User login
Pertussis Cases Spike in November
Six times as many cases of pertussis were reported in the United States for the week ending November 16, 2024, as the same week in 2023, according to new data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC).
Of the 434 cases reported for the week ending November 16, 2024, a majority (109) occurred in the East North Central region, mostly in Ohio (93). Another 70 cases occurred in the West North Central region, with 32 cases and 37 cases in Missouri and Nebraska, respectively.
None of the 75 cases in the Middle Atlantic region occurred in New Jersey or New York City; 38 were reported elsewhere in New York, and 37 in Pennsylvania. The South Atlantic region reported 55 cases, including 29 in Florida. The East South Central and West South Central regions reported 11 and 20 cases, respectively. The Mountain and Pacific regions reported 31 (20 in Arizona) and 47 (20 in Washington State) cases, respectively.
The CDC tracks pertussis cases through a national surveillance system, but many cases are likely unrecognized and unreported, according to the CDC.
Although vaccines for pertussis (whooping cough) provide protection, their effectiveness decreases over time, and the CDC expects rates to increase in vaccinated and unvaccinated populations as case levels rebound with the lifting of pandemic mitigation strategies such as masking and remote learning.
Recent CDC data reported by Medscape Medical News showed an association between lower vaccination rates and 2024’s uptick in pertussis cases.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Six times as many cases of pertussis were reported in the United States for the week ending November 16, 2024, as the same week in 2023, according to new data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC).
Of the 434 cases reported for the week ending November 16, 2024, a majority (109) occurred in the East North Central region, mostly in Ohio (93). Another 70 cases occurred in the West North Central region, with 32 cases and 37 cases in Missouri and Nebraska, respectively.
None of the 75 cases in the Middle Atlantic region occurred in New Jersey or New York City; 38 were reported elsewhere in New York, and 37 in Pennsylvania. The South Atlantic region reported 55 cases, including 29 in Florida. The East South Central and West South Central regions reported 11 and 20 cases, respectively. The Mountain and Pacific regions reported 31 (20 in Arizona) and 47 (20 in Washington State) cases, respectively.
The CDC tracks pertussis cases through a national surveillance system, but many cases are likely unrecognized and unreported, according to the CDC.
Although vaccines for pertussis (whooping cough) provide protection, their effectiveness decreases over time, and the CDC expects rates to increase in vaccinated and unvaccinated populations as case levels rebound with the lifting of pandemic mitigation strategies such as masking and remote learning.
Recent CDC data reported by Medscape Medical News showed an association between lower vaccination rates and 2024’s uptick in pertussis cases.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Six times as many cases of pertussis were reported in the United States for the week ending November 16, 2024, as the same week in 2023, according to new data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC).
Of the 434 cases reported for the week ending November 16, 2024, a majority (109) occurred in the East North Central region, mostly in Ohio (93). Another 70 cases occurred in the West North Central region, with 32 cases and 37 cases in Missouri and Nebraska, respectively.
None of the 75 cases in the Middle Atlantic region occurred in New Jersey or New York City; 38 were reported elsewhere in New York, and 37 in Pennsylvania. The South Atlantic region reported 55 cases, including 29 in Florida. The East South Central and West South Central regions reported 11 and 20 cases, respectively. The Mountain and Pacific regions reported 31 (20 in Arizona) and 47 (20 in Washington State) cases, respectively.
The CDC tracks pertussis cases through a national surveillance system, but many cases are likely unrecognized and unreported, according to the CDC.
Although vaccines for pertussis (whooping cough) provide protection, their effectiveness decreases over time, and the CDC expects rates to increase in vaccinated and unvaccinated populations as case levels rebound with the lifting of pandemic mitigation strategies such as masking and remote learning.
Recent CDC data reported by Medscape Medical News showed an association between lower vaccination rates and 2024’s uptick in pertussis cases.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Flu Vaccine Guards Household Contacts of Infected People
TOPLINE:
Vaccination lowers the risk of contracting the infection among household contacts.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers conducted a prospective cohort study of data between 2017 and 2020 to determine the estimated effectiveness of influenza vaccines in preventing secondary infections in household contacts.
- Overall, 699 people were primary contacts, or the first in a household to get infected (median age, 13 years; 54.5% women); there were 1581 household contacts (median age, 31 years; 52.7% women), and both groups were followed for 7 days.
- Participants collected daily symptom diaries and nasal swabs during the follow-up period.
- Participants also submitted their history of influenza vaccination; 50.1% of household contacts had received a shot at least 14 days before the first case of disease onset in the household.
- The risk for secondary infection and vaccine effectiveness in preventing infection among household contacts was estimated overall and by virus type, subtype, and lineage.
TAKEAWAY:
- Nearly half (48.2%) of primary cases were from children and teens between ages 5 and 17 years.
- Overall, 22% household contacts had laboratory-confirmed influenza during follow-up, of which 7% were asymptomatic.
- The overall risk for secondary infection among unvaccinated household contacts was 18.8%, with the highest risk observed among children younger than age 5 years (29.9%).
- The overall effectiveness of influenza vaccines in preventing laboratory-confirmed infections among household contacts was 21% (95% CI, 1.4%-36.7%).
- The vaccine demonstrated specific protection against influenza B infection (56.4%; 95% CI, 30.1%-72.8%), particularly among those between ages 5 and 17 years.
IN PRACTICE:
“Although complementary preventive strategies to prevent influenza in household settings may be considered, seasonal influenza vaccination is the primary strategy recommended for prevention of influenza illness and its complications,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Carlos G. Grijalva, MD, MPH, of Vanderbilt University Medical Center in Nashville, Tennessee, and was published online in JAMA Network Open.
LIMITATIONS:
The recruitment of infected individuals from clinical testing pools may have limited the generalizability of the risk for secondary infection in households in which the primary case had a milder or asymptomatic infection. The study was unable to assess the effectiveness of specific vaccine formulations, such as those receiving high doses. The stratification of estimates by influenza subtypes and lineages was challenging because of small cell sizes.
DISCLOSURES:
This study was supported by grants from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) and authors reported support from grants from the National Institute Of Allergy And Infectious Diseases. Some authors reported contracts, receiving personal fees and grants from the CDC and various pharmaceutical companies such as Merck and Sanofi.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including artificial intelligence, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Vaccination lowers the risk of contracting the infection among household contacts.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers conducted a prospective cohort study of data between 2017 and 2020 to determine the estimated effectiveness of influenza vaccines in preventing secondary infections in household contacts.
- Overall, 699 people were primary contacts, or the first in a household to get infected (median age, 13 years; 54.5% women); there were 1581 household contacts (median age, 31 years; 52.7% women), and both groups were followed for 7 days.
- Participants collected daily symptom diaries and nasal swabs during the follow-up period.
- Participants also submitted their history of influenza vaccination; 50.1% of household contacts had received a shot at least 14 days before the first case of disease onset in the household.
- The risk for secondary infection and vaccine effectiveness in preventing infection among household contacts was estimated overall and by virus type, subtype, and lineage.
TAKEAWAY:
- Nearly half (48.2%) of primary cases were from children and teens between ages 5 and 17 years.
- Overall, 22% household contacts had laboratory-confirmed influenza during follow-up, of which 7% were asymptomatic.
- The overall risk for secondary infection among unvaccinated household contacts was 18.8%, with the highest risk observed among children younger than age 5 years (29.9%).
- The overall effectiveness of influenza vaccines in preventing laboratory-confirmed infections among household contacts was 21% (95% CI, 1.4%-36.7%).
- The vaccine demonstrated specific protection against influenza B infection (56.4%; 95% CI, 30.1%-72.8%), particularly among those between ages 5 and 17 years.
IN PRACTICE:
“Although complementary preventive strategies to prevent influenza in household settings may be considered, seasonal influenza vaccination is the primary strategy recommended for prevention of influenza illness and its complications,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Carlos G. Grijalva, MD, MPH, of Vanderbilt University Medical Center in Nashville, Tennessee, and was published online in JAMA Network Open.
LIMITATIONS:
The recruitment of infected individuals from clinical testing pools may have limited the generalizability of the risk for secondary infection in households in which the primary case had a milder or asymptomatic infection. The study was unable to assess the effectiveness of specific vaccine formulations, such as those receiving high doses. The stratification of estimates by influenza subtypes and lineages was challenging because of small cell sizes.
DISCLOSURES:
This study was supported by grants from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) and authors reported support from grants from the National Institute Of Allergy And Infectious Diseases. Some authors reported contracts, receiving personal fees and grants from the CDC and various pharmaceutical companies such as Merck and Sanofi.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including artificial intelligence, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Vaccination lowers the risk of contracting the infection among household contacts.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers conducted a prospective cohort study of data between 2017 and 2020 to determine the estimated effectiveness of influenza vaccines in preventing secondary infections in household contacts.
- Overall, 699 people were primary contacts, or the first in a household to get infected (median age, 13 years; 54.5% women); there were 1581 household contacts (median age, 31 years; 52.7% women), and both groups were followed for 7 days.
- Participants collected daily symptom diaries and nasal swabs during the follow-up period.
- Participants also submitted their history of influenza vaccination; 50.1% of household contacts had received a shot at least 14 days before the first case of disease onset in the household.
- The risk for secondary infection and vaccine effectiveness in preventing infection among household contacts was estimated overall and by virus type, subtype, and lineage.
TAKEAWAY:
- Nearly half (48.2%) of primary cases were from children and teens between ages 5 and 17 years.
- Overall, 22% household contacts had laboratory-confirmed influenza during follow-up, of which 7% were asymptomatic.
- The overall risk for secondary infection among unvaccinated household contacts was 18.8%, with the highest risk observed among children younger than age 5 years (29.9%).
- The overall effectiveness of influenza vaccines in preventing laboratory-confirmed infections among household contacts was 21% (95% CI, 1.4%-36.7%).
- The vaccine demonstrated specific protection against influenza B infection (56.4%; 95% CI, 30.1%-72.8%), particularly among those between ages 5 and 17 years.
IN PRACTICE:
“Although complementary preventive strategies to prevent influenza in household settings may be considered, seasonal influenza vaccination is the primary strategy recommended for prevention of influenza illness and its complications,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Carlos G. Grijalva, MD, MPH, of Vanderbilt University Medical Center in Nashville, Tennessee, and was published online in JAMA Network Open.
LIMITATIONS:
The recruitment of infected individuals from clinical testing pools may have limited the generalizability of the risk for secondary infection in households in which the primary case had a milder or asymptomatic infection. The study was unable to assess the effectiveness of specific vaccine formulations, such as those receiving high doses. The stratification of estimates by influenza subtypes and lineages was challenging because of small cell sizes.
DISCLOSURES:
This study was supported by grants from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) and authors reported support from grants from the National Institute Of Allergy And Infectious Diseases. Some authors reported contracts, receiving personal fees and grants from the CDC and various pharmaceutical companies such as Merck and Sanofi.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including artificial intelligence, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
AMR Could Surpass Cancer as Leading Cause of Death by 2050
Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) is globally recognized as one of the greatest health threats of the 21st century, responsible for 1.27 million deaths annually. “According to the WHO, if no measures are taken promptly, AMR could lead to more deaths than cancer by 2050,” Arnaud Marchant, MD, PhD, director of the European Plotkin Institute for Vaccinology at Université libre de Bruxelles (EPIV-ULB), Anderlecht, Belgium, said in an interview with MediQuality, part of the Medscape Professional Network. “This is a huge problem, and vaccination could be part of the solution.”
EPIV-ULB marked the start of the World AMR Awareness Week (November 18-24) with an event highlighting the critical role of vaccination to counter the rise for resistant pathogens. During the event, MediQuality interviewed Marchant, along with several other experts in the field.
Antibiotics Losing Effectiveness
Marc Van Ranst, PhD, virologist at Rega Institute KU Leuven in Leuven, Belgium, echoed Marchant’s concerns. He noted that “an increasing number of bacteria are becoming resistant to more antibiotics.” “While antibiotics were once miracle drugs, they have now stopped — or almost stopped — working against certain bacteria. Although we are discovering more effective therapies, bacterial infections are increasingly likely to worsen due to AMR.”
Van Ranst issued a stark warning: “If this trend continues, it is entirely reasonable to predict that in 25 years, some antibiotics will become useless, certain bacterial infections will be much harder to treat, and deaths will outnumber those caused by cancer. It’s worth noting, however, that as cancer treatments improve, cancer-related deaths are expected to decline, further highlighting the growing burden of AMR-related fatalities.”
Viruses, Vaccines, and Resistance
Van Ranst emphasized that while AMR primarily involves bacteria, viral infections and vaccination against them also play a role in addressing the issue. “When vaccines prevent illness, they reduce the need for unnecessary antibiotic use. In the past, antibiotics were frequently prescribed for respiratory infections — typically caused by viruses — leading to misuse and heightened resistance. By preventing viral infections through vaccines, we reduce inappropriate antibiotic prescriptions and, subsequently, AMR.”
Strategic Areas of Focus
To maximize the impact of vaccination in combating AMR, Belgium must prioritize several strategic areas, according to EPIV-ULB. “Expanding vaccination coverage for recommended vaccines is crucial to effectively preventing the spread of resistant pathogens,” said Marchant.
“Innovation and development of new vaccines are also essential, including targeted research into vaccines for infections that are currently unavoidable through other means. Enhancing epidemiological surveillance through national data collection and analysis will further clarify the impact of vaccines on AMR and inform policy decisions.”
EPIV-ULB underscored the importance of educating the public and healthcare professionals. “Public awareness is essential to addressing vaccine hesitancy by providing clear information on the importance of prevention,” Marchant explained. “Healthcare professional training must also improve, encouraging preventive practices and judicious antibiotic use. Furthermore, additional research is necessary to fill data gaps and develop predictive models that can guide vaccine development in the future.”
Role of Vaccination
According to EPIV-ULB, Belgium needs a strengthened national strategy to address AMR effectively. “Complementary solutions are increasingly important as antimicrobials lose efficacy and treatments become more complex,” Marchant said. “Vaccination offers a proactive and effective preventive solution, directly and indirectly reducing the spread of resistant pathogens.”
Vaccines combat AMR through various mechanisms. “They prevent diseases such as pneumococcal pneumonia and meningitis, reducing the need for antibiotics to treat these infections,” Marchant explained. “Additionally, vaccination lowers inappropriate antibiotic use by preventing viral infections, reducing the risk of overprescribing antibiotics in cases where they are unnecessary. Lastly, herd immunity from vaccination slows the circulation of resistant pathogens, limiting their spread.”
Van Ranst urged healthcare professionals to prioritize vaccinating at-risk populations as identified by Belgium’s Superior Health Council. These include the elderly with underlying conditions and pregnant women, especially for influenza vaccines. University Hospitals Leuven in Belgium, also conducts annual vaccination campaigns for its staff, combining flu and COVID vaccines to increase uptake.
A Global Challenge
Marc Noppen, MD, PhD, director of University Hospital Brussels, Belgium, emphasized the complexity of AMR as a global issue. “The problem isn’t solely due to human antibiotic use; it also stems from veterinary medicine, plant breeding, and animal husbandry. This is a multifactorial, worldwide issue that requires public awareness. Improved vaccination strategies are one way to address AMR, particularly in this post-COVID era of heightened skepticism toward vaccines,” he explained.
Marie-Lise Verschelden from Pfizer highlighted the need for cooperation across the healthcare sector. “Belgium is fortunate to have a fantastic ecosystem of academics, clinicians, and industry experts. Collaboration, including government involvement, is critical to advancing our efforts. At Pfizer, we continue to develop new vaccines and technologies, and the COVID crisis has reinforced the critical role of vaccination in combating AMR. Through our vaccine portfolio and ongoing developments, we are well-positioned to contribute significantly to this global challenge.”
Elisabeth Van Damme from GSK reiterated that AMR is a global issue requiring joint efforts. “Existing vaccines are underutilized. Vaccination protects against certain infectious diseases, reducing the need for antibiotics. Antibiotics, in turn, are sometimes prescribed incorrectly, especially for viral infections they cannot treat. At GSK, we are already developing new vaccines to meet future needs.”
Vaccination remains a cornerstone in the fight against AMR. As pathogens grow increasingly resistant to antibiotics, coordinated efforts and innovative vaccine development are essential to mitigating this global health crisis.
This story was translated and adapted from MediQuality using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) is globally recognized as one of the greatest health threats of the 21st century, responsible for 1.27 million deaths annually. “According to the WHO, if no measures are taken promptly, AMR could lead to more deaths than cancer by 2050,” Arnaud Marchant, MD, PhD, director of the European Plotkin Institute for Vaccinology at Université libre de Bruxelles (EPIV-ULB), Anderlecht, Belgium, said in an interview with MediQuality, part of the Medscape Professional Network. “This is a huge problem, and vaccination could be part of the solution.”
EPIV-ULB marked the start of the World AMR Awareness Week (November 18-24) with an event highlighting the critical role of vaccination to counter the rise for resistant pathogens. During the event, MediQuality interviewed Marchant, along with several other experts in the field.
