User login
Sex differences in COPD symptoms predict cardiac comorbidity
Sex-specific differences in the severity of symptoms and prevalence of comorbidities in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) may point to different criteria for diagnosing cardiac comorbidities in women and men, a retrospective analysis suggests.
Among 2,046 patients in the German COSYCONET (COPD and Systemic Consequences–Comorbidities Net) cohort, most functional parameters and comorbidities and several items on the COPD Assessment Test (CAT) differed significantly between men and women.
In addition, there were sex-specific differences in the association between symptoms and cardiac disease, Franziska C. Trudzinski, MD, from the University of Heidelberg (Germany), and colleagues reported.
(Note: Although the authors used the term “gender” to distinguish male from female, this news organization has used the term “sex” in this article to refer to biological attributes of individual patients rather than personal identity.)
“[Sex]-specific differences in COPD comprised not only differences in the level of symptoms, comorbidities, and functional alterations but also differences in their mutual relationships. This was reflected in different sets of predictors for cardiac disease,” they wrote in a thematic poster presented at the American Thoracic Society’s virtual international conference.
GOLD standard
The investigators conducted an analysis of data on 795 women and 1,251 men with GOLD (Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease) class 1-3 disease from the COSYCONET COPD cohort.
They looked at the patients’ clinical history, comorbidities, lung function, CAT scores, and modified Medical Research Council (mMRC) dyspnea score.
The authors used multivariate regression analysis to model potential sex-related differences in the relationship between symptoms in general and CAT items in particular, and the pattern of comorbidities and functional alterations.
They also performed logistic regression analyses to identify predictors for cardiac disease, defined as myocardial infarction, heart failure, or coronary artery disease. The analyses were controlled for age, body mass index (BMI), smoking status, mMRC, CAT items, and z scores of forced expiratory volume in 1 second/forced vital capacity ratio.
and for CAT items of cough (item 1), phlegm (item 2), and energy (item 8; P < .05 for all comparisons).
In logistic regression analysis, predictors for cardiac disease in men were energy (CAT item 8), mMRC score, smoking status, BMI, age, and spirometric lung function.
In women, however, only age was significantly predictive for cardiac disease.
“Our findings give hints how diagnostic information might be used differently in men and women,” Dr. Trudzinski and colleagues wrote.
Reassuring data
David Mannino, MD, medical director of the COPD Foundation, who was not involved in the study, said in an interview that sex differences in COPD presentation and severity are common.
“In general, men and women report symptoms differently. For example, women don’t report a whole lot of chronic bronchitis and phlegm, although they may have it,” he said, “whereas men may report less dyspnea. It varies, but in general we know that men and women, even with the same type of disease, report symptoms differently.”
Comorbidities also differ between the sexes, he noted. Women more frequently have osteoporosis, and men more frequently have heart disease, as borne out in the study. The prevalence of heart disease among patients in the study was approximately 2.5 times higher in men than women.
“It’s reassuring, because what we’re seeing is similar to what we’ve seen in other [studies] with regards to comorbidities,” he said.
The study was sponsored by Philipps University Marburg Medical Center, Germany. The authors and Dr. Mannino have reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of the article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Sex-specific differences in the severity of symptoms and prevalence of comorbidities in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) may point to different criteria for diagnosing cardiac comorbidities in women and men, a retrospective analysis suggests.
Among 2,046 patients in the German COSYCONET (COPD and Systemic Consequences–Comorbidities Net) cohort, most functional parameters and comorbidities and several items on the COPD Assessment Test (CAT) differed significantly between men and women.
In addition, there were sex-specific differences in the association between symptoms and cardiac disease, Franziska C. Trudzinski, MD, from the University of Heidelberg (Germany), and colleagues reported.
(Note: Although the authors used the term “gender” to distinguish male from female, this news organization has used the term “sex” in this article to refer to biological attributes of individual patients rather than personal identity.)
“[Sex]-specific differences in COPD comprised not only differences in the level of symptoms, comorbidities, and functional alterations but also differences in their mutual relationships. This was reflected in different sets of predictors for cardiac disease,” they wrote in a thematic poster presented at the American Thoracic Society’s virtual international conference.
GOLD standard
The investigators conducted an analysis of data on 795 women and 1,251 men with GOLD (Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease) class 1-3 disease from the COSYCONET COPD cohort.
They looked at the patients’ clinical history, comorbidities, lung function, CAT scores, and modified Medical Research Council (mMRC) dyspnea score.
The authors used multivariate regression analysis to model potential sex-related differences in the relationship between symptoms in general and CAT items in particular, and the pattern of comorbidities and functional alterations.
They also performed logistic regression analyses to identify predictors for cardiac disease, defined as myocardial infarction, heart failure, or coronary artery disease. The analyses were controlled for age, body mass index (BMI), smoking status, mMRC, CAT items, and z scores of forced expiratory volume in 1 second/forced vital capacity ratio.
and for CAT items of cough (item 1), phlegm (item 2), and energy (item 8; P < .05 for all comparisons).
In logistic regression analysis, predictors for cardiac disease in men were energy (CAT item 8), mMRC score, smoking status, BMI, age, and spirometric lung function.
In women, however, only age was significantly predictive for cardiac disease.
“Our findings give hints how diagnostic information might be used differently in men and women,” Dr. Trudzinski and colleagues wrote.
Reassuring data
David Mannino, MD, medical director of the COPD Foundation, who was not involved in the study, said in an interview that sex differences in COPD presentation and severity are common.
“In general, men and women report symptoms differently. For example, women don’t report a whole lot of chronic bronchitis and phlegm, although they may have it,” he said, “whereas men may report less dyspnea. It varies, but in general we know that men and women, even with the same type of disease, report symptoms differently.”
Comorbidities also differ between the sexes, he noted. Women more frequently have osteoporosis, and men more frequently have heart disease, as borne out in the study. The prevalence of heart disease among patients in the study was approximately 2.5 times higher in men than women.
“It’s reassuring, because what we’re seeing is similar to what we’ve seen in other [studies] with regards to comorbidities,” he said.
The study was sponsored by Philipps University Marburg Medical Center, Germany. The authors and Dr. Mannino have reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of the article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Sex-specific differences in the severity of symptoms and prevalence of comorbidities in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) may point to different criteria for diagnosing cardiac comorbidities in women and men, a retrospective analysis suggests.
Among 2,046 patients in the German COSYCONET (COPD and Systemic Consequences–Comorbidities Net) cohort, most functional parameters and comorbidities and several items on the COPD Assessment Test (CAT) differed significantly between men and women.
In addition, there were sex-specific differences in the association between symptoms and cardiac disease, Franziska C. Trudzinski, MD, from the University of Heidelberg (Germany), and colleagues reported.
(Note: Although the authors used the term “gender” to distinguish male from female, this news organization has used the term “sex” in this article to refer to biological attributes of individual patients rather than personal identity.)
“[Sex]-specific differences in COPD comprised not only differences in the level of symptoms, comorbidities, and functional alterations but also differences in their mutual relationships. This was reflected in different sets of predictors for cardiac disease,” they wrote in a thematic poster presented at the American Thoracic Society’s virtual international conference.
GOLD standard
The investigators conducted an analysis of data on 795 women and 1,251 men with GOLD (Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease) class 1-3 disease from the COSYCONET COPD cohort.
They looked at the patients’ clinical history, comorbidities, lung function, CAT scores, and modified Medical Research Council (mMRC) dyspnea score.
The authors used multivariate regression analysis to model potential sex-related differences in the relationship between symptoms in general and CAT items in particular, and the pattern of comorbidities and functional alterations.
They also performed logistic regression analyses to identify predictors for cardiac disease, defined as myocardial infarction, heart failure, or coronary artery disease. The analyses were controlled for age, body mass index (BMI), smoking status, mMRC, CAT items, and z scores of forced expiratory volume in 1 second/forced vital capacity ratio.
and for CAT items of cough (item 1), phlegm (item 2), and energy (item 8; P < .05 for all comparisons).
In logistic regression analysis, predictors for cardiac disease in men were energy (CAT item 8), mMRC score, smoking status, BMI, age, and spirometric lung function.
In women, however, only age was significantly predictive for cardiac disease.
“Our findings give hints how diagnostic information might be used differently in men and women,” Dr. Trudzinski and colleagues wrote.
Reassuring data
David Mannino, MD, medical director of the COPD Foundation, who was not involved in the study, said in an interview that sex differences in COPD presentation and severity are common.
“In general, men and women report symptoms differently. For example, women don’t report a whole lot of chronic bronchitis and phlegm, although they may have it,” he said, “whereas men may report less dyspnea. It varies, but in general we know that men and women, even with the same type of disease, report symptoms differently.”
Comorbidities also differ between the sexes, he noted. Women more frequently have osteoporosis, and men more frequently have heart disease, as borne out in the study. The prevalence of heart disease among patients in the study was approximately 2.5 times higher in men than women.
“It’s reassuring, because what we’re seeing is similar to what we’ve seen in other [studies] with regards to comorbidities,” he said.
The study was sponsored by Philipps University Marburg Medical Center, Germany. The authors and Dr. Mannino have reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of the article first appeared on Medscape.com.
AHA/ACC guidance on ethics, professionalism in cardiovascular care
The American Heart Association and the American College of Cardiology have issued a new report on medical ethics and professionalism in cardiovascular medicine.
The report addresses a variety of topics including diversity, equity, inclusion, and belonging; racial, ethnic and gender inequities; conflicts of interest; clinician well-being; data privacy; social justice; and modern health care delivery systems.
The 54-page report is based on the proceedings of the joint 2020 Consensus Conference on Professionalism and Ethics, held Oct. 19 and 20, 2020. It was published online May 11 in Circulation and the Journal of the American College of Cardiology .
The 2020 consensus conference on professionalism and ethics came at a time even more fraught than the eras of the three previous meetings on the same topics, held in 1989, 1997, and 2004, the writing group notes.
“We have seen the COVID-19 pandemic challenge the physical and economic health of the entire country, coupled with a series of national tragedies that have awakened the call for social justice,” conference cochair C. Michael Valentine, MD, said in a news release.
“There is no better time than now to review, evaluate, and take a fresh perspective on medical ethics and professionalism,” said Dr. Valentine, professor of medicine at the Heart and Vascular Center, University of Virginia, Charlottesville.
“We hope this report will provide cardiovascular professionals and health systems with the recommendations and tools they need to address conflicts of interest; racial, ethnic, and gender inequities; and improve diversity, inclusion, and wellness among our workforce,” Dr. Valentine added. “The majority of our members are now employed and must be engaged as the leaders for change in cardiovascular care.”
Road map to improve diversity, achieve allyship
The writing committee was made up of a diverse group of cardiologists, internists, and associated health care professionals and laypeople and was organized into five task forces, each addressing a specific topic: conflicts of interest; diversity, equity, inclusion, and belonging; clinician well-being; patient autonomy, privacy, and social justice in health care; and modern health care delivery.
The report serves as a road map to achieve equity, inclusion, and belonging among cardiovascular professionals and calls for ongoing assessment of the professional culture and climate, focused on improving diversity and achieving effective allyship, the writing group says.
The report proposes continuous training to address individual, structural, and systemic racism, sexism, homophobia, classism, and ableism.
It offers recommendations for championing equity in patient care that include an annual review of practice records to look for differences in patient treatment by race, ethnicity, zip code, and primary language.
The report calls for a foundation of training in allyship and antiracism as part of medical school course requirements and experiences: A required course on social justice, race, and racism as part of the first-year curriculum; school programs and professional organizations supporting students, trainees, and members in allyship and antiracism action; and facilitating immersion and partnership with surrounding communities.
“As much as 80% of a person’s health is determined by the social and economic conditions of their environment,” consensus cochair Ivor Benjamin, MD, said in the release.
“To achieve social justice and mitigate health disparities, we must go to the margins and shift our discussions to be inclusive of populations such as rural and marginalized groups from the perspective of health equity lens for all,” said Dr. Benjamin, professor of medicine, Medical College of Wisconsin, Milwaukee.
The report also highlights the need for psychosocial support of the cardiovascular community and recommends that health care organizations prioritize regular assessment of clinicians’ well-being and engagement.
It also recommends addressing the well-being of trainees in postgraduate training programs and calls for an ombudsman program that allows for confidential reporting of mistreatment and access to support.
The report also highlights additional opportunities to:
- improve the efficiency of health information technology, such as electronic health records, and reduce the administrative burden
- identify and assist clinicians who experience mental health conditions, , or
- emphasize patient autonomy using shared decision-making and patient-centered care that is supportive of the individual patient’s values
- increase privacy protections for patient data used in research
- maintain integrity as new ways of delivering care, such as telemedicine, team-based care approaches, and physician-owned specialty centers emerge
- perform routine audits of electronic health records to promote optimal patient care, as well as ethical medical practice
- expand and make mandatory the reporting of intellectual or associational interests in addition to relationships with industry
The report’s details and recommendations will be presented and discussed Saturday, May 15, at 8:00 AM ET, during ACC.21. The session is titled Diversity and Equity: The Means to Expand Inclusion and Belonging.
The AHA will present a live webinar and six-episode podcast series (available on demand) to highlight the report’s details, dialogue, and actionable steps for cardiovascular and health care professionals, researchers, and educators.
This research had no commercial funding. The list of 40 volunteer committee members and coauthors, including their disclosures, are listed in the original report.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The American Heart Association and the American College of Cardiology have issued a new report on medical ethics and professionalism in cardiovascular medicine.
The report addresses a variety of topics including diversity, equity, inclusion, and belonging; racial, ethnic and gender inequities; conflicts of interest; clinician well-being; data privacy; social justice; and modern health care delivery systems.
The 54-page report is based on the proceedings of the joint 2020 Consensus Conference on Professionalism and Ethics, held Oct. 19 and 20, 2020. It was published online May 11 in Circulation and the Journal of the American College of Cardiology .
The 2020 consensus conference on professionalism and ethics came at a time even more fraught than the eras of the three previous meetings on the same topics, held in 1989, 1997, and 2004, the writing group notes.
“We have seen the COVID-19 pandemic challenge the physical and economic health of the entire country, coupled with a series of national tragedies that have awakened the call for social justice,” conference cochair C. Michael Valentine, MD, said in a news release.
“There is no better time than now to review, evaluate, and take a fresh perspective on medical ethics and professionalism,” said Dr. Valentine, professor of medicine at the Heart and Vascular Center, University of Virginia, Charlottesville.
“We hope this report will provide cardiovascular professionals and health systems with the recommendations and tools they need to address conflicts of interest; racial, ethnic, and gender inequities; and improve diversity, inclusion, and wellness among our workforce,” Dr. Valentine added. “The majority of our members are now employed and must be engaged as the leaders for change in cardiovascular care.”
Road map to improve diversity, achieve allyship
The writing committee was made up of a diverse group of cardiologists, internists, and associated health care professionals and laypeople and was organized into five task forces, each addressing a specific topic: conflicts of interest; diversity, equity, inclusion, and belonging; clinician well-being; patient autonomy, privacy, and social justice in health care; and modern health care delivery.
The report serves as a road map to achieve equity, inclusion, and belonging among cardiovascular professionals and calls for ongoing assessment of the professional culture and climate, focused on improving diversity and achieving effective allyship, the writing group says.
The report proposes continuous training to address individual, structural, and systemic racism, sexism, homophobia, classism, and ableism.
It offers recommendations for championing equity in patient care that include an annual review of practice records to look for differences in patient treatment by race, ethnicity, zip code, and primary language.
The report calls for a foundation of training in allyship and antiracism as part of medical school course requirements and experiences: A required course on social justice, race, and racism as part of the first-year curriculum; school programs and professional organizations supporting students, trainees, and members in allyship and antiracism action; and facilitating immersion and partnership with surrounding communities.
“As much as 80% of a person’s health is determined by the social and economic conditions of their environment,” consensus cochair Ivor Benjamin, MD, said in the release.
“To achieve social justice and mitigate health disparities, we must go to the margins and shift our discussions to be inclusive of populations such as rural and marginalized groups from the perspective of health equity lens for all,” said Dr. Benjamin, professor of medicine, Medical College of Wisconsin, Milwaukee.
The report also highlights the need for psychosocial support of the cardiovascular community and recommends that health care organizations prioritize regular assessment of clinicians’ well-being and engagement.
It also recommends addressing the well-being of trainees in postgraduate training programs and calls for an ombudsman program that allows for confidential reporting of mistreatment and access to support.
The report also highlights additional opportunities to:
- improve the efficiency of health information technology, such as electronic health records, and reduce the administrative burden
- identify and assist clinicians who experience mental health conditions, , or
- emphasize patient autonomy using shared decision-making and patient-centered care that is supportive of the individual patient’s values
- increase privacy protections for patient data used in research
- maintain integrity as new ways of delivering care, such as telemedicine, team-based care approaches, and physician-owned specialty centers emerge
- perform routine audits of electronic health records to promote optimal patient care, as well as ethical medical practice
- expand and make mandatory the reporting of intellectual or associational interests in addition to relationships with industry
The report’s details and recommendations will be presented and discussed Saturday, May 15, at 8:00 AM ET, during ACC.21. The session is titled Diversity and Equity: The Means to Expand Inclusion and Belonging.
The AHA will present a live webinar and six-episode podcast series (available on demand) to highlight the report’s details, dialogue, and actionable steps for cardiovascular and health care professionals, researchers, and educators.
This research had no commercial funding. The list of 40 volunteer committee members and coauthors, including their disclosures, are listed in the original report.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The American Heart Association and the American College of Cardiology have issued a new report on medical ethics and professionalism in cardiovascular medicine.
The report addresses a variety of topics including diversity, equity, inclusion, and belonging; racial, ethnic and gender inequities; conflicts of interest; clinician well-being; data privacy; social justice; and modern health care delivery systems.
The 54-page report is based on the proceedings of the joint 2020 Consensus Conference on Professionalism and Ethics, held Oct. 19 and 20, 2020. It was published online May 11 in Circulation and the Journal of the American College of Cardiology .
The 2020 consensus conference on professionalism and ethics came at a time even more fraught than the eras of the three previous meetings on the same topics, held in 1989, 1997, and 2004, the writing group notes.
“We have seen the COVID-19 pandemic challenge the physical and economic health of the entire country, coupled with a series of national tragedies that have awakened the call for social justice,” conference cochair C. Michael Valentine, MD, said in a news release.
“There is no better time than now to review, evaluate, and take a fresh perspective on medical ethics and professionalism,” said Dr. Valentine, professor of medicine at the Heart and Vascular Center, University of Virginia, Charlottesville.
“We hope this report will provide cardiovascular professionals and health systems with the recommendations and tools they need to address conflicts of interest; racial, ethnic, and gender inequities; and improve diversity, inclusion, and wellness among our workforce,” Dr. Valentine added. “The majority of our members are now employed and must be engaged as the leaders for change in cardiovascular care.”
Road map to improve diversity, achieve allyship
The writing committee was made up of a diverse group of cardiologists, internists, and associated health care professionals and laypeople and was organized into five task forces, each addressing a specific topic: conflicts of interest; diversity, equity, inclusion, and belonging; clinician well-being; patient autonomy, privacy, and social justice in health care; and modern health care delivery.
The report serves as a road map to achieve equity, inclusion, and belonging among cardiovascular professionals and calls for ongoing assessment of the professional culture and climate, focused on improving diversity and achieving effective allyship, the writing group says.
The report proposes continuous training to address individual, structural, and systemic racism, sexism, homophobia, classism, and ableism.
It offers recommendations for championing equity in patient care that include an annual review of practice records to look for differences in patient treatment by race, ethnicity, zip code, and primary language.
The report calls for a foundation of training in allyship and antiracism as part of medical school course requirements and experiences: A required course on social justice, race, and racism as part of the first-year curriculum; school programs and professional organizations supporting students, trainees, and members in allyship and antiracism action; and facilitating immersion and partnership with surrounding communities.
“As much as 80% of a person’s health is determined by the social and economic conditions of their environment,” consensus cochair Ivor Benjamin, MD, said in the release.
“To achieve social justice and mitigate health disparities, we must go to the margins and shift our discussions to be inclusive of populations such as rural and marginalized groups from the perspective of health equity lens for all,” said Dr. Benjamin, professor of medicine, Medical College of Wisconsin, Milwaukee.
The report also highlights the need for psychosocial support of the cardiovascular community and recommends that health care organizations prioritize regular assessment of clinicians’ well-being and engagement.
It also recommends addressing the well-being of trainees in postgraduate training programs and calls for an ombudsman program that allows for confidential reporting of mistreatment and access to support.
The report also highlights additional opportunities to:
- improve the efficiency of health information technology, such as electronic health records, and reduce the administrative burden
- identify and assist clinicians who experience mental health conditions, , or
- emphasize patient autonomy using shared decision-making and patient-centered care that is supportive of the individual patient’s values
- increase privacy protections for patient data used in research
- maintain integrity as new ways of delivering care, such as telemedicine, team-based care approaches, and physician-owned specialty centers emerge
- perform routine audits of electronic health records to promote optimal patient care, as well as ethical medical practice
- expand and make mandatory the reporting of intellectual or associational interests in addition to relationships with industry
The report’s details and recommendations will be presented and discussed Saturday, May 15, at 8:00 AM ET, during ACC.21. The session is titled Diversity and Equity: The Means to Expand Inclusion and Belonging.
The AHA will present a live webinar and six-episode podcast series (available on demand) to highlight the report’s details, dialogue, and actionable steps for cardiovascular and health care professionals, researchers, and educators.
This research had no commercial funding. The list of 40 volunteer committee members and coauthors, including their disclosures, are listed in the original report.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FIDELIO-DKD: Finerenone cuts new-onset AFib in patients with type 2 diabetes and CKD
Finerenone treatment of patients with type 2 diabetes and diabetic kidney disease was linked to a significant drop in the incidence of new-onset atrial fibrillation as a prespecified, exploratory endpoint of the FIDELIO-DKD pivotal trial that randomized more than 5,700 patients.
Treatment with finerenone linked with a 29% relative reduction compared with placebo in incident cases of atrial fibrillation (AFib), Gerasimos Filippatos, MD, reported at the annual scientific sessions of the American College of Cardiology.
The absolute reduction was modest, a 1.3% reduction from the 4.5% incidence rate on placebo to a 3.2% rate on finerenone during a median 2.6 years of follow-up. Concurrently with the report, the results appeared online (J Am Coll Cardiol. 2021 May 17. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2021.04.079).
