User login
Intermittent Fasting Linked to Higher CVD Death Risk
A new study raises a cautionary note on time-restricted eating (TRE), a type of intermittent fasting that is gaining popularity.
This was the case in the overall sample and in those with cardiovascular disease (CVD) or cancer.
Lead author Victor Wenze Zhong, PhD, cautioned that the findings “require replication and we cannot demonstrate 8-hour TRE causes cardiovascular death in this observational study.
“However, it’s important for patients, particularly those with existing heart conditions or cancer, to be aware of the positive association between an 8-hour eating window and cardiovascular death,” Dr. Zhong, professor and chair, Department of Epidemiology and Biostatistics, School of Public Health, Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine, Shanghai, China, told this news organization.
The results (Abstract P192) were presented March 18 at the American Heart Association (AHA) Epidemiology and Prevention/Lifestyle and Cardiometabolic Health Scientific Sessions 2024.
‘Provocative’ Results
Short-term randomized controlled trials have suggested that 8-hour TRE may improve cardiometabolic risk profiles, but the potential long-term effects of this eating pattern are unknown.
The observation that TRE may have short-term benefits but long-term adverse effects is “interesting and provocative” and needs further study, Christopher D. Gardner, PhD, professor of medicine at Stanford University in California, who wasn’t involved in the study, said in a conference statement, and he agreed that much more research is needed.
The researchers analyzed data on dietary patterns for 20,078 adults (mean age, 48 years; 50% men; 73% non-Hispanic White) who participated in the 2003-2018 National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys (NHANES). All of them completed two 24-hour dietary recall questionnaires within the first year of enrollment. Deaths through the end of 2019 were determined via the National Death Index.
During a median follow-up of 8 years, there were 2797 deaths due to any cause, including 840 CV deaths and 643 cancer deaths.
In the overall sample, compared with an eating duration of 12-16 hours, 8-hour TRE was significantly associated with an increased risk for CV mortality (hazard ratio [HR], 1.91; 95% CI, 1.20-3.03).
This association was also observed in adults with CVD (HR, 2.07; 95% CI, 1.14-3.78) and adults with cancer (HR, 3.04; 95% CI, 1.44-6.41).
Other eating durations were not associated with CV mortality, except for eating duration of 8 to less than 10 hours in people with CVD (HR, 1.66; 95% CI, 1.03-2.67).
No significant associations were found between eating duration and all-cause or cancer mortality in the overall sample and CVD/cancer subsamples, except that eating duration of more than 16 hours was associated with a lower risk for cancer mortality in people with cancer (HR, 0.47; 95% CI, 0.23-0.95).
Quality More Important Than Timing
Dr. Zhong noted that the study doesn’t address the underlying mechanisms driving the observed association between 8-hour TRE and CV death.
“However, we did observe that people who restricted eating to a period less than 8 hours per day had less lean muscle mass compared with those with typical eating duration of 12-16 hours. Loss of lean body mass has been linked to higher risk of cardiovascular mortality,” Dr. Zhong said.
“Based on the evidence as of now, focusing on what people eat appears to be more important than focusing on the time when they eat. There are certain dietary approaches with compelling health benefits to choose, such as DASH diet and Mediterranean diet,” Dr. Zhong said.
Intermittent fasting is “certainly an interesting concept and one on which the potential mechanisms underlying the improvements in short outcome studies and preclinical studies in animals are strongly being pursued,” Sean P. Heffron, MD, cardiologist at the Center for the Prevention of Cardiovascular Disease at NYU Langone Heart, New York, who wasn’t involved in the study, told this news organization.
Dr. Heffron expressed skepticism about the study results calling them “far from complete” and noted that data on diet was based on only 2-day diet records without correction for confounding variables.
Dr. Heffron also noted that the restricted diet group has more smokers and more men. “I would “strongly anticipate that once appropriate corrections are made, the findings will no longer persist in statistical significance,” Dr. Heffron said.
He emphasized the need for more rigorous research before making clinical recommendations. When patients ask about intermittent fasting, Dr. Heffron said he tells them, “If it works for you, that’s fine,” but he doesn’t provide a recommendation for or against it.
Funding for the study was provided by the National Key Research and Development Program of China and the National Science Foundation of China. Zhong, Dr. Heffron and Dr. Gardner have no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
A new study raises a cautionary note on time-restricted eating (TRE), a type of intermittent fasting that is gaining popularity.
This was the case in the overall sample and in those with cardiovascular disease (CVD) or cancer.
Lead author Victor Wenze Zhong, PhD, cautioned that the findings “require replication and we cannot demonstrate 8-hour TRE causes cardiovascular death in this observational study.
“However, it’s important for patients, particularly those with existing heart conditions or cancer, to be aware of the positive association between an 8-hour eating window and cardiovascular death,” Dr. Zhong, professor and chair, Department of Epidemiology and Biostatistics, School of Public Health, Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine, Shanghai, China, told this news organization.
The results (Abstract P192) were presented March 18 at the American Heart Association (AHA) Epidemiology and Prevention/Lifestyle and Cardiometabolic Health Scientific Sessions 2024.
‘Provocative’ Results
Short-term randomized controlled trials have suggested that 8-hour TRE may improve cardiometabolic risk profiles, but the potential long-term effects of this eating pattern are unknown.
The observation that TRE may have short-term benefits but long-term adverse effects is “interesting and provocative” and needs further study, Christopher D. Gardner, PhD, professor of medicine at Stanford University in California, who wasn’t involved in the study, said in a conference statement, and he agreed that much more research is needed.
The researchers analyzed data on dietary patterns for 20,078 adults (mean age, 48 years; 50% men; 73% non-Hispanic White) who participated in the 2003-2018 National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys (NHANES). All of them completed two 24-hour dietary recall questionnaires within the first year of enrollment. Deaths through the end of 2019 were determined via the National Death Index.
During a median follow-up of 8 years, there were 2797 deaths due to any cause, including 840 CV deaths and 643 cancer deaths.
In the overall sample, compared with an eating duration of 12-16 hours, 8-hour TRE was significantly associated with an increased risk for CV mortality (hazard ratio [HR], 1.91; 95% CI, 1.20-3.03).
This association was also observed in adults with CVD (HR, 2.07; 95% CI, 1.14-3.78) and adults with cancer (HR, 3.04; 95% CI, 1.44-6.41).
Other eating durations were not associated with CV mortality, except for eating duration of 8 to less than 10 hours in people with CVD (HR, 1.66; 95% CI, 1.03-2.67).
No significant associations were found between eating duration and all-cause or cancer mortality in the overall sample and CVD/cancer subsamples, except that eating duration of more than 16 hours was associated with a lower risk for cancer mortality in people with cancer (HR, 0.47; 95% CI, 0.23-0.95).
Quality More Important Than Timing
Dr. Zhong noted that the study doesn’t address the underlying mechanisms driving the observed association between 8-hour TRE and CV death.
“However, we did observe that people who restricted eating to a period less than 8 hours per day had less lean muscle mass compared with those with typical eating duration of 12-16 hours. Loss of lean body mass has been linked to higher risk of cardiovascular mortality,” Dr. Zhong said.
“Based on the evidence as of now, focusing on what people eat appears to be more important than focusing on the time when they eat. There are certain dietary approaches with compelling health benefits to choose, such as DASH diet and Mediterranean diet,” Dr. Zhong said.
Intermittent fasting is “certainly an interesting concept and one on which the potential mechanisms underlying the improvements in short outcome studies and preclinical studies in animals are strongly being pursued,” Sean P. Heffron, MD, cardiologist at the Center for the Prevention of Cardiovascular Disease at NYU Langone Heart, New York, who wasn’t involved in the study, told this news organization.
Dr. Heffron expressed skepticism about the study results calling them “far from complete” and noted that data on diet was based on only 2-day diet records without correction for confounding variables.
Dr. Heffron also noted that the restricted diet group has more smokers and more men. “I would “strongly anticipate that once appropriate corrections are made, the findings will no longer persist in statistical significance,” Dr. Heffron said.
He emphasized the need for more rigorous research before making clinical recommendations. When patients ask about intermittent fasting, Dr. Heffron said he tells them, “If it works for you, that’s fine,” but he doesn’t provide a recommendation for or against it.
Funding for the study was provided by the National Key Research and Development Program of China and the National Science Foundation of China. Zhong, Dr. Heffron and Dr. Gardner have no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
A new study raises a cautionary note on time-restricted eating (TRE), a type of intermittent fasting that is gaining popularity.
This was the case in the overall sample and in those with cardiovascular disease (CVD) or cancer.
Lead author Victor Wenze Zhong, PhD, cautioned that the findings “require replication and we cannot demonstrate 8-hour TRE causes cardiovascular death in this observational study.
“However, it’s important for patients, particularly those with existing heart conditions or cancer, to be aware of the positive association between an 8-hour eating window and cardiovascular death,” Dr. Zhong, professor and chair, Department of Epidemiology and Biostatistics, School of Public Health, Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine, Shanghai, China, told this news organization.
The results (Abstract P192) were presented March 18 at the American Heart Association (AHA) Epidemiology and Prevention/Lifestyle and Cardiometabolic Health Scientific Sessions 2024.
‘Provocative’ Results
Short-term randomized controlled trials have suggested that 8-hour TRE may improve cardiometabolic risk profiles, but the potential long-term effects of this eating pattern are unknown.
The observation that TRE may have short-term benefits but long-term adverse effects is “interesting and provocative” and needs further study, Christopher D. Gardner, PhD, professor of medicine at Stanford University in California, who wasn’t involved in the study, said in a conference statement, and he agreed that much more research is needed.
The researchers analyzed data on dietary patterns for 20,078 adults (mean age, 48 years; 50% men; 73% non-Hispanic White) who participated in the 2003-2018 National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys (NHANES). All of them completed two 24-hour dietary recall questionnaires within the first year of enrollment. Deaths through the end of 2019 were determined via the National Death Index.
During a median follow-up of 8 years, there were 2797 deaths due to any cause, including 840 CV deaths and 643 cancer deaths.
In the overall sample, compared with an eating duration of 12-16 hours, 8-hour TRE was significantly associated with an increased risk for CV mortality (hazard ratio [HR], 1.91; 95% CI, 1.20-3.03).
This association was also observed in adults with CVD (HR, 2.07; 95% CI, 1.14-3.78) and adults with cancer (HR, 3.04; 95% CI, 1.44-6.41).
Other eating durations were not associated with CV mortality, except for eating duration of 8 to less than 10 hours in people with CVD (HR, 1.66; 95% CI, 1.03-2.67).
No significant associations were found between eating duration and all-cause or cancer mortality in the overall sample and CVD/cancer subsamples, except that eating duration of more than 16 hours was associated with a lower risk for cancer mortality in people with cancer (HR, 0.47; 95% CI, 0.23-0.95).
Quality More Important Than Timing
Dr. Zhong noted that the study doesn’t address the underlying mechanisms driving the observed association between 8-hour TRE and CV death.
“However, we did observe that people who restricted eating to a period less than 8 hours per day had less lean muscle mass compared with those with typical eating duration of 12-16 hours. Loss of lean body mass has been linked to higher risk of cardiovascular mortality,” Dr. Zhong said.
“Based on the evidence as of now, focusing on what people eat appears to be more important than focusing on the time when they eat. There are certain dietary approaches with compelling health benefits to choose, such as DASH diet and Mediterranean diet,” Dr. Zhong said.
Intermittent fasting is “certainly an interesting concept and one on which the potential mechanisms underlying the improvements in short outcome studies and preclinical studies in animals are strongly being pursued,” Sean P. Heffron, MD, cardiologist at the Center for the Prevention of Cardiovascular Disease at NYU Langone Heart, New York, who wasn’t involved in the study, told this news organization.
Dr. Heffron expressed skepticism about the study results calling them “far from complete” and noted that data on diet was based on only 2-day diet records without correction for confounding variables.
Dr. Heffron also noted that the restricted diet group has more smokers and more men. “I would “strongly anticipate that once appropriate corrections are made, the findings will no longer persist in statistical significance,” Dr. Heffron said.
He emphasized the need for more rigorous research before making clinical recommendations. When patients ask about intermittent fasting, Dr. Heffron said he tells them, “If it works for you, that’s fine,” but he doesn’t provide a recommendation for or against it.
Funding for the study was provided by the National Key Research and Development Program of China and the National Science Foundation of China. Zhong, Dr. Heffron and Dr. Gardner have no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Can Treating Depression Mitigate CVD Risk?
TOPLINE:
Depression is linked to a significantly increased risk for cardiovascular disease (CVD), particularly in women, new data from a large retrospective cohort study show.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers analyzed health insurance claims from more than 4 million Japanese patients filed between 2005 and 2022.
- Participants were 18-75 (median age, 44) without a history of CVD or stroke, heart failure, or atrial fibrillation.
- Investigators followed participants for a mean period of 2.5-3.5 years to observe the number of CVD events in those who had a diagnosis of depression.
- During the follow-up period, there were 119,000 CVD events in men (14 per 10,000 person-years) and 61,800 CVD events in women (111 per 10,000 person-years).
TAKEAWAY:
- Compared with women without depression, those with depression had a 64% higher risk for CVD (hazard ratio [HR], 1.64), while men with depression had a 39% higher risk for CVD vs their counterparts without depression (HR, 1.39; P < .001).
- This association was significant even after controlling for various factors such as body mass index, diabetes, smoking, alcohol consumption, and physical inactivity.
- Investigators offered several theories about the increased risk for CVD in women with depression, including how depression during hormonal shifts can contribute to a greater impact on cardiovascular health.
IN PRACTICE:
“Healthcare professionals must recognize the important role of depression in the development of CVD and emphasize the importance of a comprehensive, patient-centered approach to its prevention and management,” study author Hidehiro Kaneko, MD, said in a press release. “Assessing the risk of CVD in depressed patients and treating and preventing depression may lead to a decrease of CVD cases.”
SOURCE:
Keitaro Senoo, MD, of the Kyoto Prefectural University of Medicine, Kyoto, Japan, led the study, which was published online on March 12 in JACC: Asia.
LIMITATIONS:
The study is observational, so causality between depression and subsequent CVD events cannot be established. In addition, depression severity is unknown.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was funded by the Ministry of Health, Labour, and Welfare, Japan, and the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science, and Technology, Japan. There were no disclosures reported.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Depression is linked to a significantly increased risk for cardiovascular disease (CVD), particularly in women, new data from a large retrospective cohort study show.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers analyzed health insurance claims from more than 4 million Japanese patients filed between 2005 and 2022.
- Participants were 18-75 (median age, 44) without a history of CVD or stroke, heart failure, or atrial fibrillation.
- Investigators followed participants for a mean period of 2.5-3.5 years to observe the number of CVD events in those who had a diagnosis of depression.
- During the follow-up period, there were 119,000 CVD events in men (14 per 10,000 person-years) and 61,800 CVD events in women (111 per 10,000 person-years).
TAKEAWAY:
- Compared with women without depression, those with depression had a 64% higher risk for CVD (hazard ratio [HR], 1.64), while men with depression had a 39% higher risk for CVD vs their counterparts without depression (HR, 1.39; P < .001).
- This association was significant even after controlling for various factors such as body mass index, diabetes, smoking, alcohol consumption, and physical inactivity.
- Investigators offered several theories about the increased risk for CVD in women with depression, including how depression during hormonal shifts can contribute to a greater impact on cardiovascular health.
IN PRACTICE:
“Healthcare professionals must recognize the important role of depression in the development of CVD and emphasize the importance of a comprehensive, patient-centered approach to its prevention and management,” study author Hidehiro Kaneko, MD, said in a press release. “Assessing the risk of CVD in depressed patients and treating and preventing depression may lead to a decrease of CVD cases.”
