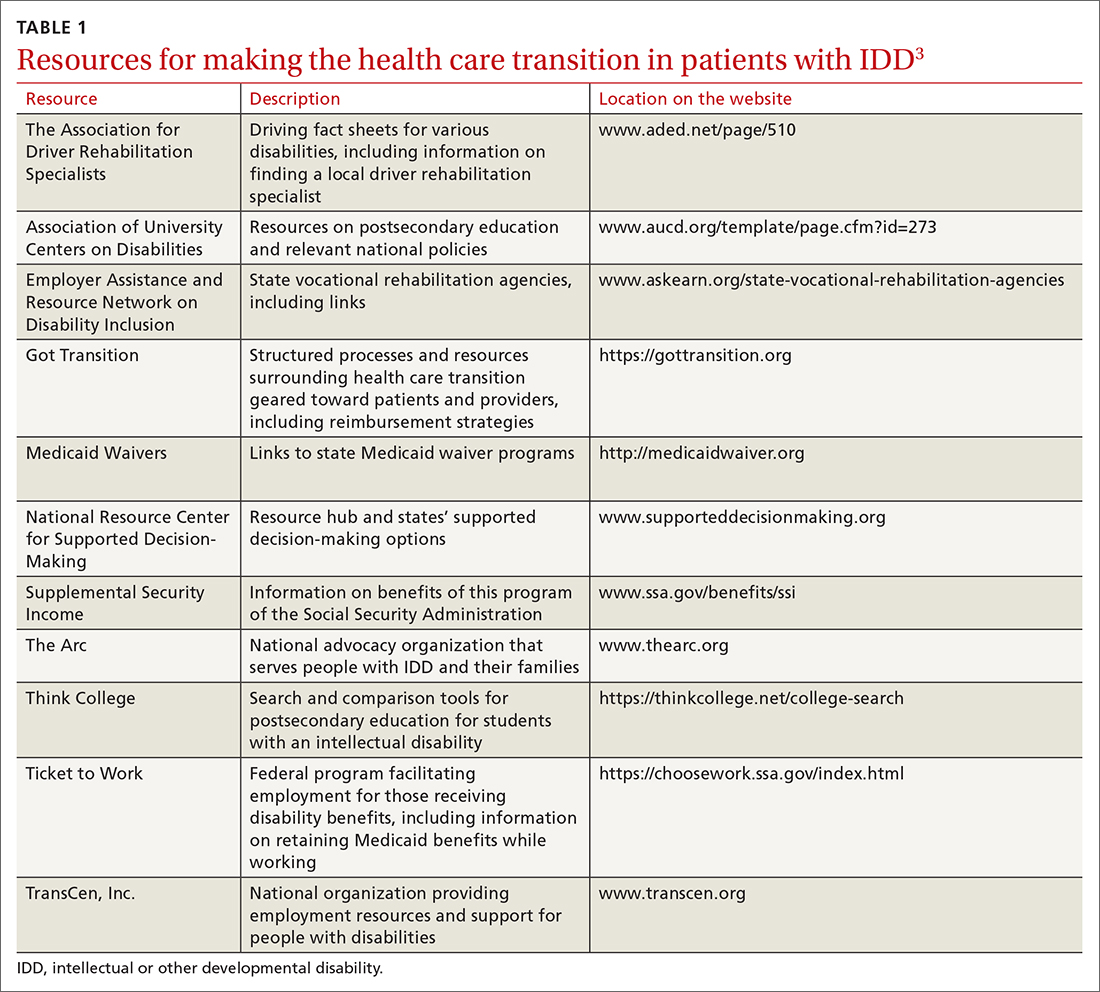
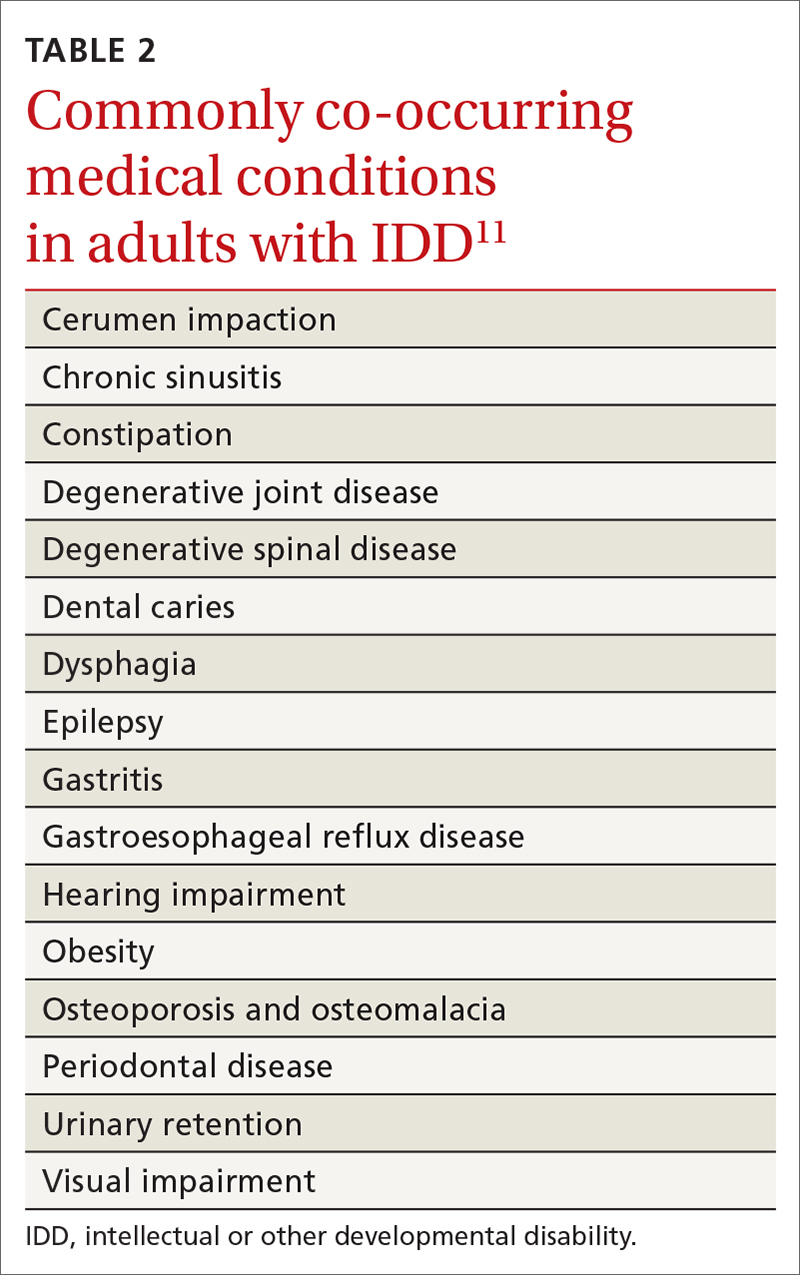
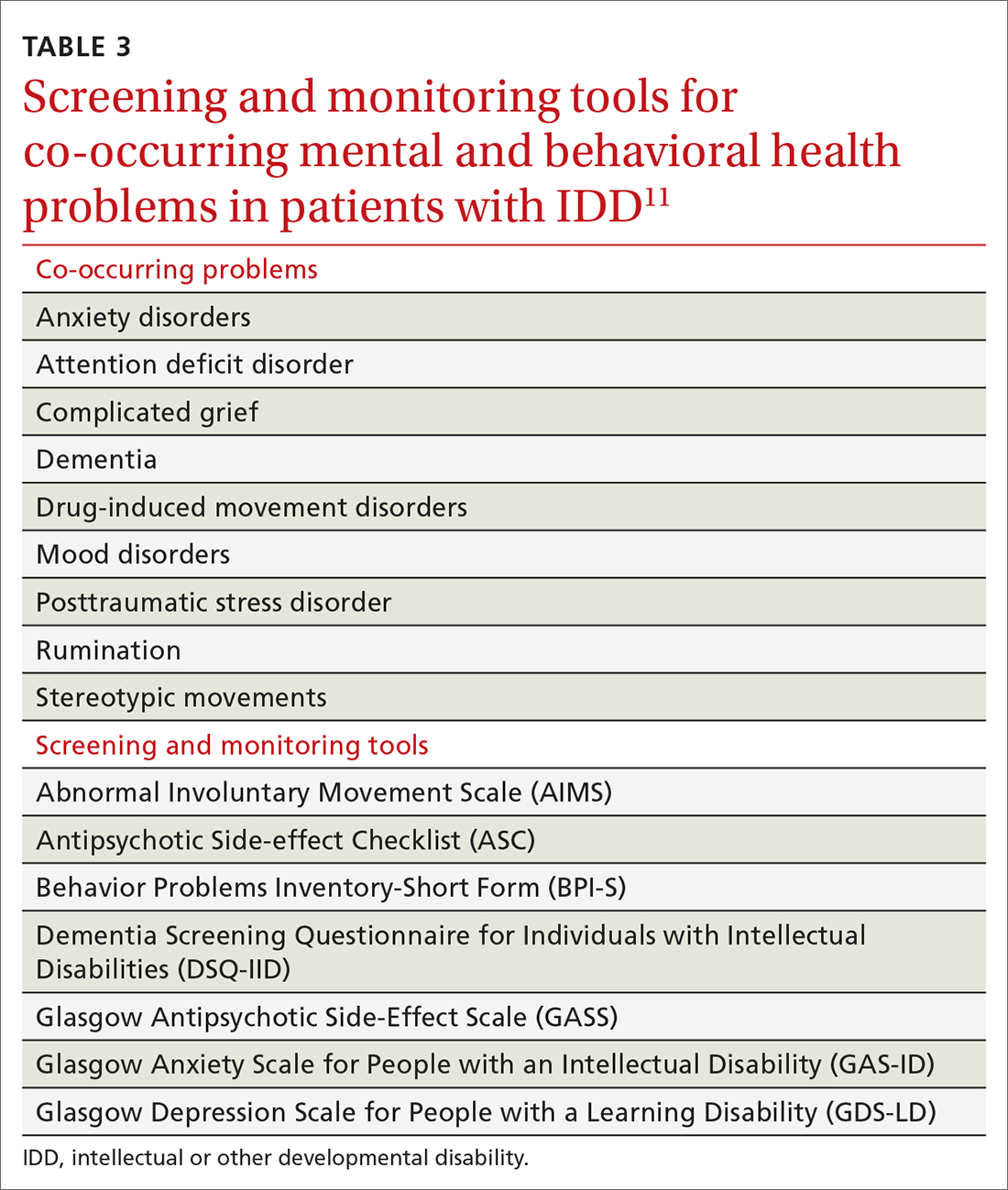
User login
‘Shocking’ early complications from teen-onset type 2 diabetes
Newly published data show alarmingly high rates and severity of early diabetes-specific complications in individuals who develop type 2 diabetes at a young age. This suggests intervention should be early and aggressive among these youngsters, said the researchers.
The results for the 500 young adult participants in the Treatment Options for Type 2 Diabetes in Adolescents and Youth 2 (TODAY 2) study were published online July 29 in the New England Journal of Medicine by the TODAY study group.
At follow-up – after originally participating in the TODAY trial when they were young teenagers – they had a mean age of 26.4 years.
At this time, more than two thirds had hypertension and half had dyslipidemia.
Overall, 60% had at least one diabetic microvascular complication (retinal disease, neuropathy, or diabetic kidney disease), and more than a quarter had two or more such complications.
“These data illustrate the serious personal and public health consequences of youth-onset type 2 diabetes in the transition to adulthood,” the researchers noted.
Don’t tread lightly just because they are young
“The fact that these youth are accumulating complications at a rapid rate and are broadly affected early in adulthood certainly suggests that aggressive therapy is needed, both for glycemic control and treatment of risk factors like hypertension and dyslipidemia,” study coauthor Philip S. Zeitler, MD, PhD, said in an interview.
“In the absence of studies specifically addressing this, we need to take a more aggressive approach than people might be inclined to, given that the age at diagnosis is young, around 14 years,” he added.
“Contrary to the inclination to be ‘gentle’ in treating them because they are kids, these data suggest that we can’t let these initial years go by without strong intervention, and we need to be prepared for polypharmacy.”
Unfortunately, as Dr. Zeitler and coauthors explained, youth-onset type 2 diabetes is characterized by a suboptimal response to currently approved diabetes medications.
New pediatric indications in the United States for drugs used to treat type 2 diabetes in adults, including the recent Food and Drug Administration approval of extended-release exenatide for children as young as 10 years of age, “helps, but only marginally,” said Dr. Zeitler, of the Clinical & Translational Research Center, Children’s Hospital Colorado, Aurora.
“In some cases, it will help get them covered by carriers, which is always good. But this is still a very limited set of medications. It doesn’t include more recently approved more potent glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) agonists, like semaglutide, and doesn’t include the sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors. Pediatricians are used to using medications off label and that is necessary here while we await further approvals,” he said.
And he noted that most individuals with youth-onset type 2 diabetes in the United States are covered by public insurance or are uninsured, depending on which state they live in. While the two major Medicaid programs in Colorado allow full access to adult formularies, that’s not the case everywhere. Moreover, patients often face further access barriers in states without expanded Medicaid.
Follow-up shows all metrics worsening over time
In TODAY 2, patients participated in an observational follow-up in their usual care settings in 2011-2020. At the start, they were receiving metformin with or without insulin for diabetes, but whether this continued and whether they were treated for other risk factors was down to individual circumstances.
Participants’ median A1c increased over time, and the percentage with A1c < 6% (< 48 mmol/mol) declined from 75% at the time of TODAY entry to just 19% at the 15-year end of follow-up.
The proportion with an A1c ≤ 10% (≤ 86 mmol/mol) rose from 0% at baseline to 34% at 15 years.
At that time, nearly 50% were taking both metformin and insulin, while more than a quarter were taking no medications.
The prevalence of hypertension increased from 19.2% at baseline to 67.5% at 15 years, while dyslipidemia rose from 20.8% to 51.6%.
Kidney disease prevalence increased from 8.0% at baseline to 54.8% at 15 years. Nerve disease rose from 1.0% to 32.4%. Retinal disease jumped from 13.7% with milder nonproliferative retinopathy in 2010-2011 to 51.0% with any eye disease in 2017-2018, including 8.8% with moderate to severe retinal changes and 3.5% with macular edema.
Overall, at the time of the last visit, 39.9% had no diabetes complications, 31.8% had one, 21.3% had two, and 7.1% had three complications.
Serious cardiovascular events in mid-20s
There were 17 adjudicated serious cardiovascular events, including four myocardial infarctions, six heart failure events, three diagnoses of coronary artery disease, and four strokes.
Six participants died, one each from myocardial infarction, kidney failure, and drug overdose, and three from sepsis.
Dr. Zeitler called the macrovascular events “shocking,” noting that although the numbers are small, for people in their mid-20s “they should be zero ... While we don’t yet know if the rates are the same or faster than in adults, even if they are the same, these kids are only in their late 20s, as opposed to adults experiencing these problems in their 50s, 60s, and 70s.
“The fact that these complications are occurring when these individuals should be in the prime of their life for both family and work has huge implications,” he stressed.
Findings have multiple causes
The reasons for the findings are both biologic and socioeconomic, Dr. Zeitler said.
“We know already that many kids with type 2 have rapid [deterioration of] beta-cell [function], which is probably very biologic. It stands to reason that an individual who can get diabetes as an adolescent probably has more fragile beta cells in some way,” he noted.
“But we also know that many other things contribute: stress, social determinants, access to quality care and medications, access to healthy foods and physical activity, availability of family supervision given the realities of families’ economic status and jobs, etc.”
It’s also known that youth with type 2 diabetes have much more severe insulin resistance than that of adults with the condition, and that “once the kids left ... the [TODAY] study, risk factor treatment in the community was less than ideal, and a lot of kids who met criteria for treatment of their blood pressure or lipids were not being treated. This is likely at least partly sociologic and partly the general pediatric hesitancy to use medications.”
He said the TODAY team will soon have some new data to show that “glycemia during the early years makes a difference, again supporting intensive intervention early on.”
The TODAY study was supported by grants from the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases. Dr. Zeitler had no further disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Newly published data show alarmingly high rates and severity of early diabetes-specific complications in individuals who develop type 2 diabetes at a young age. This suggests intervention should be early and aggressive among these youngsters, said the researchers.
The results for the 500 young adult participants in the Treatment Options for Type 2 Diabetes in Adolescents and Youth 2 (TODAY 2) study were published online July 29 in the New England Journal of Medicine by the TODAY study group.
At follow-up – after originally participating in the TODAY trial when they were young teenagers – they had a mean age of 26.4 years.
At this time, more than two thirds had hypertension and half had dyslipidemia.
Overall, 60% had at least one diabetic microvascular complication (retinal disease, neuropathy, or diabetic kidney disease), and more than a quarter had two or more such complications.
“These data illustrate the serious personal and public health consequences of youth-onset type 2 diabetes in the transition to adulthood,” the researchers noted.
Don’t tread lightly just because they are young
“The fact that these youth are accumulating complications at a rapid rate and are broadly affected early in adulthood certainly suggests that aggressive therapy is needed, both for glycemic control and treatment of risk factors like hypertension and dyslipidemia,” study coauthor Philip S. Zeitler, MD, PhD, said in an interview.
“In the absence of studies specifically addressing this, we need to take a more aggressive approach than people might be inclined to, given that the age at diagnosis is young, around 14 years,” he added.
“Contrary to the inclination to be ‘gentle’ in treating them because they are kids, these data suggest that we can’t let these initial years go by without strong intervention, and we need to be prepared for polypharmacy.”
Unfortunately, as Dr. Zeitler and coauthors explained, youth-onset type 2 diabetes is characterized by a suboptimal response to currently approved diabetes medications.
New pediatric indications in the United States for drugs used to treat type 2 diabetes in adults, including the recent Food and Drug Administration approval of extended-release exenatide for children as young as 10 years of age, “helps, but only marginally,” said Dr. Zeitler, of the Clinical & Translational Research Center, Children’s Hospital Colorado, Aurora.
“In some cases, it will help get them covered by carriers, which is always good. But this is still a very limited set of medications. It doesn’t include more recently approved more potent glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) agonists, like semaglutide, and doesn’t include the sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors. Pediatricians are used to using medications off label and that is necessary here while we await further approvals,” he said.
And he noted that most individuals with youth-onset type 2 diabetes in the United States are covered by public insurance or are uninsured, depending on which state they live in. While the two major Medicaid programs in Colorado allow full access to adult formularies, that’s not the case everywhere. Moreover, patients often face further access barriers in states without expanded Medicaid.
Follow-up shows all metrics worsening over time
In TODAY 2, patients participated in an observational follow-up in their usual care settings in 2011-2020. At the start, they were receiving metformin with or without insulin for diabetes, but whether this continued and whether they were treated for other risk factors was down to individual circumstances.
Participants’ median A1c increased over time, and the percentage with A1c < 6% (< 48 mmol/mol) declined from 75% at the time of TODAY entry to just 19% at the 15-year end of follow-up.
The proportion with an A1c ≤ 10% (≤ 86 mmol/mol) rose from 0% at baseline to 34% at 15 years.
At that time, nearly 50% were taking both metformin and insulin, while more than a quarter were taking no medications.
The prevalence of hypertension increased from 19.2% at baseline to 67.5% at 15 years, while dyslipidemia rose from 20.8% to 51.6%.
Kidney disease prevalence increased from 8.0% at baseline to 54.8% at 15 years. Nerve disease rose from 1.0% to 32.4%. Retinal disease jumped from 13.7% with milder nonproliferative retinopathy in 2010-2011 to 51.0% with any eye disease in 2017-2018, including 8.8% with moderate to severe retinal changes and 3.5% with macular edema.
Overall, at the time of the last visit, 39.9% had no diabetes complications, 31.8% had one, 21.3% had two, and 7.1% had three complications.
Serious cardiovascular events in mid-20s
There were 17 adjudicated serious cardiovascular events, including four myocardial infarctions, six heart failure events, three diagnoses of coronary artery disease, and four strokes.
Six participants died, one each from myocardial infarction, kidney failure, and drug overdose, and three from sepsis.
Dr. Zeitler called the macrovascular events “shocking,” noting that although the numbers are small, for people in their mid-20s “they should be zero ... While we don’t yet know if the rates are the same or faster than in adults, even if they are the same, these kids are only in their late 20s, as opposed to adults experiencing these problems in their 50s, 60s, and 70s.
“The fact that these complications are occurring when these individuals should be in the prime of their life for both family and work has huge implications,” he stressed.
Findings have multiple causes
The reasons for the findings are both biologic and socioeconomic, Dr. Zeitler said.
“We know already that many kids with type 2 have rapid [deterioration of] beta-cell [function], which is probably very biologic. It stands to reason that an individual who can get diabetes as an adolescent probably has more fragile beta cells in some way,” he noted.
“But we also know that many other things contribute: stress, social determinants, access to quality care and medications, access to healthy foods and physical activity, availability of family supervision given the realities of families’ economic status and jobs, etc.”
It’s also known that youth with type 2 diabetes have much more severe insulin resistance than that of adults with the condition, and that “once the kids left ... the [TODAY] study, risk factor treatment in the community was less than ideal, and a lot of kids who met criteria for treatment of their blood pressure or lipids were not being treated. This is likely at least partly sociologic and partly the general pediatric hesitancy to use medications.”
He said the TODAY team will soon have some new data to show that “glycemia during the early years makes a difference, again supporting intensive intervention early on.”
The TODAY study was supported by grants from the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases. Dr. Zeitler had no further disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Newly published data show alarmingly high rates and severity of early diabetes-specific complications in individuals who develop type 2 diabetes at a young age. This suggests intervention should be early and aggressive among these youngsters, said the researchers.
The results for the 500 young adult participants in the Treatment Options for Type 2 Diabetes in Adolescents and Youth 2 (TODAY 2) study were published online July 29 in the New England Journal of Medicine by the TODAY study group.
At follow-up – after originally participating in the TODAY trial when they were young teenagers – they had a mean age of 26.4 years.
At this time, more than two thirds had hypertension and half had dyslipidemia.
Overall, 60% had at least one diabetic microvascular complication (retinal disease, neuropathy, or diabetic kidney disease), and more than a quarter had two or more such complications.
“These data illustrate the serious personal and public health consequences of youth-onset type 2 diabetes in the transition to adulthood,” the researchers noted.
Don’t tread lightly just because they are young
“The fact that these youth are accumulating complications at a rapid rate and are broadly affected early in adulthood certainly suggests that aggressive therapy is needed, both for glycemic control and treatment of risk factors like hypertension and dyslipidemia,” study coauthor Philip S. Zeitler, MD, PhD, said in an interview.
“In the absence of studies specifically addressing this, we need to take a more aggressive approach than people might be inclined to, given that the age at diagnosis is young, around 14 years,” he added.
“Contrary to the inclination to be ‘gentle’ in treating them because they are kids, these data suggest that we can’t let these initial years go by without strong intervention, and we need to be prepared for polypharmacy.”
Unfortunately, as Dr. Zeitler and coauthors explained, youth-onset type 2 diabetes is characterized by a suboptimal response to currently approved diabetes medications.
New pediatric indications in the United States for drugs used to treat type 2 diabetes in adults, including the recent Food and Drug Administration approval of extended-release exenatide for children as young as 10 years of age, “helps, but only marginally,” said Dr. Zeitler, of the Clinical & Translational Research Center, Children’s Hospital Colorado, Aurora.
“In some cases, it will help get them covered by carriers, which is always good. But this is still a very limited set of medications. It doesn’t include more recently approved more potent glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) agonists, like semaglutide, and doesn’t include the sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors. Pediatricians are used to using medications off label and that is necessary here while we await further approvals,” he said.
And he noted that most individuals with youth-onset type 2 diabetes in the United States are covered by public insurance or are uninsured, depending on which state they live in. While the two major Medicaid programs in Colorado allow full access to adult formularies, that’s not the case everywhere. Moreover, patients often face further access barriers in states without expanded Medicaid.
Follow-up shows all metrics worsening over time
In TODAY 2, patients participated in an observational follow-up in their usual care settings in 2011-2020. At the start, they were receiving metformin with or without insulin for diabetes, but whether this continued and whether they were treated for other risk factors was down to individual circumstances.
Participants’ median A1c increased over time, and the percentage with A1c < 6% (< 48 mmol/mol) declined from 75% at the time of TODAY entry to just 19% at the 15-year end of follow-up.
The proportion with an A1c ≤ 10% (≤ 86 mmol/mol) rose from 0% at baseline to 34% at 15 years.
At that time, nearly 50% were taking both metformin and insulin, while more than a quarter were taking no medications.
The prevalence of hypertension increased from 19.2% at baseline to 67.5% at 15 years, while dyslipidemia rose from 20.8% to 51.6%.
Kidney disease prevalence increased from 8.0% at baseline to 54.8% at 15 years. Nerve disease rose from 1.0% to 32.4%. Retinal disease jumped from 13.7% with milder nonproliferative retinopathy in 2010-2011 to 51.0% with any eye disease in 2017-2018, including 8.8% with moderate to severe retinal changes and 3.5% with macular edema.
Overall, at the time of the last visit, 39.9% had no diabetes complications, 31.8% had one, 21.3% had two, and 7.1% had three complications.
Serious cardiovascular events in mid-20s
There were 17 adjudicated serious cardiovascular events, including four myocardial infarctions, six heart failure events, three diagnoses of coronary artery disease, and four strokes.
Six participants died, one each from myocardial infarction, kidney failure, and drug overdose, and three from sepsis.
Dr. Zeitler called the macrovascular events “shocking,” noting that although the numbers are small, for people in their mid-20s “they should be zero ... While we don’t yet know if the rates are the same or faster than in adults, even if they are the same, these kids are only in their late 20s, as opposed to adults experiencing these problems in their 50s, 60s, and 70s.
“The fact that these complications are occurring when these individuals should be in the prime of their life for both family and work has huge implications,” he stressed.
Findings have multiple causes
The reasons for the findings are both biologic and socioeconomic, Dr. Zeitler said.
“We know already that many kids with type 2 have rapid [deterioration of] beta-cell [function], which is probably very biologic. It stands to reason that an individual who can get diabetes as an adolescent probably has more fragile beta cells in some way,” he noted.
“But we also know that many other things contribute: stress, social determinants, access to quality care and medications, access to healthy foods and physical activity, availability of family supervision given the realities of families’ economic status and jobs, etc.”
It’s also known that youth with type 2 diabetes have much more severe insulin resistance than that of adults with the condition, and that “once the kids left ... the [TODAY] study, risk factor treatment in the community was less than ideal, and a lot of kids who met criteria for treatment of their blood pressure or lipids were not being treated. This is likely at least partly sociologic and partly the general pediatric hesitancy to use medications.”
He said the TODAY team will soon have some new data to show that “glycemia during the early years makes a difference, again supporting intensive intervention early on.”
The TODAY study was supported by grants from the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases. Dr. Zeitler had no further disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
ESC heart failure guideline to integrate bounty of new meds
Today there are so many evidence-based drug therapies for heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF) that physicians treating HF patients almost don’t know what to do them.
It’s an exciting new age that way, but to many vexingly unclear how best to merge the shiny new options with mainstay regimens based on time-honored renin-angiotensin system (RAS) inhibitors and beta-blockers.
To impart some clarity, the authors of a new HF guideline document recently took center stage at the Heart Failure Association of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC-HFA) annual meeting to preview their updated recommendations, with novel twists based on recent major trials, for the new age of HF pharmacotherapeutics.
The guideline committee considered the evidence base that existed “up until the end of March of this year,” Theresa A. McDonagh, MD, King’s College London, said during the presentation. The document “is now finalized, it’s with the publishers, and it will be presented in full with simultaneous publication at the ESC meeting” that starts August 27.
It describes a game plan, already followed by some clinicians in practice without official guidance, for initiating drugs from each of four classes in virtually all patients with HFrEF.
New indicated drugs, new perspective for HFrEF
Three of the drug categories are old acquaintances. Among them are the RAS inhibitors, which include angiotensin-receptor/neprilysin inhibitors, beta-blockers, and the mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists. The latter drugs are gaining new respect after having been underplayed in HF prescribing despite longstanding evidence of efficacy.
Completing the quartet of first-line HFrEF drug classes is a recent arrival to the HF arena, the sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors.
“We now have new data and a simplified treatment algorithm for heart failure with reduced ejection fraction based on the early administration of the four major classes of drugs,” said Marco Metra, MD, University of Brescia (Italy), previewing the medical-therapy portions of the new guideline at the ESC-HFA sessions, which launched virtually and live in Florence, Italy, on July 29.
The new game plan offers a simple answer to a once-common but complex question: How and in what order are the different drug classes initiated in patients with HFrEF? In the new document, the stated goal is to get them all on board expeditiously and safely, by any means possible.
The guideline writers did not specify a sequence, preferring to leave that decision to physicians, said Dr. Metra, who stated only two guiding principles. The first is to consider the patient’s unique circumstances. The order in which the drugs are introduced might vary, depending on, for example, whether the patient has low or high blood pressure or renal dysfunction.
Second, “it is very important that we try to give all four classes of drugs to the patient in the shortest time possible, because this saves lives,” he said.
That there is no recommendation on sequencing the drugs has led some to the wrong interpretation that all should be started at once, observed coauthor Javed Butler, MD, MPH, University of Mississippi, Jackson, as a panelist during the presentation. Far from it, he said. “The doctor with the patient in front of you can make the best decision. The idea here is to get all the therapies on as soon as possible, as safely as possible.”
“The order in which they are introduced is not really important,” agreed Vijay Chopra, MD, Max Super Specialty Hospital Saket, New Delhi, another coauthor on the panel. “The important thing is that at least some dose of all the four drugs needs to be introduced in the first 4-6 weeks, and then up-titrated.”
Other medical therapy can be more tailored, Dr. Metra noted, such as loop diuretics for patients with congestion, iron for those with iron deficiency, and other drugs depending on whether there is, for example, atrial fibrillation or coronary disease.
Adoption of emerging definitions
The document adopts the emerging characterization of HFrEF by a left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) up to 40%.
And it will leverage an expanding evidence base for medication in a segment of patients once said to have HF with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF), who had therefore lacked specific, guideline-directed medical therapies. Now, patients with an LVEF of 41%-49% will be said to have HF with mildly reduced ejection fraction (HFmrEF), a tweak to the recently introduced HF with “mid-range” LVEF that is designed to assert its nature as something to treat. The new document’s HFmrEF recommendations come with various class and level-of-evidence ratings.
That leaves HFpEF to be characterized by an LVEF of 50% in combination with structural or functional abnormalities associated with LV diastolic dysfunction or raised LV filling pressures, including raised natriuretic peptide levels.
The definitions are consistent with those proposed internationally by the ESC-HFA, the Heart Failure Society of America, and other groups in a statement published in March.
Expanded HFrEF med landscape
Since the 2016 ESC guideline on HF therapy, Dr. McDonagh said, “there’s been no substantial change in the evidence for many of the classical drugs that we use in heart failure. However, we had a lot of new and exciting evidence to consider,” especially in support of the SGLT2 inhibitors as one of the core medications in HFrEF.
The new data came from two controlled trials in particular. In DAPA-HF, patients with HFrEF who were initially without diabetes and who went on dapagliflozin (Farxiga, AstraZeneca) showed a 27% drop in cardiovascular (CV) death or worsening-HF events over a median of 18 months.
“That was followed up with very concordant results with empagliflozin [Jardiance, Boehringer Ingelheim/Eli Lilly] in HFrEF in the EMPEROR-Reduced trial,” Dr. McDonagh said. In that trial, comparable patients who took empagliflozin showed a 25% drop in a primary endpoint similar to that in DAPA-HF over the median 16-month follow-up.
Other HFrEF recommendations are for selected patients. They include ivabradine, already in the guidelines, for patients in sinus rhythm with an elevated resting heart rate who can’t take beta-blockers for whatever reason. But, Dr. McDonagh noted, “we had some new classes of drugs to consider as well.”
In particular, the oral soluble guanylate-cyclase receptor stimulator vericiguat (Verquvo) emerged about a year ago from the VICTORIA trial as a modest success for patients with HFrEF and a previous HF hospitalization. In the trial with more than 5,000 patients, treatment with vericiguat atop standard drug and device therapy was followed by a significant 10% drop in risk for CV death or HF hospitalization.
Available now or likely to be available in the United States, the European Union, Japan, and other countries, vericiguat is recommended in the new guideline for VICTORIA-like patients who don’t adequately respond to other indicated medications.
Little for HFpEF as newly defined
“Almost nothing is new” in the guidelines for HFpEF, Dr. Metra said. The document recommends screening for and treatment of any underlying disorder and comorbidities, plus diuretics for any congestion. “That’s what we have to date.”
But that evidence base might soon change. The new HFpEF recommendations could possibly be up-staged at the ESC sessions by the August 27 scheduled presentation of EMPEROR-Preserved, a randomized test of empagliflozin in HFpEF and – it could be said – HFmrEF. The trial entered patients with chronic HF and an LVEF greater than 40%.
Eli Lilly and Boehringer Ingelheim offered the world a peek at the results, which suggest the SGLT2 inhibitor had a positive impact on the primary endpoint of CV death or HF hospitalization. They announced the cursory top-line outcomes in early July as part of its regulatory obligations, noting that the trial had “met” its primary endpoint.
But many unknowns remain, including the degree of benefit and whether it varied among subgroups, and especially whether outcomes were different for HFmrEF than for HFpEF.