Antibiotics Losing Effectiveness
Marc Van Ranst, PhD, virologist at Rega Institute KU Leuven in Leuven, Belgium, echoed Marchant’s concerns. He noted that “an increasing number of bacteria are becoming resistant to more antibiotics.” “While antibiotics were once miracle drugs, they have now stopped — or almost stopped — working against certain bacteria. Although we are discovering more effective therapies, bacterial infections are increasingly likely to worsen due to AMR.”
Van Ranst issued a stark warning: “If this trend continues, it is entirely reasonable to predict that in 25 years, some antibiotics will become useless, certain bacterial infections will be much harder to treat, and deaths will outnumber those caused by cancer. It’s worth noting, however, that as cancer treatments improve, cancer-related deaths are expected to decline, further highlighting the growing burden of AMR-related fatalities.”
Viruses, Vaccines, and Resistance
Van Ranst emphasized that while AMR primarily involves bacteria, viral infections and vaccination against them also play a role in addressing the issue. “When vaccines prevent illness, they reduce the need for unnecessary antibiotic use. In the past, antibiotics were frequently prescribed for respiratory infections — typically caused by viruses — leading to misuse and heightened resistance. By preventing viral infections through vaccines, we reduce inappropriate antibiotic prescriptions and, subsequently, AMR.”
Strategic Areas of Focus
To maximize the impact of vaccination in combating AMR, Belgium must prioritize several strategic areas, according to EPIV-ULB. “Expanding vaccination coverage for recommended vaccines is crucial to effectively preventing the spread of resistant pathogens,” said Marchant.
“Innovation and development of new vaccines are also essential, including targeted research into vaccines for infections that are currently unavoidable through other means. Enhancing epidemiological surveillance through national data collection and analysis will further clarify the impact of vaccines on AMR and inform policy decisions.”
EPIV-ULB underscored the importance of educating the public and healthcare professionals. “Public awareness is essential to addressing vaccine hesitancy by providing clear information on the importance of prevention,” Marchant explained. “Healthcare professional training must also improve, encouraging preventive practices and judicious antibiotic use. Furthermore, additional research is necessary to fill data gaps and develop predictive models that can guide vaccine development in the future.”
Role of Vaccination
According to EPIV-ULB, Belgium needs a strengthened national strategy to address AMR effectively. “Complementary solutions are increasingly important as antimicrobials lose efficacy and treatments become more complex,” Marchant said. “Vaccination offers a proactive and effective preventive solution, directly and indirectly reducing the spread of resistant pathogens.”
Vaccines combat AMR through various mechanisms. “They prevent diseases such as pneumococcal pneumonia and meningitis, reducing the need for antibiotics to treat these infections,” Marchant explained. “Additionally, vaccination lowers inappropriate antibiotic use by preventing viral infections, reducing the risk of overprescribing antibiotics in cases where they are unnecessary. Lastly, herd immunity from vaccination slows the circulation of resistant pathogens, limiting their spread.”
Van Ranst urged healthcare professionals to prioritize vaccinating at-risk populations as identified by Belgium’s Superior Health Council. These include the elderly with underlying conditions and pregnant women, especially for influenza vaccines. University Hospitals Leuven in Belgium, also conducts annual vaccination campaigns for its staff, combining flu and COVID vaccines to increase uptake.
A Global Challenge
Marc Noppen, MD, PhD, director of University Hospital Brussels, Belgium, emphasized the complexity of AMR as a global issue. “The problem isn’t solely due to human antibiotic use; it also stems from veterinary medicine, plant breeding, and animal husbandry. This is a multifactorial, worldwide issue that requires public awareness. Improved vaccination strategies are one way to address AMR, particularly in this post-COVID era of heightened skepticism toward vaccines,” he explained.
Marie-Lise Verschelden from Pfizer highlighted the need for cooperation across the healthcare sector. “Belgium is fortunate to have a fantastic ecosystem of academics, clinicians, and industry experts. Collaboration, including government involvement, is critical to advancing our efforts. At Pfizer, we continue to develop new vaccines and technologies, and the COVID crisis has reinforced the critical role of vaccination in combating AMR. Through our vaccine portfolio and ongoing developments, we are well-positioned to contribute significantly to this global challenge.”
Elisabeth Van Damme from GSK reiterated that AMR is a global issue requiring joint efforts. “Existing vaccines are underutilized. Vaccination protects against certain infectious diseases, reducing the need for antibiotics. Antibiotics, in turn, are sometimes prescribed incorrectly, especially for viral infections they cannot treat. At GSK, we are already developing new vaccines to meet future needs.”
Vaccination remains a cornerstone in the fight against AMR. As pathogens grow increasingly resistant to antibiotics, coordinated efforts and innovative vaccine development are essential to mitigating this global health crisis.
This story was translated and adapted from MediQuality using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) is globally recognized as one of the greatest health threats of the 21st century, responsible for 1.27 million deaths annually. “According to the WHO, if no measures are taken promptly, AMR could lead to more deaths than cancer by 2050,” Arnaud Marchant, MD, PhD, director of the European Plotkin Institute for Vaccinology at Université libre de Bruxelles (EPIV-ULB), Anderlecht, Belgium, said in an interview with MediQuality, part of the Medscape Professional Network. “This is a huge problem, and vaccination could be part of the solution.”
EPIV-ULB marked the start of the World AMR Awareness Week (November 18-24) with an event highlighting the critical role of vaccination to counter the rise for resistant pathogens. During the event, MediQuality interviewed Marchant, along with several other experts in the field.
Antibiotics Losing Effectiveness
Marc Van Ranst, PhD, virologist at Rega Institute KU Leuven in Leuven, Belgium, echoed Marchant’s concerns. He noted that “an increasing number of bacteria are becoming resistant to more antibiotics.” “While antibiotics were once miracle drugs, they have now stopped — or almost stopped — working against certain bacteria. Although we are discovering more effective therapies, bacterial infections are increasingly likely to worsen due to AMR.”
Van Ranst issued a stark warning: “If this trend continues, it is entirely reasonable to predict that in 25 years, some antibiotics will become useless, certain bacterial infections will be much harder to treat, and deaths will outnumber those caused by cancer. It’s worth noting, however, that as cancer treatments improve, cancer-related deaths are expected to decline, further highlighting the growing burden of AMR-related fatalities.”
Viruses, Vaccines, and Resistance
Van Ranst emphasized that while AMR primarily involves bacteria, viral infections and vaccination against them also play a role in addressing the issue. “When vaccines prevent illness, they reduce the need for unnecessary antibiotic use. In the past, antibiotics were frequently prescribed for respiratory infections — typically caused by viruses — leading to misuse and heightened resistance. By preventing viral infections through vaccines, we reduce inappropriate antibiotic prescriptions and, subsequently, AMR.”
Strategic Areas of Focus
To maximize the impact of vaccination in combating AMR, Belgium must prioritize several strategic areas, according to EPIV-ULB. “Expanding vaccination coverage for recommended vaccines is crucial to effectively preventing the spread of resistant pathogens,” said Marchant.
“Innovation and development of new vaccines are also essential, including targeted research into vaccines for infections that are currently unavoidable through other means. Enhancing epidemiological surveillance through national data collection and analysis will further clarify the impact of vaccines on AMR and inform policy decisions.”
EPIV-ULB underscored the importance of educating the public and healthcare professionals. “Public awareness is essential to addressing vaccine hesitancy by providing clear information on the importance of prevention,” Marchant explained. “Healthcare professional training must also improve, encouraging preventive practices and judicious antibiotic use. Furthermore, additional research is necessary to fill data gaps and develop predictive models that can guide vaccine development in the future.”
Role of Vaccination
According to EPIV-ULB, Belgium needs a strengthened national strategy to address AMR effectively. “Complementary solutions are increasingly important as antimicrobials lose efficacy and treatments become more complex,” Marchant said. “Vaccination offers a proactive and effective preventive solution, directly and indirectly reducing the spread of resistant pathogens.”
Vaccines combat AMR through various mechanisms. “They prevent diseases such as pneumococcal pneumonia and meningitis, reducing the need for antibiotics to treat these infections,” Marchant explained. “Additionally, vaccination lowers inappropriate antibiotic use by preventing viral infections, reducing the risk of overprescribing antibiotics in cases where they are unnecessary. Lastly, herd immunity from vaccination slows the circulation of resistant pathogens, limiting their spread.”
Van Ranst urged healthcare professionals to prioritize vaccinating at-risk populations as identified by Belgium’s Superior Health Council. These include the elderly with underlying conditions and pregnant women, especially for influenza vaccines. University Hospitals Leuven in Belgium, also conducts annual vaccination campaigns for its staff, combining flu and COVID vaccines to increase uptake.
A Global Challenge
Marc Noppen, MD, PhD, director of University Hospital Brussels, Belgium, emphasized the complexity of AMR as a global issue. “The problem isn’t solely due to human antibiotic use; it also stems from veterinary medicine, plant breeding, and animal husbandry. This is a multifactorial, worldwide issue that requires public awareness. Improved vaccination strategies are one way to address AMR, particularly in this post-COVID era of heightened skepticism toward vaccines,” he explained.
Marie-Lise Verschelden from Pfizer highlighted the need for cooperation across the healthcare sector. “Belgium is fortunate to have a fantastic ecosystem of academics, clinicians, and industry experts. Collaboration, including government involvement, is critical to advancing our efforts. At Pfizer, we continue to develop new vaccines and technologies, and the COVID crisis has reinforced the critical role of vaccination in combating AMR. Through our vaccine portfolio and ongoing developments, we are well-positioned to contribute significantly to this global challenge.”
Elisabeth Van Damme from GSK reiterated that AMR is a global issue requiring joint efforts. “Existing vaccines are underutilized. Vaccination protects against certain infectious diseases, reducing the need for antibiotics. Antibiotics, in turn, are sometimes prescribed incorrectly, especially for viral infections they cannot treat. At GSK, we are already developing new vaccines to meet future needs.”
Vaccination remains a cornerstone in the fight against AMR. As pathogens grow increasingly resistant to antibiotics, coordinated efforts and innovative vaccine development are essential to mitigating this global health crisis.
This story was translated and adapted from MediQuality using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Treating Onychomycosis: Pearls from a Podiatrist
LAS VEGAS —
According to Tracey C. Vlahovic, DPM, a professor at the Samuel Merritt University College of Podiatric Medicine, Oakland, California, most cases of onychomycosis are caused by the dermatophytes Trichophyton rubrum and T mentagrophytes, although the cause can also be a mixed infection. “Dermatophytes are going to impact the nails first, and molds may come in and join the party later,” she said at the Society of Dermatology Physician Associates (SDPA) 22nd Annual Fall Dermatology Conference.
“The distal subungual onychomycosis (DSO) type is still the most common, but don’t forget that onychomycosis and nail psoriasis can happen at the same time. What we can’t lose sight of is that onychomycosis is a disease of the nail bed, which ultimately affects the nail plate; it’s not a disease of the nail plate first.”
Her diagnostic approach combines periodic acid-Schiff (PAS) staining with fungal culture “because I like to know the speciation,” she said. “PAS doesn’t give me the speciation; fungal cultures should. PCR can be expensive, but that can give me speciation.”
How Does This Happen?
Fungal DSO occurs because of exposure to a dermatophyte, which can be as simple as tinea pedis. “Perhaps it’s the environment in the shoe,” said Vlahovic, one of the authors of a textbook on onychomycosis. “That’s something I’m always concentrating on with the patient. What is your foot hygiene like? What’s your shoe and sock wear? What’s your level of physical activity? You can have trauma to the hyponychium, where the skin and the nail meet. Maybe they trim their nails too close to the skin, or maybe there’s another skin condition like psoriasis.”
The dermatophyte, she continued, enters and invades the nail at the hyponychium and uses the keratinase enzyme to digest keratin in the nail bed. Mild inflammation develops, and pH changes cause focal parakeratosis and subungual hyperkeratosis in the form of onycholysis and subungual debris. “Hyphae then invade the lamina of the nail plate, which causes brittle nails,” she said. “The compromised hyponychium creates a reservoir for molds and bacteria.”
Therapies approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for onychomycosis include the topical agents efinaconazole, tavaborole, and ciclopirox; the oral agents terbinafine and itraconazole; and laser therapy. Off-label, Vlahovic said that she sometimes uses oral fluconazole, pulsed dosing for terbinafine, and booster doses of terbinafine or any approved oral antifungal agent. Pulse dosing for itraconazole is FDA-approved for fingernails but not for toenails.
“We don’t have any oral antifungals that are approved for children, but we do have weight-based dosing,” she noted. Other off-label treatments for onychomycosis that patients may come across while browsing the internet but do not penetrate the nail plate, include products containing tolnaftate, tree oil, and undecylenic acid, “which is a very long-chain antifungal,” Vlahovic said. “It’s so huge that it can’t get through the nail plate. These products must get through the nail plate into the nail bed where the infection is.”
According to therapeutic recommendations for the treatment of toenail onychomycosis in the United States, published in 2021, terbinafine is the primary choice for oral treatment and efinaconazole 10% for topical treatment. There are no current treatment recommendations for pregnant or lactating patients. “I always defer to the obstetrician,” said Vlahovic, a coauthor of the recommendations. For pediatric patients, there are approved topical medications: Efinaconazole and tavaborole for ages 6 and up and ciclopirox for ages 12 years or older.
Treatment recommendations for adults vary based on clinical presentation and patient characteristics. Questions to consider: Are they older? Do they have diabetes? Are they able to reach their feet to apply medication? What other medications are they taking? Are there any kidney or liver issues that are cause for concern?
Another question to consider is whether they have concurrent nail psoriasis. “When I have those patients, I often treat the onychomycosis first and the nail psoriasis second,” she said.
Evidence for Lasers Weak
Though laser therapy is FDA approved for the temporary increase of clear nails in onychomycosis, Vlahovic is underwhelmed by the evidence of its use for onychomycosis. According to a systematic review of 261 studies, only 1 reported treatment success as 16.7%, and clinical cures ranged from 13% to 16%. “Many of the existing studies were so poorly done in terms of protocols; it was frustrating,” she said. “No study has reported complete cure. There’s a lack of standardization across laser companies and a lack of standardization across protocols.”
Before starting oral antifungal therapy, Vlahovic uses the Onychomycosis Severity Index to determine the number of nails involved and the proportion of nails that are affected. She also wants to know if the patient is taking any medication that might interfere with an oral antifungal and gets baseline liver function tests (LFTs) to document results in the chart. “You want to discuss the pros and cons of oral antifungal therapy, and you want to set realistic expectations,” she added. “These medications are not cosmetic products; they are meant to kill fungus. Sometimes patients lose sight of that.”
Vlahovic routinely offers pulse dosing of terbinafine, which is FDA approved at a dose of 250 mg/d for 90 days. Pulse dosing involves taking terbinafine 250 mg twice a day for 1 week, followed by a 3-week break. This cycle is repeated three or four times. A clinical trial found no significant difference in outcome between patients who received pulsed vs continuous terbinafine dosing for the treatment of dermatophyte onychomycosis.
What About Oral Antifungal Safety?
For patients who ask about the safety of oral antifungals, Vlahovic characterized them as “well tolerated and safe in an immunocompetent population.” In a meta-analysis of 122 studies of about 22,000 patients, the pooled risk for treatment discontinuation because of adverse events was 3.4% for terbinafine 250 mg/d and 4.21% for itraconazole 200 mg/d. The risk for liver injury requiring termination of treatment and the risk of having symptomatic elevation of LFTs were less than 2% for all regimens.
According to the best available published evidence, Vlahovic said, the onychomycosis recurrence rate ranges from 6% to 40%. “That’s a wild number. We really have no idea what the true recurrence rate is, and that’s a problem.”
Vlahovic disclosed having been a consultant to and an investigator for Ortho Dermatologics and Sagis Diagnostics.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
LAS VEGAS —
According to Tracey C. Vlahovic, DPM, a professor at the Samuel Merritt University College of Podiatric Medicine, Oakland, California, most cases of onychomycosis are caused by the dermatophytes Trichophyton rubrum and T mentagrophytes, although the cause can also be a mixed infection. “Dermatophytes are going to impact the nails first, and molds may come in and join the party later,” she said at the Society of Dermatology Physician Associates (SDPA) 22nd Annual Fall Dermatology Conference.
“The distal subungual onychomycosis (DSO) type is still the most common, but don’t forget that onychomycosis and nail psoriasis can happen at the same time. What we can’t lose sight of is that onychomycosis is a disease of the nail bed, which ultimately affects the nail plate; it’s not a disease of the nail plate first.”
Her diagnostic approach combines periodic acid-Schiff (PAS) staining with fungal culture “because I like to know the speciation,” she said. “PAS doesn’t give me the speciation; fungal cultures should. PCR can be expensive, but that can give me speciation.”
How Does This Happen?
Fungal DSO occurs because of exposure to a dermatophyte, which can be as simple as tinea pedis. “Perhaps it’s the environment in the shoe,” said Vlahovic, one of the authors of a textbook on onychomycosis. “That’s something I’m always concentrating on with the patient. What is your foot hygiene like? What’s your shoe and sock wear? What’s your level of physical activity? You can have trauma to the hyponychium, where the skin and the nail meet. Maybe they trim their nails too close to the skin, or maybe there’s another skin condition like psoriasis.”