SOURCE:
Keitaro Senoo, MD, of the Kyoto Prefectural University of Medicine, Kyoto, Japan, led the study, which was published online on March 12 in JACC: Asia.
LIMITATIONS:
The study is observational, so causality between depression and subsequent CVD events cannot be established. In addition, depression severity is unknown.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was funded by the Ministry of Health, Labour, and Welfare, Japan, and the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science, and Technology, Japan. There were no disclosures reported.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Depression is linked to a significantly increased risk for cardiovascular disease (CVD), particularly in women, new data from a large retrospective cohort study show.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers analyzed health insurance claims from more than 4 million Japanese patients filed between 2005 and 2022.
- Participants were 18-75 (median age, 44) without a history of CVD or stroke, heart failure, or atrial fibrillation.
- Investigators followed participants for a mean period of 2.5-3.5 years to observe the number of CVD events in those who had a diagnosis of depression.
- During the follow-up period, there were 119,000 CVD events in men (14 per 10,000 person-years) and 61,800 CVD events in women (111 per 10,000 person-years).
TAKEAWAY:
- Compared with women without depression, those with depression had a 64% higher risk for CVD (hazard ratio [HR], 1.64), while men with depression had a 39% higher risk for CVD vs their counterparts without depression (HR, 1.39; P < .001).
- This association was significant even after controlling for various factors such as body mass index, diabetes, smoking, alcohol consumption, and physical inactivity.
- Investigators offered several theories about the increased risk for CVD in women with depression, including how depression during hormonal shifts can contribute to a greater impact on cardiovascular health.
IN PRACTICE:
“Healthcare professionals must recognize the important role of depression in the development of CVD and emphasize the importance of a comprehensive, patient-centered approach to its prevention and management,” study author Hidehiro Kaneko, MD, said in a press release. “Assessing the risk of CVD in depressed patients and treating and preventing depression may lead to a decrease of CVD cases.”
SOURCE:
Keitaro Senoo, MD, of the Kyoto Prefectural University of Medicine, Kyoto, Japan, led the study, which was published online on March 12 in JACC: Asia.
LIMITATIONS:
The study is observational, so causality between depression and subsequent CVD events cannot be established. In addition, depression severity is unknown.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was funded by the Ministry of Health, Labour, and Welfare, Japan, and the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science, and Technology, Japan. There were no disclosures reported.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Phase 2 Results: Zerlasiran siRNA Drug Lowers Lp(a) by 90%
Silence Therapeutics shared positive topline 36-week data from its ongoing phase 2 study of zerlasiran, a long-acting agent directed at lowering Lp(a) levels.
In a statement, the company said the study shows a highly significant reduction from baseline in Lp(a) levels with zerlasiran compared with placebo at 36 weeks, the primary endpoint.
Zerlasiran (formerly known as SLN360), is a short interfering RNA (siRNA) agent, or “ gene silencing” therapy. It binds to and temporarily blocks the action of the LPA gene which encodes for apolipoprotein(a), a dominant and a rate-limiting component in the hepatic synthesis of the Lp(a) particle.
A previous phase 1 study showed that single subcutaneous doses of the drug, ranging from 30 mg to 600 mg, produced a dose-dependent reduction in Lp(a) plasma levels at 45-60 days.
The current double-blind placebo-controlled phase 2 trial — known as ALPACAR-360 — enrolled 178 patients at high risk for atherosclerotic cardiovascular events who had elevated levels of Lp(a), ie, ≥ 125 nmol/L (median baseline Lp(a) was approximately 215 nmol/L). They were randomized to zerlasiran or placebo.
Zerlasiran was administered at 300 mg subcutaneously every 16 or 24 weeks or at 450 mg every 24 weeks.
The 60-week study is ongoing, and secondary endpoints, including change in Lp(a) from baseline to 48 weeks (end of treatment period) and 60 weeks (end of study) and potential effects on other lipids/lipoproteins, will be evaluated.
Silence says it plans to report topline 48-week data from the ALPACAR-360 study in the second quarter of this year.
Elevated levels of Lp(a) represent a genetic risk factor for cardiovascular disease, which is believed to affect approximately 20% of the population. Although there are currently no approved Lp(a)-lowering therapies, several drug candidates are in late-stage clinical testing.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Silence Therapeutics shared positive topline 36-week data from its ongoing phase 2 study of zerlasiran, a long-acting agent directed at lowering Lp(a) levels.
In a statement, the company said the study shows a highly significant reduction from baseline in Lp(a) levels with zerlasiran compared with placebo at 36 weeks, the primary endpoint.
Zerlasiran (formerly known as SLN360), is a short interfering RNA (siRNA) agent, or “ gene silencing” therapy. It binds to and temporarily blocks the action of the LPA gene which encodes for apolipoprotein(a), a dominant and a rate-limiting component in the hepatic synthesis of the Lp(a) particle.
A previous phase 1 study showed that single subcutaneous doses of the drug, ranging from 30 mg to 600 mg, produced a dose-dependent reduction in Lp(a) plasma levels at 45-60 days.
The current double-blind placebo-controlled phase 2 trial — known as ALPACAR-360 — enrolled 178 patients at high risk for atherosclerotic cardiovascular events who had elevated levels of Lp(a), ie, ≥ 125 nmol/L (median baseline Lp(a) was approximately 215 nmol/L). They were randomized to zerlasiran or placebo.
Zerlasiran was administered at 300 mg subcutaneously every 16 or 24 weeks or at 450 mg every 24 weeks.
The 60-week study is ongoing, and secondary endpoints, including change in Lp(a) from baseline to 48 weeks (end of treatment period) and 60 weeks (end of study) and potential effects on other lipids/lipoproteins, will be evaluated.
Silence says it plans to report topline 48-week data from the ALPACAR-360 study in the second quarter of this year.
Elevated levels of Lp(a) represent a genetic risk factor for cardiovascular disease, which is believed to affect approximately 20% of the population. Although there are currently no approved Lp(a)-lowering therapies, several drug candidates are in late-stage clinical testing.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Silence Therapeutics shared positive topline 36-week data from its ongoing phase 2 study of zerlasiran, a long-acting agent directed at lowering Lp(a) levels.
In a statement, the company said the study shows a highly significant reduction from baseline in Lp(a) levels with zerlasiran compared with placebo at 36 weeks, the primary endpoint.
Zerlasiran (formerly known as SLN360), is a short interfering RNA (siRNA) agent, or “ gene silencing” therapy. It binds to and temporarily blocks the action of the LPA gene which encodes for apolipoprotein(a), a dominant and a rate-limiting component in the hepatic synthesis of the Lp(a) particle.
A previous phase 1 study showed that single subcutaneous doses of the drug, ranging from 30 mg to 600 mg, produced a dose-dependent reduction in Lp(a) plasma levels at 45-60 days.
The current double-blind placebo-controlled phase 2 trial — known as ALPACAR-360 — enrolled 178 patients at high risk for atherosclerotic cardiovascular events who had elevated levels of Lp(a), ie, ≥ 125 nmol/L (median baseline Lp(a) was approximately 215 nmol/L). They were randomized to zerlasiran or placebo.
Zerlasiran was administered at 300 mg subcutaneously every 16 or 24 weeks or at 450 mg every 24 weeks.
The 60-week study is ongoing, and secondary endpoints, including change in Lp(a) from baseline to 48 weeks (end of treatment period) and 60 weeks (end of study) and potential effects on other lipids/lipoproteins, will be evaluated.
Silence says it plans to report topline 48-week data from the ALPACAR-360 study in the second quarter of this year.
Elevated levels of Lp(a) represent a genetic risk factor for cardiovascular disease, which is believed to affect approximately 20% of the population. Although there are currently no approved Lp(a)-lowering therapies, several drug candidates are in late-stage clinical testing.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
ACC Consensus Guidance on What’s New in HFrEF Treatment
The American College of Cardiology has published a new update to its consensus decision pathway for the treatment of heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF).
Chair of the consensus document Writing Committee Thomas M. Maddox, MD, explained to this news organization that this new Decision Pathway provides a practical, streamlined update to frontline clinicians treating patients with heart failure and incorporates evidence from the 2022 AHA/ACC/HFSA Guideline for the Management of Heart Failure.
“While the AHA/ACC/HFSA Guidelines are wonderful in that they collate all the latest scientific evidence, they don’t speak as much to the practicalities of delivering the care. This is what this Decision Pathway document comes in — it is designed to help frontline clinicians with the practical reality of managing these patients,” Dr. Maddox, who is director of the Healthcare Innovation Lab at BJC HealthCare and the Washington University School of Medicine in St Louis, Missouri, commented.
The document, “Expert Consensus Decision Pathway for Optimization of Heart Failure Treatment: Answers to 10 Pivotal Issues About Heart Failure With Reduced Ejection Fraction,” was published online on March 8 in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology.
The authors provided guidance on introducing the numerous evidence-based therapies now available for HFrEF, improving adherence, overcoming treatment barriers, acknowledging contraindications and situations for which few data exist, affording expensive therapies, treating special cohorts, and making the transition to palliative care.
Rather than focusing on extensive text, the document provided practical tips, tables, and figures to make clear the steps, tools, and provisos needed to treat patients with heart failure successfully and expeditiously, they added.
Dr. Maddox reported that there are three main updated areas of advice on the treatment of heart failure in the new document.
Valsartan/Sacubitril First Line
One of the major changes involves an elevation for the status of the angiotensin receptor-neprilysin inhibitor (ARNI), Entresto (valsartan/sacubitril).
“It is now clear that this agent is superior to ACE-inhibitors or angiotensin receptor blockers in terms of reducing heart failure hospitalization and death, whereas previously it was seen as somewhat equivalent,” Dr. Maddox said. “So, barring a contraindication or another problem with getting the medication, this agent should be one of the first line medicines for all patients with heart failure and a reduced ejection fraction.”
Dual Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter 1/2 (SGLT1/2) Inhibitor
A second update involves the addition of sotagliflozin (a dual inhibitor of both SGLT1 and SGLT2) to the SGLT2 inhibitors as another first-line medication for patients with heart failure and reduced ejection fraction.
“We now have evidence that both SGLT2 and SGLT1 inhibitors are beneficial in reducing heart failure hospitalization and death. Previously we only had evidence on SGLT2 inhibitors — dapagliflozin and empagliflozin. Sotagliflozin is a newer agent, which inhibits both SGLT1 and SGLT2, and it turns out that inhibiting both are beneficial in heart failure. So, this gives us a third med in this category,” Dr. Maddox noted.
Rapid Initiation of the Four Pillars of Therapy
The document stated that more data have emerged recently to support early and rapid initiation and titration of the “four pillars” of medical therapy in heart failure to maximize the benefits of patient-reported outcomes and reduction in hospitalizations and mortality.
The four pillars of therapy are ARNI, a beta-blocker, a mineralocorticoid antagonist, and an SGLT inhibitor.
As an example, four-class medication initiation reduced the hazard of cardiovascular death or hospital admission for heart failure significantly (hazard ratio, 0.38) compared with therapy with just an angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor/angiotensin receptor blocker plus a beta-blocker, the document reported.
“What we realize now is that the more quickly we can get patients on all four of these drug classes and escalate to target doses or maximally tolerated doses ideally within 3 months, the better the outcome,” Dr. Maddox said.
“Unfortunately, right now there is very incomplete realization and recognition of that in clinical practice. So, we are trying to highlight the importance of this to encourage clinicians to be more aggressive in making this happen.”
“In all patients with heart failure and reduced ejection fraction, getting them on all four of these medicines as quickly as possible will give the best outcome. We’ve seen evidence in support of this from several broad population trials,” he added. “There are times when they can’t take all four but we should do our best to get there.”
Practical Considerations
Dr. Maddox pointed out that the Consensus Document is also trying to account for practical realities and barriers to heart failure treatment.
“When we think about these recommendations — and evidence that getting patients on all these medicines is valuable, we also focus on the fact that there are three major barriers that can get in the way of this and how to think about overcoming those barriers,” he said.
The barriers are comorbidities/side effects of medications, costs of the medicines, and systems of care that are needed to ensure patients can be treated with multiple medications in a timely fashion.
In terms of comorbidities/side effects, Dr. Maddox explained that patients with heart failure are generally older and are likely to have other comorbidities. “The more medicines we give, the more likely we are to run into side effects. So, we have produced some guidance on how to monitor for adverse effects and ways to mitigate these effects so the guideline recommended therapies can be continued without creating new harms.”
He gave the example of mineralocorticoid antagonists, which can sometimes elevate potassium levels, particularly if there is some underlying kidney disease, so clinicians are advised to recommend a low-potassium diet for these patients or the use of potassium binding agents that will also lower the amount of potassium in the blood stream; in this way, patients are able to continue the mineralocorticoid antagonist.
On costs, Dr. Maddox noted that the valsartan/sacubitril combination drug and SGLT inhibitors are new medicines and are expensive.
“They can be prohibitively expensive for patients who have suboptimal pharmacy benefits or who are uninsured.”
The Consensus Document therefore provided some guidance on ways to identify rebate programs, access insurance, and find different pathways to obtaining those drugs at a more reasonable price. It also advocated for policy changes to allow these medicines to be more accessible to more people.
More Use of Digital Tools
On the issue of systems of care, Dr. Maddox noted that the preexisting model of delivering care, which almost always involves the patient coming into the doctor’s office, invokes a high burden on both the system and most especially, the patient.
“Patients do not want to come back and forth to the doctor’s office multiple times in a few weeks. This is often a nonstarter, particularly for patients with busy lives,” he commented.
The Consensus Document advised more use of digital tools to provide remote care and contact with patients including sensors that can measure variables such as heart rate and blood pressure and video appointments.
“We are still working out what are the right models of care and how they can be performed safely and how they can be funded. But I think at the end of the day, this will give us more practical ways of getting people on multiple heart failure medicines and monitoring them safely without causing an undue burden for them logistically,” Dr. Maddox said.
He pointed out that there are a record number of medicines now available to treat heart failure, and while this is welcome, many of these patients are also on multiple other medications for other comorbidities as well.
“If you start giving patients seven, eight, or nine different medicines that they have to take every day, sometimes multiple times a day — that’s complicated medically, logistically, and financially. The potential for interaction and complications increases with every additional medication.”
Dr. Maddox also noted that patients have limits on how many medications they will accept. “It really helps if we have an engaged patient who has a good relationship with the care team to try to develop the right treatment plan that is going to meet their needs and give them the best possible health outcomes.”
It can take many visits to get the patient on all these medications and then up-titrate to target doses.
“We try and do a couple of things in each appointment. Often, we tend to start one or maybe two drugs at a time at a relatively low dose to avoid side effects, so we can be talking about 12-16 different encounters in total,” he said.
He recommended making a plan and the use of new technologies to manage each incremental step.
A Team Approach
Another issue that is discussed in the document is the use of a healthcare team to manage all the necessary appointments.
“It is no longer practical that one person can be the engineer for all this. It should be a team effort,” Dr. Maddox stated.
Responsibilities can be allocated across physicians, nurses, pharmacists, and even case managers, so that the team can take more of a population approach and develop a system to get patients on the multiple medications as quickly as possible.
“While this can still be quite a big burden for the patient, we need to figure out a system to make this as palatable as possible for them. Practices need to tailor this themselves according to what resources they have,” he added.
While most new patients will be routed to cardiologists to start their treatment plans, once on their initial medications and these have been up titrated to target levels, they should be able to be managed by primary care doctors, who will have the most holistic view of the patient and their other comorbidities, Dr. Maddox advised.
