User login
Get to Know NO: Deconstructing the Data on Nitric Oxide–Releasing Technologies for Acne
In addition to the standard fare at the 74th Annual Meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology (AAD) in Washington, DC (March 4–8, 2016), this year there were several lectures addressing the use of nitric oxide (NO) for the treatment of acne. Therefore, I would like to review how NO gets delivered and the therapeutic implications as well as provide some context and understanding of the varying NO delivery systems being investigated.
Let’s start with some basics: Why should we even consider NO, a diatomic lipophilic gaseous molecule, for acne? It may be a surprise, but you already use NO for this purpose.
- NO is produced on the surface of the skin by action of commensal bacteria and plays a physiologic role in inhibition of infection by pathogenic organisms including bacteria, fungi, and viruses, and a microbicidal role against Propionibacterium acnes.
- NO minimizes inflammation by inhibiting neutrophil chemotaxis; production of lipases by P acnes (minimizes production of immunogenic free fatty acids); production of multiple cytokines such as tumor necrosis factor α, IL-8, and IL-6; antigen-presenting cell recognition of P acnes; and multiple elements of the NLRP3 (NOD-like receptor family, pyrin domain containing 3) inflammasome, the specific inflammasome reported to be impressively activated when monocytes, and even sebocytes, are exposed to P acnes, thereby inhibiting the conversion of pro–IL-1β to IL-1β.
However, NO’s direct biological action is not enough to explain these effects. It is S-nitrosylation, the covalent modification of a protein cysteine thiol by a NO group to generate an S-nitrosothiol such as nitrosoglutathione, that explains NO’s potent modulation of gene expression and enzymatic functions.
Nitric oxide was first featured in the late-breaking research session presented by Lawrence F. Eichenfield, MD, at the AAD (Efficacy and Safety of SB204 Gel in the Treatment of Acne Vulgaris)(F053). Results were presented from a phase 2b, multicenter, randomized, double-blind study comparing the efficacy, safety, and tolerability of SB204 NO-releasing gel 4% to vehicle in participants with acne vulgaris. The investigators concluded that SB204 once daily was safe and effective for the treatment of acne vulgaris, though they did not present data on the technology itself.
The NO-releasing technology being used in SB204 is an NO donor that falls under a class of NO donors called the diazeniumdiolates, or NONOates, which have been used experimentally for more than 50 years. These compounds consist of a diolate group (N[O-]N=O) bound to a nucleophile adduct (a primary or secondary amine or polyamine) by means of a nitrogen atom. Thus, you have NO bound to a donor that under appropriate environmental conditions will release its NO following first-order kinetics. It simply releases NO, rather then generate or create it.
Two issues are to be raised in relation to Dr. Eichenfield’s presentation:
- The anti-inflammatory mechanism data cited in the study by Qin et al and discussed was not generated using the NONOate SB204.
Here is the most important point to be made: Not all NO-releasing platforms are created equal. The technology used to demonstrate the anti-inflammatory impact of NO, specifically inhibition of IL-1β through the NLRP3 inflammasome, was a different platform than SB204, and one I developed at the Albert Einstein College of Medicine (Bronx, New York) and is currently under development. This NO generator, as opposed to donor, has been shown to uniquely facilitate the formation of NO from nitrite salt through a stable and potent NO intermediate N2O3 (designated NO-np).
N2O3 can effectively facilitate trans-nitrosylation under both aerobic and anaerobic conditions, a feat my research group has found that NONOates cannot accomplish. It is both NO and its effect when placed on cellular thiols that together generate its biological impact. Therefore, it cannot be assumed that efficacy data produced from the use of NO-np would result from using any NONOate.
- A highlight of this presentation was safety. First, a reality check: When do we ever use a topical agent for only 12 weeks, as in the study discussed by Dr. Eichenfield? In fact, given the mechanism by which NO exerts its anti-inflammatory activity, the efficacy will be short-lived and require continued use.
Accumulation of amines and their metabolites released from NONOates have been shown to induce cytotoxicity in a study by Saavedra et al (J Med Chem. 1997;40:1947-1954). In the study by Blecher et al (Nanomedicine. 2012;8:1364-1371), topical application of DETA (diethylenetriamine) NONOate, another type of NONOate, actually delayed wound closure in NOD-SCID (nonobese diabetic severe combined immunodeficiency) mice as compared to untreated controls in a study by Blecher et al. Systemic infusion at concentrations required to reduce blood pressure resulted in methemoglobinemia and diminished oxygen-carrying capacity in a study by Cabrales et al (Free Radic Biol Med. 2010;49:530-538). The NONOate utilized in SB204 is encapsulated in a hydrogel particle to prevent permeation of said metabolites and donor compounds through the skin; however, a 12-week safety evaluation is certainly not long enough to determine whether local or systemic absorption has occurred. Of note, the NO-np has undergone extensive safety testing from cell culture of embryonic zebra fish to Syrian hamsters and even pigs showing no significant toxicity at any of the effective concentrations in animal studies.
Data published on the NO-np’s preclinical efficacy for the treatment of acne, infected excisions, and burn wounds were presented in 2 of my lectures at the AAD (Nanotechnology and Immunomodulators [F085] and Antimicrobial Dressings: Silver and Beyond [S056])(Chouake et al [J Drugs Dermatol. 2012;11:1471-1477]; Friedman et al [Virulence. 2011;2:217-221]; Han et al [PLoS One. 2009;4:e7804]; Marcherla et al [Front Microbiol. 2012;3:193]; Martinez et al [J Invest Dermatol. 2009;129:2463-2469]; Qin et al [J Invest Dermatol. 2015;135:2723-2731]; Blecher et al [Nanomedicine. 2012;8:1364-1371]). These data can be found within the suggested reading below.
What’s the issue?
Know the awesome biological power of NO. Know the differences between delivery systems, including donors and generators. Know the differences in therapeutic relevance, including efficacy and safety.
Do you know NO?
We want to know your views! Tell us what you think.
Suggested Readings
Multidrug-Resistant Bacterial and Fungal Skin and Soft Tissue Infections
- Ahmadi M, Lee H, Sanchez D, et al. Sustained nitric oxide releasing nanoparticles induce cell death in Candida albicans yeast and hyphal cells preventing biofilm formation in vitro and in a rodent central venous catheter model. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2016;60:2185-2194.
- Chouake J, Schairer D, Kutner A, et al. Nitrosoglutathione generating nitric oxide nanoparticles as an improved strategy for combating Pseudomonas aeruginosa–infected wounds. J Drugs Dermatol. 2012;11:1471-1477.
- Friedman A, Blecher K, Sanchez D, et al. Susceptibility of gram positive and negative bacteria to novel nitric oxide-releasing nanoparticle technology. Virulence. 2011;2:217-221.
- Friedman A, Blecher K, Schairer D, et al. Improved antimicrobial efficacy with nitric oxide releasing nanoparticle generated S-nitrosoglutathione. Nitric Oxide. 2011;25:381-386.
- Han G, Martinez LM, Mihu MR, et al. Nitric oxide releasing nanoparticles are therapeutic for Staphylococcus aureus abscesses in murine model of infection. PLoS One. 2009;4:e7804.
- Landriscina A, Rosen J, Blecher-Paz K, et al. Nitric oxide-releasing nanoparticles as a treatment for cutaneous dermatophyte infections. Sci Lett. 2015,4:193.
- Marcherla C, Sanchez DA, Ahmadi M, et al. Nitric oxide releasing nanoparticles for the treatment of Candida albicans burn infections [published online June 8, 2012]. Front Microbiol. 2012;3:193.
- Martinez L, Han G, Chacko M, et al. Antimicrobial and healing efficacy of sustained release nitric oxide nanoparticles against Staphylococcus aureus skin infections. J Invest Dermatol. 2009;129:2463-2469.
- Mihu MR, Sandkovsky U, Han G, et al. The use of nitric oxide releasing nanoparticles as a treatment against Acinetobacter baumannii in wound infections. Virulence. 2010;1:62-67.
- Mordorski B, Pelgrift R, Adler B, et al. S-nitrosocaptopril nanoparticles as nitric oxide-liberating and transnitrosylating anti-infective technology. Nanomedicine. 2015;11:283-291.
- Qin M, Landriscina A, Rosen JM, et al. Nitric oxide-releasing nanoparticles prevent Propionibacterium acnes-induced inflammation by both clearing the organism and inhibiting microbial stimulation of the innate immune response. J Invest Dermatol. 2015;135:2723-2731.
- Schairer D, Martinez L, Blecher K, et al. Nitric oxide nanoparticles: pre-clinical utility as a therapeutic for intramuscular abscesses. Virulence. 2012;3:1-6.
Wound Healing
- Blecher K, Martinez LR, Tuckman-Vernon C, et al. Nitric oxide-releasing nanoparticles accelerate wound healing in NOD-SCID mice. Nanomedicine. 2012;8:1364-1371.
- Han G, Nguyen LN, Macherla C, et al. Nitric oxide-releasing nanoparticles accelerate wound healing by promoting fibroblast migration and collagen deposition. Am J Pathol. 2012;180:1465-1473.
Erectile Dysfunction
- Han G, Tar M, Kuppam DS, et al. Nanoparticles as a novel delivery vehicle for therapeutics targeting erectile dysfunction [published online September 18, 2009. J Sex Med. 2010;7(1 pt 1):224-333.
- Tar M, CabralesP, Navati M, et al. Topically applied NO-releasing nanoparticles can increase intracorporal pressure and elicit spontaneous erections in a rat model of radical prostatectomy. J Sex Med. 2014;11:2903-2914.
Cardiovascular Disease
- Cabrales P, Han G, Nacharaju P, et al. Reversal of hemoglobin-induced vasoconstriction with sustained release of nitric oxide [published online November 5, 2010]. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2011;300:H49-H56.
- Cabrales P, Han G, Roche C, et al. Sustained release nitric oxide from long-lived circulation nanoparticles. Free Radic Biol Med. 2010;49:530-538.
- Nacharaju P, Friedman AJ, Friedman JM, et al. Exogenous nitric oxide prevents collapse during hemorrhagic shock. Resuscitation. 2011;82:607-613.
Safety of NO Donors
- Friedman A, Friedman JM. Novel biomaterials for the sustained release of nitric oxide: past, present, and future. Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2009;6:1113-1122.
- Liang H, Nacharaju P, Friedman A, et al. Nitric oxide generating/releasing materials. Future Sci OA. 2015;1. doi:10.4155/fso.15.54.
- Saavedra JE, Billiar TR, Williams DL, et al. Targeting nitric oxide (NO) delivery in vivo. design of a liver-selective NO donor prodrug that blocks tumor necrosis factor-alpha-induced apoptosis and toxicity in the liver. J Med Chem. 1997;40:1947-1954.
In addition to the standard fare at the 74th Annual Meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology (AAD) in Washington, DC (March 4–8, 2016), this year there were several lectures addressing the use of nitric oxide (NO) for the treatment of acne. Therefore, I would like to review how NO gets delivered and the therapeutic implications as well as provide some context and understanding of the varying NO delivery systems being investigated.
Let’s start with some basics: Why should we even consider NO, a diatomic lipophilic gaseous molecule, for acne? It may be a surprise, but you already use NO for this purpose.
- NO is produced on the surface of the skin by action of commensal bacteria and plays a physiologic role in inhibition of infection by pathogenic organisms including bacteria, fungi, and viruses, and a microbicidal role against Propionibacterium acnes.
- NO minimizes inflammation by inhibiting neutrophil chemotaxis; production of lipases by P acnes (minimizes production of immunogenic free fatty acids); production of multiple cytokines such as tumor necrosis factor α, IL-8, and IL-6; antigen-presenting cell recognition of P acnes; and multiple elements of the NLRP3 (NOD-like receptor family, pyrin domain containing 3) inflammasome, the specific inflammasome reported to be impressively activated when monocytes, and even sebocytes, are exposed to P acnes, thereby inhibiting the conversion of pro–IL-1β to IL-1β.
However, NO’s direct biological action is not enough to explain these effects. It is S-nitrosylation, the covalent modification of a protein cysteine thiol by a NO group to generate an S-nitrosothiol such as nitrosoglutathione, that explains NO’s potent modulation of gene expression and enzymatic functions.
Nitric oxide was first featured in the late-breaking research session presented by Lawrence F. Eichenfield, MD, at the AAD (Efficacy and Safety of SB204 Gel in the Treatment of Acne Vulgaris)(F053). Results were presented from a phase 2b, multicenter, randomized, double-blind study comparing the efficacy, safety, and tolerability of SB204 NO-releasing gel 4% to vehicle in participants with acne vulgaris. The investigators concluded that SB204 once daily was safe and effective for the treatment of acne vulgaris, though they did not present data on the technology itself.
The NO-releasing technology being used in SB204 is an NO donor that falls under a class of NO donors called the diazeniumdiolates, or NONOates, which have been used experimentally for more than 50 years. These compounds consist of a diolate group (N[O-]N=O) bound to a nucleophile adduct (a primary or secondary amine or polyamine) by means of a nitrogen atom. Thus, you have NO bound to a donor that under appropriate environmental conditions will release its NO following first-order kinetics. It simply releases NO, rather then generate or create it.
Two issues are to be raised in relation to Dr. Eichenfield’s presentation:
- The anti-inflammatory mechanism data cited in the study by Qin et al and discussed was not generated using the NONOate SB204.
Here is the most important point to be made: Not all NO-releasing platforms are created equal. The technology used to demonstrate the anti-inflammatory impact of NO, specifically inhibition of IL-1β through the NLRP3 inflammasome, was a different platform than SB204, and one I developed at the Albert Einstein College of Medicine (Bronx, New York) and is currently under development. This NO generator, as opposed to donor, has been shown to uniquely facilitate the formation of NO from nitrite salt through a stable and potent NO intermediate N2O3 (designated NO-np).
N2O3 can effectively facilitate trans-nitrosylation under both aerobic and anaerobic conditions, a feat my research group has found that NONOates cannot accomplish. It is both NO and its effect when placed on cellular thiols that together generate its biological impact. Therefore, it cannot be assumed that efficacy data produced from the use of NO-np would result from using any NONOate.
- A highlight of this presentation was safety. First, a reality check: When do we ever use a topical agent for only 12 weeks, as in the study discussed by Dr. Eichenfield? In fact, given the mechanism by which NO exerts its anti-inflammatory activity, the efficacy will be short-lived and require continued use.
Accumulation of amines and their metabolites released from NONOates have been shown to induce cytotoxicity in a study by Saavedra et al (J Med Chem. 1997;40:1947-1954). In the study by Blecher et al (Nanomedicine. 2012;8:1364-1371), topical application of DETA (diethylenetriamine) NONOate, another type of NONOate, actually delayed wound closure in NOD-SCID (nonobese diabetic severe combined immunodeficiency) mice as compared to untreated controls in a study by Blecher et al. Systemic infusion at concentrations required to reduce blood pressure resulted in methemoglobinemia and diminished oxygen-carrying capacity in a study by Cabrales et al (Free Radic Biol Med. 2010;49:530-538). The NONOate utilized in SB204 is encapsulated in a hydrogel particle to prevent permeation of said metabolites and donor compounds through the skin; however, a 12-week safety evaluation is certainly not long enough to determine whether local or systemic absorption has occurred. Of note, the NO-np has undergone extensive safety testing from cell culture of embryonic zebra fish to Syrian hamsters and even pigs showing no significant toxicity at any of the effective concentrations in animal studies.
Data published on the NO-np’s preclinical efficacy for the treatment of acne, infected excisions, and burn wounds were presented in 2 of my lectures at the AAD (Nanotechnology and Immunomodulators [F085] and Antimicrobial Dressings: Silver and Beyond [S056])(Chouake et al [J Drugs Dermatol. 2012;11:1471-1477]; Friedman et al [Virulence. 2011;2:217-221]; Han et al [PLoS One. 2009;4:e7804]; Marcherla et al [Front Microbiol. 2012;3:193]; Martinez et al [J Invest Dermatol. 2009;129:2463-2469]; Qin et al [J Invest Dermatol. 2015;135:2723-2731]; Blecher et al [Nanomedicine. 2012;8:1364-1371]). These data can be found within the suggested reading below.
What’s the issue?
Know the awesome biological power of NO. Know the differences between delivery systems, including donors and generators. Know the differences in therapeutic relevance, including efficacy and safety.
Do you know NO?
We want to know your views! Tell us what you think.
Suggested Readings
Multidrug-Resistant Bacterial and Fungal Skin and Soft Tissue Infections
- Ahmadi M, Lee H, Sanchez D, et al. Sustained nitric oxide releasing nanoparticles induce cell death in Candida albicans yeast and hyphal cells preventing biofilm formation in vitro and in a rodent central venous catheter model. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2016;60:2185-2194.
- Chouake J, Schairer D, Kutner A, et al. Nitrosoglutathione generating nitric oxide nanoparticles as an improved strategy for combating Pseudomonas aeruginosa–infected wounds. J Drugs Dermatol. 2012;11:1471-1477.