The analyses Dr. Filippatos presented also showed that whether or not patients had a history of AFib, there was no impact on either the primary benefit from finerenone treatment seen in FIDELIO-DKD, which was a significant 18% relative risk reduction compared with placebo in the combined rate of kidney failure, a 40% or greater decline from baseline in estimated glomerular filtration rate, or renal death.
Likewise, prior AFib status had no effect on the study’s key secondary endpoint, a significant 14% relative risk reduction in the combined rate of cardiovascular death, nonfatal MI, nonfatal stroke, or hospitalization for heart failure.
The primary results from FIDELIO-DKD (Efficacy and Safety of Finerenone in Subjects With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Diabetic Kidney Disease) appeared in a 2020 report (N Engl J Med. 2020 Dec 3;383[23];2219-29).
‘Side benefits can be very helpful’
“It’s important to know of finerenone’s benefits beyond the primary outcome of a trial because side benefits can be very helpful,” said Anne B. Curtis, MD, an electrophysiologist and professor and chair of medicine at the University of Buffalo (N.Y.) School of Medicine and Biomedical Sciences. “It’s not a huge benefit, but this could be an added benefit for selected patients,” she said during a press briefing. “Background studies had shown favorable remodeling of the heart [by finerenone] that could affect AFib.”
Possible mitigating effects by finerenone on inflammation and fibrosis might also mediate the drug’s apparent effect on AFib, said Dr. Filippatos, professor of cardiology and director of the Heart Failure and Cardio-Oncology Clinic at Attikon University Hospital and the University of Athens.
He noted that additional data addressing a possible AFib effect of finerenone will emerge soon from the FIGARO-DKD trial, which enrolled patients similar to those in FIDELIO-DKD but with more moderate stages of kidney disease, and from the FINEARTS-HF trial, which is examining the effect of finerenone in patients with heart failure with an ejection fraction of at least 40%.
“Heart failure and AFib go together tightly. It’s worth studying this specifically, so we can see whether there is an impact of finerenone on patients with heart failure who may not necessarily have kidney disease or diabetes,” Dr. Curtis said.
Hypothesis-generating findings
The new findings reported by Dr. Filippatos “should be considered hypothesis generating. Until we have more information, upstream therapies, including mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists [MRAs, the umbrella drug class that includes finerenone], should be used in appropriate patient populations based on defined benefits with the hope they will also reduce the development of AFib and atrial flutter over time,” Gerald V. Naccarelli, MD, and coauthors wrote in an editorial that accompanied the report (J Am Coll Cardiol. 2021 May 17. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2021.04.080).
The FIDELIO-DKD trial randomized 5,734 patients at 913 sites in 48 countries, including 461 patients with a history of AFib. The observed link of finerenone treatment with a reduced incidence of AFib appeared consistent regardless of patients’ age, sex, race, their kidney characteristics at baseline, baseline levels of systolic blood pressure, serum potassium, body mass index, A1c, or use of glucose-lowering medications.
Finerenone belongs to a new class of MRAs that have a nonsteroidal structure, in contrast with the MRAs spironolactone and eplerenone. This means that finerenone does not produce steroidal-associated adverse effects linked with certain other MRAs, such as gynecomastia, and may also differ in other actions.
FIDELIO-DKD was sponsored by Bayer, the company developing finerenone. Dr. Filippatos has received lecture fees from or participated in the direction of trials on behalf of Bayer, as well as for Amgen, Boehringer Ingelheim, Medtronic, Novartis, Servier, and Vifor. Dr. Curtis is an adviser to and receives honoraria from St. Jude Medical, and receives honoraria from Medtronic. Dr. Naccarelli has been a consultant to Acesion, ARCA, GlaxoSmithKline, Janssen, Milestone, Omeicos, and Sanofi. His coauthors had no disclosures.
Finerenone treatment of patients with type 2 diabetes and diabetic kidney disease was linked to a significant drop in the incidence of new-onset atrial fibrillation as a prespecified, exploratory endpoint of the FIDELIO-DKD pivotal trial that randomized more than 5,700 patients.
Treatment with finerenone linked with a 29% relative reduction compared with placebo in incident cases of atrial fibrillation (AFib), Gerasimos Filippatos, MD, reported at the annual scientific sessions of the American College of Cardiology.
The absolute reduction was modest, a 1.3% reduction from the 4.5% incidence rate on placebo to a 3.2% rate on finerenone during a median 2.6 years of follow-up. Concurrently with the report, the results appeared online (J Am Coll Cardiol. 2021 May 17. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2021.04.079).
The analyses Dr. Filippatos presented also showed that whether or not patients had a history of AFib, there was no impact on either the primary benefit from finerenone treatment seen in FIDELIO-DKD, which was a significant 18% relative risk reduction compared with placebo in the combined rate of kidney failure, a 40% or greater decline from baseline in estimated glomerular filtration rate, or renal death.
Likewise, prior AFib status had no effect on the study’s key secondary endpoint, a significant 14% relative risk reduction in the combined rate of cardiovascular death, nonfatal MI, nonfatal stroke, or hospitalization for heart failure.
The primary results from FIDELIO-DKD (Efficacy and Safety of Finerenone in Subjects With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Diabetic Kidney Disease) appeared in a 2020 report (N Engl J Med. 2020 Dec 3;383[23];2219-29).
‘Side benefits can be very helpful’
“It’s important to know of finerenone’s benefits beyond the primary outcome of a trial because side benefits can be very helpful,” said Anne B. Curtis, MD, an electrophysiologist and professor and chair of medicine at the University of Buffalo (N.Y.) School of Medicine and Biomedical Sciences. “It’s not a huge benefit, but this could be an added benefit for selected patients,” she said during a press briefing. “Background studies had shown favorable remodeling of the heart [by finerenone] that could affect AFib.”
Possible mitigating effects by finerenone on inflammation and fibrosis might also mediate the drug’s apparent effect on AFib, said Dr. Filippatos, professor of cardiology and director of the Heart Failure and Cardio-Oncology Clinic at Attikon University Hospital and the University of Athens.
He noted that additional data addressing a possible AFib effect of finerenone will emerge soon from the FIGARO-DKD trial, which enrolled patients similar to those in FIDELIO-DKD but with more moderate stages of kidney disease, and from the FINEARTS-HF trial, which is examining the effect of finerenone in patients with heart failure with an ejection fraction of at least 40%.
“Heart failure and AFib go together tightly. It’s worth studying this specifically, so we can see whether there is an impact of finerenone on patients with heart failure who may not necessarily have kidney disease or diabetes,” Dr. Curtis said.
Hypothesis-generating findings
The new findings reported by Dr. Filippatos “should be considered hypothesis generating. Until we have more information, upstream therapies, including mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists [MRAs, the umbrella drug class that includes finerenone], should be used in appropriate patient populations based on defined benefits with the hope they will also reduce the development of AFib and atrial flutter over time,” Gerald V. Naccarelli, MD, and coauthors wrote in an editorial that accompanied the report (J Am Coll Cardiol. 2021 May 17. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2021.04.080).
The FIDELIO-DKD trial randomized 5,734 patients at 913 sites in 48 countries, including 461 patients with a history of AFib. The observed link of finerenone treatment with a reduced incidence of AFib appeared consistent regardless of patients’ age, sex, race, their kidney characteristics at baseline, baseline levels of systolic blood pressure, serum potassium, body mass index, A1c, or use of glucose-lowering medications.
Finerenone belongs to a new class of MRAs that have a nonsteroidal structure, in contrast with the MRAs spironolactone and eplerenone. This means that finerenone does not produce steroidal-associated adverse effects linked with certain other MRAs, such as gynecomastia, and may also differ in other actions.
FIDELIO-DKD was sponsored by Bayer, the company developing finerenone. Dr. Filippatos has received lecture fees from or participated in the direction of trials on behalf of Bayer, as well as for Amgen, Boehringer Ingelheim, Medtronic, Novartis, Servier, and Vifor. Dr. Curtis is an adviser to and receives honoraria from St. Jude Medical, and receives honoraria from Medtronic. Dr. Naccarelli has been a consultant to Acesion, ARCA, GlaxoSmithKline, Janssen, Milestone, Omeicos, and Sanofi. His coauthors had no disclosures.
Finerenone treatment of patients with type 2 diabetes and diabetic kidney disease was linked to a significant drop in the incidence of new-onset atrial fibrillation as a prespecified, exploratory endpoint of the FIDELIO-DKD pivotal trial that randomized more than 5,700 patients.
Treatment with finerenone linked with a 29% relative reduction compared with placebo in incident cases of atrial fibrillation (AFib), Gerasimos Filippatos, MD, reported at the annual scientific sessions of the American College of Cardiology.
The absolute reduction was modest, a 1.3% reduction from the 4.5% incidence rate on placebo to a 3.2% rate on finerenone during a median 2.6 years of follow-up. Concurrently with the report, the results appeared online (J Am Coll Cardiol. 2021 May 17. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2021.04.079).
The analyses Dr. Filippatos presented also showed that whether or not patients had a history of AFib, there was no impact on either the primary benefit from finerenone treatment seen in FIDELIO-DKD, which was a significant 18% relative risk reduction compared with placebo in the combined rate of kidney failure, a 40% or greater decline from baseline in estimated glomerular filtration rate, or renal death.
Likewise, prior AFib status had no effect on the study’s key secondary endpoint, a significant 14% relative risk reduction in the combined rate of cardiovascular death, nonfatal MI, nonfatal stroke, or hospitalization for heart failure.
The primary results from FIDELIO-DKD (Efficacy and Safety of Finerenone in Subjects With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Diabetic Kidney Disease) appeared in a 2020 report (N Engl J Med. 2020 Dec 3;383[23];2219-29).
‘Side benefits can be very helpful’
“It’s important to know of finerenone’s benefits beyond the primary outcome of a trial because side benefits can be very helpful,” said Anne B. Curtis, MD, an electrophysiologist and professor and chair of medicine at the University of Buffalo (N.Y.) School of Medicine and Biomedical Sciences. “It’s not a huge benefit, but this could be an added benefit for selected patients,” she said during a press briefing. “Background studies had shown favorable remodeling of the heart [by finerenone] that could affect AFib.”
Possible mitigating effects by finerenone on inflammation and fibrosis might also mediate the drug’s apparent effect on AFib, said Dr. Filippatos, professor of cardiology and director of the Heart Failure and Cardio-Oncology Clinic at Attikon University Hospital and the University of Athens.
He noted that additional data addressing a possible AFib effect of finerenone will emerge soon from the FIGARO-DKD trial, which enrolled patients similar to those in FIDELIO-DKD but with more moderate stages of kidney disease, and from the FINEARTS-HF trial, which is examining the effect of finerenone in patients with heart failure with an ejection fraction of at least 40%.
“Heart failure and AFib go together tightly. It’s worth studying this specifically, so we can see whether there is an impact of finerenone on patients with heart failure who may not necessarily have kidney disease or diabetes,” Dr. Curtis said.
Hypothesis-generating findings
The new findings reported by Dr. Filippatos “should be considered hypothesis generating. Until we have more information, upstream therapies, including mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists [MRAs, the umbrella drug class that includes finerenone], should be used in appropriate patient populations based on defined benefits with the hope they will also reduce the development of AFib and atrial flutter over time,” Gerald V. Naccarelli, MD, and coauthors wrote in an editorial that accompanied the report (J Am Coll Cardiol. 2021 May 17. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2021.04.080).
The FIDELIO-DKD trial randomized 5,734 patients at 913 sites in 48 countries, including 461 patients with a history of AFib. The observed link of finerenone treatment with a reduced incidence of AFib appeared consistent regardless of patients’ age, sex, race, their kidney characteristics at baseline, baseline levels of systolic blood pressure, serum potassium, body mass index, A1c, or use of glucose-lowering medications.
Finerenone belongs to a new class of MRAs that have a nonsteroidal structure, in contrast with the MRAs spironolactone and eplerenone. This means that finerenone does not produce steroidal-associated adverse effects linked with certain other MRAs, such as gynecomastia, and may also differ in other actions.
FIDELIO-DKD was sponsored by Bayer, the company developing finerenone. Dr. Filippatos has received lecture fees from or participated in the direction of trials on behalf of Bayer, as well as for Amgen, Boehringer Ingelheim, Medtronic, Novartis, Servier, and Vifor. Dr. Curtis is an adviser to and receives honoraria from St. Jude Medical, and receives honoraria from Medtronic. Dr. Naccarelli has been a consultant to Acesion, ARCA, GlaxoSmithKline, Janssen, Milestone, Omeicos, and Sanofi. His coauthors had no disclosures.
FROM ACC 2021
Dapagliflozin misses as treatment for COVID-19 but leaves intriguing signal for benefit
In patients hospitalized with COVID-19 infection, the sodium-glucose transporter 2 inhibitor dapagliflozin showed a trend for benefit relative to placebo on multiple outcomes, including the primary outcome of time to organ failure or death, according to results from the randomized DARE-19 trial.
Because of the failure to reach statistical significance, these results have no immediate relevance, but the trends support interest in further testing SGLT2 inhibitors in acute diseases posing a high risk for organ failure, according to Mikhail Kosiborod, MD.
In a trial that did not meet its primary endpoint, Dr. Kosiborod acknowledged that positive interpretations are speculative, but he does believe that there is one immediate take-home message.
“Our results do not support discontinuation of SGLT2 inhibitors in the setting of COVID-19 as long as patients are monitored,” said Dr. Kosiborod, director of cardiometabolic research at Saint Luke’s Mid-America Heart Institute, Kansas City, Mo.
At many institutions, it has been common to discontinue SGLT2 inhibitors in patients admitted with COVID-19. One reason was the concern that drugs in this class could exacerbate organ damage, particularly if they were to induced ketoacidosis. However, only 2 (0.003%) of 613 patients treated with dapagliflozin developed ketoacidosis, and the signal for organ protection overall, although not significant, was consistent.
“Numerically, fewer patients treated with dapagliflozin experienced organ failure and death, and this was consistent across systems, including the kidney,” Dr. Kosiborod said in presenting the study at the annual scientific sessions of the American College of Cardiology.
Overall, the study suggests that, in the context of COVID-19, dapagliflozin did not show harm and might have potential benefit, he added.
DARE-19 was rapidly conceived, designed, and implemented during the early stages of the COVID-19 pandemic. Based on prior evidence that SGLT2 inhibitors “favorably affect a number of pathophysiologic pathways disrupted during acute illness” and that drugs in this class have provided organ protection in the context of heart failure, chronic kidney disease, and other cardiometabolic conditions, the study was designed to test the hypothesis that this mechanism might improve outcomes in patients hospitalized with COVID-19, Dr. Kosiborod said.
The entry criteria included confirmed or suspected COVID-19 with an onset of 4 days of fewer and one additional risk factor, such as atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease, hypertension, or type 2 diabetes. Patients with significant renal impairment or a history of diabetic ketoacidosis were excluded.
On top of standard treatments for COVID-19, patients were randomized to 10 mg dapagliflozin or placebo once daily. There were two primary endpoints. That of prevention was time to criteria for respiratory, cardiovascular, or renal organ failure or death. The second primary outcome, for recovery, was a hierarchical composite for four endpoints: death, organ failure, status at 30 days if hospitalized, and time to discharge if this occurred before day 30.
Of the 1,250 patients randomized at 95 sites in seven countries, 617 in the dapagliflozin group and 620 patients in the placebo group completed the study. Baseline characteristics, which included a mean of age of 62 years; types of comorbidities; and types of treatments were similar.
Results for two primary endpoints
The curves for the primary outcome of prevention had already separated by day 3 and continued to widen over the 30 days in which outcomes were compared. At the end of 30 days, 11.2% of the dapagliflozin group and 13.8% of the placebo group had an event. By hazard ratio, dapagliflozin was linked to 20% nonsignificant relative protection from events (hazard ratio, 0.80; 95% confidence interval, 0.58-1.10).
The trend (P = .168) for the primary endpoint for prevention was reflected in the individual components. For dapagliflozin related to placebo, there were generally similar or greater reductions in new or worsening organ failure (HR, 0.80), cardiac decompensation (HR, 0.81), respiratory decompensation (HR, 0.85), and kidney decompensation (HR, 0.65). None were statistically significant, but the confidence intervals were tight with the upper end never exceeding 1.20.
Moreover, the relative risk reduction for all-cause mortality moved in the same direction (HR, 0.77; 95% CI, 0.52-1.16).
In the hierarchical composite endpoint of recovery, there was no significant difference in the time to discharge, but again many recovery metrics numerically favored dapagliflozin with an overall difference producing a statistical trend (P = .14) similar to organ failure events and death.
In safety analyses, dapagliflozin consistently outperformed placebo across a broad array of safety measure, including any severe adverse event (65% vs. 82%), any adverse event with an outcome of death (32% vs. 48%), discontinuation caused by an adverse event (44% vs. 55%), and acute kidney injury (21% vs. 34%).
Data could fuel related studies
According to Ana Barac, MD, PhD, director of the cardio-oncology program in the Medstar Heart and Vascular Institute, Washington, these data are “thought provoking.” Although this was a negative trial, she said that it generates an “exciting hypothesis” about the potential of SGLT2 inhibitors to provide organ protection. She called for studies to pursue this path of research.
More immediately, Dr. Barac agreed that these data argue against stopping SGLT2 inhibitors in patients admitted to a hospital for COVID-19 infection.
“These data show that these drugs are not going to lead to harm, but they might lead to benefit,” she said.
For James Januzzi, MD, a cardiologist at Massachusetts General Hospital and professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School, both in Boston, DARE-19 was perhaps most impressive because of its rigorous design and execution in the midst of a pandemic.
Over the past year, “the medical literature was flooded with grossly underpowered, poorly designed, single-center studies” yielding results that have been hard to interpret, Dr. Januzzi said. Despite the fact that this study failed to confirm its hypothesis, he said the investigators deserve praise for the quality of the work.
Dr. Januzzi also believes the study is not without clinically relevant findings, particularly the fact that dapagliflozin was associated with a lower rate of adverse events than placebo. This, at least, provides reassurance about the safety of this drug in the setting of COVID-19 infection.
Dr. Kosiborod reported financial relationships with more than 10 pharmaceutical companies, including AstraZeneca, which provided funding for DARE-19. Dr. Barac reported financial relationships with Bristol-Myers Squibb and CTI BioPharma. Dr. Januzzi reported financial relationships with Boehringer Ingelheim, GE Healthcare, Johnson & Johnson, Merck, Novartis, Pfizer, and Roche.
In patients hospitalized with COVID-19 infection, the sodium-glucose transporter 2 inhibitor dapagliflozin showed a trend for benefit relative to placebo on multiple outcomes, including the primary outcome of time to organ failure or death, according to results from the randomized DARE-19 trial.
Because of the failure to reach statistical significance, these results have no immediate relevance, but the trends support interest in further testing SGLT2 inhibitors in acute diseases posing a high risk for organ failure, according to Mikhail Kosiborod, MD.
In a trial that did not meet its primary endpoint, Dr. Kosiborod acknowledged that positive interpretations are speculative, but he does believe that there is one immediate take-home message.
“Our results do not support discontinuation of SGLT2 inhibitors in the setting of COVID-19 as long as patients are monitored,” said Dr. Kosiborod, director of cardiometabolic research at Saint Luke’s Mid-America Heart Institute, Kansas City, Mo.
At many institutions, it has been common to discontinue SGLT2 inhibitors in patients admitted with COVID-19. One reason was the concern that drugs in this class could exacerbate organ damage, particularly if they were to induced ketoacidosis. However, only 2 (0.003%) of 613 patients treated with dapagliflozin developed ketoacidosis, and the signal for organ protection overall, although not significant, was consistent.
“Numerically, fewer patients treated with dapagliflozin experienced organ failure and death, and this was consistent across systems, including the kidney,” Dr. Kosiborod said in presenting the study at the annual scientific sessions of the American College of Cardiology.
Overall, the study suggests that, in the context of COVID-19, dapagliflozin did not show harm and might have potential benefit, he added.
DARE-19 was rapidly conceived, designed, and implemented during the early stages of the COVID-19 pandemic. Based on prior evidence that SGLT2 inhibitors “favorably affect a number of pathophysiologic pathways disrupted during acute illness” and that drugs in this class have provided organ protection in the context of heart failure, chronic kidney disease, and other cardiometabolic conditions, the study was designed to test the hypothesis that this mechanism might improve outcomes in patients hospitalized with COVID-19, Dr. Kosiborod said.
The entry criteria included confirmed or suspected COVID-19 with an onset of 4 days of fewer and one additional risk factor, such as atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease, hypertension, or type 2 diabetes. Patients with significant renal impairment or a history of diabetic ketoacidosis were excluded.
On top of standard treatments for COVID-19, patients were randomized to 10 mg dapagliflozin or placebo once daily. There were two primary endpoints. That of prevention was time to criteria for respiratory, cardiovascular, or renal organ failure or death. The second primary outcome, for recovery, was a hierarchical composite for four endpoints: death, organ failure, status at 30 days if hospitalized, and time to discharge if this occurred before day 30.
Of the 1,250 patients randomized at 95 sites in seven countries, 617 in the dapagliflozin group and 620 patients in the placebo group completed the study. Baseline characteristics, which included a mean of age of 62 years; types of comorbidities; and types of treatments were similar.
Results for two primary endpoints
The curves for the primary outcome of prevention had already separated by day 3 and continued to widen over the 30 days in which outcomes were compared. At the end of 30 days, 11.2% of the dapagliflozin group and 13.8% of the placebo group had an event. By hazard ratio, dapagliflozin was linked to 20% nonsignificant relative protection from events (hazard ratio, 0.80; 95% confidence interval, 0.58-1.10).
The trend (P = .168) for the primary endpoint for prevention was reflected in the individual components. For dapagliflozin related to placebo, there were generally similar or greater reductions in new or worsening organ failure (HR, 0.80), cardiac decompensation (HR, 0.81), respiratory decompensation (HR, 0.85), and kidney decompensation (HR, 0.65). None were statistically significant, but the confidence intervals were tight with the upper end never exceeding 1.20.
Moreover, the relative risk reduction for all-cause mortality moved in the same direction (HR, 0.77; 95% CI, 0.52-1.16).
