User login
Anti-Tumor Necrosis Factor Treatment for Glomerulopathy: Case Report and Review of Literature
Podocytes are terminally differentiated, highly specialized cells located in juxtaposition to the basement membrane over the abluminal surfaces of endothelial cells within the glomerular tuft. This triad structure is the site of the filtration barrier, which forms highly delicate and tightly regulated architecture to carry out the ultrafiltration function of the kidney.1 The filtration barrier is characterized by foot processes that are connected by specialized junctions called slit diaphragms.
Insults to components of the filtration barrier can initiate cascading events and perpetuate structural alterations that may eventually result in sclerotic changes.2 Common causes among children include minimal change disease (MCD) with the collapse of foot processes resulting in proteinuria, Alport syndrome due to mutation of collagen fibers within the basement membrane leading to hematuria and proteinuria, immune complex mediated nephropathy following common infections or autoimmune diseases, and focal segmental glomerulosclerosis (FSGS) that can show variable histopathology toward eventual glomerular scarring.3,4 These children often clinically have minimal, if any, signs of systemic inflammation.3-5 This has been a limiting factor for the commitment to immunomodulatory treatment, except for steroids for the treatment of MCD.6 Although prolonged steroid treatment may be efficacious, adverse effects are significant in a growing child. Alternative treatments, such as tacrolimus and rituximab have been suggested as second-line steroid-sparing agents.7,8 Not uncommonly, however, these cases are managed by supportive measures only during the progression of the natural course of the disease, which may eventually lead to renal failure, requiring transplant for survival.8,9
This case report highlights a child with a variant of uncertain significance (VUS) in genes involved in Alport syndrome and FSGS who developed an abrupt onset of proteinuria and hematuria after a respiratory illness. To our knowledge, he represents the youngest case demonstrating the benefit of targeted treatment against tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) for glomerulopathy using biologic response modifiers.
Case Description
This is currently a 7-year-old male patient who was born at 39 weeks gestation to gravida 3 para 3 following induced labor due to elevated maternal blood pressure. During the first 2 years of life, his growth and development were normal and his immunizations were up to date. The patient's medical history included upper respiratory tract infections (URIs), respiratory syncytial virus, as well as 3 bouts of pneumonia and multiple otitis media that resulted in 18 rounds of antibiotics. The child was also allergic to nuts and milk protein. The patient’s parents are of Northern European and Native American descent. There is no known family history of eye, ear, or kidney diseases.
Renal concerns were first noted at the age of 2 years and 6 months when he presented to an emergency department in Fall 2019 (week 0) for several weeks of intermittent dark-colored urine. His mother reported that the discoloration recently progressed in intensity to cola-colored, along with the onset of persistent vomiting without any fever or diarrhea. On physical examination, the patient had normal vitals: weight 14.8 kg (68th percentile), height 91 cm (24th percentile), and body surface area 0.6 m2. There was no edema, rash, or lymphadenopathy, but he appeared pale.
The patient’s initial laboratory results included: complete blood count with white blood cells (WBC) 10 x 103/L (reference range, 4.5-13.5 x 103/L); differential lymphocytes 69%; neutrophils 21%; hemoglobin 10 g/dL (reference range, 12-16 g/dL); hematocrit, 30%; (reference range, 37%-45%); platelets 437 103/L (reference range, 150-450 x 103/L); serum creatinine 0.46 mg/dL (reference range, 0.5-0.9 mg/dL); and albumin 3.1 g/dL (reference range, 3.5-5.2 g/dL). Serum electrolyte levels and liver enzymes were normal. A urine analysis revealed 3+ protein and 3+ blood with dysmorphic red blood cells (RBC) and RBC casts without WBC. The patient's spot urine protein-to-creatinine ratio was 4.3 and his renal ultrasound was normal. The patient was referred to Nephrology.
During the next 2 weeks, his protein-to-creatinine ratio progressed to 5.9 and serum albumin fell to 2.7 g/dL. His urine remained red colored, and a microscopic examination with RBC > 500 and WBC up to 10 on a high powered field. His workup was negative for antinuclear antibodies, antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody, antistreptolysin-O (ASO) and anti-DNase B. Serum C3 was low at 81 mg/dL (reference range, 90-180 mg/dL), C4 was 13.3 mg/dL (reference range, 10-40 mg/dL), and immunoglobulin G was low at 452 mg/dL (reference range 719-1475 mg/dL). A baseline audiology test revealed normal hearing.
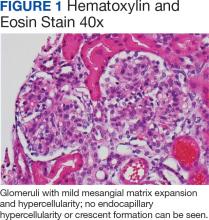
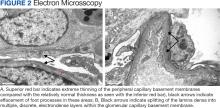
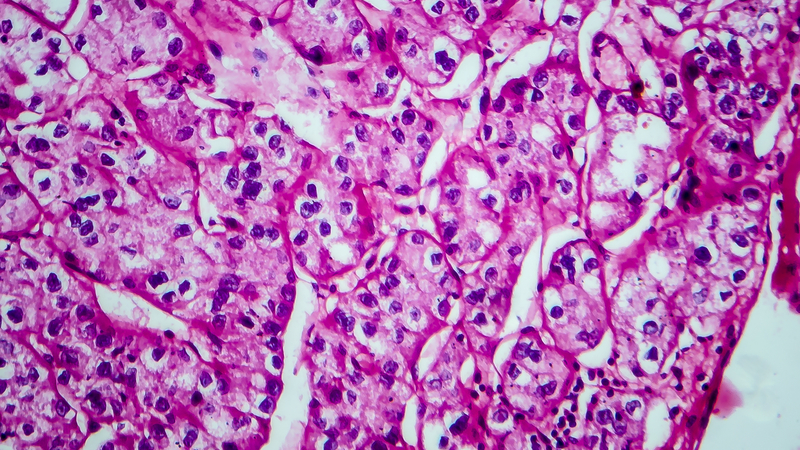
Percutaneous renal biopsy yielded about 12 glomeruli, all exhibiting mild mesangial matrix expansion and hypercellularity (Figure 1). One glomerulus had prominent parietal epithelial cells without endocapillary hypercellularity or crescent formation. There was no interstitial fibrosis or tubular atrophy. Immunofluorescence studies showed no evidence of immune complex deposition with negative staining for immunoglobulin heavy and light chains, C3 and C1q. Staining for α 2 and α 5 units of collagen was normal. Electron microscopy showed patchy areas of severe basement membrane thinning with frequent foci of mild to moderate lamina densa splitting and associated visceral epithelial cell foot process effacement (Figure 2).
These were reported as concerning findings for possible Alport syndrome by 3 independent pathology teams. The genetic testing was submitted at a commercial laboratory to screen 17 mutations, including COL4A3, COL4A4, and COL4A5. Results showed the presence of a heterozygous VUS in the COL4A4 gene (c.1055C > T; p.Pro352Leu; dbSNP ID: rs371717486; PolyPhen-2: Probably Damaging; SIFT: Deleterious) as well as the presence of a heterozygous VUS in TRPC6 gene (c2463A>T; p.Lys821Asn; dbSNP ID: rs199948731; PolyPhen-2: Benign; SIFT: Tolerated). Further genetic investigation by whole exome sequencing on approximately 20,000 genes through MNG Laboratories showed a new heterozygous VUS in the OSGEP gene [c.328T>C; p.Cys110Arg]. Additional studies ruled out mitochondrial disease, CoQ10 deficiency, and metabolic disorders upon normal findings for mitochondrial DNA, urine amino acids, plasma acylcarnitine profile, orotic acid, ammonia, and homocysteine levels.
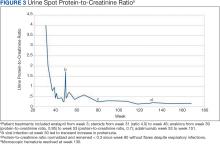
Figure 3 summarizes the patient’s treatment response during 170 weeks of follow-up (Fall 2019 to Summer 2023). The patient was started on enalapril 0.6 mg/kg daily at week 3, which continued throughout treatment. Following a rheumatology consult at week 30, the patient was started on prednisolone 3 mg/mL to assess the role of inflammation through the treatment response. An initial dose of 2 mg/kg daily (9 mL) for 1 month was followed by every other day treatment that was tapered off by week 48. To control mild but noticeably increasing proteinuria in the interim, subcutaneous anakinra 50 mg (3 mg/kg daily) was added as a steroid
DISCUSSION
This case describes a child with rapidly progressive proteinuria and hematuria following a URI who was found to have VUS mutations in 3 different genes associated with chronic kidney disease. Serology tests on the patient were negative for streptococcal antibodies and antinuclear antibodies, ruling out poststreptococcal glomerulonephritis, or systemic lupus erythematosus. His renal biopsy findings were concerning for altered podocytes, mesangial cells, and basement membrane without inflammatory infiltrate, immune complex, complements, immunoglobulin A, or vasculopathy. His blood inflammatory markers, erythrocyte sedimentation rate, C-reactive protein, and ferritin were normal when his care team initiated daily steroids.
Overall, the patient’s clinical presentation and histopathology findings were suggestive of Alport syndrome or thin basement membrane nephropathy with a high potential to progress into FSGS.10-12 Alport syndrome affects 1 in 5000 to 10,000 children annually due to S-linked inheritance of COL4A5, or autosomal recessive inheritance of COL4A3 or COL4A4 genes. It presents with hematuria and hearing loss.10 Our patient had a single copy COL4A4 gene mutation that was classified as VUS. He also had 2 additional VUS affecting the TRPC6 and OSGEP genes. TRPC6 gene mutation can be associated with FSGS through autosomal dominant inheritance. Both COL4A4 and TRPC6 gene mutations were paternally inherited. Although the patient’s father not having renal disease argues against the clinical significance of these findings, there is literature on the potential role of heterozygous COL4A4 variant mimicking thin basement membrane nephropathy that can lead to renal impairment upon copresence of superimposed conditions.13 The patient’s rapidly progressing hematuria and changes in the basement membrane were worrisome for emerging FSGS. Furthermore, VUS of TRPC6 has been reported in late onset autosomal dominant FSGS and can be associated with early onset steroid-resistant nephrotic syndrome (NS) in children.14 This concern was voiced by 3 nephrology consultants during the initial evaluation, leading to the consensus that steroid treatment for podocytopathy would not alter the patient’s long-term outcomes (ie, progression to FSGS).
Immunomodulation
Our rationale for immunomodulatory treatment was based on the abrupt onset of renal concerns following a URI, suggesting the importance of an inflammatory trigger causing altered homeostasis in a genetically susceptible host. Preclinical models show that microbial products such as lipopolysaccharides can lead to podocytopathy by several mechanisms through activation of toll-like receptor signaling. It can directly cause apoptosis by downregulation of the intracellular Akt survival pathway.15 Lipopolysaccharide can also activate the NF-αB pathway and upregulate the production of interleukin-1 (IL-1) and TNF-α in mesangial cells.16,17
Both cytokines can promote mesangial cell proliferation.18 Through autocrine and paracrine mechanisms, proinflammatory cytokines can further perpetuate somatic tissue changes and contribute to the development of podocytopathy. For instance, TNF-α can promote podocyte injury and proteinuria by downregulation of the slit diaphragm protein expression (ie, nephrin, ezrin, or podocin), and disruption of podocyte cytoskeleton.19,20 TNF-α promotes the influx and activation of macrophages and inflammatory cells. It is actively involved in chronic alterations within the glomeruli by the upregulation of matrix metalloproteases by integrins, as well as activation of myofibroblast progenitors and extracellular matrix deposition in crosstalk with transforming growth factor and other key mediators.17,21,22
For the patient described in this case report, initial improvement on steroids encouraged the pursuit of additional treatment to downregulate inflammatory pathways within the glomerular milieu. However, within the COVID-19 environment, escalating the patient’s treatment using traditional immunomodulators (ie, calcineurin inhibitors or mycophenolate mofetil) was not favored due to the risk of infection. Initially, anakinra, a recombinant IL-1 receptor antagonist, was preferred as a steroid-sparing agent for its short life and safety profile during the pandemic. At first, the patient responded well to anakinra and was allowed a steroid wean when the dose was titrated up to 6 mg/kg daily. However, anakinra did not prevent the escalation of proteinuria following a URI. After the treatment was changed to adalimumab, a fully humanized monoclonal antibody to TNF-α, the patient continued to improve and reach full remission despite experiencing a cold and the flu in the following months.
Literature Review
There is a paucity of literature on applications of biological response modifiers for idiopathic NS and FSGS.23,24 Angeletti and colleagues reported that 3 patients with severe long-standing FSGS benefited from anakinra 4 mg/kg daily to reduce proteinuria and improve kidney function. All the patients had positive C3 staining in renal biopsy and treatment response, which supported the role of C3a in inducing podocyte injury through upregulated expression of IL-1 and IL-1R.23 Trachtman and colleagues reported on the phase II FONT trial that included 14 of 21 patients aged < 18 years with advanced FSGS who were treated with adalimumab 24 mg/m2, or ≤ 40 mg every other week.24 Although, during a 6-month period, none of the 7 patients met the endpoint of reduced proteinuria by ≥ 50%, and the authors suggested that careful patient selection may improve the treatment response in future trials.24
A recent study involving transcriptomics on renal tissue samples combined with available pathology (fibrosis), urinary markers, and clinical characteristics on 285 patients with MCD or FSGS from 3 different continents identified 3 distinct clusters. Patients with evidence of activated kidney TNF pathway (n = 72, aged > 18 years) were found to have poor clinical outcomes.25 The study identified 2 urine markers associated with the TNF pathway (ie, tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases-1 and monocyte chemoattractant protein-1), which aligns with the preclinical findings previously mentioned.25
Conclusions
The patient’s condition in this case illustrates the complex nature of biologically predetermined cascading events in the emergence of glomerular disease upon environmental triggers under the influence of genetic factors.
Chronic kidney disease affects 7.7% of veterans annually, illustrating the need for new therapeutics.26 Based on our experience and literature review, upregulation of TNF-α is a root cause of glomerulopathy; further studies are warranted to evaluate the efficacy of anti-TNF biologic response modifiers for the treatment of these patients. Long-term postmarketing safety profile and steroid-sparing properties of adalimumab should allow inclusion of pediatric cases in future trials. Results may also contribute to identifying new predictive biomarkers related to the basement membrane when combined with precision nephrology to further advance patient selection and targeted treatment.25,27
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the patient’s mother for providing consent to allow publication of this case report.
1. Arif E, Nihalani D. Glomerular filtration barrier assembly: an insight. Postdoc J. 2013;1(4):33-45.
2. Garg PA. Review of podocyte biology. Am J Nephrol. 2018;47(suppl 1):3-13. doi:10.1159/000481633SUPPL
3. Warady BA, Agarwal R, Bangalore S, et al. Alport syndrome classification and management. Kidney Med. 2020;2(5):639-649. doi:10.1016/j.xkme.2020.05.014
4. Angioi A, Pani A. FSGS: from pathogenesis to the histological lesion. J Nephrol. 2016;29(4):517-523. doi:10.1007/s40620-016-0333-2
5. Roca N, Martinez C, Jatem E, Madrid A, Lopez M, Segarra A. Activation of the acute inflammatory phase response in idiopathic nephrotic syndrome: association with clinicopathological phenotypes and with response to corticosteroids. Clin Kidney J. 2021;14(4):1207-1215. doi:10.1093/ckj/sfaa247
6. Vivarelli M, Massella L, Ruggiero B, Emma F. Minimal change disease. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2017;12(2):332-345.
7. Medjeral-Thomas NR, Lawrence C, Condon M, et al. Randomized, controlled trial of tacrolimus and prednisolone monotherapy for adults with De Novo minimal change disease: a multicenter, randomized, controlled trial. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2020;15(2):209-218. doi:10.2215/CJN.06290420
8. Ye Q, Lan B, Liu H, Persson PB, Lai EY, Mao J. A critical role of the podocyte cytoskeleton in the pathogenesis of glomerular proteinuria and autoimmune podocytopathies. Acta Physiol (Oxf). 2022;235(4):e13850. doi:10.1111/apha.13850
9. Trautmann A, Schnaidt S, Lipska-Ziμtkiewicz BS, et al. Long-term outcome of steroid-resistant nephrotic syndrome in children. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2017;28:3055-3065. doi:10.1681/ASN.2016101121
10. Kashtan CE, Gross O. Clinical practice recommendations for the diagnosis and management of Alport syndrome in children, adolescents, and young adults-an update for 2020. Pediatr Nephrol. 2021;36(3):711-719. doi:10.1007/s00467-020-04819-6
11. Savige J, Rana K, Tonna S, Buzza M, Dagher H, Wang YY. Thin basement membrane nephropathy. Kidney Int. 2003;64(4):1169-78. doi:10.1046/j.1523-1755.2003.00234.x
12. Rosenberg AZ, Kopp JB. Focal segmental glomerulosclerosis. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2017; 12(3):502-517. doi:10.2215/CJN.05960616
13. Savige J. Should we diagnose autosomal dominant Alport syndrome when there is a pathogenic heterozygous COL4A3 or COL4A4 variant? Kidney Int Rep. 2018;3(6):1239-1241. doi:10.1016/j.ekir.2018.08.002
14. Gigante M, Caridi G, Montemurno E, et al. TRPC6 mutations in children with steroid-resistant nephrotic syndrome and atypical phenotype. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2011;6(7):1626-1634. doi:10.2215/CJN.07830910
15. Saurus P, Kuusela S, Lehtonen E, et al. Podocyte apoptosis is prevented by blocking the toll-like receptor pathway. Cell Death Dis. 2015;6(5):e1752. doi:10.1038/cddis.2015.125
16. Baud L, Oudinet JP, Bens M, et al. Production of tumor necrosis factor by rat mesangial cells in response to bacterial lipopolysaccharide. Kidney Int. 1989;35(5):1111-1118. doi:10.1038/ki.1989.98
17. White S, Lin L, Hu K. NF-κB and tPA signaling in kidney and other diseases. Cells. 2020;9(6):1348. doi:10.3390/cells9061348
18. Tesch GH, Lan HY, Atkins RC, Nikolic-Paterson DJ. Role of interleukin-1 in mesangial cell proliferation and matrix deposition in experimental mesangioproliferative nephritis. Am J Pathol. 1997;151(1):141-150.
19. Lai KN, Leung JCK, Chan LYY, et al. Podocyte injury induced by mesangial-derived cytokines in IgA Nephropathy. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2009;24(1):62-72. doi:10.1093/ndt/gfn441
20. Saleem MA, Kobayashi Y. Cell biology and genetics of minimal change disease. F1000 Res. 2016;5: F1000 Faculty Rev-412. doi:10.12688/f1000research.7300.1
21. Kim KP, Williams CE, Lemmon CA. Cell-matrix interactions in renal fibrosis. Kidney Dial. 2022;2(4):607-624. doi:10.3390/kidneydial2040055
22. Zvaifler NJ. Relevance of the stroma and epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) for the rheumatic diseases. Arthritis Res Ther. 2006;8(3):210. doi:10.1186/ar1963
23. Angeletti A, Magnasco A, Trivelli A, et al. Refractory minimal change disease and focal segmental glomerular sclerosis treated with Anakinra. Kidney Int Rep. 2021;7(1):121-124. doi:10.1016/j.ekir.2021.10.018
24. Trachtman H, Vento S, Herreshoff E, et al. Efficacy of galactose and adalimumab in patients with resistant focal segmental glomerulosclerosis: report of the font clinical trial group. BMC Nephrol. 2015;16:111. doi:10.1186/s12882-015-0094-5
25. Mariani LH, Eddy S, AlAkwaa FM, et al. Precision nephrology identified tumor necrosis factor activation variability in minimal change disease and focal segmental glomerulosclerosis. Kidney Int. 2023;103(3):565-579. doi:10.1016/j.kint.2022.10.023
26. Korshak L, Washington DL, Powell J, Nylen E, Kokkinos P. Kidney Disease in Veterans. US Dept of Veterans Affairs, Office of Health Equity. Updated May 13, 2020. Accessed June 28, 2024. https://www.va.gov/HEALTHEQUITY/Kidney_Disease_In_Veterans.asp
27. Malone AF, Phelan PJ, Hall G, et al. Rare hereditary COL4A3/COL4A4 variants may be mistaken for familial focal segmental glomerulosclerosis. Kidney Int. 2014;86(6):1253-1259. doi:10.1038/ki.2014.305
Podocytes are terminally differentiated, highly specialized cells located in juxtaposition to the basement membrane over the abluminal surfaces of endothelial cells within the glomerular tuft. This triad structure is the site of the filtration barrier, which forms highly delicate and tightly regulated architecture to carry out the ultrafiltration function of the kidney.1 The filtration barrier is characterized by foot processes that are connected by specialized junctions called slit diaphragms.
Insults to components of the filtration barrier can initiate cascading events and perpetuate structural alterations that may eventually result in sclerotic changes.2 Common causes among children include minimal change disease (MCD) with the collapse of foot processes resulting in proteinuria, Alport syndrome due to mutation of collagen fibers within the basement membrane leading to hematuria and proteinuria, immune complex mediated nephropathy following common infections or autoimmune diseases, and focal segmental glomerulosclerosis (FSGS) that can show variable histopathology toward eventual glomerular scarring.3,4 These children often clinically have minimal, if any, signs of systemic inflammation.3-5 This has been a limiting factor for the commitment to immunomodulatory treatment, except for steroids for the treatment of MCD.6 Although prolonged steroid treatment may be efficacious, adverse effects are significant in a growing child. Alternative treatments, such as tacrolimus and rituximab have been suggested as second-line steroid-sparing agents.7,8 Not uncommonly, however, these cases are managed by supportive measures only during the progression of the natural course of the disease, which may eventually lead to renal failure, requiring transplant for survival.8,9
This case report highlights a child with a variant of uncertain significance (VUS) in genes involved in Alport syndrome and FSGS who developed an abrupt onset of proteinuria and hematuria after a respiratory illness. To our knowledge, he represents the youngest case demonstrating the benefit of targeted treatment against tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) for glomerulopathy using biologic response modifiers.
Case Description
This is currently a 7-year-old male patient who was born at 39 weeks gestation to gravida 3 para 3 following induced labor due to elevated maternal blood pressure. During the first 2 years of life, his growth and development were normal and his immunizations were up to date. The patient's medical history included upper respiratory tract infections (URIs), respiratory syncytial virus, as well as 3 bouts of pneumonia and multiple otitis media that resulted in 18 rounds of antibiotics. The child was also allergic to nuts and milk protein. The patient’s parents are of Northern European and Native American descent. There is no known family history of eye, ear, or kidney diseases.
Renal concerns were first noted at the age of 2 years and 6 months when he presented to an emergency department in Fall 2019 (week 0) for several weeks of intermittent dark-colored urine. His mother reported that the discoloration recently progressed in intensity to cola-colored, along with the onset of persistent vomiting without any fever or diarrhea. On physical examination, the patient had normal vitals: weight 14.8 kg (68th percentile), height 91 cm (24th percentile), and body surface area 0.6 m2. There was no edema, rash, or lymphadenopathy, but he appeared pale.
The patient’s initial laboratory results included: complete blood count with white blood cells (WBC) 10 x 103/L (reference range, 4.5-13.5 x 103/L); differential lymphocytes 69%; neutrophils 21%; hemoglobin 10 g/dL (reference range, 12-16 g/dL); hematocrit, 30%; (reference range, 37%-45%); platelets 437 103/L (reference range, 150-450 x 103/L); serum creatinine 0.46 mg/dL (reference range, 0.5-0.9 mg/dL); and albumin 3.1 g/dL (reference range, 3.5-5.2 g/dL). Serum electrolyte levels and liver enzymes were normal. A urine analysis revealed 3+ protein and 3+ blood with dysmorphic red blood cells (RBC) and RBC casts without WBC. The patient's spot urine protein-to-creatinine ratio was 4.3 and his renal ultrasound was normal. The patient was referred to Nephrology.
During the next 2 weeks, his protein-to-creatinine ratio progressed to 5.9 and serum albumin fell to 2.7 g/dL. His urine remained red colored, and a microscopic examination with RBC > 500 and WBC up to 10 on a high powered field. His workup was negative for antinuclear antibodies, antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody, antistreptolysin-O (ASO) and anti-DNase B. Serum C3 was low at 81 mg/dL (reference range, 90-180 mg/dL), C4 was 13.3 mg/dL (reference range, 10-40 mg/dL), and immunoglobulin G was low at 452 mg/dL (reference range 719-1475 mg/dL). A baseline audiology test revealed normal hearing.
Percutaneous renal biopsy yielded about 12 glomeruli, all exhibiting mild mesangial matrix expansion and hypercellularity (Figure 1). One glomerulus had prominent parietal epithelial cells without endocapillary hypercellularity or crescent formation. There was no interstitial fibrosis or tubular atrophy. Immunofluorescence studies showed no evidence of immune complex deposition with negative staining for immunoglobulin heavy and light chains, C3 and C1q. Staining for α 2 and α 5 units of collagen was normal. Electron microscopy showed patchy areas of severe basement membrane thinning with frequent foci of mild to moderate lamina densa splitting and associated visceral epithelial cell foot process effacement (Figure 2).
These were reported as concerning findings for possible Alport syndrome by 3 independent pathology teams. The genetic testing was submitted at a commercial laboratory to screen 17 mutations, including COL4A3, COL4A4, and COL4A5. Results showed the presence of a heterozygous VUS in the COL4A4 gene (c.1055C > T; p.Pro352Leu; dbSNP ID: rs371717486; PolyPhen-2: Probably Damaging; SIFT: Deleterious) as well as the presence of a heterozygous VUS in TRPC6 gene (c2463A>T; p.Lys821Asn; dbSNP ID: rs199948731; PolyPhen-2: Benign; SIFT: Tolerated). Further genetic investigation by whole exome sequencing on approximately 20,000 genes through MNG Laboratories showed a new heterozygous VUS in the OSGEP gene [c.328T>C; p.Cys110Arg]. Additional studies ruled out mitochondrial disease, CoQ10 deficiency, and metabolic disorders upon normal findings for mitochondrial DNA, urine amino acids, plasma acylcarnitine profile, orotic acid, ammonia, and homocysteine levels.
Figure 3 summarizes the patient’s treatment response during 170 weeks of follow-up (Fall 2019 to Summer 2023). The patient was started on enalapril 0.6 mg/kg daily at week 3, which continued throughout treatment. Following a rheumatology consult at week 30, the patient was started on prednisolone 3 mg/mL to assess the role of inflammation through the treatment response. An initial dose of 2 mg/kg daily (9 mL) for 1 month was followed by every other day treatment that was tapered off by week 48. To control mild but noticeably increasing proteinuria in the interim, subcutaneous anakinra 50 mg (3 mg/kg daily) was added as a steroid
DISCUSSION
This case describes a child with rapidly progressive proteinuria and hematuria following a URI who was found to have VUS mutations in 3 different genes associated with chronic kidney disease. Serology tests on the patient were negative for streptococcal antibodies and antinuclear antibodies, ruling out poststreptococcal glomerulonephritis, or systemic lupus erythematosus. His renal biopsy findings were concerning for altered podocytes, mesangial cells, and basement membrane without inflammatory infiltrate, immune complex, complements, immunoglobulin A, or vasculopathy. His blood inflammatory markers, erythrocyte sedimentation rate, C-reactive protein, and ferritin were normal when his care team initiated daily steroids.
Overall, the patient’s clinical presentation and histopathology findings were suggestive of Alport syndrome or thin basement membrane nephropathy with a high potential to progress into FSGS.10-12 Alport syndrome affects 1 in 5000 to 10,000 children annually due to S-linked inheritance of COL4A5, or autosomal recessive inheritance of COL4A3 or COL4A4 genes. It presents with hematuria and hearing loss.10 Our patient had a single copy COL4A4 gene mutation that was classified as VUS. He also had 2 additional VUS affecting the TRPC6 and OSGEP genes. TRPC6 gene mutation can be associated with FSGS through autosomal dominant inheritance. Both COL4A4 and TRPC6 gene mutations were paternally inherited. Although the patient’s father not having renal disease argues against the clinical significance of these findings, there is literature on the potential role of heterozygous COL4A4 variant mimicking thin basement membrane nephropathy that can lead to renal impairment upon copresence of superimposed conditions.13 The patient’s rapidly progressing hematuria and changes in the basement membrane were worrisome for emerging FSGS. Furthermore, VUS of TRPC6 has been reported in late onset autosomal dominant FSGS and can be associated with early onset steroid-resistant nephrotic syndrome (NS) in children.14 This concern was voiced by 3 nephrology consultants during the initial evaluation, leading to the consensus that steroid treatment for podocytopathy would not alter the patient’s long-term outcomes (ie, progression to FSGS).
Immunomodulation
Our rationale for immunomodulatory treatment was based on the abrupt onset of renal concerns following a URI, suggesting the importance of an inflammatory trigger causing altered homeostasis in a genetically susceptible host. Preclinical models show that microbial products such as lipopolysaccharides can lead to podocytopathy by several mechanisms through activation of toll-like receptor signaling. It can directly cause apoptosis by downregulation of the intracellular Akt survival pathway.15 Lipopolysaccharide can also activate the NF-αB pathway and upregulate the production of interleukin-1 (IL-1) and TNF-α in mesangial cells.16,17
Both cytokines can promote mesangial cell proliferation.18 Through autocrine and paracrine mechanisms, proinflammatory cytokines can further perpetuate somatic tissue changes and contribute to the development of podocytopathy. For instance, TNF-α can promote podocyte injury and proteinuria by downregulation of the slit diaphragm protein expression (ie, nephrin, ezrin, or podocin), and disruption of podocyte cytoskeleton.19,20 TNF-α promotes the influx and activation of macrophages and inflammatory cells. It is actively involved in chronic alterations within the glomeruli by the upregulation of matrix metalloproteases by integrins, as well as activation of myofibroblast progenitors and extracellular matrix deposition in crosstalk with transforming growth factor and other key mediators.17,21,22
For the patient described in this case report, initial improvement on steroids encouraged the pursuit of additional treatment to downregulate inflammatory pathways within the glomerular milieu. However, within the COVID-19 environment, escalating the patient’s treatment using traditional immunomodulators (ie, calcineurin inhibitors or mycophenolate mofetil) was not favored due to the risk of infection. Initially, anakinra, a recombinant IL-1 receptor antagonist, was preferred as a steroid-sparing agent for its short life and safety profile during the pandemic. At first, the patient responded well to anakinra and was allowed a steroid wean when the dose was titrated up to 6 mg/kg daily. However, anakinra did not prevent the escalation of proteinuria following a URI. After the treatment was changed to adalimumab, a fully humanized monoclonal antibody to TNF-α, the patient continued to improve and reach full remission despite experiencing a cold and the flu in the following months.
Literature Review
There is a paucity of literature on applications of biological response modifiers for idiopathic NS and FSGS.23,24 Angeletti and colleagues reported that 3 patients with severe long-standing FSGS benefited from anakinra 4 mg/kg daily to reduce proteinuria and improve kidney function. All the patients had positive C3 staining in renal biopsy and treatment response, which supported the role of C3a in inducing podocyte injury through upregulated expression of IL-1 and IL-1R.23 Trachtman and colleagues reported on the phase II FONT trial that included 14 of 21 patients aged < 18 years with advanced FSGS who were treated with adalimumab 24 mg/m2, or ≤ 40 mg every other week.24 Although, during a 6-month period, none of the 7 patients met the endpoint of reduced proteinuria by ≥ 50%, and the authors suggested that careful patient selection may improve the treatment response in future trials.24
A recent study involving transcriptomics on renal tissue samples combined with available pathology (fibrosis), urinary markers, and clinical characteristics on 285 patients with MCD or FSGS from 3 different continents identified 3 distinct clusters. Patients with evidence of activated kidney TNF pathway (n = 72, aged > 18 years) were found to have poor clinical outcomes.25 The study identified 2 urine markers associated with the TNF pathway (ie, tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases-1 and monocyte chemoattractant protein-1), which aligns with the preclinical findings previously mentioned.25
Conclusions
The patient’s condition in this case illustrates the complex nature of biologically predetermined cascading events in the emergence of glomerular disease upon environmental triggers under the influence of genetic factors.
Chronic kidney disease affects 7.7% of veterans annually, illustrating the need for new therapeutics.26 Based on our experience and literature review, upregulation of TNF-α is a root cause of glomerulopathy; further studies are warranted to evaluate the efficacy of anti-TNF biologic response modifiers for the treatment of these patients. Long-term postmarketing safety profile and steroid-sparing properties of adalimumab should allow inclusion of pediatric cases in future trials. Results may also contribute to identifying new predictive biomarkers related to the basement membrane when combined with precision nephrology to further advance patient selection and targeted treatment.25,27
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the patient’s mother for providing consent to allow publication of this case report.
Podocytes are terminally differentiated, highly specialized cells located in juxtaposition to the basement membrane over the abluminal surfaces of endothelial cells within the glomerular tuft. This triad structure is the site of the filtration barrier, which forms highly delicate and tightly regulated architecture to carry out the ultrafiltration function of the kidney.1 The filtration barrier is characterized by foot processes that are connected by specialized junctions called slit diaphragms.
Insults to components of the filtration barrier can initiate cascading events and perpetuate structural alterations that may eventually result in sclerotic changes.2 Common causes among children include minimal change disease (MCD) with the collapse of foot processes resulting in proteinuria, Alport syndrome due to mutation of collagen fibers within the basement membrane leading to hematuria and proteinuria, immune complex mediated nephropathy following common infections or autoimmune diseases, and focal segmental glomerulosclerosis (FSGS) that can show variable histopathology toward eventual glomerular scarring.3,4 These children often clinically have minimal, if any, signs of systemic inflammation.3-5 This has been a limiting factor for the commitment to immunomodulatory treatment, except for steroids for the treatment of MCD.6 Although prolonged steroid treatment may be efficacious, adverse effects are significant in a growing child. Alternative treatments, such as tacrolimus and rituximab have been suggested as second-line steroid-sparing agents.7,8 Not uncommonly, however, these cases are managed by supportive measures only during the progression of the natural course of the disease, which may eventually lead to renal failure, requiring transplant for survival.8,9
This case report highlights a child with a variant of uncertain significance (VUS) in genes involved in Alport syndrome and FSGS who developed an abrupt onset of proteinuria and hematuria after a respiratory illness. To our knowledge, he represents the youngest case demonstrating the benefit of targeted treatment against tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) for glomerulopathy using biologic response modifiers.
Case Description
This is currently a 7-year-old male patient who was born at 39 weeks gestation to gravida 3 para 3 following induced labor due to elevated maternal blood pressure. During the first 2 years of life, his growth and development were normal and his immunizations were up to date. The patient's medical history included upper respiratory tract infections (URIs), respiratory syncytial virus, as well as 3 bouts of pneumonia and multiple otitis media that resulted in 18 rounds of antibiotics. The child was also allergic to nuts and milk protein. The patient’s parents are of Northern European and Native American descent. There is no known family history of eye, ear, or kidney diseases.
Renal concerns were first noted at the age of 2 years and 6 months when he presented to an emergency department in Fall 2019 (week 0) for several weeks of intermittent dark-colored urine. His mother reported that the discoloration recently progressed in intensity to cola-colored, along with the onset of persistent vomiting without any fever or diarrhea. On physical examination, the patient had normal vitals: weight 14.8 kg (68th percentile), height 91 cm (24th percentile), and body surface area 0.6 m2. There was no edema, rash, or lymphadenopathy, but he appeared pale.
The patient’s initial laboratory results included: complete blood count with white blood cells (WBC) 10 x 103/L (reference range, 4.5-13.5 x 103/L); differential lymphocytes 69%; neutrophils 21%; hemoglobin 10 g/dL (reference range, 12-16 g/dL); hematocrit, 30%; (reference range, 37%-45%); platelets 437 103/L (reference range, 150-450 x 103/L); serum creatinine 0.46 mg/dL (reference range, 0.5-0.9 mg/dL); and albumin 3.1 g/dL (reference range, 3.5-5.2 g/dL). Serum electrolyte levels and liver enzymes were normal. A urine analysis revealed 3+ protein and 3+ blood with dysmorphic red blood cells (RBC) and RBC casts without WBC. The patient's spot urine protein-to-creatinine ratio was 4.3 and his renal ultrasound was normal. The patient was referred to Nephrology.
During the next 2 weeks, his protein-to-creatinine ratio progressed to 5.9 and serum albumin fell to 2.7 g/dL. His urine remained red colored, and a microscopic examination with RBC > 500 and WBC up to 10 on a high powered field. His workup was negative for antinuclear antibodies, antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody, antistreptolysin-O (ASO) and anti-DNase B. Serum C3 was low at 81 mg/dL (reference range, 90-180 mg/dL), C4 was 13.3 mg/dL (reference range, 10-40 mg/dL), and immunoglobulin G was low at 452 mg/dL (reference range 719-1475 mg/dL). A baseline audiology test revealed normal hearing.
