User login
The Once and Future Veterans Health Administration
The Once and Future Veterans Health Administration
He who thus considers things in their first growth and origin ... will obtain the clearest view of them. Politics, Book I, Part II by Aristotle
Many seasoned observers of federal practice have signaled that the future of US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) health care is threatened as never before. Political forces and economic interests are siphoning Veterans Health Administration (VHA) capital and human resources into the community with an ineluctable push toward privatization.1
This Veterans Day, the vitality, if not the very viability of veteran health care, is in serious jeopardy, so it seems fitting to review the rationale for having institutions dedicated to the specialized medical treatment of veterans. Aristotle advises us on how to undertake this intellectual exercise in the epigraph. This column will revisit the historical origins of VA medicine to better appreciate the justification of an agency committed to this unique purpose and what may be sacrificed if it is decimated.
The provision of medical care focused on the injuries and illnesses of warriors is as old as war. The ancient Romans had among the first veterans’ hospital, named a valetudinarium. Sick and injured members of the Roman legions received state-of-the-art medical and surgical care from military doctors inside these facilities.2
In the United States, federal practice emerged almost simultaneously with the birth of a nation. Wounded troops and families of slain soldiers required rehabilitation and support from the fledgling federal government. This began a pattern of development in which each war generated novel injuries and disorders that required the VA to evolve (Table).3

Many arguments can be marshalled to demonstrate the importance of not just ensuring VA health care survives but also has the resources needed to thrive. I will highlight what I argue are the most important justifications for its existence.
The ethical argument: President Abraham Lincoln and a long line of government officials for more than 2 centuries have called the provision of high-quality health care focused on veterans a sacred trust. Failing to fulfill that promise is a violation of the deepest principles of veracity and fidelity that those who govern owe to the citizens who selflessly sacrificed time, health, and even in some cases life, for the safety and well-being of their country.4
The quality argument: Dozens of studies have found that compared to the community, many areas of veteran medical care are just plain better. Two surveys particularly salient in the aging veteran population illustrate this growing body of positive research. The most recent and largest survey of Medicare patients found that VHA hospitals surpassed community-based hospitals on all 10 metrics.5 A retrospective cohort study of mortality compared veterans transported by ambulance to VHA or community-based hospitals. The researchers found that those taken to VHA facilities had a 30-day all cause adjustment mortality 20 times lower than those taken to civilian hospitals, especially among minoritized populations who generally have higher mortality.6
The cultural argument: Glance at almost any form of communication from veterans or about their health care and you will apprehend common cultural themes. Even when frustrated that the system has not lived up to their expectations, and perhaps because of their sense of belonging, they voice ownership of VHA as their medical home. Surveys of veteran experiences have shown many feel more comfortable receiving care in the company of comrades in arms and from health care professionals with expertise and experience with veterans’ distinctive medical problems and the military values that inform their preferences for care.7
The complexity argument: Anyone who has worked even a short time in a VHA hospital or clinic knows the patients are in general more complicated than similar patients in the community. Multiple medical, geriatric, neuropsychiatric, substance use, and social comorbidities are the expectation, not the exception, as in some civilian systems. Many of the conditions common in the VHA such as traumatic brain injury, service-connected cancers, suicidal ideation, environmental exposures, and posttraumatic stress disorder would be encountered in community health care settings. The differences between VHA and community care led the RAND Corporation to caution that “Community care providers might not be equipped to handle the needs of veterans.”8
Let me bring this 1000-foot view of the crisis facing federal practice down to the literal level of my own home. For many years I have had a wonderful mechanic who has a mobile bike service. I was talking to him as he fixed my trike. I never knew he was a Vietnam era veteran, and he didn’t realize that I was a career VA health care professional at the very VHA hospital where he received care. He spontaneously told me that, “when I first got out, the VA was awful, but now it is wonderful and they are so good to me. I would not go anywhere else.” For the many veterans of that era who would echo his sentiments, we must not allow the VA to lose all it has gained since that painful time
Another philosopher, Søren Kierkegaard, wrote that “life must be understood backwards but lived forwards.”9 Our own brief back to the future journey in this editorial has, I hope, shown that VHA medical institutions and health professionals cannot be replaced with or replicated by civilian systems and clinicians. Continued attempts to do so betray the trust and risks the health and well-being of veterans. It also would deprive the country of research, innovation, and education that make unparalleled contributions to public health. Ultimately, these efforts to diminish VHA compromise the solidarity of service members with each other and with their federal practitioners. If this trend to dismantle an organization that originated with the sole purpose of caring for veterans continues, then the public expressions of respect and gratitude will sound shallower and more tentative with each passing Veterans Day.
- Quil L. Hundreds of VA clinicians warn that cuts threaten vet’s health care. National Public Radio. October 1, 2025. Accessed October 27, 2025. https://www.npr.org/2025/10/01/nx-s1-5554394/hundreds-of-va-clinicians-warn-that-cuts-threaten-vets-health-care
- Nutton V. Ancient Medicine. 2nd ed. Routledge; 2012.
- US Department of Veterans Affairs. VA History Summary. Updated June 13, 2025. Accessed October 27, 2025. https://department.va.gov/history/history-overview/
- Geppert CMA. Learning from history: the ethical foundation of VA health care. Fed Pract. 2016;33:6-7.
- US Department of Veterans Affairs. Nationwide patient survey shows VA hospitals outperform non-VA hospitals. News release. June 14, 2023. Accessed October 27, 2025. https://news.va.gov/press-room/nationwide-patient-survey-shows-va-hospitals-outperform-non-va-hospitals
- Chan DC, Danesh K, Costantini S, Card D, Taylor L, Studdert DM. Mortality among US veterans after emergency visits to Veterans Affairs and other hospitals: retrospective cohort study. BMJ. 2022;376:e068099. doi:10.1136/bmj-2021-068099
- Vigilante K, Batten SV, Shang Q, et al. Camaraderie among US veterans and their preferences for health care systems and practitioners. JAMA Netw Open. 2025;8(4):e255253. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2025.5253
- Rasmussen P, Farmer CM. The promise and challenges of VA community care: veterans’ issues in focus. Rand Health Q. 2023;10:9.
- Kierkegaard S. Journalen JJ:167 (1843) in: Søren Kierkegaards Skrifter. Vol 18. Copenhagen; 1997:306.
He who thus considers things in their first growth and origin ... will obtain the clearest view of them. Politics, Book I, Part II by Aristotle
Many seasoned observers of federal practice have signaled that the future of US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) health care is threatened as never before. Political forces and economic interests are siphoning Veterans Health Administration (VHA) capital and human resources into the community with an ineluctable push toward privatization.1
This Veterans Day, the vitality, if not the very viability of veteran health care, is in serious jeopardy, so it seems fitting to review the rationale for having institutions dedicated to the specialized medical treatment of veterans. Aristotle advises us on how to undertake this intellectual exercise in the epigraph. This column will revisit the historical origins of VA medicine to better appreciate the justification of an agency committed to this unique purpose and what may be sacrificed if it is decimated.
The provision of medical care focused on the injuries and illnesses of warriors is as old as war. The ancient Romans had among the first veterans’ hospital, named a valetudinarium. Sick and injured members of the Roman legions received state-of-the-art medical and surgical care from military doctors inside these facilities.2
In the United States, federal practice emerged almost simultaneously with the birth of a nation. Wounded troops and families of slain soldiers required rehabilitation and support from the fledgling federal government. This began a pattern of development in which each war generated novel injuries and disorders that required the VA to evolve (Table).3

Many arguments can be marshalled to demonstrate the importance of not just ensuring VA health care survives but also has the resources needed to thrive. I will highlight what I argue are the most important justifications for its existence.
The ethical argument: President Abraham Lincoln and a long line of government officials for more than 2 centuries have called the provision of high-quality health care focused on veterans a sacred trust. Failing to fulfill that promise is a violation of the deepest principles of veracity and fidelity that those who govern owe to the citizens who selflessly sacrificed time, health, and even in some cases life, for the safety and well-being of their country.4
The quality argument: Dozens of studies have found that compared to the community, many areas of veteran medical care are just plain better. Two surveys particularly salient in the aging veteran population illustrate this growing body of positive research. The most recent and largest survey of Medicare patients found that VHA hospitals surpassed community-based hospitals on all 10 metrics.5 A retrospective cohort study of mortality compared veterans transported by ambulance to VHA or community-based hospitals. The researchers found that those taken to VHA facilities had a 30-day all cause adjustment mortality 20 times lower than those taken to civilian hospitals, especially among minoritized populations who generally have higher mortality.6
The cultural argument: Glance at almost any form of communication from veterans or about their health care and you will apprehend common cultural themes. Even when frustrated that the system has not lived up to their expectations, and perhaps because of their sense of belonging, they voice ownership of VHA as their medical home. Surveys of veteran experiences have shown many feel more comfortable receiving care in the company of comrades in arms and from health care professionals with expertise and experience with veterans’ distinctive medical problems and the military values that inform their preferences for care.7
The complexity argument: Anyone who has worked even a short time in a VHA hospital or clinic knows the patients are in general more complicated than similar patients in the community. Multiple medical, geriatric, neuropsychiatric, substance use, and social comorbidities are the expectation, not the exception, as in some civilian systems. Many of the conditions common in the VHA such as traumatic brain injury, service-connected cancers, suicidal ideation, environmental exposures, and posttraumatic stress disorder would be encountered in community health care settings. The differences between VHA and community care led the RAND Corporation to caution that “Community care providers might not be equipped to handle the needs of veterans.”8
Let me bring this 1000-foot view of the crisis facing federal practice down to the literal level of my own home. For many years I have had a wonderful mechanic who has a mobile bike service. I was talking to him as he fixed my trike. I never knew he was a Vietnam era veteran, and he didn’t realize that I was a career VA health care professional at the very VHA hospital where he received care. He spontaneously told me that, “when I first got out, the VA was awful, but now it is wonderful and they are so good to me. I would not go anywhere else.” For the many veterans of that era who would echo his sentiments, we must not allow the VA to lose all it has gained since that painful time
Another philosopher, Søren Kierkegaard, wrote that “life must be understood backwards but lived forwards.”9 Our own brief back to the future journey in this editorial has, I hope, shown that VHA medical institutions and health professionals cannot be replaced with or replicated by civilian systems and clinicians. Continued attempts to do so betray the trust and risks the health and well-being of veterans. It also would deprive the country of research, innovation, and education that make unparalleled contributions to public health. Ultimately, these efforts to diminish VHA compromise the solidarity of service members with each other and with their federal practitioners. If this trend to dismantle an organization that originated with the sole purpose of caring for veterans continues, then the public expressions of respect and gratitude will sound shallower and more tentative with each passing Veterans Day.
He who thus considers things in their first growth and origin ... will obtain the clearest view of them. Politics, Book I, Part II by Aristotle
Many seasoned observers of federal practice have signaled that the future of US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) health care is threatened as never before. Political forces and economic interests are siphoning Veterans Health Administration (VHA) capital and human resources into the community with an ineluctable push toward privatization.1
This Veterans Day, the vitality, if not the very viability of veteran health care, is in serious jeopardy, so it seems fitting to review the rationale for having institutions dedicated to the specialized medical treatment of veterans. Aristotle advises us on how to undertake this intellectual exercise in the epigraph. This column will revisit the historical origins of VA medicine to better appreciate the justification of an agency committed to this unique purpose and what may be sacrificed if it is decimated.
The provision of medical care focused on the injuries and illnesses of warriors is as old as war. The ancient Romans had among the first veterans’ hospital, named a valetudinarium. Sick and injured members of the Roman legions received state-of-the-art medical and surgical care from military doctors inside these facilities.2
In the United States, federal practice emerged almost simultaneously with the birth of a nation. Wounded troops and families of slain soldiers required rehabilitation and support from the fledgling federal government. This began a pattern of development in which each war generated novel injuries and disorders that required the VA to evolve (Table).3

Many arguments can be marshalled to demonstrate the importance of not just ensuring VA health care survives but also has the resources needed to thrive. I will highlight what I argue are the most important justifications for its existence.
The ethical argument: President Abraham Lincoln and a long line of government officials for more than 2 centuries have called the provision of high-quality health care focused on veterans a sacred trust. Failing to fulfill that promise is a violation of the deepest principles of veracity and fidelity that those who govern owe to the citizens who selflessly sacrificed time, health, and even in some cases life, for the safety and well-being of their country.4
The quality argument: Dozens of studies have found that compared to the community, many areas of veteran medical care are just plain better. Two surveys particularly salient in the aging veteran population illustrate this growing body of positive research. The most recent and largest survey of Medicare patients found that VHA hospitals surpassed community-based hospitals on all 10 metrics.5 A retrospective cohort study of mortality compared veterans transported by ambulance to VHA or community-based hospitals. The researchers found that those taken to VHA facilities had a 30-day all cause adjustment mortality 20 times lower than those taken to civilian hospitals, especially among minoritized populations who generally have higher mortality.6
The cultural argument: Glance at almost any form of communication from veterans or about their health care and you will apprehend common cultural themes. Even when frustrated that the system has not lived up to their expectations, and perhaps because of their sense of belonging, they voice ownership of VHA as their medical home. Surveys of veteran experiences have shown many feel more comfortable receiving care in the company of comrades in arms and from health care professionals with expertise and experience with veterans’ distinctive medical problems and the military values that inform their preferences for care.7
The complexity argument: Anyone who has worked even a short time in a VHA hospital or clinic knows the patients are in general more complicated than similar patients in the community. Multiple medical, geriatric, neuropsychiatric, substance use, and social comorbidities are the expectation, not the exception, as in some civilian systems. Many of the conditions common in the VHA such as traumatic brain injury, service-connected cancers, suicidal ideation, environmental exposures, and posttraumatic stress disorder would be encountered in community health care settings. The differences between VHA and community care led the RAND Corporation to caution that “Community care providers might not be equipped to handle the needs of veterans.”8
Let me bring this 1000-foot view of the crisis facing federal practice down to the literal level of my own home. For many years I have had a wonderful mechanic who has a mobile bike service. I was talking to him as he fixed my trike. I never knew he was a Vietnam era veteran, and he didn’t realize that I was a career VA health care professional at the very VHA hospital where he received care. He spontaneously told me that, “when I first got out, the VA was awful, but now it is wonderful and they are so good to me. I would not go anywhere else.” For the many veterans of that era who would echo his sentiments, we must not allow the VA to lose all it has gained since that painful time
Another philosopher, Søren Kierkegaard, wrote that “life must be understood backwards but lived forwards.”9 Our own brief back to the future journey in this editorial has, I hope, shown that VHA medical institutions and health professionals cannot be replaced with or replicated by civilian systems and clinicians. Continued attempts to do so betray the trust and risks the health and well-being of veterans. It also would deprive the country of research, innovation, and education that make unparalleled contributions to public health. Ultimately, these efforts to diminish VHA compromise the solidarity of service members with each other and with their federal practitioners. If this trend to dismantle an organization that originated with the sole purpose of caring for veterans continues, then the public expressions of respect and gratitude will sound shallower and more tentative with each passing Veterans Day.
- Quil L. Hundreds of VA clinicians warn that cuts threaten vet’s health care. National Public Radio. October 1, 2025. Accessed October 27, 2025. https://www.npr.org/2025/10/01/nx-s1-5554394/hundreds-of-va-clinicians-warn-that-cuts-threaten-vets-health-care
- Nutton V. Ancient Medicine. 2nd ed. Routledge; 2012.
- US Department of Veterans Affairs. VA History Summary. Updated June 13, 2025. Accessed October 27, 2025. https://department.va.gov/history/history-overview/
- Geppert CMA. Learning from history: the ethical foundation of VA health care. Fed Pract. 2016;33:6-7.
- US Department of Veterans Affairs. Nationwide patient survey shows VA hospitals outperform non-VA hospitals. News release. June 14, 2023. Accessed October 27, 2025. https://news.va.gov/press-room/nationwide-patient-survey-shows-va-hospitals-outperform-non-va-hospitals
- Chan DC, Danesh K, Costantini S, Card D, Taylor L, Studdert DM. Mortality among US veterans after emergency visits to Veterans Affairs and other hospitals: retrospective cohort study. BMJ. 2022;376:e068099. doi:10.1136/bmj-2021-068099
- Vigilante K, Batten SV, Shang Q, et al. Camaraderie among US veterans and their preferences for health care systems and practitioners. JAMA Netw Open. 2025;8(4):e255253. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2025.5253
- Rasmussen P, Farmer CM. The promise and challenges of VA community care: veterans’ issues in focus. Rand Health Q. 2023;10:9.
- Kierkegaard S. Journalen JJ:167 (1843) in: Søren Kierkegaards Skrifter. Vol 18. Copenhagen; 1997:306.
- Quil L. Hundreds of VA clinicians warn that cuts threaten vet’s health care. National Public Radio. October 1, 2025. Accessed October 27, 2025. https://www.npr.org/2025/10/01/nx-s1-5554394/hundreds-of-va-clinicians-warn-that-cuts-threaten-vets-health-care
- Nutton V. Ancient Medicine. 2nd ed. Routledge; 2012.
- US Department of Veterans Affairs. VA History Summary. Updated June 13, 2025. Accessed October 27, 2025. https://department.va.gov/history/history-overview/
- Geppert CMA. Learning from history: the ethical foundation of VA health care. Fed Pract. 2016;33:6-7.
- US Department of Veterans Affairs. Nationwide patient survey shows VA hospitals outperform non-VA hospitals. News release. June 14, 2023. Accessed October 27, 2025. https://news.va.gov/press-room/nationwide-patient-survey-shows-va-hospitals-outperform-non-va-hospitals
- Chan DC, Danesh K, Costantini S, Card D, Taylor L, Studdert DM. Mortality among US veterans after emergency visits to Veterans Affairs and other hospitals: retrospective cohort study. BMJ. 2022;376:e068099. doi:10.1136/bmj-2021-068099
- Vigilante K, Batten SV, Shang Q, et al. Camaraderie among US veterans and their preferences for health care systems and practitioners. JAMA Netw Open. 2025;8(4):e255253. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2025.5253
- Rasmussen P, Farmer CM. The promise and challenges of VA community care: veterans’ issues in focus. Rand Health Q. 2023;10:9.
- Kierkegaard S. Journalen JJ:167 (1843) in: Søren Kierkegaards Skrifter. Vol 18. Copenhagen; 1997:306.
The Once and Future Veterans Health Administration
The Once and Future Veterans Health Administration
VHA Facilities Report Severe Staffing Shortages
VHA Facilities Report Severe Staffing Shortages
For > 10 years, the US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) Office of Inspector General (OIG) has annually surveyed Veterans Health Administration (VHA) facilities about staffing. Its recently released report is the 8th to find severe shortages—in this case, across the board. There were 4434 severe staffing shortages reported across all 139 VHA facilities in fiscal year (FY) 2025, a 50% increase from FY 2024.
In the OIG report lexicon, a severe shortage refers to "particular occupations that are difficult to fill," and is not necessarily an indication of vacancies. Vacancy refers to a "specific unoccupied position and is distinct from the designation of a severe shortage." For example, a facility could identify an occupation as a severe occupational shortage, which could have no vacant positions or 100 vacant positions.
Nearly all facilities (94%) had severe shortages for medical officers, and 79% had severe shortages for nurses even with VHA's ability to make noncompetitive appointments for those occupations. Psychology was the most frequently reported severe clinical occupational staffing shortage, reported by 79 facilities (57%), down slightly from FY 2024 (61%). One facility reported 116 clinical occupational shortages.
The report notes that the OIG does not verify or otherwise confirm the questionnaire responses, but it appears to support other data. In the first 9 months of FY 2024, the VA added 223 physicians and 3196 nurses compared with a deficit of 781 physicians and 2129 nurses over the same period in FY 2025.
VHA facilities are finding it hard to reverse the trend. According to internal documents examined by ProPublica, nearly 4 in 10 of the roughly 2000 doctors offered jobs from January through March 2025 turned them down, 4 times the rate in the same time period in 2024. VHA also lost twice as many nurses as it hired between January and June. Many potential candidates reportedly were worried about the stability of VA employment.