In the hierarchical composite endpoint of recovery, there was no significant difference in the time to discharge, but again many recovery metrics numerically favored dapagliflozin with an overall difference producing a statistical trend (P = .14) similar to organ failure events and death.
In safety analyses, dapagliflozin consistently outperformed placebo across a broad array of safety measure, including any severe adverse event (65% vs. 82%), any adverse event with an outcome of death (32% vs. 48%), discontinuation caused by an adverse event (44% vs. 55%), and acute kidney injury (21% vs. 34%).
Data could fuel related studies
According to Ana Barac, MD, PhD, director of the cardio-oncology program in the Medstar Heart and Vascular Institute, Washington, these data are “thought provoking.” Although this was a negative trial, she said that it generates an “exciting hypothesis” about the potential of SGLT2 inhibitors to provide organ protection. She called for studies to pursue this path of research.
More immediately, Dr. Barac agreed that these data argue against stopping SGLT2 inhibitors in patients admitted to a hospital for COVID-19 infection.
“These data show that these drugs are not going to lead to harm, but they might lead to benefit,” she said.
For James Januzzi, MD, a cardiologist at Massachusetts General Hospital and professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School, both in Boston, DARE-19 was perhaps most impressive because of its rigorous design and execution in the midst of a pandemic.
Over the past year, “the medical literature was flooded with grossly underpowered, poorly designed, single-center studies” yielding results that have been hard to interpret, Dr. Januzzi said. Despite the fact that this study failed to confirm its hypothesis, he said the investigators deserve praise for the quality of the work.
Dr. Januzzi also believes the study is not without clinically relevant findings, particularly the fact that dapagliflozin was associated with a lower rate of adverse events than placebo. This, at least, provides reassurance about the safety of this drug in the setting of COVID-19 infection.
Dr. Kosiborod reported financial relationships with more than 10 pharmaceutical companies, including AstraZeneca, which provided funding for DARE-19. Dr. Barac reported financial relationships with Bristol-Myers Squibb and CTI BioPharma. Dr. Januzzi reported financial relationships with Boehringer Ingelheim, GE Healthcare, Johnson & Johnson, Merck, Novartis, Pfizer, and Roche.
In patients hospitalized with COVID-19 infection, the sodium-glucose transporter 2 inhibitor dapagliflozin showed a trend for benefit relative to placebo on multiple outcomes, including the primary outcome of time to organ failure or death, according to results from the randomized DARE-19 trial.
Because of the failure to reach statistical significance, these results have no immediate relevance, but the trends support interest in further testing SGLT2 inhibitors in acute diseases posing a high risk for organ failure, according to Mikhail Kosiborod, MD.
In a trial that did not meet its primary endpoint, Dr. Kosiborod acknowledged that positive interpretations are speculative, but he does believe that there is one immediate take-home message.
“Our results do not support discontinuation of SGLT2 inhibitors in the setting of COVID-19 as long as patients are monitored,” said Dr. Kosiborod, director of cardiometabolic research at Saint Luke’s Mid-America Heart Institute, Kansas City, Mo.
At many institutions, it has been common to discontinue SGLT2 inhibitors in patients admitted with COVID-19. One reason was the concern that drugs in this class could exacerbate organ damage, particularly if they were to induced ketoacidosis. However, only 2 (0.003%) of 613 patients treated with dapagliflozin developed ketoacidosis, and the signal for organ protection overall, although not significant, was consistent.
“Numerically, fewer patients treated with dapagliflozin experienced organ failure and death, and this was consistent across systems, including the kidney,” Dr. Kosiborod said in presenting the study at the annual scientific sessions of the American College of Cardiology.
Overall, the study suggests that, in the context of COVID-19, dapagliflozin did not show harm and might have potential benefit, he added.
DARE-19 was rapidly conceived, designed, and implemented during the early stages of the COVID-19 pandemic. Based on prior evidence that SGLT2 inhibitors “favorably affect a number of pathophysiologic pathways disrupted during acute illness” and that drugs in this class have provided organ protection in the context of heart failure, chronic kidney disease, and other cardiometabolic conditions, the study was designed to test the hypothesis that this mechanism might improve outcomes in patients hospitalized with COVID-19, Dr. Kosiborod said.
The entry criteria included confirmed or suspected COVID-19 with an onset of 4 days of fewer and one additional risk factor, such as atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease, hypertension, or type 2 diabetes. Patients with significant renal impairment or a history of diabetic ketoacidosis were excluded.
On top of standard treatments for COVID-19, patients were randomized to 10 mg dapagliflozin or placebo once daily. There were two primary endpoints. That of prevention was time to criteria for respiratory, cardiovascular, or renal organ failure or death. The second primary outcome, for recovery, was a hierarchical composite for four endpoints: death, organ failure, status at 30 days if hospitalized, and time to discharge if this occurred before day 30.
Of the 1,250 patients randomized at 95 sites in seven countries, 617 in the dapagliflozin group and 620 patients in the placebo group completed the study. Baseline characteristics, which included a mean of age of 62 years; types of comorbidities; and types of treatments were similar.
Results for two primary endpoints
The curves for the primary outcome of prevention had already separated by day 3 and continued to widen over the 30 days in which outcomes were compared. At the end of 30 days, 11.2% of the dapagliflozin group and 13.8% of the placebo group had an event. By hazard ratio, dapagliflozin was linked to 20% nonsignificant relative protection from events (hazard ratio, 0.80; 95% confidence interval, 0.58-1.10).
The trend (P = .168) for the primary endpoint for prevention was reflected in the individual components. For dapagliflozin related to placebo, there were generally similar or greater reductions in new or worsening organ failure (HR, 0.80), cardiac decompensation (HR, 0.81), respiratory decompensation (HR, 0.85), and kidney decompensation (HR, 0.65). None were statistically significant, but the confidence intervals were tight with the upper end never exceeding 1.20.
Moreover, the relative risk reduction for all-cause mortality moved in the same direction (HR, 0.77; 95% CI, 0.52-1.16).
In the hierarchical composite endpoint of recovery, there was no significant difference in the time to discharge, but again many recovery metrics numerically favored dapagliflozin with an overall difference producing a statistical trend (P = .14) similar to organ failure events and death.
In safety analyses, dapagliflozin consistently outperformed placebo across a broad array of safety measure, including any severe adverse event (65% vs. 82%), any adverse event with an outcome of death (32% vs. 48%), discontinuation caused by an adverse event (44% vs. 55%), and acute kidney injury (21% vs. 34%).
Data could fuel related studies
According to Ana Barac, MD, PhD, director of the cardio-oncology program in the Medstar Heart and Vascular Institute, Washington, these data are “thought provoking.” Although this was a negative trial, she said that it generates an “exciting hypothesis” about the potential of SGLT2 inhibitors to provide organ protection. She called for studies to pursue this path of research.
More immediately, Dr. Barac agreed that these data argue against stopping SGLT2 inhibitors in patients admitted to a hospital for COVID-19 infection.
“These data show that these drugs are not going to lead to harm, but they might lead to benefit,” she said.
For James Januzzi, MD, a cardiologist at Massachusetts General Hospital and professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School, both in Boston, DARE-19 was perhaps most impressive because of its rigorous design and execution in the midst of a pandemic.
Over the past year, “the medical literature was flooded with grossly underpowered, poorly designed, single-center studies” yielding results that have been hard to interpret, Dr. Januzzi said. Despite the fact that this study failed to confirm its hypothesis, he said the investigators deserve praise for the quality of the work.
Dr. Januzzi also believes the study is not without clinically relevant findings, particularly the fact that dapagliflozin was associated with a lower rate of adverse events than placebo. This, at least, provides reassurance about the safety of this drug in the setting of COVID-19 infection.
Dr. Kosiborod reported financial relationships with more than 10 pharmaceutical companies, including AstraZeneca, which provided funding for DARE-19. Dr. Barac reported financial relationships with Bristol-Myers Squibb and CTI BioPharma. Dr. Januzzi reported financial relationships with Boehringer Ingelheim, GE Healthcare, Johnson & Johnson, Merck, Novartis, Pfizer, and Roche.
FROM ACC 2021
Novel rehab program fights frailty, boosts capacity in advanced HF
A novel physical rehabilitation program for patients with advanced heart failure that aimed to improve their ability to exercise before focusing on endurance was successful in a randomized trial in ways that seem to have eluded some earlier exercise-training studies in the setting of HF.
The often-frail patients following the training regimen, initiated before discharge from hospitalization for acute decompensation, worked on capabilities such as mobility, balance, and strength deemed necessary if exercises meant to build exercise capacity were to succeed.
A huge percentage stayed with the 12-week program, which featured personalized, one-on-one training from a physical therapist. The patients benefited, with improvements in balance, walking ability, and strength, which were followed by significant gains in 6-minute walk distance (6MWD) and measures of physical functioning, frailty, and quality of life. The patients then continued elements of the program at home out to 6 months.
At that time, death and rehospitalizations did not differ between those assigned to the regimen and similar patients who had not participated in the program, although the trial wasn’t powered for clinical events.
The rehab strategy seemed to work across a wide range of patient subgroups. In particular, there was evidence that the benefits were more pronounced in patients with HF and preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF) than in those with HF and reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF), observed Dalane W. Kitzman, MD, Wake Forest University, Winston-Salem, N.C.
Dr. Kitzman presented results from the REHAB-HF (Rehabilitation Therapy in Older Acute Heart Failure Patients) trial at the annual scientific sessions of the American College of Cardiology and is lead author on its same-day publication in the New England Journal of Medicine.
An earlier pilot program unexpectedly showed that such patients recently hospitalized with HF “have significant impairments in mobility and balance,” he explained. If so, “it would be hazardous to subject them to traditional endurance training, such as walking-based treadmill or even bicycle.”
The unusual program, said Dr. Kitzman, looks to those issues before engaging the patients in endurance exercise by addressing mobility, balance, and basic strength – enough to repeatedly stand up from a sitting position, for example. “If you’re not able to stand with confidence, then you’re not able to walk on a treadmill.”
This model of exercise rehab “is used in geriatrics research, and enables them to safely increase endurance. It’s well known from geriatric studies that if you go directly to endurance in these, frail, older patients, you have little improvement and often have injuries and falls,” he added.
Guidance from telemedicine?
The functional outcomes examined in REHAB-HF “are the ones that matter to patients the most,” observed Eileen M. Handberg, PhD, of Shands Hospital at the University of Florida, Gainesville, at a presentation on the trial for the media.
“This is about being able to get out of a chair without assistance, not falling, walking farther, and feeling better as opposed to the more traditional outcome measure that has been used in cardiac rehab trials, which has been the exercise treadmill test – which most patients don’t have the capacity to do very well anyway,” said Dr. Handberg, who is not a part of REHAB-HF.
“This opens up rehab, potentially, to the more sick, who also need a better quality of life,” she said.
However, many patients invited to participate in the trial could not because they lived too far from the program, Dr. Handberg observed. “It would be nice to see if the lessons from COVID-19 might apply to this population” by making participation possible remotely, “perhaps using family members as rehab assistance,” she said.
“I was really very impressed that you had 83% adherence to a home exercise 6 months down the road, which far eclipses what we had in HF-ACTION,” said Vera Bittner, MD, University of Alabama at Birmingham, as the invited discussant following Dr. Kitzman’s formal presentation of the trial. “And it certainly eclipses what we see in the typical cardiac rehab program.”
Both Dr. Bittner and Dr. Kitzman participated in HF-ACTION, a randomized exercise-training trial for patients with chronic, stable HFrEF who were all-around less sick than those in REHAB-HF.
Four functional domains
Historically, HF exercise or rehab trials have excluded patients hospitalized with acute decompensation, and third-party reimbursement often has not covered such programs because of a lack of supporting evidence and a supposed potential for harm, Dr. Kitzman said.
Entry to REHAB-HF required the patients to be fit enough to walk 4 meters, with or without a walker or other assistant device, and to have been in the hospital for at least 24 hours with a primary diagnosis of acute decompensated HF.
The intervention relied on exercises aimed at improving the four functional domains of strength, balance, mobility, and – when those three were sufficiently developed – endurance, Dr. Kitzman and associates wrote in their published report.
“The intervention was initiated in the hospital when feasible and was subsequently transitioned to an outpatient facility as soon as possible after discharge,” they wrote. Afterward, “a key goal of the intervention during the first 3 months [the outpatient phase] was to prepare the patient to transition to the independent maintenance phase (months 4-6).”
The study’s control patients “received frequent calls from study staff to try to approximate the increased attention received by the intervention group,” Dr. Kitzman said in an interview. “They were allowed to receive all usual care as ordered by their treating physicians. This included, if ordered, standard physical therapy or cardiac rehabilitation” in 43% of the control cohort. Of the trial’s 349 patients, those assigned to the intervention scored significantly higher on the three-component Short Physical Performance Battery (SPPB) at 12 weeks than those assigned to a usual care approach that included, for some, more conventional cardiac rehabilitation (8.3 vs. 6.9; P < .001).
The SPPB, validated in trials as a proxy for clinical outcomes includes tests of balance while standing, gait speed during a 4-minute walk, and strength. The latter is the test that measures time needed to rise from a chair five times.
They also showed consistent gains in other measures of physical functioning and quality of life by 12 weeks months.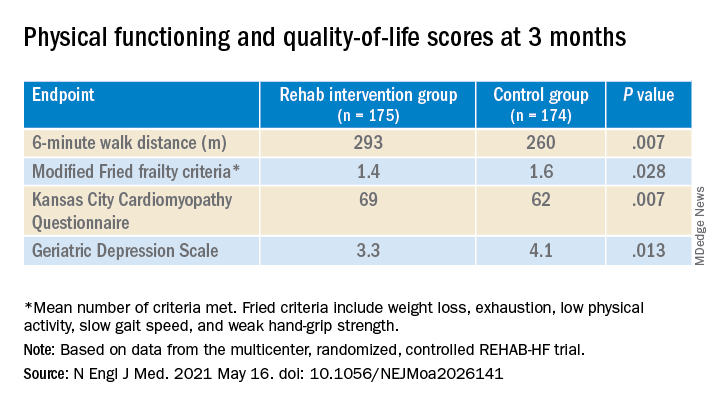
The observed SPPB treatment effect is “impressive” and “compares very favorably with previously reported estimates,” observed an accompanying editorial from Stefan D. Anker, MD, PhD, of the German Center for Cardiovascular Research and Charité Universitätsmedizin, Berlin, and Andrew J.S. Coats, DM, of the University of Warwick, Coventry, England.
“Similarly, the between-group differences seen in 6-minute walk distance (34 m) and gait speed (0.12 m/s) are clinically meaningful and sizable.”
They propose that some of the substantial quality-of-life benefit in the intervention group “may be due to better physical performance, and that part may be due to improvements in psychosocial factors and mood. It appears that exercise also resulted in patients becoming happier, or at least less depressed, as evidenced by the positive results on the Geriatric Depression Scale.”
Similar results across most subgroups
In subgroup analyses, the intervention was successful against the standard-care approach in both men and women at all ages and regardless of ejection fraction; symptom status; and whether the patient had diabetes, ischemic heart disease, or atrial fibrillation, or was obese.
Clinical outcomes were not significantly different at 6 months. The rate of death from any cause was 13% for the intervention group and 10% for the control group. There were 194 and 213 hospitalizations from any cause, respectively.
Not included in the trial’s current publication but soon to be published, Dr. Kitzman said when interviewed, is a comparison of outcomes in patients with HFpEF and HFrEF. “We found at baseline that those with HFpEF had worse impairment in physical function, quality of life, and frailty. After the intervention, there appeared to be consistently larger improvements in all outcomes, including SPPB, 6-minute walk, qualify of life, and frailty, in HFpEF versus HFrEF.”
The signals of potential benefit in HFpEF extended to clinical endpoints, he said. In contrast to similar rates of all-cause rehospitalization in HFrEF, “in patients with HFpEF, rehospitalizations were 17% lower in the intervention group, compared to the control group.” Still, he noted, the interaction P value wasn’t significant.
However, Dr. Kitzman added, mortality in the intervention group, compared with the control group, was reduced by 35% among patients with HFpEF, “but was 250% higher in HFrEF,” with a significant interaction P value.
He was careful to note that, as a phase 2 trial, REHAB-HF was underpowered for clinical events, “and even the results in the HFpEF group should not be seen as adequate evidence to change clinical care.” They were from an exploratory analysis that included relatively few events.
“Because definitive demonstration of improvement in clinical events is critical for altering clinical care guidelines and for third-party payer reimbursement decisions, we believe that a subsequent phase 3 trial is needed and are currently planning toward that,” Dr. Kitzman said.
The study was supported by research grants from the National Institutes of Health, the Kermit Glenn Phillips II Chair in Cardiovascular Medicine, and the Oristano Family Fund at Wake Forest. Dr. Kitzman disclosed receiving consulting fees or honoraria from AbbVie, AstraZeneca, Bayer Healthcare, Boehringer Ingelheim, CinRx, Corviamedical, GlaxoSmithKline, and Merck; and having an unspecified relationship with Gilead. Dr. Handberg disclosed receiving grants from Aastom Biosciences, Abbott Laboratories, Amgen, Amorcyte, AstraZeneca, Biocardia, Boehringer Ingelheim, Capricor, Cytori Therapeutics, Department of Defense, Direct Flow Medical, Everyfit, Gilead, Ionis, Medtronic, Merck, Mesoblast, Relypsa, and Sanofi-Aventis. Dr. Bittner discloses receiving consulting fees or honoraria from Pfizer and Sanofi; receiving research grants from Amgen and The Medicines Company; and having unspecified relationships with AstraZeneca, DalCor, Esperion, and Sanofi-Aventis. Dr. Anker reported receiving grants and personal fees from Abbott Vascular and Vifor; personal fees from Bayer, Boehringer Ingelheim, Novartis, Servier, Cardiac Dimensions, Thermo Fisher Scientific, AstraZeneca, Occlutech, Actimed, and Respicardia. Dr. Coats disclosed receiving personal fees from AstraZeneca, Bayer, Boehringer Ingelheim, Menarini, Novartis, Nutricia, Servier, Vifor, Abbott, Actimed, Arena, Cardiac Dimensions, Corvia, CVRx, Enopace, ESN Cleer, Faraday, WL Gore, Impulse Dynamics, and Respicardia.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A novel physical rehabilitation program for patients with advanced heart failure that aimed to improve their ability to exercise before focusing on endurance was successful in a randomized trial in ways that seem to have eluded some earlier exercise-training studies in the setting of HF.
The often-frail patients following the training regimen, initiated before discharge from hospitalization for acute decompensation, worked on capabilities such as mobility, balance, and strength deemed necessary if exercises meant to build exercise capacity were to succeed.
A huge percentage stayed with the 12-week program, which featured personalized, one-on-one training from a physical therapist. The patients benefited, with improvements in balance, walking ability, and strength, which were followed by significant gains in 6-minute walk distance (6MWD) and measures of physical functioning, frailty, and quality of life. The patients then continued elements of the program at home out to 6 months.
At that time, death and rehospitalizations did not differ between those assigned to the regimen and similar patients who had not participated in the program, although the trial wasn’t powered for clinical events.
The rehab strategy seemed to work across a wide range of patient subgroups. In particular, there was evidence that the benefits were more pronounced in patients with HF and preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF) than in those with HF and reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF), observed Dalane W. Kitzman, MD, Wake Forest University, Winston-Salem, N.C.
Dr. Kitzman presented results from the REHAB-HF (Rehabilitation Therapy in Older Acute Heart Failure Patients) trial at the annual scientific sessions of the American College of Cardiology and is lead author on its same-day publication in the New England Journal of Medicine.
An earlier pilot program unexpectedly showed that such patients recently hospitalized with HF “have significant impairments in mobility and balance,” he explained. If so, “it would be hazardous to subject them to traditional endurance training, such as walking-based treadmill or even bicycle.”
The unusual program, said Dr. Kitzman, looks to those issues before engaging the patients in endurance exercise by addressing mobility, balance, and basic strength – enough to repeatedly stand up from a sitting position, for example. “If you’re not able to stand with confidence, then you’re not able to walk on a treadmill.”
This model of exercise rehab “is used in geriatrics research, and enables them to safely increase endurance. It’s well known from geriatric studies that if you go directly to endurance in these, frail, older patients, you have little improvement and often have injuries and falls,” he added.
Guidance from telemedicine?
The functional outcomes examined in REHAB-HF “are the ones that matter to patients the most,” observed Eileen M. Handberg, PhD, of Shands Hospital at the University of Florida, Gainesville, at a presentation on the trial for the media.
“This is about being able to get out of a chair without assistance, not falling, walking farther, and feeling better as opposed to the more traditional outcome measure that has been used in cardiac rehab trials, which has been the exercise treadmill test – which most patients don’t have the capacity to do very well anyway,” said Dr. Handberg, who is not a part of REHAB-HF.
“This opens up rehab, potentially, to the more sick, who also need a better quality of life,” she said.
However, many patients invited to participate in the trial could not because they lived too far from the program, Dr. Handberg observed. “It would be nice to see if the lessons from COVID-19 might apply to this population” by making participation possible remotely, “perhaps using family members as rehab assistance,” she said.
“I was really very impressed that you had 83% adherence to a home exercise 6 months down the road, which far eclipses what we had in HF-ACTION,” said Vera Bittner, MD, University of Alabama at Birmingham, as the invited discussant following Dr. Kitzman’s formal presentation of the trial. “And it certainly eclipses what we see in the typical cardiac rehab program.”
Both Dr. Bittner and Dr. Kitzman participated in HF-ACTION, a randomized exercise-training trial for patients with chronic, stable HFrEF who were all-around less sick than those in REHAB-HF.
Four functional domains
Historically, HF exercise or rehab trials have excluded patients hospitalized with acute decompensation, and third-party reimbursement often has not covered such programs because of a lack of supporting evidence and a supposed potential for harm, Dr. Kitzman said.
Entry to REHAB-HF required the patients to be fit enough to walk 4 meters, with or without a walker or other assistant device, and to have been in the hospital for at least 24 hours with a primary diagnosis of acute decompensated HF.
The intervention relied on exercises aimed at improving the four functional domains of strength, balance, mobility, and – when those three were sufficiently developed – endurance, Dr. Kitzman and associates wrote in their published report.
“The intervention was initiated in the hospital when feasible and was subsequently transitioned to an outpatient facility as soon as possible after discharge,” they wrote. Afterward, “a key goal of the intervention during the first 3 months [the outpatient phase] was to prepare the patient to transition to the independent maintenance phase (months 4-6).”