Upgrades for familiar agents
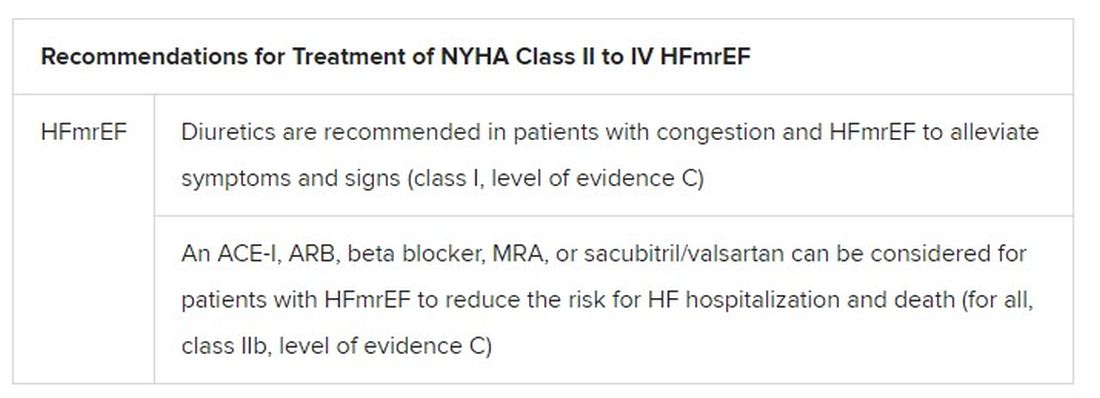
Still, HFmrEF gets noteworthy attention in the document. “For the first time, we have recommendations for these patients,” Dr. Metra said. “We already knew that diuretics are indicated for the treatment of congestion. But now, ACE inhibitors, ARBs, beta-blockers, mineralocorticoid antagonists, as well as sacubitril/valsartan, may be considered to improve outcomes in these patients.” Their upgrades in the new guidelines were based on review of trials in the CHARM program and of TOPCAT and PARAGON-HF, among others, he said.
The new document also includes “treatment algorithms based on phenotypes”; that is, comorbidities and less common HF precipitants. For example, “assessment of iron status is now mandated in all patients with heart failure,” Dr. Metra said.
AFFIRM-HF is the key trial in this arena, with its more than 1,100 iron-deficient patients with LVEF less than 50% who had been recently hospitalized for HF. A year of treatment with ferric carboxymaltose (Ferinject/Injectafer, Vifor) led to a 26% drop in risk for HF hospitalization, but without affecting mortality.
For those who are iron deficient, Dr. Metra said, “ferric carboxymaltose intravenously should be considered not only in patients with low ejection fraction and outpatients, but also in patients recently hospitalized for acute heart failure.”
The SGLT2 inhibitors are recommended in HFrEF patients with type 2 diabetes. And treatment with tafamidis (Vyndaqel, Pfizer) in patients with genetic or wild-type transthyretin cardiac amyloidosis gets a class I recommendation based on survival gains seen in the ATTR-ACT trial.
Also recommended is a full CV assessment for patients with cancer who are on cardiotoxic agents or otherwise might be at risk for chemotherapy cardiotoxicity. “Beta-blockers and ACE inhibitors should be considered in those who develop left ventricular systolic dysfunction after anticancer therapy,” Dr. Metra said.
The ongoing pandemic made its mark on the document’s genesis, as it has with most everything else. “For better or worse, we were a ‘COVID guideline,’ ” Dr. McDonagh said. The writing committee consisted of “a large task force of 31 individuals, including two patients,” and there were “only two face-to-face meetings prior to the first wave of COVID hitting Europe.”
The committee voted on each of the recommendations, “and we had to have agreement of more than 75% of the task force to assign a class of recommendation or level of evidence,” she said. “I think we did the best we could in the circumstances. We had the benefit of many discussions over Zoom, and I think at the end of the day we have achieved a consensus.”
With such a large body of participants and the 75% threshold for agreement, “you end up with perhaps a conservative guideline. But that’s not a bad thing for clinical practice, for guidelines to be conservative,” Dr. McDonagh said. “They’re mainly concerned with looking at evidence and safety.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Today there are so many evidence-based drug therapies for heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF) that physicians treating HF patients almost don’t know what to do them.
It’s an exciting new age that way, but to many vexingly unclear how best to merge the shiny new options with mainstay regimens based on time-honored renin-angiotensin system (RAS) inhibitors and beta-blockers.
To impart some clarity, the authors of a new HF guideline document recently took center stage at the Heart Failure Association of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC-HFA) annual meeting to preview their updated recommendations, with novel twists based on recent major trials, for the new age of HF pharmacotherapeutics.
The guideline committee considered the evidence base that existed “up until the end of March of this year,” Theresa A. McDonagh, MD, King’s College London, said during the presentation. The document “is now finalized, it’s with the publishers, and it will be presented in full with simultaneous publication at the ESC meeting” that starts August 27.
It describes a game plan, already followed by some clinicians in practice without official guidance, for initiating drugs from each of four classes in virtually all patients with HFrEF.
New indicated drugs, new perspective for HFrEF
Three of the drug categories are old acquaintances. Among them are the RAS inhibitors, which include angiotensin-receptor/neprilysin inhibitors, beta-blockers, and the mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists. The latter drugs are gaining new respect after having been underplayed in HF prescribing despite longstanding evidence of efficacy.
Completing the quartet of first-line HFrEF drug classes is a recent arrival to the HF arena, the sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors.
“We now have new data and a simplified treatment algorithm for heart failure with reduced ejection fraction based on the early administration of the four major classes of drugs,” said Marco Metra, MD, University of Brescia (Italy), previewing the medical-therapy portions of the new guideline at the ESC-HFA sessions, which launched virtually and live in Florence, Italy, on July 29.
The new game plan offers a simple answer to a once-common but complex question: How and in what order are the different drug classes initiated in patients with HFrEF? In the new document, the stated goal is to get them all on board expeditiously and safely, by any means possible.
The guideline writers did not specify a sequence, preferring to leave that decision to physicians, said Dr. Metra, who stated only two guiding principles. The first is to consider the patient’s unique circumstances. The order in which the drugs are introduced might vary, depending on, for example, whether the patient has low or high blood pressure or renal dysfunction.
Second, “it is very important that we try to give all four classes of drugs to the patient in the shortest time possible, because this saves lives,” he said.
That there is no recommendation on sequencing the drugs has led some to the wrong interpretation that all should be started at once, observed coauthor Javed Butler, MD, MPH, University of Mississippi, Jackson, as a panelist during the presentation. Far from it, he said. “The doctor with the patient in front of you can make the best decision. The idea here is to get all the therapies on as soon as possible, as safely as possible.”
“The order in which they are introduced is not really important,” agreed Vijay Chopra, MD, Max Super Specialty Hospital Saket, New Delhi, another coauthor on the panel. “The important thing is that at least some dose of all the four drugs needs to be introduced in the first 4-6 weeks, and then up-titrated.”
Other medical therapy can be more tailored, Dr. Metra noted, such as loop diuretics for patients with congestion, iron for those with iron deficiency, and other drugs depending on whether there is, for example, atrial fibrillation or coronary disease.
Adoption of emerging definitions
The document adopts the emerging characterization of HFrEF by a left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) up to 40%.
And it will leverage an expanding evidence base for medication in a segment of patients once said to have HF with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF), who had therefore lacked specific, guideline-directed medical therapies. Now, patients with an LVEF of 41%-49% will be said to have HF with mildly reduced ejection fraction (HFmrEF), a tweak to the recently introduced HF with “mid-range” LVEF that is designed to assert its nature as something to treat. The new document’s HFmrEF recommendations come with various class and level-of-evidence ratings.
That leaves HFpEF to be characterized by an LVEF of 50% in combination with structural or functional abnormalities associated with LV diastolic dysfunction or raised LV filling pressures, including raised natriuretic peptide levels.
The definitions are consistent with those proposed internationally by the ESC-HFA, the Heart Failure Society of America, and other groups in a statement published in March.
Expanded HFrEF med landscape
Since the 2016 ESC guideline on HF therapy, Dr. McDonagh said, “there’s been no substantial change in the evidence for many of the classical drugs that we use in heart failure. However, we had a lot of new and exciting evidence to consider,” especially in support of the SGLT2 inhibitors as one of the core medications in HFrEF.
The new data came from two controlled trials in particular. In DAPA-HF, patients with HFrEF who were initially without diabetes and who went on dapagliflozin (Farxiga, AstraZeneca) showed a 27% drop in cardiovascular (CV) death or worsening-HF events over a median of 18 months.
“That was followed up with very concordant results with empagliflozin [Jardiance, Boehringer Ingelheim/Eli Lilly] in HFrEF in the EMPEROR-Reduced trial,” Dr. McDonagh said. In that trial, comparable patients who took empagliflozin showed a 25% drop in a primary endpoint similar to that in DAPA-HF over the median 16-month follow-up.
Other HFrEF recommendations are for selected patients. They include ivabradine, already in the guidelines, for patients in sinus rhythm with an elevated resting heart rate who can’t take beta-blockers for whatever reason. But, Dr. McDonagh noted, “we had some new classes of drugs to consider as well.”
In particular, the oral soluble guanylate-cyclase receptor stimulator vericiguat (Verquvo) emerged about a year ago from the VICTORIA trial as a modest success for patients with HFrEF and a previous HF hospitalization. In the trial with more than 5,000 patients, treatment with vericiguat atop standard drug and device therapy was followed by a significant 10% drop in risk for CV death or HF hospitalization.
Available now or likely to be available in the United States, the European Union, Japan, and other countries, vericiguat is recommended in the new guideline for VICTORIA-like patients who don’t adequately respond to other indicated medications.
Little for HFpEF as newly defined
“Almost nothing is new” in the guidelines for HFpEF, Dr. Metra said. The document recommends screening for and treatment of any underlying disorder and comorbidities, plus diuretics for any congestion. “That’s what we have to date.”
But that evidence base might soon change. The new HFpEF recommendations could possibly be up-staged at the ESC sessions by the August 27 scheduled presentation of EMPEROR-Preserved, a randomized test of empagliflozin in HFpEF and – it could be said – HFmrEF. The trial entered patients with chronic HF and an LVEF greater than 40%.
Eli Lilly and Boehringer Ingelheim offered the world a peek at the results, which suggest the SGLT2 inhibitor had a positive impact on the primary endpoint of CV death or HF hospitalization. They announced the cursory top-line outcomes in early July as part of its regulatory obligations, noting that the trial had “met” its primary endpoint.
But many unknowns remain, including the degree of benefit and whether it varied among subgroups, and especially whether outcomes were different for HFmrEF than for HFpEF.
Upgrades for familiar agents
Still, HFmrEF gets noteworthy attention in the document. “For the first time, we have recommendations for these patients,” Dr. Metra said. “We already knew that diuretics are indicated for the treatment of congestion. But now, ACE inhibitors, ARBs, beta-blockers, mineralocorticoid antagonists, as well as sacubitril/valsartan, may be considered to improve outcomes in these patients.” Their upgrades in the new guidelines were based on review of trials in the CHARM program and of TOPCAT and PARAGON-HF, among others, he said.

The new document also includes “treatment algorithms based on phenotypes”; that is, comorbidities and less common HF precipitants. For example, “assessment of iron status is now mandated in all patients with heart failure,” Dr. Metra said.
AFFIRM-HF is the key trial in this arena, with its more than 1,100 iron-deficient patients with LVEF less than 50% who had been recently hospitalized for HF. A year of treatment with ferric carboxymaltose (Ferinject/Injectafer, Vifor) led to a 26% drop in risk for HF hospitalization, but without affecting mortality.
For those who are iron deficient, Dr. Metra said, “ferric carboxymaltose intravenously should be considered not only in patients with low ejection fraction and outpatients, but also in patients recently hospitalized for acute heart failure.”
The SGLT2 inhibitors are recommended in HFrEF patients with type 2 diabetes. And treatment with tafamidis (Vyndaqel, Pfizer) in patients with genetic or wild-type transthyretin cardiac amyloidosis gets a class I recommendation based on survival gains seen in the ATTR-ACT trial.
Also recommended is a full CV assessment for patients with cancer who are on cardiotoxic agents or otherwise might be at risk for chemotherapy cardiotoxicity. “Beta-blockers and ACE inhibitors should be considered in those who develop left ventricular systolic dysfunction after anticancer therapy,” Dr. Metra said.
The ongoing pandemic made its mark on the document’s genesis, as it has with most everything else. “For better or worse, we were a ‘COVID guideline,’ ” Dr. McDonagh said. The writing committee consisted of “a large task force of 31 individuals, including two patients,” and there were “only two face-to-face meetings prior to the first wave of COVID hitting Europe.”
The committee voted on each of the recommendations, “and we had to have agreement of more than 75% of the task force to assign a class of recommendation or level of evidence,” she said. “I think we did the best we could in the circumstances. We had the benefit of many discussions over Zoom, and I think at the end of the day we have achieved a consensus.”
With such a large body of participants and the 75% threshold for agreement, “you end up with perhaps a conservative guideline. But that’s not a bad thing for clinical practice, for guidelines to be conservative,” Dr. McDonagh said. “They’re mainly concerned with looking at evidence and safety.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Today there are so many evidence-based drug therapies for heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF) that physicians treating HF patients almost don’t know what to do them.
It’s an exciting new age that way, but to many vexingly unclear how best to merge the shiny new options with mainstay regimens based on time-honored renin-angiotensin system (RAS) inhibitors and beta-blockers.
To impart some clarity, the authors of a new HF guideline document recently took center stage at the Heart Failure Association of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC-HFA) annual meeting to preview their updated recommendations, with novel twists based on recent major trials, for the new age of HF pharmacotherapeutics.
The guideline committee considered the evidence base that existed “up until the end of March of this year,” Theresa A. McDonagh, MD, King’s College London, said during the presentation. The document “is now finalized, it’s with the publishers, and it will be presented in full with simultaneous publication at the ESC meeting” that starts August 27.
It describes a game plan, already followed by some clinicians in practice without official guidance, for initiating drugs from each of four classes in virtually all patients with HFrEF.
New indicated drugs, new perspective for HFrEF
Three of the drug categories are old acquaintances. Among them are the RAS inhibitors, which include angiotensin-receptor/neprilysin inhibitors, beta-blockers, and the mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists. The latter drugs are gaining new respect after having been underplayed in HF prescribing despite longstanding evidence of efficacy.
Completing the quartet of first-line HFrEF drug classes is a recent arrival to the HF arena, the sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors.
“We now have new data and a simplified treatment algorithm for heart failure with reduced ejection fraction based on the early administration of the four major classes of drugs,” said Marco Metra, MD, University of Brescia (Italy), previewing the medical-therapy portions of the new guideline at the ESC-HFA sessions, which launched virtually and live in Florence, Italy, on July 29.
The new game plan offers a simple answer to a once-common but complex question: How and in what order are the different drug classes initiated in patients with HFrEF? In the new document, the stated goal is to get them all on board expeditiously and safely, by any means possible.
The guideline writers did not specify a sequence, preferring to leave that decision to physicians, said Dr. Metra, who stated only two guiding principles. The first is to consider the patient’s unique circumstances. The order in which the drugs are introduced might vary, depending on, for example, whether the patient has low or high blood pressure or renal dysfunction.
Second, “it is very important that we try to give all four classes of drugs to the patient in the shortest time possible, because this saves lives,” he said.
That there is no recommendation on sequencing the drugs has led some to the wrong interpretation that all should be started at once, observed coauthor Javed Butler, MD, MPH, University of Mississippi, Jackson, as a panelist during the presentation. Far from it, he said. “The doctor with the patient in front of you can make the best decision. The idea here is to get all the therapies on as soon as possible, as safely as possible.”
“The order in which they are introduced is not really important,” agreed Vijay Chopra, MD, Max Super Specialty Hospital Saket, New Delhi, another coauthor on the panel. “The important thing is that at least some dose of all the four drugs needs to be introduced in the first 4-6 weeks, and then up-titrated.”
Other medical therapy can be more tailored, Dr. Metra noted, such as loop diuretics for patients with congestion, iron for those with iron deficiency, and other drugs depending on whether there is, for example, atrial fibrillation or coronary disease.
Adoption of emerging definitions
The document adopts the emerging characterization of HFrEF by a left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) up to 40%.
And it will leverage an expanding evidence base for medication in a segment of patients once said to have HF with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF), who had therefore lacked specific, guideline-directed medical therapies. Now, patients with an LVEF of 41%-49% will be said to have HF with mildly reduced ejection fraction (HFmrEF), a tweak to the recently introduced HF with “mid-range” LVEF that is designed to assert its nature as something to treat. The new document’s HFmrEF recommendations come with various class and level-of-evidence ratings.
That leaves HFpEF to be characterized by an LVEF of 50% in combination with structural or functional abnormalities associated with LV diastolic dysfunction or raised LV filling pressures, including raised natriuretic peptide levels.
The definitions are consistent with those proposed internationally by the ESC-HFA, the Heart Failure Society of America, and other groups in a statement published in March.
Expanded HFrEF med landscape
Since the 2016 ESC guideline on HF therapy, Dr. McDonagh said, “there’s been no substantial change in the evidence for many of the classical drugs that we use in heart failure. However, we had a lot of new and exciting evidence to consider,” especially in support of the SGLT2 inhibitors as one of the core medications in HFrEF.
The new data came from two controlled trials in particular. In DAPA-HF, patients with HFrEF who were initially without diabetes and who went on dapagliflozin (Farxiga, AstraZeneca) showed a 27% drop in cardiovascular (CV) death or worsening-HF events over a median of 18 months.
“That was followed up with very concordant results with empagliflozin [Jardiance, Boehringer Ingelheim/Eli Lilly] in HFrEF in the EMPEROR-Reduced trial,” Dr. McDonagh said. In that trial, comparable patients who took empagliflozin showed a 25% drop in a primary endpoint similar to that in DAPA-HF over the median 16-month follow-up.
Other HFrEF recommendations are for selected patients. They include ivabradine, already in the guidelines, for patients in sinus rhythm with an elevated resting heart rate who can’t take beta-blockers for whatever reason. But, Dr. McDonagh noted, “we had some new classes of drugs to consider as well.”
In particular, the oral soluble guanylate-cyclase receptor stimulator vericiguat (Verquvo) emerged about a year ago from the VICTORIA trial as a modest success for patients with HFrEF and a previous HF hospitalization. In the trial with more than 5,000 patients, treatment with vericiguat atop standard drug and device therapy was followed by a significant 10% drop in risk for CV death or HF hospitalization.
Available now or likely to be available in the United States, the European Union, Japan, and other countries, vericiguat is recommended in the new guideline for VICTORIA-like patients who don’t adequately respond to other indicated medications.
Little for HFpEF as newly defined
“Almost nothing is new” in the guidelines for HFpEF, Dr. Metra said. The document recommends screening for and treatment of any underlying disorder and comorbidities, plus diuretics for any congestion. “That’s what we have to date.”
But that evidence base might soon change. The new HFpEF recommendations could possibly be up-staged at the ESC sessions by the August 27 scheduled presentation of EMPEROR-Preserved, a randomized test of empagliflozin in HFpEF and – it could be said – HFmrEF. The trial entered patients with chronic HF and an LVEF greater than 40%.
Eli Lilly and Boehringer Ingelheim offered the world a peek at the results, which suggest the SGLT2 inhibitor had a positive impact on the primary endpoint of CV death or HF hospitalization. They announced the cursory top-line outcomes in early July as part of its regulatory obligations, noting that the trial had “met” its primary endpoint.
But many unknowns remain, including the degree of benefit and whether it varied among subgroups, and especially whether outcomes were different for HFmrEF than for HFpEF.
Upgrades for familiar agents
Still, HFmrEF gets noteworthy attention in the document. “For the first time, we have recommendations for these patients,” Dr. Metra said. “We already knew that diuretics are indicated for the treatment of congestion. But now, ACE inhibitors, ARBs, beta-blockers, mineralocorticoid antagonists, as well as sacubitril/valsartan, may be considered to improve outcomes in these patients.” Their upgrades in the new guidelines were based on review of trials in the CHARM program and of TOPCAT and PARAGON-HF, among others, he said.

The new document also includes “treatment algorithms based on phenotypes”; that is, comorbidities and less common HF precipitants. For example, “assessment of iron status is now mandated in all patients with heart failure,” Dr. Metra said.
AFFIRM-HF is the key trial in this arena, with its more than 1,100 iron-deficient patients with LVEF less than 50% who had been recently hospitalized for HF. A year of treatment with ferric carboxymaltose (Ferinject/Injectafer, Vifor) led to a 26% drop in risk for HF hospitalization, but without affecting mortality.
For those who are iron deficient, Dr. Metra said, “ferric carboxymaltose intravenously should be considered not only in patients with low ejection fraction and outpatients, but also in patients recently hospitalized for acute heart failure.”
The SGLT2 inhibitors are recommended in HFrEF patients with type 2 diabetes. And treatment with tafamidis (Vyndaqel, Pfizer) in patients with genetic or wild-type transthyretin cardiac amyloidosis gets a class I recommendation based on survival gains seen in the ATTR-ACT trial.
Also recommended is a full CV assessment for patients with cancer who are on cardiotoxic agents or otherwise might be at risk for chemotherapy cardiotoxicity. “Beta-blockers and ACE inhibitors should be considered in those who develop left ventricular systolic dysfunction after anticancer therapy,” Dr. Metra said.
The ongoing pandemic made its mark on the document’s genesis, as it has with most everything else. “For better or worse, we were a ‘COVID guideline,’ ” Dr. McDonagh said. The writing committee consisted of “a large task force of 31 individuals, including two patients,” and there were “only two face-to-face meetings prior to the first wave of COVID hitting Europe.”
The committee voted on each of the recommendations, “and we had to have agreement of more than 75% of the task force to assign a class of recommendation or level of evidence,” she said. “I think we did the best we could in the circumstances. We had the benefit of many discussions over Zoom, and I think at the end of the day we have achieved a consensus.”
With such a large body of participants and the 75% threshold for agreement, “you end up with perhaps a conservative guideline. But that’s not a bad thing for clinical practice, for guidelines to be conservative,” Dr. McDonagh said. “They’re mainly concerned with looking at evidence and safety.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Obesity treatment in mental illness: Is semaglutide a game changer?
It’s probably fair to say that most people would like to be thinner. More than 42% of Americans have obesity and another 30% are classified as being overweight, according to the latest statistics from the CDC.
Excess body weight is associated with many illnesses and plays a role in mental health; being heavy can take a toll on self-esteem. Many people worry that carrying excess weight makes them less attractive to potential romantic partners, and both physicians and employers treat those with obesity differently. Furthermore, in psychiatry, many of the medications we prescribe lead to weight gain.
In my clinical practice, I have listened as patients blamed themselves for their body habitus; many won’t consider biological treatments as they feel that would be “cheating” or taking an easy way out. They often point to periods in their life when they did lose weight and believe that they should be able to do it again, even if the weight loss took tremendous effort, was not sustained, and occurred decades ago.
That said, we psychiatrists often find ourselves in the position of managing obesity in our patients. I have been known to give patients who gain weight on antipsychotics either stimulants or metformin, or to add naltrexone to their Wellbutrin (bupropion) to effectively mimic a weight-loss medicine called Contrave.
Obesity a treatable medical condition
It wasn’t until 2013 that the American Medical Association recognized obesity as a medical condition.
In a New Yorker article that same year, “Diet Drugs Work: Why Won’t Doctors Prescribe Them?” Suzanne Koven wrote: “Several obesity experts told me they’ve encountered doctors who confide that they just didn’t like fat people and don’t enjoy taking care of them. Even doctors who treat obese patients feel stigmatized: ‘diet doctor’ is not a flattering term.”
Eat less, exercise more – with a blame-the-patient attitude – is still what people see as the “right” way to lose weight.
On June 4, 2021, the FDA approved semaglutide, a glucagonlike peptide–1 receptor agonist, previously used for the treatment of diabetes, for use as a weight loss agent for patients with obesity, or for those with a body mass index over 27 kg/m2 if they also have a weight-related comorbidity.
Semaglutide has three trade names, all manufactured by Novo Nordisk. The pill version is called Rybelsus and comes in 7-mg and 14-mg tablets. Ozempic is available in 0.5-mg and 1.0-mg doses and is administered weekly by subcutaneous injection for diabetes. The new, higher-dose preparation for weight loss, Wegovy, 2.4 mg, also comes as a weekly subcutaneous dose and is now available for the hefty price of $1,400 per month.
In STEP 1 trials, the higher-dose Wegovy was associated with an average 14.9% weight loss (15.3 kg) over 68 weeks, more than any other single-agent weight loss medication on the market.
GLP-1 receptor agonists work in the brain to decrease appetite, slow gastric emptying, increase insulin secretion, and stimulate brown adipose tissue thermogenesis.
Psych drugs lead to weight gain
Elaine Weiner, MD, is the medical director in the outpatient research program of the Maryland Psychiatric Research Center in Catonsville, where she treats patients with schizophrenia.
“Nearly all of our patients gain 20 pounds or more on the combinations of medications we use, mostly atypical antipsychotics,” she said. “Weight management is difficult for people who don’t have problems with motivation, but in our patients, lack of motivation is a core part of their illness, so asking them to adhere to diet and exercise regimens is of limited utility.
“Then, add to that the fact that they sometimes don’t have primary care doctors, and these issues of weight gain and metabolic syndrome come back to the psychiatrist. It is a really bad problem and we need more treatments.”
Fatima Cody Stanford, MD, MPH, MPA, is a fellowship-trained obesity medicine physician-scientist at the Massachusetts General Hospital Weight Center and Harvard Medical School, both in Boston. She has treated thousands of patients with obesity, speaks internationally on the topic of weight loss medicine, and has published over 100 peer-reviewed articles on obesity.
We spoke at length about recent changes in the field of obesity medicine and the introduction of the new GLP-1 receptor agonists.
“We as physicians have learned so little,” Dr. Stanford said. “This mantra of ‘calories in, calories out’ is not working; this is inaccurate and our focus on this has led to a rise in obesity. All calories are not created the same, and I think we are finally starting to see obesity medicine take off.”
Dr. Stanford is quick to note that obesity is a complex problem. Several different hormones are involved in regulating both appetite and satiety, processed foods promote weight gain, sleep is crucial to weight loss, and exercise helps maintain weight loss but is not usually effective in promoting it. “There are many contributors to energy storage,” she said.
The stimulant phentermine was approved in 1959. Addiction was a concern, and then in the 1990s, it was used in combination with fenfluramine to promote weight loss, a combination known as phen-fen. Fenfluramine was pulled from the market in 1997 when it was found to be associated with pulmonary hypertension and then heart valve abnormalities.
“This frightened quite a few physicians,” Dr. Stanford noted. Phentermine is still used for weight loss, either alone or together with topiramate, as a combination medication called Qsymia, nicknamed phen-top.
“Phen-top is the next best thing we have to semaglutide, and there is an average weight loss of 8%-9% of body weight. Semaglutide is going to be really significant for those people who are responders, and this has been quite well tolerated, the most common side effect being nausea,” she said.
However, she is quick to note that not everyone responds to every medication. “I use each patient’s clinical profile to determine what strategies and which medications to use.”
Cardiologists getting in the game
Michael Miller, MD, is a cardiologist at the University of Maryland, Baltimore, and author of “Heal Your Heart” (Emmaus, Pa.: Rodale, 2014). He is very enthusiastic about the approval of semaglutide.
“We are so excited because you finally can use these medicines without having to be diabetic,” Dr. Miller said. “We’re waiting on the results of the SELECT [Semaglutide Effects on Heart Disease and Stroke in Patients With Overweight or Obesity] trials looking at people who are not diabetic or who are prediabetic, to see the 5-year outcomes with regard to cardiac events.
“Usually endocrinologists prescribe these medications, but cardiologists have started to get into the game since GLP-1 receptor agonists reduce cardiovascular events.” Dr. Miller is hopeful that this medication may neutralize the weight gain caused by psychotropic medications.
Wegovy is administered via weekly injection and, like insulin, is a subcutaneous medication that patients self-administer. Will patients be amenable to injecting a medication for weight loss? Dr. Stanford said that roughly 20%-30% of her patients are hesitant when she suggests that they use liraglutide, another GLP-1 receptor agonist that is approved for weight loss, and some are very fearful of needles.
However, she also noted that during the COVID-19 pandemic, many more patients have sought treatment from obesity medicine physicians because of the association between obesity and mortality from COVID-19. Patients have been willing to consider treatments that they were not previously open to pursuing.
So if people are willing to take Wegovy and doctors are willing to prescribe it, will insurers pay for it? As of this writing, the medication is not yet available, but Ozempic, the lower-dose agent for diabetes, costs $850-$900 for a 4-week supply, according to the GoodRx website.
Liraglutide (Saxenda), the GLP-1 receptor agonist that is currently available for weight loss as a daily injectable, costs $1,300-$1,400 per month.
These medications are not covered by Medicare or Medicaid, and Dr. Stanford, who is well versed as to exactly which private insurers in Massachusetts will and will not reimburse specific medications, said her patients with insurance coverage have been known to delay retirement so that they can remain on the more expensive medications.
“For the past 8 years,” she said, “the Treat and Reduce Obesity Act has had bipartisan support in Congress but has not passed. We are still hopeful that insurers will be required to cover medical and behavioral treatments for obesity.”
As our society struggles to destigmatize so many disorders, obesity remains a highly stigmatized condition, one that our patients cannot hide and one that leads to so many other comorbid illnesses. As new treatments are approved, there will be more for physicians to offer. Semaglutide, if it becomes available to those who need it most, could be a game changer. For patients who have not had success with traditional weight-loss methods, it’s encouraging to have another option available, one that may be reasonable to try before resorting to bariatric surgery.
For decades, psychiatrists have been comfortable prescribing treatments that lead to weight gain. Now, maybe it’s time they also prescribe those that prevent it.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
It’s probably fair to say that most people would like to be thinner. More than 42% of Americans have obesity and another 30% are classified as being overweight, according to the latest statistics from the CDC.
Excess body weight is associated with many illnesses and plays a role in mental health; being heavy can take a toll on self-esteem. Many people worry that carrying excess weight makes them less attractive to potential romantic partners, and both physicians and employers treat those with obesity differently. Furthermore, in psychiatry, many of the medications we prescribe lead to weight gain.
In my clinical practice, I have listened as patients blamed themselves for their body habitus; many won’t consider biological treatments as they feel that would be “cheating” or taking an easy way out. They often point to periods in their life when they did lose weight and believe that they should be able to do it again, even if the weight loss took tremendous effort, was not sustained, and occurred decades ago.
That said, we psychiatrists often find ourselves in the position of managing obesity in our patients. I have been known to give patients who gain weight on antipsychotics either stimulants or metformin, or to add naltrexone to their Wellbutrin (bupropion) to effectively mimic a weight-loss medicine called Contrave.
Obesity a treatable medical condition
It wasn’t until 2013 that the American Medical Association recognized obesity as a medical condition.
In a New Yorker article that same year, “Diet Drugs Work: Why Won’t Doctors Prescribe Them?” Suzanne Koven wrote: “Several obesity experts told me they’ve encountered doctors who confide that they just didn’t like fat people and don’t enjoy taking care of them. Even doctors who treat obese patients feel stigmatized: ‘diet doctor’ is not a flattering term.”
Eat less, exercise more – with a blame-the-patient attitude – is still what people see as the “right” way to lose weight.
On June 4, 2021, the FDA approved semaglutide, a glucagonlike peptide–1 receptor agonist, previously used for the treatment of diabetes, for use as a weight loss agent for patients with obesity, or for those with a body mass index over 27 kg/m2 if they also have a weight-related comorbidity.
Semaglutide has three trade names, all manufactured by Novo Nordisk. The pill version is called Rybelsus and comes in 7-mg and 14-mg tablets. Ozempic is available in 0.5-mg and 1.0-mg doses and is administered weekly by subcutaneous injection for diabetes. The new, higher-dose preparation for weight loss, Wegovy, 2.4 mg, also comes as a weekly subcutaneous dose and is now available for the hefty price of $1,400 per month.
In STEP 1 trials, the higher-dose Wegovy was associated with an average 14.9% weight loss (15.3 kg) over 68 weeks, more than any other single-agent weight loss medication on the market.
GLP-1 receptor agonists work in the brain to decrease appetite, slow gastric emptying, increase insulin secretion, and stimulate brown adipose tissue thermogenesis.
Psych drugs lead to weight gain
Elaine Weiner, MD, is the medical director in the outpatient research program of the Maryland Psychiatric Research Center in Catonsville, where she treats patients with schizophrenia.
“Nearly all of our patients gain 20 pounds or more on the combinations of medications we use, mostly atypical antipsychotics,” she said. “Weight management is difficult for people who don’t have problems with motivation, but in our patients, lack of motivation is a core part of their illness, so asking them to adhere to diet and exercise regimens is of limited utility.
“Then, add to that the fact that they sometimes don’t have primary care doctors, and these issues of weight gain and metabolic syndrome come back to the psychiatrist. It is a really bad problem and we need more treatments.”
Fatima Cody Stanford, MD, MPH, MPA, is a fellowship-trained obesity medicine physician-scientist at the Massachusetts General Hospital Weight Center and Harvard Medical School, both in Boston. She has treated thousands of patients with obesity, speaks internationally on the topic of weight loss medicine, and has published over 100 peer-reviewed articles on obesity.
We spoke at length about recent changes in the field of obesity medicine and the introduction of the new GLP-1 receptor agonists.
“We as physicians have learned so little,” Dr. Stanford said. “This mantra of ‘calories in, calories out’ is not working; this is inaccurate and our focus on this has led to a rise in obesity. All calories are not created the same, and I think we are finally starting to see obesity medicine take off.”
Dr. Stanford is quick to note that obesity is a complex problem. Several different hormones are involved in regulating both appetite and satiety, processed foods promote weight gain, sleep is crucial to weight loss, and exercise helps maintain weight loss but is not usually effective in promoting it. “There are many contributors to energy storage,” she said.
The stimulant phentermine was approved in 1959. Addiction was a concern, and then in the 1990s, it was used in combination with fenfluramine to promote weight loss, a combination known as phen-fen. Fenfluramine was pulled from the market in 1997 when it was found to be associated with pulmonary hypertension and then heart valve abnormalities.
“This frightened quite a few physicians,” Dr. Stanford noted. Phentermine is still used for weight loss, either alone or together with topiramate, as a combination medication called Qsymia, nicknamed phen-top.
“Phen-top is the next best thing we have to semaglutide, and there is an average weight loss of 8%-9% of body weight. Semaglutide is going to be really significant for those people who are responders, and this has been quite well tolerated, the most common side effect being nausea,” she said.
However, she is quick to note that not everyone responds to every medication. “I use each patient’s clinical profile to determine what strategies and which medications to use.”
Cardiologists getting in the game
Michael Miller, MD, is a cardiologist at the University of Maryland, Baltimore, and author of “Heal Your Heart” (Emmaus, Pa.: Rodale, 2014). He is very enthusiastic about the approval of semaglutide.