“Following this guidance should lead to more patients receiving evidence-based care which leads to better health outcomes, but delivered in a practical way that fits with their life reality and logistical needs,” he concluded.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
The American College of Cardiology has published a new update to its consensus decision pathway for the treatment of heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF).
Chair of the consensus document Writing Committee Thomas M. Maddox, MD, explained to this news organization that this new Decision Pathway provides a practical, streamlined update to frontline clinicians treating patients with heart failure and incorporates evidence from the 2022 AHA/ACC/HFSA Guideline for the Management of Heart Failure.
“While the AHA/ACC/HFSA Guidelines are wonderful in that they collate all the latest scientific evidence, they don’t speak as much to the practicalities of delivering the care. This is what this Decision Pathway document comes in — it is designed to help frontline clinicians with the practical reality of managing these patients,” Dr. Maddox, who is director of the Healthcare Innovation Lab at BJC HealthCare and the Washington University School of Medicine in St Louis, Missouri, commented.
The document, “Expert Consensus Decision Pathway for Optimization of Heart Failure Treatment: Answers to 10 Pivotal Issues About Heart Failure With Reduced Ejection Fraction,” was published online on March 8 in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology.
The authors provided guidance on introducing the numerous evidence-based therapies now available for HFrEF, improving adherence, overcoming treatment barriers, acknowledging contraindications and situations for which few data exist, affording expensive therapies, treating special cohorts, and making the transition to palliative care.
Rather than focusing on extensive text, the document provided practical tips, tables, and figures to make clear the steps, tools, and provisos needed to treat patients with heart failure successfully and expeditiously, they added.
Dr. Maddox reported that there are three main updated areas of advice on the treatment of heart failure in the new document.
Valsartan/Sacubitril First Line
One of the major changes involves an elevation for the status of the angiotensin receptor-neprilysin inhibitor (ARNI), Entresto (valsartan/sacubitril).
“It is now clear that this agent is superior to ACE-inhibitors or angiotensin receptor blockers in terms of reducing heart failure hospitalization and death, whereas previously it was seen as somewhat equivalent,” Dr. Maddox said. “So, barring a contraindication or another problem with getting the medication, this agent should be one of the first line medicines for all patients with heart failure and a reduced ejection fraction.”
Dual Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter 1/2 (SGLT1/2) Inhibitor
A second update involves the addition of sotagliflozin (a dual inhibitor of both SGLT1 and SGLT2) to the SGLT2 inhibitors as another first-line medication for patients with heart failure and reduced ejection fraction.
“We now have evidence that both SGLT2 and SGLT1 inhibitors are beneficial in reducing heart failure hospitalization and death. Previously we only had evidence on SGLT2 inhibitors — dapagliflozin and empagliflozin. Sotagliflozin is a newer agent, which inhibits both SGLT1 and SGLT2, and it turns out that inhibiting both are beneficial in heart failure. So, this gives us a third med in this category,” Dr. Maddox noted.
Rapid Initiation of the Four Pillars of Therapy
The document stated that more data have emerged recently to support early and rapid initiation and titration of the “four pillars” of medical therapy in heart failure to maximize the benefits of patient-reported outcomes and reduction in hospitalizations and mortality.
The four pillars of therapy are ARNI, a beta-blocker, a mineralocorticoid antagonist, and an SGLT inhibitor.
As an example, four-class medication initiation reduced the hazard of cardiovascular death or hospital admission for heart failure significantly (hazard ratio, 0.38) compared with therapy with just an angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor/angiotensin receptor blocker plus a beta-blocker, the document reported.
“What we realize now is that the more quickly we can get patients on all four of these drug classes and escalate to target doses or maximally tolerated doses ideally within 3 months, the better the outcome,” Dr. Maddox said.
“Unfortunately, right now there is very incomplete realization and recognition of that in clinical practice. So, we are trying to highlight the importance of this to encourage clinicians to be more aggressive in making this happen.”
“In all patients with heart failure and reduced ejection fraction, getting them on all four of these medicines as quickly as possible will give the best outcome. We’ve seen evidence in support of this from several broad population trials,” he added. “There are times when they can’t take all four but we should do our best to get there.”
Practical Considerations
Dr. Maddox pointed out that the Consensus Document is also trying to account for practical realities and barriers to heart failure treatment.
“When we think about these recommendations — and evidence that getting patients on all these medicines is valuable, we also focus on the fact that there are three major barriers that can get in the way of this and how to think about overcoming those barriers,” he said.
The barriers are comorbidities/side effects of medications, costs of the medicines, and systems of care that are needed to ensure patients can be treated with multiple medications in a timely fashion.
In terms of comorbidities/side effects, Dr. Maddox explained that patients with heart failure are generally older and are likely to have other comorbidities. “The more medicines we give, the more likely we are to run into side effects. So, we have produced some guidance on how to monitor for adverse effects and ways to mitigate these effects so the guideline recommended therapies can be continued without creating new harms.”
He gave the example of mineralocorticoid antagonists, which can sometimes elevate potassium levels, particularly if there is some underlying kidney disease, so clinicians are advised to recommend a low-potassium diet for these patients or the use of potassium binding agents that will also lower the amount of potassium in the blood stream; in this way, patients are able to continue the mineralocorticoid antagonist.
On costs, Dr. Maddox noted that the valsartan/sacubitril combination drug and SGLT inhibitors are new medicines and are expensive.
“They can be prohibitively expensive for patients who have suboptimal pharmacy benefits or who are uninsured.”
The Consensus Document therefore provided some guidance on ways to identify rebate programs, access insurance, and find different pathways to obtaining those drugs at a more reasonable price. It also advocated for policy changes to allow these medicines to be more accessible to more people.
More Use of Digital Tools
On the issue of systems of care, Dr. Maddox noted that the preexisting model of delivering care, which almost always involves the patient coming into the doctor’s office, invokes a high burden on both the system and most especially, the patient.
“Patients do not want to come back and forth to the doctor’s office multiple times in a few weeks. This is often a nonstarter, particularly for patients with busy lives,” he commented.
The Consensus Document advised more use of digital tools to provide remote care and contact with patients including sensors that can measure variables such as heart rate and blood pressure and video appointments.
“We are still working out what are the right models of care and how they can be performed safely and how they can be funded. But I think at the end of the day, this will give us more practical ways of getting people on multiple heart failure medicines and monitoring them safely without causing an undue burden for them logistically,” Dr. Maddox said.
He pointed out that there are a record number of medicines now available to treat heart failure, and while this is welcome, many of these patients are also on multiple other medications for other comorbidities as well.
“If you start giving patients seven, eight, or nine different medicines that they have to take every day, sometimes multiple times a day — that’s complicated medically, logistically, and financially. The potential for interaction and complications increases with every additional medication.”
Dr. Maddox also noted that patients have limits on how many medications they will accept. “It really helps if we have an engaged patient who has a good relationship with the care team to try to develop the right treatment plan that is going to meet their needs and give them the best possible health outcomes.”
It can take many visits to get the patient on all these medications and then up-titrate to target doses.
“We try and do a couple of things in each appointment. Often, we tend to start one or maybe two drugs at a time at a relatively low dose to avoid side effects, so we can be talking about 12-16 different encounters in total,” he said.
He recommended making a plan and the use of new technologies to manage each incremental step.
A Team Approach
Another issue that is discussed in the document is the use of a healthcare team to manage all the necessary appointments.
“It is no longer practical that one person can be the engineer for all this. It should be a team effort,” Dr. Maddox stated.
Responsibilities can be allocated across physicians, nurses, pharmacists, and even case managers, so that the team can take more of a population approach and develop a system to get patients on the multiple medications as quickly as possible.
“While this can still be quite a big burden for the patient, we need to figure out a system to make this as palatable as possible for them. Practices need to tailor this themselves according to what resources they have,” he added.
While most new patients will be routed to cardiologists to start their treatment plans, once on their initial medications and these have been up titrated to target levels, they should be able to be managed by primary care doctors, who will have the most holistic view of the patient and their other comorbidities, Dr. Maddox advised.
“Following this guidance should lead to more patients receiving evidence-based care which leads to better health outcomes, but delivered in a practical way that fits with their life reality and logistical needs,” he concluded.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
The American College of Cardiology has published a new update to its consensus decision pathway for the treatment of heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF).
Chair of the consensus document Writing Committee Thomas M. Maddox, MD, explained to this news organization that this new Decision Pathway provides a practical, streamlined update to frontline clinicians treating patients with heart failure and incorporates evidence from the 2022 AHA/ACC/HFSA Guideline for the Management of Heart Failure.
“While the AHA/ACC/HFSA Guidelines are wonderful in that they collate all the latest scientific evidence, they don’t speak as much to the practicalities of delivering the care. This is what this Decision Pathway document comes in — it is designed to help frontline clinicians with the practical reality of managing these patients,” Dr. Maddox, who is director of the Healthcare Innovation Lab at BJC HealthCare and the Washington University School of Medicine in St Louis, Missouri, commented.
The document, “Expert Consensus Decision Pathway for Optimization of Heart Failure Treatment: Answers to 10 Pivotal Issues About Heart Failure With Reduced Ejection Fraction,” was published online on March 8 in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology.
The authors provided guidance on introducing the numerous evidence-based therapies now available for HFrEF, improving adherence, overcoming treatment barriers, acknowledging contraindications and situations for which few data exist, affording expensive therapies, treating special cohorts, and making the transition to palliative care.
Rather than focusing on extensive text, the document provided practical tips, tables, and figures to make clear the steps, tools, and provisos needed to treat patients with heart failure successfully and expeditiously, they added.
Dr. Maddox reported that there are three main updated areas of advice on the treatment of heart failure in the new document.
Valsartan/Sacubitril First Line
One of the major changes involves an elevation for the status of the angiotensin receptor-neprilysin inhibitor (ARNI), Entresto (valsartan/sacubitril).
“It is now clear that this agent is superior to ACE-inhibitors or angiotensin receptor blockers in terms of reducing heart failure hospitalization and death, whereas previously it was seen as somewhat equivalent,” Dr. Maddox said. “So, barring a contraindication or another problem with getting the medication, this agent should be one of the first line medicines for all patients with heart failure and a reduced ejection fraction.”
Dual Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter 1/2 (SGLT1/2) Inhibitor
A second update involves the addition of sotagliflozin (a dual inhibitor of both SGLT1 and SGLT2) to the SGLT2 inhibitors as another first-line medication for patients with heart failure and reduced ejection fraction.
“We now have evidence that both SGLT2 and SGLT1 inhibitors are beneficial in reducing heart failure hospitalization and death. Previously we only had evidence on SGLT2 inhibitors — dapagliflozin and empagliflozin. Sotagliflozin is a newer agent, which inhibits both SGLT1 and SGLT2, and it turns out that inhibiting both are beneficial in heart failure. So, this gives us a third med in this category,” Dr. Maddox noted.
Rapid Initiation of the Four Pillars of Therapy
The document stated that more data have emerged recently to support early and rapid initiation and titration of the “four pillars” of medical therapy in heart failure to maximize the benefits of patient-reported outcomes and reduction in hospitalizations and mortality.
The four pillars of therapy are ARNI, a beta-blocker, a mineralocorticoid antagonist, and an SGLT inhibitor.
As an example, four-class medication initiation reduced the hazard of cardiovascular death or hospital admission for heart failure significantly (hazard ratio, 0.38) compared with therapy with just an angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor/angiotensin receptor blocker plus a beta-blocker, the document reported.
“What we realize now is that the more quickly we can get patients on all four of these drug classes and escalate to target doses or maximally tolerated doses ideally within 3 months, the better the outcome,” Dr. Maddox said.
“Unfortunately, right now there is very incomplete realization and recognition of that in clinical practice. So, we are trying to highlight the importance of this to encourage clinicians to be more aggressive in making this happen.”
“In all patients with heart failure and reduced ejection fraction, getting them on all four of these medicines as quickly as possible will give the best outcome. We’ve seen evidence in support of this from several broad population trials,” he added. “There are times when they can’t take all four but we should do our best to get there.”
Practical Considerations
Dr. Maddox pointed out that the Consensus Document is also trying to account for practical realities and barriers to heart failure treatment.
“When we think about these recommendations — and evidence that getting patients on all these medicines is valuable, we also focus on the fact that there are three major barriers that can get in the way of this and how to think about overcoming those barriers,” he said.
The barriers are comorbidities/side effects of medications, costs of the medicines, and systems of care that are needed to ensure patients can be treated with multiple medications in a timely fashion.
In terms of comorbidities/side effects, Dr. Maddox explained that patients with heart failure are generally older and are likely to have other comorbidities. “The more medicines we give, the more likely we are to run into side effects. So, we have produced some guidance on how to monitor for adverse effects and ways to mitigate these effects so the guideline recommended therapies can be continued without creating new harms.”
He gave the example of mineralocorticoid antagonists, which can sometimes elevate potassium levels, particularly if there is some underlying kidney disease, so clinicians are advised to recommend a low-potassium diet for these patients or the use of potassium binding agents that will also lower the amount of potassium in the blood stream; in this way, patients are able to continue the mineralocorticoid antagonist.
On costs, Dr. Maddox noted that the valsartan/sacubitril combination drug and SGLT inhibitors are new medicines and are expensive.
“They can be prohibitively expensive for patients who have suboptimal pharmacy benefits or who are uninsured.”
The Consensus Document therefore provided some guidance on ways to identify rebate programs, access insurance, and find different pathways to obtaining those drugs at a more reasonable price. It also advocated for policy changes to allow these medicines to be more accessible to more people.
More Use of Digital Tools
On the issue of systems of care, Dr. Maddox noted that the preexisting model of delivering care, which almost always involves the patient coming into the doctor’s office, invokes a high burden on both the system and most especially, the patient.
“Patients do not want to come back and forth to the doctor’s office multiple times in a few weeks. This is often a nonstarter, particularly for patients with busy lives,” he commented.
The Consensus Document advised more use of digital tools to provide remote care and contact with patients including sensors that can measure variables such as heart rate and blood pressure and video appointments.
“We are still working out what are the right models of care and how they can be performed safely and how they can be funded. But I think at the end of the day, this will give us more practical ways of getting people on multiple heart failure medicines and monitoring them safely without causing an undue burden for them logistically,” Dr. Maddox said.
He pointed out that there are a record number of medicines now available to treat heart failure, and while this is welcome, many of these patients are also on multiple other medications for other comorbidities as well.
“If you start giving patients seven, eight, or nine different medicines that they have to take every day, sometimes multiple times a day — that’s complicated medically, logistically, and financially. The potential for interaction and complications increases with every additional medication.”
Dr. Maddox also noted that patients have limits on how many medications they will accept. “It really helps if we have an engaged patient who has a good relationship with the care team to try to develop the right treatment plan that is going to meet their needs and give them the best possible health outcomes.”
It can take many visits to get the patient on all these medications and then up-titrate to target doses.
“We try and do a couple of things in each appointment. Often, we tend to start one or maybe two drugs at a time at a relatively low dose to avoid side effects, so we can be talking about 12-16 different encounters in total,” he said.
He recommended making a plan and the use of new technologies to manage each incremental step.
A Team Approach
Another issue that is discussed in the document is the use of a healthcare team to manage all the necessary appointments.
“It is no longer practical that one person can be the engineer for all this. It should be a team effort,” Dr. Maddox stated.
Responsibilities can be allocated across physicians, nurses, pharmacists, and even case managers, so that the team can take more of a population approach and develop a system to get patients on the multiple medications as quickly as possible.
“While this can still be quite a big burden for the patient, we need to figure out a system to make this as palatable as possible for them. Practices need to tailor this themselves according to what resources they have,” he added.
