User login
Add magnesium to treatment of AF with rapid ventricular response
Background: Most large studies of magnesium sulfate for assistance with rate control in AF occurred in the postoperative setting. This study compared rate control in the ED using magnesium sulfate at high (9 g) and low (4.5 g) doses vs. placebo in combination with usual treatment with atrioventricular nodal-blocking agents.
Study design: Double-blind, prospective, randomized, controlled trial.
Setting: Three tertiary Tunisian EDs.
Synopsis: This trial in Tunisian EDs enrolled 450 patients who presented with AF with rapid ventricular response and were divided into three groups: placebo, low-dose magnesium, and high-dose magnesium. Each patient’s trial medication was given as a 100-cc infusion. Patients were then treated with AV nodal-blocking agents at the discretion of the ED physician. The primary outcome was 20% reduction in rate or heart rate of less than 90 beats per minute. Notable exclusion criteria included hypotension, altered consciousness, decompensated heart failure, MI, and renal failure.
Rate control was achieved at 4 hours in 64% of patients with low-dose magnesium, 59% with high-dose magnesium, and 43% with placebo. At 24 hours, reduction in rate was controlled for 97% of patients on the low dose, 94% on the high dose, and 83% on placebo. Adverse events were mostly flushing, which occurred more frequently with the high dose than the low dose. Major limitations of the study included a lack of statistical assessment regarding baseline similarity between the two groups and that generalizability was limited by a preference for digoxin as the AV nodal agent.
Bottom line: This trial demonstrated that 4.5 g of magnesium sulfate was a useful addition to AV nodal blockers in achieving faster rate control for atrial fibrillation with rapid ventricular response in selected ED patients.
Citation: Bouida W et al. Low-dose magnesium sulfate versus high dose in the early management of rapid atrial fibrillation: Randomized controlled double blind study. Acad Emerg Med. 2018 Jul 19. doi: 10.1111/acem.13522.
Dr. Scott is an assistant professor in the division of hospital medicine, University of New Mexico.
Background: Most large studies of magnesium sulfate for assistance with rate control in AF occurred in the postoperative setting. This study compared rate control in the ED using magnesium sulfate at high (9 g) and low (4.5 g) doses vs. placebo in combination with usual treatment with atrioventricular nodal-blocking agents.
Study design: Double-blind, prospective, randomized, controlled trial.
Setting: Three tertiary Tunisian EDs.
Synopsis: This trial in Tunisian EDs enrolled 450 patients who presented with AF with rapid ventricular response and were divided into three groups: placebo, low-dose magnesium, and high-dose magnesium. Each patient’s trial medication was given as a 100-cc infusion. Patients were then treated with AV nodal-blocking agents at the discretion of the ED physician. The primary outcome was 20% reduction in rate or heart rate of less than 90 beats per minute. Notable exclusion criteria included hypotension, altered consciousness, decompensated heart failure, MI, and renal failure.
Rate control was achieved at 4 hours in 64% of patients with low-dose magnesium, 59% with high-dose magnesium, and 43% with placebo. At 24 hours, reduction in rate was controlled for 97% of patients on the low dose, 94% on the high dose, and 83% on placebo. Adverse events were mostly flushing, which occurred more frequently with the high dose than the low dose. Major limitations of the study included a lack of statistical assessment regarding baseline similarity between the two groups and that generalizability was limited by a preference for digoxin as the AV nodal agent.
Bottom line: This trial demonstrated that 4.5 g of magnesium sulfate was a useful addition to AV nodal blockers in achieving faster rate control for atrial fibrillation with rapid ventricular response in selected ED patients.
Citation: Bouida W et al. Low-dose magnesium sulfate versus high dose in the early management of rapid atrial fibrillation: Randomized controlled double blind study. Acad Emerg Med. 2018 Jul 19. doi: 10.1111/acem.13522.
Dr. Scott is an assistant professor in the division of hospital medicine, University of New Mexico.
Background: Most large studies of magnesium sulfate for assistance with rate control in AF occurred in the postoperative setting. This study compared rate control in the ED using magnesium sulfate at high (9 g) and low (4.5 g) doses vs. placebo in combination with usual treatment with atrioventricular nodal-blocking agents.
Study design: Double-blind, prospective, randomized, controlled trial.
Setting: Three tertiary Tunisian EDs.
Synopsis: This trial in Tunisian EDs enrolled 450 patients who presented with AF with rapid ventricular response and were divided into three groups: placebo, low-dose magnesium, and high-dose magnesium. Each patient’s trial medication was given as a 100-cc infusion. Patients were then treated with AV nodal-blocking agents at the discretion of the ED physician. The primary outcome was 20% reduction in rate or heart rate of less than 90 beats per minute. Notable exclusion criteria included hypotension, altered consciousness, decompensated heart failure, MI, and renal failure.
Rate control was achieved at 4 hours in 64% of patients with low-dose magnesium, 59% with high-dose magnesium, and 43% with placebo. At 24 hours, reduction in rate was controlled for 97% of patients on the low dose, 94% on the high dose, and 83% on placebo. Adverse events were mostly flushing, which occurred more frequently with the high dose than the low dose. Major limitations of the study included a lack of statistical assessment regarding baseline similarity between the two groups and that generalizability was limited by a preference for digoxin as the AV nodal agent.
Bottom line: This trial demonstrated that 4.5 g of magnesium sulfate was a useful addition to AV nodal blockers in achieving faster rate control for atrial fibrillation with rapid ventricular response in selected ED patients.
Citation: Bouida W et al. Low-dose magnesium sulfate versus high dose in the early management of rapid atrial fibrillation: Randomized controlled double blind study. Acad Emerg Med. 2018 Jul 19. doi: 10.1111/acem.13522.
Dr. Scott is an assistant professor in the division of hospital medicine, University of New Mexico.
No raised risk of cardiovascular events for COPD patients on aclidinium
, compared with placebo, in a randomized trial of more than 3,000 patients.
Aclidinium, a long-acting muscarinic antagonist (LAMA), has been shown to reduce COPD exacerbation in the short term, but long-term effectiveness has not been examined, wrote Robert A. Wise, MD, of Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, and colleagues.
ASCENT-COPD is a multicenter, double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled, parallel-group noninferiority study conducted at 522 sites in the United States and Canada. A paper on recent data from ASCENT-COPD, published in JAMA, supports early findings reported last year at the American Thoracic Society meeting.
The researchers randomized adults with COPD to a 400-mg dose of aclidinium bromide twice daily, or placebo. The average age of the patients was 67 years; 59% were men. The median exposure time to aclidinium or placebo was 365 days during the first year of treatment, and the median exposure overall was 495 days for aclidinium patients and 478 days for placebo patients.
Of the 2,537 patients who completed the study, 69 (3.9%) in the aclidinium group and 76 (4.2%) in the placebo group experienced a major adverse cardiovascular event (MACE, defined as a composite of cardiovascular death, nonfatal myocardial infarction, and nonfatal stroke).
In addition, annual rates of moderate to severe COPD exacerbations were significantly lower in the aclidinium patients compared with placebo patients (0.44 vs. 0.57, P less than .001).
In a secondary analysis with a definition of MACE expanded to include heart failure, arrhythmias, or cerebrovascular disease, results remained similar between the groups; events occurred in 168 aclidinium patients (9.4%) and 160 placebo patients (8.9%). The rate of COPD exacerbations requiring hospitalization was significantly lower in aclidinium patients, compared with placebo patients (0.07 vs. 0.10, P = .006).
Overall, the most common treatment-emergent adverse events were similar in the aclidinium and placebo groups, respectively; pneumonia (6.1% vs. 5.8%), urinary tract infections (5.2% vs. 5.0%), and upper respiratory tract infections (4.8% vs. 5.6%). The most common serious adverse events (in at least 1% of patients) were pneumonia, atrial fibrillation, heart failure, and coronary artery disease. Dry mouth and urinary retention were rare, and occurred in less than 1% of patients in each group.
“No patient subgroup demonstrated a difference in efficacy except when analyzed by baseline COPD severity, in which the treatment benefit was observed only in patients with FEV1 [forced expiratory volume in 1 second] of 50% predicted or less,” the researchers noted. “This may be explained by the lower exacerbation rate seen in the placebo group in patients with moderate airway obstruction vs. severe or very severe obstruction,” they said.
“Outcomes of this trial add data to the long-standing controversy over the safety of LAMAs in COPD” and support the need for additional research, they said.
The study findings were limited by several factors including insufficient power to detect cause-specific mortality and the use of a LAMA with low risk of systemic effects, the researchers noted.
SOURCE: Wise R et al. JAMA. 2019. 321:1693-1701.
, compared with placebo, in a randomized trial of more than 3,000 patients.
Aclidinium, a long-acting muscarinic antagonist (LAMA), has been shown to reduce COPD exacerbation in the short term, but long-term effectiveness has not been examined, wrote Robert A. Wise, MD, of Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, and colleagues.
ASCENT-COPD is a multicenter, double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled, parallel-group noninferiority study conducted at 522 sites in the United States and Canada. A paper on recent data from ASCENT-COPD, published in JAMA, supports early findings reported last year at the American Thoracic Society meeting.
The researchers randomized adults with COPD to a 400-mg dose of aclidinium bromide twice daily, or placebo. The average age of the patients was 67 years; 59% were men. The median exposure time to aclidinium or placebo was 365 days during the first year of treatment, and the median exposure overall was 495 days for aclidinium patients and 478 days for placebo patients.
Of the 2,537 patients who completed the study, 69 (3.9%) in the aclidinium group and 76 (4.2%) in the placebo group experienced a major adverse cardiovascular event (MACE, defined as a composite of cardiovascular death, nonfatal myocardial infarction, and nonfatal stroke).
In addition, annual rates of moderate to severe COPD exacerbations were significantly lower in the aclidinium patients compared with placebo patients (0.44 vs. 0.57, P less than .001).
In a secondary analysis with a definition of MACE expanded to include heart failure, arrhythmias, or cerebrovascular disease, results remained similar between the groups; events occurred in 168 aclidinium patients (9.4%) and 160 placebo patients (8.9%). The rate of COPD exacerbations requiring hospitalization was significantly lower in aclidinium patients, compared with placebo patients (0.07 vs. 0.10, P = .006).
Overall, the most common treatment-emergent adverse events were similar in the aclidinium and placebo groups, respectively; pneumonia (6.1% vs. 5.8%), urinary tract infections (5.2% vs. 5.0%), and upper respiratory tract infections (4.8% vs. 5.6%). The most common serious adverse events (in at least 1% of patients) were pneumonia, atrial fibrillation, heart failure, and coronary artery disease. Dry mouth and urinary retention were rare, and occurred in less than 1% of patients in each group.
“No patient subgroup demonstrated a difference in efficacy except when analyzed by baseline COPD severity, in which the treatment benefit was observed only in patients with FEV1 [forced expiratory volume in 1 second] of 50% predicted or less,” the researchers noted. “This may be explained by the lower exacerbation rate seen in the placebo group in patients with moderate airway obstruction vs. severe or very severe obstruction,” they said.
