User login
RT of lymph nodes as good as dissection for the long-term
SAN ANTONIO – Both axillary radiation therapy and axillary lymph node dissection provide excellent, comparable locoregional control in patients with early-stage breast cancer who have a positive sentinel node, according to updated results of the European Organisation for Research and Treatment of Cancer’s AMAROS trial.
The 10-year cumulative incidence rate of axillary recurrence was 1.82% with radiation and 0.93% with lymph node dissection, a nonsignificant difference (hazard ratio, 1.71; P = .365). Distant metastasis–free survival and overall survival also were statistically on par. The findings reinforce the trial’s 5-year results, which additionally showed a markedly lower incidence of lymphedema with axillary radiation therapy. Lead investigator Emiel J. T. Rutgers, MD, PhD, reflected on hesitation in the uptake of axillary radiation therapy among oncologists and discussed the AMAROS results in the context of the ACOSOG Z11 trial. Dr. Rutgers, the principal investigator of the AMAROS trial and a surgical oncologist at the Netherlands Cancer Institute in Amsterdam, also described how the trial’s findings have altered practice at his institution.
Dr. Rutgers disclosed that he had no relevant conflicts of interest. The study was supported by the EORTC Charitable Trust.
SAN ANTONIO – Both axillary radiation therapy and axillary lymph node dissection provide excellent, comparable locoregional control in patients with early-stage breast cancer who have a positive sentinel node, according to updated results of the European Organisation for Research and Treatment of Cancer’s AMAROS trial.
The 10-year cumulative incidence rate of axillary recurrence was 1.82% with radiation and 0.93% with lymph node dissection, a nonsignificant difference (hazard ratio, 1.71; P = .365). Distant metastasis–free survival and overall survival also were statistically on par. The findings reinforce the trial’s 5-year results, which additionally showed a markedly lower incidence of lymphedema with axillary radiation therapy. Lead investigator Emiel J. T. Rutgers, MD, PhD, reflected on hesitation in the uptake of axillary radiation therapy among oncologists and discussed the AMAROS results in the context of the ACOSOG Z11 trial. Dr. Rutgers, the principal investigator of the AMAROS trial and a surgical oncologist at the Netherlands Cancer Institute in Amsterdam, also described how the trial’s findings have altered practice at his institution.
Dr. Rutgers disclosed that he had no relevant conflicts of interest. The study was supported by the EORTC Charitable Trust.
SAN ANTONIO – Both axillary radiation therapy and axillary lymph node dissection provide excellent, comparable locoregional control in patients with early-stage breast cancer who have a positive sentinel node, according to updated results of the European Organisation for Research and Treatment of Cancer’s AMAROS trial.
The 10-year cumulative incidence rate of axillary recurrence was 1.82% with radiation and 0.93% with lymph node dissection, a nonsignificant difference (hazard ratio, 1.71; P = .365). Distant metastasis–free survival and overall survival also were statistically on par. The findings reinforce the trial’s 5-year results, which additionally showed a markedly lower incidence of lymphedema with axillary radiation therapy. Lead investigator Emiel J. T. Rutgers, MD, PhD, reflected on hesitation in the uptake of axillary radiation therapy among oncologists and discussed the AMAROS results in the context of the ACOSOG Z11 trial. Dr. Rutgers, the principal investigator of the AMAROS trial and a surgical oncologist at the Netherlands Cancer Institute in Amsterdam, also described how the trial’s findings have altered practice at his institution.
Dr. Rutgers disclosed that he had no relevant conflicts of interest. The study was supported by the EORTC Charitable Trust.
REPORTING FROM SABCS 2018
Nothing to gain from chemo after pCR achieved
SAN ANTONIO – Women with localized breast cancer who achieve a pathological complete response (pCR) after neoadjuvant chemotherapy may have little to gain from subsequent adjuvant chemotherapy except toxicity, according to a patient-level meta-analysis of more than 27,000 women. The analysis, reported by lead investigator Laura M. Spring, MD, at the San Antonio Breast Cancer Symposium, confirmed that, compared with residual disease, pCR was associated with significantly reduced risks of event-free survival events (hazard ratio, 0.31) and death (HR, 0.22). Moreover, the EFS benefit of a pCR was similar whether women went on to receive adjuvant chemotherapy (HR, 0.36) or not (HR, 0.36) (P = .60 for difference). Dr. Spring discussed overall and subgroup findings, implications for use of neoadjuvant chemotherapy, and how these new data may inform escalation and de-escalation of adjuvant therapy.