VA spokesperson Peter Kasperowicz did not dispute the ProPublica findings but accused the news outlet of bias and "cherry-picking issues that are mostly routine." A nationwide shortage of health care workers has made hiring and retention difficult, he said.
Kasperowicz said the VA is "working to address" the number of doctors declining job offers by speeding up the hiring process and that the agency "has several strategies to navigate shortages." Those include referring veterans to telehealth and private clinicians.
In a statement released Aug. 12, Sen Richard Blumenthal (D-CT), ranking member of the Senate Committee on Veterans' Affairs, said, "This report confirms what we've warned for months—this Administration is driving dedicated VA employees to the private sector at untenable rates."
The OIG survey did not ask about facilities' rationales for identifying shortages. Moreover, the OIG says the responses don't reflect the possible impacts of "workforce reshaping efforts," such as the Deferred Resignation Program announced on January 28, 2025.
In response to the OIG report, Kasperowicz said it is "not based on actual VA health care facility vacancies and therefore is not a reliable indicator of staffing shortages." In a statement to CBS News, he added, "The report simply lists occupations facilities feel are difficult for which to recruit and retain, so the results are completely subjective, not standardized, and unreliable." According to Kasperowicz, the system-wide vacancy rates for doctors and nurses are 14% and 10%, respectively, which are in line with historical averages.
The OIG made no recommendations but "encourages VA leaders to use these review results to inform staffing initiatives and organizational change."
For > 10 years, the US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) Office of Inspector General (OIG) has annually surveyed Veterans Health Administration (VHA) facilities about staffing. Its recently released report is the 8th to find severe shortages—in this case, across the board. There were 4434 severe staffing shortages reported across all 139 VHA facilities in fiscal year (FY) 2025, a 50% increase from FY 2024.
In the OIG report lexicon, a severe shortage refers to "particular occupations that are difficult to fill," and is not necessarily an indication of vacancies. Vacancy refers to a "specific unoccupied position and is distinct from the designation of a severe shortage." For example, a facility could identify an occupation as a severe occupational shortage, which could have no vacant positions or 100 vacant positions.
Nearly all facilities (94%) had severe shortages for medical officers, and 79% had severe shortages for nurses even with VHA's ability to make noncompetitive appointments for those occupations. Psychology was the most frequently reported severe clinical occupational staffing shortage, reported by 79 facilities (57%), down slightly from FY 2024 (61%). One facility reported 116 clinical occupational shortages.
The report notes that the OIG does not verify or otherwise confirm the questionnaire responses, but it appears to support other data. In the first 9 months of FY 2024, the VA added 223 physicians and 3196 nurses compared with a deficit of 781 physicians and 2129 nurses over the same period in FY 2025.
VHA facilities are finding it hard to reverse the trend. According to internal documents examined by ProPublica, nearly 4 in 10 of the roughly 2000 doctors offered jobs from January through March 2025 turned them down, 4 times the rate in the same time period in 2024. VHA also lost twice as many nurses as it hired between January and June. Many potential candidates reportedly were worried about the stability of VA employment.
VA spokesperson Peter Kasperowicz did not dispute the ProPublica findings but accused the news outlet of bias and "cherry-picking issues that are mostly routine." A nationwide shortage of health care workers has made hiring and retention difficult, he said.
Kasperowicz said the VA is "working to address" the number of doctors declining job offers by speeding up the hiring process and that the agency "has several strategies to navigate shortages." Those include referring veterans to telehealth and private clinicians.
In a statement released Aug. 12, Sen Richard Blumenthal (D-CT), ranking member of the Senate Committee on Veterans' Affairs, said, "This report confirms what we've warned for months—this Administration is driving dedicated VA employees to the private sector at untenable rates."
The OIG survey did not ask about facilities' rationales for identifying shortages. Moreover, the OIG says the responses don't reflect the possible impacts of "workforce reshaping efforts," such as the Deferred Resignation Program announced on January 28, 2025.
In response to the OIG report, Kasperowicz said it is "not based on actual VA health care facility vacancies and therefore is not a reliable indicator of staffing shortages." In a statement to CBS News, he added, "The report simply lists occupations facilities feel are difficult for which to recruit and retain, so the results are completely subjective, not standardized, and unreliable." According to Kasperowicz, the system-wide vacancy rates for doctors and nurses are 14% and 10%, respectively, which are in line with historical averages.
The OIG made no recommendations but "encourages VA leaders to use these review results to inform staffing initiatives and organizational change."
For > 10 years, the US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) Office of Inspector General (OIG) has annually surveyed Veterans Health Administration (VHA) facilities about staffing. Its recently released report is the 8th to find severe shortages—in this case, across the board. There were 4434 severe staffing shortages reported across all 139 VHA facilities in fiscal year (FY) 2025, a 50% increase from FY 2024.
In the OIG report lexicon, a severe shortage refers to "particular occupations that are difficult to fill," and is not necessarily an indication of vacancies. Vacancy refers to a "specific unoccupied position and is distinct from the designation of a severe shortage." For example, a facility could identify an occupation as a severe occupational shortage, which could have no vacant positions or 100 vacant positions.
Nearly all facilities (94%) had severe shortages for medical officers, and 79% had severe shortages for nurses even with VHA's ability to make noncompetitive appointments for those occupations. Psychology was the most frequently reported severe clinical occupational staffing shortage, reported by 79 facilities (57%), down slightly from FY 2024 (61%). One facility reported 116 clinical occupational shortages.
The report notes that the OIG does not verify or otherwise confirm the questionnaire responses, but it appears to support other data. In the first 9 months of FY 2024, the VA added 223 physicians and 3196 nurses compared with a deficit of 781 physicians and 2129 nurses over the same period in FY 2025.
VHA facilities are finding it hard to reverse the trend. According to internal documents examined by ProPublica, nearly 4 in 10 of the roughly 2000 doctors offered jobs from January through March 2025 turned them down, 4 times the rate in the same time period in 2024. VHA also lost twice as many nurses as it hired between January and June. Many potential candidates reportedly were worried about the stability of VA employment.
VA spokesperson Peter Kasperowicz did not dispute the ProPublica findings but accused the news outlet of bias and "cherry-picking issues that are mostly routine." A nationwide shortage of health care workers has made hiring and retention difficult, he said.
Kasperowicz said the VA is "working to address" the number of doctors declining job offers by speeding up the hiring process and that the agency "has several strategies to navigate shortages." Those include referring veterans to telehealth and private clinicians.
In a statement released Aug. 12, Sen Richard Blumenthal (D-CT), ranking member of the Senate Committee on Veterans' Affairs, said, "This report confirms what we've warned for months—this Administration is driving dedicated VA employees to the private sector at untenable rates."
The OIG survey did not ask about facilities' rationales for identifying shortages. Moreover, the OIG says the responses don't reflect the possible impacts of "workforce reshaping efforts," such as the Deferred Resignation Program announced on January 28, 2025.
In response to the OIG report, Kasperowicz said it is "not based on actual VA health care facility vacancies and therefore is not a reliable indicator of staffing shortages." In a statement to CBS News, he added, "The report simply lists occupations facilities feel are difficult for which to recruit and retain, so the results are completely subjective, not standardized, and unreliable." According to Kasperowicz, the system-wide vacancy rates for doctors and nurses are 14% and 10%, respectively, which are in line with historical averages.
The OIG made no recommendations but "encourages VA leaders to use these review results to inform staffing initiatives and organizational change."
VHA Facilities Report Severe Staffing Shortages
VHA Facilities Report Severe Staffing Shortages
VA Workforce Shrinking as it Loses Collective Bargaining Rights
VA Workforce Shrinking as it Loses Collective Bargaining Rights
The US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) is on pace to cut nearly 30,000 positions by the end of fiscal year 2025, an initiative driven by a federal hiring freeze, deferred resignations, retirements, and normal attrition. According to the VA Workforce Dashboard, health care experienced the most significant net change through the first 9 months of fiscal year 2025. That included 2129 fewer registered nurses, 751 fewer physicians, and drops of 565 licensed practical nurses, 564 nurse assistants, and 1294 medical support assistants. In total, nearly 17,000 VA employees have left their jobs and 12,000 more are expected to leave by the end of September 2025.
According to VA Secretary Doug Collins, the departures have eliminated the need for the "large-scale" reduction-in-force that he proposed earlier in 2025.
The VA also announced that in accordance with an Executive Order issued by President Donald Trump, it is terminating collective bargaining rights for most of its employees, including most clinical staff not in leadership positions. The order includes the National Nurses Organizing Committee/National Nurses United, which represents 16,000 VA nurses, and the American Federation of Government Employees, which represents 320,000 VA employees. The order exempted police officers, firefighters, and security guards. The Unions have indicated they will continue to fight the changes.
VA staffing has undergone significant reversals over the past year. The VA added 223 physicians and 3196 nurses in the first 9 months of fiscal year 2024 before reversing course this year. According to the Workforce Dashboard, the VA and Veterans Health Administration combined to hire 26,984 employees in fiscal year 2025. Cumulative losses, however, totaled 54,308.
During exit interviews, VA employees noted a variety of reasons for their departure. "Personal/family matters" and "geographic relocation" were cited by many job categories. In addition, medical and dental workers also noted "poor working relationship with supervisor or coworker(s)," "desired work schedule not offered," and "job stress/pressure" among the causes. The VA has lost 148 psychologists in fiscal year 2025 who cited "lack of trust/confidence in senior leaders," as well as "policy or technology barriers to getting the work done," and "job stress/pressure" among their reasons for departure.
The US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) is on pace to cut nearly 30,000 positions by the end of fiscal year 2025, an initiative driven by a federal hiring freeze, deferred resignations, retirements, and normal attrition. According to the VA Workforce Dashboard, health care experienced the most significant net change through the first 9 months of fiscal year 2025. That included 2129 fewer registered nurses, 751 fewer physicians, and drops of 565 licensed practical nurses, 564 nurse assistants, and 1294 medical support assistants. In total, nearly 17,000 VA employees have left their jobs and 12,000 more are expected to leave by the end of September 2025.
According to VA Secretary Doug Collins, the departures have eliminated the need for the "large-scale" reduction-in-force that he proposed earlier in 2025.
The VA also announced that in accordance with an Executive Order issued by President Donald Trump, it is terminating collective bargaining rights for most of its employees, including most clinical staff not in leadership positions. The order includes the National Nurses Organizing Committee/National Nurses United, which represents 16,000 VA nurses, and the American Federation of Government Employees, which represents 320,000 VA employees. The order exempted police officers, firefighters, and security guards. The Unions have indicated they will continue to fight the changes.
VA staffing has undergone significant reversals over the past year. The VA added 223 physicians and 3196 nurses in the first 9 months of fiscal year 2024 before reversing course this year. According to the Workforce Dashboard, the VA and Veterans Health Administration combined to hire 26,984 employees in fiscal year 2025. Cumulative losses, however, totaled 54,308.
During exit interviews, VA employees noted a variety of reasons for their departure. "Personal/family matters" and "geographic relocation" were cited by many job categories. In addition, medical and dental workers also noted "poor working relationship with supervisor or coworker(s)," "desired work schedule not offered," and "job stress/pressure" among the causes. The VA has lost 148 psychologists in fiscal year 2025 who cited "lack of trust/confidence in senior leaders," as well as "policy or technology barriers to getting the work done," and "job stress/pressure" among their reasons for departure.
The US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) is on pace to cut nearly 30,000 positions by the end of fiscal year 2025, an initiative driven by a federal hiring freeze, deferred resignations, retirements, and normal attrition. According to the VA Workforce Dashboard, health care experienced the most significant net change through the first 9 months of fiscal year 2025. That included 2129 fewer registered nurses, 751 fewer physicians, and drops of 565 licensed practical nurses, 564 nurse assistants, and 1294 medical support assistants. In total, nearly 17,000 VA employees have left their jobs and 12,000 more are expected to leave by the end of September 2025.
According to VA Secretary Doug Collins, the departures have eliminated the need for the "large-scale" reduction-in-force that he proposed earlier in 2025.
The VA also announced that in accordance with an Executive Order issued by President Donald Trump, it is terminating collective bargaining rights for most of its employees, including most clinical staff not in leadership positions. The order includes the National Nurses Organizing Committee/National Nurses United, which represents 16,000 VA nurses, and the American Federation of Government Employees, which represents 320,000 VA employees. The order exempted police officers, firefighters, and security guards. The Unions have indicated they will continue to fight the changes.
VA staffing has undergone significant reversals over the past year. The VA added 223 physicians and 3196 nurses in the first 9 months of fiscal year 2024 before reversing course this year. According to the Workforce Dashboard, the VA and Veterans Health Administration combined to hire 26,984 employees in fiscal year 2025. Cumulative losses, however, totaled 54,308.
During exit interviews, VA employees noted a variety of reasons for their departure. "Personal/family matters" and "geographic relocation" were cited by many job categories. In addition, medical and dental workers also noted "poor working relationship with supervisor or coworker(s)," "desired work schedule not offered," and "job stress/pressure" among the causes. The VA has lost 148 psychologists in fiscal year 2025 who cited "lack of trust/confidence in senior leaders," as well as "policy or technology barriers to getting the work done," and "job stress/pressure" among their reasons for departure.
VA Workforce Shrinking as it Loses Collective Bargaining Rights
VA Workforce Shrinking as it Loses Collective Bargaining Rights
AVAHO Encourages Members to Make Voices Heard
Advocacy for veterans with cancer has always been a central part of the Association for VA Hematology/Oncology (AVAHO) mission, but that advocacy has now taken on a new focus: the fate of US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) employees. The advocacy portal provides templated letters, a search function to find local Senators and Members of Congress, a search function to find regional media outlets, updates on voting and elections, and information on key legislation relevant to VA health care.
To ensure its members’ concerns are heard, AVAHO is encouraging members, in their own time and as private citizens, to contact their local representatives to inform them about the real impact of recent policy changes on VA employees and the veterans they care for. Members can select any of 4 letters focused on reductions in force, cancellation of VA contracts, the return to office mandate, and the National Institutes of Health’s proposed cap on indirect cost for research grants: “AVAHO recognizes the power of the individual voice. Our members have an important role in shaping the health care services provided to veterans across our nation.”
"The contracts that have been canceled and continue to be canceled included critical services related to cancer care," AVAHO notes on its Advocacy page. "We know these impacted contracts have hindered the VA’s ability to implement research protocols, process and report pharmacogenomic results, manage Electronic Health Record Modernization workgroups responsible for safety improvements, and execute new oncology services through the Close to Me initiative, just to name a few."
Advocacy for veterans with cancer has always been a central part of the Association for VA Hematology/Oncology (AVAHO) mission, but that advocacy has now taken on a new focus: the fate of US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) employees. The advocacy portal provides templated letters, a search function to find local Senators and Members of Congress, a search function to find regional media outlets, updates on voting and elections, and information on key legislation relevant to VA health care.
To ensure its members’ concerns are heard, AVAHO is encouraging members, in their own time and as private citizens, to contact their local representatives to inform them about the real impact of recent policy changes on VA employees and the veterans they care for. Members can select any of 4 letters focused on reductions in force, cancellation of VA contracts, the return to office mandate, and the National Institutes of Health’s proposed cap on indirect cost for research grants: “AVAHO recognizes the power of the individual voice. Our members have an important role in shaping the health care services provided to veterans across our nation.”
"The contracts that have been canceled and continue to be canceled included critical services related to cancer care," AVAHO notes on its Advocacy page. "We know these impacted contracts have hindered the VA’s ability to implement research protocols, process and report pharmacogenomic results, manage Electronic Health Record Modernization workgroups responsible for safety improvements, and execute new oncology services through the Close to Me initiative, just to name a few."
Advocacy for veterans with cancer has always been a central part of the Association for VA Hematology/Oncology (AVAHO) mission, but that advocacy has now taken on a new focus: the fate of US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) employees. The advocacy portal provides templated letters, a search function to find local Senators and Members of Congress, a search function to find regional media outlets, updates on voting and elections, and information on key legislation relevant to VA health care.
To ensure its members’ concerns are heard, AVAHO is encouraging members, in their own time and as private citizens, to contact their local representatives to inform them about the real impact of recent policy changes on VA employees and the veterans they care for. Members can select any of 4 letters focused on reductions in force, cancellation of VA contracts, the return to office mandate, and the National Institutes of Health’s proposed cap on indirect cost for research grants: “AVAHO recognizes the power of the individual voice. Our members have an important role in shaping the health care services provided to veterans across our nation.”
"The contracts that have been canceled and continue to be canceled included critical services related to cancer care," AVAHO notes on its Advocacy page. "We know these impacted contracts have hindered the VA’s ability to implement research protocols, process and report pharmacogenomic results, manage Electronic Health Record Modernization workgroups responsible for safety improvements, and execute new oncology services through the Close to Me initiative, just to name a few."
VA Choice Bill Defeated in the House
A U.S. House of Representatives appropriation to fund the Veterans Choice Program surprisingly went down to defeat on Monday. The VA Choice Program is set to run out of money in September, and VA officials have been calling for Congress to provide additional funding for the program. Republican leaders, hoping to expedite the bill’s passage and thinking that it was not controversial, submitted the bill in a process that required the votes of two-thirds of the representatives. The 219-186 vote fell well short of the necessary two-thirds, and voting fell largely along party lines.
Many veterans service organizations (VSOs) were critical of the bill and called on the House to make substantial changes to it. Seven VSOs signed a joint statement calling for the bill’s defeat. “As organizations who represent and support the interests of America’s 21 million veterans, and in fulfillment of our mandate to ensure that the men and women who served are able to receive the health care and benefits they need and deserve, we are calling on Members of Congress to defeat the House vote on unacceptable choice funding legislation (S. 114, with amendments),” the statement read.
AMVETS, Disabled American Veterans , Military Officers Association of America, Military Order of the Purple Heart, Veterans of Foreign Wars, Vietnam Veterans of America, and Wounded Warrior Project all signed on to the statement. The chief complaint was that the legislation “includes funding only for the ‘choice’ program which provides additional community care options, but makes no investment in VA and uses ‘savings’ from other veterans benefits or services to ‘pay’ for the ‘choice’ program.”
The bill would have allocated $2 billion for the Veterans Choice Program, taken funding for veteran housing loan fees, and would reduce the pensions for some veterans living in nursing facilities that also could be paid for under the Medicaid program.
The fate of the bill and funding for the Veterans Choice Program remains unclear. Senate and House veterans committees seem to be far apart on how to fund the program and for efforts to make more substantive changes to the program. Although House Republicans eventually may be able to pass a bill without Democrats, in the Senate, they will need the support of at least a handful of Democrats to move the bill to the President’s desk.
A U.S. House of Representatives appropriation to fund the Veterans Choice Program surprisingly went down to defeat on Monday. The VA Choice Program is set to run out of money in September, and VA officials have been calling for Congress to provide additional funding for the program. Republican leaders, hoping to expedite the bill’s passage and thinking that it was not controversial, submitted the bill in a process that required the votes of two-thirds of the representatives. The 219-186 vote fell well short of the necessary two-thirds, and voting fell largely along party lines.
Many veterans service organizations (VSOs) were critical of the bill and called on the House to make substantial changes to it. Seven VSOs signed a joint statement calling for the bill’s defeat. “As organizations who represent and support the interests of America’s 21 million veterans, and in fulfillment of our mandate to ensure that the men and women who served are able to receive the health care and benefits they need and deserve, we are calling on Members of Congress to defeat the House vote on unacceptable choice funding legislation (S. 114, with amendments),” the statement read.
AMVETS, Disabled American Veterans , Military Officers Association of America, Military Order of the Purple Heart, Veterans of Foreign Wars, Vietnam Veterans of America, and Wounded Warrior Project all signed on to the statement. The chief complaint was that the legislation “includes funding only for the ‘choice’ program which provides additional community care options, but makes no investment in VA and uses ‘savings’ from other veterans benefits or services to ‘pay’ for the ‘choice’ program.”