“We are so excited because you finally can use these medicines without having to be diabetic,” Dr. Miller said. “We’re waiting on the results of the SELECT [Semaglutide Effects on Heart Disease and Stroke in Patients With Overweight or Obesity] trials looking at people who are not diabetic or who are prediabetic, to see the 5-year outcomes with regard to cardiac events.
“Usually endocrinologists prescribe these medications, but cardiologists have started to get into the game since GLP-1 receptor agonists reduce cardiovascular events.” Dr. Miller is hopeful that this medication may neutralize the weight gain caused by psychotropic medications.
Wegovy is administered via weekly injection and, like insulin, is a subcutaneous medication that patients self-administer. Will patients be amenable to injecting a medication for weight loss? Dr. Stanford said that roughly 20%-30% of her patients are hesitant when she suggests that they use liraglutide, another GLP-1 receptor agonist that is approved for weight loss, and some are very fearful of needles.
However, she also noted that during the COVID-19 pandemic, many more patients have sought treatment from obesity medicine physicians because of the association between obesity and mortality from COVID-19. Patients have been willing to consider treatments that they were not previously open to pursuing.
So if people are willing to take Wegovy and doctors are willing to prescribe it, will insurers pay for it? As of this writing, the medication is not yet available, but Ozempic, the lower-dose agent for diabetes, costs $850-$900 for a 4-week supply, according to the GoodRx website.
Liraglutide (Saxenda), the GLP-1 receptor agonist that is currently available for weight loss as a daily injectable, costs $1,300-$1,400 per month.
These medications are not covered by Medicare or Medicaid, and Dr. Stanford, who is well versed as to exactly which private insurers in Massachusetts will and will not reimburse specific medications, said her patients with insurance coverage have been known to delay retirement so that they can remain on the more expensive medications.
“For the past 8 years,” she said, “the Treat and Reduce Obesity Act has had bipartisan support in Congress but has not passed. We are still hopeful that insurers will be required to cover medical and behavioral treatments for obesity.”
As our society struggles to destigmatize so many disorders, obesity remains a highly stigmatized condition, one that our patients cannot hide and one that leads to so many other comorbid illnesses. As new treatments are approved, there will be more for physicians to offer. Semaglutide, if it becomes available to those who need it most, could be a game changer. For patients who have not had success with traditional weight-loss methods, it’s encouraging to have another option available, one that may be reasonable to try before resorting to bariatric surgery.
For decades, psychiatrists have been comfortable prescribing treatments that lead to weight gain. Now, maybe it’s time they also prescribe those that prevent it.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
It’s probably fair to say that most people would like to be thinner. More than 42% of Americans have obesity and another 30% are classified as being overweight, according to the latest statistics from the CDC.
Excess body weight is associated with many illnesses and plays a role in mental health; being heavy can take a toll on self-esteem. Many people worry that carrying excess weight makes them less attractive to potential romantic partners, and both physicians and employers treat those with obesity differently. Furthermore, in psychiatry, many of the medications we prescribe lead to weight gain.
In my clinical practice, I have listened as patients blamed themselves for their body habitus; many won’t consider biological treatments as they feel that would be “cheating” or taking an easy way out. They often point to periods in their life when they did lose weight and believe that they should be able to do it again, even if the weight loss took tremendous effort, was not sustained, and occurred decades ago.
That said, we psychiatrists often find ourselves in the position of managing obesity in our patients. I have been known to give patients who gain weight on antipsychotics either stimulants or metformin, or to add naltrexone to their Wellbutrin (bupropion) to effectively mimic a weight-loss medicine called Contrave.
Obesity a treatable medical condition
It wasn’t until 2013 that the American Medical Association recognized obesity as a medical condition.
In a New Yorker article that same year, “Diet Drugs Work: Why Won’t Doctors Prescribe Them?” Suzanne Koven wrote: “Several obesity experts told me they’ve encountered doctors who confide that they just didn’t like fat people and don’t enjoy taking care of them. Even doctors who treat obese patients feel stigmatized: ‘diet doctor’ is not a flattering term.”
Eat less, exercise more – with a blame-the-patient attitude – is still what people see as the “right” way to lose weight.
On June 4, 2021, the FDA approved semaglutide, a glucagonlike peptide–1 receptor agonist, previously used for the treatment of diabetes, for use as a weight loss agent for patients with obesity, or for those with a body mass index over 27 kg/m2 if they also have a weight-related comorbidity.
Semaglutide has three trade names, all manufactured by Novo Nordisk. The pill version is called Rybelsus and comes in 7-mg and 14-mg tablets. Ozempic is available in 0.5-mg and 1.0-mg doses and is administered weekly by subcutaneous injection for diabetes. The new, higher-dose preparation for weight loss, Wegovy, 2.4 mg, also comes as a weekly subcutaneous dose and is now available for the hefty price of $1,400 per month.
In STEP 1 trials, the higher-dose Wegovy was associated with an average 14.9% weight loss (15.3 kg) over 68 weeks, more than any other single-agent weight loss medication on the market.
GLP-1 receptor agonists work in the brain to decrease appetite, slow gastric emptying, increase insulin secretion, and stimulate brown adipose tissue thermogenesis.
Psych drugs lead to weight gain
Elaine Weiner, MD, is the medical director in the outpatient research program of the Maryland Psychiatric Research Center in Catonsville, where she treats patients with schizophrenia.
“Nearly all of our patients gain 20 pounds or more on the combinations of medications we use, mostly atypical antipsychotics,” she said. “Weight management is difficult for people who don’t have problems with motivation, but in our patients, lack of motivation is a core part of their illness, so asking them to adhere to diet and exercise regimens is of limited utility.
“Then, add to that the fact that they sometimes don’t have primary care doctors, and these issues of weight gain and metabolic syndrome come back to the psychiatrist. It is a really bad problem and we need more treatments.”
Fatima Cody Stanford, MD, MPH, MPA, is a fellowship-trained obesity medicine physician-scientist at the Massachusetts General Hospital Weight Center and Harvard Medical School, both in Boston. She has treated thousands of patients with obesity, speaks internationally on the topic of weight loss medicine, and has published over 100 peer-reviewed articles on obesity.
We spoke at length about recent changes in the field of obesity medicine and the introduction of the new GLP-1 receptor agonists.
“We as physicians have learned so little,” Dr. Stanford said. “This mantra of ‘calories in, calories out’ is not working; this is inaccurate and our focus on this has led to a rise in obesity. All calories are not created the same, and I think we are finally starting to see obesity medicine take off.”
Dr. Stanford is quick to note that obesity is a complex problem. Several different hormones are involved in regulating both appetite and satiety, processed foods promote weight gain, sleep is crucial to weight loss, and exercise helps maintain weight loss but is not usually effective in promoting it. “There are many contributors to energy storage,” she said.
The stimulant phentermine was approved in 1959. Addiction was a concern, and then in the 1990s, it was used in combination with fenfluramine to promote weight loss, a combination known as phen-fen. Fenfluramine was pulled from the market in 1997 when it was found to be associated with pulmonary hypertension and then heart valve abnormalities.
“This frightened quite a few physicians,” Dr. Stanford noted. Phentermine is still used for weight loss, either alone or together with topiramate, as a combination medication called Qsymia, nicknamed phen-top.
“Phen-top is the next best thing we have to semaglutide, and there is an average weight loss of 8%-9% of body weight. Semaglutide is going to be really significant for those people who are responders, and this has been quite well tolerated, the most common side effect being nausea,” she said.
However, she is quick to note that not everyone responds to every medication. “I use each patient’s clinical profile to determine what strategies and which medications to use.”
Cardiologists getting in the game
Michael Miller, MD, is a cardiologist at the University of Maryland, Baltimore, and author of “Heal Your Heart” (Emmaus, Pa.: Rodale, 2014). He is very enthusiastic about the approval of semaglutide.
“We are so excited because you finally can use these medicines without having to be diabetic,” Dr. Miller said. “We’re waiting on the results of the SELECT [Semaglutide Effects on Heart Disease and Stroke in Patients With Overweight or Obesity] trials looking at people who are not diabetic or who are prediabetic, to see the 5-year outcomes with regard to cardiac events.
“Usually endocrinologists prescribe these medications, but cardiologists have started to get into the game since GLP-1 receptor agonists reduce cardiovascular events.” Dr. Miller is hopeful that this medication may neutralize the weight gain caused by psychotropic medications.
Wegovy is administered via weekly injection and, like insulin, is a subcutaneous medication that patients self-administer. Will patients be amenable to injecting a medication for weight loss? Dr. Stanford said that roughly 20%-30% of her patients are hesitant when she suggests that they use liraglutide, another GLP-1 receptor agonist that is approved for weight loss, and some are very fearful of needles.
However, she also noted that during the COVID-19 pandemic, many more patients have sought treatment from obesity medicine physicians because of the association between obesity and mortality from COVID-19. Patients have been willing to consider treatments that they were not previously open to pursuing.
So if people are willing to take Wegovy and doctors are willing to prescribe it, will insurers pay for it? As of this writing, the medication is not yet available, but Ozempic, the lower-dose agent for diabetes, costs $850-$900 for a 4-week supply, according to the GoodRx website.
Liraglutide (Saxenda), the GLP-1 receptor agonist that is currently available for weight loss as a daily injectable, costs $1,300-$1,400 per month.
These medications are not covered by Medicare or Medicaid, and Dr. Stanford, who is well versed as to exactly which private insurers in Massachusetts will and will not reimburse specific medications, said her patients with insurance coverage have been known to delay retirement so that they can remain on the more expensive medications.
“For the past 8 years,” she said, “the Treat and Reduce Obesity Act has had bipartisan support in Congress but has not passed. We are still hopeful that insurers will be required to cover medical and behavioral treatments for obesity.”
As our society struggles to destigmatize so many disorders, obesity remains a highly stigmatized condition, one that our patients cannot hide and one that leads to so many other comorbid illnesses. As new treatments are approved, there will be more for physicians to offer. Semaglutide, if it becomes available to those who need it most, could be a game changer. For patients who have not had success with traditional weight-loss methods, it’s encouraging to have another option available, one that may be reasonable to try before resorting to bariatric surgery.
For decades, psychiatrists have been comfortable prescribing treatments that lead to weight gain. Now, maybe it’s time they also prescribe those that prevent it.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Call to Action: Multidisciplinary panel urges coordinated care for ‘NASH epidemic’
A multidisciplinary panel of U.S. experts released a “Call to Action” for improved screening, diagnosis, and treatment of patients with nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) on July 26, an effort organized by the American Gastroenterological Association in collaboration with seven other U.S. medical organizations including several endocrinology groups.
The published statement, “Preparing for the NASH Epidemic: A Call to Action,” proposes several urgent steps for the U.S. clinical community to provide better-focused and better-coordinated care for patients at risk for developing or having NAFLD or NASH, particularly among “emerging” at-risk cohorts such as patients with diabetes and obesity. It appears in the journals Gastroenterology, Diabetes Care, Metabolism: Clinical and Experimental, and Obesity.
The statement’s central pitch is that improvements in care won’t be possible unless the several medical specialties that deal with affected or at-risk patients stop working “in separate silos,” and instead create “a collective action plan,” and also organize multidisciplinary teams that “integrate primary care, hepatology, obesity medicine, endocrinology, and diabetology via well-defined care pathways.”
“The overarching goal” is a “unified, international public health response to NAFLD and NASH,” said the statement, which stemmed from a conference held in July 2020 that included representatives from not only the lead gastroenterology group but also the American Diabetes Association, the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases, the American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists, The Endocrine Society, The American Academy of Family Physicians, The Obesity Society, and the American College of Osteopathic Family Physicians.
The statement cites sobering prevalence numbers, with estimates that NAFLD exists in more than half the patients with type 2 diabetes, while NASH affects about a third, rates that translate into many millions of affected Americans, given recent estimates that the U.S. prevalence of type 2 diabetes exceeds 30 million people. And the numbers continue to rise along with increases in the prevalence of obesity and type 2 diabetes.
“It’s an enormously common disease, and there are not enough gastroenterologists, to say nothing of hepatologists, to care for every patient with NAFLD,” said Anna Mae Diehl, MD, a gastroenterologist and professor at Duke University in Durham, N.C., who was not involved with the conference nor in writing the statement.
Clinical care pathways coming soon
Another key part of this initiative is development of clinical care pathways that will have “careful explication of each step in screening, diagnosis, and treatment,” and will be designed to inform the practice of primary care physicians (PCPs) as well as clinicians from the various specialties that deal with these patients.
The clinical care pathways are on track to come out later in 2021, said Fasiha Kanwal, MD, a professor and chief of gastroenterology at Baylor College of Medicine in Houston, and lead author on the Call to Action document.
“The Pathways will include practical recommendations about whom to screen and when to refer, and the criteria primary care physicians can use for diagnosis and risk stratification,” Dr. Kanwal said in an interview. “Patients can benefit from a standardized approach.”
The new document also includes results from a recent survey about NAFLD and NASH management completed by 751 U.S. physicians, including 401 (53%) primary care physicians, 175 gastroenterologists, (23%) and 175 endocrinologists (23%; percentages total 99% because of rounding).
The results showed “significant gaps in knowledge about whom to screen and how to diagnose and treat patients at high risk for NASH,” concluded the statement’s authors. Barely more than a third of the respondents knew that almost all patients with severe obesity likely have NAFLD, and fewer than half the endocrinologists and the primary care physicians appreciated that NAFLD is very common among patients with type 2 diabetes.
‘Understanding of NAFLD is not there’
“I applaud this effort that calls attention to an emerging public health problem. This paper and survey are great ideas. The findings are not surprising, but they’re important,” said Dr. Diehl said in an interview. “Much more needs to be done” including changes in social behavior and government policies.
“The public’s understanding of NAFLD is not there,” and many physicians also have an incomplete understanding of NAFLD and more serious stages of metabolic liver disease. “Physicians know that patients with obesity are at risk for heart disease, diabetes, and stroke, but they may not always be aware that these patients can also have cirrhosis,” noted Dr. Diehl, who published in 2019 a call to action for NAFLD of her own with some associates.
“My referrals are fueled by primary care physicians who recognize patients with significant liver disease. It would be great to outline recommended practice; I have no doubt that providers will embrace this,” as well as the broader concept of multidisciplinary teams, another focus of the statement. Dr. Diehl cited the “Cancer Center model,” where an oncologist takes primary responsibility for caring for a cancer patient while coordinating care with other specialists, an approach facilitated by EMRs that allow seamless data and chart sharing and something that many health systems have either already adopted or are moving toward.
She said the NASH Call to Action may help catalyze broader application of this model to many more patients with NAFLD or NASH, and noted that some U.S. centers already use this approach – including Dr. Diehl’s program at Duke – which brings together her gastroenterology colleagues with cardiologists, radiologists, endocrinologists, and bariatric surgeons. But she noted that for most patients with metabolic liver disease, the hub clinician needs to be a PCP, especially for patients with earlier-stage disease, because the number of affected patients is so huge.
“Key steps toward establishing such teams include establishing protocols for risk stratification and referral, definition of roles and responsibilities, and buy-in from institutions and payers. Clearly a lot of work needs to occur to get to these multidisciplinary teams,” said Dr. Kanwal.
Ralph A. DeFronzo, MD, professor and deputy director of the Texas Diabetes Institute at UT Health San Antonio, who was not involved with the conference or statement, had a different take on what the future of NASH and NAFLD care may look like.
“Endocrinologists, hepatologists, and obesity experts will work within their individual specialties to diagnose and manage NASH,” he said in an interview. But he acknowledged that “an integrated effort by specialists would be important” to help “primary care physicians who are less familiar with the disease.”
Controversy over pioglitazone?
Dr. DeFronzo endorsed development of clinical care pathways as “important,” but also as a potential source of “controversy, especially with respect to treatment.”
The Call to Action statement cites lifestyle-based therapies, such as an appropriate diet; regular, moderate exercise; and elimination when possible of obesogenic medications as cornerstone interventions for patients with NAFLD or early-stage NASH, interventions that can be prescribed by PCPs. For patients with NASH and stage 2 or worse fibrosis, the statement endorses liver-directed pharmacotherapy. While noting that no agents currently carry a Food and Drug Administration–approved indication for treating NASH, the statement cites evidence that 800 IU/day of vitamin E improves steatosis in patients with NASH but not type 2 diabetes.
For patients with type 2 diabetes, the statement notes that results from five randomized trials indicated that pioglitazone could reverse steatohepatitis, findings that led to its recommendation in guidelines from a modest circle of medical groups, including the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases and the European Association for the Study of Diabetes. However, the 2021 Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes from the American Diabetes Association gives these agents limited endorsement, saying: “Pioglitazone, vitamin E treatment, and liraglutide treatment of biopsy-proven nonalcoholic steatohepatitis have each been shown to improve liver histology, but effects on longer-term clinical outcomes are not known.”
“The strongest evidence by far is for pioglitazone for treating NAFLD and NASH,” said Dr. DeFronzo, a vocal proponent of the drug for this indication. But he added that “hepatologists don’t feel comfortable with drugs from the thiazolidinedione class,” which includes pioglitazone.
“We don’t yet know how to optimally configure the health system for NAFLD and NASH to make it more efficient and helpful to patients, but models exist, and the approach is evolving,” said Dr. Diehl.
Dr. Diehl and Dr. Kanwal had no relevant disclosures. Dr. DeFronzo has been a speaker on behalf of AstraZeneca and Novo Nordisk, has been an adviser to AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Intarcia, and Janssen, and has received research funding from AstraZeneca, Janssen and Merck.
A multidisciplinary panel of U.S. experts released a “Call to Action” for improved screening, diagnosis, and treatment of patients with nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) on July 26, an effort organized by the American Gastroenterological Association in collaboration with seven other U.S. medical organizations including several endocrinology groups.
The published statement, “Preparing for the NASH Epidemic: A Call to Action,” proposes several urgent steps for the U.S. clinical community to provide better-focused and better-coordinated care for patients at risk for developing or having NAFLD or NASH, particularly among “emerging” at-risk cohorts such as patients with diabetes and obesity. It appears in the journals Gastroenterology, Diabetes Care, Metabolism: Clinical and Experimental, and Obesity.
The statement’s central pitch is that improvements in care won’t be possible unless the several medical specialties that deal with affected or at-risk patients stop working “in separate silos,” and instead create “a collective action plan,” and also organize multidisciplinary teams that “integrate primary care, hepatology, obesity medicine, endocrinology, and diabetology via well-defined care pathways.”
“The overarching goal” is a “unified, international public health response to NAFLD and NASH,” said the statement, which stemmed from a conference held in July 2020 that included representatives from not only the lead gastroenterology group but also the American Diabetes Association, the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases, the American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists, The Endocrine Society, The American Academy of Family Physicians, The Obesity Society, and the American College of Osteopathic Family Physicians.
The statement cites sobering prevalence numbers, with estimates that NAFLD exists in more than half the patients with type 2 diabetes, while NASH affects about a third, rates that translate into many millions of affected Americans, given recent estimates that the U.S. prevalence of type 2 diabetes exceeds 30 million people. And the numbers continue to rise along with increases in the prevalence of obesity and type 2 diabetes.
“It’s an enormously common disease, and there are not enough gastroenterologists, to say nothing of hepatologists, to care for every patient with NAFLD,” said Anna Mae Diehl, MD, a gastroenterologist and professor at Duke University in Durham, N.C., who was not involved with the conference nor in writing the statement.
Clinical care pathways coming soon
Another key part of this initiative is development of clinical care pathways that will have “careful explication of each step in screening, diagnosis, and treatment,” and will be designed to inform the practice of primary care physicians (PCPs) as well as clinicians from the various specialties that deal with these patients.
The clinical care pathways are on track to come out later in 2021, said Fasiha Kanwal, MD, a professor and chief of gastroenterology at Baylor College of Medicine in Houston, and lead author on the Call to Action document.
“The Pathways will include practical recommendations about whom to screen and when to refer, and the criteria primary care physicians can use for diagnosis and risk stratification,” Dr. Kanwal said in an interview. “Patients can benefit from a standardized approach.”
The new document also includes results from a recent survey about NAFLD and NASH management completed by 751 U.S. physicians, including 401 (53%) primary care physicians, 175 gastroenterologists, (23%) and 175 endocrinologists (23%; percentages total 99% because of rounding).
The results showed “significant gaps in knowledge about whom to screen and how to diagnose and treat patients at high risk for NASH,” concluded the statement’s authors. Barely more than a third of the respondents knew that almost all patients with severe obesity likely have NAFLD, and fewer than half the endocrinologists and the primary care physicians appreciated that NAFLD is very common among patients with type 2 diabetes.
‘Understanding of NAFLD is not there’
“I applaud this effort that calls attention to an emerging public health problem. This paper and survey are great ideas. The findings are not surprising, but they’re important,” said Dr. Diehl said in an interview. “Much more needs to be done” including changes in social behavior and government policies.
“The public’s understanding of NAFLD is not there,” and many physicians also have an incomplete understanding of NAFLD and more serious stages of metabolic liver disease. “Physicians know that patients with obesity are at risk for heart disease, diabetes, and stroke, but they may not always be aware that these patients can also have cirrhosis,” noted Dr. Diehl, who published in 2019 a call to action for NAFLD of her own with some associates.
“My referrals are fueled by primary care physicians who recognize patients with significant liver disease. It would be great to outline recommended practice; I have no doubt that providers will embrace this,” as well as the broader concept of multidisciplinary teams, another focus of the statement. Dr. Diehl cited the “Cancer Center model,” where an oncologist takes primary responsibility for caring for a cancer patient while coordinating care with other specialists, an approach facilitated by EMRs that allow seamless data and chart sharing and something that many health systems have either already adopted or are moving toward.
She said the NASH Call to Action may help catalyze broader application of this model to many more patients with NAFLD or NASH, and noted that some U.S. centers already use this approach – including Dr. Diehl’s program at Duke – which brings together her gastroenterology colleagues with cardiologists, radiologists, endocrinologists, and bariatric surgeons. But she noted that for most patients with metabolic liver disease, the hub clinician needs to be a PCP, especially for patients with earlier-stage disease, because the number of affected patients is so huge.
“Key steps toward establishing such teams include establishing protocols for risk stratification and referral, definition of roles and responsibilities, and buy-in from institutions and payers. Clearly a lot of work needs to occur to get to these multidisciplinary teams,” said Dr. Kanwal.
Ralph A. DeFronzo, MD, professor and deputy director of the Texas Diabetes Institute at UT Health San Antonio, who was not involved with the conference or statement, had a different take on what the future of NASH and NAFLD care may look like.
“Endocrinologists, hepatologists, and obesity experts will work within their individual specialties to diagnose and manage NASH,” he said in an interview. But he acknowledged that “an integrated effort by specialists would be important” to help “primary care physicians who are less familiar with the disease.”
Controversy over pioglitazone?
Dr. DeFronzo endorsed development of clinical care pathways as “important,” but also as a potential source of “controversy, especially with respect to treatment.”
The Call to Action statement cites lifestyle-based therapies, such as an appropriate diet; regular, moderate exercise; and elimination when possible of obesogenic medications as cornerstone interventions for patients with NAFLD or early-stage NASH, interventions that can be prescribed by PCPs. For patients with NASH and stage 2 or worse fibrosis, the statement endorses liver-directed pharmacotherapy. While noting that no agents currently carry a Food and Drug Administration–approved indication for treating NASH, the statement cites evidence that 800 IU/day of vitamin E improves steatosis in patients with NASH but not type 2 diabetes.
For patients with type 2 diabetes, the statement notes that results from five randomized trials indicated that pioglitazone could reverse steatohepatitis, findings that led to its recommendation in guidelines from a modest circle of medical groups, including the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases and the European Association for the Study of Diabetes. However, the 2021 Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes from the American Diabetes Association gives these agents limited endorsement, saying: “Pioglitazone, vitamin E treatment, and liraglutide treatment of biopsy-proven nonalcoholic steatohepatitis have each been shown to improve liver histology, but effects on longer-term clinical outcomes are not known.”
“The strongest evidence by far is for pioglitazone for treating NAFLD and NASH,” said Dr. DeFronzo, a vocal proponent of the drug for this indication. But he added that “hepatologists don’t feel comfortable with drugs from the thiazolidinedione class,” which includes pioglitazone.
“We don’t yet know how to optimally configure the health system for NAFLD and NASH to make it more efficient and helpful to patients, but models exist, and the approach is evolving,” said Dr. Diehl.
Dr. Diehl and Dr. Kanwal had no relevant disclosures. Dr. DeFronzo has been a speaker on behalf of AstraZeneca and Novo Nordisk, has been an adviser to AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Intarcia, and Janssen, and has received research funding from AstraZeneca, Janssen and Merck.
A multidisciplinary panel of U.S. experts released a “Call to Action” for improved screening, diagnosis, and treatment of patients with nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) on July 26, an effort organized by the American Gastroenterological Association in collaboration with seven other U.S. medical organizations including several endocrinology groups.
The published statement, “Preparing for the NASH Epidemic: A Call to Action,” proposes several urgent steps for the U.S. clinical community to provide better-focused and better-coordinated care for patients at risk for developing or having NAFLD or NASH, particularly among “emerging” at-risk cohorts such as patients with diabetes and obesity. It appears in the journals Gastroenterology, Diabetes Care, Metabolism: Clinical and Experimental, and Obesity.
The statement’s central pitch is that improvements in care won’t be possible unless the several medical specialties that deal with affected or at-risk patients stop working “in separate silos,” and instead create “a collective action plan,” and also organize multidisciplinary teams that “integrate primary care, hepatology, obesity medicine, endocrinology, and diabetology via well-defined care pathways.”
“The overarching goal” is a “unified, international public health response to NAFLD and NASH,” said the statement, which stemmed from a conference held in July 2020 that included representatives from not only the lead gastroenterology group but also the American Diabetes Association, the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases, the American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists, The Endocrine Society, The American Academy of Family Physicians, The Obesity Society, and the American College of Osteopathic Family Physicians.
The statement cites sobering prevalence numbers, with estimates that NAFLD exists in more than half the patients with type 2 diabetes, while NASH affects about a third, rates that translate into many millions of affected Americans, given recent estimates that the U.S. prevalence of type 2 diabetes exceeds 30 million people. And the numbers continue to rise along with increases in the prevalence of obesity and type 2 diabetes.
“It’s an enormously common disease, and there are not enough gastroenterologists, to say nothing of hepatologists, to care for every patient with NAFLD,” said Anna Mae Diehl, MD, a gastroenterologist and professor at Duke University in Durham, N.C., who was not involved with the conference nor in writing the statement.
Clinical care pathways coming soon
Another key part of this initiative is development of clinical care pathways that will have “careful explication of each step in screening, diagnosis, and treatment,” and will be designed to inform the practice of primary care physicians (PCPs) as well as clinicians from the various specialties that deal with these patients.
The clinical care pathways are on track to come out later in 2021, said Fasiha Kanwal, MD, a professor and chief of gastroenterology at Baylor College of Medicine in Houston, and lead author on the Call to Action document.
“The Pathways will include practical recommendations about whom to screen and when to refer, and the criteria primary care physicians can use for diagnosis and risk stratification,” Dr. Kanwal said in an interview. “Patients can benefit from a standardized approach.”
The new document also includes results from a recent survey about NAFLD and NASH management completed by 751 U.S. physicians, including 401 (53%) primary care physicians, 175 gastroenterologists, (23%) and 175 endocrinologists (23%; percentages total 99% because of rounding).
The results showed “significant gaps in knowledge about whom to screen and how to diagnose and treat patients at high risk for NASH,” concluded the statement’s authors. Barely more than a third of the respondents knew that almost all patients with severe obesity likely have NAFLD, and fewer than half the endocrinologists and the primary care physicians appreciated that NAFLD is very common among patients with type 2 diabetes.
‘Understanding of NAFLD is not there’
“I applaud this effort that calls attention to an emerging public health problem. This paper and survey are great ideas. The findings are not surprising, but they’re important,” said Dr. Diehl said in an interview. “Much more needs to be done” including changes in social behavior and government policies.
“The public’s understanding of NAFLD is not there,” and many physicians also have an incomplete understanding of NAFLD and more serious stages of metabolic liver disease. “Physicians know that patients with obesity are at risk for heart disease, diabetes, and stroke, but they may not always be aware that these patients can also have cirrhosis,” noted Dr. Diehl, who published in 2019 a call to action for NAFLD of her own with some associates.
“My referrals are fueled by primary care physicians who recognize patients with significant liver disease. It would be great to outline recommended practice; I have no doubt that providers will embrace this,” as well as the broader concept of multidisciplinary teams, another focus of the statement. Dr. Diehl cited the “Cancer Center model,” where an oncologist takes primary responsibility for caring for a cancer patient while coordinating care with other specialists, an approach facilitated by EMRs that allow seamless data and chart sharing and something that many health systems have either already adopted or are moving toward.
She said the NASH Call to Action may help catalyze broader application of this model to many more patients with NAFLD or NASH, and noted that some U.S. centers already use this approach – including Dr. Diehl’s program at Duke – which brings together her gastroenterology colleagues with cardiologists, radiologists, endocrinologists, and bariatric surgeons. But she noted that for most patients with metabolic liver disease, the hub clinician needs to be a PCP, especially for patients with earlier-stage disease, because the number of affected patients is so huge.
“Key steps toward establishing such teams include establishing protocols for risk stratification and referral, definition of roles and responsibilities, and buy-in from institutions and payers. Clearly a lot of work needs to occur to get to these multidisciplinary teams,” said Dr. Kanwal.
Ralph A. DeFronzo, MD, professor and deputy director of the Texas Diabetes Institute at UT Health San Antonio, who was not involved with the conference or statement, had a different take on what the future of NASH and NAFLD care may look like.
“Endocrinologists, hepatologists, and obesity experts will work within their individual specialties to diagnose and manage NASH,” he said in an interview. But he acknowledged that “an integrated effort by specialists would be important” to help “primary care physicians who are less familiar with the disease.”
Controversy over pioglitazone?
Dr. DeFronzo endorsed development of clinical care pathways as “important,” but also as a potential source of “controversy, especially with respect to treatment.”
The Call to Action statement cites lifestyle-based therapies, such as an appropriate diet; regular, moderate exercise; and elimination when possible of obesogenic medications as cornerstone interventions for patients with NAFLD or early-stage NASH, interventions that can be prescribed by PCPs. For patients with NASH and stage 2 or worse fibrosis, the statement endorses liver-directed pharmacotherapy. While noting that no agents currently carry a Food and Drug Administration–approved indication for treating NASH, the statement cites evidence that 800 IU/day of vitamin E improves steatosis in patients with NASH but not type 2 diabetes.
For patients with type 2 diabetes, the statement notes that results from five randomized trials indicated that pioglitazone could reverse steatohepatitis, findings that led to its recommendation in guidelines from a modest circle of medical groups, including the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases and the European Association for the Study of Diabetes. However, the 2021 Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes from the American Diabetes Association gives these agents limited endorsement, saying: “Pioglitazone, vitamin E treatment, and liraglutide treatment of biopsy-proven nonalcoholic steatohepatitis have each been shown to improve liver histology, but effects on longer-term clinical outcomes are not known.”
“The strongest evidence by far is for pioglitazone for treating NAFLD and NASH,” said Dr. DeFronzo, a vocal proponent of the drug for this indication. But he added that “hepatologists don’t feel comfortable with drugs from the thiazolidinedione class,” which includes pioglitazone.
“We don’t yet know how to optimally configure the health system for NAFLD and NASH to make it more efficient and helpful to patients, but models exist, and the approach is evolving,” said Dr. Diehl.
Dr. Diehl and Dr. Kanwal had no relevant disclosures. Dr. DeFronzo has been a speaker on behalf of AstraZeneca and Novo Nordisk, has been an adviser to AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Intarcia, and Janssen, and has received research funding from AstraZeneca, Janssen and Merck.
‘Wild West’ and weak evidence for weight-loss supplements
“Purported” weight-loss products –12 dietary supplements and 2 alternative therapies – lack high-quality evidence to back up claims of efficacy, a systematic review by the Obesity Society reports.
Most of the more than 300 published randomized controlled trials in the review were small and short, and only 0.5% found a statistically significant weight loss of up to 5 kg, John A. Batsis, MD, from the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, and colleagues reported in the journal Obesity.
“Despite the poor quality of these studies with high degrees of bias, most still failed to show efficacy of the product they were testing,” Srividya Kidambi, MD, from the Medical College of Wisconsin, Milwaukee, and colleagues from the Obesity Society’s Clinical Committee pointed out in an accompanying commentary.
“Yet these are the studies that are often used to support manufacturers’ claims of ‘clinically proven’ in their marketing,” they noted.
Most consumers, they continued, are unaware that these nondrug weight-loss products are not regulated by the Food and Drug Administration, but rather, if their ingredients are “generally regarded as safe,” they are treated as dietary supplements and require little or no testing to show either efficacy or safety.
“Our patients need to become aware that dietary supplements for weight loss are nothing more than a pipe dream, and as clinicians we would do well to talk with our patients and help steer them toward science-based treatments rather than the ‘Wild West’ of dietary supplements that are marketed for weight loss,” Scott Kahan, MD, MPH, coauthor of the review and commentary, told this news organization.
The dietary supplement industry has a strong lobby against legislation for more rigorous requirements for claims, noted Dr. Kahan, of the National Center for Weight and Wellness as well as George Washington University, Washington.
However, “there has to be some level of protection for consumers” who are faced with ads by “healthy skinny people saying this [product] can change your life.”
Clinical providers need to guide patients to “evidence-based interventions to support weight loss such as behavioral weight-loss interventions, [FDA-approved] medications, or bariatric surgery,” said Dr. Batsis, who also coauthored the commentary.
There is a “critical need” for more rigorous trials, and a partnership between researchers, funders, and industry, he added.
According to Dr. Kidambi and colleagues, “the use of these products will continue as long as they are allowed to be marketed with the aforementioned limited federal oversight and there is a lack of access to evidence-based obesity treatments.”
The commentary authors “call on regulatory authorities to critically examine the dietary supplement industry, including their role in promoting misleading claims and marketing products that have the potential to harm patients.”
They also urged public and private health insurance plans to “provide adequate resources for obesity management.”
And clinicians should “consider the lack of evidence for non–FDA-approved dietary supplements and therapies and guide their patients toward tested weight-management approaches.”