“Outcomes of this trial add data to the long-standing controversy over the safety of LAMAs in COPD” and support the need for additional research, they said.
The study findings were limited by several factors including insufficient power to detect cause-specific mortality and the use of a LAMA with low risk of systemic effects, the researchers noted.
SOURCE: Wise R et al. JAMA. 2019. 321:1693-1701.
, compared with placebo, in a randomized trial of more than 3,000 patients.
Aclidinium, a long-acting muscarinic antagonist (LAMA), has been shown to reduce COPD exacerbation in the short term, but long-term effectiveness has not been examined, wrote Robert A. Wise, MD, of Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, and colleagues.
ASCENT-COPD is a multicenter, double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled, parallel-group noninferiority study conducted at 522 sites in the United States and Canada. A paper on recent data from ASCENT-COPD, published in JAMA, supports early findings reported last year at the American Thoracic Society meeting.
The researchers randomized adults with COPD to a 400-mg dose of aclidinium bromide twice daily, or placebo. The average age of the patients was 67 years; 59% were men. The median exposure time to aclidinium or placebo was 365 days during the first year of treatment, and the median exposure overall was 495 days for aclidinium patients and 478 days for placebo patients.
Of the 2,537 patients who completed the study, 69 (3.9%) in the aclidinium group and 76 (4.2%) in the placebo group experienced a major adverse cardiovascular event (MACE, defined as a composite of cardiovascular death, nonfatal myocardial infarction, and nonfatal stroke).
In addition, annual rates of moderate to severe COPD exacerbations were significantly lower in the aclidinium patients compared with placebo patients (0.44 vs. 0.57, P less than .001).
In a secondary analysis with a definition of MACE expanded to include heart failure, arrhythmias, or cerebrovascular disease, results remained similar between the groups; events occurred in 168 aclidinium patients (9.4%) and 160 placebo patients (8.9%). The rate of COPD exacerbations requiring hospitalization was significantly lower in aclidinium patients, compared with placebo patients (0.07 vs. 0.10, P = .006).
Overall, the most common treatment-emergent adverse events were similar in the aclidinium and placebo groups, respectively; pneumonia (6.1% vs. 5.8%), urinary tract infections (5.2% vs. 5.0%), and upper respiratory tract infections (4.8% vs. 5.6%). The most common serious adverse events (in at least 1% of patients) were pneumonia, atrial fibrillation, heart failure, and coronary artery disease. Dry mouth and urinary retention were rare, and occurred in less than 1% of patients in each group.
“No patient subgroup demonstrated a difference in efficacy except when analyzed by baseline COPD severity, in which the treatment benefit was observed only in patients with FEV1 [forced expiratory volume in 1 second] of 50% predicted or less,” the researchers noted. “This may be explained by the lower exacerbation rate seen in the placebo group in patients with moderate airway obstruction vs. severe or very severe obstruction,” they said.
“Outcomes of this trial add data to the long-standing controversy over the safety of LAMAs in COPD” and support the need for additional research, they said.
The study findings were limited by several factors including insufficient power to detect cause-specific mortality and the use of a LAMA with low risk of systemic effects, the researchers noted.
SOURCE: Wise R et al. JAMA. 2019. 321:1693-1701.
FROM JAMA
New risk score predicts cardiac-device infection
SAN FRANCISCO – Researchers have devised a five-item scoring formula to quantify the risk for infection in patients undergoing placement, revision, or removal of a cardiac-rhythm device based on data from nearly 20,000 patients enrolled in a recent infection-prophylaxis trial.
The risk score can help identify patients who might benefit from intensified antibiotic prophylaxis, and it can also help during shared decision making with patients to better understand the risk a patient faces from infection, compared with their predicted device benefit, David H. Birnie, MD, said at the annual scientific sessions of the Heart Rhythm Society.
The new risk score produced a concordance statistic, the area under the receiver-operator characteristic curve, of 0.704. It showed that, although it could use further validation, the score as it currently stands has substantial predictive value, said Dr. Birnie, professor of medicine at the University of Ottawa and deputy chief of cardiology at the University of Ottawa Heart Institute. “It’s certainly better than anything we have now,” he said in a video interview.
Dr. Birnie and his associates used data they collected on baseline characteristics and infection outcomes of the 19,603 patients enrolled in PADIT (Prevention of Arrhythmia Device Infection Trial) who underwent a rhythm-device procedure at 1 of 28 participating Canadian centers. The primary aim of PADIT was to assess the safety and efficacy of an intensified antibiotic-prophylaxis regimen, compared with a standard regimen of a cefazolin infusion just before the procedure. The study’s primary endpoint was the incidence of hospitalization for device infection during 1-year follow-up, and while the intensified prophylactic regimen linked with a 23% relative reduction in the hospitalization rate, compared with standard treatment, the difference was not statistically significant (J Am Coll Cardiol. 2018 Dec 18;72[24]:3098-109).
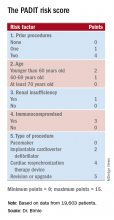
The researchers analyzed the baseline patient data and the blindly adjudicated infection outcomes and identified five factors that were independently associated with an increased infection rate. They organized the five factors and produced a formula they call the PADIT score (see chart). Those five factors are: prior procedures (the greater the number the greater the risk), age (which unexpectedly had an inverse relationship with infection incidence), depressed renal function, immuno-compromised status, and type of procedure. A patient can potentially score 0-15 points.
Among the PADIT patients a score of 0 correlated with about a 0.3% rate of hospitalization for a device-related infection during 1 year of follow-up, a score of 5 with about a 1.1% rate, a score of 6 with about a 1.8% rate, and a score of seven or more with a 3.4% infection rate over the following year. About 5% of patients had a score of 7 or more, and roughly another 5% had a score of 5 or 6, Dr. Birnie said. At his center, clinicians have begun routinely calculating scores for patients scheduled for an arrhythmia-device procedure, and they are considering routinely administering added antibiotic prophylaxis to patients with a preprocedural score of 6 or higher. They may also use the score to determine whether to use the antibacterial envelope recently reported to prevent cardiac-device infections (N Engl J Med. 2019 May 16;380[20]:1895-905).
“It’s very easy for patients to get to a PADIT score of 7 or higher,” Dr. Birnie noted. As an example, he cited a common patient, an 85-year-old with renal dysfunction who is under consideration for a second replacement of an implantable cardioverter defibrillator. The patient would score 1 point for renal insufficiency, 2 points for the type of device, and 4 points for having a prior history of two devices, and the consequent 3.4% risk for infection might counterbalance the potential benefit this elderly patient could expect from the new device. The score will be very important for targeting treatment, shared decision making, and selection of patients for future intervention trials, he concluded.
“I think this risk score will change practice by giving clinicians a better idea of a patient’s risk for infection,” commented Fred M. Kusumoto, MD, professor of medicine at the Mayo Medical School, Rochester, Minn., and director of heart rhythm services at the Mayo Clinic in Jacksonville, Fla. The PADIT score will help identify patients for whom leaving a device in place is a better option than taking it out because of their infection risk. The risk score could also help improve the cost effectiveness of preventive treatments, such as antibiotic-eluting envelopes, by targeting treatment to higher-risk patients, Dr. Kusumoto said during a press briefing.
SOURCE: Birnie DH. Heart Rhythm 2019, Absract S-LCT02-01.
I like this new infection risk score. It addresses a very clinically relevant issue. It’s important for the electrophysiology community to better understand how to best manage infections related to cardiac rhythm devices and ideally prevent them from happening.
I’m not a big fan of risk scores in general because they can sometimes detract from independent thinking about how to manage a patient. However, it is also helpful to have this type of risk-assessment information when discussing management options with a patient.
The PADIT risk score may also help identify which patients could potentially benefit the most from an antibiotic-eluting envelope when receiving an implanted cardiac-rhythm device. Recently reported results from WRAP-IT showed that routinely using envelopes cut the incidence of major infections by a relative 40%, but in absolute terms, the number needed to treat with the envelop to prevent one major infection was about 200 patients, a big number given the high cost of the envelope (N Engl J Med. 2019 May 16;380[20]:1895-905). It is therefore very interesting to think about using the PADIT risk score to better target an effective but expensive preventive measure like an antibiotic-eluting envelop to patients at the highest risk for infection.
Ulrika Birgersdotter-Green, MD , professor of medicine and director of pacemaker and ICD services at the University of California, San Diego, made these comments as a designated discussant for the report. She has been a consultant to and received honoraria from Abbott, Boston Scientific, and Medtronic.
I like this new infection risk score. It addresses a very clinically relevant issue. It’s important for the electrophysiology community to better understand how to best manage infections related to cardiac rhythm devices and ideally prevent them from happening.
I’m not a big fan of risk scores in general because they can sometimes detract from independent thinking about how to manage a patient. However, it is also helpful to have this type of risk-assessment information when discussing management options with a patient.
The PADIT risk score may also help identify which patients could potentially benefit the most from an antibiotic-eluting envelope when receiving an implanted cardiac-rhythm device. Recently reported results from WRAP-IT showed that routinely using envelopes cut the incidence of major infections by a relative 40%, but in absolute terms, the number needed to treat with the envelop to prevent one major infection was about 200 patients, a big number given the high cost of the envelope (N Engl J Med. 2019 May 16;380[20]:1895-905). It is therefore very interesting to think about using the PADIT risk score to better target an effective but expensive preventive measure like an antibiotic-eluting envelop to patients at the highest risk for infection.
Ulrika Birgersdotter-Green, MD , professor of medicine and director of pacemaker and ICD services at the University of California, San Diego, made these comments as a designated discussant for the report. She has been a consultant to and received honoraria from Abbott, Boston Scientific, and Medtronic.
I like this new infection risk score. It addresses a very clinically relevant issue. It’s important for the electrophysiology community to better understand how to best manage infections related to cardiac rhythm devices and ideally prevent them from happening.
I’m not a big fan of risk scores in general because they can sometimes detract from independent thinking about how to manage a patient. However, it is also helpful to have this type of risk-assessment information when discussing management options with a patient.
The PADIT risk score may also help identify which patients could potentially benefit the most from an antibiotic-eluting envelope when receiving an implanted cardiac-rhythm device. Recently reported results from WRAP-IT showed that routinely using envelopes cut the incidence of major infections by a relative 40%, but in absolute terms, the number needed to treat with the envelop to prevent one major infection was about 200 patients, a big number given the high cost of the envelope (N Engl J Med. 2019 May 16;380[20]:1895-905). It is therefore very interesting to think about using the PADIT risk score to better target an effective but expensive preventive measure like an antibiotic-eluting envelop to patients at the highest risk for infection.
Ulrika Birgersdotter-Green, MD , professor of medicine and director of pacemaker and ICD services at the University of California, San Diego, made these comments as a designated discussant for the report. She has been a consultant to and received honoraria from Abbott, Boston Scientific, and Medtronic.