While most new patients will be routed to cardiologists to start their treatment plans, once on their initial medications and these have been up titrated to target levels, they should be able to be managed by primary care doctors, who will have the most holistic view of the patient and their other comorbidities, Dr. Maddox advised.
“Following this guidance should lead to more patients receiving evidence-based care which leads to better health outcomes, but delivered in a practical way that fits with their life reality and logistical needs,” he concluded.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Vitamin D Supplements May Be a Double-Edged Sword
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Welcome to Impact Factor, your weekly dose of commentary on a new medical study. I’m Dr F. Perry Wilson of the Yale School of Medicine.
Imagine, if you will, the great Cathedral of Our Lady of Correlation. You walk through the majestic oak doors depicting the link between ice cream sales and shark attacks, past the rose window depicting the cardiovascular benefits of red wine, and down the aisles frescoed in dramatic images showing how Facebook usage is associated with less life satisfaction. And then you reach the altar, the holy of holies where, emblazoned in shimmering pyrite, you see the patron saint of this church: vitamin D.
Yes, if you’ve watched this space, then you know that I have little truck with the wildly popular supplement. In all of clinical research, I believe that there is no molecule with stronger data for correlation and weaker data for causation.
Low serum vitamin D levels have been linked to higher risks for heart disease, cancer, falls, COVID, dementia, C diff, and others. And yet, when we do randomized trials of vitamin D supplementation — the thing that can prove that the low level was causally linked to the outcome of interest — we get negative results.
Trials aren’t perfect, of course, and we’ll talk in a moment about a big one that had some issues. But we are at a point where we need to either be vitamin D apologists, saying, “Forget what those lying RCTs tell you and buy this supplement” — an $800 million-a-year industry, by the way — or conclude that vitamin D levels are a convenient marker of various lifestyle factors that are associated with better outcomes: markers of exercise, getting outside, eating a varied diet.
Or perhaps vitamin D supplements have real effects. It’s just that the beneficial effects are matched by the harmful ones. Stay tuned.
The Women’s Health Initiative remains among the largest randomized trials of vitamin D and calcium supplementation ever conducted — and a major contributor to the negative outcomes of vitamin D trials.
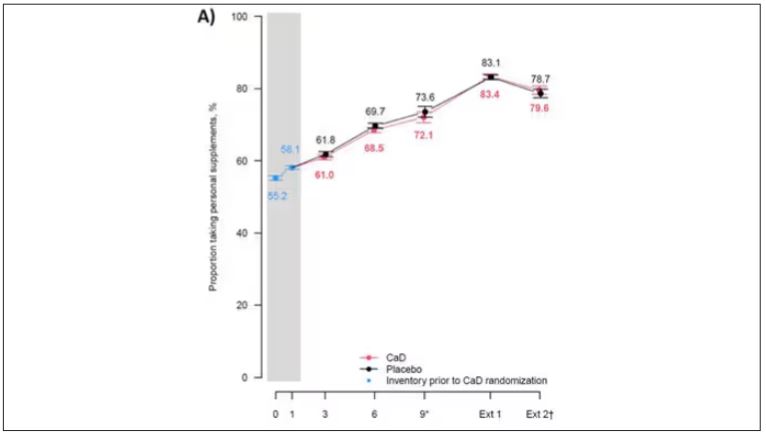
But if you dig into the inclusion and exclusion criteria for this trial, you’ll find that individuals were allowed to continue taking vitamins and supplements while they were in the trial, regardless of their randomization status. In fact, the majority took supplements at baseline, and more took supplements over time.
That means, of course, that people in the placebo group, who were getting sugar pills instead of vitamin D and calcium, may have been taking vitamin D and calcium on the side. That would certainly bias the results of the trial toward the null, which is what the primary analyses showed. To wit, the original analysis of the Women’s Health Initiative trial showed no effect of randomization to vitamin D supplementation on improving cancer or cardiovascular outcomes.
But the Women’s Health Initiative trial started 30 years ago. Today, with the benefit of decades of follow-up, we can re-investigate — and perhaps re-litigate — those findings, courtesy of this study, “Long-Term Effect of Randomization to Calcium and Vitamin D Supplementation on Health in Older Women” appearing in Annals of Internal Medicine.
Dr Cynthia Thomson, of the Mel and Enid Zuckerman College of Public Health at the University of Arizona, and colleagues led this updated analysis focused on two findings that had been hinted at, but not statistically confirmed, in other vitamin D studies: a potential for the supplement to reduce the risk for cancer, and a potential for it to increase the risk for heart disease.
The randomized trial itself only lasted 7 years. What we are seeing in this analysis of 36,282 women is outcomes that happened at any time from randomization to the end of 2023 — around 20 years after the randomization to supplementation stopped. But, the researchers would argue, that’s probably okay. Cancer and heart disease take time to develop; we see lung cancer long after people stop smoking. So a history of consistent vitamin D supplementation may indeed be protective — or harmful.
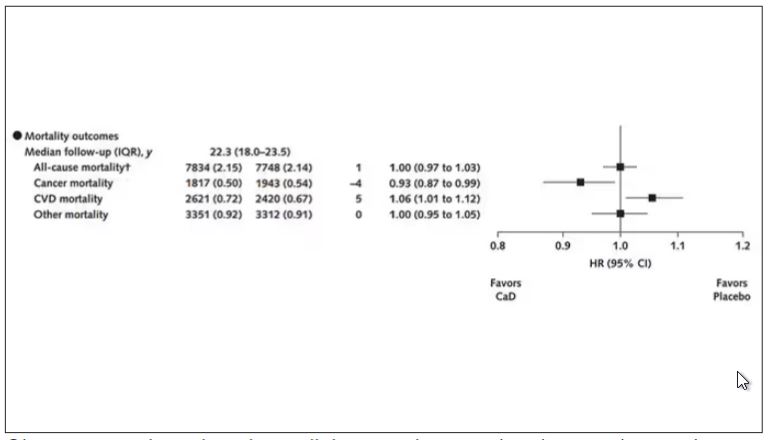
Here are the top-line results. Those randomized to vitamin D and calcium supplementation had a 7% reduction in the rate of death from cancer, driven primarily by a reduction in colorectal cancer. This was statistically significant. Also statistically significant? Those randomized to supplementation had a 6% increase in the rate of death from cardiovascular disease. Put those findings together and what do you get? Stone-cold nothing, in terms of overall mortality.
Okay, you say, but what about all that supplementation that was happening outside of the context of the trial, biasing our results toward the null?
The researchers finally clue us in.
First of all, I’ll tell you that, yes, people who were supplementing outside of the trial had higher baseline vitamin D levels — a median of 54.5 nmol/L vs 32.8 nmol/L. This may be because they were supplementing with vitamin D, but it could also be because people who take supplements tend to do other healthy things — another correlation to add to the great cathedral.
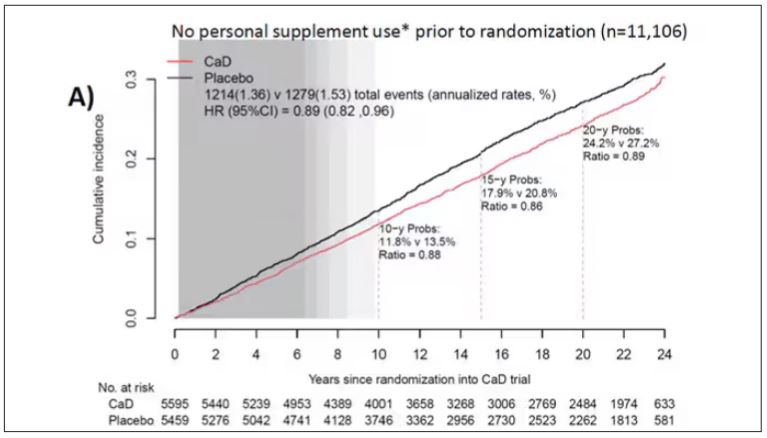
To get a better view of the real effects of randomization, the authors restricted the analysis to just those who did not use outside supplements. If vitamin D supplements help, then these are the people they should help. This group had about a 11% reduction in the incidence of cancer — statistically significant — and a 7% reduction in cancer mortality that did not meet the bar for statistical significance.
There was no increase in cardiovascular disease among this group. But this small effect on cancer was nowhere near enough to significantly reduce the rate of all-cause mortality.
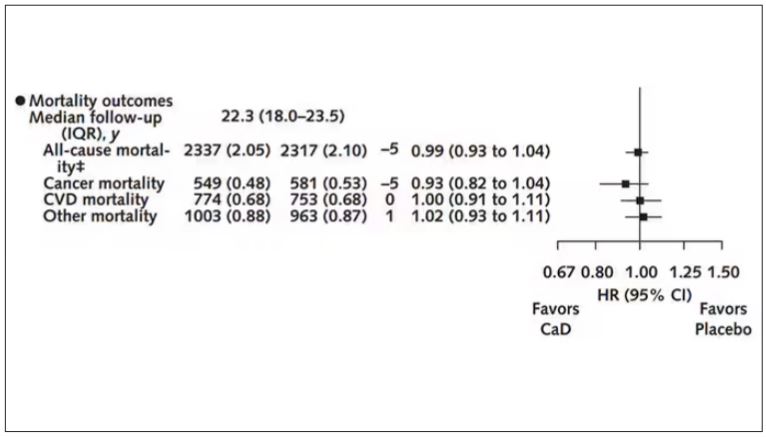
Among those using supplements, vitamin D supplementation didn’t really move the needle on any outcome.
I know what you’re thinking: How many of these women were vitamin D deficient when we got started? These results may simply be telling us that people who have normal vitamin D levels are fine to go without supplementation.
Nearly three fourths of women who were not taking supplements entered the trial with vitamin D levels below the 50 nmol/L cutoff that the authors suggest would qualify for deficiency. Around half of those who used supplements were deficient. And yet, frustratingly, I could not find data on the effect of randomization to supplementation stratified by baseline vitamin D level. I even reached out to Dr Thomson to ask about this. She replied, “We did not stratify on baseline values because the numbers are too small statistically to test this.” Sorry.
In the meantime, I can tell you that for your “average woman,” vitamin D supplementation likely has no effect on mortality. It might modestly reduce the risk for certain cancers while increasing the risk for heart disease (probably through coronary calcification). So, there might be some room for personalization here. Perhaps women with a strong family history of cancer or other risk factors would do better with supplements, and those with a high risk for heart disease would do worse. Seems like a strategy that could be tested in a clinical trial. But maybe we could ask the participants to give up their extracurricular supplement use before they enter the trial. F. Perry Wilson, MD, MSCE, has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
F. Perry Wilson, MD, MSCE, is an associate professor of medicine and public health and director of Yale’s Clinical and Translational Research Accelerator. His science communication work can be found in the Huffington Post, on NPR, and here on Medscape. He tweets @fperrywilson and his book, How Medicine Works and When It Doesn’t, is available now.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Welcome to Impact Factor, your weekly dose of commentary on a new medical study. I’m Dr F. Perry Wilson of the Yale School of Medicine.
Imagine, if you will, the great Cathedral of Our Lady of Correlation. You walk through the majestic oak doors depicting the link between ice cream sales and shark attacks, past the rose window depicting the cardiovascular benefits of red wine, and down the aisles frescoed in dramatic images showing how Facebook usage is associated with less life satisfaction. And then you reach the altar, the holy of holies where, emblazoned in shimmering pyrite, you see the patron saint of this church: vitamin D.
Yes, if you’ve watched this space, then you know that I have little truck with the wildly popular supplement. In all of clinical research, I believe that there is no molecule with stronger data for correlation and weaker data for causation.
Low serum vitamin D levels have been linked to higher risks for heart disease, cancer, falls, COVID, dementia, C diff, and others. And yet, when we do randomized trials of vitamin D supplementation — the thing that can prove that the low level was causally linked to the outcome of interest — we get negative results.
Trials aren’t perfect, of course, and we’ll talk in a moment about a big one that had some issues. But we are at a point where we need to either be vitamin D apologists, saying, “Forget what those lying RCTs tell you and buy this supplement” — an $800 million-a-year industry, by the way — or conclude that vitamin D levels are a convenient marker of various lifestyle factors that are associated with better outcomes: markers of exercise, getting outside, eating a varied diet.
Or perhaps vitamin D supplements have real effects. It’s just that the beneficial effects are matched by the harmful ones. Stay tuned.
The Women’s Health Initiative remains among the largest randomized trials of vitamin D and calcium supplementation ever conducted — and a major contributor to the negative outcomes of vitamin D trials.
But if you dig into the inclusion and exclusion criteria for this trial, you’ll find that individuals were allowed to continue taking vitamins and supplements while they were in the trial, regardless of their randomization status. In fact, the majority took supplements at baseline, and more took supplements over time.
That means, of course, that people in the placebo group, who were getting sugar pills instead of vitamin D and calcium, may have been taking vitamin D and calcium on the side. That would certainly bias the results of the trial toward the null, which is what the primary analyses showed. To wit, the original analysis of the Women’s Health Initiative trial showed no effect of randomization to vitamin D supplementation on improving cancer or cardiovascular outcomes.
But the Women’s Health Initiative trial started 30 years ago. Today, with the benefit of decades of follow-up, we can re-investigate — and perhaps re-litigate — those findings, courtesy of this study, “Long-Term Effect of Randomization to Calcium and Vitamin D Supplementation on Health in Older Women” appearing in Annals of Internal Medicine.
Dr Cynthia Thomson, of the Mel and Enid Zuckerman College of Public Health at the University of Arizona, and colleagues led this updated analysis focused on two findings that had been hinted at, but not statistically confirmed, in other vitamin D studies: a potential for the supplement to reduce the risk for cancer, and a potential for it to increase the risk for heart disease.
The randomized trial itself only lasted 7 years. What we are seeing in this analysis of 36,282 women is outcomes that happened at any time from randomization to the end of 2023 — around 20 years after the randomization to supplementation stopped. But, the researchers would argue, that’s probably okay. Cancer and heart disease take time to develop; we see lung cancer long after people stop smoking. So a history of consistent vitamin D supplementation may indeed be protective — or harmful.
Here are the top-line results. Those randomized to vitamin D and calcium supplementation had a 7% reduction in the rate of death from cancer, driven primarily by a reduction in colorectal cancer. This was statistically significant. Also statistically significant? Those randomized to supplementation had a 6% increase in the rate of death from cardiovascular disease. Put those findings together and what do you get? Stone-cold nothing, in terms of overall mortality.
Okay, you say, but what about all that supplementation that was happening outside of the context of the trial, biasing our results toward the null?
The researchers finally clue us in.
First of all, I’ll tell you that, yes, people who were supplementing outside of the trial had higher baseline vitamin D levels — a median of 54.5 nmol/L vs 32.8 nmol/L. This may be because they were supplementing with vitamin D, but it could also be because people who take supplements tend to do other healthy things — another correlation to add to the great cathedral.
To get a better view of the real effects of randomization, the authors restricted the analysis to just those who did not use outside supplements. If vitamin D supplements help, then these are the people they should help. This group had about a 11% reduction in the incidence of cancer — statistically significant — and a 7% reduction in cancer mortality that did not meet the bar for statistical significance.
There was no increase in cardiovascular disease among this group. But this small effect on cancer was nowhere near enough to significantly reduce the rate of all-cause mortality.
Among those using supplements, vitamin D supplementation didn’t really move the needle on any outcome.
I know what you’re thinking: How many of these women were vitamin D deficient when we got started? These results may simply be telling us that people who have normal vitamin D levels are fine to go without supplementation.