The dermatophyte, she continued, enters and invades the nail at the hyponychium and uses the keratinase enzyme to digest keratin in the nail bed. Mild inflammation develops, and pH changes cause focal parakeratosis and subungual hyperkeratosis in the form of onycholysis and subungual debris. “Hyphae then invade the lamina of the nail plate, which causes brittle nails,” she said. “The compromised hyponychium creates a reservoir for molds and bacteria.”
Therapies approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for onychomycosis include the topical agents efinaconazole, tavaborole, and ciclopirox; the oral agents terbinafine and itraconazole; and laser therapy. Off-label, Vlahovic said that she sometimes uses oral fluconazole, pulsed dosing for terbinafine, and booster doses of terbinafine or any approved oral antifungal agent. Pulse dosing for itraconazole is FDA-approved for fingernails but not for toenails.
“We don’t have any oral antifungals that are approved for children, but we do have weight-based dosing,” she noted. Other off-label treatments for onychomycosis that patients may come across while browsing the internet but do not penetrate the nail plate, include products containing tolnaftate, tree oil, and undecylenic acid, “which is a very long-chain antifungal,” Vlahovic said. “It’s so huge that it can’t get through the nail plate. These products must get through the nail plate into the nail bed where the infection is.”
According to therapeutic recommendations for the treatment of toenail onychomycosis in the United States, published in 2021, terbinafine is the primary choice for oral treatment and efinaconazole 10% for topical treatment. There are no current treatment recommendations for pregnant or lactating patients. “I always defer to the obstetrician,” said Vlahovic, a coauthor of the recommendations. For pediatric patients, there are approved topical medications: Efinaconazole and tavaborole for ages 6 and up and ciclopirox for ages 12 years or older.
Treatment recommendations for adults vary based on clinical presentation and patient characteristics. Questions to consider: Are they older? Do they have diabetes? Are they able to reach their feet to apply medication? What other medications are they taking? Are there any kidney or liver issues that are cause for concern?
Another question to consider is whether they have concurrent nail psoriasis. “When I have those patients, I often treat the onychomycosis first and the nail psoriasis second,” she said.
Evidence for Lasers Weak
Though laser therapy is FDA approved for the temporary increase of clear nails in onychomycosis, Vlahovic is underwhelmed by the evidence of its use for onychomycosis. According to a systematic review of 261 studies, only 1 reported treatment success as 16.7%, and clinical cures ranged from 13% to 16%. “Many of the existing studies were so poorly done in terms of protocols; it was frustrating,” she said. “No study has reported complete cure. There’s a lack of standardization across laser companies and a lack of standardization across protocols.”
Before starting oral antifungal therapy, Vlahovic uses the Onychomycosis Severity Index to determine the number of nails involved and the proportion of nails that are affected. She also wants to know if the patient is taking any medication that might interfere with an oral antifungal and gets baseline liver function tests (LFTs) to document results in the chart. “You want to discuss the pros and cons of oral antifungal therapy, and you want to set realistic expectations,” she added. “These medications are not cosmetic products; they are meant to kill fungus. Sometimes patients lose sight of that.”
Vlahovic routinely offers pulse dosing of terbinafine, which is FDA approved at a dose of 250 mg/d for 90 days. Pulse dosing involves taking terbinafine 250 mg twice a day for 1 week, followed by a 3-week break. This cycle is repeated three or four times. A clinical trial found no significant difference in outcome between patients who received pulsed vs continuous terbinafine dosing for the treatment of dermatophyte onychomycosis.
What About Oral Antifungal Safety?
For patients who ask about the safety of oral antifungals, Vlahovic characterized them as “well tolerated and safe in an immunocompetent population.” In a meta-analysis of 122 studies of about 22,000 patients, the pooled risk for treatment discontinuation because of adverse events was 3.4% for terbinafine 250 mg/d and 4.21% for itraconazole 200 mg/d. The risk for liver injury requiring termination of treatment and the risk of having symptomatic elevation of LFTs were less than 2% for all regimens.
According to the best available published evidence, Vlahovic said, the onychomycosis recurrence rate ranges from 6% to 40%. “That’s a wild number. We really have no idea what the true recurrence rate is, and that’s a problem.”
Vlahovic disclosed having been a consultant to and an investigator for Ortho Dermatologics and Sagis Diagnostics.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
LAS VEGAS —
According to Tracey C. Vlahovic, DPM, a professor at the Samuel Merritt University College of Podiatric Medicine, Oakland, California, most cases of onychomycosis are caused by the dermatophytes Trichophyton rubrum and T mentagrophytes, although the cause can also be a mixed infection. “Dermatophytes are going to impact the nails first, and molds may come in and join the party later,” she said at the Society of Dermatology Physician Associates (SDPA) 22nd Annual Fall Dermatology Conference.
“The distal subungual onychomycosis (DSO) type is still the most common, but don’t forget that onychomycosis and nail psoriasis can happen at the same time. What we can’t lose sight of is that onychomycosis is a disease of the nail bed, which ultimately affects the nail plate; it’s not a disease of the nail plate first.”
Her diagnostic approach combines periodic acid-Schiff (PAS) staining with fungal culture “because I like to know the speciation,” she said. “PAS doesn’t give me the speciation; fungal cultures should. PCR can be expensive, but that can give me speciation.”
How Does This Happen?
Fungal DSO occurs because of exposure to a dermatophyte, which can be as simple as tinea pedis. “Perhaps it’s the environment in the shoe,” said Vlahovic, one of the authors of a textbook on onychomycosis. “That’s something I’m always concentrating on with the patient. What is your foot hygiene like? What’s your shoe and sock wear? What’s your level of physical activity? You can have trauma to the hyponychium, where the skin and the nail meet. Maybe they trim their nails too close to the skin, or maybe there’s another skin condition like psoriasis.”
The dermatophyte, she continued, enters and invades the nail at the hyponychium and uses the keratinase enzyme to digest keratin in the nail bed. Mild inflammation develops, and pH changes cause focal parakeratosis and subungual hyperkeratosis in the form of onycholysis and subungual debris. “Hyphae then invade the lamina of the nail plate, which causes brittle nails,” she said. “The compromised hyponychium creates a reservoir for molds and bacteria.”
Therapies approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for onychomycosis include the topical agents efinaconazole, tavaborole, and ciclopirox; the oral agents terbinafine and itraconazole; and laser therapy. Off-label, Vlahovic said that she sometimes uses oral fluconazole, pulsed dosing for terbinafine, and booster doses of terbinafine or any approved oral antifungal agent. Pulse dosing for itraconazole is FDA-approved for fingernails but not for toenails.
“We don’t have any oral antifungals that are approved for children, but we do have weight-based dosing,” she noted. Other off-label treatments for onychomycosis that patients may come across while browsing the internet but do not penetrate the nail plate, include products containing tolnaftate, tree oil, and undecylenic acid, “which is a very long-chain antifungal,” Vlahovic said. “It’s so huge that it can’t get through the nail plate. These products must get through the nail plate into the nail bed where the infection is.”
According to therapeutic recommendations for the treatment of toenail onychomycosis in the United States, published in 2021, terbinafine is the primary choice for oral treatment and efinaconazole 10% for topical treatment. There are no current treatment recommendations for pregnant or lactating patients. “I always defer to the obstetrician,” said Vlahovic, a coauthor of the recommendations. For pediatric patients, there are approved topical medications: Efinaconazole and tavaborole for ages 6 and up and ciclopirox for ages 12 years or older.
Treatment recommendations for adults vary based on clinical presentation and patient characteristics. Questions to consider: Are they older? Do they have diabetes? Are they able to reach their feet to apply medication? What other medications are they taking? Are there any kidney or liver issues that are cause for concern?
Another question to consider is whether they have concurrent nail psoriasis. “When I have those patients, I often treat the onychomycosis first and the nail psoriasis second,” she said.
Evidence for Lasers Weak
Though laser therapy is FDA approved for the temporary increase of clear nails in onychomycosis, Vlahovic is underwhelmed by the evidence of its use for onychomycosis. According to a systematic review of 261 studies, only 1 reported treatment success as 16.7%, and clinical cures ranged from 13% to 16%. “Many of the existing studies were so poorly done in terms of protocols; it was frustrating,” she said. “No study has reported complete cure. There’s a lack of standardization across laser companies and a lack of standardization across protocols.”
Before starting oral antifungal therapy, Vlahovic uses the Onychomycosis Severity Index to determine the number of nails involved and the proportion of nails that are affected. She also wants to know if the patient is taking any medication that might interfere with an oral antifungal and gets baseline liver function tests (LFTs) to document results in the chart. “You want to discuss the pros and cons of oral antifungal therapy, and you want to set realistic expectations,” she added. “These medications are not cosmetic products; they are meant to kill fungus. Sometimes patients lose sight of that.”
Vlahovic routinely offers pulse dosing of terbinafine, which is FDA approved at a dose of 250 mg/d for 90 days. Pulse dosing involves taking terbinafine 250 mg twice a day for 1 week, followed by a 3-week break. This cycle is repeated three or four times. A clinical trial found no significant difference in outcome between patients who received pulsed vs continuous terbinafine dosing for the treatment of dermatophyte onychomycosis.
What About Oral Antifungal Safety?
For patients who ask about the safety of oral antifungals, Vlahovic characterized them as “well tolerated and safe in an immunocompetent population.” In a meta-analysis of 122 studies of about 22,000 patients, the pooled risk for treatment discontinuation because of adverse events was 3.4% for terbinafine 250 mg/d and 4.21% for itraconazole 200 mg/d. The risk for liver injury requiring termination of treatment and the risk of having symptomatic elevation of LFTs were less than 2% for all regimens.
According to the best available published evidence, Vlahovic said, the onychomycosis recurrence rate ranges from 6% to 40%. “That’s a wild number. We really have no idea what the true recurrence rate is, and that’s a problem.”
Vlahovic disclosed having been a consultant to and an investigator for Ortho Dermatologics and Sagis Diagnostics.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM SDPA 2024
Varicella Outbreaks: 2022-2024
Practitioners providing care to children are familiar with the childhood immunization schedule and routinely administer varicella vaccine at the 12-month and 4- to 5-year visits. However, when is the last time most of us or any of the current trainees have seen a case?
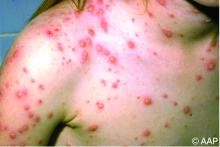
Briefly, varicella is a highly contagious disease caused by varicella-zoster virus (VZV). It is characterized by a generalized pruritic erythematous rash in various stages of development beginning as macules, progressing to papules, and ultimately becoming vesicular lesions on an erythematous base (“dewdrop on a rose petal”) and resolves with crusting of the lesion (Figure 1). It has an incubation period of 10-21 days with symptoms usually developing within 14-16 days after exposure. The vesicular rash must be differentiated from enterovirus, Staphylococcus aureus, contact dermatitis, or insect bites, which initially may be difficult. Approximately 50% of children can have symptoms including fever, malaise, anorexia, headache, and occasionally, mild abdominal pain in the 24-48 hours prior to the appearance of rash. Lesions usually first appear on the scalp, face, or trunk in successive crops over several days. A person with varicella has lesions in various stages.
In a normal host, new vesicle formation usually stops within 4 days, and most lesions have fully crusted by day 6. VZV establishes latency in sensory ganglia and may reactivate years or decades later to cause herpes zoster (HZ). Most healthy children with varicella recover without sequelae so the disease is generally regarded as benign. However, varicella can lead to serious complications and deaths in healthy as well as immunocompromised persons.
Complications of Varicella: bacterial superinfection of skin lesions most often with Streptococcus pyogenes or S aureus manifested as cellulitis, myositis, or necrotizing fasciitis; neurologic complications include cerebellar ataxia and encephalitis with the latter seen most often in adults. Pneumonia occurs most often in adults, especially those infected during pregnancy. Another concern, infection during the first 20 weeks of pregnancy can lead to fetal death or severe birth defects, including limb hypoplasia, cutaneous scarring, ocular abnormalities, and central nervous system damage (congenital varicella syndrome).
The risk for development of severe disseminated disease was first noted in the 1960s as treatments for leukemia in children improved. They were surviving their cancer only to develop severe and often fatal varicella. Today it is recognized that development of disseminated disease is a risk for all infected persons with impaired T cell function, malignancies, HIV, or receiving immunosuppressive therapy.
Reye’s syndrome is rarely seen today since taking salicylates while infected with VZV was identified as a predisposing factor for development.
VZV is only found in humans and transmission is person to person or airborne. The secondary household attack rate is approximately 90%. In contrast, the secondary attack rates in classrooms may be as low as 12%-33%. Transmission rates in the tropics for unexplained reasons are also lower.
Vaccine History: Why do we rarely see this disease anymore? Varicella, a live attenuated vaccine, was developed in 1974 by Dr. Michiaki Takahashi. It remains the only vaccine directed against a herpes group virus. In 1979, the Collaborative Varicella Vaccine Study Group was established at the National Institutes of Health (NIH) and additional safety and efficacy trials were conducted in the United States initially in leukemic patients in remission and later in healthy children, which supported Takahashi’s data. Licensure of varicella vaccine was granted in 1995. That same year, due to continuing disease and societal burden, the United States was the first country to incorporate varicella into the routine childhood immunization schedule, which resulted in significant reductions in cases. To further improve control of varicella, in 2007 vaccine recommendations were revised and a routine two-dose schedule was implemented. The impact of varicella disease pre- and post-vaccine licensure is illustrated in Figure 2. Not listed, is that in the pre-vaccine era, there were approximately 44 cases of congenital varicella syndrome annually.

As of 2023 only 23% (45/195) of nations routinely administer this vaccine and 4% (8/195) have restricted recommendations. The remaining 73% of countries do not offer the vaccine, including all countries on the African continent, and Cuba, Guatemala, Haiti, Honduras, India, Jordan, Lebanon, Philippines, Portugal, and Venezuela to list a few.
Varicella Outbreak: In October 2022, New York City (NYC) identified a varicella outbreak primarily involving persons who recently migrated from Central and South America and lived in a shelter in NYC or residential facility (n = 105); the outbreak is ongoing. As of March 8, 2024, 873 cases (53%) were among children aged 4-18 years and 91.9% had no documentation of varicella vaccine at time of symptom onset. There were 28 hospitalizations, and no deaths reported. The most common sources of transmission were the residential facilities (41.3%) and importation or possible importation (39.4%). School transmission accounted for only 1.2% of cases.
Most migrants arrived from countries where varicella vaccination is not part of the routine childhood immunization schedule. Although most cases occurred in children, almost 30% occurred in adults. Many of the migrants arrived from tropical countries where susceptibility rates are also higher in adults. This outbreak is a reminder of the importance of limiting disease transmission by maintaining high vaccination rates. To curtail this outbreak, approximately 27,000 doses of varicella vaccine were administered to the arriving migrants. In addition, MMR, COVID-19, influenza, and all routine pediatric vaccines required for school entry were administered. Temporary closure of the residential facilities were required. Education was provided to residents regarding immunizations as well as assistance to help them establish a primary care home. Multiple agencies were mobilized to successfully coordinate these efforts.
Take Home Message
1. Each country has its own routine immunization schedule. It may not include all vaccines recommended in the US schedule. When questioned I’m frequently told that immunizations are up to date, only to review records and find they are not, especially when it is related to MMR. It is often administered at 9 months and/or MR or MM is administered depending on the country. As reported here, varicella is a routine vaccine in only 45 countries.
2.
3. Once an outbreak has been identified, the infrastructure to manage and contain it must already be established. In most instances there will be a need for a rapid and often large-scale effort involving multiple agencies including local health care providers.
4. Not all diseases are reportable. Only deaths by varicella are nationally notifiable. Otherwise, cases are reported voluntarily. As of November 2, 2024, there have been 5,157 cases of varicella reported, excluding any cases from NYC.
Word is a pediatric infectious disease specialist and director of the Houston Travel Medicine Clinic. She said she had no relevant financial disclosures.
Suggested Reading
CDC. Nationally Notifiable Infectious Diseases and Conditions, United States: Weekly Tables. https://wonder.cdc.gov/nndss/nndss_weekly_tables_menu.asp.
Graham KA et al. Varicella Outbreak Among Recent Arrivals to New York City, 2022-2024. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2024 May 30;73(21):478-483. doi: 10.15585/mmwr.mm7321a1.
Marin M et al. Health and Economic Impact of the United States Varicella Vaccination Program, 1996-2020. J Infect Dis. 2022 Oct 21;226(Suppl 4):S463-S469. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jiac271.
Varicella-Zoster Virus Infections in Kimberkin DW et al, eds. Red Book: 2024 Report of the Committee on Infectious Diseases, 33rd Edition. American Academy of Pediatrics, 2024:938-951. https://www.aap.org/Red-Book-2024-Report-of-the-Committee-on-Infectious-Diseases-33rd-Edition-Paperback?srsltid=AfmBOoqyF60rR9ZwQ5jA8AouNhtRRTyPLnc_r7HWw7JVYV8v33Hr2vQS.
Practitioners providing care to children are familiar with the childhood immunization schedule and routinely administer varicella vaccine at the 12-month and 4- to 5-year visits. However, when is the last time most of us or any of the current trainees have seen a case?