Percutaneous renal biopsy yielded about 12 glomeruli, all exhibiting mild mesangial matrix expansion and hypercellularity (Figure 1). One glomerulus had prominent parietal epithelial cells without endocapillary hypercellularity or crescent formation. There was no interstitial fibrosis or tubular atrophy. Immunofluorescence studies showed no evidence of immune complex deposition with negative staining for immunoglobulin heavy and light chains, C3 and C1q. Staining for α 2 and α 5 units of collagen was normal. Electron microscopy showed patchy areas of severe basement membrane thinning with frequent foci of mild to moderate lamina densa splitting and associated visceral epithelial cell foot process effacement (Figure 2).
These were reported as concerning findings for possible Alport syndrome by 3 independent pathology teams. The genetic testing was submitted at a commercial laboratory to screen 17 mutations, including COL4A3, COL4A4, and COL4A5. Results showed the presence of a heterozygous VUS in the COL4A4 gene (c.1055C > T; p.Pro352Leu; dbSNP ID: rs371717486; PolyPhen-2: Probably Damaging; SIFT: Deleterious) as well as the presence of a heterozygous VUS in TRPC6 gene (c2463A>T; p.Lys821Asn; dbSNP ID: rs199948731; PolyPhen-2: Benign; SIFT: Tolerated). Further genetic investigation by whole exome sequencing on approximately 20,000 genes through MNG Laboratories showed a new heterozygous VUS in the OSGEP gene [c.328T>C; p.Cys110Arg]. Additional studies ruled out mitochondrial disease, CoQ10 deficiency, and metabolic disorders upon normal findings for mitochondrial DNA, urine amino acids, plasma acylcarnitine profile, orotic acid, ammonia, and homocysteine levels.
Figure 3 summarizes the patient’s treatment response during 170 weeks of follow-up (Fall 2019 to Summer 2023). The patient was started on enalapril 0.6 mg/kg daily at week 3, which continued throughout treatment. Following a rheumatology consult at week 30, the patient was started on prednisolone 3 mg/mL to assess the role of inflammation through the treatment response. An initial dose of 2 mg/kg daily (9 mL) for 1 month was followed by every other day treatment that was tapered off by week 48. To control mild but noticeably increasing proteinuria in the interim, subcutaneous anakinra 50 mg (3 mg/kg daily) was added as a steroid
DISCUSSION
This case describes a child with rapidly progressive proteinuria and hematuria following a URI who was found to have VUS mutations in 3 different genes associated with chronic kidney disease. Serology tests on the patient were negative for streptococcal antibodies and antinuclear antibodies, ruling out poststreptococcal glomerulonephritis, or systemic lupus erythematosus. His renal biopsy findings were concerning for altered podocytes, mesangial cells, and basement membrane without inflammatory infiltrate, immune complex, complements, immunoglobulin A, or vasculopathy. His blood inflammatory markers, erythrocyte sedimentation rate, C-reactive protein, and ferritin were normal when his care team initiated daily steroids.
Overall, the patient’s clinical presentation and histopathology findings were suggestive of Alport syndrome or thin basement membrane nephropathy with a high potential to progress into FSGS.10-12 Alport syndrome affects 1 in 5000 to 10,000 children annually due to S-linked inheritance of COL4A5, or autosomal recessive inheritance of COL4A3 or COL4A4 genes. It presents with hematuria and hearing loss.10 Our patient had a single copy COL4A4 gene mutation that was classified as VUS. He also had 2 additional VUS affecting the TRPC6 and OSGEP genes. TRPC6 gene mutation can be associated with FSGS through autosomal dominant inheritance. Both COL4A4 and TRPC6 gene mutations were paternally inherited. Although the patient’s father not having renal disease argues against the clinical significance of these findings, there is literature on the potential role of heterozygous COL4A4 variant mimicking thin basement membrane nephropathy that can lead to renal impairment upon copresence of superimposed conditions.13 The patient’s rapidly progressing hematuria and changes in the basement membrane were worrisome for emerging FSGS. Furthermore, VUS of TRPC6 has been reported in late onset autosomal dominant FSGS and can be associated with early onset steroid-resistant nephrotic syndrome (NS) in children.14 This concern was voiced by 3 nephrology consultants during the initial evaluation, leading to the consensus that steroid treatment for podocytopathy would not alter the patient’s long-term outcomes (ie, progression to FSGS).
Immunomodulation
Our rationale for immunomodulatory treatment was based on the abrupt onset of renal concerns following a URI, suggesting the importance of an inflammatory trigger causing altered homeostasis in a genetically susceptible host. Preclinical models show that microbial products such as lipopolysaccharides can lead to podocytopathy by several mechanisms through activation of toll-like receptor signaling. It can directly cause apoptosis by downregulation of the intracellular Akt survival pathway.15 Lipopolysaccharide can also activate the NF-αB pathway and upregulate the production of interleukin-1 (IL-1) and TNF-α in mesangial cells.16,17
Both cytokines can promote mesangial cell proliferation.18 Through autocrine and paracrine mechanisms, proinflammatory cytokines can further perpetuate somatic tissue changes and contribute to the development of podocytopathy. For instance, TNF-α can promote podocyte injury and proteinuria by downregulation of the slit diaphragm protein expression (ie, nephrin, ezrin, or podocin), and disruption of podocyte cytoskeleton.19,20 TNF-α promotes the influx and activation of macrophages and inflammatory cells. It is actively involved in chronic alterations within the glomeruli by the upregulation of matrix metalloproteases by integrins, as well as activation of myofibroblast progenitors and extracellular matrix deposition in crosstalk with transforming growth factor and other key mediators.17,21,22
For the patient described in this case report, initial improvement on steroids encouraged the pursuit of additional treatment to downregulate inflammatory pathways within the glomerular milieu. However, within the COVID-19 environment, escalating the patient’s treatment using traditional immunomodulators (ie, calcineurin inhibitors or mycophenolate mofetil) was not favored due to the risk of infection. Initially, anakinra, a recombinant IL-1 receptor antagonist, was preferred as a steroid-sparing agent for its short life and safety profile during the pandemic. At first, the patient responded well to anakinra and was allowed a steroid wean when the dose was titrated up to 6 mg/kg daily. However, anakinra did not prevent the escalation of proteinuria following a URI. After the treatment was changed to adalimumab, a fully humanized monoclonal antibody to TNF-α, the patient continued to improve and reach full remission despite experiencing a cold and the flu in the following months.
Literature Review
There is a paucity of literature on applications of biological response modifiers for idiopathic NS and FSGS.23,24 Angeletti and colleagues reported that 3 patients with severe long-standing FSGS benefited from anakinra 4 mg/kg daily to reduce proteinuria and improve kidney function. All the patients had positive C3 staining in renal biopsy and treatment response, which supported the role of C3a in inducing podocyte injury through upregulated expression of IL-1 and IL-1R.23 Trachtman and colleagues reported on the phase II FONT trial that included 14 of 21 patients aged < 18 years with advanced FSGS who were treated with adalimumab 24 mg/m2, or ≤ 40 mg every other week.24 Although, during a 6-month period, none of the 7 patients met the endpoint of reduced proteinuria by ≥ 50%, and the authors suggested that careful patient selection may improve the treatment response in future trials.24
A recent study involving transcriptomics on renal tissue samples combined with available pathology (fibrosis), urinary markers, and clinical characteristics on 285 patients with MCD or FSGS from 3 different continents identified 3 distinct clusters. Patients with evidence of activated kidney TNF pathway (n = 72, aged > 18 years) were found to have poor clinical outcomes.25 The study identified 2 urine markers associated with the TNF pathway (ie, tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases-1 and monocyte chemoattractant protein-1), which aligns with the preclinical findings previously mentioned.25
Conclusions
The patient’s condition in this case illustrates the complex nature of biologically predetermined cascading events in the emergence of glomerular disease upon environmental triggers under the influence of genetic factors.
Chronic kidney disease affects 7.7% of veterans annually, illustrating the need for new therapeutics.26 Based on our experience and literature review, upregulation of TNF-α is a root cause of glomerulopathy; further studies are warranted to evaluate the efficacy of anti-TNF biologic response modifiers for the treatment of these patients. Long-term postmarketing safety profile and steroid-sparing properties of adalimumab should allow inclusion of pediatric cases in future trials. Results may also contribute to identifying new predictive biomarkers related to the basement membrane when combined with precision nephrology to further advance patient selection and targeted treatment.25,27
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the patient’s mother for providing consent to allow publication of this case report.
1. Arif E, Nihalani D. Glomerular filtration barrier assembly: an insight. Postdoc J. 2013;1(4):33-45.
2. Garg PA. Review of podocyte biology. Am J Nephrol. 2018;47(suppl 1):3-13. doi:10.1159/000481633SUPPL
3. Warady BA, Agarwal R, Bangalore S, et al. Alport syndrome classification and management. Kidney Med. 2020;2(5):639-649. doi:10.1016/j.xkme.2020.05.014
4. Angioi A, Pani A. FSGS: from pathogenesis to the histological lesion. J Nephrol. 2016;29(4):517-523. doi:10.1007/s40620-016-0333-2
5. Roca N, Martinez C, Jatem E, Madrid A, Lopez M, Segarra A. Activation of the acute inflammatory phase response in idiopathic nephrotic syndrome: association with clinicopathological phenotypes and with response to corticosteroids. Clin Kidney J. 2021;14(4):1207-1215. doi:10.1093/ckj/sfaa247
6. Vivarelli M, Massella L, Ruggiero B, Emma F. Minimal change disease. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2017;12(2):332-345.
7. Medjeral-Thomas NR, Lawrence C, Condon M, et al. Randomized, controlled trial of tacrolimus and prednisolone monotherapy for adults with De Novo minimal change disease: a multicenter, randomized, controlled trial. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2020;15(2):209-218. doi:10.2215/CJN.06290420
8. Ye Q, Lan B, Liu H, Persson PB, Lai EY, Mao J. A critical role of the podocyte cytoskeleton in the pathogenesis of glomerular proteinuria and autoimmune podocytopathies. Acta Physiol (Oxf). 2022;235(4):e13850. doi:10.1111/apha.13850
9. Trautmann A, Schnaidt S, Lipska-Ziμtkiewicz BS, et al. Long-term outcome of steroid-resistant nephrotic syndrome in children. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2017;28:3055-3065. doi:10.1681/ASN.2016101121
10. Kashtan CE, Gross O. Clinical practice recommendations for the diagnosis and management of Alport syndrome in children, adolescents, and young adults-an update for 2020. Pediatr Nephrol. 2021;36(3):711-719. doi:10.1007/s00467-020-04819-6
11. Savige J, Rana K, Tonna S, Buzza M, Dagher H, Wang YY. Thin basement membrane nephropathy. Kidney Int. 2003;64(4):1169-78. doi:10.1046/j.1523-1755.2003.00234.x
12. Rosenberg AZ, Kopp JB. Focal segmental glomerulosclerosis. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2017; 12(3):502-517. doi:10.2215/CJN.05960616
13. Savige J. Should we diagnose autosomal dominant Alport syndrome when there is a pathogenic heterozygous COL4A3 or COL4A4 variant? Kidney Int Rep. 2018;3(6):1239-1241. doi:10.1016/j.ekir.2018.08.002
14. Gigante M, Caridi G, Montemurno E, et al. TRPC6 mutations in children with steroid-resistant nephrotic syndrome and atypical phenotype. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2011;6(7):1626-1634. doi:10.2215/CJN.07830910
15. Saurus P, Kuusela S, Lehtonen E, et al. Podocyte apoptosis is prevented by blocking the toll-like receptor pathway. Cell Death Dis. 2015;6(5):e1752. doi:10.1038/cddis.2015.125
16. Baud L, Oudinet JP, Bens M, et al. Production of tumor necrosis factor by rat mesangial cells in response to bacterial lipopolysaccharide. Kidney Int. 1989;35(5):1111-1118. doi:10.1038/ki.1989.98
17. White S, Lin L, Hu K. NF-κB and tPA signaling in kidney and other diseases. Cells. 2020;9(6):1348. doi:10.3390/cells9061348
18. Tesch GH, Lan HY, Atkins RC, Nikolic-Paterson DJ. Role of interleukin-1 in mesangial cell proliferation and matrix deposition in experimental mesangioproliferative nephritis. Am J Pathol. 1997;151(1):141-150.
19. Lai KN, Leung JCK, Chan LYY, et al. Podocyte injury induced by mesangial-derived cytokines in IgA Nephropathy. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2009;24(1):62-72. doi:10.1093/ndt/gfn441
20. Saleem MA, Kobayashi Y. Cell biology and genetics of minimal change disease. F1000 Res. 2016;5: F1000 Faculty Rev-412. doi:10.12688/f1000research.7300.1
21. Kim KP, Williams CE, Lemmon CA. Cell-matrix interactions in renal fibrosis. Kidney Dial. 2022;2(4):607-624. doi:10.3390/kidneydial2040055
22. Zvaifler NJ. Relevance of the stroma and epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) for the rheumatic diseases. Arthritis Res Ther. 2006;8(3):210. doi:10.1186/ar1963
23. Angeletti A, Magnasco A, Trivelli A, et al. Refractory minimal change disease and focal segmental glomerular sclerosis treated with Anakinra. Kidney Int Rep. 2021;7(1):121-124. doi:10.1016/j.ekir.2021.10.018
24. Trachtman H, Vento S, Herreshoff E, et al. Efficacy of galactose and adalimumab in patients with resistant focal segmental glomerulosclerosis: report of the font clinical trial group. BMC Nephrol. 2015;16:111. doi:10.1186/s12882-015-0094-5
25. Mariani LH, Eddy S, AlAkwaa FM, et al. Precision nephrology identified tumor necrosis factor activation variability in minimal change disease and focal segmental glomerulosclerosis. Kidney Int. 2023;103(3):565-579. doi:10.1016/j.kint.2022.10.023
26. Korshak L, Washington DL, Powell J, Nylen E, Kokkinos P. Kidney Disease in Veterans. US Dept of Veterans Affairs, Office of Health Equity. Updated May 13, 2020. Accessed June 28, 2024. https://www.va.gov/HEALTHEQUITY/Kidney_Disease_In_Veterans.asp
27. Malone AF, Phelan PJ, Hall G, et al. Rare hereditary COL4A3/COL4A4 variants may be mistaken for familial focal segmental glomerulosclerosis. Kidney Int. 2014;86(6):1253-1259. doi:10.1038/ki.2014.305
1. Arif E, Nihalani D. Glomerular filtration barrier assembly: an insight. Postdoc J. 2013;1(4):33-45.
2. Garg PA. Review of podocyte biology. Am J Nephrol. 2018;47(suppl 1):3-13. doi:10.1159/000481633SUPPL
3. Warady BA, Agarwal R, Bangalore S, et al. Alport syndrome classification and management. Kidney Med. 2020;2(5):639-649. doi:10.1016/j.xkme.2020.05.014
4. Angioi A, Pani A. FSGS: from pathogenesis to the histological lesion. J Nephrol. 2016;29(4):517-523. doi:10.1007/s40620-016-0333-2
5. Roca N, Martinez C, Jatem E, Madrid A, Lopez M, Segarra A. Activation of the acute inflammatory phase response in idiopathic nephrotic syndrome: association with clinicopathological phenotypes and with response to corticosteroids. Clin Kidney J. 2021;14(4):1207-1215. doi:10.1093/ckj/sfaa247
6. Vivarelli M, Massella L, Ruggiero B, Emma F. Minimal change disease. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2017;12(2):332-345.
7. Medjeral-Thomas NR, Lawrence C, Condon M, et al. Randomized, controlled trial of tacrolimus and prednisolone monotherapy for adults with De Novo minimal change disease: a multicenter, randomized, controlled trial. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2020;15(2):209-218. doi:10.2215/CJN.06290420
8. Ye Q, Lan B, Liu H, Persson PB, Lai EY, Mao J. A critical role of the podocyte cytoskeleton in the pathogenesis of glomerular proteinuria and autoimmune podocytopathies. Acta Physiol (Oxf). 2022;235(4):e13850. doi:10.1111/apha.13850
9. Trautmann A, Schnaidt S, Lipska-Ziμtkiewicz BS, et al. Long-term outcome of steroid-resistant nephrotic syndrome in children. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2017;28:3055-3065. doi:10.1681/ASN.2016101121
10. Kashtan CE, Gross O. Clinical practice recommendations for the diagnosis and management of Alport syndrome in children, adolescents, and young adults-an update for 2020. Pediatr Nephrol. 2021;36(3):711-719. doi:10.1007/s00467-020-04819-6
11. Savige J, Rana K, Tonna S, Buzza M, Dagher H, Wang YY. Thin basement membrane nephropathy. Kidney Int. 2003;64(4):1169-78. doi:10.1046/j.1523-1755.2003.00234.x
12. Rosenberg AZ, Kopp JB. Focal segmental glomerulosclerosis. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2017; 12(3):502-517. doi:10.2215/CJN.05960616
13. Savige J. Should we diagnose autosomal dominant Alport syndrome when there is a pathogenic heterozygous COL4A3 or COL4A4 variant? Kidney Int Rep. 2018;3(6):1239-1241. doi:10.1016/j.ekir.2018.08.002
14. Gigante M, Caridi G, Montemurno E, et al. TRPC6 mutations in children with steroid-resistant nephrotic syndrome and atypical phenotype. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2011;6(7):1626-1634. doi:10.2215/CJN.07830910
15. Saurus P, Kuusela S, Lehtonen E, et al. Podocyte apoptosis is prevented by blocking the toll-like receptor pathway. Cell Death Dis. 2015;6(5):e1752. doi:10.1038/cddis.2015.125
16. Baud L, Oudinet JP, Bens M, et al. Production of tumor necrosis factor by rat mesangial cells in response to bacterial lipopolysaccharide. Kidney Int. 1989;35(5):1111-1118. doi:10.1038/ki.1989.98
17. White S, Lin L, Hu K. NF-κB and tPA signaling in kidney and other diseases. Cells. 2020;9(6):1348. doi:10.3390/cells9061348
18. Tesch GH, Lan HY, Atkins RC, Nikolic-Paterson DJ. Role of interleukin-1 in mesangial cell proliferation and matrix deposition in experimental mesangioproliferative nephritis. Am J Pathol. 1997;151(1):141-150.
19. Lai KN, Leung JCK, Chan LYY, et al. Podocyte injury induced by mesangial-derived cytokines in IgA Nephropathy. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2009;24(1):62-72. doi:10.1093/ndt/gfn441
20. Saleem MA, Kobayashi Y. Cell biology and genetics of minimal change disease. F1000 Res. 2016;5: F1000 Faculty Rev-412. doi:10.12688/f1000research.7300.1
21. Kim KP, Williams CE, Lemmon CA. Cell-matrix interactions in renal fibrosis. Kidney Dial. 2022;2(4):607-624. doi:10.3390/kidneydial2040055
22. Zvaifler NJ. Relevance of the stroma and epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) for the rheumatic diseases. Arthritis Res Ther. 2006;8(3):210. doi:10.1186/ar1963
23. Angeletti A, Magnasco A, Trivelli A, et al. Refractory minimal change disease and focal segmental glomerular sclerosis treated with Anakinra. Kidney Int Rep. 2021;7(1):121-124. doi:10.1016/j.ekir.2021.10.018
24. Trachtman H, Vento S, Herreshoff E, et al. Efficacy of galactose and adalimumab in patients with resistant focal segmental glomerulosclerosis: report of the font clinical trial group. BMC Nephrol. 2015;16:111. doi:10.1186/s12882-015-0094-5
25. Mariani LH, Eddy S, AlAkwaa FM, et al. Precision nephrology identified tumor necrosis factor activation variability in minimal change disease and focal segmental glomerulosclerosis. Kidney Int. 2023;103(3):565-579. doi:10.1016/j.kint.2022.10.023
26. Korshak L, Washington DL, Powell J, Nylen E, Kokkinos P. Kidney Disease in Veterans. US Dept of Veterans Affairs, Office of Health Equity. Updated May 13, 2020. Accessed June 28, 2024. https://www.va.gov/HEALTHEQUITY/Kidney_Disease_In_Veterans.asp
27. Malone AF, Phelan PJ, Hall G, et al. Rare hereditary COL4A3/COL4A4 variants may be mistaken for familial focal segmental glomerulosclerosis. Kidney Int. 2014;86(6):1253-1259. doi:10.1038/ki.2014.305
Following the Hyperkalemia Trail: A Case Report of ECG Changes and Treatment Responses
Following the Hyperkalemia Trail: A Case Report of ECG Changes and Treatment Responses
Hyperkalemia involves elevated serum potassium levels (> 5.0 mEq/L) and represents an important electrolyte disturbance due to its potentially severe consequences, including cardiac effects that can lead to dysrhythmia and even asystole and death.1,2 In a US Medicare population, the prevalence of hyperkalemia has been estimated at 2.7% and is associated with substantial health care costs.3 The prevalence is even more marked in patients with preexisting conditions such as chronic kidney disease (CKD) and heart failure.4,5
Hyperkalemia can result from multiple factors, including impaired renal function, adrenal disease, adverse drug reactions of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors (ACEIs) and other medications, and heritable mutations.6 Hyperkalemia poses a considerable clinical risk, associated with adverse outcomes such as myocardial infarction and increased mortality in patients with CKD.5,7,8 Electrocardiographic (ECG) changes associated with hyperkalemia play a vital role in guiding clinical decisions and treatment strategies.9 Understanding the pathophysiology, risk factors, and consequences of hyperkalemia, as well as the significance of ECG changes in its management, is essential for health care practitioners.
Case Presentation
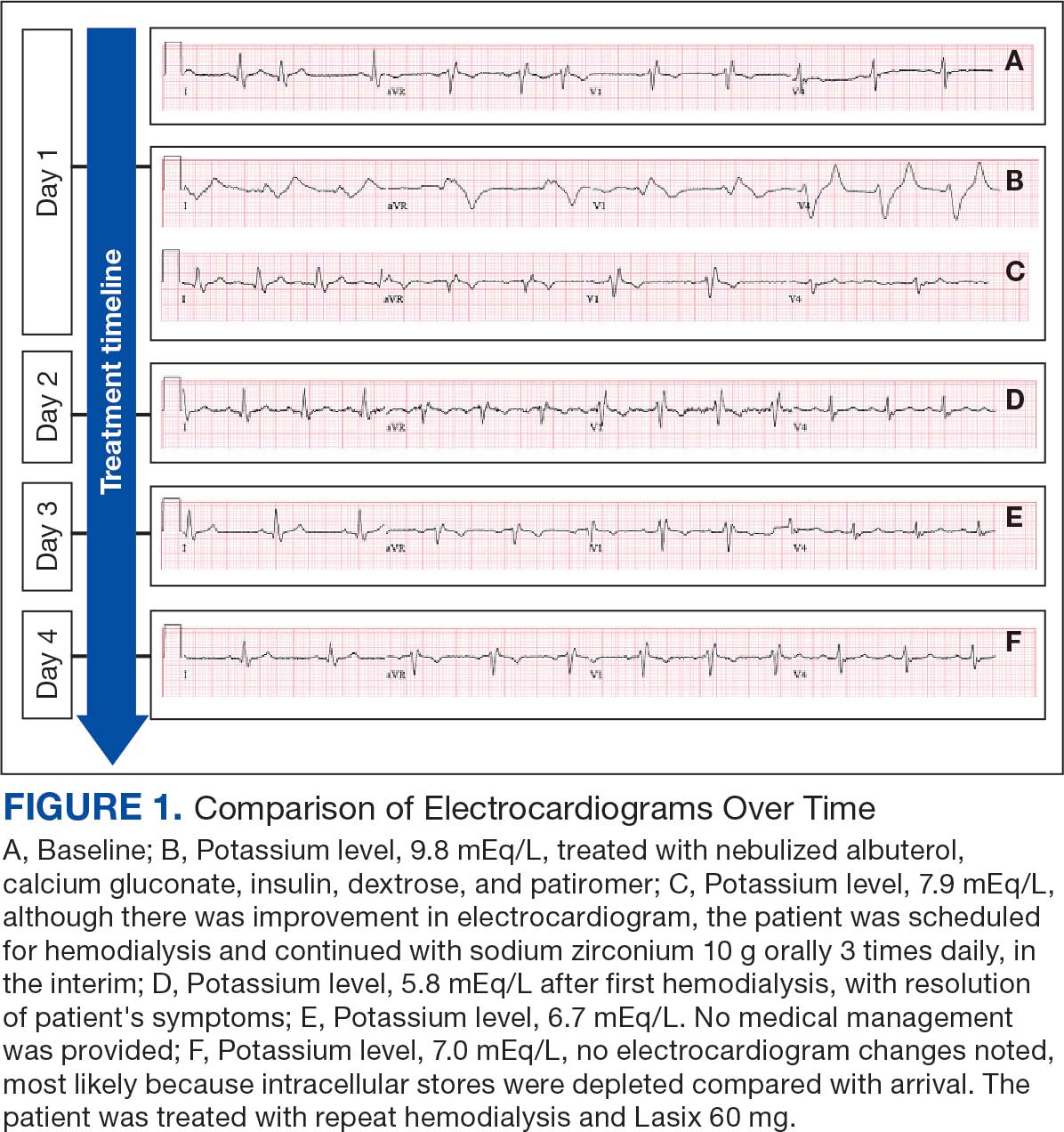
An 81-year-old Hispanic man with a history of hypertension, hypothyroidism, gout, and CKD stage 3B presented to the emergency department with progressive weakness resulting in falls and culminating in an inability to ambulate independently. Additional symptoms included nausea, diarrhea, and myalgia. His vital signs were notable for a pulse of 41 beats/min. The physical examination was remarkable for significant weakness of the bilateral upper extremities, inability to bear his own weight, and bilateral lower extremity edema. His initial ECG upon arrival showed bradycardia with wide QRS, absent P waves, and peaked T waves (Figure 1a). These findings differed from his baseline ECG taken 1 year earlier, which showed sinus rhythm with premature atrial complexes and an old right bundle branch block (Figure 1b).
Medication review revealed that the patient was currently prescribed 100 mg allopurinol daily, 2.5 mg amlodipine daily, 10 mg atorvastatin at bedtime, 4 mg doxazosin daily, 112 mcg levothyroxine daily, 100 mg losartan daily, 25 mg metoprolol daily, and 0.4 mg tamsulosin daily. The patient had also been taking over-the-counter indomethacin for knee pain.
Based on the ECG results, he was treated with 0.083%/6 mL nebulized albuterol, 4.65 Mq/250 mL saline solution intravenous (IV) calcium gluconate, 10 units IV insulin with concomitant 50%/25 mL IV dextrose and 8.4 g of oral patiromer suspension. IV furosemide was held due to concern for renal function. The decision to proceed with hemodialysis was made. Repeat laboratory tests were performed, and an ECG obtained after treatment initiation but prior to hemodialysis demonstrated improvement of rate and T wave shortening (Figure 1c). The serum potassium level dropped from 9.8 mEq/L to 7.9 mEq/L (reference range, 3.5-5.0 mEq/L) (Table 1).
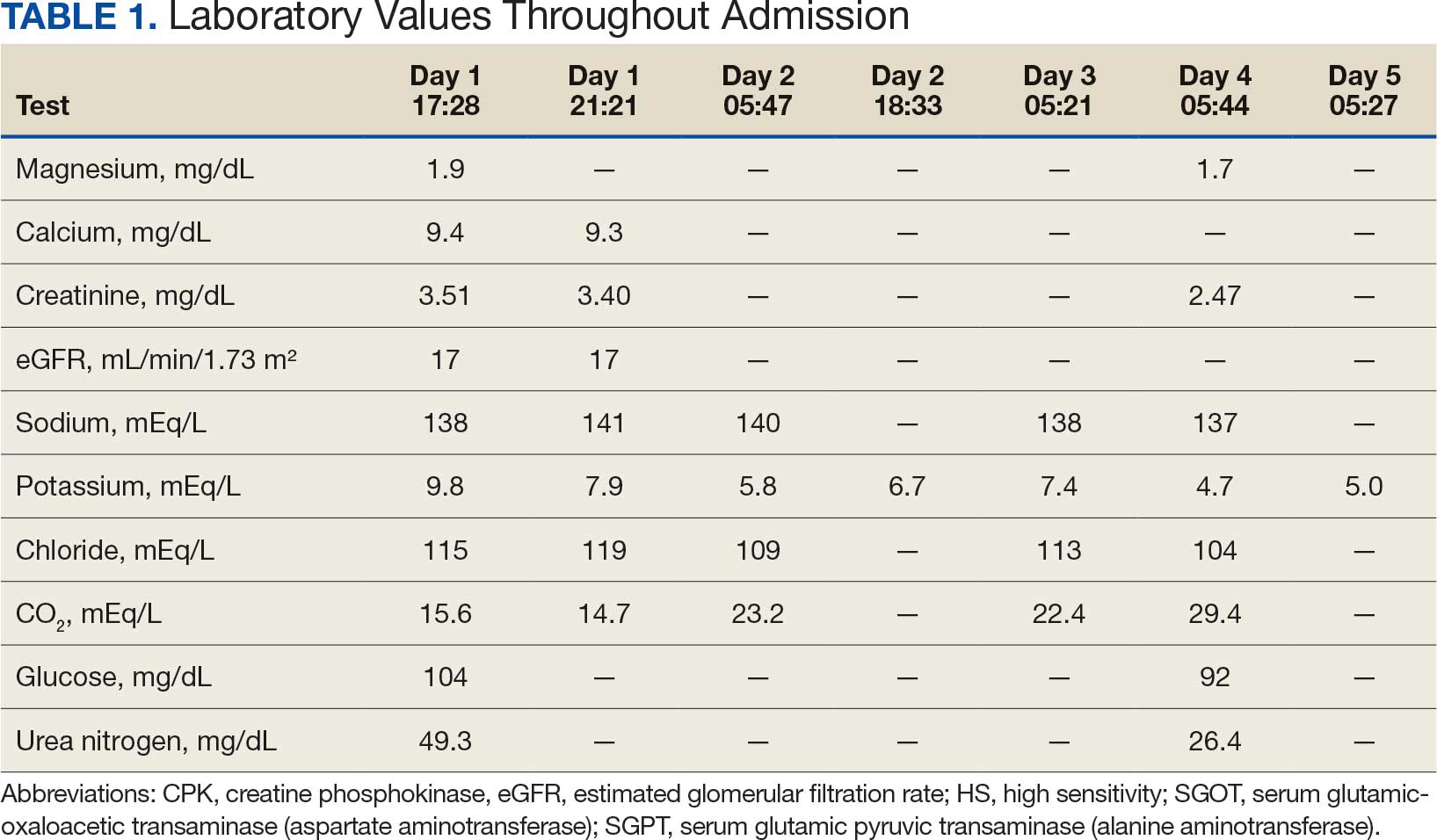
In addition to hemodialysis, sodium zirconium 10 g orally 3 times daily was added. Laboratory test results and an ECG was performed after dialysis continued to demonstrate improvement (Figure 1d). The patient’s potassium level decreased to 5.8 mEq/L, with the ECG demonstrating stability of heart rate and further improvement of the PR interval, QRS complex, and T waves.
Despite the established treatment regimen, potassium levels again rose to 6.7 mEq/L, but there were no significant changes in the ECG, and thus no medication changes were made (Figure 1e). Subsequent monitoring demonstrated a further increase in potassium to 7.4 mEq/L, with an ECG demonstrating a return to the baseline of 1 year prior. The patient underwent hemodialysis again and was given oral furosemide 60 mg every 12 hours. The potassium concentration after dialysis decreased to 4.7 mEq/L and remained stable, not going above 5.0 mEq/L on subsequent monitoring. The patient had resolution of all symptoms and was discharged.
Discussion
We have described in detail the presentation of each pathology and mechanisms of each treatment, starting with the patient’s initial condition that brought him to the emergency room—muscle weakness. Skeletal muscle weakness is a common manifestation of hyperkalemia, occurring in 20% to 40% of cases, and is more prevalent in severe elevations of potassium. Rarely, the weakness can progress to flaccid paralysis of the patient’s extremities and, in extreme cases, the diaphragm.
Muscle weakness progression occurs in a manner that resembles Guillain-Barré syndrome, starting in the lower extremities and ascending toward the upper extremities.10 This is known as secondary hyperkalemic periodic paralysis. Hyperkalemia lowers the transmembrane gradient in neurons, leading to neuronal depolarization independent of the degree of hyperkalemia. If the degree of hyperkalemia is large enough, this depolarization inactivates voltage-gated sodium channels, making neurons refractory to excitation. Electromyographical studies have shown reduction in the compounded muscle action potential.11 The transient nature of this paralysis is reflected by rapid correction of weakness and paralysis when the electrolyte disorder is corrected.
The patient in this case also presented with bradycardia. The ECG manifestations of hyperkalemia can include atrial asystole, intraventricular conduction disturbances, peaked T waves, and widened QRS complexes. However, some patients with renal insufficiency may not exhibit ECG changes despite significantly elevated serum potassium levels.12
The severity of hyperkalemia is crucial in determining the associated ECG changes, with levels > 6.0 mEq/L presenting with abnormalities.13 ECG findings alone may not always accurately reflect the severity of hyperkalemia, as up to 60% of patients with potassium levels > 6.0 mEq/L may not show ECG changes.14 Additionally, extreme hyperkalemia can lead to inconsistent ECG findings, making it challenging to rely solely on ECG for diagnosis and monitoring.8 The level of potassium that causes these effects varies widely through patient populations.
The main mechanism by which hyperkalemia affects the heart’s conduction system is through voltage differences across the conduction fibers and eventual steady-state inactivation of sodium channels. This combination of mechanisms shortens the action potential duration, allowing more cardiomyocytes to undergo synchronized depolarization. This amalgamation of cardiomyocytes repolarizing can be reflected on ECGs as peaked T waves. As the action potential decreases, there is a period during which cardiomyocytes are prone to tachyarrhythmias and ventricular fibrillation.
A reduced action potential may lead to increased rates of depolarization and thus conduction, which in some scenarios may increase heart rate. As the levels of potassium rise, intracellular accumulation impedes the entry of sodium by decreasing the cation gradient across the cell membrane. This effectively slows the sinus nodes and prolongs the QRS by slowing the overall propagation of action potentials. By this mechanism, conduction delays, blocks, or asystole are manifested. The patient in this case showed conduction delays, peaked T waves, and disappearance of P waves when he first arrived.
Hyperkalemia Treatment
Hyperkalemia develops most commonly due to acute or chronic kidney diseases, as was the case with this patient. The patient’s hyperkalemia was also augmented by the use of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), which can directly affect renal function. A properly functioning kidney is responsible for excretion of up to 90% of ingested potassium, while the remainder is excreted through the gastrointestinal (GI) tract. Definitive treatment of hyperkalemia is mitigated primarily through these 2 organ systems. The treatment also includes transitory mechanisms of potassium reduction. The goal of each method is to preserve the action potential of cardiomyocytes and myocytes. This patient presented with acute symptomatic hyperkalemia and received various medications to acutely, transitorily, and definitively treat it.
Initial therapy included calcium gluconate, which functions to stabilize the myocardial cell membrane. Hyperkalemia decreases the resting membrane action potential of excitable cells and predisposes them to early depolarization and thus dysrhythmias. Calcium decreases the threshold potential across cells and offsets the overall gradient back to near normal levels.15 Calcium can be delivered through calcium gluconate or calcium chloride. Calcium chloride is not preferred because extravasation can cause pain, blistering and tissue ischemia. Central venous access is required, potentially delaying prompt treatment. Calcium acts rapidly after administration—within 1 to 3 minutes—but only lasts 30 to 60 minutes.16 Administration of calcium gluconate can be repeated as often as necessary, but patients must be monitored for adverse effects of calcium such as nausea, abdominal pain, polydipsia, polyuria, muscle weakness, and paresthesia. Care must be taken when patients are taking digoxin, because calcium may potentiate toxicity.17 Although calcium provides immediate benefits it does little to correct the underlying cause; other medications are required to remove potassium from the body.
Two medication classes have been proven to shift potassium intracellularly. The first are β-2 agonists, such as albuterol/levalbuterol, and the second is insulin. Both work through sodium-potassium-ATPase in a direct manner. β-2 agonists stimulate sodium-potassium-ATPase to move more potassium intracellularly, but these effects have been seen only with high doses of albuterol, typically 4× the standard dose of 0.5 mg in nebulized solutions to achieve decreases in potassium of 0.3 to 0.6 mEq/L, although some trials have reported decreases of 0.62 to 0.98 mEq/L.15,18 These potassium-lowering effects of β-2 agonist are modest, but can be seen 20 to 30 minutes after administration and persist up to 1 to 2 hours. β-2 agonists are also readily affected by β blockers, which may reduce or negate the desired effect in hyperkalemia. For these reasons, a β-2 agonist should not be given as monotherapy and should be provided as an adjuvant to more independent therapies such as insulin. Insulin binds to receptors on muscle cells and increases the quantity of sodium-potassium-ATPase and glucose transporters. With this increase in influx pumps, surrounding tissues with higher resting membrane potentials can absorb the potassium load, thereby protecting cardiomyocytes.
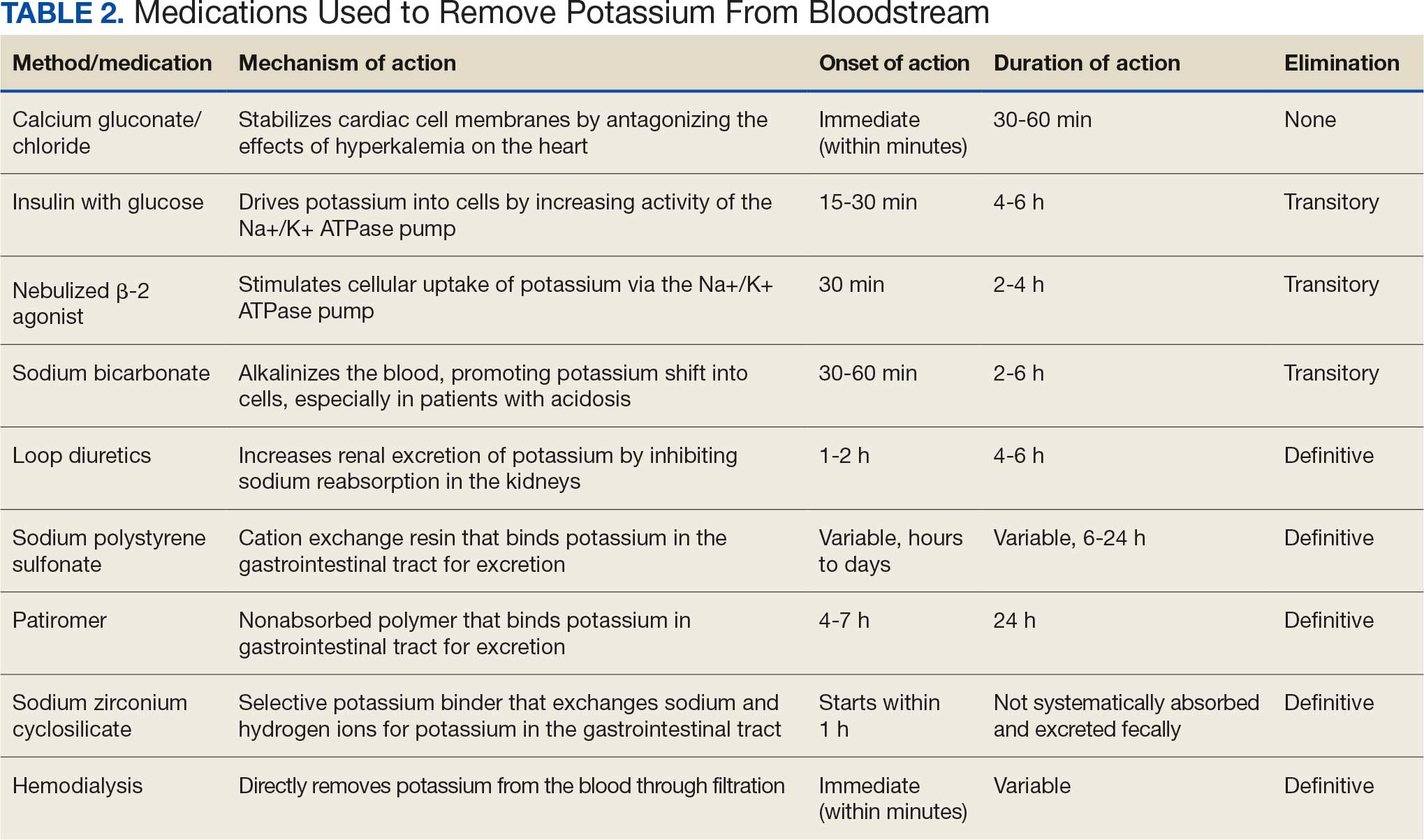
Potassium Removal
Three methods are currently available to remove potassium from the body: GI excretion, renal excretion, and direct removal from the bloodstream. Under normal physiologic conditions, the kidneys account for about 90% of the body’s ability to remove potassium. Loop diuretics facilitate the removal of potassium by increasing urine production and have an additional potassium-wasting effect. Although the onset of action of loop diuretics is typically 30 to 60 minutes after oral administration, their effect can last for several hours. In this patient, furosemide was introduced later in the treatment plan to manage recurring hyperkalemia by enhancing renal potassium excretion.
Potassium binders such as patiromer act in the GI tract, effectively reducing serum potassium levels although with a slower onset of action than furosemide, generally taking hours to days to exert its effect. Both medications illustrate a tailored approach to managing potassium levels, adapted to the evolving needs and renal function of the patient. The last method is using hemodialysis—by far the most rapid method to remove potassium, but also the most invasive. The different methods of treating hyperkalemia are summarized in Table 2. This patient required multiple days of hemodialysis to completely correct the electrolyte disorder. Upon discharge, the patient continued oral furosemide 40 mg daily and eventually discontinued hemodialysis due to stable renal function.
Often, after correcting an inciting event, potassium stores in the body eventually stabilize and do not require additional follow-up. Patients prone to hyperkalemia should be thoroughly educated on medications to avoid (NSAIDs, ACEIs/ARBs, trimethoprim), an adequate low potassium diet, and symptoms that may warrant medical attention.19
Conclusions
This case illustrates the importance of recognizing the spectrum of manifestations of hyperkalemia, which ranged from muscle weakness to cardiac dysrhythmias. Management strategies for the patient included stabilization of cardiac membranes, potassium shifting, and potassium removal, each tailored to the patient’s individual clinical findings.
The case further illustrates the critical role of continuous monitoring and dynamic adjustment of therapeutic strategies in response to evolving clinical and laboratory findings. The initial and subsequent ECGs, alongside laboratory tests, were instrumental in guiding the adjustments needed in the treatment regimen, ensuring both the efficacy and safety of the interventions. This proactive approach can mitigate the risk of recurrent hyperkalemia and its complications.
- Youn JH, McDonough AA. Recent advances in understanding integrative control of potassium homeostasis. Annu Rev Physiol. 2009;71:381-401. doi:10.1146/annurev.physiol.010908.163241 2.
- Simon LV, Hashmi MF, Farrell MW. Hyperkalemia. In: StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing; September 4, 2023. Accessed October 22, 2025.
- Mu F, Betts KA, Woolley JM, et al. Prevalence and economic burden of hyperkalemia in the United States Medicare population. Curr Med Res Opin. 2020;36:1333-1341. doi:10.1080/03007995.2020.1775072
- Loutradis C, Tolika P, Skodra A, et al. Prevalence of hyperkalemia in diabetic and non-diabetic patients with chronic kidney disease: a nested case-control study. Am J Nephrol. 2015;42:351-360. doi:10.1159/000442393
- Grodzinsky A, Goyal A, Gosch K, et al. Prevalence and prognosis of hyperkalemia in patients with acute myocardial infarction. Am J Med. 2016;129:858-865. doi:10.1016/j.amjmed.2016.03.008
- Hunter RW, Bailey MA. Hyperkalemia: pathophysiology, risk factors and consequences. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2019;34(suppl 3):iii2-iii11. doi:10.1093/ndt/gfz206
- Luo J, Brunelli SM, Jensen DE, Yang A. Association between serum potassium and outcomes in patients with reduced kidney function. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2016;11:90-100. doi:10.2215/CJN.01730215
- Montford JR, Linas S. How dangerous is hyperkalemia? J Am Soc Nephrol. 2017;28:3155-3165. doi:10.1681/ASN.2016121344
- Mattu A, Brady WJ, Robinson DA. Electrocardiographic manifestations of hyperkalemia. Am J Emerg Med. 2000;18:721-729. doi:10.1053/ajem.2000.7344
- Kimmons LA, Usery JB. Acute ascending muscle weakness secondary to medication-induced hyperkalemia. Case Rep Med. 2014;2014:789529. doi:10.1155/2014/789529
- Naik KR, Saroja AO, Khanpet MS. Reversible electrophysiological abnormalities in acute secondary hyperkalemic paralysis. Ann Indian Acad Neurol. 2012;15:339-343. doi:10.4103/0972-2327.104354
- Montague BT, Ouellette JR, Buller GK. Retrospective review of the frequency of ECG changes in hyperkalemia. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2008;3:324-330. doi:10.2215/CJN.04611007
- Larivée NL, Michaud JB, More KM, Wilson JA, Tennankore KK. Hyperkalemia: prevalence, predictors and emerging treatments. Cardiol Ther. 2023;12:35-63. doi:10.1007/s40119-022-00289-z
- Shingarev R, Allon M. A physiologic-based approach to the treatment of acute hyperkalemia. Am J Kidney Dis. 2010;56:578-584. doi:10.1053/j.ajkd.2010.03.014
- Parham WA, Mehdirad AA, Biermann KM, Fredman CS. Hyperkalemia revisited. Tex Heart Inst J. 2006;33:40-47.
- Ng KE, Lee CS. Updated treatment options in the management of hyperkalemia. U.S. Pharmacist. February 16, 2017. Accessed October 1, 2025. www.uspharmacist.com/article/updated-treatment-options-in-the-management-of-hyperkalemia
- Quick G, Bastani B. Prolonged asystolic hyperkalemic cardiac arrest with no neurologic sequelae. Ann Emerg Med. 1994;24:305-311. doi:10.1016/s0196-0644(94)70144-x 18.
- Allon M, Dunlay R, Copkney C. Nebulized albuterol for acute hyperkalemia in patients on hemodialysis. Ann Intern Med. 1989;110:426-429. doi:10.7326/0003-4819-110-6-42619.
- Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) CKD Work Group. KDIGO 2024 Clinical Practice Guideline for the Evaluation and Management of Chronic Kidney Disease. Kidney Int. 2024;105(4 suppl):S117-S314. doi:10.1016/j.kint.2023.10.018
Hyperkalemia involves elevated serum potassium levels (> 5.0 mEq/L) and represents an important electrolyte disturbance due to its potentially severe consequences, including cardiac effects that can lead to dysrhythmia and even asystole and death.1,2 In a US Medicare population, the prevalence of hyperkalemia has been estimated at 2.7% and is associated with substantial health care costs.3 The prevalence is even more marked in patients with preexisting conditions such as chronic kidney disease (CKD) and heart failure.4,5
Hyperkalemia can result from multiple factors, including impaired renal function, adrenal disease, adverse drug reactions of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors (ACEIs) and other medications, and heritable mutations.6 Hyperkalemia poses a considerable clinical risk, associated with adverse outcomes such as myocardial infarction and increased mortality in patients with CKD.5,7,8 Electrocardiographic (ECG) changes associated with hyperkalemia play a vital role in guiding clinical decisions and treatment strategies.9 Understanding the pathophysiology, risk factors, and consequences of hyperkalemia, as well as the significance of ECG changes in its management, is essential for health care practitioners.
Case Presentation
An 81-year-old Hispanic man with a history of hypertension, hypothyroidism, gout, and CKD stage 3B presented to the emergency department with progressive weakness resulting in falls and culminating in an inability to ambulate independently. Additional symptoms included nausea, diarrhea, and myalgia. His vital signs were notable for a pulse of 41 beats/min. The physical examination was remarkable for significant weakness of the bilateral upper extremities, inability to bear his own weight, and bilateral lower extremity edema. His initial ECG upon arrival showed bradycardia with wide QRS, absent P waves, and peaked T waves (Figure 1a). These findings differed from his baseline ECG taken 1 year earlier, which showed sinus rhythm with premature atrial complexes and an old right bundle branch block (Figure 1b).