The bill would have allocated $2 billion for the Veterans Choice Program, taken funding for veteran housing loan fees, and would reduce the pensions for some veterans living in nursing facilities that also could be paid for under the Medicaid program.
The fate of the bill and funding for the Veterans Choice Program remains unclear. Senate and House veterans committees seem to be far apart on how to fund the program and for efforts to make more substantive changes to the program. Although House Republicans eventually may be able to pass a bill without Democrats, in the Senate, they will need the support of at least a handful of Democrats to move the bill to the President’s desk.
A U.S. House of Representatives appropriation to fund the Veterans Choice Program surprisingly went down to defeat on Monday. The VA Choice Program is set to run out of money in September, and VA officials have been calling for Congress to provide additional funding for the program. Republican leaders, hoping to expedite the bill’s passage and thinking that it was not controversial, submitted the bill in a process that required the votes of two-thirds of the representatives. The 219-186 vote fell well short of the necessary two-thirds, and voting fell largely along party lines.
Many veterans service organizations (VSOs) were critical of the bill and called on the House to make substantial changes to it. Seven VSOs signed a joint statement calling for the bill’s defeat. “As organizations who represent and support the interests of America’s 21 million veterans, and in fulfillment of our mandate to ensure that the men and women who served are able to receive the health care and benefits they need and deserve, we are calling on Members of Congress to defeat the House vote on unacceptable choice funding legislation (S. 114, with amendments),” the statement read.
AMVETS, Disabled American Veterans , Military Officers Association of America, Military Order of the Purple Heart, Veterans of Foreign Wars, Vietnam Veterans of America, and Wounded Warrior Project all signed on to the statement. The chief complaint was that the legislation “includes funding only for the ‘choice’ program which provides additional community care options, but makes no investment in VA and uses ‘savings’ from other veterans benefits or services to ‘pay’ for the ‘choice’ program.”
The bill would have allocated $2 billion for the Veterans Choice Program, taken funding for veteran housing loan fees, and would reduce the pensions for some veterans living in nursing facilities that also could be paid for under the Medicaid program.
The fate of the bill and funding for the Veterans Choice Program remains unclear. Senate and House veterans committees seem to be far apart on how to fund the program and for efforts to make more substantive changes to the program. Although House Republicans eventually may be able to pass a bill without Democrats, in the Senate, they will need the support of at least a handful of Democrats to move the bill to the President’s desk.
Negotiating the VUCA World Through Tiered Huddles
Negotiating the VUCA World Through Tiered Huddles
To see what is in front of one’s nose needs a constant struggle.
George Orwell (1946)1
In 2019, the Veterans Health Administration (VHA) initiated a process to become a high reliability organization (HRO).2 The COVID-19 pandemic has been described in medical literature as a volatile, uncertain, complex, and ambiguous (VUCA) event, underscoring the necessity of resilient communication strategies.3 Challenges posed by 2024 Hurricanes Helene and Milton further highlighted the need for resilient communication strategies within HRO implementation.
Central to the HRO journey within the VHA has been the development of tiered huddles, an evolution of the safety huddle concept.4 Emerging organically as an effective communication mechanism across multiple facilities between 2019 and 2020, tiered huddles were, in part, spurred by the onset of COVID-19. Tiered huddles represent a proactive approach to identifying and addressing organizational threats in their early stages, thereby preventing their escalation to a VUCA-laden crisis.5 When conditions evolve beyond the horizon of tractability, where challenges are easily identified and resolved, tiered huddles serve as a resilient mechanism to restore dynamic equilibrium within the organization.6,7
This article describes how tiered huddles were integrated within Veterans Integrated Service Network (VISN) 4 and explores why these huddles are essential, particularly in the context of VUCA events. What began as a local-level tactic has now gained widespread acceptance and continues to evolve across the VHA with full support from the US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) Under Secretary for Health.8
The VHA is divided into 18 VISNs. Nine VA Medical Centers (VAMCs) and 46 outpatient clinics across Pennsylvania, Delaware, and parts of Ohio, New York, and New Jersey make up VISN 4. Disseminating vital information across VISN 4, in addition to the 17 other VISNs—including 170 VAMCs and 1193 clinics—presents a formidable challenge. As the largest integrated system in the US, the VHA is realigning its workforce to address organizational inefficiencies. An enterprise of this scale, shaped by recurrent organizational change, faces ongoing challenges in sustaining clear communication across all levels. These transitions create uncertainty for staff as roles and resources shift, underscoring the need for dependable vertical and horizontal information flow. Tiered huddles offer a steady means to support coordinated communication and strengthen the system’s ability to adapt.9
ERIE VA MEDICAL CENTER HRO JOURNEY
In 2019, John Gennaro, the Erie VAMC executive director, attended a presentation that showcased the Cleveland Clinic’s tiered huddle process, with an opportunity to observe its 5-tiered system.10 Erie VAMC already had a 3-tiered huddle system, but the Cleveland Clinic’s more robust model inspired Gennaro to propose a VISN 4 pilot program. Tiered huddles were perceived as innovative, yet not fully embraced within the VHA; nonetheless, VISN 4, much like several other VISNs, moved forward and established a VISN-level (Tier 4) huddle.8 It is important to note that there was a notional fifth-tier capability as VISN and program office leaders already participated in daily VHA-wide meetings under the auspices of the Hospital Operations Center (HOC).
Expanding the Tiered Huddle Process
The Erie VAMC huddle process begins with the unit level Managers and Frontline Staff (Tier 1), then moves to Service Chiefs and Managers (Tier 2). Tier 3 involves facility executive leadership team and service chiefs, clinical directors and top VAMC administrators (these configurations may vary depending on context). The sequencing and flow of information is bidirectional across levels, reflecting the importance of closed-loop communication to ensure staff at all levels understand that issues raised are followed up on and/or closed out (Figure 1).2
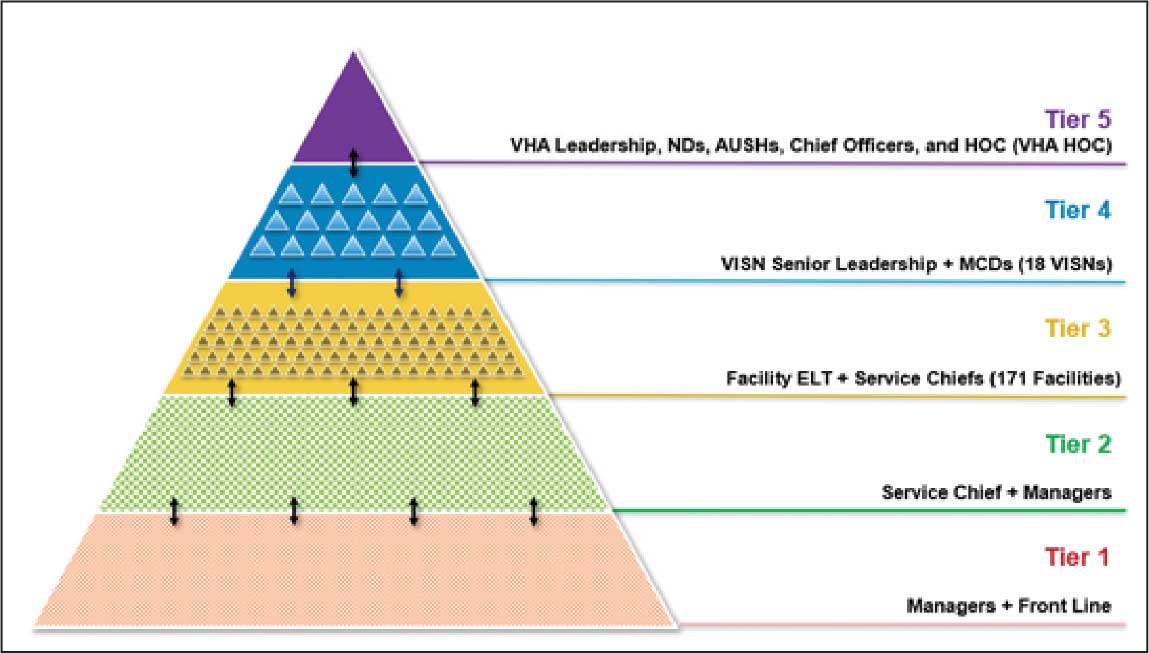
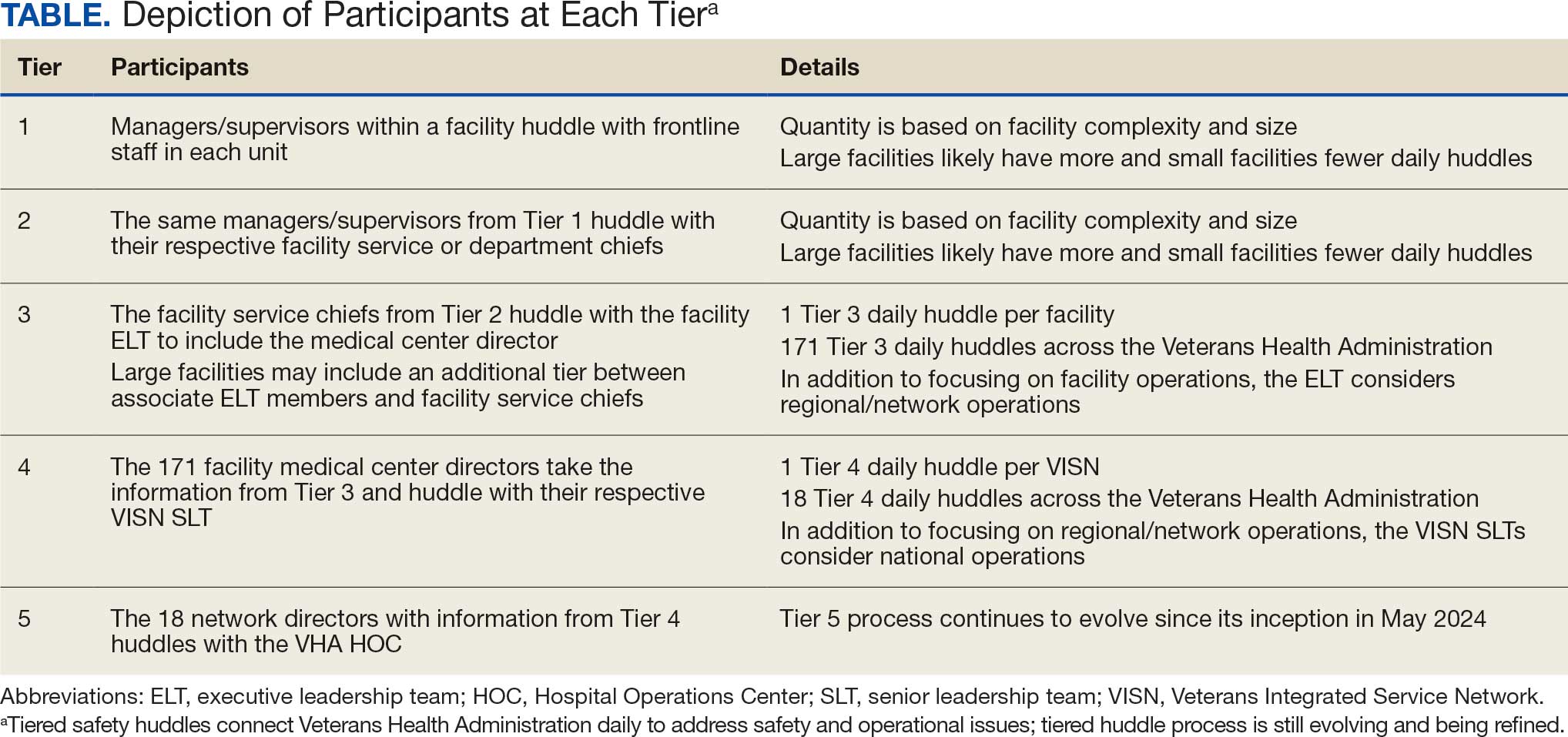
Tier 4 composition may vary among VISNs depending on size and unique mission requirements.8,11 The VISN 4 Tier 4 huddle includes the VISN director, 9 VAMC directors, and key network administrators and clinical experts. The Tier 5 huddle includes 18 VISN 4 directors with the VHA HOC (Figure 2). The tiered huddle process emphasizes team-based culture and psychological safety.12-15 Staff at all levels are encouraged to identify and transparently resolve issues, fostering a proactive and problem-solving environment across the organization. A more nuanced and detailed process across tier levels is depicted in the Table.
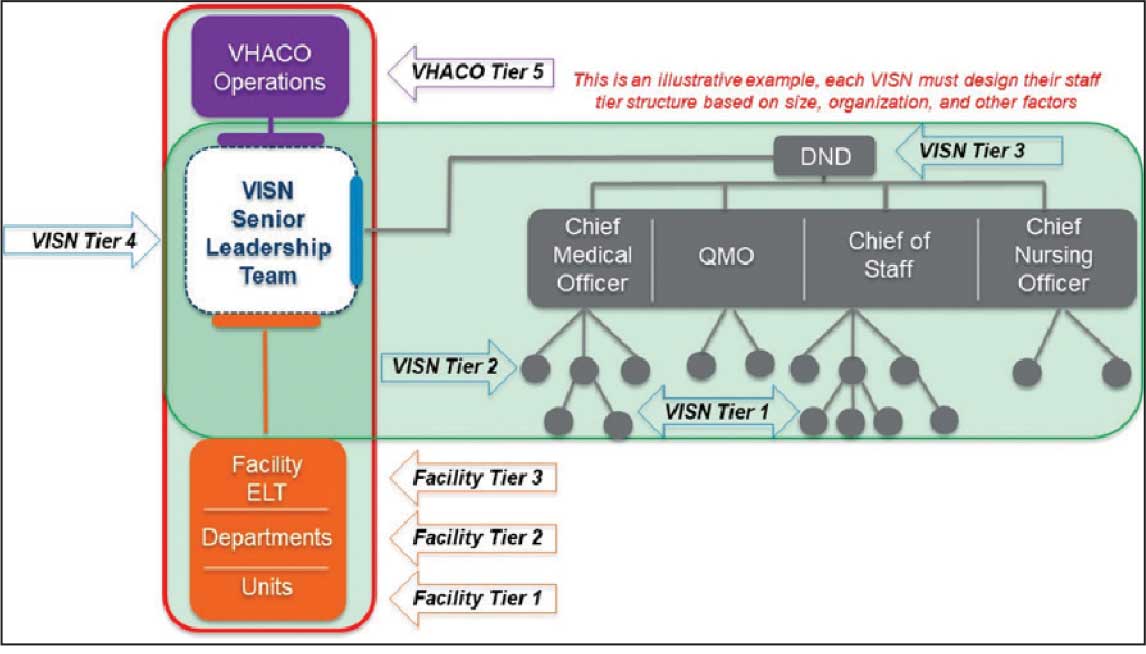
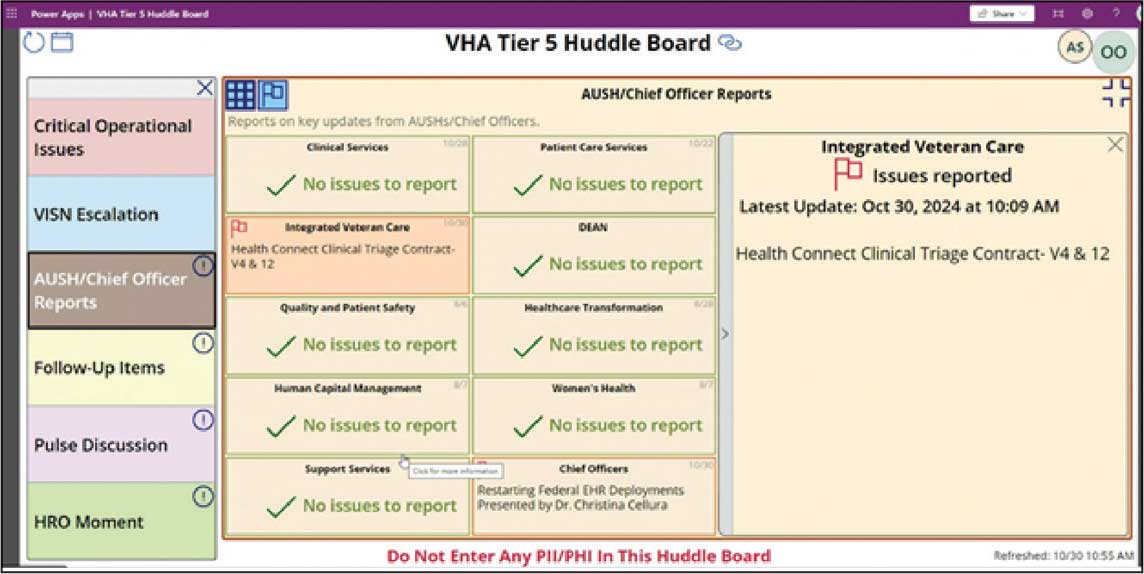
The vetting and distillation of information can present challenges as vital information ascends and spreads across organization levels. Visual management systems (VMS), whether a whiteboard or a digital platform, are key to facilitate decision-making related to what needs to be prioritized and disseminated at each tier level.2,8 At Tier 5, the HOC uses a digital VMS to provide a structured, user-friendly format for categorizing issues and topics and enhances clarity and accessibility (Figure 3). The Tier 5 VMS also facilitates tracking and reciprocal information exchange, helping to close the loop on emerging issues by monitoring their progression and resolution up and across tiers.2,8 The Tier 5 huddle process and technology supporting continue to evolve offering increasing sophistication in organizational situational awareness and responsiveness.
VUCA: A Lens for Health Care Challenges
First introduced by social scientists at the US Army War College in 1995, VUCA describes complex and unpredictable conditions often encountered in military operations.16,17 Prompted by the COVID-19 pandemic, the acronym VUCA gained recognition in health care, as leaders acknowledged the challenge of navigating rapidly changing environments. van Stralen, Byrum and Inozu, recognized authorities in high reliability, cited VUCA as the rationale for implementing HRO principles and practices. They argued that “HRO solves the problem of operations and performance in a volatile, uncertain, complex, ambiguous environment.” 18 To fully appreciate the VUCA environment and its relevance to health care, it is essential to unpack the 4 components of the acronym: volatile, uncertain, complex, and ambiguous.
Volatile refers to the speed and unpredictability of change. Health care systems are interactively complex and tightly coupled, meaning that changes in 1 part of the system can rapidly impact others.6,18,19 This high degree of interdependence amplifies volatility, especially when unexpected events occur. The rapid spread of COVID- 19 and the evolving nature of its transmission challenged health care systems’ ability to respond swiftly and effectively. Volatility also may emerge in acute medical situations, such as the rapid deterioration of a patient’s condition.
Uncertain captures the lack of predictability inherent in complex systems. In health care, uncertainty arises when there is insufficient information or when an excess of data make it difficult to discern meaningful patterns. COVID-19 and recent natural disasters have introduced profound uncertainty, as the disease’s behavior, transmission, and impact were initially unknown. Health care practitioners struggled to make decisions in real time, lacking clear guidance or precedent.3,20 While health care planning and established protocols are grounded in predictability, the COVID-19 pandemic revealed that as complexity increases, predictability diminishes. Moreover, complexity can complicate protocol selection, as situations may arise in which multiple protocols conflict or compete. The cognitive challenge of operating in this environment is analogous to what military strategists call the fog of war, where situational awareness is low and decision-makers must navigate without clarity.21 Tiered huddles, a core practice in HROs, mitigate uncertainty by fostering real-time communication and shared situational awareness among teams.20
Complex refers to the intricate interplay of multiple, interconnected factors within a system.22 In health care, this complexity is heightened by the sociotechnical nature of the field—where human, technology, and organizational elements all converge.19 Systems designed to prevent failures, such as redundancies and safety protocols, can themselves contribute to increased complexity. HRO practices such as tiered huddles are implemented to mitigate the risk of catastrophic failure by fostering collaborative sensemaking, enhanced situational awareness, and rapid problem-solving.5,20,23
Ambiguous refers to situations in which multiple interpretations, causes, or outcomes are possible. It explains how, despite following protocols, failure can still occur, or how individuals may reach different conclusions from the same data. Ambiguity does not offer binary solutions; instead, it presents a murky, multifaceted reality that requires thoughtful interpretation and adaptive responses. In these moments, leaders must act decisively, even in the absence of complete information, making trade-offs that balance immediate needs with long-term consequences.
