part on new findings presented at the European Society for Medical Oncology Congress.
Among additional lessons from those findings: PD-L1 assays are not easily interchangeable, and studies with a “one size fits all” approach should be avoided, Dr. Bianchini, head of the Breast Cancer Group – Medical Oncology and clinical translational and immunotherapy research at Ospedale San Raffaele, Milan, said at the congress.
IMPassion130 and PD-L1 assays
In the phase 3 IMpassion130 trial assessing nanoparticle, albumin-bound (nab)-paclitaxel chemotherapy + either the anti-PD-L1 monoclonal antibody atezolizumab or placebo for the first-line treatment of metastatic triple-negative breast cancer (mTNBC), investigators used, and validated, the VENTANA PD-L1 SP142 assay to evaluate PD-L1 expression in immune cells (IC). PD-L1 positivity was defined using a 1% cutoff, meaning that PD-L1-stained IC encompassed at least 1% of the tumor area.
The trial demonstrated significantly improved progression-free survival (PFS) in the atezolizumab arm, both in the intention-to-treat (ITT) analysis (7.2 vs. 5.5 months in the placebo arm; hazard ratio, 0.80), and the PD-L1-positive subgroup (7.5 vs. 5.0 months; HR, 0.62), and the results were published in November 2018 (N Engl J Med. 2018; 379:2108-21).
“IMpassion130 is the first phase 3 trial demonstrating clinical benefit of cancer immunotherapy in patients with PD-L1-positive, metastatic triple-negative breast cancer,” Hope S. Rugo, MD, said at the congress. “The combination of atezolizumab and nab-paclitaxel is now approved in the United States and Europe for this indication.”
In addition, the SP142 antibody (which binds to PD-L1), at the 1% cutoff, predicted PFS and overall survival (OS) with atezolizumab + nab-paclitaxel, compared with nab-paclitaxel + placebo; the absolute improvement in OS in the PD-L1-positive population was 7 months (HR, 0.71), whereas no impact was seen in PFS or OS in patients who were PD-L1-negative using the SP142 assay, said Dr. Rugo, professor of hematology/oncology, and director of breast oncology and clinical trials education at the University of California, San Francisco.
Based on the IMPassion130 findings, the Food and Drug Administration approved the SP142 assay, using the 1% cutoff, as a “companion diagnostic device for selecting TNBC patients for atezolizumab.”
However, questions remain about how to best identify patients who could benefit from the atezolizumab + nab-paclitaxel combination, Dr. Rugo said.
Therefore, she and her colleagues performed a retrospective post hoc subgroup analysis of data from the trial to assess the performance and analytical concordance of the SP142 assay and two other commonly used PD-L1 immunohistochemistry (IHC) assays: the VENTANA SP263 IHC assay typically used as a companion diagnostic with durvalumab, and the Dako PD-L1 IHC 22C3 assay typically used with pembrolizumab.
In addition, the investigators assessed PD-L1 prevalence and clinical activity.
“We also included an evaluation of important factors related to PD-L1 testing and ... relationship to clinical outcome,” Dr. Rugo said.
In 614 biomarker-evaluable patients, representing 68% of the IMPassion130 ITT population, PD-L1-positive prevalence was 46% with the SP142 assay, 75% with the SP263 assay (also based on a 1% IC cutoff), and 81% with the 22C3 assay (with positivity defined as a combined positive score [CPS] of 1 or more based on an algorithm including both tumor and IC counts).
“Almost all SP142-positive cases are captured by either 22C3 or SP263. However, about a third of patients’ tumors were positive for PD-L1 using only one of the other two assays,” she noted, explaining that “this leads to suboptimal analytical concordance.”
The overall percentage agreement between SP142 and the other assays was only 64%-68%, she said.
Positive percentage agreement rates of 98% for both SP263 and 22C3 suggest that the patients identified as PD-L1 positive using the SP142 assay are captured by the other two assays. However, negative percentage agreement rates were less than 45%.
The HRs for PFS were 0.60 in SP142-positive patients, 0.64 in SP263-positive patients, and 0.68 in 22C3-positive patients, and the HRs for OS were 0.74, 0.75, and 0.78, respectively.
Subgroup analyses indicated that PFS and OS benefit with atezolizumab + nab-paclitaxel vs. nab-paclitaxel alone was greater in double-positive patients (those with SP142 positivity and either SP263 or 22C3 positivity) than in patients who were SP263-positive/SP142-negative or 22C3-positive/SP142-negative.
Dr. Rugo and her colleagues also found that the benefits with atezolizumab + nab-paclitaxel in PD-L1-positive patients were apparent regardless of the source of tissue for testing (breast or distant metastases).
They concluded that the findings of the assays are not equivalent; 22C3 and SP263 identified more patients as PD-L1 positive, and SP142-positivity was encompassed in positive tests for both.
“The clinical benefit in the 22C3-positive and the SP263-positive subgroups appear to be driven by the SP142-positive subgroup, and [SP142] identifies patients with the longest median progression-free and overall survival from the addition of atezolizumab to nab-paclitaxel,” she said “The SP142 assay with an IC cutoff of 1% or greater is the approved diagnostic test used to identify patients with metastatic triple-negative breast cancer who are most likely to benefit from the addition of the checkpoint inhibitor atezolizumab to nab-paclitaxel.”
As for whether the SP142 should be the assay of choice in other settings in which it hasn’t been validated, Dr. Rugo said it is advisable to use the assay that has been validated in a positive trial.
“That’s what we would generally do ... however, recognizing that some countries are not using SP142, and some sites may not have access, certainly you encompass that population in the patients whose tumors are positive by both other assays,” she said. “The risk is that you might overtreat, and the cost of treatment is greater.”
Excess toxicity is also a concern in that situation, she said, adding that “hopefully in the future we’ll be able to figure out ways to have even more patients benefit from the addition of immunotherapy so that won’t be an issue.”
“What this data shows is that you can feel secure that you are encompassing the patient population identified by the parent trial to benefit from the addition of atezolizumab by using either of the other two assays; you’re only missing 1% – so that’s very reasonable,” she said. “The risk is that you’re overtreating; it’s quite likely that there’s a population there that isn’t benefiting as much, but that’s a balance.”
The findings from IMPassion130 with regard to OS in the unselected population that included PD-L1-negative patients (18.7 vs. 21.0 months with vs. without atezolizumab; HR, 0.86) underscore the fact that “one size does not fit all” when it comes to immunotherapy benefit, Dr. Bianchini said.
This is further demonstrated by the post hoc analysis comparing IHC assays, he said, explaining that 63% of IMPassion130 patients who were considered PD-L1-negative based on the SP142 “actually scored as PD-L1-positive by the other tests.
“So the very clinically important question is if there is any evidence from the data that [the PD-L1-negative group] benefits in a significant way from the addition of atezolizumab,” he said. “I don’t see evidence for a clinical benefit, I see evidence to look for new biomarkers to identify a potential population who will benefit.”
The “absence of evidence is not evidence of absence,” he stressed, noting that it may be possible – with the right biomarkers – to identify PD-L1-negative patients who would benefit.
What the findings do show, however, is support for the FDA decision to approve the SP142 assay with an IC cutoff of 1% as a companion diagnostic tool, and that PD-L1 is ideally assessed using samples from both the primary and metastatic site, as the IMPassion130 data “do not inform whether PD-L1 assessment in primary and metastatic sites is equally informative,” he said.
In addition, Dr. Bianchini said the findings suggest that more information is needed about using different cutoffs for SP263 and 22C3, and he cautioned against “directly translating these finding to other disease settings or immune combinations.
“Defining new biomarkers to identify who within the PD-L1-negative group might benefit from this combination remains an unmet need,” he said. “For sure, I don’t see a space for the other tests to define this population,” he added.
KEYNOTE-119, KATE2, and future directions
Both the randomized, open-label, phase 3 KEYNOTE-119 study of the checkpoint inhibitor pembrolizumab vs. single-agent chemotherapy for mTNBC, and the phase 2 KATE2 trial of the antibody-drug conjugate trastuzumab emtansine (T-DM1) + either atezolizumab or placebo in previously treated HER2-positive breast cancer patients, failed to meet their respective primary study endpoints.
But the news isn’t all bad, Dr. Bianchini said.
For example, in KEYNOTE-119, second- or third-line pembrolizumab monotherapy did not significantly improve OS vs. chemotherapy for mTNBC, but the pembrolizumab treatment effect increased as PD-L1 enrichment increased, he explained.
Pembrolizumab showed promising antitumor activity and manageable safety in mTNBC in prior trials, and was therefore further assessed in the KEYNOTE-119 study of 601 patients with centrally confirmed TNBC, 1-2 prior systemic treatments for mTNBC, progression on the latest therapy, and a prior anthracycline or taxane, Javier Cortés, MD, PhD, of Instituto Oncológico, Madrid, reported at the congress.
Pembrolizumab was given at a dose of 200 mg every 3 weeks, and chemotherapy was physician’s choice of capecitabine, eribulin, gemcitabine, or vinorelbine.
At a median follow-up of 9.9 months in the pembrolizumab group and 10.9 months in the chemotherapy group, OS did not differ significantly between the groups; this was true overall, in patients with a CPS of 10 or greater, and in those with a CPS of 1 or greater.
In all-comers, the HR for OS was 0.97, compared with 0.78 in patients with CPS of 10 or greater, and 0.86 in those with CPS of 1 or greater, Dr. Cortés said.
“One of the most interesting exploratory analyses was OS in those patients with CPS of 20 or higher,” he said, noting that median OS in that group was 14.9 vs.12.5 months with pembrolizumab vs. with chemotherapy (HR, 0.58).
Pembrolizumab did not improve overall PFS, but again, the rates improved with higher CPS. Duration of response, however, was longer with pembrolizumab vs. chemotherapy (12.2 vs. 8.3 months overall; 12.2 vs. 6.5 months for CPS of 1 or greater; and not reached vs. 7.1 months for CPS of 10 or greater).
Grade 3-5 AEs occurred in 35% vs. 49% of patients in the pembrolizumab vs. chemotherapy groups, with nine deaths occurring in each, Dr. Cortés said, adding that treatment-related AEs occurred in 14% (with one death) and 36% (with two deaths), respectively, and grade 3-4 immune-mediated AEs and infusion reactions occurred in 3.2% vs. 1.0% (no deaths), respectively.
In the double-blind, signal-seeking KATE2 trial, as reported in 2018 at the San Antonio Breast Cancer Symposium, no overall PFS improvement was seen with atezolizumab + T-DM1 (median of 8.2 vs. 6.8 months; HR, 0.82; 12-month PFS 38% vs. 34%), but again, a possible benefit was seen in PD-L1-positive patients (8.5 vs. 4.1 months; HR, 0.60).
KATE2 included 202 patients with advanced HER2-positive breast cancer that progressed after treatment with T-DM1 and a taxane. They were randomized 2:1 to receive intravenous T-DM1 at a dose of 3.6 mg/kg plus atezolizumab (1,200 mg) or placebo every 3 weeks until loss of clinical benefit or intolerable toxicity.
The “overall survival and final safety results” show that at a median follow-up of 19.0 months in the atezolizumab arm and 18.2 months in the placebo arm, with 52 OS events reported, median OS was not reached in either arm and 1-year survival was similar in the two groups (89.1% and 89.0%), Leisha A. Emens, MD, PhD, professor of medicine in hematology/oncology and co-leader of the Hillman Cancer Immunology and Immunotherapy Program at Hillman Cancer Center, University of Pittsburgh Medical Center (UPMC) reported at the congress.
The 1-year OS rate in the PD-L1-positive subgroup, however, was numerically higher with vs. without atezolizumab (94.2% vs. 87.9%), said Dr. Emens, director of translational immunotherapy for the Women’s Cancer Research Center at UPMC.
Of note, all additional biomarkers of T-cell activation and quantity analyzed, including PD-L1 gene expression, CD8 gene expression, T effector signature gene expression, and stromal tumor infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs), were enriched in the PD-L1-positive subgroup vs. the PD-L1-negative patients.
Further, OS rates in other immune biomarker subgroups (those with PD-L1 RNA expression, CD8 RNA expression, and T effector signature at or below vs. above the median, and those with TILs less than 5% vs. 5% or greater) were consistent with those in the PD-L1 IC-positive subgroup, and the biggest difference between the atezolizumab and placebo arms related to stromal TILs, she said.
The safety profile in this final analysis was consistent with the known safety profile of each drug, she added, noting that grade 3 or greater AEs occurred in 52.6% vs. 44.8% of patients in the atezolizumab vs. placebo arms, and serious AEs – primarily pyrexia – occurred in 36.1% vs 20.9%, respectively.
The rate of grade 5 AEs was similar in the groups.
T-DM1 is indicated for the treatment of HER2-positive metastatic breast cancer previously treated with trastuzumab and a taxane, either separately or in combination, Dr. Emens said.
“In addition to its cytotoxic activity, T-DM1 may potentiate tumor immunity,” she explained, adding that KATE2 was designed to assess whether combining T-DM1 with atezolizumab, an anti-PD-L1 antibody that restores anti-tumor immunity, would result in greater clinical activity than either drug alone.
Although the number of OS events was small, the data suggest an OS benefit with the addition of atezolizumab to T-DM1, specifically in the PD-L1 IC-positive patients, but follow-up was short and the study lacked statistical power, therefore additional study of HER2-targeted agents with atezolizumab in previously treated HER2-positive, PD-L1 IC-positive advanced breast cancer is warranted, Dr. Emens concluded.
Indeed, the finding of improved OS in the PD-L1-positive subgroups of both KEYNOTE-119 and KATE2, is of interest, Dr. Bianchini said.
Both trials failed to meet their primary endpoints, but a closer look into KEYNOTE-119 shows that PD-L1 as a continuous biomarker (using CPS, 22C3) was associated with a “continuous and strong trend” toward improved ORR with the addition of pembrolizumab.
The ORR was 9.6% vs. 10.6% in unselected patients, compared with 26.3% vs. 11.5% in those with CPS of 20 or greater.
“And when you look at duration of response, you see an increase not just in the number ... but the quality of the response,” he said, noting that for PFS, as well, a trend toward superiority is seen “that is consistent with all the other endpoints.”
“So overall, the application of incrementally restrictive cut-off of CPS lends weight to the exploratory analysis showing better survival from pembrolizumab in tumors with CPS more than 20,” Dr. Bianchini said, noting that the “real question,” however, is whether the finding “is worth clinical implementation.
“We know a lot about the primary tumor and immune infiltration. We’ve learned ... that if you wait and look ahead at immune infiltration in the advanced stage, you find that the tumor becomes smart,” he said, explaining that tumor/immune co-evolution leads to increased immuno-editing and immune subversion and it becomes “much harder to just hit the tumor with PD-L1, because this is not the only mechanism of immune escape.”
A review of several studies shows that in similar populations defined by biomarkers, response rates in patients treated with checkpoint inhibitors decrease in the second- and third-line setting vs. the first-line setting, he said.