Briefly, varicella is a highly contagious disease caused by varicella-zoster virus (VZV). It is characterized by a generalized pruritic erythematous rash in various stages of development beginning as macules, progressing to papules, and ultimately becoming vesicular lesions on an erythematous base (“dewdrop on a rose petal”) and resolves with crusting of the lesion (Figure 1). It has an incubation period of 10-21 days with symptoms usually developing within 14-16 days after exposure. The vesicular rash must be differentiated from enterovirus, Staphylococcus aureus, contact dermatitis, or insect bites, which initially may be difficult. Approximately 50% of children can have symptoms including fever, malaise, anorexia, headache, and occasionally, mild abdominal pain in the 24-48 hours prior to the appearance of rash. Lesions usually first appear on the scalp, face, or trunk in successive crops over several days. A person with varicella has lesions in various stages.
In a normal host, new vesicle formation usually stops within 4 days, and most lesions have fully crusted by day 6. VZV establishes latency in sensory ganglia and may reactivate years or decades later to cause herpes zoster (HZ). Most healthy children with varicella recover without sequelae so the disease is generally regarded as benign. However, varicella can lead to serious complications and deaths in healthy as well as immunocompromised persons.
Complications of Varicella: bacterial superinfection of skin lesions most often with Streptococcus pyogenes or S aureus manifested as cellulitis, myositis, or necrotizing fasciitis; neurologic complications include cerebellar ataxia and encephalitis with the latter seen most often in adults. Pneumonia occurs most often in adults, especially those infected during pregnancy. Another concern, infection during the first 20 weeks of pregnancy can lead to fetal death or severe birth defects, including limb hypoplasia, cutaneous scarring, ocular abnormalities, and central nervous system damage (congenital varicella syndrome).
The risk for development of severe disseminated disease was first noted in the 1960s as treatments for leukemia in children improved. They were surviving their cancer only to develop severe and often fatal varicella. Today it is recognized that development of disseminated disease is a risk for all infected persons with impaired T cell function, malignancies, HIV, or receiving immunosuppressive therapy.
Reye’s syndrome is rarely seen today since taking salicylates while infected with VZV was identified as a predisposing factor for development.
VZV is only found in humans and transmission is person to person or airborne. The secondary household attack rate is approximately 90%. In contrast, the secondary attack rates in classrooms may be as low as 12%-33%. Transmission rates in the tropics for unexplained reasons are also lower.
Vaccine History: Why do we rarely see this disease anymore? Varicella, a live attenuated vaccine, was developed in 1974 by Dr. Michiaki Takahashi. It remains the only vaccine directed against a herpes group virus. In 1979, the Collaborative Varicella Vaccine Study Group was established at the National Institutes of Health (NIH) and additional safety and efficacy trials were conducted in the United States initially in leukemic patients in remission and later in healthy children, which supported Takahashi’s data. Licensure of varicella vaccine was granted in 1995. That same year, due to continuing disease and societal burden, the United States was the first country to incorporate varicella into the routine childhood immunization schedule, which resulted in significant reductions in cases. To further improve control of varicella, in 2007 vaccine recommendations were revised and a routine two-dose schedule was implemented. The impact of varicella disease pre- and post-vaccine licensure is illustrated in Figure 2. Not listed, is that in the pre-vaccine era, there were approximately 44 cases of congenital varicella syndrome annually.

As of 2023 only 23% (45/195) of nations routinely administer this vaccine and 4% (8/195) have restricted recommendations. The remaining 73% of countries do not offer the vaccine, including all countries on the African continent, and Cuba, Guatemala, Haiti, Honduras, India, Jordan, Lebanon, Philippines, Portugal, and Venezuela to list a few.
Varicella Outbreak: In October 2022, New York City (NYC) identified a varicella outbreak primarily involving persons who recently migrated from Central and South America and lived in a shelter in NYC or residential facility (n = 105); the outbreak is ongoing. As of March 8, 2024, 873 cases (53%) were among children aged 4-18 years and 91.9% had no documentation of varicella vaccine at time of symptom onset. There were 28 hospitalizations, and no deaths reported. The most common sources of transmission were the residential facilities (41.3%) and importation or possible importation (39.4%). School transmission accounted for only 1.2% of cases.
Most migrants arrived from countries where varicella vaccination is not part of the routine childhood immunization schedule. Although most cases occurred in children, almost 30% occurred in adults. Many of the migrants arrived from tropical countries where susceptibility rates are also higher in adults. This outbreak is a reminder of the importance of limiting disease transmission by maintaining high vaccination rates. To curtail this outbreak, approximately 27,000 doses of varicella vaccine were administered to the arriving migrants. In addition, MMR, COVID-19, influenza, and all routine pediatric vaccines required for school entry were administered. Temporary closure of the residential facilities were required. Education was provided to residents regarding immunizations as well as assistance to help them establish a primary care home. Multiple agencies were mobilized to successfully coordinate these efforts.
Take Home Message
1. Each country has its own routine immunization schedule. It may not include all vaccines recommended in the US schedule. When questioned I’m frequently told that immunizations are up to date, only to review records and find they are not, especially when it is related to MMR. It is often administered at 9 months and/or MR or MM is administered depending on the country. As reported here, varicella is a routine vaccine in only 45 countries.
2.
3. Once an outbreak has been identified, the infrastructure to manage and contain it must already be established. In most instances there will be a need for a rapid and often large-scale effort involving multiple agencies including local health care providers.
4. Not all diseases are reportable. Only deaths by varicella are nationally notifiable. Otherwise, cases are reported voluntarily. As of November 2, 2024, there have been 5,157 cases of varicella reported, excluding any cases from NYC.
Word is a pediatric infectious disease specialist and director of the Houston Travel Medicine Clinic. She said she had no relevant financial disclosures.
Suggested Reading
CDC. Nationally Notifiable Infectious Diseases and Conditions, United States: Weekly Tables. https://wonder.cdc.gov/nndss/nndss_weekly_tables_menu.asp.
Graham KA et al. Varicella Outbreak Among Recent Arrivals to New York City, 2022-2024. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2024 May 30;73(21):478-483. doi: 10.15585/mmwr.mm7321a1.
Marin M et al. Health and Economic Impact of the United States Varicella Vaccination Program, 1996-2020. J Infect Dis. 2022 Oct 21;226(Suppl 4):S463-S469. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jiac271.
Varicella-Zoster Virus Infections in Kimberkin DW et al, eds. Red Book: 2024 Report of the Committee on Infectious Diseases, 33rd Edition. American Academy of Pediatrics, 2024:938-951. https://www.aap.org/Red-Book-2024-Report-of-the-Committee-on-Infectious-Diseases-33rd-Edition-Paperback?srsltid=AfmBOoqyF60rR9ZwQ5jA8AouNhtRRTyPLnc_r7HWw7JVYV8v33Hr2vQS.
Practitioners providing care to children are familiar with the childhood immunization schedule and routinely administer varicella vaccine at the 12-month and 4- to 5-year visits. However, when is the last time most of us or any of the current trainees have seen a case?
Briefly, varicella is a highly contagious disease caused by varicella-zoster virus (VZV). It is characterized by a generalized pruritic erythematous rash in various stages of development beginning as macules, progressing to papules, and ultimately becoming vesicular lesions on an erythematous base (“dewdrop on a rose petal”) and resolves with crusting of the lesion (Figure 1). It has an incubation period of 10-21 days with symptoms usually developing within 14-16 days after exposure. The vesicular rash must be differentiated from enterovirus, Staphylococcus aureus, contact dermatitis, or insect bites, which initially may be difficult. Approximately 50% of children can have symptoms including fever, malaise, anorexia, headache, and occasionally, mild abdominal pain in the 24-48 hours prior to the appearance of rash. Lesions usually first appear on the scalp, face, or trunk in successive crops over several days. A person with varicella has lesions in various stages.
In a normal host, new vesicle formation usually stops within 4 days, and most lesions have fully crusted by day 6. VZV establishes latency in sensory ganglia and may reactivate years or decades later to cause herpes zoster (HZ). Most healthy children with varicella recover without sequelae so the disease is generally regarded as benign. However, varicella can lead to serious complications and deaths in healthy as well as immunocompromised persons.
Complications of Varicella: bacterial superinfection of skin lesions most often with Streptococcus pyogenes or S aureus manifested as cellulitis, myositis, or necrotizing fasciitis; neurologic complications include cerebellar ataxia and encephalitis with the latter seen most often in adults. Pneumonia occurs most often in adults, especially those infected during pregnancy. Another concern, infection during the first 20 weeks of pregnancy can lead to fetal death or severe birth defects, including limb hypoplasia, cutaneous scarring, ocular abnormalities, and central nervous system damage (congenital varicella syndrome).
The risk for development of severe disseminated disease was first noted in the 1960s as treatments for leukemia in children improved. They were surviving their cancer only to develop severe and often fatal varicella. Today it is recognized that development of disseminated disease is a risk for all infected persons with impaired T cell function, malignancies, HIV, or receiving immunosuppressive therapy.
Reye’s syndrome is rarely seen today since taking salicylates while infected with VZV was identified as a predisposing factor for development.
VZV is only found in humans and transmission is person to person or airborne. The secondary household attack rate is approximately 90%. In contrast, the secondary attack rates in classrooms may be as low as 12%-33%. Transmission rates in the tropics for unexplained reasons are also lower.
Vaccine History: Why do we rarely see this disease anymore? Varicella, a live attenuated vaccine, was developed in 1974 by Dr. Michiaki Takahashi. It remains the only vaccine directed against a herpes group virus. In 1979, the Collaborative Varicella Vaccine Study Group was established at the National Institutes of Health (NIH) and additional safety and efficacy trials were conducted in the United States initially in leukemic patients in remission and later in healthy children, which supported Takahashi’s data. Licensure of varicella vaccine was granted in 1995. That same year, due to continuing disease and societal burden, the United States was the first country to incorporate varicella into the routine childhood immunization schedule, which resulted in significant reductions in cases. To further improve control of varicella, in 2007 vaccine recommendations were revised and a routine two-dose schedule was implemented. The impact of varicella disease pre- and post-vaccine licensure is illustrated in Figure 2. Not listed, is that in the pre-vaccine era, there were approximately 44 cases of congenital varicella syndrome annually.

As of 2023 only 23% (45/195) of nations routinely administer this vaccine and 4% (8/195) have restricted recommendations. The remaining 73% of countries do not offer the vaccine, including all countries on the African continent, and Cuba, Guatemala, Haiti, Honduras, India, Jordan, Lebanon, Philippines, Portugal, and Venezuela to list a few.
Varicella Outbreak: In October 2022, New York City (NYC) identified a varicella outbreak primarily involving persons who recently migrated from Central and South America and lived in a shelter in NYC or residential facility (n = 105); the outbreak is ongoing. As of March 8, 2024, 873 cases (53%) were among children aged 4-18 years and 91.9% had no documentation of varicella vaccine at time of symptom onset. There were 28 hospitalizations, and no deaths reported. The most common sources of transmission were the residential facilities (41.3%) and importation or possible importation (39.4%). School transmission accounted for only 1.2% of cases.
Most migrants arrived from countries where varicella vaccination is not part of the routine childhood immunization schedule. Although most cases occurred in children, almost 30% occurred in adults. Many of the migrants arrived from tropical countries where susceptibility rates are also higher in adults. This outbreak is a reminder of the importance of limiting disease transmission by maintaining high vaccination rates. To curtail this outbreak, approximately 27,000 doses of varicella vaccine were administered to the arriving migrants. In addition, MMR, COVID-19, influenza, and all routine pediatric vaccines required for school entry were administered. Temporary closure of the residential facilities were required. Education was provided to residents regarding immunizations as well as assistance to help them establish a primary care home. Multiple agencies were mobilized to successfully coordinate these efforts.
Take Home Message
1. Each country has its own routine immunization schedule. It may not include all vaccines recommended in the US schedule. When questioned I’m frequently told that immunizations are up to date, only to review records and find they are not, especially when it is related to MMR. It is often administered at 9 months and/or MR or MM is administered depending on the country. As reported here, varicella is a routine vaccine in only 45 countries.
2.
3. Once an outbreak has been identified, the infrastructure to manage and contain it must already be established. In most instances there will be a need for a rapid and often large-scale effort involving multiple agencies including local health care providers.
4. Not all diseases are reportable. Only deaths by varicella are nationally notifiable. Otherwise, cases are reported voluntarily. As of November 2, 2024, there have been 5,157 cases of varicella reported, excluding any cases from NYC.
Word is a pediatric infectious disease specialist and director of the Houston Travel Medicine Clinic. She said she had no relevant financial disclosures.
Suggested Reading
CDC. Nationally Notifiable Infectious Diseases and Conditions, United States: Weekly Tables. https://wonder.cdc.gov/nndss/nndss_weekly_tables_menu.asp.
Graham KA et al. Varicella Outbreak Among Recent Arrivals to New York City, 2022-2024. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2024 May 30;73(21):478-483. doi: 10.15585/mmwr.mm7321a1.
Marin M et al. Health and Economic Impact of the United States Varicella Vaccination Program, 1996-2020. J Infect Dis. 2022 Oct 21;226(Suppl 4):S463-S469. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jiac271.
Varicella-Zoster Virus Infections in Kimberkin DW et al, eds. Red Book: 2024 Report of the Committee on Infectious Diseases, 33rd Edition. American Academy of Pediatrics, 2024:938-951. https://www.aap.org/Red-Book-2024-Report-of-the-Committee-on-Infectious-Diseases-33rd-Edition-Paperback?srsltid=AfmBOoqyF60rR9ZwQ5jA8AouNhtRRTyPLnc_r7HWw7JVYV8v33Hr2vQS.
New Data: The Most Promising Treatments for Long COVID
Long COVID is a symptom-driven disease, meaning that with no cure, physicians primarily treat the symptoms their patients are experiencing. But as 2024 winds down, researchers have begun to pinpoint a number of treatments that are bringing relief to the 17 million Americans diagnosed with long COVID.
Here’s a current look at what research has identified as some of the most promising treatments.
Low-Dose Naltrexone
Some research suggests that low-dose naltrexone may be helpful for patients suffering from brain fog, pain, sleep issues, and fatigue, said Ziyad Al-Aly, MD, a global expert on long COVID and chief of research and development at the Veterans Affairs St Louis Health Care System in Missouri.
Low-dose naltrexone is an anti-inflammatory agent currently approved by the Food and Drug Administration for the treatment of alcohol and opioid dependence.
“We don’t know the mechanism for how the medication works, and for that matter, we don’t really understand what causes brain fog. But perhaps its anti-inflammatory properties seem to help, and for some patients, low-dose naltrexone has been helpful,” said Al-Aly.
A March 2024 study found that both fatigue and pain were improved in patients taking low-dose naltrexone. In another study, published in the June 2024 issue of Frontiers in Medicine, researchers found that low-dose naltrexone was associated with improvement of several clinical symptoms related to long COVID such as fatigue, poor sleep quality, brain fog, post-exertional malaise, and headache.
Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors (SSRIs) and Antidepressants
In 2023, University of Pennsylvania researchers uncovered a link between long COVID and lower levels of serotonin in the body. This helped point to the potential treatment of using SSRIs to treat the condition.
For patients who have overlapping psychiatric issues that go along with brain fog, SSRIs prescribed to treat depression and other mental health conditions, as well as the antidepressant Wellbutrin, have been shown effective at dealing with concentration issues, brain fog, and depression, said Nisha Viswanathan, MD, director of the University of California, Los Angeles (UCLA) Long COVID Program at UCLA Health.
A study published in the November 2023 issue of the journal Scientific Reports found that SSRIs led to a “considerable reduction of symptoms,” especially brain fog, fatigue, sensory overload, and overall improved functioning. Low-dose Abilify, which contains aripiprazole, an antipsychotic medication, has also been found to be effective for cognitive issues caused by long COVID.
“Abilify is traditionally used for the treatment of schizophrenia or other psychotic disorders, but in a low-dose format, there is some data to suggest that it can also be anti-inflammatory and helpful for cognitive issues like brain fog,” said Viswanathan.
Modafinil
Modafinil, a medication previously used for managing narcolepsy, has also been shown effective for the treatment of fatigue and neurocognitive deficits caused by long COVID, said Viswanathan, adding that it’s another medication that she’s found useful for a number of her patients.
It’s thought that these cognitive symptoms are caused by an inflammatory cytokine release that leads to excessive stimulation of neurotransmitters in the body. According to a June 2024 article in the American Journal of Psychiatry, “Modafinil can therapeutically act on these pathways, which possibly contributed to the symptomatic improvement.” But the medication has not been studied widely in patients with long COVID and has been shown to have interactions with other medications.
Metformin
Some research has shown that metformin, a well-known diabetes medication, reduces instances of long COVID when taken during the illness’s acute phase. It seems to boost metabolic function in patients.
“It makes sense that it would work because it seems to have anti-inflammatory effects on the body,” said Grace McComsey, MD, who leads one of the 15 nationwide long COVID centers funded by the federal RECOVER (Researching COVID to Enhance Recovery) Initiative in Cleveland, Ohio. McComsey added that it may reduce the viral persistence that causes some forms of long COVID.