Medication review revealed that the patient was currently prescribed 100 mg allopurinol daily, 2.5 mg amlodipine daily, 10 mg atorvastatin at bedtime, 4 mg doxazosin daily, 112 mcg levothyroxine daily, 100 mg losartan daily, 25 mg metoprolol daily, and 0.4 mg tamsulosin daily. The patient had also been taking over-the-counter indomethacin for knee pain.
Based on the ECG results, he was treated with 0.083%/6 mL nebulized albuterol, 4.65 Mq/250 mL saline solution intravenous (IV) calcium gluconate, 10 units IV insulin with concomitant 50%/25 mL IV dextrose and 8.4 g of oral patiromer suspension. IV furosemide was held due to concern for renal function. The decision to proceed with hemodialysis was made. Repeat laboratory tests were performed, and an ECG obtained after treatment initiation but prior to hemodialysis demonstrated improvement of rate and T wave shortening (Figure 1c). The serum potassium level dropped from 9.8 mEq/L to 7.9 mEq/L (reference range, 3.5-5.0 mEq/L) (Table 1).

In addition to hemodialysis, sodium zirconium 10 g orally 3 times daily was added. Laboratory test results and an ECG was performed after dialysis continued to demonstrate improvement (Figure 1d). The patient’s potassium level decreased to 5.8 mEq/L, with the ECG demonstrating stability of heart rate and further improvement of the PR interval, QRS complex, and T waves.
Despite the established treatment regimen, potassium levels again rose to 6.7 mEq/L, but there were no significant changes in the ECG, and thus no medication changes were made (Figure 1e). Subsequent monitoring demonstrated a further increase in potassium to 7.4 mEq/L, with an ECG demonstrating a return to the baseline of 1 year prior. The patient underwent hemodialysis again and was given oral furosemide 60 mg every 12 hours. The potassium concentration after dialysis decreased to 4.7 mEq/L and remained stable, not going above 5.0 mEq/L on subsequent monitoring. The patient had resolution of all symptoms and was discharged.
Discussion
We have described in detail the presentation of each pathology and mechanisms of each treatment, starting with the patient’s initial condition that brought him to the emergency room—muscle weakness. Skeletal muscle weakness is a common manifestation of hyperkalemia, occurring in 20% to 40% of cases, and is more prevalent in severe elevations of potassium. Rarely, the weakness can progress to flaccid paralysis of the patient’s extremities and, in extreme cases, the diaphragm.
Muscle weakness progression occurs in a manner that resembles Guillain-Barré syndrome, starting in the lower extremities and ascending toward the upper extremities.10 This is known as secondary hyperkalemic periodic paralysis. Hyperkalemia lowers the transmembrane gradient in neurons, leading to neuronal depolarization independent of the degree of hyperkalemia. If the degree of hyperkalemia is large enough, this depolarization inactivates voltage-gated sodium channels, making neurons refractory to excitation. Electromyographical studies have shown reduction in the compounded muscle action potential.11 The transient nature of this paralysis is reflected by rapid correction of weakness and paralysis when the electrolyte disorder is corrected.
The patient in this case also presented with bradycardia. The ECG manifestations of hyperkalemia can include atrial asystole, intraventricular conduction disturbances, peaked T waves, and widened QRS complexes. However, some patients with renal insufficiency may not exhibit ECG changes despite significantly elevated serum potassium levels.12
The severity of hyperkalemia is crucial in determining the associated ECG changes, with levels > 6.0 mEq/L presenting with abnormalities.13 ECG findings alone may not always accurately reflect the severity of hyperkalemia, as up to 60% of patients with potassium levels > 6.0 mEq/L may not show ECG changes.14 Additionally, extreme hyperkalemia can lead to inconsistent ECG findings, making it challenging to rely solely on ECG for diagnosis and monitoring.8 The level of potassium that causes these effects varies widely through patient populations.
The main mechanism by which hyperkalemia affects the heart’s conduction system is through voltage differences across the conduction fibers and eventual steady-state inactivation of sodium channels. This combination of mechanisms shortens the action potential duration, allowing more cardiomyocytes to undergo synchronized depolarization. This amalgamation of cardiomyocytes repolarizing can be reflected on ECGs as peaked T waves. As the action potential decreases, there is a period during which cardiomyocytes are prone to tachyarrhythmias and ventricular fibrillation.
A reduced action potential may lead to increased rates of depolarization and thus conduction, which in some scenarios may increase heart rate. As the levels of potassium rise, intracellular accumulation impedes the entry of sodium by decreasing the cation gradient across the cell membrane. This effectively slows the sinus nodes and prolongs the QRS by slowing the overall propagation of action potentials. By this mechanism, conduction delays, blocks, or asystole are manifested. The patient in this case showed conduction delays, peaked T waves, and disappearance of P waves when he first arrived.
Hyperkalemia Treatment
Hyperkalemia develops most commonly due to acute or chronic kidney diseases, as was the case with this patient. The patient’s hyperkalemia was also augmented by the use of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), which can directly affect renal function. A properly functioning kidney is responsible for excretion of up to 90% of ingested potassium, while the remainder is excreted through the gastrointestinal (GI) tract. Definitive treatment of hyperkalemia is mitigated primarily through these 2 organ systems. The treatment also includes transitory mechanisms of potassium reduction. The goal of each method is to preserve the action potential of cardiomyocytes and myocytes. This patient presented with acute symptomatic hyperkalemia and received various medications to acutely, transitorily, and definitively treat it.
Initial therapy included calcium gluconate, which functions to stabilize the myocardial cell membrane. Hyperkalemia decreases the resting membrane action potential of excitable cells and predisposes them to early depolarization and thus dysrhythmias. Calcium decreases the threshold potential across cells and offsets the overall gradient back to near normal levels.15 Calcium can be delivered through calcium gluconate or calcium chloride. Calcium chloride is not preferred because extravasation can cause pain, blistering and tissue ischemia. Central venous access is required, potentially delaying prompt treatment. Calcium acts rapidly after administration—within 1 to 3 minutes—but only lasts 30 to 60 minutes.16 Administration of calcium gluconate can be repeated as often as necessary, but patients must be monitored for adverse effects of calcium such as nausea, abdominal pain, polydipsia, polyuria, muscle weakness, and paresthesia. Care must be taken when patients are taking digoxin, because calcium may potentiate toxicity.17 Although calcium provides immediate benefits it does little to correct the underlying cause; other medications are required to remove potassium from the body.
Two medication classes have been proven to shift potassium intracellularly. The first are β-2 agonists, such as albuterol/levalbuterol, and the second is insulin. Both work through sodium-potassium-ATPase in a direct manner. β-2 agonists stimulate sodium-potassium-ATPase to move more potassium intracellularly, but these effects have been seen only with high doses of albuterol, typically 4× the standard dose of 0.5 mg in nebulized solutions to achieve decreases in potassium of 0.3 to 0.6 mEq/L, although some trials have reported decreases of 0.62 to 0.98 mEq/L.15,18 These potassium-lowering effects of β-2 agonist are modest, but can be seen 20 to 30 minutes after administration and persist up to 1 to 2 hours. β-2 agonists are also readily affected by β blockers, which may reduce or negate the desired effect in hyperkalemia. For these reasons, a β-2 agonist should not be given as monotherapy and should be provided as an adjuvant to more independent therapies such as insulin. Insulin binds to receptors on muscle cells and increases the quantity of sodium-potassium-ATPase and glucose transporters. With this increase in influx pumps, surrounding tissues with higher resting membrane potentials can absorb the potassium load, thereby protecting cardiomyocytes.
Potassium Removal
Three methods are currently available to remove potassium from the body: GI excretion, renal excretion, and direct removal from the bloodstream. Under normal physiologic conditions, the kidneys account for about 90% of the body’s ability to remove potassium. Loop diuretics facilitate the removal of potassium by increasing urine production and have an additional potassium-wasting effect. Although the onset of action of loop diuretics is typically 30 to 60 minutes after oral administration, their effect can last for several hours. In this patient, furosemide was introduced later in the treatment plan to manage recurring hyperkalemia by enhancing renal potassium excretion.
Potassium binders such as patiromer act in the GI tract, effectively reducing serum potassium levels although with a slower onset of action than furosemide, generally taking hours to days to exert its effect. Both medications illustrate a tailored approach to managing potassium levels, adapted to the evolving needs and renal function of the patient. The last method is using hemodialysis—by far the most rapid method to remove potassium, but also the most invasive. The different methods of treating hyperkalemia are summarized in Table 2. This patient required multiple days of hemodialysis to completely correct the electrolyte disorder. Upon discharge, the patient continued oral furosemide 40 mg daily and eventually discontinued hemodialysis due to stable renal function.

Often, after correcting an inciting event, potassium stores in the body eventually stabilize and do not require additional follow-up. Patients prone to hyperkalemia should be thoroughly educated on medications to avoid (NSAIDs, ACEIs/ARBs, trimethoprim), an adequate low potassium diet, and symptoms that may warrant medical attention.19
Conclusions
This case illustrates the importance of recognizing the spectrum of manifestations of hyperkalemia, which ranged from muscle weakness to cardiac dysrhythmias. Management strategies for the patient included stabilization of cardiac membranes, potassium shifting, and potassium removal, each tailored to the patient’s individual clinical findings.
The case further illustrates the critical role of continuous monitoring and dynamic adjustment of therapeutic strategies in response to evolving clinical and laboratory findings. The initial and subsequent ECGs, alongside laboratory tests, were instrumental in guiding the adjustments needed in the treatment regimen, ensuring both the efficacy and safety of the interventions. This proactive approach can mitigate the risk of recurrent hyperkalemia and its complications.
Hyperkalemia involves elevated serum potassium levels (> 5.0 mEq/L) and represents an important electrolyte disturbance due to its potentially severe consequences, including cardiac effects that can lead to dysrhythmia and even asystole and death.1,2 In a US Medicare population, the prevalence of hyperkalemia has been estimated at 2.7% and is associated with substantial health care costs.3 The prevalence is even more marked in patients with preexisting conditions such as chronic kidney disease (CKD) and heart failure.4,5
Hyperkalemia can result from multiple factors, including impaired renal function, adrenal disease, adverse drug reactions of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors (ACEIs) and other medications, and heritable mutations.6 Hyperkalemia poses a considerable clinical risk, associated with adverse outcomes such as myocardial infarction and increased mortality in patients with CKD.5,7,8 Electrocardiographic (ECG) changes associated with hyperkalemia play a vital role in guiding clinical decisions and treatment strategies.9 Understanding the pathophysiology, risk factors, and consequences of hyperkalemia, as well as the significance of ECG changes in its management, is essential for health care practitioners.
Case Presentation
An 81-year-old Hispanic man with a history of hypertension, hypothyroidism, gout, and CKD stage 3B presented to the emergency department with progressive weakness resulting in falls and culminating in an inability to ambulate independently. Additional symptoms included nausea, diarrhea, and myalgia. His vital signs were notable for a pulse of 41 beats/min. The physical examination was remarkable for significant weakness of the bilateral upper extremities, inability to bear his own weight, and bilateral lower extremity edema. His initial ECG upon arrival showed bradycardia with wide QRS, absent P waves, and peaked T waves (Figure 1a). These findings differed from his baseline ECG taken 1 year earlier, which showed sinus rhythm with premature atrial complexes and an old right bundle branch block (Figure 1b).

Medication review revealed that the patient was currently prescribed 100 mg allopurinol daily, 2.5 mg amlodipine daily, 10 mg atorvastatin at bedtime, 4 mg doxazosin daily, 112 mcg levothyroxine daily, 100 mg losartan daily, 25 mg metoprolol daily, and 0.4 mg tamsulosin daily. The patient had also been taking over-the-counter indomethacin for knee pain.
Based on the ECG results, he was treated with 0.083%/6 mL nebulized albuterol, 4.65 Mq/250 mL saline solution intravenous (IV) calcium gluconate, 10 units IV insulin with concomitant 50%/25 mL IV dextrose and 8.4 g of oral patiromer suspension. IV furosemide was held due to concern for renal function. The decision to proceed with hemodialysis was made. Repeat laboratory tests were performed, and an ECG obtained after treatment initiation but prior to hemodialysis demonstrated improvement of rate and T wave shortening (Figure 1c). The serum potassium level dropped from 9.8 mEq/L to 7.9 mEq/L (reference range, 3.5-5.0 mEq/L) (Table 1).

In addition to hemodialysis, sodium zirconium 10 g orally 3 times daily was added. Laboratory test results and an ECG was performed after dialysis continued to demonstrate improvement (Figure 1d). The patient’s potassium level decreased to 5.8 mEq/L, with the ECG demonstrating stability of heart rate and further improvement of the PR interval, QRS complex, and T waves.
Despite the established treatment regimen, potassium levels again rose to 6.7 mEq/L, but there were no significant changes in the ECG, and thus no medication changes were made (Figure 1e). Subsequent monitoring demonstrated a further increase in potassium to 7.4 mEq/L, with an ECG demonstrating a return to the baseline of 1 year prior. The patient underwent hemodialysis again and was given oral furosemide 60 mg every 12 hours. The potassium concentration after dialysis decreased to 4.7 mEq/L and remained stable, not going above 5.0 mEq/L on subsequent monitoring. The patient had resolution of all symptoms and was discharged.
Discussion
We have described in detail the presentation of each pathology and mechanisms of each treatment, starting with the patient’s initial condition that brought him to the emergency room—muscle weakness. Skeletal muscle weakness is a common manifestation of hyperkalemia, occurring in 20% to 40% of cases, and is more prevalent in severe elevations of potassium. Rarely, the weakness can progress to flaccid paralysis of the patient’s extremities and, in extreme cases, the diaphragm.
Muscle weakness progression occurs in a manner that resembles Guillain-Barré syndrome, starting in the lower extremities and ascending toward the upper extremities.10 This is known as secondary hyperkalemic periodic paralysis. Hyperkalemia lowers the transmembrane gradient in neurons, leading to neuronal depolarization independent of the degree of hyperkalemia. If the degree of hyperkalemia is large enough, this depolarization inactivates voltage-gated sodium channels, making neurons refractory to excitation. Electromyographical studies have shown reduction in the compounded muscle action potential.11 The transient nature of this paralysis is reflected by rapid correction of weakness and paralysis when the electrolyte disorder is corrected.
The patient in this case also presented with bradycardia. The ECG manifestations of hyperkalemia can include atrial asystole, intraventricular conduction disturbances, peaked T waves, and widened QRS complexes. However, some patients with renal insufficiency may not exhibit ECG changes despite significantly elevated serum potassium levels.12
The severity of hyperkalemia is crucial in determining the associated ECG changes, with levels > 6.0 mEq/L presenting with abnormalities.13 ECG findings alone may not always accurately reflect the severity of hyperkalemia, as up to 60% of patients with potassium levels > 6.0 mEq/L may not show ECG changes.14 Additionally, extreme hyperkalemia can lead to inconsistent ECG findings, making it challenging to rely solely on ECG for diagnosis and monitoring.8 The level of potassium that causes these effects varies widely through patient populations.
The main mechanism by which hyperkalemia affects the heart’s conduction system is through voltage differences across the conduction fibers and eventual steady-state inactivation of sodium channels. This combination of mechanisms shortens the action potential duration, allowing more cardiomyocytes to undergo synchronized depolarization. This amalgamation of cardiomyocytes repolarizing can be reflected on ECGs as peaked T waves. As the action potential decreases, there is a period during which cardiomyocytes are prone to tachyarrhythmias and ventricular fibrillation.
A reduced action potential may lead to increased rates of depolarization and thus conduction, which in some scenarios may increase heart rate. As the levels of potassium rise, intracellular accumulation impedes the entry of sodium by decreasing the cation gradient across the cell membrane. This effectively slows the sinus nodes and prolongs the QRS by slowing the overall propagation of action potentials. By this mechanism, conduction delays, blocks, or asystole are manifested. The patient in this case showed conduction delays, peaked T waves, and disappearance of P waves when he first arrived.
Hyperkalemia Treatment
Hyperkalemia develops most commonly due to acute or chronic kidney diseases, as was the case with this patient. The patient’s hyperkalemia was also augmented by the use of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), which can directly affect renal function. A properly functioning kidney is responsible for excretion of up to 90% of ingested potassium, while the remainder is excreted through the gastrointestinal (GI) tract. Definitive treatment of hyperkalemia is mitigated primarily through these 2 organ systems. The treatment also includes transitory mechanisms of potassium reduction. The goal of each method is to preserve the action potential of cardiomyocytes and myocytes. This patient presented with acute symptomatic hyperkalemia and received various medications to acutely, transitorily, and definitively treat it.
Initial therapy included calcium gluconate, which functions to stabilize the myocardial cell membrane. Hyperkalemia decreases the resting membrane action potential of excitable cells and predisposes them to early depolarization and thus dysrhythmias. Calcium decreases the threshold potential across cells and offsets the overall gradient back to near normal levels.15 Calcium can be delivered through calcium gluconate or calcium chloride. Calcium chloride is not preferred because extravasation can cause pain, blistering and tissue ischemia. Central venous access is required, potentially delaying prompt treatment. Calcium acts rapidly after administration—within 1 to 3 minutes—but only lasts 30 to 60 minutes.16 Administration of calcium gluconate can be repeated as often as necessary, but patients must be monitored for adverse effects of calcium such as nausea, abdominal pain, polydipsia, polyuria, muscle weakness, and paresthesia. Care must be taken when patients are taking digoxin, because calcium may potentiate toxicity.17 Although calcium provides immediate benefits it does little to correct the underlying cause; other medications are required to remove potassium from the body.
Two medication classes have been proven to shift potassium intracellularly. The first are β-2 agonists, such as albuterol/levalbuterol, and the second is insulin. Both work through sodium-potassium-ATPase in a direct manner. β-2 agonists stimulate sodium-potassium-ATPase to move more potassium intracellularly, but these effects have been seen only with high doses of albuterol, typically 4× the standard dose of 0.5 mg in nebulized solutions to achieve decreases in potassium of 0.3 to 0.6 mEq/L, although some trials have reported decreases of 0.62 to 0.98 mEq/L.15,18 These potassium-lowering effects of β-2 agonist are modest, but can be seen 20 to 30 minutes after administration and persist up to 1 to 2 hours. β-2 agonists are also readily affected by β blockers, which may reduce or negate the desired effect in hyperkalemia. For these reasons, a β-2 agonist should not be given as monotherapy and should be provided as an adjuvant to more independent therapies such as insulin. Insulin binds to receptors on muscle cells and increases the quantity of sodium-potassium-ATPase and glucose transporters. With this increase in influx pumps, surrounding tissues with higher resting membrane potentials can absorb the potassium load, thereby protecting cardiomyocytes.
Potassium Removal
Three methods are currently available to remove potassium from the body: GI excretion, renal excretion, and direct removal from the bloodstream. Under normal physiologic conditions, the kidneys account for about 90% of the body’s ability to remove potassium. Loop diuretics facilitate the removal of potassium by increasing urine production and have an additional potassium-wasting effect. Although the onset of action of loop diuretics is typically 30 to 60 minutes after oral administration, their effect can last for several hours. In this patient, furosemide was introduced later in the treatment plan to manage recurring hyperkalemia by enhancing renal potassium excretion.
Potassium binders such as patiromer act in the GI tract, effectively reducing serum potassium levels although with a slower onset of action than furosemide, generally taking hours to days to exert its effect. Both medications illustrate a tailored approach to managing potassium levels, adapted to the evolving needs and renal function of the patient. The last method is using hemodialysis—by far the most rapid method to remove potassium, but also the most invasive. The different methods of treating hyperkalemia are summarized in Table 2. This patient required multiple days of hemodialysis to completely correct the electrolyte disorder. Upon discharge, the patient continued oral furosemide 40 mg daily and eventually discontinued hemodialysis due to stable renal function.