For example, pembrolizumab response rates in the first-line and second-line or greater setting in cohort B of the KEYNOTE-086 study were 21.4% and 5.7%, respectively, compared with 12.3% in the second- to third-line setting in KEYNOTE-119, he said.
Another consideration is whether monotherapy or combination therapy is preferable, and the data suggest that regardless of how PD-L1-positivity is defined (by CPS cutoff of 1 vs. 20, for example), most patients treated with monotherapy progress within the first 3 months, he said.
“I don’t see that this is a safe approach for the majority of these patients. So without better biomarkers, combinations should always be preferred, at least to avoid early progression,” Dr. Bianchini said, adding that the open question, then, is: “If we set the new standard in the first-line as the combination of nab-paclitaxel and atezolizumab for PD-L1-positive patients defined by the VENTANA [SP142 assay], should we continue with immune checkpoint [inhibition] using different combinations?”
“Of course, at the time the trial was designed, the results of IMpassion were not available, but it’s very important, because [the findings] add to the evidence that immunotherapy is extremely relevant for some patients,” he said.
KATE2 further demonstrated the importance of PD-L1 status, he said, adding that due to its limitations, including small sample size and short follow-up, longer follow-up is needed to better evaluate duration of response and PFS.
“Despite the trial limitations, the qualitative effect seen in all clinical endpoints – overall response rate, progression-free survival, overall survival – in PD-L1-positive tumors defined by SP142 ... provided strong and robust signals supporting the investigation of immune checkpoint inhibitors in HER-positive breast cancer,” he said, noting that “many trials are ongoing in the early setting and the advanced setting.”
In addition to the lessons of these trials with respect to the interchangeability of PD-L1 IHC assays and the value of PD-L1 assessment for identifying the likelihood of benefit from immune checkpoint inhibitors, the findings highlight the possibility that PD-L1-negative tumors require different immunotherapy approaches or alternative therapeutic strategies, and underscore that the benefit of immunotherapy in PD-L1-positive patients is still restricted to a minority.
“So new studies and approaches with immuno-oncology are needed, and we need more effective biomarkers, because we need to have precision oncology applied – we need to go in that direction,” he concluded.
Dr. Bianchini reported consultancy/honorarium and or advisory board activity associated with Roche, MSD, AstraZeneca, Pfizer, Chugai, EISAI, Lilly, Novartis, Amgen, Sanofi, Neopharm, and Genomic Health. The IMPassion30 trial was funded by F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd.; Dr. Rugo reported research grants, other funding, and or travel/accommodation/expenses from Pfizer, Novartis, Eli Lilly, Merck, OBI, EISAI, Plexxikon, Genentech/Roche, MacroGenics, PUMA, Mylan, Immunomedics, Daiichi Sankyo, and Celltrion. KEYNOTE-119 was funded by Merck Sharp & Dohme Corp.; Dr. Cortés and Dr. Emens reported numerous funding relationships but none with F. Hoffman-La Roche. KATE2 was funded by F. Hoffmann-La Roche.
Sources: IMPassion130; ESMO Abstract LBA20; KEYNOTE-119: ESMO Abstract LBA21; KATE2: ESMO Abstract 305O.
REPORTING FROM ESMO 2019
Adding pertuzumab shows benefit in ERBB2-positive breast cancer
Combination pertuzumab, trastuzumab, and docetaxel provided better responses than did placebo, trastuzumab, and docetaxel in Asian patients with ERBB2-positive early or locally advanced breast cancer, according to a phase 3 trial.
The safety profile of the combination regimen was similar between the treatment arms and in accordance with that of pertuzumab alone, reported Zhimin Shao, MD, of Fudan (Shanghai) University Cancer Center, and colleagues. The study was published in JAMA Oncology.
The randomized, placebo-controlled, phase 3 PEONY study included 329 women with ERBB2-positive early or locally advanced disease. The effects of adding pertuzumab to trastuzumab and docetaxel was studied in 23 centers throughout Asia.
Prior to surgery, study subjects in the treatment arm received intravenous pertuzumab at a loading dose of 840 mg followed by 420 mg, trastuzumab at a loading dose of 8 mg/kg followed by 6 mg/kg, and 75 mg/m2 of docetaxel, while patients in the placebo arm received placebo, trastuzumab, and docetaxel. Both regimens were administered every 3 weeks for a total of four cycles.
Post surgery, study patients received intravenous fluorouracil, cyclophosphamide, and epirubicin for a total of 3 cycles, followed by pertuzumab plus trastuzumab or placebo plus trastuzumab for a total of 13 cycles.
The primary outcome was the total pathologic complete response rate assessed at the completion of surgery.
After analysis, the researchers found that total pathologic complete response rates were significantly higher for patients in the pertuzumab arm (39.3%) compared with the placebo arm (21.8%) (difference, 17.5%; P = .001).
With respect to safety, the rates of common adverse events were similar between the groups, with the exception of diarrhea (38.5% in the pertuzumab arm vs. 16.4% in the placebo arm). The incidences of serious toxicities were slightly higher in the pertuzumab arm (10.1%) compared with the placebo arm (8.2%).
“Of the most common grade 3 or higher adverse events, there was a higher incidence of neutropenia in the pertuzumab group (38.1% vs. 32.7%),” they reported.
The researchers acknowledged a key limitation of the study was the short duration of follow-up. As a result, some secondary outcome data were immature at the time of the analysis.
“The PEONY trial adds to the totality of the data showing the benefit of pertuzumab and trastuzumab with chemotherapy in ERBB2-positive early breast cancer,” they concluded.
The authors reported financial affiliations with F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd., which funded the study, and Genentech.
SOURCE: Shao Z et al. JAMA Oncol. 2019 Oct 24. doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2019.3692.
Combination pertuzumab, trastuzumab, and docetaxel provided better responses than did placebo, trastuzumab, and docetaxel in Asian patients with ERBB2-positive early or locally advanced breast cancer, according to a phase 3 trial.
The safety profile of the combination regimen was similar between the treatment arms and in accordance with that of pertuzumab alone, reported Zhimin Shao, MD, of Fudan (Shanghai) University Cancer Center, and colleagues. The study was published in JAMA Oncology.
The randomized, placebo-controlled, phase 3 PEONY study included 329 women with ERBB2-positive early or locally advanced disease. The effects of adding pertuzumab to trastuzumab and docetaxel was studied in 23 centers throughout Asia.
Prior to surgery, study subjects in the treatment arm received intravenous pertuzumab at a loading dose of 840 mg followed by 420 mg, trastuzumab at a loading dose of 8 mg/kg followed by 6 mg/kg, and 75 mg/m2 of docetaxel, while patients in the placebo arm received placebo, trastuzumab, and docetaxel. Both regimens were administered every 3 weeks for a total of four cycles.
Post surgery, study patients received intravenous fluorouracil, cyclophosphamide, and epirubicin for a total of 3 cycles, followed by pertuzumab plus trastuzumab or placebo plus trastuzumab for a total of 13 cycles.
The primary outcome was the total pathologic complete response rate assessed at the completion of surgery.
After analysis, the researchers found that total pathologic complete response rates were significantly higher for patients in the pertuzumab arm (39.3%) compared with the placebo arm (21.8%) (difference, 17.5%; P = .001).
With respect to safety, the rates of common adverse events were similar between the groups, with the exception of diarrhea (38.5% in the pertuzumab arm vs. 16.4% in the placebo arm). The incidences of serious toxicities were slightly higher in the pertuzumab arm (10.1%) compared with the placebo arm (8.2%).
“Of the most common grade 3 or higher adverse events, there was a higher incidence of neutropenia in the pertuzumab group (38.1% vs. 32.7%),” they reported.
The researchers acknowledged a key limitation of the study was the short duration of follow-up. As a result, some secondary outcome data were immature at the time of the analysis.
“The PEONY trial adds to the totality of the data showing the benefit of pertuzumab and trastuzumab with chemotherapy in ERBB2-positive early breast cancer,” they concluded.
The authors reported financial affiliations with F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd., which funded the study, and Genentech.
SOURCE: Shao Z et al. JAMA Oncol. 2019 Oct 24. doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2019.3692.
Combination pertuzumab, trastuzumab, and docetaxel provided better responses than did placebo, trastuzumab, and docetaxel in Asian patients with ERBB2-positive early or locally advanced breast cancer, according to a phase 3 trial.
The safety profile of the combination regimen was similar between the treatment arms and in accordance with that of pertuzumab alone, reported Zhimin Shao, MD, of Fudan (Shanghai) University Cancer Center, and colleagues. The study was published in JAMA Oncology.
The randomized, placebo-controlled, phase 3 PEONY study included 329 women with ERBB2-positive early or locally advanced disease. The effects of adding pertuzumab to trastuzumab and docetaxel was studied in 23 centers throughout Asia.
Prior to surgery, study subjects in the treatment arm received intravenous pertuzumab at a loading dose of 840 mg followed by 420 mg, trastuzumab at a loading dose of 8 mg/kg followed by 6 mg/kg, and 75 mg/m2 of docetaxel, while patients in the placebo arm received placebo, trastuzumab, and docetaxel. Both regimens were administered every 3 weeks for a total of four cycles.
Post surgery, study patients received intravenous fluorouracil, cyclophosphamide, and epirubicin for a total of 3 cycles, followed by pertuzumab plus trastuzumab or placebo plus trastuzumab for a total of 13 cycles.
The primary outcome was the total pathologic complete response rate assessed at the completion of surgery.
After analysis, the researchers found that total pathologic complete response rates were significantly higher for patients in the pertuzumab arm (39.3%) compared with the placebo arm (21.8%) (difference, 17.5%; P = .001).
With respect to safety, the rates of common adverse events were similar between the groups, with the exception of diarrhea (38.5% in the pertuzumab arm vs. 16.4% in the placebo arm). The incidences of serious toxicities were slightly higher in the pertuzumab arm (10.1%) compared with the placebo arm (8.2%).
“Of the most common grade 3 or higher adverse events, there was a higher incidence of neutropenia in the pertuzumab group (38.1% vs. 32.7%),” they reported.
The researchers acknowledged a key limitation of the study was the short duration of follow-up. As a result, some secondary outcome data were immature at the time of the analysis.
“The PEONY trial adds to the totality of the data showing the benefit of pertuzumab and trastuzumab with chemotherapy in ERBB2-positive early breast cancer,” they concluded.
The authors reported financial affiliations with F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd., which funded the study, and Genentech.
SOURCE: Shao Z et al. JAMA Oncol. 2019 Oct 24. doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2019.3692.
FROM JAMA ONCOLOGY
USPSTF recommendations on risk assessment, genetic counseling, and genetic testing for BRCA-related cancer
Breast cancer screening recommendations have evolved over the past decade. BRCA1/2 genes are tumor-suppressor genes. Mutations in these genes place women at an increased risk for developing breast, ovarian, fallopian tube, and peritoneal cancer. Detection of BRCA1/2 mutations through genetic screening can provide patients with more information about their cancer risk and can lead to discussion of prophylactic therapies. This includes increased screening frequency, medical therapy, and surgical interventions.
New USPSTF recommendations address who is at an increased risk for BRCA1/2 mutations. They recommend using screening tools focusing on family history that primary care physicians can utilize to determine who should be referred for genetic counseling to discuss the risks and benefits of genetic screening. The following are the task force’s two primary recommendations:
The USPSTF recommends that primary care clinicians assess women with a personal or family history of breast, ovarian, tubal, or peritoneal cancer or who have an ancestry associated with BRCA1/2 gene mutations with an appropriate brief familial risk assessment tool. Women with a positive result on the risk assessment tool should receive genetic counseling and, if indicated after counseling, genetic testing. (B recommendation)
The USPSTF recommends against routine risk assessment, genetic counseling, or genetic testing for women whose personal or family history or ancestry is not associated with potentially harmful BRCA1/2 gene mutations. (D recommendation)
Breast cancer is the second leading cause of cancer and cancer death for women in the United States. Ovarian cancer ranks fifth in cancer deaths for women in the U.S. By age 70, women with BRCA1/2 mutations have a 45%-65% cumulative lifetime risk of developing breast cancer.
Mutations in BRCA1, specifically, are associated with a 39% lifetime risk for ovarian, fallopian tube, and peritoneal cancer. In contrast, mutations in BRCA2 are associated with a 10%-17% lifetime risk.
The USPSTF also underscores the increased prevalence of BRCA1/2 mutations in the Ashkenazi Jewish population. Three out of seven familial risk assessment tools inquire about Jewish ancestry. This is because the Ashkenazi Jewish population have a higher prevalence of three founder mutations in the BRCA1/2 gene. A member of this population has a 1 in 40 chance of carrying one of these three mutations, whereas the general population has a 1 in 300 chance.
The USPSTF recommends a multistep process of screening. The first step is taking a family history of cancer. For women who have a family history of breast, ovarian, tubal, or peritoneal cancer or a personal history of these cancers, a brief familial risk assessment tool should be used to determine the need for referral for in-depth genetic counseling to determine the need for genetic testing.
It is important to recognize that the validated tools recommended by the USPSTF are specific for genetic risk assessment. General breast cancer risk assessment tools, including the National Cancer Institute Breast Cancer Risk Assessment Tool, which is based on the Gail model, are not recommended.
The sensitivity of the tools recommended by the USPSTF range between 77% and 100%. A number of tools are given as an option with no one tool being better than the other. Perhaps the easiest to implement of the validated tools recommended is the Pedigree Assessment Tool. For this tool, points are assigned for every family member with breast or ovarian cancer as indicated in the table below.
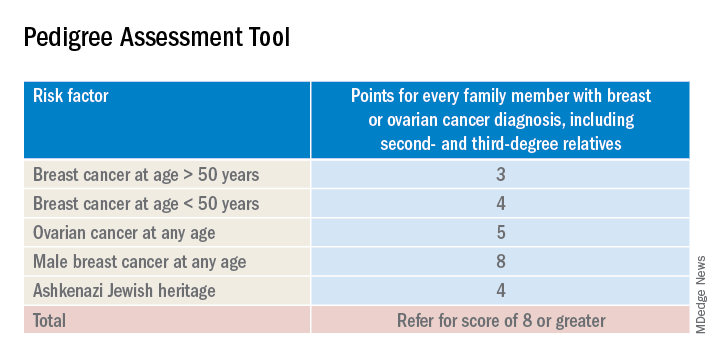
A positive result on a screening tool will lead primary care physicians to appropriately refer patients for genetic counseling. Genetic testing for BRCA1/2 mutations should be limited to those individuals whose personal and/or family history reflects an increased risk for gene mutations after detailed genetic assessment and counseling. The results of the genetic screening should assist a patient in their decision making.
Prophylactic treatment for BRCA1/2 mutation carriers are outside the scope of this recommendation. However the guidelines briefly review risk-reducing therapies including screening, medical, and surgical options. Medical therapy for patients who have BRCA1/2 mutations include the use of tamoxifen, raloxifene, and aromatase inhibitors. Surgical interventions include bilateral mastectomy and salpingo-oopherectomy.
