User login
Adding pembrolizumab to chemo doubled pCR rates in early-stage breast cancer
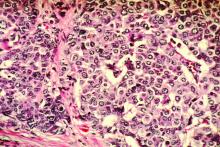
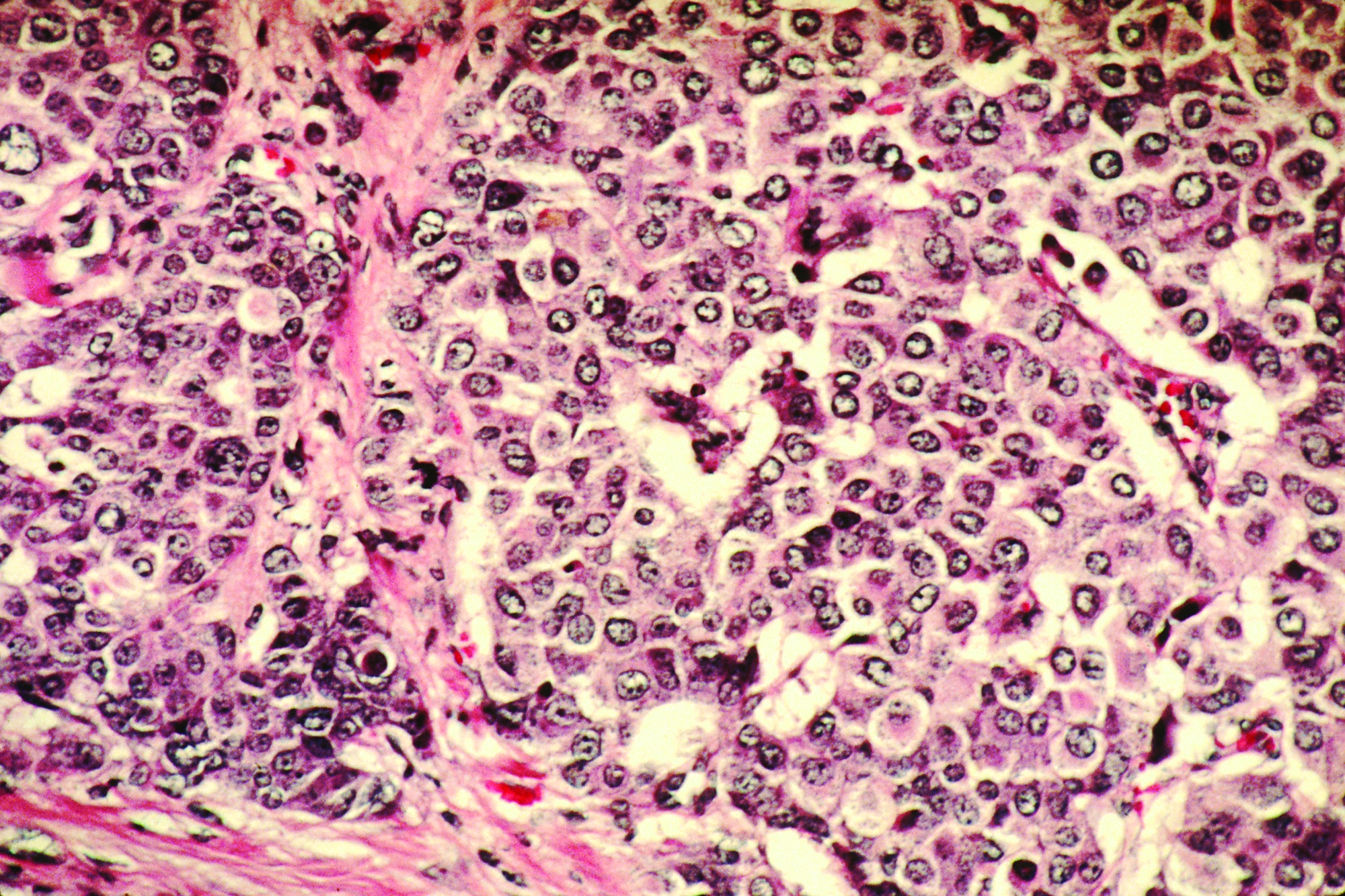
Adding pembrolizumab to neoadjuvant chemotherapy more than doubled the rate of pathologic complete response, compared with chemotherapy alone, in women with early-stage breast cancer enrolled in the phase 2 I-SPY2 trial.
Pathologic complete response (pCR) rates up to 60% were reported for patients with high-risk, stage II/III breast cancer who received pembrolizumab plus chemotherapy in I-SPY2, an ongoing platform trial designed to rapidly screen multiple agents and pinpoint those with a high probability of success.
The doubling of pCR rates was seen in all three biomarker signatures studied, including ERBB2(HER2)-negative, hormone receptor (HR)-positive/ERBB2-negative, or triple-negative breast cancer.
These results mean that pembrolizumab can “graduate” from I-SPY2 and suggest a greater than 99% predictive probability that the pembrolizumab-plus-chemotherapy approach will be superior to chemotherapy alone in a phase 3 trial, according to Rita Nanda, MD, of the University of Chicago, and colleagues.
“Notably, pembrolizumab was the first agent of 10 studied to graduate in the HR-positive/ERBB2-negative signature since I-SPY2 opened in 2010,” Dr. Nanda and colleagues wrote in JAMA Oncology.
The I-SPY2 study has enrolled adult women with stage II/III breast cancer at high risk of recurrence. The control arm included 181 patients randomized to receive standard neoadjuvant paclitaxel followed by doxorubicin plus cyclophosphamide. The pembrolizumab arm included 69 patients who received the same chemotherapy regimen plus pembrolizumab given concurrently with paclitaxel.
In ERBB2-negative patients, the estimated pCR rates were 44% in the pembrolizumab arm and 17% in the control arm. In HR-positive/ERBB2-negative patients, the estimated pCR rates were 30% and 13%, respectively. In triple-negative patients, the estimated pCR rates were 60% and 22%, respectively.
Residual cancer burden classified as extensive was less often seen in the pembrolizumab-treated patients, the investigators noted.
Event-free survival was qualitatively similar between the pembrolizumab and control arms, although the investigators cautioned against drawing conclusions based on this exploratory analysis in a small number of patients.
“Patients who achieved pCR had excellent outcomes regardless of arm,” the investigators wrote.
Immune-related adverse events (irAEs) were seen in the pembrolizumab-treated patients, although most were grade 1 or 2 and managed with dose interruption or corticosteroid therapy.
The most common irAE was thyroid dysfunction in 13% of patients, which was on par with what was seen in previously published reports. By contrast, adrenal insufficiency was observed in about 9% of patients, which is higher than in published reports for reasons that are unclear.
“Future work to characterize the risk factors for developing irAEs is warranted to improve the therapeutic index of these agents,” Dr. Nanda and colleagues wrote.
Pembrolizumab plus standard neoadjuvant chemotherapy is being evaluated in two ongoing, randomized phase 3 trials – KEYNOTE 522, which is evaluating patients with triple-negative breast cancer, and KEYNOTE 756, which is focused on high-risk, HR-positive/ERBB2-negative breast cancer.
The ongoing I-SPY2 study is supported by a grant from the National Cancer Institute as well as funding from charitable organizations, pharmaceutical companies, and private individuals. The investigators disclosed relationships with a range of pharmaceutical companies.
SOURCE: Nanda R et al. JAMA Oncol. 2020 Feb 13. doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2019.6650.
Adding pembrolizumab to neoadjuvant chemotherapy more than doubled the rate of pathologic complete response, compared with chemotherapy alone, in women with early-stage breast cancer enrolled in the phase 2 I-SPY2 trial.
Pathologic complete response (pCR) rates up to 60% were reported for patients with high-risk, stage II/III breast cancer who received pembrolizumab plus chemotherapy in I-SPY2, an ongoing platform trial designed to rapidly screen multiple agents and pinpoint those with a high probability of success.
The doubling of pCR rates was seen in all three biomarker signatures studied, including ERBB2(HER2)-negative, hormone receptor (HR)-positive/ERBB2-negative, or triple-negative breast cancer.
These results mean that pembrolizumab can “graduate” from I-SPY2 and suggest a greater than 99% predictive probability that the pembrolizumab-plus-chemotherapy approach will be superior to chemotherapy alone in a phase 3 trial, according to Rita Nanda, MD, of the University of Chicago, and colleagues.
“Notably, pembrolizumab was the first agent of 10 studied to graduate in the HR-positive/ERBB2-negative signature since I-SPY2 opened in 2010,” Dr. Nanda and colleagues wrote in JAMA Oncology.
The I-SPY2 study has enrolled adult women with stage II/III breast cancer at high risk of recurrence. The control arm included 181 patients randomized to receive standard neoadjuvant paclitaxel followed by doxorubicin plus cyclophosphamide. The pembrolizumab arm included 69 patients who received the same chemotherapy regimen plus pembrolizumab given concurrently with paclitaxel.
In ERBB2-negative patients, the estimated pCR rates were 44% in the pembrolizumab arm and 17% in the control arm. In HR-positive/ERBB2-negative patients, the estimated pCR rates were 30% and 13%, respectively. In triple-negative patients, the estimated pCR rates were 60% and 22%, respectively.
Residual cancer burden classified as extensive was less often seen in the pembrolizumab-treated patients, the investigators noted.
Event-free survival was qualitatively similar between the pembrolizumab and control arms, although the investigators cautioned against drawing conclusions based on this exploratory analysis in a small number of patients.
“Patients who achieved pCR had excellent outcomes regardless of arm,” the investigators wrote.
Immune-related adverse events (irAEs) were seen in the pembrolizumab-treated patients, although most were grade 1 or 2 and managed with dose interruption or corticosteroid therapy.
The most common irAE was thyroid dysfunction in 13% of patients, which was on par with what was seen in previously published reports. By contrast, adrenal insufficiency was observed in about 9% of patients, which is higher than in published reports for reasons that are unclear.
“Future work to characterize the risk factors for developing irAEs is warranted to improve the therapeutic index of these agents,” Dr. Nanda and colleagues wrote.
Pembrolizumab plus standard neoadjuvant chemotherapy is being evaluated in two ongoing, randomized phase 3 trials – KEYNOTE 522, which is evaluating patients with triple-negative breast cancer, and KEYNOTE 756, which is focused on high-risk, HR-positive/ERBB2-negative breast cancer.
The ongoing I-SPY2 study is supported by a grant from the National Cancer Institute as well as funding from charitable organizations, pharmaceutical companies, and private individuals. The investigators disclosed relationships with a range of pharmaceutical companies.
SOURCE: Nanda R et al. JAMA Oncol. 2020 Feb 13. doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2019.6650.
Adding pembrolizumab to neoadjuvant chemotherapy more than doubled the rate of pathologic complete response, compared with chemotherapy alone, in women with early-stage breast cancer enrolled in the phase 2 I-SPY2 trial.
Pathologic complete response (pCR) rates up to 60% were reported for patients with high-risk, stage II/III breast cancer who received pembrolizumab plus chemotherapy in I-SPY2, an ongoing platform trial designed to rapidly screen multiple agents and pinpoint those with a high probability of success.
The doubling of pCR rates was seen in all three biomarker signatures studied, including ERBB2(HER2)-negative, hormone receptor (HR)-positive/ERBB2-negative, or triple-negative breast cancer.
These results mean that pembrolizumab can “graduate” from I-SPY2 and suggest a greater than 99% predictive probability that the pembrolizumab-plus-chemotherapy approach will be superior to chemotherapy alone in a phase 3 trial, according to Rita Nanda, MD, of the University of Chicago, and colleagues.
“Notably, pembrolizumab was the first agent of 10 studied to graduate in the HR-positive/ERBB2-negative signature since I-SPY2 opened in 2010,” Dr. Nanda and colleagues wrote in JAMA Oncology.
The I-SPY2 study has enrolled adult women with stage II/III breast cancer at high risk of recurrence. The control arm included 181 patients randomized to receive standard neoadjuvant paclitaxel followed by doxorubicin plus cyclophosphamide. The pembrolizumab arm included 69 patients who received the same chemotherapy regimen plus pembrolizumab given concurrently with paclitaxel.
In ERBB2-negative patients, the estimated pCR rates were 44% in the pembrolizumab arm and 17% in the control arm. In HR-positive/ERBB2-negative patients, the estimated pCR rates were 30% and 13%, respectively. In triple-negative patients, the estimated pCR rates were 60% and 22%, respectively.
Residual cancer burden classified as extensive was less often seen in the pembrolizumab-treated patients, the investigators noted.
Event-free survival was qualitatively similar between the pembrolizumab and control arms, although the investigators cautioned against drawing conclusions based on this exploratory analysis in a small number of patients.
“Patients who achieved pCR had excellent outcomes regardless of arm,” the investigators wrote.
Immune-related adverse events (irAEs) were seen in the pembrolizumab-treated patients, although most were grade 1 or 2 and managed with dose interruption or corticosteroid therapy.
The most common irAE was thyroid dysfunction in 13% of patients, which was on par with what was seen in previously published reports. By contrast, adrenal insufficiency was observed in about 9% of patients, which is higher than in published reports for reasons that are unclear.
“Future work to characterize the risk factors for developing irAEs is warranted to improve the therapeutic index of these agents,” Dr. Nanda and colleagues wrote.
Pembrolizumab plus standard neoadjuvant chemotherapy is being evaluated in two ongoing, randomized phase 3 trials – KEYNOTE 522, which is evaluating patients with triple-negative breast cancer, and KEYNOTE 756, which is focused on high-risk, HR-positive/ERBB2-negative breast cancer.
The ongoing I-SPY2 study is supported by a grant from the National Cancer Institute as well as funding from charitable organizations, pharmaceutical companies, and private individuals. The investigators disclosed relationships with a range of pharmaceutical companies.
SOURCE: Nanda R et al. JAMA Oncol. 2020 Feb 13. doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2019.6650.
FROM JAMA ONCOLOGY
Key clinical point: Adding pembrolizumab to neoadjuvant chemotherapy more than doubled the rate of pathologic complete response (pCR) in women with early-stage breast cancer.
Major finding: In ERBB2-negative patients, the estimated pCR rates were 44% in the pembrolizumab arm and 17% in the control arm. In HR-positive/ERBB2-negative patients, the estimated pCR rates were 30% and 13%, respectively. In triple-negative patients, the estimated pCR rates were 60% and 22%, respectively.
Study details: Phase 2 trial of 69 patients treated with pembrolizumab and chemotherapy, compared with 181 chemotherapy-treated control subjects.