Nearly three fourths of women who were not taking supplements entered the trial with vitamin D levels below the 50 nmol/L cutoff that the authors suggest would qualify for deficiency. Around half of those who used supplements were deficient. And yet, frustratingly, I could not find data on the effect of randomization to supplementation stratified by baseline vitamin D level. I even reached out to Dr Thomson to ask about this. She replied, “We did not stratify on baseline values because the numbers are too small statistically to test this.” Sorry.
In the meantime, I can tell you that for your “average woman,” vitamin D supplementation likely has no effect on mortality. It might modestly reduce the risk for certain cancers while increasing the risk for heart disease (probably through coronary calcification). So, there might be some room for personalization here. Perhaps women with a strong family history of cancer or other risk factors would do better with supplements, and those with a high risk for heart disease would do worse. Seems like a strategy that could be tested in a clinical trial. But maybe we could ask the participants to give up their extracurricular supplement use before they enter the trial. F. Perry Wilson, MD, MSCE, has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
F. Perry Wilson, MD, MSCE, is an associate professor of medicine and public health and director of Yale’s Clinical and Translational Research Accelerator. His science communication work can be found in the Huffington Post, on NPR, and here on Medscape. He tweets @fperrywilson and his book, How Medicine Works and When It Doesn’t, is available now.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Welcome to Impact Factor, your weekly dose of commentary on a new medical study. I’m Dr F. Perry Wilson of the Yale School of Medicine.
Imagine, if you will, the great Cathedral of Our Lady of Correlation. You walk through the majestic oak doors depicting the link between ice cream sales and shark attacks, past the rose window depicting the cardiovascular benefits of red wine, and down the aisles frescoed in dramatic images showing how Facebook usage is associated with less life satisfaction. And then you reach the altar, the holy of holies where, emblazoned in shimmering pyrite, you see the patron saint of this church: vitamin D.
Yes, if you’ve watched this space, then you know that I have little truck with the wildly popular supplement. In all of clinical research, I believe that there is no molecule with stronger data for correlation and weaker data for causation.
Low serum vitamin D levels have been linked to higher risks for heart disease, cancer, falls, COVID, dementia, C diff, and others. And yet, when we do randomized trials of vitamin D supplementation — the thing that can prove that the low level was causally linked to the outcome of interest — we get negative results.
Trials aren’t perfect, of course, and we’ll talk in a moment about a big one that had some issues. But we are at a point where we need to either be vitamin D apologists, saying, “Forget what those lying RCTs tell you and buy this supplement” — an $800 million-a-year industry, by the way — or conclude that vitamin D levels are a convenient marker of various lifestyle factors that are associated with better outcomes: markers of exercise, getting outside, eating a varied diet.
Or perhaps vitamin D supplements have real effects. It’s just that the beneficial effects are matched by the harmful ones. Stay tuned.
The Women’s Health Initiative remains among the largest randomized trials of vitamin D and calcium supplementation ever conducted — and a major contributor to the negative outcomes of vitamin D trials.
But if you dig into the inclusion and exclusion criteria for this trial, you’ll find that individuals were allowed to continue taking vitamins and supplements while they were in the trial, regardless of their randomization status. In fact, the majority took supplements at baseline, and more took supplements over time.
That means, of course, that people in the placebo group, who were getting sugar pills instead of vitamin D and calcium, may have been taking vitamin D and calcium on the side. That would certainly bias the results of the trial toward the null, which is what the primary analyses showed. To wit, the original analysis of the Women’s Health Initiative trial showed no effect of randomization to vitamin D supplementation on improving cancer or cardiovascular outcomes.
But the Women’s Health Initiative trial started 30 years ago. Today, with the benefit of decades of follow-up, we can re-investigate — and perhaps re-litigate — those findings, courtesy of this study, “Long-Term Effect of Randomization to Calcium and Vitamin D Supplementation on Health in Older Women” appearing in Annals of Internal Medicine.
Dr Cynthia Thomson, of the Mel and Enid Zuckerman College of Public Health at the University of Arizona, and colleagues led this updated analysis focused on two findings that had been hinted at, but not statistically confirmed, in other vitamin D studies: a potential for the supplement to reduce the risk for cancer, and a potential for it to increase the risk for heart disease.
The randomized trial itself only lasted 7 years. What we are seeing in this analysis of 36,282 women is outcomes that happened at any time from randomization to the end of 2023 — around 20 years after the randomization to supplementation stopped. But, the researchers would argue, that’s probably okay. Cancer and heart disease take time to develop; we see lung cancer long after people stop smoking. So a history of consistent vitamin D supplementation may indeed be protective — or harmful.
Here are the top-line results. Those randomized to vitamin D and calcium supplementation had a 7% reduction in the rate of death from cancer, driven primarily by a reduction in colorectal cancer. This was statistically significant. Also statistically significant? Those randomized to supplementation had a 6% increase in the rate of death from cardiovascular disease. Put those findings together and what do you get? Stone-cold nothing, in terms of overall mortality.
Okay, you say, but what about all that supplementation that was happening outside of the context of the trial, biasing our results toward the null?
The researchers finally clue us in.
First of all, I’ll tell you that, yes, people who were supplementing outside of the trial had higher baseline vitamin D levels — a median of 54.5 nmol/L vs 32.8 nmol/L. This may be because they were supplementing with vitamin D, but it could also be because people who take supplements tend to do other healthy things — another correlation to add to the great cathedral.
To get a better view of the real effects of randomization, the authors restricted the analysis to just those who did not use outside supplements. If vitamin D supplements help, then these are the people they should help. This group had about a 11% reduction in the incidence of cancer — statistically significant — and a 7% reduction in cancer mortality that did not meet the bar for statistical significance.
There was no increase in cardiovascular disease among this group. But this small effect on cancer was nowhere near enough to significantly reduce the rate of all-cause mortality.
Among those using supplements, vitamin D supplementation didn’t really move the needle on any outcome.
I know what you’re thinking: How many of these women were vitamin D deficient when we got started? These results may simply be telling us that people who have normal vitamin D levels are fine to go without supplementation.
Nearly three fourths of women who were not taking supplements entered the trial with vitamin D levels below the 50 nmol/L cutoff that the authors suggest would qualify for deficiency. Around half of those who used supplements were deficient. And yet, frustratingly, I could not find data on the effect of randomization to supplementation stratified by baseline vitamin D level. I even reached out to Dr Thomson to ask about this. She replied, “We did not stratify on baseline values because the numbers are too small statistically to test this.” Sorry.
In the meantime, I can tell you that for your “average woman,” vitamin D supplementation likely has no effect on mortality. It might modestly reduce the risk for certain cancers while increasing the risk for heart disease (probably through coronary calcification). So, there might be some room for personalization here. Perhaps women with a strong family history of cancer or other risk factors would do better with supplements, and those with a high risk for heart disease would do worse. Seems like a strategy that could be tested in a clinical trial. But maybe we could ask the participants to give up their extracurricular supplement use before they enter the trial. F. Perry Wilson, MD, MSCE, has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
F. Perry Wilson, MD, MSCE, is an associate professor of medicine and public health and director of Yale’s Clinical and Translational Research Accelerator. His science communication work can be found in the Huffington Post, on NPR, and here on Medscape. He tweets @fperrywilson and his book, How Medicine Works and When It Doesn’t, is available now.
Long-Term Calcium and Vitamin D: Cancer Deaths Down, CVD Deaths Up in Older Women?
Some doctors may be scratching their heads over a new analysis reporting that combined calcium and vitamin D (CaD) supplements appear to be associated with a slight 6% increase in cardiovascular (CVD) mortality, a slight 7% decrease in cancer risk, and no effect on osteoporotic fracture in postmenopausal women.
The study, in Annals of Internal Medicine, found no effect of supplementation on all-cause mortality.
The findings emerged from an analysis of more than 20 years’ follow-up data on a randomized trial in postmenopausal women conducted as part of the Women’s Health Initiative (WHI).
Cynthia A. Thomson, PhD, RD, first author and cancer prevention scientist at the Arizona Cancer Center and a professor of health promotion sciences at the University of Arizona in Tucson said the findings recommend individualized assessment of the need for supplements for older women as they consider them in hopes of preventing fractures.
“Evaluate your patients individually and understand that there are some who may benefit from supplementation, for example, in terms of reducing colorectal cancer mortality,” Dr. Thomson said in an interview. The approach should be nuanced. “If you check the adequacy of vitamin D and calcium in their diets, supplementation may not be needed.” She added that supplementation is best considered in the context of a woman’s overall health profile, including risk factors for fracture, heart disease, and cancer, especially colorectal cancer (CRC).
Study Details
The investigators conducted postintervention follow-up of the WHI’s 7-year multicenter randomized intervention trial of CaD vs placebo.
Since existing evidence of long-term health outcomes was limited, the trial, begun in 1999 and closed in 2005, enrolled 36,282 postmenopausal women (mean age 62) with no history of breast or colorectal cancer. They were randomly assigned 1:1 to supplementation with 1000 mg of calcium carbonate (400 mg elemental calcium) plus 400 IU of vitamin D3 daily or placebo, taken twice daily in half doses.
Study outcomes were incidence of CRC, total and invasive breast cancer; disease-specific and all-cause mortality; total CVD; and hip fracture measured through December 2020, with analyses stratified by personal supplement usage.
Cancer. CaD was associated with reduced incident total cancer, CRC, and invasive breast cancer — notably among participants not taking CaD before randomization. Cancer incidence estimates varied widely, the authors noted, when stratified by supplement use before randomization. Noting that CaD seemed to have more cancer-related impact in those without prior supplementation, the authors suggested supplementation may affect cancer biology primarily by augmenting nutrient insufficiency.
An estimated 7% reduction in cancer mortality was observed after a median cumulative follow-up of 22.3 years: 1817 vs 1943 deaths (hazard ratio, 0.93; 95% CI, 0.87-0.99).
CVD. An estimated 6% increase in CVD mortality was seen in the CaD group: 2621 vs 2420 deaths (HR, 1.06; 95% CI, 1.01-1.12). Pretrial supplement users were found to be at higher CVD risk.
Hip fracture. No effect on hip fracture risk was measured, but the authors cautioned that hip fracture and CVD outcomes were available only for a subset of participants, and the effects of calcium alone vs vitamin D alone vs the combination could not be disentangled.
In a small subgroup analysis, some CaD users were seen to respond in terms of bone mineral density but since only 4 of the study’s 40 sites collected such information, the study was underpowered to examine the effect. ”Many other studies, however, show a response to supplementation in women who already have bone mineral deficits,” Dr. Thomson said.
The Calcification Question
One of the possible mechanisms of harm is that high-dose calcium supplements can increase the rate of blood coagulation and promote vascular calcification, said Emma Laing, PhD, RD, director of dietetics at the University of Georgia in Athens and a spokesperson for the Chicago-based Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics.
“Other factors that should be considered when determining a patient’s CVD risk are race, genetic predisposition, medical and social history, response to stress, and lifestyle behaviors, as well as the length of time supplements have been consumed,” added Dr. Laing, who was not involved in the WHI analysis.
“We asked ourselves if CaD supplements might contribute to calcification of the coronary arteries, since some believe this to be the case, although the literature is mixed,” said Dr. Thomson.
“So we did a shorter ancillary study in a small sample of several hundred [women] to see if there was any increase in calcification” and no difference was seen on imaging across the two arms. “However, women who were already on supplements before entering the study seemed to be at higher CVD risk,” she said.
Added study coauthor JoAnn E. Manson, MD, DrPH, chief of the division of preventive medicine at Brigham and Women’s Hospital and professor of women’s health at Harvard Medical School, both in Boston: “With no increase or decrease in coronary artery calcium at the end of the trial, we don’t believe starting or continuing calcium/vitamin D supplements should require screening for coronary artery disease.”
Some randomized trials and systematic reviews, however, have observed an increased risk of CVD in healthy patients on calcium supplements, with one Korean meta-analysis reporting a 15% increase in CVD risk in healthy postmenopausal women taking calcium supplements. Another meta-analysis found a link between calcium supplements and a greater risk of various cardiovascular outcomes, especially myocardial infarction.
Vitamin D Supplementation
As for vitamin D only supplementation, an updated meta-analysis including more than 83,000 individuals showed that it confers no cardiovascular protection and is therefore not indicated for this purpose.
Practice Considerations
Offering an outsider’s perspective, Sarah G. Candler, MD, MPH, an internist in Houston specializing in primary care for older high-risk adults, said: “Unfortunately, this latest study continues the trend of creating more questions than answers. If the adverse outcome of CVD death is a result of supplementation, it is unclear if this is due to the vitamin D, the calcium, or both. And it is unclear if this is dose dependent, time dependent, or due to concurrent risk factors unique to certain populations.
“It is recommended that patients at risk of osteoporosis based on age, sex, medications, and lifestyle be screened for osteoporosis and treated accordingly, including supplementation with CaD,” Dr. Candler said. “It remains unclear whether supplementation with CaD in the absence of osteoporosis and osteopenia is net beneficial or harmful, and at this time I would not recommend it to my patients.”
Added Dr. Manson: “The very small increase seen in cardiovascular mortality wouldn’t be a reason to discontinue supplementation among women who have been advised by their healthcare providers to take these supplements for bone health or other purposes.
“Among those at usual risk of fracture, we recommend trying to obtain adequate calcium and vitamin D from food sources first and to use supplements only for the purpose of filling gaps in intake,” Dr. Manson continued. Overall, the findings support the national recommended dietary allowances for daily calcium intake of 1200 mg and daily vitamin D intake of 600-800 IU among postmenopausal women for maintenance of bone health, she said.
While a 2022 study found that vitamin D supplementation alone did not prevent fractures in healthy adults, other research has shown that a calcium/vitamin D combination is more likely to protect the skeleton.
“Patients at risk for fractures will probably benefit from calcium and/or vitamin D supplementation if they do not meet dietary intake requirements, have malabsorption syndromes, are taking medications that affect nutrient absorption, or if they are older and not regularly exposed to sunlight,” said Dr. Laing. “A combination of biochemical, imaging, functional, and dietary intake data can help determine if a supplement is warranted.”
She stressed that additional research is needed in more diverse populations before changing practice guidelines. “However, doctors should continue to weigh the risks and benefits of prescribing supplements for each patient.”
The WHI program is funded by the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. Dr. Thomson disclosed no competing interests. Dr. Manson reported a relationship with Mars Edge. Multiple authors reported grant support from government funding agencies. The outside commentators had no relevant competing interests to disclose.
Some doctors may be scratching their heads over a new analysis reporting that combined calcium and vitamin D (CaD) supplements appear to be associated with a slight 6% increase in cardiovascular (CVD) mortality, a slight 7% decrease in cancer risk, and no effect on osteoporotic fracture in postmenopausal women.
The study, in Annals of Internal Medicine, found no effect of supplementation on all-cause mortality.
The findings emerged from an analysis of more than 20 years’ follow-up data on a randomized trial in postmenopausal women conducted as part of the Women’s Health Initiative (WHI).
Cynthia A. Thomson, PhD, RD, first author and cancer prevention scientist at the Arizona Cancer Center and a professor of health promotion sciences at the University of Arizona in Tucson said the findings recommend individualized assessment of the need for supplements for older women as they consider them in hopes of preventing fractures.
“Evaluate your patients individually and understand that there are some who may benefit from supplementation, for example, in terms of reducing colorectal cancer mortality,” Dr. Thomson said in an interview. The approach should be nuanced. “If you check the adequacy of vitamin D and calcium in their diets, supplementation may not be needed.” She added that supplementation is best considered in the context of a woman’s overall health profile, including risk factors for fracture, heart disease, and cancer, especially colorectal cancer (CRC).