- Friedman A, Blecher K, Sanchez D, et al. Susceptibility of gram positive and negative bacteria to novel nitric oxide-releasing nanoparticle technology. Virulence. 2011;2:217-221.
- Friedman A, Blecher K, Schairer D, et al. Improved antimicrobial efficacy with nitric oxide releasing nanoparticle generated S-nitrosoglutathione. Nitric Oxide. 2011;25:381-386.
- Han G, Martinez LM, Mihu MR, et al. Nitric oxide releasing nanoparticles are therapeutic for Staphylococcus aureus abscesses in murine model of infection. PLoS One. 2009;4:e7804.
- Landriscina A, Rosen J, Blecher-Paz K, et al. Nitric oxide-releasing nanoparticles as a treatment for cutaneous dermatophyte infections. Sci Lett. 2015,4:193.
- Marcherla C, Sanchez DA, Ahmadi M, et al. Nitric oxide releasing nanoparticles for the treatment of Candida albicans burn infections [published online June 8, 2012]. Front Microbiol. 2012;3:193.
- Martinez L, Han G, Chacko M, et al. Antimicrobial and healing efficacy of sustained release nitric oxide nanoparticles against Staphylococcus aureus skin infections. J Invest Dermatol. 2009;129:2463-2469.
- Mihu MR, Sandkovsky U, Han G, et al. The use of nitric oxide releasing nanoparticles as a treatment against Acinetobacter baumannii in wound infections. Virulence. 2010;1:62-67.
- Mordorski B, Pelgrift R, Adler B, et al. S-nitrosocaptopril nanoparticles as nitric oxide-liberating and transnitrosylating anti-infective technology. Nanomedicine. 2015;11:283-291.
- Qin M, Landriscina A, Rosen JM, et al. Nitric oxide-releasing nanoparticles prevent Propionibacterium acnes-induced inflammation by both clearing the organism and inhibiting microbial stimulation of the innate immune response. J Invest Dermatol. 2015;135:2723-2731.
- Schairer D, Martinez L, Blecher K, et al. Nitric oxide nanoparticles: pre-clinical utility as a therapeutic for intramuscular abscesses. Virulence. 2012;3:1-6.
Wound Healing
- Blecher K, Martinez LR, Tuckman-Vernon C, et al. Nitric oxide-releasing nanoparticles accelerate wound healing in NOD-SCID mice. Nanomedicine. 2012;8:1364-1371.
- Han G, Nguyen LN, Macherla C, et al. Nitric oxide-releasing nanoparticles accelerate wound healing by promoting fibroblast migration and collagen deposition. Am J Pathol. 2012;180:1465-1473.
Erectile Dysfunction
- Han G, Tar M, Kuppam DS, et al. Nanoparticles as a novel delivery vehicle for therapeutics targeting erectile dysfunction [published online September 18, 2009. J Sex Med. 2010;7(1 pt 1):224-333.
- Tar M, CabralesP, Navati M, et al. Topically applied NO-releasing nanoparticles can increase intracorporal pressure and elicit spontaneous erections in a rat model of radical prostatectomy. J Sex Med. 2014;11:2903-2914.
Cardiovascular Disease
- Cabrales P, Han G, Nacharaju P, et al. Reversal of hemoglobin-induced vasoconstriction with sustained release of nitric oxide [published online November 5, 2010]. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2011;300:H49-H56.
- Cabrales P, Han G, Roche C, et al. Sustained release nitric oxide from long-lived circulation nanoparticles. Free Radic Biol Med. 2010;49:530-538.
- Nacharaju P, Friedman AJ, Friedman JM, et al. Exogenous nitric oxide prevents collapse during hemorrhagic shock. Resuscitation. 2011;82:607-613.
Safety of NO Donors
- Friedman A, Friedman JM. Novel biomaterials for the sustained release of nitric oxide: past, present, and future. Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2009;6:1113-1122.
- Liang H, Nacharaju P, Friedman A, et al. Nitric oxide generating/releasing materials. Future Sci OA. 2015;1. doi:10.4155/fso.15.54.
- Saavedra JE, Billiar TR, Williams DL, et al. Targeting nitric oxide (NO) delivery in vivo. design of a liver-selective NO donor prodrug that blocks tumor necrosis factor-alpha-induced apoptosis and toxicity in the liver. J Med Chem. 1997;40:1947-1954.
In addition to the standard fare at the 74th Annual Meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology (AAD) in Washington, DC (March 4–8, 2016), this year there were several lectures addressing the use of nitric oxide (NO) for the treatment of acne. Therefore, I would like to review how NO gets delivered and the therapeutic implications as well as provide some context and understanding of the varying NO delivery systems being investigated.
Let’s start with some basics: Why should we even consider NO, a diatomic lipophilic gaseous molecule, for acne? It may be a surprise, but you already use NO for this purpose.
- NO is produced on the surface of the skin by action of commensal bacteria and plays a physiologic role in inhibition of infection by pathogenic organisms including bacteria, fungi, and viruses, and a microbicidal role against Propionibacterium acnes.
- NO minimizes inflammation by inhibiting neutrophil chemotaxis; production of lipases by P acnes (minimizes production of immunogenic free fatty acids); production of multiple cytokines such as tumor necrosis factor α, IL-8, and IL-6; antigen-presenting cell recognition of P acnes; and multiple elements of the NLRP3 (NOD-like receptor family, pyrin domain containing 3) inflammasome, the specific inflammasome reported to be impressively activated when monocytes, and even sebocytes, are exposed to P acnes, thereby inhibiting the conversion of pro–IL-1β to IL-1β.
However, NO’s direct biological action is not enough to explain these effects. It is S-nitrosylation, the covalent modification of a protein cysteine thiol by a NO group to generate an S-nitrosothiol such as nitrosoglutathione, that explains NO’s potent modulation of gene expression and enzymatic functions.
Nitric oxide was first featured in the late-breaking research session presented by Lawrence F. Eichenfield, MD, at the AAD (Efficacy and Safety of SB204 Gel in the Treatment of Acne Vulgaris)(F053). Results were presented from a phase 2b, multicenter, randomized, double-blind study comparing the efficacy, safety, and tolerability of SB204 NO-releasing gel 4% to vehicle in participants with acne vulgaris. The investigators concluded that SB204 once daily was safe and effective for the treatment of acne vulgaris, though they did not present data on the technology itself.
The NO-releasing technology being used in SB204 is an NO donor that falls under a class of NO donors called the diazeniumdiolates, or NONOates, which have been used experimentally for more than 50 years. These compounds consist of a diolate group (N[O-]N=O) bound to a nucleophile adduct (a primary or secondary amine or polyamine) by means of a nitrogen atom. Thus, you have NO bound to a donor that under appropriate environmental conditions will release its NO following first-order kinetics. It simply releases NO, rather then generate or create it.
Two issues are to be raised in relation to Dr. Eichenfield’s presentation:
- The anti-inflammatory mechanism data cited in the study by Qin et al and discussed was not generated using the NONOate SB204.
Here is the most important point to be made: Not all NO-releasing platforms are created equal. The technology used to demonstrate the anti-inflammatory impact of NO, specifically inhibition of IL-1β through the NLRP3 inflammasome, was a different platform than SB204, and one I developed at the Albert Einstein College of Medicine (Bronx, New York) and is currently under development. This NO generator, as opposed to donor, has been shown to uniquely facilitate the formation of NO from nitrite salt through a stable and potent NO intermediate N2O3 (designated NO-np).
N2O3 can effectively facilitate trans-nitrosylation under both aerobic and anaerobic conditions, a feat my research group has found that NONOates cannot accomplish. It is both NO and its effect when placed on cellular thiols that together generate its biological impact. Therefore, it cannot be assumed that efficacy data produced from the use of NO-np would result from using any NONOate.
- A highlight of this presentation was safety. First, a reality check: When do we ever use a topical agent for only 12 weeks, as in the study discussed by Dr. Eichenfield? In fact, given the mechanism by which NO exerts its anti-inflammatory activity, the efficacy will be short-lived and require continued use.
Accumulation of amines and their metabolites released from NONOates have been shown to induce cytotoxicity in a study by Saavedra et al (J Med Chem. 1997;40:1947-1954). In the study by Blecher et al (Nanomedicine. 2012;8:1364-1371), topical application of DETA (diethylenetriamine) NONOate, another type of NONOate, actually delayed wound closure in NOD-SCID (nonobese diabetic severe combined immunodeficiency) mice as compared to untreated controls in a study by Blecher et al. Systemic infusion at concentrations required to reduce blood pressure resulted in methemoglobinemia and diminished oxygen-carrying capacity in a study by Cabrales et al (Free Radic Biol Med. 2010;49:530-538). The NONOate utilized in SB204 is encapsulated in a hydrogel particle to prevent permeation of said metabolites and donor compounds through the skin; however, a 12-week safety evaluation is certainly not long enough to determine whether local or systemic absorption has occurred. Of note, the NO-np has undergone extensive safety testing from cell culture of embryonic zebra fish to Syrian hamsters and even pigs showing no significant toxicity at any of the effective concentrations in animal studies.
Data published on the NO-np’s preclinical efficacy for the treatment of acne, infected excisions, and burn wounds were presented in 2 of my lectures at the AAD (Nanotechnology and Immunomodulators [F085] and Antimicrobial Dressings: Silver and Beyond [S056])(Chouake et al [J Drugs Dermatol. 2012;11:1471-1477]; Friedman et al [Virulence. 2011;2:217-221]; Han et al [PLoS One. 2009;4:e7804]; Marcherla et al [Front Microbiol. 2012;3:193]; Martinez et al [J Invest Dermatol. 2009;129:2463-2469]; Qin et al [J Invest Dermatol. 2015;135:2723-2731]; Blecher et al [Nanomedicine. 2012;8:1364-1371]). These data can be found within the suggested reading below.
What’s the issue?
Know the awesome biological power of NO. Know the differences between delivery systems, including donors and generators. Know the differences in therapeutic relevance, including efficacy and safety.
Do you know NO?
We want to know your views! Tell us what you think.
Suggested Readings
Multidrug-Resistant Bacterial and Fungal Skin and Soft Tissue Infections
- Ahmadi M, Lee H, Sanchez D, et al. Sustained nitric oxide releasing nanoparticles induce cell death in Candida albicans yeast and hyphal cells preventing biofilm formation in vitro and in a rodent central venous catheter model. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2016;60:2185-2194.
- Chouake J, Schairer D, Kutner A, et al. Nitrosoglutathione generating nitric oxide nanoparticles as an improved strategy for combating Pseudomonas aeruginosa–infected wounds. J Drugs Dermatol. 2012;11:1471-1477.
- Friedman A, Blecher K, Sanchez D, et al. Susceptibility of gram positive and negative bacteria to novel nitric oxide-releasing nanoparticle technology. Virulence. 2011;2:217-221.
- Friedman A, Blecher K, Schairer D, et al. Improved antimicrobial efficacy with nitric oxide releasing nanoparticle generated S-nitrosoglutathione. Nitric Oxide. 2011;25:381-386.
- Han G, Martinez LM, Mihu MR, et al. Nitric oxide releasing nanoparticles are therapeutic for Staphylococcus aureus abscesses in murine model of infection. PLoS One. 2009;4:e7804.
- Landriscina A, Rosen J, Blecher-Paz K, et al. Nitric oxide-releasing nanoparticles as a treatment for cutaneous dermatophyte infections. Sci Lett. 2015,4:193.
- Marcherla C, Sanchez DA, Ahmadi M, et al. Nitric oxide releasing nanoparticles for the treatment of Candida albicans burn infections [published online June 8, 2012]. Front Microbiol. 2012;3:193.
- Martinez L, Han G, Chacko M, et al. Antimicrobial and healing efficacy of sustained release nitric oxide nanoparticles against Staphylococcus aureus skin infections. J Invest Dermatol. 2009;129:2463-2469.
- Mihu MR, Sandkovsky U, Han G, et al. The use of nitric oxide releasing nanoparticles as a treatment against Acinetobacter baumannii in wound infections. Virulence. 2010;1:62-67.
- Mordorski B, Pelgrift R, Adler B, et al. S-nitrosocaptopril nanoparticles as nitric oxide-liberating and transnitrosylating anti-infective technology. Nanomedicine. 2015;11:283-291.
- Qin M, Landriscina A, Rosen JM, et al. Nitric oxide-releasing nanoparticles prevent Propionibacterium acnes-induced inflammation by both clearing the organism and inhibiting microbial stimulation of the innate immune response. J Invest Dermatol. 2015;135:2723-2731.
- Schairer D, Martinez L, Blecher K, et al. Nitric oxide nanoparticles: pre-clinical utility as a therapeutic for intramuscular abscesses. Virulence. 2012;3:1-6.
Wound Healing
- Blecher K, Martinez LR, Tuckman-Vernon C, et al. Nitric oxide-releasing nanoparticles accelerate wound healing in NOD-SCID mice. Nanomedicine. 2012;8:1364-1371.
- Han G, Nguyen LN, Macherla C, et al. Nitric oxide-releasing nanoparticles accelerate wound healing by promoting fibroblast migration and collagen deposition. Am J Pathol. 2012;180:1465-1473.
Erectile Dysfunction
- Han G, Tar M, Kuppam DS, et al. Nanoparticles as a novel delivery vehicle for therapeutics targeting erectile dysfunction [published online September 18, 2009. J Sex Med. 2010;7(1 pt 1):224-333.
- Tar M, CabralesP, Navati M, et al. Topically applied NO-releasing nanoparticles can increase intracorporal pressure and elicit spontaneous erections in a rat model of radical prostatectomy. J Sex Med. 2014;11:2903-2914.
Cardiovascular Disease
- Cabrales P, Han G, Nacharaju P, et al. Reversal of hemoglobin-induced vasoconstriction with sustained release of nitric oxide [published online November 5, 2010]. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2011;300:H49-H56.
- Cabrales P, Han G, Roche C, et al. Sustained release nitric oxide from long-lived circulation nanoparticles. Free Radic Biol Med. 2010;49:530-538.
- Nacharaju P, Friedman AJ, Friedman JM, et al. Exogenous nitric oxide prevents collapse during hemorrhagic shock. Resuscitation. 2011;82:607-613.
Safety of NO Donors
- Friedman A, Friedman JM. Novel biomaterials for the sustained release of nitric oxide: past, present, and future. Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2009;6:1113-1122.
- Liang H, Nacharaju P, Friedman A, et al. Nitric oxide generating/releasing materials. Future Sci OA. 2015;1. doi:10.4155/fso.15.54.
- Saavedra JE, Billiar TR, Williams DL, et al. Targeting nitric oxide (NO) delivery in vivo. design of a liver-selective NO donor prodrug that blocks tumor necrosis factor-alpha-induced apoptosis and toxicity in the liver. J Med Chem. 1997;40:1947-1954.
Targeting gene rearrangements shows promise in early study
Entrectinib, an investigational drug that targets several abnormal fusion proteins, showed antitumor activity and was safe in patients with several different types of advanced solid tumors. The patients had never before been exposed to drugs targeting these same genetic alterations.
“Responses can be very rapid and durable … which include colorectal, primary brain tumor, astrocytoma, fibrosarcoma, lung, and mammary analog secretory carcinoma,” Dr. Alexander Drilon of Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center in New York said in a news conference at the annual meeting of the American Association for Cancer Research. “Dramatic intracranial activity … has been demonstrated both in primary brain tumor and also in metastatic.”
NTRK1/2/3, ROS1, and ALK gene–rearranged cancers produce fusion proteins that are ligand independent for their activity and thus constitutively active, driving tumor growth. Entrectinib is a pan-TRK, ROS1, ALK tyrosine kinase inhibitor that targets the abnormal fusion protein products of the genes, is highly potent at low concentrations, and has been designed to cross the blood-brain barrier (BBB). The targeted proteins are present across multiple cancers and are especially prevalent (greater than 80%) among some rare adult and pediatric cancers.
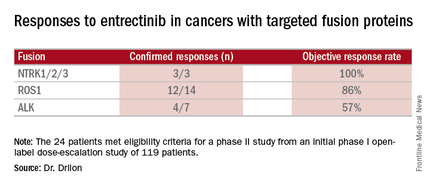
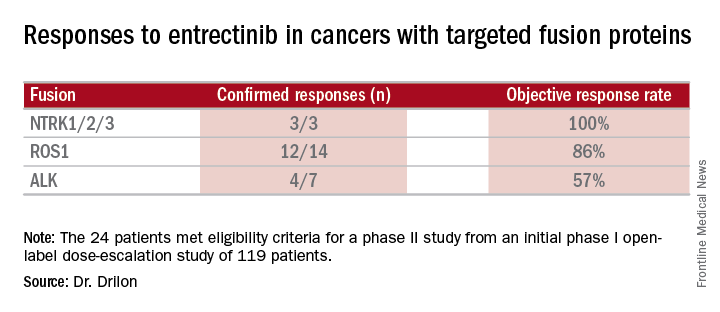
Combined data on 119 patients in two phase I trials established 600 mg orally once daily as the recommended dose to go into phase II trials. Among the 24 patients meeting eligibility criteria for a phase II trial (presence of the targeted gene fusions in their tumors, no prior treatment against these targets, and treatment at or above 600 mg daily), the confirmed response rate was 79% (19/24). Most were partial responses in terms of tumor shrinkage, but two patients had complete responses. Response rates appeared to vary according to the specific fusion protein defect.