MANAGING VUCA ENVIRONMENTS WITH TIERED HUDDLES
The tiered huddle process provides several key benefits that enable real-time issue resolution. These include the rapid dissemination of vital information, enhanced agility and resilience, and improved sensemaking within a VUCA environment. Additionally, tiered huddles prevent organizational drift by fostering heightened situational awareness. The tiered huddle process also supports leadership development, as unit-level leaders gain valuable insights into strategic decision-making through active participation. Each component is outlined in the following section.
Spread: The Challenge of Communicating
“The hallmark of a great organization is how quickly bad news travels upward,” argued Jay Forrester, the father of system dynamics.24 Unfortunately, steep power gradients and siloed organizational structures inhibit the flow of unfavorable information from frontline staff to senior leadership. This suppression is not necessarily intentional but is often a byproduct of organizational culture. Tiered huddles address the weakness of top-down communication models by promoting a reciprocal, bidirectional information exchange, with an emphasis on closed-loop communication. Open communication can foster a culture of trust and transparency, allowing leaders to make more informed decisions and respond quickly to emerging risks.
Enhancing Agility and Resilience
Tiered huddles contribute to a mindful infrastructure, an important aspect of maintaining organizational awareness and agility.21,25 A mindful infrastructure enables an organization to detect early warning signs of potential disruptions and respond to them before they escalate. In this sense, tiered huddles serve as a signal-sensing mechanism, providing the agility needed to adapt to changing circumstances and prevent patient harm. Tiered huddles facilitate self-organization, a concept from chaos theory known as autopoiesis. 26 This self-organizing capability allows teams to develop novel solutions in response to unforeseen challenges, exemplifying the adaptability and resilience needed in a VUCA environment. The diverse backgrounds of tiered huddle participants—both cognitively and culturally—enable a broader range of perspectives, which is critical for making sound decisions in complex and uncertain situations. “HROs cultivate diversity not just because it helps them notice more in complex environments, but also because it helps them adapt to the complexities they do spot,” argues Weick et al.27 This diversity of thought and experience enhances the organization’s ability to respond to complexity, much like firefighters continually adapt to the VUCA conditions they face.
Sensemaking and Sensitivity to Operations
Leaders at all levels must be attuned to what is happening both within and outside their organization. This continual sensing of the environment—looking for weak signals, threats, and opportunities—is important for HROs. This signal detection capability allows organizations to address problems in their nascent emerging state within a tractable horizon to successfully manage fluctuations. The horizon of tractability reflects a zone where weak signals and evolving issues can be identified, addressed, and resolved early before they evolve and cascade outside of safe operations. 7 Tiered huddles facilitate this process by creating a platform for team members to engage in respectful, collaborative dialogue. The diversity inherent in tiered huddles also supports sensemaking, a process of interpreting and understanding complex situations.27 In a VUCA environment, this multiperspective approach helps filter out noise and identify the most important signals. Tiered huddles can help overcome the phenomenon of dysfunctional momentum associated with cognitive lockup, fixation error, and tunnel vision, in which individuals or teams fixate on a particular solution, thus missing important alternative views.21,28 By fostering a common operating picture of the fluctuating environment, tiered huddles can enable more accurate decision-making and improve organizational resilience.
Avoiding Organizational Drift
One of the most significant contributions of tiered huddles is the ability to detect early signs of organizational drift, or subtle deviations from standard practices that can accumulate over time and lead to serious failures. By continuously monitoring for precursor conditions and weak signals, tiered huddles allow organizations to intervene early and prevent drift from becoming catastrophic.29,30 This vigilance is essential in health care, where complacency can lead to patient harm. Tiered huddles foster a culture of mindfulness and accountability, ensuring that staff stay engaged and alert to potential risks. This proactive approach is a safeguard against human error and the gradual erosion of safety standards.
Leadership Development
Tiered huddles serve as a powerful tool for leadership development. Effective leaders must be able to anticipate potential risks and foresee system failures. Involving future leaders in tiered huddles can facilitate the transfer of these critical skills. When emerging leaders at lower tiers participate in ascending-tier huddles, they gain a unique opportunity to engage in a structured, collaborative setting. This environment provides a safe space to develop and practice strategic skills, enhancing their ability to think proactively and manage complexity. By integrating future leaders into tiered huddles, organizations offer essential, hands-on experience in real-time decision making. This experiential learning is invaluable for preparing leaders to navigate the demands of a VUCA environment.
CONCLUSIONS
Since implementing the tiered huddle process, the Erie VAMC and VISN 4 have emerged as early adopters of VUCA, thus contributing to the expansion of this innovative communication approach across the VHA. Tiered huddles strengthen organizational resilience and agility, facilitate critical information flow to manage risk, and support the cultivation of future leaders. The Erie VAMC director and the VISN 4 network director regard the expansion of tiered huddles, including Tiers 4 and 5, as an adaptable model for the VHA. While tiered huddles have not yet been mandated across the VHA, a pilot at the Tier 5 HOC level was initiated on May 20, 2024. In a complex world in which VUCA events will continue to be inevitable, implementation of robust tiered huddles within complex health care systems provides the opportunity for improved responses and delivery of care.
- Orwell S, Angus I, eds. In Front of Your Nose, 1945-1950. Godine; 2000. Orwell G. The Collected Essays, Journalism, and Letters of George Orwell; vol 4.
- Murray JS, Baghdadi A, Dannenberg W, Crews P, Walsh ND. The role of high reliability organization foundational practices in building a culture of safety. Fed Pract. 2024;41:214-221. doi:10.12788/fp.0486
- Goldenhar LM, Brady PW, Sutcliffe KM, Muething SE. Huddling for high reliability and situation awareness. BMJ Qual Saf. 2013;22:899-906. doi:10.1136/bmjqs-2012-001467
- Pandit M. Critical factors for successful management of VUCA times. BMJ Lead. 2021;5:121-123. doi:10.1136/leader-2020-000305
- Mihaljevic T. Tiered daily huddles: the power of teamwork in managing large healthcare organisations. BMJ Qual Saf. 2020;29:1050-1052. doi:10.1136/bmjqs-2019-010575
- van Stralen D, Mercer TA. High-reliability organizing (HRO) in the COVID-19 liminal zone: characteristics of workers and local leaders. Neonatology Today. 2021;16:90-101. http://www.neonatologytoday.net /newsletters/nt-apr21.pdf
- Nemeth C, Wears R, Woods D, Hollnagel E, Cook R. Minding the gaps: creating resilience in health care. In: Henriksen K, Battles JB, Keyes MA, Grady ML, eds. Advances in Patient Safety: New Directions and Alternative Approaches. Vol 3: Performance and Tools. Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality; 2008.
- Merchant NB, O’Neal J, Montoya A, Cox GR, Murray JS. Creating a process for the implementation of tiered huddles in a Veterans Affairs medical center. Mil Med. 2023;188:901-906. doi:10.1093/milmed/usac073
- Starbuck WH, Farjoun M, eds. Organization at the Limit: Lessons From the Columbia Disaster. 1st ed. Wiley-Blackwell; 2005.
- Mihaljevic T. Tiered daily huddles: the power of teamwork in managing large healthcare organisations. BMJ Qual Saf. 2020;29:1050-1052. doi:10.1136/bmjqs-2019-010575
- Donnelly LF, Cherian SS, Chua KB, et al. The Daily Readiness Huddle: a process to rapidly identify issues and foster improvement through problem-solving accountability. Pediatr Radiol. 2017;47:22-30. doi:10.1007/s00247-016-3712-x
- Clark TR. The 4 Stages of Psychological Safety: Defining the Path to Inclusion and Innovation. Berrett-Koehler Publishers, Inc.; 2020.
- Edmondson AC. The Fearless Organization: Creating Psychological Safety in the Workplace for Learning, Innovation, and Growth. John Wiley & Sons; 2018.
- Edmondson AC. The Right Kind of Wrong: The Science of Failing Well. Simon Element/Simon Acumen; 2023.
- Murray JS, Kelly S, Hanover C. Promoting psychological safety in healthcare organizations. Mil Med. 2022;187:808 -810. doi:10.1093/milmed/usac041
- Barber HF. Developing strategic leadership: the US Army War College experience. J Manag Dev. 1992;11:4-12. doi:10.1108/02621719210018208
- US Army Heritage & Education Center. Who first originated the term VUCA (volatility, uncertainty, complexity and ambiguity)? Accessed November 5, 2025. https://usawc .libanswers.com/ahec/faq/84869
- van Stralen D, Byrum SL, Inozu B. High Reliability for a Highly Unreliable World: Preparing for Code Blue Through Daily Operations in Healthcare. CreateSpace Independent Publishing Platform; 2018.
- Perrow C. Normal Accidents: Living With High-Risk Technologies. Princeton University Press; 2000.
- Sculli G, Essen K. Soaring to Success: The Path to Developing High-Reliability Clinical Teams. HCPro; 2021. Accessed November 5, 2025. https://hcmarketplace.com /media/wysiwyg/CRM3_browse.pdf
- Barton MA, Sutcliffe KM, Vogus TJ, DeWitt T. Performing under uncertainty: contextualized engagement in wildland firefighting. J Contingencies Crisis Manag. 2015;23:74-83. doi:10.1111/1468-5973.12076
- Sutcliffe KM. Mindful organizing. In: Ramanujam R, Roberts KH, eds. Organizing for Reliability: A Guide for Research and Practice. Stanford University Press; 2018:61-89.
- Merchant NB, O’Neal J, Dealino-Perez C, Xiang J, Montoya A Jr, Murray JS. A high-reliability organization mindset. Am J Med Qual. 2022;37:504-510. doi:10.1097/jmq.0000000000000086
- Senge PM. The Fifth Discipline Fieldbook: Strategies and Tools for Building a Learning Organization. Crown Currency; 1994.
- Ramanujam R, Roberts KH, eds. Organizing for Reliability: A Guide for Research and Practice. Stanford University Press; 2018.
- Coveney PV. Self-organization and complexity: a new age for theory, computation and experiment. Philos Trans A Math Phys Eng Sci. 2003;361:1057-1079. doi:10.1098/rsta.2003.1191
- Weick KE, Sutcliffe KM. Managing the Unexpected: Sustained Performance in a Complex World. 3rd ed. Wiley; 2015.
- Barton M, Sutcliffe K. Overcoming dysfunctional momentum: organizational safety as a social achievement. Hum Relations. 2009;62:1327-1356. doi:10.1177/0018726709334491
- Dekker S. Drift Into Failure: From Hunting Broken Components to Understanding Complex Systems. Routledge; 2011.
- Price MR, Williams TC. When doing wrong feels so right: normalization of deviance. J Patient Saf. 2018;14:1-2. doi:10.1097/pts.0000000000000157
To see what is in front of one’s nose needs a constant struggle.
George Orwell (1946)1
In 2019, the Veterans Health Administration (VHA) initiated a process to become a high reliability organization (HRO).2 The COVID-19 pandemic has been described in medical literature as a volatile, uncertain, complex, and ambiguous (VUCA) event, underscoring the necessity of resilient communication strategies.3 Challenges posed by 2024 Hurricanes Helene and Milton further highlighted the need for resilient communication strategies within HRO implementation.
Central to the HRO journey within the VHA has been the development of tiered huddles, an evolution of the safety huddle concept.4 Emerging organically as an effective communication mechanism across multiple facilities between 2019 and 2020, tiered huddles were, in part, spurred by the onset of COVID-19. Tiered huddles represent a proactive approach to identifying and addressing organizational threats in their early stages, thereby preventing their escalation to a VUCA-laden crisis.5 When conditions evolve beyond the horizon of tractability, where challenges are easily identified and resolved, tiered huddles serve as a resilient mechanism to restore dynamic equilibrium within the organization.6,7
This article describes how tiered huddles were integrated within Veterans Integrated Service Network (VISN) 4 and explores why these huddles are essential, particularly in the context of VUCA events. What began as a local-level tactic has now gained widespread acceptance and continues to evolve across the VHA with full support from the US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) Under Secretary for Health.8
The VHA is divided into 18 VISNs. Nine VA Medical Centers (VAMCs) and 46 outpatient clinics across Pennsylvania, Delaware, and parts of Ohio, New York, and New Jersey make up VISN 4. Disseminating vital information across VISN 4, in addition to the 17 other VISNs—including 170 VAMCs and 1193 clinics—presents a formidable challenge. As the largest integrated system in the US, the VHA is realigning its workforce to address organizational inefficiencies. An enterprise of this scale, shaped by recurrent organizational change, faces ongoing challenges in sustaining clear communication across all levels. These transitions create uncertainty for staff as roles and resources shift, underscoring the need for dependable vertical and horizontal information flow. Tiered huddles offer a steady means to support coordinated communication and strengthen the system’s ability to adapt.9
ERIE VA MEDICAL CENTER HRO JOURNEY
In 2019, John Gennaro, the Erie VAMC executive director, attended a presentation that showcased the Cleveland Clinic’s tiered huddle process, with an opportunity to observe its 5-tiered system.10 Erie VAMC already had a 3-tiered huddle system, but the Cleveland Clinic’s more robust model inspired Gennaro to propose a VISN 4 pilot program. Tiered huddles were perceived as innovative, yet not fully embraced within the VHA; nonetheless, VISN 4, much like several other VISNs, moved forward and established a VISN-level (Tier 4) huddle.8 It is important to note that there was a notional fifth-tier capability as VISN and program office leaders already participated in daily VHA-wide meetings under the auspices of the Hospital Operations Center (HOC).
Expanding the Tiered Huddle Process
The Erie VAMC huddle process begins with the unit level Managers and Frontline Staff (Tier 1), then moves to Service Chiefs and Managers (Tier 2). Tier 3 involves facility executive leadership team and service chiefs, clinical directors and top VAMC administrators (these configurations may vary depending on context). The sequencing and flow of information is bidirectional across levels, reflecting the importance of closed-loop communication to ensure staff at all levels understand that issues raised are followed up on and/or closed out (Figure 1).2

Tier 4 composition may vary among VISNs depending on size and unique mission requirements.8,11 The VISN 4 Tier 4 huddle includes the VISN director, 9 VAMC directors, and key network administrators and clinical experts. The Tier 5 huddle includes 18 VISN 4 directors with the VHA HOC (Figure 2). The tiered huddle process emphasizes team-based culture and psychological safety.12-15 Staff at all levels are encouraged to identify and transparently resolve issues, fostering a proactive and problem-solving environment across the organization. A more nuanced and detailed process across tier levels is depicted in the Table.


The vetting and distillation of information can present challenges as vital information ascends and spreads across organization levels. Visual management systems (VMS), whether a whiteboard or a digital platform, are key to facilitate decision-making related to what needs to be prioritized and disseminated at each tier level.2,8 At Tier 5, the HOC uses a digital VMS to provide a structured, user-friendly format for categorizing issues and topics and enhances clarity and accessibility (Figure 3). The Tier 5 VMS also facilitates tracking and reciprocal information exchange, helping to close the loop on emerging issues by monitoring their progression and resolution up and across tiers.2,8 The Tier 5 huddle process and technology supporting continue to evolve offering increasing sophistication in organizational situational awareness and responsiveness.

VUCA: A Lens for Health Care Challenges
First introduced by social scientists at the US Army War College in 1995, VUCA describes complex and unpredictable conditions often encountered in military operations.16,17 Prompted by the COVID-19 pandemic, the acronym VUCA gained recognition in health care, as leaders acknowledged the challenge of navigating rapidly changing environments. van Stralen, Byrum and Inozu, recognized authorities in high reliability, cited VUCA as the rationale for implementing HRO principles and practices. They argued that “HRO solves the problem of operations and performance in a volatile, uncertain, complex, ambiguous environment.” 18 To fully appreciate the VUCA environment and its relevance to health care, it is essential to unpack the 4 components of the acronym: volatile, uncertain, complex, and ambiguous.
Volatile refers to the speed and unpredictability of change. Health care systems are interactively complex and tightly coupled, meaning that changes in 1 part of the system can rapidly impact others.6,18,19 This high degree of interdependence amplifies volatility, especially when unexpected events occur. The rapid spread of COVID- 19 and the evolving nature of its transmission challenged health care systems’ ability to respond swiftly and effectively. Volatility also may emerge in acute medical situations, such as the rapid deterioration of a patient’s condition.
Uncertain captures the lack of predictability inherent in complex systems. In health care, uncertainty arises when there is insufficient information or when an excess of data make it difficult to discern meaningful patterns. COVID-19 and recent natural disasters have introduced profound uncertainty, as the disease’s behavior, transmission, and impact were initially unknown. Health care practitioners struggled to make decisions in real time, lacking clear guidance or precedent.3,20 While health care planning and established protocols are grounded in predictability, the COVID-19 pandemic revealed that as complexity increases, predictability diminishes. Moreover, complexity can complicate protocol selection, as situations may arise in which multiple protocols conflict or compete. The cognitive challenge of operating in this environment is analogous to what military strategists call the fog of war, where situational awareness is low and decision-makers must navigate without clarity.21 Tiered huddles, a core practice in HROs, mitigate uncertainty by fostering real-time communication and shared situational awareness among teams.20
Complex refers to the intricate interplay of multiple, interconnected factors within a system.22 In health care, this complexity is heightened by the sociotechnical nature of the field—where human, technology, and organizational elements all converge.19 Systems designed to prevent failures, such as redundancies and safety protocols, can themselves contribute to increased complexity. HRO practices such as tiered huddles are implemented to mitigate the risk of catastrophic failure by fostering collaborative sensemaking, enhanced situational awareness, and rapid problem-solving.5,20,23
Ambiguous refers to situations in which multiple interpretations, causes, or outcomes are possible. It explains how, despite following protocols, failure can still occur, or how individuals may reach different conclusions from the same data. Ambiguity does not offer binary solutions; instead, it presents a murky, multifaceted reality that requires thoughtful interpretation and adaptive responses. In these moments, leaders must act decisively, even in the absence of complete information, making trade-offs that balance immediate needs with long-term consequences.
MANAGING VUCA ENVIRONMENTS WITH TIERED HUDDLES
The tiered huddle process provides several key benefits that enable real-time issue resolution. These include the rapid dissemination of vital information, enhanced agility and resilience, and improved sensemaking within a VUCA environment. Additionally, tiered huddles prevent organizational drift by fostering heightened situational awareness. The tiered huddle process also supports leadership development, as unit-level leaders gain valuable insights into strategic decision-making through active participation. Each component is outlined in the following section.
Spread: The Challenge of Communicating
“The hallmark of a great organization is how quickly bad news travels upward,” argued Jay Forrester, the father of system dynamics.24 Unfortunately, steep power gradients and siloed organizational structures inhibit the flow of unfavorable information from frontline staff to senior leadership. This suppression is not necessarily intentional but is often a byproduct of organizational culture. Tiered huddles address the weakness of top-down communication models by promoting a reciprocal, bidirectional information exchange, with an emphasis on closed-loop communication. Open communication can foster a culture of trust and transparency, allowing leaders to make more informed decisions and respond quickly to emerging risks.