Disclosures: The trial is supported by a grant from the National Cancer Institute as well as funding from charitable organizations, pharmaceutical companies, and private individuals. The investigators disclosed relationships with a range of pharmaceutical companies.
Source: Nanda R et al. JAMA Oncol. 2020 Feb 13.
Thrombectomy access lags for U.S. stroke patients
In 2017, roughly 3 years after evidence from several studies made endovascular thrombectomy first-line treatment for selected acute ischemic stroke patients, the treatment was available at barely more than one-third of all U.S. stroke centers, available within 30-minute access to just over 30% of Americans, and available within 15-minute access to one-fifth of U.S. residents, based on information in a comprehensive U.S. database.
These numbers showed that “current direct EVT [endovascular thrombectomy] access in the United States is suboptimal under predominate EMS routing protocols,” Amrou Sarraj, MD, and his associates wrote in an article published online in Stroke on Feb. 12. “Only in eight states did the coverage exceed 25% of the population, and nine states had coverage for less than 10% of the population. These results reflect limited access to an effective treatment modality that would improve clinical outcomes in patients with large strokes and prevent potentially devastating disability,” wrote Dr. Sarraj, chief of the general neurology service at Memorial-Hermann Hospital in Houston and coauthors.
Their analysis of data collected in 2017 by the Medicare Provider Analysis and Review (MEDPAR) database, maintained by the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services, identified two apparently effective ways to improve EVT access for acute ischemic stroke patients: First, systematically divert patients to a nearby center that offers EVT even when it means bypassing a closer stroke center that does not perform EVT when the added travel time is less than 15 minutes. Second, convert selected stroke centers that currently do not perform EVT into centers that do. Between these two approaches, the strategy of having ambulances bypass stroke centers that do not perform EVT and continuing to ones that do generally has the greater potential to boost access, the authors found. They based their analysis exclusively on their calculations of expected consequences rather than actual experience.
The calculations showed that bypassing non-EVT centers when the added bypass time computed to less than 15 minutes linked with an anticipated overall U.S. gain in access of about 17%, or 52 million people, extending the ability of acute ischemic stroke patients able to quickly reach an EVT center to about 37% of the American public. The second approach to boost access, converting the top 10% of stroke centers based on case volume that currently do not provide EVT to centers that do offer it, would result in expanded access for about 23 million additional Americans, raising the total with access to about 27% of the public, the new report said.
As part of this analysis, the MEDPAR data identified 1,941 U.S. centers providing stroke services during 2017, of which 713 (37%) had performed at least one EVT procedure. By comparison, 2015 MEDPAR data showed 577 U.S. stroke centers performing EVT, indicating that during the 2-3 years following several reports in early 2015 on the net benefits of EVT for acute ischemic stroke patients, the number of U.S. stroke centers offering this treatment had grown by a relative 24%. Based on the locations of the stroke centers that made EVT available in 2017, Dr. Sarraj and coauthors calculated that the 713 EVT-capable stroke centers provided emergency access within a 15-minute ground-ambulance trip for 61 million Americans (20% of the U.S. population), and within a 30-minute ground-transport trip to 95 million residents (31%).
Boosting these numbers by implementing a systematic bypass of stroke patients past non-EVT stroke centers to nearby centers that are EVT capable “has the benefit of ease of implementation and requires less time and resources,” the authors said. However, they also noted the heterogeneity of circumstances based on variables like population density and stroke center distribution, which means that in some locations the most effective way to boost access would be by increasing the number of stroke centers that provide EVT.
In 2018, Dr. Sarraj and associates reported results from a similar analysis of MEDPAR data that used 30-minute and 60-minute ground-transport times as the criteria for their calculations.
The study received no commercial funding. Dr. Sarraj reported receiving research funding from Stryker Neurovascular outside of this work. One coauthor reported serving in roles for the University of Texas Health System for which the institution has been funded via various industry and government grants, and another coauthor reported receiving research funding from the Patient-Centered Outcomes Research Institute, the National Institutes of Health, Genentech, and CSL Behring, as well as consulting fees from Frazer Ltd.
SOURCE: Sarraj A et al. Stroke. 2020 Feb 12. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.120.028850.
In 2017, roughly 3 years after evidence from several studies made endovascular thrombectomy first-line treatment for selected acute ischemic stroke patients, the treatment was available at barely more than one-third of all U.S. stroke centers, available within 30-minute access to just over 30% of Americans, and available within 15-minute access to one-fifth of U.S. residents, based on information in a comprehensive U.S. database.
These numbers showed that “current direct EVT [endovascular thrombectomy] access in the United States is suboptimal under predominate EMS routing protocols,” Amrou Sarraj, MD, and his associates wrote in an article published online in Stroke on Feb. 12. “Only in eight states did the coverage exceed 25% of the population, and nine states had coverage for less than 10% of the population. These results reflect limited access to an effective treatment modality that would improve clinical outcomes in patients with large strokes and prevent potentially devastating disability,” wrote Dr. Sarraj, chief of the general neurology service at Memorial-Hermann Hospital in Houston and coauthors.
Their analysis of data collected in 2017 by the Medicare Provider Analysis and Review (MEDPAR) database, maintained by the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services, identified two apparently effective ways to improve EVT access for acute ischemic stroke patients: First, systematically divert patients to a nearby center that offers EVT even when it means bypassing a closer stroke center that does not perform EVT when the added travel time is less than 15 minutes. Second, convert selected stroke centers that currently do not perform EVT into centers that do. Between these two approaches, the strategy of having ambulances bypass stroke centers that do not perform EVT and continuing to ones that do generally has the greater potential to boost access, the authors found. They based their analysis exclusively on their calculations of expected consequences rather than actual experience.
The calculations showed that bypassing non-EVT centers when the added bypass time computed to less than 15 minutes linked with an anticipated overall U.S. gain in access of about 17%, or 52 million people, extending the ability of acute ischemic stroke patients able to quickly reach an EVT center to about 37% of the American public. The second approach to boost access, converting the top 10% of stroke centers based on case volume that currently do not provide EVT to centers that do offer it, would result in expanded access for about 23 million additional Americans, raising the total with access to about 27% of the public, the new report said.
As part of this analysis, the MEDPAR data identified 1,941 U.S. centers providing stroke services during 2017, of which 713 (37%) had performed at least one EVT procedure. By comparison, 2015 MEDPAR data showed 577 U.S. stroke centers performing EVT, indicating that during the 2-3 years following several reports in early 2015 on the net benefits of EVT for acute ischemic stroke patients, the number of U.S. stroke centers offering this treatment had grown by a relative 24%. Based on the locations of the stroke centers that made EVT available in 2017, Dr. Sarraj and coauthors calculated that the 713 EVT-capable stroke centers provided emergency access within a 15-minute ground-ambulance trip for 61 million Americans (20% of the U.S. population), and within a 30-minute ground-transport trip to 95 million residents (31%).
Boosting these numbers by implementing a systematic bypass of stroke patients past non-EVT stroke centers to nearby centers that are EVT capable “has the benefit of ease of implementation and requires less time and resources,” the authors said. However, they also noted the heterogeneity of circumstances based on variables like population density and stroke center distribution, which means that in some locations the most effective way to boost access would be by increasing the number of stroke centers that provide EVT.
In 2018, Dr. Sarraj and associates reported results from a similar analysis of MEDPAR data that used 30-minute and 60-minute ground-transport times as the criteria for their calculations.
The study received no commercial funding. Dr. Sarraj reported receiving research funding from Stryker Neurovascular outside of this work. One coauthor reported serving in roles for the University of Texas Health System for which the institution has been funded via various industry and government grants, and another coauthor reported receiving research funding from the Patient-Centered Outcomes Research Institute, the National Institutes of Health, Genentech, and CSL Behring, as well as consulting fees from Frazer Ltd.
SOURCE: Sarraj A et al. Stroke. 2020 Feb 12. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.120.028850.
In 2017, roughly 3 years after evidence from several studies made endovascular thrombectomy first-line treatment for selected acute ischemic stroke patients, the treatment was available at barely more than one-third of all U.S. stroke centers, available within 30-minute access to just over 30% of Americans, and available within 15-minute access to one-fifth of U.S. residents, based on information in a comprehensive U.S. database.
These numbers showed that “current direct EVT [endovascular thrombectomy] access in the United States is suboptimal under predominate EMS routing protocols,” Amrou Sarraj, MD, and his associates wrote in an article published online in Stroke on Feb. 12. “Only in eight states did the coverage exceed 25% of the population, and nine states had coverage for less than 10% of the population. These results reflect limited access to an effective treatment modality that would improve clinical outcomes in patients with large strokes and prevent potentially devastating disability,” wrote Dr. Sarraj, chief of the general neurology service at Memorial-Hermann Hospital in Houston and coauthors.
Their analysis of data collected in 2017 by the Medicare Provider Analysis and Review (MEDPAR) database, maintained by the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services, identified two apparently effective ways to improve EVT access for acute ischemic stroke patients: First, systematically divert patients to a nearby center that offers EVT even when it means bypassing a closer stroke center that does not perform EVT when the added travel time is less than 15 minutes. Second, convert selected stroke centers that currently do not perform EVT into centers that do. Between these two approaches, the strategy of having ambulances bypass stroke centers that do not perform EVT and continuing to ones that do generally has the greater potential to boost access, the authors found. They based their analysis exclusively on their calculations of expected consequences rather than actual experience.
The calculations showed that bypassing non-EVT centers when the added bypass time computed to less than 15 minutes linked with an anticipated overall U.S. gain in access of about 17%, or 52 million people, extending the ability of acute ischemic stroke patients able to quickly reach an EVT center to about 37% of the American public. The second approach to boost access, converting the top 10% of stroke centers based on case volume that currently do not provide EVT to centers that do offer it, would result in expanded access for about 23 million additional Americans, raising the total with access to about 27% of the public, the new report said.
As part of this analysis, the MEDPAR data identified 1,941 U.S. centers providing stroke services during 2017, of which 713 (37%) had performed at least one EVT procedure. By comparison, 2015 MEDPAR data showed 577 U.S. stroke centers performing EVT, indicating that during the 2-3 years following several reports in early 2015 on the net benefits of EVT for acute ischemic stroke patients, the number of U.S. stroke centers offering this treatment had grown by a relative 24%. Based on the locations of the stroke centers that made EVT available in 2017, Dr. Sarraj and coauthors calculated that the 713 EVT-capable stroke centers provided emergency access within a 15-minute ground-ambulance trip for 61 million Americans (20% of the U.S. population), and within a 30-minute ground-transport trip to 95 million residents (31%).
Boosting these numbers by implementing a systematic bypass of stroke patients past non-EVT stroke centers to nearby centers that are EVT capable “has the benefit of ease of implementation and requires less time and resources,” the authors said. However, they also noted the heterogeneity of circumstances based on variables like population density and stroke center distribution, which means that in some locations the most effective way to boost access would be by increasing the number of stroke centers that provide EVT.
In 2018, Dr. Sarraj and associates reported results from a similar analysis of MEDPAR data that used 30-minute and 60-minute ground-transport times as the criteria for their calculations.
The study received no commercial funding. Dr. Sarraj reported receiving research funding from Stryker Neurovascular outside of this work. One coauthor reported serving in roles for the University of Texas Health System for which the institution has been funded via various industry and government grants, and another coauthor reported receiving research funding from the Patient-Centered Outcomes Research Institute, the National Institutes of Health, Genentech, and CSL Behring, as well as consulting fees from Frazer Ltd.
SOURCE: Sarraj A et al. Stroke. 2020 Feb 12. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.120.028850.
FROM STROKE
AAN publishes guideline on the treatment of sleep problems in children with autism
The guideline was published online ahead of print Feb. 12 in Neurology.
“While up to 40% of children and teens in the general population will have sleep problems at some point during their childhood, such problems usually lessen with age,” lead author Ashura Williams Buckley, MD, director of the Sleep and Neurodevelopment Service at the National Institute of Mental Health in Bethesda, Md., said in a press release. “For children and teens with autism, sleep problems are more common and more likely to persist, resulting in poor health and poor quality of life. Some sleep problems may be directly related to autism, but others are not. Regardless, autism symptoms may make sleep problems worse.”
Few evidence-based treatments are available
Dr. Williams Buckley and colleagues developed the current guideline to evaluate which pharmacologic, behavioral, and complementary and alternative medicine (CAM) interventions improve bedtime resistance, sleep onset latency, sleep continuity, total sleep time, and daytime behavior in children and adolescents with ASD. The panel evaluated 900 abstracts of articles that had been included in systematic reviews, as well as 1,087 additional abstracts. One hundred thirty-nine articles were potentially relevant, 12 met criteria for data extraction, and eight were rated class III or higher and were included in the panel’s review.
The authors observed what they called a dearth of evidence-based treatments for sleep dysregulation in ASD. Evidence indicates that melatonin, with or without cognitive–behavioral therapy (CBT), improves several sleep outcomes, compared with placebo. “Evidence for other interventions is largely lacking,” wrote Dr. Williams Buckley and colleagues. They observed a lack of long-term safety data for melatonin in children, which they considered concerning, because melatonin affects the hypothalamic–gonadal axis and can potentially influence pubertal development.
Screening for comorbid conditions and concomitant medications
The guideline recommends that clinicians assess children with ASD and sleep disturbances for coexisting conditions and concomitant medications that could be contributing to these sleep disturbances. They should ensure that children receive appropriate treatment for coexisting conditions and adjust or discontinue potentially problematic medications appropriately, according to the guideline.
Furthermore, clinicians should counsel parents or guardians about behavioral strategies as a first-line treatment for improving sleep function. These strategies could be administered alone or with pharmacologic or neutraceutical approaches as needed, according to the authors. Suggested behavioral approaches include unmodified extinction (i.e., imposing a bedtime and ignoring a child’s protests), graduated extinction (i.e., ignoring protests for a specified period before responding), positive routines (i.e., establishing pre-bedtime calming rituals), and bedtime fading (i.e., putting a child to bed close to the time he or she begins to fall asleep).
If a child’s contributing coexisting conditions and medications have been addressed and behavioral strategies have not been helpful, clinicians should offer melatonin, according to the guideline. Because over-the-counter formulations contain variable concentrations of melatonin, clinicians should write a prescription for it or recommend high-purity pharmaceutical grade melatonin. The initial dose should be 1-3 mg/day at 60-30 minutes before bedtime. The dose can be titrated to 10 mg/day. Clinicians also should counsel children and their parents about potential adverse events of melatonin and the lack of long-term safety data, according to the guideline.