All three cases of CNS disease with NTRK-rearranged cancers had intracranial responses, demonstrating that the drug crosses the BBB and is active. In one case, a 46-year-old man with brain metastases heavily pretreated for non–small cell lung cancer with an NTRK1 rearrangement experienced a dramatic response.
“The patient at that point was actually on hospice and was doing extremely poorly on supplemental oxygen,” Dr. Drilon said. “Within a few weeks, the patient had a dramatic clinical response to therapy … At day 26 there was almost a 50% reduction in tumor burden.” At day 317 scans showed he had a complete intracranial response to entrectinib, but he still has visceral disease on therapy past 1 year.
Responses often occurred within the first month of therapy, and many persisted for several months without disease progression, with one patient being followed for more than 2 years with clinical benefit. Nineteen of 24 patients have been on the therapy for more than 6 months, and the therapy appears to be safe and well tolerated.
Commenting on this study and others targeting specific genetic alterations leading to cancer, Dr. Louis Weiner, director of the Georgetown Lombardi Comprehensive Cancer Center in Washington, said, “You’re seeing a series of clinical trials described that aren’t necessarily targeting people with a particular cancer but rather people who have cancers characterized by particular molecular abnormalities.” Not all cancers will have identified molecular abnormalities driving them. “However, I think where you have these drivers, the proper thing to do is not to worry about whether [a drug] works in a given disease but rather whether it works for people with that particular abnormality,” he said.
For the future, the investigators plan a phase II trial called STARTRK-2. It is a multicenter, open-label, global basket study to include any solid tumors with the targeted rearrangements.
Dr. Drilon disclosed ties with Ignyta, which funded the study, and has received research funding from Foundation Medicine. Dr. Weiner disclosed ties with several pharmaceutical companies.
Entrectinib, an investigational drug that targets several abnormal fusion proteins, showed antitumor activity and was safe in patients with several different types of advanced solid tumors. The patients had never before been exposed to drugs targeting these same genetic alterations.
“Responses can be very rapid and durable … which include colorectal, primary brain tumor, astrocytoma, fibrosarcoma, lung, and mammary analog secretory carcinoma,” Dr. Alexander Drilon of Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center in New York said in a news conference at the annual meeting of the American Association for Cancer Research. “Dramatic intracranial activity … has been demonstrated both in primary brain tumor and also in metastatic.”
NTRK1/2/3, ROS1, and ALK gene–rearranged cancers produce fusion proteins that are ligand independent for their activity and thus constitutively active, driving tumor growth. Entrectinib is a pan-TRK, ROS1, ALK tyrosine kinase inhibitor that targets the abnormal fusion protein products of the genes, is highly potent at low concentrations, and has been designed to cross the blood-brain barrier (BBB). The targeted proteins are present across multiple cancers and are especially prevalent (greater than 80%) among some rare adult and pediatric cancers.

Combined data on 119 patients in two phase I trials established 600 mg orally once daily as the recommended dose to go into phase II trials. Among the 24 patients meeting eligibility criteria for a phase II trial (presence of the targeted gene fusions in their tumors, no prior treatment against these targets, and treatment at or above 600 mg daily), the confirmed response rate was 79% (19/24). Most were partial responses in terms of tumor shrinkage, but two patients had complete responses. Response rates appeared to vary according to the specific fusion protein defect.
All three cases of CNS disease with NTRK-rearranged cancers had intracranial responses, demonstrating that the drug crosses the BBB and is active. In one case, a 46-year-old man with brain metastases heavily pretreated for non–small cell lung cancer with an NTRK1 rearrangement experienced a dramatic response.
“The patient at that point was actually on hospice and was doing extremely poorly on supplemental oxygen,” Dr. Drilon said. “Within a few weeks, the patient had a dramatic clinical response to therapy … At day 26 there was almost a 50% reduction in tumor burden.” At day 317 scans showed he had a complete intracranial response to entrectinib, but he still has visceral disease on therapy past 1 year.
Responses often occurred within the first month of therapy, and many persisted for several months without disease progression, with one patient being followed for more than 2 years with clinical benefit. Nineteen of 24 patients have been on the therapy for more than 6 months, and the therapy appears to be safe and well tolerated.
Commenting on this study and others targeting specific genetic alterations leading to cancer, Dr. Louis Weiner, director of the Georgetown Lombardi Comprehensive Cancer Center in Washington, said, “You’re seeing a series of clinical trials described that aren’t necessarily targeting people with a particular cancer but rather people who have cancers characterized by particular molecular abnormalities.” Not all cancers will have identified molecular abnormalities driving them. “However, I think where you have these drivers, the proper thing to do is not to worry about whether [a drug] works in a given disease but rather whether it works for people with that particular abnormality,” he said.
For the future, the investigators plan a phase II trial called STARTRK-2. It is a multicenter, open-label, global basket study to include any solid tumors with the targeted rearrangements.
Dr. Drilon disclosed ties with Ignyta, which funded the study, and has received research funding from Foundation Medicine. Dr. Weiner disclosed ties with several pharmaceutical companies.
Entrectinib, an investigational drug that targets several abnormal fusion proteins, showed antitumor activity and was safe in patients with several different types of advanced solid tumors. The patients had never before been exposed to drugs targeting these same genetic alterations.
“Responses can be very rapid and durable … which include colorectal, primary brain tumor, astrocytoma, fibrosarcoma, lung, and mammary analog secretory carcinoma,” Dr. Alexander Drilon of Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center in New York said in a news conference at the annual meeting of the American Association for Cancer Research. “Dramatic intracranial activity … has been demonstrated both in primary brain tumor and also in metastatic.”
NTRK1/2/3, ROS1, and ALK gene–rearranged cancers produce fusion proteins that are ligand independent for their activity and thus constitutively active, driving tumor growth. Entrectinib is a pan-TRK, ROS1, ALK tyrosine kinase inhibitor that targets the abnormal fusion protein products of the genes, is highly potent at low concentrations, and has been designed to cross the blood-brain barrier (BBB). The targeted proteins are present across multiple cancers and are especially prevalent (greater than 80%) among some rare adult and pediatric cancers.

Combined data on 119 patients in two phase I trials established 600 mg orally once daily as the recommended dose to go into phase II trials. Among the 24 patients meeting eligibility criteria for a phase II trial (presence of the targeted gene fusions in their tumors, no prior treatment against these targets, and treatment at or above 600 mg daily), the confirmed response rate was 79% (19/24). Most were partial responses in terms of tumor shrinkage, but two patients had complete responses. Response rates appeared to vary according to the specific fusion protein defect.
All three cases of CNS disease with NTRK-rearranged cancers had intracranial responses, demonstrating that the drug crosses the BBB and is active. In one case, a 46-year-old man with brain metastases heavily pretreated for non–small cell lung cancer with an NTRK1 rearrangement experienced a dramatic response.
“The patient at that point was actually on hospice and was doing extremely poorly on supplemental oxygen,” Dr. Drilon said. “Within a few weeks, the patient had a dramatic clinical response to therapy … At day 26 there was almost a 50% reduction in tumor burden.” At day 317 scans showed he had a complete intracranial response to entrectinib, but he still has visceral disease on therapy past 1 year.
Responses often occurred within the first month of therapy, and many persisted for several months without disease progression, with one patient being followed for more than 2 years with clinical benefit. Nineteen of 24 patients have been on the therapy for more than 6 months, and the therapy appears to be safe and well tolerated.
Commenting on this study and others targeting specific genetic alterations leading to cancer, Dr. Louis Weiner, director of the Georgetown Lombardi Comprehensive Cancer Center in Washington, said, “You’re seeing a series of clinical trials described that aren’t necessarily targeting people with a particular cancer but rather people who have cancers characterized by particular molecular abnormalities.” Not all cancers will have identified molecular abnormalities driving them. “However, I think where you have these drivers, the proper thing to do is not to worry about whether [a drug] works in a given disease but rather whether it works for people with that particular abnormality,” he said.
For the future, the investigators plan a phase II trial called STARTRK-2. It is a multicenter, open-label, global basket study to include any solid tumors with the targeted rearrangements.
Dr. Drilon disclosed ties with Ignyta, which funded the study, and has received research funding from Foundation Medicine. Dr. Weiner disclosed ties with several pharmaceutical companies.
FROM THE AACR ANNUAL MEETING
Key clinical point: Entrectinib showed antitumor activity including intracranial responses.
Major finding: Patients with the targeted abnormalities had a 79% response rate.
Data source: Twenty-four patients meeting eligibility criteria for a phase II study from an initial phase I open-label dose-escalation study of 119 patients.
Disclosures: Dr. Drilon disclosed ties with Ignyta, which funded the study, and has received research funding from Foundation Medicine. Dr. Weiner disclosed ties with several pharmaceutical companies.
Smooth hair – an acne-causing epidemic
Do you ask your acne patients about which hair products they use? This common question has recently brought our attention to popular hair products that are causing an acne epidemic. Have we forgotten about “Pomade acne”? Well, it’s making a comeback. Originally described in ethnic women, new frizz-fighting hair products have resurged and so has pomade acne in all skin types and in both men and women.
Smoothing serums, heat styling sprays, leave-in products popularly known as “It’s-a-10,” “Biosilk,” “anti-frizz serums,” “heat-protectants,” “thermal setting sprays,” and “shine sprays,” contain silicone-derived ingredients and oils to control frizz, add shine, and detangle the hair. They work by smoothing the hair cuticle, and for women with difficult-to-manage hair, they have become an essential part of the daily beauty regimen.
Men are not in the clear either. Hair waxes and pomades used to style men’s hair contain greasy wax-based ingredients that also clog pores, trap bacteria, and cause inflammatory breakouts.
As a general rule in skin and body care, most products work well for what they are made to do, but when misused, they can cause mishaps. You wouldn’t moisturize your face with your hair serum would you? It seems obvious that this could cause some skin issues; however, most people will not think to correlate their acne breakouts with their hair products until we mention it. These products rub off on the face or on the pillow at night. In addition, the less we wash our hair, the more we are going to bed and getting the daytime products all over our pillowcases. Our faces are rolling around in oily, waxy, hair products all night.
Makeup is known to cause acne, and some of the makeups that are well known culprits contain the same ingredients as in hair products. Foundations, primers, and popular “BB” creams often contain cyclopentasiloxane and dimethicone. They serve a similar purpose: smoothing the skin and smoothing the hair. Both should be avoided in acne-prone patients.
Common culprits in hair products include PVP/DMAPA acrylates, cyclopentasiloxane, panthenol, dimethicone, silicone, Quaternium-70, oils, and petrolatum.
The only way to eliminate acne caused by hair products is to completely eliminate the hair product from the daily routine. However, if your patients can’t live without their hair products, here are some tips to share with them to reduce breakouts:
• Choose a hairstyle that keeps the hair away from the face, or wear hair up to avoid prolonged contact with the face, particularly while sleeping.
• Change pillowcase often (every day if possible), especially for side sleepers. Regardless of the fabric, pillowcases trap oil, dirt, and bacteria.
• Shower at night and sleep with clean hair and clean skin.
• Style hair before applying makeup. Wash hands thoroughly to remove all hair products before touching the skin.
• Cover the face prior to applying any hair sprays.
• Cover the hair at bedtime; however, tight head coverings can stimulate sweat and cause scalp breakouts.
As a general rule, any patient with difficult-to-control acne, recalcitrant acne, or acne in areas on the cheeks or hairline should eliminate these hair products in their daily routine or avoid skin contact with these products.
References
1. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2010 Apr;3(4):24-38.
2. Arch Dermatol. 1972;106 (6):843-50.
3. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2003; 48:S127-33.
4. Arch Dermatol. 1970;101(5):580-584.
5. “Cosmetics in Dermatology,” Second Edition, by Zoe Diana Draelos (New York: Churchill Livingstone, 1995).
Dr. Wesley and Dr. Talakoub are cocontributors to this column. Dr. Talakoub is in private practice in McLean, Va. Dr. Wesley practices dermatology in Beverly Hills, Calif. This month’s column is by Dr. Talakoub.
Do you ask your acne patients about which hair products they use? This common question has recently brought our attention to popular hair products that are causing an acne epidemic. Have we forgotten about “Pomade acne”? Well, it’s making a comeback. Originally described in ethnic women, new frizz-fighting hair products have resurged and so has pomade acne in all skin types and in both men and women.
Smoothing serums, heat styling sprays, leave-in products popularly known as “It’s-a-10,” “Biosilk,” “anti-frizz serums,” “heat-protectants,” “thermal setting sprays,” and “shine sprays,” contain silicone-derived ingredients and oils to control frizz, add shine, and detangle the hair. They work by smoothing the hair cuticle, and for women with difficult-to-manage hair, they have become an essential part of the daily beauty regimen.
Men are not in the clear either. Hair waxes and pomades used to style men’s hair contain greasy wax-based ingredients that also clog pores, trap bacteria, and cause inflammatory breakouts.
As a general rule in skin and body care, most products work well for what they are made to do, but when misused, they can cause mishaps. You wouldn’t moisturize your face with your hair serum would you? It seems obvious that this could cause some skin issues; however, most people will not think to correlate their acne breakouts with their hair products until we mention it. These products rub off on the face or on the pillow at night. In addition, the less we wash our hair, the more we are going to bed and getting the daytime products all over our pillowcases. Our faces are rolling around in oily, waxy, hair products all night.
Makeup is known to cause acne, and some of the makeups that are well known culprits contain the same ingredients as in hair products. Foundations, primers, and popular “BB” creams often contain cyclopentasiloxane and dimethicone. They serve a similar purpose: smoothing the skin and smoothing the hair. Both should be avoided in acne-prone patients.
Common culprits in hair products include PVP/DMAPA acrylates, cyclopentasiloxane, panthenol, dimethicone, silicone, Quaternium-70, oils, and petrolatum.
The only way to eliminate acne caused by hair products is to completely eliminate the hair product from the daily routine. However, if your patients can’t live without their hair products, here are some tips to share with them to reduce breakouts:
• Choose a hairstyle that keeps the hair away from the face, or wear hair up to avoid prolonged contact with the face, particularly while sleeping.
• Change pillowcase often (every day if possible), especially for side sleepers. Regardless of the fabric, pillowcases trap oil, dirt, and bacteria.
• Shower at night and sleep with clean hair and clean skin.
• Style hair before applying makeup. Wash hands thoroughly to remove all hair products before touching the skin.
• Cover the face prior to applying any hair sprays.
• Cover the hair at bedtime; however, tight head coverings can stimulate sweat and cause scalp breakouts.
As a general rule, any patient with difficult-to-control acne, recalcitrant acne, or acne in areas on the cheeks or hairline should eliminate these hair products in their daily routine or avoid skin contact with these products.
References
1. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2010 Apr;3(4):24-38.
2. Arch Dermatol. 1972;106 (6):843-50.
3. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2003; 48:S127-33.
4. Arch Dermatol. 1970;101(5):580-584.
5. “Cosmetics in Dermatology,” Second Edition, by Zoe Diana Draelos (New York: Churchill Livingstone, 1995).
Dr. Wesley and Dr. Talakoub are cocontributors to this column. Dr. Talakoub is in private practice in McLean, Va. Dr. Wesley practices dermatology in Beverly Hills, Calif. This month’s column is by Dr. Talakoub.
Do you ask your acne patients about which hair products they use? This common question has recently brought our attention to popular hair products that are causing an acne epidemic. Have we forgotten about “Pomade acne”? Well, it’s making a comeback. Originally described in ethnic women, new frizz-fighting hair products have resurged and so has pomade acne in all skin types and in both men and women.
Smoothing serums, heat styling sprays, leave-in products popularly known as “It’s-a-10,” “Biosilk,” “anti-frizz serums,” “heat-protectants,” “thermal setting sprays,” and “shine sprays,” contain silicone-derived ingredients and oils to control frizz, add shine, and detangle the hair. They work by smoothing the hair cuticle, and for women with difficult-to-manage hair, they have become an essential part of the daily beauty regimen.
Men are not in the clear either. Hair waxes and pomades used to style men’s hair contain greasy wax-based ingredients that also clog pores, trap bacteria, and cause inflammatory breakouts.
As a general rule in skin and body care, most products work well for what they are made to do, but when misused, they can cause mishaps. You wouldn’t moisturize your face with your hair serum would you? It seems obvious that this could cause some skin issues; however, most people will not think to correlate their acne breakouts with their hair products until we mention it. These products rub off on the face or on the pillow at night. In addition, the less we wash our hair, the more we are going to bed and getting the daytime products all over our pillowcases. Our faces are rolling around in oily, waxy, hair products all night.