Enhancing Agility and Resilience
Tiered huddles contribute to a mindful infrastructure, an important aspect of maintaining organizational awareness and agility.21,25 A mindful infrastructure enables an organization to detect early warning signs of potential disruptions and respond to them before they escalate. In this sense, tiered huddles serve as a signal-sensing mechanism, providing the agility needed to adapt to changing circumstances and prevent patient harm. Tiered huddles facilitate self-organization, a concept from chaos theory known as autopoiesis. 26 This self-organizing capability allows teams to develop novel solutions in response to unforeseen challenges, exemplifying the adaptability and resilience needed in a VUCA environment. The diverse backgrounds of tiered huddle participants—both cognitively and culturally—enable a broader range of perspectives, which is critical for making sound decisions in complex and uncertain situations. “HROs cultivate diversity not just because it helps them notice more in complex environments, but also because it helps them adapt to the complexities they do spot,” argues Weick et al.27 This diversity of thought and experience enhances the organization’s ability to respond to complexity, much like firefighters continually adapt to the VUCA conditions they face.
Sensemaking and Sensitivity to Operations
Leaders at all levels must be attuned to what is happening both within and outside their organization. This continual sensing of the environment—looking for weak signals, threats, and opportunities—is important for HROs. This signal detection capability allows organizations to address problems in their nascent emerging state within a tractable horizon to successfully manage fluctuations. The horizon of tractability reflects a zone where weak signals and evolving issues can be identified, addressed, and resolved early before they evolve and cascade outside of safe operations. 7 Tiered huddles facilitate this process by creating a platform for team members to engage in respectful, collaborative dialogue. The diversity inherent in tiered huddles also supports sensemaking, a process of interpreting and understanding complex situations.27 In a VUCA environment, this multiperspective approach helps filter out noise and identify the most important signals. Tiered huddles can help overcome the phenomenon of dysfunctional momentum associated with cognitive lockup, fixation error, and tunnel vision, in which individuals or teams fixate on a particular solution, thus missing important alternative views.21,28 By fostering a common operating picture of the fluctuating environment, tiered huddles can enable more accurate decision-making and improve organizational resilience.
Avoiding Organizational Drift
One of the most significant contributions of tiered huddles is the ability to detect early signs of organizational drift, or subtle deviations from standard practices that can accumulate over time and lead to serious failures. By continuously monitoring for precursor conditions and weak signals, tiered huddles allow organizations to intervene early and prevent drift from becoming catastrophic.29,30 This vigilance is essential in health care, where complacency can lead to patient harm. Tiered huddles foster a culture of mindfulness and accountability, ensuring that staff stay engaged and alert to potential risks. This proactive approach is a safeguard against human error and the gradual erosion of safety standards.
Leadership Development
Tiered huddles serve as a powerful tool for leadership development. Effective leaders must be able to anticipate potential risks and foresee system failures. Involving future leaders in tiered huddles can facilitate the transfer of these critical skills. When emerging leaders at lower tiers participate in ascending-tier huddles, they gain a unique opportunity to engage in a structured, collaborative setting. This environment provides a safe space to develop and practice strategic skills, enhancing their ability to think proactively and manage complexity. By integrating future leaders into tiered huddles, organizations offer essential, hands-on experience in real-time decision making. This experiential learning is invaluable for preparing leaders to navigate the demands of a VUCA environment.
CONCLUSIONS
Since implementing the tiered huddle process, the Erie VAMC and VISN 4 have emerged as early adopters of VUCA, thus contributing to the expansion of this innovative communication approach across the VHA. Tiered huddles strengthen organizational resilience and agility, facilitate critical information flow to manage risk, and support the cultivation of future leaders. The Erie VAMC director and the VISN 4 network director regard the expansion of tiered huddles, including Tiers 4 and 5, as an adaptable model for the VHA. While tiered huddles have not yet been mandated across the VHA, a pilot at the Tier 5 HOC level was initiated on May 20, 2024. In a complex world in which VUCA events will continue to be inevitable, implementation of robust tiered huddles within complex health care systems provides the opportunity for improved responses and delivery of care.
To see what is in front of one’s nose needs a constant struggle.
George Orwell (1946)1
In 2019, the Veterans Health Administration (VHA) initiated a process to become a high reliability organization (HRO).2 The COVID-19 pandemic has been described in medical literature as a volatile, uncertain, complex, and ambiguous (VUCA) event, underscoring the necessity of resilient communication strategies.3 Challenges posed by 2024 Hurricanes Helene and Milton further highlighted the need for resilient communication strategies within HRO implementation.
Central to the HRO journey within the VHA has been the development of tiered huddles, an evolution of the safety huddle concept.4 Emerging organically as an effective communication mechanism across multiple facilities between 2019 and 2020, tiered huddles were, in part, spurred by the onset of COVID-19. Tiered huddles represent a proactive approach to identifying and addressing organizational threats in their early stages, thereby preventing their escalation to a VUCA-laden crisis.5 When conditions evolve beyond the horizon of tractability, where challenges are easily identified and resolved, tiered huddles serve as a resilient mechanism to restore dynamic equilibrium within the organization.6,7
This article describes how tiered huddles were integrated within Veterans Integrated Service Network (VISN) 4 and explores why these huddles are essential, particularly in the context of VUCA events. What began as a local-level tactic has now gained widespread acceptance and continues to evolve across the VHA with full support from the US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) Under Secretary for Health.8
The VHA is divided into 18 VISNs. Nine VA Medical Centers (VAMCs) and 46 outpatient clinics across Pennsylvania, Delaware, and parts of Ohio, New York, and New Jersey make up VISN 4. Disseminating vital information across VISN 4, in addition to the 17 other VISNs—including 170 VAMCs and 1193 clinics—presents a formidable challenge. As the largest integrated system in the US, the VHA is realigning its workforce to address organizational inefficiencies. An enterprise of this scale, shaped by recurrent organizational change, faces ongoing challenges in sustaining clear communication across all levels. These transitions create uncertainty for staff as roles and resources shift, underscoring the need for dependable vertical and horizontal information flow. Tiered huddles offer a steady means to support coordinated communication and strengthen the system’s ability to adapt.9
ERIE VA MEDICAL CENTER HRO JOURNEY
In 2019, John Gennaro, the Erie VAMC executive director, attended a presentation that showcased the Cleveland Clinic’s tiered huddle process, with an opportunity to observe its 5-tiered system.10 Erie VAMC already had a 3-tiered huddle system, but the Cleveland Clinic’s more robust model inspired Gennaro to propose a VISN 4 pilot program. Tiered huddles were perceived as innovative, yet not fully embraced within the VHA; nonetheless, VISN 4, much like several other VISNs, moved forward and established a VISN-level (Tier 4) huddle.8 It is important to note that there was a notional fifth-tier capability as VISN and program office leaders already participated in daily VHA-wide meetings under the auspices of the Hospital Operations Center (HOC).
Expanding the Tiered Huddle Process
The Erie VAMC huddle process begins with the unit level Managers and Frontline Staff (Tier 1), then moves to Service Chiefs and Managers (Tier 2). Tier 3 involves facility executive leadership team and service chiefs, clinical directors and top VAMC administrators (these configurations may vary depending on context). The sequencing and flow of information is bidirectional across levels, reflecting the importance of closed-loop communication to ensure staff at all levels understand that issues raised are followed up on and/or closed out (Figure 1).2

Tier 4 composition may vary among VISNs depending on size and unique mission requirements.8,11 The VISN 4 Tier 4 huddle includes the VISN director, 9 VAMC directors, and key network administrators and clinical experts. The Tier 5 huddle includes 18 VISN 4 directors with the VHA HOC (Figure 2). The tiered huddle process emphasizes team-based culture and psychological safety.12-15 Staff at all levels are encouraged to identify and transparently resolve issues, fostering a proactive and problem-solving environment across the organization. A more nuanced and detailed process across tier levels is depicted in the Table.


The vetting and distillation of information can present challenges as vital information ascends and spreads across organization levels. Visual management systems (VMS), whether a whiteboard or a digital platform, are key to facilitate decision-making related to what needs to be prioritized and disseminated at each tier level.2,8 At Tier 5, the HOC uses a digital VMS to provide a structured, user-friendly format for categorizing issues and topics and enhances clarity and accessibility (Figure 3). The Tier 5 VMS also facilitates tracking and reciprocal information exchange, helping to close the loop on emerging issues by monitoring their progression and resolution up and across tiers.2,8 The Tier 5 huddle process and technology supporting continue to evolve offering increasing sophistication in organizational situational awareness and responsiveness.

VUCA: A Lens for Health Care Challenges
First introduced by social scientists at the US Army War College in 1995, VUCA describes complex and unpredictable conditions often encountered in military operations.16,17 Prompted by the COVID-19 pandemic, the acronym VUCA gained recognition in health care, as leaders acknowledged the challenge of navigating rapidly changing environments. van Stralen, Byrum and Inozu, recognized authorities in high reliability, cited VUCA as the rationale for implementing HRO principles and practices. They argued that “HRO solves the problem of operations and performance in a volatile, uncertain, complex, ambiguous environment.” 18 To fully appreciate the VUCA environment and its relevance to health care, it is essential to unpack the 4 components of the acronym: volatile, uncertain, complex, and ambiguous.
Volatile refers to the speed and unpredictability of change. Health care systems are interactively complex and tightly coupled, meaning that changes in 1 part of the system can rapidly impact others.6,18,19 This high degree of interdependence amplifies volatility, especially when unexpected events occur. The rapid spread of COVID- 19 and the evolving nature of its transmission challenged health care systems’ ability to respond swiftly and effectively. Volatility also may emerge in acute medical situations, such as the rapid deterioration of a patient’s condition.
Uncertain captures the lack of predictability inherent in complex systems. In health care, uncertainty arises when there is insufficient information or when an excess of data make it difficult to discern meaningful patterns. COVID-19 and recent natural disasters have introduced profound uncertainty, as the disease’s behavior, transmission, and impact were initially unknown. Health care practitioners struggled to make decisions in real time, lacking clear guidance or precedent.3,20 While health care planning and established protocols are grounded in predictability, the COVID-19 pandemic revealed that as complexity increases, predictability diminishes. Moreover, complexity can complicate protocol selection, as situations may arise in which multiple protocols conflict or compete. The cognitive challenge of operating in this environment is analogous to what military strategists call the fog of war, where situational awareness is low and decision-makers must navigate without clarity.21 Tiered huddles, a core practice in HROs, mitigate uncertainty by fostering real-time communication and shared situational awareness among teams.20
Complex refers to the intricate interplay of multiple, interconnected factors within a system.22 In health care, this complexity is heightened by the sociotechnical nature of the field—where human, technology, and organizational elements all converge.19 Systems designed to prevent failures, such as redundancies and safety protocols, can themselves contribute to increased complexity. HRO practices such as tiered huddles are implemented to mitigate the risk of catastrophic failure by fostering collaborative sensemaking, enhanced situational awareness, and rapid problem-solving.5,20,23
Ambiguous refers to situations in which multiple interpretations, causes, or outcomes are possible. It explains how, despite following protocols, failure can still occur, or how individuals may reach different conclusions from the same data. Ambiguity does not offer binary solutions; instead, it presents a murky, multifaceted reality that requires thoughtful interpretation and adaptive responses. In these moments, leaders must act decisively, even in the absence of complete information, making trade-offs that balance immediate needs with long-term consequences.
MANAGING VUCA ENVIRONMENTS WITH TIERED HUDDLES
The tiered huddle process provides several key benefits that enable real-time issue resolution. These include the rapid dissemination of vital information, enhanced agility and resilience, and improved sensemaking within a VUCA environment. Additionally, tiered huddles prevent organizational drift by fostering heightened situational awareness. The tiered huddle process also supports leadership development, as unit-level leaders gain valuable insights into strategic decision-making through active participation. Each component is outlined in the following section.
Spread: The Challenge of Communicating
“The hallmark of a great organization is how quickly bad news travels upward,” argued Jay Forrester, the father of system dynamics.24 Unfortunately, steep power gradients and siloed organizational structures inhibit the flow of unfavorable information from frontline staff to senior leadership. This suppression is not necessarily intentional but is often a byproduct of organizational culture. Tiered huddles address the weakness of top-down communication models by promoting a reciprocal, bidirectional information exchange, with an emphasis on closed-loop communication. Open communication can foster a culture of trust and transparency, allowing leaders to make more informed decisions and respond quickly to emerging risks.
Enhancing Agility and Resilience
Tiered huddles contribute to a mindful infrastructure, an important aspect of maintaining organizational awareness and agility.21,25 A mindful infrastructure enables an organization to detect early warning signs of potential disruptions and respond to them before they escalate. In this sense, tiered huddles serve as a signal-sensing mechanism, providing the agility needed to adapt to changing circumstances and prevent patient harm. Tiered huddles facilitate self-organization, a concept from chaos theory known as autopoiesis. 26 This self-organizing capability allows teams to develop novel solutions in response to unforeseen challenges, exemplifying the adaptability and resilience needed in a VUCA environment. The diverse backgrounds of tiered huddle participants—both cognitively and culturally—enable a broader range of perspectives, which is critical for making sound decisions in complex and uncertain situations. “HROs cultivate diversity not just because it helps them notice more in complex environments, but also because it helps them adapt to the complexities they do spot,” argues Weick et al.27 This diversity of thought and experience enhances the organization’s ability to respond to complexity, much like firefighters continually adapt to the VUCA conditions they face.
Sensemaking and Sensitivity to Operations
Leaders at all levels must be attuned to what is happening both within and outside their organization. This continual sensing of the environment—looking for weak signals, threats, and opportunities—is important for HROs. This signal detection capability allows organizations to address problems in their nascent emerging state within a tractable horizon to successfully manage fluctuations. The horizon of tractability reflects a zone where weak signals and evolving issues can be identified, addressed, and resolved early before they evolve and cascade outside of safe operations. 7 Tiered huddles facilitate this process by creating a platform for team members to engage in respectful, collaborative dialogue. The diversity inherent in tiered huddles also supports sensemaking, a process of interpreting and understanding complex situations.27 In a VUCA environment, this multiperspective approach helps filter out noise and identify the most important signals. Tiered huddles can help overcome the phenomenon of dysfunctional momentum associated with cognitive lockup, fixation error, and tunnel vision, in which individuals or teams fixate on a particular solution, thus missing important alternative views.21,28 By fostering a common operating picture of the fluctuating environment, tiered huddles can enable more accurate decision-making and improve organizational resilience.
Avoiding Organizational Drift
One of the most significant contributions of tiered huddles is the ability to detect early signs of organizational drift, or subtle deviations from standard practices that can accumulate over time and lead to serious failures. By continuously monitoring for precursor conditions and weak signals, tiered huddles allow organizations to intervene early and prevent drift from becoming catastrophic.29,30 This vigilance is essential in health care, where complacency can lead to patient harm. Tiered huddles foster a culture of mindfulness and accountability, ensuring that staff stay engaged and alert to potential risks. This proactive approach is a safeguard against human error and the gradual erosion of safety standards.
Leadership Development
Tiered huddles serve as a powerful tool for leadership development. Effective leaders must be able to anticipate potential risks and foresee system failures. Involving future leaders in tiered huddles can facilitate the transfer of these critical skills. When emerging leaders at lower tiers participate in ascending-tier huddles, they gain a unique opportunity to engage in a structured, collaborative setting. This environment provides a safe space to develop and practice strategic skills, enhancing their ability to think proactively and manage complexity. By integrating future leaders into tiered huddles, organizations offer essential, hands-on experience in real-time decision making. This experiential learning is invaluable for preparing leaders to navigate the demands of a VUCA environment.
CONCLUSIONS
Since implementing the tiered huddle process, the Erie VAMC and VISN 4 have emerged as early adopters of VUCA, thus contributing to the expansion of this innovative communication approach across the VHA. Tiered huddles strengthen organizational resilience and agility, facilitate critical information flow to manage risk, and support the cultivation of future leaders. The Erie VAMC director and the VISN 4 network director regard the expansion of tiered huddles, including Tiers 4 and 5, as an adaptable model for the VHA. While tiered huddles have not yet been mandated across the VHA, a pilot at the Tier 5 HOC level was initiated on May 20, 2024. In a complex world in which VUCA events will continue to be inevitable, implementation of robust tiered huddles within complex health care systems provides the opportunity for improved responses and delivery of care.
- Orwell S, Angus I, eds. In Front of Your Nose, 1945-1950. Godine; 2000. Orwell G. The Collected Essays, Journalism, and Letters of George Orwell; vol 4.
- Murray JS, Baghdadi A, Dannenberg W, Crews P, Walsh ND. The role of high reliability organization foundational practices in building a culture of safety. Fed Pract. 2024;41:214-221. doi:10.12788/fp.0486
- Goldenhar LM, Brady PW, Sutcliffe KM, Muething SE. Huddling for high reliability and situation awareness. BMJ Qual Saf. 2013;22:899-906. doi:10.1136/bmjqs-2012-001467
- Pandit M. Critical factors for successful management of VUCA times. BMJ Lead. 2021;5:121-123. doi:10.1136/leader-2020-000305
- Mihaljevic T. Tiered daily huddles: the power of teamwork in managing large healthcare organisations. BMJ Qual Saf. 2020;29:1050-1052. doi:10.1136/bmjqs-2019-010575
- van Stralen D, Mercer TA. High-reliability organizing (HRO) in the COVID-19 liminal zone: characteristics of workers and local leaders. Neonatology Today. 2021;16:90-101. http://www.neonatologytoday.net /newsletters/nt-apr21.pdf
- Nemeth C, Wears R, Woods D, Hollnagel E, Cook R. Minding the gaps: creating resilience in health care. In: Henriksen K, Battles JB, Keyes MA, Grady ML, eds. Advances in Patient Safety: New Directions and Alternative Approaches. Vol 3: Performance and Tools. Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality; 2008.
- Merchant NB, O’Neal J, Montoya A, Cox GR, Murray JS. Creating a process for the implementation of tiered huddles in a Veterans Affairs medical center. Mil Med. 2023;188:901-906. doi:10.1093/milmed/usac073
- Starbuck WH, Farjoun M, eds. Organization at the Limit: Lessons From the Columbia Disaster. 1st ed. Wiley-Blackwell; 2005.
- Mihaljevic T. Tiered daily huddles: the power of teamwork in managing large healthcare organisations. BMJ Qual Saf. 2020;29:1050-1052. doi:10.1136/bmjqs-2019-010575
- Donnelly LF, Cherian SS, Chua KB, et al. The Daily Readiness Huddle: a process to rapidly identify issues and foster improvement through problem-solving accountability. Pediatr Radiol. 2017;47:22-30. doi:10.1007/s00247-016-3712-x
- Clark TR. The 4 Stages of Psychological Safety: Defining the Path to Inclusion and Innovation. Berrett-Koehler Publishers, Inc.; 2020.
- Edmondson AC. The Fearless Organization: Creating Psychological Safety in the Workplace for Learning, Innovation, and Growth. John Wiley & Sons; 2018.
- Edmondson AC. The Right Kind of Wrong: The Science of Failing Well. Simon Element/Simon Acumen; 2023.
- Murray JS, Kelly S, Hanover C. Promoting psychological safety in healthcare organizations. Mil Med. 2022;187:808 -810. doi:10.1093/milmed/usac041
- Barber HF. Developing strategic leadership: the US Army War College experience. J Manag Dev. 1992;11:4-12. doi:10.1108/02621719210018208
- US Army Heritage & Education Center. Who first originated the term VUCA (volatility, uncertainty, complexity and ambiguity)? Accessed November 5, 2025. https://usawc .libanswers.com/ahec/faq/84869
- van Stralen D, Byrum SL, Inozu B. High Reliability for a Highly Unreliable World: Preparing for Code Blue Through Daily Operations in Healthcare. CreateSpace Independent Publishing Platform; 2018.
- Perrow C. Normal Accidents: Living With High-Risk Technologies. Princeton University Press; 2000.
- Sculli G, Essen K. Soaring to Success: The Path to Developing High-Reliability Clinical Teams. HCPro; 2021. Accessed November 5, 2025. https://hcmarketplace.com /media/wysiwyg/CRM3_browse.pdf
- Barton MA, Sutcliffe KM, Vogus TJ, DeWitt T. Performing under uncertainty: contextualized engagement in wildland firefighting. J Contingencies Crisis Manag. 2015;23:74-83. doi:10.1111/1468-5973.12076
- Sutcliffe KM. Mindful organizing. In: Ramanujam R, Roberts KH, eds. Organizing for Reliability: A Guide for Research and Practice. Stanford University Press; 2018:61-89.