SAN FRANCISCO – Researchers have devised a five-item scoring formula to quantify the risk for infection in patients undergoing placement, revision, or removal of a cardiac-rhythm device based on data from nearly 20,000 patients enrolled in a recent infection-prophylaxis trial.
The risk score can help identify patients who might benefit from intensified antibiotic prophylaxis, and it can also help during shared decision making with patients to better understand the risk a patient faces from infection, compared with their predicted device benefit, David H. Birnie, MD, said at the annual scientific sessions of the Heart Rhythm Society.
The new risk score produced a concordance statistic, the area under the receiver-operator characteristic curve, of 0.704. It showed that, although it could use further validation, the score as it currently stands has substantial predictive value, said Dr. Birnie, professor of medicine at the University of Ottawa and deputy chief of cardiology at the University of Ottawa Heart Institute. “It’s certainly better than anything we have now,” he said in a video interview.
Dr. Birnie and his associates used data they collected on baseline characteristics and infection outcomes of the 19,603 patients enrolled in PADIT (Prevention of Arrhythmia Device Infection Trial) who underwent a rhythm-device procedure at 1 of 28 participating Canadian centers. The primary aim of PADIT was to assess the safety and efficacy of an intensified antibiotic-prophylaxis regimen, compared with a standard regimen of a cefazolin infusion just before the procedure. The study’s primary endpoint was the incidence of hospitalization for device infection during 1-year follow-up, and while the intensified prophylactic regimen linked with a 23% relative reduction in the hospitalization rate, compared with standard treatment, the difference was not statistically significant (J Am Coll Cardiol. 2018 Dec 18;72[24]:3098-109).
The researchers analyzed the baseline patient data and the blindly adjudicated infection outcomes and identified five factors that were independently associated with an increased infection rate. They organized the five factors and produced a formula they call the PADIT score (see chart). Those five factors are: prior procedures (the greater the number the greater the risk), age (which unexpectedly had an inverse relationship with infection incidence), depressed renal function, immuno-compromised status, and type of procedure. A patient can potentially score 0-15 points.
Among the PADIT patients a score of 0 correlated with about a 0.3% rate of hospitalization for a device-related infection during 1 year of follow-up, a score of 5 with about a 1.1% rate, a score of 6 with about a 1.8% rate, and a score of seven or more with a 3.4% infection rate over the following year. About 5% of patients had a score of 7 or more, and roughly another 5% had a score of 5 or 6, Dr. Birnie said. At his center, clinicians have begun routinely calculating scores for patients scheduled for an arrhythmia-device procedure, and they are considering routinely administering added antibiotic prophylaxis to patients with a preprocedural score of 6 or higher. They may also use the score to determine whether to use the antibacterial envelope recently reported to prevent cardiac-device infections (N Engl J Med. 2019 May 16;380[20]:1895-905).
“It’s very easy for patients to get to a PADIT score of 7 or higher,” Dr. Birnie noted. As an example, he cited a common patient, an 85-year-old with renal dysfunction who is under consideration for a second replacement of an implantable cardioverter defibrillator. The patient would score 1 point for renal insufficiency, 2 points for the type of device, and 4 points for having a prior history of two devices, and the consequent 3.4% risk for infection might counterbalance the potential benefit this elderly patient could expect from the new device. The score will be very important for targeting treatment, shared decision making, and selection of patients for future intervention trials, he concluded.
“I think this risk score will change practice by giving clinicians a better idea of a patient’s risk for infection,” commented Fred M. Kusumoto, MD, professor of medicine at the Mayo Medical School, Rochester, Minn., and director of heart rhythm services at the Mayo Clinic in Jacksonville, Fla. The PADIT score will help identify patients for whom leaving a device in place is a better option than taking it out because of their infection risk. The risk score could also help improve the cost effectiveness of preventive treatments, such as antibiotic-eluting envelopes, by targeting treatment to higher-risk patients, Dr. Kusumoto said during a press briefing.
SOURCE: Birnie DH. Heart Rhythm 2019, Absract S-LCT02-01.
SAN FRANCISCO – Researchers have devised a five-item scoring formula to quantify the risk for infection in patients undergoing placement, revision, or removal of a cardiac-rhythm device based on data from nearly 20,000 patients enrolled in a recent infection-prophylaxis trial.
The risk score can help identify patients who might benefit from intensified antibiotic prophylaxis, and it can also help during shared decision making with patients to better understand the risk a patient faces from infection, compared with their predicted device benefit, David H. Birnie, MD, said at the annual scientific sessions of the Heart Rhythm Society.
The new risk score produced a concordance statistic, the area under the receiver-operator characteristic curve, of 0.704. It showed that, although it could use further validation, the score as it currently stands has substantial predictive value, said Dr. Birnie, professor of medicine at the University of Ottawa and deputy chief of cardiology at the University of Ottawa Heart Institute. “It’s certainly better than anything we have now,” he said in a video interview.
Dr. Birnie and his associates used data they collected on baseline characteristics and infection outcomes of the 19,603 patients enrolled in PADIT (Prevention of Arrhythmia Device Infection Trial) who underwent a rhythm-device procedure at 1 of 28 participating Canadian centers. The primary aim of PADIT was to assess the safety and efficacy of an intensified antibiotic-prophylaxis regimen, compared with a standard regimen of a cefazolin infusion just before the procedure. The study’s primary endpoint was the incidence of hospitalization for device infection during 1-year follow-up, and while the intensified prophylactic regimen linked with a 23% relative reduction in the hospitalization rate, compared with standard treatment, the difference was not statistically significant (J Am Coll Cardiol. 2018 Dec 18;72[24]:3098-109).
The researchers analyzed the baseline patient data and the blindly adjudicated infection outcomes and identified five factors that were independently associated with an increased infection rate. They organized the five factors and produced a formula they call the PADIT score (see chart). Those five factors are: prior procedures (the greater the number the greater the risk), age (which unexpectedly had an inverse relationship with infection incidence), depressed renal function, immuno-compromised status, and type of procedure. A patient can potentially score 0-15 points.
Among the PADIT patients a score of 0 correlated with about a 0.3% rate of hospitalization for a device-related infection during 1 year of follow-up, a score of 5 with about a 1.1% rate, a score of 6 with about a 1.8% rate, and a score of seven or more with a 3.4% infection rate over the following year. About 5% of patients had a score of 7 or more, and roughly another 5% had a score of 5 or 6, Dr. Birnie said. At his center, clinicians have begun routinely calculating scores for patients scheduled for an arrhythmia-device procedure, and they are considering routinely administering added antibiotic prophylaxis to patients with a preprocedural score of 6 or higher. They may also use the score to determine whether to use the antibacterial envelope recently reported to prevent cardiac-device infections (N Engl J Med. 2019 May 16;380[20]:1895-905).
“It’s very easy for patients to get to a PADIT score of 7 or higher,” Dr. Birnie noted. As an example, he cited a common patient, an 85-year-old with renal dysfunction who is under consideration for a second replacement of an implantable cardioverter defibrillator. The patient would score 1 point for renal insufficiency, 2 points for the type of device, and 4 points for having a prior history of two devices, and the consequent 3.4% risk for infection might counterbalance the potential benefit this elderly patient could expect from the new device. The score will be very important for targeting treatment, shared decision making, and selection of patients for future intervention trials, he concluded.
“I think this risk score will change practice by giving clinicians a better idea of a patient’s risk for infection,” commented Fred M. Kusumoto, MD, professor of medicine at the Mayo Medical School, Rochester, Minn., and director of heart rhythm services at the Mayo Clinic in Jacksonville, Fla. The PADIT score will help identify patients for whom leaving a device in place is a better option than taking it out because of their infection risk. The risk score could also help improve the cost effectiveness of preventive treatments, such as antibiotic-eluting envelopes, by targeting treatment to higher-risk patients, Dr. Kusumoto said during a press briefing.
SOURCE: Birnie DH. Heart Rhythm 2019, Absract S-LCT02-01.
REPORTING FROM HEART RHYTHM 2019
Key clinical point: Researchers have devised a five-item scoring formula to predict a patient’s risk for infection from an cardiac rhythm–device procedure.
Major finding: The risk score had an optimism-corrected concordance statistic of 0.704.
Study details: Investigators developed the risk score using data from PADIT, a multicenter, randomized trial with 19,603 patients.
Disclosures: PADIT received no commercial funding. Dr. Birnie had no relevant disclosures.
Source: Birnie DH. Heart Rhythm 2019, Absract S-LCT02-01.
ICYMI: Dabigatran no better than aspirin for recurrent stroke prevention
Dabigatran was slightly but not significantly superior to aspirin at the prevention of recurring stroke in patients with a recent history of embolic stroke of undetermined source over a median follow-up of 19 months (6.6% rate of recurrent stroke for dabigatran vs. 7.7% for aspirin; hazard ratio, 0.85; 95% confidence interval, 0.69-1.03; P = 0.10), according to RE-SPECT ESUS, a multicenter, randomized, double-blind trial published in the New England Journal of Medicine (2019 May 15. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1813959).
We first reported on the results of this trial when they were presented at the World Stroke Congress by lead investigator Hans-Christoph Diener, MD. Find our coverage at the link below.
Dabigatran was slightly but not significantly superior to aspirin at the prevention of recurring stroke in patients with a recent history of embolic stroke of undetermined source over a median follow-up of 19 months (6.6% rate of recurrent stroke for dabigatran vs. 7.7% for aspirin; hazard ratio, 0.85; 95% confidence interval, 0.69-1.03; P = 0.10), according to RE-SPECT ESUS, a multicenter, randomized, double-blind trial published in the New England Journal of Medicine (2019 May 15. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1813959).
We first reported on the results of this trial when they were presented at the World Stroke Congress by lead investigator Hans-Christoph Diener, MD. Find our coverage at the link below.
Dabigatran was slightly but not significantly superior to aspirin at the prevention of recurring stroke in patients with a recent history of embolic stroke of undetermined source over a median follow-up of 19 months (6.6% rate of recurrent stroke for dabigatran vs. 7.7% for aspirin; hazard ratio, 0.85; 95% confidence interval, 0.69-1.03; P = 0.10), according to RE-SPECT ESUS, a multicenter, randomized, double-blind trial published in the New England Journal of Medicine (2019 May 15. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1813959).
We first reported on the results of this trial when they were presented at the World Stroke Congress by lead investigator Hans-Christoph Diener, MD. Find our coverage at the link below.
FROM THE NEW ENGLAND JOURNAL OF MEDICINE
Aspirin shows little benefit for primary prevention of vascular disease in diabetes
Background: Multiple large, randomized, controlled trials and meta-analyses that used aspirin as primary prevention for vascular events showed decreased vascular events, but a significant counterbalanced risk of bleeding. Since diabetes carries a higher risk of vascular events, this study examines aspirin for primary prevention of vascular events in diabetic patients.
Study design: Large, randomized, controlled trial.
Setting: British registry-based study.
Synopsis: This is a 9-year randomized, controlled trial that included 15,480 British patients with diabetes without known vascular disease who were randomized to receive a 100-mg aspirin daily or placebo. Participants in each group were closely matched patients with diabetes who were recruited using registry data and were aged 40 years and older with no alternative strong indication for aspirin.