Often, after correcting an inciting event, potassium stores in the body eventually stabilize and do not require additional follow-up. Patients prone to hyperkalemia should be thoroughly educated on medications to avoid (NSAIDs, ACEIs/ARBs, trimethoprim), an adequate low potassium diet, and symptoms that may warrant medical attention.19
Conclusions
This case illustrates the importance of recognizing the spectrum of manifestations of hyperkalemia, which ranged from muscle weakness to cardiac dysrhythmias. Management strategies for the patient included stabilization of cardiac membranes, potassium shifting, and potassium removal, each tailored to the patient’s individual clinical findings.
The case further illustrates the critical role of continuous monitoring and dynamic adjustment of therapeutic strategies in response to evolving clinical and laboratory findings. The initial and subsequent ECGs, alongside laboratory tests, were instrumental in guiding the adjustments needed in the treatment regimen, ensuring both the efficacy and safety of the interventions. This proactive approach can mitigate the risk of recurrent hyperkalemia and its complications.
- Youn JH, McDonough AA. Recent advances in understanding integrative control of potassium homeostasis. Annu Rev Physiol. 2009;71:381-401. doi:10.1146/annurev.physiol.010908.163241 2.
- Simon LV, Hashmi MF, Farrell MW. Hyperkalemia. In: StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing; September 4, 2023. Accessed October 22, 2025.
- Mu F, Betts KA, Woolley JM, et al. Prevalence and economic burden of hyperkalemia in the United States Medicare population. Curr Med Res Opin. 2020;36:1333-1341. doi:10.1080/03007995.2020.1775072
- Loutradis C, Tolika P, Skodra A, et al. Prevalence of hyperkalemia in diabetic and non-diabetic patients with chronic kidney disease: a nested case-control study. Am J Nephrol. 2015;42:351-360. doi:10.1159/000442393
- Grodzinsky A, Goyal A, Gosch K, et al. Prevalence and prognosis of hyperkalemia in patients with acute myocardial infarction. Am J Med. 2016;129:858-865. doi:10.1016/j.amjmed.2016.03.008
- Hunter RW, Bailey MA. Hyperkalemia: pathophysiology, risk factors and consequences. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2019;34(suppl 3):iii2-iii11. doi:10.1093/ndt/gfz206
- Luo J, Brunelli SM, Jensen DE, Yang A. Association between serum potassium and outcomes in patients with reduced kidney function. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2016;11:90-100. doi:10.2215/CJN.01730215
- Montford JR, Linas S. How dangerous is hyperkalemia? J Am Soc Nephrol. 2017;28:3155-3165. doi:10.1681/ASN.2016121344
- Mattu A, Brady WJ, Robinson DA. Electrocardiographic manifestations of hyperkalemia. Am J Emerg Med. 2000;18:721-729. doi:10.1053/ajem.2000.7344
- Kimmons LA, Usery JB. Acute ascending muscle weakness secondary to medication-induced hyperkalemia. Case Rep Med. 2014;2014:789529. doi:10.1155/2014/789529
- Naik KR, Saroja AO, Khanpet MS. Reversible electrophysiological abnormalities in acute secondary hyperkalemic paralysis. Ann Indian Acad Neurol. 2012;15:339-343. doi:10.4103/0972-2327.104354
- Montague BT, Ouellette JR, Buller GK. Retrospective review of the frequency of ECG changes in hyperkalemia. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2008;3:324-330. doi:10.2215/CJN.04611007
- Larivée NL, Michaud JB, More KM, Wilson JA, Tennankore KK. Hyperkalemia: prevalence, predictors and emerging treatments. Cardiol Ther. 2023;12:35-63. doi:10.1007/s40119-022-00289-z
- Shingarev R, Allon M. A physiologic-based approach to the treatment of acute hyperkalemia. Am J Kidney Dis. 2010;56:578-584. doi:10.1053/j.ajkd.2010.03.014
- Parham WA, Mehdirad AA, Biermann KM, Fredman CS. Hyperkalemia revisited. Tex Heart Inst J. 2006;33:40-47.
- Ng KE, Lee CS. Updated treatment options in the management of hyperkalemia. U.S. Pharmacist. February 16, 2017. Accessed October 1, 2025. www.uspharmacist.com/article/updated-treatment-options-in-the-management-of-hyperkalemia
- Quick G, Bastani B. Prolonged asystolic hyperkalemic cardiac arrest with no neurologic sequelae. Ann Emerg Med. 1994;24:305-311. doi:10.1016/s0196-0644(94)70144-x 18.
- Allon M, Dunlay R, Copkney C. Nebulized albuterol for acute hyperkalemia in patients on hemodialysis. Ann Intern Med. 1989;110:426-429. doi:10.7326/0003-4819-110-6-42619.
- Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) CKD Work Group. KDIGO 2024 Clinical Practice Guideline for the Evaluation and Management of Chronic Kidney Disease. Kidney Int. 2024;105(4 suppl):S117-S314. doi:10.1016/j.kint.2023.10.018
- Youn JH, McDonough AA. Recent advances in understanding integrative control of potassium homeostasis. Annu Rev Physiol. 2009;71:381-401. doi:10.1146/annurev.physiol.010908.163241 2.
- Simon LV, Hashmi MF, Farrell MW. Hyperkalemia. In: StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing; September 4, 2023. Accessed October 22, 2025.
- Mu F, Betts KA, Woolley JM, et al. Prevalence and economic burden of hyperkalemia in the United States Medicare population. Curr Med Res Opin. 2020;36:1333-1341. doi:10.1080/03007995.2020.1775072
- Loutradis C, Tolika P, Skodra A, et al. Prevalence of hyperkalemia in diabetic and non-diabetic patients with chronic kidney disease: a nested case-control study. Am J Nephrol. 2015;42:351-360. doi:10.1159/000442393
- Grodzinsky A, Goyal A, Gosch K, et al. Prevalence and prognosis of hyperkalemia in patients with acute myocardial infarction. Am J Med. 2016;129:858-865. doi:10.1016/j.amjmed.2016.03.008
- Hunter RW, Bailey MA. Hyperkalemia: pathophysiology, risk factors and consequences. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2019;34(suppl 3):iii2-iii11. doi:10.1093/ndt/gfz206
- Luo J, Brunelli SM, Jensen DE, Yang A. Association between serum potassium and outcomes in patients with reduced kidney function. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2016;11:90-100. doi:10.2215/CJN.01730215
- Montford JR, Linas S. How dangerous is hyperkalemia? J Am Soc Nephrol. 2017;28:3155-3165. doi:10.1681/ASN.2016121344
- Mattu A, Brady WJ, Robinson DA. Electrocardiographic manifestations of hyperkalemia. Am J Emerg Med. 2000;18:721-729. doi:10.1053/ajem.2000.7344
- Kimmons LA, Usery JB. Acute ascending muscle weakness secondary to medication-induced hyperkalemia. Case Rep Med. 2014;2014:789529. doi:10.1155/2014/789529
- Naik KR, Saroja AO, Khanpet MS. Reversible electrophysiological abnormalities in acute secondary hyperkalemic paralysis. Ann Indian Acad Neurol. 2012;15:339-343. doi:10.4103/0972-2327.104354
- Montague BT, Ouellette JR, Buller GK. Retrospective review of the frequency of ECG changes in hyperkalemia. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2008;3:324-330. doi:10.2215/CJN.04611007
- Larivée NL, Michaud JB, More KM, Wilson JA, Tennankore KK. Hyperkalemia: prevalence, predictors and emerging treatments. Cardiol Ther. 2023;12:35-63. doi:10.1007/s40119-022-00289-z
- Shingarev R, Allon M. A physiologic-based approach to the treatment of acute hyperkalemia. Am J Kidney Dis. 2010;56:578-584. doi:10.1053/j.ajkd.2010.03.014
- Parham WA, Mehdirad AA, Biermann KM, Fredman CS. Hyperkalemia revisited. Tex Heart Inst J. 2006;33:40-47.
- Ng KE, Lee CS. Updated treatment options in the management of hyperkalemia. U.S. Pharmacist. February 16, 2017. Accessed October 1, 2025. www.uspharmacist.com/article/updated-treatment-options-in-the-management-of-hyperkalemia
- Quick G, Bastani B. Prolonged asystolic hyperkalemic cardiac arrest with no neurologic sequelae. Ann Emerg Med. 1994;24:305-311. doi:10.1016/s0196-0644(94)70144-x 18.
- Allon M, Dunlay R, Copkney C. Nebulized albuterol for acute hyperkalemia in patients on hemodialysis. Ann Intern Med. 1989;110:426-429. doi:10.7326/0003-4819-110-6-42619.
- Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) CKD Work Group. KDIGO 2024 Clinical Practice Guideline for the Evaluation and Management of Chronic Kidney Disease. Kidney Int. 2024;105(4 suppl):S117-S314. doi:10.1016/j.kint.2023.10.018
Following the Hyperkalemia Trail: A Case Report of ECG Changes and Treatment Responses
Following the Hyperkalemia Trail: A Case Report of ECG Changes and Treatment Responses
Gadolinium Intermediate Elimination and Persistent Symptoms After Magnetic Resonance Imaging Contrast Agent Exposure
Gadolinium Intermediate Elimination and Persistent Symptoms After Magnetic Resonance Imaging Contrast Agent Exposure
Magnetic resonance image (MRI) contrast agents can induce profound complications, including gadolinium encephalopathy, kidney injury, gadolinium-associated plaques, and progressive systemic fibrosis, which can be fatal.1-10 About 50% of MRIs use gadolinium-based contrast (Gd3+), a toxic rare earth metal ion that enhances imaging but requires binding with pharmaceutical ligands to reduce toxicity and promote renal elimination (Figure 1). Despite these measures, Gd3+ can persist in the body, including the brain.11,12 Wastewater treatment fails to remove these agents, making Gd3+ a growing pollutant in water and the food chain.13-15 Because Gd3+ is a rare earth metal ion in the milieu intérieur, there is an urgent need to study its biological and long-term effects (Appendix 1).
Case Presentation
A 65-year-old Vietnam-era veteran presented to nephrology at the Raymond G. Murphy Veterans Affairs Medical Center (RGMVAMC) in Albuquerque, New Mexico, for evaluation of gadolinium-induced symptoms. His medical history included metabolic syndrome, hypertension, hyperlipidemia, hypogonadism, cervical spondylosis, and an elevated prostate-specific antigen, previously assessed with a contrast-enhanced MRI in 2019 (Gadobenic acid, 19 mL). Surgical history included cervical fusion and ankle hardware.
The patient had a scheduled MRI 25 days earlier, following an elevated prostate specific antigen test result, prompting urologic surveillance and concern for malignancy. In preparation for the contrast-enhanced MRI, his right arm was cannulated with a line primed with gadobenic acid contrast. Though the technician stated the infusion had not started, the patient’s symptoms began shortly after entry into the scanner, before any programmed pulse sequences. The patient experienced claustrophobia, diaphoresis, palpitations, xerostomia, dysgeusia, shortness of breath, and a sensation of heat in his groin, chest, “kidneys,” and lower back. The MRI was terminated prematurely in response to the patient’s acute symptomatology. The patient continued experiencing new symptoms intermittently during the following week, including lightheadedness, headaches, right clavicular pain, raspy voice, edema, and a sense of doom.
The patient presented to the RGMVAMC emergency department (ED) 8 days after the MRI with worsening symptoms and was hospitalized for 10 days. During this time, he was referred to nephrology for outpatient evaluation. While awaiting his nephrology appointment, the patient presented to the RGMVAMC ED 20 days after the initial episode with ongoing symptoms. “I thought I was dying,” he said. Laboratory results and a 12-lead electrocardiogram showed a finely static background, wide P waves (> 80 ms) with notching in lead II, sinusoidal P waves in V1, R transition in V2, RR’ in V2, ST flat in lead III, and sinus bradycardia (Table 1 and Appendix 2).
The patient’s medical and surgical histories were reviewed at the nephrology evaluation 25 days following the MRI. He reported that household water was sourced from a well and that he filtered his drinking water with a reverse osmosis system. He served in the US Army for 10 years as an engineer specializing in mechanical systems, power generation, and vehicles. Following Army retirement, the patient served in the US Air Force Reserves for 15 years, working as a crew chief in pneudraulics. The patient reported stopping tobacco use 1 year before and also reported regular use of a broad array of prescription medications and dietary supplements, including dexamethasone (4 mg twice daily), fluticasone nasal spray (50 mcg per nostril, twice daily), ibuprofen (400 mg twice daily, as needed), loratadine (10 mg daily), aspirin (81 mg daily), and metoprolol succinate (50 mg nightly). In addition, he reported consistent use of cholecalciferol (3000 IU daily), another supplemental vitamin D preparation, chelated magnesium glycinate (3 tablets daily for bone issues), turmeric (1 tablet daily), a multivitamin (Living Green Liquid Gel, daily), and a mega-B complex.
Physical examination revealed a well-nourished, tall man with hypertension (145/87 mmHg) and bilateral lower extremity edema. Oral examination showed poor dentition, including missing molars (#1-3, #14-16, #17-19, #30-31), with the anterior teeth replaced by bridges supported by dental implants. The review of systems was otherwise unremarkable, with nocturia noted before the consultation.
Serum and urine gadolinium testing, (Mayo Clinic Laboratories) revealed gadolinium levels of 0.3 mcg/24 h in the urine and 0.1 ng/mL in the serum. Nonzero values indicated detectable gadolinium, suggesting retention. The patient had a prior gadolinium exposure during a 2019 MRI (about 1340 days before) and suspected a repeat exposure on day 0, although the MRI technician stated that no contrast was administered. Given his elevated vitamin D levels, the patient was advised to minimize dietary supplements, particularly vitamin D, to avoid confounding symptoms. The plan included monitoring symptoms and a follow-up evaluation with repeat laboratory tests on day 116.
At the nephrology follow-up 4 months postexposure, the patient's symptoms had primarily abated, with a marked reduction in the previously noted metallic dysgeusia. Physical examination remained consistent with prior findings. He was afebrile (97.7 °F) with a blood pressure of 111/72 mmHg, a pulse of 63 beats per minute, and an oxygen saturation of 98% on ambient air. Laboratory analysis revealed serum and urine gadolinium levels below detectable thresholds (< 0.1 ng/mL and < 0.1 mcg/24 h). A 24-hour creatinine clearance, calculated from a urine volume of 1300 mL, measured at an optimal 106 mL/min, indicating preserved renal function (Tables 2 and 3). Of note, his 24-hour oxalate was above the reference range, with a urine pH below the reference range and a high supersaturation index for calcium oxalate.
Discussion
Use of enhanced MRI has increased in the Veterans Health Administration (Figure 2). A growing range of indications for enhanced procedures (eg, cardiac MRI) has contributed to this rise. The market has grown with new gadolinium-based contrast agents, such as gadopiclenol. However, reliance on untested assumptions about the safety of newer agents and need for robust clinical trials pose potential risks to patient safety.
Without prospective evidence, the American College of Radiology (ACR) classifies gadolinium-based contrast agents into 3 groups: Group 1, associated with the highest number of nephrogenic systemic fibrosis cases; Group 2, linked to few, if any, unconfounded cases; and Group 3, where data on nephrogenic systemic fibrosis risk have been limited. As of April 2024, the ACR reclassified Group 3 agents (Ablavar/Vasovist/Angiomark and Primovist/Eovist) into Group 2. Curiously, Vueway and Elucirem were approved in late 2022 and should clearly be categorized as Group 3 (Table 4).There were 19 cases of nephrogenic systemic fibrosis or similar manifestations, 8 of which were unconfounded by other factors. These patients had been exposed to gadobutrol, often combined with other agents. Gadobutrol—like other Group 2 agents—has been associated with nephrogenic systemic fibrosis.16,17 Despite US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) documentation of rising reports, many clinicians remain unaware that nephrogenic systemic fibrosis is increasingly linked to Group 2 agents classified by the ACR.18 While declines in reported cases of nephrogenic systemic fibrosis may suggest reduced incidence, this trend may reflect diminished clinical vigilance and underreporting, particularly given emerging evidence implicating even Group 2 gadolinium-based contrast agents in delayed and underrecognized presentations. This information has yet to permeate the medical community, particularly among nephrologists. Considering these cases, revisiting the ACR guidelines may be prudent.
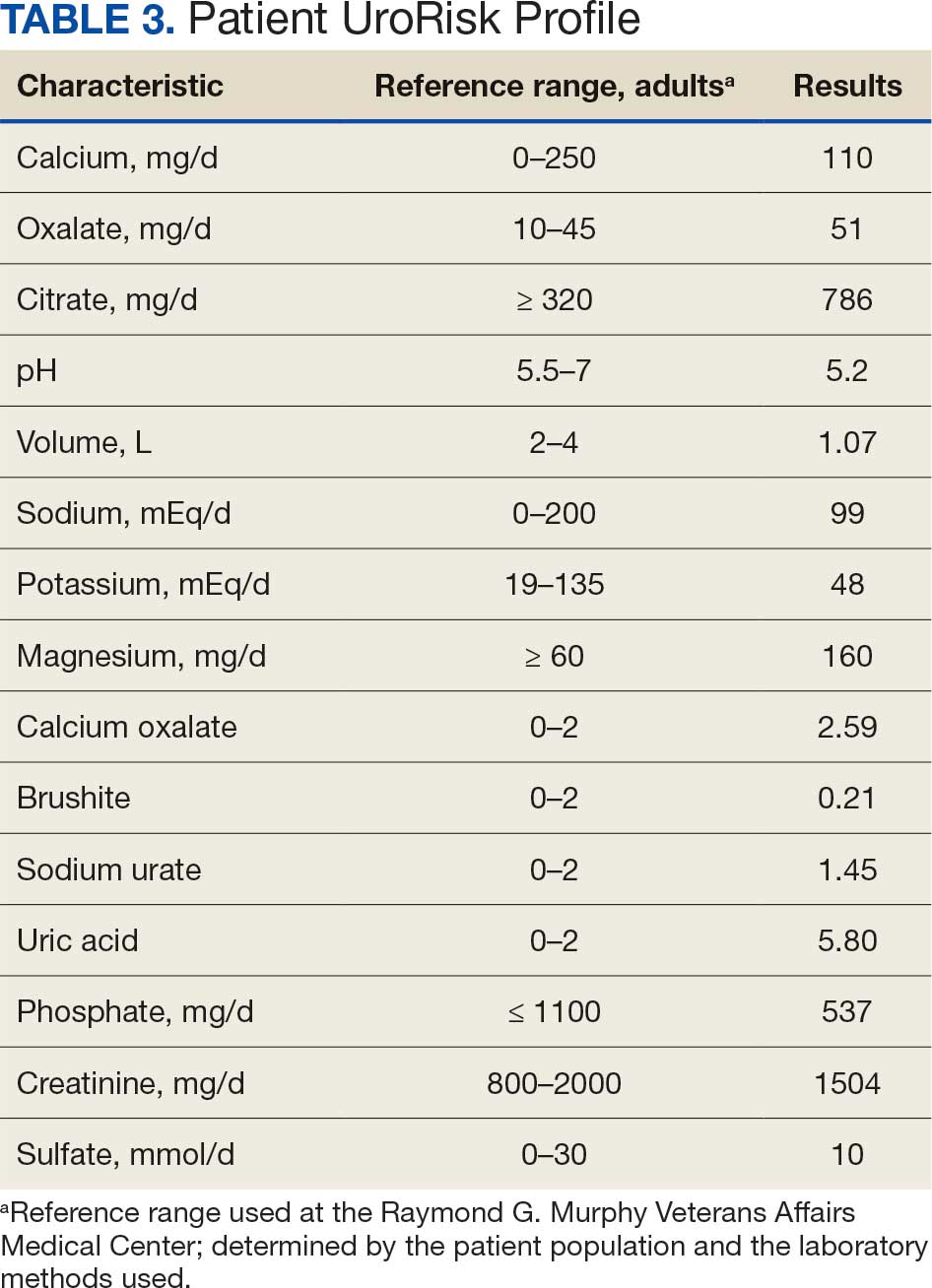
To address this growing concern, clinicians must adopt stricter vigilance and actively pursue updated information to mitigate patient risks tied to these contrast agents.
There exists an illusion of knowledge in disregarding the confounded exposures of MRI contrast agents. Ten distinct brands of contrast agents have been approved for clinical use. With repeated imaging, patients are often exposed to varying formulations of gadolinium-based agents. Yet investigators commonly discard these data points when assessing risk. By doing so, they assume—without evidence—that some formulations are inherently less likely to provoke adverse effects (AEs) than others. This untested presumption becomes perilous, especially given the limited understanding of the mechanisms underlying gadolinium-induced pathologies. As Aldous Huxley warned, “Facts do not cease to exist because they are ignored.”19
Gadolinium Persistence
Contrary to expectations, gadolinium persists in the body far longer than initially presumed. Symptoms associated with gadolinium exposure (SAGE) encapsulate the chronic, often enigmatic maladies tied to MRI contrast agents.20 The prolonged retention of this rare earth metal offers a compelling hypothesis for the etiology of SAGE. It has been hypothesized that Lewis base-rich metabolites increase susceptibility to gadolinium-based contrast agent complications.21
The blood and urine concentration elimination curves of gadolinium are exponential and categorized as fast, intermediate, and long-term.1 For urinary elimination, the function of the curves is exponential. The quantity of gadolinium in the urine at a time (t) after exposure (D[Gd](t)) is equal to the product of the amount of gadolinium in the sample (urine or blood) at the end of the fast elimination period (D[Gd](t0)) and the exponential decay with k being a rate constant.
To the authors’ knowledge, we are the only research team currently investigating the rate constant for the intermediate- and long-term phase gadolinium elimination. The Retention and Toxicity of Gadolinium-based Contrast Agents study was approved by the University of New Mexico Health Sciences Center Institutional Review Board on May 27, 2020 (IRB ID 19-660). The data for the patient in this case were compared with preliminary results for patients with exposure-to-measurement intervals < 100 days.
The patient in this case presented with detectable gadolinium levels in urine and serum shortly after an attempted contrast-enhanced MRI procedure (Figure 3). The presence of detectable gadolinium levels in the patient’s urine and serum suggests a likely exposure to a contrast agent about 27 days before his consultation. While the technician reported that no contrast was administered during the attempted MRI, it remains possible that a small amount was introduced during cannulation, potentially triggering the patient’s symptoms. Linear modeling of semilogarithmic plots for participants exposed to contrast agents within 100 days (urine: P = 1.8 × 10ˉ8, adjusted r² = 0.62; blood: P = .005, adjusted r² = 0.21) provided clearance rates (k values) for urine and blood. Extrapolating from these models to the presumed exposure date, the intercepts estimate that the patient received between 0.5% and 8% of a standard contrast dose.
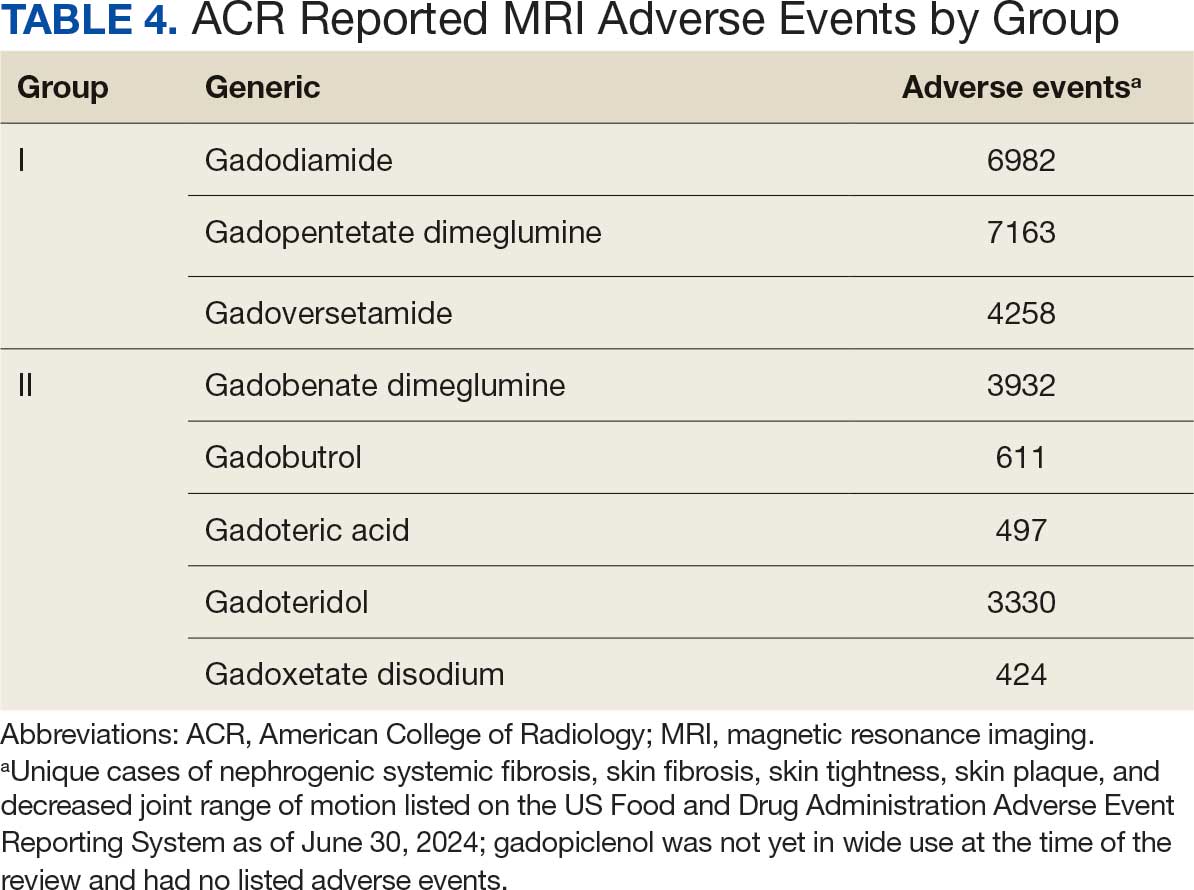
MRI contrast agents can cause skin disease. Systemic fibrosis is considered one of the most severe AEs. Skin pathophysiology involving myeloid cells is driven by elevated levels of monocyte chemoattractant protein-1, which recruits circulating fibroblasts via the C-C chemokine receptor 2.22,23 This occurs alongside activation of NADPH oxidase Nox4.4,24,25 Intracellular gadolinium-rich nanoparticles likely serve as catalysts for this reactive cascade.2,18,22,26,27 These particles assemble around intracellular lipid droplets and ferrule them in spiculated rare earth-rich shells that compromise cellular architecture.2,18,21,22,26,27 Frequently sequestered within endosomal compartments, they disrupt vesicular integrity and threaten cellular homeostasis. Interference with degradative systems such as the endolysosomal axis perturbs energy-recycling pathways—an insidious disturbance, particularly in cells with high metabolic demand. Skin-related symptoms are among the most frequently reported AEs, according to the FDA AE reporting system.18
Studies indicate repeated exposure to MRI contrast agents can lead to permanent gadolinium retention in the brain and other vital organs. Intravenous (IV) contrast agents cross the blood-brain barrier rapidly, while intrathecal administration has been linked to significant and lasting neurologic effects.18
Gadolinium is chemically bound to pharmaceutical ligands to enhance renal clearance and reduce toxicity. However, available data from human samples suggest potential ligand exchanges with undefined physiologic substances. This exchange may facilitate gadolinium precipitation and accumulation within cells into spiculated nanoparticles. Transmission electron microscopy reveals the formation of unilamellar bodies associated with mitochondriopathy and cellular damage, particularly in renal proximal tubules.2,18,22,26,27 It is proposed that intracellular nanoparticle formation represents a key mechanism driving the systemic symptoms observed in patients.1,2,18, 22,26,27
Any hypothesis based on free soluble gadolinium—or concept derived from it—should be discarded. The high affinity of pharmaceutical ligands for gadolinium suggests that the cationic rare earth metal remains predominantly in a ligand-bound, soluble form. It is hypothesized that gadolinium undergoes ligand exchange with physiologic substances, directly leading to nanoparticle formation. Current data demonstrate gadolinium precipitation according to the Le Chatelier’s principle. Since precipitated gadolinium does not readily re-equilibrate with pharmaceutical ligands, repeated administration of different contrast agent brands may contribute to nanoparticle growth.26
Meanwhile, a growing number of patients are turning to chelation therapy, a largely untested treatment. The premise of chelation therapy is rooted in several unproven assumptions.18,21 First, it assumes that clinically significant amounts of gadolinium persist in compartments such as the extracellular space, where they can be effectively chelated and cleared. Second, it presumes that free gadolinium is the primary driver of chronic symptoms, an assertion that remains scientifically unsubstantiated. Finally, chelation proponents overlook the potential harm caused by depleting essential physiological metals during the process, assuming without evidence that the scant removal of gadolinium outweighs the risk of physiological mineral depletion.
These assumptions underpin an unproven remedy that demands critical scrutiny. Recent findings reveal that gadolinium deposits in the skin and kidney often take the form of intracellular nanoparticles, directly challenging the foundation of chelation therapy. Chelation advocates must demonstrate that these intracellular gadolinium deposits neither trigger cellular toxicity nor initiate a cytokine cascade. Chelation supporters must prove that the systemic response to these foreign particles is unrelated to the symptoms reported by patients. Until then, the validity of chelation therapy remains highly questionable.
The causality of the symptoms, mainly whether IV gadolinium was administered, was examined. The null hypothesis stated that the patient was not exposed to gadolinium. However, this hypothesis was contradicted by the detection of gadolinium in the serum and urine 27 days after the potential exposure.
Two plausible explanations exist for the nonzero gadolinium levels detected in the serum and urine. The first possibility is that minute quantities of gadolinium were introduced during cannulation, with the amount being sufficient to persist in measurable concentrations 27 days postexposure. The second possibility is that the gadolinium originated from an MRI contrast agent administered 4 years earlier. In this scenario, gadolinium stored in organ reservoirs such as bone, liver, or kidneys may have been mobilized into the extracellular fluid compartment due to the administration of high-dose steroids 20 days after the recent contrast-enhanced MRI procedure attempt. Coyte et al reported elevated gadolinium levels in the serum, cord blood, breast milk, and placenta of pregnant women with prior exposure to MRI contrast agents.28 These findings suggest that gadolinium, stored in organs such as bone may be remobilized by variables affecting bone remodeling (eg, high-dose steroids).
Significantly, the patient exhibited elevated urinary oxalate levels. Previous research has found that oxalic acid reacts rapidly with MRI contrast agents, forming digadolinium trioxalate. While the gadolinium-rich nanoparticles identified in tissues such as the skin and kidney (including the human kidney) are amorphous, these in vitro findings establish a proof-of-concept: the intracellular environment facilitates gadolinium dissociation from pharmaceutical chelates.
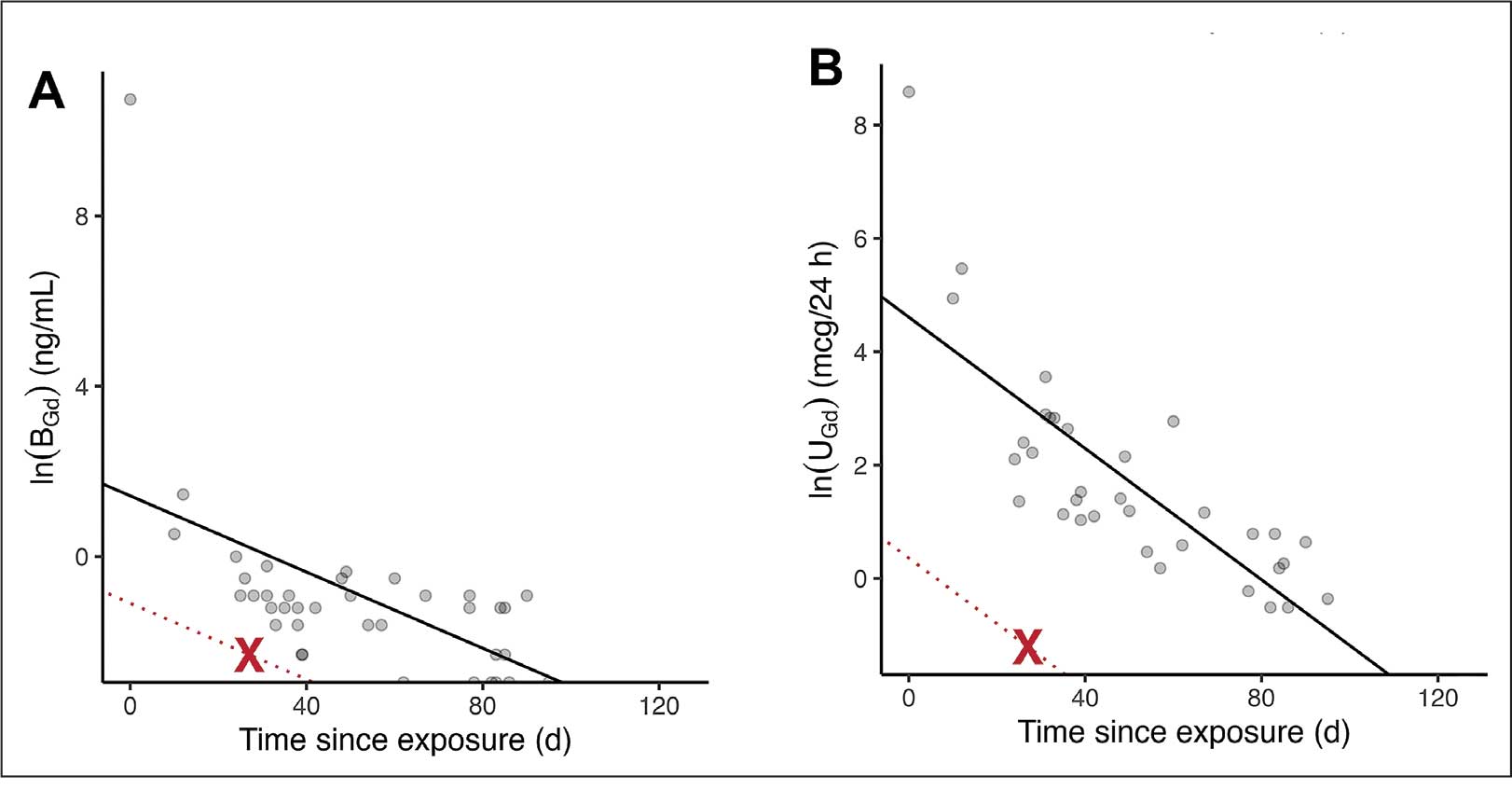
Furthermore, in vitro experiments show that proteins and lysosomal pH promote this dissociation, underscoring how human metabolic conditions—particularly oxalic acid concentration—may drive intracellular gadolinium deposition.
Patient Perspective
“They put something into my body that they cannot get out.” This stark realization underpins the patient’s profound concern about gadolinium-based contrast agents and their potential long-term effects. Reflecting on his experience, the patient expressed deep fears about the unknown future impacts: “I’m concerned about my kidneys, I’m concerned about my heart, and I’m concerned about my brain. I don’t know how this stuff is going to affect me in the future.”
He drew an unsettling parallel between gadolinium and heavy metals: “Heavy metal is poison. The body does not produce this kind of stuff on its own.” His reaction to the procedure left a lasting impression, prompting him to question the logic of using a substance that cannot be purged: “Why would you put something into someone’s body that you cannot extract? Nobody—nobody—should experience what I went through.”
The patient emphasized the lack of clear research on long-term outcomes, which compounds his anxiety: “If there was research that said, ‘Well, this is only going to affect these organs for this long,’ OK, I might be able to accept that. But there is no research like that. Nobody can tell me what’s going to happen in 5 years.”
Strengths and Limitations
A significant strength of this approach is the ability to track gadolinium elimination and symptom resolution over time, supported by unique access to intermediate and long-term clearance data from our ongoing research protocol. The investigators were equipped to back-extrapolate the exposure, which provided a rare opportunity to correlate gadolinium levels with clinical outcomes. The primary limitation is the lack of a defined clinical case definition for gadolinium toxicity and limited mechanistic understanding of SAGE, which hinders diagnosis and management.
Metabolites, proteins, and lipids rich in Lewis bases could initiate this process as substrates for intracellular gadolinium sedimentation. Future studies should investigate whether metabolic conditions such as oxalate burden or altered parathyroid hormone levels modulate gadolinium compartmentalization and tissue retention. If gadolinium-rich nanoparticle formation and accumulation disrupt cellular equilibrium, it underscores an urgent need to understand the implications of long-term gadolinium retention. The research team continues to gather evidence that the gadolinium cation remains chelated from the moment MRI contrast agents are administered through to the formation of intracellular nanoparticles. Retained gadolinium nanoparticles may act as a nidus, triggering cellular signaling cascades that lead to multisymptomatic illnesses. Intracellular and insoluble retained gadolinium challenges proponents of untested chelation therapies.
Conclusions
This case highlights emerging clinical and ethical concerns surrounding gadolinium-based contrast agent use. Clinicians may benefit from considering gadolinium retention as a contributor to persistent, unexplained symptoms—particularly in patients with recent imaging exposure. As contrast use continues to rise within federal health systems, regulatory and administrative stakeholders would do well to re-examine current safety frameworks. Informed consent should reflect what is known: gadolinium can remain in the body long after administration, potentially indefinitely. The long-term consequences of cumulative exposure remain poorly defined, but the presence of a lanthanide element in human tissue warrants greater attention from researchers and regulators alike. Interest in alternative imaging modalities and long-term safety monitoring would mark progress toward more transparent, accountable care.
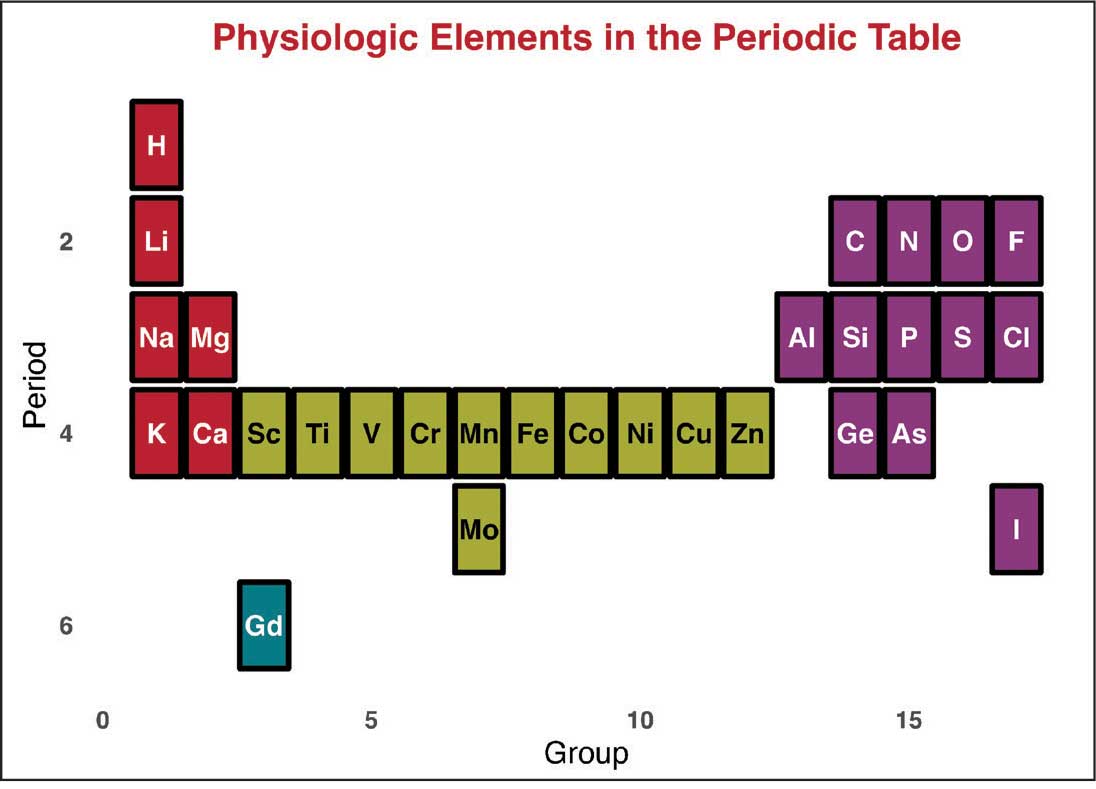
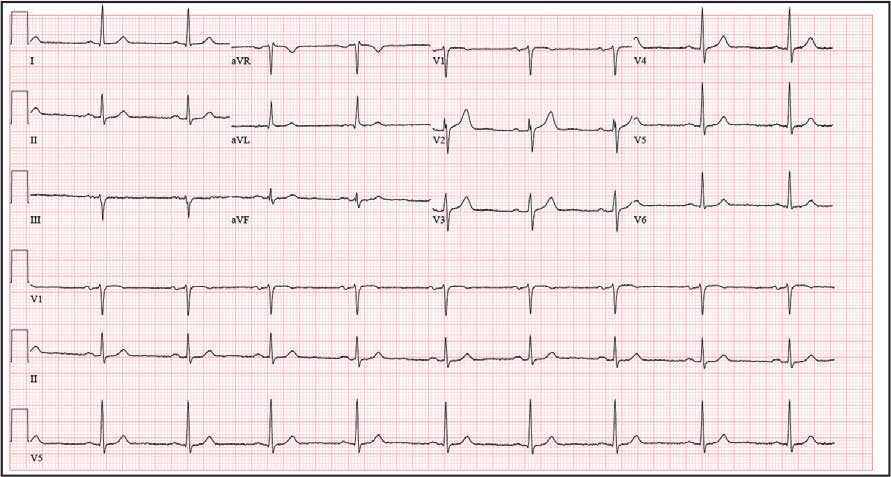
Jackson DB, MacIntyre T, Duarte-Miramontes V, et al. Gadolinium deposition disease: a case report and the prevalence of enhanced MRI procedures within the Veterans Health Administration. Fed Pract. 2022;39:218-225. doi:10.12788/fp.0258
Do C, DeAguero J, Brearley A, et al. Gadolinium-based contrast agent use, their safety, and practice evolution. Kidney360. 2020;1:561-568.doi:10.34067/kid.0000272019
Leyba K, Wagner B. Gadolinium-based contrast agents: why nephrologists need to be concerned. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 2019;28:154-162. doi:10.1097/MNH.0000000000000475
Wagner B, Drel V, Gorin Y. Pathophysiology of gadolinium-associated systemic fibrosis. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2016;311:F1-F11. doi:10.1152/ajprenal.00166.2016
Maramattom BV, Manno EM, Wijdicks EF, et al. Gadolinium encephalopathy in a patient with renal failure. Neurology. 2005;64:1276-1278.doi:10.1212/01.WNL.0000156805.45547.6E
Sam AD II, Morasch MD, Collins J, et al. Safety of gadolinium contrast angiography in patients with chronic renal insufficiency. J Vasc Surg. 2003;38:313-318. doi:10.1016/s0741-5214(03)00315-x
Schenker MP, Solomon JA, Roberts DA. Gadolinium arteriography complicated by acute pancreatitis and acute renal failure. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2001;12:393. doi:10.1016/s1051-0443(07)61925-3
Gemery J, Idelson B, Reid S, et al. Acute renal failure after arteriography with a gadolinium-based contrast agent. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1998;171:1277-1278. doi:10.2214/ajr.171.5.9798860
Akgun H, Gonlusen G, Cartwright J Jr, et al. Are gadolinium-based contrast media nephrotoxic? A renal biopsy study. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2006;130:1354-1357. doi:10.5858/2006-130-1354-AGCMNA
Gathings RM, Reddy R, Santa Cruz D, et al. Gadolinium-associated plaques: a new, distinctive clinical entity. JAMA Dermatol. 2015;151:316-319. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2014.2660
McDonald RJ, McDonald JS, Kallmes DF, et al. Gadolinium deposition in human brain tissues after contrast-enhanced MR imaging in adult patients without intracranial abnormalities. Radiology. 2017;285(2):546-554. doi:10.1148/radiol.2017161595
Kanda T, Ishii K, Kawaguchi H, et al. High signal intensity in the dentate nucleus and globus pallidus on unenhanced T1-weighted MR images: relationship with increasing cumulative dose of a gadolinium-based contrast material. Radiology. 2014;270(3):834-841. doi:10.1148/radiol.13131669
Schmidt K, Bau M, Merschel G, et al. Anthropogenic gadolinium in tap water and in tap water-based beverages from fast-food franchises in six major cities in Germany. Sci Total Environ. 2019;687:1401-1408. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.07.075
Kulaksız S, Bau M. Anthropogenic gadolinium as a microcontaminant in tap water used as drinking water in urban areas and megacities. Appl Geochem. 2011;26:1877-1885.
Brunjes R, Hofmann T. Anthropogenic gadolinium in freshwater and drinking water systems. Water Res. 2020;182:115966. doi:10.1016/j.watres.2020.115966
Endrikat J, Gutberlet M, Hoffmann KT, et al. Clinical safety of gadobutrol: review of over 25 years of use exceeding 100 million administrations. Invest Radiol. 2024;59(9):605-613. doi:10.1097/RLI.0000000000001072
Elmholdt TR, Jørgensen B, Ramsing M, et al. Two cases of nephrogenic systemic fibrosis after exposure to the macrocyclic compound gadobutrol. NDT Plus. 2010;3(3):285-287. doi:10.1093/ndtplus/sfq028
Cunningham A, Kirk M, Hong E, et al. The safety of magnetic resonance imaging contrast agents. Front Toxicol. 2024;6:1376587. doi:10.3389/ftox.2024.1376587
Huxley A. Complete Essays. Volume II, 1926-1929. Chicago; 2000:227.
McDonald RJ, Weinreb JC, Davenport MS. Symptoms associated with gadolinium exposure (SAGE): a suggested term. Radiology. 2022;302(2):270-273. doi:10.1148/radiol.2021211349
Henderson IM, Benevidez AD, Mowry CD, et al. Precipitation of gadolinium from magnetic resonance imaging contrast agents may be the Brass tacks of toxicity. Magn Reson Imaging. 2025;119:110383. doi:10.1016/j.mri.2025.110383
Do C, Drel V, Tan C, et al. Nephrogenic systemic fibrosis is mediated by myeloid C-C chemokine receptor 2. J Invest Dermatol. 2019;139(10):2134-2143. doi:10.1016/j.jid.2019.03.1145
Drel VR, Tan C, Barnes JL, et al. Centrality of bone marrow in the severity of gadolinium-based contrast-induced systemic fibrosis. FASEB J. 2016;30(9):3026-3038. doi:10.1096/fj.201500188R
Bruno F, DeAguero J, Do C, et al. Overlapping roles of NADPH oxidase 4 for diabetic and gadolinium-based contrast agent-induced systemic fibrosis. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2021;320(4):F617-F627. doi:10.1152/ajprenal.00456.2020
Wagner B, Tan C, Barnes JL, et al. Nephrogenic systemic fibrosis: evidence for oxidative stress and bone marrow-derived fibrocytes in skin, liver, and heart lesions using a 5/6 nephrectomy rodent model. Am J Pathol. 2012;181(6):1941-1952. doi:10.1016/j.ajpath.2012.08.026
DeAguero J, Howard T, Kusewitt D, et al. The onset of rare earth metallosis begins with renal gadolinium-rich nanoparticles from magnetic resonance imaging contrast agent exposure. Sci Rep. 2023;13(1):2025. doi:10.1038/s41598-023-28666-1
Do C, Ford B, Lee DY, et al. Gadolinium-based contrast agents: Stimulators of myeloid-induced renal fibrosis and major metabolic disruptors. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2019;375:32-45. doi:10.1016/j.taap.2019.05.009
Coyte RM, Darrah T, Olesik J, et al. Gadolinium during human pregnancy following administration of gadolinium chelate before pregnancy. Birth Defects Res. 2023;115(14):1264-1273. doi:10.1002/bdr2.2209
Magnetic resonance image (MRI) contrast agents can induce profound complications, including gadolinium encephalopathy, kidney injury, gadolinium-associated plaques, and progressive systemic fibrosis, which can be fatal.1-10 About 50% of MRIs use gadolinium-based contrast (Gd3+), a toxic rare earth metal ion that enhances imaging but requires binding with pharmaceutical ligands to reduce toxicity and promote renal elimination (Figure 1). Despite these measures, Gd3+ can persist in the body, including the brain.11,12 Wastewater treatment fails to remove these agents, making Gd3+ a growing pollutant in water and the food chain.13-15 Because Gd3+ is a rare earth metal ion in the milieu intérieur, there is an urgent need to study its biological and long-term effects (Appendix 1).
Case Presentation
A 65-year-old Vietnam-era veteran presented to nephrology at the Raymond G. Murphy Veterans Affairs Medical Center (RGMVAMC) in Albuquerque, New Mexico, for evaluation of gadolinium-induced symptoms. His medical history included metabolic syndrome, hypertension, hyperlipidemia, hypogonadism, cervical spondylosis, and an elevated prostate-specific antigen, previously assessed with a contrast-enhanced MRI in 2019 (Gadobenic acid, 19 mL). Surgical history included cervical fusion and ankle hardware.
The patient had a scheduled MRI 25 days earlier, following an elevated prostate specific antigen test result, prompting urologic surveillance and concern for malignancy. In preparation for the contrast-enhanced MRI, his right arm was cannulated with a line primed with gadobenic acid contrast. Though the technician stated the infusion had not started, the patient’s symptoms began shortly after entry into the scanner, before any programmed pulse sequences. The patient experienced claustrophobia, diaphoresis, palpitations, xerostomia, dysgeusia, shortness of breath, and a sensation of heat in his groin, chest, “kidneys,” and lower back. The MRI was terminated prematurely in response to the patient’s acute symptomatology. The patient continued experiencing new symptoms intermittently during the following week, including lightheadedness, headaches, right clavicular pain, raspy voice, edema, and a sense of doom.


The patient presented to the RGMVAMC emergency department (ED) 8 days after the MRI with worsening symptoms and was hospitalized for 10 days. During this time, he was referred to nephrology for outpatient evaluation. While awaiting his nephrology appointment, the patient presented to the RGMVAMC ED 20 days after the initial episode with ongoing symptoms. “I thought I was dying,” he said. Laboratory results and a 12-lead electrocardiogram showed a finely static background, wide P waves (> 80 ms) with notching in lead II, sinusoidal P waves in V1, R transition in V2, RR’ in V2, ST flat in lead III, and sinus bradycardia (Table 1 and Appendix 2).
The patient’s medical and surgical histories were reviewed at the nephrology evaluation 25 days following the MRI. He reported that household water was sourced from a well and that he filtered his drinking water with a reverse osmosis system. He served in the US Army for 10 years as an engineer specializing in mechanical systems, power generation, and vehicles. Following Army retirement, the patient served in the US Air Force Reserves for 15 years, working as a crew chief in pneudraulics. The patient reported stopping tobacco use 1 year before and also reported regular use of a broad array of prescription medications and dietary supplements, including dexamethasone (4 mg twice daily), fluticasone nasal spray (50 mcg per nostril, twice daily), ibuprofen (400 mg twice daily, as needed), loratadine (10 mg daily), aspirin (81 mg daily), and metoprolol succinate (50 mg nightly). In addition, he reported consistent use of cholecalciferol (3000 IU daily), another supplemental vitamin D preparation, chelated magnesium glycinate (3 tablets daily for bone issues), turmeric (1 tablet daily), a multivitamin (Living Green Liquid Gel, daily), and a mega-B complex.
Physical examination revealed a well-nourished, tall man with hypertension (145/87 mmHg) and bilateral lower extremity edema. Oral examination showed poor dentition, including missing molars (#1-3, #14-16, #17-19, #30-31), with the anterior teeth replaced by bridges supported by dental implants. The review of systems was otherwise unremarkable, with nocturia noted before the consultation.