Makeup is known to cause acne, and some of the makeups that are well known culprits contain the same ingredients as in hair products. Foundations, primers, and popular “BB” creams often contain cyclopentasiloxane and dimethicone. They serve a similar purpose: smoothing the skin and smoothing the hair. Both should be avoided in acne-prone patients.
Common culprits in hair products include PVP/DMAPA acrylates, cyclopentasiloxane, panthenol, dimethicone, silicone, Quaternium-70, oils, and petrolatum.
The only way to eliminate acne caused by hair products is to completely eliminate the hair product from the daily routine. However, if your patients can’t live without their hair products, here are some tips to share with them to reduce breakouts:
• Choose a hairstyle that keeps the hair away from the face, or wear hair up to avoid prolonged contact with the face, particularly while sleeping.
• Change pillowcase often (every day if possible), especially for side sleepers. Regardless of the fabric, pillowcases trap oil, dirt, and bacteria.
• Shower at night and sleep with clean hair and clean skin.
• Style hair before applying makeup. Wash hands thoroughly to remove all hair products before touching the skin.
• Cover the face prior to applying any hair sprays.
• Cover the hair at bedtime; however, tight head coverings can stimulate sweat and cause scalp breakouts.
As a general rule, any patient with difficult-to-control acne, recalcitrant acne, or acne in areas on the cheeks or hairline should eliminate these hair products in their daily routine or avoid skin contact with these products.
References
1. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2010 Apr;3(4):24-38.
2. Arch Dermatol. 1972;106 (6):843-50.
3. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2003; 48:S127-33.
4. Arch Dermatol. 1970;101(5):580-584.
5. “Cosmetics in Dermatology,” Second Edition, by Zoe Diana Draelos (New York: Churchill Livingstone, 1995).
Dr. Wesley and Dr. Talakoub are cocontributors to this column. Dr. Talakoub is in private practice in McLean, Va. Dr. Wesley practices dermatology in Beverly Hills, Calif. This month’s column is by Dr. Talakoub.
Myth of the Month: Retired myths from yesteryear
I appreciate the opportunity to share medical myths each month, hopefully to highlight topics where new knowledge and data may help change ways we approach common problems in medicine. I have been researching medical myths since the early 1990s, and some have actually evolved in such a way that they are no longer myths – that is, accepted practice now is very different than it was decades ago, and has incorporated updated research.
Some myths are timeless. The vitamin B12 myth I shared in this column last year continues to this day, despite evidence that has been present since the 1960s.
I will share with you two of my all-time favorite myths that have now been retired, where current practice now does not perpetuate these myths.
When I was in medical school, I was taught that the best way to treat a corneal abrasion was to patch the affected eye.1 Pretty much everyone who was seen in an emergency department for a corneal abrasion before the 1990s left the ED with an eye patch. This standard approach was not based on any evidence of benefit of healing or decreased pain.
Dr. Harold Jackson reported in a study of patients with corneal abrasions published in 1960 that there was no difference in healing between eyes that were patched and eyes that were left unpatched.2 The largest published study on eye patches for corneal abrasions involved 201 patients who were evaluated for corneal abrasions.3 The patients who did not receive an eye patch had less pain and quicker healing of the corneal abrasions. Other studies all showed no benefit to eye patches.4,5
A Cochrane Review published in 2006 concluded: “Treating simple corneal abrasions with a patch does not improve healing rates on the first day post-injury and does not reduce pain. In addition, use of patches results in a loss of binocular vision. Therefore, it is recommended that patches should not be used for simple corneal abrasions.”6
A more recent study by Dr. Moreno Menghini and colleagues showed no differences in healing of traumatic corneal abrasions between groups who received an eye patch, a contact lens, or no eye covering.7
Another longstanding myth that is less commonly seen now is the avoidance of use of narcotics for the treatment of acute, severe abdominal pain.
The long-term teaching was that by treating abdominal pain with narcotics, you could mask the important physical exam findings in patients presenting with an acute abdomen. The source of this myth wasn’t hard to uncover. The following are quotes from Cope’s Early Diagnosis of the Acute Abdomen 15th and 16th editions (these were the editions available back when I was a medical student in the early 1980s).
From the 15th edition: “If morphine be given, it is possible for a patient to die happy in the belief that he is on the road to recovery, and in some cases the medical attendant may for a time be induced to share the elusive hope.”8
An even stronger position was taken in the next edition of Cope’s text: “The patient cried out for relief, the relatives are insistent that something should be done, and the humane disciple of Aesculapius may think it is his first duty to diminish or banish the too obvious agony by administering a narcotic. Such a policy is a mistake. Though it may appear cruel, it is really kind to withhold morphine until a reasonable diagnosis has been made.”9
No controlled trials ever questioned this long-held belief until a study done by Dr. Alex Attard and colleagues published in 1992.10 In this study, 100 patients were evaluated by an admitting officer and given an intramuscular injection of either a narcotic or saline. Surgeons who subsequently followed the patients felt equally confident in diagnosis and management in both groups. The decision to operate or observe was incorrect in two patients in the narcotic group and nine in the saline group.
Dr. H. A. Amoli and colleagues studied whether administering morphine changed exam findings in patients with acute appendiciits.11 In a randomized, double-blind study design, half the patients received morphine and half received saline. Patients were examined by surgeons not involved in their care before and after drug administration, and their pain intensity and signs were recorded at each visit. The administration of morphine did not alter clinical signs or physician management plans.
In a study by Dr. Steven Pace and colleagues of patients presenting with acute abdominal pain, intravenous morphine or placebo was administered in 71 patients early in their presentation to the ED.12 There were no differences in accuracy of diagnosis between groups. Three diagnostic or management errors were made in each group.
I think the standard of care now for corneal abrasion treatment does not include eye patching. I also believe that the old teaching of no pain medication until the surgeon has examined the patient has also been replaced with appropriate pain management occurring early in the care plan for patients presenting with acute abdominal pain.
In the case of corneal abrasions, overwhelming data showing no benefit won out. I believe that the change in the management of acute abdominal pain was a combination of data along with advances in diagnostic imaging.
References
1. Wilkins. Emergency Medicine. 1989 Williams and Wilkins, Baltimore, Md.
2. Br Med J. 1960 Sep 3;2(5200):713.
3. Ophthalmology. 1995 Dec;102(12):1936-42.
4. Lancet. 1991 Mar 16;337(8742):643.
6. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2006 Apr 19;(2):CD004764.
7. Ophthalmic Res. 2013;50(1):13-8.
8. Cope’s Early Diagnosis of the Acute Abdomen, 15th Edition, Oxford University Press, 1979.
9. Cope’s Early Diagnosis of the Acute Abdomen, 16th Edition, Oxford University Press, 1983.
10. BMJ. 1992 Sep 5;305(6853):554-6.
11. Emerg Med J. 2008 Sep;25(9):586-9.
12. Acad Emerg Med. 1996 Dec;3(12):1086-92.
Dr. Paauw is professor of medicine in the division of general internal medicine at the University of Washington, Seattle, and he serves as third-year medical student clerkship director at the University of Washington. Contact Dr. Paauw at dpaauw@uw.edu.
I appreciate the opportunity to share medical myths each month, hopefully to highlight topics where new knowledge and data may help change ways we approach common problems in medicine. I have been researching medical myths since the early 1990s, and some have actually evolved in such a way that they are no longer myths – that is, accepted practice now is very different than it was decades ago, and has incorporated updated research.
Some myths are timeless. The vitamin B12 myth I shared in this column last year continues to this day, despite evidence that has been present since the 1960s.
I will share with you two of my all-time favorite myths that have now been retired, where current practice now does not perpetuate these myths.
When I was in medical school, I was taught that the best way to treat a corneal abrasion was to patch the affected eye.1 Pretty much everyone who was seen in an emergency department for a corneal abrasion before the 1990s left the ED with an eye patch. This standard approach was not based on any evidence of benefit of healing or decreased pain.
Dr. Harold Jackson reported in a study of patients with corneal abrasions published in 1960 that there was no difference in healing between eyes that were patched and eyes that were left unpatched.2 The largest published study on eye patches for corneal abrasions involved 201 patients who were evaluated for corneal abrasions.3 The patients who did not receive an eye patch had less pain and quicker healing of the corneal abrasions. Other studies all showed no benefit to eye patches.4,5
A Cochrane Review published in 2006 concluded: “Treating simple corneal abrasions with a patch does not improve healing rates on the first day post-injury and does not reduce pain. In addition, use of patches results in a loss of binocular vision. Therefore, it is recommended that patches should not be used for simple corneal abrasions.”6
A more recent study by Dr. Moreno Menghini and colleagues showed no differences in healing of traumatic corneal abrasions between groups who received an eye patch, a contact lens, or no eye covering.7
Another longstanding myth that is less commonly seen now is the avoidance of use of narcotics for the treatment of acute, severe abdominal pain.
The long-term teaching was that by treating abdominal pain with narcotics, you could mask the important physical exam findings in patients presenting with an acute abdomen. The source of this myth wasn’t hard to uncover. The following are quotes from Cope’s Early Diagnosis of the Acute Abdomen 15th and 16th editions (these were the editions available back when I was a medical student in the early 1980s).
From the 15th edition: “If morphine be given, it is possible for a patient to die happy in the belief that he is on the road to recovery, and in some cases the medical attendant may for a time be induced to share the elusive hope.”8
An even stronger position was taken in the next edition of Cope’s text: “The patient cried out for relief, the relatives are insistent that something should be done, and the humane disciple of Aesculapius may think it is his first duty to diminish or banish the too obvious agony by administering a narcotic. Such a policy is a mistake. Though it may appear cruel, it is really kind to withhold morphine until a reasonable diagnosis has been made.”9
No controlled trials ever questioned this long-held belief until a study done by Dr. Alex Attard and colleagues published in 1992.10 In this study, 100 patients were evaluated by an admitting officer and given an intramuscular injection of either a narcotic or saline. Surgeons who subsequently followed the patients felt equally confident in diagnosis and management in both groups. The decision to operate or observe was incorrect in two patients in the narcotic group and nine in the saline group.
Dr. H. A. Amoli and colleagues studied whether administering morphine changed exam findings in patients with acute appendiciits.11 In a randomized, double-blind study design, half the patients received morphine and half received saline. Patients were examined by surgeons not involved in their care before and after drug administration, and their pain intensity and signs were recorded at each visit. The administration of morphine did not alter clinical signs or physician management plans.
In a study by Dr. Steven Pace and colleagues of patients presenting with acute abdominal pain, intravenous morphine or placebo was administered in 71 patients early in their presentation to the ED.12 There were no differences in accuracy of diagnosis between groups. Three diagnostic or management errors were made in each group.
I think the standard of care now for corneal abrasion treatment does not include eye patching. I also believe that the old teaching of no pain medication until the surgeon has examined the patient has also been replaced with appropriate pain management occurring early in the care plan for patients presenting with acute abdominal pain.
In the case of corneal abrasions, overwhelming data showing no benefit won out. I believe that the change in the management of acute abdominal pain was a combination of data along with advances in diagnostic imaging.
References
1. Wilkins. Emergency Medicine. 1989 Williams and Wilkins, Baltimore, Md.
2. Br Med J. 1960 Sep 3;2(5200):713.
3. Ophthalmology. 1995 Dec;102(12):1936-42.
4. Lancet. 1991 Mar 16;337(8742):643.
6. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2006 Apr 19;(2):CD004764.
7. Ophthalmic Res. 2013;50(1):13-8.
8. Cope’s Early Diagnosis of the Acute Abdomen, 15th Edition, Oxford University Press, 1979.
9. Cope’s Early Diagnosis of the Acute Abdomen, 16th Edition, Oxford University Press, 1983.
10. BMJ. 1992 Sep 5;305(6853):554-6.
11. Emerg Med J. 2008 Sep;25(9):586-9.
12. Acad Emerg Med. 1996 Dec;3(12):1086-92.
Dr. Paauw is professor of medicine in the division of general internal medicine at the University of Washington, Seattle, and he serves as third-year medical student clerkship director at the University of Washington. Contact Dr. Paauw at dpaauw@uw.edu.
I appreciate the opportunity to share medical myths each month, hopefully to highlight topics where new knowledge and data may help change ways we approach common problems in medicine. I have been researching medical myths since the early 1990s, and some have actually evolved in such a way that they are no longer myths – that is, accepted practice now is very different than it was decades ago, and has incorporated updated research.
Some myths are timeless. The vitamin B12 myth I shared in this column last year continues to this day, despite evidence that has been present since the 1960s.
I will share with you two of my all-time favorite myths that have now been retired, where current practice now does not perpetuate these myths.
When I was in medical school, I was taught that the best way to treat a corneal abrasion was to patch the affected eye.1 Pretty much everyone who was seen in an emergency department for a corneal abrasion before the 1990s left the ED with an eye patch. This standard approach was not based on any evidence of benefit of healing or decreased pain.
Dr. Harold Jackson reported in a study of patients with corneal abrasions published in 1960 that there was no difference in healing between eyes that were patched and eyes that were left unpatched.2 The largest published study on eye patches for corneal abrasions involved 201 patients who were evaluated for corneal abrasions.3 The patients who did not receive an eye patch had less pain and quicker healing of the corneal abrasions. Other studies all showed no benefit to eye patches.4,5
A Cochrane Review published in 2006 concluded: “Treating simple corneal abrasions with a patch does not improve healing rates on the first day post-injury and does not reduce pain. In addition, use of patches results in a loss of binocular vision. Therefore, it is recommended that patches should not be used for simple corneal abrasions.”6
A more recent study by Dr. Moreno Menghini and colleagues showed no differences in healing of traumatic corneal abrasions between groups who received an eye patch, a contact lens, or no eye covering.7
Another longstanding myth that is less commonly seen now is the avoidance of use of narcotics for the treatment of acute, severe abdominal pain.
The long-term teaching was that by treating abdominal pain with narcotics, you could mask the important physical exam findings in patients presenting with an acute abdomen. The source of this myth wasn’t hard to uncover. The following are quotes from Cope’s Early Diagnosis of the Acute Abdomen 15th and 16th editions (these were the editions available back when I was a medical student in the early 1980s).
From the 15th edition: “If morphine be given, it is possible for a patient to die happy in the belief that he is on the road to recovery, and in some cases the medical attendant may for a time be induced to share the elusive hope.”8
An even stronger position was taken in the next edition of Cope’s text: “The patient cried out for relief, the relatives are insistent that something should be done, and the humane disciple of Aesculapius may think it is his first duty to diminish or banish the too obvious agony by administering a narcotic. Such a policy is a mistake. Though it may appear cruel, it is really kind to withhold morphine until a reasonable diagnosis has been made.”9
No controlled trials ever questioned this long-held belief until a study done by Dr. Alex Attard and colleagues published in 1992.10 In this study, 100 patients were evaluated by an admitting officer and given an intramuscular injection of either a narcotic or saline. Surgeons who subsequently followed the patients felt equally confident in diagnosis and management in both groups. The decision to operate or observe was incorrect in two patients in the narcotic group and nine in the saline group.
Dr. H. A. Amoli and colleagues studied whether administering morphine changed exam findings in patients with acute appendiciits.11 In a randomized, double-blind study design, half the patients received morphine and half received saline. Patients were examined by surgeons not involved in their care before and after drug administration, and their pain intensity and signs were recorded at each visit. The administration of morphine did not alter clinical signs or physician management plans.
In a study by Dr. Steven Pace and colleagues of patients presenting with acute abdominal pain, intravenous morphine or placebo was administered in 71 patients early in their presentation to the ED.12 There were no differences in accuracy of diagnosis between groups. Three diagnostic or management errors were made in each group.
I think the standard of care now for corneal abrasion treatment does not include eye patching. I also believe that the old teaching of no pain medication until the surgeon has examined the patient has also been replaced with appropriate pain management occurring early in the care plan for patients presenting with acute abdominal pain.
In the case of corneal abrasions, overwhelming data showing no benefit won out. I believe that the change in the management of acute abdominal pain was a combination of data along with advances in diagnostic imaging.
References
1. Wilkins. Emergency Medicine. 1989 Williams and Wilkins, Baltimore, Md.
2. Br Med J. 1960 Sep 3;2(5200):713.
3. Ophthalmology. 1995 Dec;102(12):1936-42.
4. Lancet. 1991 Mar 16;337(8742):643.
6. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2006 Apr 19;(2):CD004764.
7. Ophthalmic Res. 2013;50(1):13-8.
8. Cope’s Early Diagnosis of the Acute Abdomen, 15th Edition, Oxford University Press, 1979.
9. Cope’s Early Diagnosis of the Acute Abdomen, 16th Edition, Oxford University Press, 1983.
10. BMJ. 1992 Sep 5;305(6853):554-6.
11. Emerg Med J. 2008 Sep;25(9):586-9.
12. Acad Emerg Med. 1996 Dec;3(12):1086-92.
Dr. Paauw is professor of medicine in the division of general internal medicine at the University of Washington, Seattle, and he serves as third-year medical student clerkship director at the University of Washington. Contact Dr. Paauw at dpaauw@uw.edu.