A study published in the October 2023 issue of the journal The Lancet Infectious Diseases found that metformin seemed to reduce instances of long COVID in patients who took it after being diagnosed with acute COVID. It seems less effective in patients who already have long COVID.
Antihistamines
Other data suggest that some patients with long COVID showed improvement after taking antihistamines. Research has shown that long COVID symptoms improved in 29% of patients with long COVID.
While researchers aren’t sure why antihistamines work to quell long COVID, the thought is that, when mast cells, a white blood cell that’s part of the immune system, shed granules and cause an inflammatory reaction, they release a lot of histamines. Antihistamine medications like famotidine block histamine receptors in the body, improving symptoms like brain fog, difficulty breathing, and elevated heart rate in patients.
“For some patients, these can be a lifesaver,” said David Putrino, the Nash Family Director of the Cohen Center for Recovery from Complex Chronic Illness and a national leader in the treatment of long COVID.
Putrino cautions patients toward taking these and other medications haphazardly without fully understanding that all treatments have risks, especially if they’re taking a number of them.
“Often patients are told that there’s no risk to trying something, but physicians should be counseling their patients and reminding them that there is a risk that includes medication sensitivities and medication interactions,” said Putrino.
The good news is that doctors have begun to identify some treatments that seem to be working in their patients, but we still don’t have the large-scale clinical trials to identify which treatments will work for certain patients and why.
There’s still so much we don’t know, and for physicians on the front lines of treating long COVID, it’s still largely a guessing game. “This is a constellation of symptoms; it’s not just one thing,” said Al-Aly. And while a treatment might be wildly effective for one patient, it might be ineffective or worse, problematic, for another.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Long COVID is a symptom-driven disease, meaning that with no cure, physicians primarily treat the symptoms their patients are experiencing. But as 2024 winds down, researchers have begun to pinpoint a number of treatments that are bringing relief to the 17 million Americans diagnosed with long COVID.
Here’s a current look at what research has identified as some of the most promising treatments.
Low-Dose Naltrexone
Some research suggests that low-dose naltrexone may be helpful for patients suffering from brain fog, pain, sleep issues, and fatigue, said Ziyad Al-Aly, MD, a global expert on long COVID and chief of research and development at the Veterans Affairs St Louis Health Care System in Missouri.
Low-dose naltrexone is an anti-inflammatory agent currently approved by the Food and Drug Administration for the treatment of alcohol and opioid dependence.
“We don’t know the mechanism for how the medication works, and for that matter, we don’t really understand what causes brain fog. But perhaps its anti-inflammatory properties seem to help, and for some patients, low-dose naltrexone has been helpful,” said Al-Aly.
A March 2024 study found that both fatigue and pain were improved in patients taking low-dose naltrexone. In another study, published in the June 2024 issue of Frontiers in Medicine, researchers found that low-dose naltrexone was associated with improvement of several clinical symptoms related to long COVID such as fatigue, poor sleep quality, brain fog, post-exertional malaise, and headache.
Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors (SSRIs) and Antidepressants
In 2023, University of Pennsylvania researchers uncovered a link between long COVID and lower levels of serotonin in the body. This helped point to the potential treatment of using SSRIs to treat the condition.
For patients who have overlapping psychiatric issues that go along with brain fog, SSRIs prescribed to treat depression and other mental health conditions, as well as the antidepressant Wellbutrin, have been shown effective at dealing with concentration issues, brain fog, and depression, said Nisha Viswanathan, MD, director of the University of California, Los Angeles (UCLA) Long COVID Program at UCLA Health.
A study published in the November 2023 issue of the journal Scientific Reports found that SSRIs led to a “considerable reduction of symptoms,” especially brain fog, fatigue, sensory overload, and overall improved functioning. Low-dose Abilify, which contains aripiprazole, an antipsychotic medication, has also been found to be effective for cognitive issues caused by long COVID.
“Abilify is traditionally used for the treatment of schizophrenia or other psychotic disorders, but in a low-dose format, there is some data to suggest that it can also be anti-inflammatory and helpful for cognitive issues like brain fog,” said Viswanathan.
Modafinil
Modafinil, a medication previously used for managing narcolepsy, has also been shown effective for the treatment of fatigue and neurocognitive deficits caused by long COVID, said Viswanathan, adding that it’s another medication that she’s found useful for a number of her patients.
It’s thought that these cognitive symptoms are caused by an inflammatory cytokine release that leads to excessive stimulation of neurotransmitters in the body. According to a June 2024 article in the American Journal of Psychiatry, “Modafinil can therapeutically act on these pathways, which possibly contributed to the symptomatic improvement.” But the medication has not been studied widely in patients with long COVID and has been shown to have interactions with other medications.
Metformin
Some research has shown that metformin, a well-known diabetes medication, reduces instances of long COVID when taken during the illness’s acute phase. It seems to boost metabolic function in patients.
“It makes sense that it would work because it seems to have anti-inflammatory effects on the body,” said Grace McComsey, MD, who leads one of the 15 nationwide long COVID centers funded by the federal RECOVER (Researching COVID to Enhance Recovery) Initiative in Cleveland, Ohio. McComsey added that it may reduce the viral persistence that causes some forms of long COVID.
A study published in the October 2023 issue of the journal The Lancet Infectious Diseases found that metformin seemed to reduce instances of long COVID in patients who took it after being diagnosed with acute COVID. It seems less effective in patients who already have long COVID.
Antihistamines
Other data suggest that some patients with long COVID showed improvement after taking antihistamines. Research has shown that long COVID symptoms improved in 29% of patients with long COVID.
While researchers aren’t sure why antihistamines work to quell long COVID, the thought is that, when mast cells, a white blood cell that’s part of the immune system, shed granules and cause an inflammatory reaction, they release a lot of histamines. Antihistamine medications like famotidine block histamine receptors in the body, improving symptoms like brain fog, difficulty breathing, and elevated heart rate in patients.
“For some patients, these can be a lifesaver,” said David Putrino, the Nash Family Director of the Cohen Center for Recovery from Complex Chronic Illness and a national leader in the treatment of long COVID.
Putrino cautions patients toward taking these and other medications haphazardly without fully understanding that all treatments have risks, especially if they’re taking a number of them.
“Often patients are told that there’s no risk to trying something, but physicians should be counseling their patients and reminding them that there is a risk that includes medication sensitivities and medication interactions,” said Putrino.
The good news is that doctors have begun to identify some treatments that seem to be working in their patients, but we still don’t have the large-scale clinical trials to identify which treatments will work for certain patients and why.
There’s still so much we don’t know, and for physicians on the front lines of treating long COVID, it’s still largely a guessing game. “This is a constellation of symptoms; it’s not just one thing,” said Al-Aly. And while a treatment might be wildly effective for one patient, it might be ineffective or worse, problematic, for another.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Long COVID is a symptom-driven disease, meaning that with no cure, physicians primarily treat the symptoms their patients are experiencing. But as 2024 winds down, researchers have begun to pinpoint a number of treatments that are bringing relief to the 17 million Americans diagnosed with long COVID.
Here’s a current look at what research has identified as some of the most promising treatments.
Low-Dose Naltrexone
Some research suggests that low-dose naltrexone may be helpful for patients suffering from brain fog, pain, sleep issues, and fatigue, said Ziyad Al-Aly, MD, a global expert on long COVID and chief of research and development at the Veterans Affairs St Louis Health Care System in Missouri.
Low-dose naltrexone is an anti-inflammatory agent currently approved by the Food and Drug Administration for the treatment of alcohol and opioid dependence.
“We don’t know the mechanism for how the medication works, and for that matter, we don’t really understand what causes brain fog. But perhaps its anti-inflammatory properties seem to help, and for some patients, low-dose naltrexone has been helpful,” said Al-Aly.
A March 2024 study found that both fatigue and pain were improved in patients taking low-dose naltrexone. In another study, published in the June 2024 issue of Frontiers in Medicine, researchers found that low-dose naltrexone was associated with improvement of several clinical symptoms related to long COVID such as fatigue, poor sleep quality, brain fog, post-exertional malaise, and headache.
Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors (SSRIs) and Antidepressants
In 2023, University of Pennsylvania researchers uncovered a link between long COVID and lower levels of serotonin in the body. This helped point to the potential treatment of using SSRIs to treat the condition.
For patients who have overlapping psychiatric issues that go along with brain fog, SSRIs prescribed to treat depression and other mental health conditions, as well as the antidepressant Wellbutrin, have been shown effective at dealing with concentration issues, brain fog, and depression, said Nisha Viswanathan, MD, director of the University of California, Los Angeles (UCLA) Long COVID Program at UCLA Health.
A study published in the November 2023 issue of the journal Scientific Reports found that SSRIs led to a “considerable reduction of symptoms,” especially brain fog, fatigue, sensory overload, and overall improved functioning. Low-dose Abilify, which contains aripiprazole, an antipsychotic medication, has also been found to be effective for cognitive issues caused by long COVID.
“Abilify is traditionally used for the treatment of schizophrenia or other psychotic disorders, but in a low-dose format, there is some data to suggest that it can also be anti-inflammatory and helpful for cognitive issues like brain fog,” said Viswanathan.
Modafinil
Modafinil, a medication previously used for managing narcolepsy, has also been shown effective for the treatment of fatigue and neurocognitive deficits caused by long COVID, said Viswanathan, adding that it’s another medication that she’s found useful for a number of her patients.
It’s thought that these cognitive symptoms are caused by an inflammatory cytokine release that leads to excessive stimulation of neurotransmitters in the body. According to a June 2024 article in the American Journal of Psychiatry, “Modafinil can therapeutically act on these pathways, which possibly contributed to the symptomatic improvement.” But the medication has not been studied widely in patients with long COVID and has been shown to have interactions with other medications.
Metformin
Some research has shown that metformin, a well-known diabetes medication, reduces instances of long COVID when taken during the illness’s acute phase. It seems to boost metabolic function in patients.
“It makes sense that it would work because it seems to have anti-inflammatory effects on the body,” said Grace McComsey, MD, who leads one of the 15 nationwide long COVID centers funded by the federal RECOVER (Researching COVID to Enhance Recovery) Initiative in Cleveland, Ohio. McComsey added that it may reduce the viral persistence that causes some forms of long COVID.
A study published in the October 2023 issue of the journal The Lancet Infectious Diseases found that metformin seemed to reduce instances of long COVID in patients who took it after being diagnosed with acute COVID. It seems less effective in patients who already have long COVID.
Antihistamines
Other data suggest that some patients with long COVID showed improvement after taking antihistamines. Research has shown that long COVID symptoms improved in 29% of patients with long COVID.
While researchers aren’t sure why antihistamines work to quell long COVID, the thought is that, when mast cells, a white blood cell that’s part of the immune system, shed granules and cause an inflammatory reaction, they release a lot of histamines. Antihistamine medications like famotidine block histamine receptors in the body, improving symptoms like brain fog, difficulty breathing, and elevated heart rate in patients.
“For some patients, these can be a lifesaver,” said David Putrino, the Nash Family Director of the Cohen Center for Recovery from Complex Chronic Illness and a national leader in the treatment of long COVID.
Putrino cautions patients toward taking these and other medications haphazardly without fully understanding that all treatments have risks, especially if they’re taking a number of them.
“Often patients are told that there’s no risk to trying something, but physicians should be counseling their patients and reminding them that there is a risk that includes medication sensitivities and medication interactions,” said Putrino.
The good news is that doctors have begun to identify some treatments that seem to be working in their patients, but we still don’t have the large-scale clinical trials to identify which treatments will work for certain patients and why.
There’s still so much we don’t know, and for physicians on the front lines of treating long COVID, it’s still largely a guessing game. “This is a constellation of symptoms; it’s not just one thing,” said Al-Aly. And while a treatment might be wildly effective for one patient, it might be ineffective or worse, problematic, for another.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
It’s Not Too Late for Influenza Vaccination: Q&A With CDC’s Dr. Lisa Grohskopf
Text has been edited for length.
Are there any updates to this season’s influenza vaccine or vaccine recommendations?
Yes, we have updates to both the vaccine and the vaccine recommendations this year. Typically we have some changes each year, and this year there are two main changes in the recommendations. One relates to the composition of the vaccine for this season, and the other is a new recommendation for adult solid organ transplant recipients.
We typically have changes in the vaccine composition each season. For most seasons, one or more parts of the vaccine will change, but this year is a little different in that all of the vaccines available in the US for the 2024-2025 season are going to be three-virus, or trivalent, vaccines. They are going to be formulated to protect against three viruses: an influenza A(H1N1) virus, an influenza A(H3N2) virus, and an influenza B/Victoria lineage virus.
The reason for this change is that since the 2013-2014 season through the 2023-2024 season, we had quadrivalent vaccines that were available in the US that contained four viruses. Those vaccines contained a second influenza B virus from the Yamagata lineage (B viruses come from two main lineages).
The reason for the change to trivalent vaccines this season is that influenza B/Yamagata viruses have not been detected in global surveillance since March 2020, and so their inclusion is no longer warranted. So this season, all of the vaccines available in the US are going to be trivalent.
In addition to that change, we have an update in the influenza A(H3N2) component of the vaccine compared with last season.
The second change concerning adult solid organ transplant recipients is that Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP) now recommends that solid organ transplant recipients aged 18-64 years can receive as acceptable options either the high-dose inactivated vaccine or the adjuvanted inactivated vaccine without a preference over other age appropriate, inactivated, or recombinant vaccines.
Those vaccines are both formulated with features intended to make them more immunogenic — ie, promote a stronger immune response — and there are data for immunogenicity that suggest they could be more immunogenic in that population.
Who needs an influenza vaccine this season?
That recommendation is the same as it’s been for a number of years, which is that everybody aged 6 months or older is recommended to get a flu vaccine, with some rare exceptions, mainly concerning contraindications to vaccination.
Contraindications are detailed in the ACIP flu statement each year, and they’re relatively uncommon conditions overall, so most people are recommended, if they’re in that age group 6 months and up, to get an annual flu vaccine.
Are there groups for whom influenza vaccination is especially important?
Yes. While influenza vaccination is recommended for everybody in that age group 6 months and up — and in truth, we can never really predict who’s going to get severely ill — some people are more likely to be at risk of having serious illness or hospitalization. Those people include adults aged 65 years or older; young children; people with certain chronic health conditions such as heart disease, lung disease, and diabetes; and people from some racial and ethnic groups.
Are there any specific influenza vaccination recommendations for these groups or others?
Not for most people. In general, we have a number of different influenza vaccines each season; this year we have a total of nine brands. In general, there’s no preferential recommendation for one vaccine or type of vaccine for specific groups of people, with one exception: For people aged 65 years or older, there’s a preferential recommendation for three specific vaccines — the high-dose inactivated vaccine, Fluzone High-Dose; the recombinant vaccine, Flublok; and the adjuvanted inactivated vaccine, FLUAD.
Among those three, there’s no preference for any one of them over the other two; they’re all preferred vaccines for this age group, if available. If none of those three vaccines are available at the time that somebody aged 65 or older is there to get vaccinated, people in this age group should get any other age-appropriate influenza vaccine that is available.
When should people get vaccinated if they haven’t already?
CDC and ACIP recommend vaccination for most people, ideally by the end of October. But for those who missed the end of October, it is absolutely not too late. Providers should continue to encourage vaccination and people should get their vaccines as long as flu viruses are circulating.
The timing of the onset and the peak and the end of the flu season vary a bit from year to year. We often start to see generally activity begin to increase in the US in the fall, which is the reason for the end of October recommendation; however, flu activity doesn’t tend to peak in the US until after October. We’re talking December, January, or later, so getting vaccinated after October can still provide important protection during the peak of the season.
There does seem to be a tendency for people to think, OK, I haven’t gotten the vaccine yet, and there probably isn’t a lot of reason to do it now. But really, it’s definitely not too late, and that’s something we like to encourage people to think about, particularly as we move into December and January — it’s not too late if you missed October.
Influenza vaccination is also available in so many places. You don’t necessarily have to go to a healthcare provider’s office; there are many retail chains which offer influenza vaccines.
Is influenza spreading right now? Are activity levels increasing?
Overall influenza activity currently is low nationally, although there’s starting to be some slight increases in the pediatric age groups and, of course, we do anticipate that it will increase in the coming weeks and months.
When we get vaccinated, the protection isn’t instantaneous. The immune system needs a bit of time to react to the vaccine and to develop antibodies. That can take about 2 weeks. Even with that, now is still absolutely not too late to get a vaccine. Neither is December, for that matter. As long as the flu viruses are circulating where you are, it is still worth getting vaccinated.
What was influenza vaccination coverage like last season?
It’s a little bit early to tell for the current season, but one of the things that we do know is that since the COVID-19 pandemic, coverage has dropped compared with before the COVID-19 pandemic. Before COVID-19, influenza vaccination coverage had been slowly increasing in most groups, but it has decreased since then, and those downturns in coverage haven’t recovered to prepandemic levels. For example, during 2023-2024, about half of children and adults received a flu vaccine.
What can providers do to encourage influenza vaccination in their patients?