Dr. Spring disclosed that she has a consulting or advisory role with Novartis and that she receives institutional research funding from Tesaro. The study was supported by grants from the National Cancer Institute and Susan G. Komen.
SAN ANTONIO – Women with localized breast cancer who achieve a pathological complete response (pCR) after neoadjuvant chemotherapy may have little to gain from subsequent adjuvant chemotherapy except toxicity, according to a patient-level meta-analysis of more than 27,000 women. The analysis, reported by lead investigator Laura M. Spring, MD, at the San Antonio Breast Cancer Symposium, confirmed that, compared with residual disease, pCR was associated with significantly reduced risks of event-free survival events (hazard ratio, 0.31) and death (HR, 0.22). Moreover, the EFS benefit of a pCR was similar whether women went on to receive adjuvant chemotherapy (HR, 0.36) or not (HR, 0.36) (P = .60 for difference). Dr. Spring discussed overall and subgroup findings, implications for use of neoadjuvant chemotherapy, and how these new data may inform escalation and de-escalation of adjuvant therapy.
Dr. Spring disclosed that she has a consulting or advisory role with Novartis and that she receives institutional research funding from Tesaro. The study was supported by grants from the National Cancer Institute and Susan G. Komen.
SAN ANTONIO – Women with localized breast cancer who achieve a pathological complete response (pCR) after neoadjuvant chemotherapy may have little to gain from subsequent adjuvant chemotherapy except toxicity, according to a patient-level meta-analysis of more than 27,000 women. The analysis, reported by lead investigator Laura M. Spring, MD, at the San Antonio Breast Cancer Symposium, confirmed that, compared with residual disease, pCR was associated with significantly reduced risks of event-free survival events (hazard ratio, 0.31) and death (HR, 0.22). Moreover, the EFS benefit of a pCR was similar whether women went on to receive adjuvant chemotherapy (HR, 0.36) or not (HR, 0.36) (P = .60 for difference). Dr. Spring discussed overall and subgroup findings, implications for use of neoadjuvant chemotherapy, and how these new data may inform escalation and de-escalation of adjuvant therapy.
Dr. Spring disclosed that she has a consulting or advisory role with Novartis and that she receives institutional research funding from Tesaro. The study was supported by grants from the National Cancer Institute and Susan G. Komen.
REPORTING FROM SABCS 2018
Small absolute difference between partial and whole breast irradiation
SAN ANTONIO – A phase 3 randomized NRG Oncology trial (NSABP B-39/RTOG 0413) was unable to rule out the possibility that, after lumpectomy, partial breast irradiation is inferior to whole breast irradiation when it comes to the ipsilateral breast tumor recurrences (invasive disease or ductal carcinoma in situ), reported Frank Vicini, MD, of MHP Radiation Oncology Institute, Pontiac, Mich.
The hazard ratio for this event with the former versus latter modality was 1.22, with the 90% confidence interval (0.94-1.58) falling just outside the predefined range to declare the two modalities equivalent (0.667-1.5). However, the absolute difference in the 10-year cumulative incidence of ipsilateral breast tumor recurrences was just 0.7% (4.6% vs. 3.9%). In a video interview, Dr. Vicini discussed whether this difference is clinically important, and the implications of the trial’s findings, taken together, for offering partial breast irradiation to patients.
Dr. Vicini disclosed that he is a research adviser for ImpediMed. The study was sponsored by the National Cancer Institute.
SAN ANTONIO – A phase 3 randomized NRG Oncology trial (NSABP B-39/RTOG 0413) was unable to rule out the possibility that, after lumpectomy, partial breast irradiation is inferior to whole breast irradiation when it comes to the ipsilateral breast tumor recurrences (invasive disease or ductal carcinoma in situ), reported Frank Vicini, MD, of MHP Radiation Oncology Institute, Pontiac, Mich.
The hazard ratio for this event with the former versus latter modality was 1.22, with the 90% confidence interval (0.94-1.58) falling just outside the predefined range to declare the two modalities equivalent (0.667-1.5). However, the absolute difference in the 10-year cumulative incidence of ipsilateral breast tumor recurrences was just 0.7% (4.6% vs. 3.9%). In a video interview, Dr. Vicini discussed whether this difference is clinically important, and the implications of the trial’s findings, taken together, for offering partial breast irradiation to patients.