Screening options include earlier and more frequent mammograms and breast MRIs. Screening is largely based on family history and the USPSTF acknowledges their uncertainty when screening women with an unknown family history. Male breast cancer, pancreatic cancer, prostate cancer, and melanoma are also associated with BRCA1/2 mutations. They are not included in this recommendation.
The bottom line
USPSTF recommended that primary care physicians should use familial risk assessment tools to screen women for BRCA1/2 mutations. This includes women with a personal and/or family history of breast, ovarian, tubal, or peritoneal cancer or women with a family history of BRCA1/2 gene mutations. Patients who test positive through one of the suggested screening tools should be referred for genetic counseling. This could lead to genetic testing and subsequent prophylactic therapies and/or increased screenings if the patient so desires. It is of importance to note the USPSTF recommends against routine screening of BRCA1/2 gene mutations for women who do not meet the above requirements.
Reference
USPSTF Recommendation: Assessment, counseling, and testing for BRCA-related cancer. JAMA. 2019;322(7):652-65. doi: 10.1001/jama.2019.10987.
Dr. Style is a second-year resident in the Family Medicine Residency Program at Abington (Pa.) Jefferson Health. Dr. Skolnik is professor of family and community medicine at Jefferson Medical College, Philadelphia, and an associate director of the family medicine residency program at Abington Jefferson Health.
Breast cancer screening recommendations have evolved over the past decade. BRCA1/2 genes are tumor-suppressor genes. Mutations in these genes place women at an increased risk for developing breast, ovarian, fallopian tube, and peritoneal cancer. Detection of BRCA1/2 mutations through genetic screening can provide patients with more information about their cancer risk and can lead to discussion of prophylactic therapies. This includes increased screening frequency, medical therapy, and surgical interventions.
New USPSTF recommendations address who is at an increased risk for BRCA1/2 mutations. They recommend using screening tools focusing on family history that primary care physicians can utilize to determine who should be referred for genetic counseling to discuss the risks and benefits of genetic screening. The following are the task force’s two primary recommendations:
The USPSTF recommends that primary care clinicians assess women with a personal or family history of breast, ovarian, tubal, or peritoneal cancer or who have an ancestry associated with BRCA1/2 gene mutations with an appropriate brief familial risk assessment tool. Women with a positive result on the risk assessment tool should receive genetic counseling and, if indicated after counseling, genetic testing. (B recommendation)
The USPSTF recommends against routine risk assessment, genetic counseling, or genetic testing for women whose personal or family history or ancestry is not associated with potentially harmful BRCA1/2 gene mutations. (D recommendation)
Breast cancer is the second leading cause of cancer and cancer death for women in the United States. Ovarian cancer ranks fifth in cancer deaths for women in the U.S. By age 70, women with BRCA1/2 mutations have a 45%-65% cumulative lifetime risk of developing breast cancer.
Mutations in BRCA1, specifically, are associated with a 39% lifetime risk for ovarian, fallopian tube, and peritoneal cancer. In contrast, mutations in BRCA2 are associated with a 10%-17% lifetime risk.
The USPSTF also underscores the increased prevalence of BRCA1/2 mutations in the Ashkenazi Jewish population. Three out of seven familial risk assessment tools inquire about Jewish ancestry. This is because the Ashkenazi Jewish population have a higher prevalence of three founder mutations in the BRCA1/2 gene. A member of this population has a 1 in 40 chance of carrying one of these three mutations, whereas the general population has a 1 in 300 chance.
The USPSTF recommends a multistep process of screening. The first step is taking a family history of cancer. For women who have a family history of breast, ovarian, tubal, or peritoneal cancer or a personal history of these cancers, a brief familial risk assessment tool should be used to determine the need for referral for in-depth genetic counseling to determine the need for genetic testing.
It is important to recognize that the validated tools recommended by the USPSTF are specific for genetic risk assessment. General breast cancer risk assessment tools, including the National Cancer Institute Breast Cancer Risk Assessment Tool, which is based on the Gail model, are not recommended.
The sensitivity of the tools recommended by the USPSTF range between 77% and 100%. A number of tools are given as an option with no one tool being better than the other. Perhaps the easiest to implement of the validated tools recommended is the Pedigree Assessment Tool. For this tool, points are assigned for every family member with breast or ovarian cancer as indicated in the table below.

A positive result on a screening tool will lead primary care physicians to appropriately refer patients for genetic counseling. Genetic testing for BRCA1/2 mutations should be limited to those individuals whose personal and/or family history reflects an increased risk for gene mutations after detailed genetic assessment and counseling. The results of the genetic screening should assist a patient in their decision making.
Prophylactic treatment for BRCA1/2 mutation carriers are outside the scope of this recommendation. However the guidelines briefly review risk-reducing therapies including screening, medical, and surgical options. Medical therapy for patients who have BRCA1/2 mutations include the use of tamoxifen, raloxifene, and aromatase inhibitors. Surgical interventions include bilateral mastectomy and salpingo-oopherectomy.
Screening options include earlier and more frequent mammograms and breast MRIs. Screening is largely based on family history and the USPSTF acknowledges their uncertainty when screening women with an unknown family history. Male breast cancer, pancreatic cancer, prostate cancer, and melanoma are also associated with BRCA1/2 mutations. They are not included in this recommendation.
The bottom line
USPSTF recommended that primary care physicians should use familial risk assessment tools to screen women for BRCA1/2 mutations. This includes women with a personal and/or family history of breast, ovarian, tubal, or peritoneal cancer or women with a family history of BRCA1/2 gene mutations. Patients who test positive through one of the suggested screening tools should be referred for genetic counseling. This could lead to genetic testing and subsequent prophylactic therapies and/or increased screenings if the patient so desires. It is of importance to note the USPSTF recommends against routine screening of BRCA1/2 gene mutations for women who do not meet the above requirements.
Reference
USPSTF Recommendation: Assessment, counseling, and testing for BRCA-related cancer. JAMA. 2019;322(7):652-65. doi: 10.1001/jama.2019.10987.
Dr. Style is a second-year resident in the Family Medicine Residency Program at Abington (Pa.) Jefferson Health. Dr. Skolnik is professor of family and community medicine at Jefferson Medical College, Philadelphia, and an associate director of the family medicine residency program at Abington Jefferson Health.
Breast cancer screening recommendations have evolved over the past decade. BRCA1/2 genes are tumor-suppressor genes. Mutations in these genes place women at an increased risk for developing breast, ovarian, fallopian tube, and peritoneal cancer. Detection of BRCA1/2 mutations through genetic screening can provide patients with more information about their cancer risk and can lead to discussion of prophylactic therapies. This includes increased screening frequency, medical therapy, and surgical interventions.
New USPSTF recommendations address who is at an increased risk for BRCA1/2 mutations. They recommend using screening tools focusing on family history that primary care physicians can utilize to determine who should be referred for genetic counseling to discuss the risks and benefits of genetic screening. The following are the task force’s two primary recommendations:
The USPSTF recommends that primary care clinicians assess women with a personal or family history of breast, ovarian, tubal, or peritoneal cancer or who have an ancestry associated with BRCA1/2 gene mutations with an appropriate brief familial risk assessment tool. Women with a positive result on the risk assessment tool should receive genetic counseling and, if indicated after counseling, genetic testing. (B recommendation)
The USPSTF recommends against routine risk assessment, genetic counseling, or genetic testing for women whose personal or family history or ancestry is not associated with potentially harmful BRCA1/2 gene mutations. (D recommendation)
Breast cancer is the second leading cause of cancer and cancer death for women in the United States. Ovarian cancer ranks fifth in cancer deaths for women in the U.S. By age 70, women with BRCA1/2 mutations have a 45%-65% cumulative lifetime risk of developing breast cancer.
Mutations in BRCA1, specifically, are associated with a 39% lifetime risk for ovarian, fallopian tube, and peritoneal cancer. In contrast, mutations in BRCA2 are associated with a 10%-17% lifetime risk.
The USPSTF also underscores the increased prevalence of BRCA1/2 mutations in the Ashkenazi Jewish population. Three out of seven familial risk assessment tools inquire about Jewish ancestry. This is because the Ashkenazi Jewish population have a higher prevalence of three founder mutations in the BRCA1/2 gene. A member of this population has a 1 in 40 chance of carrying one of these three mutations, whereas the general population has a 1 in 300 chance.
The USPSTF recommends a multistep process of screening. The first step is taking a family history of cancer. For women who have a family history of breast, ovarian, tubal, or peritoneal cancer or a personal history of these cancers, a brief familial risk assessment tool should be used to determine the need for referral for in-depth genetic counseling to determine the need for genetic testing.
It is important to recognize that the validated tools recommended by the USPSTF are specific for genetic risk assessment. General breast cancer risk assessment tools, including the National Cancer Institute Breast Cancer Risk Assessment Tool, which is based on the Gail model, are not recommended.
The sensitivity of the tools recommended by the USPSTF range between 77% and 100%. A number of tools are given as an option with no one tool being better than the other. Perhaps the easiest to implement of the validated tools recommended is the Pedigree Assessment Tool. For this tool, points are assigned for every family member with breast or ovarian cancer as indicated in the table below.

A positive result on a screening tool will lead primary care physicians to appropriately refer patients for genetic counseling. Genetic testing for BRCA1/2 mutations should be limited to those individuals whose personal and/or family history reflects an increased risk for gene mutations after detailed genetic assessment and counseling. The results of the genetic screening should assist a patient in their decision making.
Prophylactic treatment for BRCA1/2 mutation carriers are outside the scope of this recommendation. However the guidelines briefly review risk-reducing therapies including screening, medical, and surgical options. Medical therapy for patients who have BRCA1/2 mutations include the use of tamoxifen, raloxifene, and aromatase inhibitors. Surgical interventions include bilateral mastectomy and salpingo-oopherectomy.
Screening options include earlier and more frequent mammograms and breast MRIs. Screening is largely based on family history and the USPSTF acknowledges their uncertainty when screening women with an unknown family history. Male breast cancer, pancreatic cancer, prostate cancer, and melanoma are also associated with BRCA1/2 mutations. They are not included in this recommendation.
The bottom line
USPSTF recommended that primary care physicians should use familial risk assessment tools to screen women for BRCA1/2 mutations. This includes women with a personal and/or family history of breast, ovarian, tubal, or peritoneal cancer or women with a family history of BRCA1/2 gene mutations. Patients who test positive through one of the suggested screening tools should be referred for genetic counseling. This could lead to genetic testing and subsequent prophylactic therapies and/or increased screenings if the patient so desires. It is of importance to note the USPSTF recommends against routine screening of BRCA1/2 gene mutations for women who do not meet the above requirements.
Reference
USPSTF Recommendation: Assessment, counseling, and testing for BRCA-related cancer. JAMA. 2019;322(7):652-65. doi: 10.1001/jama.2019.10987.
Dr. Style is a second-year resident in the Family Medicine Residency Program at Abington (Pa.) Jefferson Health. Dr. Skolnik is professor of family and community medicine at Jefferson Medical College, Philadelphia, and an associate director of the family medicine residency program at Abington Jefferson Health.
Trastuzumab benefit lasts long-term in HER2+ breast cancer
Among patients with human epidermal growth factor receptor 2–positive (HER2+) breast cancer, adding trastuzumab to adjuvant chemotherapy reduces risk of recurrence for at least 10 years, according to investigators.
The benefit of trastuzumab was greater among patients with hormone receptor–positive (HR+) disease than those with HR– disease until the 5-year timepoint, after which HR status had no significant impact on recurrence rates, reported lead author Saranya Chumsri, MD, of the Mayo Clinic in Jacksonville, Fla., and colleagues. This finding echoes a pattern similar to that of HER2– breast cancer, in which patients with HR+ disease have relatively consistent risk of recurrence over time, whereas patients with HR– disease have an early risk of recurrence that decreases after 5 years.
“To the best of our knowledge, this analysis is the first to address the risk of late relapses in subsets of HER2+ breast cancer patients who were treated with adjuvant trastuzumab,” the investigators wrote. Their report is in Journal of Clinical Oncology.
They drew data from 3,177 patients with HER2+ breast cancer who were involved in two phase 3 studies: the North Central Cancer Treatment Group N9831 and National Surgical Adjuvant Breast and Bowel Project B-31 trials. Patients involved in the analysis received either standard adjuvant chemotherapy with cyclophosphamide and doxorubicin followed by weekly paclitaxel or the same chemotherapy regimen plus concurrent trastuzumab. The primary outcome was recurrence-free survival, which was defined as time from randomization until local, regional, or distant recurrence of breast cancer or breast cancer–related death. Kaplan-Meier estimates were performed to determine recurrence-free survival, while Cox proportional hazards regression models were used to determine factors that predicted relapse.
Including a median follow-up of 8 years across all patients, the analysis showed that those with HR+ breast cancer had a significantly higher estimated rate of recurrence-free survival than that of those with HR– disease after 5 years (81.49% vs. 74.65%) and 10 years (73.84% vs. 69.22%). Overall, a comparable level of benefit was derived from adding trastuzumab regardless of HR status (interaction P = .87). However, during the first 5 years, HR positivity predicted greater benefit from adding trastuzumab, as patients with HR+ disease had a 40% lower risk of relapse than that of those with HR– disease (hazard ratio, 0.60; P less than .001). Between years 5 and 10, the statistical significance of HR status faded (P = .12), suggesting that HR status is not a predictor of long-term recurrence.
“Given concerning adverse effects and potentially smaller benefit of extended adjuvant endocrine therapy, particularly in patients with N0 or N1 disease, our findings highlight the need to develop better risk prediction models and biomarkers to identify which patients have sufficient risk for late relapse to warrant the use of extended endocrine therapy in HER2+ breast cancer,” the investigators concluded.
The study was funded by the National Institutes of Health, the Breast Cancer Research Foundation, Bankhead-Coley Research Program, the DONNA Foundation, and Genentech. Dr. Chumsri disclosed a financial relationship with Merck. Coauthors disclosed ties with Merck, Novartis, Genentech, and NanoString Technologies.
SOURCE: Chumsri et al. J Clin Oncol. 2019 Oct 17. doi: 10.1200/JCO.19.00443.
Among patients with human epidermal growth factor receptor 2–positive (HER2+) breast cancer, adding trastuzumab to adjuvant chemotherapy reduces risk of recurrence for at least 10 years, according to investigators.
The benefit of trastuzumab was greater among patients with hormone receptor–positive (HR+) disease than those with HR– disease until the 5-year timepoint, after which HR status had no significant impact on recurrence rates, reported lead author Saranya Chumsri, MD, of the Mayo Clinic in Jacksonville, Fla., and colleagues. This finding echoes a pattern similar to that of HER2– breast cancer, in which patients with HR+ disease have relatively consistent risk of recurrence over time, whereas patients with HR– disease have an early risk of recurrence that decreases after 5 years.
“To the best of our knowledge, this analysis is the first to address the risk of late relapses in subsets of HER2+ breast cancer patients who were treated with adjuvant trastuzumab,” the investigators wrote. Their report is in Journal of Clinical Oncology.