The study’s control patients “received frequent calls from study staff to try to approximate the increased attention received by the intervention group,” Dr. Kitzman said in an interview. “They were allowed to receive all usual care as ordered by their treating physicians. This included, if ordered, standard physical therapy or cardiac rehabilitation” in 43% of the control cohort. Of the trial’s 349 patients, those assigned to the intervention scored significantly higher on the three-component Short Physical Performance Battery (SPPB) at 12 weeks than those assigned to a usual care approach that included, for some, more conventional cardiac rehabilitation (8.3 vs. 6.9; P < .001).
The SPPB, validated in trials as a proxy for clinical outcomes includes tests of balance while standing, gait speed during a 4-minute walk, and strength. The latter is the test that measures time needed to rise from a chair five times.
They also showed consistent gains in other measures of physical functioning and quality of life by 12 weeks months.
The observed SPPB treatment effect is “impressive” and “compares very favorably with previously reported estimates,” observed an accompanying editorial from Stefan D. Anker, MD, PhD, of the German Center for Cardiovascular Research and Charité Universitätsmedizin, Berlin, and Andrew J.S. Coats, DM, of the University of Warwick, Coventry, England.
“Similarly, the between-group differences seen in 6-minute walk distance (34 m) and gait speed (0.12 m/s) are clinically meaningful and sizable.”
They propose that some of the substantial quality-of-life benefit in the intervention group “may be due to better physical performance, and that part may be due to improvements in psychosocial factors and mood. It appears that exercise also resulted in patients becoming happier, or at least less depressed, as evidenced by the positive results on the Geriatric Depression Scale.”
Similar results across most subgroups
In subgroup analyses, the intervention was successful against the standard-care approach in both men and women at all ages and regardless of ejection fraction; symptom status; and whether the patient had diabetes, ischemic heart disease, or atrial fibrillation, or was obese.
Clinical outcomes were not significantly different at 6 months. The rate of death from any cause was 13% for the intervention group and 10% for the control group. There were 194 and 213 hospitalizations from any cause, respectively.
Not included in the trial’s current publication but soon to be published, Dr. Kitzman said when interviewed, is a comparison of outcomes in patients with HFpEF and HFrEF. “We found at baseline that those with HFpEF had worse impairment in physical function, quality of life, and frailty. After the intervention, there appeared to be consistently larger improvements in all outcomes, including SPPB, 6-minute walk, qualify of life, and frailty, in HFpEF versus HFrEF.”
The signals of potential benefit in HFpEF extended to clinical endpoints, he said. In contrast to similar rates of all-cause rehospitalization in HFrEF, “in patients with HFpEF, rehospitalizations were 17% lower in the intervention group, compared to the control group.” Still, he noted, the interaction P value wasn’t significant.
However, Dr. Kitzman added, mortality in the intervention group, compared with the control group, was reduced by 35% among patients with HFpEF, “but was 250% higher in HFrEF,” with a significant interaction P value.
He was careful to note that, as a phase 2 trial, REHAB-HF was underpowered for clinical events, “and even the results in the HFpEF group should not be seen as adequate evidence to change clinical care.” They were from an exploratory analysis that included relatively few events.
“Because definitive demonstration of improvement in clinical events is critical for altering clinical care guidelines and for third-party payer reimbursement decisions, we believe that a subsequent phase 3 trial is needed and are currently planning toward that,” Dr. Kitzman said.
The study was supported by research grants from the National Institutes of Health, the Kermit Glenn Phillips II Chair in Cardiovascular Medicine, and the Oristano Family Fund at Wake Forest. Dr. Kitzman disclosed receiving consulting fees or honoraria from AbbVie, AstraZeneca, Bayer Healthcare, Boehringer Ingelheim, CinRx, Corviamedical, GlaxoSmithKline, and Merck; and having an unspecified relationship with Gilead. Dr. Handberg disclosed receiving grants from Aastom Biosciences, Abbott Laboratories, Amgen, Amorcyte, AstraZeneca, Biocardia, Boehringer Ingelheim, Capricor, Cytori Therapeutics, Department of Defense, Direct Flow Medical, Everyfit, Gilead, Ionis, Medtronic, Merck, Mesoblast, Relypsa, and Sanofi-Aventis. Dr. Bittner discloses receiving consulting fees or honoraria from Pfizer and Sanofi; receiving research grants from Amgen and The Medicines Company; and having unspecified relationships with AstraZeneca, DalCor, Esperion, and Sanofi-Aventis. Dr. Anker reported receiving grants and personal fees from Abbott Vascular and Vifor; personal fees from Bayer, Boehringer Ingelheim, Novartis, Servier, Cardiac Dimensions, Thermo Fisher Scientific, AstraZeneca, Occlutech, Actimed, and Respicardia. Dr. Coats disclosed receiving personal fees from AstraZeneca, Bayer, Boehringer Ingelheim, Menarini, Novartis, Nutricia, Servier, Vifor, Abbott, Actimed, Arena, Cardiac Dimensions, Corvia, CVRx, Enopace, ESN Cleer, Faraday, WL Gore, Impulse Dynamics, and Respicardia.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A novel physical rehabilitation program for patients with advanced heart failure that aimed to improve their ability to exercise before focusing on endurance was successful in a randomized trial in ways that seem to have eluded some earlier exercise-training studies in the setting of HF.
The often-frail patients following the training regimen, initiated before discharge from hospitalization for acute decompensation, worked on capabilities such as mobility, balance, and strength deemed necessary if exercises meant to build exercise capacity were to succeed.
A huge percentage stayed with the 12-week program, which featured personalized, one-on-one training from a physical therapist. The patients benefited, with improvements in balance, walking ability, and strength, which were followed by significant gains in 6-minute walk distance (6MWD) and measures of physical functioning, frailty, and quality of life. The patients then continued elements of the program at home out to 6 months.
At that time, death and rehospitalizations did not differ between those assigned to the regimen and similar patients who had not participated in the program, although the trial wasn’t powered for clinical events.
The rehab strategy seemed to work across a wide range of patient subgroups. In particular, there was evidence that the benefits were more pronounced in patients with HF and preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF) than in those with HF and reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF), observed Dalane W. Kitzman, MD, Wake Forest University, Winston-Salem, N.C.
Dr. Kitzman presented results from the REHAB-HF (Rehabilitation Therapy in Older Acute Heart Failure Patients) trial at the annual scientific sessions of the American College of Cardiology and is lead author on its same-day publication in the New England Journal of Medicine.
An earlier pilot program unexpectedly showed that such patients recently hospitalized with HF “have significant impairments in mobility and balance,” he explained. If so, “it would be hazardous to subject them to traditional endurance training, such as walking-based treadmill or even bicycle.”
The unusual program, said Dr. Kitzman, looks to those issues before engaging the patients in endurance exercise by addressing mobility, balance, and basic strength – enough to repeatedly stand up from a sitting position, for example. “If you’re not able to stand with confidence, then you’re not able to walk on a treadmill.”
This model of exercise rehab “is used in geriatrics research, and enables them to safely increase endurance. It’s well known from geriatric studies that if you go directly to endurance in these, frail, older patients, you have little improvement and often have injuries and falls,” he added.
Guidance from telemedicine?
The functional outcomes examined in REHAB-HF “are the ones that matter to patients the most,” observed Eileen M. Handberg, PhD, of Shands Hospital at the University of Florida, Gainesville, at a presentation on the trial for the media.
“This is about being able to get out of a chair without assistance, not falling, walking farther, and feeling better as opposed to the more traditional outcome measure that has been used in cardiac rehab trials, which has been the exercise treadmill test – which most patients don’t have the capacity to do very well anyway,” said Dr. Handberg, who is not a part of REHAB-HF.
“This opens up rehab, potentially, to the more sick, who also need a better quality of life,” she said.
However, many patients invited to participate in the trial could not because they lived too far from the program, Dr. Handberg observed. “It would be nice to see if the lessons from COVID-19 might apply to this population” by making participation possible remotely, “perhaps using family members as rehab assistance,” she said.
“I was really very impressed that you had 83% adherence to a home exercise 6 months down the road, which far eclipses what we had in HF-ACTION,” said Vera Bittner, MD, University of Alabama at Birmingham, as the invited discussant following Dr. Kitzman’s formal presentation of the trial. “And it certainly eclipses what we see in the typical cardiac rehab program.”
Both Dr. Bittner and Dr. Kitzman participated in HF-ACTION, a randomized exercise-training trial for patients with chronic, stable HFrEF who were all-around less sick than those in REHAB-HF.
Four functional domains
Historically, HF exercise or rehab trials have excluded patients hospitalized with acute decompensation, and third-party reimbursement often has not covered such programs because of a lack of supporting evidence and a supposed potential for harm, Dr. Kitzman said.
Entry to REHAB-HF required the patients to be fit enough to walk 4 meters, with or without a walker or other assistant device, and to have been in the hospital for at least 24 hours with a primary diagnosis of acute decompensated HF.
The intervention relied on exercises aimed at improving the four functional domains of strength, balance, mobility, and – when those three were sufficiently developed – endurance, Dr. Kitzman and associates wrote in their published report.
“The intervention was initiated in the hospital when feasible and was subsequently transitioned to an outpatient facility as soon as possible after discharge,” they wrote. Afterward, “a key goal of the intervention during the first 3 months [the outpatient phase] was to prepare the patient to transition to the independent maintenance phase (months 4-6).”
The study’s control patients “received frequent calls from study staff to try to approximate the increased attention received by the intervention group,” Dr. Kitzman said in an interview. “They were allowed to receive all usual care as ordered by their treating physicians. This included, if ordered, standard physical therapy or cardiac rehabilitation” in 43% of the control cohort. Of the trial’s 349 patients, those assigned to the intervention scored significantly higher on the three-component Short Physical Performance Battery (SPPB) at 12 weeks than those assigned to a usual care approach that included, for some, more conventional cardiac rehabilitation (8.3 vs. 6.9; P < .001).
The SPPB, validated in trials as a proxy for clinical outcomes includes tests of balance while standing, gait speed during a 4-minute walk, and strength. The latter is the test that measures time needed to rise from a chair five times.
They also showed consistent gains in other measures of physical functioning and quality of life by 12 weeks months.
The observed SPPB treatment effect is “impressive” and “compares very favorably with previously reported estimates,” observed an accompanying editorial from Stefan D. Anker, MD, PhD, of the German Center for Cardiovascular Research and Charité Universitätsmedizin, Berlin, and Andrew J.S. Coats, DM, of the University of Warwick, Coventry, England.
“Similarly, the between-group differences seen in 6-minute walk distance (34 m) and gait speed (0.12 m/s) are clinically meaningful and sizable.”
They propose that some of the substantial quality-of-life benefit in the intervention group “may be due to better physical performance, and that part may be due to improvements in psychosocial factors and mood. It appears that exercise also resulted in patients becoming happier, or at least less depressed, as evidenced by the positive results on the Geriatric Depression Scale.”
Similar results across most subgroups
In subgroup analyses, the intervention was successful against the standard-care approach in both men and women at all ages and regardless of ejection fraction; symptom status; and whether the patient had diabetes, ischemic heart disease, or atrial fibrillation, or was obese.
Clinical outcomes were not significantly different at 6 months. The rate of death from any cause was 13% for the intervention group and 10% for the control group. There were 194 and 213 hospitalizations from any cause, respectively.
Not included in the trial’s current publication but soon to be published, Dr. Kitzman said when interviewed, is a comparison of outcomes in patients with HFpEF and HFrEF. “We found at baseline that those with HFpEF had worse impairment in physical function, quality of life, and frailty. After the intervention, there appeared to be consistently larger improvements in all outcomes, including SPPB, 6-minute walk, qualify of life, and frailty, in HFpEF versus HFrEF.”
The signals of potential benefit in HFpEF extended to clinical endpoints, he said. In contrast to similar rates of all-cause rehospitalization in HFrEF, “in patients with HFpEF, rehospitalizations were 17% lower in the intervention group, compared to the control group.” Still, he noted, the interaction P value wasn’t significant.
However, Dr. Kitzman added, mortality in the intervention group, compared with the control group, was reduced by 35% among patients with HFpEF, “but was 250% higher in HFrEF,” with a significant interaction P value.
He was careful to note that, as a phase 2 trial, REHAB-HF was underpowered for clinical events, “and even the results in the HFpEF group should not be seen as adequate evidence to change clinical care.” They were from an exploratory analysis that included relatively few events.
“Because definitive demonstration of improvement in clinical events is critical for altering clinical care guidelines and for third-party payer reimbursement decisions, we believe that a subsequent phase 3 trial is needed and are currently planning toward that,” Dr. Kitzman said.
The study was supported by research grants from the National Institutes of Health, the Kermit Glenn Phillips II Chair in Cardiovascular Medicine, and the Oristano Family Fund at Wake Forest. Dr. Kitzman disclosed receiving consulting fees or honoraria from AbbVie, AstraZeneca, Bayer Healthcare, Boehringer Ingelheim, CinRx, Corviamedical, GlaxoSmithKline, and Merck; and having an unspecified relationship with Gilead. Dr. Handberg disclosed receiving grants from Aastom Biosciences, Abbott Laboratories, Amgen, Amorcyte, AstraZeneca, Biocardia, Boehringer Ingelheim, Capricor, Cytori Therapeutics, Department of Defense, Direct Flow Medical, Everyfit, Gilead, Ionis, Medtronic, Merck, Mesoblast, Relypsa, and Sanofi-Aventis. Dr. Bittner discloses receiving consulting fees or honoraria from Pfizer and Sanofi; receiving research grants from Amgen and The Medicines Company; and having unspecified relationships with AstraZeneca, DalCor, Esperion, and Sanofi-Aventis. Dr. Anker reported receiving grants and personal fees from Abbott Vascular and Vifor; personal fees from Bayer, Boehringer Ingelheim, Novartis, Servier, Cardiac Dimensions, Thermo Fisher Scientific, AstraZeneca, Occlutech, Actimed, and Respicardia. Dr. Coats disclosed receiving personal fees from AstraZeneca, Bayer, Boehringer Ingelheim, Menarini, Novartis, Nutricia, Servier, Vifor, Abbott, Actimed, Arena, Cardiac Dimensions, Corvia, CVRx, Enopace, ESN Cleer, Faraday, WL Gore, Impulse Dynamics, and Respicardia.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
New STRENGTH analysis reignites debate on omega-3 CV benefits
Questions over the cardiovascular benefits shown in the REDUCE-IT trial with icosapent ethyl, a high-dose eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) product, have been reignited with a new analysis from the STRENGTH trial showing no benefit of a high-dose combined omega-3 fatty acid product in patients who achieved the highest EPA levels and no harm in those with the highest levels of docosahexaenoic acid (DHA).
STRENGTH investigator Steven Nissen, MD, said these new results add to concerns about the positive result in the previously reported REDUCE-IT trial and suggest that “there is no strong evidence of a benefit of fish oil in preventing major cardiovascular events.”
But Dr. Nissen, who is chair of the department of cardiovascular medicine at the Cleveland Clinic in Ohio, pointed out evidence of harm, with both REDUCE-IT and STRENGTH showing an increase in atrial fibrillation with the high-dose omega-3 fatty acid products.
“Fish oils increase the risk of atrial fibrillation substantially, and there is no solid evidence that they help the heart in any way,” he stated.
The new STRENGTH analysis was presented at the annual scientific sessions of the American College of Cardiology. and was simultaneously published in JAMA Cardiology.
The REDUCE-IT trial showed a large 25% relative-risk reduction in cardiovascular events in patients taking icosapent ethyl (Vascepa, Amarin), a high-dose purified formulation of EPA, compared with patients taking a mineral oil placebo. But a similar trial, STRENGTH, showed no effect of a similar high dose of the mixed EPA/DHA product (Epanova, AstraZeneca), compared with a corn oil placebo.
The different results from these two studies have led to many questions about how the benefits seen in REDUCE-IT were brought about, and why they weren’t replicated in the STRENGTH study.
Dr. Nissen noted that several hypotheses have been proposed. These include a potential adverse effect of the mineral oil placebo in the REDUCE-IT trial, which may have elevated risk in the placebo treatment group and led to a false-positive result for icosapent ethyl. Another possibility is that the moderately higher plasma levels of EPA achieved in REDUCE-IT were responsible for the observed benefits or that the coadministration of DHA in STRENGTH may have counteracted the potential beneficial effects of EPA.
The current post hoc analysis of STRENGTH was conducted to address these latter two possibilities. It aimed to assess the association between cardiovascular outcomes and achieved levels of EPA, DHA, or changes in levels of these fatty acids.
“In our new analysis, among patients treated with fish oil, we found no evidence that EPA is beneficial or that DHA is harmful,” Dr. Nissen said.
Results of the new analysis showed an absence of a benefit from achieving high levels of EPA or harm from achieving high levels of DHA which, the authors say, “strengthens the concerns that the choice of comparator may have influenced the divergent results observed in the two trials.”
“Unlike corn oil, which is inert, mineral oil has major adverse effects, increasing LDL by 10.9% and CRP [C-reactive protein] by 32% in the REDUCE-IT trial,” Dr. Nissen said. “If you give a toxic placebo, then the active drug may falsely look really good.”
The STRENGTH trial randomly assigned 13,078 individuals at high risk for major cardiovascular events to receive 4 g daily of the EPA/DHA combined product (omega-3 carboxylic acid) or corn oil as the placebo. Main results, reported previously, showed no difference between the two groups in terms of the primary outcome – a composite of cardiovascular death, myocardial infarction, stroke, coronary revascularization, or unstable angina requiring hospitalization.
The current analysis, in 10,382 patients with available omega-3 fatty acid levels, looked at event rates according to tertiles of achieved EPA and DHA levels. The median plasma EPA level for patients taking the omega-3 product was 89 mcg/mL, with the top tertile achieving levels of 151 mcg/mL (a 443% increase). Dr. Nissen pointed out that this was higher than the median level of EPA reported in the REDUCE-IT trial (144 mcg/mL).
The median level of DHA was 91 mcg/mL, rising to 118 mcg/mL (a 68% increase) in the top tertile in the STRENGTH analysis.
Results showed no difference in the occurrence of the prespecified primary outcome among patients treated with omega-3 carboxylic acid who were in the top tertile of achieved EPA levels at 1 year (event rate, 11.3%), compared with patients treated with corn oil (11.0%), a nonsignificant difference (hazard ratio, 0.98; P = .81).
For DHA, patients in the top tertile of achieved DHA levels had an event rate of 11.4% vs. 11.0% in the corn oil group, also a nonsignificant difference (HR, 1.02; P = .85)
Sensitivity analyses based on the highest tertile of change in EPA or DHA levels showed similarly neutral results.
Because plasma levels may not reflect tissue levels of EPA or DHA, additional analyses assessed red blood cell EPA and DHA levels, neither of which showed any evidence of benefit or harm.
“These findings suggest that supplementation of omega-3 fatty acids in high-risk cardiovascular patients is neutral even at the highest achieved levels,” Dr. Nissen said. “And, in the context of increased risk of atrial fibrillation in omega-3 trials, they cast uncertainty over whether there is net benefit or harm with any omega-3 preparation,” he concluded.
He suggested that the choice of placebo comparator may play an important role in determining outcome for trials of omega-3 products, adding that further research is needed with trials specifically designed to compare corn oil with mineral oil and compare purified EPA with other formulations of omega-3 fatty acids.
At an press conference, Dr. Nissen said he could not recommend use of omega-3 fatty acid products for cardiovascular risk reduction given the uncertainty over the benefit in REDUCE-IT.
“We need replication, and the problem is STRENGTH did not replicate REDUCE-IT,” he stated.
REDUCE-IT investigator responds
The discussant of the STRENGTH analysis at the ACC presentation, Deepak L. Bhatt, MD, who was lead investigator of the REDUCE-IT trial, suggested that one conclusion could be that “an absence of a relationship in a negative trial doesn’t tell us that much other than that specific drug doesn’t work.”
Dr. Bhatt, who is executive director of interventional cardiovascular programs at Brigham and Women’s Hospital Heart & Vascular Center, Boston, said in an interview that comparisons should not be made between different trials using different products.
“I commend the STRENGTH investigators on a well-conducted trial that provided a definitive answer about the specific drug they studied, finding no benefit. But in a completely negative trial, I wouldn’t necessarily expect to see a relationship between any biomarker and outcome,” he said.
“With respect to icosapent ethyl (pure EPA), every cardiovascular trial to date has been positive: REDUCE-IT (randomized, placebo-controlled), JELIS (randomized, no placebo), EVAPORATE (randomized, placebo-controlled), CHERRY (randomized, no placebo), and some smaller ones,” Dr. Bhatt added. “Both REDUCE-IT and JELIS found associations between higher levels of EPA and lower rates of cardiovascular events, suggesting that higher EPA levels attained specifically with icosapent ethyl are beneficial.”
Pointing out that all the glucagonlike peptide–1 agonists lower glucose, for example, but not all reduce cardiovascular events, Dr. Bhatt said it was best to focus on clinical trial results and not overly focus on biomarker changes.
“Yes, the drug in STRENGTH raised EPA (and raised DHA, as well as lowering triglycerides), but the drug in REDUCE-IT and JELIS raised EPA much more, without raising DHA – and more importantly, the increase in EPA was via a totally different drug, with many different properties,” he added.
In his discussion of the study at the ACC presentation, Dr. Bhatt pointed out that in the STRENGTH trial overall there was no reduction in major adverse cardiovascular events despite a 19% reduction in triglycerides, which he said was a “very interesting disconnect.” He asked Dr. Nissen what he thought the reason was for the observation in this analysis of no relationship between EPA or DHA level and triglyceride reduction.
Dr. Nissen said that was an interesting point. “When we look at the two trials, they both reduced triglyceride levels by an almost identical amount, 19%, but we don’t see a relationship with that and EPA levels achieved.” He suggested this may be because of different threshold levels.
Dr. Bhatt also noted that high-intensity statin use was lower in the patients with higher EPA levels in the STRENGTH analysis, but Dr. Nissen countered: “I don’t think that was enough of a difference to explain the lack of an effect.”
Invited commentator on the new analysis at an ACC press conference, Eileen Handberg, PhD, said it was important to try to understand the reasons behind the different results of the STRENGTH and REDUCE-IT trials. “These new findings are important because they explain potentially why these outcomes are different,” she stated.