We know that a healthcare provider’s strong recommendation for flu vaccination is a really major factor in whether or not patients get a flu vaccine, and is more effective in increasing acceptance of vaccination than just about any other factor.
There’s a method from CDC called SHARE, which is a helpful way to help make a strong recommendation and provide information to help patients make an informed decision about whether or not they want to be vaccinated.
To implement SHARE, it’s an acronym with five parts. S is for Share the reasons why the flu vaccine is right for that patient. H is for Highlight positive experiences with flu vaccination, either personal or in practice. A is for Address patient concerns and questions about the flu vaccine, including things such as side effects, safety, and effectiveness. R is Remind patients that vaccination protects them and their loved ones from serious illness and related complications. E is Explain the potential complications and consequences of getting influenza, including serious health effects, time lost from family, work, and school, and potential financial costs.
Additional resources are accessible on CDC’s influenza resources page, including brochures, posters, and fact sheets that can help providers in encouraging and reminding people to get vaccinated.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Text has been edited for length.
Are there any updates to this season’s influenza vaccine or vaccine recommendations?
Yes, we have updates to both the vaccine and the vaccine recommendations this year. Typically we have some changes each year, and this year there are two main changes in the recommendations. One relates to the composition of the vaccine for this season, and the other is a new recommendation for adult solid organ transplant recipients.
We typically have changes in the vaccine composition each season. For most seasons, one or more parts of the vaccine will change, but this year is a little different in that all of the vaccines available in the US for the 2024-2025 season are going to be three-virus, or trivalent, vaccines. They are going to be formulated to protect against three viruses: an influenza A(H1N1) virus, an influenza A(H3N2) virus, and an influenza B/Victoria lineage virus.
The reason for this change is that since the 2013-2014 season through the 2023-2024 season, we had quadrivalent vaccines that were available in the US that contained four viruses. Those vaccines contained a second influenza B virus from the Yamagata lineage (B viruses come from two main lineages).
The reason for the change to trivalent vaccines this season is that influenza B/Yamagata viruses have not been detected in global surveillance since March 2020, and so their inclusion is no longer warranted. So this season, all of the vaccines available in the US are going to be trivalent.
In addition to that change, we have an update in the influenza A(H3N2) component of the vaccine compared with last season.
The second change concerning adult solid organ transplant recipients is that Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP) now recommends that solid organ transplant recipients aged 18-64 years can receive as acceptable options either the high-dose inactivated vaccine or the adjuvanted inactivated vaccine without a preference over other age appropriate, inactivated, or recombinant vaccines.
Those vaccines are both formulated with features intended to make them more immunogenic — ie, promote a stronger immune response — and there are data for immunogenicity that suggest they could be more immunogenic in that population.
Who needs an influenza vaccine this season?
That recommendation is the same as it’s been for a number of years, which is that everybody aged 6 months or older is recommended to get a flu vaccine, with some rare exceptions, mainly concerning contraindications to vaccination.
Contraindications are detailed in the ACIP flu statement each year, and they’re relatively uncommon conditions overall, so most people are recommended, if they’re in that age group 6 months and up, to get an annual flu vaccine.
Are there groups for whom influenza vaccination is especially important?
Yes. While influenza vaccination is recommended for everybody in that age group 6 months and up — and in truth, we can never really predict who’s going to get severely ill — some people are more likely to be at risk of having serious illness or hospitalization. Those people include adults aged 65 years or older; young children; people with certain chronic health conditions such as heart disease, lung disease, and diabetes; and people from some racial and ethnic groups.
Are there any specific influenza vaccination recommendations for these groups or others?
Not for most people. In general, we have a number of different influenza vaccines each season; this year we have a total of nine brands. In general, there’s no preferential recommendation for one vaccine or type of vaccine for specific groups of people, with one exception: For people aged 65 years or older, there’s a preferential recommendation for three specific vaccines — the high-dose inactivated vaccine, Fluzone High-Dose; the recombinant vaccine, Flublok; and the adjuvanted inactivated vaccine, FLUAD.
Among those three, there’s no preference for any one of them over the other two; they’re all preferred vaccines for this age group, if available. If none of those three vaccines are available at the time that somebody aged 65 or older is there to get vaccinated, people in this age group should get any other age-appropriate influenza vaccine that is available.
When should people get vaccinated if they haven’t already?
CDC and ACIP recommend vaccination for most people, ideally by the end of October. But for those who missed the end of October, it is absolutely not too late. Providers should continue to encourage vaccination and people should get their vaccines as long as flu viruses are circulating.
The timing of the onset and the peak and the end of the flu season vary a bit from year to year. We often start to see generally activity begin to increase in the US in the fall, which is the reason for the end of October recommendation; however, flu activity doesn’t tend to peak in the US until after October. We’re talking December, January, or later, so getting vaccinated after October can still provide important protection during the peak of the season.
There does seem to be a tendency for people to think, OK, I haven’t gotten the vaccine yet, and there probably isn’t a lot of reason to do it now. But really, it’s definitely not too late, and that’s something we like to encourage people to think about, particularly as we move into December and January — it’s not too late if you missed October.
Influenza vaccination is also available in so many places. You don’t necessarily have to go to a healthcare provider’s office; there are many retail chains which offer influenza vaccines.
Is influenza spreading right now? Are activity levels increasing?
Overall influenza activity currently is low nationally, although there’s starting to be some slight increases in the pediatric age groups and, of course, we do anticipate that it will increase in the coming weeks and months.
When we get vaccinated, the protection isn’t instantaneous. The immune system needs a bit of time to react to the vaccine and to develop antibodies. That can take about 2 weeks. Even with that, now is still absolutely not too late to get a vaccine. Neither is December, for that matter. As long as the flu viruses are circulating where you are, it is still worth getting vaccinated.
What was influenza vaccination coverage like last season?
It’s a little bit early to tell for the current season, but one of the things that we do know is that since the COVID-19 pandemic, coverage has dropped compared with before the COVID-19 pandemic. Before COVID-19, influenza vaccination coverage had been slowly increasing in most groups, but it has decreased since then, and those downturns in coverage haven’t recovered to prepandemic levels. For example, during 2023-2024, about half of children and adults received a flu vaccine.
What can providers do to encourage influenza vaccination in their patients?
We know that a healthcare provider’s strong recommendation for flu vaccination is a really major factor in whether or not patients get a flu vaccine, and is more effective in increasing acceptance of vaccination than just about any other factor.
There’s a method from CDC called SHARE, which is a helpful way to help make a strong recommendation and provide information to help patients make an informed decision about whether or not they want to be vaccinated.
To implement SHARE, it’s an acronym with five parts. S is for Share the reasons why the flu vaccine is right for that patient. H is for Highlight positive experiences with flu vaccination, either personal or in practice. A is for Address patient concerns and questions about the flu vaccine, including things such as side effects, safety, and effectiveness. R is Remind patients that vaccination protects them and their loved ones from serious illness and related complications. E is Explain the potential complications and consequences of getting influenza, including serious health effects, time lost from family, work, and school, and potential financial costs.
Additional resources are accessible on CDC’s influenza resources page, including brochures, posters, and fact sheets that can help providers in encouraging and reminding people to get vaccinated.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Text has been edited for length.
Are there any updates to this season’s influenza vaccine or vaccine recommendations?
Yes, we have updates to both the vaccine and the vaccine recommendations this year. Typically we have some changes each year, and this year there are two main changes in the recommendations. One relates to the composition of the vaccine for this season, and the other is a new recommendation for adult solid organ transplant recipients.
We typically have changes in the vaccine composition each season. For most seasons, one or more parts of the vaccine will change, but this year is a little different in that all of the vaccines available in the US for the 2024-2025 season are going to be three-virus, or trivalent, vaccines. They are going to be formulated to protect against three viruses: an influenza A(H1N1) virus, an influenza A(H3N2) virus, and an influenza B/Victoria lineage virus.
The reason for this change is that since the 2013-2014 season through the 2023-2024 season, we had quadrivalent vaccines that were available in the US that contained four viruses. Those vaccines contained a second influenza B virus from the Yamagata lineage (B viruses come from two main lineages).
The reason for the change to trivalent vaccines this season is that influenza B/Yamagata viruses have not been detected in global surveillance since March 2020, and so their inclusion is no longer warranted. So this season, all of the vaccines available in the US are going to be trivalent.
In addition to that change, we have an update in the influenza A(H3N2) component of the vaccine compared with last season.
The second change concerning adult solid organ transplant recipients is that Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP) now recommends that solid organ transplant recipients aged 18-64 years can receive as acceptable options either the high-dose inactivated vaccine or the adjuvanted inactivated vaccine without a preference over other age appropriate, inactivated, or recombinant vaccines.
Those vaccines are both formulated with features intended to make them more immunogenic — ie, promote a stronger immune response — and there are data for immunogenicity that suggest they could be more immunogenic in that population.
Who needs an influenza vaccine this season?
That recommendation is the same as it’s been for a number of years, which is that everybody aged 6 months or older is recommended to get a flu vaccine, with some rare exceptions, mainly concerning contraindications to vaccination.
Contraindications are detailed in the ACIP flu statement each year, and they’re relatively uncommon conditions overall, so most people are recommended, if they’re in that age group 6 months and up, to get an annual flu vaccine.
Are there groups for whom influenza vaccination is especially important?
Yes. While influenza vaccination is recommended for everybody in that age group 6 months and up — and in truth, we can never really predict who’s going to get severely ill — some people are more likely to be at risk of having serious illness or hospitalization. Those people include adults aged 65 years or older; young children; people with certain chronic health conditions such as heart disease, lung disease, and diabetes; and people from some racial and ethnic groups.
Are there any specific influenza vaccination recommendations for these groups or others?
Not for most people. In general, we have a number of different influenza vaccines each season; this year we have a total of nine brands. In general, there’s no preferential recommendation for one vaccine or type of vaccine for specific groups of people, with one exception: For people aged 65 years or older, there’s a preferential recommendation for three specific vaccines — the high-dose inactivated vaccine, Fluzone High-Dose; the recombinant vaccine, Flublok; and the adjuvanted inactivated vaccine, FLUAD.
Among those three, there’s no preference for any one of them over the other two; they’re all preferred vaccines for this age group, if available. If none of those three vaccines are available at the time that somebody aged 65 or older is there to get vaccinated, people in this age group should get any other age-appropriate influenza vaccine that is available.
When should people get vaccinated if they haven’t already?
CDC and ACIP recommend vaccination for most people, ideally by the end of October. But for those who missed the end of October, it is absolutely not too late. Providers should continue to encourage vaccination and people should get their vaccines as long as flu viruses are circulating.
The timing of the onset and the peak and the end of the flu season vary a bit from year to year. We often start to see generally activity begin to increase in the US in the fall, which is the reason for the end of October recommendation; however, flu activity doesn’t tend to peak in the US until after October. We’re talking December, January, or later, so getting vaccinated after October can still provide important protection during the peak of the season.
There does seem to be a tendency for people to think, OK, I haven’t gotten the vaccine yet, and there probably isn’t a lot of reason to do it now. But really, it’s definitely not too late, and that’s something we like to encourage people to think about, particularly as we move into December and January — it’s not too late if you missed October.
Influenza vaccination is also available in so many places. You don’t necessarily have to go to a healthcare provider’s office; there are many retail chains which offer influenza vaccines.
Is influenza spreading right now? Are activity levels increasing?
Overall influenza activity currently is low nationally, although there’s starting to be some slight increases in the pediatric age groups and, of course, we do anticipate that it will increase in the coming weeks and months.
When we get vaccinated, the protection isn’t instantaneous. The immune system needs a bit of time to react to the vaccine and to develop antibodies. That can take about 2 weeks. Even with that, now is still absolutely not too late to get a vaccine. Neither is December, for that matter. As long as the flu viruses are circulating where you are, it is still worth getting vaccinated.
What was influenza vaccination coverage like last season?
It’s a little bit early to tell for the current season, but one of the things that we do know is that since the COVID-19 pandemic, coverage has dropped compared with before the COVID-19 pandemic. Before COVID-19, influenza vaccination coverage had been slowly increasing in most groups, but it has decreased since then, and those downturns in coverage haven’t recovered to prepandemic levels. For example, during 2023-2024, about half of children and adults received a flu vaccine.
What can providers do to encourage influenza vaccination in their patients?
We know that a healthcare provider’s strong recommendation for flu vaccination is a really major factor in whether or not patients get a flu vaccine, and is more effective in increasing acceptance of vaccination than just about any other factor.
There’s a method from CDC called SHARE, which is a helpful way to help make a strong recommendation and provide information to help patients make an informed decision about whether or not they want to be vaccinated.
To implement SHARE, it’s an acronym with five parts. S is for Share the reasons why the flu vaccine is right for that patient. H is for Highlight positive experiences with flu vaccination, either personal or in practice. A is for Address patient concerns and questions about the flu vaccine, including things such as side effects, safety, and effectiveness. R is Remind patients that vaccination protects them and their loved ones from serious illness and related complications. E is Explain the potential complications and consequences of getting influenza, including serious health effects, time lost from family, work, and school, and potential financial costs.
Additional resources are accessible on CDC’s influenza resources page, including brochures, posters, and fact sheets that can help providers in encouraging and reminding people to get vaccinated.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
RSV Infections Take Toll on Adults
based on new data from more than 67,000 cases.
RSV remains a top cause of acute respiratory tract infections among adults in the United States, with an estimated 159,000 hospitalizations in those aged 65 years or older, wrote Suzanne N. Landi, MPH, PhD, of Pfizer in New York City, and colleagues in a study published in JAMA Network Open.
“Currently, limited estimates exist to determine the risk of hospitalization following outpatient RSV disease diagnoses in the United States,” said corresponding author Joshua T. Swan, PharmD, MPH, in an interview.
The current study was conducted to inform development of clinical trials, said Swan, senior director and category clinician in internal medicine and disease development at Pfizer, the sponsor of the study. These trials would assess the efficacy of an outpatient RSV antiviral treatment in preventing RSV-related hospitalization within 28 days among adults at a high risk for progression to severe illness, he said.
The authors reviewed data from 67,239 adults aged 18 years or older with medically attended RSV infections between October 1, 2016, and September 30, 2022. The data came from three databases: Optum (2771 patients), TriNetX (7442 patients), and Veradigm Network Electronic Health Record (VNEHR; 57,026 patients).
The primary outcome was all-cause hospitalization within 28 days of medically attended RSV.
Overall, the proportions of patients hospitalized within 28 days of infection were 6.2%, 6.0%, and 4.5% in Optum, TriNetX, and VNEHR databases, respectively.
Approximately two thirds of the patients (62%-67% across the three databases) were women, and 14.0%-54.5% were aged 65 years or older. The researchers also identified comorbidity prevalences of 20.0%-30.5% for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), 14.6%-24.4% for heart failure (HF), and 14.6%-24.4% for asthma.
A majority of the patients (ranging from 74.5% to 90.6% across the three databases) fell into a high-risk subgroup, defined as age 65 years or older with asthma, COPD, and HF. In this high-risk group, the proportions of hospitalizations were 7.6%, 8.5%, and 6.5% for Optum, TriNetX, and VNEHR, respectively.
The findings were limited by several factors, including the use only of data from outpatient settings, which cannot be used to estimate the RSV burden in the general population, and the reliance only on diagnosis or procedure codes to identify comorbidities, the researchers noted.
However, “the absolute risk of hospitalization of 1 out of 20 patients observed in our study represents significant and meaningful risk for vulnerable adults, in a disease where much of the public’s attention has historically focused on risk of hospitalization for young children,” Swan said. “These results highlight the unmet medical need for outpatient interventions and preventive measures that can reduce hospitalizations.”
Don’t Underestimate RSV Impact
The current study highlights the fact that RSV is a major cause of respiratory viral illness, said David R. Manoff, MD, associate professor of clinical thoracic medicine and surgery at Temple University, Philadelphia, in an interview.
“Historically, influenza, and, more recently, COVID-19 infection have generally been thought of as more likely to cause harm and, thus, have been more emphasized in terms of both vaccination and treatment,” said Manoff, who was not involved in the study.
The current study provides new evidence that infection with RSV can be far more serious than often recognized and a major potential source of both hospitalization and morbidity, Manoff said. In fact, data published in Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report in 2023 showed that the risks of needing oxygen, intensive care unit (ICU) admission, intubation, and death were actually higher in patients hospitalized with RSV infections than in those hospitalized with influenza or COVID-19. “
Understanding which population is hospitalized in the first place is vital to targeting prevention measures,” he added.
The new data are consistent with previous studies showing that most patients with RSV infection have primarily upper respiratory tract infection–type symptoms, but that a minority will develop lower respiratory tract disease, Manoff noted.
The findings add to the argument for implementation of RSV vaccination, especially in high-risk individuals, and support the need for RSV testing when patients present for care, he said.
However, more research is needed to reflect recent numbers, Manoff said. The study timeframe of 2016-2022 not only precedes commercially available RSV vaccines but also includes the period of increased isolation and masking seen during the COVID-19 pandemic years of 2020-2021. “We need to see if the same trends continue in the post-pandemic era.”
Additionally, the studies leading to approval of the RSV vaccine showed a reduction in hospitalization with RSV, and it is important to see how this reduction translates in real-world data and whether the RSV vaccines are reducing need for ICU admission, intubation, and death, Manoff said.