Subpar evidence, booming industry
“Annual sales of dietary supplements for weight loss are booming with an industry valued at $30 billion worldwide, despite subpar evidence” of efficacy, the commentary authors wrote by way of background.
After the Dietary Supplement Health and Education Act of 1994, the National Institutes of Health’s Office of Dietary Supplements was established “to strengthen the knowledge and understanding of dietary supplements by evaluating scientific information, stimulating and supporting research, and educating the public,” they explained.
However, dietary supplements and alternative therapies are endorsed by influencers and celebrities and marketed as a panacea for obesity and weight gain.
Literature review finds scant evidence
Consumers may believe that the “clinically proven” claims of efficacy of these “natural” weight-loss treatments have been thoroughly evaluated for safety and efficacy by the FDA, and clinicians lack information to counsel patients about this.
Therefore, although the Office of Dietary Supplements’ work has importantly advanced the science, the review authors wrote, members of the Obesity Society believed it was important to evaluate and perform a qualitative synthesis of the evidence for efficacy of non–FDA-regulated weight-loss supplements and alternative therapies to better inform clinicians and consumers.
From more than 20,000 citations of 53 dietary supplements and alternative therapies promoted for weight loss, the researchers identified 314 randomized controlled trials of 14 products that each had at least 5 randomized controlled trials.
The two types of alternative therapies in the review were mind-body interventions – which included behavioral therapies (for example, mindfulness and stress management), hypnosis, meditation, or massage – and acupuncture.
Several popular and widely used products (for example, human chorionic gonadotropin, raspberry ketones, nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide, vitamin infusions) did not meet the predefined number of published randomized controlled trials to be eligible for inclusion in the review.
The greatest number of trials were for acupuncture (45 trials), green tea (38), conjugated linoleic acid (31), ephedra with or without caffeine (31), mind-body therapies (22), and calcium and vitamin D (22). There were fewer trials of garcinia and/or hydroxycitrate (15), chitosan (9), phaseolus (7), pyruvate (7), chocolate/cocoa (6), chromium (6), guar gum (5), and phenylpropylamine (5).
Of the 314 studies, only 52 studies (16.5%) demonstrated that the products were efficacious and low risk, and only 16 studies (0.5%) reported a statistically significant between-group weight loss (0.3-4.93 kg).
For more information, in addition to their review and commentary, the authors refer clinicians to a dietary supplement label database.
The study was supported in part by grants from the National Institute on Aging. Dr. Batsis reported equity in SynchroHealth. Dr. Kidambi reported being the medical director for TOPS Center for Metabolic Health at the Medical College of Wisconsin, which is supported by TOPS. Dr. Kahan reported serving as a consultant for Novo Nordisk, Vivus, Gelesis, and Pfizer.
“Purported” weight-loss products –12 dietary supplements and 2 alternative therapies – lack high-quality evidence to back up claims of efficacy, a systematic review by the Obesity Society reports.
Most of the more than 300 published randomized controlled trials in the review were small and short, and only 0.5% found a statistically significant weight loss of up to 5 kg, John A. Batsis, MD, from the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, and colleagues reported in the journal Obesity.
“Despite the poor quality of these studies with high degrees of bias, most still failed to show efficacy of the product they were testing,” Srividya Kidambi, MD, from the Medical College of Wisconsin, Milwaukee, and colleagues from the Obesity Society’s Clinical Committee pointed out in an accompanying commentary.
“Yet these are the studies that are often used to support manufacturers’ claims of ‘clinically proven’ in their marketing,” they noted.
Most consumers, they continued, are unaware that these nondrug weight-loss products are not regulated by the Food and Drug Administration, but rather, if their ingredients are “generally regarded as safe,” they are treated as dietary supplements and require little or no testing to show either efficacy or safety.
“Our patients need to become aware that dietary supplements for weight loss are nothing more than a pipe dream, and as clinicians we would do well to talk with our patients and help steer them toward science-based treatments rather than the ‘Wild West’ of dietary supplements that are marketed for weight loss,” Scott Kahan, MD, MPH, coauthor of the review and commentary, told this news organization.
The dietary supplement industry has a strong lobby against legislation for more rigorous requirements for claims, noted Dr. Kahan, of the National Center for Weight and Wellness as well as George Washington University, Washington.
However, “there has to be some level of protection for consumers” who are faced with ads by “healthy skinny people saying this [product] can change your life.”
Clinical providers need to guide patients to “evidence-based interventions to support weight loss such as behavioral weight-loss interventions, [FDA-approved] medications, or bariatric surgery,” said Dr. Batsis, who also coauthored the commentary.
There is a “critical need” for more rigorous trials, and a partnership between researchers, funders, and industry, he added.
According to Dr. Kidambi and colleagues, “the use of these products will continue as long as they are allowed to be marketed with the aforementioned limited federal oversight and there is a lack of access to evidence-based obesity treatments.”
The commentary authors “call on regulatory authorities to critically examine the dietary supplement industry, including their role in promoting misleading claims and marketing products that have the potential to harm patients.”
They also urged public and private health insurance plans to “provide adequate resources for obesity management.”
And clinicians should “consider the lack of evidence for non–FDA-approved dietary supplements and therapies and guide their patients toward tested weight-management approaches.”
Subpar evidence, booming industry
“Annual sales of dietary supplements for weight loss are booming with an industry valued at $30 billion worldwide, despite subpar evidence” of efficacy, the commentary authors wrote by way of background.
After the Dietary Supplement Health and Education Act of 1994, the National Institutes of Health’s Office of Dietary Supplements was established “to strengthen the knowledge and understanding of dietary supplements by evaluating scientific information, stimulating and supporting research, and educating the public,” they explained.
However, dietary supplements and alternative therapies are endorsed by influencers and celebrities and marketed as a panacea for obesity and weight gain.
Literature review finds scant evidence
Consumers may believe that the “clinically proven” claims of efficacy of these “natural” weight-loss treatments have been thoroughly evaluated for safety and efficacy by the FDA, and clinicians lack information to counsel patients about this.
Therefore, although the Office of Dietary Supplements’ work has importantly advanced the science, the review authors wrote, members of the Obesity Society believed it was important to evaluate and perform a qualitative synthesis of the evidence for efficacy of non–FDA-regulated weight-loss supplements and alternative therapies to better inform clinicians and consumers.
From more than 20,000 citations of 53 dietary supplements and alternative therapies promoted for weight loss, the researchers identified 314 randomized controlled trials of 14 products that each had at least 5 randomized controlled trials.
The two types of alternative therapies in the review were mind-body interventions – which included behavioral therapies (for example, mindfulness and stress management), hypnosis, meditation, or massage – and acupuncture.
Several popular and widely used products (for example, human chorionic gonadotropin, raspberry ketones, nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide, vitamin infusions) did not meet the predefined number of published randomized controlled trials to be eligible for inclusion in the review.
The greatest number of trials were for acupuncture (45 trials), green tea (38), conjugated linoleic acid (31), ephedra with or without caffeine (31), mind-body therapies (22), and calcium and vitamin D (22). There were fewer trials of garcinia and/or hydroxycitrate (15), chitosan (9), phaseolus (7), pyruvate (7), chocolate/cocoa (6), chromium (6), guar gum (5), and phenylpropylamine (5).
Of the 314 studies, only 52 studies (16.5%) demonstrated that the products were efficacious and low risk, and only 16 studies (0.5%) reported a statistically significant between-group weight loss (0.3-4.93 kg).
For more information, in addition to their review and commentary, the authors refer clinicians to a dietary supplement label database.
The study was supported in part by grants from the National Institute on Aging. Dr. Batsis reported equity in SynchroHealth. Dr. Kidambi reported being the medical director for TOPS Center for Metabolic Health at the Medical College of Wisconsin, which is supported by TOPS. Dr. Kahan reported serving as a consultant for Novo Nordisk, Vivus, Gelesis, and Pfizer.
“Purported” weight-loss products –12 dietary supplements and 2 alternative therapies – lack high-quality evidence to back up claims of efficacy, a systematic review by the Obesity Society reports.
Most of the more than 300 published randomized controlled trials in the review were small and short, and only 0.5% found a statistically significant weight loss of up to 5 kg, John A. Batsis, MD, from the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, and colleagues reported in the journal Obesity.
“Despite the poor quality of these studies with high degrees of bias, most still failed to show efficacy of the product they were testing,” Srividya Kidambi, MD, from the Medical College of Wisconsin, Milwaukee, and colleagues from the Obesity Society’s Clinical Committee pointed out in an accompanying commentary.
“Yet these are the studies that are often used to support manufacturers’ claims of ‘clinically proven’ in their marketing,” they noted.
Most consumers, they continued, are unaware that these nondrug weight-loss products are not regulated by the Food and Drug Administration, but rather, if their ingredients are “generally regarded as safe,” they are treated as dietary supplements and require little or no testing to show either efficacy or safety.
“Our patients need to become aware that dietary supplements for weight loss are nothing more than a pipe dream, and as clinicians we would do well to talk with our patients and help steer them toward science-based treatments rather than the ‘Wild West’ of dietary supplements that are marketed for weight loss,” Scott Kahan, MD, MPH, coauthor of the review and commentary, told this news organization.
The dietary supplement industry has a strong lobby against legislation for more rigorous requirements for claims, noted Dr. Kahan, of the National Center for Weight and Wellness as well as George Washington University, Washington.
However, “there has to be some level of protection for consumers” who are faced with ads by “healthy skinny people saying this [product] can change your life.”
Clinical providers need to guide patients to “evidence-based interventions to support weight loss such as behavioral weight-loss interventions, [FDA-approved] medications, or bariatric surgery,” said Dr. Batsis, who also coauthored the commentary.
There is a “critical need” for more rigorous trials, and a partnership between researchers, funders, and industry, he added.
According to Dr. Kidambi and colleagues, “the use of these products will continue as long as they are allowed to be marketed with the aforementioned limited federal oversight and there is a lack of access to evidence-based obesity treatments.”
The commentary authors “call on regulatory authorities to critically examine the dietary supplement industry, including their role in promoting misleading claims and marketing products that have the potential to harm patients.”
They also urged public and private health insurance plans to “provide adequate resources for obesity management.”
And clinicians should “consider the lack of evidence for non–FDA-approved dietary supplements and therapies and guide their patients toward tested weight-management approaches.”
Subpar evidence, booming industry
“Annual sales of dietary supplements for weight loss are booming with an industry valued at $30 billion worldwide, despite subpar evidence” of efficacy, the commentary authors wrote by way of background.
After the Dietary Supplement Health and Education Act of 1994, the National Institutes of Health’s Office of Dietary Supplements was established “to strengthen the knowledge and understanding of dietary supplements by evaluating scientific information, stimulating and supporting research, and educating the public,” they explained.
However, dietary supplements and alternative therapies are endorsed by influencers and celebrities and marketed as a panacea for obesity and weight gain.
Literature review finds scant evidence
Consumers may believe that the “clinically proven” claims of efficacy of these “natural” weight-loss treatments have been thoroughly evaluated for safety and efficacy by the FDA, and clinicians lack information to counsel patients about this.
Therefore, although the Office of Dietary Supplements’ work has importantly advanced the science, the review authors wrote, members of the Obesity Society believed it was important to evaluate and perform a qualitative synthesis of the evidence for efficacy of non–FDA-regulated weight-loss supplements and alternative therapies to better inform clinicians and consumers.
From more than 20,000 citations of 53 dietary supplements and alternative therapies promoted for weight loss, the researchers identified 314 randomized controlled trials of 14 products that each had at least 5 randomized controlled trials.
The two types of alternative therapies in the review were mind-body interventions – which included behavioral therapies (for example, mindfulness and stress management), hypnosis, meditation, or massage – and acupuncture.
Several popular and widely used products (for example, human chorionic gonadotropin, raspberry ketones, nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide, vitamin infusions) did not meet the predefined number of published randomized controlled trials to be eligible for inclusion in the review.
The greatest number of trials were for acupuncture (45 trials), green tea (38), conjugated linoleic acid (31), ephedra with or without caffeine (31), mind-body therapies (22), and calcium and vitamin D (22). There were fewer trials of garcinia and/or hydroxycitrate (15), chitosan (9), phaseolus (7), pyruvate (7), chocolate/cocoa (6), chromium (6), guar gum (5), and phenylpropylamine (5).
Of the 314 studies, only 52 studies (16.5%) demonstrated that the products were efficacious and low risk, and only 16 studies (0.5%) reported a statistically significant between-group weight loss (0.3-4.93 kg).
For more information, in addition to their review and commentary, the authors refer clinicians to a dietary supplement label database.
The study was supported in part by grants from the National Institute on Aging. Dr. Batsis reported equity in SynchroHealth. Dr. Kidambi reported being the medical director for TOPS Center for Metabolic Health at the Medical College of Wisconsin, which is supported by TOPS. Dr. Kahan reported serving as a consultant for Novo Nordisk, Vivus, Gelesis, and Pfizer.
FROM OBESITY
Prescribe an SGLT2 inhibitor for heart failure in the absence of diabetes?
ILLUSTRATIVE CASE
A 64-year-old overweight White man with a history of hypertension, hyperlipidemia, and HF with an ejection fraction (EF) of 40% presents for primary care follow-up after a recent inpatient admission for worsened HF symptoms. At baseline, he is comfortable at rest but becomes dyspneic upon walking to another room within his home. He is already taking a mineralocorticoid receptor antagonist, a high-intensity statin, a beta-blocker, and an angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitor. What other medication should be considered to minimize his cardiovascular (CV)risk?
An estimated 1% to 2% of the world’s adult population has HF.2 Although the exact prevalence is difficult to quantify due to variations in definitions and diagnostic methods, the American Heart Association (AHA) estimated that 6.2 million Americans had HF between 2013 and 2016.3 Prevalence increases with age, with an annual incidence of approximately 35 per 1000 by age 85.4 Due to the significant morbidity and mortality associated with HF, advancements in treatment are needed.
SGLT2 inhibitors work within the proximal tubule of the kidneys, resulting in increased glucose and sodium excretion with secondary osmotic diuresis and therefore a modest reduction in serum glucose.1,2,5,6 SGLT2 inhibitors are classically prescribed for hyperglycemia treatment in type 2 diabetes. However, preliminary data suggest that this class of medication also positively impacts cardiac function. The diuresis and natriuresis effects of SGLT2 inhibitors appear to optimize cardiac output and subsequent oxygen consumption through a reduction of afterload and preload.1,2,5,6 Further, SGLT2 inhibitors may decrease inflammatory pathways and lead to a secondary reduction of cardiac remodeling via a reduction and modulation of inflammatory pathways. This reduction and modulation may also be associated with a reduction in development, and possibly a reversal, of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, cardiac fibrosis, and atherosclerosis.5,6 Some of the previously reported adverse effects of SGLT2 inhibitors include urinary tract infection, acute kidney injury, lower extremity amputation, bone fracture, and diabetic ketoacidosis.2
In several studies of patients with type 2 diabetes, SGLT2 inhibitors have shown benefit in reducing CV disease–related death and hospitalization for HF.1,2,5,6 A recent expert consensus from the American College of Cardiology (ACC) states that SGLT2 therapy should be considered for any patient with type 2 diabetes who also has established atherosclerotic CV disease, HF (a clinical syndrome as defined in ACC/AHA guidelines), or diabetic kidney disease, or who is at a high risk for atherosclerotic CV disease (ie, has signs of end-organ damage, such as left ventricular hypertrophy or retinopathy, or multiple risk factors such as advanced age, smoking, hypertension, and family history).7,8
Additionally, a 2019 randomized controlled trial (RCT) by Nassif et al showed that, compared to placebo, dapagliflozin significantly improved both patient-reported HF symptoms and cardiac natriuretic peptide levels over 12 weeks in patients with and without diabetes.9 In September 2020, UpToDate added SGLT2 inhibitors as an option for patients with continued symptoms of HF despite use of appropriate primary agents and mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists, whether or not they have type 2 diabetes; this update was based on 2 studies, 1 of which is reviewed here.10
STUDY SUMMARY
Dapagliflozin demonstrated better CV outcomes than placebo
The Dapagliflozin and Prevention of Adverse Outcomes in Heart Failure (DAPA-HF) study is an RCT that compared dapagliflozin to placebo among 4744 patients ages 18 years and older who had HF with an EF ≤ 40% and NYHA class II, III, or IV symptoms. The study included patients with (41.8%) and without diabetes. Most patients were male (76.2%-77%), White (70%), and European (44.7%-46.1%).
Patients were randomized to receive either dapagliflozin 10 mg/d or a matching placebo in addition to standard HF therapy (including an ACE inhibitor, angiotensin receptor blocker, or sacubitril-valsartan plus a beta-blocker unless contraindicated; mineralocorticoid antagonist use was encouraged). Follow-up occurred at 14 days, 60 days, 4 months, and then every 4 months, for an average of about 18 months. Patients with diabetes continued to use their glucose-lowering therapies, with dose adjustments, as needed.
Continue to: The primary outcome...
The primary outcome was a composite of worsening HF (hospitalization or urgent visit requiring intravenous HF therapy) or death from a CV cause. Secondary outcomes included a composite of hospitalization for HF or CV death; total number of hospitalizations for HF (including repeat admissions) and CV death; a change in Kansas City Cardiomyopathy Questionnaire symptom score; a composite of worsening renal function including a sustained (≥ 28 d) decline in the estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) of ≥ 50%, end-stage renal disease (defined as sustained eGFR of < 15 mL/min/1.73 m2, sustained dialysis, or renal transplantation), or renal death; and death from any cause.
The primary outcome of worsening HF or death from CV causes occurred in 386 of 2373 patients (16.3%) in the dapagliflozin group and in 502 of 2371 patients (21.2%) in the placebo group (hazard ratio [HR] = 0.74; 95% CI, 0.65-0.85; P < .001). The composite score of hospitalizations for HF plus death from a CV cause was lower in the dapagliflozin group compared to the placebo group (HR = 0.75; 95% CI, 0.65-0.85; P < .001).
A total of 276 patients (11.6%) in the dapagliflozin group and 329 patients (13.9%) in the placebo group died from any cause (HR = 0.83; 95% CI, 0.71-0.97). More patients in the dapagliflozin group than in the placebo group had an improvement in symptom score (58.3% vs 50.9%; odds ratio = 1.15; 95% CI, 1.08-1.23; P < .001). Renal composite outcome did not differ between the 2 treatment groups. Potential adverse effects included volume depletion, renal adverse event, and major hypoglycemia, which occurred at the same rate in the treatment and placebo groups. There was no difference in outcomes or adverse effects between patients with and without diabetes.1
WHAT'S NEW
Evidence supports dapagliflozin use in a new patient population
The DAPA-HF study compared dapagliflozin to placebo in HF patients both with and without diabetes and demonstrated decreased HF exacerbations and CV deaths, improved patient-reported HF symptoms, and lower all-cause mortality in the treatment group. This study supports use of dapagliflozin in a new patient population—those with HF—rather than solely in patients with diabetes, as the drug was originally marketed.
CAVEATS
Specific study population may limit generalizability
The DAPA-HF study included mostly male, White, European patients followed for an average of 18.2 months as part of initial Phase III studies funded by AstraZeneca (the pharmaceutical company that developed dapagliflozin). Given the potential conflict due to funding, all statistical results were verified by an independent academic group, and analyses were completed with an intention-to-treat model. The outlined benefits described here were only studied in a population of patients with reduced EF (≤ 40%), so the impact remains unclear for patients with preserved EF. Safety and benefits beyond 24 months were not studied in this RCT; therefore long-term data are still unknown.
Continue to: CHALLENGES TO IMPLEMENTATION
CHALLENGES TO IMPLEMENTATION
Adding an SGLT2 inhibitor may be cost prohibitive for some patients
An SGLT2 inhibitor costs, on average, $500 to $600 for a 30-day supply, which may be prohibitive for some patients.11 Integration of SGLT2 inhibitors into a patient’s medication regimen may require dose adjustments of other medications, particularly glucose-lowering therapies, and the optimal prioritization of medications is not yet known.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
The PURLs Surveillance System was supported in part by Grant Number UL1RR024999 from the National Center for Research Resources, a Clinical Translational Science Award to the University of Chicago. The content is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily represent the official views of the National Center for Research Resources or the National Institutes of Health.
1. McMurray JJV, Solomon SD, Inzucchi SE, et al. Dapagliflozin in patients with heart failure and reduced ejection fraction. N Engl J Med. 2019;381:1995-2008. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1911303
2. Lytvyn Y, Bjornstad P, Udell JA, et al. Sodium glucose cotransporter-2 inhibition in heart failure: potential mechanisms, clinical applications, and summary of clinical trials. Circulation. 2017;136:1643-1658. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.117.030012
3. Virani SS, Alonso A, Benjamin EJ, et al. Heart disease and stroke statistics—2020 update: a report from the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2020;141:e139-e596. doi: 10.1161/CIR.0000000000000757
4. Lloyd-Jones DM, Larson MG, Leip EP, et al. Lifetime risk for developing congestive heart failure: the Framingham Heart Study. Circulation. 2002;106:3068-3072. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.0000039105.49749.6f
5. Ghosh RK, Ghosh GC, Gupta M, et al. Sodium glucose co-transporter 2 inhibitors and heart failure. Am J Cardiol. 2019;124:1790-1796. doi: 10.1016/j.amjcard.2019.08.038
6. Verma S, McMurray JJV. SGLT2 inhibitors and mechanisms of cardiovascular benefit: a state-of-the-art review. Diabetologia. 2018;61:2108-2117. doi: 10.1007/s00125-018-4670-7
7. Das SR, Everett BM, Birtcher KK, et al. 2020 expert consensus decision pathway on novel therapies for cardiovascular risk reduction in patients with type 2 diabetes: a report of the American College of Cardiology Solution Set Oversight Committee. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2020;76:1117-1145. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2020.05.037
8. Yancy CW, Jessup M, Bozkurt B, et al. 2013 ACCF/AHA guideline for the management of heart failure: a report of the American College of Cardiology Foundation/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines. Circulation. 2013;128:e240-e327. doi: 10.1161/CIR.0b013e31829e8776
9. Nassif ME, Windsor SL, Tang F, et al. Dapagliflozin effects on biomarkers, symptoms, and functional status in patients with heart failure with reduced ejection fraction: The DEFINE-HF Trial. Circulation. 2019;140:1463-1476. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.119.042929
10. Colucci WS. Secondary pharmacologic therapy in heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF) in adults. UpToDate. Published October 9, 2020. Accessed June 23, 2021. www.uptodate.com/contents/secondary-pharmacologic-therapy-in-heart-failure-with-reduced-ejection-fraction-hfref-in-adults
11. Dapagliflozin. GoodRx. Accessed June 23, 2021. www.goodrx.com/dapagliflozin
ILLUSTRATIVE CASE
A 64-year-old overweight White man with a history of hypertension, hyperlipidemia, and HF with an ejection fraction (EF) of 40% presents for primary care follow-up after a recent inpatient admission for worsened HF symptoms. At baseline, he is comfortable at rest but becomes dyspneic upon walking to another room within his home. He is already taking a mineralocorticoid receptor antagonist, a high-intensity statin, a beta-blocker, and an angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitor. What other medication should be considered to minimize his cardiovascular (CV)risk?
An estimated 1% to 2% of the world’s adult population has HF.2 Although the exact prevalence is difficult to quantify due to variations in definitions and diagnostic methods, the American Heart Association (AHA) estimated that 6.2 million Americans had HF between 2013 and 2016.3 Prevalence increases with age, with an annual incidence of approximately 35 per 1000 by age 85.4 Due to the significant morbidity and mortality associated with HF, advancements in treatment are needed.
SGLT2 inhibitors work within the proximal tubule of the kidneys, resulting in increased glucose and sodium excretion with secondary osmotic diuresis and therefore a modest reduction in serum glucose.1,2,5,6 SGLT2 inhibitors are classically prescribed for hyperglycemia treatment in type 2 diabetes. However, preliminary data suggest that this class of medication also positively impacts cardiac function. The diuresis and natriuresis effects of SGLT2 inhibitors appear to optimize cardiac output and subsequent oxygen consumption through a reduction of afterload and preload.1,2,5,6 Further, SGLT2 inhibitors may decrease inflammatory pathways and lead to a secondary reduction of cardiac remodeling via a reduction and modulation of inflammatory pathways. This reduction and modulation may also be associated with a reduction in development, and possibly a reversal, of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, cardiac fibrosis, and atherosclerosis.5,6 Some of the previously reported adverse effects of SGLT2 inhibitors include urinary tract infection, acute kidney injury, lower extremity amputation, bone fracture, and diabetic ketoacidosis.2
In several studies of patients with type 2 diabetes, SGLT2 inhibitors have shown benefit in reducing CV disease–related death and hospitalization for HF.1,2,5,6 A recent expert consensus from the American College of Cardiology (ACC) states that SGLT2 therapy should be considered for any patient with type 2 diabetes who also has established atherosclerotic CV disease, HF (a clinical syndrome as defined in ACC/AHA guidelines), or diabetic kidney disease, or who is at a high risk for atherosclerotic CV disease (ie, has signs of end-organ damage, such as left ventricular hypertrophy or retinopathy, or multiple risk factors such as advanced age, smoking, hypertension, and family history).7,8
Additionally, a 2019 randomized controlled trial (RCT) by Nassif et al showed that, compared to placebo, dapagliflozin significantly improved both patient-reported HF symptoms and cardiac natriuretic peptide levels over 12 weeks in patients with and without diabetes.9 In September 2020, UpToDate added SGLT2 inhibitors as an option for patients with continued symptoms of HF despite use of appropriate primary agents and mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists, whether or not they have type 2 diabetes; this update was based on 2 studies, 1 of which is reviewed here.10
STUDY SUMMARY
Dapagliflozin demonstrated better CV outcomes than placebo
The Dapagliflozin and Prevention of Adverse Outcomes in Heart Failure (DAPA-HF) study is an RCT that compared dapagliflozin to placebo among 4744 patients ages 18 years and older who had HF with an EF ≤ 40% and NYHA class II, III, or IV symptoms. The study included patients with (41.8%) and without diabetes. Most patients were male (76.2%-77%), White (70%), and European (44.7%-46.1%).
Patients were randomized to receive either dapagliflozin 10 mg/d or a matching placebo in addition to standard HF therapy (including an ACE inhibitor, angiotensin receptor blocker, or sacubitril-valsartan plus a beta-blocker unless contraindicated; mineralocorticoid antagonist use was encouraged). Follow-up occurred at 14 days, 60 days, 4 months, and then every 4 months, for an average of about 18 months. Patients with diabetes continued to use their glucose-lowering therapies, with dose adjustments, as needed.
Continue to: The primary outcome...
The primary outcome was a composite of worsening HF (hospitalization or urgent visit requiring intravenous HF therapy) or death from a CV cause. Secondary outcomes included a composite of hospitalization for HF or CV death; total number of hospitalizations for HF (including repeat admissions) and CV death; a change in Kansas City Cardiomyopathy Questionnaire symptom score; a composite of worsening renal function including a sustained (≥ 28 d) decline in the estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) of ≥ 50%, end-stage renal disease (defined as sustained eGFR of < 15 mL/min/1.73 m2, sustained dialysis, or renal transplantation), or renal death; and death from any cause.
The primary outcome of worsening HF or death from CV causes occurred in 386 of 2373 patients (16.3%) in the dapagliflozin group and in 502 of 2371 patients (21.2%) in the placebo group (hazard ratio [HR] = 0.74; 95% CI, 0.65-0.85; P < .001). The composite score of hospitalizations for HF plus death from a CV cause was lower in the dapagliflozin group compared to the placebo group (HR = 0.75; 95% CI, 0.65-0.85; P < .001).
A total of 276 patients (11.6%) in the dapagliflozin group and 329 patients (13.9%) in the placebo group died from any cause (HR = 0.83; 95% CI, 0.71-0.97). More patients in the dapagliflozin group than in the placebo group had an improvement in symptom score (58.3% vs 50.9%; odds ratio = 1.15; 95% CI, 1.08-1.23; P < .001). Renal composite outcome did not differ between the 2 treatment groups. Potential adverse effects included volume depletion, renal adverse event, and major hypoglycemia, which occurred at the same rate in the treatment and placebo groups. There was no difference in outcomes or adverse effects between patients with and without diabetes.1
WHAT'S NEW
Evidence supports dapagliflozin use in a new patient population
The DAPA-HF study compared dapagliflozin to placebo in HF patients both with and without diabetes and demonstrated decreased HF exacerbations and CV deaths, improved patient-reported HF symptoms, and lower all-cause mortality in the treatment group. This study supports use of dapagliflozin in a new patient population—those with HF—rather than solely in patients with diabetes, as the drug was originally marketed.
CAVEATS
Specific study population may limit generalizability
The DAPA-HF study included mostly male, White, European patients followed for an average of 18.2 months as part of initial Phase III studies funded by AstraZeneca (the pharmaceutical company that developed dapagliflozin). Given the potential conflict due to funding, all statistical results were verified by an independent academic group, and analyses were completed with an intention-to-treat model. The outlined benefits described here were only studied in a population of patients with reduced EF (≤ 40%), so the impact remains unclear for patients with preserved EF. Safety and benefits beyond 24 months were not studied in this RCT; therefore long-term data are still unknown.
Continue to: CHALLENGES TO IMPLEMENTATION
CHALLENGES TO IMPLEMENTATION
Adding an SGLT2 inhibitor may be cost prohibitive for some patients
An SGLT2 inhibitor costs, on average, $500 to $600 for a 30-day supply, which may be prohibitive for some patients.11 Integration of SGLT2 inhibitors into a patient’s medication regimen may require dose adjustments of other medications, particularly glucose-lowering therapies, and the optimal prioritization of medications is not yet known.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
The PURLs Surveillance System was supported in part by Grant Number UL1RR024999 from the National Center for Research Resources, a Clinical Translational Science Award to the University of Chicago. The content is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily represent the official views of the National Center for Research Resources or the National Institutes of Health.
ILLUSTRATIVE CASE
A 64-year-old overweight White man with a history of hypertension, hyperlipidemia, and HF with an ejection fraction (EF) of 40% presents for primary care follow-up after a recent inpatient admission for worsened HF symptoms. At baseline, he is comfortable at rest but becomes dyspneic upon walking to another room within his home. He is already taking a mineralocorticoid receptor antagonist, a high-intensity statin, a beta-blocker, and an angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitor. What other medication should be considered to minimize his cardiovascular (CV)risk?
An estimated 1% to 2% of the world’s adult population has HF.2 Although the exact prevalence is difficult to quantify due to variations in definitions and diagnostic methods, the American Heart Association (AHA) estimated that 6.2 million Americans had HF between 2013 and 2016.3 Prevalence increases with age, with an annual incidence of approximately 35 per 1000 by age 85.4 Due to the significant morbidity and mortality associated with HF, advancements in treatment are needed.
SGLT2 inhibitors work within the proximal tubule of the kidneys, resulting in increased glucose and sodium excretion with secondary osmotic diuresis and therefore a modest reduction in serum glucose.1,2,5,6 SGLT2 inhibitors are classically prescribed for hyperglycemia treatment in type 2 diabetes. However, preliminary data suggest that this class of medication also positively impacts cardiac function. The diuresis and natriuresis effects of SGLT2 inhibitors appear to optimize cardiac output and subsequent oxygen consumption through a reduction of afterload and preload.1,2,5,6 Further, SGLT2 inhibitors may decrease inflammatory pathways and lead to a secondary reduction of cardiac remodeling via a reduction and modulation of inflammatory pathways. This reduction and modulation may also be associated with a reduction in development, and possibly a reversal, of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, cardiac fibrosis, and atherosclerosis.5,6 Some of the previously reported adverse effects of SGLT2 inhibitors include urinary tract infection, acute kidney injury, lower extremity amputation, bone fracture, and diabetic ketoacidosis.2
In several studies of patients with type 2 diabetes, SGLT2 inhibitors have shown benefit in reducing CV disease–related death and hospitalization for HF.1,2,5,6 A recent expert consensus from the American College of Cardiology (ACC) states that SGLT2 therapy should be considered for any patient with type 2 diabetes who also has established atherosclerotic CV disease, HF (a clinical syndrome as defined in ACC/AHA guidelines), or diabetic kidney disease, or who is at a high risk for atherosclerotic CV disease (ie, has signs of end-organ damage, such as left ventricular hypertrophy or retinopathy, or multiple risk factors such as advanced age, smoking, hypertension, and family history).7,8
Additionally, a 2019 randomized controlled trial (RCT) by Nassif et al showed that, compared to placebo, dapagliflozin significantly improved both patient-reported HF symptoms and cardiac natriuretic peptide levels over 12 weeks in patients with and without diabetes.9 In September 2020, UpToDate added SGLT2 inhibitors as an option for patients with continued symptoms of HF despite use of appropriate primary agents and mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists, whether or not they have type 2 diabetes; this update was based on 2 studies, 1 of which is reviewed here.10
STUDY SUMMARY
Dapagliflozin demonstrated better CV outcomes than placebo
The Dapagliflozin and Prevention of Adverse Outcomes in Heart Failure (DAPA-HF) study is an RCT that compared dapagliflozin to placebo among 4744 patients ages 18 years and older who had HF with an EF ≤ 40% and NYHA class II, III, or IV symptoms. The study included patients with (41.8%) and without diabetes. Most patients were male (76.2%-77%), White (70%), and European (44.7%-46.1%).
Patients were randomized to receive either dapagliflozin 10 mg/d or a matching placebo in addition to standard HF therapy (including an ACE inhibitor, angiotensin receptor blocker, or sacubitril-valsartan plus a beta-blocker unless contraindicated; mineralocorticoid antagonist use was encouraged). Follow-up occurred at 14 days, 60 days, 4 months, and then every 4 months, for an average of about 18 months. Patients with diabetes continued to use their glucose-lowering therapies, with dose adjustments, as needed.
Continue to: The primary outcome...
The primary outcome was a composite of worsening HF (hospitalization or urgent visit requiring intravenous HF therapy) or death from a CV cause. Secondary outcomes included a composite of hospitalization for HF or CV death; total number of hospitalizations for HF (including repeat admissions) and CV death; a change in Kansas City Cardiomyopathy Questionnaire symptom score; a composite of worsening renal function including a sustained (≥ 28 d) decline in the estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) of ≥ 50%, end-stage renal disease (defined as sustained eGFR of < 15 mL/min/1.73 m2, sustained dialysis, or renal transplantation), or renal death; and death from any cause.