- Merchant NB, O’Neal J, Dealino-Perez C, Xiang J, Montoya A Jr, Murray JS. A high-reliability organization mindset. Am J Med Qual. 2022;37:504-510. doi:10.1097/jmq.0000000000000086
- Senge PM. The Fifth Discipline Fieldbook: Strategies and Tools for Building a Learning Organization. Crown Currency; 1994.
- Ramanujam R, Roberts KH, eds. Organizing for Reliability: A Guide for Research and Practice. Stanford University Press; 2018.
- Coveney PV. Self-organization and complexity: a new age for theory, computation and experiment. Philos Trans A Math Phys Eng Sci. 2003;361:1057-1079. doi:10.1098/rsta.2003.1191
- Weick KE, Sutcliffe KM. Managing the Unexpected: Sustained Performance in a Complex World. 3rd ed. Wiley; 2015.
- Barton M, Sutcliffe K. Overcoming dysfunctional momentum: organizational safety as a social achievement. Hum Relations. 2009;62:1327-1356. doi:10.1177/0018726709334491
- Dekker S. Drift Into Failure: From Hunting Broken Components to Understanding Complex Systems. Routledge; 2011.
- Price MR, Williams TC. When doing wrong feels so right: normalization of deviance. J Patient Saf. 2018;14:1-2. doi:10.1097/pts.0000000000000157
- Orwell S, Angus I, eds. In Front of Your Nose, 1945-1950. Godine; 2000. Orwell G. The Collected Essays, Journalism, and Letters of George Orwell; vol 4.
- Murray JS, Baghdadi A, Dannenberg W, Crews P, Walsh ND. The role of high reliability organization foundational practices in building a culture of safety. Fed Pract. 2024;41:214-221. doi:10.12788/fp.0486
- Goldenhar LM, Brady PW, Sutcliffe KM, Muething SE. Huddling for high reliability and situation awareness. BMJ Qual Saf. 2013;22:899-906. doi:10.1136/bmjqs-2012-001467
- Pandit M. Critical factors for successful management of VUCA times. BMJ Lead. 2021;5:121-123. doi:10.1136/leader-2020-000305
- Mihaljevic T. Tiered daily huddles: the power of teamwork in managing large healthcare organisations. BMJ Qual Saf. 2020;29:1050-1052. doi:10.1136/bmjqs-2019-010575
- van Stralen D, Mercer TA. High-reliability organizing (HRO) in the COVID-19 liminal zone: characteristics of workers and local leaders. Neonatology Today. 2021;16:90-101. http://www.neonatologytoday.net /newsletters/nt-apr21.pdf
- Nemeth C, Wears R, Woods D, Hollnagel E, Cook R. Minding the gaps: creating resilience in health care. In: Henriksen K, Battles JB, Keyes MA, Grady ML, eds. Advances in Patient Safety: New Directions and Alternative Approaches. Vol 3: Performance and Tools. Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality; 2008.
- Merchant NB, O’Neal J, Montoya A, Cox GR, Murray JS. Creating a process for the implementation of tiered huddles in a Veterans Affairs medical center. Mil Med. 2023;188:901-906. doi:10.1093/milmed/usac073
- Starbuck WH, Farjoun M, eds. Organization at the Limit: Lessons From the Columbia Disaster. 1st ed. Wiley-Blackwell; 2005.
- Mihaljevic T. Tiered daily huddles: the power of teamwork in managing large healthcare organisations. BMJ Qual Saf. 2020;29:1050-1052. doi:10.1136/bmjqs-2019-010575
- Donnelly LF, Cherian SS, Chua KB, et al. The Daily Readiness Huddle: a process to rapidly identify issues and foster improvement through problem-solving accountability. Pediatr Radiol. 2017;47:22-30. doi:10.1007/s00247-016-3712-x
- Clark TR. The 4 Stages of Psychological Safety: Defining the Path to Inclusion and Innovation. Berrett-Koehler Publishers, Inc.; 2020.
- Edmondson AC. The Fearless Organization: Creating Psychological Safety in the Workplace for Learning, Innovation, and Growth. John Wiley & Sons; 2018.
- Edmondson AC. The Right Kind of Wrong: The Science of Failing Well. Simon Element/Simon Acumen; 2023.
- Murray JS, Kelly S, Hanover C. Promoting psychological safety in healthcare organizations. Mil Med. 2022;187:808 -810. doi:10.1093/milmed/usac041
- Barber HF. Developing strategic leadership: the US Army War College experience. J Manag Dev. 1992;11:4-12. doi:10.1108/02621719210018208
- US Army Heritage & Education Center. Who first originated the term VUCA (volatility, uncertainty, complexity and ambiguity)? Accessed November 5, 2025. https://usawc .libanswers.com/ahec/faq/84869
- van Stralen D, Byrum SL, Inozu B. High Reliability for a Highly Unreliable World: Preparing for Code Blue Through Daily Operations in Healthcare. CreateSpace Independent Publishing Platform; 2018.
- Perrow C. Normal Accidents: Living With High-Risk Technologies. Princeton University Press; 2000.
- Sculli G, Essen K. Soaring to Success: The Path to Developing High-Reliability Clinical Teams. HCPro; 2021. Accessed November 5, 2025. https://hcmarketplace.com /media/wysiwyg/CRM3_browse.pdf
- Barton MA, Sutcliffe KM, Vogus TJ, DeWitt T. Performing under uncertainty: contextualized engagement in wildland firefighting. J Contingencies Crisis Manag. 2015;23:74-83. doi:10.1111/1468-5973.12076
- Sutcliffe KM. Mindful organizing. In: Ramanujam R, Roberts KH, eds. Organizing for Reliability: A Guide for Research and Practice. Stanford University Press; 2018:61-89.
- Merchant NB, O’Neal J, Dealino-Perez C, Xiang J, Montoya A Jr, Murray JS. A high-reliability organization mindset. Am J Med Qual. 2022;37:504-510. doi:10.1097/jmq.0000000000000086
- Senge PM. The Fifth Discipline Fieldbook: Strategies and Tools for Building a Learning Organization. Crown Currency; 1994.
- Ramanujam R, Roberts KH, eds. Organizing for Reliability: A Guide for Research and Practice. Stanford University Press; 2018.
- Coveney PV. Self-organization and complexity: a new age for theory, computation and experiment. Philos Trans A Math Phys Eng Sci. 2003;361:1057-1079. doi:10.1098/rsta.2003.1191
- Weick KE, Sutcliffe KM. Managing the Unexpected: Sustained Performance in a Complex World. 3rd ed. Wiley; 2015.
- Barton M, Sutcliffe K. Overcoming dysfunctional momentum: organizational safety as a social achievement. Hum Relations. 2009;62:1327-1356. doi:10.1177/0018726709334491
- Dekker S. Drift Into Failure: From Hunting Broken Components to Understanding Complex Systems. Routledge; 2011.
- Price MR, Williams TC. When doing wrong feels so right: normalization of deviance. J Patient Saf. 2018;14:1-2. doi:10.1097/pts.0000000000000157
Negotiating the VUCA World Through Tiered Huddles
Negotiating the VUCA World Through Tiered Huddles
As Federal Cuts Deepen Mental Health Crisis, Philanthropy Scrambles to Fill the Gap
As Federal Cuts Deepen Mental Health Crisis, Philanthropy Scrambles to Fill the Gap
It's hardly news that the United States is experiencing a mental health crisis -- the CDC says as much. But experts in the field say that the current administration has severely compounded the problem by eliminating agency funding and national programs, slashing research grants and data resources, and creating new barriers to behavioral health care.
Philanthropic foundations aim to do what they can to address the shortfall. The numbers, however, just don't add up.
"Some big foundations and philanthropies have said they're going to increase what they give out in the next 4 years, but they'll never be able to fill the gap," said Morgan F. McDonald, MD, national director of population health at the Milbank Memorial Fund in New York City, which works with states on health policy. "Even if every one of them were to spend down their endowments, they still couldn't."
Given the financial limitations, some foundations are taking a different tack. While looking for ways to join forces with fellow nonprofits, they are providing emergency grants to bridge funding in the short term to keep research from grinding to a halt.
Budget Cuts Reach Far and Wide
Mental health research certainly didn't escape the extensive grant cancellations at the National Institutes of Health and the National Science Foundation.
"It's already affecting our ability to stay on the cutting edge of research, best practices, and treatment approaches," said Zainab Okolo, EdD, senior vice president of policy, advocacy, and government relations at The Jed Foundation in New York City, which focuses on the emotional health of teens and young adults.
The upheaval is evident in an array of government agencies. The Health Resources and Services Administration, which last year awarded $12 billion in grants to community health centers and addiction treatment services, has seen > one-fourth of its staff eliminated. The Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration has lost more than a third of its staff as federal cuts took a $1 billion bite out of its operating budget. The Education Department has halted $1 billion in grants used to hire mental health workers in school districts nationwide.
"We're very, very concerned about cuts to behavioral health systems," said Alonzo Plough, PhD, chief science officer at the Robert Wood Johnson Foundation in Princeton, New Jersey. "Doctors and nurses working in safety-net clinics are seeing tremendous reductions."
All in all, the new tax and spending law means $1 trillion in cuts to health care programs including Medicaid -- the nation's largest payer for mental health services -- Medicare, and Affordable Care Act insurance. An estimated 10 million Americans are expected to lose their health coverage as a result.
"When accessibility to care goes down, there's a chance that more people will die by suicide," said Jill Harkavy-Friedman, PhD, senior vice president of research at the American Foundation for Suicide Prevention. "But it also means people will come into care later in the course of their difficulties. Health professionals will be dealing with worse problems."
Foundations Take Emergency Measures
Even if private dollars can't replace what's been lost, philanthropic and medical foundations are stepping up.
We're seeing a lot of foundations and funders that are shifting their funding," said Alyson Niemann, CEO of Mindful Philanthropy, an organization that works with > 1000 private funders to marshal resources for mental health. This year, in response to federal cuts, "many increased funding to health and well-being, doubling or even tripling it," Niemann noted.
"They're making a great deal of effort to respond with emergency funds, really getting in the trenches and being good partners to their grantees," she said. "We've seen them asking deliberate questions, thinking about where their funding can have the most impact."
The American Psychological Foundation (APF), a longtime supporter of research and innovation, is addressing the current crisis with 2 initiatives, Michelle Quist Ryder, PhD, the organization's CEO, explained in an email. The first is APF Director Action, which funds innovative interventions at the community level. The second, Direct Action Crisis Funding Grants, will help continue research that is at risk of stalling because of budget cuts.
"Studies that are 'paused' or lose funding often cannot simply pick back up where they left off. Having to halt progress on a project can invalidate the work already completed," Ryder wrote. "These Direct Action Crisis Grants help bridge funding gaps and keep research viable."
At the same time, collaboration between foundations is becoming more widespread as they seek to maximize their impact. Philanthropic organizations are sharing ideas and best practices as well as pooling fundings.
"The goal of philanthropy is to help people," Harkavy-Friedman said. "There's strength in numbers and more dollars in numbers."
Some See Hope in Raised Voices
Despite the emergency scrambling, many of those in the trenches remain surprisingly optimistic. Some point out that the current turmoil has put a helpful spotlight on behavioral health care. Practitioners, meanwhile, have an essential role to play.
"There's a reason that things were the way they were: People advocated for many years to get where we've gotten," Harkavy-Friedman said, citing veterans' mental health care, the national violent death reporting system, and 988 as examples. "We have to raise our voices louder -- professionals in particular, because they know the impact a person in the general public many not fully grasp."
As a growing numbers of health professionals call attention to the damage wrought by deep cuts in the federal budget, foundation executives see an opportunity.
"In the mental health field, there's a deficit in the narrative, where there's a lot of focus on crisis. What we're hoping to do is shift the narrative toward 'How do we flourish together?'" Niemann said. "Sometimes deficits are where the most incredible innovations appear."
Debbie Koenig is a health writer whose work has been published by WebMD, The New York Times, and The Washington Post.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
It's hardly news that the United States is experiencing a mental health crisis -- the CDC says as much. But experts in the field say that the current administration has severely compounded the problem by eliminating agency funding and national programs, slashing research grants and data resources, and creating new barriers to behavioral health care.
Philanthropic foundations aim to do what they can to address the shortfall. The numbers, however, just don't add up.
"Some big foundations and philanthropies have said they're going to increase what they give out in the next 4 years, but they'll never be able to fill the gap," said Morgan F. McDonald, MD, national director of population health at the Milbank Memorial Fund in New York City, which works with states on health policy. "Even if every one of them were to spend down their endowments, they still couldn't."
Given the financial limitations, some foundations are taking a different tack. While looking for ways to join forces with fellow nonprofits, they are providing emergency grants to bridge funding in the short term to keep research from grinding to a halt.
Budget Cuts Reach Far and Wide
Mental health research certainly didn't escape the extensive grant cancellations at the National Institutes of Health and the National Science Foundation.
"It's already affecting our ability to stay on the cutting edge of research, best practices, and treatment approaches," said Zainab Okolo, EdD, senior vice president of policy, advocacy, and government relations at The Jed Foundation in New York City, which focuses on the emotional health of teens and young adults.
The upheaval is evident in an array of government agencies. The Health Resources and Services Administration, which last year awarded $12 billion in grants to community health centers and addiction treatment services, has seen > one-fourth of its staff eliminated. The Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration has lost more than a third of its staff as federal cuts took a $1 billion bite out of its operating budget. The Education Department has halted $1 billion in grants used to hire mental health workers in school districts nationwide.
"We're very, very concerned about cuts to behavioral health systems," said Alonzo Plough, PhD, chief science officer at the Robert Wood Johnson Foundation in Princeton, New Jersey. "Doctors and nurses working in safety-net clinics are seeing tremendous reductions."
All in all, the new tax and spending law means $1 trillion in cuts to health care programs including Medicaid -- the nation's largest payer for mental health services -- Medicare, and Affordable Care Act insurance. An estimated 10 million Americans are expected to lose their health coverage as a result.
"When accessibility to care goes down, there's a chance that more people will die by suicide," said Jill Harkavy-Friedman, PhD, senior vice president of research at the American Foundation for Suicide Prevention. "But it also means people will come into care later in the course of their difficulties. Health professionals will be dealing with worse problems."
Foundations Take Emergency Measures
Even if private dollars can't replace what's been lost, philanthropic and medical foundations are stepping up.
We're seeing a lot of foundations and funders that are shifting their funding," said Alyson Niemann, CEO of Mindful Philanthropy, an organization that works with > 1000 private funders to marshal resources for mental health. This year, in response to federal cuts, "many increased funding to health and well-being, doubling or even tripling it," Niemann noted.
"They're making a great deal of effort to respond with emergency funds, really getting in the trenches and being good partners to their grantees," she said. "We've seen them asking deliberate questions, thinking about where their funding can have the most impact."
The American Psychological Foundation (APF), a longtime supporter of research and innovation, is addressing the current crisis with 2 initiatives, Michelle Quist Ryder, PhD, the organization's CEO, explained in an email. The first is APF Director Action, which funds innovative interventions at the community level. The second, Direct Action Crisis Funding Grants, will help continue research that is at risk of stalling because of budget cuts.
"Studies that are 'paused' or lose funding often cannot simply pick back up where they left off. Having to halt progress on a project can invalidate the work already completed," Ryder wrote. "These Direct Action Crisis Grants help bridge funding gaps and keep research viable."
At the same time, collaboration between foundations is becoming more widespread as they seek to maximize their impact. Philanthropic organizations are sharing ideas and best practices as well as pooling fundings.
"The goal of philanthropy is to help people," Harkavy-Friedman said. "There's strength in numbers and more dollars in numbers."
Some See Hope in Raised Voices
Despite the emergency scrambling, many of those in the trenches remain surprisingly optimistic. Some point out that the current turmoil has put a helpful spotlight on behavioral health care. Practitioners, meanwhile, have an essential role to play.
"There's a reason that things were the way they were: People advocated for many years to get where we've gotten," Harkavy-Friedman said, citing veterans' mental health care, the national violent death reporting system, and 988 as examples. "We have to raise our voices louder -- professionals in particular, because they know the impact a person in the general public many not fully grasp."
As a growing numbers of health professionals call attention to the damage wrought by deep cuts in the federal budget, foundation executives see an opportunity.
"In the mental health field, there's a deficit in the narrative, where there's a lot of focus on crisis. What we're hoping to do is shift the narrative toward 'How do we flourish together?'" Niemann said. "Sometimes deficits are where the most incredible innovations appear."
Debbie Koenig is a health writer whose work has been published by WebMD, The New York Times, and The Washington Post.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
It's hardly news that the United States is experiencing a mental health crisis -- the CDC says as much. But experts in the field say that the current administration has severely compounded the problem by eliminating agency funding and national programs, slashing research grants and data resources, and creating new barriers to behavioral health care.
Philanthropic foundations aim to do what they can to address the shortfall. The numbers, however, just don't add up.
"Some big foundations and philanthropies have said they're going to increase what they give out in the next 4 years, but they'll never be able to fill the gap," said Morgan F. McDonald, MD, national director of population health at the Milbank Memorial Fund in New York City, which works with states on health policy. "Even if every one of them were to spend down their endowments, they still couldn't."
Given the financial limitations, some foundations are taking a different tack. While looking for ways to join forces with fellow nonprofits, they are providing emergency grants to bridge funding in the short term to keep research from grinding to a halt.
Budget Cuts Reach Far and Wide
Mental health research certainly didn't escape the extensive grant cancellations at the National Institutes of Health and the National Science Foundation.
"It's already affecting our ability to stay on the cutting edge of research, best practices, and treatment approaches," said Zainab Okolo, EdD, senior vice president of policy, advocacy, and government relations at The Jed Foundation in New York City, which focuses on the emotional health of teens and young adults.
The upheaval is evident in an array of government agencies. The Health Resources and Services Administration, which last year awarded $12 billion in grants to community health centers and addiction treatment services, has seen > one-fourth of its staff eliminated. The Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration has lost more than a third of its staff as federal cuts took a $1 billion bite out of its operating budget. The Education Department has halted $1 billion in grants used to hire mental health workers in school districts nationwide.
"We're very, very concerned about cuts to behavioral health systems," said Alonzo Plough, PhD, chief science officer at the Robert Wood Johnson Foundation in Princeton, New Jersey. "Doctors and nurses working in safety-net clinics are seeing tremendous reductions."
All in all, the new tax and spending law means $1 trillion in cuts to health care programs including Medicaid -- the nation's largest payer for mental health services -- Medicare, and Affordable Care Act insurance. An estimated 10 million Americans are expected to lose their health coverage as a result.
"When accessibility to care goes down, there's a chance that more people will die by suicide," said Jill Harkavy-Friedman, PhD, senior vice president of research at the American Foundation for Suicide Prevention. "But it also means people will come into care later in the course of their difficulties. Health professionals will be dealing with worse problems."
Foundations Take Emergency Measures
Even if private dollars can't replace what's been lost, philanthropic and medical foundations are stepping up.
We're seeing a lot of foundations and funders that are shifting their funding," said Alyson Niemann, CEO of Mindful Philanthropy, an organization that works with > 1000 private funders to marshal resources for mental health. This year, in response to federal cuts, "many increased funding to health and well-being, doubling or even tripling it," Niemann noted.
"They're making a great deal of effort to respond with emergency funds, really getting in the trenches and being good partners to their grantees," she said. "We've seen them asking deliberate questions, thinking about where their funding can have the most impact."
The American Psychological Foundation (APF), a longtime supporter of research and innovation, is addressing the current crisis with 2 initiatives, Michelle Quist Ryder, PhD, the organization's CEO, explained in an email. The first is APF Director Action, which funds innovative interventions at the community level. The second, Direct Action Crisis Funding Grants, will help continue research that is at risk of stalling because of budget cuts.