In addition, clinicians should advise children and parents that no evidence supports the routine use of weighted blankets or specialized mattress technology for improving sleep. Parents who ask about weighted blankets should be told that the reviewed trial reported no serious adverse events with this intervention, and that blankets could be a reasonable nonpharmacologic approach for some patients, according to the guideline.
Optimal outcome measures are undefined
Dr. Williams Buckley and colleagues also suggested areas for future research. Investigators have not yet defined optimal outcome measures (e.g., questionnaires, polysomnography, and actigraphy) that balance tolerability and accuracy, they wrote. Clinically important differences for most measures also have yet to be determined. Researchers should investigate whether long-term adverse events are associated with chronic melatonin use and study patients with ASD and comorbid mood disorders, wrote the authors. “Research tying the underlying neurobiology in early-life sleep disruption to behavior might help clinicians and researchers understand which treatments might work for which people with ASD,” they concluded.
The AAN supported the development of the guideline. Dr. Williams Buckley had no conflicts of interest. Six authors had conflicts of interest that the AAN deemed not significant enough to prevent their participation in the development of the guideline.
SOURCE: Williams Buckley A et al. Neurology. 2020;94:393-405. doi: 10.1212/WNL0000000000009033.
The guideline was published online ahead of print Feb. 12 in Neurology.
“While up to 40% of children and teens in the general population will have sleep problems at some point during their childhood, such problems usually lessen with age,” lead author Ashura Williams Buckley, MD, director of the Sleep and Neurodevelopment Service at the National Institute of Mental Health in Bethesda, Md., said in a press release. “For children and teens with autism, sleep problems are more common and more likely to persist, resulting in poor health and poor quality of life. Some sleep problems may be directly related to autism, but others are not. Regardless, autism symptoms may make sleep problems worse.”
Few evidence-based treatments are available
Dr. Williams Buckley and colleagues developed the current guideline to evaluate which pharmacologic, behavioral, and complementary and alternative medicine (CAM) interventions improve bedtime resistance, sleep onset latency, sleep continuity, total sleep time, and daytime behavior in children and adolescents with ASD. The panel evaluated 900 abstracts of articles that had been included in systematic reviews, as well as 1,087 additional abstracts. One hundred thirty-nine articles were potentially relevant, 12 met criteria for data extraction, and eight were rated class III or higher and were included in the panel’s review.
The authors observed what they called a dearth of evidence-based treatments for sleep dysregulation in ASD. Evidence indicates that melatonin, with or without cognitive–behavioral therapy (CBT), improves several sleep outcomes, compared with placebo. “Evidence for other interventions is largely lacking,” wrote Dr. Williams Buckley and colleagues. They observed a lack of long-term safety data for melatonin in children, which they considered concerning, because melatonin affects the hypothalamic–gonadal axis and can potentially influence pubertal development.
Screening for comorbid conditions and concomitant medications
The guideline recommends that clinicians assess children with ASD and sleep disturbances for coexisting conditions and concomitant medications that could be contributing to these sleep disturbances. They should ensure that children receive appropriate treatment for coexisting conditions and adjust or discontinue potentially problematic medications appropriately, according to the guideline.
Furthermore, clinicians should counsel parents or guardians about behavioral strategies as a first-line treatment for improving sleep function. These strategies could be administered alone or with pharmacologic or neutraceutical approaches as needed, according to the authors. Suggested behavioral approaches include unmodified extinction (i.e., imposing a bedtime and ignoring a child’s protests), graduated extinction (i.e., ignoring protests for a specified period before responding), positive routines (i.e., establishing pre-bedtime calming rituals), and bedtime fading (i.e., putting a child to bed close to the time he or she begins to fall asleep).
If a child’s contributing coexisting conditions and medications have been addressed and behavioral strategies have not been helpful, clinicians should offer melatonin, according to the guideline. Because over-the-counter formulations contain variable concentrations of melatonin, clinicians should write a prescription for it or recommend high-purity pharmaceutical grade melatonin. The initial dose should be 1-3 mg/day at 60-30 minutes before bedtime. The dose can be titrated to 10 mg/day. Clinicians also should counsel children and their parents about potential adverse events of melatonin and the lack of long-term safety data, according to the guideline.
In addition, clinicians should advise children and parents that no evidence supports the routine use of weighted blankets or specialized mattress technology for improving sleep. Parents who ask about weighted blankets should be told that the reviewed trial reported no serious adverse events with this intervention, and that blankets could be a reasonable nonpharmacologic approach for some patients, according to the guideline.
Optimal outcome measures are undefined
Dr. Williams Buckley and colleagues also suggested areas for future research. Investigators have not yet defined optimal outcome measures (e.g., questionnaires, polysomnography, and actigraphy) that balance tolerability and accuracy, they wrote. Clinically important differences for most measures also have yet to be determined. Researchers should investigate whether long-term adverse events are associated with chronic melatonin use and study patients with ASD and comorbid mood disorders, wrote the authors. “Research tying the underlying neurobiology in early-life sleep disruption to behavior might help clinicians and researchers understand which treatments might work for which people with ASD,” they concluded.
The AAN supported the development of the guideline. Dr. Williams Buckley had no conflicts of interest. Six authors had conflicts of interest that the AAN deemed not significant enough to prevent their participation in the development of the guideline.
SOURCE: Williams Buckley A et al. Neurology. 2020;94:393-405. doi: 10.1212/WNL0000000000009033.
The guideline was published online ahead of print Feb. 12 in Neurology.
“While up to 40% of children and teens in the general population will have sleep problems at some point during their childhood, such problems usually lessen with age,” lead author Ashura Williams Buckley, MD, director of the Sleep and Neurodevelopment Service at the National Institute of Mental Health in Bethesda, Md., said in a press release. “For children and teens with autism, sleep problems are more common and more likely to persist, resulting in poor health and poor quality of life. Some sleep problems may be directly related to autism, but others are not. Regardless, autism symptoms may make sleep problems worse.”
Few evidence-based treatments are available
Dr. Williams Buckley and colleagues developed the current guideline to evaluate which pharmacologic, behavioral, and complementary and alternative medicine (CAM) interventions improve bedtime resistance, sleep onset latency, sleep continuity, total sleep time, and daytime behavior in children and adolescents with ASD. The panel evaluated 900 abstracts of articles that had been included in systematic reviews, as well as 1,087 additional abstracts. One hundred thirty-nine articles were potentially relevant, 12 met criteria for data extraction, and eight were rated class III or higher and were included in the panel’s review.
The authors observed what they called a dearth of evidence-based treatments for sleep dysregulation in ASD. Evidence indicates that melatonin, with or without cognitive–behavioral therapy (CBT), improves several sleep outcomes, compared with placebo. “Evidence for other interventions is largely lacking,” wrote Dr. Williams Buckley and colleagues. They observed a lack of long-term safety data for melatonin in children, which they considered concerning, because melatonin affects the hypothalamic–gonadal axis and can potentially influence pubertal development.
Screening for comorbid conditions and concomitant medications
The guideline recommends that clinicians assess children with ASD and sleep disturbances for coexisting conditions and concomitant medications that could be contributing to these sleep disturbances. They should ensure that children receive appropriate treatment for coexisting conditions and adjust or discontinue potentially problematic medications appropriately, according to the guideline.
Furthermore, clinicians should counsel parents or guardians about behavioral strategies as a first-line treatment for improving sleep function. These strategies could be administered alone or with pharmacologic or neutraceutical approaches as needed, according to the authors. Suggested behavioral approaches include unmodified extinction (i.e., imposing a bedtime and ignoring a child’s protests), graduated extinction (i.e., ignoring protests for a specified period before responding), positive routines (i.e., establishing pre-bedtime calming rituals), and bedtime fading (i.e., putting a child to bed close to the time he or she begins to fall asleep).
If a child’s contributing coexisting conditions and medications have been addressed and behavioral strategies have not been helpful, clinicians should offer melatonin, according to the guideline. Because over-the-counter formulations contain variable concentrations of melatonin, clinicians should write a prescription for it or recommend high-purity pharmaceutical grade melatonin. The initial dose should be 1-3 mg/day at 60-30 minutes before bedtime. The dose can be titrated to 10 mg/day. Clinicians also should counsel children and their parents about potential adverse events of melatonin and the lack of long-term safety data, according to the guideline.
In addition, clinicians should advise children and parents that no evidence supports the routine use of weighted blankets or specialized mattress technology for improving sleep. Parents who ask about weighted blankets should be told that the reviewed trial reported no serious adverse events with this intervention, and that blankets could be a reasonable nonpharmacologic approach for some patients, according to the guideline.
Optimal outcome measures are undefined
Dr. Williams Buckley and colleagues also suggested areas for future research. Investigators have not yet defined optimal outcome measures (e.g., questionnaires, polysomnography, and actigraphy) that balance tolerability and accuracy, they wrote. Clinically important differences for most measures also have yet to be determined. Researchers should investigate whether long-term adverse events are associated with chronic melatonin use and study patients with ASD and comorbid mood disorders, wrote the authors. “Research tying the underlying neurobiology in early-life sleep disruption to behavior might help clinicians and researchers understand which treatments might work for which people with ASD,” they concluded.
The AAN supported the development of the guideline. Dr. Williams Buckley had no conflicts of interest. Six authors had conflicts of interest that the AAN deemed not significant enough to prevent their participation in the development of the guideline.
SOURCE: Williams Buckley A et al. Neurology. 2020;94:393-405. doi: 10.1212/WNL0000000000009033.
FROM NEUROLOGY
Key clinical point: The AAN has published a guideline on the treatment of sleep problems in children with autism.
Major finding: The guideline recommends behavioral strategies as a first-line treatment.
Study details: A review of 1,987 peer-reviewed studies.
Disclosures: The AAN funded the development of the guideline. The first author had no conflicts of interest, and the other authors had no significant conflicts.
Source: Williams Buckley A et al. Neurology. 2020;94:393-405. doi: 10.1212/WNL0000000000009033.
Glaring gap in CV event reporting in pivotal cancer trials
Clinical trials supporting Food and Drug Adminstration approval of contemporary cancer therapies frequently failed to capture major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE) and, when they did, reported rates 2.6-fold lower than noncancer trials, new research shows.
Overall, 51.3% of trials did not report MACE, with that number reaching 57.6% in trials enrolling patients with baseline cardiovascular disease (CVD).
Nearly 40% of trials did not report any CVD events in follow-up, the authors reported online Feb. 10, 2020, in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology (2020;75:620-8).
“Even in drug classes where there were established or emerging associations with cardiotoxic events, often there were no reported heart events or cardiovascular events across years of follow-up in trials that examined hundreds or even thousands of patients. That was actually pretty surprising,” senior author Daniel Addison, MD, codirector of the cardio-oncology program at the Ohio State University Medical Center, Columbus, said in an interview.
The study was prompted by a series of events that crescendoed when his team was called to the ICU to determine whether a novel targeted agent played a role in the heart decline of a patient with acute myeloid leukemia. “I had a resident ask me a very important question: ‘How do we really know for sure that the trial actually reflects the true risk of heart events?’ to which I told him, ‘it’s difficult to know,’ ” he said.
“I think many of us rely heavily on what we see in the trials, particularly when they make it to the top journals, and quite frankly, we generally take it at face value,” Dr. Addison observed.
Lower Rate of Reported Events
The investigators reviewed CV events reported in 97,365 patients (median age, 61 years; 46% female) enrolled in 189 phase 2 and 3 trials supporting FDA approval of 123 anticancer drugs from 1998 to 2018. Biologic, targeted, or immune-based therapies accounted for 72.5% of drug approvals.
Over 148,138 person-years of follow-up (median trial duration, 30 months), there were 1,148 incidents of MACE (375 heart failure, 253 MIs, 180 strokes, 65 atrial fibrillation, 29 coronary revascularizations, and 246 CVD deaths). MACE rates were higher in the intervention group than in the control group (792 vs. 356; P less than .01). Among the 64 trials that excluded patients with baseline CVD, there were 269 incidents of MACE.
To put this finding in context, the researchers examined the reported incidence of MACE among some 6,000 similarly aged participants in the Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis (MESA). The overall weighted-average incidence rate was 1,408 per 100,000 person-years among MESA participants, compared with 542 events per 100,000 person-years among oncology trial participants (716 per 100,000 in the intervention arm). This represents a reported-to-expected ratio of 0.38 – a 2.6-fold lower rate of reported events (P less than .001) – and a risk difference of 866.
Further, MACE reporting was lower by a factor of 1.7 among all cancer trial participants irrespective of baseline CVD status (reported-to-expected ratio, 0.56; risk difference, 613; P less than .001).
There was no significant difference in MACE reporting between independent or industry-sponsored trials, the authors report.
No malicious intent
“There are likely some that might lean toward not wanting to attribute blame to a new drug when the drug is in a study, but I really think that the leading factor is lack of awareness,” Dr. Addison said. “I’ve talked with several cancer collaborators around the country who run large clinical trials, and I think often, when an event may be brought to someone’s attention, there is a tendency to just write it off as kind of a generic expected event due to age, or just something that’s not really pertinent to the study. So they don’t really focus on it as much.”
“Closer collaboration between cardiologists and cancer physicians is needed to better determine true cardiac risks among patients treated with these drugs.”
Breast cancer oncologist Marc E. Lippman, MD, of Georgetown University Medical Center and Georgetown Lombardi Comprehensive Cancer Center, Washington, D.C., isn’t convinced a lack of awareness is the culprit.
“I don’t agree with that at all,” he said in an interview. “I think there are very, very clear rules and guidelines these days for adverse-event reporting. I think that’s not a very likely explanation – that it’s not on the radar.”
Part of the problem may be that some of the toxicities, particularly cardiovascular, may not emerge for years, he said. Participant screening for the trials also likely removed patients with high cardiovascular risk. “It’s very understandable to me – I’m not saying it’s good particularly – but I think it’s very understandable that, if you’re trying to develop a drug, the last thing you’d want to have is a lot of toxicity that you might have avoided by just being restrictive in who you let into the study,” Dr. Lippman said.
The underreported CVD events may also reflect the rapidly changing profile of cardiovascular toxicities associated with novel anticancer therapies.
“Providers, both cancer and noncancer, generally put cardiotoxicity in the box of anthracyclines and radiation, but particularly over the last decade, we’ve begun to understand it’s well beyond any one class of drugs,” Dr. Addison said.
“I agree completely,” Dr. Lippman said. For example, “the checkpoint inhibitors are so unbelievably different in terms of their toxicities that many people simply didn’t even know what they were getting into at first.”
One size does not fit all
Javid Moslehi, MD, director of the cardio-oncology program at Vanderbilt University, Nashville, Tenn., said echocardiography – recommended to detect changes in left ventricular function in patients exposed to anthracyclines or targeted agents like trastuzumab (Herceptin) – isn’t enough to address today’s cancer therapy–related CVD events.