Overall, aspirin provided no difference in mortality but showed an absolute 1.3% decrease in first vascular events or revascularization procedures with an absolute 1.1% increase in first occurrence of major bleeding event. Approximately 60% of the bleeding events were gastrointestinal or “other” urinary/nose bleeding, and there was no statistically significant increase in intracranial hemorrhage, hemorrhagic stroke, or vision-threatening eye bleeding. Vascular events were defined as transient ischemic attack (TIA), nonfatal MI, nonfatal ischemic stroke, or vascular death excluding intracranial hemorrhage. The major limitation of this study is that it had a composite of endpoints of different clinical significance. Furthermore, TIA as a major vascular event was added after the study began to increase statistical power, and when it is excluded, the difference for vascular events is not statistically significant.
Bottom line: Aspirin when used in primary prevention of vascular events in diabetes provides no improvement in mortality, and the benefit of prevention of vascular events must be weighed against the risks of bleeding.
Citation: The ASCEND Study Collaborative Group. Effects of aspirin for primary prevention in diabetes. N Eng J Med. 2018 Oct 18;379(16):1529-39.
Dr. Scott is an assistant professor in the division of hospital medicine, University of New Mexico.
Background: Multiple large, randomized, controlled trials and meta-analyses that used aspirin as primary prevention for vascular events showed decreased vascular events, but a significant counterbalanced risk of bleeding. Since diabetes carries a higher risk of vascular events, this study examines aspirin for primary prevention of vascular events in diabetic patients.
Study design: Large, randomized, controlled trial.
Setting: British registry-based study.
Synopsis: This is a 9-year randomized, controlled trial that included 15,480 British patients with diabetes without known vascular disease who were randomized to receive a 100-mg aspirin daily or placebo. Participants in each group were closely matched patients with diabetes who were recruited using registry data and were aged 40 years and older with no alternative strong indication for aspirin.
Overall, aspirin provided no difference in mortality but showed an absolute 1.3% decrease in first vascular events or revascularization procedures with an absolute 1.1% increase in first occurrence of major bleeding event. Approximately 60% of the bleeding events were gastrointestinal or “other” urinary/nose bleeding, and there was no statistically significant increase in intracranial hemorrhage, hemorrhagic stroke, or vision-threatening eye bleeding. Vascular events were defined as transient ischemic attack (TIA), nonfatal MI, nonfatal ischemic stroke, or vascular death excluding intracranial hemorrhage. The major limitation of this study is that it had a composite of endpoints of different clinical significance. Furthermore, TIA as a major vascular event was added after the study began to increase statistical power, and when it is excluded, the difference for vascular events is not statistically significant.
Bottom line: Aspirin when used in primary prevention of vascular events in diabetes provides no improvement in mortality, and the benefit of prevention of vascular events must be weighed against the risks of bleeding.
Citation: The ASCEND Study Collaborative Group. Effects of aspirin for primary prevention in diabetes. N Eng J Med. 2018 Oct 18;379(16):1529-39.
Dr. Scott is an assistant professor in the division of hospital medicine, University of New Mexico.
Background: Multiple large, randomized, controlled trials and meta-analyses that used aspirin as primary prevention for vascular events showed decreased vascular events, but a significant counterbalanced risk of bleeding. Since diabetes carries a higher risk of vascular events, this study examines aspirin for primary prevention of vascular events in diabetic patients.
Study design: Large, randomized, controlled trial.
Setting: British registry-based study.
Synopsis: This is a 9-year randomized, controlled trial that included 15,480 British patients with diabetes without known vascular disease who were randomized to receive a 100-mg aspirin daily or placebo. Participants in each group were closely matched patients with diabetes who were recruited using registry data and were aged 40 years and older with no alternative strong indication for aspirin.
Overall, aspirin provided no difference in mortality but showed an absolute 1.3% decrease in first vascular events or revascularization procedures with an absolute 1.1% increase in first occurrence of major bleeding event. Approximately 60% of the bleeding events were gastrointestinal or “other” urinary/nose bleeding, and there was no statistically significant increase in intracranial hemorrhage, hemorrhagic stroke, or vision-threatening eye bleeding. Vascular events were defined as transient ischemic attack (TIA), nonfatal MI, nonfatal ischemic stroke, or vascular death excluding intracranial hemorrhage. The major limitation of this study is that it had a composite of endpoints of different clinical significance. Furthermore, TIA as a major vascular event was added after the study began to increase statistical power, and when it is excluded, the difference for vascular events is not statistically significant.
Bottom line: Aspirin when used in primary prevention of vascular events in diabetes provides no improvement in mortality, and the benefit of prevention of vascular events must be weighed against the risks of bleeding.
Citation: The ASCEND Study Collaborative Group. Effects of aspirin for primary prevention in diabetes. N Eng J Med. 2018 Oct 18;379(16):1529-39.
Dr. Scott is an assistant professor in the division of hospital medicine, University of New Mexico.
Peanut contamination risk prompts Promacta recall
Novartis has recalled three lots of 12.5-mg eltrombopag (Promacta) for oral suspension following discovery of possible contamination with peanut flour at a third-party manufacturing site.
Tablets at doses of 12.5 mg, 25 mg, 50 mg, and 75 mg are unaffected by this recall because they are not manufactured in the same facility. The recalled lots of medication were distributed between January and April 2019, but so far, Novartis has not received any reports of adverse events related to the recall.
Oral suspension of eltrombopag is indicated for certain patients with chronic immune thrombocytopenia, hepatitis C–associated thrombocytopenia, and severe aplastic anemia.
More information on the recalled lots and instructions on how to return the product can be found in the full announcement, which is also available through the Food and Drug Administration website.
Novartis has recalled three lots of 12.5-mg eltrombopag (Promacta) for oral suspension following discovery of possible contamination with peanut flour at a third-party manufacturing site.
Tablets at doses of 12.5 mg, 25 mg, 50 mg, and 75 mg are unaffected by this recall because they are not manufactured in the same facility. The recalled lots of medication were distributed between January and April 2019, but so far, Novartis has not received any reports of adverse events related to the recall.
Oral suspension of eltrombopag is indicated for certain patients with chronic immune thrombocytopenia, hepatitis C–associated thrombocytopenia, and severe aplastic anemia.
More information on the recalled lots and instructions on how to return the product can be found in the full announcement, which is also available through the Food and Drug Administration website.
Novartis has recalled three lots of 12.5-mg eltrombopag (Promacta) for oral suspension following discovery of possible contamination with peanut flour at a third-party manufacturing site.
Tablets at doses of 12.5 mg, 25 mg, 50 mg, and 75 mg are unaffected by this recall because they are not manufactured in the same facility. The recalled lots of medication were distributed between January and April 2019, but so far, Novartis has not received any reports of adverse events related to the recall.
Oral suspension of eltrombopag is indicated for certain patients with chronic immune thrombocytopenia, hepatitis C–associated thrombocytopenia, and severe aplastic anemia.
More information on the recalled lots and instructions on how to return the product can be found in the full announcement, which is also available through the Food and Drug Administration website.
Severe OSA increases cardiovascular risk after surgery
Unrecognized severe obstructive sleep apnea is a risk factor for cardiovascular complications after major noncardiac surgery, according to a study published in JAMA.
The researchers state that perioperative mismanagement of obstructive sleep apnea can lead to serious medical consequences. “General anesthetics, sedatives, and postoperative analgesics are potent respiratory depressants that relax the upper airway dilator muscles and impair ventilatory response to hypoxemia and hypercapnia. Each of these events exacerbates [obstructive sleep apnea] and may predispose patients to postoperative cardiovascular complications,” said researchers who conducted the The Postoperative vascular complications in unrecognised Obstructive Sleep apnoea (POSA) study (NCT01494181).
They undertook a prospective observational cohort study involving 1,218 patients undergoing major noncardiac surgery, who were already considered at high risk of postoperative cardiovascular events – having, for example, a history of coronary artery disease, stroke, diabetes, or renal impairment. However, none had a prior diagnosis of obstructive sleep apnea.
Preoperative sleep monitoring revealed that two-thirds of the cohort had unrecognized and untreated obstructive sleep apnea, including 11.2% with severe obstructive sleep apnea.
At 30 days after surgery, patients with obstructive sleep apnea had a 49% higher risk of the primary outcome of myocardial injury, cardiac death, heart failure, thromboembolism, atrial fibrillation, or stroke, compared with those without obstructive sleep apnea.
However, this association was largely due to a significant 2.23-fold higher risk among patients with severe obstructive sleep apnea, while those with only moderate or mild sleep apnea did not show a significant increased risk of cardiovascular complications.
Patients in this study with severe obstructive sleep apnea had a 13-fold higher risk of cardiac death, 80% higher risk of myocardial injury, more than sixfold higher risk of heart failure, and nearly fourfold higher risk of atrial fibrillation.
Researchers also saw an association between obstructive sleep apnea and increased risk of infective outcomes, unplanned tracheal intubation, postoperative lung ventilation, and readmission to the ICU.
The majority of patients received nocturnal oximetry monitoring during their first 3 nights after surgery. This revealed that patients without obstructive sleep apnea had significant increases in oxygen desaturation index during their first night after surgery, while those with sleep apnea did not return to their baseline oxygen desaturation index until the third night after surgery.
“Despite a substantial decrease in ODI [oxygen desaturation index] with oxygen therapy in patients with OSA during the first 3 postoperative nights, supplemental oxygen did not modify the association between OSA and postoperative cardiovascular event,” wrote Matthew T.V. Chan, MD, of Chinese University of Hong Kong, Prince of Wales Hospital, and coauthors.
Given that the events were associated with longer durations of severe oxyhemoglobin desaturation, more aggressive interventions such as positive airway pressure or oral appliances may be required, they noted.
“However, high-level evidence demonstrating the effect of these measures on perioperative outcomes is lacking [and] further clinical trials are now required to test if additional monitoring or alternative interventions would reduce the risk,” they wrote.
The study was supported by the Health and Medical Research Fund (Hong Kong), National Healthcare Group–Khoo Teck Puat Hospital, University Health Network Foundation, University of Malaya, Malaysian Society of Anaesthesiologists, Auckland Medical Research Foundation, and ResMed. One author declared grants from private industry and a patent pending on an obstructive sleep apnea risk questionnaire used in the study.
SOURCE: Chan M et al. JAMA 2019;321[18]:1788-98. doi: 10.1001/jama.2019.4783.
This study is large, prospective, and rigorous and adds important new information to the puzzle of the impact of sleep apnea on postoperative risk, Dennis Auckley, MD, and Stavros Memtsoudis, MD, wrote in an editorial accompanying this study. The study focused on predetermined clinically significant and measurable events, used standardized and objective sleep apnea testing, and attempted to control for many of the confounders that might have influenced outcomes.
The results suggest that obstructive sleep apnea should be recognized as a major perioperative risk factor, and it should receive the same attention and optimization efforts as comorbidities such as diabetes.