Dr. Vicini disclosed that he is a research adviser for ImpediMed. The study was sponsored by the National Cancer Institute.
SAN ANTONIO – A phase 3 randomized NRG Oncology trial (NSABP B-39/RTOG 0413) was unable to rule out the possibility that, after lumpectomy, partial breast irradiation is inferior to whole breast irradiation when it comes to the ipsilateral breast tumor recurrences (invasive disease or ductal carcinoma in situ), reported Frank Vicini, MD, of MHP Radiation Oncology Institute, Pontiac, Mich.
The hazard ratio for this event with the former versus latter modality was 1.22, with the 90% confidence interval (0.94-1.58) falling just outside the predefined range to declare the two modalities equivalent (0.667-1.5). However, the absolute difference in the 10-year cumulative incidence of ipsilateral breast tumor recurrences was just 0.7% (4.6% vs. 3.9%). In a video interview, Dr. Vicini discussed whether this difference is clinically important, and the implications of the trial’s findings, taken together, for offering partial breast irradiation to patients.
Dr. Vicini disclosed that he is a research adviser for ImpediMed. The study was sponsored by the National Cancer Institute.
REPORTING FROM SABCS 2018
LCAR-B38M CAR T therapy appears durable in myeloma
SAN DIEGO – The chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy LCAR-B38M is in the race for approval in multiple myeloma following encouraging phase 1 results reported at the annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology.
In the LEGEND-2 phase 1/2 open study of 57 patients with advanced relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma treated with the investigational CAR T therapy, the overall response rate was 88% and the complete response rate was 74%. Among 42 patients who achieved complete response, 39 (68%) were negative for minimal residual disease (MRD).
With a median follow-up of 12 months, the median duration of response was 16 months and progression-free survival was 15 months. But in patients who achieved MRD-negative complete response, the median progression-free survival was extended to 24 months.
Pyrexia and cytokine release syndrome were reported in 90% or more of patients. Thrombocytopenia and leukopenia were reported in nearly half of patients.
The phase 1 study was conducted by researchers from the Second Affiliated Hospital of Xi’an Jiaotong University in Xi’an, China. The B-cell maturation antigen (BCMA)–directed CAR T-cell therapy is being jointly developed by Nanjing Legend Biotech and Janssen. A phase 2 study is currently being planned in China for LCAR-B38M. In parallel, Janssen and Legend are enrolling patients in a phase 1b/2 trial of the agent (also known as JNJ-68284528) in the United States.
The therapy joins a growing field of anti-BCMA CAR T-cell agents with promising initial trial results, including bb2121.
In a video interview at ASH, Sen Zhuang, MD, PhD, vice president of oncology clinical development at Janssen Research & Development, said this class of CAR T agents offers the potential for “very long remissions” and possibly even a “cure” for myeloma.
The LEGEND-2 study is sponsored by Nanjing Legend Biotech and two of the investigators reported employment with the company.
SAN DIEGO – The chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy LCAR-B38M is in the race for approval in multiple myeloma following encouraging phase 1 results reported at the annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology.
In the LEGEND-2 phase 1/2 open study of 57 patients with advanced relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma treated with the investigational CAR T therapy, the overall response rate was 88% and the complete response rate was 74%. Among 42 patients who achieved complete response, 39 (68%) were negative for minimal residual disease (MRD).
With a median follow-up of 12 months, the median duration of response was 16 months and progression-free survival was 15 months. But in patients who achieved MRD-negative complete response, the median progression-free survival was extended to 24 months.
Pyrexia and cytokine release syndrome were reported in 90% or more of patients. Thrombocytopenia and leukopenia were reported in nearly half of patients.
The phase 1 study was conducted by researchers from the Second Affiliated Hospital of Xi’an Jiaotong University in Xi’an, China. The B-cell maturation antigen (BCMA)–directed CAR T-cell therapy is being jointly developed by Nanjing Legend Biotech and Janssen. A phase 2 study is currently being planned in China for LCAR-B38M. In parallel, Janssen and Legend are enrolling patients in a phase 1b/2 trial of the agent (also known as JNJ-68284528) in the United States.
The therapy joins a growing field of anti-BCMA CAR T-cell agents with promising initial trial results, including bb2121.