“Initial drugs like anthracyclines or Herceptin in cardio-oncology were associated with systolic cardiac dysfunction, whereas the majority of issues we see in the cardio-oncology clinics today are vascular, metabolic, arrhythmogenic, and inflammatory,” he said in an interview. “Echocardiography misses the big and increasingly complex picture.”
His group, for example, has been studying myocarditis associated with immunotherapies, but none of the clinical trials require screening or surveillance for myocarditis with a cardiac biomarker like troponin.
The group also recently identified 303 deaths in patients exposed to ibrutinib, a drug that revolutionized the treatment of several B-cell malignancies but is associated with higher rates of atrial fibrillation, which is also associated with increased bleeding risk. “So there’s a little bit of a double whammy there, given that we often treat atrial fibrillation with anticoagulation and where we can cause complications in patients,” Dr. Moslehi noted.
Although there needs to be closer collaboration between cardiologists and oncologists on individual trials, cardiologists also have to realize that oncology care has become very personalized, he suggested.
“What’s probably relevant for the breast cancer patient may not be relevant for the prostate cancer patient and their respective treatments,” Dr. Moslehi said. “So if we were to say, ‘every person should get an echo,’ that may be less relevant to the prostate cancer patient where treatments can cause vascular and metabolic perturbations or to the patient treated with immunotherapy who may have myocarditis, where many of the echos can be normal. There’s no one-size-fits-all for these things.”
Wearable technologies like smartwatches could play a role in improving the reporting of CVD events with novel therapies but a lot more research needs to be done to validate these tools, Dr. Addison said. “But as we continue on into the 21st century, this is going to expand and may potentially help us,” he added.
In the interim, better standardization is needed of the cardiovascular events reported in oncology trials, particularly the Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events (CTCAE), said Dr. Moslehi, who also serves as chair of the American Heart Association’s subcommittee on cardio-oncology.
“Cardiovascular definitions are not exactly uniform and are not consistent with what we in cardiology consider to be important or relevant,” he said. “So I think there needs to be better standardization of these definitions, specifically within the CTCAE, which is what the oncologists use to identify adverse events.”
In a linked editorial (J Am Coll Cardiol. 2020;75:629-31), Dr. Lippman and cardiologist Nanette Bishopric, MD, of the Medstar Heart and Vascular Institute in Washington, D.C., suggested it may also be time to organize a consortium that can carry out “rigorous multicenter clinical investigations to evaluate the cardiotoxicity of emerging cancer treatments,” similar to the Thrombosis in Myocardial Infarction Study Group.
“The success of this consortium in pioneering and targeting multiple generations of drugs for the treatment of MI, involving tens of thousands of patients and thousands of collaborations across multiple national borders, is a model for how to move forward in providing the new hope of cancer cure without the trade-off of years lost to heart disease,” the editorialists concluded.
The study was supported in part by National Institutes of Health grants, including a K12-CA133250 grant to Dr. Addison. Dr. Bishopric reported being on the scientific board of C&C Biopharma. Dr. Lippman reports being on the board of directors of and holding stock in Seattle Genetics. Dr. Moslehi reported having served on advisory boards for Pfizer, Novartis, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Deciphera, Audentes Pharmaceuticals, Nektar, Takeda, Ipsen, Myokardia, AstraZeneca, GlaxoSmithKline, Intrexon, and Regeneron.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Clinical trials supporting Food and Drug Adminstration approval of contemporary cancer therapies frequently failed to capture major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE) and, when they did, reported rates 2.6-fold lower than noncancer trials, new research shows.
Overall, 51.3% of trials did not report MACE, with that number reaching 57.6% in trials enrolling patients with baseline cardiovascular disease (CVD).
Nearly 40% of trials did not report any CVD events in follow-up, the authors reported online Feb. 10, 2020, in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology (2020;75:620-8).
“Even in drug classes where there were established or emerging associations with cardiotoxic events, often there were no reported heart events or cardiovascular events across years of follow-up in trials that examined hundreds or even thousands of patients. That was actually pretty surprising,” senior author Daniel Addison, MD, codirector of the cardio-oncology program at the Ohio State University Medical Center, Columbus, said in an interview.
The study was prompted by a series of events that crescendoed when his team was called to the ICU to determine whether a novel targeted agent played a role in the heart decline of a patient with acute myeloid leukemia. “I had a resident ask me a very important question: ‘How do we really know for sure that the trial actually reflects the true risk of heart events?’ to which I told him, ‘it’s difficult to know,’ ” he said.
“I think many of us rely heavily on what we see in the trials, particularly when they make it to the top journals, and quite frankly, we generally take it at face value,” Dr. Addison observed.
Lower Rate of Reported Events
The investigators reviewed CV events reported in 97,365 patients (median age, 61 years; 46% female) enrolled in 189 phase 2 and 3 trials supporting FDA approval of 123 anticancer drugs from 1998 to 2018. Biologic, targeted, or immune-based therapies accounted for 72.5% of drug approvals.
Over 148,138 person-years of follow-up (median trial duration, 30 months), there were 1,148 incidents of MACE (375 heart failure, 253 MIs, 180 strokes, 65 atrial fibrillation, 29 coronary revascularizations, and 246 CVD deaths). MACE rates were higher in the intervention group than in the control group (792 vs. 356; P less than .01). Among the 64 trials that excluded patients with baseline CVD, there were 269 incidents of MACE.
To put this finding in context, the researchers examined the reported incidence of MACE among some 6,000 similarly aged participants in the Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis (MESA). The overall weighted-average incidence rate was 1,408 per 100,000 person-years among MESA participants, compared with 542 events per 100,000 person-years among oncology trial participants (716 per 100,000 in the intervention arm). This represents a reported-to-expected ratio of 0.38 – a 2.6-fold lower rate of reported events (P less than .001) – and a risk difference of 866.
Further, MACE reporting was lower by a factor of 1.7 among all cancer trial participants irrespective of baseline CVD status (reported-to-expected ratio, 0.56; risk difference, 613; P less than .001).
There was no significant difference in MACE reporting between independent or industry-sponsored trials, the authors report.
No malicious intent
“There are likely some that might lean toward not wanting to attribute blame to a new drug when the drug is in a study, but I really think that the leading factor is lack of awareness,” Dr. Addison said. “I’ve talked with several cancer collaborators around the country who run large clinical trials, and I think often, when an event may be brought to someone’s attention, there is a tendency to just write it off as kind of a generic expected event due to age, or just something that’s not really pertinent to the study. So they don’t really focus on it as much.”
“Closer collaboration between cardiologists and cancer physicians is needed to better determine true cardiac risks among patients treated with these drugs.”
Breast cancer oncologist Marc E. Lippman, MD, of Georgetown University Medical Center and Georgetown Lombardi Comprehensive Cancer Center, Washington, D.C., isn’t convinced a lack of awareness is the culprit.
“I don’t agree with that at all,” he said in an interview. “I think there are very, very clear rules and guidelines these days for adverse-event reporting. I think that’s not a very likely explanation – that it’s not on the radar.”
Part of the problem may be that some of the toxicities, particularly cardiovascular, may not emerge for years, he said. Participant screening for the trials also likely removed patients with high cardiovascular risk. “It’s very understandable to me – I’m not saying it’s good particularly – but I think it’s very understandable that, if you’re trying to develop a drug, the last thing you’d want to have is a lot of toxicity that you might have avoided by just being restrictive in who you let into the study,” Dr. Lippman said.
The underreported CVD events may also reflect the rapidly changing profile of cardiovascular toxicities associated with novel anticancer therapies.
“Providers, both cancer and noncancer, generally put cardiotoxicity in the box of anthracyclines and radiation, but particularly over the last decade, we’ve begun to understand it’s well beyond any one class of drugs,” Dr. Addison said.
“I agree completely,” Dr. Lippman said. For example, “the checkpoint inhibitors are so unbelievably different in terms of their toxicities that many people simply didn’t even know what they were getting into at first.”
One size does not fit all
Javid Moslehi, MD, director of the cardio-oncology program at Vanderbilt University, Nashville, Tenn., said echocardiography – recommended to detect changes in left ventricular function in patients exposed to anthracyclines or targeted agents like trastuzumab (Herceptin) – isn’t enough to address today’s cancer therapy–related CVD events.
“Initial drugs like anthracyclines or Herceptin in cardio-oncology were associated with systolic cardiac dysfunction, whereas the majority of issues we see in the cardio-oncology clinics today are vascular, metabolic, arrhythmogenic, and inflammatory,” he said in an interview. “Echocardiography misses the big and increasingly complex picture.”
His group, for example, has been studying myocarditis associated with immunotherapies, but none of the clinical trials require screening or surveillance for myocarditis with a cardiac biomarker like troponin.
The group also recently identified 303 deaths in patients exposed to ibrutinib, a drug that revolutionized the treatment of several B-cell malignancies but is associated with higher rates of atrial fibrillation, which is also associated with increased bleeding risk. “So there’s a little bit of a double whammy there, given that we often treat atrial fibrillation with anticoagulation and where we can cause complications in patients,” Dr. Moslehi noted.
Although there needs to be closer collaboration between cardiologists and oncologists on individual trials, cardiologists also have to realize that oncology care has become very personalized, he suggested.
“What’s probably relevant for the breast cancer patient may not be relevant for the prostate cancer patient and their respective treatments,” Dr. Moslehi said. “So if we were to say, ‘every person should get an echo,’ that may be less relevant to the prostate cancer patient where treatments can cause vascular and metabolic perturbations or to the patient treated with immunotherapy who may have myocarditis, where many of the echos can be normal. There’s no one-size-fits-all for these things.”
Wearable technologies like smartwatches could play a role in improving the reporting of CVD events with novel therapies but a lot more research needs to be done to validate these tools, Dr. Addison said. “But as we continue on into the 21st century, this is going to expand and may potentially help us,” he added.
In the interim, better standardization is needed of the cardiovascular events reported in oncology trials, particularly the Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events (CTCAE), said Dr. Moslehi, who also serves as chair of the American Heart Association’s subcommittee on cardio-oncology.
“Cardiovascular definitions are not exactly uniform and are not consistent with what we in cardiology consider to be important or relevant,” he said. “So I think there needs to be better standardization of these definitions, specifically within the CTCAE, which is what the oncologists use to identify adverse events.”
In a linked editorial (J Am Coll Cardiol. 2020;75:629-31), Dr. Lippman and cardiologist Nanette Bishopric, MD, of the Medstar Heart and Vascular Institute in Washington, D.C., suggested it may also be time to organize a consortium that can carry out “rigorous multicenter clinical investigations to evaluate the cardiotoxicity of emerging cancer treatments,” similar to the Thrombosis in Myocardial Infarction Study Group.
“The success of this consortium in pioneering and targeting multiple generations of drugs for the treatment of MI, involving tens of thousands of patients and thousands of collaborations across multiple national borders, is a model for how to move forward in providing the new hope of cancer cure without the trade-off of years lost to heart disease,” the editorialists concluded.
The study was supported in part by National Institutes of Health grants, including a K12-CA133250 grant to Dr. Addison. Dr. Bishopric reported being on the scientific board of C&C Biopharma. Dr. Lippman reports being on the board of directors of and holding stock in Seattle Genetics. Dr. Moslehi reported having served on advisory boards for Pfizer, Novartis, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Deciphera, Audentes Pharmaceuticals, Nektar, Takeda, Ipsen, Myokardia, AstraZeneca, GlaxoSmithKline, Intrexon, and Regeneron.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Clinical trials supporting Food and Drug Adminstration approval of contemporary cancer therapies frequently failed to capture major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE) and, when they did, reported rates 2.6-fold lower than noncancer trials, new research shows.
Overall, 51.3% of trials did not report MACE, with that number reaching 57.6% in trials enrolling patients with baseline cardiovascular disease (CVD).
Nearly 40% of trials did not report any CVD events in follow-up, the authors reported online Feb. 10, 2020, in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology (2020;75:620-8).
“Even in drug classes where there were established or emerging associations with cardiotoxic events, often there were no reported heart events or cardiovascular events across years of follow-up in trials that examined hundreds or even thousands of patients. That was actually pretty surprising,” senior author Daniel Addison, MD, codirector of the cardio-oncology program at the Ohio State University Medical Center, Columbus, said in an interview.
The study was prompted by a series of events that crescendoed when his team was called to the ICU to determine whether a novel targeted agent played a role in the heart decline of a patient with acute myeloid leukemia. “I had a resident ask me a very important question: ‘How do we really know for sure that the trial actually reflects the true risk of heart events?’ to which I told him, ‘it’s difficult to know,’ ” he said.
“I think many of us rely heavily on what we see in the trials, particularly when they make it to the top journals, and quite frankly, we generally take it at face value,” Dr. Addison observed.
Lower Rate of Reported Events
The investigators reviewed CV events reported in 97,365 patients (median age, 61 years; 46% female) enrolled in 189 phase 2 and 3 trials supporting FDA approval of 123 anticancer drugs from 1998 to 2018. Biologic, targeted, or immune-based therapies accounted for 72.5% of drug approvals.
Over 148,138 person-years of follow-up (median trial duration, 30 months), there were 1,148 incidents of MACE (375 heart failure, 253 MIs, 180 strokes, 65 atrial fibrillation, 29 coronary revascularizations, and 246 CVD deaths). MACE rates were higher in the intervention group than in the control group (792 vs. 356; P less than .01). Among the 64 trials that excluded patients with baseline CVD, there were 269 incidents of MACE.
To put this finding in context, the researchers examined the reported incidence of MACE among some 6,000 similarly aged participants in the Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis (MESA). The overall weighted-average incidence rate was 1,408 per 100,000 person-years among MESA participants, compared with 542 events per 100,000 person-years among oncology trial participants (716 per 100,000 in the intervention arm). This represents a reported-to-expected ratio of 0.38 – a 2.6-fold lower rate of reported events (P less than .001) – and a risk difference of 866.
Further, MACE reporting was lower by a factor of 1.7 among all cancer trial participants irrespective of baseline CVD status (reported-to-expected ratio, 0.56; risk difference, 613; P less than .001).
There was no significant difference in MACE reporting between independent or industry-sponsored trials, the authors report.
No malicious intent
“There are likely some that might lean toward not wanting to attribute blame to a new drug when the drug is in a study, but I really think that the leading factor is lack of awareness,” Dr. Addison said. “I’ve talked with several cancer collaborators around the country who run large clinical trials, and I think often, when an event may be brought to someone’s attention, there is a tendency to just write it off as kind of a generic expected event due to age, or just something that’s not really pertinent to the study. So they don’t really focus on it as much.”