Dr. Auckley is from the division of pulmonary, critical care and sleep medicine at MetroHealth Medical Center, Case Western Reserve University, Cleveland, and Dr. Memtsoudis is clinical professor of anesthesiology at Cornell University, New York. These comments are adapted from an editorial (JAMA 2019;231[18]:1775-6). Both declared board and executive positions with the Society of Anesthesia and Sleep Medicine. Dr. Auckley declared research funding from Medtronic, and Dr. Memtsoudis declared personal fees from Teikoku and Sandoz.
This study is large, prospective, and rigorous and adds important new information to the puzzle of the impact of sleep apnea on postoperative risk, Dennis Auckley, MD, and Stavros Memtsoudis, MD, wrote in an editorial accompanying this study. The study focused on predetermined clinically significant and measurable events, used standardized and objective sleep apnea testing, and attempted to control for many of the confounders that might have influenced outcomes.
The results suggest that obstructive sleep apnea should be recognized as a major perioperative risk factor, and it should receive the same attention and optimization efforts as comorbidities such as diabetes.
Dr. Auckley is from the division of pulmonary, critical care and sleep medicine at MetroHealth Medical Center, Case Western Reserve University, Cleveland, and Dr. Memtsoudis is clinical professor of anesthesiology at Cornell University, New York. These comments are adapted from an editorial (JAMA 2019;231[18]:1775-6). Both declared board and executive positions with the Society of Anesthesia and Sleep Medicine. Dr. Auckley declared research funding from Medtronic, and Dr. Memtsoudis declared personal fees from Teikoku and Sandoz.
This study is large, prospective, and rigorous and adds important new information to the puzzle of the impact of sleep apnea on postoperative risk, Dennis Auckley, MD, and Stavros Memtsoudis, MD, wrote in an editorial accompanying this study. The study focused on predetermined clinically significant and measurable events, used standardized and objective sleep apnea testing, and attempted to control for many of the confounders that might have influenced outcomes.
The results suggest that obstructive sleep apnea should be recognized as a major perioperative risk factor, and it should receive the same attention and optimization efforts as comorbidities such as diabetes.
Dr. Auckley is from the division of pulmonary, critical care and sleep medicine at MetroHealth Medical Center, Case Western Reserve University, Cleveland, and Dr. Memtsoudis is clinical professor of anesthesiology at Cornell University, New York. These comments are adapted from an editorial (JAMA 2019;231[18]:1775-6). Both declared board and executive positions with the Society of Anesthesia and Sleep Medicine. Dr. Auckley declared research funding from Medtronic, and Dr. Memtsoudis declared personal fees from Teikoku and Sandoz.
Unrecognized severe obstructive sleep apnea is a risk factor for cardiovascular complications after major noncardiac surgery, according to a study published in JAMA.
The researchers state that perioperative mismanagement of obstructive sleep apnea can lead to serious medical consequences. “General anesthetics, sedatives, and postoperative analgesics are potent respiratory depressants that relax the upper airway dilator muscles and impair ventilatory response to hypoxemia and hypercapnia. Each of these events exacerbates [obstructive sleep apnea] and may predispose patients to postoperative cardiovascular complications,” said researchers who conducted the The Postoperative vascular complications in unrecognised Obstructive Sleep apnoea (POSA) study (NCT01494181).
They undertook a prospective observational cohort study involving 1,218 patients undergoing major noncardiac surgery, who were already considered at high risk of postoperative cardiovascular events – having, for example, a history of coronary artery disease, stroke, diabetes, or renal impairment. However, none had a prior diagnosis of obstructive sleep apnea.
Preoperative sleep monitoring revealed that two-thirds of the cohort had unrecognized and untreated obstructive sleep apnea, including 11.2% with severe obstructive sleep apnea.
At 30 days after surgery, patients with obstructive sleep apnea had a 49% higher risk of the primary outcome of myocardial injury, cardiac death, heart failure, thromboembolism, atrial fibrillation, or stroke, compared with those without obstructive sleep apnea.
However, this association was largely due to a significant 2.23-fold higher risk among patients with severe obstructive sleep apnea, while those with only moderate or mild sleep apnea did not show a significant increased risk of cardiovascular complications.
Patients in this study with severe obstructive sleep apnea had a 13-fold higher risk of cardiac death, 80% higher risk of myocardial injury, more than sixfold higher risk of heart failure, and nearly fourfold higher risk of atrial fibrillation.
Researchers also saw an association between obstructive sleep apnea and increased risk of infective outcomes, unplanned tracheal intubation, postoperative lung ventilation, and readmission to the ICU.
The majority of patients received nocturnal oximetry monitoring during their first 3 nights after surgery. This revealed that patients without obstructive sleep apnea had significant increases in oxygen desaturation index during their first night after surgery, while those with sleep apnea did not return to their baseline oxygen desaturation index until the third night after surgery.
“Despite a substantial decrease in ODI [oxygen desaturation index] with oxygen therapy in patients with OSA during the first 3 postoperative nights, supplemental oxygen did not modify the association between OSA and postoperative cardiovascular event,” wrote Matthew T.V. Chan, MD, of Chinese University of Hong Kong, Prince of Wales Hospital, and coauthors.
Given that the events were associated with longer durations of severe oxyhemoglobin desaturation, more aggressive interventions such as positive airway pressure or oral appliances may be required, they noted.
“However, high-level evidence demonstrating the effect of these measures on perioperative outcomes is lacking [and] further clinical trials are now required to test if additional monitoring or alternative interventions would reduce the risk,” they wrote.
The study was supported by the Health and Medical Research Fund (Hong Kong), National Healthcare Group–Khoo Teck Puat Hospital, University Health Network Foundation, University of Malaya, Malaysian Society of Anaesthesiologists, Auckland Medical Research Foundation, and ResMed. One author declared grants from private industry and a patent pending on an obstructive sleep apnea risk questionnaire used in the study.
SOURCE: Chan M et al. JAMA 2019;321[18]:1788-98. doi: 10.1001/jama.2019.4783.
Unrecognized severe obstructive sleep apnea is a risk factor for cardiovascular complications after major noncardiac surgery, according to a study published in JAMA.
The researchers state that perioperative mismanagement of obstructive sleep apnea can lead to serious medical consequences. “General anesthetics, sedatives, and postoperative analgesics are potent respiratory depressants that relax the upper airway dilator muscles and impair ventilatory response to hypoxemia and hypercapnia. Each of these events exacerbates [obstructive sleep apnea] and may predispose patients to postoperative cardiovascular complications,” said researchers who conducted the The Postoperative vascular complications in unrecognised Obstructive Sleep apnoea (POSA) study (NCT01494181).
They undertook a prospective observational cohort study involving 1,218 patients undergoing major noncardiac surgery, who were already considered at high risk of postoperative cardiovascular events – having, for example, a history of coronary artery disease, stroke, diabetes, or renal impairment. However, none had a prior diagnosis of obstructive sleep apnea.
Preoperative sleep monitoring revealed that two-thirds of the cohort had unrecognized and untreated obstructive sleep apnea, including 11.2% with severe obstructive sleep apnea.
At 30 days after surgery, patients with obstructive sleep apnea had a 49% higher risk of the primary outcome of myocardial injury, cardiac death, heart failure, thromboembolism, atrial fibrillation, or stroke, compared with those without obstructive sleep apnea.
However, this association was largely due to a significant 2.23-fold higher risk among patients with severe obstructive sleep apnea, while those with only moderate or mild sleep apnea did not show a significant increased risk of cardiovascular complications.
Patients in this study with severe obstructive sleep apnea had a 13-fold higher risk of cardiac death, 80% higher risk of myocardial injury, more than sixfold higher risk of heart failure, and nearly fourfold higher risk of atrial fibrillation.
Researchers also saw an association between obstructive sleep apnea and increased risk of infective outcomes, unplanned tracheal intubation, postoperative lung ventilation, and readmission to the ICU.
The majority of patients received nocturnal oximetry monitoring during their first 3 nights after surgery. This revealed that patients without obstructive sleep apnea had significant increases in oxygen desaturation index during their first night after surgery, while those with sleep apnea did not return to their baseline oxygen desaturation index until the third night after surgery.
“Despite a substantial decrease in ODI [oxygen desaturation index] with oxygen therapy in patients with OSA during the first 3 postoperative nights, supplemental oxygen did not modify the association between OSA and postoperative cardiovascular event,” wrote Matthew T.V. Chan, MD, of Chinese University of Hong Kong, Prince of Wales Hospital, and coauthors.
Given that the events were associated with longer durations of severe oxyhemoglobin desaturation, more aggressive interventions such as positive airway pressure or oral appliances may be required, they noted.
“However, high-level evidence demonstrating the effect of these measures on perioperative outcomes is lacking [and] further clinical trials are now required to test if additional monitoring or alternative interventions would reduce the risk,” they wrote.
The study was supported by the Health and Medical Research Fund (Hong Kong), National Healthcare Group–Khoo Teck Puat Hospital, University Health Network Foundation, University of Malaya, Malaysian Society of Anaesthesiologists, Auckland Medical Research Foundation, and ResMed. One author declared grants from private industry and a patent pending on an obstructive sleep apnea risk questionnaire used in the study.
SOURCE: Chan M et al. JAMA 2019;321[18]:1788-98. doi: 10.1001/jama.2019.4783.
FROM JAMA
Arsenic exposure increases risk of left ventricular hypertrophy
Young Native Americans had increased left ventricular thickness and left ventricular hypertrophy after being exposed to arsenic, and had a greater risk if they showed signs of prehypertension or hypertension, according to recent research.
“The stronger association in subjects with elevated blood pressure suggests that individuals with preclinical heart disease might be more prone to the toxic effects of arsenic on the heart,” Gernot Pichler, MD, PhD, a cardiologist at Hospital Hietzing/Heart Center Clinic Floridsdorf in Vienna, stated in a press release.
Dr. Pichler and colleagues evaluated 1,337 individuals (mean age, 31 years; 61% female) in the Strong Heart Family Study, an extension of the Strong Heart Study that was designed to study cardiovascular disease in Native Americans. The researchers noted that, while the studies were not originally intended to evaluate arsenic exposure in these populations, “the importance of studying arsenic was recognized overtime as increasing evidence supported the role of arsenic in cardiovascular disease and the relatively high arsenic exposure in tribal communities, compared to other general populations in the United States.”
Arsenic exposure was determined through the sum of inorganic and methylated arsenic concentrations in urine, and researchers used transthoracic ECG at baseline and follow-up to compare left ventricular geometry and function. The mean follow-up was 5.6 years and baseline median sum of inorganic and methylated arsenic concentrations in urine was 4.24 (interquartile range, 2.82-6.90) mcg/g creatinine.
Prevalence of left ventricular hypertrophy was 4.6% overall, and the odds ratio of left ventricular hypertrophy per 100% increase in arsenic in the urine was 1.47 (95% confidence interval, 1.05-2.08) overall and 1.58 for individuals with prehypertension or hypertension (95% CI, 1.04-2.41).