Dr. Handberg, who is professor of medicine at the University of Florida, Gainesville, said she hoped the additional research called for by Dr. Nissen would go ahead as a head-to-head study of the two omega-3 products or of the two different placebo oils.
The STRENGTH trial was sponsored by Astra Zeneca. Dr. Nissen reports research grants from AbbVie, Amgen, Astra Zeneca, Eli Lilly, Esperion Therapeutics, MEDTRONIC, MyoKardia, Novartis, Novo Nordisk, Pfizer, and Silence Therapeutics. Dr. Bhatt reports constant fees/honoraria from CellProthera, Elsevier Practice Update Cardiology, K2P, Level Ex, Medtelligence, MJH Life Sciences, and WebMD; data safety monitoring board activities with Contego; other roles with TobeSoft, Belvoir Publications, Cardax, Cereno Scientific, Clinical Cardiology, Elsevier, HMP Global, Janssen Pharmaceuticals, Journal of Invasive Cardiology, Medscape Cardiology, Merck, MyoKardia, Novo Nordisk, PhaseBio, PLx Pharma, Regado Biosciences, and Slack Publications/Cardiology Research Foundation; and research grants from Abbott, Afimmune, Amarin, Amgen, Astra Zeneca, Bayer Healthcare Pharmaceuticals, Boehringer Ingelheim Pharmaceuticals, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Cardax, Chiesi, Eisai, Eli Lilly, Ethicon, FlowCo, Forest Laboratories, Fractyl, HLS Therapeutics, Idorsia, Ironwood, Ischemix, Lexicon, MEDTRONIC, MyoKardia, Owkin, Pfizer, PhaseBio, PLx Pharma, Regeneron, Roche, Sanofi Aventis, Synaptic, Takeda, and The Medicines Company.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Questions over the cardiovascular benefits shown in the REDUCE-IT trial with icosapent ethyl, a high-dose eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) product, have been reignited with a new analysis from the STRENGTH trial showing no benefit of a high-dose combined omega-3 fatty acid product in patients who achieved the highest EPA levels and no harm in those with the highest levels of docosahexaenoic acid (DHA).
STRENGTH investigator Steven Nissen, MD, said these new results add to concerns about the positive result in the previously reported REDUCE-IT trial and suggest that “there is no strong evidence of a benefit of fish oil in preventing major cardiovascular events.”
But Dr. Nissen, who is chair of the department of cardiovascular medicine at the Cleveland Clinic in Ohio, pointed out evidence of harm, with both REDUCE-IT and STRENGTH showing an increase in atrial fibrillation with the high-dose omega-3 fatty acid products.
“Fish oils increase the risk of atrial fibrillation substantially, and there is no solid evidence that they help the heart in any way,” he stated.
The new STRENGTH analysis was presented at the annual scientific sessions of the American College of Cardiology. and was simultaneously published in JAMA Cardiology.
The REDUCE-IT trial showed a large 25% relative-risk reduction in cardiovascular events in patients taking icosapent ethyl (Vascepa, Amarin), a high-dose purified formulation of EPA, compared with patients taking a mineral oil placebo. But a similar trial, STRENGTH, showed no effect of a similar high dose of the mixed EPA/DHA product (Epanova, AstraZeneca), compared with a corn oil placebo.
The different results from these two studies have led to many questions about how the benefits seen in REDUCE-IT were brought about, and why they weren’t replicated in the STRENGTH study.
Dr. Nissen noted that several hypotheses have been proposed. These include a potential adverse effect of the mineral oil placebo in the REDUCE-IT trial, which may have elevated risk in the placebo treatment group and led to a false-positive result for icosapent ethyl. Another possibility is that the moderately higher plasma levels of EPA achieved in REDUCE-IT were responsible for the observed benefits or that the coadministration of DHA in STRENGTH may have counteracted the potential beneficial effects of EPA.
The current post hoc analysis of STRENGTH was conducted to address these latter two possibilities. It aimed to assess the association between cardiovascular outcomes and achieved levels of EPA, DHA, or changes in levels of these fatty acids.
“In our new analysis, among patients treated with fish oil, we found no evidence that EPA is beneficial or that DHA is harmful,” Dr. Nissen said.
Results of the new analysis showed an absence of a benefit from achieving high levels of EPA or harm from achieving high levels of DHA which, the authors say, “strengthens the concerns that the choice of comparator may have influenced the divergent results observed in the two trials.”
“Unlike corn oil, which is inert, mineral oil has major adverse effects, increasing LDL by 10.9% and CRP [C-reactive protein] by 32% in the REDUCE-IT trial,” Dr. Nissen said. “If you give a toxic placebo, then the active drug may falsely look really good.”
The STRENGTH trial randomly assigned 13,078 individuals at high risk for major cardiovascular events to receive 4 g daily of the EPA/DHA combined product (omega-3 carboxylic acid) or corn oil as the placebo. Main results, reported previously, showed no difference between the two groups in terms of the primary outcome – a composite of cardiovascular death, myocardial infarction, stroke, coronary revascularization, or unstable angina requiring hospitalization.
The current analysis, in 10,382 patients with available omega-3 fatty acid levels, looked at event rates according to tertiles of achieved EPA and DHA levels. The median plasma EPA level for patients taking the omega-3 product was 89 mcg/mL, with the top tertile achieving levels of 151 mcg/mL (a 443% increase). Dr. Nissen pointed out that this was higher than the median level of EPA reported in the REDUCE-IT trial (144 mcg/mL).
The median level of DHA was 91 mcg/mL, rising to 118 mcg/mL (a 68% increase) in the top tertile in the STRENGTH analysis.
Results showed no difference in the occurrence of the prespecified primary outcome among patients treated with omega-3 carboxylic acid who were in the top tertile of achieved EPA levels at 1 year (event rate, 11.3%), compared with patients treated with corn oil (11.0%), a nonsignificant difference (hazard ratio, 0.98; P = .81).
For DHA, patients in the top tertile of achieved DHA levels had an event rate of 11.4% vs. 11.0% in the corn oil group, also a nonsignificant difference (HR, 1.02; P = .85)
Sensitivity analyses based on the highest tertile of change in EPA or DHA levels showed similarly neutral results.
Because plasma levels may not reflect tissue levels of EPA or DHA, additional analyses assessed red blood cell EPA and DHA levels, neither of which showed any evidence of benefit or harm.
“These findings suggest that supplementation of omega-3 fatty acids in high-risk cardiovascular patients is neutral even at the highest achieved levels,” Dr. Nissen said. “And, in the context of increased risk of atrial fibrillation in omega-3 trials, they cast uncertainty over whether there is net benefit or harm with any omega-3 preparation,” he concluded.
He suggested that the choice of placebo comparator may play an important role in determining outcome for trials of omega-3 products, adding that further research is needed with trials specifically designed to compare corn oil with mineral oil and compare purified EPA with other formulations of omega-3 fatty acids.
At an press conference, Dr. Nissen said he could not recommend use of omega-3 fatty acid products for cardiovascular risk reduction given the uncertainty over the benefit in REDUCE-IT.
“We need replication, and the problem is STRENGTH did not replicate REDUCE-IT,” he stated.
REDUCE-IT investigator responds
The discussant of the STRENGTH analysis at the ACC presentation, Deepak L. Bhatt, MD, who was lead investigator of the REDUCE-IT trial, suggested that one conclusion could be that “an absence of a relationship in a negative trial doesn’t tell us that much other than that specific drug doesn’t work.”
Dr. Bhatt, who is executive director of interventional cardiovascular programs at Brigham and Women’s Hospital Heart & Vascular Center, Boston, said in an interview that comparisons should not be made between different trials using different products.
“I commend the STRENGTH investigators on a well-conducted trial that provided a definitive answer about the specific drug they studied, finding no benefit. But in a completely negative trial, I wouldn’t necessarily expect to see a relationship between any biomarker and outcome,” he said.
“With respect to icosapent ethyl (pure EPA), every cardiovascular trial to date has been positive: REDUCE-IT (randomized, placebo-controlled), JELIS (randomized, no placebo), EVAPORATE (randomized, placebo-controlled), CHERRY (randomized, no placebo), and some smaller ones,” Dr. Bhatt added. “Both REDUCE-IT and JELIS found associations between higher levels of EPA and lower rates of cardiovascular events, suggesting that higher EPA levels attained specifically with icosapent ethyl are beneficial.”
Pointing out that all the glucagonlike peptide–1 agonists lower glucose, for example, but not all reduce cardiovascular events, Dr. Bhatt said it was best to focus on clinical trial results and not overly focus on biomarker changes.
“Yes, the drug in STRENGTH raised EPA (and raised DHA, as well as lowering triglycerides), but the drug in REDUCE-IT and JELIS raised EPA much more, without raising DHA – and more importantly, the increase in EPA was via a totally different drug, with many different properties,” he added.
In his discussion of the study at the ACC presentation, Dr. Bhatt pointed out that in the STRENGTH trial overall there was no reduction in major adverse cardiovascular events despite a 19% reduction in triglycerides, which he said was a “very interesting disconnect.” He asked Dr. Nissen what he thought the reason was for the observation in this analysis of no relationship between EPA or DHA level and triglyceride reduction.
Dr. Nissen said that was an interesting point. “When we look at the two trials, they both reduced triglyceride levels by an almost identical amount, 19%, but we don’t see a relationship with that and EPA levels achieved.” He suggested this may be because of different threshold levels.
Dr. Bhatt also noted that high-intensity statin use was lower in the patients with higher EPA levels in the STRENGTH analysis, but Dr. Nissen countered: “I don’t think that was enough of a difference to explain the lack of an effect.”
Invited commentator on the new analysis at an ACC press conference, Eileen Handberg, PhD, said it was important to try to understand the reasons behind the different results of the STRENGTH and REDUCE-IT trials. “These new findings are important because they explain potentially why these outcomes are different,” she stated.
Dr. Handberg, who is professor of medicine at the University of Florida, Gainesville, said she hoped the additional research called for by Dr. Nissen would go ahead as a head-to-head study of the two omega-3 products or of the two different placebo oils.
The STRENGTH trial was sponsored by Astra Zeneca. Dr. Nissen reports research grants from AbbVie, Amgen, Astra Zeneca, Eli Lilly, Esperion Therapeutics, MEDTRONIC, MyoKardia, Novartis, Novo Nordisk, Pfizer, and Silence Therapeutics. Dr. Bhatt reports constant fees/honoraria from CellProthera, Elsevier Practice Update Cardiology, K2P, Level Ex, Medtelligence, MJH Life Sciences, and WebMD; data safety monitoring board activities with Contego; other roles with TobeSoft, Belvoir Publications, Cardax, Cereno Scientific, Clinical Cardiology, Elsevier, HMP Global, Janssen Pharmaceuticals, Journal of Invasive Cardiology, Medscape Cardiology, Merck, MyoKardia, Novo Nordisk, PhaseBio, PLx Pharma, Regado Biosciences, and Slack Publications/Cardiology Research Foundation; and research grants from Abbott, Afimmune, Amarin, Amgen, Astra Zeneca, Bayer Healthcare Pharmaceuticals, Boehringer Ingelheim Pharmaceuticals, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Cardax, Chiesi, Eisai, Eli Lilly, Ethicon, FlowCo, Forest Laboratories, Fractyl, HLS Therapeutics, Idorsia, Ironwood, Ischemix, Lexicon, MEDTRONIC, MyoKardia, Owkin, Pfizer, PhaseBio, PLx Pharma, Regeneron, Roche, Sanofi Aventis, Synaptic, Takeda, and The Medicines Company.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Questions over the cardiovascular benefits shown in the REDUCE-IT trial with icosapent ethyl, a high-dose eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) product, have been reignited with a new analysis from the STRENGTH trial showing no benefit of a high-dose combined omega-3 fatty acid product in patients who achieved the highest EPA levels and no harm in those with the highest levels of docosahexaenoic acid (DHA).
STRENGTH investigator Steven Nissen, MD, said these new results add to concerns about the positive result in the previously reported REDUCE-IT trial and suggest that “there is no strong evidence of a benefit of fish oil in preventing major cardiovascular events.”
But Dr. Nissen, who is chair of the department of cardiovascular medicine at the Cleveland Clinic in Ohio, pointed out evidence of harm, with both REDUCE-IT and STRENGTH showing an increase in atrial fibrillation with the high-dose omega-3 fatty acid products.
“Fish oils increase the risk of atrial fibrillation substantially, and there is no solid evidence that they help the heart in any way,” he stated.
The new STRENGTH analysis was presented at the annual scientific sessions of the American College of Cardiology. and was simultaneously published in JAMA Cardiology.
The REDUCE-IT trial showed a large 25% relative-risk reduction in cardiovascular events in patients taking icosapent ethyl (Vascepa, Amarin), a high-dose purified formulation of EPA, compared with patients taking a mineral oil placebo. But a similar trial, STRENGTH, showed no effect of a similar high dose of the mixed EPA/DHA product (Epanova, AstraZeneca), compared with a corn oil placebo.
The different results from these two studies have led to many questions about how the benefits seen in REDUCE-IT were brought about, and why they weren’t replicated in the STRENGTH study.
Dr. Nissen noted that several hypotheses have been proposed. These include a potential adverse effect of the mineral oil placebo in the REDUCE-IT trial, which may have elevated risk in the placebo treatment group and led to a false-positive result for icosapent ethyl. Another possibility is that the moderately higher plasma levels of EPA achieved in REDUCE-IT were responsible for the observed benefits or that the coadministration of DHA in STRENGTH may have counteracted the potential beneficial effects of EPA.
The current post hoc analysis of STRENGTH was conducted to address these latter two possibilities. It aimed to assess the association between cardiovascular outcomes and achieved levels of EPA, DHA, or changes in levels of these fatty acids.
“In our new analysis, among patients treated with fish oil, we found no evidence that EPA is beneficial or that DHA is harmful,” Dr. Nissen said.
Results of the new analysis showed an absence of a benefit from achieving high levels of EPA or harm from achieving high levels of DHA which, the authors say, “strengthens the concerns that the choice of comparator may have influenced the divergent results observed in the two trials.”
“Unlike corn oil, which is inert, mineral oil has major adverse effects, increasing LDL by 10.9% and CRP [C-reactive protein] by 32% in the REDUCE-IT trial,” Dr. Nissen said. “If you give a toxic placebo, then the active drug may falsely look really good.”
The STRENGTH trial randomly assigned 13,078 individuals at high risk for major cardiovascular events to receive 4 g daily of the EPA/DHA combined product (omega-3 carboxylic acid) or corn oil as the placebo. Main results, reported previously, showed no difference between the two groups in terms of the primary outcome – a composite of cardiovascular death, myocardial infarction, stroke, coronary revascularization, or unstable angina requiring hospitalization.
The current analysis, in 10,382 patients with available omega-3 fatty acid levels, looked at event rates according to tertiles of achieved EPA and DHA levels. The median plasma EPA level for patients taking the omega-3 product was 89 mcg/mL, with the top tertile achieving levels of 151 mcg/mL (a 443% increase). Dr. Nissen pointed out that this was higher than the median level of EPA reported in the REDUCE-IT trial (144 mcg/mL).
The median level of DHA was 91 mcg/mL, rising to 118 mcg/mL (a 68% increase) in the top tertile in the STRENGTH analysis.
Results showed no difference in the occurrence of the prespecified primary outcome among patients treated with omega-3 carboxylic acid who were in the top tertile of achieved EPA levels at 1 year (event rate, 11.3%), compared with patients treated with corn oil (11.0%), a nonsignificant difference (hazard ratio, 0.98; P = .81).
For DHA, patients in the top tertile of achieved DHA levels had an event rate of 11.4% vs. 11.0% in the corn oil group, also a nonsignificant difference (HR, 1.02; P = .85)
Sensitivity analyses based on the highest tertile of change in EPA or DHA levels showed similarly neutral results.
Because plasma levels may not reflect tissue levels of EPA or DHA, additional analyses assessed red blood cell EPA and DHA levels, neither of which showed any evidence of benefit or harm.
“These findings suggest that supplementation of omega-3 fatty acids in high-risk cardiovascular patients is neutral even at the highest achieved levels,” Dr. Nissen said. “And, in the context of increased risk of atrial fibrillation in omega-3 trials, they cast uncertainty over whether there is net benefit or harm with any omega-3 preparation,” he concluded.
He suggested that the choice of placebo comparator may play an important role in determining outcome for trials of omega-3 products, adding that further research is needed with trials specifically designed to compare corn oil with mineral oil and compare purified EPA with other formulations of omega-3 fatty acids.
At an press conference, Dr. Nissen said he could not recommend use of omega-3 fatty acid products for cardiovascular risk reduction given the uncertainty over the benefit in REDUCE-IT.
“We need replication, and the problem is STRENGTH did not replicate REDUCE-IT,” he stated.
REDUCE-IT investigator responds
The discussant of the STRENGTH analysis at the ACC presentation, Deepak L. Bhatt, MD, who was lead investigator of the REDUCE-IT trial, suggested that one conclusion could be that “an absence of a relationship in a negative trial doesn’t tell us that much other than that specific drug doesn’t work.”
Dr. Bhatt, who is executive director of interventional cardiovascular programs at Brigham and Women’s Hospital Heart & Vascular Center, Boston, said in an interview that comparisons should not be made between different trials using different products.
“I commend the STRENGTH investigators on a well-conducted trial that provided a definitive answer about the specific drug they studied, finding no benefit. But in a completely negative trial, I wouldn’t necessarily expect to see a relationship between any biomarker and outcome,” he said.
“With respect to icosapent ethyl (pure EPA), every cardiovascular trial to date has been positive: REDUCE-IT (randomized, placebo-controlled), JELIS (randomized, no placebo), EVAPORATE (randomized, placebo-controlled), CHERRY (randomized, no placebo), and some smaller ones,” Dr. Bhatt added. “Both REDUCE-IT and JELIS found associations between higher levels of EPA and lower rates of cardiovascular events, suggesting that higher EPA levels attained specifically with icosapent ethyl are beneficial.”
Pointing out that all the glucagonlike peptide–1 agonists lower glucose, for example, but not all reduce cardiovascular events, Dr. Bhatt said it was best to focus on clinical trial results and not overly focus on biomarker changes.
“Yes, the drug in STRENGTH raised EPA (and raised DHA, as well as lowering triglycerides), but the drug in REDUCE-IT and JELIS raised EPA much more, without raising DHA – and more importantly, the increase in EPA was via a totally different drug, with many different properties,” he added.
In his discussion of the study at the ACC presentation, Dr. Bhatt pointed out that in the STRENGTH trial overall there was no reduction in major adverse cardiovascular events despite a 19% reduction in triglycerides, which he said was a “very interesting disconnect.” He asked Dr. Nissen what he thought the reason was for the observation in this analysis of no relationship between EPA or DHA level and triglyceride reduction.
Dr. Nissen said that was an interesting point. “When we look at the two trials, they both reduced triglyceride levels by an almost identical amount, 19%, but we don’t see a relationship with that and EPA levels achieved.” He suggested this may be because of different threshold levels.
Dr. Bhatt also noted that high-intensity statin use was lower in the patients with higher EPA levels in the STRENGTH analysis, but Dr. Nissen countered: “I don’t think that was enough of a difference to explain the lack of an effect.”
Invited commentator on the new analysis at an ACC press conference, Eileen Handberg, PhD, said it was important to try to understand the reasons behind the different results of the STRENGTH and REDUCE-IT trials. “These new findings are important because they explain potentially why these outcomes are different,” she stated.
Dr. Handberg, who is professor of medicine at the University of Florida, Gainesville, said she hoped the additional research called for by Dr. Nissen would go ahead as a head-to-head study of the two omega-3 products or of the two different placebo oils.
The STRENGTH trial was sponsored by Astra Zeneca. Dr. Nissen reports research grants from AbbVie, Amgen, Astra Zeneca, Eli Lilly, Esperion Therapeutics, MEDTRONIC, MyoKardia, Novartis, Novo Nordisk, Pfizer, and Silence Therapeutics. Dr. Bhatt reports constant fees/honoraria from CellProthera, Elsevier Practice Update Cardiology, K2P, Level Ex, Medtelligence, MJH Life Sciences, and WebMD; data safety monitoring board activities with Contego; other roles with TobeSoft, Belvoir Publications, Cardax, Cereno Scientific, Clinical Cardiology, Elsevier, HMP Global, Janssen Pharmaceuticals, Journal of Invasive Cardiology, Medscape Cardiology, Merck, MyoKardia, Novo Nordisk, PhaseBio, PLx Pharma, Regado Biosciences, and Slack Publications/Cardiology Research Foundation; and research grants from Abbott, Afimmune, Amarin, Amgen, Astra Zeneca, Bayer Healthcare Pharmaceuticals, Boehringer Ingelheim Pharmaceuticals, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Cardax, Chiesi, Eisai, Eli Lilly, Ethicon, FlowCo, Forest Laboratories, Fractyl, HLS Therapeutics, Idorsia, Ironwood, Ischemix, Lexicon, MEDTRONIC, MyoKardia, Owkin, Pfizer, PhaseBio, PLx Pharma, Regeneron, Roche, Sanofi Aventis, Synaptic, Takeda, and The Medicines Company.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM ACC 2021
Ultrasound renal denervation drops BP in patients on triple therapy
Renal denervation’s comeback as a potential treatment for patients with drug-resistant hypertension rolls on.
Renal denervation with ultrasound energy produced a significant, median 4.5–mm Hg incremental drop in daytime, ambulatory, systolic blood pressure, compared with sham-treatment after 2 months follow-up in a randomized study of 136 patients with drug-resistant hypertension maintained on a standardized, single-pill, triple-drug regimen during the study.
The results “confirm that ultrasound renal denervation can lower blood pressure across a spectrum of hypertension,” concluded Ajay J. Kirtane, MD, at the annual scientific sessions of the American College of Cardiology. Renal denervation procedures involve percutaneously placing an endovascular catheter bilaterally inside a patient’s renal arteries and using brief pulses of energy to ablate neurons involved in blood pressure regulation.
A former ‘hot concept’
“Renal denervation was a hot concept a number of years ago, but had been tested only in studies without a sham control,” and initial testing using sham controls failed to show a significant benefit from the intervention, noted Deepak L. Bhatt, MD, an interventional cardiologist and professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School in Boston who was not involved with the study. The significant reductions in systolic blood pressure reported with renal denervation, compared with control patients in this study, “are believable” because of inclusion of a true control cohort, he added. “This really exciting finding puts renal denervation squarely back on the map,” commented Dr. Bhatt during a press briefing.