The primary outcome of worsening HF or death from CV causes occurred in 386 of 2373 patients (16.3%) in the dapagliflozin group and in 502 of 2371 patients (21.2%) in the placebo group (hazard ratio [HR] = 0.74; 95% CI, 0.65-0.85; P < .001). The composite score of hospitalizations for HF plus death from a CV cause was lower in the dapagliflozin group compared to the placebo group (HR = 0.75; 95% CI, 0.65-0.85; P < .001).
A total of 276 patients (11.6%) in the dapagliflozin group and 329 patients (13.9%) in the placebo group died from any cause (HR = 0.83; 95% CI, 0.71-0.97). More patients in the dapagliflozin group than in the placebo group had an improvement in symptom score (58.3% vs 50.9%; odds ratio = 1.15; 95% CI, 1.08-1.23; P < .001). Renal composite outcome did not differ between the 2 treatment groups. Potential adverse effects included volume depletion, renal adverse event, and major hypoglycemia, which occurred at the same rate in the treatment and placebo groups. There was no difference in outcomes or adverse effects between patients with and without diabetes.1
WHAT'S NEW
Evidence supports dapagliflozin use in a new patient population
The DAPA-HF study compared dapagliflozin to placebo in HF patients both with and without diabetes and demonstrated decreased HF exacerbations and CV deaths, improved patient-reported HF symptoms, and lower all-cause mortality in the treatment group. This study supports use of dapagliflozin in a new patient population—those with HF—rather than solely in patients with diabetes, as the drug was originally marketed.
CAVEATS
Specific study population may limit generalizability
The DAPA-HF study included mostly male, White, European patients followed for an average of 18.2 months as part of initial Phase III studies funded by AstraZeneca (the pharmaceutical company that developed dapagliflozin). Given the potential conflict due to funding, all statistical results were verified by an independent academic group, and analyses were completed with an intention-to-treat model. The outlined benefits described here were only studied in a population of patients with reduced EF (≤ 40%), so the impact remains unclear for patients with preserved EF. Safety and benefits beyond 24 months were not studied in this RCT; therefore long-term data are still unknown.
Continue to: CHALLENGES TO IMPLEMENTATION
CHALLENGES TO IMPLEMENTATION
Adding an SGLT2 inhibitor may be cost prohibitive for some patients
An SGLT2 inhibitor costs, on average, $500 to $600 for a 30-day supply, which may be prohibitive for some patients.11 Integration of SGLT2 inhibitors into a patient’s medication regimen may require dose adjustments of other medications, particularly glucose-lowering therapies, and the optimal prioritization of medications is not yet known.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
The PURLs Surveillance System was supported in part by Grant Number UL1RR024999 from the National Center for Research Resources, a Clinical Translational Science Award to the University of Chicago. The content is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily represent the official views of the National Center for Research Resources or the National Institutes of Health.
1. McMurray JJV, Solomon SD, Inzucchi SE, et al. Dapagliflozin in patients with heart failure and reduced ejection fraction. N Engl J Med. 2019;381:1995-2008. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1911303
2. Lytvyn Y, Bjornstad P, Udell JA, et al. Sodium glucose cotransporter-2 inhibition in heart failure: potential mechanisms, clinical applications, and summary of clinical trials. Circulation. 2017;136:1643-1658. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.117.030012
3. Virani SS, Alonso A, Benjamin EJ, et al. Heart disease and stroke statistics—2020 update: a report from the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2020;141:e139-e596. doi: 10.1161/CIR.0000000000000757
4. Lloyd-Jones DM, Larson MG, Leip EP, et al. Lifetime risk for developing congestive heart failure: the Framingham Heart Study. Circulation. 2002;106:3068-3072. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.0000039105.49749.6f
5. Ghosh RK, Ghosh GC, Gupta M, et al. Sodium glucose co-transporter 2 inhibitors and heart failure. Am J Cardiol. 2019;124:1790-1796. doi: 10.1016/j.amjcard.2019.08.038
6. Verma S, McMurray JJV. SGLT2 inhibitors and mechanisms of cardiovascular benefit: a state-of-the-art review. Diabetologia. 2018;61:2108-2117. doi: 10.1007/s00125-018-4670-7
7. Das SR, Everett BM, Birtcher KK, et al. 2020 expert consensus decision pathway on novel therapies for cardiovascular risk reduction in patients with type 2 diabetes: a report of the American College of Cardiology Solution Set Oversight Committee. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2020;76:1117-1145. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2020.05.037
8. Yancy CW, Jessup M, Bozkurt B, et al. 2013 ACCF/AHA guideline for the management of heart failure: a report of the American College of Cardiology Foundation/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines. Circulation. 2013;128:e240-e327. doi: 10.1161/CIR.0b013e31829e8776
9. Nassif ME, Windsor SL, Tang F, et al. Dapagliflozin effects on biomarkers, symptoms, and functional status in patients with heart failure with reduced ejection fraction: The DEFINE-HF Trial. Circulation. 2019;140:1463-1476. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.119.042929
10. Colucci WS. Secondary pharmacologic therapy in heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF) in adults. UpToDate. Published October 9, 2020. Accessed June 23, 2021. www.uptodate.com/contents/secondary-pharmacologic-therapy-in-heart-failure-with-reduced-ejection-fraction-hfref-in-adults
11. Dapagliflozin. GoodRx. Accessed June 23, 2021. www.goodrx.com/dapagliflozin
1. McMurray JJV, Solomon SD, Inzucchi SE, et al. Dapagliflozin in patients with heart failure and reduced ejection fraction. N Engl J Med. 2019;381:1995-2008. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1911303
2. Lytvyn Y, Bjornstad P, Udell JA, et al. Sodium glucose cotransporter-2 inhibition in heart failure: potential mechanisms, clinical applications, and summary of clinical trials. Circulation. 2017;136:1643-1658. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.117.030012
3. Virani SS, Alonso A, Benjamin EJ, et al. Heart disease and stroke statistics—2020 update: a report from the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2020;141:e139-e596. doi: 10.1161/CIR.0000000000000757
4. Lloyd-Jones DM, Larson MG, Leip EP, et al. Lifetime risk for developing congestive heart failure: the Framingham Heart Study. Circulation. 2002;106:3068-3072. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.0000039105.49749.6f
5. Ghosh RK, Ghosh GC, Gupta M, et al. Sodium glucose co-transporter 2 inhibitors and heart failure. Am J Cardiol. 2019;124:1790-1796. doi: 10.1016/j.amjcard.2019.08.038
6. Verma S, McMurray JJV. SGLT2 inhibitors and mechanisms of cardiovascular benefit: a state-of-the-art review. Diabetologia. 2018;61:2108-2117. doi: 10.1007/s00125-018-4670-7
7. Das SR, Everett BM, Birtcher KK, et al. 2020 expert consensus decision pathway on novel therapies for cardiovascular risk reduction in patients with type 2 diabetes: a report of the American College of Cardiology Solution Set Oversight Committee. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2020;76:1117-1145. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2020.05.037
8. Yancy CW, Jessup M, Bozkurt B, et al. 2013 ACCF/AHA guideline for the management of heart failure: a report of the American College of Cardiology Foundation/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines. Circulation. 2013;128:e240-e327. doi: 10.1161/CIR.0b013e31829e8776
9. Nassif ME, Windsor SL, Tang F, et al. Dapagliflozin effects on biomarkers, symptoms, and functional status in patients with heart failure with reduced ejection fraction: The DEFINE-HF Trial. Circulation. 2019;140:1463-1476. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.119.042929
10. Colucci WS. Secondary pharmacologic therapy in heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF) in adults. UpToDate. Published October 9, 2020. Accessed June 23, 2021. www.uptodate.com/contents/secondary-pharmacologic-therapy-in-heart-failure-with-reduced-ejection-fraction-hfref-in-adults
11. Dapagliflozin. GoodRx. Accessed June 23, 2021. www.goodrx.com/dapagliflozin
PRACTICE CHANGER
Prescribe dapagliflozin, a sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 (SGLT2) inhibitor, 10 mg/d in addition to standard therapies for adult patients with heart failure (HF) with a reduced ejection fraction (≤ 40%) and New York Heart Association (NYHA) class II or greater, regardless of type 2 diabetes history, due to improved heart failure and cardiovascular outcomes.1
STRENGTH OF RECOMMENDATION
B: Based on a single randomized controlled trial.1
McMurray JJV, Solomon SD, Inzucchi SE, et al. Dapagliflozin in patients with heart failure and reduced ejection fraction. N Engl J Med. 2019;381:1995‐2008.
Transitioning patients with developmental disabilities to adult care
Some adults who have an intellectual or other developmental disability (IDD) require extensive subspecialty care; many, however, depend primarily on their family physician for the bulk of their health care. With that reliance in mind, this article provides (1) an overview of important services that family physicians can provide for their adult patients with IDD and (2) pragmatic clinical suggestions for tailoring that care. Note: We highlight only some high-impact areas of clinical focus; refer to the 2018 Canadian consensus guidelines for a comprehensive approach to optimizing primary care for this population.1
CASE
Laura S, a 24-year-old woman with Down syndrome, is visiting your clinic with her mother to establish care. Ms. S has several medical comorbidities, including type 2 diabetes, hyperlipidemia, repaired congenital heart disease, schizoaffective disorder, and hypothyroidism. She is under the care of multiple specialists, including a cardiologist and an endocrinologist. Her medications include the atypical antipsychotic risperidone, which was prescribed for her through the services of a community mental health center.
Ms. S is due for multiple preventive health screenings. She indicates that she feels nervous today talking about these screenings with a new physician.
First step in care: Proficiency in the lexicon of IDD
Three core concepts of IDD are impairment, disability, and handicap. According to the World Health Organization2:
- impairment “is any loss or abnormality of psychological, physiological, or anatomical structure or function.”
- disability “is any restriction or lack (resulting from an impairment) of ability to perform an activity in the manner or within the range considered normal for a human being.”
- handicap therefore “represents socialization of an impairment or disability, and as such it reflects the consequences for the individual—cultural, social, economic, and environmental—that stem from the presence of impairment and disability.”
Essential transition: Pediatric to adult health care
Health care transition (HCT) is the planned process of transferring care from a pediatric to an adult-based health care setting,3 comprising 3 phases:
- preparation
- transfer from pediatric to adult care
- integration into adult-based care.
Two critical components of a smooth HCT include initiating the transition early in adolescence and providing transition-support resources, which are often lacking, even in large, integrated health systems.4 Got Transition, created by the National Alliance to Advance Adolescent Health, outlines core elements of an organized HCT process (www.gottransition.org) specific to young adults with IDD, including young adults with autism spectrum disorder.5,6
Even young people who are served by a family physician and who intend to remain in that family practice as they age into adulthood require HCT services that include6:
- assessment of readiness to transition to adult care
- update of the medical history
- assessment and promotion of self-care skills
- consent discussions and optimized participation in decision-making
- transition of specialty care from pediatric to adult specialists.
Continue to: For an ideal HCT...
For an ideal HCT, full engagement of the patient, the medical home (physicians, nursing staff, and care coordinators), and the patient’s family (including the primary caregiver or guardian) is critical. In addition to preventive care visits and management of chronic disease, additional domains that require explicit attention in transitioning young people with IDD include health insurance, transportation, employment, and postsecondary education.
Young people who have special health care needs and receive high-quality HCT demonstrate improvements in adherence to care, disease-specific measures, quality of life, self-care skills, satisfaction with care, and health care utilization.7TABLE 13 lists resources identified by Berens and colleagues that are helpful in facilitating the transition.
Teach and practice disability etiquette
Societal prejudice harms people with IDD—leading to self-deprecation, alienation from the larger community, and isolation from others with IDD.8 To promote acceptance and inclusivity in residential communities, the workplace, recreational venues, and clinical settings, disability etiquette should be utilized—a set of guidelines on how to interact with patients with IDD. These include speaking to the patient directly, using clear language in an adult voice, and avoiding stereotypes about people with disabilities.9 The entire health care team, including all front-facing staff (receptionists and care and financial coordinators) and clinical staff (physicians, nurses, medical assistants), need to be educated in, and practice, disability etiquette.
Preparing for in-person visits. Pre-visit preparation, ideally by means of dialogue between health care staff and the patient or caregiver (or both), typically by telephone and in advance of the scheduled visit, is often critical for a successful first face-to-face encounter. (See “Pre-visit telephone questionnaire and script for a new adult patient with IDD,” page 287, which we developed for use in our office practice.) Outcomes of the pre-visit preparation should include identifying:
- words or actions that can trigger anxiety or panic
- de-escalation techniques, such as specific calming words and actions
- strategies for optimal communication, physical access, and physical examination.
SIDEBAR
Pre-visit telephone questionnaire and script for a new adult patient with IDD
Introduction
Hello! My name is ______________. I’m a nurse [or medical assistant] from [name of practice]. I understand that [name of patient] is coming to our office for an appointment on [date and time]. I am calling to prepare our health care team to make this first appointment successful for [name of patient] and you.
- How would [name of patient] prefer to be called?
- Who will be accompanying [name of patient] to the appointment? What parts of the appointment will that person remain for?
Describe what to expect, what the patient or caregiver should bring to the appointment, and how long the appointment will last.
- What makes [name of patient] anxious or fearful so that we might avoid doing that? Should we avoid bringing up certain topics? Should we avoid performing any procedures that are customary during a first appointment?
- Does [name of patient] have sensitivities—to light, sound, touch, etc—that we should be aware of?
Offer to have a room ready upon the patient’s arrival if remaining in the waiting area would cause too much anxiety.
- What helps calm [name of patient]? Are there some topics that put [name of patient] at ease?
- How does [name of patient] best communicate?
- Is there anything else the health care team might do to prepare for the appointment?
- Does [name of patient] need personal protective equipment, a wheelchair, oxygen, or other medical equipment upon arrival?
- What would make for a successful first appointment?
- What strategies or techniques have [name of patient’s] providers used in the past that have helped make health care visits successful?
- Is there anything else you want me to know that we haven’t talked about?
- Would it be helpful if I talked with [name of patient] now about their upcoming appointment?
Initial appointments should focus on building trust and rapport with the health care team and desensitizing the patient to the clinical environment.10 Examination techniques used with pediatric patients can be applied to this population: for example, demonstrating an examination maneuver first on the parent or caregiver; beginning the examination with the least invasive or anxiety-provoking components; and stating what you plan to do next—before you do it.
Continue to: Systematic health checks provide great value
Systematic health checks provide great value
A health check is a systematic and comprehensive health assessment that is provided annually to adults with IDD, and includes:
- specific review of signs and symptoms of health conditions that often co-occur in adults with IDD (TABLE 2Calibri11)
- screening for changes in adaptive functioning and secondary disability
- lifestyle counseling
- medication review and counseling
- immunization update
- discussion of caregiver concerns.
Regarding the last point: Many caregivers are the aging parents of the adult patient with IDD—people who have their own emerging health and support needs. You should initiate conversations about advanced planning for the needs of patients, which often involves engaging siblings and other family members to assume a greater role in caregiving.12
Benefits of the health check. A systematic review of 38 studies, comprising more than 5000 patients with IDD, found that health checks increased the detection of serious conditions, improved screening for sensory impairments, and increased the immunization rate.13 Although many patients with IDD generally understand the need for a periodic health examination, you can enhance their experience by better explaining the rationale for the health check; scheduling sufficient time for the appointment, based on the individual clinical situation; and discussing the value of laboratory testing and referrals to specialists.14
Tailoring preventive care
Many of the preventive services recommendations typically utilized by family physicians, such as guidelines from the US Preventive Services Task Force, have been developed for the general population at average risk of conditions of interest.15 Adults with IDD, depending on the cause of their developmental disability and their behavioral risk profile, might be at significantly higher (or lower) risk of cancer, heart disease, or other conditions than the general population. To address these differences, preventive care guidelines tailored to patients with certain developmental disabilities have been created, including guidelines specific to adults with Down syndrome, fragile X syndrome, Prader-Willi syndrome, Smith-Magenis syndrome, and 22q11.2 deletion (DiGeorge) syndrome.16
Clarifying the molecular genetic etiology of many developmental disabilities has led to more precise understandings about physical and behavioral health issues associated with specific developmental disabilities. For that reason, patients without a known cause for their IDD might benefit from referral to a geneticist—even in early or middle adulthood. Variables generally associated with a higher likelihood of an abnormal genetic test result include17:
- a family history of developmental disability
- a congenital malformation or dysmorphic features
- a dual diagnosis of developmental disability and co-occurring mental illness
- hypotonia
- severe or profound IDD.
Continue to: Successful implementation of preventive health screening tests...
Successful implementation of preventive health screening tests often requires ingenuity and the collective creativity of the patient, family members, staff, and family physician to allay fears and anxieties. Examples: Women who have been advised to undergo screening mammography might feel less anxious by undergoing tandem screening with their sister or mother, and colorectal cancer screening might be more easily accomplished using a fecal DNA test rather than by colonoscopy. Procedural desensitization strategies and preventive care instructional materials targeting people with IDD are posted on YouTube (for example, the “DD CARES Best Practices” series [see www.youtube.com/watch?v=EPJy4zvg4io]) and other websites.
Management of chronic disease
Evidence of health disparities in patients with IDD includes suboptimal management of chronic diseases, such as diabetes18 and hypertension,19 despite contact with a primary care physician. Nonadherence to a medication regimen might be more common in patients who live with their family or in a residential setting where there is a lower degree of supervision—that is, compared to a residence that maintains 24-hour staffing with daily nursing care and supervision. For a patient who is not so closely supervised, reviewing the medication refill history with the pharmacy, or using the so-called brown-bag technique of counting pill bottles brought to appointments, can ensure medication adherence.
CASE
As you interview Ms. S, you note that she is shy, avoids eye contact, and appears generally anxious. You calm her by noticing and complimenting her jewelry and fingernail polish. Ms. S smiles and talks about her favorite polish colors.
Her mother reports that, when Ms. S is stressed, she talks to herself alone in her bedroom. However, you do not observe evidence of schizoaffective disorder, and begin to wonder whether she needs to be taking risperidone.
Essentials of mental health care
It is estimated that one-third of adults with IDD have significant mental and behavioral health care needs.20 Patients with IDD suffer the same psychiatric disorders as the general population; some also engage in problematic behaviors, such as self-injurious actions, physical or verbal aggression (or both), property destruction, and resistance to caregiving assistance.
Continue to: Mental and behavioral health problems...
Mental and behavioral health problems can have a profound impact on the quality of life of patients with IDD, their peers, and their family and other caregivers. If untreated, these problems can lead to premature institutionalization, loss of employment or desired program participation, fractured social relationships, and caregiver withdrawal and burnout.
Initial evaluation of suspected mental and behavioral health problems begins with careful assessment for medical conditions that might be causing pain and distress, stereotypies, and other problematic behaviors. Common sources of pain and discomfort include dental and other oral disease, dysphagia, gastroesophageal reflux disease, gastritis, constipation, allergic disease, headache, musculoskeletal pathology, lower urinary tract disease, and gynecologic disorders.11 Identification and optimal treatment of medical conditions might not eliminate problematic behaviors but often decrease their frequency and intensity.
Psychoactive medications are prescribed for many patients with IDD. Many have behavioral adverse effects, such as akathisia, aggression, and disinhibition—leading to a prescribing cascade of psychoactive medication polypharmacy and escalating dosages.21 Antipsychotic medications are often initiated without a careful diagnosis, explicit outcome targets, or adequate clinical monitoring for effectiveness; in addition, they often lead to insulin resistance, metabolic syndrome, and massive weight gain.21 Even a family physician who is not the prescriber can perform an important advocacy role by critically reviewing psychoactive medications, documenting adverse effects, insisting on a clear therapeutic target, and calling for discontinuation of medications that appear to be ineffective.
Evaluation of mental and behavioral health problems requires a developmental perspective to interpret specific, observable behaviors with a proper clinical lens. For example, many patients with IDD engage in self-talk (soliloquizing) as a means of processing the world around them. This practice might escalate during a time of physical or psychological stress, and the unwary clinician might misinterpret this behavior as psychotic, leading to inappropriate prescribing of antipsychotic medication. Other psychotoform behaviors that, superficially, mimic but are typically not truly psychotic, include talk with or about imaginary friends and repetitive retelling of sometimes elaborate or grandiose tales or assertions. The failure of clinicians to recognize developmentally determined expressions of distress often leads to a misdiagnosis of schizophrenia or other psychotic illness and, consequently, inappropriate psychopharmacotherapy.
Family physicians, familiar with the use of psychiatric scales for diagnosis and treatment monitoring, should use similar scales that have been developed specifically for patients with IDD (TABLE 311). In addition, a psychiatric diagnosis manual, the Diagnostic Manual—Intellectual Disability 2, specific to people with IDD (and analogous to the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, 5th Edition) provides modification of diagnostic criteria to account for patients who have difficulty articulating their internal emotional state and inner thoughts.22
Continue to: Problematic behaviors
Problematic behaviors that are not features of a bona fide psychiatric disorder are often best understood through functional behavioral analysis, which examines antecedents and consequences of problematic behaviors and identifies their predictable outcomes, such as gaining attention, avoiding a task, or securing a desired item. Rather than being given a prescription for psychoactive medication, many adult patients with IDD and problematic behaviors might be best served by having you order consultation with a certified behavior analyst. The analyst will conduct an evaluation and, along with family or residential staff and the patient, craft a behavioral support plan to address core drivers of the undesired behavior. Behavioral support plans might be enriched by multidisciplinary input from a speech and language pathologist, habilitation professionals, occupational and physical therapists, a neuropsychologist, and others.23
Resources to help you address the physical, mental, and behavioral health problems of these patients are available online through Vanderbilt Kennedy Center’s “Toolkit for primary care providers” (https://iddtoolkit.vkcsites.org).
CASE
During your examination, you review Ms. S’s vital signs, including body mass index (BMI). You calculate that she is morbidly obese—BMI, 37—in the setting of a known comorbidity, diabetes.
Ms. S tells you that she is interested in having a healthy lifestyle, but feels frustrated because she does not know how to make the necessary changes. You discuss with her how some medications, including risperidone, can promote weight gain, and that it is important for her mental health provider to carefully reassess whether she needs to continue the drug.
Weight management in a patient population that tends to be sedentary
Patients with IDD are more likely to live a sedentary lifestyle. Compared to adults who do not have IDD, adults with IDD—especially women and patients with Down syndrome—are reported to have a higher prevalence of obesity.24
Continue to: As in the general population...
As in the general population, the greatest success in weight management involves multidisciplinary treatment, including nutritional support, physical activity, behavioral changes, and close follow-up. The importance of such an approach was borne out by the findings of a randomized controlled trial in which a multicomponent intervention—an energy-reduced diet, physical activity, and behavioral sessions—delivered to participants or their caregivers during monthly visits produced clinically meaningful 6-month weight loss.25 Health-promoting behavioral interventions that rely on a dyadic strategy, such as peer health coaches (ie, people with IDD who have been trained as a health coach) or mentors (IDD staff trained as a health coach), might be more successful at changing health behaviors among patients with IDD than traditional office-based, individual patient education and counseling.26
Similarly, undesired weight loss demands careful evaluation and management because such loss can reflect a medically significant condition, such as gastroesophageal reflux, constipation, dysphagia, neglect, and cancer.27
Boosting the amount and effectiveness of physical activity
Young people with IDD participate in physical activity less often than their neurotypical peers; as a result, they tend to be less fit and have a higher prevalence of obesity.28 Based on a meta-analysis, interventions that focus on sport and movement skills training, such as soccer, basketball, and ball-throwing programs, might be more effective than general physical activity programs.28 In addition to year-round sports training and athletic competitions, Special Olympics conducts vital health screenings of athletes and supports community-based initiatives that address bias against patients with IDD, promote inclusion, and foster social relationships (www.specialolympics.org/our-work/inclusive-health?locale=en).
Emphasize regular activity. In adulthood, fewer than 10% of patients with IDD exercise regularly.21 According to the second edition of Physical Activity Guidelines for Americans,29 “all adults, with or without a disability, should get at least 150 minutes of aerobic physical activity a week. Activities can be broken down into smaller amounts, such as about 25 minutes a day every day.”30 Supplementation with muscle-strengthening activities (eg, yoga, weight training, and resistance-band training) provides further health benefit, such as improvement in posture and prevention of future injury.31 An ideal exercise program proposed by Tyler and Baker is based on a daily, “3-2-1” schedule (ie, of every hour of activity, 30 minutes should be of aerobic exercise; 20 minutes, of strength building; and 10 minutes, of flexibility).11 By participating in any type of physical activity, there is potential for considerable health benefit in reducing psychosocial stressors, improving mental health, counteracting metabolic syndromes, and, ultimately, reducing morbidity and mortality related to physical inactivity.
CASE
With permission from Ms. S, you send your progress notes by fax to her mental health provider at the community mental health center and request a call to discuss her case—in particular, to examine potential alternatives to risperidone. With Ms. S’s input, you also co-create an exercise prescription that includes a daily 20-minute walking program with her mother.
At the follow-up visit that is scheduled in 3 months, you anticipate adding a resistance component and balance activity to the exercise prescription to enrich Ms. S’s physical activity regimen.
CORRESPONDENCE
Carl V. Tyler Jr., MD, 14601 Detroit Avenue, Lakewood, OH, 44107; catyle@ccf.org
1. Sullivan WF, Diepstra H, Heng J, et al. Primary care of adults with intellectual and developmental disabilities: 2018 Canadian consensus guidelines. Can Fam Physician. 2018;64:254-279.
2. World Health Organization. International Classification of Impairments, Disabilities, and Handicaps: A Manual of Classification Relating to the Consequences of Disease. May 1980. Accessed May 27, 2021. https://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/handle/10665/41003/9241541261_eng.pdf?sequence=1&isAllowed=y
3. Berens J, Wozow C, Peacock C. Transition to adult care. Phys Med Rehabil Clin N Am. 2020;31:159-170. doi:10.1016/j.pmr.2019.09.004
4. American Academy of Pediatrics; American Academy of Family Physicians; American College of Physicians; Transitions Clinical Report Authoring Group; Cooley WC, Sagerman PJ. Supporting the health care transition from adolescence to adulthood in the medical home. Pediatrics. 2011;128:182-200. doi:10.1542/peds.2011-0969
5. Dressler PB, Nguyen TK, Moody EJ, et al. Use of transition resources by primary care providers for youth with intellectual and developmental disabilities. Intellect Dev Disabil. 2018;56:56-68. doi:10.1352/1934-9556-56.1.56
6. The National Alliance to Advance Adolescent Health. Six Core Elements of Health Care Transition.™ Got Transition website. Accessed May 27, 2021. www.gottransition.org
7. Schmidt A, Ilango SM, McManus MA, et al. Outcomes of pediatric to adult health care transition interventions: an updated systematic review. J Pediatr Nurs. 2020; 51:92-107. doi: 10.1016/j.pedn.2020.01.002
8. Keith JM, Bennetto L, Rogge RD. The relationship between contact and attitudes: reducing prejudice toward individuals with intellectual and developmental disabilities. Res Dev Disabil. 2015;47:14-26. doi:10.1016/j.ridd.2015.07.032
9. United Spinal Association. Disability Etiquette: Tips on Interacting With People With Disabilities. 2015. Accessed June 9, 2021. www.unitedspinal.org/pdf/DisabilityEtiquette.pdf
10. Nathawad R, Hanks C. Optimizing the office visit for adolescents with special health care needs. Curr Probl Pediatr Adolesc Health Care. 2017;47:182-189. doi:10.1016/j.cppeds.2017.07.002
11. Tyler CV, Baker S. Intellectual Disabilities at Your Fingertips: A Health Care Resource. High Tide Press; 2009.
12. Williamson HJ, Perkins EA. Family caregivers of adults with intellectual and developmental disabilities: outcomes associated with U.S. services and supports. Intellect Dev Disabil. 2014;52:147-159. doi: 10.1352/1934-9556-52.2.147
13. Robertson J, Hatton C, Emerson E, et al. The impact of health checks for people with intellectual disabilities: an updated systematic review of evidence. Res Dev Disabil. 2014;35:2450-2462. doi:10.1016/j.ridd.2014.06.007
14. Perry J, Felce D, Kerr M, et al. Contact with primary care: the experience of people with intellectual disabilities. J Appl Res Intellect Disabil. 2014;27:200-211. doi: 10.1111/jar.12072
15. Recommendation topics. United States Preventive Services Task Force website. 2020. Accessed May 27, 2021. www.uspreventiveservicestaskforce.org
16. Developmental Disabilities Primary Care Initiative. Tools for the Primary Care of People with Developmental Disabilities. 1st ed. MUMS Guideline Clearinghouse; 2011.
17. Jang W, Kim Y, Han E, et al. Chromosomal microarray analysis as a first-tier clinical diagnostic test in patients with developmental delay/intellectual disability, autism spectrum disorders, and multiple congenital anomalies: a prospective multicenter study in Korea. Ann Lab Med. 2019;39:299-310. doi:10.3343/alm.2019.39.3.299
18. Shireman TI, Reichard A, Nazir N, et al. Quality of diabetes care for adults with developmental disabilities. Disabil Health J. 2010;3:179-185. doi:10.1016/j.dhjo.2009.10.004
19. Cyrus AC, Royer J, Carroll DD, et al. Anti-hypertensive medication use and actors related to adherence among adults with intellectual and developmental disabilities. Am J Intellect Dev Disabil. 2019;124:248-262. doi:10.1352/1944-7558-124.3.248
20. IDD/MI diagnosis. National Association for the Dually Diagnosed (NADD) website. 2019. Accessed May 27, 2021. https://thenadd.org/idd-mi-diagnosis
21. Matson JL, Mayville EA, Bielecki J, et al. Reliability of the Matson Evaluation of Drug Side Effects Scale (MEDS). Res Dev Disabil. 1998;19:501-506. doi:10.1016/s0891-4222(98)00021-3
22. Fletcher R, Barnhill J, Cooper SA. (2017). Diagnostic Manual-Intellectual Disability: A Textbook of Diagnosis of Mental Disorders in Persons with Intellectual Disability. 2nd ed. National Association for the Dually Diagnosed (NADD); 2017.
23. Marrus N, Hall L. Intellectual disability and language disorder. Child Adolesc Psychiatr Clin N Am. 2017;26:539-554. doi:10.1016/j.chc.2017.03.001
24. Rimmer JH, Yamaki K. Obesity and intellectual disability. Ment Retard Dev Disabil Res Rev. 2006;12;22-7. doi: 10.1002/mrdd.20091
25. Ptomey LT, Saunders RR, Saunders M, et al. Weight management in adults with intellectual and developmental disabilities: a randomized controlled trial of two dietary approaches. J Appl Res Intellect Disabil. 2018;31(suppl 1):82-96. doi:10.1111/jar.12348
26. Marks B, Sisirak J, Magallanes R, et al. Effectiveness of a HealthMessages peer-to-peer program for people with intellectual and developmental disabilities. Intellect Dev Disabil. 2019;57:242-258. doi:10.1352/1934-9556-57.3.242
27. Escudé C. Clinical Pearls in IDD Health care. HRS, Inc; 2020.
28. Kapsal NJ, Dicke T, Morin AJS, et al. Effects of physical activity on the physical and psychosocial health of youth with intellectual disabilities: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Phys Act Health. 2019;16:1187-1195. doi:10.1123/jpah.2018-0675
29. Physical Activity Guidelines for Americans. 2nd ed. US Department of Health and Human Services; 2018. Accessed May 29, 2021. https://health.gov/sites/default/files/2019-09/Physical_Activity_Guidelines_2nd_edition.pdf
30. National Center on Birth Defects and Developmental Disabilities, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Physical activity for people with disability. September 2020. Accessed May 27, 2021. www.cdc.gov/ncbddd/disabilityandhealth/features/physical-activity-for-all.html
31. Introduction to strengthening exercises. National Center on Health, Physical Activity and Disability (NCHPAD). 2020. Accessed May 27, 2021. www.nchpad.org/374/2096/Strengthening~Exercises
Some adults who have an intellectual or other developmental disability (IDD) require extensive subspecialty care; many, however, depend primarily on their family physician for the bulk of their health care. With that reliance in mind, this article provides (1) an overview of important services that family physicians can provide for their adult patients with IDD and (2) pragmatic clinical suggestions for tailoring that care. Note: We highlight only some high-impact areas of clinical focus; refer to the 2018 Canadian consensus guidelines for a comprehensive approach to optimizing primary care for this population.1
CASE
Laura S, a 24-year-old woman with Down syndrome, is visiting your clinic with her mother to establish care. Ms. S has several medical comorbidities, including type 2 diabetes, hyperlipidemia, repaired congenital heart disease, schizoaffective disorder, and hypothyroidism. She is under the care of multiple specialists, including a cardiologist and an endocrinologist. Her medications include the atypical antipsychotic risperidone, which was prescribed for her through the services of a community mental health center.
Ms. S is due for multiple preventive health screenings. She indicates that she feels nervous today talking about these screenings with a new physician.
First step in care: Proficiency in the lexicon of IDD
Three core concepts of IDD are impairment, disability, and handicap. According to the World Health Organization2:
- impairment “is any loss or abnormality of psychological, physiological, or anatomical structure or function.”
- disability “is any restriction or lack (resulting from an impairment) of ability to perform an activity in the manner or within the range considered normal for a human being.”
- handicap therefore “represents socialization of an impairment or disability, and as such it reflects the consequences for the individual—cultural, social, economic, and environmental—that stem from the presence of impairment and disability.”
Essential transition: Pediatric to adult health care
Health care transition (HCT) is the planned process of transferring care from a pediatric to an adult-based health care setting,3 comprising 3 phases:
- preparation
- transfer from pediatric to adult care
- integration into adult-based care.
Two critical components of a smooth HCT include initiating the transition early in adolescence and providing transition-support resources, which are often lacking, even in large, integrated health systems.4 Got Transition, created by the National Alliance to Advance Adolescent Health, outlines core elements of an organized HCT process (www.gottransition.org) specific to young adults with IDD, including young adults with autism spectrum disorder.5,6
Even young people who are served by a family physician and who intend to remain in that family practice as they age into adulthood require HCT services that include6:
- assessment of readiness to transition to adult care
- update of the medical history
- assessment and promotion of self-care skills
- consent discussions and optimized participation in decision-making
- transition of specialty care from pediatric to adult specialists.