Women with epilepsy conceive at normal rate
VANCOUVER – Women with epilepsy have fertility rates comparable with healthy women in the general population, according to results from the first prospective observational cohort study to make the comparison.
During the year-long Women With Epilepsy: Pregnancy Outcomes and Deliveries (WEPOD) study, 70% of women with epilepsy and 67% of healthy control women became pregnant, and there was no significant difference in the mean time to pregnancy between those with and without epilepsy (6 months vs. 9 months, respectively), Dr. Page Pennell reported at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Neurology.
Live births occurred in 82% of pregnancies of women with epilepsy and 80% of controls, while miscarriages occurred in 13% and 20%, respectively. Both of those rates are very similar to the general population. Another 5% of pregnancies in women with epilepsy were ectopic, terminated due to chromosomal abnormality, or lost to follow-up.
“These findings should reassure women with epilepsy and clinicians when counseling women with epilepsy who are planning pregnancy,” said Dr. Pennell, director of research for the division of epilepsy in the department of neurology at Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston. She is a primary investigator of the study along with Dr. Jacqueline French, professor of neurology at NYU Langone Medical Center and Dr. Cynthia Harden, system director of epilepsy services at Mount Sinai Beth Israel, both in New York.
“I think overall the findings are more in the light of myth busting. ... We don’t necessarily see a lot of problems with fertility, yet the literature suggests that the birth rates are much lower,” Dr. Harden said in an interview.
“It’s really the first solid evidence, and it’s nice because in a sea of bad news for women when it comes to family planning and achieving pregnancy and pregnancy outcomes, I think this was very positive to say that their ability to achieve pregnancy was no different than what was reported by a control population without epilepsy,” Dr. Katherine Noe, an epilepsy specialist at the Mayo Clinic in Scottsdale, Ariz., said when asked to comment on the study.
“There was certainly reason to be concerned,” said Dr. Noe, who was not involved in the study. “We have a lot of data saying that babies exposed to antiepileptic drugs are more likely to have malformations, and so you could have a baby that already early in pregnancy has severe malformations that would be more likely to end in spontaneous abortion.”
Dr. Noe said that pregnancy registry data indicate that women with epilepsy may be more likely to have a pregnancy that ends in a miscarriage. Investigators for several studies published in 2015 reported that women with epilepsy face greater risk for morbidity and adverse outcomes at the time of delivery and during pregnancy than women without epilepsy (JAMA Neurol. 2015;72[9]:981-8 and Lancet. 2016;386[10006]:1845–52). Women with epilepsy also have been thought to be more prone to infertility for various reasons, including menstrual irregularities, polycystic ovarian syndrome related to antiepileptic medications, and early menopause, she said.
Three previous studies had reported that women with epilepsy had birth rates as low as only one-quarter to one-third that of women without epilepsy. There have been many reasons reported for why that might be the case, including lower marriage rates, sexual dysfunction, lower libido (in both men and women with epilepsy), and increased number of anovulatory cycles, or greater choice to not become pregnant, Dr. Pennell said.
The WEPOD study enrolled 89 women with epilepsy and 109 healthy controls who were seeking to become pregnant and had stopped using contraception within 6 months of enrollment or were about to stop using it. The investigators excluded women with infertility, polycystic ovarian syndrome, endometriosis, endocrine disorder, and heavy smoking, or who were not in an exclusive heterosexual relationship with a significant other or spouse.
Participants received iPod touch devices with an app with which they tracked menses and intercourse, as well as antiepileptic drug use and seizures in women with epilepsy. “This was a particularly novel part of the study,” Dr. Harden said. It allowed the investigators to track adherence very well. Participants logged about 87% of their days in the app, and the investigators could see when the entries were made.
Women in both groups had a mean age of about 31 years and mean body mass index of about 25 kg/m2. Overall, 52%-58% had undergone a prior pregnancy. Women with epilepsy, compared with controls, were less often Asian (17% vs. 6%) or African American (16% vs. 1%). The education level of participants was “fairly similar” between the groups, and slightly more women with epilepsy were unemployed (21% vs. 10%). Women with epilepsy also were more often married than were controls (89% vs. 75%).
During the study, 36% of women with epilepsy were still having seizures. At enrollment, most of the women’s seizure types were generalized (30%) or focal only (63%). Dr. Pennell noted that the antiseizure medications that the women were taking were typical for women of reproductive age: lamotrigine monotherapy (44%), levetiracetam monotherapy (28%), monotherapy with a strong enzyme-inducing drug (12%), other polytherapy (10%), polytherapy with a strong enzyme-inducing drug (6%), other monotherapy (3%), or no antiseizure medication (2%). A few women either added or stopped drugs during the study. A total of 18 women with epilepsy and 15 healthy controls dropped out.
As expected, age affected the likelihood of becoming pregnant, as well as number of prior pregnancies. Body mass index did not affect the likelihood of becoming pregnant, while white race and being married increased the likelihood.
In future analyses, the investigators are planning on checking whether ovulatory rates, frequency of intercourse, and time of intercourse had any impact on pregnancy, and in women with epilepsy, they will check the effect of the type of antiseizure medication and seizure-related factors.
“I think our findings will stand with future analyses.” Dr. Harden said. “The most interesting future findings may come from within the epilepsy group,” she said, noting that older antiepileptic medications have been previously associated with difficulty conceiving.
The WEPOD study was funded by the Milken Family Foundation, the Epilepsy Therapy Project, and the Epilepsy Foundation.
VANCOUVER – Women with epilepsy have fertility rates comparable with healthy women in the general population, according to results from the first prospective observational cohort study to make the comparison.
During the year-long Women With Epilepsy: Pregnancy Outcomes and Deliveries (WEPOD) study, 70% of women with epilepsy and 67% of healthy control women became pregnant, and there was no significant difference in the mean time to pregnancy between those with and without epilepsy (6 months vs. 9 months, respectively), Dr. Page Pennell reported at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Neurology.
Live births occurred in 82% of pregnancies of women with epilepsy and 80% of controls, while miscarriages occurred in 13% and 20%, respectively. Both of those rates are very similar to the general population. Another 5% of pregnancies in women with epilepsy were ectopic, terminated due to chromosomal abnormality, or lost to follow-up.
“These findings should reassure women with epilepsy and clinicians when counseling women with epilepsy who are planning pregnancy,” said Dr. Pennell, director of research for the division of epilepsy in the department of neurology at Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston. She is a primary investigator of the study along with Dr. Jacqueline French, professor of neurology at NYU Langone Medical Center and Dr. Cynthia Harden, system director of epilepsy services at Mount Sinai Beth Israel, both in New York.
“I think overall the findings are more in the light of myth busting. ... We don’t necessarily see a lot of problems with fertility, yet the literature suggests that the birth rates are much lower,” Dr. Harden said in an interview.
“It’s really the first solid evidence, and it’s nice because in a sea of bad news for women when it comes to family planning and achieving pregnancy and pregnancy outcomes, I think this was very positive to say that their ability to achieve pregnancy was no different than what was reported by a control population without epilepsy,” Dr. Katherine Noe, an epilepsy specialist at the Mayo Clinic in Scottsdale, Ariz., said when asked to comment on the study.
“There was certainly reason to be concerned,” said Dr. Noe, who was not involved in the study. “We have a lot of data saying that babies exposed to antiepileptic drugs are more likely to have malformations, and so you could have a baby that already early in pregnancy has severe malformations that would be more likely to end in spontaneous abortion.”
Dr. Noe said that pregnancy registry data indicate that women with epilepsy may be more likely to have a pregnancy that ends in a miscarriage. Investigators for several studies published in 2015 reported that women with epilepsy face greater risk for morbidity and adverse outcomes at the time of delivery and during pregnancy than women without epilepsy (JAMA Neurol. 2015;72[9]:981-8 and Lancet. 2016;386[10006]:1845–52). Women with epilepsy also have been thought to be more prone to infertility for various reasons, including menstrual irregularities, polycystic ovarian syndrome related to antiepileptic medications, and early menopause, she said.
Three previous studies had reported that women with epilepsy had birth rates as low as only one-quarter to one-third that of women without epilepsy. There have been many reasons reported for why that might be the case, including lower marriage rates, sexual dysfunction, lower libido (in both men and women with epilepsy), and increased number of anovulatory cycles, or greater choice to not become pregnant, Dr. Pennell said.
The WEPOD study enrolled 89 women with epilepsy and 109 healthy controls who were seeking to become pregnant and had stopped using contraception within 6 months of enrollment or were about to stop using it. The investigators excluded women with infertility, polycystic ovarian syndrome, endometriosis, endocrine disorder, and heavy smoking, or who were not in an exclusive heterosexual relationship with a significant other or spouse.
Participants received iPod touch devices with an app with which they tracked menses and intercourse, as well as antiepileptic drug use and seizures in women with epilepsy. “This was a particularly novel part of the study,” Dr. Harden said. It allowed the investigators to track adherence very well. Participants logged about 87% of their days in the app, and the investigators could see when the entries were made.
Women in both groups had a mean age of about 31 years and mean body mass index of about 25 kg/m2. Overall, 52%-58% had undergone a prior pregnancy. Women with epilepsy, compared with controls, were less often Asian (17% vs. 6%) or African American (16% vs. 1%). The education level of participants was “fairly similar” between the groups, and slightly more women with epilepsy were unemployed (21% vs. 10%). Women with epilepsy also were more often married than were controls (89% vs. 75%).
During the study, 36% of women with epilepsy were still having seizures. At enrollment, most of the women’s seizure types were generalized (30%) or focal only (63%). Dr. Pennell noted that the antiseizure medications that the women were taking were typical for women of reproductive age: lamotrigine monotherapy (44%), levetiracetam monotherapy (28%), monotherapy with a strong enzyme-inducing drug (12%), other polytherapy (10%), polytherapy with a strong enzyme-inducing drug (6%), other monotherapy (3%), or no antiseizure medication (2%). A few women either added or stopped drugs during the study. A total of 18 women with epilepsy and 15 healthy controls dropped out.
As expected, age affected the likelihood of becoming pregnant, as well as number of prior pregnancies. Body mass index did not affect the likelihood of becoming pregnant, while white race and being married increased the likelihood.
In future analyses, the investigators are planning on checking whether ovulatory rates, frequency of intercourse, and time of intercourse had any impact on pregnancy, and in women with epilepsy, they will check the effect of the type of antiseizure medication and seizure-related factors.
“I think our findings will stand with future analyses.” Dr. Harden said. “The most interesting future findings may come from within the epilepsy group,” she said, noting that older antiepileptic medications have been previously associated with difficulty conceiving.
The WEPOD study was funded by the Milken Family Foundation, the Epilepsy Therapy Project, and the Epilepsy Foundation.
VANCOUVER – Women with epilepsy have fertility rates comparable with healthy women in the general population, according to results from the first prospective observational cohort study to make the comparison.
During the year-long Women With Epilepsy: Pregnancy Outcomes and Deliveries (WEPOD) study, 70% of women with epilepsy and 67% of healthy control women became pregnant, and there was no significant difference in the mean time to pregnancy between those with and without epilepsy (6 months vs. 9 months, respectively), Dr. Page Pennell reported at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Neurology.
Live births occurred in 82% of pregnancies of women with epilepsy and 80% of controls, while miscarriages occurred in 13% and 20%, respectively. Both of those rates are very similar to the general population. Another 5% of pregnancies in women with epilepsy were ectopic, terminated due to chromosomal abnormality, or lost to follow-up.
“These findings should reassure women with epilepsy and clinicians when counseling women with epilepsy who are planning pregnancy,” said Dr. Pennell, director of research for the division of epilepsy in the department of neurology at Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston. She is a primary investigator of the study along with Dr. Jacqueline French, professor of neurology at NYU Langone Medical Center and Dr. Cynthia Harden, system director of epilepsy services at Mount Sinai Beth Israel, both in New York.
“I think overall the findings are more in the light of myth busting. ... We don’t necessarily see a lot of problems with fertility, yet the literature suggests that the birth rates are much lower,” Dr. Harden said in an interview.
“It’s really the first solid evidence, and it’s nice because in a sea of bad news for women when it comes to family planning and achieving pregnancy and pregnancy outcomes, I think this was very positive to say that their ability to achieve pregnancy was no different than what was reported by a control population without epilepsy,” Dr. Katherine Noe, an epilepsy specialist at the Mayo Clinic in Scottsdale, Ariz., said when asked to comment on the study.
“There was certainly reason to be concerned,” said Dr. Noe, who was not involved in the study. “We have a lot of data saying that babies exposed to antiepileptic drugs are more likely to have malformations, and so you could have a baby that already early in pregnancy has severe malformations that would be more likely to end in spontaneous abortion.”
Dr. Noe said that pregnancy registry data indicate that women with epilepsy may be more likely to have a pregnancy that ends in a miscarriage. Investigators for several studies published in 2015 reported that women with epilepsy face greater risk for morbidity and adverse outcomes at the time of delivery and during pregnancy than women without epilepsy (JAMA Neurol. 2015;72[9]:981-8 and Lancet. 2016;386[10006]:1845–52). Women with epilepsy also have been thought to be more prone to infertility for various reasons, including menstrual irregularities, polycystic ovarian syndrome related to antiepileptic medications, and early menopause, she said.
Three previous studies had reported that women with epilepsy had birth rates as low as only one-quarter to one-third that of women without epilepsy. There have been many reasons reported for why that might be the case, including lower marriage rates, sexual dysfunction, lower libido (in both men and women with epilepsy), and increased number of anovulatory cycles, or greater choice to not become pregnant, Dr. Pennell said.
The WEPOD study enrolled 89 women with epilepsy and 109 healthy controls who were seeking to become pregnant and had stopped using contraception within 6 months of enrollment or were about to stop using it. The investigators excluded women with infertility, polycystic ovarian syndrome, endometriosis, endocrine disorder, and heavy smoking, or who were not in an exclusive heterosexual relationship with a significant other or spouse.
Participants received iPod touch devices with an app with which they tracked menses and intercourse, as well as antiepileptic drug use and seizures in women with epilepsy. “This was a particularly novel part of the study,” Dr. Harden said. It allowed the investigators to track adherence very well. Participants logged about 87% of their days in the app, and the investigators could see when the entries were made.
Women in both groups had a mean age of about 31 years and mean body mass index of about 25 kg/m2. Overall, 52%-58% had undergone a prior pregnancy. Women with epilepsy, compared with controls, were less often Asian (17% vs. 6%) or African American (16% vs. 1%). The education level of participants was “fairly similar” between the groups, and slightly more women with epilepsy were unemployed (21% vs. 10%). Women with epilepsy also were more often married than were controls (89% vs. 75%).
During the study, 36% of women with epilepsy were still having seizures. At enrollment, most of the women’s seizure types were generalized (30%) or focal only (63%). Dr. Pennell noted that the antiseizure medications that the women were taking were typical for women of reproductive age: lamotrigine monotherapy (44%), levetiracetam monotherapy (28%), monotherapy with a strong enzyme-inducing drug (12%), other polytherapy (10%), polytherapy with a strong enzyme-inducing drug (6%), other monotherapy (3%), or no antiseizure medication (2%). A few women either added or stopped drugs during the study. A total of 18 women with epilepsy and 15 healthy controls dropped out.
As expected, age affected the likelihood of becoming pregnant, as well as number of prior pregnancies. Body mass index did not affect the likelihood of becoming pregnant, while white race and being married increased the likelihood.
In future analyses, the investigators are planning on checking whether ovulatory rates, frequency of intercourse, and time of intercourse had any impact on pregnancy, and in women with epilepsy, they will check the effect of the type of antiseizure medication and seizure-related factors.
“I think our findings will stand with future analyses.” Dr. Harden said. “The most interesting future findings may come from within the epilepsy group,” she said, noting that older antiepileptic medications have been previously associated with difficulty conceiving.
The WEPOD study was funded by the Milken Family Foundation, the Epilepsy Therapy Project, and the Epilepsy Foundation.
AT THE AAN 2016 ANNUAL MEETING
Key clinical point: Women with epilepsy do not have lower ability to conceive.
Major finding: 70% of women with epilepsy and 67% of healthy control women became pregnant.
Data source: A prospective case-control study of 89 women with epilepsy and 109 healthy controls.
Disclosures: The WEPOD study was funded by the Milken Family Foundation, the Epilepsy Therapy Project, and the Epilepsy Foundation.
STAMPEDE: Metabolic surgery bests medical therapy long term
CHICAGO – The superiority of metabolic surgery over intensive medical therapy for achieving glycemic control in patients with type 2 diabetes was largely maintained at the final 5-year follow-up evaluation in the randomized, controlled STAMPEDE trial.