In a video interview at ASH, Sen Zhuang, MD, PhD, vice president of oncology clinical development at Janssen Research & Development, said this class of CAR T agents offers the potential for “very long remissions” and possibly even a “cure” for myeloma.
The LEGEND-2 study is sponsored by Nanjing Legend Biotech and two of the investigators reported employment with the company.
SAN DIEGO – The chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy LCAR-B38M is in the race for approval in multiple myeloma following encouraging phase 1 results reported at the annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology.
In the LEGEND-2 phase 1/2 open study of 57 patients with advanced relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma treated with the investigational CAR T therapy, the overall response rate was 88% and the complete response rate was 74%. Among 42 patients who achieved complete response, 39 (68%) were negative for minimal residual disease (MRD).
With a median follow-up of 12 months, the median duration of response was 16 months and progression-free survival was 15 months. But in patients who achieved MRD-negative complete response, the median progression-free survival was extended to 24 months.
Pyrexia and cytokine release syndrome were reported in 90% or more of patients. Thrombocytopenia and leukopenia were reported in nearly half of patients.
The phase 1 study was conducted by researchers from the Second Affiliated Hospital of Xi’an Jiaotong University in Xi’an, China. The B-cell maturation antigen (BCMA)–directed CAR T-cell therapy is being jointly developed by Nanjing Legend Biotech and Janssen. A phase 2 study is currently being planned in China for LCAR-B38M. In parallel, Janssen and Legend are enrolling patients in a phase 1b/2 trial of the agent (also known as JNJ-68284528) in the United States.
The therapy joins a growing field of anti-BCMA CAR T-cell agents with promising initial trial results, including bb2121.
In a video interview at ASH, Sen Zhuang, MD, PhD, vice president of oncology clinical development at Janssen Research & Development, said this class of CAR T agents offers the potential for “very long remissions” and possibly even a “cure” for myeloma.
The LEGEND-2 study is sponsored by Nanjing Legend Biotech and two of the investigators reported employment with the company.
REPORTING FROM ASH 2018
Key clinical point:
Major finding: The complete response rate was 74% with median progression-free survival of 15 months.
Study details: A phase 1/2 study of 57 patients with advanced relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma.
Disclosures: The study is sponsored by Nanjing Legend Biotech. Two of the investigators reported employment with the company.
No boost in OS with addition of capecitabine for early TNBC
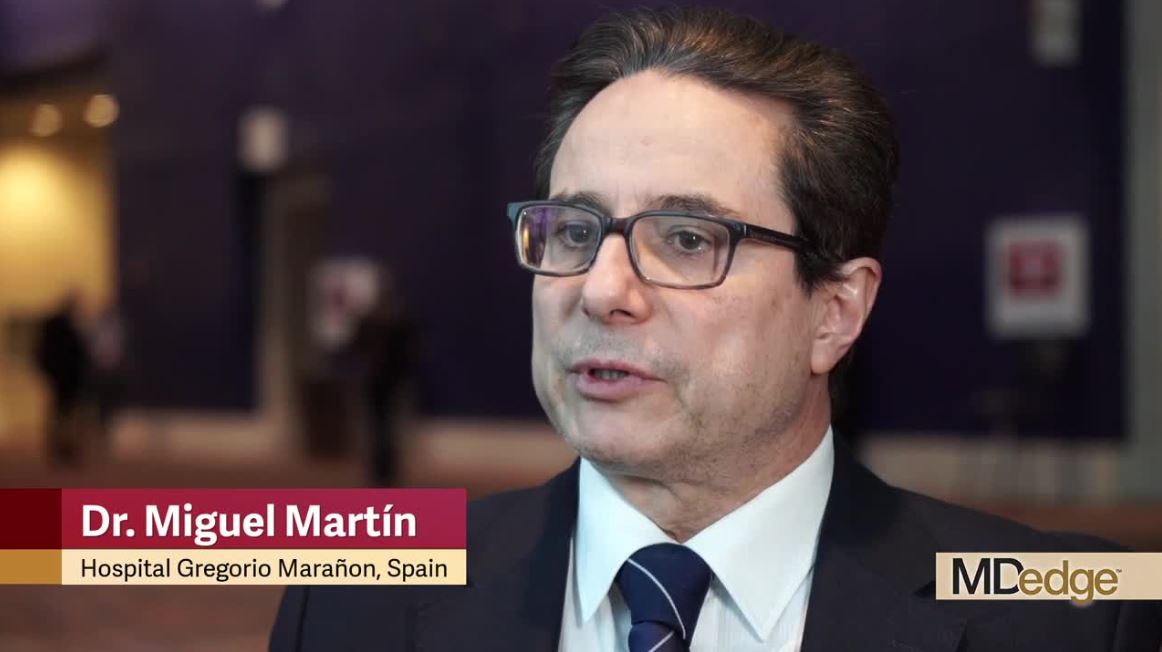
SAN ANTONIO – A phase 3 randomized controlled trial jointly conducted by GEICAM and CIBOMA is negative, showing that adding adjuvant capecitabine (Xeloda) to surgery and standard chemotherapy does not improve disease-free or overall survival in women with early-stage triple-negative breast cancer, reported lead investigator Miguel Martín, MD, PhD.