Continue to: For an ideal HCT...
For an ideal HCT, full engagement of the patient, the medical home (physicians, nursing staff, and care coordinators), and the patient’s family (including the primary caregiver or guardian) is critical. In addition to preventive care visits and management of chronic disease, additional domains that require explicit attention in transitioning young people with IDD include health insurance, transportation, employment, and postsecondary education.
Young people who have special health care needs and receive high-quality HCT demonstrate improvements in adherence to care, disease-specific measures, quality of life, self-care skills, satisfaction with care, and health care utilization.7TABLE 13 lists resources identified by Berens and colleagues that are helpful in facilitating the transition.
Teach and practice disability etiquette
Societal prejudice harms people with IDD—leading to self-deprecation, alienation from the larger community, and isolation from others with IDD.8 To promote acceptance and inclusivity in residential communities, the workplace, recreational venues, and clinical settings, disability etiquette should be utilized—a set of guidelines on how to interact with patients with IDD. These include speaking to the patient directly, using clear language in an adult voice, and avoiding stereotypes about people with disabilities.9 The entire health care team, including all front-facing staff (receptionists and care and financial coordinators) and clinical staff (physicians, nurses, medical assistants), need to be educated in, and practice, disability etiquette.
Preparing for in-person visits. Pre-visit preparation, ideally by means of dialogue between health care staff and the patient or caregiver (or both), typically by telephone and in advance of the scheduled visit, is often critical for a successful first face-to-face encounter. (See “Pre-visit telephone questionnaire and script for a new adult patient with IDD,” page 287, which we developed for use in our office practice.) Outcomes of the pre-visit preparation should include identifying:
- words or actions that can trigger anxiety or panic
- de-escalation techniques, such as specific calming words and actions
- strategies for optimal communication, physical access, and physical examination.
SIDEBAR
Pre-visit telephone questionnaire and script for a new adult patient with IDD
Introduction
Hello! My name is ______________. I’m a nurse [or medical assistant] from [name of practice]. I understand that [name of patient] is coming to our office for an appointment on [date and time]. I am calling to prepare our health care team to make this first appointment successful for [name of patient] and you.
- How would [name of patient] prefer to be called?
- Who will be accompanying [name of patient] to the appointment? What parts of the appointment will that person remain for?
Describe what to expect, what the patient or caregiver should bring to the appointment, and how long the appointment will last.
- What makes [name of patient] anxious or fearful so that we might avoid doing that? Should we avoid bringing up certain topics? Should we avoid performing any procedures that are customary during a first appointment?
- Does [name of patient] have sensitivities—to light, sound, touch, etc—that we should be aware of?
Offer to have a room ready upon the patient’s arrival if remaining in the waiting area would cause too much anxiety.
- What helps calm [name of patient]? Are there some topics that put [name of patient] at ease?
- How does [name of patient] best communicate?
- Is there anything else the health care team might do to prepare for the appointment?
- Does [name of patient] need personal protective equipment, a wheelchair, oxygen, or other medical equipment upon arrival?
- What would make for a successful first appointment?
- What strategies or techniques have [name of patient’s] providers used in the past that have helped make health care visits successful?
- Is there anything else you want me to know that we haven’t talked about?
- Would it be helpful if I talked with [name of patient] now about their upcoming appointment?
Initial appointments should focus on building trust and rapport with the health care team and desensitizing the patient to the clinical environment.10 Examination techniques used with pediatric patients can be applied to this population: for example, demonstrating an examination maneuver first on the parent or caregiver; beginning the examination with the least invasive or anxiety-provoking components; and stating what you plan to do next—before you do it.
Continue to: Systematic health checks provide great value
Systematic health checks provide great value
A health check is a systematic and comprehensive health assessment that is provided annually to adults with IDD, and includes:
- specific review of signs and symptoms of health conditions that often co-occur in adults with IDD (TABLE 2Calibri11)
- screening for changes in adaptive functioning and secondary disability
- lifestyle counseling
- medication review and counseling
- immunization update
- discussion of caregiver concerns.
Regarding the last point: Many caregivers are the aging parents of the adult patient with IDD—people who have their own emerging health and support needs. You should initiate conversations about advanced planning for the needs of patients, which often involves engaging siblings and other family members to assume a greater role in caregiving.12
Benefits of the health check. A systematic review of 38 studies, comprising more than 5000 patients with IDD, found that health checks increased the detection of serious conditions, improved screening for sensory impairments, and increased the immunization rate.13 Although many patients with IDD generally understand the need for a periodic health examination, you can enhance their experience by better explaining the rationale for the health check; scheduling sufficient time for the appointment, based on the individual clinical situation; and discussing the value of laboratory testing and referrals to specialists.14
Tailoring preventive care
Many of the preventive services recommendations typically utilized by family physicians, such as guidelines from the US Preventive Services Task Force, have been developed for the general population at average risk of conditions of interest.15 Adults with IDD, depending on the cause of their developmental disability and their behavioral risk profile, might be at significantly higher (or lower) risk of cancer, heart disease, or other conditions than the general population. To address these differences, preventive care guidelines tailored to patients with certain developmental disabilities have been created, including guidelines specific to adults with Down syndrome, fragile X syndrome, Prader-Willi syndrome, Smith-Magenis syndrome, and 22q11.2 deletion (DiGeorge) syndrome.16
Clarifying the molecular genetic etiology of many developmental disabilities has led to more precise understandings about physical and behavioral health issues associated with specific developmental disabilities. For that reason, patients without a known cause for their IDD might benefit from referral to a geneticist—even in early or middle adulthood. Variables generally associated with a higher likelihood of an abnormal genetic test result include17:
- a family history of developmental disability
- a congenital malformation or dysmorphic features
- a dual diagnosis of developmental disability and co-occurring mental illness
- hypotonia
- severe or profound IDD.
Continue to: Successful implementation of preventive health screening tests...
Successful implementation of preventive health screening tests often requires ingenuity and the collective creativity of the patient, family members, staff, and family physician to allay fears and anxieties. Examples: Women who have been advised to undergo screening mammography might feel less anxious by undergoing tandem screening with their sister or mother, and colorectal cancer screening might be more easily accomplished using a fecal DNA test rather than by colonoscopy. Procedural desensitization strategies and preventive care instructional materials targeting people with IDD are posted on YouTube (for example, the “DD CARES Best Practices” series [see www.youtube.com/watch?v=EPJy4zvg4io]) and other websites.
Management of chronic disease
Evidence of health disparities in patients with IDD includes suboptimal management of chronic diseases, such as diabetes18 and hypertension,19 despite contact with a primary care physician. Nonadherence to a medication regimen might be more common in patients who live with their family or in a residential setting where there is a lower degree of supervision—that is, compared to a residence that maintains 24-hour staffing with daily nursing care and supervision. For a patient who is not so closely supervised, reviewing the medication refill history with the pharmacy, or using the so-called brown-bag technique of counting pill bottles brought to appointments, can ensure medication adherence.
CASE
As you interview Ms. S, you note that she is shy, avoids eye contact, and appears generally anxious. You calm her by noticing and complimenting her jewelry and fingernail polish. Ms. S smiles and talks about her favorite polish colors.
Her mother reports that, when Ms. S is stressed, she talks to herself alone in her bedroom. However, you do not observe evidence of schizoaffective disorder, and begin to wonder whether she needs to be taking risperidone.
Essentials of mental health care
It is estimated that one-third of adults with IDD have significant mental and behavioral health care needs.20 Patients with IDD suffer the same psychiatric disorders as the general population; some also engage in problematic behaviors, such as self-injurious actions, physical or verbal aggression (or both), property destruction, and resistance to caregiving assistance.
Continue to: Mental and behavioral health problems...
Mental and behavioral health problems can have a profound impact on the quality of life of patients with IDD, their peers, and their family and other caregivers. If untreated, these problems can lead to premature institutionalization, loss of employment or desired program participation, fractured social relationships, and caregiver withdrawal and burnout.
Initial evaluation of suspected mental and behavioral health problems begins with careful assessment for medical conditions that might be causing pain and distress, stereotypies, and other problematic behaviors. Common sources of pain and discomfort include dental and other oral disease, dysphagia, gastroesophageal reflux disease, gastritis, constipation, allergic disease, headache, musculoskeletal pathology, lower urinary tract disease, and gynecologic disorders.11 Identification and optimal treatment of medical conditions might not eliminate problematic behaviors but often decrease their frequency and intensity.
Psychoactive medications are prescribed for many patients with IDD. Many have behavioral adverse effects, such as akathisia, aggression, and disinhibition—leading to a prescribing cascade of psychoactive medication polypharmacy and escalating dosages.21 Antipsychotic medications are often initiated without a careful diagnosis, explicit outcome targets, or adequate clinical monitoring for effectiveness; in addition, they often lead to insulin resistance, metabolic syndrome, and massive weight gain.21 Even a family physician who is not the prescriber can perform an important advocacy role by critically reviewing psychoactive medications, documenting adverse effects, insisting on a clear therapeutic target, and calling for discontinuation of medications that appear to be ineffective.
Evaluation of mental and behavioral health problems requires a developmental perspective to interpret specific, observable behaviors with a proper clinical lens. For example, many patients with IDD engage in self-talk (soliloquizing) as a means of processing the world around them. This practice might escalate during a time of physical or psychological stress, and the unwary clinician might misinterpret this behavior as psychotic, leading to inappropriate prescribing of antipsychotic medication. Other psychotoform behaviors that, superficially, mimic but are typically not truly psychotic, include talk with or about imaginary friends and repetitive retelling of sometimes elaborate or grandiose tales or assertions. The failure of clinicians to recognize developmentally determined expressions of distress often leads to a misdiagnosis of schizophrenia or other psychotic illness and, consequently, inappropriate psychopharmacotherapy.
Family physicians, familiar with the use of psychiatric scales for diagnosis and treatment monitoring, should use similar scales that have been developed specifically for patients with IDD (TABLE 311). In addition, a psychiatric diagnosis manual, the Diagnostic Manual—Intellectual Disability 2, specific to people with IDD (and analogous to the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, 5th Edition) provides modification of diagnostic criteria to account for patients who have difficulty articulating their internal emotional state and inner thoughts.22
Continue to: Problematic behaviors
Problematic behaviors that are not features of a bona fide psychiatric disorder are often best understood through functional behavioral analysis, which examines antecedents and consequences of problematic behaviors and identifies their predictable outcomes, such as gaining attention, avoiding a task, or securing a desired item. Rather than being given a prescription for psychoactive medication, many adult patients with IDD and problematic behaviors might be best served by having you order consultation with a certified behavior analyst. The analyst will conduct an evaluation and, along with family or residential staff and the patient, craft a behavioral support plan to address core drivers of the undesired behavior. Behavioral support plans might be enriched by multidisciplinary input from a speech and language pathologist, habilitation professionals, occupational and physical therapists, a neuropsychologist, and others.23
Resources to help you address the physical, mental, and behavioral health problems of these patients are available online through Vanderbilt Kennedy Center’s “Toolkit for primary care providers” (https://iddtoolkit.vkcsites.org).
CASE
During your examination, you review Ms. S’s vital signs, including body mass index (BMI). You calculate that she is morbidly obese—BMI, 37—in the setting of a known comorbidity, diabetes.
Ms. S tells you that she is interested in having a healthy lifestyle, but feels frustrated because she does not know how to make the necessary changes. You discuss with her how some medications, including risperidone, can promote weight gain, and that it is important for her mental health provider to carefully reassess whether she needs to continue the drug.
Weight management in a patient population that tends to be sedentary
Patients with IDD are more likely to live a sedentary lifestyle. Compared to adults who do not have IDD, adults with IDD—especially women and patients with Down syndrome—are reported to have a higher prevalence of obesity.24
Continue to: As in the general population...
As in the general population, the greatest success in weight management involves multidisciplinary treatment, including nutritional support, physical activity, behavioral changes, and close follow-up. The importance of such an approach was borne out by the findings of a randomized controlled trial in which a multicomponent intervention—an energy-reduced diet, physical activity, and behavioral sessions—delivered to participants or their caregivers during monthly visits produced clinically meaningful 6-month weight loss.25 Health-promoting behavioral interventions that rely on a dyadic strategy, such as peer health coaches (ie, people with IDD who have been trained as a health coach) or mentors (IDD staff trained as a health coach), might be more successful at changing health behaviors among patients with IDD than traditional office-based, individual patient education and counseling.26
Similarly, undesired weight loss demands careful evaluation and management because such loss can reflect a medically significant condition, such as gastroesophageal reflux, constipation, dysphagia, neglect, and cancer.27
Boosting the amount and effectiveness of physical activity
Young people with IDD participate in physical activity less often than their neurotypical peers; as a result, they tend to be less fit and have a higher prevalence of obesity.28 Based on a meta-analysis, interventions that focus on sport and movement skills training, such as soccer, basketball, and ball-throwing programs, might be more effective than general physical activity programs.28 In addition to year-round sports training and athletic competitions, Special Olympics conducts vital health screenings of athletes and supports community-based initiatives that address bias against patients with IDD, promote inclusion, and foster social relationships (www.specialolympics.org/our-work/inclusive-health?locale=en).
Emphasize regular activity. In adulthood, fewer than 10% of patients with IDD exercise regularly.21 According to the second edition of Physical Activity Guidelines for Americans,29 “all adults, with or without a disability, should get at least 150 minutes of aerobic physical activity a week. Activities can be broken down into smaller amounts, such as about 25 minutes a day every day.”30 Supplementation with muscle-strengthening activities (eg, yoga, weight training, and resistance-band training) provides further health benefit, such as improvement in posture and prevention of future injury.31 An ideal exercise program proposed by Tyler and Baker is based on a daily, “3-2-1” schedule (ie, of every hour of activity, 30 minutes should be of aerobic exercise; 20 minutes, of strength building; and 10 minutes, of flexibility).11 By participating in any type of physical activity, there is potential for considerable health benefit in reducing psychosocial stressors, improving mental health, counteracting metabolic syndromes, and, ultimately, reducing morbidity and mortality related to physical inactivity.
CASE
With permission from Ms. S, you send your progress notes by fax to her mental health provider at the community mental health center and request a call to discuss her case—in particular, to examine potential alternatives to risperidone. With Ms. S’s input, you also co-create an exercise prescription that includes a daily 20-minute walking program with her mother.
At the follow-up visit that is scheduled in 3 months, you anticipate adding a resistance component and balance activity to the exercise prescription to enrich Ms. S’s physical activity regimen.
CORRESPONDENCE
Carl V. Tyler Jr., MD, 14601 Detroit Avenue, Lakewood, OH, 44107; catyle@ccf.org
Some adults who have an intellectual or other developmental disability (IDD) require extensive subspecialty care; many, however, depend primarily on their family physician for the bulk of their health care. With that reliance in mind, this article provides (1) an overview of important services that family physicians can provide for their adult patients with IDD and (2) pragmatic clinical suggestions for tailoring that care. Note: We highlight only some high-impact areas of clinical focus; refer to the 2018 Canadian consensus guidelines for a comprehensive approach to optimizing primary care for this population.1
CASE
Laura S, a 24-year-old woman with Down syndrome, is visiting your clinic with her mother to establish care. Ms. S has several medical comorbidities, including type 2 diabetes, hyperlipidemia, repaired congenital heart disease, schizoaffective disorder, and hypothyroidism. She is under the care of multiple specialists, including a cardiologist and an endocrinologist. Her medications include the atypical antipsychotic risperidone, which was prescribed for her through the services of a community mental health center.
Ms. S is due for multiple preventive health screenings. She indicates that she feels nervous today talking about these screenings with a new physician.
First step in care: Proficiency in the lexicon of IDD
Three core concepts of IDD are impairment, disability, and handicap. According to the World Health Organization2:
- impairment “is any loss or abnormality of psychological, physiological, or anatomical structure or function.”
- disability “is any restriction or lack (resulting from an impairment) of ability to perform an activity in the manner or within the range considered normal for a human being.”
- handicap therefore “represents socialization of an impairment or disability, and as such it reflects the consequences for the individual—cultural, social, economic, and environmental—that stem from the presence of impairment and disability.”
Essential transition: Pediatric to adult health care
Health care transition (HCT) is the planned process of transferring care from a pediatric to an adult-based health care setting,3 comprising 3 phases:
- preparation
- transfer from pediatric to adult care
- integration into adult-based care.
Two critical components of a smooth HCT include initiating the transition early in adolescence and providing transition-support resources, which are often lacking, even in large, integrated health systems.4 Got Transition, created by the National Alliance to Advance Adolescent Health, outlines core elements of an organized HCT process (www.gottransition.org) specific to young adults with IDD, including young adults with autism spectrum disorder.5,6
Even young people who are served by a family physician and who intend to remain in that family practice as they age into adulthood require HCT services that include6:
- assessment of readiness to transition to adult care
- update of the medical history
- assessment and promotion of self-care skills
- consent discussions and optimized participation in decision-making
- transition of specialty care from pediatric to adult specialists.
Continue to: For an ideal HCT...
For an ideal HCT, full engagement of the patient, the medical home (physicians, nursing staff, and care coordinators), and the patient’s family (including the primary caregiver or guardian) is critical. In addition to preventive care visits and management of chronic disease, additional domains that require explicit attention in transitioning young people with IDD include health insurance, transportation, employment, and postsecondary education.
Young people who have special health care needs and receive high-quality HCT demonstrate improvements in adherence to care, disease-specific measures, quality of life, self-care skills, satisfaction with care, and health care utilization.7TABLE 13 lists resources identified by Berens and colleagues that are helpful in facilitating the transition.
Teach and practice disability etiquette
Societal prejudice harms people with IDD—leading to self-deprecation, alienation from the larger community, and isolation from others with IDD.8 To promote acceptance and inclusivity in residential communities, the workplace, recreational venues, and clinical settings, disability etiquette should be utilized—a set of guidelines on how to interact with patients with IDD. These include speaking to the patient directly, using clear language in an adult voice, and avoiding stereotypes about people with disabilities.9 The entire health care team, including all front-facing staff (receptionists and care and financial coordinators) and clinical staff (physicians, nurses, medical assistants), need to be educated in, and practice, disability etiquette.
Preparing for in-person visits. Pre-visit preparation, ideally by means of dialogue between health care staff and the patient or caregiver (or both), typically by telephone and in advance of the scheduled visit, is often critical for a successful first face-to-face encounter. (See “Pre-visit telephone questionnaire and script for a new adult patient with IDD,” page 287, which we developed for use in our office practice.) Outcomes of the pre-visit preparation should include identifying:
- words or actions that can trigger anxiety or panic
- de-escalation techniques, such as specific calming words and actions
- strategies for optimal communication, physical access, and physical examination.
SIDEBAR
Pre-visit telephone questionnaire and script for a new adult patient with IDD
Introduction
Hello! My name is ______________. I’m a nurse [or medical assistant] from [name of practice]. I understand that [name of patient] is coming to our office for an appointment on [date and time]. I am calling to prepare our health care team to make this first appointment successful for [name of patient] and you.
- How would [name of patient] prefer to be called?
- Who will be accompanying [name of patient] to the appointment? What parts of the appointment will that person remain for?
Describe what to expect, what the patient or caregiver should bring to the appointment, and how long the appointment will last.
- What makes [name of patient] anxious or fearful so that we might avoid doing that? Should we avoid bringing up certain topics? Should we avoid performing any procedures that are customary during a first appointment?
- Does [name of patient] have sensitivities—to light, sound, touch, etc—that we should be aware of?
Offer to have a room ready upon the patient’s arrival if remaining in the waiting area would cause too much anxiety.
- What helps calm [name of patient]? Are there some topics that put [name of patient] at ease?
- How does [name of patient] best communicate?
- Is there anything else the health care team might do to prepare for the appointment?
- Does [name of patient] need personal protective equipment, a wheelchair, oxygen, or other medical equipment upon arrival?
- What would make for a successful first appointment?
- What strategies or techniques have [name of patient’s] providers used in the past that have helped make health care visits successful?
- Is there anything else you want me to know that we haven’t talked about?
- Would it be helpful if I talked with [name of patient] now about their upcoming appointment?
Initial appointments should focus on building trust and rapport with the health care team and desensitizing the patient to the clinical environment.10 Examination techniques used with pediatric patients can be applied to this population: for example, demonstrating an examination maneuver first on the parent or caregiver; beginning the examination with the least invasive or anxiety-provoking components; and stating what you plan to do next—before you do it.
Continue to: Systematic health checks provide great value
Systematic health checks provide great value
A health check is a systematic and comprehensive health assessment that is provided annually to adults with IDD, and includes:
- specific review of signs and symptoms of health conditions that often co-occur in adults with IDD (TABLE 2Calibri11)
- screening for changes in adaptive functioning and secondary disability
- lifestyle counseling
- medication review and counseling
- immunization update
- discussion of caregiver concerns.
Regarding the last point: Many caregivers are the aging parents of the adult patient with IDD—people who have their own emerging health and support needs. You should initiate conversations about advanced planning for the needs of patients, which often involves engaging siblings and other family members to assume a greater role in caregiving.12
Benefits of the health check. A systematic review of 38 studies, comprising more than 5000 patients with IDD, found that health checks increased the detection of serious conditions, improved screening for sensory impairments, and increased the immunization rate.13 Although many patients with IDD generally understand the need for a periodic health examination, you can enhance their experience by better explaining the rationale for the health check; scheduling sufficient time for the appointment, based on the individual clinical situation; and discussing the value of laboratory testing and referrals to specialists.14
Tailoring preventive care
Many of the preventive services recommendations typically utilized by family physicians, such as guidelines from the US Preventive Services Task Force, have been developed for the general population at average risk of conditions of interest.15 Adults with IDD, depending on the cause of their developmental disability and their behavioral risk profile, might be at significantly higher (or lower) risk of cancer, heart disease, or other conditions than the general population. To address these differences, preventive care guidelines tailored to patients with certain developmental disabilities have been created, including guidelines specific to adults with Down syndrome, fragile X syndrome, Prader-Willi syndrome, Smith-Magenis syndrome, and 22q11.2 deletion (DiGeorge) syndrome.16
Clarifying the molecular genetic etiology of many developmental disabilities has led to more precise understandings about physical and behavioral health issues associated with specific developmental disabilities. For that reason, patients without a known cause for their IDD might benefit from referral to a geneticist—even in early or middle adulthood. Variables generally associated with a higher likelihood of an abnormal genetic test result include17:
- a family history of developmental disability
- a congenital malformation or dysmorphic features
- a dual diagnosis of developmental disability and co-occurring mental illness
- hypotonia
- severe or profound IDD.
Continue to: Successful implementation of preventive health screening tests...
Successful implementation of preventive health screening tests often requires ingenuity and the collective creativity of the patient, family members, staff, and family physician to allay fears and anxieties. Examples: Women who have been advised to undergo screening mammography might feel less anxious by undergoing tandem screening with their sister or mother, and colorectal cancer screening might be more easily accomplished using a fecal DNA test rather than by colonoscopy. Procedural desensitization strategies and preventive care instructional materials targeting people with IDD are posted on YouTube (for example, the “DD CARES Best Practices” series [see www.youtube.com/watch?v=EPJy4zvg4io]) and other websites.
Management of chronic disease
Evidence of health disparities in patients with IDD includes suboptimal management of chronic diseases, such as diabetes18 and hypertension,19 despite contact with a primary care physician. Nonadherence to a medication regimen might be more common in patients who live with their family or in a residential setting where there is a lower degree of supervision—that is, compared to a residence that maintains 24-hour staffing with daily nursing care and supervision. For a patient who is not so closely supervised, reviewing the medication refill history with the pharmacy, or using the so-called brown-bag technique of counting pill bottles brought to appointments, can ensure medication adherence.
CASE
As you interview Ms. S, you note that she is shy, avoids eye contact, and appears generally anxious. You calm her by noticing and complimenting her jewelry and fingernail polish. Ms. S smiles and talks about her favorite polish colors.
Her mother reports that, when Ms. S is stressed, she talks to herself alone in her bedroom. However, you do not observe evidence of schizoaffective disorder, and begin to wonder whether she needs to be taking risperidone.
Essentials of mental health care
It is estimated that one-third of adults with IDD have significant mental and behavioral health care needs.20 Patients with IDD suffer the same psychiatric disorders as the general population; some also engage in problematic behaviors, such as self-injurious actions, physical or verbal aggression (or both), property destruction, and resistance to caregiving assistance.
Continue to: Mental and behavioral health problems...
Mental and behavioral health problems can have a profound impact on the quality of life of patients with IDD, their peers, and their family and other caregivers. If untreated, these problems can lead to premature institutionalization, loss of employment or desired program participation, fractured social relationships, and caregiver withdrawal and burnout.
Initial evaluation of suspected mental and behavioral health problems begins with careful assessment for medical conditions that might be causing pain and distress, stereotypies, and other problematic behaviors. Common sources of pain and discomfort include dental and other oral disease, dysphagia, gastroesophageal reflux disease, gastritis, constipation, allergic disease, headache, musculoskeletal pathology, lower urinary tract disease, and gynecologic disorders.11 Identification and optimal treatment of medical conditions might not eliminate problematic behaviors but often decrease their frequency and intensity.
Psychoactive medications are prescribed for many patients with IDD. Many have behavioral adverse effects, such as akathisia, aggression, and disinhibition—leading to a prescribing cascade of psychoactive medication polypharmacy and escalating dosages.21 Antipsychotic medications are often initiated without a careful diagnosis, explicit outcome targets, or adequate clinical monitoring for effectiveness; in addition, they often lead to insulin resistance, metabolic syndrome, and massive weight gain.21 Even a family physician who is not the prescriber can perform an important advocacy role by critically reviewing psychoactive medications, documenting adverse effects, insisting on a clear therapeutic target, and calling for discontinuation of medications that appear to be ineffective.
Evaluation of mental and behavioral health problems requires a developmental perspective to interpret specific, observable behaviors with a proper clinical lens. For example, many patients with IDD engage in self-talk (soliloquizing) as a means of processing the world around them. This practice might escalate during a time of physical or psychological stress, and the unwary clinician might misinterpret this behavior as psychotic, leading to inappropriate prescribing of antipsychotic medication. Other psychotoform behaviors that, superficially, mimic but are typically not truly psychotic, include talk with or about imaginary friends and repetitive retelling of sometimes elaborate or grandiose tales or assertions. The failure of clinicians to recognize developmentally determined expressions of distress often leads to a misdiagnosis of schizophrenia or other psychotic illness and, consequently, inappropriate psychopharmacotherapy.
Family physicians, familiar with the use of psychiatric scales for diagnosis and treatment monitoring, should use similar scales that have been developed specifically for patients with IDD (TABLE 311). In addition, a psychiatric diagnosis manual, the Diagnostic Manual—Intellectual Disability 2, specific to people with IDD (and analogous to the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, 5th Edition) provides modification of diagnostic criteria to account for patients who have difficulty articulating their internal emotional state and inner thoughts.22
Continue to: Problematic behaviors
Problematic behaviors that are not features of a bona fide psychiatric disorder are often best understood through functional behavioral analysis, which examines antecedents and consequences of problematic behaviors and identifies their predictable outcomes, such as gaining attention, avoiding a task, or securing a desired item. Rather than being given a prescription for psychoactive medication, many adult patients with IDD and problematic behaviors might be best served by having you order consultation with a certified behavior analyst. The analyst will conduct an evaluation and, along with family or residential staff and the patient, craft a behavioral support plan to address core drivers of the undesired behavior. Behavioral support plans might be enriched by multidisciplinary input from a speech and language pathologist, habilitation professionals, occupational and physical therapists, a neuropsychologist, and others.23
Resources to help you address the physical, mental, and behavioral health problems of these patients are available online through Vanderbilt Kennedy Center’s “Toolkit for primary care providers” (https://iddtoolkit.vkcsites.org).
CASE
During your examination, you review Ms. S’s vital signs, including body mass index (BMI). You calculate that she is morbidly obese—BMI, 37—in the setting of a known comorbidity, diabetes.
Ms. S tells you that she is interested in having a healthy lifestyle, but feels frustrated because she does not know how to make the necessary changes. You discuss with her how some medications, including risperidone, can promote weight gain, and that it is important for her mental health provider to carefully reassess whether she needs to continue the drug.
Weight management in a patient population that tends to be sedentary
Patients with IDD are more likely to live a sedentary lifestyle. Compared to adults who do not have IDD, adults with IDD—especially women and patients with Down syndrome—are reported to have a higher prevalence of obesity.24
Continue to: As in the general population...
As in the general population, the greatest success in weight management involves multidisciplinary treatment, including nutritional support, physical activity, behavioral changes, and close follow-up. The importance of such an approach was borne out by the findings of a randomized controlled trial in which a multicomponent intervention—an energy-reduced diet, physical activity, and behavioral sessions—delivered to participants or their caregivers during monthly visits produced clinically meaningful 6-month weight loss.25 Health-promoting behavioral interventions that rely on a dyadic strategy, such as peer health coaches (ie, people with IDD who have been trained as a health coach) or mentors (IDD staff trained as a health coach), might be more successful at changing health behaviors among patients with IDD than traditional office-based, individual patient education and counseling.26
Similarly, undesired weight loss demands careful evaluation and management because such loss can reflect a medically significant condition, such as gastroesophageal reflux, constipation, dysphagia, neglect, and cancer.27
Boosting the amount and effectiveness of physical activity
Young people with IDD participate in physical activity less often than their neurotypical peers; as a result, they tend to be less fit and have a higher prevalence of obesity.28 Based on a meta-analysis, interventions that focus on sport and movement skills training, such as soccer, basketball, and ball-throwing programs, might be more effective than general physical activity programs.28 In addition to year-round sports training and athletic competitions, Special Olympics conducts vital health screenings of athletes and supports community-based initiatives that address bias against patients with IDD, promote inclusion, and foster social relationships (www.specialolympics.org/our-work/inclusive-health?locale=en).
Emphasize regular activity. In adulthood, fewer than 10% of patients with IDD exercise regularly.21 According to the second edition of Physical Activity Guidelines for Americans,29 “all adults, with or without a disability, should get at least 150 minutes of aerobic physical activity a week. Activities can be broken down into smaller amounts, such as about 25 minutes a day every day.”30 Supplementation with muscle-strengthening activities (eg, yoga, weight training, and resistance-band training) provides further health benefit, such as improvement in posture and prevention of future injury.31 An ideal exercise program proposed by Tyler and Baker is based on a daily, “3-2-1” schedule (ie, of every hour of activity, 30 minutes should be of aerobic exercise; 20 minutes, of strength building; and 10 minutes, of flexibility).11 By participating in any type of physical activity, there is potential for considerable health benefit in reducing psychosocial stressors, improving mental health, counteracting metabolic syndromes, and, ultimately, reducing morbidity and mortality related to physical inactivity.
CASE
With permission from Ms. S, you send your progress notes by fax to her mental health provider at the community mental health center and request a call to discuss her case—in particular, to examine potential alternatives to risperidone. With Ms. S’s input, you also co-create an exercise prescription that includes a daily 20-minute walking program with her mother.
At the follow-up visit that is scheduled in 3 months, you anticipate adding a resistance component and balance activity to the exercise prescription to enrich Ms. S’s physical activity regimen.
CORRESPONDENCE
Carl V. Tyler Jr., MD, 14601 Detroit Avenue, Lakewood, OH, 44107; catyle@ccf.org
1. Sullivan WF, Diepstra H, Heng J, et al. Primary care of adults with intellectual and developmental disabilities: 2018 Canadian consensus guidelines. Can Fam Physician. 2018;64:254-279.
2. World Health Organization. International Classification of Impairments, Disabilities, and Handicaps: A Manual of Classification Relating to the Consequences of Disease. May 1980. Accessed May 27, 2021. https://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/handle/10665/41003/9241541261_eng.pdf?sequence=1&isAllowed=y
3. Berens J, Wozow C, Peacock C. Transition to adult care. Phys Med Rehabil Clin N Am. 2020;31:159-170. doi:10.1016/j.pmr.2019.09.004
4. American Academy of Pediatrics; American Academy of Family Physicians; American College of Physicians; Transitions Clinical Report Authoring Group; Cooley WC, Sagerman PJ. Supporting the health care transition from adolescence to adulthood in the medical home. Pediatrics. 2011;128:182-200. doi:10.1542/peds.2011-0969
5. Dressler PB, Nguyen TK, Moody EJ, et al. Use of transition resources by primary care providers for youth with intellectual and developmental disabilities. Intellect Dev Disabil. 2018;56:56-68. doi:10.1352/1934-9556-56.1.56
6. The National Alliance to Advance Adolescent Health. Six Core Elements of Health Care Transition.™ Got Transition website. Accessed May 27, 2021. www.gottransition.org
7. Schmidt A, Ilango SM, McManus MA, et al. Outcomes of pediatric to adult health care transition interventions: an updated systematic review. J Pediatr Nurs. 2020; 51:92-107. doi: 10.1016/j.pedn.2020.01.002
8. Keith JM, Bennetto L, Rogge RD. The relationship between contact and attitudes: reducing prejudice toward individuals with intellectual and developmental disabilities. Res Dev Disabil. 2015;47:14-26. doi:10.1016/j.ridd.2015.07.032
9. United Spinal Association. Disability Etiquette: Tips on Interacting With People With Disabilities. 2015. Accessed June 9, 2021. www.unitedspinal.org/pdf/DisabilityEtiquette.pdf
10. Nathawad R, Hanks C. Optimizing the office visit for adolescents with special health care needs. Curr Probl Pediatr Adolesc Health Care. 2017;47:182-189. doi:10.1016/j.cppeds.2017.07.002
11. Tyler CV, Baker S. Intellectual Disabilities at Your Fingertips: A Health Care Resource. High Tide Press; 2009.
12. Williamson HJ, Perkins EA. Family caregivers of adults with intellectual and developmental disabilities: outcomes associated with U.S. services and supports. Intellect Dev Disabil. 2014;52:147-159. doi: 10.1352/1934-9556-52.2.147
13. Robertson J, Hatton C, Emerson E, et al. The impact of health checks for people with intellectual disabilities: an updated systematic review of evidence. Res Dev Disabil. 2014;35:2450-2462. doi:10.1016/j.ridd.2014.06.007
14. Perry J, Felce D, Kerr M, et al. Contact with primary care: the experience of people with intellectual disabilities. J Appl Res Intellect Disabil. 2014;27:200-211. doi: 10.1111/jar.12072
15. Recommendation topics. United States Preventive Services Task Force website. 2020. Accessed May 27, 2021. www.uspreventiveservicestaskforce.org
16. Developmental Disabilities Primary Care Initiative. Tools for the Primary Care of People with Developmental Disabilities. 1st ed. MUMS Guideline Clearinghouse; 2011.