The 150 subjects, who had “fairly severe diabetes” with an average disease duration of 8 years, were randomized to receive intensive medical therapy alone, or intensive medical therapy with Roux-en-Y gastric bypass surgery or sleeve gastrectomy surgery. The primary endpoint of hemoglobin A1c less than 6% was achieved in 5%, 29%, and 23% of patients in the groups, respectively. The difference was statistically significant in favor of both types of surgery, Dr. Philip Raymond Schauer reported at the annual meeting of the American College of Cardiology.
Furthermore, patients in the surgery groups fared better than those in the intensive medical therapy group on several other measures, including disease remission (defied as HbA1c less than 6% without diabetes medication), HbA1c less than 7% (the American Diabetes Association target for therapy), change in fasting plasma glucose from baseline, and changes in high- and low-density lipoprotein cholesterol levels, said Dr. Schauer, director of the Cleveland Clinic Bariatric and Metabolic Institute.
Patients in the surgery groups also experienced a significantly greater reduction in the use of antihypertensive medications and lipid-lowering agents, he added.
The “very dramatic drop” in HbA1c seen early on in the surgical patients was, for the most part, sustained out to 5 years, he said.
The results for both surgeries were significantly better than those for intensive medical therapy, but the results with gastric bypass were more effective at 5 years than were those for sleeve gastrectomy, he added, noting that the surgery patients had better quality of life, compared with the intensive medical therapy patients.
As for adverse events in the surgery groups, no perioperative deaths occurred, and while there were some surgical complications, none resulted in long-term disability, Dr. Schauer said.
Anemia was more common in the surgery patients, but was fairly mild. The most common complication was weight gain in 20% of patients, and the overall reoperation rate was 7%.
Of note, patients in the study had body mass index ranging from 27 to 43 kg/m2, and those with BMI less than 35 had similar benefits as those with more severe obesity. This is important, as many insurance companies won’t cover metabolic surgery for patients with BMI less than 35, he explained.
These findings represent the longest follow-up to date comparing the efficacy of the two most common metabolic surgery procedures with medical treatment of type 2 diabetes for maintaining glycemic control or reducing end-organ complications. Three-year outcomes of STAMPEDE (Surgical Treatment and Medications Potentially Eradicate Diabetes Efficiently) were reported in 2014 (N Engl J Med. 2014;370:2002-13).
The participants ranged in age from 20 to 60 years. The average HbA1c was about 9%, the average BMI was 36, and most were on at least three antidiabetic medications at baseline. Half were on insulin.
The findings are important, because of the roughly 25 million Americans with type 2 diabetes, only about half have good glycemic control on their current medical treatment strategies, Dr. Schauer said.
Though limited by the single-center study design, the STAMPEDE findings show that metabolic surgery is more effective long term than intensive medical therapy in patients with uncontrolled type 2 diabetes and should be considered a treatment option in this population, he concluded, adding that multicenter studies would be helpful for determining the generalizability of the findings.
Dr. Schauer reported receiving consulting fees/honoraria from Ethicon Endosurgery and The Medicines Company, and having ownership interest in Surgical Excellence.
CHICAGO – The superiority of metabolic surgery over intensive medical therapy for achieving glycemic control in patients with type 2 diabetes was largely maintained at the final 5-year follow-up evaluation in the randomized, controlled STAMPEDE trial.
The 150 subjects, who had “fairly severe diabetes” with an average disease duration of 8 years, were randomized to receive intensive medical therapy alone, or intensive medical therapy with Roux-en-Y gastric bypass surgery or sleeve gastrectomy surgery. The primary endpoint of hemoglobin A1c less than 6% was achieved in 5%, 29%, and 23% of patients in the groups, respectively. The difference was statistically significant in favor of both types of surgery, Dr. Philip Raymond Schauer reported at the annual meeting of the American College of Cardiology.
Furthermore, patients in the surgery groups fared better than those in the intensive medical therapy group on several other measures, including disease remission (defied as HbA1c less than 6% without diabetes medication), HbA1c less than 7% (the American Diabetes Association target for therapy), change in fasting plasma glucose from baseline, and changes in high- and low-density lipoprotein cholesterol levels, said Dr. Schauer, director of the Cleveland Clinic Bariatric and Metabolic Institute.
Patients in the surgery groups also experienced a significantly greater reduction in the use of antihypertensive medications and lipid-lowering agents, he added.
The “very dramatic drop” in HbA1c seen early on in the surgical patients was, for the most part, sustained out to 5 years, he said.
The results for both surgeries were significantly better than those for intensive medical therapy, but the results with gastric bypass were more effective at 5 years than were those for sleeve gastrectomy, he added, noting that the surgery patients had better quality of life, compared with the intensive medical therapy patients.
As for adverse events in the surgery groups, no perioperative deaths occurred, and while there were some surgical complications, none resulted in long-term disability, Dr. Schauer said.
Anemia was more common in the surgery patients, but was fairly mild. The most common complication was weight gain in 20% of patients, and the overall reoperation rate was 7%.
Of note, patients in the study had body mass index ranging from 27 to 43 kg/m2, and those with BMI less than 35 had similar benefits as those with more severe obesity. This is important, as many insurance companies won’t cover metabolic surgery for patients with BMI less than 35, he explained.
These findings represent the longest follow-up to date comparing the efficacy of the two most common metabolic surgery procedures with medical treatment of type 2 diabetes for maintaining glycemic control or reducing end-organ complications. Three-year outcomes of STAMPEDE (Surgical Treatment and Medications Potentially Eradicate Diabetes Efficiently) were reported in 2014 (N Engl J Med. 2014;370:2002-13).
The participants ranged in age from 20 to 60 years. The average HbA1c was about 9%, the average BMI was 36, and most were on at least three antidiabetic medications at baseline. Half were on insulin.
The findings are important, because of the roughly 25 million Americans with type 2 diabetes, only about half have good glycemic control on their current medical treatment strategies, Dr. Schauer said.
Though limited by the single-center study design, the STAMPEDE findings show that metabolic surgery is more effective long term than intensive medical therapy in patients with uncontrolled type 2 diabetes and should be considered a treatment option in this population, he concluded, adding that multicenter studies would be helpful for determining the generalizability of the findings.
Dr. Schauer reported receiving consulting fees/honoraria from Ethicon Endosurgery and The Medicines Company, and having ownership interest in Surgical Excellence.
CHICAGO – The superiority of metabolic surgery over intensive medical therapy for achieving glycemic control in patients with type 2 diabetes was largely maintained at the final 5-year follow-up evaluation in the randomized, controlled STAMPEDE trial.
The 150 subjects, who had “fairly severe diabetes” with an average disease duration of 8 years, were randomized to receive intensive medical therapy alone, or intensive medical therapy with Roux-en-Y gastric bypass surgery or sleeve gastrectomy surgery. The primary endpoint of hemoglobin A1c less than 6% was achieved in 5%, 29%, and 23% of patients in the groups, respectively. The difference was statistically significant in favor of both types of surgery, Dr. Philip Raymond Schauer reported at the annual meeting of the American College of Cardiology.
Furthermore, patients in the surgery groups fared better than those in the intensive medical therapy group on several other measures, including disease remission (defied as HbA1c less than 6% without diabetes medication), HbA1c less than 7% (the American Diabetes Association target for therapy), change in fasting plasma glucose from baseline, and changes in high- and low-density lipoprotein cholesterol levels, said Dr. Schauer, director of the Cleveland Clinic Bariatric and Metabolic Institute.
Patients in the surgery groups also experienced a significantly greater reduction in the use of antihypertensive medications and lipid-lowering agents, he added.
The “very dramatic drop” in HbA1c seen early on in the surgical patients was, for the most part, sustained out to 5 years, he said.
The results for both surgeries were significantly better than those for intensive medical therapy, but the results with gastric bypass were more effective at 5 years than were those for sleeve gastrectomy, he added, noting that the surgery patients had better quality of life, compared with the intensive medical therapy patients.
As for adverse events in the surgery groups, no perioperative deaths occurred, and while there were some surgical complications, none resulted in long-term disability, Dr. Schauer said.
Anemia was more common in the surgery patients, but was fairly mild. The most common complication was weight gain in 20% of patients, and the overall reoperation rate was 7%.
Of note, patients in the study had body mass index ranging from 27 to 43 kg/m2, and those with BMI less than 35 had similar benefits as those with more severe obesity. This is important, as many insurance companies won’t cover metabolic surgery for patients with BMI less than 35, he explained.
These findings represent the longest follow-up to date comparing the efficacy of the two most common metabolic surgery procedures with medical treatment of type 2 diabetes for maintaining glycemic control or reducing end-organ complications. Three-year outcomes of STAMPEDE (Surgical Treatment and Medications Potentially Eradicate Diabetes Efficiently) were reported in 2014 (N Engl J Med. 2014;370:2002-13).
The participants ranged in age from 20 to 60 years. The average HbA1c was about 9%, the average BMI was 36, and most were on at least three antidiabetic medications at baseline. Half were on insulin.
The findings are important, because of the roughly 25 million Americans with type 2 diabetes, only about half have good glycemic control on their current medical treatment strategies, Dr. Schauer said.
Though limited by the single-center study design, the STAMPEDE findings show that metabolic surgery is more effective long term than intensive medical therapy in patients with uncontrolled type 2 diabetes and should be considered a treatment option in this population, he concluded, adding that multicenter studies would be helpful for determining the generalizability of the findings.
Dr. Schauer reported receiving consulting fees/honoraria from Ethicon Endosurgery and The Medicines Company, and having ownership interest in Surgical Excellence.
AT ACC 16
Key clinical point: The superiority of metabolic surgery over intensive medical therapy for achieving glycemic control among patients with type 2 diabetes in the randomized, controlled STAMPEDE persisted at the final 5-year follow-up evaluation.
Major finding: The primary endpoint of HbA1c less than 6% was achieved in 5%, 29%, and 23% of patients in the medication and medication plus Roux-en-Y or sleeve gastrectomy groups, respectively.
Data source: The randomized, controlled STAMPEDE trial in 150 subjects.
Disclosures: Dr. Schauer reported receiving consulting fees/honoraria from Ethicon Endosurgery and The Medicines Company, and having ownership interest in Surgical Excellence.
Apply now for the 2016 Claude H. Organ, Jr., MD, FACS, Traveling Fellowship
The American College of Surgeons (ACS) is now accepting applications for the 2016 Claude H. Organ, Jr., MD, FACS, Traveling Fellowship. The deadline for all application materials is June 1.
The family and friends of the late Dr. Organ established an endowment through the ACS Foundation to provide funding for this fellowship, which is awarded annually to an outstanding young surgeon from the Society of Black Academic Surgeons, the Association of Women Surgeons, or the Surgical Section of the National Medical Association. The fellowship, in the amount of $5,000, enables a U.S. or Canadian Fellow or Associate Fellow younger than age 45 who is a member of one of these societies to attend an educational meeting or participate in an extended visit to an institution of his or her choice, tailored to his or her research interests.
Past awardees have used their fellowships to develop their careers in creative ways. The most recent fellow, Kathie-Ann Joseph, MD, MPH, FACS, associate professor of surgery, New York University School of Medicine, and chief of surgery, Bellevue Hospital Center, New York, NY, is researching how health care systems work in a major metropolitan area, with a focus on the ways that large hospitals systems manage care for underserved women.
The full requirements for the Claude H. Organ, Jr., MD, FACS, Traveling Fellowship are posted at facs.org/member-services/scholarships/special/organ. The 2016 awardee will be informed of the College’s decision by August 2016. Questions and application materials should be submitted to the attention of Kate Early, ACS Scholarships Administrator, at kearly@facs.org.
The American College of Surgeons (ACS) is now accepting applications for the 2016 Claude H. Organ, Jr., MD, FACS, Traveling Fellowship. The deadline for all application materials is June 1.
The family and friends of the late Dr. Organ established an endowment through the ACS Foundation to provide funding for this fellowship, which is awarded annually to an outstanding young surgeon from the Society of Black Academic Surgeons, the Association of Women Surgeons, or the Surgical Section of the National Medical Association. The fellowship, in the amount of $5,000, enables a U.S. or Canadian Fellow or Associate Fellow younger than age 45 who is a member of one of these societies to attend an educational meeting or participate in an extended visit to an institution of his or her choice, tailored to his or her research interests.
Past awardees have used their fellowships to develop their careers in creative ways. The most recent fellow, Kathie-Ann Joseph, MD, MPH, FACS, associate professor of surgery, New York University School of Medicine, and chief of surgery, Bellevue Hospital Center, New York, NY, is researching how health care systems work in a major metropolitan area, with a focus on the ways that large hospitals systems manage care for underserved women.
The full requirements for the Claude H. Organ, Jr., MD, FACS, Traveling Fellowship are posted at facs.org/member-services/scholarships/special/organ. The 2016 awardee will be informed of the College’s decision by August 2016. Questions and application materials should be submitted to the attention of Kate Early, ACS Scholarships Administrator, at kearly@facs.org.
The American College of Surgeons (ACS) is now accepting applications for the 2016 Claude H. Organ, Jr., MD, FACS, Traveling Fellowship. The deadline for all application materials is June 1.
The family and friends of the late Dr. Organ established an endowment through the ACS Foundation to provide funding for this fellowship, which is awarded annually to an outstanding young surgeon from the Society of Black Academic Surgeons, the Association of Women Surgeons, or the Surgical Section of the National Medical Association. The fellowship, in the amount of $5,000, enables a U.S. or Canadian Fellow or Associate Fellow younger than age 45 who is a member of one of these societies to attend an educational meeting or participate in an extended visit to an institution of his or her choice, tailored to his or her research interests.
Past awardees have used their fellowships to develop their careers in creative ways. The most recent fellow, Kathie-Ann Joseph, MD, MPH, FACS, associate professor of surgery, New York University School of Medicine, and chief of surgery, Bellevue Hospital Center, New York, NY, is researching how health care systems work in a major metropolitan area, with a focus on the ways that large hospitals systems manage care for underserved women.
The full requirements for the Claude H. Organ, Jr., MD, FACS, Traveling Fellowship are posted at facs.org/member-services/scholarships/special/organ. The 2016 awardee will be informed of the College’s decision by August 2016. Questions and application materials should be submitted to the attention of Kate Early, ACS Scholarships Administrator, at kearly@facs.org.
Your online reputation
Have you ever run across a negative or even malicious comment about you or your practice on the web, in full view of the world? You’re certainly not alone.
Chances are it was on one of those doctor rating sites, whose supposedly “objective” evaluations are anything but fair or accurate; one curmudgeon, angry about something that usually has nothing to do with your clinical skills, can use his First Amendment–protected right to trash you unfairly, as thousands of satisfied patients remain silent.
What to do? You could hire one of the many companies in the rapidly burgeoning field of online reputation management; but that can cost hundreds to thousands of dollars per month for monitoring and intervention, and there are no guarantees of success.
A better solution is to generate your own search results – positive ones – that will overwhelm any negative comments that search engines might find. Start with the social networking sites. However you feel about networking, there’s no getting around the fact that personal pages on Facebook, LinkedIn, and Twitter rank very high on major search engines. (Some consultants say a favorable LinkedIn profile is particularly helpful because of that site’s reputation as a “professional” network.) Your community activities, charitable work, interesting hobbies – anything that casts you in a favorable light – need to be mentioned prominently in your network profiles.
You can also use Google’s profiling tool (https://plus.google.com/up/accounts/) to create a sterling bio, complete with links to URLs, photos, and anything else that shows you in the best possible light. And your Google profile will be at or near the top of any Google search.
Wikipedia articles also go to the top of most searches, so if you’re notable enough to merit mention in one – or to have one of your own – see that it is done, and updated regularly. You can’t do that yourself, however; Wikipedia’s conflict of interest rules forbid writing or editing content about yourself. Someone with a theoretically “neutral point of view” will have to do it.
If you don’t yet have a website, now would be a good time. As I’ve discussed many times, a professionally designed site will be far more attractive and polished than anything you could build yourself. Furthermore, an experienced designer will employ “search engine optimization” (SEO), meaning that content will be created in a way that is readily visible to search engine users.
Leave design and SEO to the pros, but don’t delegate the content itself; as captain of the ship you are responsible for all the facts and opinions on your site. And remember that once it’s online, it’s online forever; consider the ramifications of anything you post on any site (yours or others) before hitting the “send” button. “The most damaging item about you,” one consultant told me, “could well be something you posted yourself.” Just ask any of several prominent politicians who have famously sabotaged their own careers online.
That said, don’t be shy about creating content. Make your (noncontroversial) opinions known on Facebook and Twitter. If social networks are not your thing, add a blog to your web site and write about what you know, and what interests you. If you have expertise in a particular field, write about that.
Incidentally, if the URL for your web site is not your name, you should also register your name as a separate domain name – if only to be sure that a trickster, or someone with the same name and a bad reputation, doesn’t get it.