Study Details
The investigators conducted postintervention follow-up of the WHI’s 7-year multicenter randomized intervention trial of CaD vs placebo.
Since existing evidence of long-term health outcomes was limited, the trial, begun in 1999 and closed in 2005, enrolled 36,282 postmenopausal women (mean age 62) with no history of breast or colorectal cancer. They were randomly assigned 1:1 to supplementation with 1000 mg of calcium carbonate (400 mg elemental calcium) plus 400 IU of vitamin D3 daily or placebo, taken twice daily in half doses.
Study outcomes were incidence of CRC, total and invasive breast cancer; disease-specific and all-cause mortality; total CVD; and hip fracture measured through December 2020, with analyses stratified by personal supplement usage.
Cancer. CaD was associated with reduced incident total cancer, CRC, and invasive breast cancer — notably among participants not taking CaD before randomization. Cancer incidence estimates varied widely, the authors noted, when stratified by supplement use before randomization. Noting that CaD seemed to have more cancer-related impact in those without prior supplementation, the authors suggested supplementation may affect cancer biology primarily by augmenting nutrient insufficiency.
An estimated 7% reduction in cancer mortality was observed after a median cumulative follow-up of 22.3 years: 1817 vs 1943 deaths (hazard ratio, 0.93; 95% CI, 0.87-0.99).
CVD. An estimated 6% increase in CVD mortality was seen in the CaD group: 2621 vs 2420 deaths (HR, 1.06; 95% CI, 1.01-1.12). Pretrial supplement users were found to be at higher CVD risk.
Hip fracture. No effect on hip fracture risk was measured, but the authors cautioned that hip fracture and CVD outcomes were available only for a subset of participants, and the effects of calcium alone vs vitamin D alone vs the combination could not be disentangled.
In a small subgroup analysis, some CaD users were seen to respond in terms of bone mineral density but since only 4 of the study’s 40 sites collected such information, the study was underpowered to examine the effect. ”Many other studies, however, show a response to supplementation in women who already have bone mineral deficits,” Dr. Thomson said.
The Calcification Question
One of the possible mechanisms of harm is that high-dose calcium supplements can increase the rate of blood coagulation and promote vascular calcification, said Emma Laing, PhD, RD, director of dietetics at the University of Georgia in Athens and a spokesperson for the Chicago-based Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics.
“Other factors that should be considered when determining a patient’s CVD risk are race, genetic predisposition, medical and social history, response to stress, and lifestyle behaviors, as well as the length of time supplements have been consumed,” added Dr. Laing, who was not involved in the WHI analysis.
“We asked ourselves if CaD supplements might contribute to calcification of the coronary arteries, since some believe this to be the case, although the literature is mixed,” said Dr. Thomson.
“So we did a shorter ancillary study in a small sample of several hundred [women] to see if there was any increase in calcification” and no difference was seen on imaging across the two arms. “However, women who were already on supplements before entering the study seemed to be at higher CVD risk,” she said.
Added study coauthor JoAnn E. Manson, MD, DrPH, chief of the division of preventive medicine at Brigham and Women’s Hospital and professor of women’s health at Harvard Medical School, both in Boston: “With no increase or decrease in coronary artery calcium at the end of the trial, we don’t believe starting or continuing calcium/vitamin D supplements should require screening for coronary artery disease.”
Some randomized trials and systematic reviews, however, have observed an increased risk of CVD in healthy patients on calcium supplements, with one Korean meta-analysis reporting a 15% increase in CVD risk in healthy postmenopausal women taking calcium supplements. Another meta-analysis found a link between calcium supplements and a greater risk of various cardiovascular outcomes, especially myocardial infarction.
Vitamin D Supplementation
As for vitamin D only supplementation, an updated meta-analysis including more than 83,000 individuals showed that it confers no cardiovascular protection and is therefore not indicated for this purpose.
Practice Considerations
Offering an outsider’s perspective, Sarah G. Candler, MD, MPH, an internist in Houston specializing in primary care for older high-risk adults, said: “Unfortunately, this latest study continues the trend of creating more questions than answers. If the adverse outcome of CVD death is a result of supplementation, it is unclear if this is due to the vitamin D, the calcium, or both. And it is unclear if this is dose dependent, time dependent, or due to concurrent risk factors unique to certain populations.
“It is recommended that patients at risk of osteoporosis based on age, sex, medications, and lifestyle be screened for osteoporosis and treated accordingly, including supplementation with CaD,” Dr. Candler said. “It remains unclear whether supplementation with CaD in the absence of osteoporosis and osteopenia is net beneficial or harmful, and at this time I would not recommend it to my patients.”
Added Dr. Manson: “The very small increase seen in cardiovascular mortality wouldn’t be a reason to discontinue supplementation among women who have been advised by their healthcare providers to take these supplements for bone health or other purposes.
“Among those at usual risk of fracture, we recommend trying to obtain adequate calcium and vitamin D from food sources first and to use supplements only for the purpose of filling gaps in intake,” Dr. Manson continued. Overall, the findings support the national recommended dietary allowances for daily calcium intake of 1200 mg and daily vitamin D intake of 600-800 IU among postmenopausal women for maintenance of bone health, she said.
While a 2022 study found that vitamin D supplementation alone did not prevent fractures in healthy adults, other research has shown that a calcium/vitamin D combination is more likely to protect the skeleton.
“Patients at risk for fractures will probably benefit from calcium and/or vitamin D supplementation if they do not meet dietary intake requirements, have malabsorption syndromes, are taking medications that affect nutrient absorption, or if they are older and not regularly exposed to sunlight,” said Dr. Laing. “A combination of biochemical, imaging, functional, and dietary intake data can help determine if a supplement is warranted.”
She stressed that additional research is needed in more diverse populations before changing practice guidelines. “However, doctors should continue to weigh the risks and benefits of prescribing supplements for each patient.”
The WHI program is funded by the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. Dr. Thomson disclosed no competing interests. Dr. Manson reported a relationship with Mars Edge. Multiple authors reported grant support from government funding agencies. The outside commentators had no relevant competing interests to disclose.
Some doctors may be scratching their heads over a new analysis reporting that combined calcium and vitamin D (CaD) supplements appear to be associated with a slight 6% increase in cardiovascular (CVD) mortality, a slight 7% decrease in cancer risk, and no effect on osteoporotic fracture in postmenopausal women.
The study, in Annals of Internal Medicine, found no effect of supplementation on all-cause mortality.
The findings emerged from an analysis of more than 20 years’ follow-up data on a randomized trial in postmenopausal women conducted as part of the Women’s Health Initiative (WHI).
Cynthia A. Thomson, PhD, RD, first author and cancer prevention scientist at the Arizona Cancer Center and a professor of health promotion sciences at the University of Arizona in Tucson said the findings recommend individualized assessment of the need for supplements for older women as they consider them in hopes of preventing fractures.
“Evaluate your patients individually and understand that there are some who may benefit from supplementation, for example, in terms of reducing colorectal cancer mortality,” Dr. Thomson said in an interview. The approach should be nuanced. “If you check the adequacy of vitamin D and calcium in their diets, supplementation may not be needed.” She added that supplementation is best considered in the context of a woman’s overall health profile, including risk factors for fracture, heart disease, and cancer, especially colorectal cancer (CRC).
Study Details
The investigators conducted postintervention follow-up of the WHI’s 7-year multicenter randomized intervention trial of CaD vs placebo.
Since existing evidence of long-term health outcomes was limited, the trial, begun in 1999 and closed in 2005, enrolled 36,282 postmenopausal women (mean age 62) with no history of breast or colorectal cancer. They were randomly assigned 1:1 to supplementation with 1000 mg of calcium carbonate (400 mg elemental calcium) plus 400 IU of vitamin D3 daily or placebo, taken twice daily in half doses.
Study outcomes were incidence of CRC, total and invasive breast cancer; disease-specific and all-cause mortality; total CVD; and hip fracture measured through December 2020, with analyses stratified by personal supplement usage.
Cancer. CaD was associated with reduced incident total cancer, CRC, and invasive breast cancer — notably among participants not taking CaD before randomization. Cancer incidence estimates varied widely, the authors noted, when stratified by supplement use before randomization. Noting that CaD seemed to have more cancer-related impact in those without prior supplementation, the authors suggested supplementation may affect cancer biology primarily by augmenting nutrient insufficiency.
An estimated 7% reduction in cancer mortality was observed after a median cumulative follow-up of 22.3 years: 1817 vs 1943 deaths (hazard ratio, 0.93; 95% CI, 0.87-0.99).
CVD. An estimated 6% increase in CVD mortality was seen in the CaD group: 2621 vs 2420 deaths (HR, 1.06; 95% CI, 1.01-1.12). Pretrial supplement users were found to be at higher CVD risk.
Hip fracture. No effect on hip fracture risk was measured, but the authors cautioned that hip fracture and CVD outcomes were available only for a subset of participants, and the effects of calcium alone vs vitamin D alone vs the combination could not be disentangled.
In a small subgroup analysis, some CaD users were seen to respond in terms of bone mineral density but since only 4 of the study’s 40 sites collected such information, the study was underpowered to examine the effect. ”Many other studies, however, show a response to supplementation in women who already have bone mineral deficits,” Dr. Thomson said.
The Calcification Question
One of the possible mechanisms of harm is that high-dose calcium supplements can increase the rate of blood coagulation and promote vascular calcification, said Emma Laing, PhD, RD, director of dietetics at the University of Georgia in Athens and a spokesperson for the Chicago-based Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics.
“Other factors that should be considered when determining a patient’s CVD risk are race, genetic predisposition, medical and social history, response to stress, and lifestyle behaviors, as well as the length of time supplements have been consumed,” added Dr. Laing, who was not involved in the WHI analysis.
“We asked ourselves if CaD supplements might contribute to calcification of the coronary arteries, since some believe this to be the case, although the literature is mixed,” said Dr. Thomson.
“So we did a shorter ancillary study in a small sample of several hundred [women] to see if there was any increase in calcification” and no difference was seen on imaging across the two arms. “However, women who were already on supplements before entering the study seemed to be at higher CVD risk,” she said.
Added study coauthor JoAnn E. Manson, MD, DrPH, chief of the division of preventive medicine at Brigham and Women’s Hospital and professor of women’s health at Harvard Medical School, both in Boston: “With no increase or decrease in coronary artery calcium at the end of the trial, we don’t believe starting or continuing calcium/vitamin D supplements should require screening for coronary artery disease.”
Some randomized trials and systematic reviews, however, have observed an increased risk of CVD in healthy patients on calcium supplements, with one Korean meta-analysis reporting a 15% increase in CVD risk in healthy postmenopausal women taking calcium supplements. Another meta-analysis found a link between calcium supplements and a greater risk of various cardiovascular outcomes, especially myocardial infarction.
Vitamin D Supplementation
As for vitamin D only supplementation, an updated meta-analysis including more than 83,000 individuals showed that it confers no cardiovascular protection and is therefore not indicated for this purpose.
Practice Considerations
Offering an outsider’s perspective, Sarah G. Candler, MD, MPH, an internist in Houston specializing in primary care for older high-risk adults, said: “Unfortunately, this latest study continues the trend of creating more questions than answers. If the adverse outcome of CVD death is a result of supplementation, it is unclear if this is due to the vitamin D, the calcium, or both. And it is unclear if this is dose dependent, time dependent, or due to concurrent risk factors unique to certain populations.
“It is recommended that patients at risk of osteoporosis based on age, sex, medications, and lifestyle be screened for osteoporosis and treated accordingly, including supplementation with CaD,” Dr. Candler said. “It remains unclear whether supplementation with CaD in the absence of osteoporosis and osteopenia is net beneficial or harmful, and at this time I would not recommend it to my patients.”
Added Dr. Manson: “The very small increase seen in cardiovascular mortality wouldn’t be a reason to discontinue supplementation among women who have been advised by their healthcare providers to take these supplements for bone health or other purposes.
“Among those at usual risk of fracture, we recommend trying to obtain adequate calcium and vitamin D from food sources first and to use supplements only for the purpose of filling gaps in intake,” Dr. Manson continued. Overall, the findings support the national recommended dietary allowances for daily calcium intake of 1200 mg and daily vitamin D intake of 600-800 IU among postmenopausal women for maintenance of bone health, she said.
While a 2022 study found that vitamin D supplementation alone did not prevent fractures in healthy adults, other research has shown that a calcium/vitamin D combination is more likely to protect the skeleton.
“Patients at risk for fractures will probably benefit from calcium and/or vitamin D supplementation if they do not meet dietary intake requirements, have malabsorption syndromes, are taking medications that affect nutrient absorption, or if they are older and not regularly exposed to sunlight,” said Dr. Laing. “A combination of biochemical, imaging, functional, and dietary intake data can help determine if a supplement is warranted.”
She stressed that additional research is needed in more diverse populations before changing practice guidelines. “However, doctors should continue to weigh the risks and benefits of prescribing supplements for each patient.”
The WHI program is funded by the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. Dr. Thomson disclosed no competing interests. Dr. Manson reported a relationship with Mars Edge. Multiple authors reported grant support from government funding agencies. The outside commentators had no relevant competing interests to disclose.
FROM ANNALS OF INTERNAL MEDICINE
Nurse-Led Strategy Reduces Cholesterol, BP in HIV
TOPLINE:
A multicomponent strategy of nurse-led communication, home blood pressure monitoring, evidence-based treatment algorithms, and electronic health record tools improved systolic blood pressure (SBP) and non–high-density lipoprotein (non-HDL) cholesterol levels in people living with HIV.
METHODOLOGY:
- Investigators assessed if EXTRA-CVD, a nurse-led multicomponent intervention for preventing cardiovascular diseases (CVD), could effectively improve SBP and non-HDL cholesterol levels in people living with HIV whose viral replication has been controlled effectively using antiretroviral therapy.
- They recruited 297 individuals (median age, 59 years; 20.9% women) from three academic HIV clinics in the United States with an HIV-1 viral load < 200 copies/mL who were diagnosed with both hypertension and hypercholesterolemia.
- Participants were randomly assigned to either the EXTRA-CVD intervention group or a control group comprising individuals who received general prevention education.
- SBP (the primary outcome) was calculated as the mean of two SBP measurements obtained 1 minute apart, and non-HDL cholesterol (the secondary outcome) was calculated as total cholesterol minus HDL cholesterol.
TAKEAWAY:
- Participants in the intervention vs control group reported having significantly lower SBP as early as 4 months after the nurse-led strategy (mean difference, −6.4 mm Hg; P = .002), with the improvements sustaining until 12 months (mean difference, −4.2 mm Hg; P = .04).
- At 12 months, participants in the intervention group showed a 16.9-mg/dL (P < .001) reduction in non-HDL cholesterol levels compared with those in the control group.
- The nurse-led strategy led to a greater reduction in SBP in women with HIV vs men living with HIV (5.9 mm Hg greater SBP difference at 12 months), with the difference being clinically meaningful but not statistically significant.
- This nurse-led strategy did not increase the risk for adverse events in people living with HIV.
IN PRACTICE:
“Although the EXTRA-CVD intervention was limited to BP and cholesterol, nurse-led case management might be beneficial for a range of other primary care conditions in HIV clinics. If HIV clinics choose to implement EXTRA-CVD, they might consider adding staff trained in other chronic comorbidities and/or health promotion activities,” the authors noted.
SOURCE:
This study was led by Christopher T. Longenecker, MD, University of Washington School of Medicine, Seattle, and published online on March 5, 2024, in JAMA Network Open.