17. Jang W, Kim Y, Han E, et al. Chromosomal microarray analysis as a first-tier clinical diagnostic test in patients with developmental delay/intellectual disability, autism spectrum disorders, and multiple congenital anomalies: a prospective multicenter study in Korea. Ann Lab Med. 2019;39:299-310. doi:10.3343/alm.2019.39.3.299
18. Shireman TI, Reichard A, Nazir N, et al. Quality of diabetes care for adults with developmental disabilities. Disabil Health J. 2010;3:179-185. doi:10.1016/j.dhjo.2009.10.004
19. Cyrus AC, Royer J, Carroll DD, et al. Anti-hypertensive medication use and actors related to adherence among adults with intellectual and developmental disabilities. Am J Intellect Dev Disabil. 2019;124:248-262. doi:10.1352/1944-7558-124.3.248
20. IDD/MI diagnosis. National Association for the Dually Diagnosed (NADD) website. 2019. Accessed May 27, 2021. https://thenadd.org/idd-mi-diagnosis
21. Matson JL, Mayville EA, Bielecki J, et al. Reliability of the Matson Evaluation of Drug Side Effects Scale (MEDS). Res Dev Disabil. 1998;19:501-506. doi:10.1016/s0891-4222(98)00021-3
22. Fletcher R, Barnhill J, Cooper SA. (2017). Diagnostic Manual-Intellectual Disability: A Textbook of Diagnosis of Mental Disorders in Persons with Intellectual Disability. 2nd ed. National Association for the Dually Diagnosed (NADD); 2017.
23. Marrus N, Hall L. Intellectual disability and language disorder. Child Adolesc Psychiatr Clin N Am. 2017;26:539-554. doi:10.1016/j.chc.2017.03.001
24. Rimmer JH, Yamaki K. Obesity and intellectual disability. Ment Retard Dev Disabil Res Rev. 2006;12;22-7. doi: 10.1002/mrdd.20091
25. Ptomey LT, Saunders RR, Saunders M, et al. Weight management in adults with intellectual and developmental disabilities: a randomized controlled trial of two dietary approaches. J Appl Res Intellect Disabil. 2018;31(suppl 1):82-96. doi:10.1111/jar.12348
26. Marks B, Sisirak J, Magallanes R, et al. Effectiveness of a HealthMessages peer-to-peer program for people with intellectual and developmental disabilities. Intellect Dev Disabil. 2019;57:242-258. doi:10.1352/1934-9556-57.3.242
27. Escudé C. Clinical Pearls in IDD Health care. HRS, Inc; 2020.
28. Kapsal NJ, Dicke T, Morin AJS, et al. Effects of physical activity on the physical and psychosocial health of youth with intellectual disabilities: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Phys Act Health. 2019;16:1187-1195. doi:10.1123/jpah.2018-0675
29. Physical Activity Guidelines for Americans. 2nd ed. US Department of Health and Human Services; 2018. Accessed May 29, 2021. https://health.gov/sites/default/files/2019-09/Physical_Activity_Guidelines_2nd_edition.pdf
30. National Center on Birth Defects and Developmental Disabilities, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Physical activity for people with disability. September 2020. Accessed May 27, 2021. www.cdc.gov/ncbddd/disabilityandhealth/features/physical-activity-for-all.html
31. Introduction to strengthening exercises. National Center on Health, Physical Activity and Disability (NCHPAD). 2020. Accessed May 27, 2021. www.nchpad.org/374/2096/Strengthening~Exercises
1. Sullivan WF, Diepstra H, Heng J, et al. Primary care of adults with intellectual and developmental disabilities: 2018 Canadian consensus guidelines. Can Fam Physician. 2018;64:254-279.
2. World Health Organization. International Classification of Impairments, Disabilities, and Handicaps: A Manual of Classification Relating to the Consequences of Disease. May 1980. Accessed May 27, 2021. https://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/handle/10665/41003/9241541261_eng.pdf?sequence=1&isAllowed=y
3. Berens J, Wozow C, Peacock C. Transition to adult care. Phys Med Rehabil Clin N Am. 2020;31:159-170. doi:10.1016/j.pmr.2019.09.004
4. American Academy of Pediatrics; American Academy of Family Physicians; American College of Physicians; Transitions Clinical Report Authoring Group; Cooley WC, Sagerman PJ. Supporting the health care transition from adolescence to adulthood in the medical home. Pediatrics. 2011;128:182-200. doi:10.1542/peds.2011-0969
5. Dressler PB, Nguyen TK, Moody EJ, et al. Use of transition resources by primary care providers for youth with intellectual and developmental disabilities. Intellect Dev Disabil. 2018;56:56-68. doi:10.1352/1934-9556-56.1.56
6. The National Alliance to Advance Adolescent Health. Six Core Elements of Health Care Transition.™ Got Transition website. Accessed May 27, 2021. www.gottransition.org
7. Schmidt A, Ilango SM, McManus MA, et al. Outcomes of pediatric to adult health care transition interventions: an updated systematic review. J Pediatr Nurs. 2020; 51:92-107. doi: 10.1016/j.pedn.2020.01.002
8. Keith JM, Bennetto L, Rogge RD. The relationship between contact and attitudes: reducing prejudice toward individuals with intellectual and developmental disabilities. Res Dev Disabil. 2015;47:14-26. doi:10.1016/j.ridd.2015.07.032
9. United Spinal Association. Disability Etiquette: Tips on Interacting With People With Disabilities. 2015. Accessed June 9, 2021. www.unitedspinal.org/pdf/DisabilityEtiquette.pdf
10. Nathawad R, Hanks C. Optimizing the office visit for adolescents with special health care needs. Curr Probl Pediatr Adolesc Health Care. 2017;47:182-189. doi:10.1016/j.cppeds.2017.07.002
11. Tyler CV, Baker S. Intellectual Disabilities at Your Fingertips: A Health Care Resource. High Tide Press; 2009.
12. Williamson HJ, Perkins EA. Family caregivers of adults with intellectual and developmental disabilities: outcomes associated with U.S. services and supports. Intellect Dev Disabil. 2014;52:147-159. doi: 10.1352/1934-9556-52.2.147
13. Robertson J, Hatton C, Emerson E, et al. The impact of health checks for people with intellectual disabilities: an updated systematic review of evidence. Res Dev Disabil. 2014;35:2450-2462. doi:10.1016/j.ridd.2014.06.007
14. Perry J, Felce D, Kerr M, et al. Contact with primary care: the experience of people with intellectual disabilities. J Appl Res Intellect Disabil. 2014;27:200-211. doi: 10.1111/jar.12072
15. Recommendation topics. United States Preventive Services Task Force website. 2020. Accessed May 27, 2021. www.uspreventiveservicestaskforce.org
16. Developmental Disabilities Primary Care Initiative. Tools for the Primary Care of People with Developmental Disabilities. 1st ed. MUMS Guideline Clearinghouse; 2011.
17. Jang W, Kim Y, Han E, et al. Chromosomal microarray analysis as a first-tier clinical diagnostic test in patients with developmental delay/intellectual disability, autism spectrum disorders, and multiple congenital anomalies: a prospective multicenter study in Korea. Ann Lab Med. 2019;39:299-310. doi:10.3343/alm.2019.39.3.299
18. Shireman TI, Reichard A, Nazir N, et al. Quality of diabetes care for adults with developmental disabilities. Disabil Health J. 2010;3:179-185. doi:10.1016/j.dhjo.2009.10.004
19. Cyrus AC, Royer J, Carroll DD, et al. Anti-hypertensive medication use and actors related to adherence among adults with intellectual and developmental disabilities. Am J Intellect Dev Disabil. 2019;124:248-262. doi:10.1352/1944-7558-124.3.248
20. IDD/MI diagnosis. National Association for the Dually Diagnosed (NADD) website. 2019. Accessed May 27, 2021. https://thenadd.org/idd-mi-diagnosis
21. Matson JL, Mayville EA, Bielecki J, et al. Reliability of the Matson Evaluation of Drug Side Effects Scale (MEDS). Res Dev Disabil. 1998;19:501-506. doi:10.1016/s0891-4222(98)00021-3
22. Fletcher R, Barnhill J, Cooper SA. (2017). Diagnostic Manual-Intellectual Disability: A Textbook of Diagnosis of Mental Disorders in Persons with Intellectual Disability. 2nd ed. National Association for the Dually Diagnosed (NADD); 2017.
23. Marrus N, Hall L. Intellectual disability and language disorder. Child Adolesc Psychiatr Clin N Am. 2017;26:539-554. doi:10.1016/j.chc.2017.03.001
24. Rimmer JH, Yamaki K. Obesity and intellectual disability. Ment Retard Dev Disabil Res Rev. 2006;12;22-7. doi: 10.1002/mrdd.20091
25. Ptomey LT, Saunders RR, Saunders M, et al. Weight management in adults with intellectual and developmental disabilities: a randomized controlled trial of two dietary approaches. J Appl Res Intellect Disabil. 2018;31(suppl 1):82-96. doi:10.1111/jar.12348
26. Marks B, Sisirak J, Magallanes R, et al. Effectiveness of a HealthMessages peer-to-peer program for people with intellectual and developmental disabilities. Intellect Dev Disabil. 2019;57:242-258. doi:10.1352/1934-9556-57.3.242
27. Escudé C. Clinical Pearls in IDD Health care. HRS, Inc; 2020.
28. Kapsal NJ, Dicke T, Morin AJS, et al. Effects of physical activity on the physical and psychosocial health of youth with intellectual disabilities: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Phys Act Health. 2019;16:1187-1195. doi:10.1123/jpah.2018-0675
29. Physical Activity Guidelines for Americans. 2nd ed. US Department of Health and Human Services; 2018. Accessed May 29, 2021. https://health.gov/sites/default/files/2019-09/Physical_Activity_Guidelines_2nd_edition.pdf
30. National Center on Birth Defects and Developmental Disabilities, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Physical activity for people with disability. September 2020. Accessed May 27, 2021. www.cdc.gov/ncbddd/disabilityandhealth/features/physical-activity-for-all.html
31. Introduction to strengthening exercises. National Center on Health, Physical Activity and Disability (NCHPAD). 2020. Accessed May 27, 2021. www.nchpad.org/374/2096/Strengthening~Exercises
PRACTICE RECOMMENDATIONS
› Provide young people who have an intellectual or other developmental disability (IDD) with a defined, explicit process for making the transition into the adult health care system. A
› Conduct an annual comprehensive, systematic health assessment for patients who have IDD to improve detection of serious conditions and sensory impairments. A
› Encourage young people and adults with IDD to participate in regular physical activity to reduce psychosocial stressors and counteract metabolic syndromes. A
Strength of recommendation (SOR)
A Good-quality patient-oriented evidence
B Inconsistent or limited-quality patient-oriented evidence
C Consensus, usual practice, opinion, disease-oriented evidence, case series
Admissions for eating disorders double in pandemic
Medical admissions for adolescents with restrictive eating disorders more than doubled at one hospital during the first 12 months of the COVID-19 pandemic, relative to the average number of admissions in prior years, a new study shows.
Doctors are seeing similar increases across the United States and in other countries.
Providers and health care systems “may need to rapidly adapt in response to increasing demands for care during the COVID-19 pandemic,” the researchers said in their study, which was published online in Pediatrics.
To assess whether admission patterns among adolescents with restrictive eating disorders changed during the pandemic, Alana K. Otto, MD, MPH, with the division of adolescent medicine at the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, and colleagues reviewed the charts of patients admitted to C.S. Mott Children’s Hospital, also in Ann Arbor.
Their analysis included 297 admissions among 248 patients aged 10-23 years between March 1, 2017, and March 31, 2021. Patients had an average age of about 15 years. Approximately 90% were female, and most had a diagnosis of anorexia nervosa or atypical anorexia nervosa.
Indications for medical admission included physiological instability (for example, heart rate less than 50 beats per minute while awake or blood pressure less than 90/40 mm Hg), electrolyte derangements, and acute medical complications of malnutrition such as syncope. Other possible indications included uncontrolled purging, body mass index less than 75% of the median for age and sex, acute food refusal, and failure of outpatient treatment.
Eating disorder–related admissions per month were stable prior to the pandemic. Admissions then decreased in April 2020, but subsequently increased significantly throughout the study period. In all, there were 125 admissions between April 1, 2020, and March 31, 2021. During the previous 3 years, the average number of admissions per year was 56.
Patients’ insurance status was one factor that differed before and during the pandemic. Prepandemic, about 20% of admissions were for adolescents with public insurance. During the pandemic, however, the proportion with public insurance was approximately 9%, the researchers noted. Other characteristics were generally similar.
The study was retrospective and relatively small and only looked at patients with restrictive eating disorders who were severely ill and admitted for medical stabilization. It does not reflect adolescents with eating disorders in different settings, the authors noted.
Primary care pediatricians should be familiar with indications for medical admission, such as severe bradycardia, as outlined by the Society for Adolescent Health and Medicine, they said.
Consistent trends
Unfortunately, the trend seems consistent across the nation, said Michaela M. Voss, MD, director of the the Eating Disorders Center at Children’s Mercy in Kansas City, Mo. “Our outpatient setting went from availability to get in immediately to a 6-month wait list.”
As in Michigan, Dr. Voss noted a drop in admissions as lockdowns started, followed by a spike in treatment demand that has not let up.
Dr. Voss described two of the more common presentations. In one, parents might note that their child had been getting into healthy eating and exercise before the pandemic and seemed fine. “But then COVID came, the lockdown happened, and they became overly obsessed with those things,” Dr. Voss said.
In the other presentation, kids with anxiety, depression, or OCD who lost access to their usual coping strategies and outlets developed eating disorders during the pandemic. “They focused on one of the few things they could during the lockdown, which was their own body, and then their anxiety, depression, [obsessive-compulsive disorder], and other mental health comorbidities presented as an eating disorder,” Dr. Voss said.
The increasing need for treatment over the course of the pandemic may reflect the time that it has taken for the disorders to develop, as well as the time that it takes parents to recognize the problem.
Not only are doctors seeing more cases, but patients are arriving sicker than usual, Dr. Voss said.
Major medical concerns for patients in starvation mode center on the heart, brain, and bones. In addition, refeeding syndrome poses an extreme risk, Dr. Voss noted.
The Academy for Eating Disorders has created a guide to help doctors recognize and manage risks for patients with eating disorders, which may be useful for primary care providers while they are trying to get a patient into more intensive treatment, Dr. Voss suggested. The American Academy of Pediatrics recently published a clinical report on the identification and management of eating disorders in children and adolescents.
At Johns Hopkins Hospital Children’s Center in Baltimore, “we have seen a pretty remarkable increase in the number of eating disorders in the child and adolescent space since COVID,” said Jennifer Leah Goetz, MD, a psychiatrist and medical director of the child and adolescent inpatient unit. “We have seen increasing numbers of kids presenting for acute medical stabilization and refeeding and for specific treatment for the eating disorder.”
It could be that, for people with a genetic predisposition to eating disorders, a confluence of factors related to the pandemic unmasked it. For example, children may have spent more time looking at themselves on virtual meeting platforms, which could stir lingering body image and appearance-related concerns in those who are vulnerable. And some teens who were not able to participate in athletics as usual started to watch what they eat more closely, Dr. Goetz said.
A treatment bottleneck
Patients with eating disorders “can be quite ill from a psychiatric and general medical perspective,” Dr. Goetz said. “Most psychiatrists are not particularly comfortable with the medical complications, and most internists or pediatricians are not particularly comfortable with the psychiatric complications. You end up with a patient population that can only see a really highly specialized group of individuals for care. And it is a problem. It was a problem before the pandemic, and it has been really exacerbated by what we have been going through with COVID.”
Natalie Muth, MD, MPH, RDN, a pediatrician at Children’s Primary Care Medical Group La Costa in Carlsbad, Calif., has also noticed the increase in eating disorders since COVID.
In-patient colleagues “have longer wait lists and more severe cases than they have ever seen previously,” said Dr. Muth, who chairs the American Academy of Pediatrics Section on Obesity and is an adjunct assistant professor at the University of California, Los Angeles. “In primary care, we are all having to better educate and prepare ourselves for identifying and managing patients with eating disorders.”
That could mean connecting with mental health professionals, registered dietitians, and higher levels of care. But that may be a challenge. “Accessing these resources has been more difficult due to the increasing incidence of eating disorders recently,” Dr. Muth said.
Dr. Voss acknowledged that childhood obesity is another concern for pediatricians. “However, there are appropriate and healthy and safe ways to address that,” she said. A patient with overweight or obesity who loses weight may not be doing so in a healthy way.
Clinicians should wonder if a patient’s weight is decreasing too fast. And they should ask patients questions that could help identify a problem, such as: What are they doing to cause the weight loss? Why do they want to lose the weight?
Dr. Voss added that eating disorders “do not discriminate.” While there may be a perception that all patients with eating disorders are White, upper middle–class females who are thin, “that is not the case,” Dr. Voss said. They “come in all genders, all races, all weight classes, and all ages,” she said, “and we see that variety.”
In general, there may be a need to shift how weight is discussed in clinics and society more broadly, Dr. Goetz said. Weight is an incredibly personal thing, and everyone’s genetics, metabolism, and life circumstances vary. At the same time, body mass index is not necessarily the best measure of a person’s health.
Asking a child, teen, or even an adult to go on a diet is not a benign intervention, Dr. Goetz noted. In addition, dieting is unlikely to help in the long term.
Emerging from lockdown, pressure to lose “COVID pounds” is a dangerous message for people with eating disorders, Dr. Goetz said. It also could be a dangerous message for people without eating disorders. “There are so many more interesting things about each one of us than our weight,” she added.
The study authors, Dr. Voss, Dr. Goetz, and Dr. Muth had no relevant disclosures.
Medical admissions for adolescents with restrictive eating disorders more than doubled at one hospital during the first 12 months of the COVID-19 pandemic, relative to the average number of admissions in prior years, a new study shows.
Doctors are seeing similar increases across the United States and in other countries.
Providers and health care systems “may need to rapidly adapt in response to increasing demands for care during the COVID-19 pandemic,” the researchers said in their study, which was published online in Pediatrics.
To assess whether admission patterns among adolescents with restrictive eating disorders changed during the pandemic, Alana K. Otto, MD, MPH, with the division of adolescent medicine at the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, and colleagues reviewed the charts of patients admitted to C.S. Mott Children’s Hospital, also in Ann Arbor.
Their analysis included 297 admissions among 248 patients aged 10-23 years between March 1, 2017, and March 31, 2021. Patients had an average age of about 15 years. Approximately 90% were female, and most had a diagnosis of anorexia nervosa or atypical anorexia nervosa.
Indications for medical admission included physiological instability (for example, heart rate less than 50 beats per minute while awake or blood pressure less than 90/40 mm Hg), electrolyte derangements, and acute medical complications of malnutrition such as syncope. Other possible indications included uncontrolled purging, body mass index less than 75% of the median for age and sex, acute food refusal, and failure of outpatient treatment.
Eating disorder–related admissions per month were stable prior to the pandemic. Admissions then decreased in April 2020, but subsequently increased significantly throughout the study period. In all, there were 125 admissions between April 1, 2020, and March 31, 2021. During the previous 3 years, the average number of admissions per year was 56.
Patients’ insurance status was one factor that differed before and during the pandemic. Prepandemic, about 20% of admissions were for adolescents with public insurance. During the pandemic, however, the proportion with public insurance was approximately 9%, the researchers noted. Other characteristics were generally similar.
The study was retrospective and relatively small and only looked at patients with restrictive eating disorders who were severely ill and admitted for medical stabilization. It does not reflect adolescents with eating disorders in different settings, the authors noted.
Primary care pediatricians should be familiar with indications for medical admission, such as severe bradycardia, as outlined by the Society for Adolescent Health and Medicine, they said.
Consistent trends
Unfortunately, the trend seems consistent across the nation, said Michaela M. Voss, MD, director of the the Eating Disorders Center at Children’s Mercy in Kansas City, Mo. “Our outpatient setting went from availability to get in immediately to a 6-month wait list.”
As in Michigan, Dr. Voss noted a drop in admissions as lockdowns started, followed by a spike in treatment demand that has not let up.
Dr. Voss described two of the more common presentations. In one, parents might note that their child had been getting into healthy eating and exercise before the pandemic and seemed fine. “But then COVID came, the lockdown happened, and they became overly obsessed with those things,” Dr. Voss said.
In the other presentation, kids with anxiety, depression, or OCD who lost access to their usual coping strategies and outlets developed eating disorders during the pandemic. “They focused on one of the few things they could during the lockdown, which was their own body, and then their anxiety, depression, [obsessive-compulsive disorder], and other mental health comorbidities presented as an eating disorder,” Dr. Voss said.
The increasing need for treatment over the course of the pandemic may reflect the time that it has taken for the disorders to develop, as well as the time that it takes parents to recognize the problem.
Not only are doctors seeing more cases, but patients are arriving sicker than usual, Dr. Voss said.
Major medical concerns for patients in starvation mode center on the heart, brain, and bones. In addition, refeeding syndrome poses an extreme risk, Dr. Voss noted.
The Academy for Eating Disorders has created a guide to help doctors recognize and manage risks for patients with eating disorders, which may be useful for primary care providers while they are trying to get a patient into more intensive treatment, Dr. Voss suggested. The American Academy of Pediatrics recently published a clinical report on the identification and management of eating disorders in children and adolescents.
At Johns Hopkins Hospital Children’s Center in Baltimore, “we have seen a pretty remarkable increase in the number of eating disorders in the child and adolescent space since COVID,” said Jennifer Leah Goetz, MD, a psychiatrist and medical director of the child and adolescent inpatient unit. “We have seen increasing numbers of kids presenting for acute medical stabilization and refeeding and for specific treatment for the eating disorder.”
It could be that, for people with a genetic predisposition to eating disorders, a confluence of factors related to the pandemic unmasked it. For example, children may have spent more time looking at themselves on virtual meeting platforms, which could stir lingering body image and appearance-related concerns in those who are vulnerable. And some teens who were not able to participate in athletics as usual started to watch what they eat more closely, Dr. Goetz said.
A treatment bottleneck
Patients with eating disorders “can be quite ill from a psychiatric and general medical perspective,” Dr. Goetz said. “Most psychiatrists are not particularly comfortable with the medical complications, and most internists or pediatricians are not particularly comfortable with the psychiatric complications. You end up with a patient population that can only see a really highly specialized group of individuals for care. And it is a problem. It was a problem before the pandemic, and it has been really exacerbated by what we have been going through with COVID.”
Natalie Muth, MD, MPH, RDN, a pediatrician at Children’s Primary Care Medical Group La Costa in Carlsbad, Calif., has also noticed the increase in eating disorders since COVID.
In-patient colleagues “have longer wait lists and more severe cases than they have ever seen previously,” said Dr. Muth, who chairs the American Academy of Pediatrics Section on Obesity and is an adjunct assistant professor at the University of California, Los Angeles. “In primary care, we are all having to better educate and prepare ourselves for identifying and managing patients with eating disorders.”
That could mean connecting with mental health professionals, registered dietitians, and higher levels of care. But that may be a challenge. “Accessing these resources has been more difficult due to the increasing incidence of eating disorders recently,” Dr. Muth said.
Dr. Voss acknowledged that childhood obesity is another concern for pediatricians. “However, there are appropriate and healthy and safe ways to address that,” she said. A patient with overweight or obesity who loses weight may not be doing so in a healthy way.
Clinicians should wonder if a patient’s weight is decreasing too fast. And they should ask patients questions that could help identify a problem, such as: What are they doing to cause the weight loss? Why do they want to lose the weight?
Dr. Voss added that eating disorders “do not discriminate.” While there may be a perception that all patients with eating disorders are White, upper middle–class females who are thin, “that is not the case,” Dr. Voss said. They “come in all genders, all races, all weight classes, and all ages,” she said, “and we see that variety.”
In general, there may be a need to shift how weight is discussed in clinics and society more broadly, Dr. Goetz said. Weight is an incredibly personal thing, and everyone’s genetics, metabolism, and life circumstances vary. At the same time, body mass index is not necessarily the best measure of a person’s health.
Asking a child, teen, or even an adult to go on a diet is not a benign intervention, Dr. Goetz noted. In addition, dieting is unlikely to help in the long term.
Emerging from lockdown, pressure to lose “COVID pounds” is a dangerous message for people with eating disorders, Dr. Goetz said. It also could be a dangerous message for people without eating disorders. “There are so many more interesting things about each one of us than our weight,” she added.
The study authors, Dr. Voss, Dr. Goetz, and Dr. Muth had no relevant disclosures.
Medical admissions for adolescents with restrictive eating disorders more than doubled at one hospital during the first 12 months of the COVID-19 pandemic, relative to the average number of admissions in prior years, a new study shows.
Doctors are seeing similar increases across the United States and in other countries.
Providers and health care systems “may need to rapidly adapt in response to increasing demands for care during the COVID-19 pandemic,” the researchers said in their study, which was published online in Pediatrics.
To assess whether admission patterns among adolescents with restrictive eating disorders changed during the pandemic, Alana K. Otto, MD, MPH, with the division of adolescent medicine at the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, and colleagues reviewed the charts of patients admitted to C.S. Mott Children’s Hospital, also in Ann Arbor.
Their analysis included 297 admissions among 248 patients aged 10-23 years between March 1, 2017, and March 31, 2021. Patients had an average age of about 15 years. Approximately 90% were female, and most had a diagnosis of anorexia nervosa or atypical anorexia nervosa.
Indications for medical admission included physiological instability (for example, heart rate less than 50 beats per minute while awake or blood pressure less than 90/40 mm Hg), electrolyte derangements, and acute medical complications of malnutrition such as syncope. Other possible indications included uncontrolled purging, body mass index less than 75% of the median for age and sex, acute food refusal, and failure of outpatient treatment.
Eating disorder–related admissions per month were stable prior to the pandemic. Admissions then decreased in April 2020, but subsequently increased significantly throughout the study period. In all, there were 125 admissions between April 1, 2020, and March 31, 2021. During the previous 3 years, the average number of admissions per year was 56.
Patients’ insurance status was one factor that differed before and during the pandemic. Prepandemic, about 20% of admissions were for adolescents with public insurance. During the pandemic, however, the proportion with public insurance was approximately 9%, the researchers noted. Other characteristics were generally similar.
The study was retrospective and relatively small and only looked at patients with restrictive eating disorders who were severely ill and admitted for medical stabilization. It does not reflect adolescents with eating disorders in different settings, the authors noted.
Primary care pediatricians should be familiar with indications for medical admission, such as severe bradycardia, as outlined by the Society for Adolescent Health and Medicine, they said.
Consistent trends
Unfortunately, the trend seems consistent across the nation, said Michaela M. Voss, MD, director of the the Eating Disorders Center at Children’s Mercy in Kansas City, Mo. “Our outpatient setting went from availability to get in immediately to a 6-month wait list.”
As in Michigan, Dr. Voss noted a drop in admissions as lockdowns started, followed by a spike in treatment demand that has not let up.
Dr. Voss described two of the more common presentations. In one, parents might note that their child had been getting into healthy eating and exercise before the pandemic and seemed fine. “But then COVID came, the lockdown happened, and they became overly obsessed with those things,” Dr. Voss said.
In the other presentation, kids with anxiety, depression, or OCD who lost access to their usual coping strategies and outlets developed eating disorders during the pandemic. “They focused on one of the few things they could during the lockdown, which was their own body, and then their anxiety, depression, [obsessive-compulsive disorder], and other mental health comorbidities presented as an eating disorder,” Dr. Voss said.
The increasing need for treatment over the course of the pandemic may reflect the time that it has taken for the disorders to develop, as well as the time that it takes parents to recognize the problem.
Not only are doctors seeing more cases, but patients are arriving sicker than usual, Dr. Voss said.
Major medical concerns for patients in starvation mode center on the heart, brain, and bones. In addition, refeeding syndrome poses an extreme risk, Dr. Voss noted.
The Academy for Eating Disorders has created a guide to help doctors recognize and manage risks for patients with eating disorders, which may be useful for primary care providers while they are trying to get a patient into more intensive treatment, Dr. Voss suggested. The American Academy of Pediatrics recently published a clinical report on the identification and management of eating disorders in children and adolescents.
At Johns Hopkins Hospital Children’s Center in Baltimore, “we have seen a pretty remarkable increase in the number of eating disorders in the child and adolescent space since COVID,” said Jennifer Leah Goetz, MD, a psychiatrist and medical director of the child and adolescent inpatient unit. “We have seen increasing numbers of kids presenting for acute medical stabilization and refeeding and for specific treatment for the eating disorder.”
It could be that, for people with a genetic predisposition to eating disorders, a confluence of factors related to the pandemic unmasked it. For example, children may have spent more time looking at themselves on virtual meeting platforms, which could stir lingering body image and appearance-related concerns in those who are vulnerable. And some teens who were not able to participate in athletics as usual started to watch what they eat more closely, Dr. Goetz said.
A treatment bottleneck
Patients with eating disorders “can be quite ill from a psychiatric and general medical perspective,” Dr. Goetz said. “Most psychiatrists are not particularly comfortable with the medical complications, and most internists or pediatricians are not particularly comfortable with the psychiatric complications. You end up with a patient population that can only see a really highly specialized group of individuals for care. And it is a problem. It was a problem before the pandemic, and it has been really exacerbated by what we have been going through with COVID.”
Natalie Muth, MD, MPH, RDN, a pediatrician at Children’s Primary Care Medical Group La Costa in Carlsbad, Calif., has also noticed the increase in eating disorders since COVID.
In-patient colleagues “have longer wait lists and more severe cases than they have ever seen previously,” said Dr. Muth, who chairs the American Academy of Pediatrics Section on Obesity and is an adjunct assistant professor at the University of California, Los Angeles. “In primary care, we are all having to better educate and prepare ourselves for identifying and managing patients with eating disorders.”
That could mean connecting with mental health professionals, registered dietitians, and higher levels of care. But that may be a challenge. “Accessing these resources has been more difficult due to the increasing incidence of eating disorders recently,” Dr. Muth said.
Dr. Voss acknowledged that childhood obesity is another concern for pediatricians. “However, there are appropriate and healthy and safe ways to address that,” she said. A patient with overweight or obesity who loses weight may not be doing so in a healthy way.
Clinicians should wonder if a patient’s weight is decreasing too fast. And they should ask patients questions that could help identify a problem, such as: What are they doing to cause the weight loss? Why do they want to lose the weight?
Dr. Voss added that eating disorders “do not discriminate.” While there may be a perception that all patients with eating disorders are White, upper middle–class females who are thin, “that is not the case,” Dr. Voss said. They “come in all genders, all races, all weight classes, and all ages,” she said, “and we see that variety.”
In general, there may be a need to shift how weight is discussed in clinics and society more broadly, Dr. Goetz said. Weight is an incredibly personal thing, and everyone’s genetics, metabolism, and life circumstances vary. At the same time, body mass index is not necessarily the best measure of a person’s health.
Asking a child, teen, or even an adult to go on a diet is not a benign intervention, Dr. Goetz noted. In addition, dieting is unlikely to help in the long term.
Emerging from lockdown, pressure to lose “COVID pounds” is a dangerous message for people with eating disorders, Dr. Goetz said. It also could be a dangerous message for people without eating disorders. “There are so many more interesting things about each one of us than our weight,” she added.
The study authors, Dr. Voss, Dr. Goetz, and Dr. Muth had no relevant disclosures.
FROM PEDIATRICS
ADA/EASD draft guidance aims to bring adults with type 1 diabetes out of shadows
A new draft consensus statement from the American Diabetes Association and the European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD) addresses diagnosis and management of type 1 diabetes in adults.
The impetus for the document comes from the “highly influential” EASD-ADA consensus report on the management of type 2 diabetes, which led to the realization that a comparable document was needed for adults with type 1 diabetes, said writing panel cochair Anne L. Peters, MD, professor of clinical medicine at the University of Southern California, Los Angeles.
“In recent years, there have been rapid advances in the treatment of type 1 diabetes together with a growing recognition of the psychosocial burden of living with [it],” Dr. Peters said.
She noted that although there is already some guidance available for the management of type 1 diabetes in adults, “this gets admixed into broader guidelines, and many of those are mostly derived from data in people with type 2 diabetes.”
The new draft document was coauthored by 14 content experts in type 1 diabetes, with equal numbers from the United States and Europe.
We want to be helpful to clinicians
Topics covered include diagnosis of type 1 diabetes, goals of therapy and glycemic targets, schedule of care, diabetes self-management education and additional behavioral considerations, glucose monitoring, insulin therapy, hypoglycemia, psychosocial care, diabetic ketoacidosis, pancreas and islet cell transplantation, adjunctive therapies, special populations (including pregnant women, older adults, and inpatient management), and emergent/future perspectives, including beta-cell replacement and immunotherapy.
At the end of the document are tables of glycemic targets for adults with type 1 diabetes, schedule of care, nonglycemic factors that alter A1c levels, standardized continuous glucose meter (CGM) metrics for clinical care, examples of subcutaneous insulin regimens, and the various properties of approved and nonapproved adjunctive therapies for type 1 diabetes, including metformin, pramlintide, GLP-1 agonists, and SGLT2 inhibitors.
Several colorful flowcharts are also provided, including algorithms for diagnosing and managing type 1 diabetes in adults.
Document coauthor M. Sue Kirkman, MD, of the Diabetes Care Center’s Clinical Trials Unit at the University of North Carolina, Chapel Hill, told this news organization: “We want it to be helpful to clinicians who are diagnosing type 1 diabetes in adults or caring for adults with type 1 diabetes, whether diagnosed in childhood or adulthood.”
The authors presented an overview of the document in a symposium on June 28 at the virtual ADA scientific sessions. The final version will be presented Oct. 1 at the EASD 2021 annual meeting.