“Closer collaboration between cardiologists and cancer physicians is needed to better determine true cardiac risks among patients treated with these drugs.”
Breast cancer oncologist Marc E. Lippman, MD, of Georgetown University Medical Center and Georgetown Lombardi Comprehensive Cancer Center, Washington, D.C., isn’t convinced a lack of awareness is the culprit.
“I don’t agree with that at all,” he said in an interview. “I think there are very, very clear rules and guidelines these days for adverse-event reporting. I think that’s not a very likely explanation – that it’s not on the radar.”
Part of the problem may be that some of the toxicities, particularly cardiovascular, may not emerge for years, he said. Participant screening for the trials also likely removed patients with high cardiovascular risk. “It’s very understandable to me – I’m not saying it’s good particularly – but I think it’s very understandable that, if you’re trying to develop a drug, the last thing you’d want to have is a lot of toxicity that you might have avoided by just being restrictive in who you let into the study,” Dr. Lippman said.
The underreported CVD events may also reflect the rapidly changing profile of cardiovascular toxicities associated with novel anticancer therapies.
“Providers, both cancer and noncancer, generally put cardiotoxicity in the box of anthracyclines and radiation, but particularly over the last decade, we’ve begun to understand it’s well beyond any one class of drugs,” Dr. Addison said.
“I agree completely,” Dr. Lippman said. For example, “the checkpoint inhibitors are so unbelievably different in terms of their toxicities that many people simply didn’t even know what they were getting into at first.”
One size does not fit all
Javid Moslehi, MD, director of the cardio-oncology program at Vanderbilt University, Nashville, Tenn., said echocardiography – recommended to detect changes in left ventricular function in patients exposed to anthracyclines or targeted agents like trastuzumab (Herceptin) – isn’t enough to address today’s cancer therapy–related CVD events.
“Initial drugs like anthracyclines or Herceptin in cardio-oncology were associated with systolic cardiac dysfunction, whereas the majority of issues we see in the cardio-oncology clinics today are vascular, metabolic, arrhythmogenic, and inflammatory,” he said in an interview. “Echocardiography misses the big and increasingly complex picture.”
His group, for example, has been studying myocarditis associated with immunotherapies, but none of the clinical trials require screening or surveillance for myocarditis with a cardiac biomarker like troponin.
The group also recently identified 303 deaths in patients exposed to ibrutinib, a drug that revolutionized the treatment of several B-cell malignancies but is associated with higher rates of atrial fibrillation, which is also associated with increased bleeding risk. “So there’s a little bit of a double whammy there, given that we often treat atrial fibrillation with anticoagulation and where we can cause complications in patients,” Dr. Moslehi noted.
Although there needs to be closer collaboration between cardiologists and oncologists on individual trials, cardiologists also have to realize that oncology care has become very personalized, he suggested.
“What’s probably relevant for the breast cancer patient may not be relevant for the prostate cancer patient and their respective treatments,” Dr. Moslehi said. “So if we were to say, ‘every person should get an echo,’ that may be less relevant to the prostate cancer patient where treatments can cause vascular and metabolic perturbations or to the patient treated with immunotherapy who may have myocarditis, where many of the echos can be normal. There’s no one-size-fits-all for these things.”
Wearable technologies like smartwatches could play a role in improving the reporting of CVD events with novel therapies but a lot more research needs to be done to validate these tools, Dr. Addison said. “But as we continue on into the 21st century, this is going to expand and may potentially help us,” he added.
In the interim, better standardization is needed of the cardiovascular events reported in oncology trials, particularly the Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events (CTCAE), said Dr. Moslehi, who also serves as chair of the American Heart Association’s subcommittee on cardio-oncology.
“Cardiovascular definitions are not exactly uniform and are not consistent with what we in cardiology consider to be important or relevant,” he said. “So I think there needs to be better standardization of these definitions, specifically within the CTCAE, which is what the oncologists use to identify adverse events.”
In a linked editorial (J Am Coll Cardiol. 2020;75:629-31), Dr. Lippman and cardiologist Nanette Bishopric, MD, of the Medstar Heart and Vascular Institute in Washington, D.C., suggested it may also be time to organize a consortium that can carry out “rigorous multicenter clinical investigations to evaluate the cardiotoxicity of emerging cancer treatments,” similar to the Thrombosis in Myocardial Infarction Study Group.
“The success of this consortium in pioneering and targeting multiple generations of drugs for the treatment of MI, involving tens of thousands of patients and thousands of collaborations across multiple national borders, is a model for how to move forward in providing the new hope of cancer cure without the trade-off of years lost to heart disease,” the editorialists concluded.
The study was supported in part by National Institutes of Health grants, including a K12-CA133250 grant to Dr. Addison. Dr. Bishopric reported being on the scientific board of C&C Biopharma. Dr. Lippman reports being on the board of directors of and holding stock in Seattle Genetics. Dr. Moslehi reported having served on advisory boards for Pfizer, Novartis, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Deciphera, Audentes Pharmaceuticals, Nektar, Takeda, Ipsen, Myokardia, AstraZeneca, GlaxoSmithKline, Intrexon, and Regeneron.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Model reveals genes associated with prognosis in ER+, HER2– breast cancer
ORLANDO – , according to new research.
Yara Abdou, MD, of Roswell Park Comprehensive Cancer Center in Buffalo, N.Y., and colleagues presented this work in a poster at the ASCO-SITC Clinical Immuno-Oncology Symposium.
The model used 50 cycles of machine learning to cluster 98 patients from The Cancer Genome Atlas Program into high- and low-risk groups based on mRNA expression of 26 gene groups.
The gene groups consisted of 191 genes enriched in cellular and noncellular elements of the tumor microenvironment. Mutational burden and clinical outcomes data for the patients also were considered, Dr. Abdou explained in an interview.
Kaplan-Meier curves were created for each group by K-means clustering, survival differences between the two groups were assessed, and correlations among the various gene groups were analyzed.
Five identified genes were associated with poor prognosis: LOXL2, PHEX, ACTA2, MEGF9, and TNFSF4. Fifteen genes were associated with good prognosis: CD8A, CD8B, FCRL3, GZMK, CD3E, CCL5, TP53, ICAM3, CD247, IFNG, IFNGR1, ICAM4, SHH, HLA-DOB, and CXCR3.
The Kaplan-Meier curves showed a significant difference in survival between the two groups (hazard ratio, 2.878; P = .05), confirming the validity of the risk score modeling, Dr. Abdou said.
Immune profiling showed that expression of genes associated with desmoplastic reaction, neutrophils, and immunosuppressive cytokines were higher in the high-risk group, whereas expression of genes related to immune system activation were higher in the low-risk group (P less than .05).
Stroma in the tumor microenvironment is known to affect prognosis and response to therapy in patients with breast cancer, but few mathematical models exist to determine prognosis based on mRNA expressivity in the tumor microenvironment, Dr. Abdou said, explaining the rationale for the study.
The findings suggest that when genomic profile information is available for a given patient in the clinic, this machine learning–assisted risk scoring approach could have prognostic value, she said, noting that the model also will be assessed in patients with other types of breast cancer.
Dr. Abdou reported having no disclosures.
SOURCE: Abdou Y et al. ASCO-SITC. Poster A3.
ORLANDO – , according to new research.
Yara Abdou, MD, of Roswell Park Comprehensive Cancer Center in Buffalo, N.Y., and colleagues presented this work in a poster at the ASCO-SITC Clinical Immuno-Oncology Symposium.
The model used 50 cycles of machine learning to cluster 98 patients from The Cancer Genome Atlas Program into high- and low-risk groups based on mRNA expression of 26 gene groups.
The gene groups consisted of 191 genes enriched in cellular and noncellular elements of the tumor microenvironment. Mutational burden and clinical outcomes data for the patients also were considered, Dr. Abdou explained in an interview.
Kaplan-Meier curves were created for each group by K-means clustering, survival differences between the two groups were assessed, and correlations among the various gene groups were analyzed.
Five identified genes were associated with poor prognosis: LOXL2, PHEX, ACTA2, MEGF9, and TNFSF4. Fifteen genes were associated with good prognosis: CD8A, CD8B, FCRL3, GZMK, CD3E, CCL5, TP53, ICAM3, CD247, IFNG, IFNGR1, ICAM4, SHH, HLA-DOB, and CXCR3.
The Kaplan-Meier curves showed a significant difference in survival between the two groups (hazard ratio, 2.878; P = .05), confirming the validity of the risk score modeling, Dr. Abdou said.
Immune profiling showed that expression of genes associated with desmoplastic reaction, neutrophils, and immunosuppressive cytokines were higher in the high-risk group, whereas expression of genes related to immune system activation were higher in the low-risk group (P less than .05).
Stroma in the tumor microenvironment is known to affect prognosis and response to therapy in patients with breast cancer, but few mathematical models exist to determine prognosis based on mRNA expressivity in the tumor microenvironment, Dr. Abdou said, explaining the rationale for the study.
The findings suggest that when genomic profile information is available for a given patient in the clinic, this machine learning–assisted risk scoring approach could have prognostic value, she said, noting that the model also will be assessed in patients with other types of breast cancer.
Dr. Abdou reported having no disclosures.
SOURCE: Abdou Y et al. ASCO-SITC. Poster A3.
ORLANDO – , according to new research.
Yara Abdou, MD, of Roswell Park Comprehensive Cancer Center in Buffalo, N.Y., and colleagues presented this work in a poster at the ASCO-SITC Clinical Immuno-Oncology Symposium.
The model used 50 cycles of machine learning to cluster 98 patients from The Cancer Genome Atlas Program into high- and low-risk groups based on mRNA expression of 26 gene groups.
The gene groups consisted of 191 genes enriched in cellular and noncellular elements of the tumor microenvironment. Mutational burden and clinical outcomes data for the patients also were considered, Dr. Abdou explained in an interview.
Kaplan-Meier curves were created for each group by K-means clustering, survival differences between the two groups were assessed, and correlations among the various gene groups were analyzed.
Five identified genes were associated with poor prognosis: LOXL2, PHEX, ACTA2, MEGF9, and TNFSF4. Fifteen genes were associated with good prognosis: CD8A, CD8B, FCRL3, GZMK, CD3E, CCL5, TP53, ICAM3, CD247, IFNG, IFNGR1, ICAM4, SHH, HLA-DOB, and CXCR3.
The Kaplan-Meier curves showed a significant difference in survival between the two groups (hazard ratio, 2.878; P = .05), confirming the validity of the risk score modeling, Dr. Abdou said.
Immune profiling showed that expression of genes associated with desmoplastic reaction, neutrophils, and immunosuppressive cytokines were higher in the high-risk group, whereas expression of genes related to immune system activation were higher in the low-risk group (P less than .05).
Stroma in the tumor microenvironment is known to affect prognosis and response to therapy in patients with breast cancer, but few mathematical models exist to determine prognosis based on mRNA expressivity in the tumor microenvironment, Dr. Abdou said, explaining the rationale for the study.
The findings suggest that when genomic profile information is available for a given patient in the clinic, this machine learning–assisted risk scoring approach could have prognostic value, she said, noting that the model also will be assessed in patients with other types of breast cancer.
Dr. Abdou reported having no disclosures.
SOURCE: Abdou Y et al. ASCO-SITC. Poster A3.
REPORTING FROM THE CLINICAL IMMUNO-ONCOLOGY SYMPOSIUM
Mobile stroke unit had clinical impact on EVT
In its first year of operation, a mobile stroke unit in Melbourne demonstrated substantial savings in time to commencement of both thrombolysis and endovascular thrombectomy (EVT), results from a prospective study showed.
“While previously published data from MSU [mobile stroke unit] services in Europe and North America show substantial reductions in time to thrombolysis of approximately 30-45 minutes, little is known about the clinical impact on EVT,” first author Henry Zhao, MBBS, and colleagues wrote in a study published in Stroke.
Launched in November 2017, the Melbourne MSU is based at a large comprehensive stroke center and operates with a 20-km radius, servicing about 1.7 million people within the city of Melbourne. It is staffed with an onboard neurologist or senior stroke fellow who provides primary assessment and treatment decisions, a stroke advanced practice nurse who provides clinical support and treatment administration, a clinician who provides CT imaging, and advanced life support and mobile intensive care paramedics who provide transport logistics and paramedicine support. For the current analysis, MSU patients who received reperfusion therapy were compared with control patients presenting to metropolitan Melbourne stroke units via standard ambulance within MSU operating hours. The primary outcome was median time difference in first ambulance dispatch to treatment, which the researchers used quantile regression analysis to determine. Time savings were subsequently converted to disability-adjusted life years (DALY) avoiding using published estimates.
Dr. Zhao of the Melbourne Brain Centre and department of neurology at Royal Melbourne Hospital and his colleagues reported that, in its first year of operation, the Melbourne MSU administered prehospital thrombolysis to 100 patients with a mean age of nearly 74 years. More than half of the patients (62%) were male. Compared with controls, the median time savings per MSU patient was 26 minutes for dispatch to hospital arrival and 15 minutes for hospital arrival to thrombolysis (P less than .0010 for both associations). The calculated overall time saving from dispatch to thrombolysis was 42.5 minutes.
Over the same time period, 41 MSU patients with a mean age of 76 years received EVT dispatch-to-treatment time saving of 51 minutes (P less than 0.001). This included a median time saving of 17 minutes for EVT hospital arrival to arterial puncture for MSU patients (P = .001). Overall estimated median DALYs saved through earlier provision of reperfusion therapies were 20.9 for thrombolysis and 24.6 for EVT.
“The benefit in EVT patients was primarily driven by prehospital MSU diagnosis of large vessel occlusion, which enabled bypass of a local non-EVT center directly to a comprehensive stroke center in almost 50% of patients with large vessel occlusion,” the researchers wrote. “Even when patients were located close to an EVT center, MSU pre-notification and facilitated workflows achieved a reduction in hospital arrival to arterial puncture by one-third. Furthermore, the time saving was seen despite the majority of EVT patients receiving repeat imaging in hospital to visualize the extracranial circulation.”
The study is scheduled to be presented at the International Stroke Conference on Feb. 20.
The Melbourne MSU received funding from the Australian Commonwealth Government, Victorian State Government, Royal Melbourne Hospital Neurosciences Foundation, Stroke Foundation, the Florey Institute of Neurosciences and Mental Health, the University of Melbourne, Boehringer Ingelheim, and private donation. Dr. Zhao disclosed that he has received grants from the Australian Commonwealth Government and the University of Melbourne and personal fees from Boehringer Ingelheim.