Dr. Bhatt added that, while the median 4.5–mm Hg incremental reduction in daytime, ambulatory, systolic blood pressure, compared with control patients – the study’s primary endpoint – may seem modest, “in the world of hypertension it’s a meaningful reduction” that, if sustained over the long term, would be expected to produce meaningful cuts in adverse cardiovascular events such as heart failure, stroke, and MI.
“The question is whether the effects are durable,” highlighted Dr. Bhatt, who helped lead the first sham-controlled trial of renal denervation, SYMPLICITY HTN-3, which failed to show a significant blood pressure reduction, compared with controls using radiofrequency energy to ablate renal nerves. A more recent study that used a different radiofrequency catheter and sham controls showed a significant effect on reducing systolic blood pressure in the SPYRAL HTN-OFF MED Pivotal trial, which by design did not maintain patients on any antihypertensive medications following their renal denervation procedure.
Dr. Kirtane noted that, although the median systolic blood pressure reduction, compared with controls treated by a sham procedure, was 4.5 mm Hg, the total median systolic pressure reduction after 2 months in the actively treated patients was 8.0 mm Hg when compared with their baseline blood pressure.
Concurrently with his report the results also appeared in an article posted online (Lancet. 2021 May 16;doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(21)00788-1).
Denervation coupled with a single, daily three-drug pill
The RADIANCE-HTN TRIO study ran at 53 centers in the United States and Europe, and randomized 136 adults with an office-measured blood pressure of at least 140/90 mm Hg despite being on a stable regimen of at least three antihypertensive drugs including a diuretic. The enrolled cohort averaged 52 years of age and had an average office-measured pressure of about 162/104 mm Hg despite being on an average of four agents, although only about a third of enrolled patients were on treatment with a mineralocorticoid-receptor antagonist (MRA) such as spironolactone.
At the time of enrollment and 4 weeks before their denervation procedure, all patients switched to a uniform drug regimen of a single, daily, oral pill containing the calcium channel blocker amlodipine, the angiotensin receptor blocker valsartan or olmesartan, and the diuretic hydrochlorothiazide with no other drug treatment allowed except for unusual, prespecified clinical circumstances. All patients remained on this drug regimen for the initial 2-month follow-up period unless their blood pressure exceeded 180/110 mm Hg during in-office measurement.
The denervation treatment was well tolerated, although patients reported brief, transient, and “minor” pain associated with the procedure that did not affect treatment blinding or have any lingering consequences, said Dr. Kirtane, professor of medicine at Columbia University Vagelos College of Physicians and Surgeons in New York.
A reason to use energy delivery by ultrasound rather than by radiofrequency to ablate nerves in the renal arteries is that the ultrasound approach exerts a more uniform effect, allowing effective treatment delivery without need for catheter repositioning into more distal branches of the renal arteries, said Dr. Kirtane, who is also an interventional cardiologist at NewYork-Presbyterian/Columbia University Irving Medical Center.
But each method has its advantages, he added.
He also conceded that additional questions need to be addressed regarding which patients are most appropriate for renal denervation. “We need to figure out in which patients we can apply a device-based treatment,” Dr. Kirtane said during the press briefing. Patients with what appears to be drug-resistant hypertension often do not receive treatment with a MRA because of adverse effects, and many of these patients are not usually assessed for primary aldosteronism.
In SYMPLICITY HTN-3, “about half the patients who were seemingly eligible became ineligible” when they started treatment with a MRA, noted Dr. Bhatt. “A little spironolactone can go a long way” toward resolving treatment-resistant hypertension in many patients, he said.
RADIANCE-HTN TRIO was sponsored by ReCor Medical, the company developing the tested ultrasound catheter. Dr. Kirtane has received travel expenses and meals from ReCor Medical and several other companies, and Columbia has received research funding from ReCor Medical and several other companies related to research he has conducted. Dr. Bhatt has no relationship with ReCor Medical. He has been a consultant to and received honoraria from K2P, Level Ex, and MJH Life Sciences; he has been an advisor to Cardax, Cereno Scientific, Myokardia, Novo Nordisk, Phase Bio, and PLx Pharma; and he has received research funding from numerous companies.
Renal denervation’s comeback as a potential treatment for patients with drug-resistant hypertension rolls on.
Renal denervation with ultrasound energy produced a significant, median 4.5–mm Hg incremental drop in daytime, ambulatory, systolic blood pressure, compared with sham-treatment after 2 months follow-up in a randomized study of 136 patients with drug-resistant hypertension maintained on a standardized, single-pill, triple-drug regimen during the study.
The results “confirm that ultrasound renal denervation can lower blood pressure across a spectrum of hypertension,” concluded Ajay J. Kirtane, MD, at the annual scientific sessions of the American College of Cardiology. Renal denervation procedures involve percutaneously placing an endovascular catheter bilaterally inside a patient’s renal arteries and using brief pulses of energy to ablate neurons involved in blood pressure regulation.
A former ‘hot concept’
“Renal denervation was a hot concept a number of years ago, but had been tested only in studies without a sham control,” and initial testing using sham controls failed to show a significant benefit from the intervention, noted Deepak L. Bhatt, MD, an interventional cardiologist and professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School in Boston who was not involved with the study. The significant reductions in systolic blood pressure reported with renal denervation, compared with control patients in this study, “are believable” because of inclusion of a true control cohort, he added. “This really exciting finding puts renal denervation squarely back on the map,” commented Dr. Bhatt during a press briefing.
Dr. Bhatt added that, while the median 4.5–mm Hg incremental reduction in daytime, ambulatory, systolic blood pressure, compared with control patients – the study’s primary endpoint – may seem modest, “in the world of hypertension it’s a meaningful reduction” that, if sustained over the long term, would be expected to produce meaningful cuts in adverse cardiovascular events such as heart failure, stroke, and MI.
“The question is whether the effects are durable,” highlighted Dr. Bhatt, who helped lead the first sham-controlled trial of renal denervation, SYMPLICITY HTN-3, which failed to show a significant blood pressure reduction, compared with controls using radiofrequency energy to ablate renal nerves. A more recent study that used a different radiofrequency catheter and sham controls showed a significant effect on reducing systolic blood pressure in the SPYRAL HTN-OFF MED Pivotal trial, which by design did not maintain patients on any antihypertensive medications following their renal denervation procedure.
Dr. Kirtane noted that, although the median systolic blood pressure reduction, compared with controls treated by a sham procedure, was 4.5 mm Hg, the total median systolic pressure reduction after 2 months in the actively treated patients was 8.0 mm Hg when compared with their baseline blood pressure.
Concurrently with his report the results also appeared in an article posted online (Lancet. 2021 May 16;doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(21)00788-1).
Denervation coupled with a single, daily three-drug pill
The RADIANCE-HTN TRIO study ran at 53 centers in the United States and Europe, and randomized 136 adults with an office-measured blood pressure of at least 140/90 mm Hg despite being on a stable regimen of at least three antihypertensive drugs including a diuretic. The enrolled cohort averaged 52 years of age and had an average office-measured pressure of about 162/104 mm Hg despite being on an average of four agents, although only about a third of enrolled patients were on treatment with a mineralocorticoid-receptor antagonist (MRA) such as spironolactone.
At the time of enrollment and 4 weeks before their denervation procedure, all patients switched to a uniform drug regimen of a single, daily, oral pill containing the calcium channel blocker amlodipine, the angiotensin receptor blocker valsartan or olmesartan, and the diuretic hydrochlorothiazide with no other drug treatment allowed except for unusual, prespecified clinical circumstances. All patients remained on this drug regimen for the initial 2-month follow-up period unless their blood pressure exceeded 180/110 mm Hg during in-office measurement.
The denervation treatment was well tolerated, although patients reported brief, transient, and “minor” pain associated with the procedure that did not affect treatment blinding or have any lingering consequences, said Dr. Kirtane, professor of medicine at Columbia University Vagelos College of Physicians and Surgeons in New York.
A reason to use energy delivery by ultrasound rather than by radiofrequency to ablate nerves in the renal arteries is that the ultrasound approach exerts a more uniform effect, allowing effective treatment delivery without need for catheter repositioning into more distal branches of the renal arteries, said Dr. Kirtane, who is also an interventional cardiologist at NewYork-Presbyterian/Columbia University Irving Medical Center.
But each method has its advantages, he added.
He also conceded that additional questions need to be addressed regarding which patients are most appropriate for renal denervation. “We need to figure out in which patients we can apply a device-based treatment,” Dr. Kirtane said during the press briefing. Patients with what appears to be drug-resistant hypertension often do not receive treatment with a MRA because of adverse effects, and many of these patients are not usually assessed for primary aldosteronism.
In SYMPLICITY HTN-3, “about half the patients who were seemingly eligible became ineligible” when they started treatment with a MRA, noted Dr. Bhatt. “A little spironolactone can go a long way” toward resolving treatment-resistant hypertension in many patients, he said.
RADIANCE-HTN TRIO was sponsored by ReCor Medical, the company developing the tested ultrasound catheter. Dr. Kirtane has received travel expenses and meals from ReCor Medical and several other companies, and Columbia has received research funding from ReCor Medical and several other companies related to research he has conducted. Dr. Bhatt has no relationship with ReCor Medical. He has been a consultant to and received honoraria from K2P, Level Ex, and MJH Life Sciences; he has been an advisor to Cardax, Cereno Scientific, Myokardia, Novo Nordisk, Phase Bio, and PLx Pharma; and he has received research funding from numerous companies.
Renal denervation’s comeback as a potential treatment for patients with drug-resistant hypertension rolls on.
Renal denervation with ultrasound energy produced a significant, median 4.5–mm Hg incremental drop in daytime, ambulatory, systolic blood pressure, compared with sham-treatment after 2 months follow-up in a randomized study of 136 patients with drug-resistant hypertension maintained on a standardized, single-pill, triple-drug regimen during the study.
The results “confirm that ultrasound renal denervation can lower blood pressure across a spectrum of hypertension,” concluded Ajay J. Kirtane, MD, at the annual scientific sessions of the American College of Cardiology. Renal denervation procedures involve percutaneously placing an endovascular catheter bilaterally inside a patient’s renal arteries and using brief pulses of energy to ablate neurons involved in blood pressure regulation.
A former ‘hot concept’
“Renal denervation was a hot concept a number of years ago, but had been tested only in studies without a sham control,” and initial testing using sham controls failed to show a significant benefit from the intervention, noted Deepak L. Bhatt, MD, an interventional cardiologist and professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School in Boston who was not involved with the study. The significant reductions in systolic blood pressure reported with renal denervation, compared with control patients in this study, “are believable” because of inclusion of a true control cohort, he added. “This really exciting finding puts renal denervation squarely back on the map,” commented Dr. Bhatt during a press briefing.
Dr. Bhatt added that, while the median 4.5–mm Hg incremental reduction in daytime, ambulatory, systolic blood pressure, compared with control patients – the study’s primary endpoint – may seem modest, “in the world of hypertension it’s a meaningful reduction” that, if sustained over the long term, would be expected to produce meaningful cuts in adverse cardiovascular events such as heart failure, stroke, and MI.
“The question is whether the effects are durable,” highlighted Dr. Bhatt, who helped lead the first sham-controlled trial of renal denervation, SYMPLICITY HTN-3, which failed to show a significant blood pressure reduction, compared with controls using radiofrequency energy to ablate renal nerves. A more recent study that used a different radiofrequency catheter and sham controls showed a significant effect on reducing systolic blood pressure in the SPYRAL HTN-OFF MED Pivotal trial, which by design did not maintain patients on any antihypertensive medications following their renal denervation procedure.
Dr. Kirtane noted that, although the median systolic blood pressure reduction, compared with controls treated by a sham procedure, was 4.5 mm Hg, the total median systolic pressure reduction after 2 months in the actively treated patients was 8.0 mm Hg when compared with their baseline blood pressure.
Concurrently with his report the results also appeared in an article posted online (Lancet. 2021 May 16;doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(21)00788-1).
Denervation coupled with a single, daily three-drug pill
The RADIANCE-HTN TRIO study ran at 53 centers in the United States and Europe, and randomized 136 adults with an office-measured blood pressure of at least 140/90 mm Hg despite being on a stable regimen of at least three antihypertensive drugs including a diuretic. The enrolled cohort averaged 52 years of age and had an average office-measured pressure of about 162/104 mm Hg despite being on an average of four agents, although only about a third of enrolled patients were on treatment with a mineralocorticoid-receptor antagonist (MRA) such as spironolactone.
At the time of enrollment and 4 weeks before their denervation procedure, all patients switched to a uniform drug regimen of a single, daily, oral pill containing the calcium channel blocker amlodipine, the angiotensin receptor blocker valsartan or olmesartan, and the diuretic hydrochlorothiazide with no other drug treatment allowed except for unusual, prespecified clinical circumstances. All patients remained on this drug regimen for the initial 2-month follow-up period unless their blood pressure exceeded 180/110 mm Hg during in-office measurement.
The denervation treatment was well tolerated, although patients reported brief, transient, and “minor” pain associated with the procedure that did not affect treatment blinding or have any lingering consequences, said Dr. Kirtane, professor of medicine at Columbia University Vagelos College of Physicians and Surgeons in New York.
A reason to use energy delivery by ultrasound rather than by radiofrequency to ablate nerves in the renal arteries is that the ultrasound approach exerts a more uniform effect, allowing effective treatment delivery without need for catheter repositioning into more distal branches of the renal arteries, said Dr. Kirtane, who is also an interventional cardiologist at NewYork-Presbyterian/Columbia University Irving Medical Center.
But each method has its advantages, he added.
He also conceded that additional questions need to be addressed regarding which patients are most appropriate for renal denervation. “We need to figure out in which patients we can apply a device-based treatment,” Dr. Kirtane said during the press briefing. Patients with what appears to be drug-resistant hypertension often do not receive treatment with a MRA because of adverse effects, and many of these patients are not usually assessed for primary aldosteronism.
In SYMPLICITY HTN-3, “about half the patients who were seemingly eligible became ineligible” when they started treatment with a MRA, noted Dr. Bhatt. “A little spironolactone can go a long way” toward resolving treatment-resistant hypertension in many patients, he said.
RADIANCE-HTN TRIO was sponsored by ReCor Medical, the company developing the tested ultrasound catheter. Dr. Kirtane has received travel expenses and meals from ReCor Medical and several other companies, and Columbia has received research funding from ReCor Medical and several other companies related to research he has conducted. Dr. Bhatt has no relationship with ReCor Medical. He has been a consultant to and received honoraria from K2P, Level Ex, and MJH Life Sciences; he has been an advisor to Cardax, Cereno Scientific, Myokardia, Novo Nordisk, Phase Bio, and PLx Pharma; and he has received research funding from numerous companies.
FROM ACC 2021
FLOWER-MI: FFR-guided complete revascularization shows no advantage in STEMI
For patients with ST-elevated myocardial infarction (STEMI) undergoing complete revascularization, percutaneous coronary interventions (PCI) guided by fractional flow reserve (FFR) relative to angiography-guided PCI do not result in significantly lower risk of death or events, according to data from the randomized FLOWER-MI trial.
Rather, the events at 1 year were numerically lower among those randomized to the angiography-guided approach, according to the principal investigator of the trial, Etienne Puymirat, MD, PhD.
Prior studies showing an advantage for FFR-guided PCI in patients with coronary syndromes provided the hypothesis that FFR-guided PCI would also be superior for guiding PCI in STEMI patients. In the multicenter FAME trial, for example, FFR-guided PCI for patients with multivessel disease was associated with fewer stent placements (P < .001) and a nearly 30% lower rate of events at 1 year (P = .02).
While the advantage of complete revascularization, meaning PCI treatment of nonculprit as well as culprit lesions, has already been shown to be a better strategy than treatment of culprit lesions alone, FLOWER-MI is the first large study to compare FFR to angiography for guiding this approach to STEMI patients with multivessel disease, said Dr. Puymirat of Hôpital Européen George Pompidou, Paris, at the annual scientific sessions of the American College of Cardiology.
In this trial, involving multiple centers in France, STEMI patients were eligible for randomization if they had successful PCI of a culprit lesion and 50% or greater stenosis in at least one additional nonculprit lesion. The complete revascularization, whether patients were randomized to PCI guided by angiography or FFR, was performed during the index hospital admission. Patient management and follow-up was otherwise the same.
After a small number of exclusions, the intention-to-treat populations were 577 patients in the angiography-guided group and 586 in the FFR-guided group. The characteristics of the groups were well matched with an average age of about 62 years and similar rates of risk factors, such as hypertension and diabetes.
Angiography guidance just as good
The primary outcome was a composite of all-cause mortality, nonfatal MI, and unplanned revascularization. By hazard ratio, the risk of having one of these events within 1 year of PCI was numerically greater, at 32 in the FFR-guided group and 24 in the angiography-guided group, but the difference was not statistically significant (1.32; P = .31).
However, the total rate of events was low (5.5% vs. 4.2% for the angiography-guided and FFR-guided groups, respectively) and the confidence intervals were wide (95% CI, 0.78-2.23). This was also true of the components of the primary outcome.
No signal for a difference between strategies could be derived from these components, which included a higher rate of MI in the FFR-guided group (3.1% vs. 1.7%) but a lower rate of death (1.5% vs. 1.7%).
Unplanned hospitalizations leading to revascularization rates were also low (1.9% and 2.6% for angiography-guided and FFR-guided PCI, respectively), although it was reported that the rate of revascularization for nonculprit lesions was about twice as high in the FFR group (53.3% vs. 27.3%).
At 1 year, there were also low rates and no significant differences in a list of secondary outcomes that included hospitalization for recurrent ischemia or heart failure, stent thrombosis, and revascularization. As within the primary composite outcome, no pattern could be seen in the secondary events, some of which were numerically more common in the FFR-guided group and some numerically lower.
In a cost-efficacy analysis, the median per-patient cost of the FFR-guided strategy was about 500 Euros ($607) greater (8,832 vs. 8,322; P < .01), leading Dr. Puymirat to conclude that “the use of FFR for nonculprit lesions appears to be less effective but more expensive,” at least by costs derived in France.
Lack of statistical power limits interpretation
The conclusion of FLOWER-MI is that FFR-guided PCI in complete revascularization of nonculprit lesions in STEMI patients is not superior to an angiography-guided approach, but Dr. Puymirat cautioned that the low number of events precludes a definitive message.
William Fearon, MD, professor of cardiovascular medicine at Stanford (Calif.) University Medical Center, agreed. Based on his calculations, the trial was substantially underpowered. Evaluating the details of treatment in the FFR group, Dr. Fearon pointed out that a nonculprit lesion with a FFR of 0.80 or less was identified in about 55% of patients. Ultimately, 66% in the FFR group received PCI, eliminating the key distinction between strategies for the majority of patients enrolled.
“Only about one-third of the FFR-guided patients, or about 200 patients, did not receive nonculprit PCI, and therefore only in this small group could we expect a difference in outcomes from the angio-guided group,” Dr. Fearon said.
Fewer stents were placed in the FFR-guided than angiography-guided group (1.01 vs. 1.5), but Dr. Fearon suggested that it would be very difficult to show a difference in risk of events in a study of this size when event rates at 1 year reached only about 5%.
In response, Dr. Puymirat acknowledged that the rate of events for this trial, which was designed in 2015, were lower than expected. In recalculating the power needed based on the rate of events observed in FLOWER-MI, he estimated that about 8,000 patients would have been needed to show a meaningful difference in these PCI strategies.
Dr. Puymirat reports financial relationships with more than a dozen pharmaceutical companies, including Abbott, which provided some of the funding for this trial. Dr. Fearon reports financial relationships with Abbott, CathWorks, HeartFlow, and Medtronic.
For patients with ST-elevated myocardial infarction (STEMI) undergoing complete revascularization, percutaneous coronary interventions (PCI) guided by fractional flow reserve (FFR) relative to angiography-guided PCI do not result in significantly lower risk of death or events, according to data from the randomized FLOWER-MI trial.
Rather, the events at 1 year were numerically lower among those randomized to the angiography-guided approach, according to the principal investigator of the trial, Etienne Puymirat, MD, PhD.
Prior studies showing an advantage for FFR-guided PCI in patients with coronary syndromes provided the hypothesis that FFR-guided PCI would also be superior for guiding PCI in STEMI patients. In the multicenter FAME trial, for example, FFR-guided PCI for patients with multivessel disease was associated with fewer stent placements (P < .001) and a nearly 30% lower rate of events at 1 year (P = .02).
While the advantage of complete revascularization, meaning PCI treatment of nonculprit as well as culprit lesions, has already been shown to be a better strategy than treatment of culprit lesions alone, FLOWER-MI is the first large study to compare FFR to angiography for guiding this approach to STEMI patients with multivessel disease, said Dr. Puymirat of Hôpital Européen George Pompidou, Paris, at the annual scientific sessions of the American College of Cardiology.
In this trial, involving multiple centers in France, STEMI patients were eligible for randomization if they had successful PCI of a culprit lesion and 50% or greater stenosis in at least one additional nonculprit lesion. The complete revascularization, whether patients were randomized to PCI guided by angiography or FFR, was performed during the index hospital admission. Patient management and follow-up was otherwise the same.
After a small number of exclusions, the intention-to-treat populations were 577 patients in the angiography-guided group and 586 in the FFR-guided group. The characteristics of the groups were well matched with an average age of about 62 years and similar rates of risk factors, such as hypertension and diabetes.
Angiography guidance just as good
The primary outcome was a composite of all-cause mortality, nonfatal MI, and unplanned revascularization. By hazard ratio, the risk of having one of these events within 1 year of PCI was numerically greater, at 32 in the FFR-guided group and 24 in the angiography-guided group, but the difference was not statistically significant (1.32; P = .31).
However, the total rate of events was low (5.5% vs. 4.2% for the angiography-guided and FFR-guided groups, respectively) and the confidence intervals were wide (95% CI, 0.78-2.23). This was also true of the components of the primary outcome.
No signal for a difference between strategies could be derived from these components, which included a higher rate of MI in the FFR-guided group (3.1% vs. 1.7%) but a lower rate of death (1.5% vs. 1.7%).