Set up an RSS news feed for yourself, so you’ll know immediately anytime your name pops up in news or gossip sites, or on blogs. If something untrue is posted about you, take action. Reputable news sites and blogs have their own reputations to protect, and so can usually be persuaded to correct anything that is demonstrably false. Try to get the error removed entirely, or corrected within the original article. An erratum on the last page of the next edition will be ignored, and will leave the false information online, intact.
Unfair comments on doctor rating sites are unlikely to be removed unless they are blatantly libelous; but there is nothing wrong with encouraging happy patients to write favorable reviews. Turnabout is fair play.
Dr. Eastern practices dermatology and dermatologic surgery in Belleville, N.J. He is the author of numerous articles and textbook chapters, and is a longtime monthly columnist for Dermatology News. Write to him at dermnews@frontlinemedcom.com.
Have you ever run across a negative or even malicious comment about you or your practice on the web, in full view of the world? You’re certainly not alone.
Chances are it was on one of those doctor rating sites, whose supposedly “objective” evaluations are anything but fair or accurate; one curmudgeon, angry about something that usually has nothing to do with your clinical skills, can use his First Amendment–protected right to trash you unfairly, as thousands of satisfied patients remain silent.
What to do? You could hire one of the many companies in the rapidly burgeoning field of online reputation management; but that can cost hundreds to thousands of dollars per month for monitoring and intervention, and there are no guarantees of success.
A better solution is to generate your own search results – positive ones – that will overwhelm any negative comments that search engines might find. Start with the social networking sites. However you feel about networking, there’s no getting around the fact that personal pages on Facebook, LinkedIn, and Twitter rank very high on major search engines. (Some consultants say a favorable LinkedIn profile is particularly helpful because of that site’s reputation as a “professional” network.) Your community activities, charitable work, interesting hobbies – anything that casts you in a favorable light – need to be mentioned prominently in your network profiles.
You can also use Google’s profiling tool (https://plus.google.com/up/accounts/) to create a sterling bio, complete with links to URLs, photos, and anything else that shows you in the best possible light. And your Google profile will be at or near the top of any Google search.
Wikipedia articles also go to the top of most searches, so if you’re notable enough to merit mention in one – or to have one of your own – see that it is done, and updated regularly. You can’t do that yourself, however; Wikipedia’s conflict of interest rules forbid writing or editing content about yourself. Someone with a theoretically “neutral point of view” will have to do it.
If you don’t yet have a website, now would be a good time. As I’ve discussed many times, a professionally designed site will be far more attractive and polished than anything you could build yourself. Furthermore, an experienced designer will employ “search engine optimization” (SEO), meaning that content will be created in a way that is readily visible to search engine users.
Leave design and SEO to the pros, but don’t delegate the content itself; as captain of the ship you are responsible for all the facts and opinions on your site. And remember that once it’s online, it’s online forever; consider the ramifications of anything you post on any site (yours or others) before hitting the “send” button. “The most damaging item about you,” one consultant told me, “could well be something you posted yourself.” Just ask any of several prominent politicians who have famously sabotaged their own careers online.
That said, don’t be shy about creating content. Make your (noncontroversial) opinions known on Facebook and Twitter. If social networks are not your thing, add a blog to your web site and write about what you know, and what interests you. If you have expertise in a particular field, write about that.
Incidentally, if the URL for your web site is not your name, you should also register your name as a separate domain name – if only to be sure that a trickster, or someone with the same name and a bad reputation, doesn’t get it.
Set up an RSS news feed for yourself, so you’ll know immediately anytime your name pops up in news or gossip sites, or on blogs. If something untrue is posted about you, take action. Reputable news sites and blogs have their own reputations to protect, and so can usually be persuaded to correct anything that is demonstrably false. Try to get the error removed entirely, or corrected within the original article. An erratum on the last page of the next edition will be ignored, and will leave the false information online, intact.
Unfair comments on doctor rating sites are unlikely to be removed unless they are blatantly libelous; but there is nothing wrong with encouraging happy patients to write favorable reviews. Turnabout is fair play.
Dr. Eastern practices dermatology and dermatologic surgery in Belleville, N.J. He is the author of numerous articles and textbook chapters, and is a longtime monthly columnist for Dermatology News. Write to him at dermnews@frontlinemedcom.com.
Have you ever run across a negative or even malicious comment about you or your practice on the web, in full view of the world? You’re certainly not alone.
Chances are it was on one of those doctor rating sites, whose supposedly “objective” evaluations are anything but fair or accurate; one curmudgeon, angry about something that usually has nothing to do with your clinical skills, can use his First Amendment–protected right to trash you unfairly, as thousands of satisfied patients remain silent.
What to do? You could hire one of the many companies in the rapidly burgeoning field of online reputation management; but that can cost hundreds to thousands of dollars per month for monitoring and intervention, and there are no guarantees of success.
A better solution is to generate your own search results – positive ones – that will overwhelm any negative comments that search engines might find. Start with the social networking sites. However you feel about networking, there’s no getting around the fact that personal pages on Facebook, LinkedIn, and Twitter rank very high on major search engines. (Some consultants say a favorable LinkedIn profile is particularly helpful because of that site’s reputation as a “professional” network.) Your community activities, charitable work, interesting hobbies – anything that casts you in a favorable light – need to be mentioned prominently in your network profiles.
You can also use Google’s profiling tool (https://plus.google.com/up/accounts/) to create a sterling bio, complete with links to URLs, photos, and anything else that shows you in the best possible light. And your Google profile will be at or near the top of any Google search.
Wikipedia articles also go to the top of most searches, so if you’re notable enough to merit mention in one – or to have one of your own – see that it is done, and updated regularly. You can’t do that yourself, however; Wikipedia’s conflict of interest rules forbid writing or editing content about yourself. Someone with a theoretically “neutral point of view” will have to do it.
If you don’t yet have a website, now would be a good time. As I’ve discussed many times, a professionally designed site will be far more attractive and polished than anything you could build yourself. Furthermore, an experienced designer will employ “search engine optimization” (SEO), meaning that content will be created in a way that is readily visible to search engine users.
Leave design and SEO to the pros, but don’t delegate the content itself; as captain of the ship you are responsible for all the facts and opinions on your site. And remember that once it’s online, it’s online forever; consider the ramifications of anything you post on any site (yours or others) before hitting the “send” button. “The most damaging item about you,” one consultant told me, “could well be something you posted yourself.” Just ask any of several prominent politicians who have famously sabotaged their own careers online.
That said, don’t be shy about creating content. Make your (noncontroversial) opinions known on Facebook and Twitter. If social networks are not your thing, add a blog to your web site and write about what you know, and what interests you. If you have expertise in a particular field, write about that.
Incidentally, if the URL for your web site is not your name, you should also register your name as a separate domain name – if only to be sure that a trickster, or someone with the same name and a bad reputation, doesn’t get it.
Set up an RSS news feed for yourself, so you’ll know immediately anytime your name pops up in news or gossip sites, or on blogs. If something untrue is posted about you, take action. Reputable news sites and blogs have their own reputations to protect, and so can usually be persuaded to correct anything that is demonstrably false. Try to get the error removed entirely, or corrected within the original article. An erratum on the last page of the next edition will be ignored, and will leave the false information online, intact.
Unfair comments on doctor rating sites are unlikely to be removed unless they are blatantly libelous; but there is nothing wrong with encouraging happy patients to write favorable reviews. Turnabout is fair play.
Dr. Eastern practices dermatology and dermatologic surgery in Belleville, N.J. He is the author of numerous articles and textbook chapters, and is a longtime monthly columnist for Dermatology News. Write to him at dermnews@frontlinemedcom.com.
Earlier bariatric surgery may improve cardiovascular outcomes
CHICAGO – Sooner may be better than later when it comes to the timing of bariatric surgery in patients with morbid obesity.
Of 828 patients with body mass index of at least 35 kg/m2 who underwent laparoscopic adjustable gastric banding performed by a single surgeon and were followed for up to 11 years (mean of 10 years), 423 were aged 45 years or younger, and 405 were over age 45 years at the time of surgery. A comparison of outcomes between the two age groups showed that older age at the time of surgery was an independent predictor of cardiovascular events (hazard ratio, 1.8), Maharaj Singh, Ph.D., a biostatistician at the Aurora Research Institute, Milwaukee, reported in a poster at the annual meeting of the American College of Cardiology.
Despite a similar reduction in body weight after gastric banding surgery, the older patients experienced more cardiovascular events: myocardial infarction occurred in 0.2% and 1.7% of patients in the younger and older age groups, respectively, pulmonary embolism occurred in 0.7% and 4.3%, congestive heart failure occurred in 2.8% and 7.8%, and stroke occurred in 3.7% and 7.6%, Dr. Singh said.
“Although the older group had more comorbidities, these were accounted for by multivariate analysis and age over 45 years remained an independent predictor of poor cardiovascular outcomes,” senior coauthor Dr. Arshad Jahangir, professor of medicine at the University of Wisconsin–Madison, said in an interview.
Other independent predictors of adverse cardiovascular outcomes in the study were sleep apnea (hazard ratio, 4), history of hypertension (HR, 1.9), and depression, (HR, 1.8), Dr. Jahangir said.
“Gender, race, and diabetes mellitus did not independently predict cardiovascular events,” he said.
Weight loss after bariatric surgery has been shown to reduce the risk of adverse cardiovascular events, but it has remained unclear whether the reduction in risk varies based on age at the time of surgery, he said.
The current findings suggest that the effects of laparoscopic adjustable gastric banding–induced weight loss on cardiovascular outcomes are greater in patients who undergo the surgery at a younger age, he said, adding that the findings also “raise important questions about whether better control of sleep apnea, hypertension, and depression could help further reduce cardiovascular events in morbidly obese individuals undergoing bariatric surgery and should be addressed in a prospective study of these patients.”
The authors reported having no disclosures.
CHICAGO – Sooner may be better than later when it comes to the timing of bariatric surgery in patients with morbid obesity.
Of 828 patients with body mass index of at least 35 kg/m2 who underwent laparoscopic adjustable gastric banding performed by a single surgeon and were followed for up to 11 years (mean of 10 years), 423 were aged 45 years or younger, and 405 were over age 45 years at the time of surgery. A comparison of outcomes between the two age groups showed that older age at the time of surgery was an independent predictor of cardiovascular events (hazard ratio, 1.8), Maharaj Singh, Ph.D., a biostatistician at the Aurora Research Institute, Milwaukee, reported in a poster at the annual meeting of the American College of Cardiology.
Despite a similar reduction in body weight after gastric banding surgery, the older patients experienced more cardiovascular events: myocardial infarction occurred in 0.2% and 1.7% of patients in the younger and older age groups, respectively, pulmonary embolism occurred in 0.7% and 4.3%, congestive heart failure occurred in 2.8% and 7.8%, and stroke occurred in 3.7% and 7.6%, Dr. Singh said.
“Although the older group had more comorbidities, these were accounted for by multivariate analysis and age over 45 years remained an independent predictor of poor cardiovascular outcomes,” senior coauthor Dr. Arshad Jahangir, professor of medicine at the University of Wisconsin–Madison, said in an interview.
Other independent predictors of adverse cardiovascular outcomes in the study were sleep apnea (hazard ratio, 4), history of hypertension (HR, 1.9), and depression, (HR, 1.8), Dr. Jahangir said.
“Gender, race, and diabetes mellitus did not independently predict cardiovascular events,” he said.
Weight loss after bariatric surgery has been shown to reduce the risk of adverse cardiovascular events, but it has remained unclear whether the reduction in risk varies based on age at the time of surgery, he said.
The current findings suggest that the effects of laparoscopic adjustable gastric banding–induced weight loss on cardiovascular outcomes are greater in patients who undergo the surgery at a younger age, he said, adding that the findings also “raise important questions about whether better control of sleep apnea, hypertension, and depression could help further reduce cardiovascular events in morbidly obese individuals undergoing bariatric surgery and should be addressed in a prospective study of these patients.”
The authors reported having no disclosures.
CHICAGO – Sooner may be better than later when it comes to the timing of bariatric surgery in patients with morbid obesity.
Of 828 patients with body mass index of at least 35 kg/m2 who underwent laparoscopic adjustable gastric banding performed by a single surgeon and were followed for up to 11 years (mean of 10 years), 423 were aged 45 years or younger, and 405 were over age 45 years at the time of surgery. A comparison of outcomes between the two age groups showed that older age at the time of surgery was an independent predictor of cardiovascular events (hazard ratio, 1.8), Maharaj Singh, Ph.D., a biostatistician at the Aurora Research Institute, Milwaukee, reported in a poster at the annual meeting of the American College of Cardiology.
Despite a similar reduction in body weight after gastric banding surgery, the older patients experienced more cardiovascular events: myocardial infarction occurred in 0.2% and 1.7% of patients in the younger and older age groups, respectively, pulmonary embolism occurred in 0.7% and 4.3%, congestive heart failure occurred in 2.8% and 7.8%, and stroke occurred in 3.7% and 7.6%, Dr. Singh said.
“Although the older group had more comorbidities, these were accounted for by multivariate analysis and age over 45 years remained an independent predictor of poor cardiovascular outcomes,” senior coauthor Dr. Arshad Jahangir, professor of medicine at the University of Wisconsin–Madison, said in an interview.
Other independent predictors of adverse cardiovascular outcomes in the study were sleep apnea (hazard ratio, 4), history of hypertension (HR, 1.9), and depression, (HR, 1.8), Dr. Jahangir said.
“Gender, race, and diabetes mellitus did not independently predict cardiovascular events,” he said.
Weight loss after bariatric surgery has been shown to reduce the risk of adverse cardiovascular events, but it has remained unclear whether the reduction in risk varies based on age at the time of surgery, he said.
The current findings suggest that the effects of laparoscopic adjustable gastric banding–induced weight loss on cardiovascular outcomes are greater in patients who undergo the surgery at a younger age, he said, adding that the findings also “raise important questions about whether better control of sleep apnea, hypertension, and depression could help further reduce cardiovascular events in morbidly obese individuals undergoing bariatric surgery and should be addressed in a prospective study of these patients.”
The authors reported having no disclosures.
AT ACC 16
Key clinical point: Morbidly obese patients who underwent bariatric surgery before age 45 years had a reduced risk of adverse cardiovascular outcomes vs. those aged 45 or older at the time of surgery, despite similar weight loss.
Major finding: Older vs. younger age at the time of surgery was an independent predictor of cardiovascular events (hazard ratio, 1.8).
Data source: A review of outcomes in 828 laparoscopic adjustable gastric banding patients.
Disclosures: The authors reported having no disclosures.
AAN updates botulinum toxin guidelines for most established uses
VANCOUVER – A new American Academy of Neurology practice guideline on the efficacy and safety evidence for botulinum toxin treatment of blepharospasm, cervical dystonia, spasticity, and headache has updated the last recommendations published in 2008, but leaves some relevant clinical concerns and off-label uses unaddressed.
The 2016 update, published April 18 in Neurology, adds new individual evidence for the use of the four branded formulations of the two commercially available botulinum toxin serotypes, A and B, for the aforementioned indications rather than lumping all recommendations for botulinum toxin together as in the 2008 guidelines. However, questions remain on the differences between the different products in clinical practice, especially since the formulations show little clinical difference in head-to-head comparisons for some of the indications, especially for the serotype A formulations.
In a press briefing on the new guidelines at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Neurology, guidelines coauthor Dr. Mark Hallett noted that nothing really surprised the experienced 14-member committee that put the guidelines together. “The reason that we chose these four different diseases is because we already had the sense that they were going to change in the particular ways that they did. We didn’t know exactly, of course, what was going to happen, but we had a sense that there were sufficient data that it was worth looking at them.”
For blepharospasm, the totality of evidence suggests that onabotulinumtoxinA (onaBoNT-A; Botox) and incobotulinumtoxinA (incoBoNT-A; Xeomin) injections should be considered and are probably safe and effective (level B recommendation), while abobotulinumtoxinA (aboBoNT-A; Dysport) may be considered (level C) and is possibly effective. The evidence shows that incoBoNT-A and onaBoNT-A have equivalent efficacy and aboBoNT-A and onaBoNT-A are possibly equivalent. There was not enough evidence to determine the efficacy of rimabotulinumtoxinB for blepharospasm (rimaBoNT-B; Myobloc).
The rigorousness of clinical trials in evaluating the efficacy and safety of botulinum toxin has evolved since the Food and Drug Administration approved onaBoNT-A and incoBoNT-A to treat blepharospasm, but no new trials have been conducted to give it a higher level of recommendation despite their well-known magnitude of benefit, said Dr. Hallett, chief of the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke medical neurology branch and its human motor control section.
New evidence added to the already well-established data on the effectiveness of botulinum toxin for cervical dystonia suggest that onaBoNT-A and incoBoNT-A are probably safe and effective and should be considered. In addition, aboBoNT-A and rimaBoNT-B have already proven effectiveness and safety and should be offered. The lack of class I studies for onaBoNT-A and incoBoNT-A led to the lower level of recommendation for them despite an extensive clinical history of their use in cervical dystonia, the guideline committee wrote (Neurology. 2016 Apr 18. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000002560).