The study was funded by Pfizer, and Swan is a Pfizer employee. Manoff had no financial conflicts to disclose.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
based on new data from more than 67,000 cases.
RSV remains a top cause of acute respiratory tract infections among adults in the United States, with an estimated 159,000 hospitalizations in those aged 65 years or older, wrote Suzanne N. Landi, MPH, PhD, of Pfizer in New York City, and colleagues in a study published in JAMA Network Open.
“Currently, limited estimates exist to determine the risk of hospitalization following outpatient RSV disease diagnoses in the United States,” said corresponding author Joshua T. Swan, PharmD, MPH, in an interview.
The current study was conducted to inform development of clinical trials, said Swan, senior director and category clinician in internal medicine and disease development at Pfizer, the sponsor of the study. These trials would assess the efficacy of an outpatient RSV antiviral treatment in preventing RSV-related hospitalization within 28 days among adults at a high risk for progression to severe illness, he said.
The authors reviewed data from 67,239 adults aged 18 years or older with medically attended RSV infections between October 1, 2016, and September 30, 2022. The data came from three databases: Optum (2771 patients), TriNetX (7442 patients), and Veradigm Network Electronic Health Record (VNEHR; 57,026 patients).
The primary outcome was all-cause hospitalization within 28 days of medically attended RSV.
Overall, the proportions of patients hospitalized within 28 days of infection were 6.2%, 6.0%, and 4.5% in Optum, TriNetX, and VNEHR databases, respectively.
Approximately two thirds of the patients (62%-67% across the three databases) were women, and 14.0%-54.5% were aged 65 years or older. The researchers also identified comorbidity prevalences of 20.0%-30.5% for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), 14.6%-24.4% for heart failure (HF), and 14.6%-24.4% for asthma.
A majority of the patients (ranging from 74.5% to 90.6% across the three databases) fell into a high-risk subgroup, defined as age 65 years or older with asthma, COPD, and HF. In this high-risk group, the proportions of hospitalizations were 7.6%, 8.5%, and 6.5% for Optum, TriNetX, and VNEHR, respectively.
The findings were limited by several factors, including the use only of data from outpatient settings, which cannot be used to estimate the RSV burden in the general population, and the reliance only on diagnosis or procedure codes to identify comorbidities, the researchers noted.
However, “the absolute risk of hospitalization of 1 out of 20 patients observed in our study represents significant and meaningful risk for vulnerable adults, in a disease where much of the public’s attention has historically focused on risk of hospitalization for young children,” Swan said. “These results highlight the unmet medical need for outpatient interventions and preventive measures that can reduce hospitalizations.”
Don’t Underestimate RSV Impact
The current study highlights the fact that RSV is a major cause of respiratory viral illness, said David R. Manoff, MD, associate professor of clinical thoracic medicine and surgery at Temple University, Philadelphia, in an interview.
“Historically, influenza, and, more recently, COVID-19 infection have generally been thought of as more likely to cause harm and, thus, have been more emphasized in terms of both vaccination and treatment,” said Manoff, who was not involved in the study.
The current study provides new evidence that infection with RSV can be far more serious than often recognized and a major potential source of both hospitalization and morbidity, Manoff said. In fact, data published in Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report in 2023 showed that the risks of needing oxygen, intensive care unit (ICU) admission, intubation, and death were actually higher in patients hospitalized with RSV infections than in those hospitalized with influenza or COVID-19. “
Understanding which population is hospitalized in the first place is vital to targeting prevention measures,” he added.
The new data are consistent with previous studies showing that most patients with RSV infection have primarily upper respiratory tract infection–type symptoms, but that a minority will develop lower respiratory tract disease, Manoff noted.
The findings add to the argument for implementation of RSV vaccination, especially in high-risk individuals, and support the need for RSV testing when patients present for care, he said.
However, more research is needed to reflect recent numbers, Manoff said. The study timeframe of 2016-2022 not only precedes commercially available RSV vaccines but also includes the period of increased isolation and masking seen during the COVID-19 pandemic years of 2020-2021. “We need to see if the same trends continue in the post-pandemic era.”
Additionally, the studies leading to approval of the RSV vaccine showed a reduction in hospitalization with RSV, and it is important to see how this reduction translates in real-world data and whether the RSV vaccines are reducing need for ICU admission, intubation, and death, Manoff said.
The study was funded by Pfizer, and Swan is a Pfizer employee. Manoff had no financial conflicts to disclose.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
based on new data from more than 67,000 cases.
RSV remains a top cause of acute respiratory tract infections among adults in the United States, with an estimated 159,000 hospitalizations in those aged 65 years or older, wrote Suzanne N. Landi, MPH, PhD, of Pfizer in New York City, and colleagues in a study published in JAMA Network Open.
“Currently, limited estimates exist to determine the risk of hospitalization following outpatient RSV disease diagnoses in the United States,” said corresponding author Joshua T. Swan, PharmD, MPH, in an interview.
The current study was conducted to inform development of clinical trials, said Swan, senior director and category clinician in internal medicine and disease development at Pfizer, the sponsor of the study. These trials would assess the efficacy of an outpatient RSV antiviral treatment in preventing RSV-related hospitalization within 28 days among adults at a high risk for progression to severe illness, he said.
The authors reviewed data from 67,239 adults aged 18 years or older with medically attended RSV infections between October 1, 2016, and September 30, 2022. The data came from three databases: Optum (2771 patients), TriNetX (7442 patients), and Veradigm Network Electronic Health Record (VNEHR; 57,026 patients).
The primary outcome was all-cause hospitalization within 28 days of medically attended RSV.
Overall, the proportions of patients hospitalized within 28 days of infection were 6.2%, 6.0%, and 4.5% in Optum, TriNetX, and VNEHR databases, respectively.
Approximately two thirds of the patients (62%-67% across the three databases) were women, and 14.0%-54.5% were aged 65 years or older. The researchers also identified comorbidity prevalences of 20.0%-30.5% for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), 14.6%-24.4% for heart failure (HF), and 14.6%-24.4% for asthma.
A majority of the patients (ranging from 74.5% to 90.6% across the three databases) fell into a high-risk subgroup, defined as age 65 years or older with asthma, COPD, and HF. In this high-risk group, the proportions of hospitalizations were 7.6%, 8.5%, and 6.5% for Optum, TriNetX, and VNEHR, respectively.
The findings were limited by several factors, including the use only of data from outpatient settings, which cannot be used to estimate the RSV burden in the general population, and the reliance only on diagnosis or procedure codes to identify comorbidities, the researchers noted.
However, “the absolute risk of hospitalization of 1 out of 20 patients observed in our study represents significant and meaningful risk for vulnerable adults, in a disease where much of the public’s attention has historically focused on risk of hospitalization for young children,” Swan said. “These results highlight the unmet medical need for outpatient interventions and preventive measures that can reduce hospitalizations.”
Don’t Underestimate RSV Impact
The current study highlights the fact that RSV is a major cause of respiratory viral illness, said David R. Manoff, MD, associate professor of clinical thoracic medicine and surgery at Temple University, Philadelphia, in an interview.
“Historically, influenza, and, more recently, COVID-19 infection have generally been thought of as more likely to cause harm and, thus, have been more emphasized in terms of both vaccination and treatment,” said Manoff, who was not involved in the study.
The current study provides new evidence that infection with RSV can be far more serious than often recognized and a major potential source of both hospitalization and morbidity, Manoff said. In fact, data published in Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report in 2023 showed that the risks of needing oxygen, intensive care unit (ICU) admission, intubation, and death were actually higher in patients hospitalized with RSV infections than in those hospitalized with influenza or COVID-19. “
Understanding which population is hospitalized in the first place is vital to targeting prevention measures,” he added.
The new data are consistent with previous studies showing that most patients with RSV infection have primarily upper respiratory tract infection–type symptoms, but that a minority will develop lower respiratory tract disease, Manoff noted.
The findings add to the argument for implementation of RSV vaccination, especially in high-risk individuals, and support the need for RSV testing when patients present for care, he said.
However, more research is needed to reflect recent numbers, Manoff said. The study timeframe of 2016-2022 not only precedes commercially available RSV vaccines but also includes the period of increased isolation and masking seen during the COVID-19 pandemic years of 2020-2021. “We need to see if the same trends continue in the post-pandemic era.”
Additionally, the studies leading to approval of the RSV vaccine showed a reduction in hospitalization with RSV, and it is important to see how this reduction translates in real-world data and whether the RSV vaccines are reducing need for ICU admission, intubation, and death, Manoff said.
The study was funded by Pfizer, and Swan is a Pfizer employee. Manoff had no financial conflicts to disclose.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM JAMA NETWORK OPEN
Family Doctors Can Intervene to Treat and Prevent STIs
VANCOUVER, BRITISH COLUMBIA — Family physicians should familiarize themselves with doxycycline post-exposure prophylaxis (doxy PEP) as a prescription for patients who frequently have unprotected sex (including oral, anal, and vaginal) with multiple partners, according to a presentation at the Family Medicine Forum (FMF) 2024. Doxy PEP decreases the risk for bacterial sexually transmitted infections (STIs).
Many family physicians may be unaware of doxy PEP as a means of avoiding STIs. “Doxy PEP is an incredible tool that can be used within 72 hours of unprotected sex to reduce bacterial STI risk,” said James Owen, MD, assistant professor of family and community medicine at the University of Toronto in Ontario, Canada.
The US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention point to data from three randomized, controlled trials that demonstrate the ability of doxy PEP to decrease syphilis and chlamydia infections by more than 70% and decrease gonococcal infections by about 50%, said Jordan Goodridge, MD, assistant professor of family and community medicine at the University of Toronto.
Optimizing Doxy PEP
Doxy PEP (200 mg) is most effective when administered in the first 24 hours after unprotected sex, explained Goodridge. It is recommended that patients repeat the 200-mg dose if they are sexually active again within 24 hours.
To ensure optimal absorption of doxy PEP, the drug should not be taken with antacids or multivitamins, said Goodridge. Antacids “can bind to doxycycline and prevent it from being absorbed,” he said.
A key concern about doxy PEP is the development of antimicrobial resistance, noted Goodridge. “We don’t have long-term studies to give us an idea about what this risk is, to quantify it. The studies we have are relatively short, generally less than a year, and didn’t suggest that there was a huge risk [for antimicrobial resistance].”
Moreover, doxycycline is teratogenic, and its use is contraindicated in pregnancy, said Goodridge. If a pregnant patient is being treated for syphilis, then penicillin is the treatment of choice. For pregnant patients with penicillin allergy, Public Health Agency of Canada guidelines call for penicillin desensitization followed by penicillin.
The rate of syphilis has been rising in Canadian women of reproductive age, thus increasing the potential for congenital syphilis, noted Goodridge.
Benefits of HPV Vaccine
The 9-valent HPV vaccine is recommended in Canada for patients aged 9-26 years, but those aged 27 years or older at ongoing risk for HPV exposure may receive the 9-valent HPV vaccine after discussion with their healthcare providers, noted Owen.
High-risk patients can benefit from the vaccine even though they have likely had exposure to HPV, he added. “If someone has multiple sexual partners, they have probably been exposed to HPV at some point,” said Owen. “You still could reduce a patient’s risk for being exposed to certain oncogenic strains [of HPV]. Certainly, within our practices, we’re often giving it [that is, the HPV vaccine] to higher-risk individuals, including men having sex with men.”
HIV Prevention
“Condoms are still a mainstay of HIV and STI prevention, but condom use is going down,” said Owen.
In a national survey commissioned by the Toronto-based organization LetsStopAIDS and including more than 1100 Canadians aged 18-24 years, 24% of respondents said they use condoms “all the time.” In 2020, by contrast, more than half (53%) of respondents reported that they use condoms all the time.
Updated Canadian guidelines on the use of HIV pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP) are expected to be released in 2025 and will address questions about how frequently individuals taking HIV PrEP should be tested to ensure a negative HIV result. The guidelines will also provide guidance as to whether HIV serology or HIV viral load should be captured, said Owen. Patients in Canada who take HIV PrEP are now generally screened for HIV every 3 months.
A new HIV PrEP tool that has become available to Canadian clinicians is the injectable drug cabotegravir, which is dosed every 2 months.
Owen and Goodridge reported having no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
VANCOUVER, BRITISH COLUMBIA — Family physicians should familiarize themselves with doxycycline post-exposure prophylaxis (doxy PEP) as a prescription for patients who frequently have unprotected sex (including oral, anal, and vaginal) with multiple partners, according to a presentation at the Family Medicine Forum (FMF) 2024. Doxy PEP decreases the risk for bacterial sexually transmitted infections (STIs).
Many family physicians may be unaware of doxy PEP as a means of avoiding STIs. “Doxy PEP is an incredible tool that can be used within 72 hours of unprotected sex to reduce bacterial STI risk,” said James Owen, MD, assistant professor of family and community medicine at the University of Toronto in Ontario, Canada.
The US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention point to data from three randomized, controlled trials that demonstrate the ability of doxy PEP to decrease syphilis and chlamydia infections by more than 70% and decrease gonococcal infections by about 50%, said Jordan Goodridge, MD, assistant professor of family and community medicine at the University of Toronto.
Optimizing Doxy PEP
Doxy PEP (200 mg) is most effective when administered in the first 24 hours after unprotected sex, explained Goodridge. It is recommended that patients repeat the 200-mg dose if they are sexually active again within 24 hours.
To ensure optimal absorption of doxy PEP, the drug should not be taken with antacids or multivitamins, said Goodridge. Antacids “can bind to doxycycline and prevent it from being absorbed,” he said.
A key concern about doxy PEP is the development of antimicrobial resistance, noted Goodridge. “We don’t have long-term studies to give us an idea about what this risk is, to quantify it. The studies we have are relatively short, generally less than a year, and didn’t suggest that there was a huge risk [for antimicrobial resistance].”
Moreover, doxycycline is teratogenic, and its use is contraindicated in pregnancy, said Goodridge. If a pregnant patient is being treated for syphilis, then penicillin is the treatment of choice. For pregnant patients with penicillin allergy, Public Health Agency of Canada guidelines call for penicillin desensitization followed by penicillin.
The rate of syphilis has been rising in Canadian women of reproductive age, thus increasing the potential for congenital syphilis, noted Goodridge.
Benefits of HPV Vaccine
The 9-valent HPV vaccine is recommended in Canada for patients aged 9-26 years, but those aged 27 years or older at ongoing risk for HPV exposure may receive the 9-valent HPV vaccine after discussion with their healthcare providers, noted Owen.
High-risk patients can benefit from the vaccine even though they have likely had exposure to HPV, he added. “If someone has multiple sexual partners, they have probably been exposed to HPV at some point,” said Owen. “You still could reduce a patient’s risk for being exposed to certain oncogenic strains [of HPV]. Certainly, within our practices, we’re often giving it [that is, the HPV vaccine] to higher-risk individuals, including men having sex with men.”
HIV Prevention
“Condoms are still a mainstay of HIV and STI prevention, but condom use is going down,” said Owen.
In a national survey commissioned by the Toronto-based organization LetsStopAIDS and including more than 1100 Canadians aged 18-24 years, 24% of respondents said they use condoms “all the time.” In 2020, by contrast, more than half (53%) of respondents reported that they use condoms all the time.
Updated Canadian guidelines on the use of HIV pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP) are expected to be released in 2025 and will address questions about how frequently individuals taking HIV PrEP should be tested to ensure a negative HIV result. The guidelines will also provide guidance as to whether HIV serology or HIV viral load should be captured, said Owen. Patients in Canada who take HIV PrEP are now generally screened for HIV every 3 months.
A new HIV PrEP tool that has become available to Canadian clinicians is the injectable drug cabotegravir, which is dosed every 2 months.
Owen and Goodridge reported having no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
VANCOUVER, BRITISH COLUMBIA — Family physicians should familiarize themselves with doxycycline post-exposure prophylaxis (doxy PEP) as a prescription for patients who frequently have unprotected sex (including oral, anal, and vaginal) with multiple partners, according to a presentation at the Family Medicine Forum (FMF) 2024. Doxy PEP decreases the risk for bacterial sexually transmitted infections (STIs).
Many family physicians may be unaware of doxy PEP as a means of avoiding STIs. “Doxy PEP is an incredible tool that can be used within 72 hours of unprotected sex to reduce bacterial STI risk,” said James Owen, MD, assistant professor of family and community medicine at the University of Toronto in Ontario, Canada.
The US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention point to data from three randomized, controlled trials that demonstrate the ability of doxy PEP to decrease syphilis and chlamydia infections by more than 70% and decrease gonococcal infections by about 50%, said Jordan Goodridge, MD, assistant professor of family and community medicine at the University of Toronto.
Optimizing Doxy PEP
Doxy PEP (200 mg) is most effective when administered in the first 24 hours after unprotected sex, explained Goodridge. It is recommended that patients repeat the 200-mg dose if they are sexually active again within 24 hours.
To ensure optimal absorption of doxy PEP, the drug should not be taken with antacids or multivitamins, said Goodridge. Antacids “can bind to doxycycline and prevent it from being absorbed,” he said.