“People drinking water from private wells, which are not regulated, need to be aware that arsenic may increase the risk for cardiovascular disease,” said Dr. Pichler. “Testing those wells is a critical first step to take action and prevent exposure.”
Prospective and cross-sectional analyses both showed changes in left ventricular geometry – such as in the left atrial systolic diameter, interventricular septum, and left ventricular posterior wall thickness and mass index – were associated with exposure to arsenic. In addition, left ventricular function factors such as isovolumic relaxation time and stroke volume were also affected by arsenic exposure. However, the researchers noted that their study was limited by a single method of arsenic exposure and having no long-term follow-up for participants.
“The study raises the question of whether the changes in heart structure are reversible if exposure is reduced. Some changes have occurred in water sources in the study communities, and it will be important to check the potential health impact of reducing arsenic exposure,” said Dr. Pichler.
This study was funded by the National Institute of Health Sciences and grants from the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. The authors reported no relevant conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Pichler G et al. Circ Cardiovasc Imaging. 2019 May 1. doi: 10.1161/CIRCIMAGING.119.009018.
The results from Pichler et al. show the effects of recent arsenic exposure on left ventricular (LV) hypertrophy, but other questions remain as to the long-term effects of arsenic and its interactions with other environmental metals, Rajiv Chowdhury, MBBS, PhD, and Kim van Daalen, BSc, MPhil, wrote in a related editorial.
It has been established that chronic, low to moderate inorganic arsenic exposure may be linked to cardiovascular disease (CVD) and risk factors such as hypertension and diabetes, but it is unclear how different exposure pathways contribute as well as what pathophysiological mechanisms contribute to CVD, and whether arsenic directly or indirectly contributes to cardiac functioning or a worse cardiometabolic profile, respectively, they wrote.
While the results contribute to the understanding of arsenic exposure through drinking water and its relationship to LV function and geometry, urinary arsenic reflects recent exposure and cannot measure arsenic exposure over a period of time. The study also does not account for an individual’s CVD risk or LV functioning/geometry with daily exposure to co-occurring environmental metals, particularly heavy metals, together with arsenic. Factors such as genetics, age, gender, and nutrition also impact an individual’s reaction to arsenic, and studies should be able to differentiate inorganic arsenic obtained from food and other sources.
While “this elegant analysis ... helps to clarify the observational associations of [arsenic] with LV geometry and function, it stimulates further complimentary work,” they wrote. “Such studies would be essential since CVD remains the single leading cause of adult premature death worldwide, and millions of individuals globally are exposed to arsenic and other metal contaminants.”
Dr. Chowdhury and Dr. Daalen are from the cardiovascular epidemiology unit in the department of public health and primary care at the University of Cambridge (England).
The results from Pichler et al. show the effects of recent arsenic exposure on left ventricular (LV) hypertrophy, but other questions remain as to the long-term effects of arsenic and its interactions with other environmental metals, Rajiv Chowdhury, MBBS, PhD, and Kim van Daalen, BSc, MPhil, wrote in a related editorial.
It has been established that chronic, low to moderate inorganic arsenic exposure may be linked to cardiovascular disease (CVD) and risk factors such as hypertension and diabetes, but it is unclear how different exposure pathways contribute as well as what pathophysiological mechanisms contribute to CVD, and whether arsenic directly or indirectly contributes to cardiac functioning or a worse cardiometabolic profile, respectively, they wrote.
While the results contribute to the understanding of arsenic exposure through drinking water and its relationship to LV function and geometry, urinary arsenic reflects recent exposure and cannot measure arsenic exposure over a period of time. The study also does not account for an individual’s CVD risk or LV functioning/geometry with daily exposure to co-occurring environmental metals, particularly heavy metals, together with arsenic. Factors such as genetics, age, gender, and nutrition also impact an individual’s reaction to arsenic, and studies should be able to differentiate inorganic arsenic obtained from food and other sources.
While “this elegant analysis ... helps to clarify the observational associations of [arsenic] with LV geometry and function, it stimulates further complimentary work,” they wrote. “Such studies would be essential since CVD remains the single leading cause of adult premature death worldwide, and millions of individuals globally are exposed to arsenic and other metal contaminants.”
Dr. Chowdhury and Dr. Daalen are from the cardiovascular epidemiology unit in the department of public health and primary care at the University of Cambridge (England).
The results from Pichler et al. show the effects of recent arsenic exposure on left ventricular (LV) hypertrophy, but other questions remain as to the long-term effects of arsenic and its interactions with other environmental metals, Rajiv Chowdhury, MBBS, PhD, and Kim van Daalen, BSc, MPhil, wrote in a related editorial.
It has been established that chronic, low to moderate inorganic arsenic exposure may be linked to cardiovascular disease (CVD) and risk factors such as hypertension and diabetes, but it is unclear how different exposure pathways contribute as well as what pathophysiological mechanisms contribute to CVD, and whether arsenic directly or indirectly contributes to cardiac functioning or a worse cardiometabolic profile, respectively, they wrote.
While the results contribute to the understanding of arsenic exposure through drinking water and its relationship to LV function and geometry, urinary arsenic reflects recent exposure and cannot measure arsenic exposure over a period of time. The study also does not account for an individual’s CVD risk or LV functioning/geometry with daily exposure to co-occurring environmental metals, particularly heavy metals, together with arsenic. Factors such as genetics, age, gender, and nutrition also impact an individual’s reaction to arsenic, and studies should be able to differentiate inorganic arsenic obtained from food and other sources.
While “this elegant analysis ... helps to clarify the observational associations of [arsenic] with LV geometry and function, it stimulates further complimentary work,” they wrote. “Such studies would be essential since CVD remains the single leading cause of adult premature death worldwide, and millions of individuals globally are exposed to arsenic and other metal contaminants.”
Dr. Chowdhury and Dr. Daalen are from the cardiovascular epidemiology unit in the department of public health and primary care at the University of Cambridge (England).
Young Native Americans had increased left ventricular thickness and left ventricular hypertrophy after being exposed to arsenic, and had a greater risk if they showed signs of prehypertension or hypertension, according to recent research.
“The stronger association in subjects with elevated blood pressure suggests that individuals with preclinical heart disease might be more prone to the toxic effects of arsenic on the heart,” Gernot Pichler, MD, PhD, a cardiologist at Hospital Hietzing/Heart Center Clinic Floridsdorf in Vienna, stated in a press release.
Dr. Pichler and colleagues evaluated 1,337 individuals (mean age, 31 years; 61% female) in the Strong Heart Family Study, an extension of the Strong Heart Study that was designed to study cardiovascular disease in Native Americans. The researchers noted that, while the studies were not originally intended to evaluate arsenic exposure in these populations, “the importance of studying arsenic was recognized overtime as increasing evidence supported the role of arsenic in cardiovascular disease and the relatively high arsenic exposure in tribal communities, compared to other general populations in the United States.”
Arsenic exposure was determined through the sum of inorganic and methylated arsenic concentrations in urine, and researchers used transthoracic ECG at baseline and follow-up to compare left ventricular geometry and function. The mean follow-up was 5.6 years and baseline median sum of inorganic and methylated arsenic concentrations in urine was 4.24 (interquartile range, 2.82-6.90) mcg/g creatinine.
Prevalence of left ventricular hypertrophy was 4.6% overall, and the odds ratio of left ventricular hypertrophy per 100% increase in arsenic in the urine was 1.47 (95% confidence interval, 1.05-2.08) overall and 1.58 for individuals with prehypertension or hypertension (95% CI, 1.04-2.41).
“People drinking water from private wells, which are not regulated, need to be aware that arsenic may increase the risk for cardiovascular disease,” said Dr. Pichler. “Testing those wells is a critical first step to take action and prevent exposure.”
Prospective and cross-sectional analyses both showed changes in left ventricular geometry – such as in the left atrial systolic diameter, interventricular septum, and left ventricular posterior wall thickness and mass index – were associated with exposure to arsenic. In addition, left ventricular function factors such as isovolumic relaxation time and stroke volume were also affected by arsenic exposure. However, the researchers noted that their study was limited by a single method of arsenic exposure and having no long-term follow-up for participants.
“The study raises the question of whether the changes in heart structure are reversible if exposure is reduced. Some changes have occurred in water sources in the study communities, and it will be important to check the potential health impact of reducing arsenic exposure,” said Dr. Pichler.
This study was funded by the National Institute of Health Sciences and grants from the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. The authors reported no relevant conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Pichler G et al. Circ Cardiovasc Imaging. 2019 May 1. doi: 10.1161/CIRCIMAGING.119.009018.
Young Native Americans had increased left ventricular thickness and left ventricular hypertrophy after being exposed to arsenic, and had a greater risk if they showed signs of prehypertension or hypertension, according to recent research.
“The stronger association in subjects with elevated blood pressure suggests that individuals with preclinical heart disease might be more prone to the toxic effects of arsenic on the heart,” Gernot Pichler, MD, PhD, a cardiologist at Hospital Hietzing/Heart Center Clinic Floridsdorf in Vienna, stated in a press release.
Dr. Pichler and colleagues evaluated 1,337 individuals (mean age, 31 years; 61% female) in the Strong Heart Family Study, an extension of the Strong Heart Study that was designed to study cardiovascular disease in Native Americans. The researchers noted that, while the studies were not originally intended to evaluate arsenic exposure in these populations, “the importance of studying arsenic was recognized overtime as increasing evidence supported the role of arsenic in cardiovascular disease and the relatively high arsenic exposure in tribal communities, compared to other general populations in the United States.”
Arsenic exposure was determined through the sum of inorganic and methylated arsenic concentrations in urine, and researchers used transthoracic ECG at baseline and follow-up to compare left ventricular geometry and function. The mean follow-up was 5.6 years and baseline median sum of inorganic and methylated arsenic concentrations in urine was 4.24 (interquartile range, 2.82-6.90) mcg/g creatinine.
Prevalence of left ventricular hypertrophy was 4.6% overall, and the odds ratio of left ventricular hypertrophy per 100% increase in arsenic in the urine was 1.47 (95% confidence interval, 1.05-2.08) overall and 1.58 for individuals with prehypertension or hypertension (95% CI, 1.04-2.41).
“People drinking water from private wells, which are not regulated, need to be aware that arsenic may increase the risk for cardiovascular disease,” said Dr. Pichler. “Testing those wells is a critical first step to take action and prevent exposure.”
Prospective and cross-sectional analyses both showed changes in left ventricular geometry – such as in the left atrial systolic diameter, interventricular septum, and left ventricular posterior wall thickness and mass index – were associated with exposure to arsenic. In addition, left ventricular function factors such as isovolumic relaxation time and stroke volume were also affected by arsenic exposure. However, the researchers noted that their study was limited by a single method of arsenic exposure and having no long-term follow-up for participants.
“The study raises the question of whether the changes in heart structure are reversible if exposure is reduced. Some changes have occurred in water sources in the study communities, and it will be important to check the potential health impact of reducing arsenic exposure,” said Dr. Pichler.