Serum and urine gadolinium testing, (Mayo Clinic Laboratories) revealed gadolinium levels of 0.3 mcg/24 h in the urine and 0.1 ng/mL in the serum. Nonzero values indicated detectable gadolinium, suggesting retention. The patient had a prior gadolinium exposure during a 2019 MRI (about 1340 days before) and suspected a repeat exposure on day 0, although the MRI technician stated that no contrast was administered. Given his elevated vitamin D levels, the patient was advised to minimize dietary supplements, particularly vitamin D, to avoid confounding symptoms. The plan included monitoring symptoms and a follow-up evaluation with repeat laboratory tests on day 116.
At the nephrology follow-up 4 months postexposure, the patient's symptoms had primarily abated, with a marked reduction in the previously noted metallic dysgeusia. Physical examination remained consistent with prior findings. He was afebrile (97.7 °F) with a blood pressure of 111/72 mmHg, a pulse of 63 beats per minute, and an oxygen saturation of 98% on ambient air. Laboratory analysis revealed serum and urine gadolinium levels below detectable thresholds (< 0.1 ng/mL and < 0.1 mcg/24 h). A 24-hour creatinine clearance, calculated from a urine volume of 1300 mL, measured at an optimal 106 mL/min, indicating preserved renal function (Tables 2 and 3). Of note, his 24-hour oxalate was above the reference range, with a urine pH below the reference range and a high supersaturation index for calcium oxalate.
Discussion
Use of enhanced MRI has increased in the Veterans Health Administration (Figure 2). A growing range of indications for enhanced procedures (eg, cardiac MRI) has contributed to this rise. The market has grown with new gadolinium-based contrast agents, such as gadopiclenol. However, reliance on untested assumptions about the safety of newer agents and need for robust clinical trials pose potential risks to patient safety.
Without prospective evidence, the American College of Radiology (ACR) classifies gadolinium-based contrast agents into 3 groups: Group 1, associated with the highest number of nephrogenic systemic fibrosis cases; Group 2, linked to few, if any, unconfounded cases; and Group 3, where data on nephrogenic systemic fibrosis risk have been limited. As of April 2024, the ACR reclassified Group 3 agents (Ablavar/Vasovist/Angiomark and Primovist/Eovist) into Group 2. Curiously, Vueway and Elucirem were approved in late 2022 and should clearly be categorized as Group 3 (Table 4).There were 19 cases of nephrogenic systemic fibrosis or similar manifestations, 8 of which were unconfounded by other factors. These patients had been exposed to gadobutrol, often combined with other agents. Gadobutrol—like other Group 2 agents—has been associated with nephrogenic systemic fibrosis.16,17 Despite US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) documentation of rising reports, many clinicians remain unaware that nephrogenic systemic fibrosis is increasingly linked to Group 2 agents classified by the ACR.18 While declines in reported cases of nephrogenic systemic fibrosis may suggest reduced incidence, this trend may reflect diminished clinical vigilance and underreporting, particularly given emerging evidence implicating even Group 2 gadolinium-based contrast agents in delayed and underrecognized presentations. This information has yet to permeate the medical community, particularly among nephrologists. Considering these cases, revisiting the ACR guidelines may be prudent.

To address this growing concern, clinicians must adopt stricter vigilance and actively pursue updated information to mitigate patient risks tied to these contrast agents.
There exists an illusion of knowledge in disregarding the confounded exposures of MRI contrast agents. Ten distinct brands of contrast agents have been approved for clinical use. With repeated imaging, patients are often exposed to varying formulations of gadolinium-based agents. Yet investigators commonly discard these data points when assessing risk. By doing so, they assume—without evidence—that some formulations are inherently less likely to provoke adverse effects (AEs) than others. This untested presumption becomes perilous, especially given the limited understanding of the mechanisms underlying gadolinium-induced pathologies. As Aldous Huxley warned, “Facts do not cease to exist because they are ignored.”19
Gadolinium Persistence
Contrary to expectations, gadolinium persists in the body far longer than initially presumed. Symptoms associated with gadolinium exposure (SAGE) encapsulate the chronic, often enigmatic maladies tied to MRI contrast agents.20 The prolonged retention of this rare earth metal offers a compelling hypothesis for the etiology of SAGE. It has been hypothesized that Lewis base-rich metabolites increase susceptibility to gadolinium-based contrast agent complications.21
The blood and urine concentration elimination curves of gadolinium are exponential and categorized as fast, intermediate, and long-term.1 For urinary elimination, the function of the curves is exponential. The quantity of gadolinium in the urine at a time (t) after exposure (D[Gd](t)) is equal to the product of the amount of gadolinium in the sample (urine or blood) at the end of the fast elimination period (D[Gd](t0)) and the exponential decay with k being a rate constant.
To the authors’ knowledge, we are the only research team currently investigating the rate constant for the intermediate- and long-term phase gadolinium elimination. The Retention and Toxicity of Gadolinium-based Contrast Agents study was approved by the University of New Mexico Health Sciences Center Institutional Review Board on May 27, 2020 (IRB ID 19-660). The data for the patient in this case were compared with preliminary results for patients with exposure-to-measurement intervals < 100 days.
The patient in this case presented with detectable gadolinium levels in urine and serum shortly after an attempted contrast-enhanced MRI procedure (Figure 3). The presence of detectable gadolinium levels in the patient’s urine and serum suggests a likely exposure to a contrast agent about 27 days before his consultation. While the technician reported that no contrast was administered during the attempted MRI, it remains possible that a small amount was introduced during cannulation, potentially triggering the patient’s symptoms. Linear modeling of semilogarithmic plots for participants exposed to contrast agents within 100 days (urine: P = 1.8 × 10ˉ8, adjusted r² = 0.62; blood: P = .005, adjusted r² = 0.21) provided clearance rates (k values) for urine and blood. Extrapolating from these models to the presumed exposure date, the intercepts estimate that the patient received between 0.5% and 8% of a standard contrast dose.

MRI contrast agents can cause skin disease. Systemic fibrosis is considered one of the most severe AEs. Skin pathophysiology involving myeloid cells is driven by elevated levels of monocyte chemoattractant protein-1, which recruits circulating fibroblasts via the C-C chemokine receptor 2.22,23 This occurs alongside activation of NADPH oxidase Nox4.4,24,25 Intracellular gadolinium-rich nanoparticles likely serve as catalysts for this reactive cascade.2,18,22,26,27 These particles assemble around intracellular lipid droplets and ferrule them in spiculated rare earth-rich shells that compromise cellular architecture.2,18,21,22,26,27 Frequently sequestered within endosomal compartments, they disrupt vesicular integrity and threaten cellular homeostasis. Interference with degradative systems such as the endolysosomal axis perturbs energy-recycling pathways—an insidious disturbance, particularly in cells with high metabolic demand. Skin-related symptoms are among the most frequently reported AEs, according to the FDA AE reporting system.18
Studies indicate repeated exposure to MRI contrast agents can lead to permanent gadolinium retention in the brain and other vital organs. Intravenous (IV) contrast agents cross the blood-brain barrier rapidly, while intrathecal administration has been linked to significant and lasting neurologic effects.18
Gadolinium is chemically bound to pharmaceutical ligands to enhance renal clearance and reduce toxicity. However, available data from human samples suggest potential ligand exchanges with undefined physiologic substances. This exchange may facilitate gadolinium precipitation and accumulation within cells into spiculated nanoparticles. Transmission electron microscopy reveals the formation of unilamellar bodies associated with mitochondriopathy and cellular damage, particularly in renal proximal tubules.2,18,22,26,27 It is proposed that intracellular nanoparticle formation represents a key mechanism driving the systemic symptoms observed in patients.1,2,18, 22,26,27
Any hypothesis based on free soluble gadolinium—or concept derived from it—should be discarded. The high affinity of pharmaceutical ligands for gadolinium suggests that the cationic rare earth metal remains predominantly in a ligand-bound, soluble form. It is hypothesized that gadolinium undergoes ligand exchange with physiologic substances, directly leading to nanoparticle formation. Current data demonstrate gadolinium precipitation according to the Le Chatelier’s principle. Since precipitated gadolinium does not readily re-equilibrate with pharmaceutical ligands, repeated administration of different contrast agent brands may contribute to nanoparticle growth.26
Meanwhile, a growing number of patients are turning to chelation therapy, a largely untested treatment. The premise of chelation therapy is rooted in several unproven assumptions.18,21 First, it assumes that clinically significant amounts of gadolinium persist in compartments such as the extracellular space, where they can be effectively chelated and cleared. Second, it presumes that free gadolinium is the primary driver of chronic symptoms, an assertion that remains scientifically unsubstantiated. Finally, chelation proponents overlook the potential harm caused by depleting essential physiological metals during the process, assuming without evidence that the scant removal of gadolinium outweighs the risk of physiological mineral depletion.

These assumptions underpin an unproven remedy that demands critical scrutiny. Recent findings reveal that gadolinium deposits in the skin and kidney often take the form of intracellular nanoparticles, directly challenging the foundation of chelation therapy. Chelation advocates must demonstrate that these intracellular gadolinium deposits neither trigger cellular toxicity nor initiate a cytokine cascade. Chelation supporters must prove that the systemic response to these foreign particles is unrelated to the symptoms reported by patients. Until then, the validity of chelation therapy remains highly questionable.
The causality of the symptoms, mainly whether IV gadolinium was administered, was examined. The null hypothesis stated that the patient was not exposed to gadolinium. However, this hypothesis was contradicted by the detection of gadolinium in the serum and urine 27 days after the potential exposure.
Two plausible explanations exist for the nonzero gadolinium levels detected in the serum and urine. The first possibility is that minute quantities of gadolinium were introduced during cannulation, with the amount being sufficient to persist in measurable concentrations 27 days postexposure. The second possibility is that the gadolinium originated from an MRI contrast agent administered 4 years earlier. In this scenario, gadolinium stored in organ reservoirs such as bone, liver, or kidneys may have been mobilized into the extracellular fluid compartment due to the administration of high-dose steroids 20 days after the recent contrast-enhanced MRI procedure attempt. Coyte et al reported elevated gadolinium levels in the serum, cord blood, breast milk, and placenta of pregnant women with prior exposure to MRI contrast agents.28 These findings suggest that gadolinium, stored in organs such as bone may be remobilized by variables affecting bone remodeling (eg, high-dose steroids).
Significantly, the patient exhibited elevated urinary oxalate levels. Previous research has found that oxalic acid reacts rapidly with MRI contrast agents, forming digadolinium trioxalate. While the gadolinium-rich nanoparticles identified in tissues such as the skin and kidney (including the human kidney) are amorphous, these in vitro findings establish a proof-of-concept: the intracellular environment facilitates gadolinium dissociation from pharmaceutical chelates.

Furthermore, in vitro experiments show that proteins and lysosomal pH promote this dissociation, underscoring how human metabolic conditions—particularly oxalic acid concentration—may drive intracellular gadolinium deposition.
Patient Perspective
“They put something into my body that they cannot get out.” This stark realization underpins the patient’s profound concern about gadolinium-based contrast agents and their potential long-term effects. Reflecting on his experience, the patient expressed deep fears about the unknown future impacts: “I’m concerned about my kidneys, I’m concerned about my heart, and I’m concerned about my brain. I don’t know how this stuff is going to affect me in the future.”
He drew an unsettling parallel between gadolinium and heavy metals: “Heavy metal is poison. The body does not produce this kind of stuff on its own.” His reaction to the procedure left a lasting impression, prompting him to question the logic of using a substance that cannot be purged: “Why would you put something into someone’s body that you cannot extract? Nobody—nobody—should experience what I went through.”
The patient emphasized the lack of clear research on long-term outcomes, which compounds his anxiety: “If there was research that said, ‘Well, this is only going to affect these organs for this long,’ OK, I might be able to accept that. But there is no research like that. Nobody can tell me what’s going to happen in 5 years.”
Strengths and Limitations
A significant strength of this approach is the ability to track gadolinium elimination and symptom resolution over time, supported by unique access to intermediate and long-term clearance data from our ongoing research protocol. The investigators were equipped to back-extrapolate the exposure, which provided a rare opportunity to correlate gadolinium levels with clinical outcomes. The primary limitation is the lack of a defined clinical case definition for gadolinium toxicity and limited mechanistic understanding of SAGE, which hinders diagnosis and management.
Metabolites, proteins, and lipids rich in Lewis bases could initiate this process as substrates for intracellular gadolinium sedimentation. Future studies should investigate whether metabolic conditions such as oxalate burden or altered parathyroid hormone levels modulate gadolinium compartmentalization and tissue retention. If gadolinium-rich nanoparticle formation and accumulation disrupt cellular equilibrium, it underscores an urgent need to understand the implications of long-term gadolinium retention. The research team continues to gather evidence that the gadolinium cation remains chelated from the moment MRI contrast agents are administered through to the formation of intracellular nanoparticles. Retained gadolinium nanoparticles may act as a nidus, triggering cellular signaling cascades that lead to multisymptomatic illnesses. Intracellular and insoluble retained gadolinium challenges proponents of untested chelation therapies.
Conclusions
This case highlights emerging clinical and ethical concerns surrounding gadolinium-based contrast agent use. Clinicians may benefit from considering gadolinium retention as a contributor to persistent, unexplained symptoms—particularly in patients with recent imaging exposure. As contrast use continues to rise within federal health systems, regulatory and administrative stakeholders would do well to re-examine current safety frameworks. Informed consent should reflect what is known: gadolinium can remain in the body long after administration, potentially indefinitely. The long-term consequences of cumulative exposure remain poorly defined, but the presence of a lanthanide element in human tissue warrants greater attention from researchers and regulators alike. Interest in alternative imaging modalities and long-term safety monitoring would mark progress toward more transparent, accountable care.


Magnetic resonance image (MRI) contrast agents can induce profound complications, including gadolinium encephalopathy, kidney injury, gadolinium-associated plaques, and progressive systemic fibrosis, which can be fatal.1-10 About 50% of MRIs use gadolinium-based contrast (Gd3+), a toxic rare earth metal ion that enhances imaging but requires binding with pharmaceutical ligands to reduce toxicity and promote renal elimination (Figure 1). Despite these measures, Gd3+ can persist in the body, including the brain.11,12 Wastewater treatment fails to remove these agents, making Gd3+ a growing pollutant in water and the food chain.13-15 Because Gd3+ is a rare earth metal ion in the milieu intérieur, there is an urgent need to study its biological and long-term effects (Appendix 1).
Case Presentation
A 65-year-old Vietnam-era veteran presented to nephrology at the Raymond G. Murphy Veterans Affairs Medical Center (RGMVAMC) in Albuquerque, New Mexico, for evaluation of gadolinium-induced symptoms. His medical history included metabolic syndrome, hypertension, hyperlipidemia, hypogonadism, cervical spondylosis, and an elevated prostate-specific antigen, previously assessed with a contrast-enhanced MRI in 2019 (Gadobenic acid, 19 mL). Surgical history included cervical fusion and ankle hardware.
The patient had a scheduled MRI 25 days earlier, following an elevated prostate specific antigen test result, prompting urologic surveillance and concern for malignancy. In preparation for the contrast-enhanced MRI, his right arm was cannulated with a line primed with gadobenic acid contrast. Though the technician stated the infusion had not started, the patient’s symptoms began shortly after entry into the scanner, before any programmed pulse sequences. The patient experienced claustrophobia, diaphoresis, palpitations, xerostomia, dysgeusia, shortness of breath, and a sensation of heat in his groin, chest, “kidneys,” and lower back. The MRI was terminated prematurely in response to the patient’s acute symptomatology. The patient continued experiencing new symptoms intermittently during the following week, including lightheadedness, headaches, right clavicular pain, raspy voice, edema, and a sense of doom.


The patient presented to the RGMVAMC emergency department (ED) 8 days after the MRI with worsening symptoms and was hospitalized for 10 days. During this time, he was referred to nephrology for outpatient evaluation. While awaiting his nephrology appointment, the patient presented to the RGMVAMC ED 20 days after the initial episode with ongoing symptoms. “I thought I was dying,” he said. Laboratory results and a 12-lead electrocardiogram showed a finely static background, wide P waves (> 80 ms) with notching in lead II, sinusoidal P waves in V1, R transition in V2, RR’ in V2, ST flat in lead III, and sinus bradycardia (Table 1 and Appendix 2).
The patient’s medical and surgical histories were reviewed at the nephrology evaluation 25 days following the MRI. He reported that household water was sourced from a well and that he filtered his drinking water with a reverse osmosis system. He served in the US Army for 10 years as an engineer specializing in mechanical systems, power generation, and vehicles. Following Army retirement, the patient served in the US Air Force Reserves for 15 years, working as a crew chief in pneudraulics. The patient reported stopping tobacco use 1 year before and also reported regular use of a broad array of prescription medications and dietary supplements, including dexamethasone (4 mg twice daily), fluticasone nasal spray (50 mcg per nostril, twice daily), ibuprofen (400 mg twice daily, as needed), loratadine (10 mg daily), aspirin (81 mg daily), and metoprolol succinate (50 mg nightly). In addition, he reported consistent use of cholecalciferol (3000 IU daily), another supplemental vitamin D preparation, chelated magnesium glycinate (3 tablets daily for bone issues), turmeric (1 tablet daily), a multivitamin (Living Green Liquid Gel, daily), and a mega-B complex.
Physical examination revealed a well-nourished, tall man with hypertension (145/87 mmHg) and bilateral lower extremity edema. Oral examination showed poor dentition, including missing molars (#1-3, #14-16, #17-19, #30-31), with the anterior teeth replaced by bridges supported by dental implants. The review of systems was otherwise unremarkable, with nocturia noted before the consultation.

Serum and urine gadolinium testing, (Mayo Clinic Laboratories) revealed gadolinium levels of 0.3 mcg/24 h in the urine and 0.1 ng/mL in the serum. Nonzero values indicated detectable gadolinium, suggesting retention. The patient had a prior gadolinium exposure during a 2019 MRI (about 1340 days before) and suspected a repeat exposure on day 0, although the MRI technician stated that no contrast was administered. Given his elevated vitamin D levels, the patient was advised to minimize dietary supplements, particularly vitamin D, to avoid confounding symptoms. The plan included monitoring symptoms and a follow-up evaluation with repeat laboratory tests on day 116.
At the nephrology follow-up 4 months postexposure, the patient's symptoms had primarily abated, with a marked reduction in the previously noted metallic dysgeusia. Physical examination remained consistent with prior findings. He was afebrile (97.7 °F) with a blood pressure of 111/72 mmHg, a pulse of 63 beats per minute, and an oxygen saturation of 98% on ambient air. Laboratory analysis revealed serum and urine gadolinium levels below detectable thresholds (< 0.1 ng/mL and < 0.1 mcg/24 h). A 24-hour creatinine clearance, calculated from a urine volume of 1300 mL, measured at an optimal 106 mL/min, indicating preserved renal function (Tables 2 and 3). Of note, his 24-hour oxalate was above the reference range, with a urine pH below the reference range and a high supersaturation index for calcium oxalate.
Discussion
Use of enhanced MRI has increased in the Veterans Health Administration (Figure 2). A growing range of indications for enhanced procedures (eg, cardiac MRI) has contributed to this rise. The market has grown with new gadolinium-based contrast agents, such as gadopiclenol. However, reliance on untested assumptions about the safety of newer agents and need for robust clinical trials pose potential risks to patient safety.
Without prospective evidence, the American College of Radiology (ACR) classifies gadolinium-based contrast agents into 3 groups: Group 1, associated with the highest number of nephrogenic systemic fibrosis cases; Group 2, linked to few, if any, unconfounded cases; and Group 3, where data on nephrogenic systemic fibrosis risk have been limited. As of April 2024, the ACR reclassified Group 3 agents (Ablavar/Vasovist/Angiomark and Primovist/Eovist) into Group 2. Curiously, Vueway and Elucirem were approved in late 2022 and should clearly be categorized as Group 3 (Table 4).There were 19 cases of nephrogenic systemic fibrosis or similar manifestations, 8 of which were unconfounded by other factors. These patients had been exposed to gadobutrol, often combined with other agents. Gadobutrol—like other Group 2 agents—has been associated with nephrogenic systemic fibrosis.16,17 Despite US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) documentation of rising reports, many clinicians remain unaware that nephrogenic systemic fibrosis is increasingly linked to Group 2 agents classified by the ACR.18 While declines in reported cases of nephrogenic systemic fibrosis may suggest reduced incidence, this trend may reflect diminished clinical vigilance and underreporting, particularly given emerging evidence implicating even Group 2 gadolinium-based contrast agents in delayed and underrecognized presentations. This information has yet to permeate the medical community, particularly among nephrologists. Considering these cases, revisiting the ACR guidelines may be prudent.

To address this growing concern, clinicians must adopt stricter vigilance and actively pursue updated information to mitigate patient risks tied to these contrast agents.
There exists an illusion of knowledge in disregarding the confounded exposures of MRI contrast agents. Ten distinct brands of contrast agents have been approved for clinical use. With repeated imaging, patients are often exposed to varying formulations of gadolinium-based agents. Yet investigators commonly discard these data points when assessing risk. By doing so, they assume—without evidence—that some formulations are inherently less likely to provoke adverse effects (AEs) than others. This untested presumption becomes perilous, especially given the limited understanding of the mechanisms underlying gadolinium-induced pathologies. As Aldous Huxley warned, “Facts do not cease to exist because they are ignored.”19
Gadolinium Persistence
Contrary to expectations, gadolinium persists in the body far longer than initially presumed. Symptoms associated with gadolinium exposure (SAGE) encapsulate the chronic, often enigmatic maladies tied to MRI contrast agents.20 The prolonged retention of this rare earth metal offers a compelling hypothesis for the etiology of SAGE. It has been hypothesized that Lewis base-rich metabolites increase susceptibility to gadolinium-based contrast agent complications.21
The blood and urine concentration elimination curves of gadolinium are exponential and categorized as fast, intermediate, and long-term.1 For urinary elimination, the function of the curves is exponential. The quantity of gadolinium in the urine at a time (t) after exposure (D[Gd](t)) is equal to the product of the amount of gadolinium in the sample (urine or blood) at the end of the fast elimination period (D[Gd](t0)) and the exponential decay with k being a rate constant.
To the authors’ knowledge, we are the only research team currently investigating the rate constant for the intermediate- and long-term phase gadolinium elimination. The Retention and Toxicity of Gadolinium-based Contrast Agents study was approved by the University of New Mexico Health Sciences Center Institutional Review Board on May 27, 2020 (IRB ID 19-660). The data for the patient in this case were compared with preliminary results for patients with exposure-to-measurement intervals < 100 days.
The patient in this case presented with detectable gadolinium levels in urine and serum shortly after an attempted contrast-enhanced MRI procedure (Figure 3). The presence of detectable gadolinium levels in the patient’s urine and serum suggests a likely exposure to a contrast agent about 27 days before his consultation. While the technician reported that no contrast was administered during the attempted MRI, it remains possible that a small amount was introduced during cannulation, potentially triggering the patient’s symptoms. Linear modeling of semilogarithmic plots for participants exposed to contrast agents within 100 days (urine: P = 1.8 × 10ˉ8, adjusted r² = 0.62; blood: P = .005, adjusted r² = 0.21) provided clearance rates (k values) for urine and blood. Extrapolating from these models to the presumed exposure date, the intercepts estimate that the patient received between 0.5% and 8% of a standard contrast dose.

MRI contrast agents can cause skin disease. Systemic fibrosis is considered one of the most severe AEs. Skin pathophysiology involving myeloid cells is driven by elevated levels of monocyte chemoattractant protein-1, which recruits circulating fibroblasts via the C-C chemokine receptor 2.22,23 This occurs alongside activation of NADPH oxidase Nox4.4,24,25 Intracellular gadolinium-rich nanoparticles likely serve as catalysts for this reactive cascade.2,18,22,26,27 These particles assemble around intracellular lipid droplets and ferrule them in spiculated rare earth-rich shells that compromise cellular architecture.2,18,21,22,26,27 Frequently sequestered within endosomal compartments, they disrupt vesicular integrity and threaten cellular homeostasis. Interference with degradative systems such as the endolysosomal axis perturbs energy-recycling pathways—an insidious disturbance, particularly in cells with high metabolic demand. Skin-related symptoms are among the most frequently reported AEs, according to the FDA AE reporting system.18
Studies indicate repeated exposure to MRI contrast agents can lead to permanent gadolinium retention in the brain and other vital organs. Intravenous (IV) contrast agents cross the blood-brain barrier rapidly, while intrathecal administration has been linked to significant and lasting neurologic effects.18
Gadolinium is chemically bound to pharmaceutical ligands to enhance renal clearance and reduce toxicity. However, available data from human samples suggest potential ligand exchanges with undefined physiologic substances. This exchange may facilitate gadolinium precipitation and accumulation within cells into spiculated nanoparticles. Transmission electron microscopy reveals the formation of unilamellar bodies associated with mitochondriopathy and cellular damage, particularly in renal proximal tubules.2,18,22,26,27 It is proposed that intracellular nanoparticle formation represents a key mechanism driving the systemic symptoms observed in patients.1,2,18, 22,26,27
Any hypothesis based on free soluble gadolinium—or concept derived from it—should be discarded. The high affinity of pharmaceutical ligands for gadolinium suggests that the cationic rare earth metal remains predominantly in a ligand-bound, soluble form. It is hypothesized that gadolinium undergoes ligand exchange with physiologic substances, directly leading to nanoparticle formation. Current data demonstrate gadolinium precipitation according to the Le Chatelier’s principle. Since precipitated gadolinium does not readily re-equilibrate with pharmaceutical ligands, repeated administration of different contrast agent brands may contribute to nanoparticle growth.26
Meanwhile, a growing number of patients are turning to chelation therapy, a largely untested treatment. The premise of chelation therapy is rooted in several unproven assumptions.18,21 First, it assumes that clinically significant amounts of gadolinium persist in compartments such as the extracellular space, where they can be effectively chelated and cleared. Second, it presumes that free gadolinium is the primary driver of chronic symptoms, an assertion that remains scientifically unsubstantiated. Finally, chelation proponents overlook the potential harm caused by depleting essential physiological metals during the process, assuming without evidence that the scant removal of gadolinium outweighs the risk of physiological mineral depletion.

These assumptions underpin an unproven remedy that demands critical scrutiny. Recent findings reveal that gadolinium deposits in the skin and kidney often take the form of intracellular nanoparticles, directly challenging the foundation of chelation therapy. Chelation advocates must demonstrate that these intracellular gadolinium deposits neither trigger cellular toxicity nor initiate a cytokine cascade. Chelation supporters must prove that the systemic response to these foreign particles is unrelated to the symptoms reported by patients. Until then, the validity of chelation therapy remains highly questionable.
The causality of the symptoms, mainly whether IV gadolinium was administered, was examined. The null hypothesis stated that the patient was not exposed to gadolinium. However, this hypothesis was contradicted by the detection of gadolinium in the serum and urine 27 days after the potential exposure.
Two plausible explanations exist for the nonzero gadolinium levels detected in the serum and urine. The first possibility is that minute quantities of gadolinium were introduced during cannulation, with the amount being sufficient to persist in measurable concentrations 27 days postexposure. The second possibility is that the gadolinium originated from an MRI contrast agent administered 4 years earlier. In this scenario, gadolinium stored in organ reservoirs such as bone, liver, or kidneys may have been mobilized into the extracellular fluid compartment due to the administration of high-dose steroids 20 days after the recent contrast-enhanced MRI procedure attempt. Coyte et al reported elevated gadolinium levels in the serum, cord blood, breast milk, and placenta of pregnant women with prior exposure to MRI contrast agents.28 These findings suggest that gadolinium, stored in organs such as bone may be remobilized by variables affecting bone remodeling (eg, high-dose steroids).
Significantly, the patient exhibited elevated urinary oxalate levels. Previous research has found that oxalic acid reacts rapidly with MRI contrast agents, forming digadolinium trioxalate. While the gadolinium-rich nanoparticles identified in tissues such as the skin and kidney (including the human kidney) are amorphous, these in vitro findings establish a proof-of-concept: the intracellular environment facilitates gadolinium dissociation from pharmaceutical chelates.

Furthermore, in vitro experiments show that proteins and lysosomal pH promote this dissociation, underscoring how human metabolic conditions—particularly oxalic acid concentration—may drive intracellular gadolinium deposition.
Patient Perspective
“They put something into my body that they cannot get out.” This stark realization underpins the patient’s profound concern about gadolinium-based contrast agents and their potential long-term effects. Reflecting on his experience, the patient expressed deep fears about the unknown future impacts: “I’m concerned about my kidneys, I’m concerned about my heart, and I’m concerned about my brain. I don’t know how this stuff is going to affect me in the future.”
He drew an unsettling parallel between gadolinium and heavy metals: “Heavy metal is poison. The body does not produce this kind of stuff on its own.” His reaction to the procedure left a lasting impression, prompting him to question the logic of using a substance that cannot be purged: “Why would you put something into someone’s body that you cannot extract? Nobody—nobody—should experience what I went through.”
The patient emphasized the lack of clear research on long-term outcomes, which compounds his anxiety: “If there was research that said, ‘Well, this is only going to affect these organs for this long,’ OK, I might be able to accept that. But there is no research like that. Nobody can tell me what’s going to happen in 5 years.”
Strengths and Limitations
A significant strength of this approach is the ability to track gadolinium elimination and symptom resolution over time, supported by unique access to intermediate and long-term clearance data from our ongoing research protocol. The investigators were equipped to back-extrapolate the exposure, which provided a rare opportunity to correlate gadolinium levels with clinical outcomes. The primary limitation is the lack of a defined clinical case definition for gadolinium toxicity and limited mechanistic understanding of SAGE, which hinders diagnosis and management.
Metabolites, proteins, and lipids rich in Lewis bases could initiate this process as substrates for intracellular gadolinium sedimentation. Future studies should investigate whether metabolic conditions such as oxalate burden or altered parathyroid hormone levels modulate gadolinium compartmentalization and tissue retention. If gadolinium-rich nanoparticle formation and accumulation disrupt cellular equilibrium, it underscores an urgent need to understand the implications of long-term gadolinium retention. The research team continues to gather evidence that the gadolinium cation remains chelated from the moment MRI contrast agents are administered through to the formation of intracellular nanoparticles. Retained gadolinium nanoparticles may act as a nidus, triggering cellular signaling cascades that lead to multisymptomatic illnesses. Intracellular and insoluble retained gadolinium challenges proponents of untested chelation therapies.
Conclusions
This case highlights emerging clinical and ethical concerns surrounding gadolinium-based contrast agent use. Clinicians may benefit from considering gadolinium retention as a contributor to persistent, unexplained symptoms—particularly in patients with recent imaging exposure. As contrast use continues to rise within federal health systems, regulatory and administrative stakeholders would do well to re-examine current safety frameworks. Informed consent should reflect what is known: gadolinium can remain in the body long after administration, potentially indefinitely. The long-term consequences of cumulative exposure remain poorly defined, but the presence of a lanthanide element in human tissue warrants greater attention from researchers and regulators alike. Interest in alternative imaging modalities and long-term safety monitoring would mark progress toward more transparent, accountable care.