SOURCE: Zhao H et al. Stroke. 2020 Feb 12. doi: 10.1161/strokeaha.119.027843.
In its first year of operation, a mobile stroke unit in Melbourne demonstrated substantial savings in time to commencement of both thrombolysis and endovascular thrombectomy (EVT), results from a prospective study showed.
“While previously published data from MSU [mobile stroke unit] services in Europe and North America show substantial reductions in time to thrombolysis of approximately 30-45 minutes, little is known about the clinical impact on EVT,” first author Henry Zhao, MBBS, and colleagues wrote in a study published in Stroke.
Launched in November 2017, the Melbourne MSU is based at a large comprehensive stroke center and operates with a 20-km radius, servicing about 1.7 million people within the city of Melbourne. It is staffed with an onboard neurologist or senior stroke fellow who provides primary assessment and treatment decisions, a stroke advanced practice nurse who provides clinical support and treatment administration, a clinician who provides CT imaging, and advanced life support and mobile intensive care paramedics who provide transport logistics and paramedicine support. For the current analysis, MSU patients who received reperfusion therapy were compared with control patients presenting to metropolitan Melbourne stroke units via standard ambulance within MSU operating hours. The primary outcome was median time difference in first ambulance dispatch to treatment, which the researchers used quantile regression analysis to determine. Time savings were subsequently converted to disability-adjusted life years (DALY) avoiding using published estimates.
Dr. Zhao of the Melbourne Brain Centre and department of neurology at Royal Melbourne Hospital and his colleagues reported that, in its first year of operation, the Melbourne MSU administered prehospital thrombolysis to 100 patients with a mean age of nearly 74 years. More than half of the patients (62%) were male. Compared with controls, the median time savings per MSU patient was 26 minutes for dispatch to hospital arrival and 15 minutes for hospital arrival to thrombolysis (P less than .0010 for both associations). The calculated overall time saving from dispatch to thrombolysis was 42.5 minutes.
Over the same time period, 41 MSU patients with a mean age of 76 years received EVT dispatch-to-treatment time saving of 51 minutes (P less than 0.001). This included a median time saving of 17 minutes for EVT hospital arrival to arterial puncture for MSU patients (P = .001). Overall estimated median DALYs saved through earlier provision of reperfusion therapies were 20.9 for thrombolysis and 24.6 for EVT.
“The benefit in EVT patients was primarily driven by prehospital MSU diagnosis of large vessel occlusion, which enabled bypass of a local non-EVT center directly to a comprehensive stroke center in almost 50% of patients with large vessel occlusion,” the researchers wrote. “Even when patients were located close to an EVT center, MSU pre-notification and facilitated workflows achieved a reduction in hospital arrival to arterial puncture by one-third. Furthermore, the time saving was seen despite the majority of EVT patients receiving repeat imaging in hospital to visualize the extracranial circulation.”
The study is scheduled to be presented at the International Stroke Conference on Feb. 20.
The Melbourne MSU received funding from the Australian Commonwealth Government, Victorian State Government, Royal Melbourne Hospital Neurosciences Foundation, Stroke Foundation, the Florey Institute of Neurosciences and Mental Health, the University of Melbourne, Boehringer Ingelheim, and private donation. Dr. Zhao disclosed that he has received grants from the Australian Commonwealth Government and the University of Melbourne and personal fees from Boehringer Ingelheim.
SOURCE: Zhao H et al. Stroke. 2020 Feb 12. doi: 10.1161/strokeaha.119.027843.
In its first year of operation, a mobile stroke unit in Melbourne demonstrated substantial savings in time to commencement of both thrombolysis and endovascular thrombectomy (EVT), results from a prospective study showed.
“While previously published data from MSU [mobile stroke unit] services in Europe and North America show substantial reductions in time to thrombolysis of approximately 30-45 minutes, little is known about the clinical impact on EVT,” first author Henry Zhao, MBBS, and colleagues wrote in a study published in Stroke.
Launched in November 2017, the Melbourne MSU is based at a large comprehensive stroke center and operates with a 20-km radius, servicing about 1.7 million people within the city of Melbourne. It is staffed with an onboard neurologist or senior stroke fellow who provides primary assessment and treatment decisions, a stroke advanced practice nurse who provides clinical support and treatment administration, a clinician who provides CT imaging, and advanced life support and mobile intensive care paramedics who provide transport logistics and paramedicine support. For the current analysis, MSU patients who received reperfusion therapy were compared with control patients presenting to metropolitan Melbourne stroke units via standard ambulance within MSU operating hours. The primary outcome was median time difference in first ambulance dispatch to treatment, which the researchers used quantile regression analysis to determine. Time savings were subsequently converted to disability-adjusted life years (DALY) avoiding using published estimates.
Dr. Zhao of the Melbourne Brain Centre and department of neurology at Royal Melbourne Hospital and his colleagues reported that, in its first year of operation, the Melbourne MSU administered prehospital thrombolysis to 100 patients with a mean age of nearly 74 years. More than half of the patients (62%) were male. Compared with controls, the median time savings per MSU patient was 26 minutes for dispatch to hospital arrival and 15 minutes for hospital arrival to thrombolysis (P less than .0010 for both associations). The calculated overall time saving from dispatch to thrombolysis was 42.5 minutes.
Over the same time period, 41 MSU patients with a mean age of 76 years received EVT dispatch-to-treatment time saving of 51 minutes (P less than 0.001). This included a median time saving of 17 minutes for EVT hospital arrival to arterial puncture for MSU patients (P = .001). Overall estimated median DALYs saved through earlier provision of reperfusion therapies were 20.9 for thrombolysis and 24.6 for EVT.
“The benefit in EVT patients was primarily driven by prehospital MSU diagnosis of large vessel occlusion, which enabled bypass of a local non-EVT center directly to a comprehensive stroke center in almost 50% of patients with large vessel occlusion,” the researchers wrote. “Even when patients were located close to an EVT center, MSU pre-notification and facilitated workflows achieved a reduction in hospital arrival to arterial puncture by one-third. Furthermore, the time saving was seen despite the majority of EVT patients receiving repeat imaging in hospital to visualize the extracranial circulation.”
The study is scheduled to be presented at the International Stroke Conference on Feb. 20.
The Melbourne MSU received funding from the Australian Commonwealth Government, Victorian State Government, Royal Melbourne Hospital Neurosciences Foundation, Stroke Foundation, the Florey Institute of Neurosciences and Mental Health, the University of Melbourne, Boehringer Ingelheim, and private donation. Dr. Zhao disclosed that he has received grants from the Australian Commonwealth Government and the University of Melbourne and personal fees from Boehringer Ingelheim.
SOURCE: Zhao H et al. Stroke. 2020 Feb 12. doi: 10.1161/strokeaha.119.027843.
FROM STROKE
Key clinical point: A mobile stroke unit (MSU) substantially reduced time to reperfusion therapies.
Major finding: Compared with controls, the median time savings per MSU patient was 26 minutes for dispatch to hospital arrival and 15 minutes for hospital arrival to thrombolysis (P less than .0010 for both associations).
Study details: A prospective study of 100 stroke patients.
Disclosures: The Melbourne MSU received funding from the Australian Commonwealth Government, Victorian State Government, Royal Melbourne Hospital Neurosciences Foundation, Stroke Foundation, the Florey Institute of Neurosciences and Mental Health, the University of Melbourne, Boehringer Ingelheim, and private donation. Dr. Zhao disclosed that he has received grants from the Australian Commonwealth Government and the University of Melbourne and personal fees from Boehringer Ingelheim.
Source: Zhao H et al. Stroke. 2020 Feb 12. doi: 10.1161/strokeaha.119.027843.
FDA: Cell phones still look safe
according to a review by the Food and Drug Administration.
The FDA reviewed the published literature from 2008 to 2018 and concluded that the data don’t support any quantifiable adverse health risks from RFR. However, the evidence is not without limitations.
The FDA’s evaluation included evidence from in vivo animal studies from Jan. 1, 2008, to Aug. 1, 2018, and epidemiologic studies in humans from Jan. 1, 2008, to May 8, 2018. Both kinds of evidence had limitations, but neither produced strong indications of any causal risks from cell phone use.
The FDA noted that in vivo animal studies are limited by variability of methods and RFR exposure, which make comparisons of results difficult. These studies are also impacted by the indirect effects of temperature increases (the only currently established biological effect of RFR) and stress experienced by the animals, which make teasing out the direct effects of RFR difficult.
The FDA noted that strong epidemiologic studies can provide more relevant and accurate information than in vivo studies, but epidemiologic studies are not without limitations. For example, most have participants track and self-report their cell phone use. There’s also no way to directly track certain factors of RFR exposure, such as frequency, duration, or intensity.
Even with those caveats in mind, the FDA wrote that, “based on the studies that are described in detail in this report, there is insufficient evidence to support a causal association between RFR exposure and tumorigenesis. There is a lack of clear dose-response relationship, a lack of consistent findings or specificity, and a lack of biological mechanistic plausibility.”
The full review is available on the FDA website.
according to a review by the Food and Drug Administration.
The FDA reviewed the published literature from 2008 to 2018 and concluded that the data don’t support any quantifiable adverse health risks from RFR. However, the evidence is not without limitations.
The FDA’s evaluation included evidence from in vivo animal studies from Jan. 1, 2008, to Aug. 1, 2018, and epidemiologic studies in humans from Jan. 1, 2008, to May 8, 2018. Both kinds of evidence had limitations, but neither produced strong indications of any causal risks from cell phone use.
The FDA noted that in vivo animal studies are limited by variability of methods and RFR exposure, which make comparisons of results difficult. These studies are also impacted by the indirect effects of temperature increases (the only currently established biological effect of RFR) and stress experienced by the animals, which make teasing out the direct effects of RFR difficult.
The FDA noted that strong epidemiologic studies can provide more relevant and accurate information than in vivo studies, but epidemiologic studies are not without limitations. For example, most have participants track and self-report their cell phone use. There’s also no way to directly track certain factors of RFR exposure, such as frequency, duration, or intensity.
Even with those caveats in mind, the FDA wrote that, “based on the studies that are described in detail in this report, there is insufficient evidence to support a causal association between RFR exposure and tumorigenesis. There is a lack of clear dose-response relationship, a lack of consistent findings or specificity, and a lack of biological mechanistic plausibility.”
The full review is available on the FDA website.
according to a review by the Food and Drug Administration.
The FDA reviewed the published literature from 2008 to 2018 and concluded that the data don’t support any quantifiable adverse health risks from RFR. However, the evidence is not without limitations.
The FDA’s evaluation included evidence from in vivo animal studies from Jan. 1, 2008, to Aug. 1, 2018, and epidemiologic studies in humans from Jan. 1, 2008, to May 8, 2018. Both kinds of evidence had limitations, but neither produced strong indications of any causal risks from cell phone use.
The FDA noted that in vivo animal studies are limited by variability of methods and RFR exposure, which make comparisons of results difficult. These studies are also impacted by the indirect effects of temperature increases (the only currently established biological effect of RFR) and stress experienced by the animals, which make teasing out the direct effects of RFR difficult.
The FDA noted that strong epidemiologic studies can provide more relevant and accurate information than in vivo studies, but epidemiologic studies are not without limitations. For example, most have participants track and self-report their cell phone use. There’s also no way to directly track certain factors of RFR exposure, such as frequency, duration, or intensity.
Even with those caveats in mind, the FDA wrote that, “based on the studies that are described in detail in this report, there is insufficient evidence to support a causal association between RFR exposure and tumorigenesis. There is a lack of clear dose-response relationship, a lack of consistent findings or specificity, and a lack of biological mechanistic plausibility.”
The full review is available on the FDA website.
Pharmacologic prophylaxis fails in pediatric migraine
Clinicians hoped that medications used in adults – such as antidepressants, antiepileptics, antihypertensive agents, calcium channel blockers, and food supplements – would find similar success in children. Unfortunately, researchers found only short-term signs of efficacy over placebo, with no benefit lasting more than 6 months.
The study, conducted by a team led by Cosima Locher, PhD, of Boston Children’s Hospital, included 23 double-blind, randomized, controlled trials with a total of 2,217 patients; the mean age was 11 years. They compared 12 pharmacologic agents with each other or with placebo in the study, published online in JAMA Pediatrics.
In a main efficacy analysis that included 19 studies, only two treatments outperformed placebo: propranolol (standardized mean difference, 0.60; 95% confidence interval, 0.03-1.17) and topiramate (SMD, 0.59; 95% CI, 0.03-1.15). There were no statistically significant between-treatment differences.
The results had an overall low to moderate certainty.
When propranolol was compared to placebo, the 95% prediction interval (–0.62 to 1.82) was wider than the significant confidence interval (0.03-1.17), and comprised both beneficial and detrimental effects. A similar result was found with topiramate, with a prediction interval of –0.62 to 1.80 extending into nonsignificant effects (95% CI, 0.03-1.15). In both cases, significant effects were found only when the prediction interval was 70%.
In a long-term analysis (greater than 6 months), no treatment outperformed placebo.
The treatments generally were acceptable. The researchers found no significant difference in tolerability between any of the treatments and each other or placebo. Safety data analyzed from 13 trials revealed no significant differences between treatments and placebo.
“Because specific effects of drugs are associated with the size of the placebo effect, the lack of drug efficacy in our NMA [network meta-analysis] could be owing to a comparatively high placebo effect in children. In fact, there is indirect evidence [from other studies] that the placebo effect is more pronounced in children and adolescents than in adults,” Dr. Locher and associates said. They suggested that studies were needed to quantify the placebo effect in pediatric migraine, and if it was large, to develop innovative therapies making use of this.
The findings should lead to some changes in practice, Boris Zernikow, MD, PhD, of Children’s and Adolescents’ Hospital Datteln (Germany) wrote in an accompanying editorial.
Pharmacological prophylactic treatment of childhood migraine should be an exception rather than the rule, and nonpharmacologic approaches should be emphasized, particularly because the placebo effect is magnified in children, he said.
Many who suffer migraines in childhood will continue to be affected in adulthood, so pediatric intervention is a good opportunity to instill effective strategies. These include: using abortive medication early in an attack and using antimigraine medications for only that specific type of headache; engaging in physical activity to reduce migraine attacks; getting sufficient sleep; and learning relaxation and other psychological approaches to counter migraines.
Dr. Zernikow had no relevant financial disclosures. One study author received grants from Amgen and other support from Grunenthal and Akelos. The study received funding from the Sara Page Mayo Endowment for Pediatric Pain Research, Education, and Treatment; the Swiss National Science Foundation; the Schweizer-Arau-Foundation; and the Theophrastus Foundation.