They drew data from 3,177 patients with HER2+ breast cancer who were involved in two phase 3 studies: the North Central Cancer Treatment Group N9831 and National Surgical Adjuvant Breast and Bowel Project B-31 trials. Patients involved in the analysis received either standard adjuvant chemotherapy with cyclophosphamide and doxorubicin followed by weekly paclitaxel or the same chemotherapy regimen plus concurrent trastuzumab. The primary outcome was recurrence-free survival, which was defined as time from randomization until local, regional, or distant recurrence of breast cancer or breast cancer–related death. Kaplan-Meier estimates were performed to determine recurrence-free survival, while Cox proportional hazards regression models were used to determine factors that predicted relapse.
Including a median follow-up of 8 years across all patients, the analysis showed that those with HR+ breast cancer had a significantly higher estimated rate of recurrence-free survival than that of those with HR– disease after 5 years (81.49% vs. 74.65%) and 10 years (73.84% vs. 69.22%). Overall, a comparable level of benefit was derived from adding trastuzumab regardless of HR status (interaction P = .87). However, during the first 5 years, HR positivity predicted greater benefit from adding trastuzumab, as patients with HR+ disease had a 40% lower risk of relapse than that of those with HR– disease (hazard ratio, 0.60; P less than .001). Between years 5 and 10, the statistical significance of HR status faded (P = .12), suggesting that HR status is not a predictor of long-term recurrence.
“Given concerning adverse effects and potentially smaller benefit of extended adjuvant endocrine therapy, particularly in patients with N0 or N1 disease, our findings highlight the need to develop better risk prediction models and biomarkers to identify which patients have sufficient risk for late relapse to warrant the use of extended endocrine therapy in HER2+ breast cancer,” the investigators concluded.
The study was funded by the National Institutes of Health, the Breast Cancer Research Foundation, Bankhead-Coley Research Program, the DONNA Foundation, and Genentech. Dr. Chumsri disclosed a financial relationship with Merck. Coauthors disclosed ties with Merck, Novartis, Genentech, and NanoString Technologies.
SOURCE: Chumsri et al. J Clin Oncol. 2019 Oct 17. doi: 10.1200/JCO.19.00443.
Among patients with human epidermal growth factor receptor 2–positive (HER2+) breast cancer, adding trastuzumab to adjuvant chemotherapy reduces risk of recurrence for at least 10 years, according to investigators.
The benefit of trastuzumab was greater among patients with hormone receptor–positive (HR+) disease than those with HR– disease until the 5-year timepoint, after which HR status had no significant impact on recurrence rates, reported lead author Saranya Chumsri, MD, of the Mayo Clinic in Jacksonville, Fla., and colleagues. This finding echoes a pattern similar to that of HER2– breast cancer, in which patients with HR+ disease have relatively consistent risk of recurrence over time, whereas patients with HR– disease have an early risk of recurrence that decreases after 5 years.
“To the best of our knowledge, this analysis is the first to address the risk of late relapses in subsets of HER2+ breast cancer patients who were treated with adjuvant trastuzumab,” the investigators wrote. Their report is in Journal of Clinical Oncology.
They drew data from 3,177 patients with HER2+ breast cancer who were involved in two phase 3 studies: the North Central Cancer Treatment Group N9831 and National Surgical Adjuvant Breast and Bowel Project B-31 trials. Patients involved in the analysis received either standard adjuvant chemotherapy with cyclophosphamide and doxorubicin followed by weekly paclitaxel or the same chemotherapy regimen plus concurrent trastuzumab. The primary outcome was recurrence-free survival, which was defined as time from randomization until local, regional, or distant recurrence of breast cancer or breast cancer–related death. Kaplan-Meier estimates were performed to determine recurrence-free survival, while Cox proportional hazards regression models were used to determine factors that predicted relapse.
Including a median follow-up of 8 years across all patients, the analysis showed that those with HR+ breast cancer had a significantly higher estimated rate of recurrence-free survival than that of those with HR– disease after 5 years (81.49% vs. 74.65%) and 10 years (73.84% vs. 69.22%). Overall, a comparable level of benefit was derived from adding trastuzumab regardless of HR status (interaction P = .87). However, during the first 5 years, HR positivity predicted greater benefit from adding trastuzumab, as patients with HR+ disease had a 40% lower risk of relapse than that of those with HR– disease (hazard ratio, 0.60; P less than .001). Between years 5 and 10, the statistical significance of HR status faded (P = .12), suggesting that HR status is not a predictor of long-term recurrence.
“Given concerning adverse effects and potentially smaller benefit of extended adjuvant endocrine therapy, particularly in patients with N0 or N1 disease, our findings highlight the need to develop better risk prediction models and biomarkers to identify which patients have sufficient risk for late relapse to warrant the use of extended endocrine therapy in HER2+ breast cancer,” the investigators concluded.
The study was funded by the National Institutes of Health, the Breast Cancer Research Foundation, Bankhead-Coley Research Program, the DONNA Foundation, and Genentech. Dr. Chumsri disclosed a financial relationship with Merck. Coauthors disclosed ties with Merck, Novartis, Genentech, and NanoString Technologies.
SOURCE: Chumsri et al. J Clin Oncol. 2019 Oct 17. doi: 10.1200/JCO.19.00443.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF CLINICAL ONCOLOGY
Adding veliparib to chemotherapy improves PFS in BRCA-mutated breast cancer
BARCELONA – Adding veliparib to chemotherapy improved progression-free survival and provided a more durable benefit than did chemotherapy alone for HER2-negative advanced germline BRCA-associated breast cancer in the randomized, placebo-controlled, phase 3 BROCADE3 study.
Investigator-assessed median progression-free survival (PFS), the primary study endpoint, was 14.5 vs. 12.6 months in 337 patients randomized to receive the poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase inhibitor (PARPi) veliparib along with carboplatin/paclitaxel (CP) and 172 who received placebo and CP (hazard ratio, 0.71), Veronique C. Diéras, MD, reported at the European Society for Medical Oncology Congress.
“The benefit looks durable; more patients in the veliparib arm were still progression free at 2 years (34% vs. 20%), and at 3 years (26% vs. 11%),” said Dr. Diéras of Institut Curie, Paris, and Centre Eugene Marquis, Rennes, France.
The PFS benefit was confirmed by independent central review, and was apparent in all subgroups analyzed, except perhaps in patients with prior brain metastases, who comprised a very small group, she noted.
Among the secondary study endpoints were median overall survival (33.5 vs. 28.2 months at an interim analysis; HR, 0.95), clinical benefit rate (90.7% and 93.2% at 24 weeks), and objective response rate (75.8% and 74.1%).
“This is very important to note,” she said, referring to the high percentage of patients who benefited from CP alone. “But, again, if we look at the duration of response, in the veliparib arm the median duration of response was 14.7 months, whereas it was 11 months in the placebo arm.”
Participants in the double-blind trial were adults with a median age of 47 years who were randomized 2:1 to CP with veliparib or placebo for the treatment of germline BRCA1- or BRCA2-mutated metastatic breast cancer and had received no more than two prior lines of cytotoxic therapy; 48% were estrogen receptor– and/or progesterone receptor–negative, 8% had prior platinum therapy, 4% had a history of central nervous system metastases, and 19% had prior chemotherapy for metastatic disease.
They received placebo or veliparib at an oral dose of 120 mg twice daily on days −2 to 5 with carboplatin (area under the curve 6 on day 1) and weekly paclitaxel (80 mg/m2 on days 1, 8, and 15) in 21-day cycles until disease progression, and as allowed per study protocol, 44% crossed over from the placebo to veliparib group, Dr. Diéras said.
Common adverse events in the veliparib and placebo groups, respectively, included neutropenia (in 89% and 91% of patients), thrombocytopenia (81% and 71%), anemia (80% and 70%), and nausea (73% and 64%), she said, adding that the most common grade 3 adverse events were anemia (42% and 40%), neutropenia (81% and 84%), and thrombocytopenia (40% and 28%).
However, less than 10% of patients discontinued the study drug because of adverse events, she noted.
“In fact, the addition of veliparib to cytotoxic chemotherapy didn’t impair the administration of cytotoxic chemotherapy,” she said, adding that the mean number of CP cycles was 11 in both arms.
Select adverse events of special interest in the veliparib and placebo groups, respectively, included infection within 14 days of neutropenia (any grade, 37% and 36%; grade 3+, 5.4% and 1.8%), hemorrhage within 14 days of thrombocytopenia (any grade, 10% and 7%; grade 3+, 0.3% and 0%), and myelodysplastic syndromes (0.3% in both groups, with 0 grade 3+ events), she said.
“We know that germline BRCA-mutated breast cancers have increased sensitivity to platinum agents. Moreover, according to the concept of synthetic lethality, we do know also that these mutated tumors are very good candidates for PARP inhibition, so there is a strong rationale to combine a PARP inhibitor with cytotoxic chemotherapy with platinum,” she said.
Early studies of such combinations have been challenging because of exacerbation of myelosuppression, which may be the result of “the PARP trapping activity of some compounds,” but veliparib potently inhibits PARP with minimal PARP trapping, and thus may be better tolerated in combination with CP, she explained.
“In fact, in a phase 2 randomized trial – BROCADE2 – we did observe numerical increases in PFS and overall survival with [veliparib+CP],” she said.
In BROCADE3, the addition to veliparib to CP provided “a statistically significant and clinically meaningful benefit in patients with HER-negative advanced breast cancer and a germline BRCA mutation” without substantially altering the toxicity profile of C/P, she said.
“Considering these results, in my opinion, patients harboring BRCA mutations with advanced breast cancer [who are] candidates for chemotherapy should be offered this treatment option,” she concluded.
Invited discussant Sherene Loi, MBBS, PhD, head of the Translational Breast Cancer Genomics and Therapeutics Laboratory at Peter MacCallum Cancer Center, Victoria, Australia, said the investigators should be commended for conducting this phase 3 trial, and agreed that the approach is “reasonable to consider in a patient who does need chemotherapy.”
However, Dr. Loi said, it remains unclear if the PFS benefit seen in BROCADE3 is “due to the combination upfront and/or the monotherapy,” and suggested waiting for additional data before considering veliparib + CP as the new standard of care for germline BRCA1- and BRCA2-mutated advanced breast cancer.
“Current ESMO guidelines advise that single-agent chemotherapy be given sequentially in the absence of visceral crisis, therefore I think it’s important to await further for mature OS data and patient-reported outcomes,” she said, adding that it is also important to wait for the correlative analyses to “try to understand the rate of BRCA reversions and other resistance mechanisms in plasma.”
BROCADE3 was funded by AbbVie. Dr. Diéras reported advisory/consultancy roles for several pharmaceutical companies including AbbVie. Dr. Loi reported relationships with numerous pharmaceutical companies.
SOURCE: Diéras V et al. ESMO 2019, Abstract LBA9.
BARCELONA – Adding veliparib to chemotherapy improved progression-free survival and provided a more durable benefit than did chemotherapy alone for HER2-negative advanced germline BRCA-associated breast cancer in the randomized, placebo-controlled, phase 3 BROCADE3 study.
Investigator-assessed median progression-free survival (PFS), the primary study endpoint, was 14.5 vs. 12.6 months in 337 patients randomized to receive the poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase inhibitor (PARPi) veliparib along with carboplatin/paclitaxel (CP) and 172 who received placebo and CP (hazard ratio, 0.71), Veronique C. Diéras, MD, reported at the European Society for Medical Oncology Congress.
“The benefit looks durable; more patients in the veliparib arm were still progression free at 2 years (34% vs. 20%), and at 3 years (26% vs. 11%),” said Dr. Diéras of Institut Curie, Paris, and Centre Eugene Marquis, Rennes, France.
The PFS benefit was confirmed by independent central review, and was apparent in all subgroups analyzed, except perhaps in patients with prior brain metastases, who comprised a very small group, she noted.
Among the secondary study endpoints were median overall survival (33.5 vs. 28.2 months at an interim analysis; HR, 0.95), clinical benefit rate (90.7% and 93.2% at 24 weeks), and objective response rate (75.8% and 74.1%).
“This is very important to note,” she said, referring to the high percentage of patients who benefited from CP alone. “But, again, if we look at the duration of response, in the veliparib arm the median duration of response was 14.7 months, whereas it was 11 months in the placebo arm.”
Participants in the double-blind trial were adults with a median age of 47 years who were randomized 2:1 to CP with veliparib or placebo for the treatment of germline BRCA1- or BRCA2-mutated metastatic breast cancer and had received no more than two prior lines of cytotoxic therapy; 48% were estrogen receptor– and/or progesterone receptor–negative, 8% had prior platinum therapy, 4% had a history of central nervous system metastases, and 19% had prior chemotherapy for metastatic disease.
They received placebo or veliparib at an oral dose of 120 mg twice daily on days −2 to 5 with carboplatin (area under the curve 6 on day 1) and weekly paclitaxel (80 mg/m2 on days 1, 8, and 15) in 21-day cycles until disease progression, and as allowed per study protocol, 44% crossed over from the placebo to veliparib group, Dr. Diéras said.
Common adverse events in the veliparib and placebo groups, respectively, included neutropenia (in 89% and 91% of patients), thrombocytopenia (81% and 71%), anemia (80% and 70%), and nausea (73% and 64%), she said, adding that the most common grade 3 adverse events were anemia (42% and 40%), neutropenia (81% and 84%), and thrombocytopenia (40% and 28%).
However, less than 10% of patients discontinued the study drug because of adverse events, she noted.
“In fact, the addition of veliparib to cytotoxic chemotherapy didn’t impair the administration of cytotoxic chemotherapy,” she said, adding that the mean number of CP cycles was 11 in both arms.
Select adverse events of special interest in the veliparib and placebo groups, respectively, included infection within 14 days of neutropenia (any grade, 37% and 36%; grade 3+, 5.4% and 1.8%), hemorrhage within 14 days of thrombocytopenia (any grade, 10% and 7%; grade 3+, 0.3% and 0%), and myelodysplastic syndromes (0.3% in both groups, with 0 grade 3+ events), she said.
“We know that germline BRCA-mutated breast cancers have increased sensitivity to platinum agents. Moreover, according to the concept of synthetic lethality, we do know also that these mutated tumors are very good candidates for PARP inhibition, so there is a strong rationale to combine a PARP inhibitor with cytotoxic chemotherapy with platinum,” she said.
Early studies of such combinations have been challenging because of exacerbation of myelosuppression, which may be the result of “the PARP trapping activity of some compounds,” but veliparib potently inhibits PARP with minimal PARP trapping, and thus may be better tolerated in combination with CP, she explained.
“In fact, in a phase 2 randomized trial – BROCADE2 – we did observe numerical increases in PFS and overall survival with [veliparib+CP],” she said.
In BROCADE3, the addition to veliparib to CP provided “a statistically significant and clinically meaningful benefit in patients with HER-negative advanced breast cancer and a germline BRCA mutation” without substantially altering the toxicity profile of C/P, she said.