Jackson DB, MacIntyre T, Duarte-Miramontes V, et al. Gadolinium deposition disease: a case report and the prevalence of enhanced MRI procedures within the Veterans Health Administration. Fed Pract. 2022;39:218-225. doi:10.12788/fp.0258
Do C, DeAguero J, Brearley A, et al. Gadolinium-based contrast agent use, their safety, and practice evolution. Kidney360. 2020;1:561-568.doi:10.34067/kid.0000272019
Leyba K, Wagner B. Gadolinium-based contrast agents: why nephrologists need to be concerned. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 2019;28:154-162. doi:10.1097/MNH.0000000000000475
Wagner B, Drel V, Gorin Y. Pathophysiology of gadolinium-associated systemic fibrosis. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2016;311:F1-F11. doi:10.1152/ajprenal.00166.2016
Maramattom BV, Manno EM, Wijdicks EF, et al. Gadolinium encephalopathy in a patient with renal failure. Neurology. 2005;64:1276-1278.doi:10.1212/01.WNL.0000156805.45547.6E
Sam AD II, Morasch MD, Collins J, et al. Safety of gadolinium contrast angiography in patients with chronic renal insufficiency. J Vasc Surg. 2003;38:313-318. doi:10.1016/s0741-5214(03)00315-x
Schenker MP, Solomon JA, Roberts DA. Gadolinium arteriography complicated by acute pancreatitis and acute renal failure. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2001;12:393. doi:10.1016/s1051-0443(07)61925-3
Gemery J, Idelson B, Reid S, et al. Acute renal failure after arteriography with a gadolinium-based contrast agent. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1998;171:1277-1278. doi:10.2214/ajr.171.5.9798860
Akgun H, Gonlusen G, Cartwright J Jr, et al. Are gadolinium-based contrast media nephrotoxic? A renal biopsy study. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2006;130:1354-1357. doi:10.5858/2006-130-1354-AGCMNA
Gathings RM, Reddy R, Santa Cruz D, et al. Gadolinium-associated plaques: a new, distinctive clinical entity. JAMA Dermatol. 2015;151:316-319. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2014.2660
McDonald RJ, McDonald JS, Kallmes DF, et al. Gadolinium deposition in human brain tissues after contrast-enhanced MR imaging in adult patients without intracranial abnormalities. Radiology. 2017;285(2):546-554. doi:10.1148/radiol.2017161595
Kanda T, Ishii K, Kawaguchi H, et al. High signal intensity in the dentate nucleus and globus pallidus on unenhanced T1-weighted MR images: relationship with increasing cumulative dose of a gadolinium-based contrast material. Radiology. 2014;270(3):834-841. doi:10.1148/radiol.13131669
Schmidt K, Bau M, Merschel G, et al. Anthropogenic gadolinium in tap water and in tap water-based beverages from fast-food franchises in six major cities in Germany. Sci Total Environ. 2019;687:1401-1408. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.07.075
Kulaksız S, Bau M. Anthropogenic gadolinium as a microcontaminant in tap water used as drinking water in urban areas and megacities. Appl Geochem. 2011;26:1877-1885.
Brunjes R, Hofmann T. Anthropogenic gadolinium in freshwater and drinking water systems. Water Res. 2020;182:115966. doi:10.1016/j.watres.2020.115966
Endrikat J, Gutberlet M, Hoffmann KT, et al. Clinical safety of gadobutrol: review of over 25 years of use exceeding 100 million administrations. Invest Radiol. 2024;59(9):605-613. doi:10.1097/RLI.0000000000001072
Elmholdt TR, Jørgensen B, Ramsing M, et al. Two cases of nephrogenic systemic fibrosis after exposure to the macrocyclic compound gadobutrol. NDT Plus. 2010;3(3):285-287. doi:10.1093/ndtplus/sfq028
Cunningham A, Kirk M, Hong E, et al. The safety of magnetic resonance imaging contrast agents. Front Toxicol. 2024;6:1376587. doi:10.3389/ftox.2024.1376587
Huxley A. Complete Essays. Volume II, 1926-1929. Chicago; 2000:227.
McDonald RJ, Weinreb JC, Davenport MS. Symptoms associated with gadolinium exposure (SAGE): a suggested term. Radiology. 2022;302(2):270-273. doi:10.1148/radiol.2021211349
Henderson IM, Benevidez AD, Mowry CD, et al. Precipitation of gadolinium from magnetic resonance imaging contrast agents may be the Brass tacks of toxicity. Magn Reson Imaging. 2025;119:110383. doi:10.1016/j.mri.2025.110383
Do C, Drel V, Tan C, et al. Nephrogenic systemic fibrosis is mediated by myeloid C-C chemokine receptor 2. J Invest Dermatol. 2019;139(10):2134-2143. doi:10.1016/j.jid.2019.03.1145
Drel VR, Tan C, Barnes JL, et al. Centrality of bone marrow in the severity of gadolinium-based contrast-induced systemic fibrosis. FASEB J. 2016;30(9):3026-3038. doi:10.1096/fj.201500188R
Bruno F, DeAguero J, Do C, et al. Overlapping roles of NADPH oxidase 4 for diabetic and gadolinium-based contrast agent-induced systemic fibrosis. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2021;320(4):F617-F627. doi:10.1152/ajprenal.00456.2020
Wagner B, Tan C, Barnes JL, et al. Nephrogenic systemic fibrosis: evidence for oxidative stress and bone marrow-derived fibrocytes in skin, liver, and heart lesions using a 5/6 nephrectomy rodent model. Am J Pathol. 2012;181(6):1941-1952. doi:10.1016/j.ajpath.2012.08.026
DeAguero J, Howard T, Kusewitt D, et al. The onset of rare earth metallosis begins with renal gadolinium-rich nanoparticles from magnetic resonance imaging contrast agent exposure. Sci Rep. 2023;13(1):2025. doi:10.1038/s41598-023-28666-1
Do C, Ford B, Lee DY, et al. Gadolinium-based contrast agents: Stimulators of myeloid-induced renal fibrosis and major metabolic disruptors. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2019;375:32-45. doi:10.1016/j.taap.2019.05.009
Coyte RM, Darrah T, Olesik J, et al. Gadolinium during human pregnancy following administration of gadolinium chelate before pregnancy. Birth Defects Res. 2023;115(14):1264-1273. doi:10.1002/bdr2.2209
Jackson DB, MacIntyre T, Duarte-Miramontes V, et al. Gadolinium deposition disease: a case report and the prevalence of enhanced MRI procedures within the Veterans Health Administration. Fed Pract. 2022;39:218-225. doi:10.12788/fp.0258
Do C, DeAguero J, Brearley A, et al. Gadolinium-based contrast agent use, their safety, and practice evolution. Kidney360. 2020;1:561-568.doi:10.34067/kid.0000272019
Leyba K, Wagner B. Gadolinium-based contrast agents: why nephrologists need to be concerned. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 2019;28:154-162. doi:10.1097/MNH.0000000000000475
Wagner B, Drel V, Gorin Y. Pathophysiology of gadolinium-associated systemic fibrosis. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2016;311:F1-F11. doi:10.1152/ajprenal.00166.2016
Maramattom BV, Manno EM, Wijdicks EF, et al. Gadolinium encephalopathy in a patient with renal failure. Neurology. 2005;64:1276-1278.doi:10.1212/01.WNL.0000156805.45547.6E
Sam AD II, Morasch MD, Collins J, et al. Safety of gadolinium contrast angiography in patients with chronic renal insufficiency. J Vasc Surg. 2003;38:313-318. doi:10.1016/s0741-5214(03)00315-x
Schenker MP, Solomon JA, Roberts DA. Gadolinium arteriography complicated by acute pancreatitis and acute renal failure. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2001;12:393. doi:10.1016/s1051-0443(07)61925-3
Gemery J, Idelson B, Reid S, et al. Acute renal failure after arteriography with a gadolinium-based contrast agent. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1998;171:1277-1278. doi:10.2214/ajr.171.5.9798860
Akgun H, Gonlusen G, Cartwright J Jr, et al. Are gadolinium-based contrast media nephrotoxic? A renal biopsy study. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2006;130:1354-1357. doi:10.5858/2006-130-1354-AGCMNA
Gathings RM, Reddy R, Santa Cruz D, et al. Gadolinium-associated plaques: a new, distinctive clinical entity. JAMA Dermatol. 2015;151:316-319. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2014.2660
McDonald RJ, McDonald JS, Kallmes DF, et al. Gadolinium deposition in human brain tissues after contrast-enhanced MR imaging in adult patients without intracranial abnormalities. Radiology. 2017;285(2):546-554. doi:10.1148/radiol.2017161595
Kanda T, Ishii K, Kawaguchi H, et al. High signal intensity in the dentate nucleus and globus pallidus on unenhanced T1-weighted MR images: relationship with increasing cumulative dose of a gadolinium-based contrast material. Radiology. 2014;270(3):834-841. doi:10.1148/radiol.13131669
Schmidt K, Bau M, Merschel G, et al. Anthropogenic gadolinium in tap water and in tap water-based beverages from fast-food franchises in six major cities in Germany. Sci Total Environ. 2019;687:1401-1408. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.07.075
Kulaksız S, Bau M. Anthropogenic gadolinium as a microcontaminant in tap water used as drinking water in urban areas and megacities. Appl Geochem. 2011;26:1877-1885.
Brunjes R, Hofmann T. Anthropogenic gadolinium in freshwater and drinking water systems. Water Res. 2020;182:115966. doi:10.1016/j.watres.2020.115966
Endrikat J, Gutberlet M, Hoffmann KT, et al. Clinical safety of gadobutrol: review of over 25 years of use exceeding 100 million administrations. Invest Radiol. 2024;59(9):605-613. doi:10.1097/RLI.0000000000001072
Elmholdt TR, Jørgensen B, Ramsing M, et al. Two cases of nephrogenic systemic fibrosis after exposure to the macrocyclic compound gadobutrol. NDT Plus. 2010;3(3):285-287. doi:10.1093/ndtplus/sfq028
Cunningham A, Kirk M, Hong E, et al. The safety of magnetic resonance imaging contrast agents. Front Toxicol. 2024;6:1376587. doi:10.3389/ftox.2024.1376587
Huxley A. Complete Essays. Volume II, 1926-1929. Chicago; 2000:227.
McDonald RJ, Weinreb JC, Davenport MS. Symptoms associated with gadolinium exposure (SAGE): a suggested term. Radiology. 2022;302(2):270-273. doi:10.1148/radiol.2021211349
Henderson IM, Benevidez AD, Mowry CD, et al. Precipitation of gadolinium from magnetic resonance imaging contrast agents may be the Brass tacks of toxicity. Magn Reson Imaging. 2025;119:110383. doi:10.1016/j.mri.2025.110383
Do C, Drel V, Tan C, et al. Nephrogenic systemic fibrosis is mediated by myeloid C-C chemokine receptor 2. J Invest Dermatol. 2019;139(10):2134-2143. doi:10.1016/j.jid.2019.03.1145
Drel VR, Tan C, Barnes JL, et al. Centrality of bone marrow in the severity of gadolinium-based contrast-induced systemic fibrosis. FASEB J. 2016;30(9):3026-3038. doi:10.1096/fj.201500188R
Bruno F, DeAguero J, Do C, et al. Overlapping roles of NADPH oxidase 4 for diabetic and gadolinium-based contrast agent-induced systemic fibrosis. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2021;320(4):F617-F627. doi:10.1152/ajprenal.00456.2020
Wagner B, Tan C, Barnes JL, et al. Nephrogenic systemic fibrosis: evidence for oxidative stress and bone marrow-derived fibrocytes in skin, liver, and heart lesions using a 5/6 nephrectomy rodent model. Am J Pathol. 2012;181(6):1941-1952. doi:10.1016/j.ajpath.2012.08.026
DeAguero J, Howard T, Kusewitt D, et al. The onset of rare earth metallosis begins with renal gadolinium-rich nanoparticles from magnetic resonance imaging contrast agent exposure. Sci Rep. 2023;13(1):2025. doi:10.1038/s41598-023-28666-1
Do C, Ford B, Lee DY, et al. Gadolinium-based contrast agents: Stimulators of myeloid-induced renal fibrosis and major metabolic disruptors. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2019;375:32-45. doi:10.1016/j.taap.2019.05.009
Coyte RM, Darrah T, Olesik J, et al. Gadolinium during human pregnancy following administration of gadolinium chelate before pregnancy. Birth Defects Res. 2023;115(14):1264-1273. doi:10.1002/bdr2.2209
Gadolinium Intermediate Elimination and Persistent Symptoms After Magnetic Resonance Imaging Contrast Agent Exposure
Gadolinium Intermediate Elimination and Persistent Symptoms After Magnetic Resonance Imaging Contrast Agent Exposure
Treating Metastatic RCC: From Risk Assessment to Therapy Selection
Treating Metastatic RCC: From Risk Assessment to Therapy Selection
Treatment of metastatic renal cell carcinoma (RCC) is complex and requires careful analysis of risk and treatment options, an oncologist said at the July Association of VA Hematology and Oncology (AVAHO) seminar in Long Beach, California, regarding treating veterans with kidney cancer.
“We’ve come a long way in treating this disease, but individualizing therapy remains critical, especially in complex populations like our veterans,” said Matthew B. Rettig, MD, chief of Hematology-Oncology at the Veterans Affairs Greater Los Angeles Healthcare System and professor of Medicine and Urology at UCLA.
Rettig emphasized 2 critical early questions clinicians should consider when encountering metastatic RCC. First: Can the patient be treated with localized interventions such as metastasectomy, radiation therapy, or nephrectomy? These can be curative, Rettig said.
And second: Does the patient currently need systemic therapy? “[There are] a small subset of patients,” Rettig said, “who go into a durable, complete remission, dare I say ‘cure,’ with immunotherapeutic-based approaches.”
Rettig highlighted the International Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma Database Consortium criteria as a guide for clinicians as they determine the best strategy for treatment. The Database Consortium estimates survival in various lines of therapy by incorporating 6 prognostic factors: anemia, hypercalcemia, neutrophilia, thrombocytosis, performance status, and time from diagnosis to treatment.
These criteria classify patients into favorable, intermediate, or poor risk categories that can guide first-line systemic therapy. The criteria also provide estimates of median survival.
Rettig noted a “huge percentage” of veterans mirror the intermediate-risk demographics of clinical trial cohorts but often present with greater comorbidity burdens: “That plays into whether we treat and how we treat,” he said.
Rettig highlighted kidney cancer guidelines from the National Comprehensive Cancer Network and noted that several trials examined first-line use of combinations of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) and checkpoint inhibitors.
There’s a general theme in the findings, he said: “You have OS (overall survival) and PFS (progression-free survival) benefit in the intermediate/poor risk group, but only PFS benefit in the patients who have favorable-risk disease. And you see higher objective response rates with the combinations.
“If you have a patient who's highly symptomatic or has an organ system threatened by a metastasis, you'd want to use a combination that elicits a higher objective response rate,” Rettig added.
A TKI is going to be the most appropriate second-line therapy for patients who received a prior checkpoint inhibitor, Rettig said.
“Don't change to another checkpoint inhibitor,” he said. “We have enough phase 3 data that indicates checkpoint inhibitors are no longer really adding to benefit once they’ve had a checkpoint inhibitor.”
Rettig said to even consider checkpoint inhibitors for patients who are checkpoint inhibitor-naïve, especially given the potential for durable remissions. As for third-line therapy, he said, “we have both belzutifan and tivozanib, which have been shown to improve PFS. More studies are ongoing.”
There are many adverse events linked to TKIs, Rettig said, including cardiovascular problems, thrombosis, hypertension, heart failure, torsades de pointes, QT prolongation, and gastrointestinal toxicity. TKIs tend to be the major drivers of adverse events in combination therapy.
Rettig emphasized the shorter half-life of the TKI axitinib, which he said allows for easier management of toxicities: “That’s why it’s preferred in the VA RCC clinical pathway.”
Rettig discloses relationships with Ambrx, Amgen, AVEO, Bayer, INmune Bio, Johnson & Johnson Health Care Systems, Lantheus, Merck, Myovant, Novartis, ORIC, and Progenics.
Treatment of metastatic renal cell carcinoma (RCC) is complex and requires careful analysis of risk and treatment options, an oncologist said at the July Association of VA Hematology and Oncology (AVAHO) seminar in Long Beach, California, regarding treating veterans with kidney cancer.
“We’ve come a long way in treating this disease, but individualizing therapy remains critical, especially in complex populations like our veterans,” said Matthew B. Rettig, MD, chief of Hematology-Oncology at the Veterans Affairs Greater Los Angeles Healthcare System and professor of Medicine and Urology at UCLA.
Rettig emphasized 2 critical early questions clinicians should consider when encountering metastatic RCC. First: Can the patient be treated with localized interventions such as metastasectomy, radiation therapy, or nephrectomy? These can be curative, Rettig said.
And second: Does the patient currently need systemic therapy? “[There are] a small subset of patients,” Rettig said, “who go into a durable, complete remission, dare I say ‘cure,’ with immunotherapeutic-based approaches.”
Rettig highlighted the International Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma Database Consortium criteria as a guide for clinicians as they determine the best strategy for treatment. The Database Consortium estimates survival in various lines of therapy by incorporating 6 prognostic factors: anemia, hypercalcemia, neutrophilia, thrombocytosis, performance status, and time from diagnosis to treatment.
These criteria classify patients into favorable, intermediate, or poor risk categories that can guide first-line systemic therapy. The criteria also provide estimates of median survival.
Rettig noted a “huge percentage” of veterans mirror the intermediate-risk demographics of clinical trial cohorts but often present with greater comorbidity burdens: “That plays into whether we treat and how we treat,” he said.
Rettig highlighted kidney cancer guidelines from the National Comprehensive Cancer Network and noted that several trials examined first-line use of combinations of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) and checkpoint inhibitors.
There’s a general theme in the findings, he said: “You have OS (overall survival) and PFS (progression-free survival) benefit in the intermediate/poor risk group, but only PFS benefit in the patients who have favorable-risk disease. And you see higher objective response rates with the combinations.
“If you have a patient who's highly symptomatic or has an organ system threatened by a metastasis, you'd want to use a combination that elicits a higher objective response rate,” Rettig added.
A TKI is going to be the most appropriate second-line therapy for patients who received a prior checkpoint inhibitor, Rettig said.
“Don't change to another checkpoint inhibitor,” he said. “We have enough phase 3 data that indicates checkpoint inhibitors are no longer really adding to benefit once they’ve had a checkpoint inhibitor.”
Rettig said to even consider checkpoint inhibitors for patients who are checkpoint inhibitor-naïve, especially given the potential for durable remissions. As for third-line therapy, he said, “we have both belzutifan and tivozanib, which have been shown to improve PFS. More studies are ongoing.”
There are many adverse events linked to TKIs, Rettig said, including cardiovascular problems, thrombosis, hypertension, heart failure, torsades de pointes, QT prolongation, and gastrointestinal toxicity. TKIs tend to be the major drivers of adverse events in combination therapy.
Rettig emphasized the shorter half-life of the TKI axitinib, which he said allows for easier management of toxicities: “That’s why it’s preferred in the VA RCC clinical pathway.”
Rettig discloses relationships with Ambrx, Amgen, AVEO, Bayer, INmune Bio, Johnson & Johnson Health Care Systems, Lantheus, Merck, Myovant, Novartis, ORIC, and Progenics.
Treatment of metastatic renal cell carcinoma (RCC) is complex and requires careful analysis of risk and treatment options, an oncologist said at the July Association of VA Hematology and Oncology (AVAHO) seminar in Long Beach, California, regarding treating veterans with kidney cancer.
“We’ve come a long way in treating this disease, but individualizing therapy remains critical, especially in complex populations like our veterans,” said Matthew B. Rettig, MD, chief of Hematology-Oncology at the Veterans Affairs Greater Los Angeles Healthcare System and professor of Medicine and Urology at UCLA.
Rettig emphasized 2 critical early questions clinicians should consider when encountering metastatic RCC. First: Can the patient be treated with localized interventions such as metastasectomy, radiation therapy, or nephrectomy? These can be curative, Rettig said.
And second: Does the patient currently need systemic therapy? “[There are] a small subset of patients,” Rettig said, “who go into a durable, complete remission, dare I say ‘cure,’ with immunotherapeutic-based approaches.”
Rettig highlighted the International Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma Database Consortium criteria as a guide for clinicians as they determine the best strategy for treatment. The Database Consortium estimates survival in various lines of therapy by incorporating 6 prognostic factors: anemia, hypercalcemia, neutrophilia, thrombocytosis, performance status, and time from diagnosis to treatment.
These criteria classify patients into favorable, intermediate, or poor risk categories that can guide first-line systemic therapy. The criteria also provide estimates of median survival.
Rettig noted a “huge percentage” of veterans mirror the intermediate-risk demographics of clinical trial cohorts but often present with greater comorbidity burdens: “That plays into whether we treat and how we treat,” he said.
Rettig highlighted kidney cancer guidelines from the National Comprehensive Cancer Network and noted that several trials examined first-line use of combinations of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) and checkpoint inhibitors.
There’s a general theme in the findings, he said: “You have OS (overall survival) and PFS (progression-free survival) benefit in the intermediate/poor risk group, but only PFS benefit in the patients who have favorable-risk disease. And you see higher objective response rates with the combinations.
“If you have a patient who's highly symptomatic or has an organ system threatened by a metastasis, you'd want to use a combination that elicits a higher objective response rate,” Rettig added.
A TKI is going to be the most appropriate second-line therapy for patients who received a prior checkpoint inhibitor, Rettig said.
“Don't change to another checkpoint inhibitor,” he said. “We have enough phase 3 data that indicates checkpoint inhibitors are no longer really adding to benefit once they’ve had a checkpoint inhibitor.”
Rettig said to even consider checkpoint inhibitors for patients who are checkpoint inhibitor-naïve, especially given the potential for durable remissions. As for third-line therapy, he said, “we have both belzutifan and tivozanib, which have been shown to improve PFS. More studies are ongoing.”
There are many adverse events linked to TKIs, Rettig said, including cardiovascular problems, thrombosis, hypertension, heart failure, torsades de pointes, QT prolongation, and gastrointestinal toxicity. TKIs tend to be the major drivers of adverse events in combination therapy.
Rettig emphasized the shorter half-life of the TKI axitinib, which he said allows for easier management of toxicities: “That’s why it’s preferred in the VA RCC clinical pathway.”
Rettig discloses relationships with Ambrx, Amgen, AVEO, Bayer, INmune Bio, Johnson & Johnson Health Care Systems, Lantheus, Merck, Myovant, Novartis, ORIC, and Progenics.
Treating Metastatic RCC: From Risk Assessment to Therapy Selection
Treating Metastatic RCC: From Risk Assessment to Therapy Selection
Renal Cell Carcinoma: What You Need to Know About Hereditary Syndromes
Renal Cell Carcinoma: What You Need to Know About Hereditary Syndromes
The role of hereditary syndromes in renal cell carcinoma (RCC) might be easily missed, a kidney cancer specialist said during a recent Association of VA Hematology and Oncology (AVAHO) seminar in Long Beach, California, though careful clinical evaluation can uncover genetic traits that may affect treatment and familial risk.
“The importance of finding or identifying hereditary forms of kidney cancer really should not be underestimated,” said urologist Brian Shuch, MD, director of the UCLA Kidney Cancer Program, on treating veterans with kidney cancer.
According to Shuch, recent data suggest that about 4.5% of patients with RCC have a hereditary syndrome: “A lot of times, these hide in plain sight. You have to really look deep and try to figure things out and understand that maybe they have a hereditary form of kidney cancer.”
It is important to consider early genetic testing, Shuch said. Red flags for hereditary syndromes include early-onset RCC (age ≤ 45 years), multifocal tumors, bilateral tumors (especially in younger individuals), or a relevant family personal history, he said.
Unusual skin conditions are also potential signs, Shuch said. These can include leiomyomas, fibrofolliculomas, and angiofibromas: “Patients have lots of lumps or bumps.”
“When I look at a patient, I go head to toe and ask if there any issues with your vision, any issues with your hearing, any issues swallowing,” he explained at the meeting. “Do you have any problems with heart issues, adrenal issues? You’ve got to go through each organ, and it can lead you to different things.”
Shuch highlighted Von Hippel-Lindau (VHL) syndrome, which affects 1 in 25,000 people. About 80% to 90% of these patients have a family history, Shuch said.
But the others do not. “Unfortunately, some get diagnosed later in life because they don’t get cascade testing starting at aged 2, which is recommended. These are the patients who might be coming into the ER with a hemangioblastoma or picking up the phone and all of a sudden being deaf in one ear due to an endolymphatic sac tumor.
“We want to limit metastatic spread and preserve the kidneys,” Shuch said. “We don’t want to be doing radical nephrectomies. We want to avoid chronic kidney disease, prevent end-stage renal disease, and maximize quality of life.”
It’s a good idea to avoid surgical removal unless a patient’s tumor grows to be > 3 cm, a line that indicates risk of metastases, he said.
In terms of treatment, Shuch highlighted a 2021 study that showed benefit in VHL from belzutifan (Welireg), an oral HIF-2 α inhibitor approved by the US Food and Drug Administration. The medication significantly reduced the need for surgical intervention.
“Patients go on this drug, and surgeons are putting their scalpels down,” said Shuch, who worked on the 2021 study.
Other hereditary syndromes include the rare hereditary papillary RCC, and Birt-Hogg-Dubé syndrome, believed to affect 1 in 200,000 people but may be more common, he said.
Birt-Hogg-Dubé syndrome is linked to lung cysts, lung collapse, and skin manifestations. The 3 cm surgery rule is appropriate in these cases, Shuch said, and metastases are rare.
Another condition, hereditary leiomyomatosis and RCC, is the most dangerous hereditary form. Originally thought to affect 1 in 200,000 people, hereditary leiomyomatosis and RCC is similar to Birt-Hogg-Dubé syndrome in that it is believed to be more common.
“You will see this,” Shuch predicted.
Shuch advised colleagues to intervene early and take a large margin during surgery.
He also highlighted familial paraganglioma syndrome, which is associated with gastrointestinal stromal tumors, and Cowden syndrome, which is linked to skin manifestations and breast, thyroid, and endometrial cancer.
Shuch reported that he had no disclosures.
The role of hereditary syndromes in renal cell carcinoma (RCC) might be easily missed, a kidney cancer specialist said during a recent Association of VA Hematology and Oncology (AVAHO) seminar in Long Beach, California, though careful clinical evaluation can uncover genetic traits that may affect treatment and familial risk.
“The importance of finding or identifying hereditary forms of kidney cancer really should not be underestimated,” said urologist Brian Shuch, MD, director of the UCLA Kidney Cancer Program, on treating veterans with kidney cancer.
According to Shuch, recent data suggest that about 4.5% of patients with RCC have a hereditary syndrome: “A lot of times, these hide in plain sight. You have to really look deep and try to figure things out and understand that maybe they have a hereditary form of kidney cancer.”
It is important to consider early genetic testing, Shuch said. Red flags for hereditary syndromes include early-onset RCC (age ≤ 45 years), multifocal tumors, bilateral tumors (especially in younger individuals), or a relevant family personal history, he said.
Unusual skin conditions are also potential signs, Shuch said. These can include leiomyomas, fibrofolliculomas, and angiofibromas: “Patients have lots of lumps or bumps.”
“When I look at a patient, I go head to toe and ask if there any issues with your vision, any issues with your hearing, any issues swallowing,” he explained at the meeting. “Do you have any problems with heart issues, adrenal issues? You’ve got to go through each organ, and it can lead you to different things.”
Shuch highlighted Von Hippel-Lindau (VHL) syndrome, which affects 1 in 25,000 people. About 80% to 90% of these patients have a family history, Shuch said.
But the others do not. “Unfortunately, some get diagnosed later in life because they don’t get cascade testing starting at aged 2, which is recommended. These are the patients who might be coming into the ER with a hemangioblastoma or picking up the phone and all of a sudden being deaf in one ear due to an endolymphatic sac tumor.
“We want to limit metastatic spread and preserve the kidneys,” Shuch said. “We don’t want to be doing radical nephrectomies. We want to avoid chronic kidney disease, prevent end-stage renal disease, and maximize quality of life.”
It’s a good idea to avoid surgical removal unless a patient’s tumor grows to be > 3 cm, a line that indicates risk of metastases, he said.
In terms of treatment, Shuch highlighted a 2021 study that showed benefit in VHL from belzutifan (Welireg), an oral HIF-2 α inhibitor approved by the US Food and Drug Administration. The medication significantly reduced the need for surgical intervention.
“Patients go on this drug, and surgeons are putting their scalpels down,” said Shuch, who worked on the 2021 study.
Other hereditary syndromes include the rare hereditary papillary RCC, and Birt-Hogg-Dubé syndrome, believed to affect 1 in 200,000 people but may be more common, he said.
Birt-Hogg-Dubé syndrome is linked to lung cysts, lung collapse, and skin manifestations. The 3 cm surgery rule is appropriate in these cases, Shuch said, and metastases are rare.
Another condition, hereditary leiomyomatosis and RCC, is the most dangerous hereditary form. Originally thought to affect 1 in 200,000 people, hereditary leiomyomatosis and RCC is similar to Birt-Hogg-Dubé syndrome in that it is believed to be more common.
“You will see this,” Shuch predicted.
Shuch advised colleagues to intervene early and take a large margin during surgery.
He also highlighted familial paraganglioma syndrome, which is associated with gastrointestinal stromal tumors, and Cowden syndrome, which is linked to skin manifestations and breast, thyroid, and endometrial cancer.
Shuch reported that he had no disclosures.
The role of hereditary syndromes in renal cell carcinoma (RCC) might be easily missed, a kidney cancer specialist said during a recent Association of VA Hematology and Oncology (AVAHO) seminar in Long Beach, California, though careful clinical evaluation can uncover genetic traits that may affect treatment and familial risk.
“The importance of finding or identifying hereditary forms of kidney cancer really should not be underestimated,” said urologist Brian Shuch, MD, director of the UCLA Kidney Cancer Program, on treating veterans with kidney cancer.
According to Shuch, recent data suggest that about 4.5% of patients with RCC have a hereditary syndrome: “A lot of times, these hide in plain sight. You have to really look deep and try to figure things out and understand that maybe they have a hereditary form of kidney cancer.”
It is important to consider early genetic testing, Shuch said. Red flags for hereditary syndromes include early-onset RCC (age ≤ 45 years), multifocal tumors, bilateral tumors (especially in younger individuals), or a relevant family personal history, he said.
Unusual skin conditions are also potential signs, Shuch said. These can include leiomyomas, fibrofolliculomas, and angiofibromas: “Patients have lots of lumps or bumps.”
“When I look at a patient, I go head to toe and ask if there any issues with your vision, any issues with your hearing, any issues swallowing,” he explained at the meeting. “Do you have any problems with heart issues, adrenal issues? You’ve got to go through each organ, and it can lead you to different things.”
Shuch highlighted Von Hippel-Lindau (VHL) syndrome, which affects 1 in 25,000 people. About 80% to 90% of these patients have a family history, Shuch said.
But the others do not. “Unfortunately, some get diagnosed later in life because they don’t get cascade testing starting at aged 2, which is recommended. These are the patients who might be coming into the ER with a hemangioblastoma or picking up the phone and all of a sudden being deaf in one ear due to an endolymphatic sac tumor.
“We want to limit metastatic spread and preserve the kidneys,” Shuch said. “We don’t want to be doing radical nephrectomies. We want to avoid chronic kidney disease, prevent end-stage renal disease, and maximize quality of life.”
It’s a good idea to avoid surgical removal unless a patient’s tumor grows to be > 3 cm, a line that indicates risk of metastases, he said.
In terms of treatment, Shuch highlighted a 2021 study that showed benefit in VHL from belzutifan (Welireg), an oral HIF-2 α inhibitor approved by the US Food and Drug Administration. The medication significantly reduced the need for surgical intervention.
“Patients go on this drug, and surgeons are putting their scalpels down,” said Shuch, who worked on the 2021 study.
Other hereditary syndromes include the rare hereditary papillary RCC, and Birt-Hogg-Dubé syndrome, believed to affect 1 in 200,000 people but may be more common, he said.
Birt-Hogg-Dubé syndrome is linked to lung cysts, lung collapse, and skin manifestations. The 3 cm surgery rule is appropriate in these cases, Shuch said, and metastases are rare.
Another condition, hereditary leiomyomatosis and RCC, is the most dangerous hereditary form. Originally thought to affect 1 in 200,000 people, hereditary leiomyomatosis and RCC is similar to Birt-Hogg-Dubé syndrome in that it is believed to be more common.
“You will see this,” Shuch predicted.
Shuch advised colleagues to intervene early and take a large margin during surgery.
He also highlighted familial paraganglioma syndrome, which is associated with gastrointestinal stromal tumors, and Cowden syndrome, which is linked to skin manifestations and breast, thyroid, and endometrial cancer.
Shuch reported that he had no disclosures.
Renal Cell Carcinoma: What You Need to Know About Hereditary Syndromes
Renal Cell Carcinoma: What You Need to Know About Hereditary Syndromes
Elusive Edema: A Case of Nephrotic Syndrome Mimicking Decompensated Cirrhosis
Elusive Edema: A Case of Nephrotic Syndrome Mimicking Decompensated Cirrhosis
Histology is the gold standard for cirrhosis diagnosis. However, a combination of clinical history, physical examination findings, and supportive laboratory and radiographic features is generally sufficient to make the diagnosis. Routine ultrasound and computed tomography (CT) imaging often identifies a nodular liver contour with sequelae of portal hypertension, including splenomegaly, varices, and ascites, which can suggest cirrhosis when supported by laboratory parameters and clinical features. As a result, the diagnosis is typically made clinically.1 Many patients with compensated cirrhosis go undetected. The presence of a decompensation event (ascites, spontaneous bacterial peritonitis, variceal hemorrhage, or hepatic encephalopathy) often leads to index diagnosis when patients were previously compensated. When a patient presents with suspected decompensated cirrhosis, it is important to consider other diagnoses with similar presentations and ensure that multiple disease processes are not contributing to the symptoms.
CASE PRESENTATION
A 64-year-old male with a history of intravenous (IV) methamphetamine use and prior incarceration presented with a 3-week history of progressively worsening generalized swelling. Prior to the onset of his symptoms, the patient injured his right lower extremity (RLE) in a bicycle accident, resulting in edema that progressed to bilateral lower extremity (BLE) edema and worsening fatigue, despite resolution of the initial injury. The patient gained weight though he could not quantify the amount. He experienced progressive hunger, thirst, and fatigue as well as increased sleep. Additionally, the patient experienced worsening dyspnea on exertion and orthopnea. He started using 2 pillows instead of 1 pillow at night.
The patient reported no fevers, chills, sputum production, chest pain, or paroxysmal nocturnal dyspnea. He had no known history of sexually transmitted infections, no significant history of alcohol use, and occasional tobacco and marijuana use. He had been incarcerated > 10 years before and last used IV methamphetamine 3 years before. He did not regularly take any medications.
The patient’s vital signs included a temperature of 98.2 °F; 78/min heart rate; 15/min respiratory rate; 159/109 mm Hg blood pressure; and 98% oxygen saturation on room air. He had gained 20 lbs in the past 4 months. He had pitting edema in both legs and arms, as well as periorbital swelling, but no jugular venous distention, abnormal heart sounds, or murmurs. Breath sounds were distant but clear to auscultation. His abdomen was distended with normal bowel sounds and no fluid wave; mild epigastric tenderness was present, but no intra-abdominal masses were palpated. He had spider angiomata on the upper chest but no other stigmata of cirrhosis, such as caput medusae or jaundice. Tattoos were noted.
Laboratory test results showed a platelet count of 178 x 103/μL (reference range, 140- 440 ~ 103μL).Creatinine was 0.80 mg/dL (reference range, < 1.28 mg/dL), with an estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) of 99 mL/min/1.73 m2 using the Chronic Kidney Disease-Epidemiology equation (reference range, > 60 mL/min/1.73 m2), (reference range, > 60 mL/min/1.73 m2), and Cystatin C was 1.14 mg/L (reference range, < 1.15 mg/L). His electrolytes and complete blood count were within normal limits, including sodium, 134 mmol/L; potassium, 4.4 mmol/L; chloride, 108 mmol/L; and carbon dioxide, 22.5 mmol/L.
Additional test results included alkaline phosphatase, 126 U/L (reference range, < 94 U/L); alanine transaminase, 41 U/L (reference range, < 45 U/L); aspartate aminotransferase, 70 U/L (reference range, < 35 U/L); total bilirubin, 0.6 mg/dL (reference range, < 1 mg/dL); albumin, 1.8 g/dL (reference range, 3.2-4.8 g/dL); and total protein, 6.3 g/dL (reference range, 5.9-8.3 g/dL). The patient’s international normalized ratio was 0.96 (reference range, 0.8-1.1), and brain natriuretic peptide was normal at 56 pg/mL. No prior laboratory results were available for comparison.
Urine toxicology was positive for amphetamines. Urinalysis demonstrated large occult blood, with a red blood cell count of 26/ HPF (reference range, 0/HPF) and proteinuria (100 mg/dL; reference range, negative), without bacteria, nitrites, or leukocyte esterase. Urine white blood cell count was 10/ HPF (reference range, 0/HPF), and fine granular casts and hyaline casts were present.
A noncontrast CT of the abdomen and pelvis in the emergency department showed an irregular liver contour with diffuse nodularity, multiple portosystemic collaterals, moderate abdominal and pelvic ascites, small bilateral pleural effusions with associated atelectasis, and anasarca consistent with cirrhosis (Figure 1). The patient was admitted to the internal medicine service for workup and management of newly diagnosed cirrhosis.
Paracentesis revealed straw-colored fluid with an ascitic fluid neutrophil count of 17/μL, a protein level of < 3 g/dL and albumin level of < 1.5 g/dL. Gram stain of the ascitic fluid showed a moderate white blood cell count with no organisms. Fluid culture showed no microbial growth.
Initial workup for cirrhosis demonstrated a positive total hepatitis A antibody. The patient had a nonreactive hepatitis B surface antigen and surface antibody, but a reactive hepatitis B core antibody; a hepatitis B DNA level was not ordered. He had a reactive hepatitis C antibody with a viral load of 4,490,000 II/mL (genotype 1a). The patient’s iron level was 120 μg/dL, with a calculated total iron-binding capacity (TIBC) of 126.2 μg/dL. His transferrin saturation (TSAT) (serum iron divided by TIBC) was 95%. The patient had nonreactive antinuclear antibody and antimitochondrial antibody tests and a positive antismooth muscle antibody test with a titer of 1:40. His α-fetoprotein (AFP) level was 505 ng/mL (reference range, < 8 ng/mL).
Follow-up MRI of the abdomen and pelvis showed cirrhotic morphology with large volume ascites and portosystemic collaterals, consistent with portal hypertension. Additionally, it showed multiple scattered peripheral sub centimeter hyperenhancing foci, most likely representing benign lesions.
The patient's spot urine protein-creatinine ratio was 3.76. To better quantify proteinuria, a 24-hour urine collection was performed and revealed 12.8 g/d of urine protein (reference range, 0-0.17 g/d). His serum triglyceride level was 175 mg/dL (reference range, 40-60 mg/dL); total cholesterol was 177 mg/ dL (reference range, ≤ 200 mg/dL); low density lipoprotein cholesterol was 98 mg/ dL (reference range, ≤ 130 mg/dL); and highdensity lipoprotein cholesterol was 43.8 mg/ dL (reference range, ≥ 40 mg/dL); C3 complement level was 71 mg/dL (reference range, 82-185 mg/dL); and C4 complement level was 22 mg/dL (reference range, 15-53 mg/ dL). His rheumatoid factor was < 14 IU/mL. Tests for rapid plasma reagin and HIV antigen- antibody were nonreactive, and the phospholipase A2 receptor antibody test was negative. The patient tested positive for QuantiFERON-TB Gold and qualitative cryoglobulin, which indicated a cryocrit of 1%.
A renal biopsy was performed, revealing diffuse podocyte foot process effacement and glomerulonephritis with low-grade C3 and immunoglobulin (Ig) G deposits, consistent with early membranoproliferative glomerulonephritis (MPGN) (Figures 2 and 3).
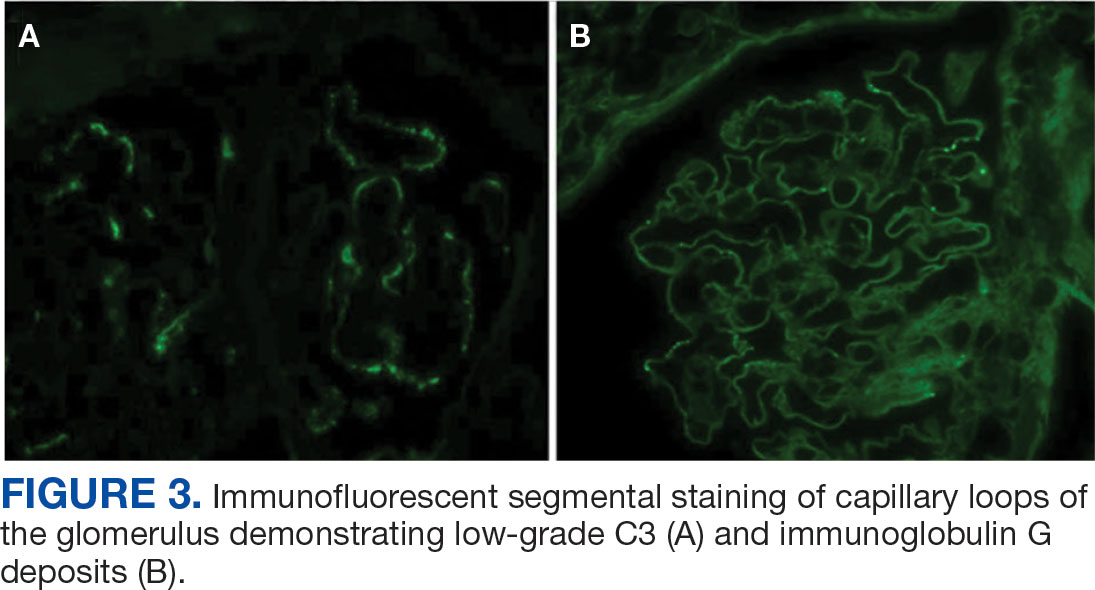
The patient was initially diuresed with IV furosemide without significant urine output. He was then diuresed with IV 25% albumin (total, 25 g), followed by IV furosemide 40 mg twice daily, which led to significant urine output and resolution of his anasarca. Given the patient’s hypoalbuminemic state, IV albumin was necessary to deliver furosemide to the proximal tubule. He was started on lisinopril for renal protection and discharged with spironolactone and furosemide for fluid management in the context of cirrhosis.
The patient was evaluated by the Liver Nodule Clinic, which includes specialists from hepatology, medical oncology, radiation oncology, interventional radiology, and diagnostic radiology. The team considered the patient’s medical history and characteristics of the nodules on imaging. Notable aspects of the patient’s history included hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection and an elevated AFP level, although imaging showed no lesion concerning for malignancy. Given these findings, the patient was scheduled for a liver biopsy to establish a tissue diagnosis of cirrhosis. Hepatology, nephrology, and infectious disease specialists coordinated to plan the management and treatment of latent tuberculosis (TB), chronic HCV, MPGN, compensated cirrhosis, and suspicious liver lesions.
The patient chose to handle management and treatment as an outpatient. He was discharged with furosemide and spironolactone for anasarca management, and amlodipine and lisinopril for his hypertension and MPGN. Follow-up appointments were scheduled with infectious disease for management of latent TB and HCV, nephrology for MPGN, gastroenterology for cirrhosis, and interventional radiology for liver biopsy. Unfortunately, the patient was unhoused with limited access to transportation, which prevented timely follow-up. Given these social factors, immunosuppression was not started. Additionally, he did not start on HCV therapy because the viral load was still pending at time of discharge.
DISCUSSION
The diagnosis of decompensated cirrhosis was prematurely established, resulting in a diagnostic delay, a form of diagnostic error. However, on hospital day 2, the initial hypothesis of decompensated cirrhosis as the sole driver of the patient’s presentation was reconsidered due to the disconnect between the severity of hypoalbuminemia and diffuse edema (anasarca), and the absence of laboratory evidence of hepatic decompensation (normal international normalized ratio, bilirubin, and low but normal platelet count). Although image findings supported cirrhosis, laboratory markers did not indicate hepatic decompensation. The severity of hypoalbuminemia and anasarca, along with an indeterminate Serum-Ascites Albumin Gradient, prompted the patient’s care team to consider other causes, specifically, nephrotic syndrome.
The patien’s spot protein-to-creatinine ratio was 3.76 (reference range < 0.2 mg/mg creatinine), but a 24-hour urine protein collection was 12.8 g/day (reference range < 150 mg/day). While most spot urine protein- to-creatinine ratios (UPCR) correlate with a 24-hour urine collection, discrepancies can occur, as in this case. It is important to recognize that the spot UPCR assumes that patients are excreting 1000 mg of creatinine daily in their urine, which is not always the case. In addition, changes in urine osmolality can lead to different values. The gold standard for proteinuria is a 24-hour urine collection for protein and creatinine.
The patient’s nephrotic-range proteinuria and severe hypoalbuminemia are not solely explained by cirrhosis. In addition, the patient’s lower extremity edema pointed to nephrotic syndrome. The differential diagnosis for nephrotic syndrome includes both primary and secondary forms of membranous nephropathy, minimal change disease, focal segmental glomerulosclerosis, and MPGN, a histopathological diagnosis that requires distinguishing between immune complex-mediated and complement-mediated forms. Other causes of nephrotic syndrome that do not fit in any of these buckets include amyloidosis, IgA nephropathy, and diabetes mellitus (DM). Despite DM being a common cause of nephrotic range proteinuria, it rarely leads to full nephrotic syndrome.
When considering the diagnosis, we reframed the patient’s clinical syndrome as compensated cirrhosis plus nephrotic syndrome. This approach prioritized identifying a cause that could explain both cirrhosis (from any cause) leading to IgA nephropathy or injection drug use serving as a risk factor for cirrhosis and nephrotic syndrome through HCV or AA amyloidosis, respectively. This problem representation guided us to the correct diagnosis. There are multiple renal diseases associated with HCV infection, including MPGN, membranous nephropathy, focal segmental glomerulosclerosis, and IgA nephropathy.2 MPGN and mixed cryoglobulinemia are the most common. In the past, MPGN was classified as type I, II, and III.
The patient’s urine toxicology revealed recent amphetamine use, which can also lead to acute kidney injury through rhabdomyolysis or acute interstitial nephritis (AIN).3 In the cases of rhabdomyolysis, urinalysis would show positive heme without any red blood cell on microscopic analysis, which was not present in this case. AIN commonly manifests as acute kidney injury, pyuria, and proteinuria but without a decrease in complement levels.4 While the patient’s urine sediment included white blood cell (10/high-power field), the presence of microscopic hematuria, decreased complement levels, and proteinuria in the context of HCV positivity makes MPGN more likely than AIN.
Recently, there has been greater emphasis on using immunofluorescence for kidney biopsies. MPGN is now classified into 2 main categories: MPGN with mesangial immunoglobulins and C3 deposits in the capillary walls, and MPGN with C3 deposits but without Ig.5 MPGN with Ig-complement deposits is seen in autoimmune diseases and infections and is associated with dysproteinemias.
The renal biopsy in this patient was consistent with MPGN with immunofluorescence, a common finding in patients with infection. By synthesizing these data, we concluded that the patient represented a case of chronic HCV infection that led to MPGN with cryoglobulinemia. The normal C4 and negative RF do not suggest cryoglobulinemic crisis. Compensated cirrhosis was seen on imaging, pending liver biopsy.
Treatment
The management of MPGN secondary to HCV infection relies on the treatment of the underlying infection and clearance of viral load. Direct-acting antivirals have been used successfully in the treatment of HCV-associated MPGN. When cryoglobulinemia is present, immunosuppressive therapy is recommended. These regimens commonly include rituximab and steroids.5 Rituximab is also used for nephrotic syndrome associated with MPGN, as recommended in the 2018 Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes guidelines.6
When initiating rituximab therapy in a patient who tests positive for hepatitis B (HBcAb positive or HBsAb positive), it is recommended to follow the established guidelines, which include treating them with entecavir for prophylaxis to prevent reactivation or a flare of hepatitis B.7 The patient in this case needed close follow-up in the nephrology and hepatology clinic. Immunosuppressive therapy was not pursued while the patient was admitted to the hospital due to instability with housing, transportation, and difficulty in ensuring close follow-up.
CONCLUSIONS
Clinicians should maintain a broad differential even in the face of confirmatory imaging and other objective findings. In the case of anasarca, nephrotic syndrome should be considered. Key causes of nephrotic syndromes include MPGN, membranous nephropathy, minimal change disease, and focal segmental glomerulosclerosis. MPGN is a histopathological diagnosis, and it is essential to identify if it is secondary to immune complexes or only complement mediated because Ig-complement deposits are seen in autoimmune disease and infection. The management of MPGN due to HCV infection relies on antiviral therapy. In the presence of cryoglobulinemia, immunosuppressive therapy is recommended.
- Tapper EB, Parikh ND. Diagnosis and management of cirrhosis and its complications: a review. JAMA. 2023;329(18):1589–1602. doi:10.1001/jama.2023.5997
- Ozkok A, Yildiz A. Hepatitis C virus associated glomerulopathies. World J Gastroenterol. 2014;20(24):7544-7554. doi:10.3748/wjg.v20.i24.7544
- Foley RJ, Kapatkin K, Vrani R, Weinman EJ. Amphetamineinduced acute renal failure. South Med J. 1984;77(2):258- 260. doi:10.1097/00007611-198402000-00035
- Rossert J. Drug - induced acute interstitial nephritis. Kidney Int. 2001;60(2):804-817. doi:10.1046/j.1523-1755.2001.060002804.x
- Sethi S, Fervenza FC. Membranoproliferative glomerulonephritis: pathogenetic heterogeneity and proposal for a new classification. Semin Nephrol. 2011;31(4):341-348. doi:10.1016/j.semnephrol.2011.06.005
- Jadoul M, Berenguer MC, Doss W, et al. Executive summary of the 2018 KDIGO hepatitis C in CKD guideline: welcoming advances in evaluation and management. Kidney Int. 2018;94(4):663-673. doi:10.1016/j.kint.2018.06.011
- Myint A, Tong MJ, Beaven SW. Reactivation of hepatitis b virus: a review of clinical guidelines. Clin Liver Dis (Hoboken). 2020;15(4):162-167. doi:10.1002/cld.883
Histology is the gold standard for cirrhosis diagnosis. However, a combination of clinical history, physical examination findings, and supportive laboratory and radiographic features is generally sufficient to make the diagnosis. Routine ultrasound and computed tomography (CT) imaging often identifies a nodular liver contour with sequelae of portal hypertension, including splenomegaly, varices, and ascites, which can suggest cirrhosis when supported by laboratory parameters and clinical features. As a result, the diagnosis is typically made clinically.1 Many patients with compensated cirrhosis go undetected. The presence of a decompensation event (ascites, spontaneous bacterial peritonitis, variceal hemorrhage, or hepatic encephalopathy) often leads to index diagnosis when patients were previously compensated. When a patient presents with suspected decompensated cirrhosis, it is important to consider other diagnoses with similar presentations and ensure that multiple disease processes are not contributing to the symptoms.
CASE PRESENTATION
A 64-year-old male with a history of intravenous (IV) methamphetamine use and prior incarceration presented with a 3-week history of progressively worsening generalized swelling. Prior to the onset of his symptoms, the patient injured his right lower extremity (RLE) in a bicycle accident, resulting in edema that progressed to bilateral lower extremity (BLE) edema and worsening fatigue, despite resolution of the initial injury. The patient gained weight though he could not quantify the amount. He experienced progressive hunger, thirst, and fatigue as well as increased sleep. Additionally, the patient experienced worsening dyspnea on exertion and orthopnea. He started using 2 pillows instead of 1 pillow at night.
The patient reported no fevers, chills, sputum production, chest pain, or paroxysmal nocturnal dyspnea. He had no known history of sexually transmitted infections, no significant history of alcohol use, and occasional tobacco and marijuana use. He had been incarcerated > 10 years before and last used IV methamphetamine 3 years before. He did not regularly take any medications.
The patient’s vital signs included a temperature of 98.2 °F; 78/min heart rate; 15/min respiratory rate; 159/109 mm Hg blood pressure; and 98% oxygen saturation on room air. He had gained 20 lbs in the past 4 months. He had pitting edema in both legs and arms, as well as periorbital swelling, but no jugular venous distention, abnormal heart sounds, or murmurs. Breath sounds were distant but clear to auscultation. His abdomen was distended with normal bowel sounds and no fluid wave; mild epigastric tenderness was present, but no intra-abdominal masses were palpated. He had spider angiomata on the upper chest but no other stigmata of cirrhosis, such as caput medusae or jaundice. Tattoos were noted.
Laboratory test results showed a platelet count of 178 x 103/μL (reference range, 140- 440 ~ 103μL).Creatinine was 0.80 mg/dL (reference range, < 1.28 mg/dL), with an estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) of 99 mL/min/1.73 m2 using the Chronic Kidney Disease-Epidemiology equation (reference range, > 60 mL/min/1.73 m2), (reference range, > 60 mL/min/1.73 m2), and Cystatin C was 1.14 mg/L (reference range, < 1.15 mg/L). His electrolytes and complete blood count were within normal limits, including sodium, 134 mmol/L; potassium, 4.4 mmol/L; chloride, 108 mmol/L; and carbon dioxide, 22.5 mmol/L.
Additional test results included alkaline phosphatase, 126 U/L (reference range, < 94 U/L); alanine transaminase, 41 U/L (reference range, < 45 U/L); aspartate aminotransferase, 70 U/L (reference range, < 35 U/L); total bilirubin, 0.6 mg/dL (reference range, < 1 mg/dL); albumin, 1.8 g/dL (reference range, 3.2-4.8 g/dL); and total protein, 6.3 g/dL (reference range, 5.9-8.3 g/dL). The patient’s international normalized ratio was 0.96 (reference range, 0.8-1.1), and brain natriuretic peptide was normal at 56 pg/mL. No prior laboratory results were available for comparison.
Urine toxicology was positive for amphetamines. Urinalysis demonstrated large occult blood, with a red blood cell count of 26/ HPF (reference range, 0/HPF) and proteinuria (100 mg/dL; reference range, negative), without bacteria, nitrites, or leukocyte esterase. Urine white blood cell count was 10/ HPF (reference range, 0/HPF), and fine granular casts and hyaline casts were present.
A noncontrast CT of the abdomen and pelvis in the emergency department showed an irregular liver contour with diffuse nodularity, multiple portosystemic collaterals, moderate abdominal and pelvic ascites, small bilateral pleural effusions with associated atelectasis, and anasarca consistent with cirrhosis (Figure 1). The patient was admitted to the internal medicine service for workup and management of newly diagnosed cirrhosis.