Unplanned hospitalizations leading to revascularization rates were also low (1.9% and 2.6% for angiography-guided and FFR-guided PCI, respectively), although it was reported that the rate of revascularization for nonculprit lesions was about twice as high in the FFR group (53.3% vs. 27.3%).
At 1 year, there were also low rates and no significant differences in a list of secondary outcomes that included hospitalization for recurrent ischemia or heart failure, stent thrombosis, and revascularization. As within the primary composite outcome, no pattern could be seen in the secondary events, some of which were numerically more common in the FFR-guided group and some numerically lower.
In a cost-efficacy analysis, the median per-patient cost of the FFR-guided strategy was about 500 Euros ($607) greater (8,832 vs. 8,322; P < .01), leading Dr. Puymirat to conclude that “the use of FFR for nonculprit lesions appears to be less effective but more expensive,” at least by costs derived in France.
Lack of statistical power limits interpretation
The conclusion of FLOWER-MI is that FFR-guided PCI in complete revascularization of nonculprit lesions in STEMI patients is not superior to an angiography-guided approach, but Dr. Puymirat cautioned that the low number of events precludes a definitive message.
William Fearon, MD, professor of cardiovascular medicine at Stanford (Calif.) University Medical Center, agreed. Based on his calculations, the trial was substantially underpowered. Evaluating the details of treatment in the FFR group, Dr. Fearon pointed out that a nonculprit lesion with a FFR of 0.80 or less was identified in about 55% of patients. Ultimately, 66% in the FFR group received PCI, eliminating the key distinction between strategies for the majority of patients enrolled.
“Only about one-third of the FFR-guided patients, or about 200 patients, did not receive nonculprit PCI, and therefore only in this small group could we expect a difference in outcomes from the angio-guided group,” Dr. Fearon said.
Fewer stents were placed in the FFR-guided than angiography-guided group (1.01 vs. 1.5), but Dr. Fearon suggested that it would be very difficult to show a difference in risk of events in a study of this size when event rates at 1 year reached only about 5%.
In response, Dr. Puymirat acknowledged that the rate of events for this trial, which was designed in 2015, were lower than expected. In recalculating the power needed based on the rate of events observed in FLOWER-MI, he estimated that about 8,000 patients would have been needed to show a meaningful difference in these PCI strategies.
Dr. Puymirat reports financial relationships with more than a dozen pharmaceutical companies, including Abbott, which provided some of the funding for this trial. Dr. Fearon reports financial relationships with Abbott, CathWorks, HeartFlow, and Medtronic.
For patients with ST-elevated myocardial infarction (STEMI) undergoing complete revascularization, percutaneous coronary interventions (PCI) guided by fractional flow reserve (FFR) relative to angiography-guided PCI do not result in significantly lower risk of death or events, according to data from the randomized FLOWER-MI trial.
Rather, the events at 1 year were numerically lower among those randomized to the angiography-guided approach, according to the principal investigator of the trial, Etienne Puymirat, MD, PhD.
Prior studies showing an advantage for FFR-guided PCI in patients with coronary syndromes provided the hypothesis that FFR-guided PCI would also be superior for guiding PCI in STEMI patients. In the multicenter FAME trial, for example, FFR-guided PCI for patients with multivessel disease was associated with fewer stent placements (P < .001) and a nearly 30% lower rate of events at 1 year (P = .02).
While the advantage of complete revascularization, meaning PCI treatment of nonculprit as well as culprit lesions, has already been shown to be a better strategy than treatment of culprit lesions alone, FLOWER-MI is the first large study to compare FFR to angiography for guiding this approach to STEMI patients with multivessel disease, said Dr. Puymirat of Hôpital Européen George Pompidou, Paris, at the annual scientific sessions of the American College of Cardiology.
In this trial, involving multiple centers in France, STEMI patients were eligible for randomization if they had successful PCI of a culprit lesion and 50% or greater stenosis in at least one additional nonculprit lesion. The complete revascularization, whether patients were randomized to PCI guided by angiography or FFR, was performed during the index hospital admission. Patient management and follow-up was otherwise the same.
After a small number of exclusions, the intention-to-treat populations were 577 patients in the angiography-guided group and 586 in the FFR-guided group. The characteristics of the groups were well matched with an average age of about 62 years and similar rates of risk factors, such as hypertension and diabetes.
Angiography guidance just as good
The primary outcome was a composite of all-cause mortality, nonfatal MI, and unplanned revascularization. By hazard ratio, the risk of having one of these events within 1 year of PCI was numerically greater, at 32 in the FFR-guided group and 24 in the angiography-guided group, but the difference was not statistically significant (1.32; P = .31).
However, the total rate of events was low (5.5% vs. 4.2% for the angiography-guided and FFR-guided groups, respectively) and the confidence intervals were wide (95% CI, 0.78-2.23). This was also true of the components of the primary outcome.
No signal for a difference between strategies could be derived from these components, which included a higher rate of MI in the FFR-guided group (3.1% vs. 1.7%) but a lower rate of death (1.5% vs. 1.7%).
Unplanned hospitalizations leading to revascularization rates were also low (1.9% and 2.6% for angiography-guided and FFR-guided PCI, respectively), although it was reported that the rate of revascularization for nonculprit lesions was about twice as high in the FFR group (53.3% vs. 27.3%).
At 1 year, there were also low rates and no significant differences in a list of secondary outcomes that included hospitalization for recurrent ischemia or heart failure, stent thrombosis, and revascularization. As within the primary composite outcome, no pattern could be seen in the secondary events, some of which were numerically more common in the FFR-guided group and some numerically lower.
In a cost-efficacy analysis, the median per-patient cost of the FFR-guided strategy was about 500 Euros ($607) greater (8,832 vs. 8,322; P < .01), leading Dr. Puymirat to conclude that “the use of FFR for nonculprit lesions appears to be less effective but more expensive,” at least by costs derived in France.
Lack of statistical power limits interpretation
The conclusion of FLOWER-MI is that FFR-guided PCI in complete revascularization of nonculprit lesions in STEMI patients is not superior to an angiography-guided approach, but Dr. Puymirat cautioned that the low number of events precludes a definitive message.
William Fearon, MD, professor of cardiovascular medicine at Stanford (Calif.) University Medical Center, agreed. Based on his calculations, the trial was substantially underpowered. Evaluating the details of treatment in the FFR group, Dr. Fearon pointed out that a nonculprit lesion with a FFR of 0.80 or less was identified in about 55% of patients. Ultimately, 66% in the FFR group received PCI, eliminating the key distinction between strategies for the majority of patients enrolled.
“Only about one-third of the FFR-guided patients, or about 200 patients, did not receive nonculprit PCI, and therefore only in this small group could we expect a difference in outcomes from the angio-guided group,” Dr. Fearon said.
Fewer stents were placed in the FFR-guided than angiography-guided group (1.01 vs. 1.5), but Dr. Fearon suggested that it would be very difficult to show a difference in risk of events in a study of this size when event rates at 1 year reached only about 5%.
In response, Dr. Puymirat acknowledged that the rate of events for this trial, which was designed in 2015, were lower than expected. In recalculating the power needed based on the rate of events observed in FLOWER-MI, he estimated that about 8,000 patients would have been needed to show a meaningful difference in these PCI strategies.
Dr. Puymirat reports financial relationships with more than a dozen pharmaceutical companies, including Abbott, which provided some of the funding for this trial. Dr. Fearon reports financial relationships with Abbott, CathWorks, HeartFlow, and Medtronic.
FROM ACC 2021
Nasal spray resurrected after showing clinical benefits for PSVT
Significant improvement in the control of symptoms related to paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia (PSVT) is resurrecting etripamil as a self-administered nasal spray a year after it failed to meet the primary endpoint in a phase 3 trial, according to a new analysis from this same study presented at the annual scientific sessions of the American College of Cardiology.
In the phase 3 NODE-301 trial, presented at the 2020 Heart Rhythm Society annual meeting, etripamil did not show an advantage over placebo at 5 hours for achieving sinus rhythm. Nevertheless, a new presentation of the secondary outcomes suggests substantial clinical benefit.
These advantages include significant reductions in PSVT symptoms, a trend for fewer emergency room visits, and a degree of patient satisfaction that appears meaningful, according to Bruce S. Stambler, MD, an electrophysiologist affiliated with Piedmont Heart Institute, Atlanta.
The data, despite the phase 3 trial results, “support continued development of etripamil nasal spray acute treatment of PSVT,” Dr. Stambler said.
Etripamil is an L-type calcium channel blocker. When administered by nasal spray, it reaches peak effects within about 10 minutes. But the action is short, with a decline in antiarrhythmia effects beginning about 30 minutes after the peak effect.
In the NODE-301 trial, which employed a 2:1 randomization ratio, 138 patients self-administered 70 mg of etripamil or placebo immediately upon experiencing a suspected episode of PSVT.
Up until 45 minutes, the proportion of episodes that converted to sinus rhythm was about 66% greater (hazard ratio, 1.66; P = .02) on etripamil than placebo, but the advantage was then lost. By predefined primary endpoint of 5 hours, when 100% of placebo patients but not all etripamil patients had converted, there was a slight but nonstatistical advantage for placebo (HR 1.08; P = .1212).
However, because of the rapid onset and then the rapid offset of this agent, the 5-hour time point for comparing effects might not have been the optimal duration to compare effects, according to Dr. Stambler.
On the basis of safety of etripamil, which was not associated with any significant adverse events in NODE-301, and the early clinical effect, the investigators have looked again at the data.
For relief of patient-reported symptoms and patient-reported satisfaction, which were secondary endpoints of the study, the data support a clinical role, according to this new analysis.
Specifically, there were large differences on a 7-point scale for all of the measured symptoms of PSVT in favor of etripamil, including rapid pulse (P = .002), palpitations (P = .0001), dizziness (P = 0.01), shortness of breath (P = 0.008), and anxiety (P = 0.006). A numerical advantage for chest pain did not reach significance.
“In general, patients reported scores of 4 to 5 on this scale, which corresponds to ‘not satisfied’ to ‘satisfied,’ while the placebo-treated patients reported scores of 2 to 3, which corresponds to ‘dissatisfied’ or ‘very dissatisfied,’ ” Dr. Stambler reported.
The favorable patient experience is also reflected in the Treatment Satisfaction with Questionnaire for Medication (TSQM-9), which was another NODE-301 endpoint. Evaluated when patients were still blinded to their assigned therapy, the advantage of etripamil over placebo for both global satisfaction (P = .007) and treatment effectiveness (P = .002) were also highly statistically significant.
The subjective experience of patients appeared to be reflected in objective measures. When the two groups were compared for interventions in an emergency room, the need was reduced by about half (12.1% vs. 24.5%; P = .051) among those treated with etripamil. Although this just missed the conventional measure of statistical significance, it was close. Similarly, patients randomized to etripamil required numerically fewer rescue medications (14.0% vs. 26.5%; P = .059).
Adenosine was the most common of the rescue medications, according to Dr. Stambler. He said there was no difference between the groups in use of rescue oral therapies.
When comparing etripamil and placebo in the subgroup that did visit an emergency room for PSVT, there was a delay in ER visits among those randomized to etripamil (116 vs. 79 minutes; P < 0.05), suggesting that this agent reduced the sense of urgency when PSVT symptoms develop, according to Dr. Stambler.
On average, the patients who enrolled in this trial had a PSVT history of about 1.5 years. In the year prior to enrollment, the mean number of ER visits was about nine.
In the trial design, patients were required to take a test dose of etripamil under observation by a physician before being sent home with their assigned therapy, but Dr. Stambler does not believe that the requirement, if the drug is approved, will be in the label.
Unexpectedly, many patients had symptom relief even without converting to sinus rhythm, Dr. Stambler acknowledged. He speculated that the reduction in heart rate associated with etripamil might have provided a relief of symptoms sufficient to relieve anxiety, producing the relative advantage for patient satisfaction.
Jodie L. Hurwitz, MD, director of the electrophysiology lab at Medical City Hospital, Dallas, indicated that there is a need for new options for PSVT. An expert panelist during the session where these data were presented, she was particularly interested in rapid symptom relief.
“It would be great to have a therapy that could be self-administered at home. Patients would like it, too,” she said.
Mary N. Walsh, MD, a heart failure specialist affiliated with Indiana University, Indianapolis, sees a potential role of a self-administered therapy like etripamil in conjunction with wearable devices. She noted that the proportion of patients using these devices to monitor arrhythmias is increasing, providing a role for an easily transportable therapy that could be used quickly when symptoms develop.
However, after the negative phase 3 trial, more data must now be collected to satisfy the regulatory authorities that this agent is safe and effective. Dr. Stambler said that the developer is now committed to pursue these studies.
Dr. Stambler has a financial relationship with Milestone Pharmaceuticals, which is developing etripamil nasal spray and was the sponsor of this trial. Dr. Walsh and Dr. Hurwitz have no potential relevant conflicts of interest.
Significant improvement in the control of symptoms related to paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia (PSVT) is resurrecting etripamil as a self-administered nasal spray a year after it failed to meet the primary endpoint in a phase 3 trial, according to a new analysis from this same study presented at the annual scientific sessions of the American College of Cardiology.
In the phase 3 NODE-301 trial, presented at the 2020 Heart Rhythm Society annual meeting, etripamil did not show an advantage over placebo at 5 hours for achieving sinus rhythm. Nevertheless, a new presentation of the secondary outcomes suggests substantial clinical benefit.
These advantages include significant reductions in PSVT symptoms, a trend for fewer emergency room visits, and a degree of patient satisfaction that appears meaningful, according to Bruce S. Stambler, MD, an electrophysiologist affiliated with Piedmont Heart Institute, Atlanta.
The data, despite the phase 3 trial results, “support continued development of etripamil nasal spray acute treatment of PSVT,” Dr. Stambler said.
Etripamil is an L-type calcium channel blocker. When administered by nasal spray, it reaches peak effects within about 10 minutes. But the action is short, with a decline in antiarrhythmia effects beginning about 30 minutes after the peak effect.
In the NODE-301 trial, which employed a 2:1 randomization ratio, 138 patients self-administered 70 mg of etripamil or placebo immediately upon experiencing a suspected episode of PSVT.
Up until 45 minutes, the proportion of episodes that converted to sinus rhythm was about 66% greater (hazard ratio, 1.66; P = .02) on etripamil than placebo, but the advantage was then lost. By predefined primary endpoint of 5 hours, when 100% of placebo patients but not all etripamil patients had converted, there was a slight but nonstatistical advantage for placebo (HR 1.08; P = .1212).
However, because of the rapid onset and then the rapid offset of this agent, the 5-hour time point for comparing effects might not have been the optimal duration to compare effects, according to Dr. Stambler.
On the basis of safety of etripamil, which was not associated with any significant adverse events in NODE-301, and the early clinical effect, the investigators have looked again at the data.
For relief of patient-reported symptoms and patient-reported satisfaction, which were secondary endpoints of the study, the data support a clinical role, according to this new analysis.
Specifically, there were large differences on a 7-point scale for all of the measured symptoms of PSVT in favor of etripamil, including rapid pulse (P = .002), palpitations (P = .0001), dizziness (P = 0.01), shortness of breath (P = 0.008), and anxiety (P = 0.006). A numerical advantage for chest pain did not reach significance.
“In general, patients reported scores of 4 to 5 on this scale, which corresponds to ‘not satisfied’ to ‘satisfied,’ while the placebo-treated patients reported scores of 2 to 3, which corresponds to ‘dissatisfied’ or ‘very dissatisfied,’ ” Dr. Stambler reported.
The favorable patient experience is also reflected in the Treatment Satisfaction with Questionnaire for Medication (TSQM-9), which was another NODE-301 endpoint. Evaluated when patients were still blinded to their assigned therapy, the advantage of etripamil over placebo for both global satisfaction (P = .007) and treatment effectiveness (P = .002) were also highly statistically significant.
The subjective experience of patients appeared to be reflected in objective measures. When the two groups were compared for interventions in an emergency room, the need was reduced by about half (12.1% vs. 24.5%; P = .051) among those treated with etripamil. Although this just missed the conventional measure of statistical significance, it was close. Similarly, patients randomized to etripamil required numerically fewer rescue medications (14.0% vs. 26.5%; P = .059).
Adenosine was the most common of the rescue medications, according to Dr. Stambler. He said there was no difference between the groups in use of rescue oral therapies.
When comparing etripamil and placebo in the subgroup that did visit an emergency room for PSVT, there was a delay in ER visits among those randomized to etripamil (116 vs. 79 minutes; P < 0.05), suggesting that this agent reduced the sense of urgency when PSVT symptoms develop, according to Dr. Stambler.
On average, the patients who enrolled in this trial had a PSVT history of about 1.5 years. In the year prior to enrollment, the mean number of ER visits was about nine.
In the trial design, patients were required to take a test dose of etripamil under observation by a physician before being sent home with their assigned therapy, but Dr. Stambler does not believe that the requirement, if the drug is approved, will be in the label.
Unexpectedly, many patients had symptom relief even without converting to sinus rhythm, Dr. Stambler acknowledged. He speculated that the reduction in heart rate associated with etripamil might have provided a relief of symptoms sufficient to relieve anxiety, producing the relative advantage for patient satisfaction.
Jodie L. Hurwitz, MD, director of the electrophysiology lab at Medical City Hospital, Dallas, indicated that there is a need for new options for PSVT. An expert panelist during the session where these data were presented, she was particularly interested in rapid symptom relief.
“It would be great to have a therapy that could be self-administered at home. Patients would like it, too,” she said.
Mary N. Walsh, MD, a heart failure specialist affiliated with Indiana University, Indianapolis, sees a potential role of a self-administered therapy like etripamil in conjunction with wearable devices. She noted that the proportion of patients using these devices to monitor arrhythmias is increasing, providing a role for an easily transportable therapy that could be used quickly when symptoms develop.
However, after the negative phase 3 trial, more data must now be collected to satisfy the regulatory authorities that this agent is safe and effective. Dr. Stambler said that the developer is now committed to pursue these studies.
Dr. Stambler has a financial relationship with Milestone Pharmaceuticals, which is developing etripamil nasal spray and was the sponsor of this trial. Dr. Walsh and Dr. Hurwitz have no potential relevant conflicts of interest.
Significant improvement in the control of symptoms related to paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia (PSVT) is resurrecting etripamil as a self-administered nasal spray a year after it failed to meet the primary endpoint in a phase 3 trial, according to a new analysis from this same study presented at the annual scientific sessions of the American College of Cardiology.
In the phase 3 NODE-301 trial, presented at the 2020 Heart Rhythm Society annual meeting, etripamil did not show an advantage over placebo at 5 hours for achieving sinus rhythm. Nevertheless, a new presentation of the secondary outcomes suggests substantial clinical benefit.
These advantages include significant reductions in PSVT symptoms, a trend for fewer emergency room visits, and a degree of patient satisfaction that appears meaningful, according to Bruce S. Stambler, MD, an electrophysiologist affiliated with Piedmont Heart Institute, Atlanta.
The data, despite the phase 3 trial results, “support continued development of etripamil nasal spray acute treatment of PSVT,” Dr. Stambler said.
Etripamil is an L-type calcium channel blocker. When administered by nasal spray, it reaches peak effects within about 10 minutes. But the action is short, with a decline in antiarrhythmia effects beginning about 30 minutes after the peak effect.
In the NODE-301 trial, which employed a 2:1 randomization ratio, 138 patients self-administered 70 mg of etripamil or placebo immediately upon experiencing a suspected episode of PSVT.
Up until 45 minutes, the proportion of episodes that converted to sinus rhythm was about 66% greater (hazard ratio, 1.66; P = .02) on etripamil than placebo, but the advantage was then lost. By predefined primary endpoint of 5 hours, when 100% of placebo patients but not all etripamil patients had converted, there was a slight but nonstatistical advantage for placebo (HR 1.08; P = .1212).
However, because of the rapid onset and then the rapid offset of this agent, the 5-hour time point for comparing effects might not have been the optimal duration to compare effects, according to Dr. Stambler.
On the basis of safety of etripamil, which was not associated with any significant adverse events in NODE-301, and the early clinical effect, the investigators have looked again at the data.
For relief of patient-reported symptoms and patient-reported satisfaction, which were secondary endpoints of the study, the data support a clinical role, according to this new analysis.
Specifically, there were large differences on a 7-point scale for all of the measured symptoms of PSVT in favor of etripamil, including rapid pulse (P = .002), palpitations (P = .0001), dizziness (P = 0.01), shortness of breath (P = 0.008), and anxiety (P = 0.006). A numerical advantage for chest pain did not reach significance.
“In general, patients reported scores of 4 to 5 on this scale, which corresponds to ‘not satisfied’ to ‘satisfied,’ while the placebo-treated patients reported scores of 2 to 3, which corresponds to ‘dissatisfied’ or ‘very dissatisfied,’ ” Dr. Stambler reported.
The favorable patient experience is also reflected in the Treatment Satisfaction with Questionnaire for Medication (TSQM-9), which was another NODE-301 endpoint. Evaluated when patients were still blinded to their assigned therapy, the advantage of etripamil over placebo for both global satisfaction (P = .007) and treatment effectiveness (P = .002) were also highly statistically significant.
The subjective experience of patients appeared to be reflected in objective measures. When the two groups were compared for interventions in an emergency room, the need was reduced by about half (12.1% vs. 24.5%; P = .051) among those treated with etripamil. Although this just missed the conventional measure of statistical significance, it was close. Similarly, patients randomized to etripamil required numerically fewer rescue medications (14.0% vs. 26.5%; P = .059).
Adenosine was the most common of the rescue medications, according to Dr. Stambler. He said there was no difference between the groups in use of rescue oral therapies.
When comparing etripamil and placebo in the subgroup that did visit an emergency room for PSVT, there was a delay in ER visits among those randomized to etripamil (116 vs. 79 minutes; P < 0.05), suggesting that this agent reduced the sense of urgency when PSVT symptoms develop, according to Dr. Stambler.
On average, the patients who enrolled in this trial had a PSVT history of about 1.5 years. In the year prior to enrollment, the mean number of ER visits was about nine.
In the trial design, patients were required to take a test dose of etripamil under observation by a physician before being sent home with their assigned therapy, but Dr. Stambler does not believe that the requirement, if the drug is approved, will be in the label.
Unexpectedly, many patients had symptom relief even without converting to sinus rhythm, Dr. Stambler acknowledged. He speculated that the reduction in heart rate associated with etripamil might have provided a relief of symptoms sufficient to relieve anxiety, producing the relative advantage for patient satisfaction.