LIMITATIONS:
Because this trial was conducted at well-resourced, major academic HIV clinics, the results may not be applicable to other populations, such as smaller community-based clinics or HIV care outside the United States. The sensitivity analyses performed in this study may not have fully accounted for the bias introduced by the differential attrition in the intervention group.
DISCLOSURES:
This study was supported by grants from the National Institutes of Health (NIH). The authors declared receiving grants and personal fees from or having other ties with the NIH and other sources.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
A multicomponent strategy of nurse-led communication, home blood pressure monitoring, evidence-based treatment algorithms, and electronic health record tools improved systolic blood pressure (SBP) and non–high-density lipoprotein (non-HDL) cholesterol levels in people living with HIV.
METHODOLOGY:
- Investigators assessed if EXTRA-CVD, a nurse-led multicomponent intervention for preventing cardiovascular diseases (CVD), could effectively improve SBP and non-HDL cholesterol levels in people living with HIV whose viral replication has been controlled effectively using antiretroviral therapy.
- They recruited 297 individuals (median age, 59 years; 20.9% women) from three academic HIV clinics in the United States with an HIV-1 viral load < 200 copies/mL who were diagnosed with both hypertension and hypercholesterolemia.
- Participants were randomly assigned to either the EXTRA-CVD intervention group or a control group comprising individuals who received general prevention education.
- SBP (the primary outcome) was calculated as the mean of two SBP measurements obtained 1 minute apart, and non-HDL cholesterol (the secondary outcome) was calculated as total cholesterol minus HDL cholesterol.
TAKEAWAY:
- Participants in the intervention vs control group reported having significantly lower SBP as early as 4 months after the nurse-led strategy (mean difference, −6.4 mm Hg; P = .002), with the improvements sustaining until 12 months (mean difference, −4.2 mm Hg; P = .04).
- At 12 months, participants in the intervention group showed a 16.9-mg/dL (P < .001) reduction in non-HDL cholesterol levels compared with those in the control group.
- The nurse-led strategy led to a greater reduction in SBP in women with HIV vs men living with HIV (5.9 mm Hg greater SBP difference at 12 months), with the difference being clinically meaningful but not statistically significant.
- This nurse-led strategy did not increase the risk for adverse events in people living with HIV.
IN PRACTICE:
“Although the EXTRA-CVD intervention was limited to BP and cholesterol, nurse-led case management might be beneficial for a range of other primary care conditions in HIV clinics. If HIV clinics choose to implement EXTRA-CVD, they might consider adding staff trained in other chronic comorbidities and/or health promotion activities,” the authors noted.
SOURCE:
This study was led by Christopher T. Longenecker, MD, University of Washington School of Medicine, Seattle, and published online on March 5, 2024, in JAMA Network Open.
LIMITATIONS:
Because this trial was conducted at well-resourced, major academic HIV clinics, the results may not be applicable to other populations, such as smaller community-based clinics or HIV care outside the United States. The sensitivity analyses performed in this study may not have fully accounted for the bias introduced by the differential attrition in the intervention group.
DISCLOSURES:
This study was supported by grants from the National Institutes of Health (NIH). The authors declared receiving grants and personal fees from or having other ties with the NIH and other sources.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
A multicomponent strategy of nurse-led communication, home blood pressure monitoring, evidence-based treatment algorithms, and electronic health record tools improved systolic blood pressure (SBP) and non–high-density lipoprotein (non-HDL) cholesterol levels in people living with HIV.
METHODOLOGY:
- Investigators assessed if EXTRA-CVD, a nurse-led multicomponent intervention for preventing cardiovascular diseases (CVD), could effectively improve SBP and non-HDL cholesterol levels in people living with HIV whose viral replication has been controlled effectively using antiretroviral therapy.
- They recruited 297 individuals (median age, 59 years; 20.9% women) from three academic HIV clinics in the United States with an HIV-1 viral load < 200 copies/mL who were diagnosed with both hypertension and hypercholesterolemia.
- Participants were randomly assigned to either the EXTRA-CVD intervention group or a control group comprising individuals who received general prevention education.
- SBP (the primary outcome) was calculated as the mean of two SBP measurements obtained 1 minute apart, and non-HDL cholesterol (the secondary outcome) was calculated as total cholesterol minus HDL cholesterol.
TAKEAWAY:
- Participants in the intervention vs control group reported having significantly lower SBP as early as 4 months after the nurse-led strategy (mean difference, −6.4 mm Hg; P = .002), with the improvements sustaining until 12 months (mean difference, −4.2 mm Hg; P = .04).
- At 12 months, participants in the intervention group showed a 16.9-mg/dL (P < .001) reduction in non-HDL cholesterol levels compared with those in the control group.
- The nurse-led strategy led to a greater reduction in SBP in women with HIV vs men living with HIV (5.9 mm Hg greater SBP difference at 12 months), with the difference being clinically meaningful but not statistically significant.
- This nurse-led strategy did not increase the risk for adverse events in people living with HIV.
IN PRACTICE:
“Although the EXTRA-CVD intervention was limited to BP and cholesterol, nurse-led case management might be beneficial for a range of other primary care conditions in HIV clinics. If HIV clinics choose to implement EXTRA-CVD, they might consider adding staff trained in other chronic comorbidities and/or health promotion activities,” the authors noted.
SOURCE:
This study was led by Christopher T. Longenecker, MD, University of Washington School of Medicine, Seattle, and published online on March 5, 2024, in JAMA Network Open.
LIMITATIONS:
Because this trial was conducted at well-resourced, major academic HIV clinics, the results may not be applicable to other populations, such as smaller community-based clinics or HIV care outside the United States. The sensitivity analyses performed in this study may not have fully accounted for the bias introduced by the differential attrition in the intervention group.
DISCLOSURES:
This study was supported by grants from the National Institutes of Health (NIH). The authors declared receiving grants and personal fees from or having other ties with the NIH and other sources.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Higher Dietary Niacin Tied to Lower Mortality Risk in MASLD
TOPLINE:
Higher dietary niacin intake is associated with a lower risk for all-cause mortality among people with metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD), but there is no connection between niacin consumption and cardiovascular disease (CVD) mortality, a recent study suggested.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers analyzed data from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (2003-2018) for 4315 adults with MASLD (mean age, 52.5 years; 55%, men; 67%, non-Hispanic White).
- Dietary niacin intake levels were based on two 24-hour dietary recall interviews to report the types and quantities of foods that participants consumed in the 24 hours prior to the interviews.
- Participants were categorized by tertile of dietary niacin intake: Tertile 1 (n = 1440), < 18.4 mg; tertile 2 (n = 1441), 18.5-26.6 mg; and tertile 3 (n = 1434), > 26.7 mg.
TAKEAWAY:
- During a median follow-up of 8.8 years, 566 deaths occurred, of which 197 were attributed to CVD.
- Compared with participants with a niacin intake of 18.4 mg or lower (the lowest tertile), the multivariable-adjusted hazard ratios (HRs) for participants with a niacin intake of 26.7 mg or higher (the highest tertile) were 0.70 for all-cause mortality and 0.65 for CVD mortality.
- For the subgroup with diabetes compared with the reference group (the first tertile), the HR of all-cause mortality in the third tertile was 0.82.
- When the subgroup without diabetes was compared with the reference group, the HR of all-cause mortality in the third tertile was 0.58, suggesting a significant interaction between niacin and diabetes with the risk of all-cause mortality.
- An inverse association between dietary niacin intake and all-cause mortality was seen in sensitivity analyses, when excluding a participant who died within 2 years of follow-up.
IN PRACTICE:
“Higher dietary niacin intake was associated with a lower risk of all-cause mortality,” but not CVD, among individuals with MASLD, and “the dose-response association…needs to be further investigated to determine optimal intake level,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study, led by Jie Pan, MD, Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou, China, was published online in JAMA Network Open.
LIMITATIONS:
Physical activity data were missing and could not be adjusted for. The National Death Index used by the researchers has only “modest” ability to accurately classify CVD mortality, and the dietary data were subject to recall bias.
DISCLOSURES:
One author was supported by a grant from the National Nature Science Foundation of China. No other conflicts of interest were reported.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Higher dietary niacin intake is associated with a lower risk for all-cause mortality among people with metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD), but there is no connection between niacin consumption and cardiovascular disease (CVD) mortality, a recent study suggested.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers analyzed data from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (2003-2018) for 4315 adults with MASLD (mean age, 52.5 years; 55%, men; 67%, non-Hispanic White).
- Dietary niacin intake levels were based on two 24-hour dietary recall interviews to report the types and quantities of foods that participants consumed in the 24 hours prior to the interviews.
- Participants were categorized by tertile of dietary niacin intake: Tertile 1 (n = 1440), < 18.4 mg; tertile 2 (n = 1441), 18.5-26.6 mg; and tertile 3 (n = 1434), > 26.7 mg.
TAKEAWAY:
- During a median follow-up of 8.8 years, 566 deaths occurred, of which 197 were attributed to CVD.
- Compared with participants with a niacin intake of 18.4 mg or lower (the lowest tertile), the multivariable-adjusted hazard ratios (HRs) for participants with a niacin intake of 26.7 mg or higher (the highest tertile) were 0.70 for all-cause mortality and 0.65 for CVD mortality.
- For the subgroup with diabetes compared with the reference group (the first tertile), the HR of all-cause mortality in the third tertile was 0.82.
- When the subgroup without diabetes was compared with the reference group, the HR of all-cause mortality in the third tertile was 0.58, suggesting a significant interaction between niacin and diabetes with the risk of all-cause mortality.
- An inverse association between dietary niacin intake and all-cause mortality was seen in sensitivity analyses, when excluding a participant who died within 2 years of follow-up.
IN PRACTICE:
“Higher dietary niacin intake was associated with a lower risk of all-cause mortality,” but not CVD, among individuals with MASLD, and “the dose-response association…needs to be further investigated to determine optimal intake level,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study, led by Jie Pan, MD, Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou, China, was published online in JAMA Network Open.
LIMITATIONS:
Physical activity data were missing and could not be adjusted for. The National Death Index used by the researchers has only “modest” ability to accurately classify CVD mortality, and the dietary data were subject to recall bias.
DISCLOSURES:
One author was supported by a grant from the National Nature Science Foundation of China. No other conflicts of interest were reported.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Higher dietary niacin intake is associated with a lower risk for all-cause mortality among people with metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD), but there is no connection between niacin consumption and cardiovascular disease (CVD) mortality, a recent study suggested.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers analyzed data from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (2003-2018) for 4315 adults with MASLD (mean age, 52.5 years; 55%, men; 67%, non-Hispanic White).
- Dietary niacin intake levels were based on two 24-hour dietary recall interviews to report the types and quantities of foods that participants consumed in the 24 hours prior to the interviews.
- Participants were categorized by tertile of dietary niacin intake: Tertile 1 (n = 1440), < 18.4 mg; tertile 2 (n = 1441), 18.5-26.6 mg; and tertile 3 (n = 1434), > 26.7 mg.
TAKEAWAY:
- During a median follow-up of 8.8 years, 566 deaths occurred, of which 197 were attributed to CVD.
- Compared with participants with a niacin intake of 18.4 mg or lower (the lowest tertile), the multivariable-adjusted hazard ratios (HRs) for participants with a niacin intake of 26.7 mg or higher (the highest tertile) were 0.70 for all-cause mortality and 0.65 for CVD mortality.
- For the subgroup with diabetes compared with the reference group (the first tertile), the HR of all-cause mortality in the third tertile was 0.82.
- When the subgroup without diabetes was compared with the reference group, the HR of all-cause mortality in the third tertile was 0.58, suggesting a significant interaction between niacin and diabetes with the risk of all-cause mortality.
- An inverse association between dietary niacin intake and all-cause mortality was seen in sensitivity analyses, when excluding a participant who died within 2 years of follow-up.
IN PRACTICE:
“Higher dietary niacin intake was associated with a lower risk of all-cause mortality,” but not CVD, among individuals with MASLD, and “the dose-response association…needs to be further investigated to determine optimal intake level,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study, led by Jie Pan, MD, Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou, China, was published online in JAMA Network Open.
LIMITATIONS:
Physical activity data were missing and could not be adjusted for. The National Death Index used by the researchers has only “modest” ability to accurately classify CVD mortality, and the dietary data were subject to recall bias.
DISCLOSURES:
One author was supported by a grant from the National Nature Science Foundation of China. No other conflicts of interest were reported.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Hypertension Stable in US, Antihypertensive Med Use Rises
TOPLINE:
Hypertension prevalence remained stable in the United States at 30% after guidelines updated in 2017 lowered the threshold for the condition, while antihypertensive medication use rose about 3%, new research from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) shows.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers analyzed data from the Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance System, a telephone survey of US adults aged 18 years and older.
- Self-reported diagnosed hypertension was defined as an affirmative response to the question, “Have you ever been told by a doctor, nurse, or other health professional that you have high blood pressure?”
- To determine treatment, respondents who answered the first question affirmatively were then asked, “Are you currently taking medicine for your high blood pressure?”
- Hypertension and treatment were assessed by age group (18-44, 45-64, and > 65 years), sex, race, ethnicity, level of education, and state of residence.
TAKEAWAY:
- The final analytic samples for 2017, 2019, and 2021 included 425,417, 392,100, and 410,318 participants, respectively.
- From 2017 to 2021, the overall age-standardized prevalence of hypertension did not change, remaining at almost exactly 30%.
- The age-standardized prevalence of antihypertensive medication use among individuals with hypertension increased by 3.1 percentage points, from 59.8% to 62.9%.
- Increases in medication use were seen in most sociodemographic groups; for example, in 2021, the prevalence was higher among women than among men (68.5% vs 59.4%), among adults aged ≥ 65 years than among those aged 18-44 years (92.5% vs 42.5%), and among Black patients than among White patients (71.3% vs 62%).
- Increases in medication use were also seen by state; use increased in 11 states, ranging from 52.2% in Utah to 72.8% in Mississippi in 2021, and did not decrease significantly in any state.
IN PRACTICE:
“These findings can be used to increase awareness of hypertension and promote lifestyle modifications and antihypertensive medication use to optimize blood pressure control and reduce disparities in prevalence and control,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Ahlia Sekkarie, PhD, of CDC’s Division for Heart Disease and Stroke Prevention, and published online in Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report.
LIMITATIONS:
The study had several limitations. The findings were based on self-report. Median response rates of less than 50% could lead to under- or overestimates of prevalence. Parts of the population, such as those in long-term care facilities or without a telephone, were not included in the analysis. Some demographic categories had small sample sizes; therefore, prevalence changes might not be detectable.
DISCLOSURES:
No specific funding was reported. The authors reported no potential conflicts of interest.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Hypertension prevalence remained stable in the United States at 30% after guidelines updated in 2017 lowered the threshold for the condition, while antihypertensive medication use rose about 3%, new research from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) shows.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers analyzed data from the Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance System, a telephone survey of US adults aged 18 years and older.
- Self-reported diagnosed hypertension was defined as an affirmative response to the question, “Have you ever been told by a doctor, nurse, or other health professional that you have high blood pressure?”
- To determine treatment, respondents who answered the first question affirmatively were then asked, “Are you currently taking medicine for your high blood pressure?”
- Hypertension and treatment were assessed by age group (18-44, 45-64, and > 65 years), sex, race, ethnicity, level of education, and state of residence.
TAKEAWAY:
- The final analytic samples for 2017, 2019, and 2021 included 425,417, 392,100, and 410,318 participants, respectively.
- From 2017 to 2021, the overall age-standardized prevalence of hypertension did not change, remaining at almost exactly 30%.
- The age-standardized prevalence of antihypertensive medication use among individuals with hypertension increased by 3.1 percentage points, from 59.8% to 62.9%.