Paracentesis revealed straw-colored fluid with an ascitic fluid neutrophil count of 17/μL, a protein level of < 3 g/dL and albumin level of < 1.5 g/dL. Gram stain of the ascitic fluid showed a moderate white blood cell count with no organisms. Fluid culture showed no microbial growth.
Initial workup for cirrhosis demonstrated a positive total hepatitis A antibody. The patient had a nonreactive hepatitis B surface antigen and surface antibody, but a reactive hepatitis B core antibody; a hepatitis B DNA level was not ordered. He had a reactive hepatitis C antibody with a viral load of 4,490,000 II/mL (genotype 1a). The patient’s iron level was 120 μg/dL, with a calculated total iron-binding capacity (TIBC) of 126.2 μg/dL. His transferrin saturation (TSAT) (serum iron divided by TIBC) was 95%. The patient had nonreactive antinuclear antibody and antimitochondrial antibody tests and a positive antismooth muscle antibody test with a titer of 1:40. His α-fetoprotein (AFP) level was 505 ng/mL (reference range, < 8 ng/mL).
Follow-up MRI of the abdomen and pelvis showed cirrhotic morphology with large volume ascites and portosystemic collaterals, consistent with portal hypertension. Additionally, it showed multiple scattered peripheral sub centimeter hyperenhancing foci, most likely representing benign lesions.
The patient's spot urine protein-creatinine ratio was 3.76. To better quantify proteinuria, a 24-hour urine collection was performed and revealed 12.8 g/d of urine protein (reference range, 0-0.17 g/d). His serum triglyceride level was 175 mg/dL (reference range, 40-60 mg/dL); total cholesterol was 177 mg/ dL (reference range, ≤ 200 mg/dL); low density lipoprotein cholesterol was 98 mg/ dL (reference range, ≤ 130 mg/dL); and highdensity lipoprotein cholesterol was 43.8 mg/ dL (reference range, ≥ 40 mg/dL); C3 complement level was 71 mg/dL (reference range, 82-185 mg/dL); and C4 complement level was 22 mg/dL (reference range, 15-53 mg/ dL). His rheumatoid factor was < 14 IU/mL. Tests for rapid plasma reagin and HIV antigen- antibody were nonreactive, and the phospholipase A2 receptor antibody test was negative. The patient tested positive for QuantiFERON-TB Gold and qualitative cryoglobulin, which indicated a cryocrit of 1%.
A renal biopsy was performed, revealing diffuse podocyte foot process effacement and glomerulonephritis with low-grade C3 and immunoglobulin (Ig) G deposits, consistent with early membranoproliferative glomerulonephritis (MPGN) (Figures 2 and 3).


The patient was initially diuresed with IV furosemide without significant urine output. He was then diuresed with IV 25% albumin (total, 25 g), followed by IV furosemide 40 mg twice daily, which led to significant urine output and resolution of his anasarca. Given the patient’s hypoalbuminemic state, IV albumin was necessary to deliver furosemide to the proximal tubule. He was started on lisinopril for renal protection and discharged with spironolactone and furosemide for fluid management in the context of cirrhosis.
The patient was evaluated by the Liver Nodule Clinic, which includes specialists from hepatology, medical oncology, radiation oncology, interventional radiology, and diagnostic radiology. The team considered the patient’s medical history and characteristics of the nodules on imaging. Notable aspects of the patient’s history included hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection and an elevated AFP level, although imaging showed no lesion concerning for malignancy. Given these findings, the patient was scheduled for a liver biopsy to establish a tissue diagnosis of cirrhosis. Hepatology, nephrology, and infectious disease specialists coordinated to plan the management and treatment of latent tuberculosis (TB), chronic HCV, MPGN, compensated cirrhosis, and suspicious liver lesions.
The patient chose to handle management and treatment as an outpatient. He was discharged with furosemide and spironolactone for anasarca management, and amlodipine and lisinopril for his hypertension and MPGN. Follow-up appointments were scheduled with infectious disease for management of latent TB and HCV, nephrology for MPGN, gastroenterology for cirrhosis, and interventional radiology for liver biopsy. Unfortunately, the patient was unhoused with limited access to transportation, which prevented timely follow-up. Given these social factors, immunosuppression was not started. Additionally, he did not start on HCV therapy because the viral load was still pending at time of discharge.
DISCUSSION
The diagnosis of decompensated cirrhosis was prematurely established, resulting in a diagnostic delay, a form of diagnostic error. However, on hospital day 2, the initial hypothesis of decompensated cirrhosis as the sole driver of the patient’s presentation was reconsidered due to the disconnect between the severity of hypoalbuminemia and diffuse edema (anasarca), and the absence of laboratory evidence of hepatic decompensation (normal international normalized ratio, bilirubin, and low but normal platelet count). Although image findings supported cirrhosis, laboratory markers did not indicate hepatic decompensation. The severity of hypoalbuminemia and anasarca, along with an indeterminate Serum-Ascites Albumin Gradient, prompted the patient’s care team to consider other causes, specifically, nephrotic syndrome.
The patien’s spot protein-to-creatinine ratio was 3.76 (reference range < 0.2 mg/mg creatinine), but a 24-hour urine protein collection was 12.8 g/day (reference range < 150 mg/day). While most spot urine protein- to-creatinine ratios (UPCR) correlate with a 24-hour urine collection, discrepancies can occur, as in this case. It is important to recognize that the spot UPCR assumes that patients are excreting 1000 mg of creatinine daily in their urine, which is not always the case. In addition, changes in urine osmolality can lead to different values. The gold standard for proteinuria is a 24-hour urine collection for protein and creatinine.
The patient’s nephrotic-range proteinuria and severe hypoalbuminemia are not solely explained by cirrhosis. In addition, the patient’s lower extremity edema pointed to nephrotic syndrome. The differential diagnosis for nephrotic syndrome includes both primary and secondary forms of membranous nephropathy, minimal change disease, focal segmental glomerulosclerosis, and MPGN, a histopathological diagnosis that requires distinguishing between immune complex-mediated and complement-mediated forms. Other causes of nephrotic syndrome that do not fit in any of these buckets include amyloidosis, IgA nephropathy, and diabetes mellitus (DM). Despite DM being a common cause of nephrotic range proteinuria, it rarely leads to full nephrotic syndrome.
When considering the diagnosis, we reframed the patient’s clinical syndrome as compensated cirrhosis plus nephrotic syndrome. This approach prioritized identifying a cause that could explain both cirrhosis (from any cause) leading to IgA nephropathy or injection drug use serving as a risk factor for cirrhosis and nephrotic syndrome through HCV or AA amyloidosis, respectively. This problem representation guided us to the correct diagnosis. There are multiple renal diseases associated with HCV infection, including MPGN, membranous nephropathy, focal segmental glomerulosclerosis, and IgA nephropathy.2 MPGN and mixed cryoglobulinemia are the most common. In the past, MPGN was classified as type I, II, and III.
The patient’s urine toxicology revealed recent amphetamine use, which can also lead to acute kidney injury through rhabdomyolysis or acute interstitial nephritis (AIN).3 In the cases of rhabdomyolysis, urinalysis would show positive heme without any red blood cell on microscopic analysis, which was not present in this case. AIN commonly manifests as acute kidney injury, pyuria, and proteinuria but without a decrease in complement levels.4 While the patient’s urine sediment included white blood cell (10/high-power field), the presence of microscopic hematuria, decreased complement levels, and proteinuria in the context of HCV positivity makes MPGN more likely than AIN.
Recently, there has been greater emphasis on using immunofluorescence for kidney biopsies. MPGN is now classified into 2 main categories: MPGN with mesangial immunoglobulins and C3 deposits in the capillary walls, and MPGN with C3 deposits but without Ig.5 MPGN with Ig-complement deposits is seen in autoimmune diseases and infections and is associated with dysproteinemias.
The renal biopsy in this patient was consistent with MPGN with immunofluorescence, a common finding in patients with infection. By synthesizing these data, we concluded that the patient represented a case of chronic HCV infection that led to MPGN with cryoglobulinemia. The normal C4 and negative RF do not suggest cryoglobulinemic crisis. Compensated cirrhosis was seen on imaging, pending liver biopsy.
Treatment
The management of MPGN secondary to HCV infection relies on the treatment of the underlying infection and clearance of viral load. Direct-acting antivirals have been used successfully in the treatment of HCV-associated MPGN. When cryoglobulinemia is present, immunosuppressive therapy is recommended. These regimens commonly include rituximab and steroids.5 Rituximab is also used for nephrotic syndrome associated with MPGN, as recommended in the 2018 Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes guidelines.6
When initiating rituximab therapy in a patient who tests positive for hepatitis B (HBcAb positive or HBsAb positive), it is recommended to follow the established guidelines, which include treating them with entecavir for prophylaxis to prevent reactivation or a flare of hepatitis B.7 The patient in this case needed close follow-up in the nephrology and hepatology clinic. Immunosuppressive therapy was not pursued while the patient was admitted to the hospital due to instability with housing, transportation, and difficulty in ensuring close follow-up.
CONCLUSIONS
Clinicians should maintain a broad differential even in the face of confirmatory imaging and other objective findings. In the case of anasarca, nephrotic syndrome should be considered. Key causes of nephrotic syndromes include MPGN, membranous nephropathy, minimal change disease, and focal segmental glomerulosclerosis. MPGN is a histopathological diagnosis, and it is essential to identify if it is secondary to immune complexes or only complement mediated because Ig-complement deposits are seen in autoimmune disease and infection. The management of MPGN due to HCV infection relies on antiviral therapy. In the presence of cryoglobulinemia, immunosuppressive therapy is recommended.
Histology is the gold standard for cirrhosis diagnosis. However, a combination of clinical history, physical examination findings, and supportive laboratory and radiographic features is generally sufficient to make the diagnosis. Routine ultrasound and computed tomography (CT) imaging often identifies a nodular liver contour with sequelae of portal hypertension, including splenomegaly, varices, and ascites, which can suggest cirrhosis when supported by laboratory parameters and clinical features. As a result, the diagnosis is typically made clinically.1 Many patients with compensated cirrhosis go undetected. The presence of a decompensation event (ascites, spontaneous bacterial peritonitis, variceal hemorrhage, or hepatic encephalopathy) often leads to index diagnosis when patients were previously compensated. When a patient presents with suspected decompensated cirrhosis, it is important to consider other diagnoses with similar presentations and ensure that multiple disease processes are not contributing to the symptoms.
CASE PRESENTATION
A 64-year-old male with a history of intravenous (IV) methamphetamine use and prior incarceration presented with a 3-week history of progressively worsening generalized swelling. Prior to the onset of his symptoms, the patient injured his right lower extremity (RLE) in a bicycle accident, resulting in edema that progressed to bilateral lower extremity (BLE) edema and worsening fatigue, despite resolution of the initial injury. The patient gained weight though he could not quantify the amount. He experienced progressive hunger, thirst, and fatigue as well as increased sleep. Additionally, the patient experienced worsening dyspnea on exertion and orthopnea. He started using 2 pillows instead of 1 pillow at night.
The patient reported no fevers, chills, sputum production, chest pain, or paroxysmal nocturnal dyspnea. He had no known history of sexually transmitted infections, no significant history of alcohol use, and occasional tobacco and marijuana use. He had been incarcerated > 10 years before and last used IV methamphetamine 3 years before. He did not regularly take any medications.
The patient’s vital signs included a temperature of 98.2 °F; 78/min heart rate; 15/min respiratory rate; 159/109 mm Hg blood pressure; and 98% oxygen saturation on room air. He had gained 20 lbs in the past 4 months. He had pitting edema in both legs and arms, as well as periorbital swelling, but no jugular venous distention, abnormal heart sounds, or murmurs. Breath sounds were distant but clear to auscultation. His abdomen was distended with normal bowel sounds and no fluid wave; mild epigastric tenderness was present, but no intra-abdominal masses were palpated. He had spider angiomata on the upper chest but no other stigmata of cirrhosis, such as caput medusae or jaundice. Tattoos were noted.
Laboratory test results showed a platelet count of 178 x 103/μL (reference range, 140- 440 ~ 103μL).Creatinine was 0.80 mg/dL (reference range, < 1.28 mg/dL), with an estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) of 99 mL/min/1.73 m2 using the Chronic Kidney Disease-Epidemiology equation (reference range, > 60 mL/min/1.73 m2), (reference range, > 60 mL/min/1.73 m2), and Cystatin C was 1.14 mg/L (reference range, < 1.15 mg/L). His electrolytes and complete blood count were within normal limits, including sodium, 134 mmol/L; potassium, 4.4 mmol/L; chloride, 108 mmol/L; and carbon dioxide, 22.5 mmol/L.
Additional test results included alkaline phosphatase, 126 U/L (reference range, < 94 U/L); alanine transaminase, 41 U/L (reference range, < 45 U/L); aspartate aminotransferase, 70 U/L (reference range, < 35 U/L); total bilirubin, 0.6 mg/dL (reference range, < 1 mg/dL); albumin, 1.8 g/dL (reference range, 3.2-4.8 g/dL); and total protein, 6.3 g/dL (reference range, 5.9-8.3 g/dL). The patient’s international normalized ratio was 0.96 (reference range, 0.8-1.1), and brain natriuretic peptide was normal at 56 pg/mL. No prior laboratory results were available for comparison.
Urine toxicology was positive for amphetamines. Urinalysis demonstrated large occult blood, with a red blood cell count of 26/ HPF (reference range, 0/HPF) and proteinuria (100 mg/dL; reference range, negative), without bacteria, nitrites, or leukocyte esterase. Urine white blood cell count was 10/ HPF (reference range, 0/HPF), and fine granular casts and hyaline casts were present.
A noncontrast CT of the abdomen and pelvis in the emergency department showed an irregular liver contour with diffuse nodularity, multiple portosystemic collaterals, moderate abdominal and pelvic ascites, small bilateral pleural effusions with associated atelectasis, and anasarca consistent with cirrhosis (Figure 1). The patient was admitted to the internal medicine service for workup and management of newly diagnosed cirrhosis.

Paracentesis revealed straw-colored fluid with an ascitic fluid neutrophil count of 17/μL, a protein level of < 3 g/dL and albumin level of < 1.5 g/dL. Gram stain of the ascitic fluid showed a moderate white blood cell count with no organisms. Fluid culture showed no microbial growth.
Initial workup for cirrhosis demonstrated a positive total hepatitis A antibody. The patient had a nonreactive hepatitis B surface antigen and surface antibody, but a reactive hepatitis B core antibody; a hepatitis B DNA level was not ordered. He had a reactive hepatitis C antibody with a viral load of 4,490,000 II/mL (genotype 1a). The patient’s iron level was 120 μg/dL, with a calculated total iron-binding capacity (TIBC) of 126.2 μg/dL. His transferrin saturation (TSAT) (serum iron divided by TIBC) was 95%. The patient had nonreactive antinuclear antibody and antimitochondrial antibody tests and a positive antismooth muscle antibody test with a titer of 1:40. His α-fetoprotein (AFP) level was 505 ng/mL (reference range, < 8 ng/mL).
Follow-up MRI of the abdomen and pelvis showed cirrhotic morphology with large volume ascites and portosystemic collaterals, consistent with portal hypertension. Additionally, it showed multiple scattered peripheral sub centimeter hyperenhancing foci, most likely representing benign lesions.
The patient's spot urine protein-creatinine ratio was 3.76. To better quantify proteinuria, a 24-hour urine collection was performed and revealed 12.8 g/d of urine protein (reference range, 0-0.17 g/d). His serum triglyceride level was 175 mg/dL (reference range, 40-60 mg/dL); total cholesterol was 177 mg/ dL (reference range, ≤ 200 mg/dL); low density lipoprotein cholesterol was 98 mg/ dL (reference range, ≤ 130 mg/dL); and highdensity lipoprotein cholesterol was 43.8 mg/ dL (reference range, ≥ 40 mg/dL); C3 complement level was 71 mg/dL (reference range, 82-185 mg/dL); and C4 complement level was 22 mg/dL (reference range, 15-53 mg/ dL). His rheumatoid factor was < 14 IU/mL. Tests for rapid plasma reagin and HIV antigen- antibody were nonreactive, and the phospholipase A2 receptor antibody test was negative. The patient tested positive for QuantiFERON-TB Gold and qualitative cryoglobulin, which indicated a cryocrit of 1%.
A renal biopsy was performed, revealing diffuse podocyte foot process effacement and glomerulonephritis with low-grade C3 and immunoglobulin (Ig) G deposits, consistent with early membranoproliferative glomerulonephritis (MPGN) (Figures 2 and 3).