SOURCES: Locher C et al. JAMA Pediatrics. 2020 Feb 10. doi: 10.1001/jamapediatrics.2019.5856; Zernikow B. JAMA Pediatrics. 2020 Feb 10. doi: 10.1001/jamapediatrics.2019.5907.
Clinicians hoped that medications used in adults – such as antidepressants, antiepileptics, antihypertensive agents, calcium channel blockers, and food supplements – would find similar success in children. Unfortunately, researchers found only short-term signs of efficacy over placebo, with no benefit lasting more than 6 months.
The study, conducted by a team led by Cosima Locher, PhD, of Boston Children’s Hospital, included 23 double-blind, randomized, controlled trials with a total of 2,217 patients; the mean age was 11 years. They compared 12 pharmacologic agents with each other or with placebo in the study, published online in JAMA Pediatrics.
In a main efficacy analysis that included 19 studies, only two treatments outperformed placebo: propranolol (standardized mean difference, 0.60; 95% confidence interval, 0.03-1.17) and topiramate (SMD, 0.59; 95% CI, 0.03-1.15). There were no statistically significant between-treatment differences.
The results had an overall low to moderate certainty.
When propranolol was compared to placebo, the 95% prediction interval (–0.62 to 1.82) was wider than the significant confidence interval (0.03-1.17), and comprised both beneficial and detrimental effects. A similar result was found with topiramate, with a prediction interval of –0.62 to 1.80 extending into nonsignificant effects (95% CI, 0.03-1.15). In both cases, significant effects were found only when the prediction interval was 70%.
In a long-term analysis (greater than 6 months), no treatment outperformed placebo.
The treatments generally were acceptable. The researchers found no significant difference in tolerability between any of the treatments and each other or placebo. Safety data analyzed from 13 trials revealed no significant differences between treatments and placebo.
“Because specific effects of drugs are associated with the size of the placebo effect, the lack of drug efficacy in our NMA [network meta-analysis] could be owing to a comparatively high placebo effect in children. In fact, there is indirect evidence [from other studies] that the placebo effect is more pronounced in children and adolescents than in adults,” Dr. Locher and associates said. They suggested that studies were needed to quantify the placebo effect in pediatric migraine, and if it was large, to develop innovative therapies making use of this.
The findings should lead to some changes in practice, Boris Zernikow, MD, PhD, of Children’s and Adolescents’ Hospital Datteln (Germany) wrote in an accompanying editorial.
Pharmacological prophylactic treatment of childhood migraine should be an exception rather than the rule, and nonpharmacologic approaches should be emphasized, particularly because the placebo effect is magnified in children, he said.
Many who suffer migraines in childhood will continue to be affected in adulthood, so pediatric intervention is a good opportunity to instill effective strategies. These include: using abortive medication early in an attack and using antimigraine medications for only that specific type of headache; engaging in physical activity to reduce migraine attacks; getting sufficient sleep; and learning relaxation and other psychological approaches to counter migraines.
Dr. Zernikow had no relevant financial disclosures. One study author received grants from Amgen and other support from Grunenthal and Akelos. The study received funding from the Sara Page Mayo Endowment for Pediatric Pain Research, Education, and Treatment; the Swiss National Science Foundation; the Schweizer-Arau-Foundation; and the Theophrastus Foundation.
SOURCES: Locher C et al. JAMA Pediatrics. 2020 Feb 10. doi: 10.1001/jamapediatrics.2019.5856; Zernikow B. JAMA Pediatrics. 2020 Feb 10. doi: 10.1001/jamapediatrics.2019.5907.
Clinicians hoped that medications used in adults – such as antidepressants, antiepileptics, antihypertensive agents, calcium channel blockers, and food supplements – would find similar success in children. Unfortunately, researchers found only short-term signs of efficacy over placebo, with no benefit lasting more than 6 months.
The study, conducted by a team led by Cosima Locher, PhD, of Boston Children’s Hospital, included 23 double-blind, randomized, controlled trials with a total of 2,217 patients; the mean age was 11 years. They compared 12 pharmacologic agents with each other or with placebo in the study, published online in JAMA Pediatrics.
In a main efficacy analysis that included 19 studies, only two treatments outperformed placebo: propranolol (standardized mean difference, 0.60; 95% confidence interval, 0.03-1.17) and topiramate (SMD, 0.59; 95% CI, 0.03-1.15). There were no statistically significant between-treatment differences.
The results had an overall low to moderate certainty.
When propranolol was compared to placebo, the 95% prediction interval (–0.62 to 1.82) was wider than the significant confidence interval (0.03-1.17), and comprised both beneficial and detrimental effects. A similar result was found with topiramate, with a prediction interval of –0.62 to 1.80 extending into nonsignificant effects (95% CI, 0.03-1.15). In both cases, significant effects were found only when the prediction interval was 70%.
In a long-term analysis (greater than 6 months), no treatment outperformed placebo.
The treatments generally were acceptable. The researchers found no significant difference in tolerability between any of the treatments and each other or placebo. Safety data analyzed from 13 trials revealed no significant differences between treatments and placebo.
“Because specific effects of drugs are associated with the size of the placebo effect, the lack of drug efficacy in our NMA [network meta-analysis] could be owing to a comparatively high placebo effect in children. In fact, there is indirect evidence [from other studies] that the placebo effect is more pronounced in children and adolescents than in adults,” Dr. Locher and associates said. They suggested that studies were needed to quantify the placebo effect in pediatric migraine, and if it was large, to develop innovative therapies making use of this.
The findings should lead to some changes in practice, Boris Zernikow, MD, PhD, of Children’s and Adolescents’ Hospital Datteln (Germany) wrote in an accompanying editorial.
Pharmacological prophylactic treatment of childhood migraine should be an exception rather than the rule, and nonpharmacologic approaches should be emphasized, particularly because the placebo effect is magnified in children, he said.
Many who suffer migraines in childhood will continue to be affected in adulthood, so pediatric intervention is a good opportunity to instill effective strategies. These include: using abortive medication early in an attack and using antimigraine medications for only that specific type of headache; engaging in physical activity to reduce migraine attacks; getting sufficient sleep; and learning relaxation and other psychological approaches to counter migraines.
Dr. Zernikow had no relevant financial disclosures. One study author received grants from Amgen and other support from Grunenthal and Akelos. The study received funding from the Sara Page Mayo Endowment for Pediatric Pain Research, Education, and Treatment; the Swiss National Science Foundation; the Schweizer-Arau-Foundation; and the Theophrastus Foundation.
SOURCES: Locher C et al. JAMA Pediatrics. 2020 Feb 10. doi: 10.1001/jamapediatrics.2019.5856; Zernikow B. JAMA Pediatrics. 2020 Feb 10. doi: 10.1001/jamapediatrics.2019.5907.
FROM JAMA PEDIATRICS
Breast cancer treatments veer from guidelines
Women with breast cancer may be receiving treatments that are discordant with guideline recommendations for genetic subtypes of disease, based on a retrospective analysis of more than 20,000 patients.
Radiotherapy and chemotherapy practices were particularly out of alignment with guidelines, reported lead author Allison W. Kurian, MD, of Stanford (Calif.) University, and colleagues.
“Integrating genetic testing into breast cancer care has been complex and challenging,” the investigators wrote in JAMA Oncology. “There is wide variability in which clinicians order testing and disclose results, in the clinical significance of results, and in how clinicians interpret results to patients.”
According to the investigators, while germline testing is on the rise, little is known about how these test results are translating to clinical care.
To learn more, the investigators evaluated data from 20,568 women with stage 0-III breast cancer who entered the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results registries of Georgia and California between 2014 and 2016.
Three treatment types were evaluated: surgery (bilateral vs. unilateral mastectomy), radiotherapy after lumpectomy, and chemotherapy. Treatment selection was compared with test results for breast cancer–associated genes, such as BRCA1/2, TP53, PTEN, and others. Associations were then compared with guideline recommendations.
Data analysis suggested that many clinicians were correctly using genetic test results to guide surgical decisions. For example, almost two-thirds (61.7%) of women with a BRCA mutation underwent bilateral mastectomy, compared with one-quarter (24.3%) who were BRCA negative (odds ratio, 5.52). For other pathogenic variants, the rate of bilateral mastectomy was still elevated, albeit to a lesser degree (OR, 2.41).
Generally, these practices align with recommendations, the investigators wrote, noting that research supports bilateral mastectomy with BRCA1/2, TP53, and PTEN variants, while data are lacking for other genetic subtypes.
Radiotherapy and chemotherapy practices were more discordant with guidelines. For example, women with a BRCA mutation were 78% less likely to receive radiotherapy after lumpectomy (OR, 0.22) and 76% more likely to receive chemotherapy for early-stage, hormone-positive disease (OR, 1.76). According to investigators, these findings suggest possible trends in undertreatment and overtreatment, respectively.
“We believe more research is needed to confirm our results and to evaluate long-term outcomes of pathogenic variant carriers to understand treatment decision making and consequences,” the investigators concluded.
The study was funded by the National Institutes of Health and the California Department of Public Health. The investigators reported relationships with Myriad Genetics, Genomic Health, Roche, and other companies.
SOURCE: Kurian AW et al. JAMA Oncol. 2020 Feb 6. doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2019.6400.
Women with breast cancer may be receiving treatments that are discordant with guideline recommendations for genetic subtypes of disease, based on a retrospective analysis of more than 20,000 patients.
Radiotherapy and chemotherapy practices were particularly out of alignment with guidelines, reported lead author Allison W. Kurian, MD, of Stanford (Calif.) University, and colleagues.
“Integrating genetic testing into breast cancer care has been complex and challenging,” the investigators wrote in JAMA Oncology. “There is wide variability in which clinicians order testing and disclose results, in the clinical significance of results, and in how clinicians interpret results to patients.”
According to the investigators, while germline testing is on the rise, little is known about how these test results are translating to clinical care.
To learn more, the investigators evaluated data from 20,568 women with stage 0-III breast cancer who entered the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results registries of Georgia and California between 2014 and 2016.
Three treatment types were evaluated: surgery (bilateral vs. unilateral mastectomy), radiotherapy after lumpectomy, and chemotherapy. Treatment selection was compared with test results for breast cancer–associated genes, such as BRCA1/2, TP53, PTEN, and others. Associations were then compared with guideline recommendations.
Data analysis suggested that many clinicians were correctly using genetic test results to guide surgical decisions. For example, almost two-thirds (61.7%) of women with a BRCA mutation underwent bilateral mastectomy, compared with one-quarter (24.3%) who were BRCA negative (odds ratio, 5.52). For other pathogenic variants, the rate of bilateral mastectomy was still elevated, albeit to a lesser degree (OR, 2.41).
Generally, these practices align with recommendations, the investigators wrote, noting that research supports bilateral mastectomy with BRCA1/2, TP53, and PTEN variants, while data are lacking for other genetic subtypes.
Radiotherapy and chemotherapy practices were more discordant with guidelines. For example, women with a BRCA mutation were 78% less likely to receive radiotherapy after lumpectomy (OR, 0.22) and 76% more likely to receive chemotherapy for early-stage, hormone-positive disease (OR, 1.76). According to investigators, these findings suggest possible trends in undertreatment and overtreatment, respectively.
“We believe more research is needed to confirm our results and to evaluate long-term outcomes of pathogenic variant carriers to understand treatment decision making and consequences,” the investigators concluded.
The study was funded by the National Institutes of Health and the California Department of Public Health. The investigators reported relationships with Myriad Genetics, Genomic Health, Roche, and other companies.
SOURCE: Kurian AW et al. JAMA Oncol. 2020 Feb 6. doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2019.6400.
Women with breast cancer may be receiving treatments that are discordant with guideline recommendations for genetic subtypes of disease, based on a retrospective analysis of more than 20,000 patients.
Radiotherapy and chemotherapy practices were particularly out of alignment with guidelines, reported lead author Allison W. Kurian, MD, of Stanford (Calif.) University, and colleagues.
“Integrating genetic testing into breast cancer care has been complex and challenging,” the investigators wrote in JAMA Oncology. “There is wide variability in which clinicians order testing and disclose results, in the clinical significance of results, and in how clinicians interpret results to patients.”
According to the investigators, while germline testing is on the rise, little is known about how these test results are translating to clinical care.
To learn more, the investigators evaluated data from 20,568 women with stage 0-III breast cancer who entered the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results registries of Georgia and California between 2014 and 2016.
Three treatment types were evaluated: surgery (bilateral vs. unilateral mastectomy), radiotherapy after lumpectomy, and chemotherapy. Treatment selection was compared with test results for breast cancer–associated genes, such as BRCA1/2, TP53, PTEN, and others. Associations were then compared with guideline recommendations.
Data analysis suggested that many clinicians were correctly using genetic test results to guide surgical decisions. For example, almost two-thirds (61.7%) of women with a BRCA mutation underwent bilateral mastectomy, compared with one-quarter (24.3%) who were BRCA negative (odds ratio, 5.52). For other pathogenic variants, the rate of bilateral mastectomy was still elevated, albeit to a lesser degree (OR, 2.41).
Generally, these practices align with recommendations, the investigators wrote, noting that research supports bilateral mastectomy with BRCA1/2, TP53, and PTEN variants, while data are lacking for other genetic subtypes.
Radiotherapy and chemotherapy practices were more discordant with guidelines. For example, women with a BRCA mutation were 78% less likely to receive radiotherapy after lumpectomy (OR, 0.22) and 76% more likely to receive chemotherapy for early-stage, hormone-positive disease (OR, 1.76). According to investigators, these findings suggest possible trends in undertreatment and overtreatment, respectively.
“We believe more research is needed to confirm our results and to evaluate long-term outcomes of pathogenic variant carriers to understand treatment decision making and consequences,” the investigators concluded.
The study was funded by the National Institutes of Health and the California Department of Public Health. The investigators reported relationships with Myriad Genetics, Genomic Health, Roche, and other companies.
SOURCE: Kurian AW et al. JAMA Oncol. 2020 Feb 6. doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2019.6400.
FROM JAMA ONCOLOGY
Palliative care improves QoL for patients with Parkinson’s disease and related disorders
, according to results from a randomized clinical trial in JAMA Neurology.
The benefits of palliative care even extended to patients’ caregivers, who also appeared to benefit from outpatient palliative care at the 12-month mark, according to lead author Benzi M. Kluger, MD, of the department of neurology, University of Colorado at Denver, Aurora, and colleagues.