“Considering these results, in my opinion, patients harboring BRCA mutations with advanced breast cancer [who are] candidates for chemotherapy should be offered this treatment option,” she concluded.
Invited discussant Sherene Loi, MBBS, PhD, head of the Translational Breast Cancer Genomics and Therapeutics Laboratory at Peter MacCallum Cancer Center, Victoria, Australia, said the investigators should be commended for conducting this phase 3 trial, and agreed that the approach is “reasonable to consider in a patient who does need chemotherapy.”
However, Dr. Loi said, it remains unclear if the PFS benefit seen in BROCADE3 is “due to the combination upfront and/or the monotherapy,” and suggested waiting for additional data before considering veliparib + CP as the new standard of care for germline BRCA1- and BRCA2-mutated advanced breast cancer.
“Current ESMO guidelines advise that single-agent chemotherapy be given sequentially in the absence of visceral crisis, therefore I think it’s important to await further for mature OS data and patient-reported outcomes,” she said, adding that it is also important to wait for the correlative analyses to “try to understand the rate of BRCA reversions and other resistance mechanisms in plasma.”
BROCADE3 was funded by AbbVie. Dr. Diéras reported advisory/consultancy roles for several pharmaceutical companies including AbbVie. Dr. Loi reported relationships with numerous pharmaceutical companies.
SOURCE: Diéras V et al. ESMO 2019, Abstract LBA9.
BARCELONA – Adding veliparib to chemotherapy improved progression-free survival and provided a more durable benefit than did chemotherapy alone for HER2-negative advanced germline BRCA-associated breast cancer in the randomized, placebo-controlled, phase 3 BROCADE3 study.
Investigator-assessed median progression-free survival (PFS), the primary study endpoint, was 14.5 vs. 12.6 months in 337 patients randomized to receive the poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase inhibitor (PARPi) veliparib along with carboplatin/paclitaxel (CP) and 172 who received placebo and CP (hazard ratio, 0.71), Veronique C. Diéras, MD, reported at the European Society for Medical Oncology Congress.
“The benefit looks durable; more patients in the veliparib arm were still progression free at 2 years (34% vs. 20%), and at 3 years (26% vs. 11%),” said Dr. Diéras of Institut Curie, Paris, and Centre Eugene Marquis, Rennes, France.
The PFS benefit was confirmed by independent central review, and was apparent in all subgroups analyzed, except perhaps in patients with prior brain metastases, who comprised a very small group, she noted.
Among the secondary study endpoints were median overall survival (33.5 vs. 28.2 months at an interim analysis; HR, 0.95), clinical benefit rate (90.7% and 93.2% at 24 weeks), and objective response rate (75.8% and 74.1%).
“This is very important to note,” she said, referring to the high percentage of patients who benefited from CP alone. “But, again, if we look at the duration of response, in the veliparib arm the median duration of response was 14.7 months, whereas it was 11 months in the placebo arm.”
Participants in the double-blind trial were adults with a median age of 47 years who were randomized 2:1 to CP with veliparib or placebo for the treatment of germline BRCA1- or BRCA2-mutated metastatic breast cancer and had received no more than two prior lines of cytotoxic therapy; 48% were estrogen receptor– and/or progesterone receptor–negative, 8% had prior platinum therapy, 4% had a history of central nervous system metastases, and 19% had prior chemotherapy for metastatic disease.
They received placebo or veliparib at an oral dose of 120 mg twice daily on days −2 to 5 with carboplatin (area under the curve 6 on day 1) and weekly paclitaxel (80 mg/m2 on days 1, 8, and 15) in 21-day cycles until disease progression, and as allowed per study protocol, 44% crossed over from the placebo to veliparib group, Dr. Diéras said.
Common adverse events in the veliparib and placebo groups, respectively, included neutropenia (in 89% and 91% of patients), thrombocytopenia (81% and 71%), anemia (80% and 70%), and nausea (73% and 64%), she said, adding that the most common grade 3 adverse events were anemia (42% and 40%), neutropenia (81% and 84%), and thrombocytopenia (40% and 28%).
However, less than 10% of patients discontinued the study drug because of adverse events, she noted.
“In fact, the addition of veliparib to cytotoxic chemotherapy didn’t impair the administration of cytotoxic chemotherapy,” she said, adding that the mean number of CP cycles was 11 in both arms.
Select adverse events of special interest in the veliparib and placebo groups, respectively, included infection within 14 days of neutropenia (any grade, 37% and 36%; grade 3+, 5.4% and 1.8%), hemorrhage within 14 days of thrombocytopenia (any grade, 10% and 7%; grade 3+, 0.3% and 0%), and myelodysplastic syndromes (0.3% in both groups, with 0 grade 3+ events), she said.
“We know that germline BRCA-mutated breast cancers have increased sensitivity to platinum agents. Moreover, according to the concept of synthetic lethality, we do know also that these mutated tumors are very good candidates for PARP inhibition, so there is a strong rationale to combine a PARP inhibitor with cytotoxic chemotherapy with platinum,” she said.
Early studies of such combinations have been challenging because of exacerbation of myelosuppression, which may be the result of “the PARP trapping activity of some compounds,” but veliparib potently inhibits PARP with minimal PARP trapping, and thus may be better tolerated in combination with CP, she explained.
“In fact, in a phase 2 randomized trial – BROCADE2 – we did observe numerical increases in PFS and overall survival with [veliparib+CP],” she said.
In BROCADE3, the addition to veliparib to CP provided “a statistically significant and clinically meaningful benefit in patients with HER-negative advanced breast cancer and a germline BRCA mutation” without substantially altering the toxicity profile of C/P, she said.
“Considering these results, in my opinion, patients harboring BRCA mutations with advanced breast cancer [who are] candidates for chemotherapy should be offered this treatment option,” she concluded.
Invited discussant Sherene Loi, MBBS, PhD, head of the Translational Breast Cancer Genomics and Therapeutics Laboratory at Peter MacCallum Cancer Center, Victoria, Australia, said the investigators should be commended for conducting this phase 3 trial, and agreed that the approach is “reasonable to consider in a patient who does need chemotherapy.”
However, Dr. Loi said, it remains unclear if the PFS benefit seen in BROCADE3 is “due to the combination upfront and/or the monotherapy,” and suggested waiting for additional data before considering veliparib + CP as the new standard of care for germline BRCA1- and BRCA2-mutated advanced breast cancer.
“Current ESMO guidelines advise that single-agent chemotherapy be given sequentially in the absence of visceral crisis, therefore I think it’s important to await further for mature OS data and patient-reported outcomes,” she said, adding that it is also important to wait for the correlative analyses to “try to understand the rate of BRCA reversions and other resistance mechanisms in plasma.”
BROCADE3 was funded by AbbVie. Dr. Diéras reported advisory/consultancy roles for several pharmaceutical companies including AbbVie. Dr. Loi reported relationships with numerous pharmaceutical companies.
SOURCE: Diéras V et al. ESMO 2019, Abstract LBA9.
REPORTING FROM ESMO 2019
Risk of contralateral breast cancer highest for women under 40
Stray radiation exposure could be responsible for up to 28% of the contralateral breast cancer that occurs years after radiotherapy of the primary tumor.
The risk is highest among women initially treated when younger than 40 years, who had at lest 5 years’ lapse between the first and second occurrences, and had a higher genetic risk score, Gordon P. Watt, PhD, and colleagues reported in JAMA Network Open.
“These findings may support clinical decision making related to radiation treatment, particularly among women for whom other modalities may be considered,” wrote Dr. Watt of Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, New York, and coauthors. “For example, young women with a high [genetic risk] may consider partial-breast radiation therapy, rather than whole-breast radiation therapy when appropriate, opt for radiation therapy techniques that reduce integral dose (e.g., proton beam), or decide for non–radiation therapy–based locoregional management (e.g., mastectomy). These findings may be especially important in younger women with medially located breast cancers, where the scatter dose to the contralateral breast is likely to be higher.”
The investigators enrolled women who received a diagnosis for a first invasive local or regional breast cancer when they were younger than 55 years in a case-control study to investigate whether the NHEJ genetic risk score (GRS) could predict a woman’s risk of developing contralateral breast cancer after irradiation of a primary breast cancer. The risk score comprises 93 single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) located in or near the seven genes in the NHEJ pathway, including DCLRE1C, LIG4, NHEJ1, PRKDC, XRCC4, XRCC5, and XRCC6. Dr. Watts’ team investigated risks associated with 69 of the SNPs.
The study comprised 3,732 women who were recruited from 2000 to 2012, with primary diagnosis occurring from 1985 to 2008. Of these, 1,521 had contralateral breast cancer; the remainder had unilateral disease and were used as controls.
At first diagnosis, they were aged a median of 46 years, although age ranged from 23 to 54 years. Most of the primary tumors (84%) were ductal. Among the recurrences, 9% were in situ, 63% local, 23% regional, and 2% distant. Stage was unknown on the remainder. Among these recurrent tumors, 54% were estrogen receptor positive and 24% were progesterone receptor positive, with unknown status on the remainder.
For women aged younger than 40 years at the time of the primary tumor, and at least 5 years out from treatment, radiation increased the risk of contralateral disease by 70%. But there was no significant risk to younger women with less than 5 years’ latency, or to women diagnosed at 40 years or older regardless of the time since treatment.
Age played a similar role when considering location-specific stray radiation dose. The risk was doubled in younger women who were exposed to at least 1 Gy and at least 5 years out from treatment, but there was no significantly increased risk to women older at first diagnosis.
Nor were the individual SNPs associated with increased risk. “The NHEJ GRS was approximately normally distributed and was dichotomized at the overall median for analysis; the median (range) GRS in the case group was 75 alleles and the median GRS in the control group was 74 alleles,” the investigators wrote.
But when examined by total GRS score, differences emerged.
“In the high NHEJ GRS group, among women who received the first diagnosis when they were younger than 40 years with a latency of 5 years or more, a stray radiation dose of 1.0 Gy or more was associated with threefold greater contralateral breast cancer risk, compared with no radiation exposure. In contrast, for women with an NHEJ GRS of 74 alleles or fewer in the same age and latency group, there was no association between radiation dose and contralateral breast cancer,” they wrote.
Again, there was no increased risk for women aged older than 40 years at first diagnosis.
“Based on these results, after a latency of 5 years or longer among women who received their first breast cancer diagnosis when they were younger than 40 years with a high NHEJ GRS, the population-attributable risk fraction of contralateral breast cancer attributable to stray radiation exposure to the contralateral breast was 28%. The corresponding population attributable risk fraction among women who received their first diagnosis when they were younger than 40 years after a latency of 5 years or more with a low NHEJ GRS was 18%,” the investigators wrote.
Five of the seven NHEJ pathway genes appeared to be driving these increased risks: LIG4, NHEJ1, XRCC4, XRCC5, and XRCC6. The expression quantitative trait loci (eQTLs) in each gene were always associated with a single direction of association; all risk alleles in XRCC4 were associated with decreased expression and all risk alleles in LIG4 were associated with increased expression.
“The consistent association of multiple NHEJ GRS risk alleles with eQTLs in a single direction suggests that the NHEJ GRS may be capturing the effect of SNP alleles on the transcription of one or more genes in the NHEJ pathway. This supports the hypothesis that the variation in this pathway may alter double-stranded DNA damage response, thereby increasing the risk of tumor development. However, the results from [the Genotype-Tissue Expression database] are drawn from multiple tissues that may not be appropriate proxies for breast tissue and the impact of genetic variation in the overall NHEJ pathway is likely to be complex,” the investigators wrote.
Dr. Watt had no financial disclosures. The research was funded by the National Cancer Institute.
SOURCE: Watt GP et al. JAMA Netw Open. 2019 Sep 27. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2019.12259.
Stray radiation exposure could be responsible for up to 28% of the contralateral breast cancer that occurs years after radiotherapy of the primary tumor.
The risk is highest among women initially treated when younger than 40 years, who had at lest 5 years’ lapse between the first and second occurrences, and had a higher genetic risk score, Gordon P. Watt, PhD, and colleagues reported in JAMA Network Open.
“These findings may support clinical decision making related to radiation treatment, particularly among women for whom other modalities may be considered,” wrote Dr. Watt of Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, New York, and coauthors. “For example, young women with a high [genetic risk] may consider partial-breast radiation therapy, rather than whole-breast radiation therapy when appropriate, opt for radiation therapy techniques that reduce integral dose (e.g., proton beam), or decide for non–radiation therapy–based locoregional management (e.g., mastectomy). These findings may be especially important in younger women with medially located breast cancers, where the scatter dose to the contralateral breast is likely to be higher.”
The investigators enrolled women who received a diagnosis for a first invasive local or regional breast cancer when they were younger than 55 years in a case-control study to investigate whether the NHEJ genetic risk score (GRS) could predict a woman’s risk of developing contralateral breast cancer after irradiation of a primary breast cancer. The risk score comprises 93 single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) located in or near the seven genes in the NHEJ pathway, including DCLRE1C, LIG4, NHEJ1, PRKDC, XRCC4, XRCC5, and XRCC6. Dr. Watts’ team investigated risks associated with 69 of the SNPs.
The study comprised 3,732 women who were recruited from 2000 to 2012, with primary diagnosis occurring from 1985 to 2008. Of these, 1,521 had contralateral breast cancer; the remainder had unilateral disease and were used as controls.
At first diagnosis, they were aged a median of 46 years, although age ranged from 23 to 54 years. Most of the primary tumors (84%) were ductal. Among the recurrences, 9% were in situ, 63% local, 23% regional, and 2% distant. Stage was unknown on the remainder. Among these recurrent tumors, 54% were estrogen receptor positive and 24% were progesterone receptor positive, with unknown status on the remainder.
For women aged younger than 40 years at the time of the primary tumor, and at least 5 years out from treatment, radiation increased the risk of contralateral disease by 70%. But there was no significant risk to younger women with less than 5 years’ latency, or to women diagnosed at 40 years or older regardless of the time since treatment.
Age played a similar role when considering location-specific stray radiation dose. The risk was doubled in younger women who were exposed to at least 1 Gy and at least 5 years out from treatment, but there was no significantly increased risk to women older at first diagnosis.
Nor were the individual SNPs associated with increased risk. “The NHEJ GRS was approximately normally distributed and was dichotomized at the overall median for analysis; the median (range) GRS in the case group was 75 alleles and the median GRS in the control group was 74 alleles,” the investigators wrote.
But when examined by total GRS score, differences emerged.
“In the high NHEJ GRS group, among women who received the first diagnosis when they were younger than 40 years with a latency of 5 years or more, a stray radiation dose of 1.0 Gy or more was associated with threefold greater contralateral breast cancer risk, compared with no radiation exposure. In contrast, for women with an NHEJ GRS of 74 alleles or fewer in the same age and latency group, there was no association between radiation dose and contralateral breast cancer,” they wrote.
Again, there was no increased risk for women aged older than 40 years at first diagnosis.