This study was funded by the National Institute of Health Sciences and grants from the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. The authors reported no relevant conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Pichler G et al. Circ Cardiovasc Imaging. 2019 May 1. doi: 10.1161/CIRCIMAGING.119.009018.
FROM CIRCULATION: CARDIOVASCULAR IMAGING
Ankylosing spondylitis patients taking COX-2 inhibitors may see fewer cardiovascular events
MADISON, WISC. – Patients with ankylosing spondylitis had a small but significant reduction in risk for cardiovascular events if they were taking cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) inhibitors, according to a new systematic review and meta-analysis.
The reduced risk observed in this analysis (risk ratio, 0.48; 95% confidence interval, 0.33-0.70) contrasts with the increased risk for cardiovascular events seen with COX-2 inhibitor use in the general population, said Paras Karmacharya, MBBS, speaking in an interview at the annual meeting of the Spondyloarthritis Research and Treatment Network (SPARTAN). The overall effect was highly statistically significant (P = .0001), and the finding provides “reassuring” data for a population that’s known to have an elevated risk for cardiovascular events, he said.
“[W]e found in the subgroup analysis that COX-2 inhibitors were associated with a reduced risk of cardiovascular events as a whole,” an association also seen when looking just at ischemic stroke, Dr. Karmacharya said. “So that was sort of surprising; in the general population, there are some concerns about using COX-2 inhibitors.”
Looking at data for the nine studies that met criteria for inclusion in the meta-analysis, Dr. Karmacharya, a rheumatology fellow at the Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minn., and his collaborators calculated risk ratios for a composite outcome of all cardiovascular events (CVE) for all individuals taking NSAIDs, compared with individuals with ankylosing spondylitis (AS) who were not taking NSAIDs. Here, they found a relative risk of 0.94 (95% CI, 0.50-1.75; P = .84).
Next, the investigators calculated a relative risk of 0.78 for the composite CVE outcome just for those taking nonselective NSAIDs (95% CI, 0.44-1.38; P = .40).
Along with NSAIDs, Dr. Karmacharya and his coauthors also looked at the relationship between tumor necrosis factor inhibitors (TNFIs) and cardiovascular events. They found a significantly increased risk for the composite endpoint among AS patients taking TNFIs (RR, 1.60; 95% CI, 1.05-2.41; P = .03), but the comparison was limited to only one study.
In their analysis, the investigators also broke out risk of acute coronary syndrome (ACS)/ischemic heart disease. “The only place where we found some increased risk was ACS and ischemic heart disease, and that was with nonselective NSAIDS,” Dr. Karmacharya said (RR, 1.21; 95% CI, 1.06-1.39; P = .005). No significant changes in relative risk for ACS and ischemic heart disease were seen for the total group of NSAID users, for the subgroups taking COX-2 inhibitors, or for those taking TNFIs.
Finally, the investigators found a relative risk of 0.58 for stroke among the full group of NSAID users and a relative risk of 0.59 for those taking COX-2 inhibitors, but no reduced risk for the subgroup taking nonselective NSAIDs (P = .02, .04, and .37, respectively).
“While NSAIDs are known to be associated with an increased risk of CVE in the general population, whether the anti-inflammatory effects of NSAIDs reduce or modify the CVE risk in AS is controversial,” Dr. Karmacharya and his collaborators wrote. In this context, the meta-analysis provides a useful perspective for rheumatologists who care for AS patients, Dr. Karmacharya said: “I think it’s important, because most of these patients are on NSAIDs long-term.”
However, all of the studies included in the meta-analysis were observational, with no randomized, controlled trials meeting inclusion criteria. Also, some analyses presented in the poster involved as few as two studies, so findings should be interpreted with caution, he added. “We don’t have a lot of studies included in the analysis. ... so we need more data for sure, but I think what data we have so far look reassuring.”
Dr. Karmacharya reported that he had no conflicts of interest, and reported no outside sources of funding.
MADISON, WISC. – Patients with ankylosing spondylitis had a small but significant reduction in risk for cardiovascular events if they were taking cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) inhibitors, according to a new systematic review and meta-analysis.
The reduced risk observed in this analysis (risk ratio, 0.48; 95% confidence interval, 0.33-0.70) contrasts with the increased risk for cardiovascular events seen with COX-2 inhibitor use in the general population, said Paras Karmacharya, MBBS, speaking in an interview at the annual meeting of the Spondyloarthritis Research and Treatment Network (SPARTAN). The overall effect was highly statistically significant (P = .0001), and the finding provides “reassuring” data for a population that’s known to have an elevated risk for cardiovascular events, he said.
“[W]e found in the subgroup analysis that COX-2 inhibitors were associated with a reduced risk of cardiovascular events as a whole,” an association also seen when looking just at ischemic stroke, Dr. Karmacharya said. “So that was sort of surprising; in the general population, there are some concerns about using COX-2 inhibitors.”
Looking at data for the nine studies that met criteria for inclusion in the meta-analysis, Dr. Karmacharya, a rheumatology fellow at the Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minn., and his collaborators calculated risk ratios for a composite outcome of all cardiovascular events (CVE) for all individuals taking NSAIDs, compared with individuals with ankylosing spondylitis (AS) who were not taking NSAIDs. Here, they found a relative risk of 0.94 (95% CI, 0.50-1.75; P = .84).
Next, the investigators calculated a relative risk of 0.78 for the composite CVE outcome just for those taking nonselective NSAIDs (95% CI, 0.44-1.38; P = .40).
Along with NSAIDs, Dr. Karmacharya and his coauthors also looked at the relationship between tumor necrosis factor inhibitors (TNFIs) and cardiovascular events. They found a significantly increased risk for the composite endpoint among AS patients taking TNFIs (RR, 1.60; 95% CI, 1.05-2.41; P = .03), but the comparison was limited to only one study.
In their analysis, the investigators also broke out risk of acute coronary syndrome (ACS)/ischemic heart disease. “The only place where we found some increased risk was ACS and ischemic heart disease, and that was with nonselective NSAIDS,” Dr. Karmacharya said (RR, 1.21; 95% CI, 1.06-1.39; P = .005). No significant changes in relative risk for ACS and ischemic heart disease were seen for the total group of NSAID users, for the subgroups taking COX-2 inhibitors, or for those taking TNFIs.
Finally, the investigators found a relative risk of 0.58 for stroke among the full group of NSAID users and a relative risk of 0.59 for those taking COX-2 inhibitors, but no reduced risk for the subgroup taking nonselective NSAIDs (P = .02, .04, and .37, respectively).
“While NSAIDs are known to be associated with an increased risk of CVE in the general population, whether the anti-inflammatory effects of NSAIDs reduce or modify the CVE risk in AS is controversial,” Dr. Karmacharya and his collaborators wrote. In this context, the meta-analysis provides a useful perspective for rheumatologists who care for AS patients, Dr. Karmacharya said: “I think it’s important, because most of these patients are on NSAIDs long-term.”
However, all of the studies included in the meta-analysis were observational, with no randomized, controlled trials meeting inclusion criteria. Also, some analyses presented in the poster involved as few as two studies, so findings should be interpreted with caution, he added. “We don’t have a lot of studies included in the analysis. ... so we need more data for sure, but I think what data we have so far look reassuring.”
Dr. Karmacharya reported that he had no conflicts of interest, and reported no outside sources of funding.
MADISON, WISC. – Patients with ankylosing spondylitis had a small but significant reduction in risk for cardiovascular events if they were taking cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) inhibitors, according to a new systematic review and meta-analysis.
The reduced risk observed in this analysis (risk ratio, 0.48; 95% confidence interval, 0.33-0.70) contrasts with the increased risk for cardiovascular events seen with COX-2 inhibitor use in the general population, said Paras Karmacharya, MBBS, speaking in an interview at the annual meeting of the Spondyloarthritis Research and Treatment Network (SPARTAN). The overall effect was highly statistically significant (P = .0001), and the finding provides “reassuring” data for a population that’s known to have an elevated risk for cardiovascular events, he said.
“[W]e found in the subgroup analysis that COX-2 inhibitors were associated with a reduced risk of cardiovascular events as a whole,” an association also seen when looking just at ischemic stroke, Dr. Karmacharya said. “So that was sort of surprising; in the general population, there are some concerns about using COX-2 inhibitors.”
Looking at data for the nine studies that met criteria for inclusion in the meta-analysis, Dr. Karmacharya, a rheumatology fellow at the Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minn., and his collaborators calculated risk ratios for a composite outcome of all cardiovascular events (CVE) for all individuals taking NSAIDs, compared with individuals with ankylosing spondylitis (AS) who were not taking NSAIDs. Here, they found a relative risk of 0.94 (95% CI, 0.50-1.75; P = .84).
Next, the investigators calculated a relative risk of 0.78 for the composite CVE outcome just for those taking nonselective NSAIDs (95% CI, 0.44-1.38; P = .40).
Along with NSAIDs, Dr. Karmacharya and his coauthors also looked at the relationship between tumor necrosis factor inhibitors (TNFIs) and cardiovascular events. They found a significantly increased risk for the composite endpoint among AS patients taking TNFIs (RR, 1.60; 95% CI, 1.05-2.41; P = .03), but the comparison was limited to only one study.
In their analysis, the investigators also broke out risk of acute coronary syndrome (ACS)/ischemic heart disease. “The only place where we found some increased risk was ACS and ischemic heart disease, and that was with nonselective NSAIDS,” Dr. Karmacharya said (RR, 1.21; 95% CI, 1.06-1.39; P = .005). No significant changes in relative risk for ACS and ischemic heart disease were seen for the total group of NSAID users, for the subgroups taking COX-2 inhibitors, or for those taking TNFIs.
Finally, the investigators found a relative risk of 0.58 for stroke among the full group of NSAID users and a relative risk of 0.59 for those taking COX-2 inhibitors, but no reduced risk for the subgroup taking nonselective NSAIDs (P = .02, .04, and .37, respectively).
“While NSAIDs are known to be associated with an increased risk of CVE in the general population, whether the anti-inflammatory effects of NSAIDs reduce or modify the CVE risk in AS is controversial,” Dr. Karmacharya and his collaborators wrote. In this context, the meta-analysis provides a useful perspective for rheumatologists who care for AS patients, Dr. Karmacharya said: “I think it’s important, because most of these patients are on NSAIDs long-term.”
However, all of the studies included in the meta-analysis were observational, with no randomized, controlled trials meeting inclusion criteria. Also, some analyses presented in the poster involved as few as two studies, so findings should be interpreted with caution, he added. “We don’t have a lot of studies included in the analysis. ... so we need more data for sure, but I think what data we have so far look reassuring.”
Dr. Karmacharya reported that he had no conflicts of interest, and reported no outside sources of funding.
REPORTING FROM SPARTAN 2019
Key clinical point: Individuals with ankylosing spondylitis (AS) who took cyclooxygenase 2 (COX-2) inhibitors had a reduced risk of cardiovascular events, compared with AS patients who were not using COX-2 inhibitors.
Major finding: Individuals with AS taking COX-2 inhibitors had a risk ratio of 0.48 for cardiovascular events (95% CI, 0.33-0.70; P = .001).