A key concern about doxy PEP is the development of antimicrobial resistance, noted Goodridge. “We don’t have long-term studies to give us an idea about what this risk is, to quantify it. The studies we have are relatively short, generally less than a year, and didn’t suggest that there was a huge risk [for antimicrobial resistance].”
Moreover, doxycycline is teratogenic, and its use is contraindicated in pregnancy, said Goodridge. If a pregnant patient is being treated for syphilis, then penicillin is the treatment of choice. For pregnant patients with penicillin allergy, Public Health Agency of Canada guidelines call for penicillin desensitization followed by penicillin.
The rate of syphilis has been rising in Canadian women of reproductive age, thus increasing the potential for congenital syphilis, noted Goodridge.
Benefits of HPV Vaccine
The 9-valent HPV vaccine is recommended in Canada for patients aged 9-26 years, but those aged 27 years or older at ongoing risk for HPV exposure may receive the 9-valent HPV vaccine after discussion with their healthcare providers, noted Owen.
High-risk patients can benefit from the vaccine even though they have likely had exposure to HPV, he added. “If someone has multiple sexual partners, they have probably been exposed to HPV at some point,” said Owen. “You still could reduce a patient’s risk for being exposed to certain oncogenic strains [of HPV]. Certainly, within our practices, we’re often giving it [that is, the HPV vaccine] to higher-risk individuals, including men having sex with men.”
HIV Prevention
“Condoms are still a mainstay of HIV and STI prevention, but condom use is going down,” said Owen.
In a national survey commissioned by the Toronto-based organization LetsStopAIDS and including more than 1100 Canadians aged 18-24 years, 24% of respondents said they use condoms “all the time.” In 2020, by contrast, more than half (53%) of respondents reported that they use condoms all the time.
Updated Canadian guidelines on the use of HIV pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP) are expected to be released in 2025 and will address questions about how frequently individuals taking HIV PrEP should be tested to ensure a negative HIV result. The guidelines will also provide guidance as to whether HIV serology or HIV viral load should be captured, said Owen. Patients in Canada who take HIV PrEP are now generally screened for HIV every 3 months.
A new HIV PrEP tool that has become available to Canadian clinicians is the injectable drug cabotegravir, which is dosed every 2 months.
Owen and Goodridge reported having no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM FMF 2024
Canadian Scientists Keep Watchful Eye on H5N1 Human Case
Now that Canada has confirmed its first human case of highly pathogenic avian influenza (HPAI) linked to H5N1, virologists and infectious disease experts are urging caution around surveillance, infection control, and the potential for spread among mammals and humans.
Public health officials at the National Microbiology Laboratory in Winnipeg, Manitoba, Canada, confirmed that the virus strain is related to the ones circulating among poultry in British Columbia.
So far, the case appears to be isolated, and no additional infections have been detected among the teen’s family, friends, or healthcare workers. But Canadian and American scientists who have studied the genetic sequence of the virus have found mutations that could make it easier to infect humans. Even if this strain remains contained after the teen’s case resolves, the mere fact that mutations have occurred could be a cause for concern about future strains.
“HPAI is one of those diseases that scientists, public health specialists, animal health specialists, and physicians have been watching closely for 20 years due to its epidemic and pandemic potential, including impacts to agriculture, food security, and financial security,” Isaac Bogoch, MD, associate professor of medicine at the University of Toronto and infectious disease specialist with the University Health Network, Toronto, Ontario, Canada, said in an interview.
“The last couple of years have been notable in that the H5N1 outbreak among wild birds and migratory birds has been larger, and the spillover to dairy cows and humans in the US is obviously concerning,” he said. “As we see more viral reassortment and more mammals are impacted, the more opportunities there are for this to go awry.”
Current H5N1 Outlook
Canadian public health officials and virologists are still unsure how the teen in British Columbia became infected, Bogoch said. The case has prompted concern due to the disease severity and need for hospitalization, while other cases across North America have remained mild.
The United States has reported 53 human cases as of November 21, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. In all but one case, the infections occurred among dairy or poultry workers, primarily in California, Colorado, and Washington. In all these cases, patients have reported mild symptoms, including mild respiratory issues and conjunctivitis. None have been hospitalized.
In Canada, the teen was infected with a strain of the virus circulating in wild birds. This strain has also been found in poultry outbreaks in British Columbia and Washington during the past month. So far, the risk for infection remains low for the public, according to the Public Health Agency of Canada.
“This detection was picked up via hospital-based influenza surveillance, confirming that human influenza surveillance in British Columbia and Canada is effective at detecting avian influenza A (H5N1),” Theresa Tam, MD, Canada’s chief public health officer, said in a statement. “We must continue to remain vigilant in our efforts to prevent the spread of avian influenza between animals and to humans.”
For now, Canadian virologists are watching developments closely and urging caution among those who encounter wild or migratory birds but not recommending major changes overall.
“The fact that we have a first human case in Canada is not at all surprising, given what is happening in the US and Europe, as well as what is happening in domestic bird flocks in British Columbia,” said Brian Ward, MD, professor of medicine at McGill University, researcher with McGill’s JD MacLean Centre for Tropical Diseases, and co-director of McGill’s Vaccine Study Centre, Montreal, Quebec, Canada.
“Millions of migratory waterfowl are flying over Canada right now, many of which may be carrying or infected with the virus,” he said. “The bottom line is that increasing evidence of mammal-to-mammal spread among dairy cows, elephant seals, and mink and ermine farms is worrisome, but we don’t need to sound the sirens yet.”
Future Outbreak Measures
Looking ahead, though, the developing situation feels more threatening than benign, given the ongoing spread among dairy cattle in the United States, said Bogoch. “It’s difficult to get the genie back in the bottle. I had hoped to see the cases slow down this year, but we just haven’t seen that.”
The fact that surveillance measures such as wastewater sampling have been scaled back in some areas of Canada is cause for concern, Bogoch added.
“We have great foundations for surveillance and action; we just need to make sure they are supported adequately, that groups communicate (across too many silos), and that there are quick responses,” said Scott Weese, DVM, professor of pathobiology at the Ontario Veterinary College and director of the University of Guelph’s Centre for Public Health and Zoonoses in Ontario.
“With cattle in the US, I think it’s highlighted what can happen if the initial response is not very aggressive. There could have been a lot more proactive response to H5N1 in dairy cattle, but there are so many competing interests and unwillingness to take necessary steps that the virus continues to spread,” he said. “Hopefully we’ve learned from that. However, as is often the case, the science is sometimes the easy part. Getting people to take the required actions is the challenge.”
On a personal level, masks and social distancing work well against influenza virus, including both seasonal and avian strains, said Ward. On a broader level, healthcare providers can monitor patients and support testing, where appropriate.
“The most important thing for people to know is that there is going to be another pandemic. It might or might not be due to a variant of H5N1, but it will come at some time,” said Allison McGeer, MD, professor of laboratory medicine and pathobiology at the University of Toronto and an infectious disease specialist with the Sinai Health System, Toronto.
Healthcare providers should follow ongoing updates to public health guidance, support surveillance where possible, and work with hospital leadership and infection control officials to ensure that pandemic plans are in place, she said.
“They may not be needed in the next few months, but they will be needed,” McGeer said. “We know a lot more about influenza than we did about SARS-CoV-2, so we have more tools to mitigate the impact, but we need to have them ready and know how to use them effectively.”
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Now that Canada has confirmed its first human case of highly pathogenic avian influenza (HPAI) linked to H5N1, virologists and infectious disease experts are urging caution around surveillance, infection control, and the potential for spread among mammals and humans.
Public health officials at the National Microbiology Laboratory in Winnipeg, Manitoba, Canada, confirmed that the virus strain is related to the ones circulating among poultry in British Columbia.
So far, the case appears to be isolated, and no additional infections have been detected among the teen’s family, friends, or healthcare workers. But Canadian and American scientists who have studied the genetic sequence of the virus have found mutations that could make it easier to infect humans. Even if this strain remains contained after the teen’s case resolves, the mere fact that mutations have occurred could be a cause for concern about future strains.
“HPAI is one of those diseases that scientists, public health specialists, animal health specialists, and physicians have been watching closely for 20 years due to its epidemic and pandemic potential, including impacts to agriculture, food security, and financial security,” Isaac Bogoch, MD, associate professor of medicine at the University of Toronto and infectious disease specialist with the University Health Network, Toronto, Ontario, Canada, said in an interview.
“The last couple of years have been notable in that the H5N1 outbreak among wild birds and migratory birds has been larger, and the spillover to dairy cows and humans in the US is obviously concerning,” he said. “As we see more viral reassortment and more mammals are impacted, the more opportunities there are for this to go awry.”
Current H5N1 Outlook
Canadian public health officials and virologists are still unsure how the teen in British Columbia became infected, Bogoch said. The case has prompted concern due to the disease severity and need for hospitalization, while other cases across North America have remained mild.
The United States has reported 53 human cases as of November 21, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. In all but one case, the infections occurred among dairy or poultry workers, primarily in California, Colorado, and Washington. In all these cases, patients have reported mild symptoms, including mild respiratory issues and conjunctivitis. None have been hospitalized.
In Canada, the teen was infected with a strain of the virus circulating in wild birds. This strain has also been found in poultry outbreaks in British Columbia and Washington during the past month. So far, the risk for infection remains low for the public, according to the Public Health Agency of Canada.
“This detection was picked up via hospital-based influenza surveillance, confirming that human influenza surveillance in British Columbia and Canada is effective at detecting avian influenza A (H5N1),” Theresa Tam, MD, Canada’s chief public health officer, said in a statement. “We must continue to remain vigilant in our efforts to prevent the spread of avian influenza between animals and to humans.”
For now, Canadian virologists are watching developments closely and urging caution among those who encounter wild or migratory birds but not recommending major changes overall.
“The fact that we have a first human case in Canada is not at all surprising, given what is happening in the US and Europe, as well as what is happening in domestic bird flocks in British Columbia,” said Brian Ward, MD, professor of medicine at McGill University, researcher with McGill’s JD MacLean Centre for Tropical Diseases, and co-director of McGill’s Vaccine Study Centre, Montreal, Quebec, Canada.
“Millions of migratory waterfowl are flying over Canada right now, many of which may be carrying or infected with the virus,” he said. “The bottom line is that increasing evidence of mammal-to-mammal spread among dairy cows, elephant seals, and mink and ermine farms is worrisome, but we don’t need to sound the sirens yet.”
Future Outbreak Measures
Looking ahead, though, the developing situation feels more threatening than benign, given the ongoing spread among dairy cattle in the United States, said Bogoch. “It’s difficult to get the genie back in the bottle. I had hoped to see the cases slow down this year, but we just haven’t seen that.”
The fact that surveillance measures such as wastewater sampling have been scaled back in some areas of Canada is cause for concern, Bogoch added.
“We have great foundations for surveillance and action; we just need to make sure they are supported adequately, that groups communicate (across too many silos), and that there are quick responses,” said Scott Weese, DVM, professor of pathobiology at the Ontario Veterinary College and director of the University of Guelph’s Centre for Public Health and Zoonoses in Ontario.
“With cattle in the US, I think it’s highlighted what can happen if the initial response is not very aggressive. There could have been a lot more proactive response to H5N1 in dairy cattle, but there are so many competing interests and unwillingness to take necessary steps that the virus continues to spread,” he said. “Hopefully we’ve learned from that. However, as is often the case, the science is sometimes the easy part. Getting people to take the required actions is the challenge.”
On a personal level, masks and social distancing work well against influenza virus, including both seasonal and avian strains, said Ward. On a broader level, healthcare providers can monitor patients and support testing, where appropriate.
“The most important thing for people to know is that there is going to be another pandemic. It might or might not be due to a variant of H5N1, but it will come at some time,” said Allison McGeer, MD, professor of laboratory medicine and pathobiology at the University of Toronto and an infectious disease specialist with the Sinai Health System, Toronto.
Healthcare providers should follow ongoing updates to public health guidance, support surveillance where possible, and work with hospital leadership and infection control officials to ensure that pandemic plans are in place, she said.
“They may not be needed in the next few months, but they will be needed,” McGeer said. “We know a lot more about influenza than we did about SARS-CoV-2, so we have more tools to mitigate the impact, but we need to have them ready and know how to use them effectively.”
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Now that Canada has confirmed its first human case of highly pathogenic avian influenza (HPAI) linked to H5N1, virologists and infectious disease experts are urging caution around surveillance, infection control, and the potential for spread among mammals and humans.
Public health officials at the National Microbiology Laboratory in Winnipeg, Manitoba, Canada, confirmed that the virus strain is related to the ones circulating among poultry in British Columbia.
So far, the case appears to be isolated, and no additional infections have been detected among the teen’s family, friends, or healthcare workers. But Canadian and American scientists who have studied the genetic sequence of the virus have found mutations that could make it easier to infect humans. Even if this strain remains contained after the teen’s case resolves, the mere fact that mutations have occurred could be a cause for concern about future strains.
“HPAI is one of those diseases that scientists, public health specialists, animal health specialists, and physicians have been watching closely for 20 years due to its epidemic and pandemic potential, including impacts to agriculture, food security, and financial security,” Isaac Bogoch, MD, associate professor of medicine at the University of Toronto and infectious disease specialist with the University Health Network, Toronto, Ontario, Canada, said in an interview.
“The last couple of years have been notable in that the H5N1 outbreak among wild birds and migratory birds has been larger, and the spillover to dairy cows and humans in the US is obviously concerning,” he said. “As we see more viral reassortment and more mammals are impacted, the more opportunities there are for this to go awry.”
Current H5N1 Outlook
Canadian public health officials and virologists are still unsure how the teen in British Columbia became infected, Bogoch said. The case has prompted concern due to the disease severity and need for hospitalization, while other cases across North America have remained mild.
The United States has reported 53 human cases as of November 21, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. In all but one case, the infections occurred among dairy or poultry workers, primarily in California, Colorado, and Washington. In all these cases, patients have reported mild symptoms, including mild respiratory issues and conjunctivitis. None have been hospitalized.
In Canada, the teen was infected with a strain of the virus circulating in wild birds. This strain has also been found in poultry outbreaks in British Columbia and Washington during the past month. So far, the risk for infection remains low for the public, according to the Public Health Agency of Canada.
“This detection was picked up via hospital-based influenza surveillance, confirming that human influenza surveillance in British Columbia and Canada is effective at detecting avian influenza A (H5N1),” Theresa Tam, MD, Canada’s chief public health officer, said in a statement. “We must continue to remain vigilant in our efforts to prevent the spread of avian influenza between animals and to humans.”
For now, Canadian virologists are watching developments closely and urging caution among those who encounter wild or migratory birds but not recommending major changes overall.
“The fact that we have a first human case in Canada is not at all surprising, given what is happening in the US and Europe, as well as what is happening in domestic bird flocks in British Columbia,” said Brian Ward, MD, professor of medicine at McGill University, researcher with McGill’s JD MacLean Centre for Tropical Diseases, and co-director of McGill’s Vaccine Study Centre, Montreal, Quebec, Canada.
“Millions of migratory waterfowl are flying over Canada right now, many of which may be carrying or infected with the virus,” he said. “The bottom line is that increasing evidence of mammal-to-mammal spread among dairy cows, elephant seals, and mink and ermine farms is worrisome, but we don’t need to sound the sirens yet.”
Future Outbreak Measures
Looking ahead, though, the developing situation feels more threatening than benign, given the ongoing spread among dairy cattle in the United States, said Bogoch. “It’s difficult to get the genie back in the bottle. I had hoped to see the cases slow down this year, but we just haven’t seen that.”
The fact that surveillance measures such as wastewater sampling have been scaled back in some areas of Canada is cause for concern, Bogoch added.
“We have great foundations for surveillance and action; we just need to make sure they are supported adequately, that groups communicate (across too many silos), and that there are quick responses,” said Scott Weese, DVM, professor of pathobiology at the Ontario Veterinary College and director of the University of Guelph’s Centre for Public Health and Zoonoses in Ontario.
“With cattle in the US, I think it’s highlighted what can happen if the initial response is not very aggressive. There could have been a lot more proactive response to H5N1 in dairy cattle, but there are so many competing interests and unwillingness to take necessary steps that the virus continues to spread,” he said. “Hopefully we’ve learned from that. However, as is often the case, the science is sometimes the easy part. Getting people to take the required actions is the challenge.”
On a personal level, masks and social distancing work well against influenza virus, including both seasonal and avian strains, said Ward. On a broader level, healthcare providers can monitor patients and support testing, where appropriate.
“The most important thing for people to know is that there is going to be another pandemic. It might or might not be due to a variant of H5N1, but it will come at some time,” said Allison McGeer, MD, professor of laboratory medicine and pathobiology at the University of Toronto and an infectious disease specialist with the Sinai Health System, Toronto.
Healthcare providers should follow ongoing updates to public health guidance, support surveillance where possible, and work with hospital leadership and infection control officials to ensure that pandemic plans are in place, she said.
“They may not be needed in the next few months, but they will be needed,” McGeer said. “We know a lot more about influenza than we did about SARS-CoV-2, so we have more tools to mitigate the impact, but we need to have them ready and know how to use them effectively.”
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.