In adults with upper-limb spasticity, all three serotype A formulations – onaBoNT-A, aboBoNT-A, and incoBoNT-A – are effective and safe in reducing symptoms and improving passive limb function. All three achieved level A evidence to recommend that they should be offered. One comparative trial showed enough evidence to say that onaBoNT-A is probably superior to tizanidine for reducing upper-extremity tone and should be considered before it. RimaBoNT-B has level B evidence to advise that it should be considered and is probably safe and effective. None of the formulations have enough data to determine their efficacy on active limb function.
Fewer trials have examined the safety and effectiveness of botulinum toxin formulations for reducing lower leg spasticity in adults. The guidelines panel found enough evidence to recommend that aboBoNT-A and onaBoNT-A are safe and effective and should be offered (level A). There were no trials with high enough level of quality to determine whether incoBoNT-A or rimaBoNT-B were effective for lower-leg spasticity. None of the four agents had enough evidence to support their ability to improve active function associated with lower-limb spasticity.
At the press briefing, guidelines first author Dr. David M. Simpson expressed hope that a more refined methodology for evaluating spasticity might be achieved in future trials of botulinum toxin to detect the potentially subtle effects the agents may have on certain patients who are more likely to achieve benefits in active limb function. Currently, trials use a standardized set of outcomes to try to detect differences in patients with wide-ranging severity of symptoms and types of injury that led to spasticity. Dr. Simpson is professor of neurology at Mount Sinai in New York, as well as director of the neuromuscular diseases division and director of the clinical neurophysiology laboratories.
Positive results for onaBoNT-A in two pivotal trials in chronic migraine that were published since the last guidelines give the formulation the only FDA-approved indication for a botulinum toxin in chronic migraine and earned it a level A recommendation from the guidelines committee. However, in the trials it had a relatively small magnitude of efficacy in reducing the number of headache days by 15% versus placebo. The guidelines also advise not using onaBoNT-A in episodic migraine based on three negative trials. No high-quality trials have evaluated any formulation to change the overall 2008 guidelines’ advice that botulinum toxin is probably ineffective for treating chronic tension-type headaches.
Familiarity with appropriate dosing and side effects may allow clinicians to use the products off-label for indications in the guidelines for which clinical trials were not available, Dr. Richard L. Barbano of the movement disorders division at the University of Rochester noted in an editorial about the guidelines (Neurol Clin Pract. 2016 Apr 18. doi: 10.1212/CPJ.0000000000000244). “Off-label use is common in clinical practice. Little data exist to indicate that any of the different formulations, with attention to appropriate dosing and side effects, would not be effective in treating these other conditions. There are also a number of other neurologic conditions not discussed in the guideline in which botulinum toxin has shown efficacy, such as hemifacial spasm and other focal dystonias. Lack of sufficient high-level evidence to support a level A or B guideline recommendation does not negate their potential utility and likewise, there is little evidence to recommend one formulation over another.”
“In some circumstances where the drugs are relatively equivalent, some people prefer to stick with one so they get used to it more, and they can have more of a sense of what the dosing is, given that the doses may be different with the compounds and have different side effects,” Dr. Hallett said in an interview, noting that availability and price also might enter into a clinician’s decision on what to do.
Dr. Barbano also said that cost and value are becoming more important, and neurologists should consider when botulinum toxin therapy should be chosen among existing alternative treatment options, particularly for chronic migraine.
The guidelines are endorsed by the American Association of Neuromuscular & Electrodiagnostic Medicine and the American Society of Plastic Surgeons.
Dr. Hallett reported serving as chair of the Neurotoxin Institute Advisory Council and has received research grants from Allergan and Merz Pharmaceuticals. Dr. Simpson reported receiving research grants from and served as a consultant for Allergan, Ipsen, Merz Pharmaceuticals, and Acorda Therapeutics. Five other coauthors of the guidelines disclosed relationships with manufacturers of botulinum toxin formulations. Dr. Barbano reported serving on a scientific advisory board for Allergan and receiving research support from Allergan, Vaccinex, and Biotie.
VANCOUVER – A new American Academy of Neurology practice guideline on the efficacy and safety evidence for botulinum toxin treatment of blepharospasm, cervical dystonia, spasticity, and headache has updated the last recommendations published in 2008, but leaves some relevant clinical concerns and off-label uses unaddressed.
The 2016 update, published April 18 in Neurology, adds new individual evidence for the use of the four branded formulations of the two commercially available botulinum toxin serotypes, A and B, for the aforementioned indications rather than lumping all recommendations for botulinum toxin together as in the 2008 guidelines. However, questions remain on the differences between the different products in clinical practice, especially since the formulations show little clinical difference in head-to-head comparisons for some of the indications, especially for the serotype A formulations.
In a press briefing on the new guidelines at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Neurology, guidelines coauthor Dr. Mark Hallett noted that nothing really surprised the experienced 14-member committee that put the guidelines together. “The reason that we chose these four different diseases is because we already had the sense that they were going to change in the particular ways that they did. We didn’t know exactly, of course, what was going to happen, but we had a sense that there were sufficient data that it was worth looking at them.”
For blepharospasm, the totality of evidence suggests that onabotulinumtoxinA (onaBoNT-A; Botox) and incobotulinumtoxinA (incoBoNT-A; Xeomin) injections should be considered and are probably safe and effective (level B recommendation), while abobotulinumtoxinA (aboBoNT-A; Dysport) may be considered (level C) and is possibly effective. The evidence shows that incoBoNT-A and onaBoNT-A have equivalent efficacy and aboBoNT-A and onaBoNT-A are possibly equivalent. There was not enough evidence to determine the efficacy of rimabotulinumtoxinB for blepharospasm (rimaBoNT-B; Myobloc).
The rigorousness of clinical trials in evaluating the efficacy and safety of botulinum toxin has evolved since the Food and Drug Administration approved onaBoNT-A and incoBoNT-A to treat blepharospasm, but no new trials have been conducted to give it a higher level of recommendation despite their well-known magnitude of benefit, said Dr. Hallett, chief of the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke medical neurology branch and its human motor control section.
New evidence added to the already well-established data on the effectiveness of botulinum toxin for cervical dystonia suggest that onaBoNT-A and incoBoNT-A are probably safe and effective and should be considered. In addition, aboBoNT-A and rimaBoNT-B have already proven effectiveness and safety and should be offered. The lack of class I studies for onaBoNT-A and incoBoNT-A led to the lower level of recommendation for them despite an extensive clinical history of their use in cervical dystonia, the guideline committee wrote (Neurology. 2016 Apr 18. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000002560).
In adults with upper-limb spasticity, all three serotype A formulations – onaBoNT-A, aboBoNT-A, and incoBoNT-A – are effective and safe in reducing symptoms and improving passive limb function. All three achieved level A evidence to recommend that they should be offered. One comparative trial showed enough evidence to say that onaBoNT-A is probably superior to tizanidine for reducing upper-extremity tone and should be considered before it. RimaBoNT-B has level B evidence to advise that it should be considered and is probably safe and effective. None of the formulations have enough data to determine their efficacy on active limb function.
Fewer trials have examined the safety and effectiveness of botulinum toxin formulations for reducing lower leg spasticity in adults. The guidelines panel found enough evidence to recommend that aboBoNT-A and onaBoNT-A are safe and effective and should be offered (level A). There were no trials with high enough level of quality to determine whether incoBoNT-A or rimaBoNT-B were effective for lower-leg spasticity. None of the four agents had enough evidence to support their ability to improve active function associated with lower-limb spasticity.
At the press briefing, guidelines first author Dr. David M. Simpson expressed hope that a more refined methodology for evaluating spasticity might be achieved in future trials of botulinum toxin to detect the potentially subtle effects the agents may have on certain patients who are more likely to achieve benefits in active limb function. Currently, trials use a standardized set of outcomes to try to detect differences in patients with wide-ranging severity of symptoms and types of injury that led to spasticity. Dr. Simpson is professor of neurology at Mount Sinai in New York, as well as director of the neuromuscular diseases division and director of the clinical neurophysiology laboratories.
Positive results for onaBoNT-A in two pivotal trials in chronic migraine that were published since the last guidelines give the formulation the only FDA-approved indication for a botulinum toxin in chronic migraine and earned it a level A recommendation from the guidelines committee. However, in the trials it had a relatively small magnitude of efficacy in reducing the number of headache days by 15% versus placebo. The guidelines also advise not using onaBoNT-A in episodic migraine based on three negative trials. No high-quality trials have evaluated any formulation to change the overall 2008 guidelines’ advice that botulinum toxin is probably ineffective for treating chronic tension-type headaches.
Familiarity with appropriate dosing and side effects may allow clinicians to use the products off-label for indications in the guidelines for which clinical trials were not available, Dr. Richard L. Barbano of the movement disorders division at the University of Rochester noted in an editorial about the guidelines (Neurol Clin Pract. 2016 Apr 18. doi: 10.1212/CPJ.0000000000000244). “Off-label use is common in clinical practice. Little data exist to indicate that any of the different formulations, with attention to appropriate dosing and side effects, would not be effective in treating these other conditions. There are also a number of other neurologic conditions not discussed in the guideline in which botulinum toxin has shown efficacy, such as hemifacial spasm and other focal dystonias. Lack of sufficient high-level evidence to support a level A or B guideline recommendation does not negate their potential utility and likewise, there is little evidence to recommend one formulation over another.”
“In some circumstances where the drugs are relatively equivalent, some people prefer to stick with one so they get used to it more, and they can have more of a sense of what the dosing is, given that the doses may be different with the compounds and have different side effects,” Dr. Hallett said in an interview, noting that availability and price also might enter into a clinician’s decision on what to do.
Dr. Barbano also said that cost and value are becoming more important, and neurologists should consider when botulinum toxin therapy should be chosen among existing alternative treatment options, particularly for chronic migraine.
The guidelines are endorsed by the American Association of Neuromuscular & Electrodiagnostic Medicine and the American Society of Plastic Surgeons.
Dr. Hallett reported serving as chair of the Neurotoxin Institute Advisory Council and has received research grants from Allergan and Merz Pharmaceuticals. Dr. Simpson reported receiving research grants from and served as a consultant for Allergan, Ipsen, Merz Pharmaceuticals, and Acorda Therapeutics. Five other coauthors of the guidelines disclosed relationships with manufacturers of botulinum toxin formulations. Dr. Barbano reported serving on a scientific advisory board for Allergan and receiving research support from Allergan, Vaccinex, and Biotie.
VANCOUVER – A new American Academy of Neurology practice guideline on the efficacy and safety evidence for botulinum toxin treatment of blepharospasm, cervical dystonia, spasticity, and headache has updated the last recommendations published in 2008, but leaves some relevant clinical concerns and off-label uses unaddressed.
The 2016 update, published April 18 in Neurology, adds new individual evidence for the use of the four branded formulations of the two commercially available botulinum toxin serotypes, A and B, for the aforementioned indications rather than lumping all recommendations for botulinum toxin together as in the 2008 guidelines. However, questions remain on the differences between the different products in clinical practice, especially since the formulations show little clinical difference in head-to-head comparisons for some of the indications, especially for the serotype A formulations.
In a press briefing on the new guidelines at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Neurology, guidelines coauthor Dr. Mark Hallett noted that nothing really surprised the experienced 14-member committee that put the guidelines together. “The reason that we chose these four different diseases is because we already had the sense that they were going to change in the particular ways that they did. We didn’t know exactly, of course, what was going to happen, but we had a sense that there were sufficient data that it was worth looking at them.”
For blepharospasm, the totality of evidence suggests that onabotulinumtoxinA (onaBoNT-A; Botox) and incobotulinumtoxinA (incoBoNT-A; Xeomin) injections should be considered and are probably safe and effective (level B recommendation), while abobotulinumtoxinA (aboBoNT-A; Dysport) may be considered (level C) and is possibly effective. The evidence shows that incoBoNT-A and onaBoNT-A have equivalent efficacy and aboBoNT-A and onaBoNT-A are possibly equivalent. There was not enough evidence to determine the efficacy of rimabotulinumtoxinB for blepharospasm (rimaBoNT-B; Myobloc).
The rigorousness of clinical trials in evaluating the efficacy and safety of botulinum toxin has evolved since the Food and Drug Administration approved onaBoNT-A and incoBoNT-A to treat blepharospasm, but no new trials have been conducted to give it a higher level of recommendation despite their well-known magnitude of benefit, said Dr. Hallett, chief of the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke medical neurology branch and its human motor control section.
New evidence added to the already well-established data on the effectiveness of botulinum toxin for cervical dystonia suggest that onaBoNT-A and incoBoNT-A are probably safe and effective and should be considered. In addition, aboBoNT-A and rimaBoNT-B have already proven effectiveness and safety and should be offered. The lack of class I studies for onaBoNT-A and incoBoNT-A led to the lower level of recommendation for them despite an extensive clinical history of their use in cervical dystonia, the guideline committee wrote (Neurology. 2016 Apr 18. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000002560).
In adults with upper-limb spasticity, all three serotype A formulations – onaBoNT-A, aboBoNT-A, and incoBoNT-A – are effective and safe in reducing symptoms and improving passive limb function. All three achieved level A evidence to recommend that they should be offered. One comparative trial showed enough evidence to say that onaBoNT-A is probably superior to tizanidine for reducing upper-extremity tone and should be considered before it. RimaBoNT-B has level B evidence to advise that it should be considered and is probably safe and effective. None of the formulations have enough data to determine their efficacy on active limb function.
Fewer trials have examined the safety and effectiveness of botulinum toxin formulations for reducing lower leg spasticity in adults. The guidelines panel found enough evidence to recommend that aboBoNT-A and onaBoNT-A are safe and effective and should be offered (level A). There were no trials with high enough level of quality to determine whether incoBoNT-A or rimaBoNT-B were effective for lower-leg spasticity. None of the four agents had enough evidence to support their ability to improve active function associated with lower-limb spasticity.
At the press briefing, guidelines first author Dr. David M. Simpson expressed hope that a more refined methodology for evaluating spasticity might be achieved in future trials of botulinum toxin to detect the potentially subtle effects the agents may have on certain patients who are more likely to achieve benefits in active limb function. Currently, trials use a standardized set of outcomes to try to detect differences in patients with wide-ranging severity of symptoms and types of injury that led to spasticity. Dr. Simpson is professor of neurology at Mount Sinai in New York, as well as director of the neuromuscular diseases division and director of the clinical neurophysiology laboratories.
Positive results for onaBoNT-A in two pivotal trials in chronic migraine that were published since the last guidelines give the formulation the only FDA-approved indication for a botulinum toxin in chronic migraine and earned it a level A recommendation from the guidelines committee. However, in the trials it had a relatively small magnitude of efficacy in reducing the number of headache days by 15% versus placebo. The guidelines also advise not using onaBoNT-A in episodic migraine based on three negative trials. No high-quality trials have evaluated any formulation to change the overall 2008 guidelines’ advice that botulinum toxin is probably ineffective for treating chronic tension-type headaches.
Familiarity with appropriate dosing and side effects may allow clinicians to use the products off-label for indications in the guidelines for which clinical trials were not available, Dr. Richard L. Barbano of the movement disorders division at the University of Rochester noted in an editorial about the guidelines (Neurol Clin Pract. 2016 Apr 18. doi: 10.1212/CPJ.0000000000000244). “Off-label use is common in clinical practice. Little data exist to indicate that any of the different formulations, with attention to appropriate dosing and side effects, would not be effective in treating these other conditions. There are also a number of other neurologic conditions not discussed in the guideline in which botulinum toxin has shown efficacy, such as hemifacial spasm and other focal dystonias. Lack of sufficient high-level evidence to support a level A or B guideline recommendation does not negate their potential utility and likewise, there is little evidence to recommend one formulation over another.”
“In some circumstances where the drugs are relatively equivalent, some people prefer to stick with one so they get used to it more, and they can have more of a sense of what the dosing is, given that the doses may be different with the compounds and have different side effects,” Dr. Hallett said in an interview, noting that availability and price also might enter into a clinician’s decision on what to do.
Dr. Barbano also said that cost and value are becoming more important, and neurologists should consider when botulinum toxin therapy should be chosen among existing alternative treatment options, particularly for chronic migraine.
The guidelines are endorsed by the American Association of Neuromuscular & Electrodiagnostic Medicine and the American Society of Plastic Surgeons.
Dr. Hallett reported serving as chair of the Neurotoxin Institute Advisory Council and has received research grants from Allergan and Merz Pharmaceuticals. Dr. Simpson reported receiving research grants from and served as a consultant for Allergan, Ipsen, Merz Pharmaceuticals, and Acorda Therapeutics. Five other coauthors of the guidelines disclosed relationships with manufacturers of botulinum toxin formulations. Dr. Barbano reported serving on a scientific advisory board for Allergan and receiving research support from Allergan, Vaccinex, and Biotie.
AT THE AAN 2016 ANNUAL MEETING