Study details: Systematic review and meta-analysis of nine observational studies that variably examined the association between NSAID use and tumor necrosis factor inhibitor use and cardiovascular events among individuals with AS.
Disclosures: The authors reported no conflicts of interest and no outside sources of funding.
Source: Karmacharya P. et al. SPARTAN 2019.
Higher plasma cell-free DNA tracks with worse PAH survival
NEW ORLEANS – Cell-free (cf) DNA looked like an informative biomarker for both the severity of pulmonary artery hypertension and the survival prognosis for patients with this disease, based on results from two preliminary studies involving a total of 173 people.
“Plasma levels of cell-free DNA are elevated in patients with pulmonary artery hypertension, compared with healthy controls, and may predict disease severity and mortality,” Samuel B. Brusca, MD, said at the at the annual meeting of the American College of Cardiology.
A growing biomedical literature has documented a role for cfDNA in tracking the course of cancer, septic shock, and transplanted organs (Transplantation. 2019 Feb;103[2]:273-83) (Cell-Free DNA: Applications in Different Diseases, in “Cell-free DNA as Diagnostic Markers.” [New York: Humana Press, 2018, pp. 3-12]). Based on this background Dr. Brusca and his associates decided to examine whether plasma levels of cfDNA linked with pulmonary artery hypertension (PAH) severity and survival.
Their first study included seven patients with mild PAH (defined as patients with a tricuspid annular plane systolic excursion [TAPSE] of more than 18 mm and a maximum oxygen uptake [VO2] of at least 75% of predicted), eight with severe PAH (a TAPSE of 18 mm or less and a VO2 of less than 75%), and seven healthy adult controls. Measurement of plasma cfDNA showed an average level of 19.4 ng/mL among the healthy controls (prior reports had indicated that 10-20 ng/mL were normal levels), 22.0 ng/mL among patients with mild PAH, and 36.2 ng/mL in those with severe PAH. The level among the severe PAH patients was significantly higher than the level in controls by two different statistical tests, said Dr. Brusca, a critical care medicine physician at the National Institutes of Health Clinical Center in Bethesda, Md.
The second analysis by Dr. Brusca and his associates included 151 PAH patients followed by physicians at the Clinical Center for an average of 40 months. Their analysis tracked survival of these patients relative to their baseline levels of cfDNA and divided into tertiles. Patients in the lowest tertile had a starting cfDNA level of up to 39 ng/mL, those in the middle tertile had levels of 39.1-64.0 ng/mL, and those in the top tertile had levels of at least 64.1 ng/mL. A Kaplan-Meier analysis showed statistically significant differences in survival rates between each of the tertiles. Patients in the lowest tertile had a 5-year actuarial survival rate of about 65%, those in the middle tertile had a survival rate of about 48%, and those in the tertile with the highest level of cfDNA had a survival rate of about 28%.
Additional studies of cfDNA are needed in larger numbers of PAH patients, and cfDNA levels should be compared with levels of other, more established biomarkers, such as inflammatory cytokines, Dr. Brusca said in an interview.
Dr. Brusca had no disclosures. The study received no commercial funding.
SOURCE: Brusca SB et al. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2019 March 12;73(9 Suppl 1):1897.
I was very excited to hear Dr. Brusca’s report on using cell-free (cf) DNA to track the severity of pulmonary artery hypertension and survival of these patients. I’m now using cfDNA frequently to monitor heart transplant patients, and the information it provides has been very valuable. But cfDNA may be even better suited to assessing patients with pulmonary artery hypertension (PAH) because it’s a vascular disease, and increases in cfDNA appears to reflect damage to the vascular endothelium. It’s a brilliant application of this technology. Brain natriuretic peptide and troponin are markers of right heart damage, but cfDNA appears to be able to track the progression of the vascular component of PAH. It appears to be the first disease-specific biomarker we have for PAH. It’s time to start routinely measuring levels of cfDNA in trials so we can gather more data on the clinical correlates of changing levels of this biomarker.
I was very excited to hear Dr. Brusca’s report on using cell-free (cf) DNA to track the severity of pulmonary artery hypertension and survival of these patients. I’m now using cfDNA frequently to monitor heart transplant patients, and the information it provides has been very valuable. But cfDNA may be even better suited to assessing patients with pulmonary artery hypertension (PAH) because it’s a vascular disease, and increases in cfDNA appears to reflect damage to the vascular endothelium. It’s a brilliant application of this technology. Brain natriuretic peptide and troponin are markers of right heart damage, but cfDNA appears to be able to track the progression of the vascular component of PAH. It appears to be the first disease-specific biomarker we have for PAH. It’s time to start routinely measuring levels of cfDNA in trials so we can gather more data on the clinical correlates of changing levels of this biomarker.
I was very excited to hear Dr. Brusca’s report on using cell-free (cf) DNA to track the severity of pulmonary artery hypertension and survival of these patients. I’m now using cfDNA frequently to monitor heart transplant patients, and the information it provides has been very valuable. But cfDNA may be even better suited to assessing patients with pulmonary artery hypertension (PAH) because it’s a vascular disease, and increases in cfDNA appears to reflect damage to the vascular endothelium. It’s a brilliant application of this technology. Brain natriuretic peptide and troponin are markers of right heart damage, but cfDNA appears to be able to track the progression of the vascular component of PAH. It appears to be the first disease-specific biomarker we have for PAH. It’s time to start routinely measuring levels of cfDNA in trials so we can gather more data on the clinical correlates of changing levels of this biomarker.
NEW ORLEANS – Cell-free (cf) DNA looked like an informative biomarker for both the severity of pulmonary artery hypertension and the survival prognosis for patients with this disease, based on results from two preliminary studies involving a total of 173 people.
“Plasma levels of cell-free DNA are elevated in patients with pulmonary artery hypertension, compared with healthy controls, and may predict disease severity and mortality,” Samuel B. Brusca, MD, said at the at the annual meeting of the American College of Cardiology.
A growing biomedical literature has documented a role for cfDNA in tracking the course of cancer, septic shock, and transplanted organs (Transplantation. 2019 Feb;103[2]:273-83) (Cell-Free DNA: Applications in Different Diseases, in “Cell-free DNA as Diagnostic Markers.” [New York: Humana Press, 2018, pp. 3-12]). Based on this background Dr. Brusca and his associates decided to examine whether plasma levels of cfDNA linked with pulmonary artery hypertension (PAH) severity and survival.
Their first study included seven patients with mild PAH (defined as patients with a tricuspid annular plane systolic excursion [TAPSE] of more than 18 mm and a maximum oxygen uptake [VO2] of at least 75% of predicted), eight with severe PAH (a TAPSE of 18 mm or less and a VO2 of less than 75%), and seven healthy adult controls. Measurement of plasma cfDNA showed an average level of 19.4 ng/mL among the healthy controls (prior reports had indicated that 10-20 ng/mL were normal levels), 22.0 ng/mL among patients with mild PAH, and 36.2 ng/mL in those with severe PAH. The level among the severe PAH patients was significantly higher than the level in controls by two different statistical tests, said Dr. Brusca, a critical care medicine physician at the National Institutes of Health Clinical Center in Bethesda, Md.
The second analysis by Dr. Brusca and his associates included 151 PAH patients followed by physicians at the Clinical Center for an average of 40 months. Their analysis tracked survival of these patients relative to their baseline levels of cfDNA and divided into tertiles. Patients in the lowest tertile had a starting cfDNA level of up to 39 ng/mL, those in the middle tertile had levels of 39.1-64.0 ng/mL, and those in the top tertile had levels of at least 64.1 ng/mL. A Kaplan-Meier analysis showed statistically significant differences in survival rates between each of the tertiles. Patients in the lowest tertile had a 5-year actuarial survival rate of about 65%, those in the middle tertile had a survival rate of about 48%, and those in the tertile with the highest level of cfDNA had a survival rate of about 28%.
Additional studies of cfDNA are needed in larger numbers of PAH patients, and cfDNA levels should be compared with levels of other, more established biomarkers, such as inflammatory cytokines, Dr. Brusca said in an interview.
Dr. Brusca had no disclosures. The study received no commercial funding.
SOURCE: Brusca SB et al. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2019 March 12;73(9 Suppl 1):1897.
NEW ORLEANS – Cell-free (cf) DNA looked like an informative biomarker for both the severity of pulmonary artery hypertension and the survival prognosis for patients with this disease, based on results from two preliminary studies involving a total of 173 people.
“Plasma levels of cell-free DNA are elevated in patients with pulmonary artery hypertension, compared with healthy controls, and may predict disease severity and mortality,” Samuel B. Brusca, MD, said at the at the annual meeting of the American College of Cardiology.
A growing biomedical literature has documented a role for cfDNA in tracking the course of cancer, septic shock, and transplanted organs (Transplantation. 2019 Feb;103[2]:273-83) (Cell-Free DNA: Applications in Different Diseases, in “Cell-free DNA as Diagnostic Markers.” [New York: Humana Press, 2018, pp. 3-12]). Based on this background Dr. Brusca and his associates decided to examine whether plasma levels of cfDNA linked with pulmonary artery hypertension (PAH) severity and survival.
Their first study included seven patients with mild PAH (defined as patients with a tricuspid annular plane systolic excursion [TAPSE] of more than 18 mm and a maximum oxygen uptake [VO2] of at least 75% of predicted), eight with severe PAH (a TAPSE of 18 mm or less and a VO2 of less than 75%), and seven healthy adult controls. Measurement of plasma cfDNA showed an average level of 19.4 ng/mL among the healthy controls (prior reports had indicated that 10-20 ng/mL were normal levels), 22.0 ng/mL among patients with mild PAH, and 36.2 ng/mL in those with severe PAH. The level among the severe PAH patients was significantly higher than the level in controls by two different statistical tests, said Dr. Brusca, a critical care medicine physician at the National Institutes of Health Clinical Center in Bethesda, Md.
The second analysis by Dr. Brusca and his associates included 151 PAH patients followed by physicians at the Clinical Center for an average of 40 months. Their analysis tracked survival of these patients relative to their baseline levels of cfDNA and divided into tertiles. Patients in the lowest tertile had a starting cfDNA level of up to 39 ng/mL, those in the middle tertile had levels of 39.1-64.0 ng/mL, and those in the top tertile had levels of at least 64.1 ng/mL. A Kaplan-Meier analysis showed statistically significant differences in survival rates between each of the tertiles. Patients in the lowest tertile had a 5-year actuarial survival rate of about 65%, those in the middle tertile had a survival rate of about 48%, and those in the tertile with the highest level of cfDNA had a survival rate of about 28%.
Additional studies of cfDNA are needed in larger numbers of PAH patients, and cfDNA levels should be compared with levels of other, more established biomarkers, such as inflammatory cytokines, Dr. Brusca said in an interview.
Dr. Brusca had no disclosures. The study received no commercial funding.
SOURCE: Brusca SB et al. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2019 March 12;73(9 Suppl 1):1897.
REPORTING FROM ACC 2019