The draft document and video of the ADA meeting presentation are both available on the ADA website.
New algorithm to reduce misdiagnosis of type 1 diabetes in adults
Misdiagnosis of adult-onset type 1 diabetes is common, occurring in up to 40% of those who develop the condition after age 30 years, said J. Hans de Vries, MD, PhD, medical director, Profil Institute for Metabolic Research, Neuss, Germany.
There are multiple reasons for this, including the fact that obesity and type 2 diabetes are becoming more prevalent at younger ages, C-peptide levels may still be relatively high at the time of clinical type 1 diabetes onset, and islet autoantibodies don’t have 100% positive predictive value.
“No single feature confirms type 1 diabetes in isolation,” Dr. de Vries noted.
The document provides a detailed diagnostic algorithm specifically for adults in whom type 1 diabetes is suspected, starting with autoantibody measurement. If the diagnosis isn’t confirmed that way, the algorithm advises investigating for monogenic diabetes, including use of a maturity-onset diabetes of the young (MODY) calculator and subsequent C-peptide measurement.
Measurement of C-peptide is also recommended if the diabetes type is still uncertain more than 3 years after diabetes onset in those treated with insulin, because by that point it is likely to be <200 pmol/L in people with type 1 diabetes.
Clear statements on diabetes technology, preferred insulins
The draft document clearly states that physiologic insulin replacement using a pump or multiple daily injections, CGM, and analog rather than human insulin are standards of care for adults with type 1 diabetes. Use of hybrid closed-loop insulin delivery systems is advised when available, as they offer the “greatest benefits.”
However, the document also notes that in cases of cost barriers, subcutaneous regimens of human regular and NPH insulin may be used. It cautions, though, that these may result in higher glucose variability, higher risk of hypoglycemia, and less lifestyle flexibility.
Dr. Kirkman told this news organization: “Using human insulins such as NPH and Regular in type 1 diabetes is definitely not preferred, but sometimes due to people’s inability to afford analogs we have to use them. People need to know how to use them safely.”
As for the do-it-yourself insulin delivery systems, which many with type 1 diabetes now use with open-source software algorithms that reverse-engineer older pumps, the document advises that health care providers shouldn’t actively recommend them as they’re not approved by regulatory authorities, but should also “respect the individual’s right to make informed choices and continue to offer support,” Dr. Kirkman said when presenting the insulin therapy section.
Psychosocial aspects of type 1 diabetes ‘underappreciated’
Special emphasis is placed on psychosocial support, which may be overlooked in adults, Dr. Kirkman noted.
“Clinicians probably underappreciate what people with type 1 diabetes go through on a daily basis. A lot of the evidence out there regarding psychosocial issues is in children and families of children with type 1 diabetes, or in adults with type 2 diabetes ... Maximizing quality of life needs to be at the forefront of care, not just focusing on glycemic goals.”
Indeed, between 20% and 40% of people with type 1 diabetes experience diabetes-related emotional distress – including 15% with depression – particularly at the time of diagnosis and when complications develop, noted Frank J. Snoek, PhD, professor of medical psychology at Amsterdam University Medical Center, the Netherlands.
To address this, the draft advises that “self-management difficulties, psychological, and social problems” be screened periodically and monitored using validated screening tools.
“Health care providers should be proficient at asking questions about and discussing emotional health, psychological needs, and social challenges as part of the consultation,” Dr. Snoek said.
Dr. Peters disclosed ties with Abbott Diabetes Care, AstraZeneca, Lilly, Medscape, Novo Nordisk, Vertex, and Zealand, Omada, and Teladoc. Dr. Kirkman has received research support from Novo Nordisk and Bayer. Dr. de Vries disclosed ties with Adocia, Novo Nordisk, Zealand, Eli Lilly, and Afon Technology. Dr. Snoek reported ties with Roche Diabetes, Novo Nordisk, Sanofi, and Eli Lilly.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A new draft consensus statement from the American Diabetes Association and the European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD) addresses diagnosis and management of type 1 diabetes in adults.
The impetus for the document comes from the “highly influential” EASD-ADA consensus report on the management of type 2 diabetes, which led to the realization that a comparable document was needed for adults with type 1 diabetes, said writing panel cochair Anne L. Peters, MD, professor of clinical medicine at the University of Southern California, Los Angeles.
“In recent years, there have been rapid advances in the treatment of type 1 diabetes together with a growing recognition of the psychosocial burden of living with [it],” Dr. Peters said.
She noted that although there is already some guidance available for the management of type 1 diabetes in adults, “this gets admixed into broader guidelines, and many of those are mostly derived from data in people with type 2 diabetes.”
The new draft document was coauthored by 14 content experts in type 1 diabetes, with equal numbers from the United States and Europe.
We want to be helpful to clinicians
Topics covered include diagnosis of type 1 diabetes, goals of therapy and glycemic targets, schedule of care, diabetes self-management education and additional behavioral considerations, glucose monitoring, insulin therapy, hypoglycemia, psychosocial care, diabetic ketoacidosis, pancreas and islet cell transplantation, adjunctive therapies, special populations (including pregnant women, older adults, and inpatient management), and emergent/future perspectives, including beta-cell replacement and immunotherapy.
At the end of the document are tables of glycemic targets for adults with type 1 diabetes, schedule of care, nonglycemic factors that alter A1c levels, standardized continuous glucose meter (CGM) metrics for clinical care, examples of subcutaneous insulin regimens, and the various properties of approved and nonapproved adjunctive therapies for type 1 diabetes, including metformin, pramlintide, GLP-1 agonists, and SGLT2 inhibitors.
Several colorful flowcharts are also provided, including algorithms for diagnosing and managing type 1 diabetes in adults.
Document coauthor M. Sue Kirkman, MD, of the Diabetes Care Center’s Clinical Trials Unit at the University of North Carolina, Chapel Hill, told this news organization: “We want it to be helpful to clinicians who are diagnosing type 1 diabetes in adults or caring for adults with type 1 diabetes, whether diagnosed in childhood or adulthood.”
The authors presented an overview of the document in a symposium on June 28 at the virtual ADA scientific sessions. The final version will be presented Oct. 1 at the EASD 2021 annual meeting.
The draft document and video of the ADA meeting presentation are both available on the ADA website.
New algorithm to reduce misdiagnosis of type 1 diabetes in adults
Misdiagnosis of adult-onset type 1 diabetes is common, occurring in up to 40% of those who develop the condition after age 30 years, said J. Hans de Vries, MD, PhD, medical director, Profil Institute for Metabolic Research, Neuss, Germany.
There are multiple reasons for this, including the fact that obesity and type 2 diabetes are becoming more prevalent at younger ages, C-peptide levels may still be relatively high at the time of clinical type 1 diabetes onset, and islet autoantibodies don’t have 100% positive predictive value.
“No single feature confirms type 1 diabetes in isolation,” Dr. de Vries noted.
The document provides a detailed diagnostic algorithm specifically for adults in whom type 1 diabetes is suspected, starting with autoantibody measurement. If the diagnosis isn’t confirmed that way, the algorithm advises investigating for monogenic diabetes, including use of a maturity-onset diabetes of the young (MODY) calculator and subsequent C-peptide measurement.
Measurement of C-peptide is also recommended if the diabetes type is still uncertain more than 3 years after diabetes onset in those treated with insulin, because by that point it is likely to be <200 pmol/L in people with type 1 diabetes.
Clear statements on diabetes technology, preferred insulins
The draft document clearly states that physiologic insulin replacement using a pump or multiple daily injections, CGM, and analog rather than human insulin are standards of care for adults with type 1 diabetes. Use of hybrid closed-loop insulin delivery systems is advised when available, as they offer the “greatest benefits.”
However, the document also notes that in cases of cost barriers, subcutaneous regimens of human regular and NPH insulin may be used. It cautions, though, that these may result in higher glucose variability, higher risk of hypoglycemia, and less lifestyle flexibility.
Dr. Kirkman told this news organization: “Using human insulins such as NPH and Regular in type 1 diabetes is definitely not preferred, but sometimes due to people’s inability to afford analogs we have to use them. People need to know how to use them safely.”
As for the do-it-yourself insulin delivery systems, which many with type 1 diabetes now use with open-source software algorithms that reverse-engineer older pumps, the document advises that health care providers shouldn’t actively recommend them as they’re not approved by regulatory authorities, but should also “respect the individual’s right to make informed choices and continue to offer support,” Dr. Kirkman said when presenting the insulin therapy section.
Psychosocial aspects of type 1 diabetes ‘underappreciated’
Special emphasis is placed on psychosocial support, which may be overlooked in adults, Dr. Kirkman noted.
“Clinicians probably underappreciate what people with type 1 diabetes go through on a daily basis. A lot of the evidence out there regarding psychosocial issues is in children and families of children with type 1 diabetes, or in adults with type 2 diabetes ... Maximizing quality of life needs to be at the forefront of care, not just focusing on glycemic goals.”
Indeed, between 20% and 40% of people with type 1 diabetes experience diabetes-related emotional distress – including 15% with depression – particularly at the time of diagnosis and when complications develop, noted Frank J. Snoek, PhD, professor of medical psychology at Amsterdam University Medical Center, the Netherlands.
To address this, the draft advises that “self-management difficulties, psychological, and social problems” be screened periodically and monitored using validated screening tools.
“Health care providers should be proficient at asking questions about and discussing emotional health, psychological needs, and social challenges as part of the consultation,” Dr. Snoek said.
Dr. Peters disclosed ties with Abbott Diabetes Care, AstraZeneca, Lilly, Medscape, Novo Nordisk, Vertex, and Zealand, Omada, and Teladoc. Dr. Kirkman has received research support from Novo Nordisk and Bayer. Dr. de Vries disclosed ties with Adocia, Novo Nordisk, Zealand, Eli Lilly, and Afon Technology. Dr. Snoek reported ties with Roche Diabetes, Novo Nordisk, Sanofi, and Eli Lilly.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A new draft consensus statement from the American Diabetes Association and the European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD) addresses diagnosis and management of type 1 diabetes in adults.
The impetus for the document comes from the “highly influential” EASD-ADA consensus report on the management of type 2 diabetes, which led to the realization that a comparable document was needed for adults with type 1 diabetes, said writing panel cochair Anne L. Peters, MD, professor of clinical medicine at the University of Southern California, Los Angeles.
“In recent years, there have been rapid advances in the treatment of type 1 diabetes together with a growing recognition of the psychosocial burden of living with [it],” Dr. Peters said.
She noted that although there is already some guidance available for the management of type 1 diabetes in adults, “this gets admixed into broader guidelines, and many of those are mostly derived from data in people with type 2 diabetes.”
The new draft document was coauthored by 14 content experts in type 1 diabetes, with equal numbers from the United States and Europe.
We want to be helpful to clinicians
Topics covered include diagnosis of type 1 diabetes, goals of therapy and glycemic targets, schedule of care, diabetes self-management education and additional behavioral considerations, glucose monitoring, insulin therapy, hypoglycemia, psychosocial care, diabetic ketoacidosis, pancreas and islet cell transplantation, adjunctive therapies, special populations (including pregnant women, older adults, and inpatient management), and emergent/future perspectives, including beta-cell replacement and immunotherapy.
At the end of the document are tables of glycemic targets for adults with type 1 diabetes, schedule of care, nonglycemic factors that alter A1c levels, standardized continuous glucose meter (CGM) metrics for clinical care, examples of subcutaneous insulin regimens, and the various properties of approved and nonapproved adjunctive therapies for type 1 diabetes, including metformin, pramlintide, GLP-1 agonists, and SGLT2 inhibitors.
Several colorful flowcharts are also provided, including algorithms for diagnosing and managing type 1 diabetes in adults.
Document coauthor M. Sue Kirkman, MD, of the Diabetes Care Center’s Clinical Trials Unit at the University of North Carolina, Chapel Hill, told this news organization: “We want it to be helpful to clinicians who are diagnosing type 1 diabetes in adults or caring for adults with type 1 diabetes, whether diagnosed in childhood or adulthood.”
The authors presented an overview of the document in a symposium on June 28 at the virtual ADA scientific sessions. The final version will be presented Oct. 1 at the EASD 2021 annual meeting.
The draft document and video of the ADA meeting presentation are both available on the ADA website.
New algorithm to reduce misdiagnosis of type 1 diabetes in adults
Misdiagnosis of adult-onset type 1 diabetes is common, occurring in up to 40% of those who develop the condition after age 30 years, said J. Hans de Vries, MD, PhD, medical director, Profil Institute for Metabolic Research, Neuss, Germany.
There are multiple reasons for this, including the fact that obesity and type 2 diabetes are becoming more prevalent at younger ages, C-peptide levels may still be relatively high at the time of clinical type 1 diabetes onset, and islet autoantibodies don’t have 100% positive predictive value.
“No single feature confirms type 1 diabetes in isolation,” Dr. de Vries noted.
The document provides a detailed diagnostic algorithm specifically for adults in whom type 1 diabetes is suspected, starting with autoantibody measurement. If the diagnosis isn’t confirmed that way, the algorithm advises investigating for monogenic diabetes, including use of a maturity-onset diabetes of the young (MODY) calculator and subsequent C-peptide measurement.
Measurement of C-peptide is also recommended if the diabetes type is still uncertain more than 3 years after diabetes onset in those treated with insulin, because by that point it is likely to be <200 pmol/L in people with type 1 diabetes.
Clear statements on diabetes technology, preferred insulins
The draft document clearly states that physiologic insulin replacement using a pump or multiple daily injections, CGM, and analog rather than human insulin are standards of care for adults with type 1 diabetes. Use of hybrid closed-loop insulin delivery systems is advised when available, as they offer the “greatest benefits.”
However, the document also notes that in cases of cost barriers, subcutaneous regimens of human regular and NPH insulin may be used. It cautions, though, that these may result in higher glucose variability, higher risk of hypoglycemia, and less lifestyle flexibility.
Dr. Kirkman told this news organization: “Using human insulins such as NPH and Regular in type 1 diabetes is definitely not preferred, but sometimes due to people’s inability to afford analogs we have to use them. People need to know how to use them safely.”
As for the do-it-yourself insulin delivery systems, which many with type 1 diabetes now use with open-source software algorithms that reverse-engineer older pumps, the document advises that health care providers shouldn’t actively recommend them as they’re not approved by regulatory authorities, but should also “respect the individual’s right to make informed choices and continue to offer support,” Dr. Kirkman said when presenting the insulin therapy section.
Psychosocial aspects of type 1 diabetes ‘underappreciated’
Special emphasis is placed on psychosocial support, which may be overlooked in adults, Dr. Kirkman noted.
“Clinicians probably underappreciate what people with type 1 diabetes go through on a daily basis. A lot of the evidence out there regarding psychosocial issues is in children and families of children with type 1 diabetes, or in adults with type 2 diabetes ... Maximizing quality of life needs to be at the forefront of care, not just focusing on glycemic goals.”
Indeed, between 20% and 40% of people with type 1 diabetes experience diabetes-related emotional distress – including 15% with depression – particularly at the time of diagnosis and when complications develop, noted Frank J. Snoek, PhD, professor of medical psychology at Amsterdam University Medical Center, the Netherlands.
To address this, the draft advises that “self-management difficulties, psychological, and social problems” be screened periodically and monitored using validated screening tools.
“Health care providers should be proficient at asking questions about and discussing emotional health, psychological needs, and social challenges as part of the consultation,” Dr. Snoek said.
Dr. Peters disclosed ties with Abbott Diabetes Care, AstraZeneca, Lilly, Medscape, Novo Nordisk, Vertex, and Zealand, Omada, and Teladoc. Dr. Kirkman has received research support from Novo Nordisk and Bayer. Dr. de Vries disclosed ties with Adocia, Novo Nordisk, Zealand, Eli Lilly, and Afon Technology. Dr. Snoek reported ties with Roche Diabetes, Novo Nordisk, Sanofi, and Eli Lilly.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
New agents for youth-onset type 2 diabetes ‘finally in sight’
There are limited treatment options for children and youth with type 2 diabetes, but a few novel therapies beyond metformin are on the horizon, experts said at the annual scientific sessions of the American Diabetes Association.
“Type 2 diabetes in youth only emerged as a well-recognized pediatric medical problem in the 1990s and the first decade of the 21st century,” session chair Kenneth C. Copeland, MD, said in an interview.
“Fortunately, a number of clinical trials of antidiabetic pharmacologic agents in diabetic youth have now been completed, demonstrating both safety and efficacy, and at long last, a ... variety of agents are finally in sight,” he noted.
Type 2 diabetes in youth is profoundly different from type 2 diabetes in adults, added Dr. Copeland, pediatrics professor emeritus, University of Oklahoma, Oklahoma City. In youth, its course is typically aggressive and refractive to treatment.
Concerted efforts at lifestyle intervention are important but insufficient, and a response to metformin, even when initiated at diagnosis, is often short lived, he added.
Because of the rapid glycemic deterioration that is typical of type 2 diabetes in youth and leads to the full array of diabetic complications, early aggressive pharmacologic treatment is indicated.
“We all look forward to this next decade ushering in new treatment options, spanning the spectrum from obesity prevention to complex pharmacologic intervention,” Dr. Copeland summarized.
Increasing prevalence of T2D in youth, limited therapies
Rates of type 2 diabetes in youth continue to increase, especially among non-White groups, and most of these individuals have less than optimal diabetes control, Elvira Isganaitis, MD, MPH, a pediatric endocrinologist at the Joslin Diabetes Center and assistant professor of pediatrics at Harvard Medical School, both in Boston, told the meeting.
Although the Food and Drug Administration has approved more than 25 drugs to treat type 2 diabetes in adults, “unfortunately,” metformin is the only oral medication approved to treat the disease in a pediatric population, “and a majority of youth either do not respond to it or do not tolerate it,” she said in an interview.
Dr. Copeland observed that “the TODAY study demonstrated conclusively that, despite an often dramatic initial improvement in glycemic control upon initiation of pharmacologic and lifestyle intervention, this initial response was followed by a rapid deterioration of beta-cell function and glycemic failure, indicating that additional pharmacologic agents were sorely needed for this population.”
The RISE study also showed that, compared with adults, youth had more rapid beta-cell deterioration despite treatment.
Until the June 2019 FDA approval of the injectable glucagonlike peptide–1 receptor agonist liraglutide (Victoza, Novo Nordisk) for children 10 years or older, “except for insulin, metformin was the only antidiabetic medication available for use in youth, severely limiting treatment options,” he added.
Liraglutide ‘a huge breakthrough,’ other options on the horizon
The FDA approval of liraglutide was “a huge breakthrough” as the first noninsulin drug for pediatric type 2 diabetes since metformin was approved for pediatric use in 2000, Dr. Isganaitis said.
The ELLIPSE study, on which the approval was based, showed liraglutide was effective at lowering hemoglobin A1c and was generally well tolerated, although it was associated with a higher incidence of gastrointestinal symptoms.
In December 2020, the FDA also approved liraglutide (Saxenda) for the treatment of obesity in youth age 12 and older (at a dose of 3 mg as opposed to the 1.8-mg dose of liraglutide [Victoza]), “which is wonderful news considering that the majority of pediatric patients with type 2 diabetes also have obesity,” Dr. Isganaitis added.
“The results of studies of liraglutide on glycemia in diabetic youth are impressive, with both an additional benefit of weight loss and without unacceptable identified risks or side effects,” Dr. Copeland concurred.
Waiting in the wings
Dr. Isganaitis reported that a few phase 3 clinical trials of other therapies for pediatric patients with type 2 diabetes are in the wings.
The 24-week phase 3 T2GO clinical trial of the sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitor dapagliflozin (AstraZeneca) versus placebo in 72 patients with type 2 diabetes aged 10-24 years was completed in April 2020, and the data are being analyzed.
An AstraZeneca-sponsored phase 3 trial of the safety and efficacy of a weekly injection of the GLP-1 receptor agonist exenatide in 10- to 17-year-olds with type 2 diabetes (n = 82) has also been completed and data are being analyzed.
A Takeda-sponsored phase 3 pediatric study of the dipeptidyl peptidase–4 inhibitor alogliptin in 10- to 17-year-olds with type 2 diabetes (n = 150) is estimated to be completed by February 2022.
And the phase 3 DINAMO trial, sponsored by Boehringer Ingelheim, which is evaluating the efficacy and safety of the SGLT2 inhibitor empagliflozin (10 mg/25 mg) versus the DPP-4 inhibitor linagliptin (5 mg) versus placebo over 26 weeks in 10- to 17-year-olds with type 2 diabetes (estimated 186 participants), is expected to be completed in May 2023.
“I hope that these medications will demonstrate efficacy and allow pediatric patients with type 2 diabetes to have more treatment options,” Dr. Isganaitis concluded.
Type 2 diabetes more aggressive than type 1 diabetes in kids
According to Dr. Isganaitis, “there is a widely held misconception among the general public and even among some physicians that type 2 diabetes is somehow less worrisome or ‘milder’ than a diagnosis of type 1 diabetes.”
However, the risk of complications and severe morbidity is higher with a diagnosis of type 2 diabetes versus type 1 diabetes in a child, so “this condition needs to be managed intensively with a multidisciplinary team including pediatric endocrinology, nutrition [support], diabetes educators, and mental health support,” she emphasized.
Many people also believe that “type 2 diabetes in kids is a ‘lifestyle disease,’ ” she continued, “but in fact, there is a strong role for genetics.”
The ADA Presidents’ Select Abstract “paints a picture of youth-onset type 2 diabetes as a disease intermediate in extremity between monogenic diabetes [caused by mutations in a single gene] and type 2 diabetes [caused by multiple genes and lifestyle factors such as obesity], in which genetic variants in both insulin secretion and insulin response pathways are implicated.”
Along the same lines, Dr. Isganaitis presented an oral abstract at the meeting that showed that, among youth with newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes, those whose mothers had diabetes had faster disease progression and earlier onset of diabetes complications.
Dr. Isganaitis has reported no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Copeland has reported serving on data monitoring committees for Boehringer Ingelheim and Novo Nordisk, and on an advisory committee for a research study for Daiichi Sankyo.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
There are limited treatment options for children and youth with type 2 diabetes, but a few novel therapies beyond metformin are on the horizon, experts said at the annual scientific sessions of the American Diabetes Association.
“Type 2 diabetes in youth only emerged as a well-recognized pediatric medical problem in the 1990s and the first decade of the 21st century,” session chair Kenneth C. Copeland, MD, said in an interview.
“Fortunately, a number of clinical trials of antidiabetic pharmacologic agents in diabetic youth have now been completed, demonstrating both safety and efficacy, and at long last, a ... variety of agents are finally in sight,” he noted.
Type 2 diabetes in youth is profoundly different from type 2 diabetes in adults, added Dr. Copeland, pediatrics professor emeritus, University of Oklahoma, Oklahoma City. In youth, its course is typically aggressive and refractive to treatment.
Concerted efforts at lifestyle intervention are important but insufficient, and a response to metformin, even when initiated at diagnosis, is often short lived, he added.
Because of the rapid glycemic deterioration that is typical of type 2 diabetes in youth and leads to the full array of diabetic complications, early aggressive pharmacologic treatment is indicated.
“We all look forward to this next decade ushering in new treatment options, spanning the spectrum from obesity prevention to complex pharmacologic intervention,” Dr. Copeland summarized.
Increasing prevalence of T2D in youth, limited therapies
Rates of type 2 diabetes in youth continue to increase, especially among non-White groups, and most of these individuals have less than optimal diabetes control, Elvira Isganaitis, MD, MPH, a pediatric endocrinologist at the Joslin Diabetes Center and assistant professor of pediatrics at Harvard Medical School, both in Boston, told the meeting.
Although the Food and Drug Administration has approved more than 25 drugs to treat type 2 diabetes in adults, “unfortunately,” metformin is the only oral medication approved to treat the disease in a pediatric population, “and a majority of youth either do not respond to it or do not tolerate it,” she said in an interview.
Dr. Copeland observed that “the TODAY study demonstrated conclusively that, despite an often dramatic initial improvement in glycemic control upon initiation of pharmacologic and lifestyle intervention, this initial response was followed by a rapid deterioration of beta-cell function and glycemic failure, indicating that additional pharmacologic agents were sorely needed for this population.”
The RISE study also showed that, compared with adults, youth had more rapid beta-cell deterioration despite treatment.
Until the June 2019 FDA approval of the injectable glucagonlike peptide–1 receptor agonist liraglutide (Victoza, Novo Nordisk) for children 10 years or older, “except for insulin, metformin was the only antidiabetic medication available for use in youth, severely limiting treatment options,” he added.
Liraglutide ‘a huge breakthrough,’ other options on the horizon
The FDA approval of liraglutide was “a huge breakthrough” as the first noninsulin drug for pediatric type 2 diabetes since metformin was approved for pediatric use in 2000, Dr. Isganaitis said.
The ELLIPSE study, on which the approval was based, showed liraglutide was effective at lowering hemoglobin A1c and was generally well tolerated, although it was associated with a higher incidence of gastrointestinal symptoms.
In December 2020, the FDA also approved liraglutide (Saxenda) for the treatment of obesity in youth age 12 and older (at a dose of 3 mg as opposed to the 1.8-mg dose of liraglutide [Victoza]), “which is wonderful news considering that the majority of pediatric patients with type 2 diabetes also have obesity,” Dr. Isganaitis added.
“The results of studies of liraglutide on glycemia in diabetic youth are impressive, with both an additional benefit of weight loss and without unacceptable identified risks or side effects,” Dr. Copeland concurred.
Waiting in the wings
Dr. Isganaitis reported that a few phase 3 clinical trials of other therapies for pediatric patients with type 2 diabetes are in the wings.
The 24-week phase 3 T2GO clinical trial of the sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitor dapagliflozin (AstraZeneca) versus placebo in 72 patients with type 2 diabetes aged 10-24 years was completed in April 2020, and the data are being analyzed.
An AstraZeneca-sponsored phase 3 trial of the safety and efficacy of a weekly injection of the GLP-1 receptor agonist exenatide in 10- to 17-year-olds with type 2 diabetes (n = 82) has also been completed and data are being analyzed.
A Takeda-sponsored phase 3 pediatric study of the dipeptidyl peptidase–4 inhibitor alogliptin in 10- to 17-year-olds with type 2 diabetes (n = 150) is estimated to be completed by February 2022.
And the phase 3 DINAMO trial, sponsored by Boehringer Ingelheim, which is evaluating the efficacy and safety of the SGLT2 inhibitor empagliflozin (10 mg/25 mg) versus the DPP-4 inhibitor linagliptin (5 mg) versus placebo over 26 weeks in 10- to 17-year-olds with type 2 diabetes (estimated 186 participants), is expected to be completed in May 2023.
“I hope that these medications will demonstrate efficacy and allow pediatric patients with type 2 diabetes to have more treatment options,” Dr. Isganaitis concluded.
Type 2 diabetes more aggressive than type 1 diabetes in kids
According to Dr. Isganaitis, “there is a widely held misconception among the general public and even among some physicians that type 2 diabetes is somehow less worrisome or ‘milder’ than a diagnosis of type 1 diabetes.”
However, the risk of complications and severe morbidity is higher with a diagnosis of type 2 diabetes versus type 1 diabetes in a child, so “this condition needs to be managed intensively with a multidisciplinary team including pediatric endocrinology, nutrition [support], diabetes educators, and mental health support,” she emphasized.
Many people also believe that “type 2 diabetes in kids is a ‘lifestyle disease,’ ” she continued, “but in fact, there is a strong role for genetics.”
The ADA Presidents’ Select Abstract “paints a picture of youth-onset type 2 diabetes as a disease intermediate in extremity between monogenic diabetes [caused by mutations in a single gene] and type 2 diabetes [caused by multiple genes and lifestyle factors such as obesity], in which genetic variants in both insulin secretion and insulin response pathways are implicated.”
Along the same lines, Dr. Isganaitis presented an oral abstract at the meeting that showed that, among youth with newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes, those whose mothers had diabetes had faster disease progression and earlier onset of diabetes complications.
Dr. Isganaitis has reported no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Copeland has reported serving on data monitoring committees for Boehringer Ingelheim and Novo Nordisk, and on an advisory committee for a research study for Daiichi Sankyo.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
There are limited treatment options for children and youth with type 2 diabetes, but a few novel therapies beyond metformin are on the horizon, experts said at the annual scientific sessions of the American Diabetes Association.
“Type 2 diabetes in youth only emerged as a well-recognized pediatric medical problem in the 1990s and the first decade of the 21st century,” session chair Kenneth C. Copeland, MD, said in an interview.
“Fortunately, a number of clinical trials of antidiabetic pharmacologic agents in diabetic youth have now been completed, demonstrating both safety and efficacy, and at long last, a ... variety of agents are finally in sight,” he noted.
Type 2 diabetes in youth is profoundly different from type 2 diabetes in adults, added Dr. Copeland, pediatrics professor emeritus, University of Oklahoma, Oklahoma City. In youth, its course is typically aggressive and refractive to treatment.
Concerted efforts at lifestyle intervention are important but insufficient, and a response to metformin, even when initiated at diagnosis, is often short lived, he added.
Because of the rapid glycemic deterioration that is typical of type 2 diabetes in youth and leads to the full array of diabetic complications, early aggressive pharmacologic treatment is indicated.
“We all look forward to this next decade ushering in new treatment options, spanning the spectrum from obesity prevention to complex pharmacologic intervention,” Dr. Copeland summarized.
Increasing prevalence of T2D in youth, limited therapies
Rates of type 2 diabetes in youth continue to increase, especially among non-White groups, and most of these individuals have less than optimal diabetes control, Elvira Isganaitis, MD, MPH, a pediatric endocrinologist at the Joslin Diabetes Center and assistant professor of pediatrics at Harvard Medical School, both in Boston, told the meeting.
Although the Food and Drug Administration has approved more than 25 drugs to treat type 2 diabetes in adults, “unfortunately,” metformin is the only oral medication approved to treat the disease in a pediatric population, “and a majority of youth either do not respond to it or do not tolerate it,” she said in an interview.
Dr. Copeland observed that “the TODAY study demonstrated conclusively that, despite an often dramatic initial improvement in glycemic control upon initiation of pharmacologic and lifestyle intervention, this initial response was followed by a rapid deterioration of beta-cell function and glycemic failure, indicating that additional pharmacologic agents were sorely needed for this population.”
The RISE study also showed that, compared with adults, youth had more rapid beta-cell deterioration despite treatment.
Until the June 2019 FDA approval of the injectable glucagonlike peptide–1 receptor agonist liraglutide (Victoza, Novo Nordisk) for children 10 years or older, “except for insulin, metformin was the only antidiabetic medication available for use in youth, severely limiting treatment options,” he added.
Liraglutide ‘a huge breakthrough,’ other options on the horizon
The FDA approval of liraglutide was “a huge breakthrough” as the first noninsulin drug for pediatric type 2 diabetes since metformin was approved for pediatric use in 2000, Dr. Isganaitis said.
The ELLIPSE study, on which the approval was based, showed liraglutide was effective at lowering hemoglobin A1c and was generally well tolerated, although it was associated with a higher incidence of gastrointestinal symptoms.
In December 2020, the FDA also approved liraglutide (Saxenda) for the treatment of obesity in youth age 12 and older (at a dose of 3 mg as opposed to the 1.8-mg dose of liraglutide [Victoza]), “which is wonderful news considering that the majority of pediatric patients with type 2 diabetes also have obesity,” Dr. Isganaitis added.
“The results of studies of liraglutide on glycemia in diabetic youth are impressive, with both an additional benefit of weight loss and without unacceptable identified risks or side effects,” Dr. Copeland concurred.
Waiting in the wings
Dr. Isganaitis reported that a few phase 3 clinical trials of other therapies for pediatric patients with type 2 diabetes are in the wings.
The 24-week phase 3 T2GO clinical trial of the sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitor dapagliflozin (AstraZeneca) versus placebo in 72 patients with type 2 diabetes aged 10-24 years was completed in April 2020, and the data are being analyzed.
An AstraZeneca-sponsored phase 3 trial of the safety and efficacy of a weekly injection of the GLP-1 receptor agonist exenatide in 10- to 17-year-olds with type 2 diabetes (n = 82) has also been completed and data are being analyzed.
A Takeda-sponsored phase 3 pediatric study of the dipeptidyl peptidase–4 inhibitor alogliptin in 10- to 17-year-olds with type 2 diabetes (n = 150) is estimated to be completed by February 2022.
And the phase 3 DINAMO trial, sponsored by Boehringer Ingelheim, which is evaluating the efficacy and safety of the SGLT2 inhibitor empagliflozin (10 mg/25 mg) versus the DPP-4 inhibitor linagliptin (5 mg) versus placebo over 26 weeks in 10- to 17-year-olds with type 2 diabetes (estimated 186 participants), is expected to be completed in May 2023.
“I hope that these medications will demonstrate efficacy and allow pediatric patients with type 2 diabetes to have more treatment options,” Dr. Isganaitis concluded.
Type 2 diabetes more aggressive than type 1 diabetes in kids
According to Dr. Isganaitis, “there is a widely held misconception among the general public and even among some physicians that type 2 diabetes is somehow less worrisome or ‘milder’ than a diagnosis of type 1 diabetes.”
However, the risk of complications and severe morbidity is higher with a diagnosis of type 2 diabetes versus type 1 diabetes in a child, so “this condition needs to be managed intensively with a multidisciplinary team including pediatric endocrinology, nutrition [support], diabetes educators, and mental health support,” she emphasized.
Many people also believe that “type 2 diabetes in kids is a ‘lifestyle disease,’ ” she continued, “but in fact, there is a strong role for genetics.”
The ADA Presidents’ Select Abstract “paints a picture of youth-onset type 2 diabetes as a disease intermediate in extremity between monogenic diabetes [caused by mutations in a single gene] and type 2 diabetes [caused by multiple genes and lifestyle factors such as obesity], in which genetic variants in both insulin secretion and insulin response pathways are implicated.”
Along the same lines, Dr. Isganaitis presented an oral abstract at the meeting that showed that, among youth with newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes, those whose mothers had diabetes had faster disease progression and earlier onset of diabetes complications.
Dr. Isganaitis has reported no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Copeland has reported serving on data monitoring committees for Boehringer Ingelheim and Novo Nordisk, and on an advisory committee for a research study for Daiichi Sankyo.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.