“Based on these results, after a latency of 5 years or longer among women who received their first breast cancer diagnosis when they were younger than 40 years with a high NHEJ GRS, the population-attributable risk fraction of contralateral breast cancer attributable to stray radiation exposure to the contralateral breast was 28%. The corresponding population attributable risk fraction among women who received their first diagnosis when they were younger than 40 years after a latency of 5 years or more with a low NHEJ GRS was 18%,” the investigators wrote.
Five of the seven NHEJ pathway genes appeared to be driving these increased risks: LIG4, NHEJ1, XRCC4, XRCC5, and XRCC6. The expression quantitative trait loci (eQTLs) in each gene were always associated with a single direction of association; all risk alleles in XRCC4 were associated with decreased expression and all risk alleles in LIG4 were associated with increased expression.
“The consistent association of multiple NHEJ GRS risk alleles with eQTLs in a single direction suggests that the NHEJ GRS may be capturing the effect of SNP alleles on the transcription of one or more genes in the NHEJ pathway. This supports the hypothesis that the variation in this pathway may alter double-stranded DNA damage response, thereby increasing the risk of tumor development. However, the results from [the Genotype-Tissue Expression database] are drawn from multiple tissues that may not be appropriate proxies for breast tissue and the impact of genetic variation in the overall NHEJ pathway is likely to be complex,” the investigators wrote.
Dr. Watt had no financial disclosures. The research was funded by the National Cancer Institute.
SOURCE: Watt GP et al. JAMA Netw Open. 2019 Sep 27. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2019.12259.
Stray radiation exposure could be responsible for up to 28% of the contralateral breast cancer that occurs years after radiotherapy of the primary tumor.
The risk is highest among women initially treated when younger than 40 years, who had at lest 5 years’ lapse between the first and second occurrences, and had a higher genetic risk score, Gordon P. Watt, PhD, and colleagues reported in JAMA Network Open.
“These findings may support clinical decision making related to radiation treatment, particularly among women for whom other modalities may be considered,” wrote Dr. Watt of Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, New York, and coauthors. “For example, young women with a high [genetic risk] may consider partial-breast radiation therapy, rather than whole-breast radiation therapy when appropriate, opt for radiation therapy techniques that reduce integral dose (e.g., proton beam), or decide for non–radiation therapy–based locoregional management (e.g., mastectomy). These findings may be especially important in younger women with medially located breast cancers, where the scatter dose to the contralateral breast is likely to be higher.”
The investigators enrolled women who received a diagnosis for a first invasive local or regional breast cancer when they were younger than 55 years in a case-control study to investigate whether the NHEJ genetic risk score (GRS) could predict a woman’s risk of developing contralateral breast cancer after irradiation of a primary breast cancer. The risk score comprises 93 single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) located in or near the seven genes in the NHEJ pathway, including DCLRE1C, LIG4, NHEJ1, PRKDC, XRCC4, XRCC5, and XRCC6. Dr. Watts’ team investigated risks associated with 69 of the SNPs.
The study comprised 3,732 women who were recruited from 2000 to 2012, with primary diagnosis occurring from 1985 to 2008. Of these, 1,521 had contralateral breast cancer; the remainder had unilateral disease and were used as controls.
At first diagnosis, they were aged a median of 46 years, although age ranged from 23 to 54 years. Most of the primary tumors (84%) were ductal. Among the recurrences, 9% were in situ, 63% local, 23% regional, and 2% distant. Stage was unknown on the remainder. Among these recurrent tumors, 54% were estrogen receptor positive and 24% were progesterone receptor positive, with unknown status on the remainder.
For women aged younger than 40 years at the time of the primary tumor, and at least 5 years out from treatment, radiation increased the risk of contralateral disease by 70%. But there was no significant risk to younger women with less than 5 years’ latency, or to women diagnosed at 40 years or older regardless of the time since treatment.
Age played a similar role when considering location-specific stray radiation dose. The risk was doubled in younger women who were exposed to at least 1 Gy and at least 5 years out from treatment, but there was no significantly increased risk to women older at first diagnosis.
Nor were the individual SNPs associated with increased risk. “The NHEJ GRS was approximately normally distributed and was dichotomized at the overall median for analysis; the median (range) GRS in the case group was 75 alleles and the median GRS in the control group was 74 alleles,” the investigators wrote.
But when examined by total GRS score, differences emerged.
“In the high NHEJ GRS group, among women who received the first diagnosis when they were younger than 40 years with a latency of 5 years or more, a stray radiation dose of 1.0 Gy or more was associated with threefold greater contralateral breast cancer risk, compared with no radiation exposure. In contrast, for women with an NHEJ GRS of 74 alleles or fewer in the same age and latency group, there was no association between radiation dose and contralateral breast cancer,” they wrote.
Again, there was no increased risk for women aged older than 40 years at first diagnosis.
“Based on these results, after a latency of 5 years or longer among women who received their first breast cancer diagnosis when they were younger than 40 years with a high NHEJ GRS, the population-attributable risk fraction of contralateral breast cancer attributable to stray radiation exposure to the contralateral breast was 28%. The corresponding population attributable risk fraction among women who received their first diagnosis when they were younger than 40 years after a latency of 5 years or more with a low NHEJ GRS was 18%,” the investigators wrote.
Five of the seven NHEJ pathway genes appeared to be driving these increased risks: LIG4, NHEJ1, XRCC4, XRCC5, and XRCC6. The expression quantitative trait loci (eQTLs) in each gene were always associated with a single direction of association; all risk alleles in XRCC4 were associated with decreased expression and all risk alleles in LIG4 were associated with increased expression.
“The consistent association of multiple NHEJ GRS risk alleles with eQTLs in a single direction suggests that the NHEJ GRS may be capturing the effect of SNP alleles on the transcription of one or more genes in the NHEJ pathway. This supports the hypothesis that the variation in this pathway may alter double-stranded DNA damage response, thereby increasing the risk of tumor development. However, the results from [the Genotype-Tissue Expression database] are drawn from multiple tissues that may not be appropriate proxies for breast tissue and the impact of genetic variation in the overall NHEJ pathway is likely to be complex,” the investigators wrote.
Dr. Watt had no financial disclosures. The research was funded by the National Cancer Institute.
SOURCE: Watt GP et al. JAMA Netw Open. 2019 Sep 27. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2019.12259.
FROM JAMA NETWORK OPEN
Multigene testing for all patients with breast cancer may be cost-effective, life-saving
High-risk multigene testing for all patients with breast cancer may be a cost-effective way to reduce rates of breast cancer and ovarian cancer, according to investigators.
A microsimulation modeling study suggested that moving from standard BRCA testing based on clinical criteria or family history to widespread adoption of multigene testing could potentially save more than 2,400 lives per year in the United States, reported lead author Li Sun, MSc, of the London School of Hygiene & Tropical Medicine, and colleagues.
“Moving toward unselected BC testing may give an impetus for prevention in unaffected family members along with clinical implications for the patient with BC. Pathogenic variant carriers with newly diagnosed BC can opt for bilateral mastectomy rather than breast conservation at initial BC surgery,” the investigators wrote in JAMA Oncology. They noted that, presently, only 20%-30% of eligible patients are actually tested. “Testing all patients with breast cancer at diagnosis can increase testing access and uptake and identify many more pathogenic variant carriers for screening and prevention.”
To see if such a broad roll-out would be economically and medically feasible and beneficial, the investigators performed a modeling study involving 11,836 women with breast cancer, with data drawn from four large databases in the United Kingdom, the United States, and Australia.
The model compared annual costs, number of detected cases of breast cancer and ovarian cancer, and related rates of mortality between standard BRCA testing based on clinical criteria or family history versus high-risk multigene testing (BRCA1/BRCA2/PALB2) for all patients with breast cancer.
Resultant incremental cost-effectiveness ratios (ICERs) showed that in both the United Kingdom and the United States, multigene testing would cost, on average, significantly less than minimum willingness-to-pay thresholds of £30,000 per quality-adjusted life-year (QALY) and $100,000/QALY, respectively. In the United Kingdom, the estimated cost of multigene testing was £10,464/QALY from a payer’s perspective and £7,216/QALY from a societal perspective, the latter of which incorporates economic costs beyond the health care system. In the United States, these values rose to $65,661/QALY (payer perspective) and $61,618/QALY (societal perspective). Probabilistic sensitivity analysis suggested that multigene testing would be cost-effective for almost all health system simulations in the United Kingdom (98%-99%) and approximately two-thirds of those in the United States (64%-68%).
Epidemiologically, in the United Kingdom, multigene testing could potentially prevent 2,101 cases of breast cancer and ovarian cancer and 633 deaths per year, while in the United States, 9,733 cases might be prevented, with 2,406 lives saved.
“Our analysis suggests that an unselected testing strategy is extremely cost-effective for U.K. and U.S. health systems and provides a basis for change in current guidelines and policy to implement this strategy,” the investigators said.
The study was funded by the National Cancer Institute, the State of Washington, the Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center, and others. The investigators reported additional relationships with AstraZeneca, the Manchester National Institute for Health Research Biomedical Research Centre, Cancer Research UK, an others.
SOURCE: Sun et al. JAMA Oncol. 2019 Oct 3. doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2019.3323.
Although detection of more pathogenic variants among patients with breast cancer may initially appear beneficial, the hidden risks and costs associated with broader multigene testing would likely outweigh the benefits.
Present guidelines, such as those provided by the National Comprehensive Cancer Network, already include effective strategies for detecting BRCA1/2 variants, as only 0.6% of patients who do not meet screening guidelines are estimated to test positive
Beyond BRCA1/2, the clinical relevance of pathogenic variants becomes dubious, as many genetic aberrations are not actionable. Furthermore, misinterpretation of unfamiliar results may increase risks of treatment decisions that might actually harm patients. While some argue that broader testing could have benefits for family members, this is poorly supported with evidence.
Behind the allegedly falling costs of genetic sequencing, true costs are hidden with corporate policies that reduce patient financial liability. It is worth noting that two publicly held testing companies recently reported annual revenues of $144 million and $498 million, representing money drawn largely from third-party payers covering guideline-recommended testing. Instead of concrete science, the popularity of multigene testing is more likely driven by active marketing and technological convenience. More independent studies are needed.
Mark Robson, MD, is with the department of breast cancer medicine and clinical genetics at Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center in New York. Susan Domchek, MD is with the Basser Center for BRCA at the University of Pennsylvania in Philadelphia. Dr. Robson disclosed financial relationships with AstraZeneca, McKesson, and Pfizer. Dr. Domchek reported personal fees from Clovis, AstraZeneca, and BMS. Their remarks are adapted from an editorial (JAMA Oncol. 2019 Oct 3. doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2019.4004).
Although detection of more pathogenic variants among patients with breast cancer may initially appear beneficial, the hidden risks and costs associated with broader multigene testing would likely outweigh the benefits.
Present guidelines, such as those provided by the National Comprehensive Cancer Network, already include effective strategies for detecting BRCA1/2 variants, as only 0.6% of patients who do not meet screening guidelines are estimated to test positive
Beyond BRCA1/2, the clinical relevance of pathogenic variants becomes dubious, as many genetic aberrations are not actionable. Furthermore, misinterpretation of unfamiliar results may increase risks of treatment decisions that might actually harm patients. While some argue that broader testing could have benefits for family members, this is poorly supported with evidence.
Behind the allegedly falling costs of genetic sequencing, true costs are hidden with corporate policies that reduce patient financial liability. It is worth noting that two publicly held testing companies recently reported annual revenues of $144 million and $498 million, representing money drawn largely from third-party payers covering guideline-recommended testing. Instead of concrete science, the popularity of multigene testing is more likely driven by active marketing and technological convenience. More independent studies are needed.
Mark Robson, MD, is with the department of breast cancer medicine and clinical genetics at Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center in New York. Susan Domchek, MD is with the Basser Center for BRCA at the University of Pennsylvania in Philadelphia. Dr. Robson disclosed financial relationships with AstraZeneca, McKesson, and Pfizer. Dr. Domchek reported personal fees from Clovis, AstraZeneca, and BMS. Their remarks are adapted from an editorial (JAMA Oncol. 2019 Oct 3. doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2019.4004).
Although detection of more pathogenic variants among patients with breast cancer may initially appear beneficial, the hidden risks and costs associated with broader multigene testing would likely outweigh the benefits.
Present guidelines, such as those provided by the National Comprehensive Cancer Network, already include effective strategies for detecting BRCA1/2 variants, as only 0.6% of patients who do not meet screening guidelines are estimated to test positive
Beyond BRCA1/2, the clinical relevance of pathogenic variants becomes dubious, as many genetic aberrations are not actionable. Furthermore, misinterpretation of unfamiliar results may increase risks of treatment decisions that might actually harm patients. While some argue that broader testing could have benefits for family members, this is poorly supported with evidence.
Behind the allegedly falling costs of genetic sequencing, true costs are hidden with corporate policies that reduce patient financial liability. It is worth noting that two publicly held testing companies recently reported annual revenues of $144 million and $498 million, representing money drawn largely from third-party payers covering guideline-recommended testing. Instead of concrete science, the popularity of multigene testing is more likely driven by active marketing and technological convenience. More independent studies are needed.
Mark Robson, MD, is with the department of breast cancer medicine and clinical genetics at Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center in New York. Susan Domchek, MD is with the Basser Center for BRCA at the University of Pennsylvania in Philadelphia. Dr. Robson disclosed financial relationships with AstraZeneca, McKesson, and Pfizer. Dr. Domchek reported personal fees from Clovis, AstraZeneca, and BMS. Their remarks are adapted from an editorial (JAMA Oncol. 2019 Oct 3. doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2019.4004).
High-risk multigene testing for all patients with breast cancer may be a cost-effective way to reduce rates of breast cancer and ovarian cancer, according to investigators.
A microsimulation modeling study suggested that moving from standard BRCA testing based on clinical criteria or family history to widespread adoption of multigene testing could potentially save more than 2,400 lives per year in the United States, reported lead author Li Sun, MSc, of the London School of Hygiene & Tropical Medicine, and colleagues.
“Moving toward unselected BC testing may give an impetus for prevention in unaffected family members along with clinical implications for the patient with BC. Pathogenic variant carriers with newly diagnosed BC can opt for bilateral mastectomy rather than breast conservation at initial BC surgery,” the investigators wrote in JAMA Oncology. They noted that, presently, only 20%-30% of eligible patients are actually tested. “Testing all patients with breast cancer at diagnosis can increase testing access and uptake and identify many more pathogenic variant carriers for screening and prevention.”
To see if such a broad roll-out would be economically and medically feasible and beneficial, the investigators performed a modeling study involving 11,836 women with breast cancer, with data drawn from four large databases in the United Kingdom, the United States, and Australia.
The model compared annual costs, number of detected cases of breast cancer and ovarian cancer, and related rates of mortality between standard BRCA testing based on clinical criteria or family history versus high-risk multigene testing (BRCA1/BRCA2/PALB2) for all patients with breast cancer.