Jodie L. Hurwitz, MD, director of the electrophysiology lab at Medical City Hospital, Dallas, indicated that there is a need for new options for PSVT. An expert panelist during the session where these data were presented, she was particularly interested in rapid symptom relief.
“It would be great to have a therapy that could be self-administered at home. Patients would like it, too,” she said.
Mary N. Walsh, MD, a heart failure specialist affiliated with Indiana University, Indianapolis, sees a potential role of a self-administered therapy like etripamil in conjunction with wearable devices. She noted that the proportion of patients using these devices to monitor arrhythmias is increasing, providing a role for an easily transportable therapy that could be used quickly when symptoms develop.
However, after the negative phase 3 trial, more data must now be collected to satisfy the regulatory authorities that this agent is safe and effective. Dr. Stambler said that the developer is now committed to pursue these studies.
Dr. Stambler has a financial relationship with Milestone Pharmaceuticals, which is developing etripamil nasal spray and was the sponsor of this trial. Dr. Walsh and Dr. Hurwitz have no potential relevant conflicts of interest.
FROM ACC 2021
LAAOS III: Surgical LAA closure cuts AFib stroke risk by one third
Left atrial appendage occlusion performed at the time of other heart surgery reduces the risk for stroke by about one-third in high-risk patients with atrial fibrillation (AFib), according to results of the Left Atrial Appendage Occlusion Study III (LAAOS III).
At 3.8 years’ follow-up, the primary endpoint of ischemic stroke or systemic embolism occurred in 4.8% of patients randomly assigned to left atrial appendage occlusion (LAAO) and 7.0% of those with no occlusion. This translated into a 33% relative risk reduction (hazard ratio, 0.67; 95% confidence interval, 0.53-0.85; P = .001).
In a landmark analysis, the effect was present early on but was more pronounced after the first 30 days, reducing the relative risk by 42% (HR, 0.58; 95% CI, 0.42-0.80), the researchers report.
The reduction in ongoing stroke risk was on top of oral anticoagulation (OAC) and consistent across all subgroups, Richard Whitlock, MD, PhD, professor of surgery, McMaster University, Hamilton, Ont., reported in a late-breaking trial session at the annual scientific sessions of the American College of Cardiology.
The procedure was safe and added, on average, just 6 minutes to cardiopulmonary bypass time, according to the results, simultaneously published in the New England Journal of Medicine.
“Any patient who comes to the operating room who fits the profile of a LAAOS III patient – so has atrial fibrillation and an elevated stroke risk based on their CHA2DS2-VASc score – the appendage should come off,” he said in an interview.
Commenting during the formal discussion, panelist Michael J. Mack, MD, of Baylor Health Care System in Houston, said, “This is potentially a game-changing, practice-changing study” but asked if there are any patients who shouldn’t undergo LAAO, such as those with heart failure (HF).
Dr. Whitlock said about 10%-15% of patients coming for heart surgery have a history of AFib and “as surgeons, you do need to individualize therapy. If you have a very frail patient, have concerns about tissue quality, you really need to think about how you would occlude the left atrial appendage or if you would occlude.”
Reassuringly, he noted, the data show no increase in HF hospitalizations and a beneficial effect on stroke among patients with HF and those with low ejection fractions, below 50%.
Observational data on surgical occlusion have been inconsistent, and current guidelines offer a weak recommendation in patients with AFib who have a contraindication to long-term anticoagulation. This is the first study to definitively prove that ischemic stroke is reduced by managing the left atrial appendage, he said in an interview.
“The previous percutaneous trials failed to demonstrate that; they demonstrated noninferiority but it was driven primarily by the avoidance of hemorrhagic events or strokes through taking patients off oral anticoagulation,” he said.
The results should translate into a class I guideline recommendation, he added. “This opens up a new paradigm of treatment for atrial fibrillation and stroke prevention in that it is really the first study that has looked at the additive effects of managing the left atrial appendage in addition to oral anticoagulation, and it’s protective on top of oral anticoagulation. That is a paradigm shift.”
In an accompanying editorial, Richard L. Page, MD, University of Vermont in Burlington, said the trial provides no insight on the possible benefit of surgical occlusion in patients unable to receive anticoagulation or with a lower CHA2DS2-VASc score, but he agreed a class I recommendation is likely for the population studied.
“I hope and anticipate that the results of this paper will strengthen the guideline indications for surgical left atrial appendage occlusion and will increase the number of cardiac surgeons who routinely perform this add-on procedure,” he said. “While many already perform this procedure, cardiac surgeons should now feel more comfortable that surgical left atrial appendage occlusion is indicated and supported by high-quality randomized data.”
Unfortunately, LAAOS III does not answer the question of whether patients can come off anticoagulation, but it does show surgical occlusion provides added protection from strokes, which can be huge with atrial fibrillation, Dr. Whitlock said.
“I spoke with a patient today who is an active 66-year-old individual on a [direct oral anticoagulant], and his stroke risk has been further reduced by 30%-40%, so he was ecstatic to hear the results,” Dr. Whitlock said. “I think it’s peace of mind.”
Global, nonindustry effort
LAAOS III investigators at 105 centers in 27 countries enrolled 4,811 patients undergoing cardiac surgery (mean age, 71 years; 68% male) who had a CHA2DS2-VASc score of at least 2.
In all, 4,770 were randomly assigned to no LAAO or occlusion via the preferred technique of amputation with suture closure of the stump as well as stapler occlusion, or epicardial device closure with the AtriClip (AtriCure) or TigerPaw (Maquet Medical). The treating team, researchers, and patients were blinded to assignment.
Patients were followed every 6 months with a validated stroke questionnaire. The trial was stopped early by the data safety monitoring board after the second interim analysis.
The mean CHA2DS2-VASc score was 4.2, one-third of patients had permanent AFib, 9% had a history of stroke, and more than two-thirds underwent a valve procedure, which makes LAAOS III unique, as many previous trials excluded valvular AFib, Dr. Whitlock pointed out.
Operative outcomes in the LAAO and no-LAAO groups were as follows:
- Bypass time: mean, 119 minutes vs. 113 minutes.
- Cross-clamp time: mean, 86 minutes vs. 82 minutes.
- Chest tube output: median, 520 mL vs. 500 mL.
- Reoperation for bleeding: both, 4.0%.
- Prolonged hospitalization due to HF: 5 vs. 14 events.
- 30-day mortality: 3.7% vs 4.0%.
The primary safety outcome of HF hospitalization at 3.8 years occurred in 7.7% of patients with LAAO and 6.8% without occlusion (HR, 1.13; 95% CI, 0.92-1.40), despite concerns that taking off the appendage could worsen HF risk by impairing renal clearance of salt and water.
“There’s observational data on either side of the fence, so it was an important endpoint that people were concerned about,” Dr. Whitlock told this news organization. “We had a data collection firm dedicated to admission for heart failure to really tease that out and, in the end, we saw no adverse effect.”
Although rates of ischemic stroke at 3.8 years were lower with LAAO than without (4.2% vs. 6.6%; HR, 0.62; 95% CI, 0.48-0.80), there was no difference in systemic embolism (0.3% for both) or death (22.6% vs. 22.5%).
In LAAOS III, fewer than 2% of the deaths were attributed to stroke, which is consistent with large stroke registries, Dr. Whitlock said. “Stroke is not what causes people with atrial fibrillation to die; it’s actually the progression on to heart failure.”
The positive effect on stroke was consistent across all subgroups, including sex, age, rheumatic heart disease, type of OAC at baseline, CHA2DS2-VASc score (≤4 vs. >4), type of surgery, history of heart failure or hypertension, and prior stroke/transient ischemic attack/systemic embolism.
Panelist Anne B. Curtis, MD, State University of New York at Buffalo, expressed surprise that about half of patients at baseline were not receiving anticoagulation and questioned whether event rates varied among those who did and didn’t stay on OAC.
Dr. Whitlock noted that OAC is often underused in AFib and that analyses showed the effects were consistent whether patients were on or off anticoagulants.
The study was sponsored by the Population Health Research Institute, McMaster University. Dr. Whitlock reported no relevant disclosures. Dr. Curtis reported consultant fees/honoraria from Abbott, Janssen, Medtronic, Milestone Pharmaceuticals, and Sanofi Aventis, and data safety monitoring board participation for Medtronic.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Left atrial appendage occlusion performed at the time of other heart surgery reduces the risk for stroke by about one-third in high-risk patients with atrial fibrillation (AFib), according to results of the Left Atrial Appendage Occlusion Study III (LAAOS III).
At 3.8 years’ follow-up, the primary endpoint of ischemic stroke or systemic embolism occurred in 4.8% of patients randomly assigned to left atrial appendage occlusion (LAAO) and 7.0% of those with no occlusion. This translated into a 33% relative risk reduction (hazard ratio, 0.67; 95% confidence interval, 0.53-0.85; P = .001).
In a landmark analysis, the effect was present early on but was more pronounced after the first 30 days, reducing the relative risk by 42% (HR, 0.58; 95% CI, 0.42-0.80), the researchers report.
The reduction in ongoing stroke risk was on top of oral anticoagulation (OAC) and consistent across all subgroups, Richard Whitlock, MD, PhD, professor of surgery, McMaster University, Hamilton, Ont., reported in a late-breaking trial session at the annual scientific sessions of the American College of Cardiology.
The procedure was safe and added, on average, just 6 minutes to cardiopulmonary bypass time, according to the results, simultaneously published in the New England Journal of Medicine.
“Any patient who comes to the operating room who fits the profile of a LAAOS III patient – so has atrial fibrillation and an elevated stroke risk based on their CHA2DS2-VASc score – the appendage should come off,” he said in an interview.
Commenting during the formal discussion, panelist Michael J. Mack, MD, of Baylor Health Care System in Houston, said, “This is potentially a game-changing, practice-changing study” but asked if there are any patients who shouldn’t undergo LAAO, such as those with heart failure (HF).
Dr. Whitlock said about 10%-15% of patients coming for heart surgery have a history of AFib and “as surgeons, you do need to individualize therapy. If you have a very frail patient, have concerns about tissue quality, you really need to think about how you would occlude the left atrial appendage or if you would occlude.”
Reassuringly, he noted, the data show no increase in HF hospitalizations and a beneficial effect on stroke among patients with HF and those with low ejection fractions, below 50%.
Observational data on surgical occlusion have been inconsistent, and current guidelines offer a weak recommendation in patients with AFib who have a contraindication to long-term anticoagulation. This is the first study to definitively prove that ischemic stroke is reduced by managing the left atrial appendage, he said in an interview.
“The previous percutaneous trials failed to demonstrate that; they demonstrated noninferiority but it was driven primarily by the avoidance of hemorrhagic events or strokes through taking patients off oral anticoagulation,” he said.
The results should translate into a class I guideline recommendation, he added. “This opens up a new paradigm of treatment for atrial fibrillation and stroke prevention in that it is really the first study that has looked at the additive effects of managing the left atrial appendage in addition to oral anticoagulation, and it’s protective on top of oral anticoagulation. That is a paradigm shift.”
In an accompanying editorial, Richard L. Page, MD, University of Vermont in Burlington, said the trial provides no insight on the possible benefit of surgical occlusion in patients unable to receive anticoagulation or with a lower CHA2DS2-VASc score, but he agreed a class I recommendation is likely for the population studied.
“I hope and anticipate that the results of this paper will strengthen the guideline indications for surgical left atrial appendage occlusion and will increase the number of cardiac surgeons who routinely perform this add-on procedure,” he said. “While many already perform this procedure, cardiac surgeons should now feel more comfortable that surgical left atrial appendage occlusion is indicated and supported by high-quality randomized data.”
Unfortunately, LAAOS III does not answer the question of whether patients can come off anticoagulation, but it does show surgical occlusion provides added protection from strokes, which can be huge with atrial fibrillation, Dr. Whitlock said.
“I spoke with a patient today who is an active 66-year-old individual on a [direct oral anticoagulant], and his stroke risk has been further reduced by 30%-40%, so he was ecstatic to hear the results,” Dr. Whitlock said. “I think it’s peace of mind.”
Global, nonindustry effort
LAAOS III investigators at 105 centers in 27 countries enrolled 4,811 patients undergoing cardiac surgery (mean age, 71 years; 68% male) who had a CHA2DS2-VASc score of at least 2.
In all, 4,770 were randomly assigned to no LAAO or occlusion via the preferred technique of amputation with suture closure of the stump as well as stapler occlusion, or epicardial device closure with the AtriClip (AtriCure) or TigerPaw (Maquet Medical). The treating team, researchers, and patients were blinded to assignment.
Patients were followed every 6 months with a validated stroke questionnaire. The trial was stopped early by the data safety monitoring board after the second interim analysis.
The mean CHA2DS2-VASc score was 4.2, one-third of patients had permanent AFib, 9% had a history of stroke, and more than two-thirds underwent a valve procedure, which makes LAAOS III unique, as many previous trials excluded valvular AFib, Dr. Whitlock pointed out.
Operative outcomes in the LAAO and no-LAAO groups were as follows:
- Bypass time: mean, 119 minutes vs. 113 minutes.
- Cross-clamp time: mean, 86 minutes vs. 82 minutes.
- Chest tube output: median, 520 mL vs. 500 mL.
- Reoperation for bleeding: both, 4.0%.
- Prolonged hospitalization due to HF: 5 vs. 14 events.
- 30-day mortality: 3.7% vs 4.0%.
The primary safety outcome of HF hospitalization at 3.8 years occurred in 7.7% of patients with LAAO and 6.8% without occlusion (HR, 1.13; 95% CI, 0.92-1.40), despite concerns that taking off the appendage could worsen HF risk by impairing renal clearance of salt and water.
“There’s observational data on either side of the fence, so it was an important endpoint that people were concerned about,” Dr. Whitlock told this news organization. “We had a data collection firm dedicated to admission for heart failure to really tease that out and, in the end, we saw no adverse effect.”
Although rates of ischemic stroke at 3.8 years were lower with LAAO than without (4.2% vs. 6.6%; HR, 0.62; 95% CI, 0.48-0.80), there was no difference in systemic embolism (0.3% for both) or death (22.6% vs. 22.5%).
In LAAOS III, fewer than 2% of the deaths were attributed to stroke, which is consistent with large stroke registries, Dr. Whitlock said. “Stroke is not what causes people with atrial fibrillation to die; it’s actually the progression on to heart failure.”
The positive effect on stroke was consistent across all subgroups, including sex, age, rheumatic heart disease, type of OAC at baseline, CHA2DS2-VASc score (≤4 vs. >4), type of surgery, history of heart failure or hypertension, and prior stroke/transient ischemic attack/systemic embolism.
Panelist Anne B. Curtis, MD, State University of New York at Buffalo, expressed surprise that about half of patients at baseline were not receiving anticoagulation and questioned whether event rates varied among those who did and didn’t stay on OAC.
Dr. Whitlock noted that OAC is often underused in AFib and that analyses showed the effects were consistent whether patients were on or off anticoagulants.
The study was sponsored by the Population Health Research Institute, McMaster University. Dr. Whitlock reported no relevant disclosures. Dr. Curtis reported consultant fees/honoraria from Abbott, Janssen, Medtronic, Milestone Pharmaceuticals, and Sanofi Aventis, and data safety monitoring board participation for Medtronic.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Left atrial appendage occlusion performed at the time of other heart surgery reduces the risk for stroke by about one-third in high-risk patients with atrial fibrillation (AFib), according to results of the Left Atrial Appendage Occlusion Study III (LAAOS III).
At 3.8 years’ follow-up, the primary endpoint of ischemic stroke or systemic embolism occurred in 4.8% of patients randomly assigned to left atrial appendage occlusion (LAAO) and 7.0% of those with no occlusion. This translated into a 33% relative risk reduction (hazard ratio, 0.67; 95% confidence interval, 0.53-0.85; P = .001).
In a landmark analysis, the effect was present early on but was more pronounced after the first 30 days, reducing the relative risk by 42% (HR, 0.58; 95% CI, 0.42-0.80), the researchers report.
The reduction in ongoing stroke risk was on top of oral anticoagulation (OAC) and consistent across all subgroups, Richard Whitlock, MD, PhD, professor of surgery, McMaster University, Hamilton, Ont., reported in a late-breaking trial session at the annual scientific sessions of the American College of Cardiology.
The procedure was safe and added, on average, just 6 minutes to cardiopulmonary bypass time, according to the results, simultaneously published in the New England Journal of Medicine.
“Any patient who comes to the operating room who fits the profile of a LAAOS III patient – so has atrial fibrillation and an elevated stroke risk based on their CHA2DS2-VASc score – the appendage should come off,” he said in an interview.
Commenting during the formal discussion, panelist Michael J. Mack, MD, of Baylor Health Care System in Houston, said, “This is potentially a game-changing, practice-changing study” but asked if there are any patients who shouldn’t undergo LAAO, such as those with heart failure (HF).
Dr. Whitlock said about 10%-15% of patients coming for heart surgery have a history of AFib and “as surgeons, you do need to individualize therapy. If you have a very frail patient, have concerns about tissue quality, you really need to think about how you would occlude the left atrial appendage or if you would occlude.”
Reassuringly, he noted, the data show no increase in HF hospitalizations and a beneficial effect on stroke among patients with HF and those with low ejection fractions, below 50%.
Observational data on surgical occlusion have been inconsistent, and current guidelines offer a weak recommendation in patients with AFib who have a contraindication to long-term anticoagulation. This is the first study to definitively prove that ischemic stroke is reduced by managing the left atrial appendage, he said in an interview.
“The previous percutaneous trials failed to demonstrate that; they demonstrated noninferiority but it was driven primarily by the avoidance of hemorrhagic events or strokes through taking patients off oral anticoagulation,” he said.
The results should translate into a class I guideline recommendation, he added. “This opens up a new paradigm of treatment for atrial fibrillation and stroke prevention in that it is really the first study that has looked at the additive effects of managing the left atrial appendage in addition to oral anticoagulation, and it’s protective on top of oral anticoagulation. That is a paradigm shift.”
In an accompanying editorial, Richard L. Page, MD, University of Vermont in Burlington, said the trial provides no insight on the possible benefit of surgical occlusion in patients unable to receive anticoagulation or with a lower CHA2DS2-VASc score, but he agreed a class I recommendation is likely for the population studied.
“I hope and anticipate that the results of this paper will strengthen the guideline indications for surgical left atrial appendage occlusion and will increase the number of cardiac surgeons who routinely perform this add-on procedure,” he said. “While many already perform this procedure, cardiac surgeons should now feel more comfortable that surgical left atrial appendage occlusion is indicated and supported by high-quality randomized data.”
Unfortunately, LAAOS III does not answer the question of whether patients can come off anticoagulation, but it does show surgical occlusion provides added protection from strokes, which can be huge with atrial fibrillation, Dr. Whitlock said.
“I spoke with a patient today who is an active 66-year-old individual on a [direct oral anticoagulant], and his stroke risk has been further reduced by 30%-40%, so he was ecstatic to hear the results,” Dr. Whitlock said. “I think it’s peace of mind.”
Global, nonindustry effort
LAAOS III investigators at 105 centers in 27 countries enrolled 4,811 patients undergoing cardiac surgery (mean age, 71 years; 68% male) who had a CHA2DS2-VASc score of at least 2.
In all, 4,770 were randomly assigned to no LAAO or occlusion via the preferred technique of amputation with suture closure of the stump as well as stapler occlusion, or epicardial device closure with the AtriClip (AtriCure) or TigerPaw (Maquet Medical). The treating team, researchers, and patients were blinded to assignment.
Patients were followed every 6 months with a validated stroke questionnaire. The trial was stopped early by the data safety monitoring board after the second interim analysis.
The mean CHA2DS2-VASc score was 4.2, one-third of patients had permanent AFib, 9% had a history of stroke, and more than two-thirds underwent a valve procedure, which makes LAAOS III unique, as many previous trials excluded valvular AFib, Dr. Whitlock pointed out.
Operative outcomes in the LAAO and no-LAAO groups were as follows:
- Bypass time: mean, 119 minutes vs. 113 minutes.
- Cross-clamp time: mean, 86 minutes vs. 82 minutes.
- Chest tube output: median, 520 mL vs. 500 mL.
- Reoperation for bleeding: both, 4.0%.
- Prolonged hospitalization due to HF: 5 vs. 14 events.
- 30-day mortality: 3.7% vs 4.0%.
The primary safety outcome of HF hospitalization at 3.8 years occurred in 7.7% of patients with LAAO and 6.8% without occlusion (HR, 1.13; 95% CI, 0.92-1.40), despite concerns that taking off the appendage could worsen HF risk by impairing renal clearance of salt and water.
“There’s observational data on either side of the fence, so it was an important endpoint that people were concerned about,” Dr. Whitlock told this news organization. “We had a data collection firm dedicated to admission for heart failure to really tease that out and, in the end, we saw no adverse effect.”
Although rates of ischemic stroke at 3.8 years were lower with LAAO than without (4.2% vs. 6.6%; HR, 0.62; 95% CI, 0.48-0.80), there was no difference in systemic embolism (0.3% for both) or death (22.6% vs. 22.5%).
In LAAOS III, fewer than 2% of the deaths were attributed to stroke, which is consistent with large stroke registries, Dr. Whitlock said. “Stroke is not what causes people with atrial fibrillation to die; it’s actually the progression on to heart failure.”
The positive effect on stroke was consistent across all subgroups, including sex, age, rheumatic heart disease, type of OAC at baseline, CHA2DS2-VASc score (≤4 vs. >4), type of surgery, history of heart failure or hypertension, and prior stroke/transient ischemic attack/systemic embolism.
Panelist Anne B. Curtis, MD, State University of New York at Buffalo, expressed surprise that about half of patients at baseline were not receiving anticoagulation and questioned whether event rates varied among those who did and didn’t stay on OAC.
Dr. Whitlock noted that OAC is often underused in AFib and that analyses showed the effects were consistent whether patients were on or off anticoagulants.
The study was sponsored by the Population Health Research Institute, McMaster University. Dr. Whitlock reported no relevant disclosures. Dr. Curtis reported consultant fees/honoraria from Abbott, Janssen, Medtronic, Milestone Pharmaceuticals, and Sanofi Aventis, and data safety monitoring board participation for Medtronic.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM ACC 2021