"Studies that are 'paused' or lose funding often cannot simply pick back up where they left off. Having to halt progress on a project can invalidate the work already completed," Ryder wrote. "These Direct Action Crisis Grants help bridge funding gaps and keep research viable."
At the same time, collaboration between foundations is becoming more widespread as they seek to maximize their impact. Philanthropic organizations are sharing ideas and best practices as well as pooling fundings.
"The goal of philanthropy is to help people," Harkavy-Friedman said. "There's strength in numbers and more dollars in numbers."
Some See Hope in Raised Voices
Despite the emergency scrambling, many of those in the trenches remain surprisingly optimistic. Some point out that the current turmoil has put a helpful spotlight on behavioral health care. Practitioners, meanwhile, have an essential role to play.
"There's a reason that things were the way they were: People advocated for many years to get where we've gotten," Harkavy-Friedman said, citing veterans' mental health care, the national violent death reporting system, and 988 as examples. "We have to raise our voices louder -- professionals in particular, because they know the impact a person in the general public many not fully grasp."
As a growing numbers of health professionals call attention to the damage wrought by deep cuts in the federal budget, foundation executives see an opportunity.
"In the mental health field, there's a deficit in the narrative, where there's a lot of focus on crisis. What we're hoping to do is shift the narrative toward 'How do we flourish together?'" Niemann said. "Sometimes deficits are where the most incredible innovations appear."
Debbie Koenig is a health writer whose work has been published by WebMD, The New York Times, and The Washington Post.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
As Federal Cuts Deepen Mental Health Crisis, Philanthropy Scrambles to Fill the Gap
As Federal Cuts Deepen Mental Health Crisis, Philanthropy Scrambles to Fill the Gap
Indian Health Service: Business as Usual During Shutdown
Despite the ongoing shutdown of the US federal government, the Indian Health Service (IHS) continues to maintain the status quo while operating on an island of relatively insulated stability.
“IHS will continue to operate business-as-usual during a lapse of appropriations,” US Department of Health and Human Services press secretary Emily G. Hilliard said at a recent meeting with the National Congress of American Indians (NCAI). “100% of IHS staff will report for work, and health care services across Indian Country will not be impacted.”
The protective cocoon around IHS and its services provided is largely due to advance appropriations, and lessons learned from previous government shutdowns. During the historically long 35-day government shutdown in 2018 and 2019, all federal government operations had to halt operations unless they were deemed indispensable. IHS was not considered indispensable and consequently, about 60% of IHS employees did not receive a paycheck.
In preparation for another potential shutdown in 2023, IHS was more proactive. “Because of the fact that now we have advanced appropriations for Indian Health Services, on Oct. 1, whether or not there’s a federal budget in place, will continue providing services,” then-HHS Secretary Xavier Becerra, said at the time.
The safeguards have held for the current shutdown, aided by tribal pressure. As the federal shutdown loomed in September, a delegation led by NCAI spent 3 days lobbying Congress—focusing primarily on the new leadership in the Senate Indian Affairs Committee—to guarantee some protection for federal employees who work with tribal governments.
At the quarterly meeting of the United Indian Nations of Oklahoma (UINO) in Tulsa, Rear Adm. Travis Watts, director of the IHS Oklahoma City Area and a citizen of the Choctaw Nation of Oklahoma, told attendees, “The advance appropriations allow us to keep our doors open at this particular time. We want to thank the tribal nations for their advocacy for those advance appropriations.”
IHS is funded through 2026. All 14,801 IHS staff will be paid through advance appropriations, multi-year or supplemental appropriations, third-party collections, or carryover balances.
However, according to the proposed 2026 budget some key health-related funding is at risk, including about $128 million in Tribal set-aside funding for mental and behavioral health funding: $60 million from the Tribal Opioid Response Grants, $22.75 million from Tribal Behavioral Health Grants, $14.5 million from Medication-Assisted Treatment for Prescription and Opioid Addiction, and $3.4 million Tribal set-aside for the Zero Suicide program. Six IHS accounts are not funded by advance appropriations: Electronic Health Record System, Indian Health Care Improvement Fund, Contract Support Costs, Payments for Tribal Leases, Sanitation Facilities Construction, and Health Care Facilities Construction.
In a public statement, Cherokee Nation Principal Chief Chuck Hoskin Jr. said, “[W]e’re hopeful that Congress’ foresight to provide an advance appropriation for the Indian Health Service will prevent any severe disruptions as experienced during the 2013 and 2018 shutdowns. I urge both sides of the aisle to work on a path forward and reopen the government as soon as possible and call on the administration to honor the government’s Treaty and Trust responsibilities, avoid needless cuts to Tribal programs and personnel, and use its authorities to minimize harm to tribes and tribal citizens.”
Hoskin Jr. cautioned, though, that not every tribe has the same resources. Many smaller, direct-service tribes depend entirely on IHS to deliver care.
“Thank goodness for forward funding,” he said. “But we have to make that permanent in federal statute. No one in this country should be at the mercy of political dysfunction to get health care.
Despite the ongoing shutdown of the US federal government, the Indian Health Service (IHS) continues to maintain the status quo while operating on an island of relatively insulated stability.
“IHS will continue to operate business-as-usual during a lapse of appropriations,” US Department of Health and Human Services press secretary Emily G. Hilliard said at a recent meeting with the National Congress of American Indians (NCAI). “100% of IHS staff will report for work, and health care services across Indian Country will not be impacted.”
The protective cocoon around IHS and its services provided is largely due to advance appropriations, and lessons learned from previous government shutdowns. During the historically long 35-day government shutdown in 2018 and 2019, all federal government operations had to halt operations unless they were deemed indispensable. IHS was not considered indispensable and consequently, about 60% of IHS employees did not receive a paycheck.
In preparation for another potential shutdown in 2023, IHS was more proactive. “Because of the fact that now we have advanced appropriations for Indian Health Services, on Oct. 1, whether or not there’s a federal budget in place, will continue providing services,” then-HHS Secretary Xavier Becerra, said at the time.
The safeguards have held for the current shutdown, aided by tribal pressure. As the federal shutdown loomed in September, a delegation led by NCAI spent 3 days lobbying Congress—focusing primarily on the new leadership in the Senate Indian Affairs Committee—to guarantee some protection for federal employees who work with tribal governments.
At the quarterly meeting of the United Indian Nations of Oklahoma (UINO) in Tulsa, Rear Adm. Travis Watts, director of the IHS Oklahoma City Area and a citizen of the Choctaw Nation of Oklahoma, told attendees, “The advance appropriations allow us to keep our doors open at this particular time. We want to thank the tribal nations for their advocacy for those advance appropriations.”
IHS is funded through 2026. All 14,801 IHS staff will be paid through advance appropriations, multi-year or supplemental appropriations, third-party collections, or carryover balances.
However, according to the proposed 2026 budget some key health-related funding is at risk, including about $128 million in Tribal set-aside funding for mental and behavioral health funding: $60 million from the Tribal Opioid Response Grants, $22.75 million from Tribal Behavioral Health Grants, $14.5 million from Medication-Assisted Treatment for Prescription and Opioid Addiction, and $3.4 million Tribal set-aside for the Zero Suicide program. Six IHS accounts are not funded by advance appropriations: Electronic Health Record System, Indian Health Care Improvement Fund, Contract Support Costs, Payments for Tribal Leases, Sanitation Facilities Construction, and Health Care Facilities Construction.
In a public statement, Cherokee Nation Principal Chief Chuck Hoskin Jr. said, “[W]e’re hopeful that Congress’ foresight to provide an advance appropriation for the Indian Health Service will prevent any severe disruptions as experienced during the 2013 and 2018 shutdowns. I urge both sides of the aisle to work on a path forward and reopen the government as soon as possible and call on the administration to honor the government’s Treaty and Trust responsibilities, avoid needless cuts to Tribal programs and personnel, and use its authorities to minimize harm to tribes and tribal citizens.”
Hoskin Jr. cautioned, though, that not every tribe has the same resources. Many smaller, direct-service tribes depend entirely on IHS to deliver care.
“Thank goodness for forward funding,” he said. “But we have to make that permanent in federal statute. No one in this country should be at the mercy of political dysfunction to get health care.
Despite the ongoing shutdown of the US federal government, the Indian Health Service (IHS) continues to maintain the status quo while operating on an island of relatively insulated stability.
“IHS will continue to operate business-as-usual during a lapse of appropriations,” US Department of Health and Human Services press secretary Emily G. Hilliard said at a recent meeting with the National Congress of American Indians (NCAI). “100% of IHS staff will report for work, and health care services across Indian Country will not be impacted.”
The protective cocoon around IHS and its services provided is largely due to advance appropriations, and lessons learned from previous government shutdowns. During the historically long 35-day government shutdown in 2018 and 2019, all federal government operations had to halt operations unless they were deemed indispensable. IHS was not considered indispensable and consequently, about 60% of IHS employees did not receive a paycheck.
In preparation for another potential shutdown in 2023, IHS was more proactive. “Because of the fact that now we have advanced appropriations for Indian Health Services, on Oct. 1, whether or not there’s a federal budget in place, will continue providing services,” then-HHS Secretary Xavier Becerra, said at the time.
The safeguards have held for the current shutdown, aided by tribal pressure. As the federal shutdown loomed in September, a delegation led by NCAI spent 3 days lobbying Congress—focusing primarily on the new leadership in the Senate Indian Affairs Committee—to guarantee some protection for federal employees who work with tribal governments.
At the quarterly meeting of the United Indian Nations of Oklahoma (UINO) in Tulsa, Rear Adm. Travis Watts, director of the IHS Oklahoma City Area and a citizen of the Choctaw Nation of Oklahoma, told attendees, “The advance appropriations allow us to keep our doors open at this particular time. We want to thank the tribal nations for their advocacy for those advance appropriations.”
IHS is funded through 2026. All 14,801 IHS staff will be paid through advance appropriations, multi-year or supplemental appropriations, third-party collections, or carryover balances.
However, according to the proposed 2026 budget some key health-related funding is at risk, including about $128 million in Tribal set-aside funding for mental and behavioral health funding: $60 million from the Tribal Opioid Response Grants, $22.75 million from Tribal Behavioral Health Grants, $14.5 million from Medication-Assisted Treatment for Prescription and Opioid Addiction, and $3.4 million Tribal set-aside for the Zero Suicide program. Six IHS accounts are not funded by advance appropriations: Electronic Health Record System, Indian Health Care Improvement Fund, Contract Support Costs, Payments for Tribal Leases, Sanitation Facilities Construction, and Health Care Facilities Construction.
In a public statement, Cherokee Nation Principal Chief Chuck Hoskin Jr. said, “[W]e’re hopeful that Congress’ foresight to provide an advance appropriation for the Indian Health Service will prevent any severe disruptions as experienced during the 2013 and 2018 shutdowns. I urge both sides of the aisle to work on a path forward and reopen the government as soon as possible and call on the administration to honor the government’s Treaty and Trust responsibilities, avoid needless cuts to Tribal programs and personnel, and use its authorities to minimize harm to tribes and tribal citizens.”
Hoskin Jr. cautioned, though, that not every tribe has the same resources. Many smaller, direct-service tribes depend entirely on IHS to deliver care.
“Thank goodness for forward funding,” he said. “But we have to make that permanent in federal statute. No one in this country should be at the mercy of political dysfunction to get health care.
Physicians Face Medicare Telehealth Woes Amid Federal Government Shutdown
Physicians Face Medicare Telehealth Woes Amid Federal Government Shutdown
The ongoing US government partial shutdown has unintended consequences for seniors and their doctors as most telehealth appointments are now no longer being covered by Medicare.
That's because without a budget deal, federal lawmakers did not renew some pandemic-era telehealth flexibilities allowing Medicare beneficiaries to have medical appointments with doctors over audio or video at home.
This policy was first put into place under the first Trump Administration in 2020 during the COVID-19 pandemic. Previously, Medicare covered very limited telehealth services for rural patients.
For the past 5 years, lawmakers have always managed to renew the telehealth flexibilities in every government funding bill before the expiration date. This year, however, they expired for the first time on October 1.
Federal lawmakers remain at odds on the 2026 federal funding bill, meaning the shutdown could last into more days and even weeks.
But with Congress in a standoff, clinicians and patients outside Washington, DC, are already grappling with the consequences of the funding impasse.
Clinicians, Patients Already Feeling Effects
For the South Dakota-based Sanford Health System, which is the largest rural health system in the country, the past week without the Medicare telehealth waivers being in place has caused a lot of anxiety and uncertainty for both patients and clinicians.
Dave Newman, an endocrinologist and chief medical officer of virtual care at Sanford, said the health system decided to keep providing Medicare telehealth appointments to patients for now.
"We're maintaining telehealth access because we know that's the best thing for our patients. We've got full confidence that reimbursement will follow, but patients can't wait for Congress to act at this point," Newman told Medscape Medical News. "They still need access to their specialists. They still need access to their primary care providers, and this is one of the only ways that a lot of our patients get access. For them, it's either virtual care or no care at all."
Newman said as the shutdown continues, Sanford may reconsidered whether it can keep providing these appointments without reimbursement.
Some health systems have stopped providing an Medicare telehealth appointments, said Alexis Apple, director of federal affairs at the American Telemedicine Association. That means patients must appear in person for their doctor's appointment or cancel.
NYU Langone Health system's website currently has a banner that reads: "Due to the federal government shutdown, Medicare and Medicaid patients are unable to schedule new telehealth/video visits. If you already have a visit scheduled, it will continue as planned. If not, contact your doctor's office to schedule an in-person appointment.
"It's creating lots of confusion in the industry from patients, providers, hospital systems. You know, what do we do next? How do we grapple with this shutdown?" said Apple. "Patients have been able to receive care within their homes over the past 5 years, and now, all of a sudden, they've been stripped of that access."
Medicare patients who continue telehealth after October 1 may find out they're on the hook for the bill, if Congress doesn't act, said Apple.
Some physicians worry that commercial insurance payers may follow suit and no longer cover virtual appointments. Medicare, which is the largest health care payer in the country, is often seen as the standard for what services should be covered.
Patients and doctors have come to rely on telehealth as an integral part of health care, said Richard Chou, an anesthesiologist at the US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) in Sacramento, California.
"You're seeing that postpandemic, telehealth is kind of a new way of doing things. It's part of the day for us as doctors," said Chou. He said tha tmany of his VA patients do their preliminary surgery appointments via telehealth before coming into the facility.
"Telehealth is that bridge to making sure patients get the care they need, and when these patients don't get that preliminary care they need, this builds up and builds up," said Chou. "And next thing you know, you have people flooding the emergency rooms, and we can't have that."
Will Telehealth Reimbursement See a Permanent Fix?
With Congressional budget negotiations at an impasse, it remains unclear when the shutdown will end.
Health care spending disagreements weigh heavily in negotiations. Democrats are currently unwilling to give the votes to pass the 60-vote threshold in the Senate unless Republicans agree to extend Affordable Care Act subsidies that expire at the end of the year. Democrats also want to reverse the Medicaid cuts that were part of the large Republican domestic tax and spending bill passed by Congress earlier this year.
When lawmakers do reach an agreement and reopen the government, it's likely telehealth flexibilities will be included in any package but for how long remains in question.
A newly introduced bipartisan bill would permanently allow Medicare patients to access telehealth appointments in their homes. But the legislation has been estimated to be very costly.
Federal data does show that telehealth appointments have been popular with Medicare recipients and increased over time since telehealth became more accessible.
"I used to say that virtual care was the future of medicine, and now it's just kind of the present of medicine. It used to be like a cool technology that we used to advertise, now it's just the standard of care," said Newman. "We think that permanent coverage would mean stability for both patients and providers."
Victoria Knight is a freelance reporter based in Washington, DC.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The ongoing US government partial shutdown has unintended consequences for seniors and their doctors as most telehealth appointments are now no longer being covered by Medicare.
That's because without a budget deal, federal lawmakers did not renew some pandemic-era telehealth flexibilities allowing Medicare beneficiaries to have medical appointments with doctors over audio or video at home.
This policy was first put into place under the first Trump Administration in 2020 during the COVID-19 pandemic. Previously, Medicare covered very limited telehealth services for rural patients.
For the past 5 years, lawmakers have always managed to renew the telehealth flexibilities in every government funding bill before the expiration date. This year, however, they expired for the first time on October 1.
Federal lawmakers remain at odds on the 2026 federal funding bill, meaning the shutdown could last into more days and even weeks.
But with Congress in a standoff, clinicians and patients outside Washington, DC, are already grappling with the consequences of the funding impasse.
Clinicians, Patients Already Feeling Effects
For the South Dakota-based Sanford Health System, which is the largest rural health system in the country, the past week without the Medicare telehealth waivers being in place has caused a lot of anxiety and uncertainty for both patients and clinicians.
Dave Newman, an endocrinologist and chief medical officer of virtual care at Sanford, said the health system decided to keep providing Medicare telehealth appointments to patients for now.
"We're maintaining telehealth access because we know that's the best thing for our patients. We've got full confidence that reimbursement will follow, but patients can't wait for Congress to act at this point," Newman told Medscape Medical News. "They still need access to their specialists. They still need access to their primary care providers, and this is one of the only ways that a lot of our patients get access. For them, it's either virtual care or no care at all."
Newman said as the shutdown continues, Sanford may reconsidered whether it can keep providing these appointments without reimbursement.
Some health systems have stopped providing an Medicare telehealth appointments, said Alexis Apple, director of federal affairs at the American Telemedicine Association. That means patients must appear in person for their doctor's appointment or cancel.
NYU Langone Health system's website currently has a banner that reads: "Due to the federal government shutdown, Medicare and Medicaid patients are unable to schedule new telehealth/video visits. If you already have a visit scheduled, it will continue as planned. If not, contact your doctor's office to schedule an in-person appointment.
"It's creating lots of confusion in the industry from patients, providers, hospital systems. You know, what do we do next? How do we grapple with this shutdown?" said Apple. "Patients have been able to receive care within their homes over the past 5 years, and now, all of a sudden, they've been stripped of that access."
Medicare patients who continue telehealth after October 1 may find out they're on the hook for the bill, if Congress doesn't act, said Apple.
Some physicians worry that commercial insurance payers may follow suit and no longer cover virtual appointments. Medicare, which is the largest health care payer in the country, is often seen as the standard for what services should be covered.
Patients and doctors have come to rely on telehealth as an integral part of health care, said Richard Chou, an anesthesiologist at the US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) in Sacramento, California.
"You're seeing that postpandemic, telehealth is kind of a new way of doing things. It's part of the day for us as doctors," said Chou. He said tha tmany of his VA patients do their preliminary surgery appointments via telehealth before coming into the facility.
"Telehealth is that bridge to making sure patients get the care they need, and when these patients don't get that preliminary care they need, this builds up and builds up," said Chou. "And next thing you know, you have people flooding the emergency rooms, and we can't have that."
Will Telehealth Reimbursement See a Permanent Fix?
With Congressional budget negotiations at an impasse, it remains unclear when the shutdown will end.
Health care spending disagreements weigh heavily in negotiations. Democrats are currently unwilling to give the votes to pass the 60-vote threshold in the Senate unless Republicans agree to extend Affordable Care Act subsidies that expire at the end of the year. Democrats also want to reverse the Medicaid cuts that were part of the large Republican domestic tax and spending bill passed by Congress earlier this year.
When lawmakers do reach an agreement and reopen the government, it's likely telehealth flexibilities will be included in any package but for how long remains in question.
A newly introduced bipartisan bill would permanently allow Medicare patients to access telehealth appointments in their homes. But the legislation has been estimated to be very costly.
Federal data does show that telehealth appointments have been popular with Medicare recipients and increased over time since telehealth became more accessible.
"I used to say that virtual care was the future of medicine, and now it's just kind of the present of medicine. It used to be like a cool technology that we used to advertise, now it's just the standard of care," said Newman. "We think that permanent coverage would mean stability for both patients and providers."
Victoria Knight is a freelance reporter based in Washington, DC.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The ongoing US government partial shutdown has unintended consequences for seniors and their doctors as most telehealth appointments are now no longer being covered by Medicare.