Resultant incremental cost-effectiveness ratios (ICERs) showed that in both the United Kingdom and the United States, multigene testing would cost, on average, significantly less than minimum willingness-to-pay thresholds of £30,000 per quality-adjusted life-year (QALY) and $100,000/QALY, respectively. In the United Kingdom, the estimated cost of multigene testing was £10,464/QALY from a payer’s perspective and £7,216/QALY from a societal perspective, the latter of which incorporates economic costs beyond the health care system. In the United States, these values rose to $65,661/QALY (payer perspective) and $61,618/QALY (societal perspective). Probabilistic sensitivity analysis suggested that multigene testing would be cost-effective for almost all health system simulations in the United Kingdom (98%-99%) and approximately two-thirds of those in the United States (64%-68%).
Epidemiologically, in the United Kingdom, multigene testing could potentially prevent 2,101 cases of breast cancer and ovarian cancer and 633 deaths per year, while in the United States, 9,733 cases might be prevented, with 2,406 lives saved.
“Our analysis suggests that an unselected testing strategy is extremely cost-effective for U.K. and U.S. health systems and provides a basis for change in current guidelines and policy to implement this strategy,” the investigators said.
The study was funded by the National Cancer Institute, the State of Washington, the Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center, and others. The investigators reported additional relationships with AstraZeneca, the Manchester National Institute for Health Research Biomedical Research Centre, Cancer Research UK, an others.
SOURCE: Sun et al. JAMA Oncol. 2019 Oct 3. doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2019.3323.
High-risk multigene testing for all patients with breast cancer may be a cost-effective way to reduce rates of breast cancer and ovarian cancer, according to investigators.
A microsimulation modeling study suggested that moving from standard BRCA testing based on clinical criteria or family history to widespread adoption of multigene testing could potentially save more than 2,400 lives per year in the United States, reported lead author Li Sun, MSc, of the London School of Hygiene & Tropical Medicine, and colleagues.
“Moving toward unselected BC testing may give an impetus for prevention in unaffected family members along with clinical implications for the patient with BC. Pathogenic variant carriers with newly diagnosed BC can opt for bilateral mastectomy rather than breast conservation at initial BC surgery,” the investigators wrote in JAMA Oncology. They noted that, presently, only 20%-30% of eligible patients are actually tested. “Testing all patients with breast cancer at diagnosis can increase testing access and uptake and identify many more pathogenic variant carriers for screening and prevention.”
To see if such a broad roll-out would be economically and medically feasible and beneficial, the investigators performed a modeling study involving 11,836 women with breast cancer, with data drawn from four large databases in the United Kingdom, the United States, and Australia.
The model compared annual costs, number of detected cases of breast cancer and ovarian cancer, and related rates of mortality between standard BRCA testing based on clinical criteria or family history versus high-risk multigene testing (BRCA1/BRCA2/PALB2) for all patients with breast cancer.
Resultant incremental cost-effectiveness ratios (ICERs) showed that in both the United Kingdom and the United States, multigene testing would cost, on average, significantly less than minimum willingness-to-pay thresholds of £30,000 per quality-adjusted life-year (QALY) and $100,000/QALY, respectively. In the United Kingdom, the estimated cost of multigene testing was £10,464/QALY from a payer’s perspective and £7,216/QALY from a societal perspective, the latter of which incorporates economic costs beyond the health care system. In the United States, these values rose to $65,661/QALY (payer perspective) and $61,618/QALY (societal perspective). Probabilistic sensitivity analysis suggested that multigene testing would be cost-effective for almost all health system simulations in the United Kingdom (98%-99%) and approximately two-thirds of those in the United States (64%-68%).
Epidemiologically, in the United Kingdom, multigene testing could potentially prevent 2,101 cases of breast cancer and ovarian cancer and 633 deaths per year, while in the United States, 9,733 cases might be prevented, with 2,406 lives saved.
“Our analysis suggests that an unselected testing strategy is extremely cost-effective for U.K. and U.S. health systems and provides a basis for change in current guidelines and policy to implement this strategy,” the investigators said.
The study was funded by the National Cancer Institute, the State of Washington, the Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center, and others. The investigators reported additional relationships with AstraZeneca, the Manchester National Institute for Health Research Biomedical Research Centre, Cancer Research UK, an others.
SOURCE: Sun et al. JAMA Oncol. 2019 Oct 3. doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2019.3323.
FROM JAMA ONCOLOGY
Ribociclib/fulvestrant boosts survival in advanced breast cancer
BARCELONA – In postmenopausal women with hormone receptor–positive, HER2-negative advanced breast cancer, the combination of ribociclib (Kisqali) and fulvestrant (Faslodex) was associated with a significant survival benefit, compared with fulvestrant alone, investigators reported.
Among 726 postmenopausal patients in MONALEESA-3 randomly assigned to receive either ribociclib or placebo plus fulvestrant who were followed for a median of 39.4 months, the median overall survival (OS) was not reached for patients assigned to ribociclib, compared with 40 months for patients in the control (fulvestrant-only) arm, reported Dennis J. Slamon, MD, PhD from the University of California, Los Angeles
“The combined data set of MONALEESA-3 and MONALEESA-7 represent some 1,400 patients, and the largest body of evidence for overall survival for any [cyclin-dependent kinases 4/6] inhibitor, and these data demonstrate a consistent, meaningful prolongation of survival irrespective of menopausal status, pre or post, and irrespective of whether the patient is treated in the first line or the second line,” he said at the European Society for Medical Oncology Congress.
Results of the MONALEESA-7 trial, which showed an overall survival advantage for adding ribociclib to endocrine therapy in premenopausal women with hormone receptor–positive, HER2-negative breast cancer, were reported at the 2019 annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology.
MONALEESA-3 investigators enrolled 726 postmenopausal women with hormone receptor–positive/HER2-negative advanced breast cancer who had received not more than one prior line of endocrine therapy for advanced disease, stratified them by the presence of liver and/or lung metastases and prior endocrine therapy, and then randomly assigned them to receive intramuscular fulvestrant 500 mg every 28 days, with an additional dose on day 15 of cycle one, plus either ribociclib 600 mg per day, 3 weeks on and 1 week off for every cycle, or placebo.
Dr. Slamon presented results of the primary endpoint of progression-free survival at the 2018 ASCO annual meeting, which showed a median PFS with ribociclib plus fulvestrant of 20.5 months versus 12.8 months for fulvestrant alone (hazard ratio, 5.93; P less than .0001). The overall survival data presented by Dr. Slamon at ESMO 2019 were not mature at that time.
As noted, at a median follow-up of 39.4 months, median overall survival was not reached in the combination arm, compared with 40 months in the fulvestrant/placebo arm, translating into a HR for risk of death with ribociclib of 0.724 (P = .00455).
Estimated OS rates at 36 months were 67% in the ribociclib arm versus 58.2% in the placebo arm, and at 42 months were 57.8% and 45.9%, respectively.
The survival benefit appeared consistent both for patients treated in the first line (median OS not reached vs. 45.1 months; HR, 0.70) and for those treated after early relapse of therapy for early breast or in the second line (median OS, 40.2 vs. 32.5 months, respectively; HR, 0.73). In both comparisons, however, the 95% confidence interval crossed 1, indicating that the results were not statistically significant.
An analysis of OS by subgroup indicated significant benefit or trends for most categories except Asian race, and treatment in Asia or Latin America, although the numbers of patients in each of those subgroups was less than 20, making it difficult to draw significant inferences from the findings, Dr. Slamon cautioned.
A descriptive analysis of updated PFS results were very similar to those previously reported, with a median of 20.6 months with ribociclib versus 12.8 months with placebo (HR, 0.587). Median PFS by line of therapy was 33.6 versus 19.2 months, respectively, in the first line, and 14.5 versus 9.1 months in the second line (HR, 0.546 and 0.571; P values not shown).
“CDK4/6 inhibitors not only improve progression-free survival in first- and second-line metastatic breast cancer, it also translates into an overall survival improvement. What more do we really want?” said invited discussant Sybil Loibl, MD, from Goethe University in Frankfurt, Germany.
“Outcome improves irrespective of pretreatment, menopausal status, endocrine sensitivity and site of metastases, which is good knowledge for our patients,” she said.
To date there are no biomarkers identified that can select subgroups that could experience particular benefit from CDK4/6 inhibitors. It may require a meta-analysis of all available clinical trial data on these agents in both the first and second line therapy to reveal potential differences among subgroups, she said.
MONALEESA-3 is supported by Novartis. Dr. Slamon disclosed a consulting or advisory role, research funding, honoraria, and travel expenses from Novartis and others. Dr. Loibl disclosed honoraria and research grants from Novartis and others.
SOURCE: Slamon DJ et al. ESMO 2019, Abstract LBA7_PR.
BARCELONA – In postmenopausal women with hormone receptor–positive, HER2-negative advanced breast cancer, the combination of ribociclib (Kisqali) and fulvestrant (Faslodex) was associated with a significant survival benefit, compared with fulvestrant alone, investigators reported.
Among 726 postmenopausal patients in MONALEESA-3 randomly assigned to receive either ribociclib or placebo plus fulvestrant who were followed for a median of 39.4 months, the median overall survival (OS) was not reached for patients assigned to ribociclib, compared with 40 months for patients in the control (fulvestrant-only) arm, reported Dennis J. Slamon, MD, PhD from the University of California, Los Angeles
“The combined data set of MONALEESA-3 and MONALEESA-7 represent some 1,400 patients, and the largest body of evidence for overall survival for any [cyclin-dependent kinases 4/6] inhibitor, and these data demonstrate a consistent, meaningful prolongation of survival irrespective of menopausal status, pre or post, and irrespective of whether the patient is treated in the first line or the second line,” he said at the European Society for Medical Oncology Congress.
Results of the MONALEESA-7 trial, which showed an overall survival advantage for adding ribociclib to endocrine therapy in premenopausal women with hormone receptor–positive, HER2-negative breast cancer, were reported at the 2019 annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology.
MONALEESA-3 investigators enrolled 726 postmenopausal women with hormone receptor–positive/HER2-negative advanced breast cancer who had received not more than one prior line of endocrine therapy for advanced disease, stratified them by the presence of liver and/or lung metastases and prior endocrine therapy, and then randomly assigned them to receive intramuscular fulvestrant 500 mg every 28 days, with an additional dose on day 15 of cycle one, plus either ribociclib 600 mg per day, 3 weeks on and 1 week off for every cycle, or placebo.
Dr. Slamon presented results of the primary endpoint of progression-free survival at the 2018 ASCO annual meeting, which showed a median PFS with ribociclib plus fulvestrant of 20.5 months versus 12.8 months for fulvestrant alone (hazard ratio, 5.93; P less than .0001). The overall survival data presented by Dr. Slamon at ESMO 2019 were not mature at that time.
As noted, at a median follow-up of 39.4 months, median overall survival was not reached in the combination arm, compared with 40 months in the fulvestrant/placebo arm, translating into a HR for risk of death with ribociclib of 0.724 (P = .00455).
Estimated OS rates at 36 months were 67% in the ribociclib arm versus 58.2% in the placebo arm, and at 42 months were 57.8% and 45.9%, respectively.
The survival benefit appeared consistent both for patients treated in the first line (median OS not reached vs. 45.1 months; HR, 0.70) and for those treated after early relapse of therapy for early breast or in the second line (median OS, 40.2 vs. 32.5 months, respectively; HR, 0.73). In both comparisons, however, the 95% confidence interval crossed 1, indicating that the results were not statistically significant.
An analysis of OS by subgroup indicated significant benefit or trends for most categories except Asian race, and treatment in Asia or Latin America, although the numbers of patients in each of those subgroups was less than 20, making it difficult to draw significant inferences from the findings, Dr. Slamon cautioned.
A descriptive analysis of updated PFS results were very similar to those previously reported, with a median of 20.6 months with ribociclib versus 12.8 months with placebo (HR, 0.587). Median PFS by line of therapy was 33.6 versus 19.2 months, respectively, in the first line, and 14.5 versus 9.1 months in the second line (HR, 0.546 and 0.571; P values not shown).
“CDK4/6 inhibitors not only improve progression-free survival in first- and second-line metastatic breast cancer, it also translates into an overall survival improvement. What more do we really want?” said invited discussant Sybil Loibl, MD, from Goethe University in Frankfurt, Germany.
“Outcome improves irrespective of pretreatment, menopausal status, endocrine sensitivity and site of metastases, which is good knowledge for our patients,” she said.
To date there are no biomarkers identified that can select subgroups that could experience particular benefit from CDK4/6 inhibitors. It may require a meta-analysis of all available clinical trial data on these agents in both the first and second line therapy to reveal potential differences among subgroups, she said.
MONALEESA-3 is supported by Novartis. Dr. Slamon disclosed a consulting or advisory role, research funding, honoraria, and travel expenses from Novartis and others. Dr. Loibl disclosed honoraria and research grants from Novartis and others.
SOURCE: Slamon DJ et al. ESMO 2019, Abstract LBA7_PR.
BARCELONA – In postmenopausal women with hormone receptor–positive, HER2-negative advanced breast cancer, the combination of ribociclib (Kisqali) and fulvestrant (Faslodex) was associated with a significant survival benefit, compared with fulvestrant alone, investigators reported.
Among 726 postmenopausal patients in MONALEESA-3 randomly assigned to receive either ribociclib or placebo plus fulvestrant who were followed for a median of 39.4 months, the median overall survival (OS) was not reached for patients assigned to ribociclib, compared with 40 months for patients in the control (fulvestrant-only) arm, reported Dennis J. Slamon, MD, PhD from the University of California, Los Angeles
“The combined data set of MONALEESA-3 and MONALEESA-7 represent some 1,400 patients, and the largest body of evidence for overall survival for any [cyclin-dependent kinases 4/6] inhibitor, and these data demonstrate a consistent, meaningful prolongation of survival irrespective of menopausal status, pre or post, and irrespective of whether the patient is treated in the first line or the second line,” he said at the European Society for Medical Oncology Congress.
Results of the MONALEESA-7 trial, which showed an overall survival advantage for adding ribociclib to endocrine therapy in premenopausal women with hormone receptor–positive, HER2-negative breast cancer, were reported at the 2019 annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology.
MONALEESA-3 investigators enrolled 726 postmenopausal women with hormone receptor–positive/HER2-negative advanced breast cancer who had received not more than one prior line of endocrine therapy for advanced disease, stratified them by the presence of liver and/or lung metastases and prior endocrine therapy, and then randomly assigned them to receive intramuscular fulvestrant 500 mg every 28 days, with an additional dose on day 15 of cycle one, plus either ribociclib 600 mg per day, 3 weeks on and 1 week off for every cycle, or placebo.
Dr. Slamon presented results of the primary endpoint of progression-free survival at the 2018 ASCO annual meeting, which showed a median PFS with ribociclib plus fulvestrant of 20.5 months versus 12.8 months for fulvestrant alone (hazard ratio, 5.93; P less than .0001). The overall survival data presented by Dr. Slamon at ESMO 2019 were not mature at that time.
As noted, at a median follow-up of 39.4 months, median overall survival was not reached in the combination arm, compared with 40 months in the fulvestrant/placebo arm, translating into a HR for risk of death with ribociclib of 0.724 (P = .00455).