At the San Antonio Breast Cancer Symposium, he discussed the overall findings and intriguing subgroup results suggesting that there was a benefit in women with tumors having the nonbasal phenotype. Dr. Martín also detailed implications in the context of the CREATE-X trial findings and the era of personalized medicine, and outlined next avenues of research.
The trial was supported by Roche, which also provided capecitabine. Dr. Martín disclosed that he has received speakers honoraria from Pfizer and Lilly; honoraria for participation in advisory boards from AstraZeneca, Novartis, Roche-Genentech, Pfizer, GlaxoSmithKline, PharmaMar, Taiho Oncology, and Lilly; and research grants from Novartis and Roche.
SAN ANTONIO – A phase 3 randomized controlled trial jointly conducted by GEICAM and CIBOMA is negative, showing that adding adjuvant capecitabine (Xeloda) to surgery and standard chemotherapy does not improve disease-free or overall survival in women with early-stage triple-negative breast cancer, reported lead investigator Miguel Martín, MD, PhD.
At the San Antonio Breast Cancer Symposium, he discussed the overall findings and intriguing subgroup results suggesting that there was a benefit in women with tumors having the nonbasal phenotype. Dr. Martín also detailed implications in the context of the CREATE-X trial findings and the era of personalized medicine, and outlined next avenues of research.
The trial was supported by Roche, which also provided capecitabine. Dr. Martín disclosed that he has received speakers honoraria from Pfizer and Lilly; honoraria for participation in advisory boards from AstraZeneca, Novartis, Roche-Genentech, Pfizer, GlaxoSmithKline, PharmaMar, Taiho Oncology, and Lilly; and research grants from Novartis and Roche.
SAN ANTONIO – A phase 3 randomized controlled trial jointly conducted by GEICAM and CIBOMA is negative, showing that adding adjuvant capecitabine (Xeloda) to surgery and standard chemotherapy does not improve disease-free or overall survival in women with early-stage triple-negative breast cancer, reported lead investigator Miguel Martín, MD, PhD.
At the San Antonio Breast Cancer Symposium, he discussed the overall findings and intriguing subgroup results suggesting that there was a benefit in women with tumors having the nonbasal phenotype. Dr. Martín also detailed implications in the context of the CREATE-X trial findings and the era of personalized medicine, and outlined next avenues of research.
The trial was supported by Roche, which also provided capecitabine. Dr. Martín disclosed that he has received speakers honoraria from Pfizer and Lilly; honoraria for participation in advisory boards from AstraZeneca, Novartis, Roche-Genentech, Pfizer, GlaxoSmithKline, PharmaMar, Taiho Oncology, and Lilly; and research grants from Novartis and Roche.