That's because without a budget deal, federal lawmakers did not renew some pandemic-era telehealth flexibilities allowing Medicare beneficiaries to have medical appointments with doctors over audio or video at home.
This policy was first put into place under the first Trump Administration in 2020 during the COVID-19 pandemic. Previously, Medicare covered very limited telehealth services for rural patients.
For the past 5 years, lawmakers have always managed to renew the telehealth flexibilities in every government funding bill before the expiration date. This year, however, they expired for the first time on October 1.
Federal lawmakers remain at odds on the 2026 federal funding bill, meaning the shutdown could last into more days and even weeks.
But with Congress in a standoff, clinicians and patients outside Washington, DC, are already grappling with the consequences of the funding impasse.
Clinicians, Patients Already Feeling Effects
For the South Dakota-based Sanford Health System, which is the largest rural health system in the country, the past week without the Medicare telehealth waivers being in place has caused a lot of anxiety and uncertainty for both patients and clinicians.
Dave Newman, an endocrinologist and chief medical officer of virtual care at Sanford, said the health system decided to keep providing Medicare telehealth appointments to patients for now.
"We're maintaining telehealth access because we know that's the best thing for our patients. We've got full confidence that reimbursement will follow, but patients can't wait for Congress to act at this point," Newman told Medscape Medical News. "They still need access to their specialists. They still need access to their primary care providers, and this is one of the only ways that a lot of our patients get access. For them, it's either virtual care or no care at all."
Newman said as the shutdown continues, Sanford may reconsidered whether it can keep providing these appointments without reimbursement.
Some health systems have stopped providing an Medicare telehealth appointments, said Alexis Apple, director of federal affairs at the American Telemedicine Association. That means patients must appear in person for their doctor's appointment or cancel.
NYU Langone Health system's website currently has a banner that reads: "Due to the federal government shutdown, Medicare and Medicaid patients are unable to schedule new telehealth/video visits. If you already have a visit scheduled, it will continue as planned. If not, contact your doctor's office to schedule an in-person appointment.
"It's creating lots of confusion in the industry from patients, providers, hospital systems. You know, what do we do next? How do we grapple with this shutdown?" said Apple. "Patients have been able to receive care within their homes over the past 5 years, and now, all of a sudden, they've been stripped of that access."
Medicare patients who continue telehealth after October 1 may find out they're on the hook for the bill, if Congress doesn't act, said Apple.
Some physicians worry that commercial insurance payers may follow suit and no longer cover virtual appointments. Medicare, which is the largest health care payer in the country, is often seen as the standard for what services should be covered.
Patients and doctors have come to rely on telehealth as an integral part of health care, said Richard Chou, an anesthesiologist at the US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) in Sacramento, California.
"You're seeing that postpandemic, telehealth is kind of a new way of doing things. It's part of the day for us as doctors," said Chou. He said tha tmany of his VA patients do their preliminary surgery appointments via telehealth before coming into the facility.
"Telehealth is that bridge to making sure patients get the care they need, and when these patients don't get that preliminary care they need, this builds up and builds up," said Chou. "And next thing you know, you have people flooding the emergency rooms, and we can't have that."
Will Telehealth Reimbursement See a Permanent Fix?
With Congressional budget negotiations at an impasse, it remains unclear when the shutdown will end.
Health care spending disagreements weigh heavily in negotiations. Democrats are currently unwilling to give the votes to pass the 60-vote threshold in the Senate unless Republicans agree to extend Affordable Care Act subsidies that expire at the end of the year. Democrats also want to reverse the Medicaid cuts that were part of the large Republican domestic tax and spending bill passed by Congress earlier this year.
When lawmakers do reach an agreement and reopen the government, it's likely telehealth flexibilities will be included in any package but for how long remains in question.
A newly introduced bipartisan bill would permanently allow Medicare patients to access telehealth appointments in their homes. But the legislation has been estimated to be very costly.
Federal data does show that telehealth appointments have been popular with Medicare recipients and increased over time since telehealth became more accessible.
"I used to say that virtual care was the future of medicine, and now it's just kind of the present of medicine. It used to be like a cool technology that we used to advertise, now it's just the standard of care," said Newman. "We think that permanent coverage would mean stability for both patients and providers."
Victoria Knight is a freelance reporter based in Washington, DC.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Physicians Face Medicare Telehealth Woes Amid Federal Government Shutdown
Physicians Face Medicare Telehealth Woes Amid Federal Government Shutdown
Architect of VA Transformation Urges Innovation Amid Uncertainty
Architect of VA Transformation Urges Innovation Amid Uncertainty
PHOENIX – Three decades after he initiated the transformation of the Veterans Health Administration (VHA) into a model research and clinical health care system, former US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) Under Secretary of Health Kenneth W. Kizer, MD, MPH, urged cancer specialists to embrace this challenging moment as an opportunity for bold innovation.
At the annual meeting of the Association of VA Hematology/Oncology (AVAHO), Kizer acknowledged that the VA faces an “uncertain and turbulent time” in areas such as funding, staffing, community care implementation, and the rollout of a new electronic health record system.
He also noted the grim rise of global instability, economic turmoil, climate change, infectious diseases, political violence, and mass shootings.
“This can be stressful. It can create negative energy. But this uncertainty can also be liberating, and it can prompt positive energy and innovation, depending on choices that we make,” said Kizer, who also has served as California’s top health official prior to leading the VHA from 1994 to 1999.
From “Bloated Bureaucracy’ to High-Quality Health Care System
Kizer has been credited with revitalizing VHA care through a greater commitment to quality, and harkened to his work with the VA as an example of how bold goals can lead to bold innovation.
“What were the perceptions of VA health care in 1994? Well, they weren’t very good, frankly,” Kizer recalled. He described the VA as having a reputation at that time as “highly dysfunctional” with “a very bloated and entrenched bureaucracy.” As for quality of care, it “wasn’t viewed as very good.”
The system’s problems were so severe that patients would park motorhomes in VA medical center parking lots as they waited for care. “While they might have an appointment for one day, they may not be seen for 3 or 4 or 5 days. So they would stay in their motorhome until they finally got into their clinic appointment,” Kizer said.
Overall, “the public viewed the VA as this bleak backwater of incompetence and difference and inefficiency, and there were very strong calls to privatize the VA,” Kizer said.
Kizer asked colleagues about what he should do after he was asked to take the under secretary job. “With one exception, they all said, don’t go near it. Don’t touch it. Walk away. That it’s impossible to change the organization.
“I looked at the VA and I saw an opportunity. When I told [members of the President Bill] Clinton [Administration] yes, my bold aim was that I would like to pursue this was to make VHA a model of excellent health care, an exemplary health care system. Most everyone else thought that I was totally delusional, but sometimes it’s good to be delusional.”
Revolutionary Changes Despite Opposition
Kizer sought reforms in 5 major strategic objectives, all without explicit congressional approval: creating an accountable management structure, decentralizing decision-making, integrating care, implementing universal primary care, and pursuing eligibility reform to create the current 8-tier VA system.
One major innovation was the implementation of community-based outpatient clinics (CBOCs): “Those were strongly opposed initially,” Kizer said. “Everyone, the veteran community in particular, had been led to believe that the only good care was in the hospital.”
The resistance was substantial. “There was a lot of opposition when we said we’re going to move out into the community where you live to make [care] easier to access,” Kizer said.
To make things more difficult, Congress wouldn’t fund the project: “For the first 3 years, every CBOC had to be funded by redirected savings from other things that we could do within the system,” he said. “All of this was through redirected savings and finding ways to save and reinvest.”
Innovation From the Ground Up
Kizer emphasized that many breakthrough innovations came from frontline staff rather than executive mandates. He cited the example of Barcode Medication Administration, which originated from a nurse in Topeka, Kan.
The nurse saw a barcode scanner put to work at a rental car company where it was used to check cars in and out. She wondered, “Why can’t we do this with medications when they’re given on the floor? We followed up on it, pursued those things, tested it out, it worked.”
The results were dramatic. “I was told at a meeting that they had achieved close to 80% reduction in medication errors,” Kizer said. After verifying the results personally, he “authorized $20 million, and we moved forward with it systemwide.”
This experience reinforced his belief in harvesting ideas from staff at all levels.
Innovation remains part of the VA’s culture “despite what some people would have you believe,” Kizer said. Recently, the VA has made major advances in areas such as patient transportation and the climate crisis, he said.
Inside the Recipe for Innovation
Boldness, persistence, adaptability, and tolerance for risk are necessary ingredients for high-risk goals, Kizer said. Ambition is also part of the picture.
He highlighted examples such as the Apollo moon landing, the first sub-4-minute mile, and the first swim across the English Channel by a woman.
In medicine, Kizer pointed to a national patient safety campaign that saved an estimated 122,000 lives. He also mentioned recent progress in organ transplantation such as recommendations from the National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine to establish national performance goals and the Organ Procurement and Transplantation Network’s target of 60,000 deceased donor transplants by 2026.
Bold doesn’t mean being reckless or careless, Kizer said. “But it does require innovation. And it does require that you try some new things, some of which aren’t going to work out.”
The key mindset, he explained, is to “embrace the unknown” because “you often really don’t know how you will accomplish the aim when you start. But you’ll figure it out as you go.”
Kizer highlighted 2 opposing strategies to handling challenging times.
According to him, the “negative energy” approach focuses on frustrations, limitations, and asking “Why is this happening to me?”
In contrast, a “positive energy” approach expects problems, focuses on available resources and capabilities, and asks, “What are the opportunities that these changes are creating for me?”
Kizer made it crystal clear which option he prefers.
Dr. Kizer disclosed that his comments represent his opinions only, and he noted his ongoing connections to the VA.
PHOENIX – Three decades after he initiated the transformation of the Veterans Health Administration (VHA) into a model research and clinical health care system, former US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) Under Secretary of Health Kenneth W. Kizer, MD, MPH, urged cancer specialists to embrace this challenging moment as an opportunity for bold innovation.
At the annual meeting of the Association of VA Hematology/Oncology (AVAHO), Kizer acknowledged that the VA faces an “uncertain and turbulent time” in areas such as funding, staffing, community care implementation, and the rollout of a new electronic health record system.
He also noted the grim rise of global instability, economic turmoil, climate change, infectious diseases, political violence, and mass shootings.
“This can be stressful. It can create negative energy. But this uncertainty can also be liberating, and it can prompt positive energy and innovation, depending on choices that we make,” said Kizer, who also has served as California’s top health official prior to leading the VHA from 1994 to 1999.
From “Bloated Bureaucracy’ to High-Quality Health Care System
Kizer has been credited with revitalizing VHA care through a greater commitment to quality, and harkened to his work with the VA as an example of how bold goals can lead to bold innovation.
“What were the perceptions of VA health care in 1994? Well, they weren’t very good, frankly,” Kizer recalled. He described the VA as having a reputation at that time as “highly dysfunctional” with “a very bloated and entrenched bureaucracy.” As for quality of care, it “wasn’t viewed as very good.”
The system’s problems were so severe that patients would park motorhomes in VA medical center parking lots as they waited for care. “While they might have an appointment for one day, they may not be seen for 3 or 4 or 5 days. So they would stay in their motorhome until they finally got into their clinic appointment,” Kizer said.
Overall, “the public viewed the VA as this bleak backwater of incompetence and difference and inefficiency, and there were very strong calls to privatize the VA,” Kizer said.
Kizer asked colleagues about what he should do after he was asked to take the under secretary job. “With one exception, they all said, don’t go near it. Don’t touch it. Walk away. That it’s impossible to change the organization.
“I looked at the VA and I saw an opportunity. When I told [members of the President Bill] Clinton [Administration] yes, my bold aim was that I would like to pursue this was to make VHA a model of excellent health care, an exemplary health care system. Most everyone else thought that I was totally delusional, but sometimes it’s good to be delusional.”
Revolutionary Changes Despite Opposition
Kizer sought reforms in 5 major strategic objectives, all without explicit congressional approval: creating an accountable management structure, decentralizing decision-making, integrating care, implementing universal primary care, and pursuing eligibility reform to create the current 8-tier VA system.
One major innovation was the implementation of community-based outpatient clinics (CBOCs): “Those were strongly opposed initially,” Kizer said. “Everyone, the veteran community in particular, had been led to believe that the only good care was in the hospital.”
The resistance was substantial. “There was a lot of opposition when we said we’re going to move out into the community where you live to make [care] easier to access,” Kizer said.
To make things more difficult, Congress wouldn’t fund the project: “For the first 3 years, every CBOC had to be funded by redirected savings from other things that we could do within the system,” he said. “All of this was through redirected savings and finding ways to save and reinvest.”
Innovation From the Ground Up
Kizer emphasized that many breakthrough innovations came from frontline staff rather than executive mandates. He cited the example of Barcode Medication Administration, which originated from a nurse in Topeka, Kan.
The nurse saw a barcode scanner put to work at a rental car company where it was used to check cars in and out. She wondered, “Why can’t we do this with medications when they’re given on the floor? We followed up on it, pursued those things, tested it out, it worked.”
The results were dramatic. “I was told at a meeting that they had achieved close to 80% reduction in medication errors,” Kizer said. After verifying the results personally, he “authorized $20 million, and we moved forward with it systemwide.”
This experience reinforced his belief in harvesting ideas from staff at all levels.
Innovation remains part of the VA’s culture “despite what some people would have you believe,” Kizer said. Recently, the VA has made major advances in areas such as patient transportation and the climate crisis, he said.
Inside the Recipe for Innovation
Boldness, persistence, adaptability, and tolerance for risk are necessary ingredients for high-risk goals, Kizer said. Ambition is also part of the picture.
He highlighted examples such as the Apollo moon landing, the first sub-4-minute mile, and the first swim across the English Channel by a woman.
In medicine, Kizer pointed to a national patient safety campaign that saved an estimated 122,000 lives. He also mentioned recent progress in organ transplantation such as recommendations from the National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine to establish national performance goals and the Organ Procurement and Transplantation Network’s target of 60,000 deceased donor transplants by 2026.
Bold doesn’t mean being reckless or careless, Kizer said. “But it does require innovation. And it does require that you try some new things, some of which aren’t going to work out.”
The key mindset, he explained, is to “embrace the unknown” because “you often really don’t know how you will accomplish the aim when you start. But you’ll figure it out as you go.”
Kizer highlighted 2 opposing strategies to handling challenging times.
According to him, the “negative energy” approach focuses on frustrations, limitations, and asking “Why is this happening to me?”
In contrast, a “positive energy” approach expects problems, focuses on available resources and capabilities, and asks, “What are the opportunities that these changes are creating for me?”
Kizer made it crystal clear which option he prefers.
Dr. Kizer disclosed that his comments represent his opinions only, and he noted his ongoing connections to the VA.
PHOENIX – Three decades after he initiated the transformation of the Veterans Health Administration (VHA) into a model research and clinical health care system, former US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) Under Secretary of Health Kenneth W. Kizer, MD, MPH, urged cancer specialists to embrace this challenging moment as an opportunity for bold innovation.
At the annual meeting of the Association of VA Hematology/Oncology (AVAHO), Kizer acknowledged that the VA faces an “uncertain and turbulent time” in areas such as funding, staffing, community care implementation, and the rollout of a new electronic health record system.
He also noted the grim rise of global instability, economic turmoil, climate change, infectious diseases, political violence, and mass shootings.
“This can be stressful. It can create negative energy. But this uncertainty can also be liberating, and it can prompt positive energy and innovation, depending on choices that we make,” said Kizer, who also has served as California’s top health official prior to leading the VHA from 1994 to 1999.
From “Bloated Bureaucracy’ to High-Quality Health Care System
Kizer has been credited with revitalizing VHA care through a greater commitment to quality, and harkened to his work with the VA as an example of how bold goals can lead to bold innovation.
“What were the perceptions of VA health care in 1994? Well, they weren’t very good, frankly,” Kizer recalled. He described the VA as having a reputation at that time as “highly dysfunctional” with “a very bloated and entrenched bureaucracy.” As for quality of care, it “wasn’t viewed as very good.”
The system’s problems were so severe that patients would park motorhomes in VA medical center parking lots as they waited for care. “While they might have an appointment for one day, they may not be seen for 3 or 4 or 5 days. So they would stay in their motorhome until they finally got into their clinic appointment,” Kizer said.
Overall, “the public viewed the VA as this bleak backwater of incompetence and difference and inefficiency, and there were very strong calls to privatize the VA,” Kizer said.
Kizer asked colleagues about what he should do after he was asked to take the under secretary job. “With one exception, they all said, don’t go near it. Don’t touch it. Walk away. That it’s impossible to change the organization.
“I looked at the VA and I saw an opportunity. When I told [members of the President Bill] Clinton [Administration] yes, my bold aim was that I would like to pursue this was to make VHA a model of excellent health care, an exemplary health care system. Most everyone else thought that I was totally delusional, but sometimes it’s good to be delusional.”
Revolutionary Changes Despite Opposition
Kizer sought reforms in 5 major strategic objectives, all without explicit congressional approval: creating an accountable management structure, decentralizing decision-making, integrating care, implementing universal primary care, and pursuing eligibility reform to create the current 8-tier VA system.
One major innovation was the implementation of community-based outpatient clinics (CBOCs): “Those were strongly opposed initially,” Kizer said. “Everyone, the veteran community in particular, had been led to believe that the only good care was in the hospital.”
The resistance was substantial. “There was a lot of opposition when we said we’re going to move out into the community where you live to make [care] easier to access,” Kizer said.
To make things more difficult, Congress wouldn’t fund the project: “For the first 3 years, every CBOC had to be funded by redirected savings from other things that we could do within the system,” he said. “All of this was through redirected savings and finding ways to save and reinvest.”
Innovation From the Ground Up
Kizer emphasized that many breakthrough innovations came from frontline staff rather than executive mandates. He cited the example of Barcode Medication Administration, which originated from a nurse in Topeka, Kan.
The nurse saw a barcode scanner put to work at a rental car company where it was used to check cars in and out. She wondered, “Why can’t we do this with medications when they’re given on the floor? We followed up on it, pursued those things, tested it out, it worked.”
The results were dramatic. “I was told at a meeting that they had achieved close to 80% reduction in medication errors,” Kizer said. After verifying the results personally, he “authorized $20 million, and we moved forward with it systemwide.”
This experience reinforced his belief in harvesting ideas from staff at all levels.
Innovation remains part of the VA’s culture “despite what some people would have you believe,” Kizer said. Recently, the VA has made major advances in areas such as patient transportation and the climate crisis, he said.
Inside the Recipe for Innovation
Boldness, persistence, adaptability, and tolerance for risk are necessary ingredients for high-risk goals, Kizer said. Ambition is also part of the picture.
He highlighted examples such as the Apollo moon landing, the first sub-4-minute mile, and the first swim across the English Channel by a woman.
In medicine, Kizer pointed to a national patient safety campaign that saved an estimated 122,000 lives. He also mentioned recent progress in organ transplantation such as recommendations from the National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine to establish national performance goals and the Organ Procurement and Transplantation Network’s target of 60,000 deceased donor transplants by 2026.
Bold doesn’t mean being reckless or careless, Kizer said. “But it does require innovation. And it does require that you try some new things, some of which aren’t going to work out.”
The key mindset, he explained, is to “embrace the unknown” because “you often really don’t know how you will accomplish the aim when you start. But you’ll figure it out as you go.”
Kizer highlighted 2 opposing strategies to handling challenging times.
According to him, the “negative energy” approach focuses on frustrations, limitations, and asking “Why is this happening to me?”
In contrast, a “positive energy” approach expects problems, focuses on available resources and capabilities, and asks, “What are the opportunities that these changes are creating for me?”
Kizer made it crystal clear which option he prefers.
Dr. Kizer disclosed that his comments represent his opinions only, and he noted his ongoing connections to the VA.
Architect of VA Transformation Urges Innovation Amid Uncertainty
Architect of VA Transformation Urges Innovation Amid Uncertainty