Estimated OS rates at 36 months were 67% in the ribociclib arm versus 58.2% in the placebo arm, and at 42 months were 57.8% and 45.9%, respectively.
The survival benefit appeared consistent both for patients treated in the first line (median OS not reached vs. 45.1 months; HR, 0.70) and for those treated after early relapse of therapy for early breast or in the second line (median OS, 40.2 vs. 32.5 months, respectively; HR, 0.73). In both comparisons, however, the 95% confidence interval crossed 1, indicating that the results were not statistically significant.
An analysis of OS by subgroup indicated significant benefit or trends for most categories except Asian race, and treatment in Asia or Latin America, although the numbers of patients in each of those subgroups was less than 20, making it difficult to draw significant inferences from the findings, Dr. Slamon cautioned.
A descriptive analysis of updated PFS results were very similar to those previously reported, with a median of 20.6 months with ribociclib versus 12.8 months with placebo (HR, 0.587). Median PFS by line of therapy was 33.6 versus 19.2 months, respectively, in the first line, and 14.5 versus 9.1 months in the second line (HR, 0.546 and 0.571; P values not shown).
“CDK4/6 inhibitors not only improve progression-free survival in first- and second-line metastatic breast cancer, it also translates into an overall survival improvement. What more do we really want?” said invited discussant Sybil Loibl, MD, from Goethe University in Frankfurt, Germany.
“Outcome improves irrespective of pretreatment, menopausal status, endocrine sensitivity and site of metastases, which is good knowledge for our patients,” she said.
To date there are no biomarkers identified that can select subgroups that could experience particular benefit from CDK4/6 inhibitors. It may require a meta-analysis of all available clinical trial data on these agents in both the first and second line therapy to reveal potential differences among subgroups, she said.
MONALEESA-3 is supported by Novartis. Dr. Slamon disclosed a consulting or advisory role, research funding, honoraria, and travel expenses from Novartis and others. Dr. Loibl disclosed honoraria and research grants from Novartis and others.
SOURCE: Slamon DJ et al. ESMO 2019, Abstract LBA7_PR.
REPORTING FROM ESMO 2019
Cancer burden: Multiple metrics needed to clarify the big picture
A new analysis of 40 years of U.S. cancer data underscores the importance of looking at multiple metrics to discern the complex interplay of factors influencing cancer burden in the population. Findings showed that the epidemiologic signature – a composite of two or three key metrics – differed across cancer types and was favorable in some cases and unfavorable in others.
“Epidemiologic signatures that illustrate trends in population-based data on cancer burden provide insight into true cancer occurrence, overdiagnosis, and treatment advances,” explain the analysts, led by H. Gilbert Welch, MD, MPH, Center for Surgery and Public Health, Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston. “They are important indicators of the potential contribution of environmental exposures, primary preventive interventions, new treatments, and changing diagnostic and screening practices.”
Dr. Welch and colleagues analyzed data for the years 1975 through 2015, assessing juxtaposed trends in incidence, mortality, and, when available, metastatic incidence (cancer already metastatic at diagnosis) for 11 cancers individually and for all cancers combined. Incidence data combining invasive and in situ cancers were obtained from the original nine Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results (SEER) registries, and mortality data were obtained from the National Vital Statistics System.
The analysts then explored implications of the epidemiologic signatures as they pertain to true cancer occurrence (the underlying incidence of clinically meaningful cancer), overdiagnosis (detection of cancers that will not cause symptoms or death), and treatment advances.
Individual cancers
Findings of the analysis, published in a special report in the New England Journal of Medicine, revealed three broad categories of epidemiologic signatures having different implications for the public health and oncology fields.
Desirable signatures showed, for example, declining mortality against a backdrop of stable incidence over the 40-year period, signaling improved treatment, as seen for chronic myeloid leukemia following introduction of imatinib (Gleevec), according to the analysts. Lung cancer incidence and mortality rose and fell in tandem, reflecting an increase in smoking followed by a decrease in response to prevention efforts. Stomach, cervical, and colorectal cancers had both falling incidence – likely reflecting a true decline in occurrence related to prevention and/or screening detection and subsequent treatment of precancerous lesions – and falling mortality.
Undesirable signatures showed a rising incidence juxtaposed with stable mortality and stable or rising metastatic incidence, signaling likely overdiagnosis, Dr. Welch and colleagues proposed. Three cancers—thyroid cancer, kidney cancer, and melanoma—fell into this category; for thyroid cancer and melanoma, fairly recent upticks in metastatic incidence may reflect upstaging.
Finally, some signatures showed mixed signals, with rising incidence and falling mortality. Breast cancer incidence rose and stabilized, coinciding with introduction of screening mammography, and possibly reflecting an increase in true cancer occurrence or overdiagnosis (with stable metastatic incidence favoring the latter), the analysts speculate. Declining mortality since the 1990s may be due to improved treatment or screening, or both. Prostate cancer incidence rose sharply with introduction of prostate-specific antigen screening but then fell to initial levels, suggesting sensitivity of this cancer to diagnostic scrutiny. Falling metastatic incidence indicates screening leads to earlier diagnosis in some cases, while declining mortality starting in the 1990s may again reflect improved treatment or screening, or both.
All cancers
The epidemiologic signature for all cancers combined differed somewhat by sex. Women had a rising incidence during the 1980s that was mainly driven by lung and breast cancers, according to Dr. Welch and colleagues; a continued rise since the mid-1990s was largely driven by melanoma, kidney cancer, and thyroid cancer. Declining mortality since 1990 has been primarily due to reductions in deaths from breast and colorectal cancers, and, more recently, lung cancer.
Men had a “volatile pattern” in the incidence of all cancers combined that was attributable to prostate cancer trends; drops in lung and colorectal cancer incidences were offset by rises in melanoma and kidney cancer incidences, the analysts proposed. Declining mortality since 1990 was more marked than that among women and reflects a longer period of decline in lung cancer mortality, plus reductions in deaths from prostate cancer and colorectal cancer.
“Falling mortality means that there has been real progress against cancer in the past 40 years – largely reflecting improved treatment and the decline of a uniquely powerful causal factor: cigarette smoking,” Dr. Welch and colleagues noted. “The lack of an accompanying fall in incidence is an unfortunate side effect of early cancer-detection efforts.”
Dr. Welch reported that he had no relevant disclosures. The analysis did not receive any specific funding.
SOURCE: Welch HG et al. N Engl J Med. 2019;381:1378-86. doi: 10.1056/NEJMsr1905447.
A new analysis of 40 years of U.S. cancer data underscores the importance of looking at multiple metrics to discern the complex interplay of factors influencing cancer burden in the population. Findings showed that the epidemiologic signature – a composite of two or three key metrics – differed across cancer types and was favorable in some cases and unfavorable in others.
“Epidemiologic signatures that illustrate trends in population-based data on cancer burden provide insight into true cancer occurrence, overdiagnosis, and treatment advances,” explain the analysts, led by H. Gilbert Welch, MD, MPH, Center for Surgery and Public Health, Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston. “They are important indicators of the potential contribution of environmental exposures, primary preventive interventions, new treatments, and changing diagnostic and screening practices.”
Dr. Welch and colleagues analyzed data for the years 1975 through 2015, assessing juxtaposed trends in incidence, mortality, and, when available, metastatic incidence (cancer already metastatic at diagnosis) for 11 cancers individually and for all cancers combined. Incidence data combining invasive and in situ cancers were obtained from the original nine Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results (SEER) registries, and mortality data were obtained from the National Vital Statistics System.
The analysts then explored implications of the epidemiologic signatures as they pertain to true cancer occurrence (the underlying incidence of clinically meaningful cancer), overdiagnosis (detection of cancers that will not cause symptoms or death), and treatment advances.
Individual cancers
Findings of the analysis, published in a special report in the New England Journal of Medicine, revealed three broad categories of epidemiologic signatures having different implications for the public health and oncology fields.
Desirable signatures showed, for example, declining mortality against a backdrop of stable incidence over the 40-year period, signaling improved treatment, as seen for chronic myeloid leukemia following introduction of imatinib (Gleevec), according to the analysts. Lung cancer incidence and mortality rose and fell in tandem, reflecting an increase in smoking followed by a decrease in response to prevention efforts. Stomach, cervical, and colorectal cancers had both falling incidence – likely reflecting a true decline in occurrence related to prevention and/or screening detection and subsequent treatment of precancerous lesions – and falling mortality.
Undesirable signatures showed a rising incidence juxtaposed with stable mortality and stable or rising metastatic incidence, signaling likely overdiagnosis, Dr. Welch and colleagues proposed. Three cancers—thyroid cancer, kidney cancer, and melanoma—fell into this category; for thyroid cancer and melanoma, fairly recent upticks in metastatic incidence may reflect upstaging.
Finally, some signatures showed mixed signals, with rising incidence and falling mortality. Breast cancer incidence rose and stabilized, coinciding with introduction of screening mammography, and possibly reflecting an increase in true cancer occurrence or overdiagnosis (with stable metastatic incidence favoring the latter), the analysts speculate. Declining mortality since the 1990s may be due to improved treatment or screening, or both. Prostate cancer incidence rose sharply with introduction of prostate-specific antigen screening but then fell to initial levels, suggesting sensitivity of this cancer to diagnostic scrutiny. Falling metastatic incidence indicates screening leads to earlier diagnosis in some cases, while declining mortality starting in the 1990s may again reflect improved treatment or screening, or both.
All cancers
The epidemiologic signature for all cancers combined differed somewhat by sex. Women had a rising incidence during the 1980s that was mainly driven by lung and breast cancers, according to Dr. Welch and colleagues; a continued rise since the mid-1990s was largely driven by melanoma, kidney cancer, and thyroid cancer. Declining mortality since 1990 has been primarily due to reductions in deaths from breast and colorectal cancers, and, more recently, lung cancer.
Men had a “volatile pattern” in the incidence of all cancers combined that was attributable to prostate cancer trends; drops in lung and colorectal cancer incidences were offset by rises in melanoma and kidney cancer incidences, the analysts proposed. Declining mortality since 1990 was more marked than that among women and reflects a longer period of decline in lung cancer mortality, plus reductions in deaths from prostate cancer and colorectal cancer.
“Falling mortality means that there has been real progress against cancer in the past 40 years – largely reflecting improved treatment and the decline of a uniquely powerful causal factor: cigarette smoking,” Dr. Welch and colleagues noted. “The lack of an accompanying fall in incidence is an unfortunate side effect of early cancer-detection efforts.”
Dr. Welch reported that he had no relevant disclosures. The analysis did not receive any specific funding.
SOURCE: Welch HG et al. N Engl J Med. 2019;381:1378-86. doi: 10.1056/NEJMsr1905447.
A new analysis of 40 years of U.S. cancer data underscores the importance of looking at multiple metrics to discern the complex interplay of factors influencing cancer burden in the population. Findings showed that the epidemiologic signature – a composite of two or three key metrics – differed across cancer types and was favorable in some cases and unfavorable in others.
“Epidemiologic signatures that illustrate trends in population-based data on cancer burden provide insight into true cancer occurrence, overdiagnosis, and treatment advances,” explain the analysts, led by H. Gilbert Welch, MD, MPH, Center for Surgery and Public Health, Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston. “They are important indicators of the potential contribution of environmental exposures, primary preventive interventions, new treatments, and changing diagnostic and screening practices.”
Dr. Welch and colleagues analyzed data for the years 1975 through 2015, assessing juxtaposed trends in incidence, mortality, and, when available, metastatic incidence (cancer already metastatic at diagnosis) for 11 cancers individually and for all cancers combined. Incidence data combining invasive and in situ cancers were obtained from the original nine Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results (SEER) registries, and mortality data were obtained from the National Vital Statistics System.
The analysts then explored implications of the epidemiologic signatures as they pertain to true cancer occurrence (the underlying incidence of clinically meaningful cancer), overdiagnosis (detection of cancers that will not cause symptoms or death), and treatment advances.
Individual cancers
Findings of the analysis, published in a special report in the New England Journal of Medicine, revealed three broad categories of epidemiologic signatures having different implications for the public health and oncology fields.
Desirable signatures showed, for example, declining mortality against a backdrop of stable incidence over the 40-year period, signaling improved treatment, as seen for chronic myeloid leukemia following introduction of imatinib (Gleevec), according to the analysts. Lung cancer incidence and mortality rose and fell in tandem, reflecting an increase in smoking followed by a decrease in response to prevention efforts. Stomach, cervical, and colorectal cancers had both falling incidence – likely reflecting a true decline in occurrence related to prevention and/or screening detection and subsequent treatment of precancerous lesions – and falling mortality.
Undesirable signatures showed a rising incidence juxtaposed with stable mortality and stable or rising metastatic incidence, signaling likely overdiagnosis, Dr. Welch and colleagues proposed. Three cancers—thyroid cancer, kidney cancer, and melanoma—fell into this category; for thyroid cancer and melanoma, fairly recent upticks in metastatic incidence may reflect upstaging.
Finally, some signatures showed mixed signals, with rising incidence and falling mortality. Breast cancer incidence rose and stabilized, coinciding with introduction of screening mammography, and possibly reflecting an increase in true cancer occurrence or overdiagnosis (with stable metastatic incidence favoring the latter), the analysts speculate. Declining mortality since the 1990s may be due to improved treatment or screening, or both. Prostate cancer incidence rose sharply with introduction of prostate-specific antigen screening but then fell to initial levels, suggesting sensitivity of this cancer to diagnostic scrutiny. Falling metastatic incidence indicates screening leads to earlier diagnosis in some cases, while declining mortality starting in the 1990s may again reflect improved treatment or screening, or both.
All cancers
The epidemiologic signature for all cancers combined differed somewhat by sex. Women had a rising incidence during the 1980s that was mainly driven by lung and breast cancers, according to Dr. Welch and colleagues; a continued rise since the mid-1990s was largely driven by melanoma, kidney cancer, and thyroid cancer. Declining mortality since 1990 has been primarily due to reductions in deaths from breast and colorectal cancers, and, more recently, lung cancer.
Men had a “volatile pattern” in the incidence of all cancers combined that was attributable to prostate cancer trends; drops in lung and colorectal cancer incidences were offset by rises in melanoma and kidney cancer incidences, the analysts proposed. Declining mortality since 1990 was more marked than that among women and reflects a longer period of decline in lung cancer mortality, plus reductions in deaths from prostate cancer and colorectal cancer.
“Falling mortality means that there has been real progress against cancer in the past 40 years – largely reflecting improved treatment and the decline of a uniquely powerful causal factor: cigarette smoking,” Dr. Welch and colleagues noted. “The lack of an accompanying fall in incidence is an unfortunate side effect of early cancer-detection efforts.”
Dr. Welch reported that he had no relevant disclosures. The analysis did not receive any specific funding.
SOURCE: Welch HG et al. N Engl J Med. 2019;381:1378-86. doi: 10.1056/NEJMsr1905447.
FROM NEW ENGLAND JOURNAL OF MEDICINE