REPORTING FROM SABCS 2018
2018: A banner year for hematology drug approvals
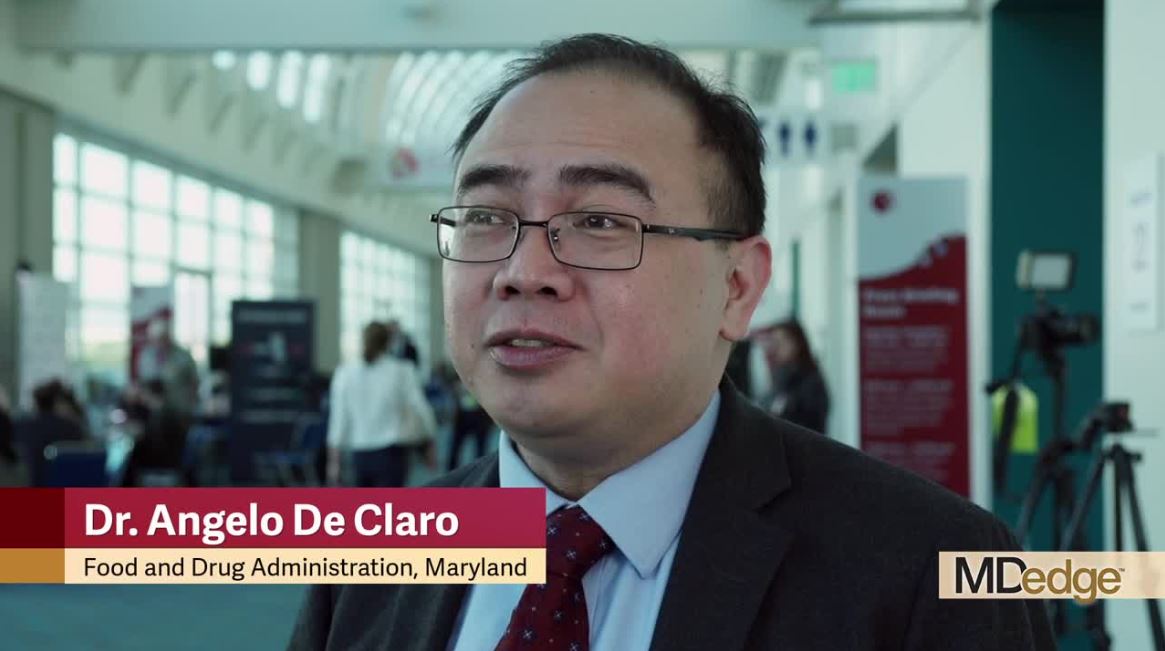
SAN DIEGO – It was banner year for new hematology drug approvals, according to R. Angelo de Claro, MD, of the Food and Drug Administration.
, including 12 first-time approvals, 5 new biosimilars, and 15 new indications for previously approved drugs, Dr. de Claro, clinical team leader in the FDA’s division of hematology products in Silver Spring, Md., said during an overview of the approvals at the annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology.
These include six new approvals for first-line treatment, and eight for pediatric indications, he said.
Highlights were discussed at two ASH-FDA joint symposia at the meeting, including one focused on the malignant hematology approvals, and another on the nonmalignant hematology approvals. In a video interview, Dr. de Claro provides some additional insight into their importance and about what might lie ahead.
“I think what’s exciting is that you have drug development occurring in more common conditions such as chronic lymphocytic leukemia, as well as in rare conditions, including hairy cell leukemia – and the first-ever approval in hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis,” he said. “It’s been very busy at the FDA; stay tuned ... the year’s not done yet. There could be more coming and we certainly anticipate more applications in the future.”
Dr. de Claro is an FDA employee. He reported having no other relevant disclosures.
SAN DIEGO – It was banner year for new hematology drug approvals, according to R. Angelo de Claro, MD, of the Food and Drug Administration.
, including 12 first-time approvals, 5 new biosimilars, and 15 new indications for previously approved drugs, Dr. de Claro, clinical team leader in the FDA’s division of hematology products in Silver Spring, Md., said during an overview of the approvals at the annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology.
These include six new approvals for first-line treatment, and eight for pediatric indications, he said.
Highlights were discussed at two ASH-FDA joint symposia at the meeting, including one focused on the malignant hematology approvals, and another on the nonmalignant hematology approvals. In a video interview, Dr. de Claro provides some additional insight into their importance and about what might lie ahead.
“I think what’s exciting is that you have drug development occurring in more common conditions such as chronic lymphocytic leukemia, as well as in rare conditions, including hairy cell leukemia – and the first-ever approval in hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis,” he said. “It’s been very busy at the FDA; stay tuned ... the year’s not done yet. There could be more coming and we certainly anticipate more applications in the future.”
Dr. de Claro is an FDA employee. He reported having no other relevant disclosures.
SAN DIEGO – It was banner year for new hematology drug approvals, according to R. Angelo de Claro, MD, of the Food and Drug Administration.