- Increases in medication use were seen in most sociodemographic groups; for example, in 2021, the prevalence was higher among women than among men (68.5% vs 59.4%), among adults aged ≥ 65 years than among those aged 18-44 years (92.5% vs 42.5%), and among Black patients than among White patients (71.3% vs 62%).
- Increases in medication use were also seen by state; use increased in 11 states, ranging from 52.2% in Utah to 72.8% in Mississippi in 2021, and did not decrease significantly in any state.
IN PRACTICE:
“These findings can be used to increase awareness of hypertension and promote lifestyle modifications and antihypertensive medication use to optimize blood pressure control and reduce disparities in prevalence and control,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Ahlia Sekkarie, PhD, of CDC’s Division for Heart Disease and Stroke Prevention, and published online in Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report.
LIMITATIONS:
The study had several limitations. The findings were based on self-report. Median response rates of less than 50% could lead to under- or overestimates of prevalence. Parts of the population, such as those in long-term care facilities or without a telephone, were not included in the analysis. Some demographic categories had small sample sizes; therefore, prevalence changes might not be detectable.
DISCLOSURES:
No specific funding was reported. The authors reported no potential conflicts of interest.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Hypertension prevalence remained stable in the United States at 30% after guidelines updated in 2017 lowered the threshold for the condition, while antihypertensive medication use rose about 3%, new research from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) shows.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers analyzed data from the Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance System, a telephone survey of US adults aged 18 years and older.
- Self-reported diagnosed hypertension was defined as an affirmative response to the question, “Have you ever been told by a doctor, nurse, or other health professional that you have high blood pressure?”
- To determine treatment, respondents who answered the first question affirmatively were then asked, “Are you currently taking medicine for your high blood pressure?”
- Hypertension and treatment were assessed by age group (18-44, 45-64, and > 65 years), sex, race, ethnicity, level of education, and state of residence.
TAKEAWAY:
- The final analytic samples for 2017, 2019, and 2021 included 425,417, 392,100, and 410,318 participants, respectively.
- From 2017 to 2021, the overall age-standardized prevalence of hypertension did not change, remaining at almost exactly 30%.
- The age-standardized prevalence of antihypertensive medication use among individuals with hypertension increased by 3.1 percentage points, from 59.8% to 62.9%.
- Increases in medication use were seen in most sociodemographic groups; for example, in 2021, the prevalence was higher among women than among men (68.5% vs 59.4%), among adults aged ≥ 65 years than among those aged 18-44 years (92.5% vs 42.5%), and among Black patients than among White patients (71.3% vs 62%).
- Increases in medication use were also seen by state; use increased in 11 states, ranging from 52.2% in Utah to 72.8% in Mississippi in 2021, and did not decrease significantly in any state.
IN PRACTICE:
“These findings can be used to increase awareness of hypertension and promote lifestyle modifications and antihypertensive medication use to optimize blood pressure control and reduce disparities in prevalence and control,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Ahlia Sekkarie, PhD, of CDC’s Division for Heart Disease and Stroke Prevention, and published online in Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report.
LIMITATIONS:
The study had several limitations. The findings were based on self-report. Median response rates of less than 50% could lead to under- or overestimates of prevalence. Parts of the population, such as those in long-term care facilities or without a telephone, were not included in the analysis. Some demographic categories had small sample sizes; therefore, prevalence changes might not be detectable.
DISCLOSURES:
No specific funding was reported. The authors reported no potential conflicts of interest.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Smoking Cessation Before Age 40 Years Brings Great Benefits
Chronic smoking remains a major cause of premature mortality on a global scale. Despite intensified efforts to combat this scourge, a quarter of deaths among middle-aged adults in Europe and North America are attributed to it. However, over the past decades, antismoking campaigns have borne fruit, and many smokers have quit before the age of 40 years, enabling some case-control studies.
Among those abstainers who made the right choice, the excess mortality attributable to smoking over a lifetime would be reduced by 90% compared with controls who continued smoking. The estimated benefit is clear, but the analysis lacks nuance. Is smoking cessation beneficial even at older ages? If so, is the effect measurable in terms of magnitude and speed of the effect? An article published online in The New England Journal of Medicine Evidence provided some answers to these questions.
Four-Cohort Meta-Analysis
The study was a meta-analysis of individual data collected within four national cohort studies that were linked to each country’s death registry. Two of these studies were nationally representative. The National Health Interview Survey involved a sample of US citizens living in the community, aged 20-79 years, who were included annually in the cohort between 1997 and 2018. The second, the Canadian Community Health Survey, included subjects in the same age group, with samples analyzed between 2000 and 2014.
In Norway, three cohort studies conducted between 1974 and 2003, in which participants aged 25-79 years were included, were combined to form the Norwegian Health Screening Survey. These were the Counties Study (1974-1988), the 40 Years Study (1985-1999), and the Cohort of Norway (1994-2003), respectively. The fourth cohort was established through recruitment via the UK Biobank, with adults aged 40-73 years invited to participate in the survey. The data analysis ultimately covered a relatively heterogeneous total population of 1.48 million adults, all from high-income countries and followed for 15 years. It relied on the Cox proportional hazards model applied to each study, considering smoker vs nonsmoker status, as well as the time elapsed since smoking cessation (less than 3 years, between 3 and 9 years, or at least 10 years). Statistical adjustments made in the context of multivariate Cox analysis considered age, education, alcohol consumption, and obesity.
Excess Mortality Confirmed
At the end of follow-up, 122,697 deaths were recorded. The comparison of smokers and nonsmokers confirmed smoking-related excess mortality, with adjusted hazard ratios (HRs) estimated at 2.80 for women and 2.70 for men. Smoking shortened life expectancy in the 40- to 79-year-age group by 12 years for women and 13 years for men, in terms of overall mortality. In terms of smoking-attributable specific mortality, the corresponding figures reached 24 and 26 years, respectively. Respiratory diseases ranked highest in both sexes (HR, 7.6 for women and 6.3 for men), followed by cardiovascular diseases (HR, 3.1 for women and 2.9 for men) and cancers (HR, 2.8 for women and 3.1 for men).
The Earlier, the Better
Smoking cessation halves overall excess mortality. Above all, quitting before age 40 years brings overall mortality back to the level of nonsmokers as early as the third year after quitting. The excess mortality decreases even more as the cessation period is prolonged, even after age 40 years. Thus, cessation ≥ 10 years in smokers aged 40-49 years almost cancels out overall excess mortality (-99% in women, -96% in men). The trend is almost as favorable in the older age group (50-59 years), with corresponding figures of -95% and -92%, respectively.
Long-term survival increases in the early years after cessation, especially if it occurs at a younger age, but the benefit remains tangible even in older smokers. Thus, cessation of less than 3 years, effective in patients aged 50-59 years, reduces overall excess mortality by 63% in women and 54% in men. In patients aged 60-79 years, the figures are -40% and -33%, respectively.
Naturally, the earlier the cessation, the greater the number of years gained. It is 12 years for cessation before age 40 years, reduced to 6 years for cessation between 40 and 49 years, and 2.5 years when it is even later (50-59 years). These quantitative results are approximate, given the methodology (a meta-analysis) and some heterogeneity in the studies, as well as the multitude of potential confounding factors that have not all been considered. Nevertheless, the results probably contain a kernel of truth, and their optimistic implications should be highlighted to encourage smokers to abstain, even older ones. Better late than never, even if the benefit of cessation is maximal when it occurs as early as possible, knowing that a minimum of 3 years of cessation would be sufficient to gain years of life.
This story was translated from JIM, which is part of the Medscape professional network, using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Chronic smoking remains a major cause of premature mortality on a global scale. Despite intensified efforts to combat this scourge, a quarter of deaths among middle-aged adults in Europe and North America are attributed to it. However, over the past decades, antismoking campaigns have borne fruit, and many smokers have quit before the age of 40 years, enabling some case-control studies.
Among those abstainers who made the right choice, the excess mortality attributable to smoking over a lifetime would be reduced by 90% compared with controls who continued smoking. The estimated benefit is clear, but the analysis lacks nuance. Is smoking cessation beneficial even at older ages? If so, is the effect measurable in terms of magnitude and speed of the effect? An article published online in The New England Journal of Medicine Evidence provided some answers to these questions.
Four-Cohort Meta-Analysis
The study was a meta-analysis of individual data collected within four national cohort studies that were linked to each country’s death registry. Two of these studies were nationally representative. The National Health Interview Survey involved a sample of US citizens living in the community, aged 20-79 years, who were included annually in the cohort between 1997 and 2018. The second, the Canadian Community Health Survey, included subjects in the same age group, with samples analyzed between 2000 and 2014.
In Norway, three cohort studies conducted between 1974 and 2003, in which participants aged 25-79 years were included, were combined to form the Norwegian Health Screening Survey. These were the Counties Study (1974-1988), the 40 Years Study (1985-1999), and the Cohort of Norway (1994-2003), respectively. The fourth cohort was established through recruitment via the UK Biobank, with adults aged 40-73 years invited to participate in the survey. The data analysis ultimately covered a relatively heterogeneous total population of 1.48 million adults, all from high-income countries and followed for 15 years. It relied on the Cox proportional hazards model applied to each study, considering smoker vs nonsmoker status, as well as the time elapsed since smoking cessation (less than 3 years, between 3 and 9 years, or at least 10 years). Statistical adjustments made in the context of multivariate Cox analysis considered age, education, alcohol consumption, and obesity.
Excess Mortality Confirmed
At the end of follow-up, 122,697 deaths were recorded. The comparison of smokers and nonsmokers confirmed smoking-related excess mortality, with adjusted hazard ratios (HRs) estimated at 2.80 for women and 2.70 for men. Smoking shortened life expectancy in the 40- to 79-year-age group by 12 years for women and 13 years for men, in terms of overall mortality. In terms of smoking-attributable specific mortality, the corresponding figures reached 24 and 26 years, respectively. Respiratory diseases ranked highest in both sexes (HR, 7.6 for women and 6.3 for men), followed by cardiovascular diseases (HR, 3.1 for women and 2.9 for men) and cancers (HR, 2.8 for women and 3.1 for men).
The Earlier, the Better
Smoking cessation halves overall excess mortality. Above all, quitting before age 40 years brings overall mortality back to the level of nonsmokers as early as the third year after quitting. The excess mortality decreases even more as the cessation period is prolonged, even after age 40 years. Thus, cessation ≥ 10 years in smokers aged 40-49 years almost cancels out overall excess mortality (-99% in women, -96% in men). The trend is almost as favorable in the older age group (50-59 years), with corresponding figures of -95% and -92%, respectively.
Long-term survival increases in the early years after cessation, especially if it occurs at a younger age, but the benefit remains tangible even in older smokers. Thus, cessation of less than 3 years, effective in patients aged 50-59 years, reduces overall excess mortality by 63% in women and 54% in men. In patients aged 60-79 years, the figures are -40% and -33%, respectively.
Naturally, the earlier the cessation, the greater the number of years gained. It is 12 years for cessation before age 40 years, reduced to 6 years for cessation between 40 and 49 years, and 2.5 years when it is even later (50-59 years). These quantitative results are approximate, given the methodology (a meta-analysis) and some heterogeneity in the studies, as well as the multitude of potential confounding factors that have not all been considered. Nevertheless, the results probably contain a kernel of truth, and their optimistic implications should be highlighted to encourage smokers to abstain, even older ones. Better late than never, even if the benefit of cessation is maximal when it occurs as early as possible, knowing that a minimum of 3 years of cessation would be sufficient to gain years of life.
This story was translated from JIM, which is part of the Medscape professional network, using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Chronic smoking remains a major cause of premature mortality on a global scale. Despite intensified efforts to combat this scourge, a quarter of deaths among middle-aged adults in Europe and North America are attributed to it. However, over the past decades, antismoking campaigns have borne fruit, and many smokers have quit before the age of 40 years, enabling some case-control studies.
Among those abstainers who made the right choice, the excess mortality attributable to smoking over a lifetime would be reduced by 90% compared with controls who continued smoking. The estimated benefit is clear, but the analysis lacks nuance. Is smoking cessation beneficial even at older ages? If so, is the effect measurable in terms of magnitude and speed of the effect? An article published online in The New England Journal of Medicine Evidence provided some answers to these questions.
Four-Cohort Meta-Analysis
The study was a meta-analysis of individual data collected within four national cohort studies that were linked to each country’s death registry. Two of these studies were nationally representative. The National Health Interview Survey involved a sample of US citizens living in the community, aged 20-79 years, who were included annually in the cohort between 1997 and 2018. The second, the Canadian Community Health Survey, included subjects in the same age group, with samples analyzed between 2000 and 2014.
In Norway, three cohort studies conducted between 1974 and 2003, in which participants aged 25-79 years were included, were combined to form the Norwegian Health Screening Survey. These were the Counties Study (1974-1988), the 40 Years Study (1985-1999), and the Cohort of Norway (1994-2003), respectively. The fourth cohort was established through recruitment via the UK Biobank, with adults aged 40-73 years invited to participate in the survey. The data analysis ultimately covered a relatively heterogeneous total population of 1.48 million adults, all from high-income countries and followed for 15 years. It relied on the Cox proportional hazards model applied to each study, considering smoker vs nonsmoker status, as well as the time elapsed since smoking cessation (less than 3 years, between 3 and 9 years, or at least 10 years). Statistical adjustments made in the context of multivariate Cox analysis considered age, education, alcohol consumption, and obesity.
Excess Mortality Confirmed
At the end of follow-up, 122,697 deaths were recorded. The comparison of smokers and nonsmokers confirmed smoking-related excess mortality, with adjusted hazard ratios (HRs) estimated at 2.80 for women and 2.70 for men. Smoking shortened life expectancy in the 40- to 79-year-age group by 12 years for women and 13 years for men, in terms of overall mortality. In terms of smoking-attributable specific mortality, the corresponding figures reached 24 and 26 years, respectively. Respiratory diseases ranked highest in both sexes (HR, 7.6 for women and 6.3 for men), followed by cardiovascular diseases (HR, 3.1 for women and 2.9 for men) and cancers (HR, 2.8 for women and 3.1 for men).
The Earlier, the Better
Smoking cessation halves overall excess mortality. Above all, quitting before age 40 years brings overall mortality back to the level of nonsmokers as early as the third year after quitting. The excess mortality decreases even more as the cessation period is prolonged, even after age 40 years. Thus, cessation ≥ 10 years in smokers aged 40-49 years almost cancels out overall excess mortality (-99% in women, -96% in men). The trend is almost as favorable in the older age group (50-59 years), with corresponding figures of -95% and -92%, respectively.
Long-term survival increases in the early years after cessation, especially if it occurs at a younger age, but the benefit remains tangible even in older smokers. Thus, cessation of less than 3 years, effective in patients aged 50-59 years, reduces overall excess mortality by 63% in women and 54% in men. In patients aged 60-79 years, the figures are -40% and -33%, respectively.
Naturally, the earlier the cessation, the greater the number of years gained. It is 12 years for cessation before age 40 years, reduced to 6 years for cessation between 40 and 49 years, and 2.5 years when it is even later (50-59 years). These quantitative results are approximate, given the methodology (a meta-analysis) and some heterogeneity in the studies, as well as the multitude of potential confounding factors that have not all been considered. Nevertheless, the results probably contain a kernel of truth, and their optimistic implications should be highlighted to encourage smokers to abstain, even older ones. Better late than never, even if the benefit of cessation is maximal when it occurs as early as possible, knowing that a minimum of 3 years of cessation would be sufficient to gain years of life.
This story was translated from JIM, which is part of the Medscape professional network, using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.