Between November 2015 and September 2017, Dr. Kluger and colleagues included 210 patients into the trial from three participating academic tertiary care centers who had “moderate to high palliative care needs” as assessed by the Palliative Care Needs Assessment Tool, which the researchers said are “common reasons for referral” and “reflect a desire to meet patient-centered needs rather than disease-centered markers.” Patients were primarily non-Hispanic white men with a mean age of about 70 years. The researchers also included 175 caregivers in the trial, most of whom were women, spouses to the patients, and in their caregiver role for over 5.5 years.
Patients with PDRD were randomized to receive standard care – usual care through their primary care physician and a neurologist – or “integrated outpatient palliative care,” from a team consisting of a palliative neurologist, nurse, social worker, chaplain, and board-certified palliative medicine physician. The goal of palliative care was addressing “nonmotor symptoms, goals of care, anticipatory guidance, difficult emotions, and caregiver support,” which patients received every 3 months through an in-person outpatient visit or telemedicine.
Quality of life for patients was measured through the Quality of Life in Alzheimer’s Disease (QoL-AD) scale, and caregiver burden was assessed with the Zarit Burden Interview (ZBI-12). The researchers also measured symptom burden and other QoL measures using the Edmonton Symptom Assessment Scale–Revised for Parkinson’s Disease, Parkinson’s Disease Questionnaire, Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale, Prolonged Grief Disorder questionnaire, and Functional Assessment of Chronic Illness Therapy–Spiritual Well-Being.
Overall, 87 of 105 (82.1%) of patients in the palliative care group went to all their outpatient palliative care visits, and 19 of 106 (17.9%) patients received palliative care through telemedicine. Patients in the palliative care group also attended more neurology visits (4.66 visits) than those in the standard care (3.16 visits) group.
Quality of life significantly improved for patients in the palliative care group, compared with patients receiving standard care only at 6 months (0.66 vs. –0.84; between-group difference, 1.87; 95% confidence interval, 0.47-3.27; P = .009) and at 12 months (0.68 vs. –0.42; between-group difference, 1.36; 95% CI, −0.01 to 2.73; P = .05). These results remained significant at 6 months and 12 months after researchers used multiple imputation to fill in missing data. While there was no significant difference in caregiver burden between groups at 6 months, there was a statistically significant difference at 12 months favoring the palliative care group (between-group difference, −2.60; 95% CI, −4.58 to −0.61; P = .01).
Patients receiving palliative care also had better nonmotor symptom burden, motor symptom severity, and were more likely to complete advance directives, compared with patients receiving standard care alone. “We hypothesize that motor improvements may have reflected an unanticipated benefit of our palliative care team’s general goal of encouraging activities that promoted joy, meaning, and connection,” Dr. Kluger and colleagues said. Researchers also noted that the intervention patients with greater need for palliative care tended to benefit more than patients with patients with lower palliative care needs.
“Because the palliative care intervention is time-intensive and resource-intensive, future studies should optimize triage tools and consider alternative models of care delivery, such as telemedicine or care navigators, to provide key aspects of the intervention at lower cost,” they said.
In a related editorial, Bastiaan R. Bloem, MD, PhD, from the Center of Expertise for Parkinson & Movement Disorders, at Radboud University Medical Center, in the Netherlands, and colleagues acknowledged that the study by Kluger et al. is “timely and practical” because it introduces a system for outpatient palliative care for patients with PDRD at a time when there is “growing awareness that palliative care may also benefit persons with neurodegenerative diseases like Parkinson’s disease.”
The study is also important because it highlights that patients at varying stages of disease, including mild disease, may benefit from an integrated outpatient palliative model, which is not usually considered when determining candidates for palliative care in other scenarios, such as in patients with cancer. Future studies are warranted to assess how palliative care models can be implemented in different disease states and health care settings, they said.
“These new studies should continue to highlight the fact that palliative care is not about terminal diseases and dying,” Dr. Bloem and colleagues concluded. “As Kluger and colleagues indicate in their important clinical trial, palliative care is about how to live well.”
Six authors reported receiving a grant from the Patient-Centered Outcomes Research Institute, which was the funding source for the study. Two authors reported receiving grants from the University Hospital Foundation during the study. One author reported receiving grants from Allergan and Merz Pharma and is a consultant for GE Pharmaceuticals and Sunovion Pharmaceuticals; another reported receiving grants from the Archstone Foundation, the California Health Care Foundation, the Cambia Health Foundation, the Gordon and Betty Moore Foundation, the National Institute of Nursing Research, the Stupski Foundation, and the UniHealth Foundation. Dr. Bloem and a colleague reported their institution received a center of excellence grant from the Parkinson’s Foundation.
SOURCE: Kluger B et al. JAMA Neurol. doi: 10.1001/jamaneurol.2019.4992.
, according to results from a randomized clinical trial in JAMA Neurology.
The benefits of palliative care even extended to patients’ caregivers, who also appeared to benefit from outpatient palliative care at the 12-month mark, according to lead author Benzi M. Kluger, MD, of the department of neurology, University of Colorado at Denver, Aurora, and colleagues.
Between November 2015 and September 2017, Dr. Kluger and colleagues included 210 patients into the trial from three participating academic tertiary care centers who had “moderate to high palliative care needs” as assessed by the Palliative Care Needs Assessment Tool, which the researchers said are “common reasons for referral” and “reflect a desire to meet patient-centered needs rather than disease-centered markers.” Patients were primarily non-Hispanic white men with a mean age of about 70 years. The researchers also included 175 caregivers in the trial, most of whom were women, spouses to the patients, and in their caregiver role for over 5.5 years.
Patients with PDRD were randomized to receive standard care – usual care through their primary care physician and a neurologist – or “integrated outpatient palliative care,” from a team consisting of a palliative neurologist, nurse, social worker, chaplain, and board-certified palliative medicine physician. The goal of palliative care was addressing “nonmotor symptoms, goals of care, anticipatory guidance, difficult emotions, and caregiver support,” which patients received every 3 months through an in-person outpatient visit or telemedicine.
Quality of life for patients was measured through the Quality of Life in Alzheimer’s Disease (QoL-AD) scale, and caregiver burden was assessed with the Zarit Burden Interview (ZBI-12). The researchers also measured symptom burden and other QoL measures using the Edmonton Symptom Assessment Scale–Revised for Parkinson’s Disease, Parkinson’s Disease Questionnaire, Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale, Prolonged Grief Disorder questionnaire, and Functional Assessment of Chronic Illness Therapy–Spiritual Well-Being.
Overall, 87 of 105 (82.1%) of patients in the palliative care group went to all their outpatient palliative care visits, and 19 of 106 (17.9%) patients received palliative care through telemedicine. Patients in the palliative care group also attended more neurology visits (4.66 visits) than those in the standard care (3.16 visits) group.
Quality of life significantly improved for patients in the palliative care group, compared with patients receiving standard care only at 6 months (0.66 vs. –0.84; between-group difference, 1.87; 95% confidence interval, 0.47-3.27; P = .009) and at 12 months (0.68 vs. –0.42; between-group difference, 1.36; 95% CI, −0.01 to 2.73; P = .05). These results remained significant at 6 months and 12 months after researchers used multiple imputation to fill in missing data. While there was no significant difference in caregiver burden between groups at 6 months, there was a statistically significant difference at 12 months favoring the palliative care group (between-group difference, −2.60; 95% CI, −4.58 to −0.61; P = .01).
Patients receiving palliative care also had better nonmotor symptom burden, motor symptom severity, and were more likely to complete advance directives, compared with patients receiving standard care alone. “We hypothesize that motor improvements may have reflected an unanticipated benefit of our palliative care team’s general goal of encouraging activities that promoted joy, meaning, and connection,” Dr. Kluger and colleagues said. Researchers also noted that the intervention patients with greater need for palliative care tended to benefit more than patients with patients with lower palliative care needs.
“Because the palliative care intervention is time-intensive and resource-intensive, future studies should optimize triage tools and consider alternative models of care delivery, such as telemedicine or care navigators, to provide key aspects of the intervention at lower cost,” they said.
In a related editorial, Bastiaan R. Bloem, MD, PhD, from the Center of Expertise for Parkinson & Movement Disorders, at Radboud University Medical Center, in the Netherlands, and colleagues acknowledged that the study by Kluger et al. is “timely and practical” because it introduces a system for outpatient palliative care for patients with PDRD at a time when there is “growing awareness that palliative care may also benefit persons with neurodegenerative diseases like Parkinson’s disease.”
The study is also important because it highlights that patients at varying stages of disease, including mild disease, may benefit from an integrated outpatient palliative model, which is not usually considered when determining candidates for palliative care in other scenarios, such as in patients with cancer. Future studies are warranted to assess how palliative care models can be implemented in different disease states and health care settings, they said.
“These new studies should continue to highlight the fact that palliative care is not about terminal diseases and dying,” Dr. Bloem and colleagues concluded. “As Kluger and colleagues indicate in their important clinical trial, palliative care is about how to live well.”
Six authors reported receiving a grant from the Patient-Centered Outcomes Research Institute, which was the funding source for the study. Two authors reported receiving grants from the University Hospital Foundation during the study. One author reported receiving grants from Allergan and Merz Pharma and is a consultant for GE Pharmaceuticals and Sunovion Pharmaceuticals; another reported receiving grants from the Archstone Foundation, the California Health Care Foundation, the Cambia Health Foundation, the Gordon and Betty Moore Foundation, the National Institute of Nursing Research, the Stupski Foundation, and the UniHealth Foundation. Dr. Bloem and a colleague reported their institution received a center of excellence grant from the Parkinson’s Foundation.
SOURCE: Kluger B et al. JAMA Neurol. doi: 10.1001/jamaneurol.2019.4992.
, according to results from a randomized clinical trial in JAMA Neurology.
The benefits of palliative care even extended to patients’ caregivers, who also appeared to benefit from outpatient palliative care at the 12-month mark, according to lead author Benzi M. Kluger, MD, of the department of neurology, University of Colorado at Denver, Aurora, and colleagues.
Between November 2015 and September 2017, Dr. Kluger and colleagues included 210 patients into the trial from three participating academic tertiary care centers who had “moderate to high palliative care needs” as assessed by the Palliative Care Needs Assessment Tool, which the researchers said are “common reasons for referral” and “reflect a desire to meet patient-centered needs rather than disease-centered markers.” Patients were primarily non-Hispanic white men with a mean age of about 70 years. The researchers also included 175 caregivers in the trial, most of whom were women, spouses to the patients, and in their caregiver role for over 5.5 years.
Patients with PDRD were randomized to receive standard care – usual care through their primary care physician and a neurologist – or “integrated outpatient palliative care,” from a team consisting of a palliative neurologist, nurse, social worker, chaplain, and board-certified palliative medicine physician. The goal of palliative care was addressing “nonmotor symptoms, goals of care, anticipatory guidance, difficult emotions, and caregiver support,” which patients received every 3 months through an in-person outpatient visit or telemedicine.
Quality of life for patients was measured through the Quality of Life in Alzheimer’s Disease (QoL-AD) scale, and caregiver burden was assessed with the Zarit Burden Interview (ZBI-12). The researchers also measured symptom burden and other QoL measures using the Edmonton Symptom Assessment Scale–Revised for Parkinson’s Disease, Parkinson’s Disease Questionnaire, Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale, Prolonged Grief Disorder questionnaire, and Functional Assessment of Chronic Illness Therapy–Spiritual Well-Being.
Overall, 87 of 105 (82.1%) of patients in the palliative care group went to all their outpatient palliative care visits, and 19 of 106 (17.9%) patients received palliative care through telemedicine. Patients in the palliative care group also attended more neurology visits (4.66 visits) than those in the standard care (3.16 visits) group.
Quality of life significantly improved for patients in the palliative care group, compared with patients receiving standard care only at 6 months (0.66 vs. –0.84; between-group difference, 1.87; 95% confidence interval, 0.47-3.27; P = .009) and at 12 months (0.68 vs. –0.42; between-group difference, 1.36; 95% CI, −0.01 to 2.73; P = .05). These results remained significant at 6 months and 12 months after researchers used multiple imputation to fill in missing data. While there was no significant difference in caregiver burden between groups at 6 months, there was a statistically significant difference at 12 months favoring the palliative care group (between-group difference, −2.60; 95% CI, −4.58 to −0.61; P = .01).
Patients receiving palliative care also had better nonmotor symptom burden, motor symptom severity, and were more likely to complete advance directives, compared with patients receiving standard care alone. “We hypothesize that motor improvements may have reflected an unanticipated benefit of our palliative care team’s general goal of encouraging activities that promoted joy, meaning, and connection,” Dr. Kluger and colleagues said. Researchers also noted that the intervention patients with greater need for palliative care tended to benefit more than patients with patients with lower palliative care needs.
“Because the palliative care intervention is time-intensive and resource-intensive, future studies should optimize triage tools and consider alternative models of care delivery, such as telemedicine or care navigators, to provide key aspects of the intervention at lower cost,” they said.
In a related editorial, Bastiaan R. Bloem, MD, PhD, from the Center of Expertise for Parkinson & Movement Disorders, at Radboud University Medical Center, in the Netherlands, and colleagues acknowledged that the study by Kluger et al. is “timely and practical” because it introduces a system for outpatient palliative care for patients with PDRD at a time when there is “growing awareness that palliative care may also benefit persons with neurodegenerative diseases like Parkinson’s disease.”
The study is also important because it highlights that patients at varying stages of disease, including mild disease, may benefit from an integrated outpatient palliative model, which is not usually considered when determining candidates for palliative care in other scenarios, such as in patients with cancer. Future studies are warranted to assess how palliative care models can be implemented in different disease states and health care settings, they said.
“These new studies should continue to highlight the fact that palliative care is not about terminal diseases and dying,” Dr. Bloem and colleagues concluded. “As Kluger and colleagues indicate in their important clinical trial, palliative care is about how to live well.”
Six authors reported receiving a grant from the Patient-Centered Outcomes Research Institute, which was the funding source for the study. Two authors reported receiving grants from the University Hospital Foundation during the study. One author reported receiving grants from Allergan and Merz Pharma and is a consultant for GE Pharmaceuticals and Sunovion Pharmaceuticals; another reported receiving grants from the Archstone Foundation, the California Health Care Foundation, the Cambia Health Foundation, the Gordon and Betty Moore Foundation, the National Institute of Nursing Research, the Stupski Foundation, and the UniHealth Foundation. Dr. Bloem and a colleague reported their institution received a center of excellence grant from the Parkinson’s Foundation.
SOURCE: Kluger B et al. JAMA Neurol. doi: 10.1001/jamaneurol.2019.4992.
FROM JAMA NEUROLOGY