, including 12 first-time approvals, 5 new biosimilars, and 15 new indications for previously approved drugs, Dr. de Claro, clinical team leader in the FDA’s division of hematology products in Silver Spring, Md., said during an overview of the approvals at the annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology.
These include six new approvals for first-line treatment, and eight for pediatric indications, he said.
Highlights were discussed at two ASH-FDA joint symposia at the meeting, including one focused on the malignant hematology approvals, and another on the nonmalignant hematology approvals. In a video interview, Dr. de Claro provides some additional insight into their importance and about what might lie ahead.
“I think what’s exciting is that you have drug development occurring in more common conditions such as chronic lymphocytic leukemia, as well as in rare conditions, including hairy cell leukemia – and the first-ever approval in hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis,” he said. “It’s been very busy at the FDA; stay tuned ... the year’s not done yet. There could be more coming and we certainly anticipate more applications in the future.”
Dr. de Claro is an FDA employee. He reported having no other relevant disclosures.
REPORTING FROM ASH 2018
KATHERINE: T-DM1 doubles HER2-positive invasive disease-free survival
SAN ANTONIO – Swapping trastuzumab out for the drug-antibody conjugate trastuzumab emtansine (T-DM1; Kadcyla) as adjuvant therapy resulted in a halving in the risk of invasive disease or death in patients with HER2-positive early breast cancer with residual invasive disease after neoadjuvant chemotherapy and HER2-targeted therapy, including trastuzumab.
For the primary endpoint in the KATHERINE trial of invasive disease-free survival – defined as freedom from ipsilateral invasive breast tumor recurrence, ipsilateral locoregional invasive breast cancer recurrence, contralateral invasive breast cancer, distant recurrence, or death from any cause – T-DM1 was associated with a hazard ratio of 0.50 (P less than .001).
The 3-year invasive disease-free survival rate for 743 patients treated with T-DMI 1 was 88.3%, compared with 77% for 743 patients treated with trastuzumab, reported Charles E. Geyer Jr., MD, from Virginia Commonwealth University, Richmond, at the San Antonio Breast Cancer Symposium.
In a video interview, Dr. Geyer discussed results of KATHERINE, which suggest that T-DM1 should be considered as a new standard of care in this patient population.
Dr. Geyer reported travel support from Roche and AstraZeneca, medical writing support from AbbVie and Roche, and honoraria from Celgene.
SAN ANTONIO – Swapping trastuzumab out for the drug-antibody conjugate trastuzumab emtansine (T-DM1; Kadcyla) as adjuvant therapy resulted in a halving in the risk of invasive disease or death in patients with HER2-positive early breast cancer with residual invasive disease after neoadjuvant chemotherapy and HER2-targeted therapy, including trastuzumab.
For the primary endpoint in the KATHERINE trial of invasive disease-free survival – defined as freedom from ipsilateral invasive breast tumor recurrence, ipsilateral locoregional invasive breast cancer recurrence, contralateral invasive breast cancer, distant recurrence, or death from any cause – T-DM1 was associated with a hazard ratio of 0.50 (P less than .001).
The 3-year invasive disease-free survival rate for 743 patients treated with T-DMI 1 was 88.3%, compared with 77% for 743 patients treated with trastuzumab, reported Charles E. Geyer Jr., MD, from Virginia Commonwealth University, Richmond, at the San Antonio Breast Cancer Symposium.
In a video interview, Dr. Geyer discussed results of KATHERINE, which suggest that T-DM1 should be considered as a new standard of care in this patient population.
Dr. Geyer reported travel support from Roche and AstraZeneca, medical writing support from AbbVie and Roche, and honoraria from Celgene.
SAN ANTONIO – Swapping trastuzumab out for the drug-antibody conjugate trastuzumab emtansine (T-DM1; Kadcyla) as adjuvant therapy resulted in a halving in the risk of invasive disease or death in patients with HER2-positive early breast cancer with residual invasive disease after neoadjuvant chemotherapy and HER2-targeted therapy, including trastuzumab.
For the primary endpoint in the KATHERINE trial of invasive disease-free survival – defined as freedom from ipsilateral invasive breast tumor recurrence, ipsilateral locoregional invasive breast cancer recurrence, contralateral invasive breast cancer, distant recurrence, or death from any cause – T-DM1 was associated with a hazard ratio of 0.50 (P less than .001).