The patient was initially diuresed with IV furosemide without significant urine output. He was then diuresed with IV 25% albumin (total, 25 g), followed by IV furosemide 40 mg twice daily, which led to significant urine output and resolution of his anasarca. Given the patient’s hypoalbuminemic state, IV albumin was necessary to deliver furosemide to the proximal tubule. He was started on lisinopril for renal protection and discharged with spironolactone and furosemide for fluid management in the context of cirrhosis.
The patient was evaluated by the Liver Nodule Clinic, which includes specialists from hepatology, medical oncology, radiation oncology, interventional radiology, and diagnostic radiology. The team considered the patient’s medical history and characteristics of the nodules on imaging. Notable aspects of the patient’s history included hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection and an elevated AFP level, although imaging showed no lesion concerning for malignancy. Given these findings, the patient was scheduled for a liver biopsy to establish a tissue diagnosis of cirrhosis. Hepatology, nephrology, and infectious disease specialists coordinated to plan the management and treatment of latent tuberculosis (TB), chronic HCV, MPGN, compensated cirrhosis, and suspicious liver lesions.
The patient chose to handle management and treatment as an outpatient. He was discharged with furosemide and spironolactone for anasarca management, and amlodipine and lisinopril for his hypertension and MPGN. Follow-up appointments were scheduled with infectious disease for management of latent TB and HCV, nephrology for MPGN, gastroenterology for cirrhosis, and interventional radiology for liver biopsy. Unfortunately, the patient was unhoused with limited access to transportation, which prevented timely follow-up. Given these social factors, immunosuppression was not started. Additionally, he did not start on HCV therapy because the viral load was still pending at time of discharge.
DISCUSSION
The diagnosis of decompensated cirrhosis was prematurely established, resulting in a diagnostic delay, a form of diagnostic error. However, on hospital day 2, the initial hypothesis of decompensated cirrhosis as the sole driver of the patient’s presentation was reconsidered due to the disconnect between the severity of hypoalbuminemia and diffuse edema (anasarca), and the absence of laboratory evidence of hepatic decompensation (normal international normalized ratio, bilirubin, and low but normal platelet count). Although image findings supported cirrhosis, laboratory markers did not indicate hepatic decompensation. The severity of hypoalbuminemia and anasarca, along with an indeterminate Serum-Ascites Albumin Gradient, prompted the patient’s care team to consider other causes, specifically, nephrotic syndrome.
The patien’s spot protein-to-creatinine ratio was 3.76 (reference range < 0.2 mg/mg creatinine), but a 24-hour urine protein collection was 12.8 g/day (reference range < 150 mg/day). While most spot urine protein- to-creatinine ratios (UPCR) correlate with a 24-hour urine collection, discrepancies can occur, as in this case. It is important to recognize that the spot UPCR assumes that patients are excreting 1000 mg of creatinine daily in their urine, which is not always the case. In addition, changes in urine osmolality can lead to different values. The gold standard for proteinuria is a 24-hour urine collection for protein and creatinine.
The patient’s nephrotic-range proteinuria and severe hypoalbuminemia are not solely explained by cirrhosis. In addition, the patient’s lower extremity edema pointed to nephrotic syndrome. The differential diagnosis for nephrotic syndrome includes both primary and secondary forms of membranous nephropathy, minimal change disease, focal segmental glomerulosclerosis, and MPGN, a histopathological diagnosis that requires distinguishing between immune complex-mediated and complement-mediated forms. Other causes of nephrotic syndrome that do not fit in any of these buckets include amyloidosis, IgA nephropathy, and diabetes mellitus (DM). Despite DM being a common cause of nephrotic range proteinuria, it rarely leads to full nephrotic syndrome.
When considering the diagnosis, we reframed the patient’s clinical syndrome as compensated cirrhosis plus nephrotic syndrome. This approach prioritized identifying a cause that could explain both cirrhosis (from any cause) leading to IgA nephropathy or injection drug use serving as a risk factor for cirrhosis and nephrotic syndrome through HCV or AA amyloidosis, respectively. This problem representation guided us to the correct diagnosis. There are multiple renal diseases associated with HCV infection, including MPGN, membranous nephropathy, focal segmental glomerulosclerosis, and IgA nephropathy.2 MPGN and mixed cryoglobulinemia are the most common. In the past, MPGN was classified as type I, II, and III.
The patient’s urine toxicology revealed recent amphetamine use, which can also lead to acute kidney injury through rhabdomyolysis or acute interstitial nephritis (AIN).3 In the cases of rhabdomyolysis, urinalysis would show positive heme without any red blood cell on microscopic analysis, which was not present in this case. AIN commonly manifests as acute kidney injury, pyuria, and proteinuria but without a decrease in complement levels.4 While the patient’s urine sediment included white blood cell (10/high-power field), the presence of microscopic hematuria, decreased complement levels, and proteinuria in the context of HCV positivity makes MPGN more likely than AIN.
Recently, there has been greater emphasis on using immunofluorescence for kidney biopsies. MPGN is now classified into 2 main categories: MPGN with mesangial immunoglobulins and C3 deposits in the capillary walls, and MPGN with C3 deposits but without Ig.5 MPGN with Ig-complement deposits is seen in autoimmune diseases and infections and is associated with dysproteinemias.
The renal biopsy in this patient was consistent with MPGN with immunofluorescence, a common finding in patients with infection. By synthesizing these data, we concluded that the patient represented a case of chronic HCV infection that led to MPGN with cryoglobulinemia. The normal C4 and negative RF do not suggest cryoglobulinemic crisis. Compensated cirrhosis was seen on imaging, pending liver biopsy.
Treatment
The management of MPGN secondary to HCV infection relies on the treatment of the underlying infection and clearance of viral load. Direct-acting antivirals have been used successfully in the treatment of HCV-associated MPGN. When cryoglobulinemia is present, immunosuppressive therapy is recommended. These regimens commonly include rituximab and steroids.5 Rituximab is also used for nephrotic syndrome associated with MPGN, as recommended in the 2018 Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes guidelines.6
When initiating rituximab therapy in a patient who tests positive for hepatitis B (HBcAb positive or HBsAb positive), it is recommended to follow the established guidelines, which include treating them with entecavir for prophylaxis to prevent reactivation or a flare of hepatitis B.7 The patient in this case needed close follow-up in the nephrology and hepatology clinic. Immunosuppressive therapy was not pursued while the patient was admitted to the hospital due to instability with housing, transportation, and difficulty in ensuring close follow-up.
CONCLUSIONS
Clinicians should maintain a broad differential even in the face of confirmatory imaging and other objective findings. In the case of anasarca, nephrotic syndrome should be considered. Key causes of nephrotic syndromes include MPGN, membranous nephropathy, minimal change disease, and focal segmental glomerulosclerosis. MPGN is a histopathological diagnosis, and it is essential to identify if it is secondary to immune complexes or only complement mediated because Ig-complement deposits are seen in autoimmune disease and infection. The management of MPGN due to HCV infection relies on antiviral therapy. In the presence of cryoglobulinemia, immunosuppressive therapy is recommended.
- Tapper EB, Parikh ND. Diagnosis and management of cirrhosis and its complications: a review. JAMA. 2023;329(18):1589–1602. doi:10.1001/jama.2023.5997
- Ozkok A, Yildiz A. Hepatitis C virus associated glomerulopathies. World J Gastroenterol. 2014;20(24):7544-7554. doi:10.3748/wjg.v20.i24.7544
- Foley RJ, Kapatkin K, Vrani R, Weinman EJ. Amphetamineinduced acute renal failure. South Med J. 1984;77(2):258- 260. doi:10.1097/00007611-198402000-00035
- Rossert J. Drug - induced acute interstitial nephritis. Kidney Int. 2001;60(2):804-817. doi:10.1046/j.1523-1755.2001.060002804.x
- Sethi S, Fervenza FC. Membranoproliferative glomerulonephritis: pathogenetic heterogeneity and proposal for a new classification. Semin Nephrol. 2011;31(4):341-348. doi:10.1016/j.semnephrol.2011.06.005
- Jadoul M, Berenguer MC, Doss W, et al. Executive summary of the 2018 KDIGO hepatitis C in CKD guideline: welcoming advances in evaluation and management. Kidney Int. 2018;94(4):663-673. doi:10.1016/j.kint.2018.06.011
- Myint A, Tong MJ, Beaven SW. Reactivation of hepatitis b virus: a review of clinical guidelines. Clin Liver Dis (Hoboken). 2020;15(4):162-167. doi:10.1002/cld.883
- Tapper EB, Parikh ND. Diagnosis and management of cirrhosis and its complications: a review. JAMA. 2023;329(18):1589–1602. doi:10.1001/jama.2023.5997
- Ozkok A, Yildiz A. Hepatitis C virus associated glomerulopathies. World J Gastroenterol. 2014;20(24):7544-7554. doi:10.3748/wjg.v20.i24.7544
- Foley RJ, Kapatkin K, Vrani R, Weinman EJ. Amphetamineinduced acute renal failure. South Med J. 1984;77(2):258- 260. doi:10.1097/00007611-198402000-00035
- Rossert J. Drug - induced acute interstitial nephritis. Kidney Int. 2001;60(2):804-817. doi:10.1046/j.1523-1755.2001.060002804.x
- Sethi S, Fervenza FC. Membranoproliferative glomerulonephritis: pathogenetic heterogeneity and proposal for a new classification. Semin Nephrol. 2011;31(4):341-348. doi:10.1016/j.semnephrol.2011.06.005
- Jadoul M, Berenguer MC, Doss W, et al. Executive summary of the 2018 KDIGO hepatitis C in CKD guideline: welcoming advances in evaluation and management. Kidney Int. 2018;94(4):663-673. doi:10.1016/j.kint.2018.06.011
- Myint A, Tong MJ, Beaven SW. Reactivation of hepatitis b virus: a review of clinical guidelines. Clin Liver Dis (Hoboken). 2020;15(4):162-167. doi:10.1002/cld.883
Elusive Edema: A Case of Nephrotic Syndrome Mimicking Decompensated Cirrhosis
Elusive Edema: A Case of Nephrotic Syndrome Mimicking Decompensated Cirrhosis
Intensive BP Control May Benefit CKD Patients in Real World
TOPLINE:
The cardiovascular benefits observed with intensive blood pressure (BP) control in patients with hypertension and elevated cardiovascular risk from the Systolic Blood Pressure Intervention Trial (SPRINT) can be largely replicated in real-world settings among patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD), highlighting the advantages of adopting intensive BP targets.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers conducted a comparative effectiveness study to determine if the beneficial and adverse effects of intensive vs standard BP control observed in SPRINT were replicable in patients with CKD and hypertension in clinical practice.
- They identified 85,938 patients (mean age, 75.7 years; 95.0% men) and 13,983 patients (mean age, 77.4 years; 38.4% men) from the Veterans Health Administration (VHA) and Kaiser Permanente of Southern California (KPSC) databases, respectively.
- The treatment effect was estimated by combining baseline covariate, treatment, and outcome data of participants from the SPRINT with covariate data from the VHA and KPSC databases.
- The primary outcomes included major cardiovascular events, all-cause death, cognitive impairment, CKD progression, and adverse events at 4 years.
TAKEAWAY:
- Compared with SPRINT participants, those in the VHA and KPSC databases were older, had less prevalent cardiovascular disease, higher albuminuria, and used more statins.
- The benefits of intensive vs standard BP control on major cardiovascular events, all-cause mortality, and certain adverse events (hypotension, syncope, bradycardia, acute kidney injury, and electrolyte abnormality) were transferable from the trial to the VHA and KPSC populations.
- The treatment effect of intensive BP management on CKD progression was transportable to the KPSC population but not to the VHA population. However, the trial’s impact on cognitive outcomes, such as dementia, was not transportable to either the VHA or KPSC populations.
- On the absolute scale, intensive vs standard BP treatment showed greater cardiovascular benefits and fewer safety concerns in the VHA and KPSC populations than in the SPRINT.
IN PRACTICE:
“This example highlights the potential for transportability methods to provide insights that can bridge evidence gaps and inform the application of novel therapies to patients with CKD who are treated in everyday practice,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
This study was led by Manjula Kurella Tamura, MD, MPH, Division of Nephrology, Department of Medicine, Stanford University School of Medicine, Palo Alto, California. It was published online on January 7, 2025, in JAMA Network Open.
LIMITATIONS:
Transportability analyses could not account for characteristics that were not well-documented in electronic health records, such as limited life expectancy. The study was conducted before the widespread use of sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors, glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonists, and nonsteroidal mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists, making it unclear whether intensive BP treatment would result in similar benefits with current pharmacotherapy regimens. Eligibility for this study was based on BP measurements in routine practice, which tend to be more variable than those collected in research settings.
DISCLOSURES:
This study was supported by grants from the National Institutes of Health. Some authors disclosed serving as a consultant and receiving grants, personal fees, and consulting fees from pharmaceutical companies and other sources.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
The cardiovascular benefits observed with intensive blood pressure (BP) control in patients with hypertension and elevated cardiovascular risk from the Systolic Blood Pressure Intervention Trial (SPRINT) can be largely replicated in real-world settings among patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD), highlighting the advantages of adopting intensive BP targets.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers conducted a comparative effectiveness study to determine if the beneficial and adverse effects of intensive vs standard BP control observed in SPRINT were replicable in patients with CKD and hypertension in clinical practice.
- They identified 85,938 patients (mean age, 75.7 years; 95.0% men) and 13,983 patients (mean age, 77.4 years; 38.4% men) from the Veterans Health Administration (VHA) and Kaiser Permanente of Southern California (KPSC) databases, respectively.
- The treatment effect was estimated by combining baseline covariate, treatment, and outcome data of participants from the SPRINT with covariate data from the VHA and KPSC databases.
- The primary outcomes included major cardiovascular events, all-cause death, cognitive impairment, CKD progression, and adverse events at 4 years.
TAKEAWAY:
- Compared with SPRINT participants, those in the VHA and KPSC databases were older, had less prevalent cardiovascular disease, higher albuminuria, and used more statins.
- The benefits of intensive vs standard BP control on major cardiovascular events, all-cause mortality, and certain adverse events (hypotension, syncope, bradycardia, acute kidney injury, and electrolyte abnormality) were transferable from the trial to the VHA and KPSC populations.
- The treatment effect of intensive BP management on CKD progression was transportable to the KPSC population but not to the VHA population. However, the trial’s impact on cognitive outcomes, such as dementia, was not transportable to either the VHA or KPSC populations.
- On the absolute scale, intensive vs standard BP treatment showed greater cardiovascular benefits and fewer safety concerns in the VHA and KPSC populations than in the SPRINT.
IN PRACTICE:
“This example highlights the potential for transportability methods to provide insights that can bridge evidence gaps and inform the application of novel therapies to patients with CKD who are treated in everyday practice,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
This study was led by Manjula Kurella Tamura, MD, MPH, Division of Nephrology, Department of Medicine, Stanford University School of Medicine, Palo Alto, California. It was published online on January 7, 2025, in JAMA Network Open.
LIMITATIONS:
Transportability analyses could not account for characteristics that were not well-documented in electronic health records, such as limited life expectancy. The study was conducted before the widespread use of sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors, glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonists, and nonsteroidal mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists, making it unclear whether intensive BP treatment would result in similar benefits with current pharmacotherapy regimens. Eligibility for this study was based on BP measurements in routine practice, which tend to be more variable than those collected in research settings.
DISCLOSURES:
This study was supported by grants from the National Institutes of Health. Some authors disclosed serving as a consultant and receiving grants, personal fees, and consulting fees from pharmaceutical companies and other sources.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
The cardiovascular benefits observed with intensive blood pressure (BP) control in patients with hypertension and elevated cardiovascular risk from the Systolic Blood Pressure Intervention Trial (SPRINT) can be largely replicated in real-world settings among patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD), highlighting the advantages of adopting intensive BP targets.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers conducted a comparative effectiveness study to determine if the beneficial and adverse effects of intensive vs standard BP control observed in SPRINT were replicable in patients with CKD and hypertension in clinical practice.
- They identified 85,938 patients (mean age, 75.7 years; 95.0% men) and 13,983 patients (mean age, 77.4 years; 38.4% men) from the Veterans Health Administration (VHA) and Kaiser Permanente of Southern California (KPSC) databases, respectively.
- The treatment effect was estimated by combining baseline covariate, treatment, and outcome data of participants from the SPRINT with covariate data from the VHA and KPSC databases.
- The primary outcomes included major cardiovascular events, all-cause death, cognitive impairment, CKD progression, and adverse events at 4 years.
TAKEAWAY:
- Compared with SPRINT participants, those in the VHA and KPSC databases were older, had less prevalent cardiovascular disease, higher albuminuria, and used more statins.
- The benefits of intensive vs standard BP control on major cardiovascular events, all-cause mortality, and certain adverse events (hypotension, syncope, bradycardia, acute kidney injury, and electrolyte abnormality) were transferable from the trial to the VHA and KPSC populations.
- The treatment effect of intensive BP management on CKD progression was transportable to the KPSC population but not to the VHA population. However, the trial’s impact on cognitive outcomes, such as dementia, was not transportable to either the VHA or KPSC populations.
- On the absolute scale, intensive vs standard BP treatment showed greater cardiovascular benefits and fewer safety concerns in the VHA and KPSC populations than in the SPRINT.
IN PRACTICE:
“This example highlights the potential for transportability methods to provide insights that can bridge evidence gaps and inform the application of novel therapies to patients with CKD who are treated in everyday practice,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
This study was led by Manjula Kurella Tamura, MD, MPH, Division of Nephrology, Department of Medicine, Stanford University School of Medicine, Palo Alto, California. It was published online on January 7, 2025, in JAMA Network Open.
LIMITATIONS:
Transportability analyses could not account for characteristics that were not well-documented in electronic health records, such as limited life expectancy. The study was conducted before the widespread use of sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors, glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonists, and nonsteroidal mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists, making it unclear whether intensive BP treatment would result in similar benefits with current pharmacotherapy regimens. Eligibility for this study was based on BP measurements in routine practice, which tend to be more variable than those collected in research settings.
DISCLOSURES:
This study was supported by grants from the National Institutes of Health. Some authors disclosed serving as a consultant and receiving grants, personal fees, and consulting fees from pharmaceutical companies and other sources.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Lowering Urate May Protect Kidneys in Gout Patients With CKD
TOPLINE:
Achieving serum urate to below 6 mg/dL with urate-lowering therapy (ULT) in patients with gout and chronic kidney disease (CKD) stage III is not linked to an increased risk for severe or end-stage kidney disease.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers emulated analyses of a hypothetical target trial using a cloning, censoring, and weighting approach to evaluate the association between achieving target serum urate level with ULT and the progression of CKD in patients with gout and CKD stage III.
- They included 14,972 patients (mean age, 73.1 years; 37.7% women) from a general practice database who had a mean baseline serum urate level of 8.9 mg/dL and initiated ULTs such as allopurinol or febuxostat.
- Participants were divided into two groups: Those who achieved a target serum urate level < 6 mg/dL and those who did not within 1 year after the initiation of ULT; the mean follow-up duration was a little more than 3 years in both groups.
- The primary outcome was the occurrence of severe or end-stage kidney disease over 5 years of initiating ULT, defined by an estimated glomerular filtration rate below 30 mL/min per 1.73 m2 on two occasions more than 90 days apart within 1 year, or at least one Read code for CKD stages IV or V, dialysis, or kidney transplant.
- A prespecified noninferiority margin for the hazard ratio was set at 1.2 to compare the outcomes between those who achieved the target serum urate level < 6 mg/dL and those who did not.
TAKEAWAY:
- Among the patients who initiated ULT, 31.8% achieved a target serum urate level < 6 mg/dL within 1 year.
- The 5-year risk for severe or end-stage kidney disease was lower (10.32%) in participants with gout and stage III CKD who achieved the target serum urate level than in those who did not (12.73%).
- The adjusted 5-year risk difference for severe to end-stage kidney disease was not inferior in patients who achieved the target serum urate level vs those who did not (adjusted hazard ratio [aHR], 0.89; 95% CI, 0.80-0.98; P for noninferiority < .001); results were consistent for end-stage kidney disease alone (aHR, 0.67; P for noninferiority = .001).
- Similarly, in participants with gout and CKD stages II-III, the 5-year risks for severe or end-stage kidney disease (aHR, 0.91) and end-stage kidney disease alone (aHR, 0.73) were noninferior in the group that did vs that did not achieve target serum urate levels, with P for noninferiority being < .001 and .003, respectively.
IN PRACTICE:
“Our findings suggest that lowering serum urate levels to < 6 mg/dL is generally well tolerated and may even slow CKD progression in these individuals. Initiatives to optimize the use and adherence to ULT could benefit clinicians and patients,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
This study was led by Yilun Wang, MD, PhD, Xiangya Hospital, Central South University, Changsha, China. It was published online in JAMA Internal Medicine.
LIMITATIONS:
Residual confounding may still have been present despite rigorous methods to control it, as is common in observational studies. Participants who achieved target serum urate levels may have received better healthcare, adhered to other treatments more consistently, and used ULT for a longer duration. The findings may have limited generalizability, as participants who did not achieve target serum urate levels prior to initiation were excluded.
DISCLOSURES:
This study was supported by the China National Key Research and Development Plan, the National Natural Science Foundation of China, the Project Program of the National Clinical Research Center for Geriatric Disorders, and other sources. Two authors reported receiving personal fees and/or grants from multiple pharmaceutical companies.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including artificial intelligence, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Achieving serum urate to below 6 mg/dL with urate-lowering therapy (ULT) in patients with gout and chronic kidney disease (CKD) stage III is not linked to an increased risk for severe or end-stage kidney disease.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers emulated analyses of a hypothetical target trial using a cloning, censoring, and weighting approach to evaluate the association between achieving target serum urate level with ULT and the progression of CKD in patients with gout and CKD stage III.
- They included 14,972 patients (mean age, 73.1 years; 37.7% women) from a general practice database who had a mean baseline serum urate level of 8.9 mg/dL and initiated ULTs such as allopurinol or febuxostat.
- Participants were divided into two groups: Those who achieved a target serum urate level < 6 mg/dL and those who did not within 1 year after the initiation of ULT; the mean follow-up duration was a little more than 3 years in both groups.
- The primary outcome was the occurrence of severe or end-stage kidney disease over 5 years of initiating ULT, defined by an estimated glomerular filtration rate below 30 mL/min per 1.73 m2 on two occasions more than 90 days apart within 1 year, or at least one Read code for CKD stages IV or V, dialysis, or kidney transplant.
- A prespecified noninferiority margin for the hazard ratio was set at 1.2 to compare the outcomes between those who achieved the target serum urate level < 6 mg/dL and those who did not.
TAKEAWAY:
- Among the patients who initiated ULT, 31.8% achieved a target serum urate level < 6 mg/dL within 1 year.
- The 5-year risk for severe or end-stage kidney disease was lower (10.32%) in participants with gout and stage III CKD who achieved the target serum urate level than in those who did not (12.73%).
- The adjusted 5-year risk difference for severe to end-stage kidney disease was not inferior in patients who achieved the target serum urate level vs those who did not (adjusted hazard ratio [aHR], 0.89; 95% CI, 0.80-0.98; P for noninferiority < .001); results were consistent for end-stage kidney disease alone (aHR, 0.67; P for noninferiority = .001).
- Similarly, in participants with gout and CKD stages II-III, the 5-year risks for severe or end-stage kidney disease (aHR, 0.91) and end-stage kidney disease alone (aHR, 0.73) were noninferior in the group that did vs that did not achieve target serum urate levels, with P for noninferiority being < .001 and .003, respectively.
IN PRACTICE:
“Our findings suggest that lowering serum urate levels to < 6 mg/dL is generally well tolerated and may even slow CKD progression in these individuals. Initiatives to optimize the use and adherence to ULT could benefit clinicians and patients,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
This study was led by Yilun Wang, MD, PhD, Xiangya Hospital, Central South University, Changsha, China. It was published online in JAMA Internal Medicine.
LIMITATIONS:
Residual confounding may still have been present despite rigorous methods to control it, as is common in observational studies. Participants who achieved target serum urate levels may have received better healthcare, adhered to other treatments more consistently, and used ULT for a longer duration. The findings may have limited generalizability, as participants who did not achieve target serum urate levels prior to initiation were excluded.
DISCLOSURES:
This study was supported by the China National Key Research and Development Plan, the National Natural Science Foundation of China, the Project Program of the National Clinical Research Center for Geriatric Disorders, and other sources. Two authors reported receiving personal fees and/or grants from multiple pharmaceutical companies.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including artificial intelligence, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Achieving serum urate to below 6 mg/dL with urate-lowering therapy (ULT) in patients with gout and chronic kidney disease (CKD) stage III is not linked to an increased risk for severe or end-stage kidney disease.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers emulated analyses of a hypothetical target trial using a cloning, censoring, and weighting approach to evaluate the association between achieving target serum urate level with ULT and the progression of CKD in patients with gout and CKD stage III.
- They included 14,972 patients (mean age, 73.1 years; 37.7% women) from a general practice database who had a mean baseline serum urate level of 8.9 mg/dL and initiated ULTs such as allopurinol or febuxostat.
- Participants were divided into two groups: Those who achieved a target serum urate level < 6 mg/dL and those who did not within 1 year after the initiation of ULT; the mean follow-up duration was a little more than 3 years in both groups.
- The primary outcome was the occurrence of severe or end-stage kidney disease over 5 years of initiating ULT, defined by an estimated glomerular filtration rate below 30 mL/min per 1.73 m2 on two occasions more than 90 days apart within 1 year, or at least one Read code for CKD stages IV or V, dialysis, or kidney transplant.
- A prespecified noninferiority margin for the hazard ratio was set at 1.2 to compare the outcomes between those who achieved the target serum urate level < 6 mg/dL and those who did not.
TAKEAWAY:
- Among the patients who initiated ULT, 31.8% achieved a target serum urate level < 6 mg/dL within 1 year.
- The 5-year risk for severe or end-stage kidney disease was lower (10.32%) in participants with gout and stage III CKD who achieved the target serum urate level than in those who did not (12.73%).
- The adjusted 5-year risk difference for severe to end-stage kidney disease was not inferior in patients who achieved the target serum urate level vs those who did not (adjusted hazard ratio [aHR], 0.89; 95% CI, 0.80-0.98; P for noninferiority < .001); results were consistent for end-stage kidney disease alone (aHR, 0.67; P for noninferiority = .001).
- Similarly, in participants with gout and CKD stages II-III, the 5-year risks for severe or end-stage kidney disease (aHR, 0.91) and end-stage kidney disease alone (aHR, 0.73) were noninferior in the group that did vs that did not achieve target serum urate levels, with P for noninferiority being < .001 and .003, respectively.
IN PRACTICE:
“Our findings suggest that lowering serum urate levels to < 6 mg/dL is generally well tolerated and may even slow CKD progression in these individuals. Initiatives to optimize the use and adherence to ULT could benefit clinicians and patients,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
This study was led by Yilun Wang, MD, PhD, Xiangya Hospital, Central South University, Changsha, China. It was published online in JAMA Internal Medicine.
LIMITATIONS:
Residual confounding may still have been present despite rigorous methods to control it, as is common in observational studies. Participants who achieved target serum urate levels may have received better healthcare, adhered to other treatments more consistently, and used ULT for a longer duration. The findings may have limited generalizability, as participants who did not achieve target serum urate levels prior to initiation were excluded.
DISCLOSURES:
This study was supported by the China National Key Research and Development Plan, the National Natural Science Foundation of China, the Project Program of the National Clinical Research Center for Geriatric Disorders, and other sources. Two authors reported receiving personal fees and/or grants from multiple pharmaceutical companies.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including artificial intelligence, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
How to Avoid Freaking Out About Kidney Function
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Matthew F. Watto, MD: I’m Dr Matthew Frank Watto, here with my great friend and America’s primary care physician, Dr Paul Nelson Williams.
We had a great discussion with Kidney Boy, Dr Joel Topf, everyone’s favorite nephrologist, and he taught us how to manage blood pressure in chronic kidney disease (CKD).
Paul N. Williams, MD: Dr Topf focuses more on albuminuria than we are used to doing. It’s probably one of the most important prognostic indicators of how a patient is going to do from a renal standpoint.
Historically, I’ve tended to focus on the estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR), and the lower that number gets, the more I sweat, but albuminuria is probably equally, if not more, important as a way of prognosticating whether a patient is going to progress to dialysis or transplant. He directed us towards this nifty little calculator, kidneyfailurerisk.com, where you plug in the patient’s age, eGFR, and degree of albuminuria, and it spits out their risk of progressing to hemodialysis or renal transplantation over the next 5 years. It’s a nice way to concretely explain to patients their risk for progression.
Instead of telling the patient, “You are high risk,” Dr Topf will say, “Your risk is 6% of needing dialysis in the next 5 years.” You can even use these thresholds to gauge when to refer a patient. If someone has a 5-year risk between 3% and 5% or higher, that patient should probably be seeing a nephrologist.
If their 2-year risk is greater than 20%, that patient probably should be evaluated for transplantation. This gives us have more concrete numbers to work with rather than just saying, “Your kidneys aren’t working as well as we would like and you should see a kidney doctor.” Patients have a better sense of how serious things might be.
Watto: It’s just easier for them to understand. Dr Topf made the point that we used to have a heat map based on the stage of CKD that would tell you how high a patient’s risk was compared with other people. But patients don’t really understand relative risk, so Dr Topf tells them their absolute risk for ending up on dialysis over the next 2-5 years.
Patients come in and they are worried because they looked at their lab results and see that their creatinine level is red, or their eGFR is low. They think, It says I have stage 3a CKD.
We should probably have the stages of CKD start at stage 3, which should be called stage 1 so it doesn’t sound as bad. Patients think they are halfway to dialysis; they are already at stage 3 and didn’t even know their kidneys were a problem.
Dr Topf said that cystatin C (something I only recently started ordering) can be obtained, and sometimes you can recategorize the patient, especially those with an eGFR between 45 and 60. The cystatin C can predict their renal function better than the creatinine-based equations. If you are using the creatinine equation, he recommends using the 2021 equations.
Another nice thing about cystatin C is that it isn’t tripped up in younger patients with a lot of muscle mass. You just have to watch out for inflammation, which can throw the test off. For example, when a patient is in the intensive care unit, it’s probably not that helpful, but for your outpatients, cystatin C works well.
Williams: I’ve been using it a fair amount in my patients with more muscle mass. And some patients have been taking creatine as a supplement, and that can alter the numbers as well. This is a nice way to get them out of CKD stage 2 or 3 and back where they belong, with normal healthy functioning kidneys.
Watto: Now, Paul, if we find a patient with more advanced CKD — let’s say stage 4, whether by cystatin C or serum creatinine, and their eGFR is less than 30 — should we start peeling off the angiotensin-converting enzyme ACE inhibitor or the angiotensin receptor blocker (ARB)? Those drugs can raise potassium. What should we do here?
Williams: That’s the temptation, Matt, and I feel like that was the old orthodoxy, back in residency. It didn’t take much for us to start taking off ACE inhibitors or ARBs once the kidney function started to drop, but it turns out you may be doing more harm than good.
Some data have shown that if you peel off those medications, you actually increase mortality and cardiovascular risk. So, in general, if you can keep them going, the patient will be better off. Hang onto the ACE inhibitors or ARBs as long as you are able to, because they confer a fair amount of benefit.
Watto: As long as the potassium isn’t in red on your lab’s range. It might go up to 5.2 or 5.4, but as long as it’s stable, that should be OK. You probably wouldn’t initiate an ACE inhibitor or ARB or spironolactone with a potassium level above 5, but if it’s below 5 when you start and it goes up slightly after you start the drug, that could be acceptable.
Another thing we talked about was when a patient progresses to CKD and ends up on dialysis, how helpful are those intradialysis blood pressures in predicting cardiovascular outcomes?
Williams: For someone who’s performing the dialysis, probably really helpful. In the outpatient setting to predict cardiovascular risk, probably less so. Dr Topf makes the point that the readings are done either shortly after or right when the patient is about to have a large-bore catheter inserted into their arm. And then they have liters of fluid drained out of them. So those numbers are going to have huge amounts of variability. You would not base the patient’s blood pressure treatment solely on those numbers. But regardless of what the numbers are, or even regardless of your office numbers, hopefully you’re working with a nephrologist to make sure that you’re actually in concert and not fighting each other with the blood pressure medications.
Watto: Dr Topf said that a lot of the hypertension in dialysis is because of too much volume. If you can get the volume down, you might be able to peel off blood pressure medications instead of adding more. But some patients have issues with cramping; it’s uncomfortable and not everyone tolerates it.
I was really surprised to learn that beta blockers, specifically atenolol, have some evidence of improving cardiovascular outcomes in patients on dialysis. Dr Topf speculated that this was because they are largely dying of cardiovascular disease, so maybe that’s why, but that’s one of the places, the only places I can think of aside from thyroid disease, where atenolol really shines.
If you want to hear this fantastic episode and all the great pearls, then click on this link.
Matthew F. Watto, MD, Clinical Assistant Professor, Department of Medicine, Perelman School of Medicine at University of Pennsylvania; Internist, Department of Medicine, Hospital Medicine Section, Pennsylvania Hospital, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Paul N. Williams, MD, has disclosed ties with The Curbsiders.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Matthew F. Watto, MD: I’m Dr Matthew Frank Watto, here with my great friend and America’s primary care physician, Dr Paul Nelson Williams.
We had a great discussion with Kidney Boy, Dr Joel Topf, everyone’s favorite nephrologist, and he taught us how to manage blood pressure in chronic kidney disease (CKD).
Paul N. Williams, MD: Dr Topf focuses more on albuminuria than we are used to doing. It’s probably one of the most important prognostic indicators of how a patient is going to do from a renal standpoint.
Historically, I’ve tended to focus on the estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR), and the lower that number gets, the more I sweat, but albuminuria is probably equally, if not more, important as a way of prognosticating whether a patient is going to progress to dialysis or transplant. He directed us towards this nifty little calculator, kidneyfailurerisk.com, where you plug in the patient’s age, eGFR, and degree of albuminuria, and it spits out their risk of progressing to hemodialysis or renal transplantation over the next 5 years. It’s a nice way to concretely explain to patients their risk for progression.
Instead of telling the patient, “You are high risk,” Dr Topf will say, “Your risk is 6% of needing dialysis in the next 5 years.” You can even use these thresholds to gauge when to refer a patient. If someone has a 5-year risk between 3% and 5% or higher, that patient should probably be seeing a nephrologist.
If their 2-year risk is greater than 20%, that patient probably should be evaluated for transplantation. This gives us have more concrete numbers to work with rather than just saying, “Your kidneys aren’t working as well as we would like and you should see a kidney doctor.” Patients have a better sense of how serious things might be.
Watto: It’s just easier for them to understand. Dr Topf made the point that we used to have a heat map based on the stage of CKD that would tell you how high a patient’s risk was compared with other people. But patients don’t really understand relative risk, so Dr Topf tells them their absolute risk for ending up on dialysis over the next 2-5 years.
Patients come in and they are worried because they looked at their lab results and see that their creatinine level is red, or their eGFR is low. They think, It says I have stage 3a CKD.
We should probably have the stages of CKD start at stage 3, which should be called stage 1 so it doesn’t sound as bad. Patients think they are halfway to dialysis; they are already at stage 3 and didn’t even know their kidneys were a problem.
Dr Topf said that cystatin C (something I only recently started ordering) can be obtained, and sometimes you can recategorize the patient, especially those with an eGFR between 45 and 60. The cystatin C can predict their renal function better than the creatinine-based equations. If you are using the creatinine equation, he recommends using the 2021 equations.
Another nice thing about cystatin C is that it isn’t tripped up in younger patients with a lot of muscle mass. You just have to watch out for inflammation, which can throw the test off. For example, when a patient is in the intensive care unit, it’s probably not that helpful, but for your outpatients, cystatin C works well.
Williams: I’ve been using it a fair amount in my patients with more muscle mass. And some patients have been taking creatine as a supplement, and that can alter the numbers as well. This is a nice way to get them out of CKD stage 2 or 3 and back where they belong, with normal healthy functioning kidneys.
Watto: Now, Paul, if we find a patient with more advanced CKD — let’s say stage 4, whether by cystatin C or serum creatinine, and their eGFR is less than 30 — should we start peeling off the angiotensin-converting enzyme ACE inhibitor or the angiotensin receptor blocker (ARB)? Those drugs can raise potassium. What should we do here?
Williams: That’s the temptation, Matt, and I feel like that was the old orthodoxy, back in residency. It didn’t take much for us to start taking off ACE inhibitors or ARBs once the kidney function started to drop, but it turns out you may be doing more harm than good.
Some data have shown that if you peel off those medications, you actually increase mortality and cardiovascular risk. So, in general, if you can keep them going, the patient will be better off. Hang onto the ACE inhibitors or ARBs as long as you are able to, because they confer a fair amount of benefit.
Watto: As long as the potassium isn’t in red on your lab’s range. It might go up to 5.2 or 5.4, but as long as it’s stable, that should be OK. You probably wouldn’t initiate an ACE inhibitor or ARB or spironolactone with a potassium level above 5, but if it’s below 5 when you start and it goes up slightly after you start the drug, that could be acceptable.
Another thing we talked about was when a patient progresses to CKD and ends up on dialysis, how helpful are those intradialysis blood pressures in predicting cardiovascular outcomes?
Williams: For someone who’s performing the dialysis, probably really helpful. In the outpatient setting to predict cardiovascular risk, probably less so. Dr Topf makes the point that the readings are done either shortly after or right when the patient is about to have a large-bore catheter inserted into their arm. And then they have liters of fluid drained out of them. So those numbers are going to have huge amounts of variability. You would not base the patient’s blood pressure treatment solely on those numbers. But regardless of what the numbers are, or even regardless of your office numbers, hopefully you’re working with a nephrologist to make sure that you’re actually in concert and not fighting each other with the blood pressure medications.
Watto: Dr Topf said that a lot of the hypertension in dialysis is because of too much volume. If you can get the volume down, you might be able to peel off blood pressure medications instead of adding more. But some patients have issues with cramping; it’s uncomfortable and not everyone tolerates it.
I was really surprised to learn that beta blockers, specifically atenolol, have some evidence of improving cardiovascular outcomes in patients on dialysis. Dr Topf speculated that this was because they are largely dying of cardiovascular disease, so maybe that’s why, but that’s one of the places, the only places I can think of aside from thyroid disease, where atenolol really shines.
If you want to hear this fantastic episode and all the great pearls, then click on this link.
Matthew F. Watto, MD, Clinical Assistant Professor, Department of Medicine, Perelman School of Medicine at University of Pennsylvania; Internist, Department of Medicine, Hospital Medicine Section, Pennsylvania Hospital, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Paul N. Williams, MD, has disclosed ties with The Curbsiders.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Matthew F. Watto, MD: I’m Dr Matthew Frank Watto, here with my great friend and America’s primary care physician, Dr Paul Nelson Williams.
We had a great discussion with Kidney Boy, Dr Joel Topf, everyone’s favorite nephrologist, and he taught us how to manage blood pressure in chronic kidney disease (CKD).
Paul N. Williams, MD: Dr Topf focuses more on albuminuria than we are used to doing. It’s probably one of the most important prognostic indicators of how a patient is going to do from a renal standpoint.
Historically, I’ve tended to focus on the estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR), and the lower that number gets, the more I sweat, but albuminuria is probably equally, if not more, important as a way of prognosticating whether a patient is going to progress to dialysis or transplant. He directed us towards this nifty little calculator, kidneyfailurerisk.com, where you plug in the patient’s age, eGFR, and degree of albuminuria, and it spits out their risk of progressing to hemodialysis or renal transplantation over the next 5 years. It’s a nice way to concretely explain to patients their risk for progression.
Instead of telling the patient, “You are high risk,” Dr Topf will say, “Your risk is 6% of needing dialysis in the next 5 years.” You can even use these thresholds to gauge when to refer a patient. If someone has a 5-year risk between 3% and 5% or higher, that patient should probably be seeing a nephrologist.
If their 2-year risk is greater than 20%, that patient probably should be evaluated for transplantation. This gives us have more concrete numbers to work with rather than just saying, “Your kidneys aren’t working as well as we would like and you should see a kidney doctor.” Patients have a better sense of how serious things might be.
Watto: It’s just easier for them to understand. Dr Topf made the point that we used to have a heat map based on the stage of CKD that would tell you how high a patient’s risk was compared with other people. But patients don’t really understand relative risk, so Dr Topf tells them their absolute risk for ending up on dialysis over the next 2-5 years.
Patients come in and they are worried because they looked at their lab results and see that their creatinine level is red, or their eGFR is low. They think, It says I have stage 3a CKD.
We should probably have the stages of CKD start at stage 3, which should be called stage 1 so it doesn’t sound as bad. Patients think they are halfway to dialysis; they are already at stage 3 and didn’t even know their kidneys were a problem.
Dr Topf said that cystatin C (something I only recently started ordering) can be obtained, and sometimes you can recategorize the patient, especially those with an eGFR between 45 and 60. The cystatin C can predict their renal function better than the creatinine-based equations. If you are using the creatinine equation, he recommends using the 2021 equations.
Another nice thing about cystatin C is that it isn’t tripped up in younger patients with a lot of muscle mass. You just have to watch out for inflammation, which can throw the test off. For example, when a patient is in the intensive care unit, it’s probably not that helpful, but for your outpatients, cystatin C works well.
Williams: I’ve been using it a fair amount in my patients with more muscle mass. And some patients have been taking creatine as a supplement, and that can alter the numbers as well. This is a nice way to get them out of CKD stage 2 or 3 and back where they belong, with normal healthy functioning kidneys.
Watto: Now, Paul, if we find a patient with more advanced CKD — let’s say stage 4, whether by cystatin C or serum creatinine, and their eGFR is less than 30 — should we start peeling off the angiotensin-converting enzyme ACE inhibitor or the angiotensin receptor blocker (ARB)? Those drugs can raise potassium. What should we do here?
Williams: That’s the temptation, Matt, and I feel like that was the old orthodoxy, back in residency. It didn’t take much for us to start taking off ACE inhibitors or ARBs once the kidney function started to drop, but it turns out you may be doing more harm than good.
Some data have shown that if you peel off those medications, you actually increase mortality and cardiovascular risk. So, in general, if you can keep them going, the patient will be better off. Hang onto the ACE inhibitors or ARBs as long as you are able to, because they confer a fair amount of benefit.
Watto: As long as the potassium isn’t in red on your lab’s range. It might go up to 5.2 or 5.4, but as long as it’s stable, that should be OK. You probably wouldn’t initiate an ACE inhibitor or ARB or spironolactone with a potassium level above 5, but if it’s below 5 when you start and it goes up slightly after you start the drug, that could be acceptable.
Another thing we talked about was when a patient progresses to CKD and ends up on dialysis, how helpful are those intradialysis blood pressures in predicting cardiovascular outcomes?
Williams: For someone who’s performing the dialysis, probably really helpful. In the outpatient setting to predict cardiovascular risk, probably less so. Dr Topf makes the point that the readings are done either shortly after or right when the patient is about to have a large-bore catheter inserted into their arm. And then they have liters of fluid drained out of them. So those numbers are going to have huge amounts of variability. You would not base the patient’s blood pressure treatment solely on those numbers. But regardless of what the numbers are, or even regardless of your office numbers, hopefully you’re working with a nephrologist to make sure that you’re actually in concert and not fighting each other with the blood pressure medications.
Watto: Dr Topf said that a lot of the hypertension in dialysis is because of too much volume. If you can get the volume down, you might be able to peel off blood pressure medications instead of adding more. But some patients have issues with cramping; it’s uncomfortable and not everyone tolerates it.
I was really surprised to learn that beta blockers, specifically atenolol, have some evidence of improving cardiovascular outcomes in patients on dialysis. Dr Topf speculated that this was because they are largely dying of cardiovascular disease, so maybe that’s why, but that’s one of the places, the only places I can think of aside from thyroid disease, where atenolol really shines.
If you want to hear this fantastic episode and all the great pearls, then click on this link.
Matthew F. Watto, MD, Clinical Assistant Professor, Department of Medicine, Perelman School of Medicine at University of Pennsylvania; Internist, Department of Medicine, Hospital Medicine Section, Pennsylvania Hospital, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Paul N. Williams, MD, has disclosed ties with The Curbsiders.
An 81-Year-Old White Woman Presented With a 2-Week History of a Painful Lesion on Her Left Calf
Calciphylaxis, also known as calcific uremic arteriolopathy, is a rare condition most commonly observed in patients with end-stage renal disease (ESRD). Because of the non-healing nature of the wounds and need for frequent hospitalizations, there is a significant risk of sepsis with a 1-year mortality rate greater than 50%.
Beyond ESRD, calciphylaxis is also associated with obesity, diabetes, hypoalbuminemia, autoimmune conditions, hepatic disease, malignancies, and dialysis. Rates in patients on dialysis have been increasing, ranging from 1% to 4%. Certain medications have also been implicated in the development of calciphylaxis, including warfarin, steroids, calcium-based phosphate binders, vitamin D, and iron. There is also an association with White individuals and more cases have been reported in females.
Pathophysiology of this condition includes calcification of the medial layer of arterioles and small arteries near the skin. Damage to vessel endothelium and formation of microthrombi contribute to the ischemia, which results in necrosis and ulceration of the skin. Elevated calcium and phosphate have been associated with these findings; however, these lab abnormalities alone are typically not enough to cause calciphylaxis. Vascular calcification inhibitors such as fetuin-A, osteoprotegerin, and matrix G1a protein may play a role in pathogenesis, with individuals lacking these factors potentially being at a greater risk. Specifically, matrix G1a protein is dependent on vitamin K dependent carboxylation, which may elucidate why warfarin has been implicated in the development of calciphylaxis because of interference with this pathway.
Upon presentation, patients will have painful ischemic plaques on the skin or painful subcutaneous nodules. Long-standing lesions may have a necrotic eschar or secondary infection, or may be associated with livedo reticularis. Areas with a greater concentration of adipose tissue such as the abdomen, thighs, and buttocks are most commonly affected, but lesions may appear anywhere. A biopsy may be done, but a clinical diagnosis is often sufficient as biopsies carry risks of prolonged healing and infection.
The differential diagnosis includes warfarin skin necrosis, cholesterol embolization, vasculitis, antiphospholipid syndrome, and cellulitis. Although this is a cutaneous manifestation, calciphylaxis is indicative of a systemic problem and requires multidisciplinary intervention.
Patients who present with calciphylaxis require a complete metabolic panel, liver function tests, coagulation studies, and albumin tests. Depending on the presentation, imaging studies such as nuclear medicine scans may be used if extensive soft tissue involvement is suspected.
Clinical management includes carefully avoiding electrolyte imbalances, initiating dialysis if necessary, discontinuing potentially offending supplements and medications, and administering proper wound care and pain management. Debridement of necrotic tissue may be necessary and should be initiated early as this has been associated with a 6-month increase in survival. Physicians should have a low threshold for starting antibiotics if secondary infection is suspected, but prophylaxis is not recommended. Sodium thiosulfate has been used off-label, but the mechanism of action is unknown and some meta-analyses indicate this treatment is not significantly associated with improvement of skin lesions. Interventions such as hyperbaric oxygen have also been used, but there is still more research to be done on these modalities.
The case and photo were submitted by Lucas Shapiro, BS, Nova Southeastern University College of Osteopathic Medicine, and Dr. Bilu Martin.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, Fort Lauderdale, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at mdedge.com/dermatology. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to dermnews@mdedge.com.
References
Kodumudi V et al. Adv Ther. 2020 Dec;37(12):4797-4807. doi: 10.1007/s12325-020-01504-w.
Seethapathy H et al. Adv Chronic Kidney Dis. 2019 Nov;26(6):484-490. doi: 10.1053/j.ackd.2019.09.005.
Turek M et al. Am J Case Rep. 2021 Jun 7:22:e930026. doi: 10.12659/AJCR.930026.
Wen W at al. JAMA Netw Open. 2023;6(4):e2310068. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.10068.
Westphal SG, Plumb T. Calciphylaxis. [Updated 2023 Aug 8]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2024 Jan-. Available from: www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK519020/.
Calciphylaxis, also known as calcific uremic arteriolopathy, is a rare condition most commonly observed in patients with end-stage renal disease (ESRD). Because of the non-healing nature of the wounds and need for frequent hospitalizations, there is a significant risk of sepsis with a 1-year mortality rate greater than 50%.
Beyond ESRD, calciphylaxis is also associated with obesity, diabetes, hypoalbuminemia, autoimmune conditions, hepatic disease, malignancies, and dialysis. Rates in patients on dialysis have been increasing, ranging from 1% to 4%. Certain medications have also been implicated in the development of calciphylaxis, including warfarin, steroids, calcium-based phosphate binders, vitamin D, and iron. There is also an association with White individuals and more cases have been reported in females.
Pathophysiology of this condition includes calcification of the medial layer of arterioles and small arteries near the skin. Damage to vessel endothelium and formation of microthrombi contribute to the ischemia, which results in necrosis and ulceration of the skin. Elevated calcium and phosphate have been associated with these findings; however, these lab abnormalities alone are typically not enough to cause calciphylaxis. Vascular calcification inhibitors such as fetuin-A, osteoprotegerin, and matrix G1a protein may play a role in pathogenesis, with individuals lacking these factors potentially being at a greater risk. Specifically, matrix G1a protein is dependent on vitamin K dependent carboxylation, which may elucidate why warfarin has been implicated in the development of calciphylaxis because of interference with this pathway.
Upon presentation, patients will have painful ischemic plaques on the skin or painful subcutaneous nodules. Long-standing lesions may have a necrotic eschar or secondary infection, or may be associated with livedo reticularis. Areas with a greater concentration of adipose tissue such as the abdomen, thighs, and buttocks are most commonly affected, but lesions may appear anywhere. A biopsy may be done, but a clinical diagnosis is often sufficient as biopsies carry risks of prolonged healing and infection.
The differential diagnosis includes warfarin skin necrosis, cholesterol embolization, vasculitis, antiphospholipid syndrome, and cellulitis. Although this is a cutaneous manifestation, calciphylaxis is indicative of a systemic problem and requires multidisciplinary intervention.
Patients who present with calciphylaxis require a complete metabolic panel, liver function tests, coagulation studies, and albumin tests. Depending on the presentation, imaging studies such as nuclear medicine scans may be used if extensive soft tissue involvement is suspected.
Clinical management includes carefully avoiding electrolyte imbalances, initiating dialysis if necessary, discontinuing potentially offending supplements and medications, and administering proper wound care and pain management. Debridement of necrotic tissue may be necessary and should be initiated early as this has been associated with a 6-month increase in survival. Physicians should have a low threshold for starting antibiotics if secondary infection is suspected, but prophylaxis is not recommended. Sodium thiosulfate has been used off-label, but the mechanism of action is unknown and some meta-analyses indicate this treatment is not significantly associated with improvement of skin lesions. Interventions such as hyperbaric oxygen have also been used, but there is still more research to be done on these modalities.
The case and photo were submitted by Lucas Shapiro, BS, Nova Southeastern University College of Osteopathic Medicine, and Dr. Bilu Martin.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, Fort Lauderdale, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at mdedge.com/dermatology. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to dermnews@mdedge.com.
References
Kodumudi V et al. Adv Ther. 2020 Dec;37(12):4797-4807. doi: 10.1007/s12325-020-01504-w.
Seethapathy H et al. Adv Chronic Kidney Dis. 2019 Nov;26(6):484-490. doi: 10.1053/j.ackd.2019.09.005.
Turek M et al. Am J Case Rep. 2021 Jun 7:22:e930026. doi: 10.12659/AJCR.930026.
Wen W at al. JAMA Netw Open. 2023;6(4):e2310068. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.10068.
Westphal SG, Plumb T. Calciphylaxis. [Updated 2023 Aug 8]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2024 Jan-. Available from: www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK519020/.
Calciphylaxis, also known as calcific uremic arteriolopathy, is a rare condition most commonly observed in patients with end-stage renal disease (ESRD). Because of the non-healing nature of the wounds and need for frequent hospitalizations, there is a significant risk of sepsis with a 1-year mortality rate greater than 50%.
Beyond ESRD, calciphylaxis is also associated with obesity, diabetes, hypoalbuminemia, autoimmune conditions, hepatic disease, malignancies, and dialysis. Rates in patients on dialysis have been increasing, ranging from 1% to 4%. Certain medications have also been implicated in the development of calciphylaxis, including warfarin, steroids, calcium-based phosphate binders, vitamin D, and iron. There is also an association with White individuals and more cases have been reported in females.
Pathophysiology of this condition includes calcification of the medial layer of arterioles and small arteries near the skin. Damage to vessel endothelium and formation of microthrombi contribute to the ischemia, which results in necrosis and ulceration of the skin. Elevated calcium and phosphate have been associated with these findings; however, these lab abnormalities alone are typically not enough to cause calciphylaxis. Vascular calcification inhibitors such as fetuin-A, osteoprotegerin, and matrix G1a protein may play a role in pathogenesis, with individuals lacking these factors potentially being at a greater risk. Specifically, matrix G1a protein is dependent on vitamin K dependent carboxylation, which may elucidate why warfarin has been implicated in the development of calciphylaxis because of interference with this pathway.
Upon presentation, patients will have painful ischemic plaques on the skin or painful subcutaneous nodules. Long-standing lesions may have a necrotic eschar or secondary infection, or may be associated with livedo reticularis. Areas with a greater concentration of adipose tissue such as the abdomen, thighs, and buttocks are most commonly affected, but lesions may appear anywhere. A biopsy may be done, but a clinical diagnosis is often sufficient as biopsies carry risks of prolonged healing and infection.
The differential diagnosis includes warfarin skin necrosis, cholesterol embolization, vasculitis, antiphospholipid syndrome, and cellulitis. Although this is a cutaneous manifestation, calciphylaxis is indicative of a systemic problem and requires multidisciplinary intervention.
Patients who present with calciphylaxis require a complete metabolic panel, liver function tests, coagulation studies, and albumin tests. Depending on the presentation, imaging studies such as nuclear medicine scans may be used if extensive soft tissue involvement is suspected.
Clinical management includes carefully avoiding electrolyte imbalances, initiating dialysis if necessary, discontinuing potentially offending supplements and medications, and administering proper wound care and pain management. Debridement of necrotic tissue may be necessary and should be initiated early as this has been associated with a 6-month increase in survival. Physicians should have a low threshold for starting antibiotics if secondary infection is suspected, but prophylaxis is not recommended. Sodium thiosulfate has been used off-label, but the mechanism of action is unknown and some meta-analyses indicate this treatment is not significantly associated with improvement of skin lesions. Interventions such as hyperbaric oxygen have also been used, but there is still more research to be done on these modalities.
The case and photo were submitted by Lucas Shapiro, BS, Nova Southeastern University College of Osteopathic Medicine, and Dr. Bilu Martin.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, Fort Lauderdale, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at mdedge.com/dermatology. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to dermnews@mdedge.com.
References
Kodumudi V et al. Adv Ther. 2020 Dec;37(12):4797-4807. doi: 10.1007/s12325-020-01504-w.
Seethapathy H et al. Adv Chronic Kidney Dis. 2019 Nov;26(6):484-490. doi: 10.1053/j.ackd.2019.09.005.
Turek M et al. Am J Case Rep. 2021 Jun 7:22:e930026. doi: 10.12659/AJCR.930026.
Wen W at al. JAMA Netw Open. 2023;6(4):e2310068. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.10068.
Westphal SG, Plumb T. Calciphylaxis. [Updated 2023 Aug 8]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2024 Jan-. Available from: www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK519020/.
An 81-year-old White woman with a medical history significant for end stage renal disease (ESRD) on dialysis, diabetes, and a cerebrovascular accident presented with a 2-week history of a very painful lesion on her left calf. Upon physical exam, she was also noted to have tender subcutaneous nodules on her left anterolateral thigh that had been present for several weeks.
What's your diagnosis?