The 3-year invasive disease-free survival rate for 743 patients treated with T-DMI 1 was 88.3%, compared with 77% for 743 patients treated with trastuzumab, reported Charles E. Geyer Jr., MD, from Virginia Commonwealth University, Richmond, at the San Antonio Breast Cancer Symposium.
In a video interview, Dr. Geyer discussed results of KATHERINE, which suggest that T-DM1 should be considered as a new standard of care in this patient population.
Dr. Geyer reported travel support from Roche and AstraZeneca, medical writing support from AbbVie and Roche, and honoraria from Celgene.
REPORTING FROM SABCS 2018
December 2018 Highlights
Innovations in Dermatology: Laboratory Monitoring With Isotretinoin



FLT3 inhibitor moves forward in newly diagnosed AML
SAN DIEGO – In an ongoing phase 1 study, the oral FMS-like tyrosine kinase 3
The dose escalation/expansion study coupled the oral agent with induction and consolidation chemotherapy and was aimed at establishing the dosing and safety of gilteritinib.
The findings – reported at the annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology – mean that the FLT3 inhibitor will next be compared with the current standard of care, which has a 60%-65% remission rate, according to Keith W. Pratz, MD, of Johns Hopkins University in Baltimore.
“The later-phase clinical studies that we will be doing with gilteritinib will look to compare midostaurin-based chemotherapy with gilteritinib and looking for outcomes, with hopes of improving upon this 60%-65% remission rate,” Dr. Pratz said in a video interview.
Gilteritinib was recently approved by the Food and Drug Administration for relapsed/refractory AML patients with FLT3 mutations.
Dr. Pratz said the approval will provide a needed new treatment option in that patient population, which has had a low response rate to conventional therapy, in the range of 10%-15%.
“There really wasn’t a standard approved therapy prior to this and this will be what is given to most patients who have a FLT3 mutation and relapse,” he said.
Dr. Pratz reported consultancy and research funding from Astellas, which markets gilteritinib, as well as other companies.
SAN DIEGO – In an ongoing phase 1 study, the oral FMS-like tyrosine kinase 3
The dose escalation/expansion study coupled the oral agent with induction and consolidation chemotherapy and was aimed at establishing the dosing and safety of gilteritinib.
The findings – reported at the annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology – mean that the FLT3 inhibitor will next be compared with the current standard of care, which has a 60%-65% remission rate, according to Keith W. Pratz, MD, of Johns Hopkins University in Baltimore.
“The later-phase clinical studies that we will be doing with gilteritinib will look to compare midostaurin-based chemotherapy with gilteritinib and looking for outcomes, with hopes of improving upon this 60%-65% remission rate,” Dr. Pratz said in a video interview.
Gilteritinib was recently approved by the Food and Drug Administration for relapsed/refractory AML patients with FLT3 mutations.
Dr. Pratz said the approval will provide a needed new treatment option in that patient population, which has had a low response rate to conventional therapy, in the range of 10%-15%.
“There really wasn’t a standard approved therapy prior to this and this will be what is given to most patients who have a FLT3 mutation and relapse,” he said.
Dr. Pratz reported consultancy and research funding from Astellas, which markets gilteritinib, as well as other companies.
SAN DIEGO – In an ongoing phase 1 study, the oral FMS-like tyrosine kinase 3
The dose escalation/expansion study coupled the oral agent with induction and consolidation chemotherapy and was aimed at establishing the dosing and safety of gilteritinib.
The findings – reported at the annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology – mean that the FLT3 inhibitor will next be compared with the current standard of care, which has a 60%-65% remission rate, according to Keith W. Pratz, MD, of Johns Hopkins University in Baltimore.
“The later-phase clinical studies that we will be doing with gilteritinib will look to compare midostaurin-based chemotherapy with gilteritinib and looking for outcomes, with hopes of improving upon this 60%-65% remission rate,” Dr. Pratz said in a video interview.
Gilteritinib was recently approved by the Food and Drug Administration for relapsed/refractory AML patients with FLT3 mutations.
Dr. Pratz said the approval will provide a needed new treatment option in that patient population, which has had a low response rate to conventional therapy, in the range of 10%-15%.
“There really wasn’t a standard approved therapy prior to this and this will be what is given to most patients who have a FLT3 mutation and relapse,” he said.
Dr. Pratz reported consultancy and research funding from Astellas, which markets gilteritinib, as well as other companies.
REPORTING FROM ASH 2018